GAIT ANALYSIS. Professor Areerat Suputtitada,M.D.
|
|
|
- Rebecca Woods
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GAIT ANALYSIS Department of Rehabilitation Medicine,Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University,Bangkok,Thailand 1
2 Scope in 60 mins Gait cycle: Terminology Motion analysis machines Gait determinants Gait control structures Abnormal gait Cases studies 2
3 One gait cycle 3
4 Spatial-Temporal Parameters 4 Step length 78 cm. Stride length 156 cm. Cadence 120 steps per min or 60 strides per min Stride width 5-11 cm. Foot angle 6-7 degree.
5 Gait in the young The walking base is wider. The stride length and speed are lower and the cycle time is shorter (higher cadence). 5 Small children have no heel strike, initial contact being made by the flat foot. There is very little stance phase knee flexion. The whole leg is externally rotated during the swing phase. There is an absence of reciprocal arm swinging. Mature gait is at 7 yrs old.
6 Gait velocity Cadence Gait in the elderly Stride length ('marche à petit pas') Swing phase, double-support phase Posture stooped Walking base Vertical joint movement Lateral joint movement 6
7 DILEMMA 7 Gait changes product of normal aging? Gait changes product of (age-related) disorders? Consequence: what is 'normal' gait in the elderly? Practical approach: describe suspect findings identify additional findings establish specific diagnosis or contribute findings to ageing
8 Normal data of elderly 8
9 Movements in Sagittal Plane 9 Pelvis anterior and posterior tilting Knee flexion and extension Ankle dorsiflexion and plantar flexion
10 Movements in Coronal Plane 10 Pelvis obliquity up or down Hip abduction and adduction Foot varus and valgus
11 Movements in Transverse Plane 11 Pelvis protraction and retraction Hip internal and external rotation Knee internal and external rotation Foot: In Toeing and Out Toeing
12 Clinical Gait Analysis History taking/physical examination/special tests Videotape examination: slow motion and freezing - frame Measurement of general gait parameters: cadence (steps/min), stride length (m), speed (m/s) Kinematic analysis Kinetic measurement Electromyography 12
13 Video Observation 13 Low cost/easier Advantages Permanent record for subsequent analysis. Slow motion, freeze frame facilities and time coding can all enhance greatly the accuracy of observation Disadvantages Difficult to assess rotational movement No kinematic data: joint angle No information on forces/muscle firing
14 Gait and Motion Analysis Machines 1. High speed camera and computer 14 Arrange the cameras to cover the entire measurement volume Cameras must be mounted firmly on tripods or other stable structures Isolate camera from movements or vibrations of any sort. 2. Marker, 2.5mm 40mm 3. Visual 3D software Oqus ( Hz)
15 Gait and Motion Analysis Machines 2. Force plate Pressure plate
16 Visual 3D Analysis 16 Speed, stride and cycle time Step length and step time Stance phase and swing phase Center of pressure and ground force Joint angles/force/moment/ power/velocity Segment center of gravity position Segment distal/proximal joint position
17 Kinematic analysis 17
18 Wireless EMG 18 EMG allows to directly look into the muscle. It allows measurement of muscular performance. Helps in decision making both before and after treatment. Helps patients to find and train their muscles. Allows analysis to improve sports activities. Detect muscle response in ergonomic activities.
19 Electromyography 19
20 Kinetic measurement 20
21 Attributes of Normal Walking Stability in stance Foot clearance in swing Pre-positioning of foot for initial contact Adequate step length Energy conservation 21
22 Gait Determinants-Energy conservation 1. Pelvic rotation Four degree each in the horizontal plane Forward leg movement with less lower CG Maximal rotation during double supportthe lowest point of CG in gait cycle 22
23 Gait Determinants 2. Pelvic tilt Pelvis downward during swing phase. Gluteus medius of stance limb contracts to hold pelvis in swing limb not drop too much. Vertical movement 5 degree. 23
24 Gait Determinants Early knee flexion Knee flexion 15 degree during stance phase 4,5 Knee and ankle motion Weight transfer from heel to toe in sinusoidal motion 6. Motion of CG in the horizontal plane Motion of CG 2 inches from stance phase in one limb to another limb
25 Ankle and foot during push off 25 Ankle rockers
26 Gait Determinants 26 Sinusoidal movement in vertical and horizontal plane 2 inches each Highest at midstance Lowest at double support Most lateral at midstance Energy conservation
27 basal ganglia coordination of movement elements cerebellum sequencing of movement elements alpha-mn activation gamma-mn activation GAIT CONTROL STRUCTURES contraction motor cortex spine and joints frontal lobe 27 parietal lobe visuo-acousticospatial integrat. brainstem brainstem orthostatic reflexes spinal cord PNS muscles spinal reflexes spinal cord PNS muscles spine and joints muscle spindel afferences force joint position visual system vestibular system acoustic system movement
28 GAIT CONTROL STRUCTURES frontal lobe basal ganglia motor cortex parietal lobe 28 visual system cerebellum brainstem brainstem vestibular system spinal cord spinal cord acoustic system PNS PNS muscles muscles spine and joints spine and joints
29 JOINTS 29 Osteoarthrisis Spinal degeneration Spondylitis HLA B27 Stiff gait
30 GAIT CONTROL STRUCTURES frontal lobe basal ganglia motor cortex parietal lobe 30 visual system cerebellum brainstem brainstem vestibular system spinal cord spinal cord acoustic system PNS PNS muscles muscles spine and joints spine and joints
31 MUSCLE 31 Polymyositis/dermatom. Polymyalgia rheumatica Myopathy Ischemia Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis CK, skin changes, paraneoplastic pain, CK normal CK, EMG peripheral arterial occlusive disease gait disorder not usually presenting feature Paretic gait
32 GAIT CONTROL STRUCTURES frontal lobe basal ganglia motor cortex parietal lobe 32 visual system cerebellum brainstem brainstem vestibular system spinal cord spinal cord acoustic system PNS PNS muscles muscles spine and joints spine and joints
33 NERVE Polyneuropathy diabetis mellitus, alcoholism, neoplasms, dysproteinemia CIDP: conduction blocks Mononeuropathy diabetis mellitus Plexopathy neoplasms Polyradiculitis Guillain-Barré syndrome: CSF protein, GM antibodies Cauda syndrome spinal stenosis: MR imaging Post-polio syndrome history 33 Paretic gait
34 GAIT CONTROL STRUCTURES frontal lobe basal ganglia motor cortex parietal lobe 34 visual system cerebellum brainstem brainstem vestibular system spinal cord spinal cord acoustic system PNS PNS muscles muscles spine and joints spine and joints
35 Myelopathy Syrinx Tumors SPINAL CORD 35 Her. spastic paraparesis cervical myelopathy pathological fractures: osteoporosis metastasis multiple sclerosis intramedullary extramedullary meningeoma Spastic gait Ataxic gait
36 GAIT CONTROL STRUCTURES frontal lobe basal ganglia motor cortex parietal lobe 36 visual system cerebellum brainstem brainstem vestibular system spinal cord spinal cord acoustic system PNS PNS muscles muscles spine and joints spine and joints
37 BRAIN STEM 37 Progressive supranuclear palsy Infarction Vertebrobasilar insufficiency downward gaze bradykinesia dementia Toppling gait falls without prevention severe dysequilibrium
38 GAIT CONTROL STRUCTURES frontal lobe basal ganglia motor cortex parietal lobe 38 visual system cerebellum brainstem brainstem vestibular system spinal cord spinal cord acoustic system PNS PNS muscles muscles spine and joints spine and joints
39 CERBELLUM 39 Toxic cerebellopathy Drug-induced cp. Paraneoplastic cp. Radiation-induced cp. Infarction alcohol phenytoin Ataxic gait
40 basal ganglia GAIT CONTROL STRUCTURES frontal lobe 40 motor cortex parietal lobe visual system cerebellum brainstem brainstem vestibular system spinal cord spinal cord acoustic system PNS PNS muscles muscles spine and joints spine and joints
41 MOTOR CORTEX 41 Infarction/haemorrage Tumors Falx meningeoma hemiparesis hemiparesis paraparesis stiff gait
42 basal ganglia GAIT CONTROL STRUCTURES frontal lobe 42 motor cortex parietal lobe visual system cerebellum brainstem brainstem vestibular system spinal cord spinal cord acoustic system PNS PNS muscles muscles spine and joints spine and joints
43 BASAL GANGLIA 1 43 Parkinsonian syndromes idiopathic Parkinson's disease (IPD) multiple system atrophy (MSA) Freezing gait with festination
44 BASAL GANGLIA 2 44 Dystonia idiopathic d. tardive d. Stiff gait
45 BASAL GANGLIA 3 45 Chorea dementia Ataxic gait coordination, dysmetria, wide-based, irregular movements
46 basal ganglia GAIT CONTROL STRUCTURES frontal lobe 46 motor cortex parietal lobe visual system cerebellum brainstem brainstem vestibular system spinal cord spinal cord acoustic system PNS PNS muscles muscles spine and joints spine and joints
47 FRONTAL LOBE 47 Tumors Normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) gait initiation apathy disinhibition reasoning Hakim trias: gait disorder dementia urine incontinence Freezing gait without festination
48 GAIT CONTROL STRUCTURES frontal lobe basal ganglia motor cortex parietal lobe 48 visual system cerebellum brainstem brainstem vestibular system spinal cord spinal cord acoustic system PNS PNS muscles muscles spine and joints spine and joints
49 PARIETAL LOBE 49 Infarction/haemorrhagia Tumors Chronic subdural haematoma Veering gait gait deviation in one direction Cautious gait slow, short-stepped, shuffling normal: base, freezing, gait initiation
50 basal ganglia GAIT CONTROL STRUCTURES frontal lobe 50 motor cortex parietal lobe visual system cerebellum brainstem brainstem vestibular system spinal cord spinal cord acoustic system PNS PNS muscles muscles spine and joints spine and joints
51 VISUAL SYSTEM 51 visual acuity visual field age-related acuity accomodation contrast sensitivity glare sensitivity dark adaptation depth perception retinal degeneration cataract hemianopia Cautious gait
52 basal ganglia GAIT CONTROL STRUCTURES frontal lobe 52 motor cortex parietal lobe visual system cerebellum brainstem brainstem vestibular system spinal cord spinal cord acoustic system PNS PNS muscles muscles spine and joints spine and joints
53 VESTIBULAR SYSTEM 53 Acoustic neurinoma tinnitus deafness gait disorder Veering gait gait deviation in one direction
54 basal ganglia GAIT CONTROL STRUCTURES frontal lobe 54 motor cortex parietal lobe visual system cerebellum brainstem brainstem vestibular system spinal cord spinal cord acoustic system PNS PNS muscles muscles spine and joints spine and joints
55 ACOUSTIC SYSTEM 55 Presbyacusis Cautious gait
56 FREEZING GAIT 56 Findings Mechanism gait initiation turning blockades at narrowings normal: base access to brainstem locomotor centres FG with festination/hastening Impairment basal ganglia FG without festination/hastening Impairment frontal lobe parietal lobe vermis atrophy (gait ignition failure)
57 Parkinson 57
58 HIERARCHY OF GAIT CONTROL STRUCTURES frontal lobe gait initiation 58 parietal lobe visuo-spatialacoustic integration visual system visual gait control basal ganglia coordination of movement elements vestibular system vestibular gait control brainstem orthostatic reflexes cerebellum sequencing of movement elements spinal cord afferent conduction efferent conduction spinal reflexes PNS muscles muscle spindles afferences joint afferences motoneurons force production spine and joints mechanics
59 Simplified Gait Analysis Check Sheet 59 Moseley & Moore et al 1993
60 Case study 60
61 Case study 61
62 Case study 62
63 Case study 63
64 Case study 64
65 Case study 65
66 Case study 66
67 Case study 67
68 Case study 68
69 Quit What is the most likely diagnosis in a patient with the stance duration of 55%? A. Ataxia B. Antalgic gait C. Balance problem D. Child 69
70 Normal stance=60%. 55% is shortened stance. Answer Ataxia and balance problems trend to result in increased stance duration. Children have longer stance times compared to adults. Stance is shortened due to pain (antalgic gait). 70
71 What is the muscle? 71
72 Answers 72
73 Take Home Messages 73 Clinical gait analysis is used together with the history, physical examination and other special investigations to perform a detailed assessment of a patient with abnormal gait. It usually consists of 5 elements: videotape examination, measurement of general gait parameters, kinematic analysis, kinetic measurement, and elctromyograpky (EMG). The human eye is simply not fast enough to capture and process all of the events that occur during an average gait cycle. Video recording of walking can providing a permanent record of the walk for subsequent analysis. Slow motion, freeze frame facilities and time coding can all enhance greatly the accuracy of observation. Computerized gait analysis by combining kinematic and kinetic data, is possible to calculate the joint moments and powers in three dimensions. The joint angle, moment and power,and the EMG for specific muscles,provide a detailed description of the mechanics of gait. Such information enhances much better decisions to be reached on the best way to treat the patients.
74 74
Normal and Pathological Gait
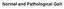 Normal and Pathological Gait Introduction Human gait locomotion Bipedal, biphasic forward propulsion of centre of gravity of the human body, in which there are alternate sinuous movements of different
Normal and Pathological Gait Introduction Human gait locomotion Bipedal, biphasic forward propulsion of centre of gravity of the human body, in which there are alternate sinuous movements of different
ASSESMENT Introduction REPORTS Running Reports Walking Reports Written Report
 ASSESMENT REPORTS Introduction Left panel Avatar Playback Right Panel Patient Gait Parameters Report Tab Click on parameter to view avatar at that point in time 2 Introduction Software will compare gait
ASSESMENT REPORTS Introduction Left panel Avatar Playback Right Panel Patient Gait Parameters Report Tab Click on parameter to view avatar at that point in time 2 Introduction Software will compare gait
Normal and Abnormal Gait
 Normal and Abnormal Gait Adrielle Fry, MD EvergreenHealth, Division of Sport and Spine University of Washington Board Review Course March 6, 2017 What are we going to cover? Definitions and key concepts
Normal and Abnormal Gait Adrielle Fry, MD EvergreenHealth, Division of Sport and Spine University of Washington Board Review Course March 6, 2017 What are we going to cover? Definitions and key concepts
Purpose. Outline. Angle definition. Objectives:
 Disclosure Information AACPDM 69 th Annual Meeting October 21-24, 2015 Speaker Names: Sylvia Õunpuu, MSc and Kristan Pierz, MD Gait Analysis Data Interpretation: Understanding Kinematic Relationships Within
Disclosure Information AACPDM 69 th Annual Meeting October 21-24, 2015 Speaker Names: Sylvia Õunpuu, MSc and Kristan Pierz, MD Gait Analysis Data Interpretation: Understanding Kinematic Relationships Within
INTRODUCTION TO GAIT ANALYSIS DATA
 INTRODUCTION TO GAIT ANALYSIS DATA 1. Phases of gait a. Stance (% gc) i. Loading response (10%) ii. Mid- and terminal stance (%) iii. Pre-swing (10%) b. Swing (% gc) i. Initial swing ii. Mid-swing iii.
INTRODUCTION TO GAIT ANALYSIS DATA 1. Phases of gait a. Stance (% gc) i. Loading response (10%) ii. Mid- and terminal stance (%) iii. Pre-swing (10%) b. Swing (% gc) i. Initial swing ii. Mid-swing iii.
video Purpose Pathological Gait Objectives: Primary, Secondary and Compensatory Gait Deviations in CP AACPDM IC #3 1
 s in CP Disclosure Information AACPDM 71st Annual Meeting September 13-16, 2017 Speaker Names: Sylvia Ounpuu, MSc and Kristan Pierz, MD Differentiating Between, Secondary and Compensatory Mechanisms in
s in CP Disclosure Information AACPDM 71st Annual Meeting September 13-16, 2017 Speaker Names: Sylvia Ounpuu, MSc and Kristan Pierz, MD Differentiating Between, Secondary and Compensatory Mechanisms in
The Starting Point. Prosthetic Alignment in the Transtibial Amputee. Outline. COM Motion in the Coronal Plane
 Prosthetic Alignment in the Transtibial Amputee The Starting Point David C. Morgenroth, MD, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine University of Washington VAPSHCS Outline COM Motion in the Coronal Plane
Prosthetic Alignment in the Transtibial Amputee The Starting Point David C. Morgenroth, MD, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine University of Washington VAPSHCS Outline COM Motion in the Coronal Plane
Gait. Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 12 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 Gait Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 12 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Definitions Locomotion = the act of moving from one place to the other Gait = the manner of walking Definitions Walking = a smooth, highly coordinated,
Gait Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 12 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Definitions Locomotion = the act of moving from one place to the other Gait = the manner of walking Definitions Walking = a smooth, highly coordinated,
Neurorehabil Neural Repair Oct 23. [Epub ahead of print]
![Neurorehabil Neural Repair Oct 23. [Epub ahead of print] Neurorehabil Neural Repair Oct 23. [Epub ahead of print]](/thumbs/86/94477916.jpg) APPENDICE Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2009 Oct 23. [Epub ahead of print] Segmental Muscle Vibration Improves Walking in Chronic Stroke Patients With Foot Drop: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Paoloni M,
APPENDICE Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2009 Oct 23. [Epub ahead of print] Segmental Muscle Vibration Improves Walking in Chronic Stroke Patients With Foot Drop: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Paoloni M,
Normal Gait and Dynamic Function purpose of the foot in ambulation. Normal Gait and Dynamic Function purpose of the foot in ambulation
 Normal Gait and Dynamic Function purpose of the foot in ambulation Edward P. Mulligan, PT, DPT, OCS, SCS, ATC Assistant Professor; Residency Chair UT Southwestern School of Health Professions Department
Normal Gait and Dynamic Function purpose of the foot in ambulation Edward P. Mulligan, PT, DPT, OCS, SCS, ATC Assistant Professor; Residency Chair UT Southwestern School of Health Professions Department
Spasticity in gait. Wessex ACPIN Spasticity Presentation Alison Clarke
 Spasticity in gait Clinicians recognise spasticity but the elements of spasticity contributing to gait patterns are often difficult to identify: Variability of muscle tone Observation/recording General
Spasticity in gait Clinicians recognise spasticity but the elements of spasticity contributing to gait patterns are often difficult to identify: Variability of muscle tone Observation/recording General
Normal Gait. Definitions. Definitions Analysis of Stance Phase Analysis of Swing Phase Additional Determinants of Gait Abnormal Gait.
 Normal Gait Definitions Analysis of Stance Phase Analysis of Swing Phase Additional Determinants of Gait Abnormal Gait Muscular Weakness/Paralysis Joint/Muscle ROM Limitation Neurologic Involvement Pain
Normal Gait Definitions Analysis of Stance Phase Analysis of Swing Phase Additional Determinants of Gait Abnormal Gait Muscular Weakness/Paralysis Joint/Muscle ROM Limitation Neurologic Involvement Pain
Assessments SIMPLY GAIT. Posture and Gait. Observing Posture and Gait. Postural Assessment. Postural Assessment 6/28/2016
 Assessments 2 SIMPLY GAIT Understanding movement Evaluations of factors that help therapist form professional judgments Include health, palpatory, range of motion, postural, and gait assessments Assessments
Assessments 2 SIMPLY GAIT Understanding movement Evaluations of factors that help therapist form professional judgments Include health, palpatory, range of motion, postural, and gait assessments Assessments
Gait Analysis at Your Fingertips:
 Gait Analysis at Your Fingertips: Enhancing Observational Gait Analysis Using Mobile Device Technology and the Edinburgh Visual Gait Scale Jon R. Davids, MD; Shriners Hospitals for Children Northern California;
Gait Analysis at Your Fingertips: Enhancing Observational Gait Analysis Using Mobile Device Technology and the Edinburgh Visual Gait Scale Jon R. Davids, MD; Shriners Hospitals for Children Northern California;
Step 3: Ask the patient Can you walk without help? I will stay with you in case of any problems. Notice any cerebellar dysarthria during his reply.
 STEPS OF EXAMINATION CNS - GAIT Step 1: Approach the patient Read the instructions carefully for clues Shake hands, introduce yourself Ask few questions Could you tell me your name please? Are you right-
STEPS OF EXAMINATION CNS - GAIT Step 1: Approach the patient Read the instructions carefully for clues Shake hands, introduce yourself Ask few questions Could you tell me your name please? Are you right-
Gait Analyser. Description of Walking Performance
 Gait Analyser Description of Walking Performance This brochure will help you to understand clearly the parameters described in the report of the Gait Analyser, provide you with tips to implement the walking
Gait Analyser Description of Walking Performance This brochure will help you to understand clearly the parameters described in the report of the Gait Analyser, provide you with tips to implement the walking
Brian Snyder MD/PhD Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School
 Brian Snyder MD/PhD Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Observe patient s gait pattern as walk into room Systematic musculoskeletal exam (range of motion, joint alignment while standing) Neurologic
Brian Snyder MD/PhD Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Observe patient s gait pattern as walk into room Systematic musculoskeletal exam (range of motion, joint alignment while standing) Neurologic
G-EOL. Discover the simplicity of gait therapy intended for daily use
 G-EOL Discover the simplicity of gait therapy intended for daily use Reha Technology a passion for robotic-assisted gait therapy For over 10 years, Reha Technology has been successfully developing innovative,
G-EOL Discover the simplicity of gait therapy intended for daily use Reha Technology a passion for robotic-assisted gait therapy For over 10 years, Reha Technology has been successfully developing innovative,
Mobility Lab provides sensitive, valid and reliable outcome measures.
 Mobility Lab provides sensitive, valid and reliable outcome measures. ith hundreds of universities and hospitals using this system worldwide, Mobility Lab is the most trusted wearable gait and balance
Mobility Lab provides sensitive, valid and reliable outcome measures. ith hundreds of universities and hospitals using this system worldwide, Mobility Lab is the most trusted wearable gait and balance
Foot mechanics & implications on training, posture and movement
 Foot mechanics & implications on training, posture and movement Three Arches Three Arches These arches are not reciprocal. When the foot pronates ALL arches should fall. If the medial arch falls and the
Foot mechanics & implications on training, posture and movement Three Arches Three Arches These arches are not reciprocal. When the foot pronates ALL arches should fall. If the medial arch falls and the
Ankle biomechanics demonstrates excessive and prolonged time to peak rearfoot eversion (see Foot Complex graph). We would not necessarily expect
 Case Study #1 The first case study is a runner presenting with bilateral shin splints with pain and tenderness along the medial aspect of the tibia. The symptoms have increased significantly over the last
Case Study #1 The first case study is a runner presenting with bilateral shin splints with pain and tenderness along the medial aspect of the tibia. The symptoms have increased significantly over the last
-Elastic strain energy (duty factor decreases at higher speeds). Higher forces act on feet. More tendon stretch. More energy stored in tendon.
 As velocity increases ( ) (i.e. increasing Froude number v 2 / gl) the component of the energy cost of transport associated with: -Internal kinetic energy (limbs accelerated to higher angular velocity).
As velocity increases ( ) (i.e. increasing Froude number v 2 / gl) the component of the energy cost of transport associated with: -Internal kinetic energy (limbs accelerated to higher angular velocity).
Gait analysis through sound
 Invited article Niigata Journal of Health and Welfare Vol. 15, No. 1 Gait analysis through sound Kaoru Abe Graduate School of Health and Welfare, Niigata University of Health and Welfare, Niigata, Japan
Invited article Niigata Journal of Health and Welfare Vol. 15, No. 1 Gait analysis through sound Kaoru Abe Graduate School of Health and Welfare, Niigata University of Health and Welfare, Niigata, Japan
Palacký Univerzity in Olomouc Faculty of Physical Culture
 Project: Sophisticated biomechanic diagnostics of human movement Registration number: CZ.1.07/2.3.00/09.0209 Palacký Univerzity in Olomouc Faculty of Physical Culture Tento projekt je spolufinancován Evropským
Project: Sophisticated biomechanic diagnostics of human movement Registration number: CZ.1.07/2.3.00/09.0209 Palacký Univerzity in Olomouc Faculty of Physical Culture Tento projekt je spolufinancován Evropským
Human Gait. 1 Exceptions include frogs and toads, who have biped gait, though it is unlike human gait
 Human Gait Kinesiology, as well as motion picture photography of human subjects at rest and in motion, is required for a detailed study and application of the knowledge of human gait. For an average clinician
Human Gait Kinesiology, as well as motion picture photography of human subjects at rest and in motion, is required for a detailed study and application of the knowledge of human gait. For an average clinician
video Outline Pre-requisites of Typical Gait Case Studies Case 1 L5 Myelomeningocele Case 1 L5 Myelomeningocele
 Outline Evaluation of Orthosis Function in Children with Neuromuscular Disorders Using Motion Analysis Outcomes Terminology Methods Typically developing Case examples variety of pathologies Sylvia Õunpuu,
Outline Evaluation of Orthosis Function in Children with Neuromuscular Disorders Using Motion Analysis Outcomes Terminology Methods Typically developing Case examples variety of pathologies Sylvia Õunpuu,
WalkOn product range. Dynamic Ankle-Foot Orthoses. Information for specialist dealers
 WalkOn product range Dynamic Ankle-Foot Orthoses Information for specialist dealers WalkOn Flex WalkOn WalkOn Trimable WalkOn Reaction WalkOn Reaction plus One range Many different applications The WalkOn
WalkOn product range Dynamic Ankle-Foot Orthoses Information for specialist dealers WalkOn Flex WalkOn WalkOn Trimable WalkOn Reaction WalkOn Reaction plus One range Many different applications The WalkOn
Joint session ESPRM/ESMAC/SIMFER/SIAMOC Study of the Movement in clinic of the Rehabilitation Venice 25 May 2010
 Joint session ESPRM/ESMAC/SIMFER/SIAMOC Study of the Movement in clinic of the Rehabilitation Venice 25 May 2010 Gait Analysis in the Rehabilitation field M.G. Benedetti MD LAM Movement Analysis Laboratory
Joint session ESPRM/ESMAC/SIMFER/SIAMOC Study of the Movement in clinic of the Rehabilitation Venice 25 May 2010 Gait Analysis in the Rehabilitation field M.G. Benedetti MD LAM Movement Analysis Laboratory
10/24/2016. The Puzzle of Pain NMT and the Dynamic Foot Judith DeLany, LMT. Judith DeLany, LMT. NMTCenter.com. NMTCenter.com
 The Puzzle of Pain NMT and the Dynamic Foot Judith DeLany, LMT NMTCenter.com Judith DeLany, LMT NMTCenter.com Define gait cycle and its periods Consider key elements in gait Discuss foot design Consequences
The Puzzle of Pain NMT and the Dynamic Foot Judith DeLany, LMT NMTCenter.com Judith DeLany, LMT NMTCenter.com Define gait cycle and its periods Consider key elements in gait Discuss foot design Consequences
WALKING AIDS AND GAIT TRAINING
 WALKING AIDS AND GAIT TRAINING By:Dr. Chaman Lal B.S.PT, DPT, Dip. in sports Injuries, MPPS(PAK), PG in Clinical Electroneurophysiology (AKUH), Registered.EEGT (USA), Member of ABRET, AANEM & ASET (USA).
WALKING AIDS AND GAIT TRAINING By:Dr. Chaman Lal B.S.PT, DPT, Dip. in sports Injuries, MPPS(PAK), PG in Clinical Electroneurophysiology (AKUH), Registered.EEGT (USA), Member of ABRET, AANEM & ASET (USA).
Coaching the Triple Jump Boo Schexnayder
 I. Understanding the Event A. The Run and Its Purpose B. Hip Undulation and the Phases C. Making the Connection II. III. IV. The Approach Run A. Phases B. Technical Features 1. Posture 2. Progressive Body
I. Understanding the Event A. The Run and Its Purpose B. Hip Undulation and the Phases C. Making the Connection II. III. IV. The Approach Run A. Phases B. Technical Features 1. Posture 2. Progressive Body
ANNEXURE II. Consent Form
 ANNEXURE II Consent Form I, voluntarily agree to participate in the research work entitled Gait Pattern in Post Stroke Hemiparetic Patients: Analysis and Correction. All my questions have been satisfactorily
ANNEXURE II Consent Form I, voluntarily agree to participate in the research work entitled Gait Pattern in Post Stroke Hemiparetic Patients: Analysis and Correction. All my questions have been satisfactorily
Positive running posture sums up the right technique for top speed
 Positive running, a model for high speed running Frans Bosch positive running posture sums up the right technique for top speed building blocks in running: Pelvic rotation for- and backward and hamstring
Positive running, a model for high speed running Frans Bosch positive running posture sums up the right technique for top speed building blocks in running: Pelvic rotation for- and backward and hamstring
Serve the only stroke in which the player has full control over its outcome. Bahamonde (2000) The higher the velocity, the smaller the margin of
 Lower Extremity Performance of Tennis Serve Reporter: Chin-Fu Hsu Adviser: Lin-Hwa Wang OUTLINE Introduction Kinetic Chain Serve Types Lower Extremity Movement Summary Future Work INTRODUCTION Serve the
Lower Extremity Performance of Tennis Serve Reporter: Chin-Fu Hsu Adviser: Lin-Hwa Wang OUTLINE Introduction Kinetic Chain Serve Types Lower Extremity Movement Summary Future Work INTRODUCTION Serve the
Athlete Profiling. Injury Prevention
 Athlete Profiling Injury Prevention Fraser McKinney Physiotherapist Special interest in: Basketball Athletics Race Walking Research Performance markers (screening / HR assessments / biomechanics) Athlete
Athlete Profiling Injury Prevention Fraser McKinney Physiotherapist Special interest in: Basketball Athletics Race Walking Research Performance markers (screening / HR assessments / biomechanics) Athlete
The technique of reciprocal walking using the hip guidance orthosis (hgo) with crutches
 The technique of reciprocal walking using the hip guidance orthosis (hgo) with crutches P. B. BUTLER, R. E. MAJOR and J. H. PATRICK Orthotic Research and Locomotor Assessment Unit, The Robert Jones and
The technique of reciprocal walking using the hip guidance orthosis (hgo) with crutches P. B. BUTLER, R. E. MAJOR and J. H. PATRICK Orthotic Research and Locomotor Assessment Unit, The Robert Jones and
Motor function analysis: from animal models to patients
 Motor function analysis: from animal models to patients ZNZ lecture 27.04.2016 Linard Filli Sensorimotor Lab University Hospital Zurich Linard.Filli@usz.ch Content of lecture Basic neuroanatomy of motor
Motor function analysis: from animal models to patients ZNZ lecture 27.04.2016 Linard Filli Sensorimotor Lab University Hospital Zurich Linard.Filli@usz.ch Content of lecture Basic neuroanatomy of motor
Running injuries - what are the most important factors
 Created as a free resource by Clinical Edge Based on Physio Edge podcast 59 with Greg Lehman, Tom Goom and Dr Christian Barton Get your free trial of online Physio education at Why do runners get injured?
Created as a free resource by Clinical Edge Based on Physio Edge podcast 59 with Greg Lehman, Tom Goom and Dr Christian Barton Get your free trial of online Physio education at Why do runners get injured?
EXSC 408L Fall '03 Problem Set #2 Linear Motion. Linear Motion
 Problems: 1. Once you have recorded the calibration frame for a data collection, why is it important to make sure the camera does not shut off? hat happens if the camera automatically shuts off after being
Problems: 1. Once you have recorded the calibration frame for a data collection, why is it important to make sure the camera does not shut off? hat happens if the camera automatically shuts off after being
GROUND REACTION FORCE DOMINANT VERSUS NON-DOMINANT SINGLE LEG STEP OFF
 GROUND REACTION FORCE DOMINANT VERSUS NON-DOMINANT SINGLE LEG STEP OFF Sara Gharabaghli, Rebecca Krogstad, Sara Lynch, Sofia Saavedra, and Tamara Wright California State University, San Marcos, San Marcos,
GROUND REACTION FORCE DOMINANT VERSUS NON-DOMINANT SINGLE LEG STEP OFF Sara Gharabaghli, Rebecca Krogstad, Sara Lynch, Sofia Saavedra, and Tamara Wright California State University, San Marcos, San Marcos,
Aeris Performance 2. Product Manual
 Aeris Performance 2 Product Manual Instructions The Aeris Performance 2 is designed to be maintenance free. The foot is water resistant; however, if the foot is submerged in water, the foot and foot shell
Aeris Performance 2 Product Manual Instructions The Aeris Performance 2 is designed to be maintenance free. The foot is water resistant; however, if the foot is submerged in water, the foot and foot shell
C-Brace Orthotronic Mobility System
 C-Brace Orthotronic Mobility System You ll always remember your first step Information for practitioners C-Brace Orthotics reinvented Until now, you and your patients with conditions like incomplete spinal
C-Brace Orthotronic Mobility System You ll always remember your first step Information for practitioners C-Brace Orthotics reinvented Until now, you and your patients with conditions like incomplete spinal
Does Ski Width Influence Muscle Action in an Elite Skier? A Case Study. Montana State University Movement Science Laboratory Bozeman, MT 59717
 Does Ski Width Influence Muscle Action in an Elite Skier? A Case Study John G. Seifert 1, Heidi Nunnikhoven 1, Cory Snyder 1, Ronald Kipp 2 1 Montana State University Movement Science Laboratory Bozeman,
Does Ski Width Influence Muscle Action in an Elite Skier? A Case Study John G. Seifert 1, Heidi Nunnikhoven 1, Cory Snyder 1, Ronald Kipp 2 1 Montana State University Movement Science Laboratory Bozeman,
Transformation of nonfunctional spinal circuits into functional states after the loss of brain input
 Transformation of nonfunctional spinal circuits into functional states after the loss of brain input G. Courtine, Y. P. Gerasimenko, R. van den Brand, A. Yew, P. Musienko, H. Zhong, B. Song, Y. Ao, R.
Transformation of nonfunctional spinal circuits into functional states after the loss of brain input G. Courtine, Y. P. Gerasimenko, R. van den Brand, A. Yew, P. Musienko, H. Zhong, B. Song, Y. Ao, R.
Axis of rotation is always perpendicular to the plane of movement
 Sports scientists and medical practitioners use formal terms to describe directionality, joint movement, and muscle movement. These universal terms let us use fewer words when describing movement, teaching,
Sports scientists and medical practitioners use formal terms to describe directionality, joint movement, and muscle movement. These universal terms let us use fewer words when describing movement, teaching,
The Lateralized Foot & Ankle Pattern and the Pronated Left Chest
 The Lateralized Foot & Ankle Pattern and the Pronated Left Chest Presented by: James Anderson, MPT, PRC Director of Affiliate Programs, Faculty & Board of Certification Postural Restoration Institute Pronate
The Lateralized Foot & Ankle Pattern and the Pronated Left Chest Presented by: James Anderson, MPT, PRC Director of Affiliate Programs, Faculty & Board of Certification Postural Restoration Institute Pronate
Posture influences ground reaction force: implications for crouch gait
 University of Tennessee, Knoxville From the SelectedWorks of Jeffrey A. Reinbolt July 14, 2010 Posture influences ground reaction force: implications for crouch gait H. X. Hoang Jeffrey A. Reinbolt, University
University of Tennessee, Knoxville From the SelectedWorks of Jeffrey A. Reinbolt July 14, 2010 Posture influences ground reaction force: implications for crouch gait H. X. Hoang Jeffrey A. Reinbolt, University
An investigation of kinematic and kinetic variables for the description of prosthetic gait using the ENOCH system
 An investigation of kinematic and kinetic variables for the description of prosthetic gait using the ENOCH system K. OBERG and H. LANSHAMMAR* Amputee Training and Research Unit, University Hospital, Fack,
An investigation of kinematic and kinetic variables for the description of prosthetic gait using the ENOCH system K. OBERG and H. LANSHAMMAR* Amputee Training and Research Unit, University Hospital, Fack,
Supplementary Figure S1
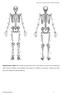 Supplementary Figure S1: Anterior and posterior views of the marker set used in the running gait trials. Forty-six markers were attached to the subject (15 markers on each leg, 4 markers on each arm, and
Supplementary Figure S1: Anterior and posterior views of the marker set used in the running gait trials. Forty-six markers were attached to the subject (15 markers on each leg, 4 markers on each arm, and
Biomechanics and Models of Locomotion
 Physics-Based Models for People Tracking: Biomechanics and Models of Locomotion Marcus Brubaker 1 Leonid Sigal 1,2 David J Fleet 1 1 University of Toronto 2 Disney Research, Pittsburgh Biomechanics Biomechanics
Physics-Based Models for People Tracking: Biomechanics and Models of Locomotion Marcus Brubaker 1 Leonid Sigal 1,2 David J Fleet 1 1 University of Toronto 2 Disney Research, Pittsburgh Biomechanics Biomechanics
Element DS. Product Manual
 Element DS Product Manual Instructions The Element DS is designed to be maintenance free. The foot is water resistant; however, if the foot is submerged in water, the foot and foot shell should be rinsed
Element DS Product Manual Instructions The Element DS is designed to be maintenance free. The foot is water resistant; however, if the foot is submerged in water, the foot and foot shell should be rinsed
Normal Gait Smooth, rhythmic, efficient Gait cycle consists of one stride by each leg In normal walking, one foot is always on ground
 Normal Gait Smooth, rhythmic, efficient Gait cycle consists of one stride by each leg In normal walking, one foot is always on ground (running both feet leave ground) Gait Cycle Maturation of Gait Small
Normal Gait Smooth, rhythmic, efficient Gait cycle consists of one stride by each leg In normal walking, one foot is always on ground (running both feet leave ground) Gait Cycle Maturation of Gait Small
Comparison of Kinematics and Kinetics During Drop and Drop Jump Performance
 schouweiler, hess UW-L Journal of Undergraduate Research XIII (21) Comparison of Kinematics and Kinetics During Drop and Drop Jump Performance Ryan Schouweiler, Karina Hess Faculty Sponsor: Thomas Kernozek,
schouweiler, hess UW-L Journal of Undergraduate Research XIII (21) Comparison of Kinematics and Kinetics During Drop and Drop Jump Performance Ryan Schouweiler, Karina Hess Faculty Sponsor: Thomas Kernozek,
Gait Lab Testing and Treatment Planning in Brain Injury Grant E. Myers, PT, DPT, CSCS. Gait Lab Testing and Treatment Planning in Brain Injury
 Gait Lab Testing and Treatment Planning in Brain Injury What do we associate this technology with? Movies Avatar Grant Myers PT, DPT, CSCS, CMP Gait Laboratory Services Scripps Memorial Hospital Encinitas
Gait Lab Testing and Treatment Planning in Brain Injury What do we associate this technology with? Movies Avatar Grant Myers PT, DPT, CSCS, CMP Gait Laboratory Services Scripps Memorial Hospital Encinitas
GAIT ANALYSIS IN CEREBRAL PALSY USING VICON SYSTEM
 Proceedings in Manufacturing Systems, Volume 7, Issue 2, 2012 ISSN 2067-9238 GAIT ANALYSIS IN CEREBRAL PALSY USING VICON SYSTEM Raluca Dana TUGUI 1,*, Dinu ANTONESCU 2, Mircea Iulian NISTOR 3, Doina BUCUR
Proceedings in Manufacturing Systems, Volume 7, Issue 2, 2012 ISSN 2067-9238 GAIT ANALYSIS IN CEREBRAL PALSY USING VICON SYSTEM Raluca Dana TUGUI 1,*, Dinu ANTONESCU 2, Mircea Iulian NISTOR 3, Doina BUCUR
Increasing ankle push-off work with a powered prosthesis does not necessarily reduce metabolic rate for transtibial amputees
 Supplementary Materials Increasing ankle push-off work with a powered prosthesis does not necessarily reduce metabolic rate for transtibial amputees Roberto E. Quesada, Joshua M. Caputo,, and Steven H.
Supplementary Materials Increasing ankle push-off work with a powered prosthesis does not necessarily reduce metabolic rate for transtibial amputees Roberto E. Quesada, Joshua M. Caputo,, and Steven H.
WORKBOOK/MUSTANG. Featuring: The R82 Next Step Development Plan. mustang. R82 Education
 WORKBOOK/MUSTANG Featuring: The R82 Next Step Development Plan mustang R82 Education CLINICAL WORK BOOK/MUSTANG PAGE 2 PAGE 3 What is Mustang? Mustang is a highly adaptable walking aid for children and
WORKBOOK/MUSTANG Featuring: The R82 Next Step Development Plan mustang R82 Education CLINICAL WORK BOOK/MUSTANG PAGE 2 PAGE 3 What is Mustang? Mustang is a highly adaptable walking aid for children and
Running Injuries in Adolescents Jeffrey Shilt, M.D. Part 1 Page 1
 Running Injuries in Adolescents Jeffrey Shilt, M.D. Chief Surgical Officer, The Woodlands, Texas Children's Hospital Associate Professor, Orthopedic and Scoliosis Surgery, Baylor College of Medicine Part
Running Injuries in Adolescents Jeffrey Shilt, M.D. Chief Surgical Officer, The Woodlands, Texas Children's Hospital Associate Professor, Orthopedic and Scoliosis Surgery, Baylor College of Medicine Part
ScienceDirect. Improvement of three-dimensional motion analyzer system for the development of Indonesian gait database
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Manufacturing 2 (2015 ) 268 274 2nd International Materials, Industrial, and Manufacturing Engineering Conference, MIMEC2015, 4-6 February
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Manufacturing 2 (2015 ) 268 274 2nd International Materials, Industrial, and Manufacturing Engineering Conference, MIMEC2015, 4-6 February
The motion axis of the ankle joint forms an angle of 80 with the horizontal plane and 15 to 20 with the frontal plane.
 The foot is connected to the leg in the ankle joint. The ankle joint is a single-axle hinge-joint. Its motion axis is essentially a straight line connecting the peaks of the medial and lateral malleus.
The foot is connected to the leg in the ankle joint. The ankle joint is a single-axle hinge-joint. Its motion axis is essentially a straight line connecting the peaks of the medial and lateral malleus.
A7HLE71CO PHYSICAL THERAPY
 I A7HLE71CO Runner's Video Gait Analysis Matthew Wolin, 12/4/2018 Footwear: Altra Torin 3.0 Treadmill speed: 7.0 mph VGA Analyst: Chris Jensen, PT, MPT, OCS, CKPT POSTERIOR VIEW FINDINGS: (mid-stance)..
I A7HLE71CO Runner's Video Gait Analysis Matthew Wolin, 12/4/2018 Footwear: Altra Torin 3.0 Treadmill speed: 7.0 mph VGA Analyst: Chris Jensen, PT, MPT, OCS, CKPT POSTERIOR VIEW FINDINGS: (mid-stance)..
AEROBIC GYMNASTICS Code of Points APPENDIX II Guide to Judging Execution and Difficulty
 FÉDÉRATION INTERNATIONALE DE GYMNASTIQUE FONDÉE EN 1881 AEROBIC GYMNASTICS Code of Points 2009 2012 DRAFT OCTOBER 2008 APPENDIX II Guide to Judging Execution and Difficulty Page 1 of 80 INTRODUCTION This
FÉDÉRATION INTERNATIONALE DE GYMNASTIQUE FONDÉE EN 1881 AEROBIC GYMNASTICS Code of Points 2009 2012 DRAFT OCTOBER 2008 APPENDIX II Guide to Judging Execution and Difficulty Page 1 of 80 INTRODUCTION This
AllPro Foot. Posterior Mount Product Manual
 AllPro Foot Posterior Mount Product Manual Instructions The AllPro PM foot system has been designed and manufactured for specific patient weights. Failure to follow the weight guidelines and/or overload
AllPro Foot Posterior Mount Product Manual Instructions The AllPro PM foot system has been designed and manufactured for specific patient weights. Failure to follow the weight guidelines and/or overload
Performance of three walking orthoses for the paralysed: a case study using gait analysis
 Prosthetics and Orthotics International, 1990, 14, 103 110 Performance of three walking orthoses for the paralysed: a case study using gait analysis R. J. JEFFERSON and M. W. WHITTLE Oxford Orthopaedic
Prosthetics and Orthotics International, 1990, 14, 103 110 Performance of three walking orthoses for the paralysed: a case study using gait analysis R. J. JEFFERSON and M. W. WHITTLE Oxford Orthopaedic
Equine Cannon Angle System
 Equine Cannon System How to interpret the results December 2010 Page 1 of 14 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 The Sagittal Plane... 4 The Coronal Plane... 5 Results Format... 6 How to Interpret the
Equine Cannon System How to interpret the results December 2010 Page 1 of 14 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 The Sagittal Plane... 4 The Coronal Plane... 5 Results Format... 6 How to Interpret the
Aeris Activity. Product Manual
 Aeris Activity Product Manual Instructions The Aeris Activity Foot System has been designed and manufactured for specific patient weights. Failure to follow the weight guidelines and/or overload conditions
Aeris Activity Product Manual Instructions The Aeris Activity Foot System has been designed and manufactured for specific patient weights. Failure to follow the weight guidelines and/or overload conditions
Running from injury 2
 Created as a free resource by Clinical Edge Based on Physio Edge podcast 049 with Dr Rich Willy Get your free trial of online Physio education by clicking here Running injuries & assessment Running assessment
Created as a free resource by Clinical Edge Based on Physio Edge podcast 049 with Dr Rich Willy Get your free trial of online Physio education by clicking here Running injuries & assessment Running assessment
EDUCATION COURSES. Stride. Initial Swing (high knee) Mid stance Toe off Mid swing Initial contact
 EDUCATION COURSES RUNNING ANALYSIS Our purpose is performance enhancement. Improving speed and acceleration is the key to success in most ground-based sports. The ability to run from 0-5-10-20m as fast
EDUCATION COURSES RUNNING ANALYSIS Our purpose is performance enhancement. Improving speed and acceleration is the key to success in most ground-based sports. The ability to run from 0-5-10-20m as fast
A Functional Approach to Improving Ankle Dorsiflexion. Knock on Effects
 Keith Thornhill PT A Functional Approach to Improving Ankle Dorsiflexion Today's article is a guest post from Keith Thornhill, current team physiotherapist at Munster Rugby (Ireland). In my experience
Keith Thornhill PT A Functional Approach to Improving Ankle Dorsiflexion Today's article is a guest post from Keith Thornhill, current team physiotherapist at Munster Rugby (Ireland). In my experience
Biomechanical Analysis of Race Walking Compared to Normal Walking and Running Gait
 University of Kentucky UKnowledge Theses and Dissertations--Kinesiology and Health Promotion Kinesiology and Health Promotion 2015 Biomechanical Analysis of Race Walking Compared to Normal Walking and
University of Kentucky UKnowledge Theses and Dissertations--Kinesiology and Health Promotion Kinesiology and Health Promotion 2015 Biomechanical Analysis of Race Walking Compared to Normal Walking and
Coaching the Hurdles
 Coaching the Hurdles Monica Gary, Sprints & Hurdles Coach Purdue University Important components to consider in hurdle training: a. Rhythm for the hurdler is the primary concern for the coach -short rhythm
Coaching the Hurdles Monica Gary, Sprints & Hurdles Coach Purdue University Important components to consider in hurdle training: a. Rhythm for the hurdler is the primary concern for the coach -short rhythm
The importance of physical activity throughout an individual's life is indisputable. As healthcare
 What to Expect When They re Expecting: A Look at Biomechanical Changes in Walking/Running During Pregnancy Jennifer Bruer-Vandeweert, Megan Hotchkiss, Jamie Kronenberg, Kristin Olson Dr. Rumit Singh Kakar,
What to Expect When They re Expecting: A Look at Biomechanical Changes in Walking/Running During Pregnancy Jennifer Bruer-Vandeweert, Megan Hotchkiss, Jamie Kronenberg, Kristin Olson Dr. Rumit Singh Kakar,
KICKBIKE Your key to optimum sports performance
 KICKBIKE Your key to optimum sports performance Efficient Running is essential to optimum performance of most sports we play. Whether we want to maximize our speed, maximize our endurance, or both, an
KICKBIKE Your key to optimum sports performance Efficient Running is essential to optimum performance of most sports we play. Whether we want to maximize our speed, maximize our endurance, or both, an
Kinetic chain checkpoints
 Kinetic chain checkpoints Observations: Foot/ankle Knee Lumbo-Pelvic-Hip-Complex (LPHC) Shoulder and Cervical Spine (upper body) Each joint region has a specific and optimal motion based on its structure
Kinetic chain checkpoints Observations: Foot/ankle Knee Lumbo-Pelvic-Hip-Complex (LPHC) Shoulder and Cervical Spine (upper body) Each joint region has a specific and optimal motion based on its structure
Complex movement patterns of a bipedal walk
 1 Complex movement patterns of a bipedal walk Objectives After completing this lesson, you will be able to: Describe the complex movement patterns of a bipedal walk. Describe the biomechanics of walking
1 Complex movement patterns of a bipedal walk Objectives After completing this lesson, you will be able to: Describe the complex movement patterns of a bipedal walk. Describe the biomechanics of walking
SCHEINWORKS Measuring and Analysis Systems by
 Pressure Measurement Systems for standing and walking analysis Germany since 1879 Pressure Measurement Systems for standing and walking analysis Documentation of Gait image Stance Symmetry of all parameters
Pressure Measurement Systems for standing and walking analysis Germany since 1879 Pressure Measurement Systems for standing and walking analysis Documentation of Gait image Stance Symmetry of all parameters
NeuroOrthopaedics lower extremity
 NeuroOrthopaedics lower extremity Medical devices for drop foot Information for technicians and therapists NeuroOrthopaedics lower extremity Ottobock 1 The right device for every user Around the world,
NeuroOrthopaedics lower extremity Medical devices for drop foot Information for technicians and therapists NeuroOrthopaedics lower extremity Ottobock 1 The right device for every user Around the world,
Clinical view on ambulation in patients with Spinal Cord Injury
 Clinical view on ambulation in patients with Spinal Cord Injury Sasa Moslavac Spinal Unit, Special Medical Rehabilitation Hospital, Varazdinske Toplice,, Croatia 1 Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) to walk again
Clinical view on ambulation in patients with Spinal Cord Injury Sasa Moslavac Spinal Unit, Special Medical Rehabilitation Hospital, Varazdinske Toplice,, Croatia 1 Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) to walk again
Analysis of Gait Characteristics Changes in Normal Walking and Fast Walking Of the Elderly People
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 08, Issue 7 (July. 2018), V (V) 34-41 www.iosrjen.org Analysis of Gait Characteristics Changes in and Of the Elderly
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 08, Issue 7 (July. 2018), V (V) 34-41 www.iosrjen.org Analysis of Gait Characteristics Changes in and Of the Elderly
ABCA Research Committee
 ABCA Research Committee Title: What the Best in Baseball Do A longitudinal / cross-sectional biomechanical study of the best hitters and pitchers in the game of baseball. Purpose: The purpose of this study
ABCA Research Committee Title: What the Best in Baseball Do A longitudinal / cross-sectional biomechanical study of the best hitters and pitchers in the game of baseball. Purpose: The purpose of this study
Brief Biomechanical Analysis on the Walking of Spinal Cord Injury Patients with a Lower Limb Exoskeleton Robot
 13 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics June 24-26, 13 Seattle, Washington USA Brief Biomechanical Analysis on the Walking of Spinal Cord Injury Patients with a Lower Limb Exoskeleton
13 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics June 24-26, 13 Seattle, Washington USA Brief Biomechanical Analysis on the Walking of Spinal Cord Injury Patients with a Lower Limb Exoskeleton
Dynamic Warm up. the age of the athlete current physical condition and prior exercise experience
 Dynamic Warm up 10-20 minutes May be dependent on: the age of the athlete current physical condition and prior exercise experience Prepares the body for the demands of a work out or practice Increases
Dynamic Warm up 10-20 minutes May be dependent on: the age of the athlete current physical condition and prior exercise experience Prepares the body for the demands of a work out or practice Increases
The Influence of Load Carrying Modes on Gait variables of Healthy Indian Women
 The Influence of Load Carrying Modes on Gait variables of Healthy Indian Women *Guha Thakurta A, Iqbal R and De A National Institute of Industrial Engineering, Powai, Vihar Lake, Mumbai-400087, India,
The Influence of Load Carrying Modes on Gait variables of Healthy Indian Women *Guha Thakurta A, Iqbal R and De A National Institute of Industrial Engineering, Powai, Vihar Lake, Mumbai-400087, India,
Steffen Willwacher, Katina Fischer, Gert Peter Brüggemann Institute of Biomechanics and Orthopaedics, German Sport University, Cologne, Germany
 P01-3 ID126 SURFACE STIFFNESS AFFECTS JOINT LOADING IN RUNNING Steffen Willwacher, Katina Fischer, Gert Peter Brüggemann Institute of Biomechanics and Orthopaedics, German Sport University, Cologne, Germany
P01-3 ID126 SURFACE STIFFNESS AFFECTS JOINT LOADING IN RUNNING Steffen Willwacher, Katina Fischer, Gert Peter Brüggemann Institute of Biomechanics and Orthopaedics, German Sport University, Cologne, Germany
Lumbar Decompression Surgery: Correction of foot drop
 Lumbar Decompression Surgery: Correction of foot drop By Rebecca Marshall Specialist Physiotherapist FES service Mobility and Specialised Rehabilitation Centre Sheffield December 2017 Talk Content History/clinical
Lumbar Decompression Surgery: Correction of foot drop By Rebecca Marshall Specialist Physiotherapist FES service Mobility and Specialised Rehabilitation Centre Sheffield December 2017 Talk Content History/clinical
Stability Trainer. New! Balance Products. Rocker and Wobble Boards. New!
 New! Stability Trainer Balance Products Rocker and Wobble Boards New! www.thera-band.com Rocker and Wobble Boards The Hygenic Corporation 1245 Home Avenue, Akron, Ohio 44310 USA 330.633.8460 1.800.321.2135
New! Stability Trainer Balance Products Rocker and Wobble Boards New! www.thera-band.com Rocker and Wobble Boards The Hygenic Corporation 1245 Home Avenue, Akron, Ohio 44310 USA 330.633.8460 1.800.321.2135
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF EXOSKELETON FOR ANKLE AND KNEE JOINT
 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF EXOSKELETON FOR ANKLE AND KNEE JOINT PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S0925 COLLEGE : NEW HORIZON COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, BANGALORE BRANCH : MECHANICAL ENGINEERING GUIDES : DR GANESHA PRASAD
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF EXOSKELETON FOR ANKLE AND KNEE JOINT PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S0925 COLLEGE : NEW HORIZON COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, BANGALORE BRANCH : MECHANICAL ENGINEERING GUIDES : DR GANESHA PRASAD
A bit of background. Session Schedule 3:00-3:10: Introduction & session overview. Overarching research theme: CPTA
 A Cognitive-Biomechanical Perspective for the Management of Common Chronic Musculoskeletal Conditions Skulpan Asavasopon, PT, PhD Loma Linda University Christopher M. Powers, PT, PhD, FAPTA University
A Cognitive-Biomechanical Perspective for the Management of Common Chronic Musculoskeletal Conditions Skulpan Asavasopon, PT, PhD Loma Linda University Christopher M. Powers, PT, PhD, FAPTA University
Quantification and localization of gait variability as biomarkers for mild traumatic brain injury
 University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations Summer 21 Quantification and localization of gait variability as biomarkers for mild traumatic brain injury Rosalind Lauren Smith University
University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations Summer 21 Quantification and localization of gait variability as biomarkers for mild traumatic brain injury Rosalind Lauren Smith University
GCD Variables. Steps and Strides. Walking Speed. Cadence. Stride Length
 Variables Steps and Strides Each time a leg goes forward, it makes a step the right leg moves forward to make a right step and then the left leg moved forward for a left step. When a right and left step
Variables Steps and Strides Each time a leg goes forward, it makes a step the right leg moves forward to make a right step and then the left leg moved forward for a left step. When a right and left step
1B1 Meridium. Reclaim your way. Information for practitioners. Meridium Ottobock 1
 1B1 Meridium Reclaim your way. Information for practitioners Meridium Ottobock 1 Reclaim your way. With the development of the individualized Meridium prosthetic foot, Ottobock has incorporated the latest
1B1 Meridium Reclaim your way. Information for practitioners Meridium Ottobock 1 Reclaim your way. With the development of the individualized Meridium prosthetic foot, Ottobock has incorporated the latest
Secondary gait compensations in individuals without neuromuscular involvement following a unilateral imposed equinus constraint
 Gait and Posture 20 (2004) 238 244 Secondary gait compensations in individuals without neuromuscular involvement following a unilateral imposed equinus constraint Michael J. Goodman a, Jason L. Menown
Gait and Posture 20 (2004) 238 244 Secondary gait compensations in individuals without neuromuscular involvement following a unilateral imposed equinus constraint Michael J. Goodman a, Jason L. Menown
+ t1 t2 moment-time curves
 Part 6 - Angular Kinematics / Angular Impulse 1. While jumping over a hurdle, an athlete s hip angle was measured to be 2.41 radians. Within 0.15 seconds, the hurdler s hip angle changed to be 3.29 radians.
Part 6 - Angular Kinematics / Angular Impulse 1. While jumping over a hurdle, an athlete s hip angle was measured to be 2.41 radians. Within 0.15 seconds, the hurdler s hip angle changed to be 3.29 radians.
Alignment & Stance in High Performance Skiing
 Alignment & Stance in High Performance Skiing Ron LeMaster Ron LeMaster What I ve Learned in 10 Years A lot! Good alignment is not well defined Alignment and stance are the subjects of many technical misconceptions
Alignment & Stance in High Performance Skiing Ron LeMaster Ron LeMaster What I ve Learned in 10 Years A lot! Good alignment is not well defined Alignment and stance are the subjects of many technical misconceptions
GAITS (AN AUGENBLICK APPROACH)
 1 4:15-5:30 PM Abnormal Gaits: An Eyeblink Diagnosis SPEAKER Salvatore Mangione, MD Disclosures The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Salvatore Mangione, MD: No financial relationships
1 4:15-5:30 PM Abnormal Gaits: An Eyeblink Diagnosis SPEAKER Salvatore Mangione, MD Disclosures The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Salvatore Mangione, MD: No financial relationships
Current issues regarding induced acceleration analysis of walking using the integration method to decompose the GRF
 Current issues regarding induced acceleration analysis of walking using the integration method to decompose the GRF George Chen May 17, 2002 Stanford Neuromuscular Biomechanics Lab Group Muscle contribution
Current issues regarding induced acceleration analysis of walking using the integration method to decompose the GRF George Chen May 17, 2002 Stanford Neuromuscular Biomechanics Lab Group Muscle contribution
Structure (Down plane)
 By Lauren Russell Structure (Down plane) The body (toes, knees, hips, wrists and shoulders) is aligned parallel to the intended target line. The torso is tilted over the ball from the hips whilst maintaining
By Lauren Russell Structure (Down plane) The body (toes, knees, hips, wrists and shoulders) is aligned parallel to the intended target line. The torso is tilted over the ball from the hips whilst maintaining
ITF Coaches Education Programme Coaching High Performance Players Course Power and the Tennis Serve.
 ITF Coaches Education Programme Coaching High Performance Players Course Power and the Tennis Serve. By Machar Reid & Miguel Crespo A Powerful Serve A Key Ingredient of Successful Tennis Performance Preparation
ITF Coaches Education Programme Coaching High Performance Players Course Power and the Tennis Serve. By Machar Reid & Miguel Crespo A Powerful Serve A Key Ingredient of Successful Tennis Performance Preparation
The Promise of Achieving Higher Standards in Children s Health. The Gait and Motion Analysis Laboratory Referral Guide
 The Promise of Achieving Higher Standards in Children s Health Nemours/Alfred I. dupont Hospital for Children has consistently been ranked among the best in the nation for pediatric orthopedics by U.S
The Promise of Achieving Higher Standards in Children s Health Nemours/Alfred I. dupont Hospital for Children has consistently been ranked among the best in the nation for pediatric orthopedics by U.S
Walking Tall - What Your Client's Gait Can
 Session # 488 Walking Tall - What Your Client's Gait Can Tell You Before They Even Speak! Presented by, CHEK Faculty What is Gait? Gait is the scientific term that describes walking. Also one of the seven
Session # 488 Walking Tall - What Your Client's Gait Can Tell You Before They Even Speak! Presented by, CHEK Faculty What is Gait? Gait is the scientific term that describes walking. Also one of the seven
