GA A23188 CRYOGENIC TARGET SYSTEM FOR Z-PINCH MACHINES
|
|
|
- Ella French
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GA A23188 CRYOGENIC TARGET SYSTEM FOR Z-PINCH MACHINES by C.R. GIBSON, N.B. ALEXANDER, J.V. DEL BENE, D.T. GOODIN, and G.E. BESENBRUCH JULY 1999
2 GA A23188 CRYOGENIC TARGET SYSTEM FOR Z-PINCH MACHINES by C.R. GIBSON, N.B. ALEXANDER, J.V. DEL BENE, D.T. GOODIN, and G.E. BESENBRUCH This is a preprint of a paper to be presented at the Cryogenic Engineering Conference and International Cryogenic Materials Conference, Montreal, Canada, and to be published in Advances in Cryogenic Engineering. GA PROJECT JULY 1999
3 CRYOGENIC TARGET SYSTEM FOR Z-PINCH MACHINE C.R. Gibson, et al. CRYOGENIC TARGET SYSTEM FOR Z-PINCH MACHINES C.R. Gibson, N.B. Alexander, J.V. Del Bene, D.T. Goodin, and G.E. Besenbruch General Atomics San Diego, California 92121, USA ABSTRACT Recent advances in the technology of fast pulsed electrical power and load design have led to growing interest in the use of z-pinch machines as x-ray sources for fusion applications. 1 To achieve high yield, z-pinch machines require the use of cryogenic targets. These targets contain a spherical polymer capsule with a layer of solid deuterium-tritium (DT) on the inside wall. This DT layer is obtained by first permeation filling the capsule with high pressure DT gas at room temperature. The filled capsule is then cooled to approximately 19 K to solidify the DT. The uniform layer is created through a process called beta layering, which involves placing the capsule in a very uniform temperature environment and allowing the natural heating due to beta decay of the tritium to provide the thermal energy to redistribute the DT into a uniform layer. General Atomics has performed preconceptual design studies of a system designed to fill a target with DT, cool it down to cryogenic temperatures, and then insert it into a z-pinch chamber. The baseline system design uses a supercritical helium stream to cool the target. The helium is compressed by a room temperature compressor and cooled using both liquid nitrogen and liquid helium reservoirs. The cold supercritical helium then travels to the target through an umbilical tube several meters long. This umbilical allows the target to be at the center of the chamber while the cryogenic equipment is safely outside. This paper will describe the preconceptual design of a z-pinch cryogenic target system and present the supporting thermal analysis. INTRODUCTION The z-pinch was one of the first plasma confinement concepts to be studied in the early days of controlled fusion energy research. In such a device, a large current flows axially down a cylindrical array of wires, as shown in Fig. 1. The current creates a large circumferential magnetic field producing a Lorentz force which implodes the wire array towards the center of the cylinder. The wires vaporize from the ohmic heating into a plasma which continues to carry the current. The Lorentz force accelerates the plasma inward to the center of the wire array where it is highly compressed and heated. This, in turn, causes the plasma to emit x-rays. In the last three years, the x-ray output energy from Sandia National Laboratory s Z-Machine has increased from 0.1 to almost 2.0 MJ. This is the culmination of many decades of experimenting with z-pinches and pulsed power devices. The Z-Machine now produces the world s most powerful and energetic x-rays and can be used as a driver to GENERAL ATOMICS REPORT GA A
4 C.R. Gibson, et al. CRYOGENIC TARGET SYSTEM FOR Z-PINCH MACHINE Magnetic Field Current Figure 1. Sketch of z-pinch wire array showing the axial current and circumferential magnetic field. study inertial confinement fusion (ICF). The x-rays can be used to compress capsules filled with a mixture of deuterium and tritium (DT). For an ICF device to reach ignition, the DT must be a solid (~19 K) and must form a smooth, symmetrical layer on the inside of the capsule wall. Sandia National Laboratory has proposed two follow-on z-pinch devices for the Z-Machine. The X-1 Advanced Radiation Source is designed to have a x-ray output of 16 MJ. This is enough energy to explore ignition and even high gain fusion. The ZX machine is an intermediate step between Z and X-1 and has a design output of 7 MJ. Z-Pinch Cryogenic Target Systems Both X-1 and ZX require cryogenic targets to meet their design goals. General Atomics in cooperation with the University of Rochester and Los Alamos National Laboratory, has designed a cryogenic target delivery system for the OMEGA laser at the University of Rochester s Laboratory for Laser Energetics. 2 This system has been fabricated and is in final testing in Rochester. The first laser shot of a cryogenic target is scheduled for September Using the experience gained on the OMEGA system, we have produced design concepts for the proposed z-pinch machines. One major difference between OMEGA and the proposed z-pinch machines is the amount of damage caused by the shot. For OMEGA, everything within about one centimeter of the target is vaporized or severely damaged. For X-1, this radius will be about 50 cm. All components inside this spherical volume must be replaced after each shot. In addition, all unshielded regions inside the experiment chamber will be subject to shrapnel damage. This requirement forces all non-expendable equipment to be located safely outside of the chamber. Z-PINCH CRYOGENIC TARGET SYSTEM A pre-conceptual point design for a z-pinch cryogenic target system has been produced, as shown in Fig. 2. The system consists of the z-pinch target, the target cooling cryostat, the fill station, the insertion robot, and the auxiliary cooler. Z-Pinch Target Design Target designers working at Sandia and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratories have developed several z-pinch target designs. 3 A one-sided dynamic hohlraum design is shown in Fig. 3. The dynamic hohlraum design has the target centered inside of the wire array. During the shot, the high atomic number plasma is accelerated inward forming, in effect, a dynamic hohlraum wall. This wall implodes and stagnates on the foam cylinder emitting x-rays onto the capsule for its implosion. 2 GENERAL ATOMICS REPORT GA A23188
5 CRYOGENIC TARGET SYSTEM FOR Z-PINCH MACHINE C.R. Gibson, et al. Auxiliary Cooler Experiment Chamber Fill Station Target Cooling Cryostat Insertion Robot Figure 2. The z-pinch cryogenic target system includes a DT fill station, a target cooling cryostat, an experiment chamber, an insertion robot, and an auxiliary cooler. Auxiliary Cooler Capsule Hohlraum Wire Array Foam and Helium Gas Supercritical Heliumcooling Lines Figure 3. One-Sided dynamic hohlraum design. At the center of the target is a spherical capsule holding the DT fuel. The target assembly is designed to cool the capsule to just below the triple point of DT (~19 K) in an isothermal environment (±0.1 K). Under these conditions, the DT will form a very symmetrical solid layer inside the capsule by a process called beta layering. 4 Heat energy from the beta decay of the tritium results in a redistribution of the DT into a uniform layer. This occurs due to the high vapor pressure of solid DT near its triple point. Non-uniformities in layer thickness cause local temperature variations, which translate into differences in local saturated vapor pressures. This results in net material movement from warm to cold spots until a smooth isothermal surface is created. Immediately outside the capsule are two layers of foam of densities between 3 and 50 mg/cc. The first layer is spherical in shape while the second layer is cylindrical. These open cell foams serve to stagnate the wire plasma implosion and must include some helium gas to conduct the beta decay heat away from the capsule. GENERAL ATOMICS REPORT GA A
6 C.R. Gibson, et al. CRYOGENIC TARGET SYSTEM FOR Z-PINCH MACHINE Surrounding the cylindrical foam is the cylindrical hohlraum wall. This wall is made of gold and is 2 to 4 µm thick. From a cryogenic point of view, the hohlraum wall acts like a thermal shield to keep the capsule cold and to conduct away heat. Windows may be placed in the hohlraum wall to allow access to the capsule for characterization. Cooling tubes are attached to the bottom of the hohlraum wall to provide cooling. Supercritical helium at a pressure of approximately 15 atm and a temperature of about 13 K flows through the tubes. The helium is cooled to cryogenic temperatures in the target cooling cryostat as described in the following section. An auxiliary cooler is attached to the top of the target to provide more uniform cooling. The target is designed to be inserted into the wire array from the bottom. To prevent a thermal short, the target is spaced away from the surrounding structure by a nominal 0.5 mm gap. A low thermal conductivity locking mechanism accurately positions the target assembly. The pre-conceptual design of a cryogenic two-sided static hohlraum is shown in Fig. 4. The static hohlraum design has two sets of wire arrays located above and below the hohlraum and its capsule. The two wire arrays are connected in parallel to one power feed. During the shot, the wires are accelerated inward onto the foam cylinders heating them to ~100 ev. The x-ray radiation produced by the heating of this static cylinder then flows axially into the hohlraum and capsule. The cryogenic design is similar to the dynamic hohlraum except that the axial length has been greatly increased. The interior spaces of the hohlraum are filled with CH foam and/or helium gas. The long aspect ratio of this target makes cooling this target more challenging than the dynamic hohlraum. Z-Pinch Target Thermal Analysis A finite-element thermal analysis has been performed on the one-sided dynamic hohlraum design shown in Fig. 3. There are two major thermal issues that must be addressed in the design of a z-pinch target. One is how the heat from radioactive beta decay of tritium inside the capsule is removed. The second issue is how to provide a sufficiently uniform thermal environment (±0.1 K) around the capsule to produce a uniform solid DT layer. Auxiliary Cooler Foam and Helium Gas Wire Array Capsule Hohlraum Supercritical Heliumcooling Lines Figure 4. Two-sided static hohlraum design. 4 GENERAL ATOMICS REPORT GA A23188
7 CRYOGENIC TARGET SYSTEM FOR Z-PINCH MACHINE C.R. Gibson, et al. The thermal analysis results show that the foam surrounding the capsule must be filled with helium gas. The foam alone does not have sufficient thermal conductivity to remove the heat from the tritium beta decay and still allow the target to be at 19 K. Since theexperimental chamber must be under a high vacuum, the hohlraum walls surrounding the capsule must therefore be gas tight. The thermal analysis also shows that cooling only from the bottom of the target cannot create the isothermal environment required for producing a uniform layer by beta layering. An auxiliary cooler has, therefore, been added to the design. This device attaches to the top of the target after the target has been placed in the center of the wire array by the insertion robot. The thermal analysis has shown that with the auxiliary cooler, a temperature uniformity of ±0.1 K can be achieved at the capsule wall. Target Cooling Cryostat The target cooling cryostat, shown in Fig. 5, is used during the fill, transport and insertion of z-pinch targets. It consists of three main parts: the extendible target holder, the liquid cryogen dewars and the umbilical. The target is assembled separately at room temperature and then placed by hand on the target cooling cryostat s extendible target holder. This device elevates the target from its storage spot inside the cryostat to an elevation above the top of the cryostat. It is used to place the target into the fill station for target filling and partially into the experiment chamber. The extendible target holder consists of a welded stainless steel bellows which is extended by pressurizing the inside with helium gas. Precision rails guide the target holder and allow only vertical motion. Three possible target cooling techniques, shown in Fig. 6, have been examined. Conduction cooling the target from a liquid helium reservoir [Fig. 6(a)] is conceptually the simplest approach, however there are several disadvantages. The reservoir must either be designed to be replaced after each shot or it must be located far away from the target. In addition, since the target must be kept cold at all times after filling, the reservoir must be inserted into the evacuated experiment chamber at the same time as the target. The other two concepts studied use flowing supercritical helium to transfer the heat from the target to the cooling source. Supercritical helium at approximately 1.5 MPa (15 atm) is first passed through a heat exchanger submerged in liquid nitrogen to cool the gas to about 77 K. The Target Extendible Target Holder Cryogenic Umbilical Transport Cart Liquid Helium Tank Liquid Nitrogen Tank Figure 5. The target cooling cryostat moves the filled target from fill station to experiment chamber. GENERAL ATOMICS REPORT GA A
8 C.R. Gibson, et al. CRYOGENIC TARGET SYSTEM FOR Z-PINCH MACHINE Liquid Helium Reservoir Heater Copper Braid Holhraum Helium Compressor Liquid Nitrogen Reservoir Heat Exchanger Heat Exchanger Liquid Nitrogen Reservoir Outside Experiment Chamber Heater Inside Experiment Chamber Holhraum Helium Compressor Liquid Nitrogen Reservoir Cryocooler First Stage Second Stage Heater Holhraum (a) Conduction Cooling from Liquid Helium Reservoir (b) Supercritical Helium Cooled by Liquid Helium (c) Supercritical Helium Cooled by Cryocooler Figure 6. Several cooling schemes for target cooling were investigated. gas is then cooled to about 13 K by either liquid helium [Fig. 6(b)] or a mechanical cryocooler [Fig. 6(c)]. Several counterflow heat exchangers can be added to precool the gas with the return stream thereby increasing the efficiency of the system. Supercritical helium is used because of its low viscosity and excellent heat transfer characteristics. In addition, the flow oscillation and excessive pressure drop problems encountered with two-phase helium flow are avoided. The target cooling cryostat is located on a cart which moves between the fill station and the experiment chamber. The cart contains the helium compressor, support utilities, and instrumentation for the target cooling cryostat. The baseline target cooling cryostat design presented here uses a supercritical helium stream cooled by liquid nitrogen and liquid helium as shown in Fig. 6(c). A preliminary thermal analysis predicts this system will reach steady state equilibrium in about 4 h. With a helium flow rate of 0.1 gm/s, the pressure drop through the system is about 0.4 MPa (4 atm) and the consumption rates are 0.3 L/h of liquid nitrogen and 6 L/h of liquid helium. The umbilical carries supercritical helium between the liquid cryogen dewars and the target. This design allows the target cooling cryostat to remain safely outside the experiment chamberduring the shot. It consists of a helium supply tube, a helium return tube, and leads for temperature sensors and heaters on the hohlraum. The umbilical must extend from a span of about 0.5 m when inside the target cooling cryostat to approximately 5 m when the target is inside the wire array. This is accomplished by using a tightly coiled umbilical similar to a spring. Proof-of-concept tests were performed on 2 m long by 3.18 mm (0.125 in.) diameter tubing of various cryogenically compatible materials wound into a 9 cm (3.5 in.) diameter spiral. The sample umbilical with the best performance was made from a 304 stainless steel tube with a 0.71 mm (0.028 in.) wall. This sample umbilical showed the characteristics required for a full length umbilical: elastic deformations for small axial deflections and no kinking for large deflections. Fill Station The fill station includes several pieces of equipment, as shown in Fig. 7, which are designed to fill a polymer capsule by permeation of high pressure [up to 150 MPa (1500 atm)] DT gas through the capsule wall. The target cooling cryostat, with a target inside, is mated with the fill station. The extendible target holder is raised up to insert the target inside a permeation cell. The cell is then rotated 60 to engage a breech lock mechanism for containment of the high pressure DT. The cell is slowly pressurized with DT at a rate calculated to equal the rate of permeation through the capsule wall. The maximum pressure is determined by the required solid DT layer thickness. Once that pressure is reached, the permeation cell is gradually cooled to condense the DT. Both the permeation cell and 6 GENERAL ATOMICS REPORT GA A23188
9 CRYOGENIC TARGET SYSTEM FOR Z-PINCH MACHINE C.R. Gibson, et al. Supercritical Helium Cooling Lines High Pressure DT Line Vacuum Vessel Glovebox Wall Permeation Cell Target Cooling Cryostat Figure 7. Target cooling cryostat extends target up into fill station for permeation filling. target base include cooling tubes. The DT not trapped inside the capsule can now be pumped out of the cell. The breech lock mechanism is then disengaged and the target is lowered back down inside the target cooling cryostat. After the gate valve is closed, the target cooling cryostat can be disconnected from the Fill Station and transported to the experiment chamber. Insertion Robot The insertion robot is used to transfer targets from the target cooling cryostat to the center of the wire array, as shown in Fig. 2. Since the polymer capsule wall is not strong enough to withstand the room temperature pressure of the DT gas, the target must be kept at cryogenic temperatures until the shot. In order to maintain the cryogenic temperatures, the target must also be kept in a vacuum environment. Thus, any manipulation of the target must be done remotely. After the target cooling cryostat is mated with the experiment chamber, the extendible target holder raises the target into the experiment chamber. The insertion robot then grasps the bottom of the target, lifts it into the experiment chamber, and places it on a long vertical end effector for placement within the wire array. The umbilical cooling lines spool out as the target is lifted, maintaining thermal contact between the target cooling cryostat and the target. The robot can also be used to position blast shields. Before the shot, the robot is removed from the experiment chamber to prevent neutron activation and damage from shrapnel. GENERAL ATOMICS REPORT GA A
10 C.R. Gibson, et al. CRYOGENIC TARGET SYSTEM FOR Z-PINCH MACHINE Auxiliary Cooler After the target is placed within the wire array, an auxiliary cooler extends from the top of the experiment chamberand makes thermal contact with the target. The arm which places the cooling tip in place is withdrawn to outside the experiment chamber. The auxiliary cooler allows both the bottom and top of the target to be actively cooled in order to create a uniform temperature environment required for beta layering the DT. In this baseline design, the cooling is provided by a supercritical helium loop similar to the one cooling the target base. SUMMARY The concepts described should allow the successful fielding of cryogenic targets on z-pinch machines, such as the existing z-machine or the proposed zx or x-1 facilities. ACKNOWLEDGMENT This is a report of work supported by General Atomics Internal Research and Development funds. The authors wish to acknowledge the many discussions with target designers at Sandia and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratories. REFERENCES 1. G. Yonas, Fusion and the z-pinch, Scientific American 279, 40 (1998). 2. C.R. Gibson, et al., Design of the fill/transfer station cryostat for the OMEGA cryogenic target system, Advances in Cryogenic Engineering 43, 605 (1998). 3. R.E. Olson, et al., Indirect-drive ICF target concepts for the X-1 z-pinch facility, Fusion Technology 35, 260 (1999). 4. J.K. Hoffer, et al., Forming a perfectly uniform shell of solid DT fusion fuel by the beta layering process, Proc 14th International Conf. on Plasma Physics and Controlled Nuclear Fusion, September (1992) p GENERAL ATOMICS REPORT GA A23188
An Investigative and Synoptic Review on Helium Liquefaction Using a Commercial 4 K Gifford- McMahon Cryocooler
 An Investigative and Synoptic Review on Helium Liquefaction Using a Commercial 4 K Gifford- McMahon Cryocooler Mahesh N 1, S A Mohan Krishna 2 1 PG Student, Vidyavardhaka College of Engineering, Mysore,
An Investigative and Synoptic Review on Helium Liquefaction Using a Commercial 4 K Gifford- McMahon Cryocooler Mahesh N 1, S A Mohan Krishna 2 1 PG Student, Vidyavardhaka College of Engineering, Mysore,
AN EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON HELIUM LIQUEFACTION USING TWO-STAGE GIFFORD McMAHON CRYOCOOLER
 P P P International Journal of Scientific Engineering and Applied Science (IJSEAS) - Volume-1, Issue-6, September 2015 AN EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON HELIUM LIQUEFACTION USING TWO-STAGE GIFFORD McMAHON
P P P International Journal of Scientific Engineering and Applied Science (IJSEAS) - Volume-1, Issue-6, September 2015 AN EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON HELIUM LIQUEFACTION USING TWO-STAGE GIFFORD McMAHON
RC102 & RC110 Sample in Vacuum Continuous Flow Cryogenic Workstation Cryostats
 RC102 & RC110 Sample in Vacuum Continuous Flow Cryogenic Workstation Cryostats www.cryoindustries.com INDUSTRIES RC102 & RC110 Sample in Vacuum Continuous Flow Cryogenic Workstation Cryostats Designed
RC102 & RC110 Sample in Vacuum Continuous Flow Cryogenic Workstation Cryostats www.cryoindustries.com INDUSTRIES RC102 & RC110 Sample in Vacuum Continuous Flow Cryogenic Workstation Cryostats Designed
Dynamic Operation of a 4 K Pulse Tube Cryocooler with Inverter Compressors
 Dynamic Operation of a 4 K Pulse Tube Cryocooler with Inverter Compressors C. Wang Cryomech, Inc. Syracuse, NY 13211 ABSTRACT This paper introduces the concept of operating a 4 K pulse tube cryocooler
Dynamic Operation of a 4 K Pulse Tube Cryocooler with Inverter Compressors C. Wang Cryomech, Inc. Syracuse, NY 13211 ABSTRACT This paper introduces the concept of operating a 4 K pulse tube cryocooler
Development of High Efficiency 4K Two-Stage Pulse Tube Cryocooler
 Development of High Efficiency 4K Two-Stage Pulse Tube Cryocooler M. Xu, H. Takayama and K. Nakano Sumitomo Heavy Industries, Ltd. Nishi-tokyo-city, Tokyo, Japan 188-8585 ABSTRACT Sumitomo Heavy Industries
Development of High Efficiency 4K Two-Stage Pulse Tube Cryocooler M. Xu, H. Takayama and K. Nakano Sumitomo Heavy Industries, Ltd. Nishi-tokyo-city, Tokyo, Japan 188-8585 ABSTRACT Sumitomo Heavy Industries
Initial Performance of the High-Pressure DT-Filling Portion of the Cryogenic Target Handling System
 INITIAL ERFORANCE OF THE HIGH-RESSURE DT-FILLING ORTION OF THE CRYOGENIC TARGET HANDLING SYSTE Initial erformance of the High-ressure DT-Filling ortion of the Cryogenic Target Handling System Cryogenic
INITIAL ERFORANCE OF THE HIGH-RESSURE DT-FILLING ORTION OF THE CRYOGENIC TARGET HANDLING SYSTE Initial erformance of the High-ressure DT-Filling ortion of the Cryogenic Target Handling System Cryogenic
SPECIFICATION FOR AN MRBR 9.4 TESLA/310MM/AS CRYO-COOLED MAGNET SYSTEM
 SPECIFICATION FOR AN MRBR 9.4 TESLA/310MM/AS CRYO-COOLED MAGNET SYSTEM Prepared by:- Magnex Scientific Limited The Magnet Technology Centre 6 Mead Road Oxford Industrial Park Yarnton, Oxford OX5 1QU, UK
SPECIFICATION FOR AN MRBR 9.4 TESLA/310MM/AS CRYO-COOLED MAGNET SYSTEM Prepared by:- Magnex Scientific Limited The Magnet Technology Centre 6 Mead Road Oxford Industrial Park Yarnton, Oxford OX5 1QU, UK
Microscopy Cryogenic WORKSTATION. Performance by Design
 CRYO Microscopy Cryogenic WORKSTATION Optical cryostat for use in microscopy and spectroscopy Performance by Design RC102-CFM Microscopy Cryostat offers fast cooldown, high efficiency, excellent temperature
CRYO Microscopy Cryogenic WORKSTATION Optical cryostat for use in microscopy and spectroscopy Performance by Design RC102-CFM Microscopy Cryostat offers fast cooldown, high efficiency, excellent temperature
Magnet and RF Cavity Test Stand Design. Tom Peterson, SLAC USPAS January, 2017
 Magnet and RF Cavity Test Stand Design, SLAC Outline Test dewars and test stands Saturated bath test dewars Double bath test dewars SRF test cryostats SRF cryomodule test stands Horizontal magnet test
Magnet and RF Cavity Test Stand Design, SLAC Outline Test dewars and test stands Saturated bath test dewars Double bath test dewars SRF test cryostats SRF cryomodule test stands Horizontal magnet test
D R A F T. Operating Procedures for the NPDGamma Liquid Hydrogen Target at the BL 13. Version 1.00
 D R A F T Operating Procedures for the NPDGamma Liquid Hydrogen Target at the BL 13 Version 1.00 October 06, 2010 Operating Procedures for the NPDGamma Liquid Hydrogen Target V1.00 6/10/10 2 Table of Content
D R A F T Operating Procedures for the NPDGamma Liquid Hydrogen Target at the BL 13 Version 1.00 October 06, 2010 Operating Procedures for the NPDGamma Liquid Hydrogen Target V1.00 6/10/10 2 Table of Content
JANIS OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS FOR SUPERCONDUCTING MAGNET CRYOSTATS
 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS FOR SUPERCONDUCTING MAGNET CRYOSTATS INTRODUCTION The Janis Research Company's Superconducting Magnet/Cryostat System is one of the most versatile tools available to the scientist
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS FOR SUPERCONDUCTING MAGNET CRYOSTATS INTRODUCTION The Janis Research Company's Superconducting Magnet/Cryostat System is one of the most versatile tools available to the scientist
DRAFT. Operating Procedures for the NPDGamma Liquid Hydrogen Target in TA-53, Building MPF-35
 Operating Procedures for the NPDGamma Liquid Hydrogen Target V0.03 11/26/05 1 DRAFT Operating Procedures for the NPDGamma Liquid Hydrogen Target in TA-53, Building MPF-35 Version 0.03 November 26, 2005
Operating Procedures for the NPDGamma Liquid Hydrogen Target V0.03 11/26/05 1 DRAFT Operating Procedures for the NPDGamma Liquid Hydrogen Target in TA-53, Building MPF-35 Version 0.03 November 26, 2005
First Experimental Data of the Cryogenic Safety Test Facility PICARD
 First Experimental Data of the Cryogenic Safety Test Facility PICARD C. Heidt, A. Henriques, M. Stamm and S. Grohmann 26 th International Cryogenic Engineering Conference 2016 in New Delhi, India KIT,
First Experimental Data of the Cryogenic Safety Test Facility PICARD C. Heidt, A. Henriques, M. Stamm and S. Grohmann 26 th International Cryogenic Engineering Conference 2016 in New Delhi, India KIT,
Development of high pressure-high vacuum-high conductance piston valve for gas-filled radiation detectors
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series Development of high pressure-high vacuum-high conductance piston valve for gas-filled radiation detectors To cite this article: D N Prasad et al 2008 J. Phys.: Conf.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series Development of high pressure-high vacuum-high conductance piston valve for gas-filled radiation detectors To cite this article: D N Prasad et al 2008 J. Phys.: Conf.
HIGH SPATIAL RESOLUTION NEUTRON IMAGING OF INERTIAL FUSION TARGET PLASMAS USING BUBBLE DETECTORS
 GA A25378 HIGH SPATIAL RESOLUTION NEUTRON IMAGING OF INERTIAL FUSION TARGET PLASMAS USING BUBBLE DETECTORS FINAL REPORT FOR THE PERIOD NOVEMBER 1, 2002 THROUGH OCTOBER 31, 2005 by R.K. FISHER Prepared
GA A25378 HIGH SPATIAL RESOLUTION NEUTRON IMAGING OF INERTIAL FUSION TARGET PLASMAS USING BUBBLE DETECTORS FINAL REPORT FOR THE PERIOD NOVEMBER 1, 2002 THROUGH OCTOBER 31, 2005 by R.K. FISHER Prepared
Vibration-Free Joule-Thomson Cryocoolers for Distributed Microcooling
 Vibration-Free Joule-Thomson Cryocoolers for Distributed Microcooling W. Chen, M. Zagarola Creare Inc. Hanover, NH, USA ABSTRACT This paper reports on an innovative concept for a space-borne Joule-Thomson
Vibration-Free Joule-Thomson Cryocoolers for Distributed Microcooling W. Chen, M. Zagarola Creare Inc. Hanover, NH, USA ABSTRACT This paper reports on an innovative concept for a space-borne Joule-Thomson
The Hydrogen Isotope Separation System
 The Hydrogen Isotope Separation System Introduction The Laboratory for Laser Energetics (LLE) routinely fields 86-nm-diam, thin-walled plastic shells filled with deuterium tritium (DT) gas or DT ice layered
The Hydrogen Isotope Separation System Introduction The Laboratory for Laser Energetics (LLE) routinely fields 86-nm-diam, thin-walled plastic shells filled with deuterium tritium (DT) gas or DT ice layered
PURE SUBSTANCE. Nitrogen and gaseous air are pure substances.
 CLASS Third Units PURE SUBSTANCE Pure substance: A substance that has a fixed chemical composition throughout. Air is a mixture of several gases, but it is considered to be a pure substance. Nitrogen and
CLASS Third Units PURE SUBSTANCE Pure substance: A substance that has a fixed chemical composition throughout. Air is a mixture of several gases, but it is considered to be a pure substance. Nitrogen and
l.b An Advanced Cryogenic Target-Positioning System
 l.b PROGRESS IN LASER FUSION An Advanced Cryogenic Target-Positioning System The past quarter has seen the completion of a difficult, multiyear project to provide a cryogenic (cryo) target capability for
l.b PROGRESS IN LASER FUSION An Advanced Cryogenic Target-Positioning System The past quarter has seen the completion of a difficult, multiyear project to provide a cryogenic (cryo) target capability for
Earlier Lecture. In the earlier lecture, we have seen Kapitza & Heylandt systems which are the modifications of the Claude System.
 17 1 Earlier Lecture In the earlier lecture, we have seen Kapitza & Heylandt systems which are the modifications of the Claude System. Collins system is an extension of the Claude system to reach lower
17 1 Earlier Lecture In the earlier lecture, we have seen Kapitza & Heylandt systems which are the modifications of the Claude System. Collins system is an extension of the Claude system to reach lower
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 14 Fluids Fluids at rest pressure vs. depth Pascal s principle Archimedes s principle Buoynat forces Fluids in motion: Continuity & Bernoulli equations 1. How deep
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 14 Fluids Fluids at rest pressure vs. depth Pascal s principle Archimedes s principle Buoynat forces Fluids in motion: Continuity & Bernoulli equations 1. How deep
Current Leads for Cryogenic Systems
 Current Leads for Cryogenic Systems American Magnetics Inc. s (AMI) Vapor Cooled Current Leads provide reliable and consistent electrical current transfer from room temperature (300K) to a Liquid Helium
Current Leads for Cryogenic Systems American Magnetics Inc. s (AMI) Vapor Cooled Current Leads provide reliable and consistent electrical current transfer from room temperature (300K) to a Liquid Helium
Oil-Lubricated Compressors for Regenerative Cryocoolers Using an Elastic Membrane
 Oil-Lubricated Compressors for Regenerative Cryocoolers Using an Elastic Membrane E.C. Luo, Z.H. Wu, G.Y. Yu, J.Y. Hu, and W. Dai Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry Chinese Academy of Sciences
Oil-Lubricated Compressors for Regenerative Cryocoolers Using an Elastic Membrane E.C. Luo, Z.H. Wu, G.Y. Yu, J.Y. Hu, and W. Dai Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry Chinese Academy of Sciences
Overview of Earlier Lecture
 4 1 Overview of Earlier Lecture Hydrogen Helium Phase Diagram of Helium Super fluid Helium 2 Outline of the Lecture Uses of Helium 4 Thermomechanical, Mechanocaloric, Fountain, Rollin Film Effects. Sound
4 1 Overview of Earlier Lecture Hydrogen Helium Phase Diagram of Helium Super fluid Helium 2 Outline of the Lecture Uses of Helium 4 Thermomechanical, Mechanocaloric, Fountain, Rollin Film Effects. Sound
Loss of Vacuum Experiments on a Superfluid Helium Vessel
 1 Loss of Vacuum Experiments on a Superfluid Helium Vessel Stephen M. Harrison 1 Abstract The Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS) is a particle physics experiment for use on the International Space Station
1 Loss of Vacuum Experiments on a Superfluid Helium Vessel Stephen M. Harrison 1 Abstract The Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS) is a particle physics experiment for use on the International Space Station
Helium-Liquefaction by Cryocooler for High-Field Magnet Cooling
 Helium-Liquefaction by Cryocooler for High-Field Magnet Cooling Y.S. Choi 1,,.A. Painter 3, D.L. Kim, B.S. Lee, H.S. Yang, H.W. Weijers 3, G.E. Miller 3 and J.R. Miller 3 1. KBSI-NHMFL Collaboration Center
Helium-Liquefaction by Cryocooler for High-Field Magnet Cooling Y.S. Choi 1,,.A. Painter 3, D.L. Kim, B.S. Lee, H.S. Yang, H.W. Weijers 3, G.E. Miller 3 and J.R. Miller 3 1. KBSI-NHMFL Collaboration Center
Procedure of Xenon Transfer
 Procedure of Xenon Transfer Feng Zhou,MIT CC: Martina Green February 28, 2005 In this write up, we discuss the procedure on how to transfer xenon to a designed gas storage vessel that supplies xenon to
Procedure of Xenon Transfer Feng Zhou,MIT CC: Martina Green February 28, 2005 In this write up, we discuss the procedure on how to transfer xenon to a designed gas storage vessel that supplies xenon to
ENGINEERING DESIGN OF CRYOCONDENSATION PUMPS FOR THE DIII-D
 ENGINEERING DESIGN OF CRYOCONDENSATION PUMPS FOR THE DIII-D RADIATIVE DIVERTOR PROGRA~~ ECEIVED MAR 0 3 1997 by A.S. BOZEK, C.B. BAXI, J.V. DEL BENE, G.J. LAUGHON, E.E. REIS, H.D. SHATOFF, and J.P. SMITH
ENGINEERING DESIGN OF CRYOCONDENSATION PUMPS FOR THE DIII-D RADIATIVE DIVERTOR PROGRA~~ ECEIVED MAR 0 3 1997 by A.S. BOZEK, C.B. BAXI, J.V. DEL BENE, G.J. LAUGHON, E.E. REIS, H.D. SHATOFF, and J.P. SMITH
Laser-Induced Bubbles in Glycerol-Water Mixtures
 Laser-Induced Bubbles in Glycerol-Water Mixtures Allison R. McCarn, Erin M. Englert, and Gary A. Williams Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of California, Los Angeles, California 90095, USA
Laser-Induced Bubbles in Glycerol-Water Mixtures Allison R. McCarn, Erin M. Englert, and Gary A. Williams Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of California, Los Angeles, California 90095, USA
Flexible Metal Hose Products
 Flexible Metal Hose Products Specialty Flexible Hose Solutions of Stainless Steel The AEROCOM Advantage Aerocom offers engineered solutions that address specific flexible piping challenges such as vibration,
Flexible Metal Hose Products Specialty Flexible Hose Solutions of Stainless Steel The AEROCOM Advantage Aerocom offers engineered solutions that address specific flexible piping challenges such as vibration,
Characterizing a Cu/Mn Alloy for Extracting Oxygen from Inert Gas. Streams
 Characterizing a Cu/Mn Alloy for Extracting Oxygen from Inert Gas Streams Grace Lenhard Prattsburgh Central School LLE advisors: Walter Shmayda and Matthew Sharpe Laboratory for Laser Energetics University
Characterizing a Cu/Mn Alloy for Extracting Oxygen from Inert Gas Streams Grace Lenhard Prattsburgh Central School LLE advisors: Walter Shmayda and Matthew Sharpe Laboratory for Laser Energetics University
FAILURE AND HAZARD ANALYSIS OF THE NPDGAMMA LH2 TARGET SYSTEM
 FAILURE AND HAZARD ANALYSIS OF THE NPDGAMMA LH2 TARGET SYSTEM Revision: 0.00 Edited by: Seppo Penttila, November 10, 2010 1. General The RSS 8305.0 Installation, Commissioning, and Operation of the NPDGamma
FAILURE AND HAZARD ANALYSIS OF THE NPDGAMMA LH2 TARGET SYSTEM Revision: 0.00 Edited by: Seppo Penttila, November 10, 2010 1. General The RSS 8305.0 Installation, Commissioning, and Operation of the NPDGamma
CRYO INDUSTRIES. Liquid Helium Research Dewars
 Liquid Helium Research Dewars Liquid Helium Research Dewars Cryo Industries Liquid Helium Research Dewars are finely designed and manufactured using the highest quality materials. A Liquid Helium reservoir
Liquid Helium Research Dewars Liquid Helium Research Dewars Cryo Industries Liquid Helium Research Dewars are finely designed and manufactured using the highest quality materials. A Liquid Helium reservoir
Figure 1: Hydrostatic Pressure Forces Are Perpendicular to the Surface
 Pressure Hulls and Canisters 2 Cornerstone Electronics Technology and Robotics III (Notes primarily from Underwater Robotics Science Design and Fabrication, an excellent book for the design, fabrication,
Pressure Hulls and Canisters 2 Cornerstone Electronics Technology and Robotics III (Notes primarily from Underwater Robotics Science Design and Fabrication, an excellent book for the design, fabrication,
Cryogenics of SRF Spoke Cavity Development at SMTF
 Cryogenics of SRF Spoke Cavity Development at SMTF Michael White SRF Development Technical Division Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory May 11, 2006 Overview of Topics SMTF Overview CTF Cryogen Supply
Cryogenics of SRF Spoke Cavity Development at SMTF Michael White SRF Development Technical Division Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory May 11, 2006 Overview of Topics SMTF Overview CTF Cryogen Supply
EXPERIENCE WITH A PRE-SERIES SUPERFLUID HELIUM TEST BENCH FOR LHC MAGNETS
 EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH European Laboratory for Particle Physics Large Hadron Collider Project LHC Project Report 388 EXPERIENCE WITH A PRE-SERIES SUPERFLUID HELIUM TEST BENCH FOR LHC
EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH European Laboratory for Particle Physics Large Hadron Collider Project LHC Project Report 388 EXPERIENCE WITH A PRE-SERIES SUPERFLUID HELIUM TEST BENCH FOR LHC
Chapter 13 Fluids. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 13 Fluids Phases of Matter Density and Specific Gravity Pressure in Fluids Atmospheric Pressure and Gauge Pressure Pascal s Principle Units of Chapter 13 Measurement of Pressure; Gauges and the
Chapter 13 Fluids Phases of Matter Density and Specific Gravity Pressure in Fluids Atmospheric Pressure and Gauge Pressure Pascal s Principle Units of Chapter 13 Measurement of Pressure; Gauges and the
VACGEN. Vacuum Components. Product Overview
 VACGEN Product Overview WHY CHOOSE US? In 1964 the Vacuum Generators company was formed in East Grinstead, UK, by Dr Bernard Eastwell and Vic Treasure with a single product - the CR38 all metal right angled
VACGEN Product Overview WHY CHOOSE US? In 1964 the Vacuum Generators company was formed in East Grinstead, UK, by Dr Bernard Eastwell and Vic Treasure with a single product - the CR38 all metal right angled
ITER_D_R8752R v.1.1. IDM UID D_R8752R v.1.1
 IDM UID D_R8752R v.1.1 Technical Specifications: Supply of Elastomer sealed Ultra High Vacuum Valves for the ITER Project. Technical Specifications: Supply of Elastomer sealed Ultra High Vacuum Valves
IDM UID D_R8752R v.1.1 Technical Specifications: Supply of Elastomer sealed Ultra High Vacuum Valves for the ITER Project. Technical Specifications: Supply of Elastomer sealed Ultra High Vacuum Valves
Technical Specifications of Hydrogen Isotope Handling and Recovery System
 SECTION - C TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS OF STORES AND DRAWINGS. Technical Specifications of Hydrogen Isotope Handling and Recovery System INSTITUTE FOR PLASMA RESEARCH GANDHINAGAR, GUJARAT 382428 ANNEXURE-I
SECTION - C TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS OF STORES AND DRAWINGS. Technical Specifications of Hydrogen Isotope Handling and Recovery System INSTITUTE FOR PLASMA RESEARCH GANDHINAGAR, GUJARAT 382428 ANNEXURE-I
hydro-pac, inc. Low-Pressure Gas Compressors 1500 to 6000 PSI
 hydro-pac, inc. LX-SERIES Low-Pressure Gas Compressors 1500 to 6000 PSI hydro-pac, inc. LX-SERIES Features Hydro-Pac LX-SERIES Gas Compressors feature: Oil-free non lubricated gas pistons and cylinders
hydro-pac, inc. LX-SERIES Low-Pressure Gas Compressors 1500 to 6000 PSI hydro-pac, inc. LX-SERIES Features Hydro-Pac LX-SERIES Gas Compressors feature: Oil-free non lubricated gas pistons and cylinders
[USING THE VITROBOT April 9, Using the Vitrobot
 Using the Vitrobot The Vitrobot Mk 3 (aka Mark III, Mark 3, etc.) can control both the local temperature and the local humidity during the process of plunge-freezing a grid for cryoem. It does require
Using the Vitrobot The Vitrobot Mk 3 (aka Mark III, Mark 3, etc.) can control both the local temperature and the local humidity during the process of plunge-freezing a grid for cryoem. It does require
Detecting Hydrogen in Helium Streams. Samuel Goodman. Pittsford Mendon High School. Rochester, New York. Advisor: Dr.
 1 Detecting Hydrogen in Helium Streams Samuel Goodman Pittsford Mendon High School Rochester, New York Advisor: Dr. Walter Shmayda Laboratory for Laser Energetics University of Rochester Rochester, New
1 Detecting Hydrogen in Helium Streams Samuel Goodman Pittsford Mendon High School Rochester, New York Advisor: Dr. Walter Shmayda Laboratory for Laser Energetics University of Rochester Rochester, New
R.Maingi, G.L. Jackson, M.R. Wade,? M.A. Mahdavi, P.K.Mioduszewski,?
 DIVERTOR PARTICLE EXHAUST AND WALL INVENTORY ON DllCD R.Maingi, G.L. Jackson, M.R. Wade,? M.A. Mahdavi, P.K.Mioduszewski,? G. Haas,# M.J. Schaffer, J.T. Hogan,i C.C. Klepperi General Atomics, P.0.Box 85608,
DIVERTOR PARTICLE EXHAUST AND WALL INVENTORY ON DllCD R.Maingi, G.L. Jackson, M.R. Wade,? M.A. Mahdavi, P.K.Mioduszewski,? G. Haas,# M.J. Schaffer, J.T. Hogan,i C.C. Klepperi General Atomics, P.0.Box 85608,
HW-1: Due by 5:00 pm EDT on Wednesday 13 June 2018 to GradeScope.
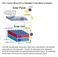 HW-1: Due by 5:00 pm EDT on Wednesday 13 June 2018 to GradeScope. The solar cell/solar panel shown above depict how a semiconductor can transform solar power into electrical power. Consider the solar panel
HW-1: Due by 5:00 pm EDT on Wednesday 13 June 2018 to GradeScope. The solar cell/solar panel shown above depict how a semiconductor can transform solar power into electrical power. Consider the solar panel
JT Micro Compressor Test Results
 JT Micro Compressor Test Results J.R. Olson, P. Champagne, E. Roth, T. Nast Advanced Technology Center, Lockheed Martin Space Systems Palo Alto, CA 94304, USA ABSTRACT We report the results of operational
JT Micro Compressor Test Results J.R. Olson, P. Champagne, E. Roth, T. Nast Advanced Technology Center, Lockheed Martin Space Systems Palo Alto, CA 94304, USA ABSTRACT We report the results of operational
Load Responsive Multilayer Insulation Performance Testing
 Load Responsive Multilayer Insulation Performance Testing S. Dye 1, A. Kopelove 1, and G. L. Mills 2 1 Quest Thermal Group, 6452 Fig Street Suite A, Arvada, CO 80004 USA 2 Ball Aerospace & Technologies
Load Responsive Multilayer Insulation Performance Testing S. Dye 1, A. Kopelove 1, and G. L. Mills 2 1 Quest Thermal Group, 6452 Fig Street Suite A, Arvada, CO 80004 USA 2 Ball Aerospace & Technologies
Old-Exam.Questions-Ch-14 T072 T071
 Old-Exam.Questions-Ch-14 T072 Q23. Water is pumped out of a swimming pool at a speed of 5.0 m/s through a uniform hose of radius 1.0 cm. Find the mass of water pumped out of the pool in one minute. (Density
Old-Exam.Questions-Ch-14 T072 Q23. Water is pumped out of a swimming pool at a speed of 5.0 m/s through a uniform hose of radius 1.0 cm. Find the mass of water pumped out of the pool in one minute. (Density
Table of Contents Want full page pictures with most important parts labeled in the beginning.
 1 Table of Contents Want full page pictures with most important parts labeled in the beginning. Precool Procedures (Perform before cooling down): 1. Check N2 and 4He gas tanks to be sure that there is
1 Table of Contents Want full page pictures with most important parts labeled in the beginning. Precool Procedures (Perform before cooling down): 1. Check N2 and 4He gas tanks to be sure that there is
Cryogenic Engineering Prof. M. D. Atrey Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay
 Cryogenic Engineering Prof. M. D. Atrey Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. # 29 Cryocoolers Ideal Stirling cycle So, welcome to the 29th lecture on
Cryogenic Engineering Prof. M. D. Atrey Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. # 29 Cryocoolers Ideal Stirling cycle So, welcome to the 29th lecture on
CERTIFICATES OF COMPETENCY IN THE MERCHANT NAVY MARINE ENGINEER OFFICER
 CERTIFICATES OF COMPETENCY IN THE MERCHANT NAVY MARINE ENGINEER OFFICER EXAMINATIONS ADMINISTERED BY THE SCOTTISH QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY ON BEHALF OF THE MARITIME AND COASTGUARD AGENCY STCW 95 CHIEF
CERTIFICATES OF COMPETENCY IN THE MERCHANT NAVY MARINE ENGINEER OFFICER EXAMINATIONS ADMINISTERED BY THE SCOTTISH QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY ON BEHALF OF THE MARITIME AND COASTGUARD AGENCY STCW 95 CHIEF
Generating Calibration Gas Standards
 Technical Note 1001 Metronics Inc. Generating Calibration Gas Standards with Dynacal Permeation Devices Permeation devices provide an excellent method of producing known gas concentrations in the PPM and
Technical Note 1001 Metronics Inc. Generating Calibration Gas Standards with Dynacal Permeation Devices Permeation devices provide an excellent method of producing known gas concentrations in the PPM and
Performance Testing of a High Capacity Compressor for a 20K 20W Cryocooler
 #93 1 Performance Testing of a High Capacity Compressor for a 20K 20W Cryocooler K. Cragin, D. Deserranno, M. Zagarola Creare LLC Hanover, NH 03755 ABSTRACT Creare is currently developing for NASA a high
#93 1 Performance Testing of a High Capacity Compressor for a 20K 20W Cryocooler K. Cragin, D. Deserranno, M. Zagarola Creare LLC Hanover, NH 03755 ABSTRACT Creare is currently developing for NASA a high
CFD Simulation and Experimental Validation of a Diaphragm Pressure Wave Generator
 CFD Simulation and Experimental Validation of a Diaphragm Pressure Wave Generator T. Huang 1, A. Caughley 2, R. Young 2 and V. Chamritski 1 1 HTS-110 Ltd Lower Hutt, New Zealand 2 Industrial Research Ltd
CFD Simulation and Experimental Validation of a Diaphragm Pressure Wave Generator T. Huang 1, A. Caughley 2, R. Young 2 and V. Chamritski 1 1 HTS-110 Ltd Lower Hutt, New Zealand 2 Industrial Research Ltd
Pressure Measurement
 Pressure Measurement Manometers Sensors, Transducers Ashish J. Modi Lecturer, Dept. of Mech.Engg., Shri S.V.M. inst. Of Technology, Bharuch Pressure Pressure is a force per unit area exerted by a fluid
Pressure Measurement Manometers Sensors, Transducers Ashish J. Modi Lecturer, Dept. of Mech.Engg., Shri S.V.M. inst. Of Technology, Bharuch Pressure Pressure is a force per unit area exerted by a fluid
The JET Gas Baking Plant for DT Operation and Analysis of Tritium Permeation and Baking Gas Activation in DTE1
 JET CP(98)57 The JET Gas Baking Plant for DT Operation and Analysis of Tritium Permeation and Baking Gas Activation in DTE1 R J H Pearce, P Andrew, S Bryan, J L Hemmerich. JET Joint Undertaking, Abingdon,
JET CP(98)57 The JET Gas Baking Plant for DT Operation and Analysis of Tritium Permeation and Baking Gas Activation in DTE1 R J H Pearce, P Andrew, S Bryan, J L Hemmerich. JET Joint Undertaking, Abingdon,
INSTRUMENTS A THERMAL MASS FLOW SENSOR USING A CONSTANT DIFFERENTIAL TEMPERATURE ABOVE THE AMBIENT GAS TEMPERATURE
 TELEDYNE HASTINGS TECHNICAL PAPERS INSTRUMENTS A THERMAL MASS FLOW SENSOR USING A CONSTANT DIFFERENTIAL TEMPERATURE ABOVE THE AMBIENT GAS TEMPERATURE Proceedings of FEDSM 98 1998 ASME Fluids Engineering
TELEDYNE HASTINGS TECHNICAL PAPERS INSTRUMENTS A THERMAL MASS FLOW SENSOR USING A CONSTANT DIFFERENTIAL TEMPERATURE ABOVE THE AMBIENT GAS TEMPERATURE Proceedings of FEDSM 98 1998 ASME Fluids Engineering
Problems of Chapter 3
 Problems of Chapter 3 Section 3.1 Molecular Model of an Ideal Gas 3. A sealed cubical container 20 cm on a side contains three times Avogadro s number of molecules at a temperature of 20 C. Find the force
Problems of Chapter 3 Section 3.1 Molecular Model of an Ideal Gas 3. A sealed cubical container 20 cm on a side contains three times Avogadro s number of molecules at a temperature of 20 C. Find the force
Micro Channel Recuperator for a Reverse Brayton Cycle Cryocooler
 Micro Channel Recuperator for a Reverse Brayton Cycle Cryocooler C. Becnel, J. Lagrone, and K. Kelly Mezzo Technologies Baton Rouge, LA USA 70806 ABSTRACT The Missile Defense Agency has supported a research
Micro Channel Recuperator for a Reverse Brayton Cycle Cryocooler C. Becnel, J. Lagrone, and K. Kelly Mezzo Technologies Baton Rouge, LA USA 70806 ABSTRACT The Missile Defense Agency has supported a research
Unit 24: Applications of Pneumatics and Hydraulics
 Unit 24: Applications of Pneumatics and Hydraulics Unit code: J/601/1496 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15 OUTCOME 2 TUTORIAL 9 ACCUMULATORS The material needed for outcome 2 is very extensive so there are
Unit 24: Applications of Pneumatics and Hydraulics Unit code: J/601/1496 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15 OUTCOME 2 TUTORIAL 9 ACCUMULATORS The material needed for outcome 2 is very extensive so there are
PRad Target. Chris Keith JLab Target Group
 PRad Target Chris Keith JLab Target Group Target Overview & Components Target Software Hazard Analysis and Mitigation Target Status, Performance& Remaining Work Installation Schedule Nov. 12, 2015 PRad
PRad Target Chris Keith JLab Target Group Target Overview & Components Target Software Hazard Analysis and Mitigation Target Status, Performance& Remaining Work Installation Schedule Nov. 12, 2015 PRad
Experimental Verification of Integrated Pressure Suppression Systems in Fusion Reactors at In-Vessel Loss-of -Coolant Events
 Experimental Verification of Integrated Pressure Suppression Systems in Fusion Reactors at In-Vessel Loss-of -Coolant Events K. Takase 1), H. Akimoto 1) 1) Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI),
Experimental Verification of Integrated Pressure Suppression Systems in Fusion Reactors at In-Vessel Loss-of -Coolant Events K. Takase 1), H. Akimoto 1) 1) Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI),
Pump out insert (condenser and still lines) overnight with turbo pump
 Running the Dilution Fridge Before starting a run: Pump out insert (condenser and still lines) overnight with turbo pump Make sure LN and LHe traps are clean pump out with He4 rotary pump Start He3 rotary
Running the Dilution Fridge Before starting a run: Pump out insert (condenser and still lines) overnight with turbo pump Make sure LN and LHe traps are clean pump out with He4 rotary pump Start He3 rotary
CNS In-Pool Assembly Mechanical Design for OYSTER Project
 CNS In-Pool Assembly Mechanical Design for OYSTER Project JINBOK CHOI, JUNGHYUN RYU Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute (KAERI) 111 Deadeok-daero 989Beon-gil, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon, Republic of Korea
CNS In-Pool Assembly Mechanical Design for OYSTER Project JINBOK CHOI, JUNGHYUN RYU Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute (KAERI) 111 Deadeok-daero 989Beon-gil, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon, Republic of Korea
National Accelerator Laboratory
 Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory FERMILAB-Conf-97/268 A 1400 Liter 1.8K Test Facility T.J. Peterson, R.J. Rabehl and C.D. Sylvester Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory P.O. Box 500, Batavia, Illinois
Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory FERMILAB-Conf-97/268 A 1400 Liter 1.8K Test Facility T.J. Peterson, R.J. Rabehl and C.D. Sylvester Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory P.O. Box 500, Batavia, Illinois
Procedure for Operating Columbia (Nevis) LHe Electron Bubble Chamber Cryostat. Version 5.1
 Project: Novel Electron Bubble Particle Detector Procedure for Operating Columbia (Nevis) LHe Electron Bubble Chamber Cryostat Version 5.1 (Using side filling line) Hand Processed Changes HPC No. Date
Project: Novel Electron Bubble Particle Detector Procedure for Operating Columbia (Nevis) LHe Electron Bubble Chamber Cryostat Version 5.1 (Using side filling line) Hand Processed Changes HPC No. Date
Irrigation &Hydraulics Department lb / ft to kg/lit.
 CAIRO UNIVERSITY FLUID MECHANICS Faculty of Engineering nd Year CIVIL ENG. Irrigation &Hydraulics Department 010-011 1. FLUID PROPERTIES 1. Identify the dimensions and units for the following engineering
CAIRO UNIVERSITY FLUID MECHANICS Faculty of Engineering nd Year CIVIL ENG. Irrigation &Hydraulics Department 010-011 1. FLUID PROPERTIES 1. Identify the dimensions and units for the following engineering
Short Introduction to Cryo-Pumps and Refrigerators. Dr Graham Rogers Leybold UK Ltd.
 Short Introduction to Cryo-Pumps and Refrigerators Dr Graham Rogers Leybold UK Ltd. Cryo Pumps Topics Physical principles of cryo-pumping Design and control of modern refrigerator cryo-pumps UHV and XHV
Short Introduction to Cryo-Pumps and Refrigerators Dr Graham Rogers Leybold UK Ltd. Cryo Pumps Topics Physical principles of cryo-pumping Design and control of modern refrigerator cryo-pumps UHV and XHV
Storage and transfer of cryofluids
 Storage and transfer of cryofluids Christian Gianese Guilty 1: Arsène d Arsonval (1851-1940) He invented a glass container with double wall, the vacuum being done in the space between the outer and inner
Storage and transfer of cryofluids Christian Gianese Guilty 1: Arsène d Arsonval (1851-1940) He invented a glass container with double wall, the vacuum being done in the space between the outer and inner
Variable Temperature Storage Dewar Mount Inserts
 Variable Temperature Storage Dewar Mount Inserts All inserts are available for either Liquid Helium or Liquid Nitrogen Dewars! DStat - External cryostat with insert leg DStatMag - Super Conducting Magnet
Variable Temperature Storage Dewar Mount Inserts All inserts are available for either Liquid Helium or Liquid Nitrogen Dewars! DStat - External cryostat with insert leg DStatMag - Super Conducting Magnet
Trapped Bubble Dynamics in Cryogenic Fluids. Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of California, Los Angeles, CA 90095, USA
 Trapped Bubble Dynamics in Cryogenic Fluids O. Baghdassarian, H. Cho y,e.varoquaux Λ, and G. A. Williams Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of California, Los Angeles, CA 90095, USA Initial
Trapped Bubble Dynamics in Cryogenic Fluids O. Baghdassarian, H. Cho y,e.varoquaux Λ, and G. A. Williams Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of California, Los Angeles, CA 90095, USA Initial
Enter your parameter set number (1-27)
 1- Helium balloons fly and balloons with air sink. Assume that we want to get a balloon that is just floating in the air, neither rising nor falling, when a small weight is placed hanging in the balloon.
1- Helium balloons fly and balloons with air sink. Assume that we want to get a balloon that is just floating in the air, neither rising nor falling, when a small weight is placed hanging in the balloon.
Cryostream 800 Series
 Cryostream 800 Series Cryostream 800 Series Nearly 30 years after the invention of the first Cryostream Cooler, Oxford Cryosystems is proud to announce the launch of the new 800 series Cryostream. The
Cryostream 800 Series Cryostream 800 Series Nearly 30 years after the invention of the first Cryostream Cooler, Oxford Cryosystems is proud to announce the launch of the new 800 series Cryostream. The
Thermodynamics ERT 206 Properties of Pure Substance HANNA ILYANI ZULHAIMI
 Thermodynamics ERT 206 Properties of Pure Substance HANNA ILYANI ZULHAIMI Outline: Pure Substance Phases of pure substance Phase change process of pure substance Saturation temperature and saturation pressure
Thermodynamics ERT 206 Properties of Pure Substance HANNA ILYANI ZULHAIMI Outline: Pure Substance Phases of pure substance Phase change process of pure substance Saturation temperature and saturation pressure
HCMTCB MATERIALS SAMPLING & TESTING PERFORMANCE CHECKLIST
 HCMTCB MATERIALS SAMPLING & TESTING PERFORMANCE CHECKLIST Release Date: January 7, 2014 Sampling Coarse Aggregate PERFORMANCE CHECKLIST AASHTO T-2 Sampling of Aggregates Sampling From A Stockpile 1 When
HCMTCB MATERIALS SAMPLING & TESTING PERFORMANCE CHECKLIST Release Date: January 7, 2014 Sampling Coarse Aggregate PERFORMANCE CHECKLIST AASHTO T-2 Sampling of Aggregates Sampling From A Stockpile 1 When
Design, Static Structural & Model Analysis of Water Ring Vacuum Pump Impeller
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 6, Issue 03, 2018 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Design, Static Structural & Model Analysis of Water Ring Vacuum Pump Impeller Ajay A.
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 6, Issue 03, 2018 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Design, Static Structural & Model Analysis of Water Ring Vacuum Pump Impeller Ajay A.
Detector Carrier Gas Comments Detector anode purge or reference gas. Electron Capture Nitrogen Maximum sensitivity Nitrogen Argon/Methane
 Gas requirements Gases for packed columns The carrier gas you use depends upon the type of detector and the performance requirements. Table 520-1 lists gas recommendations for packed column use. In general,
Gas requirements Gases for packed columns The carrier gas you use depends upon the type of detector and the performance requirements. Table 520-1 lists gas recommendations for packed column use. In general,
Digester Processes. 1. Raw Sludge Pumping System
 Digester Processes 1. Raw Sludge Pumping System Removes accumulated sludge from the primary clarifiers, pumped through 1 of 2 pipes either 150 or 200mm in diameter (Fig. 1.1). Fig 1.1 Pipes feeding Digesters
Digester Processes 1. Raw Sludge Pumping System Removes accumulated sludge from the primary clarifiers, pumped through 1 of 2 pipes either 150 or 200mm in diameter (Fig. 1.1). Fig 1.1 Pipes feeding Digesters
Specifications of Cryogenic vacuum jacketed valves
 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS OF STORES AND DRAWINGS. SECTION - C Technical Specifications for Supply of Cryogenic Vacuum ed Control Valves Specifications of Cryogenic vacuum jacketed valves Contents 1 INTRODUCTION
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS OF STORES AND DRAWINGS. SECTION - C Technical Specifications for Supply of Cryogenic Vacuum ed Control Valves Specifications of Cryogenic vacuum jacketed valves Contents 1 INTRODUCTION
mass of container full of air = g mass of container with extra air = g volume of air released = cm 3
 1992 Q32 The air pressure inside the passenger cabin of an airliner is 9 x 10 4 Pa when the airliner is at its cruising height. The pressure of the outside atmosphere at this height is 4 x 10 4 Pa. Calculate
1992 Q32 The air pressure inside the passenger cabin of an airliner is 9 x 10 4 Pa when the airliner is at its cruising height. The pressure of the outside atmosphere at this height is 4 x 10 4 Pa. Calculate
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS Combination Permeameter ELE International Chartmoor Road, Chartwell Business Park Leighton Buzzard, Bedfordshire, LU7 4WG England phone: +44 (0) 1525 249200 fax: +44 (0) 1525 249249
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS Combination Permeameter ELE International Chartmoor Road, Chartwell Business Park Leighton Buzzard, Bedfordshire, LU7 4WG England phone: +44 (0) 1525 249200 fax: +44 (0) 1525 249249
Fermilab MTF Cryogenic System & Vertical RF Cavity Test Facility. Yuenian Huang, on behalf of Fermilab, TD/TID May 11, 2006
 Fermilab MTF Cryogenic System & Vertical RF Cavity Test Facility Yuenian Huang, on behalf of Fermilab, TD/TID May 11, 2006 1 Magnet Test Facility (MTF) Tevatron magnet test stands Testing temperature range
Fermilab MTF Cryogenic System & Vertical RF Cavity Test Facility Yuenian Huang, on behalf of Fermilab, TD/TID May 11, 2006 1 Magnet Test Facility (MTF) Tevatron magnet test stands Testing temperature range
Truck-mounted Mass Flow Metering for LPG Delivery
 Truck-mounted Mass Flow Metering for LPG Delivery Itron, Inc. 1310 Emerald Rd. Greenwood, SC 29646 Introduction The mathematician Gustave De Coriolis first described the Coriolis Effect, which is an inertial
Truck-mounted Mass Flow Metering for LPG Delivery Itron, Inc. 1310 Emerald Rd. Greenwood, SC 29646 Introduction The mathematician Gustave De Coriolis first described the Coriolis Effect, which is an inertial
A Depletion Compensated Wet Bath Simulator For Calibrating Evidential Breath Alcohol Analyzers
 A Depletion Compensated Wet Bath Simulator For Calibrating Evidential Breath Alcohol Analyzers Slemeyer, A. University of Applied Sciences of Giessen, Dept. of Electrical Engineering 1 Wiesenstr. 14, D-35390
A Depletion Compensated Wet Bath Simulator For Calibrating Evidential Breath Alcohol Analyzers Slemeyer, A. University of Applied Sciences of Giessen, Dept. of Electrical Engineering 1 Wiesenstr. 14, D-35390
PRELIMINARY PIPE STRESS ANALYSIS OF HIGH PRESSURE, HIGH TEMPERATURE EXPERIMENTAL HELIUM COOLING SYSTEM
 A.K. VERMA, B.K. YADAV, A. GANDHI, A. SARASWAT, S. VERMA, E.R. KUMAR PRELIMINARY PIPE STRESS ANALYSIS OF HIGH PRESSURE, HIGH TEMPERATURE EXPERIMENTAL HELIUM COOLING SYSTEM A.K.VERMA Institute for Plasma
A.K. VERMA, B.K. YADAV, A. GANDHI, A. SARASWAT, S. VERMA, E.R. KUMAR PRELIMINARY PIPE STRESS ANALYSIS OF HIGH PRESSURE, HIGH TEMPERATURE EXPERIMENTAL HELIUM COOLING SYSTEM A.K.VERMA Institute for Plasma
COURSE NUMBER: ME 321 Fluid Mechanics I Fluid statics. Course teacher Dr. M. Mahbubur Razzaque Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BUET
 COURSE NUMBER: ME 321 Fluid Mechanics I Fluid statics Course teacher Dr. M. Mahbubur Razzaque Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BUET 1 Fluid statics Fluid statics is the study of fluids in
COURSE NUMBER: ME 321 Fluid Mechanics I Fluid statics Course teacher Dr. M. Mahbubur Razzaque Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BUET 1 Fluid statics Fluid statics is the study of fluids in
Performance of the Liquid Hydrogen Target
 Performance of the Liquid Hydrogen Target Presented by Chad Gillis Indiana University at NPDGamma Collaboration Meeting July 2012, Oak Ridge, Tennessee Since upgrading the target for operation at the SNS,
Performance of the Liquid Hydrogen Target Presented by Chad Gillis Indiana University at NPDGamma Collaboration Meeting July 2012, Oak Ridge, Tennessee Since upgrading the target for operation at the SNS,
Introduction of Vacuum Science & Technology. Diffusion pumps used on the Calutron mass spectrometers during the Manhattan Project.
 Introduction of Vacuum Science & Technology Diffusion pumps used on the Calutron mass spectrometers during the Manhattan Project. 1 What is a vacuum? 760 mm Hg Vacuum ATM A vacuum is defined as less than
Introduction of Vacuum Science & Technology Diffusion pumps used on the Calutron mass spectrometers during the Manhattan Project. 1 What is a vacuum? 760 mm Hg Vacuum ATM A vacuum is defined as less than
DESIGN AND PERFORMANCE OF THE NEW SARTORIUS 1 KG VACUUM MASS COMPARATOR AT PTB
 XVIII IMEKO ORLD CONGRESS Metrology for a Sustainable Development September, 17 22, 2006, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil DESIGN AND PERFORMANCE OF THE NE SARTORIUS 1 KG VACUUM MASS COMPARATOR AT PTB M. Borys 1,
XVIII IMEKO ORLD CONGRESS Metrology for a Sustainable Development September, 17 22, 2006, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil DESIGN AND PERFORMANCE OF THE NE SARTORIUS 1 KG VACUUM MASS COMPARATOR AT PTB M. Borys 1,
SALT RSS-NIR MID-TERM REVIEW MAY 20 & 21, 2009 THERMAL SYSTEM DESIGN
 SALT RSS-NIR MID-TERM REVIEW MAY 20 & 21, 2009 THERMAL SYSTEM DESIGN DOUG ADLER UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN NIR THERMAL SYSTEMS Three primary thermal systems: Predewar, Dewar, and Electronics NIR instrument
SALT RSS-NIR MID-TERM REVIEW MAY 20 & 21, 2009 THERMAL SYSTEM DESIGN DOUG ADLER UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN NIR THERMAL SYSTEMS Three primary thermal systems: Predewar, Dewar, and Electronics NIR instrument
ASSIGNMENT 2 CHE 3473
 DUE: May 23 ASSIGNMENT 2 CHE 3473 #Problem 1: 3.3 #Problem 2: 3.4 #Problem 3: 3.5 #Problem 4: 3.6 #Problem 5: 3.7 #Problem 6: 3.8 #Problem 7: 3.11 #Problem 8: 3.15 #Problem 9: 3.22 #Problem 10: 3.32 #Problem
DUE: May 23 ASSIGNMENT 2 CHE 3473 #Problem 1: 3.3 #Problem 2: 3.4 #Problem 3: 3.5 #Problem 4: 3.6 #Problem 5: 3.7 #Problem 6: 3.8 #Problem 7: 3.11 #Problem 8: 3.15 #Problem 9: 3.22 #Problem 10: 3.32 #Problem
Specifications for the CMI 2409 Magnetocardiograph
 Specifications for the CMI 2409 Magnetocardiograph Revision date April 14, 2006 1 518-381-1000 (tel) The CMI-2409 system consists of a holder (A), a patient bed (B) and a workstation (not shown in the
Specifications for the CMI 2409 Magnetocardiograph Revision date April 14, 2006 1 518-381-1000 (tel) The CMI-2409 system consists of a holder (A), a patient bed (B) and a workstation (not shown in the
GLOSSARY OF TERMS. Adiabatic Compression Compression process when all heat of compression is retained in the gas being compressed.
 GLOSSARY OF TERMS Absolute pressure Total pressure measured from absolute zero i.e. a perfect vacuum. As a practical matter, gauge pressure plus atmospheric pressure. Absolute temperature Temperature measured
GLOSSARY OF TERMS Absolute pressure Total pressure measured from absolute zero i.e. a perfect vacuum. As a practical matter, gauge pressure plus atmospheric pressure. Absolute temperature Temperature measured
ASSIGNMENT 2 CHE 3473
 DUE: May 21 ASSIGNMENT 2 CHE 3473 #Problem 1 Read Chapter 3. ALL OF IT. Time yourself and report the time. #Problem 2: 3.2 #Problem 3: 3.3 #Problem 4: 3.5 #Problem 5: 3.6 #Problem 6: 3.7 #Problem 7: 3.8
DUE: May 21 ASSIGNMENT 2 CHE 3473 #Problem 1 Read Chapter 3. ALL OF IT. Time yourself and report the time. #Problem 2: 3.2 #Problem 3: 3.3 #Problem 4: 3.5 #Problem 5: 3.6 #Problem 6: 3.7 #Problem 7: 3.8
Vacuum Jacketed Piping Solutions
 Acme Cryogenics VACUUM INSULATED PIPE Vacuum Jacketed Piping Solutions Preferred piping solution for the safe, reliable, cost-effective transfer of cryogenic liquids - such as liquidifed nitrogen, oxygen,
Acme Cryogenics VACUUM INSULATED PIPE Vacuum Jacketed Piping Solutions Preferred piping solution for the safe, reliable, cost-effective transfer of cryogenic liquids - such as liquidifed nitrogen, oxygen,
QUALIFICATION OF SUB-ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE SENSORS FOR THE CRYOMAGNET BAYONET HEAT EXCHANGERS OF THE LARGE HADRON COLLIDER
 EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH European Laboratory for Particle Physics Large Hadron Collider Project LHC Project Report 980 QUALIFICATION OF SUB-ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE SENSORS FOR THE CRYOMAGNET
EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH European Laboratory for Particle Physics Large Hadron Collider Project LHC Project Report 980 QUALIFICATION OF SUB-ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE SENSORS FOR THE CRYOMAGNET
Cooling Characteristics of GM-type Pulse Tube Refrigerator with Neon as Working Gas
 Cooling Characteristics of GM-type Pulse Tube Refrigerator with Neon as Working Gas J. Ko, Y.J. Hong, H. Kim, H. Yeom, S.J. Park, D.Y. Koh Korea Institute of Machinery & Materials Daejeon, Korea (S), 305-343
Cooling Characteristics of GM-type Pulse Tube Refrigerator with Neon as Working Gas J. Ko, Y.J. Hong, H. Kim, H. Yeom, S.J. Park, D.Y. Koh Korea Institute of Machinery & Materials Daejeon, Korea (S), 305-343
Experimental Analysis on Vortex Tube Refrigerator Using Different Conical Valve Angles
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 7-067X, p-issn: 7-00X, www.ijerd.com Volume 3, Issue 4 (August ), PP. 33-39 Experimental Analysis on Vortex Tube Refrigerator Using
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 7-067X, p-issn: 7-00X, www.ijerd.com Volume 3, Issue 4 (August ), PP. 33-39 Experimental Analysis on Vortex Tube Refrigerator Using
Chapter 4, Problem 30.
 Chapter 4, Problem 30. A well-insulated rigid tank contains 5 kg of a saturated liquid vapor mixture of water at l00 kpa. Initially, three-quarters of the mass is in the liquid phase. An electric resistor
Chapter 4, Problem 30. A well-insulated rigid tank contains 5 kg of a saturated liquid vapor mixture of water at l00 kpa. Initially, three-quarters of the mass is in the liquid phase. An electric resistor
Compiled by: B Beard. Approved by: SH Carstens. Description of requirements and procedures for compact provers to be used as verification standards.
 1. Scope Description of requirements and procedures for compact provers to be used as verification standards. 2. Reference documents Trade Metrology Act SANS1698 3. Policy A. BASIC REQUIREMENTS Compact
1. Scope Description of requirements and procedures for compact provers to be used as verification standards. 2. Reference documents Trade Metrology Act SANS1698 3. Policy A. BASIC REQUIREMENTS Compact
