GAIT MEASUREMENTS AND MOTOR RECOVERY AFTER STROKE. Plamen S. Mateev, Ina M. Tarkka, Ekaterina B. Titianova
|
|
|
- Noah Underwood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Pliska Stud. Math. Bulgar. 16 (2004), STUDIA MATHEMATICA BULGARICA GAIT MEASUREMENTS AND MOTOR RECOVERY AFTER STROKE Plamen S. Mateev, Ina M. Tarkka, Ekaterina B. Titianova Gait analysis is one of the methods used for estimation of the degree of restoration of motor recovery after stroke. The purpose of the present study was to examine the diagnostic value of the footprint parameters and their relationship with the functional ambulation profile (FAP) scores provided automatically by the pressure sensor walkway system for gait examination. The patterns of walking were studied in a group of 23 patients with chronic unilateral stroke and 72 healthy subjects. Among the measured gait variables the peak times of the footprints were found as most informative parameters. Their predictive value was compared with some other gait indicators for motor recovery after stroke. 1. Introduction Gait abnormalities after chronic unilateral stroke have been clinically evaluated and described by a number of investigators using different methods [1],[3],[6],[7]. Most of the techniques however are time consuming or otherwise insufficient for collecting reliable data. Recent technology has resulted in flexible and portable walkways with embedded pressure sensitive sensors. The pressure sensor system records the location of activated sensors and the time of their activation and deactivation. It provides the spatial and temporal variables of gait along with a dynamic pressure mapping of each footprint during walking [4],[5]. The clinical applicability of this technique is under investigation Mathematics Subject Classification: 62P10, 92C20 Key words: gait analysis, recovery after stroke
3 122 P. Mateev, I. Tarkka, E. Titianova The purpose of the present study was to examine the diagnostic value of the pressure sensor system GAITRite for distinguish gait abnormalities after stroke using the estimation of footprint parameters and functional ambulation profile (FAP) scores provided automatically by the equipment. 2. Gait Equipment and Recordings All gait measurements were performed with a portable GAITRite system (MAP/ CIR Inc., Havertown, PA). This system consists of an electronic walkway of 4.57 m with an active area of m, where the sensor pads are encapsulated. 13,824 sensors, each 1 cm in diameter, are arranged in a grid pattern. Detail information about the methodology is given in [8]. The system continuously scans the sensors, provides information about the geometry of the footprints in 2-D space and gives a dynamic pressure mapping during walking by recording the location of activated sensors and the time of sensor activation/deactivation. At least one complete stride for each side inside the walkway is required to complete the computation. Measurements of the spatial and temporal gait variables are based on the geometric centers of heels for each of the 3 consecutive footprints (Figure 1). The subjects were asked to walk twice across the walkway without shoes. The average of both trials was analyzed. The walking distance (cm) and the ambulation time (s) were obtained from the heel centers of the first and last footprints. Figure 1: The series of three footprints. Each footprint is divided into 12 trapezoids. Points A, D and G are the geometric centers of the heel for each footprint [2].
4 Gait Measurements and Motor Recovery after Stroke 123 The Functional Ambulation Profile (FAP) scores are calculated by the system as a general indicator for the tested patient. The algorithm of FAP calculation includes following steps [2]: 1) For each limb the step length (measured electronically by the walkway) is divided by the leg length (measured manually) to produce the Step Length/Leg Length ratio (SL/LL), at the patient s preferred velocity. The velocity, collected over the 3.66 meters of the GAITRite active area is divided by the patient s mean leg length to produce the mean normalized velocity expressed in Leg Lengths per second (LL/sec). 2) For each limb, the SL/LL ratio, the step time and the mean normalized velocity are then compared on a model of regression lines to determine their deviations from the normal. This constitutes 44% of the total score, or 22% for each limb s performance. 3) The degree of asymmetry is calculated by subtracting the SL/LL ratios of each limb and then compared to normal, representing 8% of the total score. 4) The dynamic base of support, measured by the GAITRite walkway is also compared to normal, representing 8% of the total score. 5) Use of assisting devices such as orthoses, splints etc. represent 5% of the total score. Ambulatory aids such as canes, crutches, or walkers represent 5% of the total score. The final score is derived subtracting points from a maximum score of 100. The maximum score of 100 is obtained at ordinary speed when step extremity ratios and step times are symmetrical and a dynamic base of support is less than 10 cm (see [5], [8]). So defined FAP score is not sufficiently convincing and manual operations are necessarily. Our hypothesis is that among measured parameters exist more informative ones. According the recording system, the footprint was divided into 12 trapezoids, 6 for the lateral part and 6 for the medial part. Each trapezoid, includes a specific number of sensors and the order for assigning sensor activation is heel-to-toe. The following parameters were evaluated for each trapezoid: segmental integrated pressure over time (P*t) (expressed as a percent of the overall integrated pressure over time), peak time (s) (first time point of each trapezoid when one or more sensors within a segment is at the maximum switching level), active area (expressed as a percent of the sum of the active sensors within one segment) and peak pressure (the maximum switching level expressed as a percent of the overall maximum switching level at the peak time in a segment). Detailed explanation of technology of the footprint measurements is given in [9].
5 124 P. Mateev, I. Tarkka, E. Titianova All mentioned variables were tested as predictors in models for degree of motor recovery. 3. The Sample For the purpose of the study 3 experimental groups were measured: The first group (A) consisted from 23 patients (16 men and 7 women, mean age 54.8 ± 6.9 years, range years; mean height ± 8.8 cm, mean weight 82.8 ± 18.9 kg) with residual hemiparesis due to stroke. Some patients had survived unilateral cerebral infarction in the middle cerebral artery territory and others had a unilateral cerebral hemorrhage. They walked with a preferred ordinary speed. The second group (B) included 62 clinically healthy subjects (21 men and 41 women, mean age ± 11.0 years, range years, mean height 1.70 ± m, mean weight ± 11.6 kg).they were non homogeneous set of people without explicit illness and walked with a preferred ordinary speed. In the third group (C) were enrolled 10 clinically healthy subjects (5 men and 5 women, mean age 50.9 ± 4.4 years, range years, mean height 1.69 ± 0.09 m, mean weight 77.6 ± 23.4kg). Fifty measurements were taken at 5 different speeds (from very slow to very fast). The velocity performance was divided into 5 categories: < 40 cm/s, cm/s, cm/s, cm/s and > 160 cm/s. All patients and healthy subjects were engaged in a small training session and they gave an informed consent prior to the study. 4. Results and discussion The description of the algorithm calculating the FAP score is not enough to be reproduced. Nevertheless it is clear that the value of the FAP score depends on the velocity of the tested person. The scatter plot of Velocity and FAP score of patients of group (A) and volunteers in group (C) illustrate our suspicions (Figure 2. The FAP score falls when velocity is small as well higher than 160 cm/s. Decreasing the velocity is not sufficient to distinguish the ailing from healthy persons. Most of the reported gait measurements are unidimensional (velocity, cadence, FAP scores etc.) or bidimensional (left and right stance time, swing time, step length, etc.) averaged characteristics. The latter are commonly used to indicate some gait asymmetry. As shown earlier, there were four indicators, reported by the system for every one of the twelve trapezoids of each footprint. We chose one of them, namely
6 Gait Measurements and Motor Recovery after Stroke 125 Figure 2: Scatter plot of Velocity versus FAP score points. The dependence follows a nonlinear function. The FAP scores fall when velocity were smaller than 80 cm/s and higher than 160 cm/s. Peak-time, as more informative for some deviations of the manner of the steps. Our choice was based on numerical experiments with correlation matrix of those four sets of parameters evaluated on the three experimental groups and their combinations. As an example, for the peak time using the homogenous group (C) we found that the first principal component explains 85% of total variance. Another control group (B) is more variable and only 45% are explained from first two principal components. The combination of the groups (A) and (C) gives 81% explained variation for two factors (principal components). The scatter plot (Figure 3) of that two groups ((A) and (C)) over the two factors suggests that the two groups may be distinguished using peak-time characteristics. Adding group (A) to group (C) increased the number of factors in the analysis from one (when only (C) was included in analysis) to two. There were not such effect combining the groups (A) and (B). Our hypothesis was confirmed in the next phase of the investigations, namely the linear discriminant analysis. First we applied the procedure to the groups (A) and (C) as training sample. As a result (see table 1) we had 98% correct classification of the group (C) and 82.6% correct classification in the group (A). The total correct classification was 93.15%. Posterior probabilities of the control group (B) gave 59 right classifications of 62 examined persons or %. A similar attempt was performed using groups (A) and (B) as training sample. The classification of the both groups was a little bit better, but posterior probabilities on control group (C) now is extremely indicative(see table 2).
7 126 P. Mateev, I. Tarkka, E. Titianova Figure 3: The principal component analysis of the footprint peak times in patients and controls. The projection of the all footprint peak time observations of the two common factors differentiated stroke gait from normal walking. Classified as good bad Correct Group walkers walkers classifications (A) (23 bad) % (C) (50 good) % Total 93.15% (B) (62 good) % Table 1: The classification table: the groups (A) and (C) as training sample. 5. Conclusions Our study reveals that a pressure sensor system GAITRite is a reliable screening instrument for detection of gait abnormalities after chronic unilateral stroke based on the footprint peak time measurements. By testing the volunteers at different walking velocities as a training sample more reliable information for gait quality is possible to obtain. There are optimistic conjectures that a better diagnostics are to be attained. First, using more flexible nonlinear algorhytm [10] for estimation of discrimination rule. Second, detailed information from the equipment including dynamics of the gait and higher order statistics.
8 Gait Measurements and Motor Recovery after Stroke 127 Classified as good bad Correct Group walkers walkers classifications (A) (23 bad) % (B) (62 good) % Total 96.47% (C) (5 10 good) % velocity categories: < 40 cm/s % cm/s % cm/s % cm/s % > 160 cm/s % Table 2: The classification table: groups (A) and (B) as training sample 6. Acknowledgment Neither an author nor any author s institution has received any commercial financial support related to this study. The company manufacturing this equipment or the distributor were not involved in any way in this study. The authors thank Mr. Paavo Kononen, MSc, and Mrs. Aila Keinanen, RN, for their help during the collection of the data. The Academy of Finland and Bulgarian Academy of Science and the Brain Research and Rehabilitation Center Neuron, Kuopio, Finland provided financial support for this work. R E F E R E N C E S [1] T. P. Andriacchi, J. A. Ogle, J. O. Galante. Walking speed as a basis for normal and abnormal gait measurements. Biomech. 10 (1977) [2] GAITRite Operating manual. GAITRite portable gait analysis system. CIR/MAP Inc., 1625 East Darby Rd., Havertown, PA 19083, USA. [3] M. Marks, G. Hirschberg. Analysis of the hemiparetic gait. Ann NY Acad Sci. 74 (1958), [4] A. L. McDonough, M. Batavia, F. C. Chen, et al. The validity and the reliability of the GAITRite system s measurements: a preliminary evaluation. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 82 (2001),
9 128 P. Mateev, I. Tarkka, E. Titianova [5] A. J. Nelson, L. J. Certo, L. Lembo, et al. The functional ambulation performance of elderly fallers and non-fallers walking at their preferred velocity. NeuroRehab 3 (1999), [6] E. J. Roth, C. Merbitz, K. Mroczek, S. A. Dugan, W. W. Suh. Hemiplegic gait. Relationship between walking speed and other temporal parameters. Stroke. 76 (1997), [7] E. B. Titianova, I.Tarkka. Asymmetry in walking performance and postural sway in patients with chronic unilateral infarction. J. Rehabil Res Dev. 32 (1995), [8] E. B. Titianova, K. Pitkanen, J. Sivenius, I. M. Tarkka. Gait characteristics and functional ambulation profile in patients with chronic unilateral stroke. Am. J. Phys. Med.Rehabil. 82 (2003), [9] E. B. Titianova, P. S. Mateev, I. M. Tarkka. Footprint analysis of gait using a pressure sensor system. J EMG & Kinesiol. 14 (2) (2004), [10] D. Vandev. Interactive Discriminant Analysis in MATLAB, Proc. Seminar on Statistical Data Analysis SDA 2003, June, Sozopol (2003) (in this volume). Plamen S. Mateev Ph.D. Institute of Mathematics and Informatics, Bulgarian Academy of Science, G.Bonchev Str. blok 8, BG Sofia pmat@math.bas.bg Ina M. Tarkka, Ph.D. Brain Research and Rehabilitation Center Neuron Kortejoki FIN Kuopio ina.tarkka@neuron.fi Ekaterina B. Titianova, M.D.,Ph.D., Specialized University Hospital of Neurology and Psychiatry St. Naum, BG Sofia titianova@yahoo.com
Gait Analyser. Description of Walking Performance
 Gait Analyser Description of Walking Performance This brochure will help you to understand clearly the parameters described in the report of the Gait Analyser, provide you with tips to implement the walking
Gait Analyser Description of Walking Performance This brochure will help you to understand clearly the parameters described in the report of the Gait Analyser, provide you with tips to implement the walking
Ambulatory monitoring of gait quality with wearable inertial sensors
 Ambulatory monitoring of gait quality with wearable inertial sensors Dr. Philippe Terrier, PhD June 2016 Summary 1. Why? Reasons for measuring gait in real life conditions 2. What? Real-life assessment
Ambulatory monitoring of gait quality with wearable inertial sensors Dr. Philippe Terrier, PhD June 2016 Summary 1. Why? Reasons for measuring gait in real life conditions 2. What? Real-life assessment
PURPOSE. METHODS Design
 7 Murrary, M.P.; Sepic, S.B.; Gardner, G.M.; and Mollinger, L.A., "Gait patterns of above-knee amputees using constant-friction knee components," Bull Prosthet Res, 17(2):35-45, 1980. 8 Godfrey, C.M.;
7 Murrary, M.P.; Sepic, S.B.; Gardner, G.M.; and Mollinger, L.A., "Gait patterns of above-knee amputees using constant-friction knee components," Bull Prosthet Res, 17(2):35-45, 1980. 8 Godfrey, C.M.;
KJSB. Evaluation of Gait Assistive Devices in Patients with Parkinson's Disease ORIGINAL INTRODUCTION. Mi-Young Kim 1, Bee-Oh Lim 2
 KJSB Korean Journal of Sport Biomechanics 2016; 26(3): 309-314 http://dx.doi.org/10.5103/kjsb.2016.26.3.309 http://e-kjsb.org eissn 2093-9752 ORIGINAL Evaluation of Gait Assistive Devices in Patients with
KJSB Korean Journal of Sport Biomechanics 2016; 26(3): 309-314 http://dx.doi.org/10.5103/kjsb.2016.26.3.309 http://e-kjsb.org eissn 2093-9752 ORIGINAL Evaluation of Gait Assistive Devices in Patients with
Analysis of Foot Pressure Variation with Change in Stride Length
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-853, p-issn: 2279-861.Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. IV (Oct. 214), PP 46-51 Dr. Charudatta V. Shinde, M.S. MCh ( Orthopaedics ), Dr. Weijie
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-853, p-issn: 2279-861.Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. IV (Oct. 214), PP 46-51 Dr. Charudatta V. Shinde, M.S. MCh ( Orthopaedics ), Dr. Weijie
THE INFLUENCE OF SLOW RECOVERY INSOLE ON PLANTAR PRESSURE AND CONTACT AREA DURING WALKING
 March 12, 2015 5:39:44pm WSPC/170-JMMB 1540005 ISSN: 0219-51942nd Reading Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology Vol. 15, No. 2 (2015) 1540005 (6 pages) c World Scientific Publishing Company DOI:
March 12, 2015 5:39:44pm WSPC/170-JMMB 1540005 ISSN: 0219-51942nd Reading Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology Vol. 15, No. 2 (2015) 1540005 (6 pages) c World Scientific Publishing Company DOI:
Walking speemtmmkubjects and amputees: aspects of validity of gait analysis
 Prostheticsand Orthoti~Inte~national, 1993, 17, 78-82 Walking speemtmmkubjects and : aspects of validity of gait analysis A. M. BOONSTRA*, V. FIDLER** and W. H. EISMA* *Department of Rehabilitation Medicine,
Prostheticsand Orthoti~Inte~national, 1993, 17, 78-82 Walking speemtmmkubjects and : aspects of validity of gait analysis A. M. BOONSTRA*, V. FIDLER** and W. H. EISMA* *Department of Rehabilitation Medicine,
Mobility Lab provides sensitive, valid and reliable outcome measures.
 Mobility Lab provides sensitive, valid and reliable outcome measures. ith hundreds of universities and hospitals using this system worldwide, Mobility Lab is the most trusted wearable gait and balance
Mobility Lab provides sensitive, valid and reliable outcome measures. ith hundreds of universities and hospitals using this system worldwide, Mobility Lab is the most trusted wearable gait and balance
MEASUREMENTS OF TEMPORAL and spatial gait parameters
 1648 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Agreement Between the GAITRite Walkway System and a Stopwatch Footfall Count Method for Measurement of Temporal and Spatial Gait Parameters James W. Youdas, PT, MS, John H. Hollman,
1648 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Agreement Between the GAITRite Walkway System and a Stopwatch Footfall Count Method for Measurement of Temporal and Spatial Gait Parameters James W. Youdas, PT, MS, John H. Hollman,
Factors of Influence on the Walking Ability of Children with Spastic Cerebral Palsy
 Factors of Influence on the Walking Ability of Children with Spastic Cerebral Palsy J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 10: 1 5, 1998 ATSUSHI FURUKAWA, RPT 1), EIJI NII, MD, PhD 1), HIROYASU IWATSUKI, RPT 2), MASAKI NISHIYAMA,
Factors of Influence on the Walking Ability of Children with Spastic Cerebral Palsy J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 10: 1 5, 1998 ATSUSHI FURUKAWA, RPT 1), EIJI NII, MD, PhD 1), HIROYASU IWATSUKI, RPT 2), MASAKI NISHIYAMA,
An investigation of kinematic and kinetic variables for the description of prosthetic gait using the ENOCH system
 An investigation of kinematic and kinetic variables for the description of prosthetic gait using the ENOCH system K. OBERG and H. LANSHAMMAR* Amputee Training and Research Unit, University Hospital, Fack,
An investigation of kinematic and kinetic variables for the description of prosthetic gait using the ENOCH system K. OBERG and H. LANSHAMMAR* Amputee Training and Research Unit, University Hospital, Fack,
REPLACING REDUNDANT STABILOMETRY PARAMETERS WITH RATIO AND MAXIMUM DEVIATION PARAMETERS
 Proceedings of the 12th IASTED International Conference Biomedical Engineering (BioMed 2016) February 15-16, 2016 Innsbruck, Austria REPLACING REDUNDANT STABILOMETRY PARAMETERS WITH RATIO AND MAXIMUM DEVIATION
Proceedings of the 12th IASTED International Conference Biomedical Engineering (BioMed 2016) February 15-16, 2016 Innsbruck, Austria REPLACING REDUNDANT STABILOMETRY PARAMETERS WITH RATIO AND MAXIMUM DEVIATION
KINEMATIC QUANTIFICATION OF GAIT SYMMETRY BASED ON BILATERAL CYCLOGRAMS
 KINEMATIC QUANTIFICATION OF GAIT SYMMETRY BASED ON BILATERAL CYCLOGRAMS Ambarish Goswami Honda Research Institute Mountain View, California, USA agoswami@honda-ri.com Abstract Symmetry is considered to
KINEMATIC QUANTIFICATION OF GAIT SYMMETRY BASED ON BILATERAL CYCLOGRAMS Ambarish Goswami Honda Research Institute Mountain View, California, USA agoswami@honda-ri.com Abstract Symmetry is considered to
QUANTIFICATION OF ASYMMETRICAL STEPPING POST-STROKE AND ITS RELATIONSHIP TO HEMIPARETIC WALKING PERFORMANCE
 QUANTIFICATION OF ASYMMETRICAL STEPPING POST-STROKE AND ITS RELATIONSHIP TO HEMIPARETIC WALKING PERFORMANCE By CHITRA LAKSHMI KINATINKARA BALASUBRAMANIAN A DISSERTATION PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL
QUANTIFICATION OF ASYMMETRICAL STEPPING POST-STROKE AND ITS RELATIONSHIP TO HEMIPARETIC WALKING PERFORMANCE By CHITRA LAKSHMI KINATINKARA BALASUBRAMANIAN A DISSERTATION PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL
Spasticity in gait. Wessex ACPIN Spasticity Presentation Alison Clarke
 Spasticity in gait Clinicians recognise spasticity but the elements of spasticity contributing to gait patterns are often difficult to identify: Variability of muscle tone Observation/recording General
Spasticity in gait Clinicians recognise spasticity but the elements of spasticity contributing to gait patterns are often difficult to identify: Variability of muscle tone Observation/recording General
MOTOR CONTROL DYSFUNCTION often requires that
 43 Temporal Stride and Force Analysis of Cane-Assisted Gait in People With Hemiplegic Stroke Chia-Ling Chen, MD, PhD, Hsieh-Ching Chen, PhD, May-Kuen Wong, MD, Fuk-Tan Tang, MD, Rong-Shun Chen, PhD ABSTRACT.
43 Temporal Stride and Force Analysis of Cane-Assisted Gait in People With Hemiplegic Stroke Chia-Ling Chen, MD, PhD, Hsieh-Ching Chen, PhD, May-Kuen Wong, MD, Fuk-Tan Tang, MD, Rong-Shun Chen, PhD ABSTRACT.
Different methods are available to assess gait variations
 Journal of Motor Behavior, Vol. 43, No. 2, 2011 Copyright C Taylor & Francis Group, LLC RAPID COMMUNICATION Validity of Functional Ambulation Performance Score for the Evaluation of Spatiotemporal Parameters
Journal of Motor Behavior, Vol. 43, No. 2, 2011 Copyright C Taylor & Francis Group, LLC RAPID COMMUNICATION Validity of Functional Ambulation Performance Score for the Evaluation of Spatiotemporal Parameters
Inter and intra-limb processes of gait control.
 Inter and intra-limb processes of gait control. Simon B. Taylor, Rezaul K. Begg and Russell J. Best Biomechanics Unit, Centre for Rehabilitation, Exercise and Sport Science. Victoria University, Melbourne,
Inter and intra-limb processes of gait control. Simon B. Taylor, Rezaul K. Begg and Russell J. Best Biomechanics Unit, Centre for Rehabilitation, Exercise and Sport Science. Victoria University, Melbourne,
Balance Item Score (0-4)
 BERG BALANCE SCALE Patient Name: Rater Name: Date: Balance Item Score (0-4) 1. Sitting unsupported 2. Change of position: sitting to standing 3. Change of position standing to sitting 4. Transfers 5. Standing
BERG BALANCE SCALE Patient Name: Rater Name: Date: Balance Item Score (0-4) 1. Sitting unsupported 2. Change of position: sitting to standing 3. Change of position standing to sitting 4. Transfers 5. Standing
Changes in Gait Characteristics Following a Concussion
 Georgia Southern University Digital Commons@Georgia Southern Electronic Theses & Dissertations Graduate Studies, Jack N. Averitt College of Spring 2012 Changes in Gait Characteristics Following a Concussion
Georgia Southern University Digital Commons@Georgia Southern Electronic Theses & Dissertations Graduate Studies, Jack N. Averitt College of Spring 2012 Changes in Gait Characteristics Following a Concussion
Fall Prevention Midterm Report. Akram Alsamarae Lindsay Petku 03/09/2014 Dr. Mansoor Nasir
 Fall Prevention Midterm Report Akram Alsamarae Lindsay Petku 03/09/2014 Dr. Mansoor Nasir Updates to timeline Last semester we created a timeline that included important milestones. We have narrowed down
Fall Prevention Midterm Report Akram Alsamarae Lindsay Petku 03/09/2014 Dr. Mansoor Nasir Updates to timeline Last semester we created a timeline that included important milestones. We have narrowed down
Self-fulfilling prophecy? Current affairs. Reality check 11/29/2011
 Standardized Treadmill Training: Raising Expectations for Gait Training Post Stroke Karen McCain, PT, DPT, NCS Patricia Smith, PT, PhD, NCS University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas David
Standardized Treadmill Training: Raising Expectations for Gait Training Post Stroke Karen McCain, PT, DPT, NCS Patricia Smith, PT, PhD, NCS University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas David
Fluid Flow. Link. Flow» P 1 P 2 Figure 1. Flow Model
 Fluid Flow Equipment: Water reservoir, output tubes of various dimensions (length, diameter), beaker, electronic scale for each table. Computer and Logger Pro software. Lots of ice.temperature probe on
Fluid Flow Equipment: Water reservoir, output tubes of various dimensions (length, diameter), beaker, electronic scale for each table. Computer and Logger Pro software. Lots of ice.temperature probe on
Shock absorbing material on the shoes of long leg braces for paraplegic walking
 Prosthetics and Orthotics International, 1990, 14, 27-32 Shock absorbing material on the shoes of long leg braces for paraplegic walking F. BIERLING-SØRENSEN, H. RYDE, *F. BOJSEN-MØLLER AND **E. LYQUIST
Prosthetics and Orthotics International, 1990, 14, 27-32 Shock absorbing material on the shoes of long leg braces for paraplegic walking F. BIERLING-SØRENSEN, H. RYDE, *F. BOJSEN-MØLLER AND **E. LYQUIST
Clinical view on ambulation in patients with Spinal Cord Injury
 Clinical view on ambulation in patients with Spinal Cord Injury Sasa Moslavac Spinal Unit, Special Medical Rehabilitation Hospital, Varazdinske Toplice,, Croatia 1 Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) to walk again
Clinical view on ambulation in patients with Spinal Cord Injury Sasa Moslavac Spinal Unit, Special Medical Rehabilitation Hospital, Varazdinske Toplice,, Croatia 1 Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) to walk again
Neurorehabil Neural Repair Oct 23. [Epub ahead of print]
![Neurorehabil Neural Repair Oct 23. [Epub ahead of print] Neurorehabil Neural Repair Oct 23. [Epub ahead of print]](/thumbs/86/94477916.jpg) APPENDICE Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2009 Oct 23. [Epub ahead of print] Segmental Muscle Vibration Improves Walking in Chronic Stroke Patients With Foot Drop: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Paoloni M,
APPENDICE Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2009 Oct 23. [Epub ahead of print] Segmental Muscle Vibration Improves Walking in Chronic Stroke Patients With Foot Drop: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Paoloni M,
Development of Gait at Slow, Free, and Fast Speeds in 3- and 5-Year-Old Children
 Development of Gait at Slow, Free, and Fast Speeds in 3- and 5-Year-Old Children RUTH ROSE-JACOBS The purpose of this study was to describe and statistically analyze 3- and 5- year-old children's gait
Development of Gait at Slow, Free, and Fast Speeds in 3- and 5-Year-Old Children RUTH ROSE-JACOBS The purpose of this study was to describe and statistically analyze 3- and 5- year-old children's gait
Maximum walking speeds obtained using treadmill and overground robot system in persons with post-stroke hemiplegia
 Capó-Lugo et al. Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation 2012, 9:80 JOURNAL OF NEUROENGINEERING JNERAND REHABILITATION RESEARCH Maximum walking speeds obtained using treadmill and overground robot
Capó-Lugo et al. Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation 2012, 9:80 JOURNAL OF NEUROENGINEERING JNERAND REHABILITATION RESEARCH Maximum walking speeds obtained using treadmill and overground robot
GAIT RECOVERY IN HEALTHY SUBJECTS: PERTURBATIONS TO THE KNEE MOTION WITH A SMART KNEE BRACE. by Mehmet Temel
 GAIT RECOVERY IN HEALTHY SUBJECTS: PERTURBATIONS TO THE KNEE MOTION WITH A SMART KNEE BRACE by Mehmet Temel A thesis submitted to the Faculty of the University of Delaware in partial fulfillment of the
GAIT RECOVERY IN HEALTHY SUBJECTS: PERTURBATIONS TO THE KNEE MOTION WITH A SMART KNEE BRACE by Mehmet Temel A thesis submitted to the Faculty of the University of Delaware in partial fulfillment of the
GAIT ANALYSIS OF SUBJECTS WITH ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT RUPTURE USING MEDILOGIC SOLE PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION MEASUREMENT SYSTEM
 GAIT ANALYSIS OF SUBJECTS WITH ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT RUPTURE USING MEDILOGIC SOLE PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION MEASUREMENT SYSTEM D. Höftberger 1, A. Kozek 1, J. Langer 1, J. Obergruber 1 1 Fachhochschule
GAIT ANALYSIS OF SUBJECTS WITH ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT RUPTURE USING MEDILOGIC SOLE PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION MEASUREMENT SYSTEM D. Höftberger 1, A. Kozek 1, J. Langer 1, J. Obergruber 1 1 Fachhochschule
FALL-RELATED HIP FRACTURES contribute substantially. Age-Related Changes in Spatial and Temporal Gait Variables
 31 Age-Related Changes in Spatial and Temporal Gait Variables Penny C. Grabiner, BSN, S. Tina Biswas, BSE, Mark D. Grabiner, PhD ABSTRACT. Grabiner PC, Biswas ST, Grabiner MD. Agerelated changes in spatial
31 Age-Related Changes in Spatial and Temporal Gait Variables Penny C. Grabiner, BSN, S. Tina Biswas, BSE, Mark D. Grabiner, PhD ABSTRACT. Grabiner PC, Biswas ST, Grabiner MD. Agerelated changes in spatial
Relationship between Ground Reaction Force and Stability Level of the Lower Extremity in Runners Background: Objective: Design and Setting:
 Relationship between Ground Reaction Force and Stability Level of the Lower Extremity in Runners Kimitake Sato, Monique Butcher-Mokha Barry University Miami Shores, FL Background: Neuromuscular control
Relationship between Ground Reaction Force and Stability Level of the Lower Extremity in Runners Kimitake Sato, Monique Butcher-Mokha Barry University Miami Shores, FL Background: Neuromuscular control
Evaluation of gait symmetry in poliomyelitis subjects : Comparison of a
 Evaluation of gait symmetry in poliomyelitis subjects : Comparison of a conventional knee ankle foot orthosis (KAFO) and a new powered KAFO. Arazpour, M, Ahmadi, F, Bahramizadeh, M, Samadiam, M, Mousavi,
Evaluation of gait symmetry in poliomyelitis subjects : Comparison of a conventional knee ankle foot orthosis (KAFO) and a new powered KAFO. Arazpour, M, Ahmadi, F, Bahramizadeh, M, Samadiam, M, Mousavi,
Motor function analysis: from animal models to patients
 Motor function analysis: from animal models to patients ZNZ lecture 27.04.2016 Linard Filli Sensorimotor Lab University Hospital Zurich Linard.Filli@usz.ch Content of lecture Basic neuroanatomy of motor
Motor function analysis: from animal models to patients ZNZ lecture 27.04.2016 Linard Filli Sensorimotor Lab University Hospital Zurich Linard.Filli@usz.ch Content of lecture Basic neuroanatomy of motor
Equine Cannon Angle System
 Equine Cannon System How to interpret the results December 2010 Page 1 of 14 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 The Sagittal Plane... 4 The Coronal Plane... 5 Results Format... 6 How to Interpret the
Equine Cannon System How to interpret the results December 2010 Page 1 of 14 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 The Sagittal Plane... 4 The Coronal Plane... 5 Results Format... 6 How to Interpret the
Cycling Volume Estimation Methods for Safety Analysis
 Cycling Volume Estimation Methods for Safety Analysis XI ICTCT extra Workshop in Vancouver, Canada Session: Methods and Simulation Date: March, 01 The Highway Safety Manual (HSM) documents many safety
Cycling Volume Estimation Methods for Safety Analysis XI ICTCT extra Workshop in Vancouver, Canada Session: Methods and Simulation Date: March, 01 The Highway Safety Manual (HSM) documents many safety
The Influence of Load Carrying Modes on Gait variables of Healthy Indian Women
 The Influence of Load Carrying Modes on Gait variables of Healthy Indian Women *Guha Thakurta A, Iqbal R and De A National Institute of Industrial Engineering, Powai, Vihar Lake, Mumbai-400087, India,
The Influence of Load Carrying Modes on Gait variables of Healthy Indian Women *Guha Thakurta A, Iqbal R and De A National Institute of Industrial Engineering, Powai, Vihar Lake, Mumbai-400087, India,
Corrected FIM effectiveness as an index independent of FIM score on admission
 7 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2014) Original Article Corrected FIM effectiveness as an index independent of FIM score on admission Makoto Tokunaga, MD, PhD, 1 Ryoji Nakanishi,
7 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2014) Original Article Corrected FIM effectiveness as an index independent of FIM score on admission Makoto Tokunaga, MD, PhD, 1 Ryoji Nakanishi,
Chapter 5: Methods and Philosophy of Statistical Process Control
 Chapter 5: Methods and Philosophy of Statistical Process Control Learning Outcomes After careful study of this chapter You should be able to: Understand chance and assignable causes of variation, Explain
Chapter 5: Methods and Philosophy of Statistical Process Control Learning Outcomes After careful study of this chapter You should be able to: Understand chance and assignable causes of variation, Explain
The Impact of Walker Style on Gait Characteristics in Non-assistive Device Dependent older Adults
 St. Catherine University SOPHIA Doctor of Physical Therapy Research Papers Physical Therapy 5-2017 The Impact of Walker Style on Gait Characteristics in Non-assistive Device Dependent older Adults Matthew
St. Catherine University SOPHIA Doctor of Physical Therapy Research Papers Physical Therapy 5-2017 The Impact of Walker Style on Gait Characteristics in Non-assistive Device Dependent older Adults Matthew
8th Grade. Data.
 1 8th Grade Data 2015 11 20 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Two Variable Data Line of Best Fit Determining the Prediction Equation Two Way Table Glossary Teacher
1 8th Grade Data 2015 11 20 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Two Variable Data Line of Best Fit Determining the Prediction Equation Two Way Table Glossary Teacher
Woodie Guthrie - Huntington disease (HD) Symptoms of HD. Changes in driving behavior. Driving simulator performance. Driving simulator performance
 Validation of driving simulation to assess on-road performance in Huntington disease H. Devos, A. Nieuwboer, W. Vandenberghe, M. Tant, W. De Weerdt, E. Uc 7th Internation Symposium on Human Factors in
Validation of driving simulation to assess on-road performance in Huntington disease H. Devos, A. Nieuwboer, W. Vandenberghe, M. Tant, W. De Weerdt, E. Uc 7th Internation Symposium on Human Factors in
C-Brace Reimbursement Guide
 Reimbursement Guide Information for practitioners and payers Product Information Effective September 24, 2018 The The is the first microprocessor stance and swing phase controlled orthosis (SSCO ). This
Reimbursement Guide Information for practitioners and payers Product Information Effective September 24, 2018 The The is the first microprocessor stance and swing phase controlled orthosis (SSCO ). This
The Scientific Bulletin of VALAHIA University MATERIALS and MECHANICS Nr. 5 (year 8) 2010
 STATISTIC PROCESSING OF MEASUREMENTS DONE WITH CALORCRO EQUIPMENT FOR ASSESSING THE GAIT ENERGETIC EXPENDITURE AT HEALTHY SUBJECTS AND PATIENTS SUFFERING FROM OSTEOARTHRITIS OF LOWER LIMBS G. CAPRIS 1),
STATISTIC PROCESSING OF MEASUREMENTS DONE WITH CALORCRO EQUIPMENT FOR ASSESSING THE GAIT ENERGETIC EXPENDITURE AT HEALTHY SUBJECTS AND PATIENTS SUFFERING FROM OSTEOARTHRITIS OF LOWER LIMBS G. CAPRIS 1),
Effects of dual task on turning ability in stroke survivors and older adults
 Effects of dual task on turning ability in stroke survivors and older adults Hollands, K, Agnihotri, D and Tyson, SF http://dx.doi.org/1.116/j.gaitpost.214.6.19 Title Authors Type URL Effects of dual task
Effects of dual task on turning ability in stroke survivors and older adults Hollands, K, Agnihotri, D and Tyson, SF http://dx.doi.org/1.116/j.gaitpost.214.6.19 Title Authors Type URL Effects of dual task
EFFECT OF SHOE RAISE ALONG WITH MOTOR RELEARNING PROGRAMME (MRP) ON AMBULATION IN CHRONIC STROKE
 Int J Physiother. Vol 3(3), 297-303, June (2016) ISSN: 2348-8336 ORIGINAL ARTICLE EFFECT OF SHOE RAISE ALONG WITH MOTOR RELEARNING PROGRAMME () ON AMBULATION IN CHRONIC STROKE IJPHY ABSTRACT ¹Dr.Gajanan
Int J Physiother. Vol 3(3), 297-303, June (2016) ISSN: 2348-8336 ORIGINAL ARTICLE EFFECT OF SHOE RAISE ALONG WITH MOTOR RELEARNING PROGRAMME () ON AMBULATION IN CHRONIC STROKE IJPHY ABSTRACT ¹Dr.Gajanan
SCIENTIFIC COMMITTEE SEVENTH REGULAR SESSION August 2011 Pohnpei, Federated States of Micronesia
 SCIENTIFIC COMMITTEE SEVENTH REGULAR SESSION 9-17 August 2011 Pohnpei, Federated States of Micronesia CPUE of skipjack for the Japanese offshore pole and line using GPS and catch data WCPFC-SC7-2011/SA-WP-09
SCIENTIFIC COMMITTEE SEVENTH REGULAR SESSION 9-17 August 2011 Pohnpei, Federated States of Micronesia CPUE of skipjack for the Japanese offshore pole and line using GPS and catch data WCPFC-SC7-2011/SA-WP-09
Test-Retest Reliability of the StepWatch Activity Monitor Outputs in Individuals
 Test-Retest Reliability of the StepWatch Activity Monitor Outputs in Individuals with Chronic Stroke Suzie Mudge, MHSc; N. Susan Stott, PhD Department of Surgery, University of Auckland Address for correspondence:
Test-Retest Reliability of the StepWatch Activity Monitor Outputs in Individuals with Chronic Stroke Suzie Mudge, MHSc; N. Susan Stott, PhD Department of Surgery, University of Auckland Address for correspondence:
Ultrasonic motion analysis system - measurement of temporal and spatial gait parameters Huitema, RB; Hof, At L.; Postema, K
 University of Groningen Ultrasonic motion analysis system - measurement of temporal and spatial gait parameters Huitema, RB; Hof, At L.; Postema, K Published in: Journal of biomechanics IMPORTANT NOTE:
University of Groningen Ultrasonic motion analysis system - measurement of temporal and spatial gait parameters Huitema, RB; Hof, At L.; Postema, K Published in: Journal of biomechanics IMPORTANT NOTE:
An Analysis of the Travel Conditions on the U. S. 52 Bypass. Bypass in Lafayette, Indiana.
 An Analysis of the Travel Conditions on the U. S. 52 Bypass in Lafayette, Indiana T. B. T readway Research Assistant J. C. O ppenlander Research Engineer Joint Highway Research Project Purdue University
An Analysis of the Travel Conditions on the U. S. 52 Bypass in Lafayette, Indiana T. B. T readway Research Assistant J. C. O ppenlander Research Engineer Joint Highway Research Project Purdue University
Spastic Paretic Stiff-Legged Gait Joint Kinetics
 Authors: D. Casey Kerrigan, MD, MS Mark E. Karvosky, MA Patrick O. Riley, PhD Affiliations: From the Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation (DCK, POR), Harvard Medical School, and Spaulding
Authors: D. Casey Kerrigan, MD, MS Mark E. Karvosky, MA Patrick O. Riley, PhD Affiliations: From the Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation (DCK, POR), Harvard Medical School, and Spaulding
Title: Gait Performances in Children with Tourette Syndrome: A Preliminary Study
 Title: Gait Performances in Children with Tourette Syndrome: A Preliminary Study Authors: Wen-Yu Liu, PhD, PT 1 ; Pei-Hsuan Lin, PT 1 ; Hen-Yu Lien, PhD 1, PT; Huei-Shyong Wang, MD 2 ; Alice May-Kuen,
Title: Gait Performances in Children with Tourette Syndrome: A Preliminary Study Authors: Wen-Yu Liu, PhD, PT 1 ; Pei-Hsuan Lin, PT 1 ; Hen-Yu Lien, PhD 1, PT; Huei-Shyong Wang, MD 2 ; Alice May-Kuen,
siot-shoe: A Smart IoT-shoe for Gait Assistance (Miami University)
 siot-shoe: A Smart IoT-shoe for Gait Assistance (Miami University) Abstract Mark Sullivan, Casey Knox, Juan Ding Gait analysis through the Internet of Things (IoT) is able to provide an overall assessment
siot-shoe: A Smart IoT-shoe for Gait Assistance (Miami University) Abstract Mark Sullivan, Casey Knox, Juan Ding Gait analysis through the Internet of Things (IoT) is able to provide an overall assessment
WalkOn product range. Dynamic Ankle-Foot Orthoses. Information for specialist dealers
 WalkOn product range Dynamic Ankle-Foot Orthoses Information for specialist dealers WalkOn Flex WalkOn WalkOn Trimable WalkOn Reaction WalkOn Reaction plus One range Many different applications The WalkOn
WalkOn product range Dynamic Ankle-Foot Orthoses Information for specialist dealers WalkOn Flex WalkOn WalkOn Trimable WalkOn Reaction WalkOn Reaction plus One range Many different applications The WalkOn
Title: Title: Effects of Dual Task on Turning Ability in Stroke Survivors and Older Adults
 Title: Title: Effects of Dual Task on Turning Ability in Stroke Survivors and Older Adults Author: K.L. Hollands D. Agnihotri S.F. Tyson PII: S0966-6362(14)00639-0 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.1016/j.gaitpost.2014.06.019
Title: Title: Effects of Dual Task on Turning Ability in Stroke Survivors and Older Adults Author: K.L. Hollands D. Agnihotri S.F. Tyson PII: S0966-6362(14)00639-0 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.1016/j.gaitpost.2014.06.019
Effect of airflow direction on human perception of draught
 Effect of airflow direction on human perception of draught J. Toftum, G. Zhou, A. Melikov Laboratory of Indoor Environment and Energy Department of Energy Engineering Technical University of Denmark Abstract
Effect of airflow direction on human perception of draught J. Toftum, G. Zhou, A. Melikov Laboratory of Indoor Environment and Energy Department of Energy Engineering Technical University of Denmark Abstract
ASSESMENT Introduction REPORTS Running Reports Walking Reports Written Report
 ASSESMENT REPORTS Introduction Left panel Avatar Playback Right Panel Patient Gait Parameters Report Tab Click on parameter to view avatar at that point in time 2 Introduction Software will compare gait
ASSESMENT REPORTS Introduction Left panel Avatar Playback Right Panel Patient Gait Parameters Report Tab Click on parameter to view avatar at that point in time 2 Introduction Software will compare gait
Stride Time Calculation from EMG and Foot Switch Data and Finding Corelation between Them for Prosthetic Control
 2012 International Conference on Environment Science and Engieering IPCBEE vol.3 2(2012) (2012)IACSIT Press, Singapoore Stride Time Calculation from EMG and Foot Switch Data and Finding Corelation between
2012 International Conference on Environment Science and Engieering IPCBEE vol.3 2(2012) (2012)IACSIT Press, Singapoore Stride Time Calculation from EMG and Foot Switch Data and Finding Corelation between
Legendre et al Appendices and Supplements, p. 1
 Legendre et al. 2010 Appendices and Supplements, p. 1 Appendices and Supplement to: Legendre, P., M. De Cáceres, and D. Borcard. 2010. Community surveys through space and time: testing the space-time interaction
Legendre et al. 2010 Appendices and Supplements, p. 1 Appendices and Supplement to: Legendre, P., M. De Cáceres, and D. Borcard. 2010. Community surveys through space and time: testing the space-time interaction
UNCORRECTED PROOF. George Chen a,b, Carolynn Patten a,c, *, Dhara H. Kothari a, Felix E. Zajac a,b,c
 1 Gait & Posture xxx (2004) xxx xxx www.elsevier.com/locate/gaitpost 2 3 4 5 Gait deviations associated with post-stroke hemiparesis: improvement during treadmill walking using weight support, speed, support
1 Gait & Posture xxx (2004) xxx xxx www.elsevier.com/locate/gaitpost 2 3 4 5 Gait deviations associated with post-stroke hemiparesis: improvement during treadmill walking using weight support, speed, support
Improving pedestrian dynamics modelling using fuzzy logic
 Improving pedestrian dynamics modelling using fuzzy logic Phillip Tomé 1, François Bonzon 1, Bertrand Merminod 1, and Kamiar Aminian 2 1 EPFL Geodetic Engineering Lab (TOPO) Station 18 1015 Lausanne Switzerland
Improving pedestrian dynamics modelling using fuzzy logic Phillip Tomé 1, François Bonzon 1, Bertrand Merminod 1, and Kamiar Aminian 2 1 EPFL Geodetic Engineering Lab (TOPO) Station 18 1015 Lausanne Switzerland
Figure 1 betois (bending torsion insole system) system with five measuring points and A/D- converter.
 Bending and Torsional Moments - A new measuring system for gait analysis Nora Dawin & Annette Kerkhoff & Klaus Peikenkamp, University of Applied Sciences Münster, Germany Abstract The Laboratory of Biomechanics
Bending and Torsional Moments - A new measuring system for gait analysis Nora Dawin & Annette Kerkhoff & Klaus Peikenkamp, University of Applied Sciences Münster, Germany Abstract The Laboratory of Biomechanics
Gait Analysis at Your Fingertips:
 Gait Analysis at Your Fingertips: Enhancing Observational Gait Analysis Using Mobile Device Technology and the Edinburgh Visual Gait Scale Jon R. Davids, MD; Shriners Hospitals for Children Northern California;
Gait Analysis at Your Fingertips: Enhancing Observational Gait Analysis Using Mobile Device Technology and the Edinburgh Visual Gait Scale Jon R. Davids, MD; Shriners Hospitals for Children Northern California;
Reliable and clinically meaningful assessment and
 Reliability and Validity of Bilateral Thigh and Foot Accelerometry Measures of Walking in Healthy and Hemiparetic Subjects Kaveh Saremi, MD, Jon Marehbian, Xiaohong Yan, Jean-Philippe Regnaux, PhD, Robert
Reliability and Validity of Bilateral Thigh and Foot Accelerometry Measures of Walking in Healthy and Hemiparetic Subjects Kaveh Saremi, MD, Jon Marehbian, Xiaohong Yan, Jean-Philippe Regnaux, PhD, Robert
Inertial compensation for belt acceleration in an instrumented treadmill
 Inertial compensation for belt acceleration in an instrumented treadmill Sandra K. Hnat, Antonie J. van den Bogert Department of Mechanical Engineering, Cleveland State University Cleveland, OH 44115,
Inertial compensation for belt acceleration in an instrumented treadmill Sandra K. Hnat, Antonie J. van den Bogert Department of Mechanical Engineering, Cleveland State University Cleveland, OH 44115,
Rehabilitating Asymmetric Gait Using Asymmetry. Tyagi Ramakrishnan
 Rehabilitating Asymmetric Gait Using Asymmetry by Tyagi Ramakrishnan A dissertation submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Mechanical Engineering
Rehabilitating Asymmetric Gait Using Asymmetry by Tyagi Ramakrishnan A dissertation submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Mechanical Engineering
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Gait Posture. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2009 May 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Gait Posture. 2008 May ; 27(4): 710 714. Two simple methods for determining gait events during treadmill and overground walking using
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Gait Posture. 2008 May ; 27(4): 710 714. Two simple methods for determining gait events during treadmill and overground walking using
THE EFFECT OF BINDING POSITION ON KINETIC VARIABLES IN ALPINE SKIING
 THE EFFECT OF BINDING POSITION ON KINETIC VARIABLES IN ALPINE SKIING H. SCHWAMEDER 1, B. M. NIGG 2, V. v. TSCHARNER 2, D. STEFANYSHYN 2 1 Institute of Sports Sciences, University of Salzburg 2 Human Performance
THE EFFECT OF BINDING POSITION ON KINETIC VARIABLES IN ALPINE SKIING H. SCHWAMEDER 1, B. M. NIGG 2, V. v. TSCHARNER 2, D. STEFANYSHYN 2 1 Institute of Sports Sciences, University of Salzburg 2 Human Performance
An investigation of lower-extremity functional asymmetry for nonpreferred able-bodied walking speeds
 Original Research An investigation of lower-extremity functional asymmetry for nonpreferred able-bodied walking speeds JOHN RICE* and MATTHEW K. SEELEY Department of Exercise Sciences; 106 SFH; Brigham
Original Research An investigation of lower-extremity functional asymmetry for nonpreferred able-bodied walking speeds JOHN RICE* and MATTHEW K. SEELEY Department of Exercise Sciences; 106 SFH; Brigham
Use of cluster analysis for gait pattern classification of patients in the early and late recovery phases following stroke
 Gait and Posture 18 (2003) 114/125 www.elsevier.com/locate/gaitpost Use of cluster analysis for gait pattern classification of patients in the early and late recovery phases following stroke Sara Mulroy
Gait and Posture 18 (2003) 114/125 www.elsevier.com/locate/gaitpost Use of cluster analysis for gait pattern classification of patients in the early and late recovery phases following stroke Sara Mulroy
Center of Mass Acceleration as a Surrogate for Force Production After Spinal Cord Injury Effects of Inclined Treadmill Walking
 Center of Mass Acceleration as a Surrogate for Force Production After Spinal Cord Injury Effects of Inclined Treadmill Walking Mark G. Bowden, PhD, PT Research Health Scientist, Ralph H. Johnson VA Medical
Center of Mass Acceleration as a Surrogate for Force Production After Spinal Cord Injury Effects of Inclined Treadmill Walking Mark G. Bowden, PhD, PT Research Health Scientist, Ralph H. Johnson VA Medical
C-Brace Reimbursement Guide
 C-Brace Reimbursement Guide Information for practitioners and payers Product Information The C-Brace The C-Brace is the first microprocessor stance and swing phase controlled orthosis (SSCO). This highly
C-Brace Reimbursement Guide Information for practitioners and payers Product Information The C-Brace The C-Brace is the first microprocessor stance and swing phase controlled orthosis (SSCO). This highly
Can Asymmetric Running Patterns Be Predicted By Assessment of Asymmetric Standing Posture? A Case Study in Elite College Runners
 REVIEW ARTICLE Can Asymmetric Running Patterns Be Predicted By Assessment of Asymmetric Standing Posture? A Case Study in Elite College Runners Paige E. Skorseth; Patrick T. Knott, PhD, PA-C Abstract Objective:
REVIEW ARTICLE Can Asymmetric Running Patterns Be Predicted By Assessment of Asymmetric Standing Posture? A Case Study in Elite College Runners Paige E. Skorseth; Patrick T. Knott, PhD, PA-C Abstract Objective:
Evaluation of footfall induced vibration in building floor
 Evaluation of footfall induced vibration in building floor T. Nguyen 1, E. Gad 2, J. Wilson 3, N. Lythgo 4 and N. Haritos 5 1. Corresponding Author. PhD student, Faculty of Engineering and Industrial Sciences,
Evaluation of footfall induced vibration in building floor T. Nguyen 1, E. Gad 2, J. Wilson 3, N. Lythgo 4 and N. Haritos 5 1. Corresponding Author. PhD student, Faculty of Engineering and Industrial Sciences,
SHOT ON GOAL. Name: Football scoring a goal and trigonometry Ian Edwards Luther College Teachers Teaching with Technology
 SHOT ON GOAL Name: Football scoring a goal and trigonometry 2006 Ian Edwards Luther College Teachers Teaching with Technology Shot on Goal Trigonometry page 2 THE TASKS You are an assistant coach with
SHOT ON GOAL Name: Football scoring a goal and trigonometry 2006 Ian Edwards Luther College Teachers Teaching with Technology Shot on Goal Trigonometry page 2 THE TASKS You are an assistant coach with
Effect of Age and Sex on Gait Characteristics in the Korean Elderly People
 Iran J Public Health, Vol. 47, No.5, May 2018, pp.666-673 Original Article Effect of Age and Sex on Gait Characteristics in the Korean People Yang Sun PARK 1, Ji-Won KIM 2, Yuri KWON 2, Moon-Seok KWON
Iran J Public Health, Vol. 47, No.5, May 2018, pp.666-673 Original Article Effect of Age and Sex on Gait Characteristics in the Korean People Yang Sun PARK 1, Ji-Won KIM 2, Yuri KWON 2, Moon-Seok KWON
University of Kassel Swim Start Research
 University of Kassel Swim Start Research Sebastian Fischer & Armin Kibele Institute for Sports and Sport Science, University of Kassel, Germany Research Fields: Swim Start research I. Materials and Equipment
University of Kassel Swim Start Research Sebastian Fischer & Armin Kibele Institute for Sports and Sport Science, University of Kassel, Germany Research Fields: Swim Start research I. Materials and Equipment
The Starting Point. Prosthetic Alignment in the Transtibial Amputee. Outline. COM Motion in the Coronal Plane
 Prosthetic Alignment in the Transtibial Amputee The Starting Point David C. Morgenroth, MD, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine University of Washington VAPSHCS Outline COM Motion in the Coronal Plane
Prosthetic Alignment in the Transtibial Amputee The Starting Point David C. Morgenroth, MD, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine University of Washington VAPSHCS Outline COM Motion in the Coronal Plane
Diabetes and Orthoses. Rob Bradbury Talar Made
 Diabetes and Orthoses Rob Bradbury Talar Made Diabetes High prevalence disease 4-6% in UK (over 2.5 mill diagnosed and a further 0.5 ) 6+% in USA 40% in some parts of Middle East (may be higher in Indian
Diabetes and Orthoses Rob Bradbury Talar Made Diabetes High prevalence disease 4-6% in UK (over 2.5 mill diagnosed and a further 0.5 ) 6+% in USA 40% in some parts of Middle East (may be higher in Indian
Can trawling effort be identified from satellite-based VMS data?
 Not to be cited without prior reference to the author International Council for the Exploration of the Seas Theme session N: Technologies for monitoring fishing activities and observing catch Can trawling
Not to be cited without prior reference to the author International Council for the Exploration of the Seas Theme session N: Technologies for monitoring fishing activities and observing catch Can trawling
JAPMA Article In Press
 JAPMA Article In Press This article has undergone peer review, copyediting, and author review but is not a final version and may differ from the published version. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7547/15-051
JAPMA Article In Press This article has undergone peer review, copyediting, and author review but is not a final version and may differ from the published version. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7547/15-051
Investigation of Suction Process of Scroll Compressors
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2006 Investigation of Suction Process of Scroll Compressors Michael M. Cui Trane Jack Sauls
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2006 Investigation of Suction Process of Scroll Compressors Michael M. Cui Trane Jack Sauls
23 RD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON BALLISTICS TARRAGONA, SPAIN APRIL 2007
 23 RD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON BALLISTICS TARRAGONA, SPAIN 16-20 APRIL 2007 AN INVESTIGATION INTO THE INTERRELATION BETWEEN THE INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL BALLISTICS OF FIRING A TP-T TANK AMMUNITION M. H.
23 RD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON BALLISTICS TARRAGONA, SPAIN 16-20 APRIL 2007 AN INVESTIGATION INTO THE INTERRELATION BETWEEN THE INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL BALLISTICS OF FIRING A TP-T TANK AMMUNITION M. H.
GOLF SWING CONSISTENCY IN ELITE COLLEGIATE GOLFERS
 GOLF SWING CONSISTENCY IN ELITE COLLEGIATE GOLFERS Preliminary Findings Prepared by: Daniel Goldstein, PT, OCS, SCS, ATC John Stemm, PT, CSCS Study Location: NCAA Men s Golf Championship 2003 Karsten Creek
GOLF SWING CONSISTENCY IN ELITE COLLEGIATE GOLFERS Preliminary Findings Prepared by: Daniel Goldstein, PT, OCS, SCS, ATC John Stemm, PT, CSCS Study Location: NCAA Men s Golf Championship 2003 Karsten Creek
Part 1: Inspiratory and expiratory pressures
 BIOEN 327 Autumn 2013 Experimental procedures Throughout these experiments, record in your notebook the purpose of the experiments, the methods you used, and the results. Where possible, make predictions
BIOEN 327 Autumn 2013 Experimental procedures Throughout these experiments, record in your notebook the purpose of the experiments, the methods you used, and the results. Where possible, make predictions
Relationships between walking velocity and distance and the symmetry of temporospatial parameters in chronic post-stroke subjects
 Acta of Bioengineering and Biomechanics Vol. 19, No. 3, 2017 Original paper DOI: 10.5277//ABB-00694-2016-02 Relationships between walking velocity and distance and the symmetry of temporospatial parameters
Acta of Bioengineering and Biomechanics Vol. 19, No. 3, 2017 Original paper DOI: 10.5277//ABB-00694-2016-02 Relationships between walking velocity and distance and the symmetry of temporospatial parameters
Supplementary Figure S1
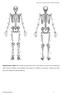 Supplementary Figure S1: Anterior and posterior views of the marker set used in the running gait trials. Forty-six markers were attached to the subject (15 markers on each leg, 4 markers on each arm, and
Supplementary Figure S1: Anterior and posterior views of the marker set used in the running gait trials. Forty-six markers were attached to the subject (15 markers on each leg, 4 markers on each arm, and
The Effects of Simulated Knee Arthrodesis and Temporal Acclimation on Gait Kinematics
 The Effects of Simulated Knee Arthrodesis and Temporal Acclimation on Gait Kinematics Eric M. Lucas, MS 1, Randy Hutchison, PhD 2, Justin Marro, MS 1, Taylor Gambon 1, John D. DesJardins, PhD 1. 1 Clemson
The Effects of Simulated Knee Arthrodesis and Temporal Acclimation on Gait Kinematics Eric M. Lucas, MS 1, Randy Hutchison, PhD 2, Justin Marro, MS 1, Taylor Gambon 1, John D. DesJardins, PhD 1. 1 Clemson
DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF A GAIT CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM FOR OLDER ADULTS BY MOVEMENT CONTROL AND BIOMECHANICAL FACTORS. Wen-Ni Wennie Huang
 DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF A GAIT CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM FOR OLDER ADULTS BY MOVEMENT CONTROL AND BIOMECHANICAL FACTORS by Wen-Ni Wennie Huang B. S. in Physical Therapy, Queen s University, Canada, 1997
DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF A GAIT CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM FOR OLDER ADULTS BY MOVEMENT CONTROL AND BIOMECHANICAL FACTORS by Wen-Ni Wennie Huang B. S. in Physical Therapy, Queen s University, Canada, 1997
Using GPOPS-II to optimize sum of squared torques of a double pendulum as a prosthesis leg. Abstract
 Using GPOPS-II to optimize sum of squared torques of a double pendulum as a prosthesis leg Abstract Milad Zarei MCE 593 Prosthesis Design & Control A two-dimensional, two links pendulum is developed to
Using GPOPS-II to optimize sum of squared torques of a double pendulum as a prosthesis leg Abstract Milad Zarei MCE 593 Prosthesis Design & Control A two-dimensional, two links pendulum is developed to
The Optimal Downhill Slope for Acute Overspeed Running
 International Journal of Sports Physiology and Performance, 2008, 3, 88-93 2008 Human Kinetics, Inc. The Optimal Downhill Slope for Acute Overspeed Running William P. Ebben Purpose: This study evaluated
International Journal of Sports Physiology and Performance, 2008, 3, 88-93 2008 Human Kinetics, Inc. The Optimal Downhill Slope for Acute Overspeed Running William P. Ebben Purpose: This study evaluated
Gait Analysis by High School Students
 Gait Analysis by High School Students André Heck 1 and Caroline van Dongen 2 1 AMSTEL Institute, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, heck@science.uva.nl 2 St. Antoniuscollege, Gouda, The
Gait Analysis by High School Students André Heck 1 and Caroline van Dongen 2 1 AMSTEL Institute, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, heck@science.uva.nl 2 St. Antoniuscollege, Gouda, The
Activity Overview. Footprints In The Sand Inquiry MO-BILITY. Activity 2E. Activity Objectives: Activity Description: Activity Background: LESSON 2
 Footprints In The Sand Inquiry Activity 2E Activity Objectives: Working in collaborative groups, students will be able to: assume assigned roles to complete a given task examine the various parts of the
Footprints In The Sand Inquiry Activity 2E Activity Objectives: Working in collaborative groups, students will be able to: assume assigned roles to complete a given task examine the various parts of the
2600T Series Pressure Transmitters Plugged Impulse Line Detection Diagnostic. Pressure Measurement Engineered solutions for all applications
 Application Description AG/266PILD-EN Rev. C 2600T Series Pressure Transmitters Plugged Impulse Line Detection Diagnostic Pressure Measurement Engineered solutions for all applications Increase plant productivity
Application Description AG/266PILD-EN Rev. C 2600T Series Pressure Transmitters Plugged Impulse Line Detection Diagnostic Pressure Measurement Engineered solutions for all applications Increase plant productivity
The overarching aim of the work presented in this thesis was to assess and
 CHAPTER 7 EPILOGUE Chapter 7 The overarching aim of the work presented in this thesis was to assess and understand the effort for balance control in terms of the metabolic cost of walking in able-bodied
CHAPTER 7 EPILOGUE Chapter 7 The overarching aim of the work presented in this thesis was to assess and understand the effort for balance control in terms of the metabolic cost of walking in able-bodied
or
 INTRODUCTION The consequences of postural dyscontrol are pervasive and have a significant impact on activities of daily living, community mobility and social, work and leisure pursuits. The Community Balance
INTRODUCTION The consequences of postural dyscontrol are pervasive and have a significant impact on activities of daily living, community mobility and social, work and leisure pursuits. The Community Balance
Key words: biomechanics, injury, technique, measurement, strength, evaluation
 Becker, T., & Havriluk, R. (2006). Bilateral and anterior-posterior muscular imbalances in swimmers. In J. P. Vilas-Boas, F. Alves, A. Marques (Eds.), Biomechanics and Medicine in Swimming X. Portuguese
Becker, T., & Havriluk, R. (2006). Bilateral and anterior-posterior muscular imbalances in swimmers. In J. P. Vilas-Boas, F. Alves, A. Marques (Eds.), Biomechanics and Medicine in Swimming X. Portuguese
Boyle s Law. Pressure-Volume Relationship in Gases. Figure 1
 Boyle s Law Pressure-Volume Relationship in Gases The primary objective of this experiment is to determine the relationship between the pressure and volume of a confined gas. The gas we use will be air,
Boyle s Law Pressure-Volume Relationship in Gases The primary objective of this experiment is to determine the relationship between the pressure and volume of a confined gas. The gas we use will be air,
IMPORTANT: All features subject to change without notice.
 4.0.1 Table of Contents 1. Contents 4 2. Quick Start 4 3. Icon Key 5 4. Changing GaitSens View / Exiting GaitSens 5 5. Select User 6 6. Validate Setup 7 7. Therapist View 8 8. My Goals 9 9. Replay Session
4.0.1 Table of Contents 1. Contents 4 2. Quick Start 4 3. Icon Key 5 4. Changing GaitSens View / Exiting GaitSens 5 5. Select User 6 6. Validate Setup 7 7. Therapist View 8 8. My Goals 9 9. Replay Session
Medicine Meets Virtual Reality 21
 University of Nebraska Omaha DigitalCommons@UNO Faculty Books and Monographs 2014 Medicine Meets Virtual Reality 21 James D. Westwood Susan W. Westwood Li Felländer-Tsai Cali M. Fidopiastis Randy S. Haluck
University of Nebraska Omaha DigitalCommons@UNO Faculty Books and Monographs 2014 Medicine Meets Virtual Reality 21 James D. Westwood Susan W. Westwood Li Felländer-Tsai Cali M. Fidopiastis Randy S. Haluck
