A new theory for downslope windstorms and trapped lee wave François Lott Lab. Météorologie Dynamique, Ecole Normale Supérieure, Paris
|
|
|
- Eugene Marshall
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A new theory for downslope windstorms and trapped lee wave François Lott Lab. Météorologie Dynamique, Ecole Normale Supérieure, Paris 1)Motivation: trapped lee waves 2)Model description 3)Downslope windstorms and Foehn 4)Trapped lee-waves and low level flow stability
2 1) Motivation: trapped lee waves Turning points are not sufficient for the existence of trapped lee-waves, R matters (Smith et al. 2002) and Jiang et al. 2006): Often R is small ( R <<1), except when the boundary layer is unstable! A good reason for R <<1: the background wind is null in z=0, there is a critical level for mountain waves! The gravity waves somehow see the presence of this critical level (Lott 2007)
3 1) Motivation: trapped lee waves For a viscous bound. R depends on the surface Richardson number J R ~1 can only occur when J<0.25 and in the inviscid limit (Lott 2007) Case of a small linear damping : J>0.25 w= ^w e ikx Monochromatic GW z= N 0 U 0 z U(z) Near the surface (Booker and Bretherton 1967): ŵ a 1 ( z i ϵ ) 1 / 2 i J 14 a 2 ( z i ϵ) 1 /2 i J 1 4 the boundary condition: w (z=0)=0 yields 1 R = a 2 a 1 = ( iϵ)i J 0.25 =e π J 0.25 It decreases when J increases. J -1/2 We will return to the unstable case J<0.25 latter
4 How to integrate a mountain forcing in those results (the linear boundary condition w(0)=u(0)dh/dx reduces to 0=0)! 2D Boussinesq non-dimensional U =tanh z/ J, N 2 =1 J= d N U 0, Downslope windstorms and trapped lee wave, F. Lott 2) Model description non-dim shear depth Mountain :h= H n 1 x 2 /F r 2 H N = H N, non dim mount. height U 0 F r = L N,Froude or non dim mountain length U 0 Linear inflow solution: w (x,z)= f (k)ŵc (k, z)e ikx dk Nonlinear boundary condition: w (h)=u (h) dh dx ~Long (1953)
5 ŵ c (k, z) satisfies: d ^w c d z ( 2) 1 1 U2 2 2 k U J ^w =0 c which has an analytical solution, satisfying mz/ J ^w c e when Downslope windstorms and trapped lee wave, F. Lott 2) Model description Linear inflow solution: w (x,z)= f (k)ŵc (k, z)e ikx dk ŵ c a 1 (k)z 1/2 i μ 1/ 2 iμ a 2 (k) z when m 2 =k 2 1and μ 2 =J 0.25 z z 0 Nonlinear boundary condition determine f(k): Nonlinear boundary condition: w (h)=u (h) dh dx f (k) (a 1 (k)h (x) 1 / 2 iμ a 2 (k)h (x) 1/2i μ ) e ikx dk=h dh dx ϵ 0 This inversion can be done when there is dissipation ~Long (1953)
6 3) Prediction of dowslope windstorms and Foehn w(x,z): structure of a mountain wave with vertical wavelength becoming small near the ground Results for J=2, H ND =0.2, F r =10 No trapped waves, despite the fact that S(z)= U U 2 2 J decreases with altitude Remember ŵ z 0 z 1 /2 e i J 0.25 log z This also means that the horizontal wind becomes very Large near the surface û z 0 z 1 /2 e i J 0.25 log z This leads to the strong downslope winds Strong downslope winds No upper level wave breaking Dry Foehn
7 3) Prediction of dowslope windstorms and Foehn Uniform wind, H ND =0.2, F r =10 These results essentially Result from the smallness of the background horizontal wind near z=0 Here simulations with U=1 No strong downslope winds or jumps when U=1
8 3) Prediction of dowslope windstorms and Foehn Downslope wind amplitude: Max ( u(x, z) ) z<h n /2 U (H N ) 0< x<2f r Z BLYR 5 ϵ/ F r Boundary layer depth: being the linear damping parameter Downslope windstorms and dry Foehn are favored in stable flows
9 4) Trapped lee waves and low level flow stability R ~1 can only occur when J<0.25 and in the inviscid limit (Lott 2007) Near the surface: ŵ a 1 ( z i ϵ ) 1 / J a 2 ( z iϵ) 1/ J The BC: w (z=0)=0 yields a 2 a 1 =ϵ 0.25 J The EP flux ^u ^w 2 = 0.25 J 2k a 1 2 ϵ 0.25 J goes to zero when goes to zero: R 1 Also, modes with a 2 =0 exists in our profiles: the longest neutral modes of KH instability (Drazin 1958)
10 4) Trapped lee waves and low level flow stability Stable (J<0.25), waves stay confined over the ridge Trapped waves decaying downstream Transition Unstable (J<0.25), pure trapped lee waves develop downstream Pure trapped waves= longest neutral mode of KH instability (Drazin 1958)
11 A new theory for downslope windstorms and trapped lee wave François Lott Lab. Météorologie Dynamique, Ecole Normale Supérieure, Paris Critical level dynamics induces downslope windstorms and Foehn when J>1 Trapped lee waves start to appear when J<1 Pure trapped lee waves when J<0.25 are near KH instability KH instabilities: Trapped mountain waves: U(z) N 2 >0 U(z) N 2 >0 U(z)>0 N 2 >0 U(z)>0 N 2 >0 Always Unstable (actually J=0) Conditionnaly Unstable (if J<0.25) 0 R =1 always 0 R =1 becomes conditional to J<0.25)
12 A new theory for downslope windstorms and trapped lee wave François Lott Lab. Météorologie Dynamique, Ecole Normale Supérieure, Paris Critical level dynamics induces downslope windstorms and Foehn when J>1 Trapped lee waves start to appear when J<1 Pure trapped lee waves when J<0.25 are near KH instability KH instabilities: Trapped mountain waves: U(z) N 2 >0 U(z) N 2 >0 U(z)>0 N 2 >0 U(z)>0 N 2 >0 Always Unstable (actually J=0) Conditionnaly Unstable (if J<0.25) 0 R =1 always (actually J=0 At the surface) 0 R =1 becomes conditional to J<0.25)
Gravity waves in stable atmospheric boundary layers
 Gravity waves in stable atmospheric boundary layers Carmen J. Nappo CJN Research Meteorology Knoxville, Tennessee 37919, USA Abstract Gravity waves permeate the stable atmospheric planetary boundary layer,
Gravity waves in stable atmospheric boundary layers Carmen J. Nappo CJN Research Meteorology Knoxville, Tennessee 37919, USA Abstract Gravity waves permeate the stable atmospheric planetary boundary layer,
ESCI 343 Atmospheric Dynamics II Lesson 10 - Topographic Waves
 ESCI 343 Atmospheric Dynamics II Lesson 10 - Topographic Waves Reference: An Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology (3 rd edition), J.R. Holton Reading: Holton, Section 7.4. STATIONARY WAVES Waves will appear
ESCI 343 Atmospheric Dynamics II Lesson 10 - Topographic Waves Reference: An Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology (3 rd edition), J.R. Holton Reading: Holton, Section 7.4. STATIONARY WAVES Waves will appear
Trapped lee waves: a currently neglected source of low-level orographic drag
 Trapped lee waves: a currently neglected source of low-level orographic drag Miguel A. C. Teixeira, Jose L. Argain, Pedro M. A. Miranda 3, University of Reading, Reading, UK Physics, University of Algarve,
Trapped lee waves: a currently neglected source of low-level orographic drag Miguel A. C. Teixeira, Jose L. Argain, Pedro M. A. Miranda 3, University of Reading, Reading, UK Physics, University of Algarve,
Downslope Wind Storms
 Downslope Wind Storms How does acceleration over the wing affect pressure field? Equation of Motion for frictionless flow: V t = l k α p+g If we assume a horizontally homogeneous, hydrostatic reference
Downslope Wind Storms How does acceleration over the wing affect pressure field? Equation of Motion for frictionless flow: V t = l k α p+g If we assume a horizontally homogeneous, hydrostatic reference
Modelling atmospheric stability with CFD: The importance of tall profiles
 ENERGY Modelling atmospheric stability with CFD: The importance of tall profiles VindKraftNet Seminar on Profiles Jean-François Corbett, Global Head of CFD Service 1 SAFER, SMARTER, GREENER DNV GL CFD
ENERGY Modelling atmospheric stability with CFD: The importance of tall profiles VindKraftNet Seminar on Profiles Jean-François Corbett, Global Head of CFD Service 1 SAFER, SMARTER, GREENER DNV GL CFD
Gravity Waves in Shear and
 Gravity Waves in Shear and Implications for Organized Convection Sam Stechmann (Wisconsin) and Andy Majda (NYU) (paper in J. Atmos. Sci., 29) Workshop on Modelling Monsoon Intraseasonal Variability Busan,
Gravity Waves in Shear and Implications for Organized Convection Sam Stechmann (Wisconsin) and Andy Majda (NYU) (paper in J. Atmos. Sci., 29) Workshop on Modelling Monsoon Intraseasonal Variability Busan,
Lecture 7. More on BL wind profiles and turbulent eddy structures. In this lecture
 Lecture 7. More on BL wind profiles and turbulent eddy structures In this lecture Stability and baroclinicity effects on PBL wind and temperature profiles Large-eddy structures and entrainment in shear-driven
Lecture 7. More on BL wind profiles and turbulent eddy structures In this lecture Stability and baroclinicity effects on PBL wind and temperature profiles Large-eddy structures and entrainment in shear-driven
Large-Scale Flow Response to the Breaking of Mountain Gravity Waves François Lott, LMD, Ecole Normale Supérieure;
 Large-Scale Flow Response to the Breaking of Mountain Gravity Waves François Lott, LMD, Ecole Normale Supérieure; flott@lmd.ens.fr 1) General: gravity waves and their impact on climate 2) Regional and
Large-Scale Flow Response to the Breaking of Mountain Gravity Waves François Lott, LMD, Ecole Normale Supérieure; flott@lmd.ens.fr 1) General: gravity waves and their impact on climate 2) Regional and
Impact of non hydrostatic effects and trapped lee waves on mountain wave drag in directionally sheared flow
 Impact of non hydrostatic effects and trapped lee waves on mountain wave drag in directionally sheared flow Article Accepted Version Yu, C. L. and Teixeira, M. A. C. (25) Impact of nonhydrostatic effects
Impact of non hydrostatic effects and trapped lee waves on mountain wave drag in directionally sheared flow Article Accepted Version Yu, C. L. and Teixeira, M. A. C. (25) Impact of nonhydrostatic effects
Non orographic and orographic gravity waves above Antarctica and the Southern Ocean
 Non orographic and orographic gravity waves above Antarctica and the Southern Ocean Riwal Plougonven Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique, IPSL Ecole Normale Supérieure Work involving: Albert Hertzog,
Non orographic and orographic gravity waves above Antarctica and the Southern Ocean Riwal Plougonven Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique, IPSL Ecole Normale Supérieure Work involving: Albert Hertzog,
Effect of channel slope on flow characteristics of undular hydraulic jumps
 River Basin Management III 33 Effect of channel slope on flow characteristics of undular hydraulic jumps H. Gotoh, Y. Yasuda & I. Ohtsu Department of Civil Engineering, College of Science and Technology,
River Basin Management III 33 Effect of channel slope on flow characteristics of undular hydraulic jumps H. Gotoh, Y. Yasuda & I. Ohtsu Department of Civil Engineering, College of Science and Technology,
Kathleen Dohan. Wind-Driven Surface Currents. Earth and Space Research, Seattle, WA
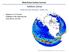 Updates to OSCAR and challenges with capturing the wind-driven currents. Wind-Driven Surface Currents Kathleen Dohan Earth and Space Research, Seattle, WA ENSO OSCAR Surface currents from satellite fields
Updates to OSCAR and challenges with capturing the wind-driven currents. Wind-Driven Surface Currents Kathleen Dohan Earth and Space Research, Seattle, WA ENSO OSCAR Surface currents from satellite fields
LOCAL WINDS. Prof. Stephan De Wekker Department of Env. Sciences Guest lecture EVSC 1300
 LOCAL WINDS Prof. Stephan De Wekker (dewekker@virginia.edu) Department of Env. Sciences Guest lecture EVSC 1300 SEA BREEZE 980 mb 990 mb 1000 mb LAND BREEZE The convergence of two lake breezes and
LOCAL WINDS Prof. Stephan De Wekker (dewekker@virginia.edu) Department of Env. Sciences Guest lecture EVSC 1300 SEA BREEZE 980 mb 990 mb 1000 mb LAND BREEZE The convergence of two lake breezes and
Modeling of Mountain Waves in T-REX
 10.6 Modeling of Mountain Waves in T-REX Steven E. Koch 1,2, Ligia R. Bernardet 1,2, Brian D. Jamison 1,3, and John M. Brown 1 1 NOAA / Earth Systems Research Laboratory (ESRL), Boulder, Colorado 2 Developmental
10.6 Modeling of Mountain Waves in T-REX Steven E. Koch 1,2, Ligia R. Bernardet 1,2, Brian D. Jamison 1,3, and John M. Brown 1 1 NOAA / Earth Systems Research Laboratory (ESRL), Boulder, Colorado 2 Developmental
Large-amplitude internal wave generation in the lee of step-shaped topography
 1 Large-amplitude internal wave generation in the lee of step-shaped topography B. R. Sutherland University of Alberta, Edmonton, Canada. Short title: LARGE-AMPLITUDE INTERNAL WAVE GENERATION... 2 Abstract.
1 Large-amplitude internal wave generation in the lee of step-shaped topography B. R. Sutherland University of Alberta, Edmonton, Canada. Short title: LARGE-AMPLITUDE INTERNAL WAVE GENERATION... 2 Abstract.
Chapter 2. Turbulence and the Planetary Boundary Layer
 Chapter 2. Turbulence and the Planetary Boundary Layer In the chapter we will first have a qualitative overview of the PBL then learn the concept of Reynolds averaging and derive the Reynolds averaged
Chapter 2. Turbulence and the Planetary Boundary Layer In the chapter we will first have a qualitative overview of the PBL then learn the concept of Reynolds averaging and derive the Reynolds averaged
An experimental study of internal wave generation through evanescent regions
 An experimental study of internal wave generation through evanescent regions Allison Lee, Julie Crockett Department of Mechanical Engineering Brigham Young University Abstract Internal waves are a complex
An experimental study of internal wave generation through evanescent regions Allison Lee, Julie Crockett Department of Mechanical Engineering Brigham Young University Abstract Internal waves are a complex
Lee Waves and Mountain Waves
 Lee Waves and Mountain Waves Dale R. Durran University of Washington, Seattle, USA December 7, 2013 KEYWORDS: Mountain waves, gravity waves, lee waves Introduction Buoyancy perturbations develop when stably
Lee Waves and Mountain Waves Dale R. Durran University of Washington, Seattle, USA December 7, 2013 KEYWORDS: Mountain waves, gravity waves, lee waves Introduction Buoyancy perturbations develop when stably
Transport and mixing in the extratropical tropopause region in a high vertical resolution GCM
 Transport and mixing in the extratropical tropopause region in a high vertical resolution GCM (Miyazaki et al. JAS 2010a,2010b) Kazuyuki Miyazaki Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute (KNMI) Japan
Transport and mixing in the extratropical tropopause region in a high vertical resolution GCM (Miyazaki et al. JAS 2010a,2010b) Kazuyuki Miyazaki Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute (KNMI) Japan
CVEN Computer Applications in Engineering and Construction. Programming Assignment #4 Analysis of Wave Data Using Root-Finding Methods
 CVEN 30-501 Computer Applications in Engineering and Construction Programming Assignment #4 Analysis of Wave Data Using Root-Finding Methods Date distributed: 9/30/016 Date due: 10/14/016 at 3:00 PM (electronic
CVEN 30-501 Computer Applications in Engineering and Construction Programming Assignment #4 Analysis of Wave Data Using Root-Finding Methods Date distributed: 9/30/016 Date due: 10/14/016 at 3:00 PM (electronic
Salmon: Introduction to ocean waves
 10 Breakers, bores and longshore currents There is lots more to say about linear, shallow-water waves, but now we want to say something about the more general, nonlinear case. To keep the math as simple
10 Breakers, bores and longshore currents There is lots more to say about linear, shallow-water waves, but now we want to say something about the more general, nonlinear case. To keep the math as simple
Mountain Forced Flows
 Mountain Forced Flows Jeremy A. Gibbs University of Oklahoma gibbz@ou.edu February 3, 2015 1 / 45 Overview Orographic Precipitation Common Ingredients of Heavy Orographic Precipitation Formation and Enhancement
Mountain Forced Flows Jeremy A. Gibbs University of Oklahoma gibbz@ou.edu February 3, 2015 1 / 45 Overview Orographic Precipitation Common Ingredients of Heavy Orographic Precipitation Formation and Enhancement
The total precipitation (P) is determined by the average rainfall rate (R) and the duration (D),
 Orographic precipitation Common ingredients of heavy orographic precipitation The total precipitation (P) is determined by the average rainfall rate (R) and the duration (D), P = RD. (1) The rainfall rate
Orographic precipitation Common ingredients of heavy orographic precipitation The total precipitation (P) is determined by the average rainfall rate (R) and the duration (D), P = RD. (1) The rainfall rate
The Dissipation of Trapped Lee Waves. Part I: Leakage of Inviscid Waves into the Stratosphere
 APRIL 2015 D U R R A N E T A L. 1569 The Dissipation of Trapped Lee Waves. Part I: Leakage of Inviscid Waves into the Stratosphere DALE R. DURRAN, MATTHEW O. G. HILLS,* AND PETER N. BLOSSEY Department
APRIL 2015 D U R R A N E T A L. 1569 The Dissipation of Trapped Lee Waves. Part I: Leakage of Inviscid Waves into the Stratosphere DALE R. DURRAN, MATTHEW O. G. HILLS,* AND PETER N. BLOSSEY Department
A majority of these phenomena are mesocale and are induced by stably stratified flow over orography.
 Chapter 2. Mountain forced flows 2.1. Mountain waves Well-known weather phenomena directly related to flow over orography include mountain waves lee waves and clouds rotors and rotor clouds severe downslope
Chapter 2. Mountain forced flows 2.1. Mountain waves Well-known weather phenomena directly related to flow over orography include mountain waves lee waves and clouds rotors and rotor clouds severe downslope
The Use of Bulk and Profile Methods for Determining Surface Heat Fluxes in the Presence of Glacier Winds
 3 The Use of Bulk and Profile Methods for Determining Surface Heat Fluxes in the Presence of Glacier Winds A -D second-order closure model and in situ observations on a melting glacier surface are used
3 The Use of Bulk and Profile Methods for Determining Surface Heat Fluxes in the Presence of Glacier Winds A -D second-order closure model and in situ observations on a melting glacier surface are used
A Numerical Simulation of Convectively Induced Turbulence (CIT) above Deep Convection
 A Numerical Simulation of Convectively Induced Turbulence (CIT) above Deep Convection Jung-Hoon Kim and Hye-Yeong Chun Department of Atmospheric Sciences Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea 1. Introduction
A Numerical Simulation of Convectively Induced Turbulence (CIT) above Deep Convection Jung-Hoon Kim and Hye-Yeong Chun Department of Atmospheric Sciences Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea 1. Introduction
Forest Winds in Complex Terrain
 Forest Winds in Complex Terrain Ilda Albuquerque 1 Contents Project Description Motivation Forest Complex Terrain Forested Complex Terrain 2 Project Description WAUDIT (Wind Resource Assessment Audit and
Forest Winds in Complex Terrain Ilda Albuquerque 1 Contents Project Description Motivation Forest Complex Terrain Forested Complex Terrain 2 Project Description WAUDIT (Wind Resource Assessment Audit and
Upstream-Propagating Wave Modes in Moist and Dry Flow over Topography
 3060 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 69 Upstream-Propagating Wave Modes in Moist and Dry Flow over Topography TEDDIE L. KELLER, RICHARD ROTUNNO, MATTHIAS STEINER, AND
3060 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 69 Upstream-Propagating Wave Modes in Moist and Dry Flow over Topography TEDDIE L. KELLER, RICHARD ROTUNNO, MATTHIAS STEINER, AND
Goal: Develop quantitative understanding of ENSO genesis, evolution, and impacts
 The Delayed Oscillator Zebiak and Cane (1987) Model Other Theories Theory of ENSO teleconnections Goal: Develop quantitative understanding of ENSO genesis, evolution, and impacts The delayed oscillator
The Delayed Oscillator Zebiak and Cane (1987) Model Other Theories Theory of ENSO teleconnections Goal: Develop quantitative understanding of ENSO genesis, evolution, and impacts The delayed oscillator
The Influence of Ocean Surface Waves on Offshore Wind Turbine Aerodynamics. Ali Al Sam
 The Influence of Ocean Surface Waves on Offshore Wind Turbine Aerodynamics Ali Al Sam What I m going to wear today? Do I need to leave early to get to work? Taking buss or riding bike? Where will we drink
The Influence of Ocean Surface Waves on Offshore Wind Turbine Aerodynamics Ali Al Sam What I m going to wear today? Do I need to leave early to get to work? Taking buss or riding bike? Where will we drink
Gravity waves and bores. Material kindly provided by Dr. Steven Koch GSD NOAA (Boulder, CO)
 Gravity waves and bores Material kindly provided by Dr. Steven Koch GSD NOAA (Boulder, CO) Presented at Iowa State University 11 April 2005 What is a gravity wave? An oscillation caused by the displacement
Gravity waves and bores Material kindly provided by Dr. Steven Koch GSD NOAA (Boulder, CO) Presented at Iowa State University 11 April 2005 What is a gravity wave? An oscillation caused by the displacement
Influence of rounding corners on unsteady flow and heat transfer around a square cylinder
 Influence of rounding corners on unsteady flow and heat transfer around a square cylinder S. K. Singh Deptt. of Mech. Engg., M. B. M. Engg. College / J. N. V. University, Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India Abstract
Influence of rounding corners on unsteady flow and heat transfer around a square cylinder S. K. Singh Deptt. of Mech. Engg., M. B. M. Engg. College / J. N. V. University, Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India Abstract
Bora flow over the complex terrain of the mid- Adriatic area
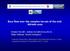 Bora flow over the complex terrain of the mid- Adriatic area Kristian Horvath 1, kristian.horvath@cirus.dhz.hr, Željko Večenaj 2, Branko Grisogono 2 1 Research Department, Meteorological and Hydrological
Bora flow over the complex terrain of the mid- Adriatic area Kristian Horvath 1, kristian.horvath@cirus.dhz.hr, Željko Večenaj 2, Branko Grisogono 2 1 Research Department, Meteorological and Hydrological
ITTC Recommended Procedures and Guidelines
 Page 1 of 6 Table of Contents 1. PURPOSE...2 2. PARAMETERS...2 2.1 General Considerations...2 3 DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE...2 3.1 Model Design and Construction...2 3.2 Measurements...3 3.5 Execution of
Page 1 of 6 Table of Contents 1. PURPOSE...2 2. PARAMETERS...2 2.1 General Considerations...2 3 DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE...2 3.1 Model Design and Construction...2 3.2 Measurements...3 3.5 Execution of
Thorsten Mauritsen *, Gunilla Svensson Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden
 J.1 WAVE FLOW SIMULATIONS OVER ARCTIC LEADS Thorsten Mauritsen *, Gunilla Svensson Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden Branko Grisogono Department of Geophysics, Faculty of Science, Zagreb, Croatia
J.1 WAVE FLOW SIMULATIONS OVER ARCTIC LEADS Thorsten Mauritsen *, Gunilla Svensson Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden Branko Grisogono Department of Geophysics, Faculty of Science, Zagreb, Croatia
Orographic Clouds. "...towering up the darkening mountain's side... It mantles round the mid-way height..."320
 Chapter 12 Orographic Clouds "...towering up the darkening mountain's side... It mantles round the mid-way height..."320 In previous chapters, we have seen a variety of dynamical features that govern the
Chapter 12 Orographic Clouds "...towering up the darkening mountain's side... It mantles round the mid-way height..."320 In previous chapters, we have seen a variety of dynamical features that govern the
Xiaoli Guo Larsén,* Søren Larsen and Andrea N. Hahmann Risø National Laboratory for Sustainable Energy, Roskilde, Denmark
 Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 138: 274 279, January 2012 A Notes and Correspondence Origin of the waves in A case-study of mesoscale spectra of wind and
Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 138: 274 279, January 2012 A Notes and Correspondence Origin of the waves in A case-study of mesoscale spectra of wind and
Trapped mountain waves during a light aircraft accident
 Australian Meteorological and Oceanographic Journal 63 (2013) 377 389 Trapped mountain waves during a light aircraft accident Teresa J. Parker 1 and Todd P. Lane 2 1 Monash Weather and Climate, School
Australian Meteorological and Oceanographic Journal 63 (2013) 377 389 Trapped mountain waves during a light aircraft accident Teresa J. Parker 1 and Todd P. Lane 2 1 Monash Weather and Climate, School
Hong Kong International Airport North Runway South Runway
 P.1 Atmospheric Waves Associated with a Valley of Lantau Island: Observation, Theory and Numerical Simulation P.W. Chan * Hong Kong Observatory, Hong Kong, China 1. INTRODUCTION The Hong Kong Observatory
P.1 Atmospheric Waves Associated with a Valley of Lantau Island: Observation, Theory and Numerical Simulation P.W. Chan * Hong Kong Observatory, Hong Kong, China 1. INTRODUCTION The Hong Kong Observatory
Super-parameterization of boundary layer roll vortices in tropical cyclone models
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Super-parameterization of boundary layer roll vortices in tropical cyclone models PI Isaac Ginis Graduate School of Oceanography
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Super-parameterization of boundary layer roll vortices in tropical cyclone models PI Isaac Ginis Graduate School of Oceanography
Stefan Emeis
 The Physics of Wind Park Optimization Stefan Emeis stefan.emeis@kit.edu INSTITUTE OF METEOROLOGY AND CLIMATE RESEARCH, Photo: Vattenfall/C. Steiness KIT University of the State of Baden-Wuerttemberg and
The Physics of Wind Park Optimization Stefan Emeis stefan.emeis@kit.edu INSTITUTE OF METEOROLOGY AND CLIMATE RESEARCH, Photo: Vattenfall/C. Steiness KIT University of the State of Baden-Wuerttemberg and
Wave Breaking. Wave Breaking
 Wave Breaking The release of energy derived from the wind, along a narrow coastal zone - geomorphic work done by wind, really, translated through medium of water. Wave Breaking Wave breaking is responsible
Wave Breaking The release of energy derived from the wind, along a narrow coastal zone - geomorphic work done by wind, really, translated through medium of water. Wave Breaking Wave breaking is responsible
Student name: + is valid for C =. The vorticity
 13.012 Marine Hydrodynamics for Ocean Engineers Fall 2004 Quiz #1 Student name: This is a closed book examination. You are allowed 1 sheet of 8.5 x 11 paper with notes. For the problems in Section A, fill
13.012 Marine Hydrodynamics for Ocean Engineers Fall 2004 Quiz #1 Student name: This is a closed book examination. You are allowed 1 sheet of 8.5 x 11 paper with notes. For the problems in Section A, fill
10.6 The Dynamics of Drainage Flows Developed on a Low Angle Slope in a Large Valley Sharon Zhong 1 and C. David Whiteman 2
 10.6 The Dynamics of Drainage Flows Developed on a Low Angle Slope in a Large Valley Sharon Zhong 1 and C. David Whiteman 2 1Department of Geosciences, University of Houston, Houston, TX 2Pacific Northwest
10.6 The Dynamics of Drainage Flows Developed on a Low Angle Slope in a Large Valley Sharon Zhong 1 and C. David Whiteman 2 1Department of Geosciences, University of Houston, Houston, TX 2Pacific Northwest
A flow regime diagram for forecasting lee waves, rotors and downslope winds
 Meteorol. Appl. 13, 179 195 (2006) doi:10.1017/s1350482706002088 A flow regime diagram for forecasting lee waves, rotors and downslope winds P. F. Sheridan & S. B. Vosper Met Office, FitzRoy Road, Exeter
Meteorol. Appl. 13, 179 195 (2006) doi:10.1017/s1350482706002088 A flow regime diagram for forecasting lee waves, rotors and downslope winds P. F. Sheridan & S. B. Vosper Met Office, FitzRoy Road, Exeter
WESEP 594 Research Seminar
 WESEP 594 Research Seminar Aaron J Rosenberg Department of Aerospace Engineering Iowa State University Major: WESEP Co-major: Aerospace Engineering Motivation Increase Wind Energy Capture Betz limit: 59.3%
WESEP 594 Research Seminar Aaron J Rosenberg Department of Aerospace Engineering Iowa State University Major: WESEP Co-major: Aerospace Engineering Motivation Increase Wind Energy Capture Betz limit: 59.3%
Turbulence generation by mountain wave breaking in flows with directional wind shear
 Turbulence generation by mountain wave breaking in flows with directional wind shear Article Accepted Version Guarino, M. V., Teixeira, M. A. C. and Ambaum, M. H. P. (2016) Turbulence generation by mountain
Turbulence generation by mountain wave breaking in flows with directional wind shear Article Accepted Version Guarino, M. V., Teixeira, M. A. C. and Ambaum, M. H. P. (2016) Turbulence generation by mountain
VI. Static Stability. Consider a parcel of unsaturated air. Assume the actual lapse rate is less than the dry adiabatic lapse rate: Γ < Γ d
 VI. Static Stability Consider a parcel of unsaturated air. Assume the actual lapse rate is less than the dry adiabatic lapse rate: Γ < Γ d VI. Static Stability Consider a parcel of unsaturated air. Assume
VI. Static Stability Consider a parcel of unsaturated air. Assume the actual lapse rate is less than the dry adiabatic lapse rate: Γ < Γ d VI. Static Stability Consider a parcel of unsaturated air. Assume
LONG WAVE RUN-UP OVER SUBMERGED REEF AND BREAKWATER
 LONG WAVE RUN-UP OVER SUBMERGED REEF AND BREAKWATER A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE GRADUATE DIVISION OF THE UNIVERSITY OF HAWAIʻI IN PARTIAL FULFILMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE
LONG WAVE RUN-UP OVER SUBMERGED REEF AND BREAKWATER A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE GRADUATE DIVISION OF THE UNIVERSITY OF HAWAIʻI IN PARTIAL FULFILMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE
3. Observed initial growth of short waves from radar measurements in tanks (Larson and Wright, 1975). The dependence of the exponential amplification
 Geophysica (1997), 33(2), 9-14 Laboratory Measurements of Stress Modulation by Wave Groups M.G. Skafel and M.A. Donelan* National Water Research Institute Canada Centre for Inland Waters Burlington, Ontario,
Geophysica (1997), 33(2), 9-14 Laboratory Measurements of Stress Modulation by Wave Groups M.G. Skafel and M.A. Donelan* National Water Research Institute Canada Centre for Inland Waters Burlington, Ontario,
The effect of back spin on a table tennis ball moving in a viscous fluid.
 How can planes fly? The phenomenon of lift can be produced in an ideal (non-viscous) fluid by the addition of a free vortex (circulation) around a cylinder in a rectilinear flow stream. This is known as
How can planes fly? The phenomenon of lift can be produced in an ideal (non-viscous) fluid by the addition of a free vortex (circulation) around a cylinder in a rectilinear flow stream. This is known as
Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics
 Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics Volume 9, 2010 http://acousticalsociety.org/ 159th Meeting Acoustical Society of America/NOISE-CON 2010 Baltimore, Maryland 19-23 April 2010 Session 1pBB: Biomedical
Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics Volume 9, 2010 http://acousticalsociety.org/ 159th Meeting Acoustical Society of America/NOISE-CON 2010 Baltimore, Maryland 19-23 April 2010 Session 1pBB: Biomedical
Laboratory generation of internal waves from. sinusoidal topography
 Laboratory generation of internal waves from sinusoidal topography D. A. Aguilar a, B. R. Sutherland a,, D. J. Muraki b a Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences, University of Alberta, Edmonton,
Laboratory generation of internal waves from sinusoidal topography D. A. Aguilar a, B. R. Sutherland a,, D. J. Muraki b a Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences, University of Alberta, Edmonton,
Large-eddy simulation study of effects of clearing in forest on wind turbines
 Large-eddy simulation study of effects of clearing in forest on wind turbines J. Matsfelt 1 and L. Davidson 1 1 Chalmers University of Technology, Dep. of Mechanics and Maritime Sciences, Div. of Fluid
Large-eddy simulation study of effects of clearing in forest on wind turbines J. Matsfelt 1 and L. Davidson 1 1 Chalmers University of Technology, Dep. of Mechanics and Maritime Sciences, Div. of Fluid
Flow modelling hills complex terrain and other issues
 Flow modelling hills, complex terrain and other issues Modelling approaches sorted after complexity Rules of thumbs Codes and standards Linear model, 1 st order turbulence closure LINCOM/Wasp Reynolds-averaged
Flow modelling hills, complex terrain and other issues Modelling approaches sorted after complexity Rules of thumbs Codes and standards Linear model, 1 st order turbulence closure LINCOM/Wasp Reynolds-averaged
Testing TELEMAC-2D suitability for tsunami propagation from source to near shore
 Testing TELEMAC-2D suitability for tsunami propagation from source to near shore Alan Cooper, Giovanni Cuomo, Sébastien Bourban, Michael Turnbull, David Roscoe HR Wallingford Ltd, Howbery Park, Wallingford,
Testing TELEMAC-2D suitability for tsunami propagation from source to near shore Alan Cooper, Giovanni Cuomo, Sébastien Bourban, Michael Turnbull, David Roscoe HR Wallingford Ltd, Howbery Park, Wallingford,
Feature Articles. Annyong ha shimnikka
 Acoustics Shock Vibration Signal Processing October 2002 Newsletter Annyong ha shimnikka Feature Articles Vibration waves are one of the mechanisms by which nature displays its awesome power. Mountain
Acoustics Shock Vibration Signal Processing October 2002 Newsletter Annyong ha shimnikka Feature Articles Vibration waves are one of the mechanisms by which nature displays its awesome power. Mountain
18 Flight Hazards over High Ground
 18 Flight Hazards over High Ground meteorology 18.1 Mountain Effect on Fronts When a warm front passes a mountain range, the air, is lifted over the mountain and will strengthen the formation of cloud
18 Flight Hazards over High Ground meteorology 18.1 Mountain Effect on Fronts When a warm front passes a mountain range, the air, is lifted over the mountain and will strengthen the formation of cloud
Short-period gravity waves over a high-latitude observation site: Rothera, Antarctica
 Short-period gravity waves over a high-latitude observation site: Rothera, Antarctica K. Nielsen, D. Broutman, M. Taylor, D. Siskind, S. Eckermann, K. Hoppel, R. Hibbins, M. Jarvis, N. Mitchell, J. Russell
Short-period gravity waves over a high-latitude observation site: Rothera, Antarctica K. Nielsen, D. Broutman, M. Taylor, D. Siskind, S. Eckermann, K. Hoppel, R. Hibbins, M. Jarvis, N. Mitchell, J. Russell
On the Interpretation of Scatterometer Winds near Sea Surface Temperature Fronts
 On the Interpretation of Scatterometer Winds near Sea Surface Temperature Fronts Jim Edson University of Connecticut Amanda Plagge & Doug Vandemark University of New Hampshire IOVWST Meeting Utrecht, NL
On the Interpretation of Scatterometer Winds near Sea Surface Temperature Fronts Jim Edson University of Connecticut Amanda Plagge & Doug Vandemark University of New Hampshire IOVWST Meeting Utrecht, NL
Vertical Motion and Atmospheric Stability
 Lesson 4 Vertical Motion and Atmospheric Stability This lesson describes the vertical structure of the atmosphere, atmospheric stability and the corresponding vertical motion. Adiabatic diagrams are introduced
Lesson 4 Vertical Motion and Atmospheric Stability This lesson describes the vertical structure of the atmosphere, atmospheric stability and the corresponding vertical motion. Adiabatic diagrams are introduced
Slide 1 / The distance traveled by a wave in one period is called? Frequency Period Speed of wave Wavelength Amplitude
 Slide 1 / 20 1 The distance traveled by a wave in one period is called? Frequency Period Speed of wave Wavelength mplitude Slide 2 / 20 2 Which of the following is the speed of a wave traveling with a
Slide 1 / 20 1 The distance traveled by a wave in one period is called? Frequency Period Speed of wave Wavelength mplitude Slide 2 / 20 2 Which of the following is the speed of a wave traveling with a
Waves Multiple Choice
 Waves Multiple Choice PSI Physics Name: 1. The distance traveled by a wave in one period is called? A. Frequency B. Period C. Speed of wave D. Wavelength E. Amplitude 2. Which of the following is the speed
Waves Multiple Choice PSI Physics Name: 1. The distance traveled by a wave in one period is called? A. Frequency B. Period C. Speed of wave D. Wavelength E. Amplitude 2. Which of the following is the speed
ISOLATION OF NON-HYDROSTATIC REGIONS WITHIN A BASIN
 ISOLATION OF NON-HYDROSTATIC REGIONS WITHIN A BASIN Bridget M. Wadzuk 1 (Member, ASCE) and Ben R. Hodges 2 (Member, ASCE) ABSTRACT Modeling of dynamic pressure appears necessary to achieve a more robust
ISOLATION OF NON-HYDROSTATIC REGIONS WITHIN A BASIN Bridget M. Wadzuk 1 (Member, ASCE) and Ben R. Hodges 2 (Member, ASCE) ABSTRACT Modeling of dynamic pressure appears necessary to achieve a more robust
General Physics 1 Lab - PHY 2048L Lab 6: Wave Mechanics Wave on a String / Optical Tweezers PhET Lab Date. Wave on a String
 General Physics 1 Lab - PHY 2048L Name Lab 6: Wave Mechanics Wave on a String / Optical Tweezers PhET Lab Date Author: Harsh Jain / PhET Source: Wave on a String http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/wave-on-a-string
General Physics 1 Lab - PHY 2048L Name Lab 6: Wave Mechanics Wave on a String / Optical Tweezers PhET Lab Date Author: Harsh Jain / PhET Source: Wave on a String http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/wave-on-a-string
Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
 43 Module 3: Lecture - 5 on Compressibility and Consolidation Contents Stresses in soil from surface loads; Terzaghi s 1-D consolidation theory; Application in different boundary conditions; Ramp loading;
43 Module 3: Lecture - 5 on Compressibility and Consolidation Contents Stresses in soil from surface loads; Terzaghi s 1-D consolidation theory; Application in different boundary conditions; Ramp loading;
Control of surge and pitch motions of a rectangular floating body using internal sloshing phenomena. Minho Ha and *Cheolung Cheong 1)
 Control of surge and pitch motions of a rectangular floating body using internal sloshing phenomena Minho Ha and *Cheolung Cheong 1) School of Mechanical Engineering, PNU, Busan 609-735, Korea 1) ccheong@pusan.ac.kr
Control of surge and pitch motions of a rectangular floating body using internal sloshing phenomena Minho Ha and *Cheolung Cheong 1) School of Mechanical Engineering, PNU, Busan 609-735, Korea 1) ccheong@pusan.ac.kr
Applications of ELCIRC at LNEC
 stratification in the Guadiana estuary tidal propagation in the Óbidos lagoon Lígia Pinto Anabela Oliveira André B. Fortunato 2 O utline Stratification in the Guadiana estuary The Guadiana estuary Objectives
stratification in the Guadiana estuary tidal propagation in the Óbidos lagoon Lígia Pinto Anabela Oliveira André B. Fortunato 2 O utline Stratification in the Guadiana estuary The Guadiana estuary Objectives
Ship waves in Tallinn Bay: Experimental and numerical study
 Ship waves in Tallinn Bay: Experimental and numerical study Tomas Torsvik Bergen Center for Computational Science UNIFOB AS In collaboration with Tarmo Soomere Wave Engineering Centre for Nonlinear studies
Ship waves in Tallinn Bay: Experimental and numerical study Tomas Torsvik Bergen Center for Computational Science UNIFOB AS In collaboration with Tarmo Soomere Wave Engineering Centre for Nonlinear studies
Numerical Simulation of Internal Waves in the Littoral Ocean
 Numerical Simulation of Internal Waves in the Littoral Ocean Robert L. Street Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305-4020 phone: (650) 723-4969 fax: (650)
Numerical Simulation of Internal Waves in the Littoral Ocean Robert L. Street Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305-4020 phone: (650) 723-4969 fax: (650)
Title. Author(s)HOSSEINI, M.; FARSHADMANESH, P. Issue Date Doc URL. Type. Note. File Information
 Title EVALUATING THE EFFECT OF MULTIPLE VERTICAL ORTHOGONA PHENOMENON IN RECTANGULAR TANKS SUBJECTED TO 3-DIMEN EXCITATIONS Author(s)HOSSEINI, M.; FARSHADMANESH, P. Issue Date 2013-09-11 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/54196
Title EVALUATING THE EFFECT OF MULTIPLE VERTICAL ORTHOGONA PHENOMENON IN RECTANGULAR TANKS SUBJECTED TO 3-DIMEN EXCITATIONS Author(s)HOSSEINI, M.; FARSHADMANESH, P. Issue Date 2013-09-11 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/54196
Airy Wave Theory 2: Wave Orbitals and Energy. Compilation of Airy Equations
 Airy Wave Theory 2: Wave Orbitals and Energy Compilation of Airy Equations 1 Orbital Motion of Water Particles Airy Wave Theory also predicts water particle orbital path trajectories. Orbital path divided
Airy Wave Theory 2: Wave Orbitals and Energy Compilation of Airy Equations 1 Orbital Motion of Water Particles Airy Wave Theory also predicts water particle orbital path trajectories. Orbital path divided
Investigation on Deep-Array Wake Losses Under Stable Atmospheric Conditions
 Investigation on Deep-Array Wake Losses Under Stable Atmospheric Conditions Yavor Hristov, Mark Zagar, Seonghyeon Hahn, Gregory Oxley Plant Siting and Forecasting Vestas Wind Systems A/S Introduction Introduction
Investigation on Deep-Array Wake Losses Under Stable Atmospheric Conditions Yavor Hristov, Mark Zagar, Seonghyeon Hahn, Gregory Oxley Plant Siting and Forecasting Vestas Wind Systems A/S Introduction Introduction
PhD student, January 2010-December 2013
 Numerical modeling of wave current interactions ata a local scaleand and studyof turbulence closuremodel effects MARIA JOÃO TELES PhD student, January 2010-December 2013 Supervisor: António Pires-Silva,
Numerical modeling of wave current interactions ata a local scaleand and studyof turbulence closuremodel effects MARIA JOÃO TELES PhD student, January 2010-December 2013 Supervisor: António Pires-Silva,
Unsteady Wave-Driven Circulation Cells Relevant to Rip Currents and Coastal Engineering
 Unsteady Wave-Driven Circulation Cells Relevant to Rip Currents and Coastal Engineering Andrew Kennedy Dept of Civil and Coastal Engineering 365 Weil Hall University of Florida Gainesville, FL 32611 phone:
Unsteady Wave-Driven Circulation Cells Relevant to Rip Currents and Coastal Engineering Andrew Kennedy Dept of Civil and Coastal Engineering 365 Weil Hall University of Florida Gainesville, FL 32611 phone:
Investigation of Upstream Boundary Layer Influence on Mountain Wave Breaking and Lee Wave Rotors Using a Large-Eddy Simulation
 OCTOBER 2009 S M I T H A N D S K Y L L I N G S T A D 3147 Investigation of Upstream Boundary Layer Influence on Mountain Wave Breaking and Lee Wave Rotors Using a Large-Eddy Simulation CRAIG M. SMITH AND
OCTOBER 2009 S M I T H A N D S K Y L L I N G S T A D 3147 Investigation of Upstream Boundary Layer Influence on Mountain Wave Breaking and Lee Wave Rotors Using a Large-Eddy Simulation CRAIG M. SMITH AND
CHAPTER 185 SAND TRANSPORT UNDER GROUPING WAVES
 CHAPTER 185 SAND TRANSPORT UNDER GROUPING WAVES Shinji Sato 1 Abstract Laboratory experiments as well as numerical modeling were conducted for sand transport under non-breaking grouping waves. Experiments
CHAPTER 185 SAND TRANSPORT UNDER GROUPING WAVES Shinji Sato 1 Abstract Laboratory experiments as well as numerical modeling were conducted for sand transport under non-breaking grouping waves. Experiments
Theory of Flight Stalls. References: FTGU pages 18, 35-38
 Theory of Flight 6.07 Stalls References: FTGU pages 18, 35-38 Review 1. What are the two main types of drag? 2. Is it possible to eliminate induced drag? Why or why not? 3. What is one way to increase
Theory of Flight 6.07 Stalls References: FTGU pages 18, 35-38 Review 1. What are the two main types of drag? 2. Is it possible to eliminate induced drag? Why or why not? 3. What is one way to increase
Pushover analysis with ZSOIL taking soil into account. Stéphane Commend GeoMod Ing. SA, Lausanne
 Pushover analysis with ZSOIL taking soil into account Stéphane Commend GeoMod Ing. SA, Lausanne scommend@geomod.ch Contents Motivation Why pushover? Why take soil into account? Brief recall of pushover
Pushover analysis with ZSOIL taking soil into account Stéphane Commend GeoMod Ing. SA, Lausanne scommend@geomod.ch Contents Motivation Why pushover? Why take soil into account? Brief recall of pushover
PARAMETRIZATION OF WAVE TRANSFORMATION ABOVE SUBMERGED BAR BASED ON PHYSICAL AND NUMERICAL TESTS
 Proceedings of the 6 th International Conference on the Application of Physical Modelling in Coastal and Port Engineering and Science (Coastlab16) Ottawa, Canada, May 10-13, 2016 Copyright : Creative Commons
Proceedings of the 6 th International Conference on the Application of Physical Modelling in Coastal and Port Engineering and Science (Coastlab16) Ottawa, Canada, May 10-13, 2016 Copyright : Creative Commons
Atmospheric Stability. GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 10 Ahrens: Chapter 6
 Atmospheric Stability GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 10 Ahrens: Chapter 6 Last lecture: Thanks to Dr. Stewart! Hydrologic cycle! Humidity! Diabatic: convection, conduction, radiation; mixing! Adiabatic: change
Atmospheric Stability GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 10 Ahrens: Chapter 6 Last lecture: Thanks to Dr. Stewart! Hydrologic cycle! Humidity! Diabatic: convection, conduction, radiation; mixing! Adiabatic: change
1. Large-scale temperature inversions.
 Lecture 18. Local and regional pollution issues: plumes of pollution. Objectives: 1. Large-scale temperature inversions. 2. Plumes of pollution. Readings: Turco: p.128-135; Brimblecombe: p.130-138 1. Large-scale
Lecture 18. Local and regional pollution issues: plumes of pollution. Objectives: 1. Large-scale temperature inversions. 2. Plumes of pollution. Readings: Turco: p.128-135; Brimblecombe: p.130-138 1. Large-scale
A new mechanism of oceanatmosphere coupling in midlatitudes
 A new mechanism of oceanatmosphere coupling in midlatitudes Arnaud Czaja & Nicholas Blunt Imperial College, London Grantham Institute for Climate Change 1. Motivation Two key questions By which mechanism(s)
A new mechanism of oceanatmosphere coupling in midlatitudes Arnaud Czaja & Nicholas Blunt Imperial College, London Grantham Institute for Climate Change 1. Motivation Two key questions By which mechanism(s)
Observed Roughness Lengths for Momentum and Temperature on a Melting Glacier Surface
 5 Observed Roughness Lengths for Momentum and Temperature on a Melting Glacier Surface The roughness lengths for momentum and temperature are calculated on a melting glacier surface. Data from a five level
5 Observed Roughness Lengths for Momentum and Temperature on a Melting Glacier Surface The roughness lengths for momentum and temperature are calculated on a melting glacier surface. Data from a five level
ATMS 310 Tropical Dynamics
 ATMS 310 Tropical Dynamics Introduction Throughout the semester we have focused on mid-latitude dynamics. This is not to say that the dynamics of other parts of the world, such as the tropics, are any
ATMS 310 Tropical Dynamics Introduction Throughout the semester we have focused on mid-latitude dynamics. This is not to say that the dynamics of other parts of the world, such as the tropics, are any
Comparison of data and model predictions of current, wave and radar cross-section modulation by seabed sand waves
 Comparison of data and model predictions of current, wave and radar cross-section modulation by seabed sand waves Cees de Valk, ARGOSS Summary SAR Imaging of seabed features Seabed Sand waves Objectives
Comparison of data and model predictions of current, wave and radar cross-section modulation by seabed sand waves Cees de Valk, ARGOSS Summary SAR Imaging of seabed features Seabed Sand waves Objectives
Quantification of the Effects of Turbulence in Wind on the Flutter Stability of Suspension Bridges
 Quantification of the Effects of Turbulence in Wind on the Flutter Stability of Suspension Bridges T. Abbas 1 and G. Morgenthal 2 1 PhD candidate, Graduate College 1462, Department of Civil Engineering,
Quantification of the Effects of Turbulence in Wind on the Flutter Stability of Suspension Bridges T. Abbas 1 and G. Morgenthal 2 1 PhD candidate, Graduate College 1462, Department of Civil Engineering,
Atmospheric dynamics and meteorology
 Atmospheric dynamics and meteorology B. Legras, http://www.lmd.ens.fr/legras II Potential vorticity, tropopause and baroclinic instability (supposed to be known: notions on the conservation of potential
Atmospheric dynamics and meteorology B. Legras, http://www.lmd.ens.fr/legras II Potential vorticity, tropopause and baroclinic instability (supposed to be known: notions on the conservation of potential
 et al. [25], Noack et al. [26] for circular cylinder flows, Van Oudheusden [27] for square cylinder and Durgesh [28] for a flat plate model. The first two modes appear as phase-shifted versions of each
et al. [25], Noack et al. [26] for circular cylinder flows, Van Oudheusden [27] for square cylinder and Durgesh [28] for a flat plate model. The first two modes appear as phase-shifted versions of each
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING Volume 1, No 4, 2010
 Effect of geometric dimensions on the transmission coefficient of floating breakwaters Mohammad Hosein Tadayon, Khosro Bargi 2, Hesam Sharifian, S. Reza Hoseini - Ph.D student, Department of Civil Engineering,
Effect of geometric dimensions on the transmission coefficient of floating breakwaters Mohammad Hosein Tadayon, Khosro Bargi 2, Hesam Sharifian, S. Reza Hoseini - Ph.D student, Department of Civil Engineering,
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON THE HYDRODYNAMIC BEHAVIORS OF TWO CONCENTRIC CYLINDERS
 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON THE HYDRODYNAMIC BEHAVIORS OF TWO CONCENTRIC CYLINDERS *Jeong-Rok Kim 1), Hyeok-Jun Koh ), Won-Sun Ruy 3) and Il-Hyoung Cho ) 1), 3), ) Department of Ocean System Engineering, Jeju
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON THE HYDRODYNAMIC BEHAVIORS OF TWO CONCENTRIC CYLINDERS *Jeong-Rok Kim 1), Hyeok-Jun Koh ), Won-Sun Ruy 3) and Il-Hyoung Cho ) 1), 3), ) Department of Ocean System Engineering, Jeju
Atmospheric Factors Governing Banded Orographic Convection
 3758 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 62 Atmospheric Factors Governing Banded Orographic Convection DANIEL J. KIRSHBAUM National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder,
3758 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 62 Atmospheric Factors Governing Banded Orographic Convection DANIEL J. KIRSHBAUM National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder,
Patchy mixing in the Indian Ocean
 CPT: Representing internal-wave driven mixing in global ocean models The Team: Matthew Alford (UW) Brian Arbic (U Michigan) Frank Bryan (NCAR) Eric Chassignet (FSU) Gokhan Danabasoglu (NCAR) Peter Gent
CPT: Representing internal-wave driven mixing in global ocean models The Team: Matthew Alford (UW) Brian Arbic (U Michigan) Frank Bryan (NCAR) Eric Chassignet (FSU) Gokhan Danabasoglu (NCAR) Peter Gent
4.3 Oblique Shocks and Expansions Fans: The Supercritical Marine Layer.
 4.3 Oblique Shocks and Expansions Fans: The Supercritical Marine Layer. The marine layer is a relatively dense and well-mixed layer of moist air that lies above the sea surface and is often capped by a
4.3 Oblique Shocks and Expansions Fans: The Supercritical Marine Layer. The marine layer is a relatively dense and well-mixed layer of moist air that lies above the sea surface and is often capped by a
Air Flow Exchange Velocity of Urban Canyon Cavities due to Thermal Spatial Differences
 Air Flow Exchange Velocity of Urban Canyon Cavities due to Thermal Spatial Differences Marta Oliveira Panão 1, Helder Gonçalves 1 and Paulo Ferrão 1 Renewable Energy Department, INETI, Lisbon, Portugal
Air Flow Exchange Velocity of Urban Canyon Cavities due to Thermal Spatial Differences Marta Oliveira Panão 1, Helder Gonçalves 1 and Paulo Ferrão 1 Renewable Energy Department, INETI, Lisbon, Portugal
Synthetic aperture radar observations of sea surface signatures of atmospheric gravity waves over Southeast Asian coastal waters
 Synthetic aperture radar observations of sea surface signatures of atmospheric gravity waves over Southeast Asian coastal waters Werner Alpers Institute of Oceanography, University of Hamburg, Hamburg,
Synthetic aperture radar observations of sea surface signatures of atmospheric gravity waves over Southeast Asian coastal waters Werner Alpers Institute of Oceanography, University of Hamburg, Hamburg,
WAVE BREAKING OVER LOCAL TOPOGRAPHY DURING THE MAP IOP 15 MISTRAL EVENT: OBSERVATIONS AND HIGH-RESOLUTION NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS
 WAVE BREAKING OVER LOCAL TOPOGRAPHY DURING THE MAP IOP 15 MISTRAL EVENT: OBSERVATIONS AND HIGH-RESOLUTION NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS Vincent Guénard 1, Gilles Tedeschi 1, Philippe Drobinski 2, Jean Luc Caccia
WAVE BREAKING OVER LOCAL TOPOGRAPHY DURING THE MAP IOP 15 MISTRAL EVENT: OBSERVATIONS AND HIGH-RESOLUTION NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS Vincent Guénard 1, Gilles Tedeschi 1, Philippe Drobinski 2, Jean Luc Caccia
THE GAP AND KATABATIC CONTRIBUTIONS FOR THE MAP IOP 15 MISTRAL WINDSTORM. Université Sud Toulon-Var, LSEET-LEPI-CNRS, Toulon, France
 P7.1 THE GAP AND KATABATIC CONTRIBUTIONS FOR THE MAP IOP 15 MISTRAL WINDSTORM Vincent Guénard * 1, Philippe Drobinski 2, Jean Luc Caccia 1 1 Université Sud Toulon-Var, LSEET-LEPI-CNRS, Toulon, France 2
P7.1 THE GAP AND KATABATIC CONTRIBUTIONS FOR THE MAP IOP 15 MISTRAL WINDSTORM Vincent Guénard * 1, Philippe Drobinski 2, Jean Luc Caccia 1 1 Université Sud Toulon-Var, LSEET-LEPI-CNRS, Toulon, France 2
DUE TO EXTERNAL FORCES
 17B.6 DNS ON GROWTH OF A VERTICAL VORTEX IN CONVECTION DUE TO EXTERNAL FORCES Ryota Iijima* and Tetsuro Tamura Tokyo Institute of Technology, Yokohama, Japan 1. INTRODUCTION Various types of vertical vortices,
17B.6 DNS ON GROWTH OF A VERTICAL VORTEX IN CONVECTION DUE TO EXTERNAL FORCES Ryota Iijima* and Tetsuro Tamura Tokyo Institute of Technology, Yokohama, Japan 1. INTRODUCTION Various types of vertical vortices,
