El Nino/La Nina. What is El Nino? From NOAA website
|
|
|
- Emma Ramsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 El Nino/La Nina What is El Nino? From NOAA website El Nino was originally recognized by fishermen off the coast of South America as the appearance of unusually warm water in the Pacific Ocean, occurring near the beginning of the year. El Nino means The Little Boy or Christ child in Spanish. This name was used as a tendency of the phenomenon to arrive around Christmas. La Nina means The Little Girl. La Nina is sometimes called El Viejo, anti-el Nino, or simply a cold event or a cold episode. ENSO is the Southern Oscillation Index El Niño is a disruption of the ocean-atmosphere system in the tropical Pacific having important consequences for weather around the globe. Among these consequences are increased rainfall across the southern tier of the US and in Peru, which has caused destructive flooding, and drought in the West Pacific, sometimes associated with devastating brush fires in Australia. Observations of conditions in the tropical Pacific are considered essential for the prediction of short term (a few months to 1 year) climate variations. To provide necessary data, NOAA operates a network of buoys which measure temperature, currents and winds in the equatorial band. These buoys daily transmit data which are available to researchers & forecasters around the world in real time. In normal, non-el Niño conditions, the trade winds blow towards the west across the tropical Pacific. These winds pile up warm surface water in the west Pacific, so that the sea surface is about 1/2 meter higher at Indonesia than at Ecuador. The sea surface temperature is about 8 degrees C higher in the west, with cool temperatures off South America, due to an upwelling of cold water from deeper levels. This cold water is nutrient-rich, supporting high levels of primary productivity, diverse marine ecosystems, and major fisheries. Rainfall is found in rising air over the warmest water, and the east Pacific is relatively dry. The observations at 110 W (left diagram of 110 W conditions) show that the cool water (below about 17 degrees C, the black band in these plots) is within 50m of the surface. During El Niño, the trade winds relax in the central and western Pacific leading to a depression of the thermocline in the eastern Pacific, and an elevation of the thermocline in the west. The observations at 110W show, for example, that during , the 17- degree isotherm dropped to about 150m depth. This reduced the efficiency of upwelling to cool the suface and cut off the supply of nutrient rich thermocline water to the euphotic zone. The result was a rise in sea surface temperature and a drastic decline in primary productivity, the latter of which adversely affected higher trophic levels of the food
2 chain, including commercial fisheries in this region. The weakening of easterly tradewinds during El Niño is evident in this figure as well. Rainfall follows the warm water eastward, with associated flooding in Peru and drought in Indonesia and Australia. The eastward displacement of the atmospheric heat source overlaying the warmest water results in large changes in the global atmospheric circulation, which in turn force changes in weather in regions far removed from the tropical Pacific. Recognizing El Niño El Niño can be seen in Sea Surface Temperature in the Equatorial Pacific Ocean El Niño can be seen in measurements of the sea surface temp. In Dec. 1993, the sea surface temp & the winds were near normal, with warm water in the Western Pacific Ocean, & cool water, called the "cold tongue" in the Eastern Pacific Ocean. The winds in the Western Pacific are very weak & the winds in the Eastern Pacific are blowing towards the west (towards Indonesia). Dec was an anomaly, the warm water spread from the western Pacific Ocean towards the east (in the direction of South America), the "cold tongue" weakened, & the winds in the western Pacific, usually weak, are blowing strongly towards the east, pushing the warm water eastward. The anomalies show clearly that the water in the center of Pacific Ocean is much warmer than in a normal December. Dec was a strong La Niña event. The cold tongue is cooler than usual by about 3 Centigrade. The cold La Niña events sometimes (but not always) follow El Niño events. Typically, El Niño occurs more frequently than La Niña. A list of El Niño and La Niña years is provided by the National Center for Environmental Prediction (NCEP). El Niño and La Niña events vary in strength. For example, the La Niña in 1987 was stronger than the La Niña in 1995, and the El Niño is unusually strong. La Niña impact on the global climate Global climate La Niña impacts tend to be opposite those of El Niño impacts. In the tropics, ocean temperature variations in La Niña tend to be opposite those of El Niño. At higher latitudes, El Niño and La Niña are among a number of factors that influence climate. However, the impacts of El Niño and La Niña at these latitudes are most clearly seen in wintertime. In the continental US, during El Niño years, temperatures in the winter are warmer than normal in the North Central States, and cooler than normal in the Southeast and the Southwest. During a La Niña year, winter temperatures are warmer than normal in the Southeast and cooler than normal in the Northwest.
3 My Thoughts on EI Nino 2007 Don Anderson; February, 2007 Gathered from a wide spectrum of documents on the subject. Prepared primarily in response to requests from cruising sailboats about to depart west coast ports for the Marquesas and on west to other parts of French Polynesia and the far Southwestern Pacific. Conclusion It is unlikely that the current El Niño episode will have any significant effect on normal weather patterns throughout the Pacific, at least through May The Next El Niño Episode. We are presently experiencing a mild El Niño episode. The equatorial upper-ocean heat content (average temperature departures in the upper 300 m of the ocean) peaked in late November 2006 and has been decreasing rapidly since that time, with the latest values being negative for the first time since early April These trends in surface and subsurface ocean temperatures indicate that the warm episode (El Niño) is weakening. It is still possible for some areas to experience El Niño-related effects during the next month, primarily in the region of the central tropical Pacific. Most of the statistical and coupled models, including the NCEP Climate Forecast System (CFS), indicate that SST anomalies will continue to decrease and that ENSO-neutral conditions are likely to develop during March-May There is considerable uncertainty in the forecasts for periods after May Introduction. There is a very large amount of data on the effect of an El Niño episode on land masses but a paucity of data on its effect on ocean passages of the world. This is because there are literally tens of thousands of meteorological and other weather recording sites on land, but very few along the ocean passages. Furthermore, the studies aimed at predicting the effect of an El Niño on weather are driven by the need to predict events and thereby reduce losses to life and property, most of which reside on land. No doubt the advent of satellite imaging, especially the surface wind vector computational capability of NOAA s latest satellite, the QuikSCAT Scatterometer launched in 1999, will allow the development of more precise predictions of El Niño and La Niña episodes on the vast ocean expanses of the globe. Impact on Passages Mexico/Central America to French Polynesia, March-May 2007 My guess is that conditions will be about normal, i.e. wind and sea conditions should be expected to be similar to what one finds in the pilot charts for any given month. Nothing unusual should be expected for the ITCZ.
4 Impact on Passages French Polynesia to Western Pacific, August-November 2007 I don t know. It s too early to say. It simply bears watching closely by cruisers contemplating remaining in French Polynesia or making the run west toward New Caledonia and/or points SW toward New Zealand. Basis for My Thoughts. I m a scientist but not a professional meteorologist, so here are my notes taken from a large number of professional meteorologist s opinions and publications. They are the principal basis for my present thoughts on the subject. The La Niña-El Niño Cycle. The La Niña-El Niño cycle is referred to as the El Niño/Southern Oscillation (ENSO). It is a coupled atmosphere-ocean phenomenon that is believed to be triggered by anomalous bursts of westerly winds that originate in the western Pacific. These anomalous westerlies with concomitant reduction in intensity of the NE and SE trade winds, reverse the normal westerly movement of warm surface waters in the equatorial Pacific. This eastward movement of warm surface waters reduces the normal upwelling of deep cold waters along the coasts of Peru and Ecuador. This reduced upwelling enhances the increase in the coastal sea surface temperatures. During a La Niña episode, stronger than normal trade winds prevail across the Pacific. My records developed while doing weather routing for yachts on passages from Mexico or Central America to the Western Pacific between March and September last year (2001) showed NE and SE trade winds frequently on the order of 25 to 30 knots for several periods lasting a week or more. These wind speeds are stronger than average and are consistent with a La Niña condition when atmospheric pressure is high in the Eastern Tropical Pacific and low in the Western Tropical Pacific. These stronger than normal trades causes warm water to build up in the Western Pacific. The trade winds then decrease and the warm water moves back across the Equatorial Pacific towards the coasts of Ecuador and Peru. This eastward movement of warmer water strengthens the warm eastward North Equatorial Countercurrent while weakening the cold westward South Equatorial Current. The result is an increase in warmer upper level water along the shores of Ecuador and Peru thereby causing an El Niño condition. Although the onset of an El Niño is signaled by warming of the waters in the Western Pacific, the El Niño phenomenon over water is felt most strongly in coastal waters of Peru where it has been occurring at approximately 3 to 6 year intervals for over a thousand years and where it was named for the Christmas season when it always begins, hence El Niño, the Christ Child. El Niño sea surface temperature anomalies off Peru reach their maximum of up to +7 C during extreme episodes. During an El Niño episode, the warmer equatorial waters enhance the Hadley circulation, named for the English meteorologist George Hadley. In 1735 he put forward a hypothesis to explain the persistent trade winds. He suggested a meridional atmospheric circulation where the warm tropical air ascended and moved toward the polar regions
5 while the cold polar air descended and moved toward the equator. This circulation, coupled with the rotational effect (Coriolis force) of the earth, bent the tropical air mass toward the west, thereby causing the easterly flow of the trades. Any enhancement of the Hadley circulation tends to weaken the trade winds while increasing the intensity of the mid latitude westerlies. Impact of an El Niño on Land Mass Areas. As the warmer surface water moves eastward across the Equatorial Pacific, it leaves behind it increased drought in Indonesia, New Guinea and Northeastern Australia increasing the probability of brush fires and crop and livestock losses. As the warm waters intensify in the Eastern Pacific they bring increased thunderstorms with torrential rains to Ecuador and Northern Peru resulting in widespread flooding with consequent severe loss of life and property. The North Pacific, during an El Niño episode, experiences more frequent storms with increased intensity between October and March. The 1982/83 El Niño was the most intense in the past 55-year record. During that El Niño episode, Eastern Australia suffered the worst drought in 200 years while Ecuador suffered record rainfall of over thirteen times normal. Drought conditions extended from the Philippines to Hawaii. During the same period, California coastal areas suffered extensive damage from unusually high sea levels and record wave heights caused by unusually intense storms. A rare winter storm with gale force winds from the south struck the Baja California peninsular on December 8, 1982 causing the complete loss of 27 cruisers in the Cabo San Lucas anchorage. The El Niño episode was a strong one that brought three times the normal rainfall to Ventura County, California. Consequences of El Niño to Pacific Marine Environment. During an El Niño episode normal upwelling of cold water off Peru is shut down so that nutrients are no longer brought to the surface. The consequence is that fishing dies but the fish do not; they migrate to greater depths. The secondary consequence is a greatly increased mortality rate in seabirds and sea lions. During the 1982/83 El Niño episode, seventeen million birds disappeared from Christmas Island (01 N 160 W). They left the nestlings presumably in search of food. Consequences of El Niño along the Pacific Equatorial Trough. The warmer Equatorial Pacific waters cause heating of the lower atmosphere that in turn increases its buoyancy leading to increased convection This means an increase in intensity of the Intertropical Convergence Zones both north and south of the equator. These zones, now more often referred to as Near Equatorial Tradewind Convergence Zones (NETWZ), exist as a band around the world s oceans between about 15N and 10S, moving north and south with the sun, lagging it by about two months. They are characterized by clumps of cumulonimbus clouds with low ceilings but towering to 45,000 feet, torrential rain with low visibility and squally conditions with winds
6 commonly on the order of 35 kts. During an El Niño episode, there is an increase in frequency and intensity of thunderstorm activity, with extremely heavy increased amounts of rain, as much as five times normal annual precipitation. The north-south extent of the ITCZ decreases. During extreme episodes, such as occurred in 1882, the trade winds reverse direction and sea level rises of almost 12 inches occur along the entire Republic of Kiribati (a string of about 50 islands strung along the equator between about 155 W and 170 E. Dense fog develops over the Central Pacific. The normally westward-setting surface current reverses direction. Effect of El Niño on Tropical Cyclones. The South Pacific tropical cyclone season is December through April. The majority of tropical cyclones originate west of 170W in the Near Equatorial Trough. They typically travel at speeds of 12 to 17 knots. During an El Niño episode the warmer waters increase the number of thunderstorms with consequent enhancement of tropical cyclone activity. On the her hand, during an El Niño episode, the upper level winds over the United States change direction and inhibit hurricane development in the North Atlantic, Caribbean and Gulf of Mexico. For example, during the 1997/98 El Niño episode, one of the strongest on record, there were only seven tropical storms, three hurricanes and one severe hurricane in the Western Atlantic. In the Northern Pacific between 1989 and 1995 there were 230 major cyclonic storms (hurricanes and typhoons). During the period 1995 through 2000 there were only 183. Two of the most damaging hurricanes to hit Hawaii in modern times were Iwa in 1982 and Iniki in These two years were strong El Niño years and showed the largest sea surface temperature positive anomalies in the record between 1945 and During this 55-year period there were 12 El Niño episodes each lasting 12 to 18 months. During normal years the North Pacific tropical cyclones, most of them born a few hundred miles SW of Acapulco, travel WNW towards Hawaii and rarely have sustained gale force winds west of 145W. During strong El Niño episodes, tropical cyclones of storm or hurricane force intensity may track well past the dateline. During strong El Niño episodes, tropical cyclones in the South Pacific may extend east of the dateline as far as the Marquesas, The Gambier in the Southeastern Tuamotus and even further to the southwest as far as the Pitcairn Group. In 1982, French Polynesia experienced six major tropical cyclones. The first occurred in November at the beginning of the season and was the most devastating. Conclusion It is unlikely that the current El Niño episode will have any significant effect on normal weather patterns throughout the Pacific, at least through May 2007.
The General Circulation and El Niño. Dr. Christopher M. Godfrey University of North Carolina at Asheville
 The General Circulation and El Niño Dr. Christopher M. Godfrey University of North Carolina at Asheville Global Circulation Model Air flow broken up into 3 cells Easterlies in the tropics (trade winds)
The General Circulation and El Niño Dr. Christopher M. Godfrey University of North Carolina at Asheville Global Circulation Model Air flow broken up into 3 cells Easterlies in the tropics (trade winds)
- terminology. Further Reading: Chapter 07 of the text book. Outline. - characteristics of ENSO. -impacts
 (1 of 14) Further Reading: Chapter 07 of the text book Outline - terminology - characteristics of ENSO -impacts (2 of 14) Today: Introduction We want to look at another source of variability in the atmosphere
(1 of 14) Further Reading: Chapter 07 of the text book Outline - terminology - characteristics of ENSO -impacts (2 of 14) Today: Introduction We want to look at another source of variability in the atmosphere
Lecture 13 El Niño/La Niña Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction. Idealized 3-Cell Model of Wind Patterns on a Rotating Earth. Previous Lecture!
 Lecture 13 El Niño/La Niña Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction Previous Lecture! Global Winds General Circulation of winds at the surface and aloft Polar Jet Stream Subtropical Jet Stream Monsoons 1 2 Radiation
Lecture 13 El Niño/La Niña Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction Previous Lecture! Global Winds General Circulation of winds at the surface and aloft Polar Jet Stream Subtropical Jet Stream Monsoons 1 2 Radiation
REMINDERS: UPCOMING REVIEW SESSIONS: - Thursday, Feb 27, 6:30-8:00pm in HSS 1330
 REMINDERS: Midterm 2: Friday, February 28 - lecture material covering chapters 6, 7, and 15 (since first midterm and through Wed lecture) - same Format as first midterm UPCOMING REVIEW SESSIONS: - Thursday,
REMINDERS: Midterm 2: Friday, February 28 - lecture material covering chapters 6, 7, and 15 (since first midterm and through Wed lecture) - same Format as first midterm UPCOMING REVIEW SESSIONS: - Thursday,
OCN 201 Lab Fall 2009 OCN 201. Lab 9 - El Niño
 OCN 201 Lab Fall 2009 OCN 201 Lab 9 - El Niño El Niño is probably one of the most widely publicized oceanic phenomena. If there s one single reason for that it s probably the fact that El Niño s presence
OCN 201 Lab Fall 2009 OCN 201 Lab 9 - El Niño El Niño is probably one of the most widely publicized oceanic phenomena. If there s one single reason for that it s probably the fact that El Niño s presence
March 4 th, 2019 Sample Current Affairs
 March 4 th, 2019 Sample Current Affairs 1. A weak El Niño is developing in the equatorial Pacific Ocean, which is expected to continue for a few months at least. What is El Nino? What causes El Nino? What
March 4 th, 2019 Sample Current Affairs 1. A weak El Niño is developing in the equatorial Pacific Ocean, which is expected to continue for a few months at least. What is El Nino? What causes El Nino? What
Module 3, Investigation 1: Briefing 1 What are the effects of ENSO?
 Background The changing temperatures of the tropical Pacific Ocean affect climate variability all over Earth. Ocean warming and cooling dramatically affect human activities by changing weather patterns
Background The changing temperatures of the tropical Pacific Ocean affect climate variability all over Earth. Ocean warming and cooling dramatically affect human activities by changing weather patterns
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore L A NIÑA El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) For the complete encyclopedic
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore L A NIÑA El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) For the complete encyclopedic
Ocean Inter-annual Variability: El Niño and La Niña. How does El Niño influence the oceans and climate patterns?
 Name: Date: Guiding Question: Ocean Inter-annual Variability: El Niño and La Niña How does El Niño influence the oceans and climate patterns? Introduction What is El Niño/La Niña? The El Niño/La Niña cycle
Name: Date: Guiding Question: Ocean Inter-annual Variability: El Niño and La Niña How does El Niño influence the oceans and climate patterns? Introduction What is El Niño/La Niña? The El Niño/La Niña cycle
Lecture 13. Global Wind Patterns and the Oceans EOM
 Lecture 13. Global Wind Patterns and the Oceans EOM Global Wind Patterns and the Oceans Drag from wind exerts a force called wind stress on the ocean surface in the direction of the wind. The currents
Lecture 13. Global Wind Patterns and the Oceans EOM Global Wind Patterns and the Oceans Drag from wind exerts a force called wind stress on the ocean surface in the direction of the wind. The currents
Lecture 24. El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Part 1
 Lecture 24 El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Part 1 The most dominant phenomenon in the interannual variation of the tropical oceanatmosphere system is the El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) over the
Lecture 24 El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Part 1 The most dominant phenomenon in the interannual variation of the tropical oceanatmosphere system is the El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) over the
El Nino and Global Warming
 El Nino and Global Warming El Niño and Global Warming El Niño Climate Trade winds Barometric pressure Southern oscillation WHAT YOU WILL LEARN 1. You will identify the cause of El Niño events. 2. You will
El Nino and Global Warming El Niño and Global Warming El Niño Climate Trade winds Barometric pressure Southern oscillation WHAT YOU WILL LEARN 1. You will identify the cause of El Niño events. 2. You will
GEOS 201 Lab 13 Climate of Change InTeGrate Module Case studies 2.2 & 3.1
 Discerning Patterns: Does the North Atlantic oscillate? Climate variability, or short term climate change, can wreak havoc around the world. Dramatic year to year shifts in weather can have unanticipated
Discerning Patterns: Does the North Atlantic oscillate? Climate variability, or short term climate change, can wreak havoc around the world. Dramatic year to year shifts in weather can have unanticipated
ESCI 107 The Atmosphere Lesson 11 Global Circulation
 Reading: Meteorology Today, Chapter 10 THE GLOBAL CIRCULATION ESCI 107 The Atmosphere Lesson 11 Global Circulation Latitudinal heat imbalance The tropics receive more radiation than they emit. The polar
Reading: Meteorology Today, Chapter 10 THE GLOBAL CIRCULATION ESCI 107 The Atmosphere Lesson 11 Global Circulation Latitudinal heat imbalance The tropics receive more radiation than they emit. The polar
Currents. History. Pressure Cells 3/13/17. El Nino Southern Oscillation ENSO. Teleconnections and Oscillations. Neutral Conditions
 Teleconnections and Oscillations Teleconnection climate anomalies being related to each other over a large scale Oscillations: Macroscale movement of atmospheric systems that can influence weather, climate,
Teleconnections and Oscillations Teleconnection climate anomalies being related to each other over a large scale Oscillations: Macroscale movement of atmospheric systems that can influence weather, climate,
Trade winds How do they affect the tropical oceans? 10/9/13. Take away concepts and ideas. El Niño - Southern Oscillation (ENSO)
 El Niño - Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Ocean-atmosphere interactions Take away concepts and ideas What is El Niño, La Niña? Trade wind and Walker circulation. What is the Southern Oscillation? Tropical
El Niño - Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Ocean-atmosphere interactions Take away concepts and ideas What is El Niño, La Niña? Trade wind and Walker circulation. What is the Southern Oscillation? Tropical
Current: large mass of continuously moving ocean water
 Ocean Currents Current: large mass of continuously moving ocean water Surface Currents--Wind Circulation These waters make up about 10% of all the water in the ocean. These waters are the upper 400 meters
Ocean Currents Current: large mass of continuously moving ocean water Surface Currents--Wind Circulation These waters make up about 10% of all the water in the ocean. These waters are the upper 400 meters
Lecture 29. The El-Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) La Niña = the girl; corresponds to the opposite climate situation
 Lecture 29 The El-Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) El Niño is Spanish for Christ child, the name given by fishermen to a warm ocean current off the coast of Peru/Ecuador that in some years occurs near
Lecture 29 The El-Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) El Niño is Spanish for Christ child, the name given by fishermen to a warm ocean current off the coast of Peru/Ecuador that in some years occurs near
El Niño / Southern Oscillation (ENSO) and inter-annual climate variability
 El Niño / Southern Oscillation (ENSO) and inter-annual climate variability seasonal cycle what is normal? monthly average conditions through a calendar year sea level pressure and surface winds surface
El Niño / Southern Oscillation (ENSO) and inter-annual climate variability seasonal cycle what is normal? monthly average conditions through a calendar year sea level pressure and surface winds surface
El Niño Lecture Notes
 El Niño Lecture Notes There is a huge link between the atmosphere & ocean. The oceans influence the atmosphere to affect climate, but the atmosphere also influences the ocean, which can also affect climate.
El Niño Lecture Notes There is a huge link between the atmosphere & ocean. The oceans influence the atmosphere to affect climate, but the atmosphere also influences the ocean, which can also affect climate.
Variability in the tropical oceans - Monitoring and prediction of El Niño and La Niña -
 Variability in the tropical oceans - Monitoring and prediction of El Niño and La Niña - Jun ichi HIROSAWA Climate Prediction Division Japan Meteorological Agency SST anomaly in Nov. 1997 1 ( ) Outline
Variability in the tropical oceans - Monitoring and prediction of El Niño and La Niña - Jun ichi HIROSAWA Climate Prediction Division Japan Meteorological Agency SST anomaly in Nov. 1997 1 ( ) Outline
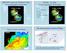
APPENDIX B NOAA DROUGHT ANALYSIS 29 OCTOBER 2007
 APPENDIX B NOAA DROUGHT ANALYSIS 29 OCTOBER 2007 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP October 29, 2007 Outline Overview Recent
APPENDIX B NOAA DROUGHT ANALYSIS 29 OCTOBER 2007 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP October 29, 2007 Outline Overview Recent
Name: OBJECTIVES: By the end of today s lesson, you will be able to
 7 th Grade Science Unit: Water s Cycles and Patterns Lesson: WCP 21 Name: Date: Monday, October 3, 2016 Homeroom: _ OBJECTIVES: By the end of today s lesson, you will be able to SWBAT Explain how currents
7 th Grade Science Unit: Water s Cycles and Patterns Lesson: WCP 21 Name: Date: Monday, October 3, 2016 Homeroom: _ OBJECTIVES: By the end of today s lesson, you will be able to SWBAT Explain how currents
9/25/2014. Scales of Atmospheric Motion. Scales of Atmospheric Motion. Chapter 7: Circulation of the Atmosphere
 Chapter 7: Circulation of the Atmosphere The Atmosphere: An Introduction to Meteorology, 12 th Lutgens Tarbuck Lectures by: Heather Gallacher, Cleveland State University Scales of Atmospheric Motion Small-
Chapter 7: Circulation of the Atmosphere The Atmosphere: An Introduction to Meteorology, 12 th Lutgens Tarbuck Lectures by: Heather Gallacher, Cleveland State University Scales of Atmospheric Motion Small-
IX. Upper Ocean Circulation
 IX. Upper Ocean Circulation World Ocean Covers 71% of Earth s surface Contains 97% of surface water Arctic Ocean NH: 61% ocean, 39% land Pacific Ocean Atlantic Ocean Southern Ocean Indian Ocean SH: 81%
IX. Upper Ocean Circulation World Ocean Covers 71% of Earth s surface Contains 97% of surface water Arctic Ocean NH: 61% ocean, 39% land Pacific Ocean Atlantic Ocean Southern Ocean Indian Ocean SH: 81%
Class Notes: Week 10. April 9 th,2019. Topics: Front and Mid-Latitude Wave Cyclones El Niño / La Niña Mid-term 2 review
 Class Notes: Week 10 April 9 th,2019 Topics: Front and Mid-Latitude Wave Cyclones El Niño / La Niña Mid-term 2 review Front- is a boundary between 2 different types of air masses Air masses with different
Class Notes: Week 10 April 9 th,2019 Topics: Front and Mid-Latitude Wave Cyclones El Niño / La Niña Mid-term 2 review Front- is a boundary between 2 different types of air masses Air masses with different
Lecture 13 March 24, 2010, Wednesday. Atmospheric Pressure & Wind: Part 4
 Lecture 13 March 24, 2010, Wednesday Atmospheric Pressure & Wind: Part 4 Synoptic scale winds Mesoscale winds Microscale winds Air-sea interactions The largest synoptic scale wind. Monsoon: Arabic for
Lecture 13 March 24, 2010, Wednesday Atmospheric Pressure & Wind: Part 4 Synoptic scale winds Mesoscale winds Microscale winds Air-sea interactions The largest synoptic scale wind. Monsoon: Arabic for
Recent Atmospheric and Oceanic Circulation Changes Affecting Winter Weather in North America. Dr. Art Douglas Professor Emeritus Creighton University
 Recent Atmospheric and Oceanic Circulation Changes Affecting Winter Weather in North America Dr. Art Douglas Professor Emeritus Creighton University Outline 1. The 2018 El Nino: A Northern Hemisphere induced
Recent Atmospheric and Oceanic Circulation Changes Affecting Winter Weather in North America Dr. Art Douglas Professor Emeritus Creighton University Outline 1. The 2018 El Nino: A Northern Hemisphere induced
Equatorial upwelling. Example of regional winds of small scale
 Example of regional winds of small scale Sea and land breezes Note on Fig. 8.11. Shows the case for southern hemisphere! Coastal upwelling and downwelling. Upwelling is caused by along shore winds, that
Example of regional winds of small scale Sea and land breezes Note on Fig. 8.11. Shows the case for southern hemisphere! Coastal upwelling and downwelling. Upwelling is caused by along shore winds, that
El Niño Unit (2.5 pts)
 T. James Noyes, El Camino College El Niño Unit (Topic 9B) page 1 Name: Section: El Niño Unit (2.5 pts) El Niño is a warm ocean current that flows along the Equator and towards the west coast of South America
T. James Noyes, El Camino College El Niño Unit (Topic 9B) page 1 Name: Section: El Niño Unit (2.5 pts) El Niño is a warm ocean current that flows along the Equator and towards the west coast of South America
Global Circulations. GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 15 Ahrens: Chapter 10
 Global Circulations GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 15 Ahrens: Chapter 10 Last lecture Microscale (turbulence) Mesoscale (land/sea breeze) Synoptic scale (monsoon) Global scale (3 cell circulation) Three Cell Model
Global Circulations GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 15 Ahrens: Chapter 10 Last lecture Microscale (turbulence) Mesoscale (land/sea breeze) Synoptic scale (monsoon) Global scale (3 cell circulation) Three Cell Model
Pacific Climate Variability
 Pacific Climate Variability Pacific Islands Climate Education Partnership You may have heard the term climate variability. What does the term climate variability mean? What are the causes and effects of
Pacific Climate Variability Pacific Islands Climate Education Partnership You may have heard the term climate variability. What does the term climate variability mean? What are the causes and effects of
Upcoming Events of Interest
 Ecosystems 31 January 2007 9th class meeting Sky Islands El Nino Ecosystems 31 Jan READINGS: Sky Islands, El Nino (on website) EO Wilson book chapter Friday 02 Feb: EO Wilson book chapter (same as above)
Ecosystems 31 January 2007 9th class meeting Sky Islands El Nino Ecosystems 31 Jan READINGS: Sky Islands, El Nino (on website) EO Wilson book chapter Friday 02 Feb: EO Wilson book chapter (same as above)
Chapter. Air Pressure and Wind
 Chapter Air Pressure and Wind 19.1 Understanding Air Pressure Air Pressure Defined Air pressure is the pressure exerted by the weight of air. 19.1 Understanding Air Pressure Air Pressure Defined Air pressure
Chapter Air Pressure and Wind 19.1 Understanding Air Pressure Air Pressure Defined Air pressure is the pressure exerted by the weight of air. 19.1 Understanding Air Pressure Air Pressure Defined Air pressure
Chapter 10: Global Wind Systems
 Chapter 10: Global Wind Systems Three-cell model of atmospheric circulation Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) Typical surface wind patterns Upper-level pressure and winds Climatological sea-level pressure
Chapter 10: Global Wind Systems Three-cell model of atmospheric circulation Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) Typical surface wind patterns Upper-level pressure and winds Climatological sea-level pressure
ORESU-G ORESU-G
 ORESU-G-97-008 ORESU-G 97-008 The Pacific Northwest: a Region of Transitions The unusual oceanic and atmospheric conditions of the Pacific Northwest create a remarkable and dynamic setting unlike any other
ORESU-G-97-008 ORESU-G 97-008 The Pacific Northwest: a Region of Transitions The unusual oceanic and atmospheric conditions of the Pacific Northwest create a remarkable and dynamic setting unlike any other
ENSO Wrap-Up. Current state of the Pacific and Indian Ocean
 18-11-2014 ENSO Wrap-Up Current state of the Pacific and Indian Ocean Tropical Pacific Ocean moves closer to El Niño The Pacific Ocean has shown some renewed signs of El Niño development in recent weeks.
18-11-2014 ENSO Wrap-Up Current state of the Pacific and Indian Ocean Tropical Pacific Ocean moves closer to El Niño The Pacific Ocean has shown some renewed signs of El Niño development in recent weeks.
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 8 March 2010
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 8 March 2010 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 8 March 2010 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
Module 3, Investigation 1: Briefing 1 What are the effects of ENSO?
 Module 3, Investigation 1: Briefing 1 Background The changing temperatures of the tropical Pacific Ocean affect climate variability all over Earth. Ocean warming and cooling dramatically affect human activities
Module 3, Investigation 1: Briefing 1 Background The changing temperatures of the tropical Pacific Ocean affect climate variability all over Earth. Ocean warming and cooling dramatically affect human activities
Review for the second quarter. Mechanisms for cloud formation
 Review for the second quarter Mechanisms for cloud formation 1 Rising air expands and cools; Sinking air compresses and warms. (18) (24) Dry adiabatic lapse rate (10 o C/km): the rate of temperature decrease
Review for the second quarter Mechanisms for cloud formation 1 Rising air expands and cools; Sinking air compresses and warms. (18) (24) Dry adiabatic lapse rate (10 o C/km): the rate of temperature decrease
Ocean Currents that Redistribute Heat Globally
 Ocean Currents that Redistribute Heat Globally Ocean Circulation Ocean Currents Fig. CO7 OCEAN CURRENTS Surface ocean currents are similar to wind patterns: 1. Driven by Coriolis forces 2. Driven by winds
Ocean Currents that Redistribute Heat Globally Ocean Circulation Ocean Currents Fig. CO7 OCEAN CURRENTS Surface ocean currents are similar to wind patterns: 1. Driven by Coriolis forces 2. Driven by winds
Air Pressure and Wind
 Air Pressure and Wind 19.1 Understanding Air Pressure Air Pressure Defined Air pressure is the pressure exerted by the weight of air. Air pressure is exerted in all directions down, up, and sideways. The
Air Pressure and Wind 19.1 Understanding Air Pressure Air Pressure Defined Air pressure is the pressure exerted by the weight of air. Air pressure is exerted in all directions down, up, and sideways. The
Winds and Ocean Circulations
 Winds and Ocean Circulations AT 351 Lab 5 February 20, 2008 Sea Surface Temperatures 1 Temperature Structure of the Ocean Ocean Currents 2 What causes ocean circulation? The direction of most ocean currents
Winds and Ocean Circulations AT 351 Lab 5 February 20, 2008 Sea Surface Temperatures 1 Temperature Structure of the Ocean Ocean Currents 2 What causes ocean circulation? The direction of most ocean currents
Introduction to Oceanography OCE 1001
 Introduction to Oceanography OCE 1001 Lecture Notes Chantale Bégin & Jessica Fry Version 2.1 10. Ocean Circulation (Trujillo, Chapter 7) Major ocean currents are stable and predictable; they have been
Introduction to Oceanography OCE 1001 Lecture Notes Chantale Bégin & Jessica Fry Version 2.1 10. Ocean Circulation (Trujillo, Chapter 7) Major ocean currents are stable and predictable; they have been
McKnight's Physical Geography 11e
 Chapter 2 Lecture McKnight's Physical Geography 11e Lectures Chapter 5 Atmospheric Pressure and Wind Michael Commons Ohio Northern University Atmospheric Pressure and Wind The Nature of Atmospheric Pressure
Chapter 2 Lecture McKnight's Physical Geography 11e Lectures Chapter 5 Atmospheric Pressure and Wind Michael Commons Ohio Northern University Atmospheric Pressure and Wind The Nature of Atmospheric Pressure
The Setting - Climatology of the Hawaiian Archipelago. Link to Video of Maui Waves
 The Setting - Climatology of the Hawaiian Archipelago Link to Video of Maui Waves What caused this week s weather? What caused this weekend s weather? Today s Objective: Provide overview and description
The Setting - Climatology of the Hawaiian Archipelago Link to Video of Maui Waves What caused this week s weather? What caused this weekend s weather? Today s Objective: Provide overview and description
CHAPTER 7 Ocean Circulation
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 CHAPTER 7 Ocean Circulation Words Ocean currents Moving seawater Surface ocean currents Transfer heat from warmer to cooler areas Similar to pattern of major wind belts
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 CHAPTER 7 Ocean Circulation Words Ocean currents Moving seawater Surface ocean currents Transfer heat from warmer to cooler areas Similar to pattern of major wind belts
Atmospheric Circulation. Recall Vertical Circulation
 Today s topics: Atmospheric circulation: generation of wind patterns on a rotating Earth Seasonal patterns of climate: Monsoons and El Niño Tropical Cyclones: Hurricanes and typhoons Atmospheric Circulation
Today s topics: Atmospheric circulation: generation of wind patterns on a rotating Earth Seasonal patterns of climate: Monsoons and El Niño Tropical Cyclones: Hurricanes and typhoons Atmospheric Circulation
ENSO: El Niño Southern Oscillation
 ENSO: El Niño Southern Oscillation La Niña the little girl El Niño the little boy, the child LO: explain a complete ENSO cycle and assess the net affects on fish recruitment John K. Horne University of
ENSO: El Niño Southern Oscillation La Niña the little girl El Niño the little boy, the child LO: explain a complete ENSO cycle and assess the net affects on fish recruitment John K. Horne University of
and the Link between Oceans, Atmosphere, and Weather
 Geography Worksheet Instructions Using a map, atlas, or any other materials your teacher suggests, label the following on the blank map provided. 1. Label East, West, North, and South. 2. Label the following
Geography Worksheet Instructions Using a map, atlas, or any other materials your teacher suggests, label the following on the blank map provided. 1. Label East, West, North, and South. 2. Label the following
Climate briefing. Wellington region, February Alex Pezza and Mike Thompson Environmental Science Department
 Climate briefing Wellington region, February 2016 Alex Pezza and Mike Thompson Environmental Science Department For more information, contact the Greater Wellington Regional Council: Wellington PO Box
Climate briefing Wellington region, February 2016 Alex Pezza and Mike Thompson Environmental Science Department For more information, contact the Greater Wellington Regional Council: Wellington PO Box
Global Impacts of El Niño on Agriculture
 Global Impacts of El Niño on Agriculture Presented to the University of Arkansas Division of Agriculture s Food and Agribusiness Series Webinar Series Presented by: Mark Brusberg and Brian Morris USDA
Global Impacts of El Niño on Agriculture Presented to the University of Arkansas Division of Agriculture s Food and Agribusiness Series Webinar Series Presented by: Mark Brusberg and Brian Morris USDA
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 4 September 2012
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 4 September 2012 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 4 September 2012 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
Section 1. Global Wind Patterns and Weather. What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate. Learning Outcomes
 Chapter 5 Winds, Oceans, Weather, and Climate Section 1 Global Wind Patterns and Weather What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Determine the effects of Earth s rotation and the uneven
Chapter 5 Winds, Oceans, Weather, and Climate Section 1 Global Wind Patterns and Weather What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Determine the effects of Earth s rotation and the uneven
MFE 659 Lecture 2b El Niño/La Niña Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction. El Niño La Niña Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction. Intro to Ocean Circulation
 MFE 659 Lecture 2b El Niño/La Niña Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction El Niño La Niña Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction Outline Ocean Circulation El Niño La Niña Southern Oscillation ENSO 1 2 Intro to Ocean Circulation
MFE 659 Lecture 2b El Niño/La Niña Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction El Niño La Niña Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction Outline Ocean Circulation El Niño La Niña Southern Oscillation ENSO 1 2 Intro to Ocean Circulation
3/22/11. General Circulation of the Atmosphere. General Circulation of the Atmosphere
 Chapter 10 General refers to the average air flow, actual winds will vary considerably. Average conditions help identify driving forces. The basic cause of the general circulation is unequal heating of
Chapter 10 General refers to the average air flow, actual winds will vary considerably. Average conditions help identify driving forces. The basic cause of the general circulation is unequal heating of
General Introduction to Climate Drivers and BoM Climate Services Products
 General Introduction to Climate Drivers and BoM Climate Services Products Climate Information Services Australian Bureau of Meteorology Yuriy Kuleshov El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) El Niño Southern
General Introduction to Climate Drivers and BoM Climate Services Products Climate Information Services Australian Bureau of Meteorology Yuriy Kuleshov El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) El Niño Southern
Shoes, Rubber Duckies,, and El Niño
 Shoes, Rubber Duckies,, and El Niño How they are related By Laura Maliszewski and Liz Strojny New Gifts found in the Ocean Instead of that chest full of gold... Did you know you could find that new rubber
Shoes, Rubber Duckies,, and El Niño How they are related By Laura Maliszewski and Liz Strojny New Gifts found in the Ocean Instead of that chest full of gold... Did you know you could find that new rubber
Lornshill Academy. Geography Department Higher Revision Physical Environments - Atmosphere
 Lornshill Academy Geography Department Higher Revision Physical Environments - Atmosphere Physical Environments Atmosphere Global heat budget The earth s energy comes from solar radiation, this incoming
Lornshill Academy Geography Department Higher Revision Physical Environments - Atmosphere Physical Environments Atmosphere Global heat budget The earth s energy comes from solar radiation, this incoming
Chapter 7: Circulation And The Atmosphere
 Chapter 7: Circulation And The Atmosphere Highly integrated wind system Main Circulation Currents: series of deep rivers of air encircling the planet Various perturbations or vortices (hurricanes, tornados,
Chapter 7: Circulation And The Atmosphere Highly integrated wind system Main Circulation Currents: series of deep rivers of air encircling the planet Various perturbations or vortices (hurricanes, tornados,
Weather drivers in South Australia
 August 2008 Key facts Weather drivers in South Australia Major weather drivers in South Australia are: El Niño - Southern Oscillation frontal systems cut-off lows blocking highs Indian Ocean Dipole cloudbands
August 2008 Key facts Weather drivers in South Australia Major weather drivers in South Australia are: El Niño - Southern Oscillation frontal systems cut-off lows blocking highs Indian Ocean Dipole cloudbands
El Niño and the Winter Weather Outlook
 El Niño and the 2015-2016 Winter Weather Outlook 2015 NASEO Annual Meeting http://www.ospo.noaa.gov/products/ocean/sst/anomaly/ NWS Boston February 10, 2015 Jimmy Taeger Meteorologist National Weather
El Niño and the 2015-2016 Winter Weather Outlook 2015 NASEO Annual Meeting http://www.ospo.noaa.gov/products/ocean/sst/anomaly/ NWS Boston February 10, 2015 Jimmy Taeger Meteorologist National Weather
Leeuwin Current - Reading
 Leeuwin Current At 5,500 kilometres, the Leeuwin is our longest ocean current! One of Australia s most influential natural features, the Leeuwin Current, has been confirmed as the longest continuous coastal
Leeuwin Current At 5,500 kilometres, the Leeuwin is our longest ocean current! One of Australia s most influential natural features, the Leeuwin Current, has been confirmed as the longest continuous coastal
Canada s vast size creates a diverse range of weather conditions and climatic conditions. Warming trend for last 10 years Wet Spring Dry five summers
 Chapter 4 Weather and Climate Canada s vast size creates a diverse range of weather conditions and climatic conditions. Weather examples: Rainy today Snow tomorrow Fog on Wednesday 23 degree C today High
Chapter 4 Weather and Climate Canada s vast size creates a diverse range of weather conditions and climatic conditions. Weather examples: Rainy today Snow tomorrow Fog on Wednesday 23 degree C today High
Section 6. The Surface Circulation of the Ocean. What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate. Learning Outcomes
 Chapter 5 Winds, Oceans, Weather, and Climate Section 6 The Surface Circulation of the Ocean What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Understand the general paths of surface ocean currents.
Chapter 5 Winds, Oceans, Weather, and Climate Section 6 The Surface Circulation of the Ocean What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Understand the general paths of surface ocean currents.
18.1 Understanding Air Pressure 18.1 Understanding Air Pressure Air Pressure Defined Measuring Air Pressure Air pressure barometer
 18.1 Understanding Air Pressure 18.1 Understanding Air Pressure Air Pressure Defined Air pressure is the pressure exerted by the weight of air. Air pressure is exerted in all directions down, up, and sideways.
18.1 Understanding Air Pressure 18.1 Understanding Air Pressure Air Pressure Defined Air pressure is the pressure exerted by the weight of air. Air pressure is exerted in all directions down, up, and sideways.
Goals for today: continuing Ch 8: Atmospheric Circulation and Pressure Distributions. 26 Oct., 2011
 Goals for today: 26 Oct., 2011 continuing Ch 8: Atmospheric Circulation and Pressure Distributions Examples of synoptic scale and mesoscale circulation systems that are driven by geographic diversity in
Goals for today: 26 Oct., 2011 continuing Ch 8: Atmospheric Circulation and Pressure Distributions Examples of synoptic scale and mesoscale circulation systems that are driven by geographic diversity in
Weather drivers in Victoria
 August 2008 Weather drivers in Victoria Key facts Major weather drivers in Victoria are: El Niño - Southern Oscillation frontal systems cut-off lows blocking highs Southern Annular Mode cloudbands Figure
August 2008 Weather drivers in Victoria Key facts Major weather drivers in Victoria are: El Niño - Southern Oscillation frontal systems cut-off lows blocking highs Southern Annular Mode cloudbands Figure
Understanding El Nino-Monsoon teleconnections
 Understanding El Nino-Monsoon teleconnections Dr Neena Joseph Mani Earth & Climate Science INSA Anniversary General meeting, Session: Science in IISER Pune 27 th December 2017 Mean State of the equatorial
Understanding El Nino-Monsoon teleconnections Dr Neena Joseph Mani Earth & Climate Science INSA Anniversary General meeting, Session: Science in IISER Pune 27 th December 2017 Mean State of the equatorial
Tropical Pacific Ocean remains on track for El Niño in 2014
 1 of 10 3/06/2014 3:33 PM ENSO Wrap-Up Current state of the Pacific and Indian Ocean Tropical Pacific Ocean remains on track for El Niño in 2014 Issued on Tuesday 3 June 2014 Product Code IDCKGEWWOO The
1 of 10 3/06/2014 3:33 PM ENSO Wrap-Up Current state of the Pacific and Indian Ocean Tropical Pacific Ocean remains on track for El Niño in 2014 Issued on Tuesday 3 June 2014 Product Code IDCKGEWWOO The
For Class Today How does ocean water circulate? Ocean currents, surface currents, gyres, currents & climate, upwelling, deep ocean circulation
 For Class Today Modified Cornell Notes on section 16.1 (pg. 448-453) **Follow the guide in your ISN and previous notes for help** Heading: How does ocean water circulate? Left hand side categories: Ocean
For Class Today Modified Cornell Notes on section 16.1 (pg. 448-453) **Follow the guide in your ISN and previous notes for help** Heading: How does ocean water circulate? Left hand side categories: Ocean
Lecture 15 General Circulation of the Atmosphere and Ocean
 Lecture 15 General Circulation of the Atmosphere and Ocean Non-rotating model of atmospheric general circulation Hadley (1735) Cell is induced by uneven distribution of solar heating. Conceptual models
Lecture 15 General Circulation of the Atmosphere and Ocean Non-rotating model of atmospheric general circulation Hadley (1735) Cell is induced by uneven distribution of solar heating. Conceptual models
Factors Affecting Wind
 Understanding Air Pressure Average air pressure at sea level is about 1 kg per cm 2 (14.7 lbs/in 2 ) Roughly the same pressure that is produced by a column of water 10 m (33 ft) high The pressurized suits
Understanding Air Pressure Average air pressure at sea level is about 1 kg per cm 2 (14.7 lbs/in 2 ) Roughly the same pressure that is produced by a column of water 10 m (33 ft) high The pressurized suits
Wednesday, September 27, 2017 Test Monday, about half-way through grading. No D2L Assessment this week, watch for one next week
 Wednesday, September 27, 2017 Test Monday, about half-way through grading No D2L Assessment this week, watch for one next week Homework 3 Climate Variability (due Monday, October 9) Quick comment on Coriolis
Wednesday, September 27, 2017 Test Monday, about half-way through grading No D2L Assessment this week, watch for one next week Homework 3 Climate Variability (due Monday, October 9) Quick comment on Coriolis
Global Winds AOSC 200 Tim Canty
 Global Winds AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Global Wind Patterns Deserts Jet Stream Monsoons Ocean transport Ocean cycles Lecture 16 Oct 24
Global Winds AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Global Wind Patterns Deserts Jet Stream Monsoons Ocean transport Ocean cycles Lecture 16 Oct 24
How fast will be the phase-transition of 15/16 El Nino?
 How fast will be the phase-transition of 15/16 El Nino? YOO-GEUN HAM D E P A R T M E N T O F O C E A N O G R A P H Y, C H O N N A M N A T I O N A L U N I V E R S I T Y 2015/16 El Nino outlook One of strongest
How fast will be the phase-transition of 15/16 El Nino? YOO-GEUN HAM D E P A R T M E N T O F O C E A N O G R A P H Y, C H O N N A M N A T I O N A L U N I V E R S I T Y 2015/16 El Nino outlook One of strongest
10% water in the world is tied up in the surface ocean currents. (above the pycnocline) Primary source is wind: Westerlies, Trades, Polar Easterlies
 Oceanography Chapter 9 10% water in the world is tied up in the surface ocean currents. (above the pycnocline) Primary source is wind: Westerlies, Trades, Polar Easterlies Coriolis deflects winds (and
Oceanography Chapter 9 10% water in the world is tied up in the surface ocean currents. (above the pycnocline) Primary source is wind: Westerlies, Trades, Polar Easterlies Coriolis deflects winds (and
Climate Science INTER-ANNUAL TO DECADAL CLIMATE VARIABILITY/COASTAL UPWELLING AND COASTAL CLIMATES. MONITORING EL NIÑO and LA NIÑA
 Climate Science INTER-ANNUAL TO DECADAL CLIMATE VARIABILITY/COASTAL UPWELLING AND COASTAL CLIMATES MONITORING EL NIÑO and LA NIÑA Background: Before 1982, few Americans had ever heard of the term El Niño,
Climate Science INTER-ANNUAL TO DECADAL CLIMATE VARIABILITY/COASTAL UPWELLING AND COASTAL CLIMATES MONITORING EL NIÑO and LA NIÑA Background: Before 1982, few Americans had ever heard of the term El Niño,
Duckies have been found in Hawaii, Alaska, S. America, Scotland, Washington state and Australia as of 2012.
 Duckies have been found in Hawaii, Alaska, S. America, Scotland, Washington state and Australia as of 2012. We learned that it takes 3 years to complete one circuit of the North Pacific Gyre flow in the
Duckies have been found in Hawaii, Alaska, S. America, Scotland, Washington state and Australia as of 2012. We learned that it takes 3 years to complete one circuit of the North Pacific Gyre flow in the
Name Date L.O: SWBAT explain what breezes, planetary winds, ocean currents & monsoons are.
 Name Date L.O: SWBAT explain what breezes, planetary winds, ocean currents & monsoons are. 1. A cool breeze is blowing toward the land from the ocean on a warm, cloudless summer day. This condition is
Name Date L.O: SWBAT explain what breezes, planetary winds, ocean currents & monsoons are. 1. A cool breeze is blowing toward the land from the ocean on a warm, cloudless summer day. This condition is
Record-breaking La Niña events
 Record-breaking La Niña events An analysis of the La Niña life cycle and the impacts and significance of the 2010 11 and 2011 12 La Niña events in Australia Contents Introduction At a glance: the impact
Record-breaking La Niña events An analysis of the La Niña life cycle and the impacts and significance of the 2010 11 and 2011 12 La Niña events in Australia Contents Introduction At a glance: the impact
The Child. Mean Annual SST Cycle 11/19/12
 Introduction to Climatology GEOGRAPHY 300 El Niño-Southern Oscillation Tom Giambelluca University of Hawai i at Mānoa and Pacific Decadal Oscillation ENSO: El Niño-Southern Oscillation PDO: Pacific Decadal
Introduction to Climatology GEOGRAPHY 300 El Niño-Southern Oscillation Tom Giambelluca University of Hawai i at Mānoa and Pacific Decadal Oscillation ENSO: El Niño-Southern Oscillation PDO: Pacific Decadal
Analysis of 2012 Indian Ocean Dipole Behavior
 Analysis of 2012 Indian Ocean Dipole Behavior Mo Lan National University of Singapore Supervisor: Tomoki TOZUKA Department of Earth and Planetary Science, University of Tokyo Abstract The Indian Ocean
Analysis of 2012 Indian Ocean Dipole Behavior Mo Lan National University of Singapore Supervisor: Tomoki TOZUKA Department of Earth and Planetary Science, University of Tokyo Abstract The Indian Ocean
Overview. Learning Goals. Prior Knowledge. UWHS Climate Science. Grade Level Time Required Part I 30 minutes Part II 2+ hours Part III
 Draft 2/2014 UWHS Climate Science Unit 3: Natural Variability Chapter 5 in Kump et al Nancy Flowers Overview This module provides a hands-on learning experience where students will analyze sea surface
Draft 2/2014 UWHS Climate Science Unit 3: Natural Variability Chapter 5 in Kump et al Nancy Flowers Overview This module provides a hands-on learning experience where students will analyze sea surface
Name Class Date. Use the terms from the following list to complete the sentences below. Each term may be used only once. Some terms may not be used.
 Assessment Chapter Test B The Movement of Ocean Water USING KEY TERMS Use the terms from the following list to complete the sentences below. Each term may be used only once. Some terms may not be used.
Assessment Chapter Test B The Movement of Ocean Water USING KEY TERMS Use the terms from the following list to complete the sentences below. Each term may be used only once. Some terms may not be used.
ATMS 310 Tropical Dynamics
 ATMS 310 Tropical Dynamics Introduction Throughout the semester we have focused on mid-latitude dynamics. This is not to say that the dynamics of other parts of the world, such as the tropics, are any
ATMS 310 Tropical Dynamics Introduction Throughout the semester we have focused on mid-latitude dynamics. This is not to say that the dynamics of other parts of the world, such as the tropics, are any
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint. Chapter 18 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens
 Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 18 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 18 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Enviro Sci 1A03 Quiz 3
 Enviro Sci 1A03 Quiz 3 Question 1 (1 point) Which of the following measure wind direction and speed? Question 1 options: a) aerovane b) anemometer c) wind vane d) all of the above Question 2 (1 point)
Enviro Sci 1A03 Quiz 3 Question 1 (1 point) Which of the following measure wind direction and speed? Question 1 options: a) aerovane b) anemometer c) wind vane d) all of the above Question 2 (1 point)
The Movement of Ocean Water. Currents
 The Movement of Ocean Water Currents Ocean Current movement of ocean water that follows a regular pattern influenced by: weather Earth s rotation position of continents Surface current horizontal movement
The Movement of Ocean Water Currents Ocean Current movement of ocean water that follows a regular pattern influenced by: weather Earth s rotation position of continents Surface current horizontal movement
ATS150: Global Climate Change. Oceans and Climate. Icebergs. Scott Denning CSU 1
 The Oceans Wind-Driven Gyre Circulations Icebergs Scott Denning CSU 1 Surface Balance of Forces friction coriolis wind stress resultant current Wind stress accelerates surface water Friction couples surface
The Oceans Wind-Driven Gyre Circulations Icebergs Scott Denning CSU 1 Surface Balance of Forces friction coriolis wind stress resultant current Wind stress accelerates surface water Friction couples surface
Atmospheric Circulation (Ch. 8) Ocean & Atmosphere are intertwined Gases & waters freely exchanged Wind Weather Climate
 Atmospheric Circulation (Ch. 8) Ocean & Atmosphere are intertwined Gases & waters freely exchanged Wind Weather Climate Atmospheric Structure Consists of Layers Separated by Temperature Stratosphere: Temperature
Atmospheric Circulation (Ch. 8) Ocean & Atmosphere are intertwined Gases & waters freely exchanged Wind Weather Climate Atmospheric Structure Consists of Layers Separated by Temperature Stratosphere: Temperature
ENSO Jigsaw [Key Science Knowledge Module]
![ENSO Jigsaw [Key Science Knowledge Module] ENSO Jigsaw [Key Science Knowledge Module]](/thumbs/83/88958439.jpg) ` 3 Teacher Edition 2-3 days ENSO Jigsaw [Key Science Knowledge Module] Activity Overview This module is the most important learning module in terms of the physical science aspects associated with the
` 3 Teacher Edition 2-3 days ENSO Jigsaw [Key Science Knowledge Module] Activity Overview This module is the most important learning module in terms of the physical science aspects associated with the
Hui Wang, Mike Young, and Liming Zhou School of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, Georgia
 Water Cycle between Ocean and Land and Its Influence on Climate Variability over the South American-Atlantic Regions as Determined by SeaWinds Scatterometers Rong Fu Hui Wang, Mike Young, and Liming Zhou
Water Cycle between Ocean and Land and Its Influence on Climate Variability over the South American-Atlantic Regions as Determined by SeaWinds Scatterometers Rong Fu Hui Wang, Mike Young, and Liming Zhou
8 th Grade Science Meteorology Review
 8 th Grade Science Meteorology Review #1 Where does Earth get the energy that produces global weather patterns? A: The sun B: Humidity C: Air masses D: Cyclones A. The Sun #2 Do all of the areas on Earth
8 th Grade Science Meteorology Review #1 Where does Earth get the energy that produces global weather patterns? A: The sun B: Humidity C: Air masses D: Cyclones A. The Sun #2 Do all of the areas on Earth
Lecture 18: El Niño. Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics EESS 146B/246B
 Lecture 18: El Niño Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics EESS 146B/246B El Niño Transient equatorial motions: Kelvin and Rossby waves. Positive feedback mechanism associated with air-sea coupling. Atmospheric
Lecture 18: El Niño Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics EESS 146B/246B El Niño Transient equatorial motions: Kelvin and Rossby waves. Positive feedback mechanism associated with air-sea coupling. Atmospheric
Atmosphere & Weather. Earth Science
 Atmosphere & Weather Earth Science Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Earth s energy is provided by the SUN! Energy is important to us because it 1. Drives winds and ocean currents. 2. Allows plants to
Atmosphere & Weather Earth Science Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Earth s energy is provided by the SUN! Energy is important to us because it 1. Drives winds and ocean currents. 2. Allows plants to
Lesson: Ocean Circulation
 Lesson: Ocean Circulation By Keith Meldahl Corresponding to Chapter 9: Ocean Circulation As this figure shows, there is a connection between the prevailing easterly and westerly winds (discussed in Chapter
Lesson: Ocean Circulation By Keith Meldahl Corresponding to Chapter 9: Ocean Circulation As this figure shows, there is a connection between the prevailing easterly and westerly winds (discussed in Chapter
& La Niña Southern Oscillation Index
 El Niño & La Niña Southern Oscillation Index Today: first of the natural changes Lectures 1) El Nino/La Nina: year- decadal changes in climate system 2) Next: Short term natural changes (centuries to millenia)
El Niño & La Niña Southern Oscillation Index Today: first of the natural changes Lectures 1) El Nino/La Nina: year- decadal changes in climate system 2) Next: Short term natural changes (centuries to millenia)
ESS15 Lecture 12. Review, tropical oceans & El Nino, and the thermohaline ocean circulation. Please see new reading material on website.
 ESS15 Lecture 12 Review, tropical oceans & El Nino, and the thermohaline ocean circulation. Please see new reading material on website. Review. I-clicker exercise: In this graph of Earth s energy imbalances
ESS15 Lecture 12 Review, tropical oceans & El Nino, and the thermohaline ocean circulation. Please see new reading material on website. Review. I-clicker exercise: In this graph of Earth s energy imbalances
Nevis Hulme Gairloch High School John Smith Invergordon Academy. Gairloch High School / Invergordon Academy
 Nevis Hulme Gairloch High School John Smith Invergordon Academy 1 Gairloch High School / Invergordon Academy ATMOSPHERIC CIRCULATION The Three Cell Model Global Winds The ITCZ The purpose of this presentation
Nevis Hulme Gairloch High School John Smith Invergordon Academy 1 Gairloch High School / Invergordon Academy ATMOSPHERIC CIRCULATION The Three Cell Model Global Winds The ITCZ The purpose of this presentation
