CRG(13)7. UK Lung DCD Retrieval Protocol
|
|
|
- Tyler Arthur Lester
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UK Lung DCD Retrieval Protocol Background In 2010 more than a third of all deceased organ donors in the UK were DCD donors. The lung is eminently suited to DCD retrieval because of its relative tolerance to warm ischaemia and the potential avoidance of some of the deleterious effects of brain stem death. Accepting a possible publication bias, the reported outcomes after lung transplant from DCD donors are at least as good, and possibly better, than for DBD donors. In some European countries, notably the Netherlands, with high rates of DCD donation, these donors contribute up to a third of all lung transplants. But in the UK, they comprise less than 10% of lung transplants. Many of the controversies surrounding DCD donation were resolved in the combined ICS and BTS document Donation after Circulatory Death sponsored by the Department of Health and NHSBT. But there remain differences, particularly with regard to the retrieval process, and post-mortem lung inflation and ventilation. On the transplant side, there is confusion over acceptance criteria and allocation policies. Retrieval team availability is sometimes patchy and one centre does not have DCD retrieval capability. This was recognised at CTAG in autumn of 2010, and a working group, consisting of Karen Redmond, John Dunning, Ali Machaal, Jorge Mascaro, and chaired by John Dark, was established. Its remit included defining acceptance criteria and contraindications, proposing an allocation algorithm and developing guidelines for the actual retrieval. The aim was to construct a working document, congruent with the other publications in the field, which would accelerate use of DCD lungs for transplant. At the same time an audit of DCD lung Tx Activity was carried out by NHSBT, with particular regard to the reasons for non-use. Acceptance Criteria All donors <65 who do not have any of the contraindications listed below: Absolute contraindications to retrieval agreed for all organs Active invasive cancer in the last 3 years excluding non-melanoma skin cancer and primary brain tumour Haematological malignancy myeloma, lymphoma, leukaemia Untreated systemic infection Variant CJD HIV disease (but not HIV infection) Absolute contraindications to retrieval for lung Chest trauma with extensive bilateral lung contusions Convincing radiological evidence of bilateral pneumonic consolidation Pre-existing structural lung changes (e.g. emphysematous or multiple large bullae) Previous complex intra-pleural thoracic surgery or dense adhesions prohibiting safe procurement Bronchoscopy (if available) showing inflammation/soiling of the airway, and recurrent secretions in the distal airway after adequate toilet Sustained peak airway pressure > 30 cmh2o Note: The decision with regard to EVLP is taken by the implanting centre, not by the offering SN-OD or the retrieving centre. If EVLP is not being considered, the following requirements are required: Systemic arterial PO2> 40 kpa on 100% FiO2 and 5 cmh2o PEEP, or equivalent FiO2:PaO2 within 12 hours Bronchoscopy (if available, see below) no severe inflammation of the airway, or recurrent secretions in the distal airway after adequate toilet.
2 These criteria are consistent with Organ Donation after Circulatory Death and with the DEVELOP- UK protocol Information on Referral Organ Donation after Circulatory Death specified that Donor assessment and recipient identification rely in part on a series of blood tests. It is both acceptable and lawful for samples of blood to be taken from the donor to allow these various tests to be carried out (including FBC, U/E, LFT, blood gases, virology screening, HLA-typing, and blood group) and this should be done as soon as possible to minimise delays. It is vital that all blood samples are correctly and fully labelled, particularly if they are to be sent for analysis in laboratories other than those of the donor hospital For lung donation, we consider that the following information additional to that determining suitability is available on offer Age Sex Height Blood group HLA Tissue Type* Serological result for HIV, HBV, HCV* *or the time this will be available is stated The following information to determine the likelihood of death occurring: primary diagnosis and past medical history The use and dose of inotropes Presence of a gag reflex Presence of a cough reflex Respiratory rate when disconnected from the ventilator The fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2) Arterial oxygen saturation and ph Ventilation mode Planned time of withdrawal of treatment Planned mode of withdrawal of treatment ie extubation, reduction of inotropes The following should also be available, but with varying detail Arterial blood gases, ideally on 100% and PEEP 5 cm H20. Not all ITU s will report this, but the ABG and FIO2 of the last blood gas, within less than 12 hours of retrieval, should be available Chest X-ray; within 24 hours of retrieval. Chest X-ray report (on the basis of which some of the contraindications, ie extensive bilateral lower lobe consolidation) should be available Bronchoscopy; the consensus document states Bronchoscopy to assess the potential for lung donation may be appropriate, if it does not cause the patient distress. This needs specific discussion with the patient s family. Bronchoscopy should be requested as a routine, although there is no obligation for the ITU to carry this out. There is no need for gram staining of tracheal or central airway secretions. Allocation Time may be limited, and organs are being lost because of delays in allocation. The consensus document states: At present most organs are offered to transplant centres sequentially rather than simultaneously. This can result in considerable delays that place an intolerable and unnecessary burden on referring units and donor families.
3 Simultaneous offering to all relevant centres would reduce these delays significantly, and must be addressed by NHSBT as a matter of urgency The simplest routine is to use current Zones (on the basis that all teams can retrieve and assess DCD lungs). The Zonal centre has primacy of use, but a provisional offer is made by NHSBT Duty Office to all the other 4 centres simultaneously. It was agreed at CTAG that offers will be made according to the regular sequence, at 5 minute intervals. Offering simultaneously can only be done by fax, which is not satisfactory. If the primary zonal centre does not accept the organs, allocation will go according to the sequence at that time. But all centres will be expected to give a yes or no answer to the provisional offer. We did not discuss the time allowed; this is a detail to be worked out If the zonal centre turns down the organ, as long as there is no contraindication, the decision to proceed falls on the accepting centre Process of Retrieval The Donor ITU team The retrieval team and the SN-OD are not involved in any way with the management of the donor, so there is a reliance on the donor ITU team. Ventilator management should be with a lung-protective regime, 5-6 ml/kg tidal volume and PEEP of 8cm H2o In an ideal situation, there will have been a bronchoscopy, with report of state of airway mucosa and secretions, recent ABG s and a chest X-ray within 12 hours. A nasogastric tube should be placed unless there is likliehood of distress to the donor A suitably experienced clinician will be available throughout the process of withdrawal of treatment, and will be responsible for confirming death promptly when it occurs. This individual may agree to re-intubate the donor after death (if there has been extubation). The donor hospital team should have a robust protocol in this regard. The situation with regard to re-intubation by the donor hospital team must be ascertained before the Retrieval team leave their base. If the donor hospital team will not reintubate the donor, the retrieval team MUST include someone appropriately skilled. The Retrieval Team Withdrawal of treatment may take place in A&E, ITU, an anaesthetic room or an operating theatre. The team should be present in or adjacent to the operating theatre to be used for the retrieval surgery. They should not be in the same room as the donor until 5 minutes after asystole and after certification of death. The local arrangements with the SN-OD with regard to withdrawal of treatment, the presence of the family, time to arrival in the operating room and personnel to re-intubate should be confirmed. Potential difficulties with intubation should be identified at this stage. The Retrieval surgeon should check the consent, height & weight, X-ray chest, blood group and virology of donor and Complete National Transplant Database Form A discussion should take place with the abdominal retrieval team with regard to how the surgery should be planned. It must be recognised that the greatest urgency for the abdominal team is cannulation and cooling of the abdominal organs. The focus for the Thoracic team is protection of the airway and inflation of the lungs. The two teams must agree details such as when the chest is opened and when the thoracic team will inspect and cannulate the lungs. The need for rapid cooling of the abdominal organs must be recognised
4 If possible, discussions should be held with the donor team about the use of the operating theatre anaesthetic machine to deliver continuous PEEP After withdrawal of treatment, maintain regular contact with the SN-OD with regard to the haemodynamics and saturations on the donor. If cardiac arrest does not occur within 120 minutes, the situation should be discussed with the implanting team. A decision may be made to abandon the retrieval at this stage if the donor is stable The point at which systolic blood pressure falls below 50 mmhg, or the saturations fall below 70% should be noted. If more than an hour passes with pressure and saturation at this level there is concern about warm ischaemia and the retrieval should be abandoned. A warm ischaemia time of more than 30 minutes is an indication for the use of EVLP After cardiac arrest: The time of death must be noted On arrival in the operating theatre, the donor should be reintubated with a cuffed endotracheal tube; this may be preceded by a rigid bronchoscopy, depending on the skills available. Intra-abdominal manipulation may cause aspiration, so early protection of the airway is important. Thorough airway toilet should be performed as soon as possible. Once reintubated, atelectatic lung may be recruited with a single breath, perhaps 30-40mmHg pressure for 40 seconds, ideally using the anaesthetic machine CPAP should be maintained at 5 cm H2O and continuous O2, once again ideally with the theatre anaesthetic machine Cyclical ventilation must not be used at this stage. Once the chest is open, and spontaneous cardiac contraction is impossible, further single recruitment manoeuvres may be required, at the direction of the retrieval surgeon. The time of lung inflation should be noted. Warm ischaemia is lessened at this stage, but many teams feel that early flushing of the lungs is still important, so the chest is rapidly opened. The lungs are examined for collapse, consolidation, mass lesions and pleural adhesions. If there is a suspicion of airways disease, the degree of collapse when the lungs are disconnected should be noted The pulmonary artery is cannulated (and the right ventricle may be opened to remove clot) Antegrade perfusion is started with 1 litre of warm (room temperature) perfadex. The left atrium is widely opened and clot washed out of the pulmonary veins At this stage, distribution of perfusate is aided by gentle cyclical ventilation of the lungs When the antegrade perfusion is complete, the pulmonary veins are gently cannulated for retrograde perfusion, ml down each one, until the effluent from the PA is clear. The lungs are best removed collapsed. When only the trachea is intact, the lungs are cautiously reinflated prior to storage. If EVLP is to be used, ensure there is at least 10cm of trachea. After removal, the lungs are again examined. Information about the degree of inflation, the collapse test, any areas of consolidation or masses, clot in the pulmonary artery, the uniformity of flushing and any palpable oedema will be required by the implanting team. This must be communicated in a timely manner; the decision to proceed to direct transplant, to EVLP, or to abandon the retrieval is based on this The lungs are packed as for a standard retrieval, with the routine blood specimens and paperwork Note: It has been agreed that the lungs will not be reinflated until 10 minutes has elapsed since the time of death, to avoid any chance of auto-resucitation. Similarly, cyclical ventilation will not be used until the left atrium is open and there is no longer any chance of cardiac activity
5 Normothermic Regional Perfusion (NRP) A number of liver teams have introduced perfusion of the abdominal organs with oxygenated blood, using an ECMO-like circuit, in category lll and IV DCD donors. This approach may reduce liver ischaemia, and give an opportunity for pre-retrieval viability testing. Clamping of the descending aorta to prevent any possibility of re-starting brain perfusion is an absolute requirement. If an abdominal team wishes to use NRP in a DCD donor who is also a potential lung donor, they must first discuss the details with the cardiothoracic team. Rapid laparotomy coincides with protection of the airway as in a standard retrieval. The abdominal team will cannulate the abdominal aorta and IVC and the cardiothoracic team will then clamp the lower thoracic aorta and then immediately proceed to flush the lungs in situ. Limited topical cooling should be used. The intra-pericardial IVC should be clamped at an early stage to reduce the chance of entraining air into the perfusion circuit. Whilst abdominal perfusion continues, the thoracic team remove the lungs, for retrograde perfusion on the back table. They must then secure complete haemostasis in the chest (bearing in mind that the donor is by now systemically heparinised, and must not stand down until both they and the abdominal team are satisfied that there is no significant bleeding into the chest John Dark 06/02/2013
APPENDIX 5. Donor Heart Perfusion & Preservation Protocol for NORS Teams in the UK
 APPENDIX 5 Donor Heart Perfusion & Preservation Protocol for NORS Teams in the UK 1. Systemically anticoagulate donors with 30,000 units of IV heparin 2. Venting of the IVC (chest or abdomen) as agreed
APPENDIX 5 Donor Heart Perfusion & Preservation Protocol for NORS Teams in the UK 1. Systemically anticoagulate donors with 30,000 units of IV heparin 2. Venting of the IVC (chest or abdomen) as agreed
General indications for ex vivo lung perfusion (EVLP) are
 Ex Vivo Lung Perfusion Marcelo Cypel, MD, MSc, and Shaf Keshavjee, MD, MSc The number of patients listed for lung transplantation largely exceeds the number of available transplantable organs because of
Ex Vivo Lung Perfusion Marcelo Cypel, MD, MSc, and Shaf Keshavjee, MD, MSc The number of patients listed for lung transplantation largely exceeds the number of available transplantable organs because of
Summary of Significant Changes. Policy
 This Management Process Description replaces MPD1043/6 Copy Number Summary of Significant Changes Effective 03/10/16 Removal of references to retrieval zones Points 2.2 and 5.9: Clarification of responsibilities
This Management Process Description replaces MPD1043/6 Copy Number Summary of Significant Changes Effective 03/10/16 Removal of references to retrieval zones Points 2.2 and 5.9: Clarification of responsibilities
VENTILATORS PURPOSE OBJECTIVES
 VENTILATORS PURPOSE To familiarize and acquaint the transfer Paramedic with the skills and knowledge necessary to adequately maintain a ventilator in the interfacility transfer environment. COGNITIVE OBJECTIVES
VENTILATORS PURPOSE To familiarize and acquaint the transfer Paramedic with the skills and knowledge necessary to adequately maintain a ventilator in the interfacility transfer environment. COGNITIVE OBJECTIVES
NORS Mobilisation Single Process
 This document has been developed to support stakeholders involved in NORS mobilisation. This is a highlevel description of the process referred to in SOP4574 - Logistics & NORS Mobilisation Manual - Hub
This document has been developed to support stakeholders involved in NORS mobilisation. This is a highlevel description of the process referred to in SOP4574 - Logistics & NORS Mobilisation Manual - Hub
NOTE: If not used, provider must document reason(s) for deferring mechanical ventilation in a patient with an advanced airway
 APPENDIX: TITLE: Mechanical Ventilator Use REVISED: November 1, 2017 I. Introduction: Mechanical Ventilation is the use of an automated device to deliver positive pressure ventilation to a patient. Proper
APPENDIX: TITLE: Mechanical Ventilator Use REVISED: November 1, 2017 I. Introduction: Mechanical Ventilation is the use of an automated device to deliver positive pressure ventilation to a patient. Proper
Mechanical Ventilation
 Mechanical Ventilation Chapter 4 Mechanical Ventilation Equipment When providing mechanical ventilation for pediatric casualties, it is important to select the appropriately sized bag-valve mask or endotracheal
Mechanical Ventilation Chapter 4 Mechanical Ventilation Equipment When providing mechanical ventilation for pediatric casualties, it is important to select the appropriately sized bag-valve mask or endotracheal
ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENT. First 24 hours: All patients with ARDS criteria were ventilated during 24 hours with low V T (6-8 ml/kg
 APPENDIX 1 Appendix 1. Complete respiratory protocol. First 24 hours: All patients with ARDS criteria were ventilated during 24 hours with low V T (6-8 ml/kg predicted body weight (PBW)) (NEJM 2000; 342
APPENDIX 1 Appendix 1. Complete respiratory protocol. First 24 hours: All patients with ARDS criteria were ventilated during 24 hours with low V T (6-8 ml/kg predicted body weight (PBW)) (NEJM 2000; 342
National Standards. for Organ Retrieval. from Deceased Donors
 MPD1043/8 National Standards for Organ Retrieval from Deceased Donors 1 Index Summary of Changes Glossary Useful Information Rationale & Policy Statement Donor Assessment & Offering NORS Co-ordination
MPD1043/8 National Standards for Organ Retrieval from Deceased Donors 1 Index Summary of Changes Glossary Useful Information Rationale & Policy Statement Donor Assessment & Offering NORS Co-ordination
excellence in care Procedure Management of patients with difficult oxygenation. For Review Aug 2015
 Difficult Oxygenation HELI.CLI.12 Purpose This procedure describes the processes and procedures for a lung protective strategy in the mechanical ventilation of patients that are difficult to oxygenate
Difficult Oxygenation HELI.CLI.12 Purpose This procedure describes the processes and procedures for a lung protective strategy in the mechanical ventilation of patients that are difficult to oxygenate
4/2/2017. Sophisticated Modes of Mechanical Ventilation - When and How to Use Them. Case Study 1. Case Study 1. ph 7.17 PCO 2 55 PO 2 62 HCO 3
 Sophisticated Modes of Mechanical entilation - When and How to Use Them Dr. Leanna R. Miller DNP, RN, CCRN-CMC, PCCN-CSC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Case Study 1 A 55 year-old man
Sophisticated Modes of Mechanical entilation - When and How to Use Them Dr. Leanna R. Miller DNP, RN, CCRN-CMC, PCCN-CSC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Case Study 1 A 55 year-old man
Donation after Neurological Death NDD General Information
 Donation after Neurological Death NDD General Information Prior to recovering organs, BC Transplant will have confirmed the following: suitability of the potential organ donor consent for donation two
Donation after Neurological Death NDD General Information Prior to recovering organs, BC Transplant will have confirmed the following: suitability of the potential organ donor consent for donation two
VENTILATION STRATEGIES FOR THE CRITICALLY UNWELL
 VENTILATION STRATEGIES FOR THE CRITICALLY UNWELL Dr Nick Taylor Visiting Emergency Specialist Teaching Hospital Karapitiya Senior Specialist and Director ED Training Clinical Lecturer, Australian National
VENTILATION STRATEGIES FOR THE CRITICALLY UNWELL Dr Nick Taylor Visiting Emergency Specialist Teaching Hospital Karapitiya Senior Specialist and Director ED Training Clinical Lecturer, Australian National
EMS INTER-FACILITY TRANSPORT WITH MECHANICAL VENTILATOR COURSE OBJECTIVES
 GENERAL PROVISIONS: EMS INTER-FACILITY TRANSPORT WITH MECHANICAL VENTILATOR COURSE OBJECTIVES Individuals providing Inter-facility transport with Mechanical Ventilator must have successfully completed
GENERAL PROVISIONS: EMS INTER-FACILITY TRANSPORT WITH MECHANICAL VENTILATOR COURSE OBJECTIVES Individuals providing Inter-facility transport with Mechanical Ventilator must have successfully completed
Day-to-day management of Tracheostomies & Laryngectomies
 Suctioning Suctioning the airway is an essential part of routine care of the tracheostomy and laryngectomy patient. Sputum is continually produced in health and our native airways deal with this load without
Suctioning Suctioning the airway is an essential part of routine care of the tracheostomy and laryngectomy patient. Sputum is continually produced in health and our native airways deal with this load without
McHENRY WESTERN LAKE COUNTY EMS SYSTEM FALL 2014 CONTINUING EDUCATION MANDATORY FOR ALL PRIMARY AND PROBATIONARY ALS SYSTEM PROVIDERS.
 McHENRY WESTERN LAKE COUNTY EMS SYSTEM FALL 2014 CONTINUING EDUCATION MANDATORY FOR ALL PRIMARY AND PROBATIONARY ALS SYSTEM PROVIDERS ResQPOD In a cardiac arrest blood flow to the organs stop. Key to survival
McHENRY WESTERN LAKE COUNTY EMS SYSTEM FALL 2014 CONTINUING EDUCATION MANDATORY FOR ALL PRIMARY AND PROBATIONARY ALS SYSTEM PROVIDERS ResQPOD In a cardiac arrest blood flow to the organs stop. Key to survival
6 th Accredited Advanced Mechanical Ventilation Course for Anesthesiologists. Course Test Results for the accreditation of the acquired knowledge
 6 th Accredited Advanced Mechanical Ventilation Course for Anesthesiologists Course Test Results for the accreditation of the acquired knowledge Q. Concerning the mechanics of the newborn s respiratory
6 th Accredited Advanced Mechanical Ventilation Course for Anesthesiologists Course Test Results for the accreditation of the acquired knowledge Q. Concerning the mechanics of the newborn s respiratory
Difficult Oxygenation Distribution: Sydney X Illawarra X Orange X
 HELICOPTER OPERATING PROCEDURE HOP No: C/12 Issued: May 2011 Page: 1 of 5 Revision No: Original Difficult Oxygenation Distribution: Sydney X Illawarra X Orange X TRIM No: 09/300 Document No: D10/9973 X
HELICOPTER OPERATING PROCEDURE HOP No: C/12 Issued: May 2011 Page: 1 of 5 Revision No: Original Difficult Oxygenation Distribution: Sydney X Illawarra X Orange X TRIM No: 09/300 Document No: D10/9973 X
3100A Competency Exam
 NAME DATE (Circle the appropriate answer) 3100A Competency Exam 1. Of the following, which best describes the mechanics of ventilation used by the 3100A? a. Active inspiration with passive exhalation b.
NAME DATE (Circle the appropriate answer) 3100A Competency Exam 1. Of the following, which best describes the mechanics of ventilation used by the 3100A? a. Active inspiration with passive exhalation b.
Notes on BIPAP/CPAP. M.Berry Emergency physician St Vincent s Hospital, Sydney
 Notes on BIPAP/CPAP M.Berry Emergency physician St Vincent s Hospital, Sydney 2 DEFINITIONS Non-Invasive Positive Pressure Ventilation (NIPPV) Encompasses both CPAP and BiPAP Offers ventilation support
Notes on BIPAP/CPAP M.Berry Emergency physician St Vincent s Hospital, Sydney 2 DEFINITIONS Non-Invasive Positive Pressure Ventilation (NIPPV) Encompasses both CPAP and BiPAP Offers ventilation support
Instructions/Procedure for Use of the Speaking Valve
 Instructions/Procedure for Use of the Speaking Valve Notes on the use of the speaking valve for ventilator-dependent and non-ventilator dependent patients The speaking valve is a one-way valve that allows
Instructions/Procedure for Use of the Speaking Valve Notes on the use of the speaking valve for ventilator-dependent and non-ventilator dependent patients The speaking valve is a one-way valve that allows
RESUSCITATION. If baby very floppy and heart rate slow, assist breathing immediately. If baby not breathing adequately by 90 sec, assist breathing
 RESUSCITATION Check equipment daily, and before resuscitation Follow Resuscitation Council UK Guidelines www.resus.org.uk DRY AND COVER Cord clamping see Cord clamping below >28 weeks gestation, dry baby,
RESUSCITATION Check equipment daily, and before resuscitation Follow Resuscitation Council UK Guidelines www.resus.org.uk DRY AND COVER Cord clamping see Cord clamping below >28 weeks gestation, dry baby,
Neonatal tidal volume targeted ventilation
 Neonatal tidal volume targeted ventilation Colin Morley Retired Professor of Neonatal Medicine, Royal Women s Hospital, Melbourne, Australia. Honorary Visiting Fellow, Dept Obstetrics and Gynaecology,
Neonatal tidal volume targeted ventilation Colin Morley Retired Professor of Neonatal Medicine, Royal Women s Hospital, Melbourne, Australia. Honorary Visiting Fellow, Dept Obstetrics and Gynaecology,
APNOEA AND PRE-OXYGENATION
 APNOEA AND PRE-OXYGENATION Original article by Dr Andrew Biffen, Dr Richard Hughes Torbay Hospital, UK INTRODUCTION The purpose of pre-oxygenation is to increase physiological stores of oxygen in order
APNOEA AND PRE-OXYGENATION Original article by Dr Andrew Biffen, Dr Richard Hughes Torbay Hospital, UK INTRODUCTION The purpose of pre-oxygenation is to increase physiological stores of oxygen in order
Clinical Skills. Administering Oxygen
 Clinical Skills Administering Oxygen Updated July 2017 Clare Cann Original 2012 Carole Loveridge, Lecturer in Women`s Health Aims and Objectives Aims and Objectives The aim of this module is to facilitate
Clinical Skills Administering Oxygen Updated July 2017 Clare Cann Original 2012 Carole Loveridge, Lecturer in Women`s Health Aims and Objectives Aims and Objectives The aim of this module is to facilitate
Inspiration 7i Ventilator
 Inspiration 7i Ventilator Clinician Focused Products is not just a tag line, rather a belief system. Low cost of ownership High performance PSOL and active exhalation Comprehensive graphics and trending
Inspiration 7i Ventilator Clinician Focused Products is not just a tag line, rather a belief system. Low cost of ownership High performance PSOL and active exhalation Comprehensive graphics and trending
INTRODUCTION TO BI-VENT (APRV) INTRODUCTION TO BI-VENT (APRV) PROGRAM OBJECTIVES
 INTRODUCTION TO BI-VENT (APRV) INTRODUCTION TO BI-VENT (APRV) PROGRAM OBJECTIVES PROVIDE THE DEFINITION FOR BI-VENT EXPLAIN THE BENEFITS OF BI-VENT EXPLAIN SET PARAMETERS IDENTIFY RECRUITMENT IN APRV USING
INTRODUCTION TO BI-VENT (APRV) INTRODUCTION TO BI-VENT (APRV) PROGRAM OBJECTIVES PROVIDE THE DEFINITION FOR BI-VENT EXPLAIN THE BENEFITS OF BI-VENT EXPLAIN SET PARAMETERS IDENTIFY RECRUITMENT IN APRV USING
Basics of Mechanical Ventilation. Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity
 Basics of Mechanical Ventilation Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity Overview of topics 1. Goals 2. Settings 3. Modes 4. Advantages and disadvantages
Basics of Mechanical Ventilation Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity Overview of topics 1. Goals 2. Settings 3. Modes 4. Advantages and disadvantages
Point-of-Care Testing: A Cardiovascular Perfusionist s Perspective
 Point-of-Care Testing: A Cardiovascular Perfusionist s Perspective Cory M. Alwardt, PhD, CCP Chief Perfusionist/ECMO Coordinator Assistant Professor of Surgery Mayo Clinic Hospital, Phoenix alwardt.cory@mayo.edu
Point-of-Care Testing: A Cardiovascular Perfusionist s Perspective Cory M. Alwardt, PhD, CCP Chief Perfusionist/ECMO Coordinator Assistant Professor of Surgery Mayo Clinic Hospital, Phoenix alwardt.cory@mayo.edu
SUPPLEMENTARY APPENDIX. Ary Serpa Neto MD MSc, Fabienne D Simonis MD, Carmen SV Barbas MD PhD, Michelle Biehl MD, Rogier M Determann MD PhD, Jonathan
 1 LUNG PROTECTIVE VENTILATION WITH LOW TIDAL VOLUMES AND THE OCCURRENCE OF PULMONARY COMPLICATIONS IN PATIENTS WITHOUT ARDS: a systematic review and individual patient data metaanalysis SUPPLEMENTARY APPENDIX
1 LUNG PROTECTIVE VENTILATION WITH LOW TIDAL VOLUMES AND THE OCCURRENCE OF PULMONARY COMPLICATIONS IN PATIENTS WITHOUT ARDS: a systematic review and individual patient data metaanalysis SUPPLEMENTARY APPENDIX
Automatic Transport Ventilators. ICU Quality Ventilation on the Street.
 Automatic Transport Ventilators ICU Quality Ventilation on the Street. Kevin Bowden, March 20 th 2014 Ventilator Definition A ventilator is an automatic mechanical device designed to provide all or part
Automatic Transport Ventilators ICU Quality Ventilation on the Street. Kevin Bowden, March 20 th 2014 Ventilator Definition A ventilator is an automatic mechanical device designed to provide all or part
Initiation and Management of Airway Pressure Release Ventilation (APRV)
 Initiation and Management of Airway Pressure Release Ventilation (APRV) Eric Kriner RRT Pulmonary Critical Care Clinical Specialist Pulmonary Services Department Medstar Washington Hospital Center Disclosures
Initiation and Management of Airway Pressure Release Ventilation (APRV) Eric Kriner RRT Pulmonary Critical Care Clinical Specialist Pulmonary Services Department Medstar Washington Hospital Center Disclosures
Endotracheal Suctioning: In Line ETT
 Approved by: Endotracheal Suctioning: In Line ETT Gail Cameron Senior Director Operations, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Dr. Paul Byrne Medical Director, Neonatology Neonatal Policy & Procedures
Approved by: Endotracheal Suctioning: In Line ETT Gail Cameron Senior Director Operations, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Dr. Paul Byrne Medical Director, Neonatology Neonatal Policy & Procedures
STANDARDIZED PROCEDURE NEONATAL INTUBATION (Neonatal)
 I. Definition This procedure is done in order to establish access to the airway in order to assist ventilation by the use of either endotracheal tube (ET tube) and bag, ET tube and continuous positive
I. Definition This procedure is done in order to establish access to the airway in order to assist ventilation by the use of either endotracheal tube (ET tube) and bag, ET tube and continuous positive
Clinical guideline for Ventilator Hyperinflation as a physiotherapy technique, in adult mechanically ventilated patients
 Title of Guideline Contact Name Division and Speciality Clinical guideline for Ventilator Hyperinflation as a physiotherapy technique, in adult mechanically ventilated patients Rebecca Storer (Band 7 Physiotherapist,
Title of Guideline Contact Name Division and Speciality Clinical guideline for Ventilator Hyperinflation as a physiotherapy technique, in adult mechanically ventilated patients Rebecca Storer (Band 7 Physiotherapist,
Chapter 4: Ventilation Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE
 Instant download and all chapters Test Bank Respiratory Care Anatomy and Physiology Foundations for Clinical Practice 3rd Edition Will Beachey https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-respiratory-care-anatomy-physiologyfoundations-clinical-practice-3rd-edition-will-beachey/
Instant download and all chapters Test Bank Respiratory Care Anatomy and Physiology Foundations for Clinical Practice 3rd Edition Will Beachey https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-respiratory-care-anatomy-physiologyfoundations-clinical-practice-3rd-edition-will-beachey/
THE PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF NORMAL LUNGS
 Thorax (1952), 7, 285. THE PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF NORMAL LUNGS REMOVED AFTER DEATH BY M. B. McILROY From the Medical Professorial Unit, St. Bartholomew's Hospital, London (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION OCTOBER
Thorax (1952), 7, 285. THE PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF NORMAL LUNGS REMOVED AFTER DEATH BY M. B. McILROY From the Medical Professorial Unit, St. Bartholomew's Hospital, London (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION OCTOBER
The aim of this guideline is to describe the indications and procedure for using high flow nasal prong oxygen
 High flow nasal prong HFNP oxygen therapy o Introduction & aim o Indications o Contraindications o Management equipment setup patient management o Weaning o Complications Introduction Humidified high flow
High flow nasal prong HFNP oxygen therapy o Introduction & aim o Indications o Contraindications o Management equipment setup patient management o Weaning o Complications Introduction Humidified high flow
RESPIRATORY CARE POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL. a) Persistent hypoxemia despite improved ventilatory pattern and elevated Fl02
 The University of Mississippi AND PROCEDURE MANUAL Effective Date: June 30, 1990 Revised Date: December 2009 MANUAL CODE Page 1 of 5 PREPARED BY: Respiratory Care Policy and Procedure Review Committee
The University of Mississippi AND PROCEDURE MANUAL Effective Date: June 30, 1990 Revised Date: December 2009 MANUAL CODE Page 1 of 5 PREPARED BY: Respiratory Care Policy and Procedure Review Committee
Respiratory Signs: Tachypnea (RR>30/min), Desaturation, Shallow breathing, Use of accessory muscles Breathing sound: Wheezing, Rhonchi, Crepitation.
 Respiratory Signs: Tachypnea (RR>30/min), Desaturation, Shallow breathing, Use of accessory muscles Breathing sound: Wheezing, Rhonchi, Crepitation. Paradoxical breathing Hyper-resonance on percussion:
Respiratory Signs: Tachypnea (RR>30/min), Desaturation, Shallow breathing, Use of accessory muscles Breathing sound: Wheezing, Rhonchi, Crepitation. Paradoxical breathing Hyper-resonance on percussion:
Airways and Resuscitators. CRC 330 Cardiorespiratory Care University of South Alabama
 Airways and Resuscitators CRC 330 Cardiorespiratory Care University of South Alabama Causes of Upper Airway Obstruction CNS depressionanesthesia, drug overdose Cardiac arrest Loss of consciousness Foreign
Airways and Resuscitators CRC 330 Cardiorespiratory Care University of South Alabama Causes of Upper Airway Obstruction CNS depressionanesthesia, drug overdose Cardiac arrest Loss of consciousness Foreign
Why we should care (I)
 What the $*!# is Lung Protective Ventilation and Why Should I be Using it in the OR? Disclosures KATHERINE PALMIERI, MD, MBA 64 TH ANNUAL POSTGRADUATE SYMPOSIUM UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS MEDICAL CENTER DEPARTMENT
What the $*!# is Lung Protective Ventilation and Why Should I be Using it in the OR? Disclosures KATHERINE PALMIERI, MD, MBA 64 TH ANNUAL POSTGRADUATE SYMPOSIUM UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS MEDICAL CENTER DEPARTMENT
Simulation 10: 27 Year-Old Male Trauma Patient
 Simulation 10: 27 Year-Old Male Trauma Patient Flow Chart Opening Scenario Section 1 Type: IG Handed off 27 YO male with blunt chest trauma/pulmonary contusions on PC A/C ventilation; PIP = 30 cm H2O,
Simulation 10: 27 Year-Old Male Trauma Patient Flow Chart Opening Scenario Section 1 Type: IG Handed off 27 YO male with blunt chest trauma/pulmonary contusions on PC A/C ventilation; PIP = 30 cm H2O,
Section 2.9 Decannulation
 Bite- sized training from the GTC Section 2.9 Decannulation This is one of a series of bite- sized chunks of educational material developed by the Global Tracheostomy Collaborative. The GTC has developed
Bite- sized training from the GTC Section 2.9 Decannulation This is one of a series of bite- sized chunks of educational material developed by the Global Tracheostomy Collaborative. The GTC has developed
Avalanche Victim Resuscitation Checklist
 Avalanche Victim Resuscitation Checklist Changing process for saving lives ICAR MEDCOM: Kottmann A, Blancher M, Boyd J, Spichiger T, Brugger H Dr A. Kottmann Avalanche Time Hazard Life or death Stressfull
Avalanche Victim Resuscitation Checklist Changing process for saving lives ICAR MEDCOM: Kottmann A, Blancher M, Boyd J, Spichiger T, Brugger H Dr A. Kottmann Avalanche Time Hazard Life or death Stressfull
Standard Operating Procedure
 Standard Operating Procedure SOP ID C04 Version 1.0 Title Approved by Capnography: MobiMed Clinical Effectiveness Group Date Issued 1 st February 2013 Review Date 31 st January 2015 Directorate Clinical
Standard Operating Procedure SOP ID C04 Version 1.0 Title Approved by Capnography: MobiMed Clinical Effectiveness Group Date Issued 1 st February 2013 Review Date 31 st January 2015 Directorate Clinical
Monitoring, Ventilation & Capnography
 Why do we need to monitor? Monitoring, Ventilation & Capnography Keith Simpson BVSc MRCVS MIET(Electronics) Torquay, Devon. Under anaesthesia animals no longer have the ability to adequately control their
Why do we need to monitor? Monitoring, Ventilation & Capnography Keith Simpson BVSc MRCVS MIET(Electronics) Torquay, Devon. Under anaesthesia animals no longer have the ability to adequately control their
A V A L A N C H E R E S C U E
 AVALANCHE RESCUE The On-Site Triage And Evacuation Of Avalanche Victims Statistics De Quervain s Mortality Curve 1945 to 1979 and 1979 to 1989 2,611 cases, buried at average 1.06 m After 1 hour 30-40%
AVALANCHE RESCUE The On-Site Triage And Evacuation Of Avalanche Victims Statistics De Quervain s Mortality Curve 1945 to 1979 and 1979 to 1989 2,611 cases, buried at average 1.06 m After 1 hour 30-40%
Mechanical Ventilation of the Patient with ARDS
 1 Mechanical Ventilation of the Patient with ARDS Dean Hess, PhD, RRT, FAARC Assistant Professor of Anesthesia Harvard Medical School Assistant Director of Respiratory Care Massachusetts General Hospital
1 Mechanical Ventilation of the Patient with ARDS Dean Hess, PhD, RRT, FAARC Assistant Professor of Anesthesia Harvard Medical School Assistant Director of Respiratory Care Massachusetts General Hospital
Patient Information for the: Humanitarian Device for use in the Control of Air Leaks
 Patient Information for the: Humanitarian Device for use in the Control of Air Leaks Glossary Airway: The tubes in the lungs that pass air to and from the lung tissue. Anesthesia: Technique to make the
Patient Information for the: Humanitarian Device for use in the Control of Air Leaks Glossary Airway: The tubes in the lungs that pass air to and from the lung tissue. Anesthesia: Technique to make the
Invasive mechanical ventilation:
 Invasive mechanical ventilation definition mechanical ventilation: using an apparatus to facilitate transport of oxygen and CO2 between the atmosphere and the alveoli for the purpose of enhancing pulmonary
Invasive mechanical ventilation definition mechanical ventilation: using an apparatus to facilitate transport of oxygen and CO2 between the atmosphere and the alveoli for the purpose of enhancing pulmonary
PART EIGHT HIGH FREQUENCY PERCUSSIVE OSCILLATION (HFPOV )
 PART EIGHT HIGH FREQUENCY PERCUSSIVE OSCILLATION (HFPOV ) Note: For maximal comparative understanding, FIRST read PART SEVEN which defines the concept of High Frequency Oscillatory Ventilation (HFOV).
PART EIGHT HIGH FREQUENCY PERCUSSIVE OSCILLATION (HFPOV ) Note: For maximal comparative understanding, FIRST read PART SEVEN which defines the concept of High Frequency Oscillatory Ventilation (HFOV).
Recommendations for Standards. Monitoring. Cardiopulmonary Bypass
 Recommendations for Standards of Monitoring during Cardiopulmonary Bypass Membership of the working party (2006) Ian Curle Fiona Gibson Jonathan Hyde Alex Shipolini David Smith J P van Besouw Kate Wark
Recommendations for Standards of Monitoring during Cardiopulmonary Bypass Membership of the working party (2006) Ian Curle Fiona Gibson Jonathan Hyde Alex Shipolini David Smith J P van Besouw Kate Wark
Solutions. Digital pressure management solutions. Copyright 2013 GaleMed Corporation
 Solutions Digital pressure management solutions Content 1. About GiO Solutions 2. What is Gio 3. Clinical Applications 4. Product Range 5. Features 6. Specifications 7. Accessories 8. Order Information
Solutions Digital pressure management solutions Content 1. About GiO Solutions 2. What is Gio 3. Clinical Applications 4. Product Range 5. Features 6. Specifications 7. Accessories 8. Order Information
HOBIT Trial Checklist
 ED INITIAL IDENTIFICATION AND NOTIFICATION OF HOBIT TRIAL PATIENTS HOBIT eligibility met pending head CT results If patient has pacemaker/aicd/insulin pump/other implantable device, verify that the device
ED INITIAL IDENTIFICATION AND NOTIFICATION OF HOBIT TRIAL PATIENTS HOBIT eligibility met pending head CT results If patient has pacemaker/aicd/insulin pump/other implantable device, verify that the device
CPR + AED Topic 6 TECS TECS FIRE & SAFETY TRAINING PTE LTD
 CPR + AED Topic 6 1 Anatomy and physiology of the circulatory system 2 Principles of Resuscitation Principles of resuscitation / Determine if CPR is necessary by examining casualty, which include the following:
CPR + AED Topic 6 1 Anatomy and physiology of the circulatory system 2 Principles of Resuscitation Principles of resuscitation / Determine if CPR is necessary by examining casualty, which include the following:
The Basics of Ventilator Management. Overview. How we breath 3/23/2019
 The Basics of Ventilator Management What are we really trying to do here Peter Lutz, MD Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Pulmonary Associates, Mobile, Al Overview Approach to the physiology of the
The Basics of Ventilator Management What are we really trying to do here Peter Lutz, MD Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Pulmonary Associates, Mobile, Al Overview Approach to the physiology of the
AUTOVENT 4000 VENTILATOR
 OVERVIEW AUTOVENT 4000 Only properly trained and approved Escambia County Bureau of Public Safety Paramedics are to use the AutoVent 4000 ventilator manufactured by LSP to transport patients already on
OVERVIEW AUTOVENT 4000 Only properly trained and approved Escambia County Bureau of Public Safety Paramedics are to use the AutoVent 4000 ventilator manufactured by LSP to transport patients already on
HONG KONG COLLEGE OF ANAESTHESIOLOGISTS TECHNICAL GUIDINES RECOMMENDATIONS ON CHECKING ANAESTHESIA DELIVERY SYSTEMS
 RECOMMENDATIONS ON CHECKING ANAESTHESIA DELIVERY SYSTEMS 1. INTRODUCTION An anaesthesia delivery system includes any machine, equipment or apparatus which supplies gases, vapours, local anaesthesia and/or
RECOMMENDATIONS ON CHECKING ANAESTHESIA DELIVERY SYSTEMS 1. INTRODUCTION An anaesthesia delivery system includes any machine, equipment or apparatus which supplies gases, vapours, local anaesthesia and/or
Chapter 9 Airway Respirations Metabolism Oxygen Requirements Respiratory Anatomy Respiratory Anatomy Respiratory Anatomy Diaphragm
 1 Chapter 9 Airway 2 Respirations Every cell of the body requires to survive Oxygen must come in and carbon must go out 3 Metabolism Metabolism--Process where the body s cells convert food to Adequate
1 Chapter 9 Airway 2 Respirations Every cell of the body requires to survive Oxygen must come in and carbon must go out 3 Metabolism Metabolism--Process where the body s cells convert food to Adequate
MINI- COURSE on Management of OXYGEN in babies with RESPIRATORY DISTRESS
 MINI- COURSE on Management of OXYGEN in babies with RESPIRATORY DISTRESS Instructions: Read each sheet and answer any questions as honestly as possible The first sheets have 5 questions to allow you to
MINI- COURSE on Management of OXYGEN in babies with RESPIRATORY DISTRESS Instructions: Read each sheet and answer any questions as honestly as possible The first sheets have 5 questions to allow you to
OPEN LUNG APPROACH CONCEPT OF MECHANICAL VENTILATION
 OPEN LUNG APPROACH CONCEPT OF MECHANICAL VENTILATION L. Rudo Mathivha Intensive Care Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Aacademic Hospital & the University of the Witwatersrand OUTLINE Introduction Goals & Indications
OPEN LUNG APPROACH CONCEPT OF MECHANICAL VENTILATION L. Rudo Mathivha Intensive Care Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Aacademic Hospital & the University of the Witwatersrand OUTLINE Introduction Goals & Indications
Mechanical Ventilation. Which of the following is true regarding ventilation? Basics of Ventilation
 Mechanical Ventilation Jeffrey L. Wilt, MD, FACP, FCCP Associate Professor of Medicine Michigan State University Associate Program Director MSU-Grand Rapids Internal Medicine Residency Which of the following
Mechanical Ventilation Jeffrey L. Wilt, MD, FACP, FCCP Associate Professor of Medicine Michigan State University Associate Program Director MSU-Grand Rapids Internal Medicine Residency Which of the following
Mechanical Ventilation. Mechanical Ventilation is a Drug!!! is a drug. MV: Indications for use. MV as a Drug: Outline. MV: Indications for use
 Mechanical Ventilation is a Drug!!! Mechanical Ventilation is a drug I am an employee of Philips Healthcare Hospital Respiratory Care Group and they help me pay for my kids education Jim Laging, RRT, RCP
Mechanical Ventilation is a Drug!!! Mechanical Ventilation is a drug I am an employee of Philips Healthcare Hospital Respiratory Care Group and they help me pay for my kids education Jim Laging, RRT, RCP
Indications for Mechanical Ventilation. Mechanical Ventilation. Indications for Mechanical Ventilation. Modes. Modes: Volume cycled
 Mechanical Ventilation Eric A. Libré, MD VCU School of Medicine Inova Fairfax Hospital and VHC Indications for Mechanical Ventilation Inadequate ventilatory effort Rising pco2 with resp acidosis (7.25)
Mechanical Ventilation Eric A. Libré, MD VCU School of Medicine Inova Fairfax Hospital and VHC Indications for Mechanical Ventilation Inadequate ventilatory effort Rising pco2 with resp acidosis (7.25)
London Respiratory Team
 London Respiratory Team By email 28 March 2012 Ambulatory Oxygen for London This guide has been produced to help healthcare maximise the benefit of the new oxygen contract for patients and to reduce waste.
London Respiratory Team By email 28 March 2012 Ambulatory Oxygen for London This guide has been produced to help healthcare maximise the benefit of the new oxygen contract for patients and to reduce waste.
SEP-1 Additional Notes for Abstraction for Version 5.0b
 SEP-1 Additional Notes for Abstraction for Version 5.0b Data Element Administrative Contraindication to Care Blood Culture Collection Date Blood Culture Collection Time Broad Spectrum or Other Antibiotic
SEP-1 Additional Notes for Abstraction for Version 5.0b Data Element Administrative Contraindication to Care Blood Culture Collection Date Blood Culture Collection Time Broad Spectrum or Other Antibiotic
PROBLEM SET 9. SOLUTIONS April 23, 2004
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.542J: Quantitative Physiology: Organ Transport Systems Instructors: Roger Mark and Jose Venegas MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Departments
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.542J: Quantitative Physiology: Organ Transport Systems Instructors: Roger Mark and Jose Venegas MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Departments
Selecting the Ventilator and the Mode. Chapter 6
 Selecting the Ventilator and the Mode Chapter 6 Criteria for Ventilator Selection Why does the patient need ventilatory support? Does the ventilation problem require a special mode? What therapeutic goals
Selecting the Ventilator and the Mode Chapter 6 Criteria for Ventilator Selection Why does the patient need ventilatory support? Does the ventilation problem require a special mode? What therapeutic goals
ORA Role Resource Document
 Introduction Organ Recovery Assistants (ORA) are a very important part of the BC Transplant retrieval team. The ORA s primary roles in the organ retrieval surgery are to assist the SRS and OR staff during
Introduction Organ Recovery Assistants (ORA) are a very important part of the BC Transplant retrieval team. The ORA s primary roles in the organ retrieval surgery are to assist the SRS and OR staff during
G622. APPLIED SCIENCE Monitoring the Activity of the Human Body ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE. Thursday 27 May 2010 Afternoon. Duration: 1 hour 30 minutes
 ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE APPLIED SCIENCE Monitoring the Activity of the Human Body G622 *OCE/17533* Candidates answer on the Question Paper OCR Supplied Materials: None Other Materials Required: Electronic
ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE APPLIED SCIENCE Monitoring the Activity of the Human Body G622 *OCE/17533* Candidates answer on the Question Paper OCR Supplied Materials: None Other Materials Required: Electronic
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE
 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: ENDO TRACHEAL SUCTIONING OF THE ADULT PATIENT (suc03) Nursing, Respiratory DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: 11/82 12/18 1 of 5 RESPONSIBILITY: RN,
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: ENDO TRACHEAL SUCTIONING OF THE ADULT PATIENT (suc03) Nursing, Respiratory DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: 11/82 12/18 1 of 5 RESPONSIBILITY: RN,
Let s talk about Capnography
 Let s talk about Capnography This is one of a series of articles by Keith Simpson BVSc MRCVS MIET (Electronics) discussing the practical aspects of some common monitoring techniques. Capnometry is the
Let s talk about Capnography This is one of a series of articles by Keith Simpson BVSc MRCVS MIET (Electronics) discussing the practical aspects of some common monitoring techniques. Capnometry is the
Committee on Issues in Organ Donor Intervention Research. Presented by: Richard D. Hasz Vice President, Clinical Services
 Committee on Issues in Organ Donor Intervention Research Presented by: Richard D. Hasz Vice President, Clinical Services Living Organ Donors 5,527 U.S. National Trends in Organ Donation Living vs. Deceased
Committee on Issues in Organ Donor Intervention Research Presented by: Richard D. Hasz Vice President, Clinical Services Living Organ Donors 5,527 U.S. National Trends in Organ Donation Living vs. Deceased
Capnography in the Veterinary Technician Toolbox. Katie Pinner BS, LVT Bush Advanced Veterinary Imaging Richmond, VA
 Capnography in the Veterinary Technician Toolbox Katie Pinner BS, LVT Bush Advanced Veterinary Imaging Richmond, VA What are Respiration and Ventilation? Respiration includes all those chemical and physical
Capnography in the Veterinary Technician Toolbox Katie Pinner BS, LVT Bush Advanced Veterinary Imaging Richmond, VA What are Respiration and Ventilation? Respiration includes all those chemical and physical
o An experienced and trained assistant is available to help you with induction.
 Safe Surgery and Safe Anaesthesiia for Patiient Safety Check Liist before iinduciing anaesthesiia: o An experienced and trained assistant is available to help you with induction. o You have the correct
Safe Surgery and Safe Anaesthesiia for Patiient Safety Check Liist before iinduciing anaesthesiia: o An experienced and trained assistant is available to help you with induction. o You have the correct
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY. Anaesthesiology Block 18 (GNK 586) Prof Pierre Fourie
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Anaesthesiology Block 18 (GNK 586) Prof Pierre Fourie Outline Ventilation Diffusion Perfusion Ventilation-Perfusion relationship Work of breathing Control of Ventilation 2 This image
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Anaesthesiology Block 18 (GNK 586) Prof Pierre Fourie Outline Ventilation Diffusion Perfusion Ventilation-Perfusion relationship Work of breathing Control of Ventilation 2 This image
UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS FIELD MEDICAL TRAINING BATTALION Camp Lejeune, NC
 UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS FIELD MEDICAL TRAINING BATTALION Camp Lejeune, NC 28542-0042 FMST 504 Conduct Triage TERMINAL LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Given multiple casualties in a tactical environment, conduct
UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS FIELD MEDICAL TRAINING BATTALION Camp Lejeune, NC 28542-0042 FMST 504 Conduct Triage TERMINAL LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Given multiple casualties in a tactical environment, conduct
APRV: Moving beyond ARDSnet
 APRV: Moving beyond ARDSnet Matthew Lissauer, MD Associate Professor of Surgery Medical Director, Surgical Critical Care Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey What is APRV? APRV is different from
APRV: Moving beyond ARDSnet Matthew Lissauer, MD Associate Professor of Surgery Medical Director, Surgical Critical Care Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey What is APRV? APRV is different from
Circulatory And Respiration
 Circulatory And Respiration Composition Of Blood Blood Heart 200mmHg 120mmHg Aorta Artery Arteriole 50mmHg Capillary Bed Venule Vein Vena Cava Heart Differences Between Arteries and Veins Veins transport
Circulatory And Respiration Composition Of Blood Blood Heart 200mmHg 120mmHg Aorta Artery Arteriole 50mmHg Capillary Bed Venule Vein Vena Cava Heart Differences Between Arteries and Veins Veins transport
IDEAL FOR SHORT- TO MEDIUM- TERM ANAESTHESIA OR VENTILATION. Anaesthesia Tracheal Tubes
 IDEAL FOR SHORT- TO MEDIUM- TERM ANAESTHESIA OR VENTILATION Anaesthesia Tracheal Tubes Common Features Clear tube material Allows visualisation of condensed exhaled air indicating tracheal intubation.
IDEAL FOR SHORT- TO MEDIUM- TERM ANAESTHESIA OR VENTILATION Anaesthesia Tracheal Tubes Common Features Clear tube material Allows visualisation of condensed exhaled air indicating tracheal intubation.
War Surgery Dr. Abdulwahid INTRODUCTION: AIRWAY, BREATHING
 War Surgery Dr. Abdulwahid INTRODUCTION: AIRWAY, BREATHING The aims of war surgery: Save life Avoid infectious complications Save limbs Minimize residual disability The outcome is influenced by: Type of
War Surgery Dr. Abdulwahid INTRODUCTION: AIRWAY, BREATHING The aims of war surgery: Save life Avoid infectious complications Save limbs Minimize residual disability The outcome is influenced by: Type of
Immersion pulmonary oedema: is it confused with drowning?
 Immersion pulmonary oedema: is it confused with drowning? Dr Peter Wilmshurst Consultant Cardiologist Royal Stoke University Hospital & UK Diving Medical Committee Drowning and pulmonary oedema Drowning
Immersion pulmonary oedema: is it confused with drowning? Dr Peter Wilmshurst Consultant Cardiologist Royal Stoke University Hospital & UK Diving Medical Committee Drowning and pulmonary oedema Drowning
Balloon Gastrostomy (BG) Tube
 Balloon Gastrostomy (BG) Tube Post insertion advice Please follow hospital/ Consultant advice for care of the tube and stoma site for the first 28 days (if the BG tube has been placed as a first gastrostomy
Balloon Gastrostomy (BG) Tube Post insertion advice Please follow hospital/ Consultant advice for care of the tube and stoma site for the first 28 days (if the BG tube has been placed as a first gastrostomy
 http://www.priory.com/cmol/hfov.htm INTRODUCTION The vast majority of patients who are admitted to an Intensive Care Unit (ICU) will need artificial ventilation (Jones et al 1998). The usual means through
http://www.priory.com/cmol/hfov.htm INTRODUCTION The vast majority of patients who are admitted to an Intensive Care Unit (ICU) will need artificial ventilation (Jones et al 1998). The usual means through
PART ONE CHAPTER ONE PRIMARY CONSIDERATIONS RELATING TO THE PHYSIOLOGICAL AND PHYSICAL ASPECTS OF THE MECHANICAL VENTILATION OF THE LUNG
 PART ONE CHAPTER ONE PRIMARY CONSIDERATIONS RELATING TO THE PHYSIOLOGICAL AND PHYSICAL ASPECTS OF THE MECHANICAL VENTILATION OF THE LUNG POSSIBLE ORIGIN OF THE MECHANICAL VENTILATION OF THE LUNG- The first
PART ONE CHAPTER ONE PRIMARY CONSIDERATIONS RELATING TO THE PHYSIOLOGICAL AND PHYSICAL ASPECTS OF THE MECHANICAL VENTILATION OF THE LUNG POSSIBLE ORIGIN OF THE MECHANICAL VENTILATION OF THE LUNG- The first
First Response Learning Module 2 Based on ILCOR and ANZCOR Victorian Newborn Resuscitation Project Updated March 2018
 First Response Learning Module 2 Based on ILCOR and ANZCOR 2016 Learning objectives Following completion of the theoretical & practical components of this module, the participant will be able to demonstrate
First Response Learning Module 2 Based on ILCOR and ANZCOR 2016 Learning objectives Following completion of the theoretical & practical components of this module, the participant will be able to demonstrate
OXYGEN THERAPY. (Non-invasive O2 therapy in patient >8yrs)
 OXYGEN THERAPY (Non-invasive O2 therapy in patient >8yrs) Learning aims Indications and precautions for O2 therapy Targets of therapy Standard notation O2 delivery devices Taps, tanks and tubing Notation
OXYGEN THERAPY (Non-invasive O2 therapy in patient >8yrs) Learning aims Indications and precautions for O2 therapy Targets of therapy Standard notation O2 delivery devices Taps, tanks and tubing Notation
1.060 Set-Up and Priming of the Bypass Circuit. Perfusion Technology Department. Perfusionists
 TITLE/DESCRIPTION: DEPARTMENT: PERSONNEL: 1.060 Set-Up and Priming of the Bypass Circuit Perfusion Technology Department Perfusionists EFFECTIVE DATE: 8/97 REVISED: 09/07, 04/09, 9/17 PURPOSE: The function
TITLE/DESCRIPTION: DEPARTMENT: PERSONNEL: 1.060 Set-Up and Priming of the Bypass Circuit Perfusion Technology Department Perfusionists EFFECTIVE DATE: 8/97 REVISED: 09/07, 04/09, 9/17 PURPOSE: The function
Operating Instructions for Microprocessor Controlled Ventilators
 Page 1 of 5 Operating Instructions for Microprocessor Controlled Ventilators Purpose Audience Scope Physician's Order To provide guidelines for the procedure for the use of microprocessor controlled ventilators.
Page 1 of 5 Operating Instructions for Microprocessor Controlled Ventilators Purpose Audience Scope Physician's Order To provide guidelines for the procedure for the use of microprocessor controlled ventilators.
COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL. Effective Date: August 31, 2006
 COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION Emergency Procedures POLICY NUMBER: 702 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: CARDIOPULMONARY RESUSCITATION (CPR) 1. PURPOSE: To provide
COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION Emergency Procedures POLICY NUMBER: 702 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: CARDIOPULMONARY RESUSCITATION (CPR) 1. PURPOSE: To provide
 Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Venepuncture. Clinical Skills. Venepuncture. Dr Brian Jenkins (Clinical Skills Lead) Sian Williams (Clinical Skills Manager)
 Clinical Skills Venepuncture Dr Brian Jenkins (Clinical Skills Lead) Sian Williams (Clinical Skills Manager) Aims and Objectives Aims and Objectives The aim of this module is to facilitate learning regarding
Clinical Skills Venepuncture Dr Brian Jenkins (Clinical Skills Lead) Sian Williams (Clinical Skills Manager) Aims and Objectives Aims and Objectives The aim of this module is to facilitate learning regarding
Health Professional Info
 Health Professional Info Mouthpiece Ventilation (MPV) What is MPV? MPV is a less intrusive form of noninvasive ventilation that uses a portable home mechanical ventilator (HMV) with a single-limb open-circuit
Health Professional Info Mouthpiece Ventilation (MPV) What is MPV? MPV is a less intrusive form of noninvasive ventilation that uses a portable home mechanical ventilator (HMV) with a single-limb open-circuit
Respiration. The resspiratory system
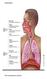 Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
Recommendations on Checking Anaesthesia Delivery Systems
 Page 1 of 11 Recommendations on Checking Anaesthesia Delivery Version Effective Date 1 Oct 1992 (reviewed Feb 07, Feb 02) 2 2004 3 Nov 2011 4 Dec 2016 Document No. HKCA T1 v4 Prepared by College Guidelines
Page 1 of 11 Recommendations on Checking Anaesthesia Delivery Version Effective Date 1 Oct 1992 (reviewed Feb 07, Feb 02) 2 2004 3 Nov 2011 4 Dec 2016 Document No. HKCA T1 v4 Prepared by College Guidelines
V8600 Ventilator. Integrated Invasive & Noninvasive Ventilation
 V8600 Ventilator Integrated Invasive & Noninvasive Ventilation 0123 V8600 Ventilator Invasive Ventilation With state-of-the-art turbine technology, V8600 helps achieve sequential ventilation in various
V8600 Ventilator Integrated Invasive & Noninvasive Ventilation 0123 V8600 Ventilator Invasive Ventilation With state-of-the-art turbine technology, V8600 helps achieve sequential ventilation in various
Gas Exchange in Animals. Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2. Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial
 Gas Exchange in Animals Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2 Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial Respiratory surface! skin, gills, lungs Circulatory System O2/CO2
Gas Exchange in Animals Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2 Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial Respiratory surface! skin, gills, lungs Circulatory System O2/CO2
QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE
 cm H O 2 cm H O 2 cm HO 2 PSI cm H O 2 ON OFF UPPER LIMIT LOWER LIMIT UPPER LIMIT LOWER LIMIT LIFE PULSE HIGH-FREQUENCY VENTILATOR QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE 01388-08.11 MONITOR PIP JET VALVE ALARMS READY SILENCE
cm H O 2 cm H O 2 cm HO 2 PSI cm H O 2 ON OFF UPPER LIMIT LOWER LIMIT UPPER LIMIT LOWER LIMIT LIFE PULSE HIGH-FREQUENCY VENTILATOR QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE 01388-08.11 MONITOR PIP JET VALVE ALARMS READY SILENCE
Learning objectives. First Response Learning Module 2 Based on ILCOR and ANZCOR 2016
 First Response Learning Module 2 Based on ILCOR and ANZCOR 2016 Learning objectives Following completion of the theoretical & practical components of this module, the participant will be able to demonstrate
First Response Learning Module 2 Based on ILCOR and ANZCOR 2016 Learning objectives Following completion of the theoretical & practical components of this module, the participant will be able to demonstrate
