Keywords Amputation, electromyography, kinematics of cycling, leg asymmetry, motion capture, transtibial prosthesis.
|
|
|
- Branden Wilson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Biomechanics of Cycling with a Transtibial Prosthesis: A Case Study of a Professional Cyclist D. Koutny, D. Palousek, P. Stoklasek, J. Rosicky, L. Tepla, M. Prochazkova, Z. Svoboda, P. Krejci Abstract The article deals with biomechanics of cyclist with unilateral transtibial amputation. Transtibial amputation completely removes ankle and part of muscles of a lower leg which are responsible for production of force during pedaling and causes significant geometric and power asymmetry between the limbs during cycling movement. The primary goal of this work is to assess the effects of length adjustment of the crank on the kinematics and muscle activity of cyclist. The paper presents experimental work, which aims to find a suitable ratio of the length of kinematic components to improve overall athletic performance. The study presents the results of the kinematic analysis of the cycling movement with different crank length realized by tracking camera system together with the results of muscle activity measurements captured by electromyography and measurement of forces in the cranks by strain gauges. Keywords Amputation, electromyography, kinematics of cycling, leg asymmetry, motion capture, transtibial prosthesis. A I. INTRODUCTION LTHOUGH modern cycling leg prosthesis intended for top sport are manufactured with advanced technologies from lightweight and durable materials, geometric deviations arise between prosthetic and healthy limbs during their use while pedaling. These deviations are characterized by angular rotation in the hip and knee. For proper bicycle ride and optimal (balanced) output of muscular energy, it is needed to reduce or completely suppress these deviations. This can be achieved by length modification of the components of the kinematic chain, which consists of a residual limb, prosthesis and pedal crank [1], [2]. Although cycling for people with amputations is considered as very beneficial health sport, it can have, particularly in performance at top level, a number of negative effects on the musculoskeletal system of the organism caused by unilateral loading. During cycling, there is no direct contact with the legs and ground and therefore there is no subsequent overloading of joints due to body weight or impact loading of D. Koutny, D. Palousek, P. Stoklasek, and P. Krejci are with the Brno University of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Institute of Machine and Industrial Design, Technicka 2, Brno, Czech Republic ( koutny@fme.vutbr.cz; palousek@fme.vutbr.cz, p.100klasek@ gmail.com, krejci@fme.vutbr.cz). J. Rosicky is with the University of Ostrava, Faculty of Health Studies, Department of Rehabilitation, Syllabova 19, Ostrava 3, Czech Republic ( jiri.rosicky@osu.cz). Z. Svoboda, M. Prochazkova, and L. Tepla are with the Palacký University, Faculty of Physical Culture, Department of Natural Sciences in Kinanthropology, Křížkovského 8, Olomouc, Czech Republic ( zdenek.svoboda@upol.cz, marketa.prochazkova@upol.cz, lucie.tepla01@ upol.cz). musculoskeletal system as in other sports, however top cycling is associated with the emergence of various injuries and musculoskeletal problems [3], [4]. Appropriate crank arm length compensation under prosthetic limb would partially reduce uneven loading of muscles of whole body and thus have a positive effect on the body and health of racing cyclist. Childers et al. [1], [2], [5] investigated the influence of various external factors on bicycling for individuals with unilateral transtibial amputation (bicycle positioning, crank shortening, stiffness of the prosthesis). Their work shows, that the shortening of the crank under prosthetic limb reduces force and geometric deviations between the legs, positively affects stereotype of pedaling and may contribute to a decrease in muscle loading of amputated limb. The authors also point to the fact that for the performance cycling in terms of transmission of higher driving forces is better to design and produce rigid prosthesis without flexible members simulating the ankle joint. Moderate geometric and power asymmetry between the legs during cyclical movement is apparent also at healthy athletes. Carpes et al. [6], investigated asymmetry of the limbs during running and cycling. He pointed out a few interesting facts asymmetry during pedaling of healthy athletes is probably connected with the limb dominance and is significantly reduced by increase of the load while pedaling (e.g. suitable change of gear ratio). In the research, Carpes also mentions that the elimination of the power imbalances between limbs is one of the most important factors for optimization of athletic performance, because it plays a significant role in the uniform production of driving torque. The phenomenon of force asymmetry of healthy cyclists during pedaling is probably caused by neuromuscular changes in the limbs after suffered injuries and is directly related to the influence of the limb dominance. The influence of speed changes during pedaling on the motion asymmetry of lower limbs of healthy cyclists was done in other studies [7], [8]. The authors also concluded that the increase of the load while pedaling (by change of gear ratios) leads to reduction of the power and geometrical deviations between the legs. There is large number of parameters that can be set and changed on the bike. Almost every element on the bike may be set incorrectly; which can result in improper involvement of the muscles during the pedaling cycle and therefore inefficient use of muscle potential. Appropriate setting of the bike (especially to the optimum saddle height) was studied by Burkett and Mellifont [9]. Their study describes the collaboration with the six-member Australian Paralympic 812
2 cycling team during preparation for the Paralympic games. Half of the team reduced the seat height in the range of 10-19mm, the second half increased the saddle height in the range of 3-12mm. These changes have had an impact on the range of motion (ROM) in the hip joint, but did not show any change in the performance of cyclists when driving in the same conditions. This relatively simple resetting reduced the height of the rider in the frontal plane, which may cause in longer races achievement of better performance (higher speed), especially in terms of improvement of the overall aerodynamics of the rider. The authors mention that the integration of sports science combined with expert guidance and appropriate training program can have a positive impact on the overall performance of sports cyclists with amputation, their safety and health. II. METHODS Further described experiments involved a male performance cyclist, 37 years old, 70kg, 188cm, with handicap: C4 - unilateral below-knee amputation of the right leg. Cyclist uses custom-made transtibial cycling prosthesis and carbon-fiber socket without mechanical members supplemented with duralumin adapter with a cleat to fasten directly to the pedal surface. The prosthesis is attached to the stumb by vacuum clamping system on a silicone liner Iceross Seal-In X5 (Össur, Reykjavik, Iceland). Fig. 1 Prosthesis structure The aim of the experimental part of this case study was to investigate the effects of length adjustment of the crank on the kinematics and muscle activity of cyclist. A motion capture system and measurement of muscle activity in the legs were used during riding in the seated position and in the climbing position. Both measurements were performed synchronously under the supervision of trained personnel under the same riding conditions. To ride in the seated position a riding parameters of 140 W and 70 rpm were chosen and for a ride in the climbing position 160 W and 80 rpm were used. These parameters were monitored on the rear bicycle wheel with a wireless performance and speed sensor by cyclo-computer Cycle Ops Power (Cycle Ops, Madison, USA). Rear wheel of the racing bike was clamped in a magnetic trainer. The six30 seconds measurements were performed for three different settings of bicycle crank length (three in seated and three in climbing position). The bicycle crank length of 175mm (original crank length), 167.5mm and 160mm were used. Fig. 2 Seated position (left) and climbing position (right) A. Kinematic Analysis For all measurements of kinematics was used a six-camera Vicon MX system (Vicon Motion Systems, Oxford, UK) with a frequency of 200Hz scanning. For evaluation of the kinematic parameters program Vicon Nexus 1.0 (Vicon Motion Systems, Oxford, UK) with a Plug In Gait model was used. On the lower limbs and pelvis of the cyclist a 14 reflective markers were placed (8 on the healthy limb 6 on side of prosthetic limb). On the side of prosthetic limb there was not necessary to trace the movement of the heel and toe. Fig. 3 Reflective markers on health limb (left), on prosthesis (right) The values of angular rotation in selected joints were evaluated in 5 consecutive cycles (5x turning a right crank about the 360 ). On the basis of these results a percentage difference between the angular rotation in the hip and knee of prosthetic limb in comparison of the healthy limb were expressed. For both lower limbs were observed values of the angular rotation of the hip joint (the angle between the femur and vertical line) and knee joint (for the healthy limb: the angle between the femur and tibia, for the prosthetic leg: the angle between the femur and prosthetic pylon). 813
3 Prototype of wireless module Strain gauge Fig. 4 Graphical representation of measured angles B. EMG Measurements For all measurements of muscle activity an EMG sensors Trigno Wireless Systems (Delsys, Boston, USA) were used. Surface electrodes (TrignoTM Wireless) were applied on the midpoint of the contracted muscles belly, parallel to the muscle fibers on the following muscles: the biceps femoris, semitendinosus, gluteus maximus, quadriceps femoris part m. vastus medialis and m. vastus lateralis. The skin was shaved and cleaned with and ECG&EEG abrasive skin prepping gel (NuprepTM) to reduced skin impedance. All electrodes were fixed on the skin with adhesive tapes. For evaluation of the EMG signal an EMG works program (Delsys, Boston, USA) was used. The raw EMG signals were amplified (gain = 2500), band pass filtered ( Hz), an analog-to-digital converted at a sampling rate frequency of 4000/296 Hz. The EMG signal was also full-wave rectified and smoothed (Butterworth filter, second-order, cut-off frequency of 12 Hz). Finally root mean square procedure (window length 0.125; windows overlap ) was applied. EMG activity between the muscle activity in amputated limb in comparison of the healthy limb recorded during the test situation was expressed relative to the threshold muscle activity. The threshold muscle activity was calculated as average + two standard deviations of muscle activity recorded in resting cycling position. The activity level of each muscle was calculated for five consecutives crank cycles and normalized to the threshold value of each muscle. C. Strain Gauge Measurements For comparison of the influence of the crank shortening on the actual produced force during pedaling a separate measurement of the forces in the bicycle cranks was done. The measurement of the dominant bending strain in the crank arm was done by strain gauges connected in full-bridge arrangement compensating tension and torsion. Placement of strain gauges was determined on the basis on finite element analysis of the crank. For signal transmission from the strain gaugesan onsite developed wireless system was used (Fig. 5). Signal and data processing were done in Matlab software. Fig. 5 Wireless strain gauge measurement of cranksforces A. Kinematic Analysis III. RESULTS The results of kinematic measurement for riding in the seated position are shown in Tables I-III, the results of kinematic measurement for riding in the in the climbing position are shown in Tables IV to VI. TABLE I HIP AND KNEE ANGLES - CRANK LENGTH 175MM, SEATED POSITION health limb amputated limb TABLE II HIP AND KNEE ANGLES - CRANK LENGTH 167.5MM, SEATED POSITION health limb amputated limb TABLE III HIP AND KNEE ANGLES - CRANK LENGTH 160 MM, SEATED POSITION health limb amputated limb Fig. 6 ROM geometric asymmetries seated position 814
4 TABLE IV HIP AND KNEE ANGLES - CRANK LENGTH 175 MM, CLIMBING POSITION health limb amputated limb TABLE V HIP AND KNEE ANGLES - CRANK LENGTH 167.5MM, CLIMBING POSITION health limb amputated limb TABLE VI HIP AND KNEE ANGLES - CRANK LENGTH 160 MM, CLIMBING POSITION health limb amputated limb Fig. 7 ROM geometric asymmetries climbing position B. EMG Measurements The evaluation of the measurement results of muscle activity is based on the threshold values of individual muscles recorded in the resting cyclist position. Fig. 9 Muscle activity in health limb seated position The evaluation of muscle activity of individual muscles for the seated position showed the following findings: Muscle activity of amputated limb is much higher than the healthy limb muscle activity. Any change in muscle activity in the muscles of amputated limb also affects the muscle activity of healthy limb. Due to the shortened length of the crank arm, while riding in the seated position, there is a decrease in muscle activity of the quadriceps femoris and gluteus maximusat both limbs. Due to the shortened length of the crank, while riding in the seated position, theree is an increase in muscle activity of biceps fem. and semitendinosus in both limbs (Figs. 8 and 9). In terms of balanced muscular activity for the ride in the seated position, shortening of the crank to 160 mm appears to be optimal. Fig. 10 Muscle activity in amputed limb climbing position Fig. 8 Muscle activity in amputated limb seated position 815
5 Fig. 11 Muscle activity in health limb climbing position The evaluation of muscle activity of individual muscles for the climbing position showed the following findings: Muscle activity of amputated limb is much higher than the muscle activity of healthy limb. When shortening the length of the crank to 160mm for riding in climbing position muscle activity of the amputated limb in the gluteus max. decreases, while activity of other observed muscles increase. In terms of balanced muscular activity for the ride in climbing position, shortening of the crank to 167.5mm appears to be optimal. C. Strain Gauge Measurements The forces produced by health and prosthetic limbs during the pedaling shows expected significant difference between the limbs. The force produced by prosthetic limb is about 42% lower than the health limb. As can be seen on the Figs. 12 and 13, the values of forces are not influenced by the change of crank length. However, the measurement was done independently on the EMG; therefore, further verification by complex measurement needs to be done. Fig. 13 Forces in the cranks seated position, 175mm IV. CONCLUSION This article shows the influence of the crank length adjustments on the geometric deviations between the movement of prosthetic and healthy limbs during cycling of the handicapped performance cyclist. Based on the results of kinematic analysis, EMG measurement and evaluation of subjective perceptions of the participating cyclist, the most suitable variant was the crank with the length of mm. Shortening of the bike's crank at the prosthetic limb can bring more symmetrical involvement of the limbs during the pedaling and therefore possible improvement of athletic performance of the cyclist with transtibial prosthesis. Shortening of the bike's crankat the prosthetic limb also has a positive effect on the activity of the muscles of the lower limbs during pedaling. Due to the shortening of crank length, activity of most of the monitored muscles decreased in comparison with the original state. However, the forces on the cranks did not significantly change with crank shortening. This can lead to lower muscle exhaustion and to overall better performance during the long races. ACKNOWLEDGMENT The work was supported by European Regional Development Fund in the framework of the research project NETME Centre under the Operational Programme Research and Development for Innovation. Registered no: CZ.1.05/2.1.00/ , ID code: ED0002/01/01, project name: NETME Centre New Technologies for Mechanical Engineering and project of specific research FSI-S-11-30/1454. The authors acknowledge the patience of the subject that participated in this case study and the MCAE Systems, s.r.o. for modification of the cranks. All authors report no conflicts of interest. Fig. 12 Forces in the cranks seated position, 167.5mm REFERENCES [1] Childers, W. L.; Kistenberg, R. S.; Gregor, R. J. The biomechanics of cycling with a transtibial amputation: Recommendations for prosthetic 816
6 design and direction for future research. Prosthetics and orthotics international, 2009, 33.3: [2] Childers, W. L. Motor control in person with trans-tibial amputation during cycling Dissertation. Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Applied Physiology. [3] Schwellnus, M.; Derman, E. Common injuries in cycling: Prevention, diagnosis and management. SA Fam Pract. 2005, 47, 7, p [4] Clarsen, B; Krosshaug, T; BAHR, R. Overuse injuries in professional road cyclists. The American journal of sports medicine, 2010, 38.12: [5] Childers, W. L.; Gregor, R. J. Effectiveness of force production in persons with unilateral transtibial amputation during cycling. Prosthetics and orthotics international, 2011, 35.4: [6] Carpes, F. P.; Mota, C. B.; Faria, I. E. On the bilateral asymmetry during running and cycling A review considering leg preference. Physical Therapy in Sport, 2010, 11.4: [7] Smak, W.; Neptune, R. R.; Hull, M. L. The influence of pedaling rate on bilateral asymmetry in cycling. Journal of biomechanics, 1999, : 906. [8] Sanderson, D. J. The influence of cadence and power output on the biomechanics of force application during steady-rate cycling in competitive and recreational cyclists. Journal of sports sciences, 1991, 9.2: [9] Burkett, B.; Mellifont, R. Sport science and coaching in Paralympic cycling. International Journal of Sports Science and Coaching, 2008, 3.1:
Palacký Univerzity in Olomouc Faculty of Physical Culture
 Project: Sophisticated biomechanic diagnostics of human movement Registration number: CZ.1.07/2.3.00/09.0209 Palacký Univerzity in Olomouc Faculty of Physical Culture Tento projekt je spolufinancován Evropským
Project: Sophisticated biomechanic diagnostics of human movement Registration number: CZ.1.07/2.3.00/09.0209 Palacký Univerzity in Olomouc Faculty of Physical Culture Tento projekt je spolufinancován Evropským
Available online at Prediction of energy efficient pedal forces in cycling using musculoskeletal simulation models
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Engineering 2 00 (2010) (2009) 3211 3215 000 000 Engineering www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia 8 th Conference of the International Sports Engineering Association
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Engineering 2 00 (2010) (2009) 3211 3215 000 000 Engineering www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia 8 th Conference of the International Sports Engineering Association
A Pilot Study on Electromyographic Analysis of Single and Double Revolution Jumps in Figure Skating
 Journal of Exercise Science and Physiotherapy, Vol. 5, No. 1: 14-19, 2009 A Pilot Study on Electromyographic Analysis of Single and Double Revolution Jumps in Figure Skating Taylor¹, C. L. and Psycharakis²,
Journal of Exercise Science and Physiotherapy, Vol. 5, No. 1: 14-19, 2009 A Pilot Study on Electromyographic Analysis of Single and Double Revolution Jumps in Figure Skating Taylor¹, C. L. and Psycharakis²,
Joint Torque Evaluation of Lower Limbs in Bicycle Pedaling
 11th conference of the International Sports Engineering Association, ISEA 216 Delft University of Technology; July 12 th Joint Torque Evaluation of Lower Limbs in Bicycle Pedaling Hiroki Yamazaki Akihiro
11th conference of the International Sports Engineering Association, ISEA 216 Delft University of Technology; July 12 th Joint Torque Evaluation of Lower Limbs in Bicycle Pedaling Hiroki Yamazaki Akihiro
Does Ski Width Influence Muscle Action in an Elite Skier? A Case Study. Montana State University Movement Science Laboratory Bozeman, MT 59717
 Does Ski Width Influence Muscle Action in an Elite Skier? A Case Study John G. Seifert 1, Heidi Nunnikhoven 1, Cory Snyder 1, Ronald Kipp 2 1 Montana State University Movement Science Laboratory Bozeman,
Does Ski Width Influence Muscle Action in an Elite Skier? A Case Study John G. Seifert 1, Heidi Nunnikhoven 1, Cory Snyder 1, Ronald Kipp 2 1 Montana State University Movement Science Laboratory Bozeman,
Available online at ScienceDirect. The 2014 conference of the International Sports Engineering Association
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 72 ( 2014 ) 150 155 The 2014 conference of the International Sports Engineering Association Impact of electrical assistance
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 72 ( 2014 ) 150 155 The 2014 conference of the International Sports Engineering Association Impact of electrical assistance
Muscles force and joints load simulation of bicycle riding using multibody models
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 13 (2011) 81 87 5 th Asia-Pacific Congress on Sports Technology (APCST) Muscles force and joints load simulation of bicycle riding using multibody
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 13 (2011) 81 87 5 th Asia-Pacific Congress on Sports Technology (APCST) Muscles force and joints load simulation of bicycle riding using multibody
Supplementary Figure S1
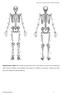 Supplementary Figure S1: Anterior and posterior views of the marker set used in the running gait trials. Forty-six markers were attached to the subject (15 markers on each leg, 4 markers on each arm, and
Supplementary Figure S1: Anterior and posterior views of the marker set used in the running gait trials. Forty-six markers were attached to the subject (15 markers on each leg, 4 markers on each arm, and
PROPRIO FOOT INTRODUCTION KEY FEATURES ÖSSUR DYNAMIC SOLUTIONS
 INTRODUCTION PROPRIO FOOT is an adaptive prosthetic device for low to moderately active below-knee amputees that mimics natural foot motion. Motor-powered ankle motion increases ground clearance and reduces
INTRODUCTION PROPRIO FOOT is an adaptive prosthetic device for low to moderately active below-knee amputees that mimics natural foot motion. Motor-powered ankle motion increases ground clearance and reduces
Pedaling Asymmetries in Cyclists With Unilateral Transtibial Amputation: Effect of Prosthetic Foot Stiffness
 Journal of Applied Biomechanics, 2011, 27, 314-321 2011 Human Kinetics, Inc. Pedaling Asymmetries in Cyclists With Unilateral Transtibial Amputation: Effect of Prosthetic Foot Stiffness W. Lee Childers,
Journal of Applied Biomechanics, 2011, 27, 314-321 2011 Human Kinetics, Inc. Pedaling Asymmetries in Cyclists With Unilateral Transtibial Amputation: Effect of Prosthetic Foot Stiffness W. Lee Childers,
Effects of Mass and Momentum of Inertia Alternation on Individual Muscle Forces During Swing Phase of Transtibial Amputee Gait
 Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 56, No. 3, pp. E92-E97, 21 Effects of Mass and Momentum of Inertia Alternation on Individual Muscle Forces During Swing Phase of Transtibial Amputee Gait YAGHOUB DABIRI 1, SIAMAK
Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 56, No. 3, pp. E92-E97, 21 Effects of Mass and Momentum of Inertia Alternation on Individual Muscle Forces During Swing Phase of Transtibial Amputee Gait YAGHOUB DABIRI 1, SIAMAK
GROUND REACTION FORCE DOMINANT VERSUS NON-DOMINANT SINGLE LEG STEP OFF
 GROUND REACTION FORCE DOMINANT VERSUS NON-DOMINANT SINGLE LEG STEP OFF Sara Gharabaghli, Rebecca Krogstad, Sara Lynch, Sofia Saavedra, and Tamara Wright California State University, San Marcos, San Marcos,
GROUND REACTION FORCE DOMINANT VERSUS NON-DOMINANT SINGLE LEG STEP OFF Sara Gharabaghli, Rebecca Krogstad, Sara Lynch, Sofia Saavedra, and Tamara Wright California State University, San Marcos, San Marcos,
A Novel Gear-shifting Strategy Used on Smart Bicycles
 2012 International Conference on Industrial and Intelligent Information (ICIII 2012) IPCSIT vol.31 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore A Novel Gear-shifting Strategy Used on Smart Bicycles Tsung-Yin
2012 International Conference on Industrial and Intelligent Information (ICIII 2012) IPCSIT vol.31 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore A Novel Gear-shifting Strategy Used on Smart Bicycles Tsung-Yin
Personal Bicycle Fitting Report Rider Information
 5/19/2011 Retül Notes Report Specialized Dolce PRE-FIT NOTES Courtney is a recreational cyclist coming in today for a fit on her road bike. She enjoys riding with friends and in group rides. She has had
5/19/2011 Retül Notes Report Specialized Dolce PRE-FIT NOTES Courtney is a recreational cyclist coming in today for a fit on her road bike. She enjoys riding with friends and in group rides. She has had
Myths and Science in Cycling
 Myths and Science in Cycling John McDaniel, PhD Kent State University Jim Martin, PhD - U of Utah Steve Elmer, PhD- Michigan Tech Who am I PhD in Exercise Physiology under Dr. Jim Martin at the University
Myths and Science in Cycling John McDaniel, PhD Kent State University Jim Martin, PhD - U of Utah Steve Elmer, PhD- Michigan Tech Who am I PhD in Exercise Physiology under Dr. Jim Martin at the University
An investigation of kinematic and kinetic variables for the description of prosthetic gait using the ENOCH system
 An investigation of kinematic and kinetic variables for the description of prosthetic gait using the ENOCH system K. OBERG and H. LANSHAMMAR* Amputee Training and Research Unit, University Hospital, Fack,
An investigation of kinematic and kinetic variables for the description of prosthetic gait using the ENOCH system K. OBERG and H. LANSHAMMAR* Amputee Training and Research Unit, University Hospital, Fack,
1C11 Terion K2. Confidence with every step. Information for Practitioners
 1C11 Terion K2 Confidence with every step Information for Practitioners Confidence with every step For prosthesis users who need a high level of stability With the 1C11 Terion K2, Ottobock has developed
1C11 Terion K2 Confidence with every step Information for Practitioners Confidence with every step For prosthesis users who need a high level of stability With the 1C11 Terion K2, Ottobock has developed
1. Zinn, L. (2009). Zinn and the Art of Road Bike Maintenance, 3rd Ed. Boulder, CO: Velo Press.
 Bike Fit Clinic 3/11/2014 James Cunningham, PT, DPT, OCS 1. Zinn, L. (2009). Zinn and the Art of Road Bike Maintenance, 3rd Ed. Boulder, CO: Velo Press. Basic frame guidelines Should be able to have at
Bike Fit Clinic 3/11/2014 James Cunningham, PT, DPT, OCS 1. Zinn, L. (2009). Zinn and the Art of Road Bike Maintenance, 3rd Ed. Boulder, CO: Velo Press. Basic frame guidelines Should be able to have at
Your Life. Your Adventure. Triton Family of Products
 Your Life. Your Adventure. Triton Family of Products Ready for any challenge The search is over! Now your high-mobility patients can choose from a variety of superb options to fit their active lifestyles.
Your Life. Your Adventure. Triton Family of Products Ready for any challenge The search is over! Now your high-mobility patients can choose from a variety of superb options to fit their active lifestyles.
The Starting Point. Prosthetic Alignment in the Transtibial Amputee. Outline. COM Motion in the Coronal Plane
 Prosthetic Alignment in the Transtibial Amputee The Starting Point David C. Morgenroth, MD, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine University of Washington VAPSHCS Outline COM Motion in the Coronal Plane
Prosthetic Alignment in the Transtibial Amputee The Starting Point David C. Morgenroth, MD, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine University of Washington VAPSHCS Outline COM Motion in the Coronal Plane
Bicycle Fit Services
 Bicycle Fit Services Fitting Services (click to go to) - Premium 3D Motion Capture Bike Fit ~ $399 - Complete 3D Motion Capture Bike Fit ~ $299 - Multi-Bike Complete 3D Motion Capture Bike Fit ~ $474-2D
Bicycle Fit Services Fitting Services (click to go to) - Premium 3D Motion Capture Bike Fit ~ $399 - Complete 3D Motion Capture Bike Fit ~ $299 - Multi-Bike Complete 3D Motion Capture Bike Fit ~ $474-2D
SHUFFLE TURN OF HUMANOID ROBOT SIMULATION BASED ON EMG MEASUREMENT
 SHUFFLE TURN OF HUMANOID ROBOT SIMULATION BASED ON EMG MEASUREMENT MASANAO KOEDA, TAKAYUKI SERIZAWA, AND YUTA MATSUI Osaka Electro-Communication University, Faculty of Information Science and Arts, Department
SHUFFLE TURN OF HUMANOID ROBOT SIMULATION BASED ON EMG MEASUREMENT MASANAO KOEDA, TAKAYUKI SERIZAWA, AND YUTA MATSUI Osaka Electro-Communication University, Faculty of Information Science and Arts, Department
Gait Analysis by High School Students
 Gait Analysis by High School Students André Heck 1 and Caroline van Dongen 2 1 AMSTEL Institute, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, heck@science.uva.nl 2 St. Antoniuscollege, Gouda, The
Gait Analysis by High School Students André Heck 1 and Caroline van Dongen 2 1 AMSTEL Institute, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, heck@science.uva.nl 2 St. Antoniuscollege, Gouda, The
Optimization of an off-road bicycle with four-bar linkage rear suspension
 Proceedings of MUSME 2008, the International Symposium on Multibody Systems and Mechatronics San Juan (Argentina), 8-12 April 2008 Paper n. 02-MUSME08 Optimization of an off-road bicycle with four-bar
Proceedings of MUSME 2008, the International Symposium on Multibody Systems and Mechatronics San Juan (Argentina), 8-12 April 2008 Paper n. 02-MUSME08 Optimization of an off-road bicycle with four-bar
Electromyography Study on Lower Limb Muscle Synchronizations Strategies during Walking and Sitto-Stand Tasks on High-Heeled Shoes
 Electromyography Study on Lower Limb Muscle Synchronizations Strategies during Walking and Sitto-Stand Tasks on High-Heeled Shoes A Dissertation submitted for The partial fulfillment of Master of Engineering
Electromyography Study on Lower Limb Muscle Synchronizations Strategies during Walking and Sitto-Stand Tasks on High-Heeled Shoes A Dissertation submitted for The partial fulfillment of Master of Engineering
Biomechanical Analysis of Taekwondo Kicking Technique, Performance & Training Effects
 Preface Taekwondo is a free-fighting, combat sport that is popular in Hong Kong. It is an international sport, with over 18 million participants worldwide, and is one of the new Olympic sports in the Sydney
Preface Taekwondo is a free-fighting, combat sport that is popular in Hong Kong. It is an international sport, with over 18 million participants worldwide, and is one of the new Olympic sports in the Sydney
KOTARO SASAKI Curriculum Vitae
 KOTARO SASAKI Curriculum Vitae Department of Mechanical & Biomedical Engineering Boise State University 1910 University Dr. Boise ID 83725-2075 Phone: (208) 426-4027 Email: kosasaki@boisestate.edu EDUCATION
KOTARO SASAKI Curriculum Vitae Department of Mechanical & Biomedical Engineering Boise State University 1910 University Dr. Boise ID 83725-2075 Phone: (208) 426-4027 Email: kosasaki@boisestate.edu EDUCATION
Aerodynamic study of a cyclist s moving legs using an innovative approach
 Aerodynamic study of a cyclist s moving legs using an innovative approach Francesco Pozzetti 30 September 2017 Abstract During a period of four weeks in September, I completed a research project in fluid
Aerodynamic study of a cyclist s moving legs using an innovative approach Francesco Pozzetti 30 September 2017 Abstract During a period of four weeks in September, I completed a research project in fluid
Chapter 1 - Injury overview Chapter 2 - Fit for Running Assessment Chapter 3 - Soft Tissue Mobilization... 21
 Table of Contents Introduction Chapter 1 - Injury overview... 6 Chapter 2 - Fit for Running Assessment... 13 Chapter 3 - Soft Tissue Mobilization... 21 Chapter 4 - Dynamic Warm-up... 28 Chapter 5 - Strengthening...
Table of Contents Introduction Chapter 1 - Injury overview... 6 Chapter 2 - Fit for Running Assessment... 13 Chapter 3 - Soft Tissue Mobilization... 21 Chapter 4 - Dynamic Warm-up... 28 Chapter 5 - Strengthening...
Steffen Willwacher, Katina Fischer, Gert Peter Brüggemann Institute of Biomechanics and Orthopaedics, German Sport University, Cologne, Germany
 P01-3 ID126 SURFACE STIFFNESS AFFECTS JOINT LOADING IN RUNNING Steffen Willwacher, Katina Fischer, Gert Peter Brüggemann Institute of Biomechanics and Orthopaedics, German Sport University, Cologne, Germany
P01-3 ID126 SURFACE STIFFNESS AFFECTS JOINT LOADING IN RUNNING Steffen Willwacher, Katina Fischer, Gert Peter Brüggemann Institute of Biomechanics and Orthopaedics, German Sport University, Cologne, Germany
INVESTIGATION OF POWER OUTPUT ON A NOVEL BICYCLE DRIVE IN COMPARISON WITH THE COMMON BICYCLE DRIVE
 117 Biomechanics Symposia 2001 / University of San Francisco INVESTIGATION OF POWER OUTPUT ON A NOVEL BICYCLE DRIVE IN COMPARISON WITH THE COMMON BICYCLE DRIVE T. Angeli and R. Pawlik Institute for Machine
117 Biomechanics Symposia 2001 / University of San Francisco INVESTIGATION OF POWER OUTPUT ON A NOVEL BICYCLE DRIVE IN COMPARISON WITH THE COMMON BICYCLE DRIVE T. Angeli and R. Pawlik Institute for Machine
THE ANKLE-HIP TRANSVERSE PLANE COUPLING DURING THE STANCE PHASE OF NORMAL WALKING
 THE ANKLE-HIP TRANSVERSE PLANE COUPLING DURING THE STANCE PHASE OF NORMAL WALKING Thales R. Souza, Rafael Z. Pinto, Renato G. Trede, Nadja C. Pereira, Renata N. Kirkwood and Sérgio T. Fonseca. Movement
THE ANKLE-HIP TRANSVERSE PLANE COUPLING DURING THE STANCE PHASE OF NORMAL WALKING Thales R. Souza, Rafael Z. Pinto, Renato G. Trede, Nadja C. Pereira, Renata N. Kirkwood and Sérgio T. Fonseca. Movement
Ground Forces Impact on Release of Rotational Shot Put Technique
 Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Theses and Dissertations 2014-12-01 Ground Forces Impact on Release of Rotational Shot Put Technique Niklas B. Arrhenius Brigham Young University - Provo
Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Theses and Dissertations 2014-12-01 Ground Forces Impact on Release of Rotational Shot Put Technique Niklas B. Arrhenius Brigham Young University - Provo
Increasing ankle push-off work with a powered prosthesis does not necessarily reduce metabolic rate for transtibial amputees
 Supplementary Materials Increasing ankle push-off work with a powered prosthesis does not necessarily reduce metabolic rate for transtibial amputees Roberto E. Quesada, Joshua M. Caputo,, and Steven H.
Supplementary Materials Increasing ankle push-off work with a powered prosthesis does not necessarily reduce metabolic rate for transtibial amputees Roberto E. Quesada, Joshua M. Caputo,, and Steven H.
Positive running posture sums up the right technique for top speed
 Positive running, a model for high speed running Frans Bosch positive running posture sums up the right technique for top speed building blocks in running: Pelvic rotation for- and backward and hamstring
Positive running, a model for high speed running Frans Bosch positive running posture sums up the right technique for top speed building blocks in running: Pelvic rotation for- and backward and hamstring
CHAPTER IV FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF THE KNEE JOINT WITHOUT A MEDICAL IMPLANT
 39 CHAPTER IV FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF THE KNEE JOINT WITHOUT A MEDICAL IMPLANT 4.1 Modeling in Biomechanics The human body, apart of all its other functions is a mechanical mechanism and a structure,
39 CHAPTER IV FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF THE KNEE JOINT WITHOUT A MEDICAL IMPLANT 4.1 Modeling in Biomechanics The human body, apart of all its other functions is a mechanical mechanism and a structure,
1B1 Meridium. Reclaim your way. Information for practitioners. Meridium Ottobock 1
 1B1 Meridium Reclaim your way. Information for practitioners Meridium Ottobock 1 Reclaim your way. With the development of the individualized Meridium prosthetic foot, Ottobock has incorporated the latest
1B1 Meridium Reclaim your way. Information for practitioners Meridium Ottobock 1 Reclaim your way. With the development of the individualized Meridium prosthetic foot, Ottobock has incorporated the latest
Hands should be positioned at approximately shoulder width with a comfortable grip.
 The Basics Bike Fit The bicycle should be adapted to fit your body and not the other way around. There are many styles of bicycles that can be modified to meet your needs. Weight distribution should be
The Basics Bike Fit The bicycle should be adapted to fit your body and not the other way around. There are many styles of bicycles that can be modified to meet your needs. Weight distribution should be
Posture influences ground reaction force: implications for crouch gait
 University of Tennessee, Knoxville From the SelectedWorks of Jeffrey A. Reinbolt July 14, 2010 Posture influences ground reaction force: implications for crouch gait H. X. Hoang Jeffrey A. Reinbolt, University
University of Tennessee, Knoxville From the SelectedWorks of Jeffrey A. Reinbolt July 14, 2010 Posture influences ground reaction force: implications for crouch gait H. X. Hoang Jeffrey A. Reinbolt, University
Design and manufacturing basalt and carbon fiber road bike frame.
 MATERIALES COMPUESTOS 15 1 Design and manufacturing basalt and carbon road bike frame. E. Romero, RACORMANCE Composites Bikes. J. Justo, F. París Group of Elasticity and Strength of Materials, University
MATERIALES COMPUESTOS 15 1 Design and manufacturing basalt and carbon road bike frame. E. Romero, RACORMANCE Composites Bikes. J. Justo, F. París Group of Elasticity and Strength of Materials, University
HPA Power Transmission. Everardo Uribe
 HPA Power Transmission There are several forces the HPA has to overcome, most of these forces will have to be overcome by the power transmission component. The main force will of course be aerodynamic
HPA Power Transmission There are several forces the HPA has to overcome, most of these forces will have to be overcome by the power transmission component. The main force will of course be aerodynamic
PRO-FLEX. Less load, more dynamics
 PRO-FLEX Less load, more dynamics CARBON Unique Pivot Technology and ankle torque deliver 27º ankle motion with progressive stiffness for a more physiological gait. Immediate adaptation to ramps, stairs
PRO-FLEX Less load, more dynamics CARBON Unique Pivot Technology and ankle torque deliver 27º ankle motion with progressive stiffness for a more physiological gait. Immediate adaptation to ramps, stairs
empower Reclaim your power. Information for technicians empower Ottobock 1
 empower Reclaim your power. Information for technicians empower Ottobock 1 empower Powered propulsion for more freedom in life The empower Ankle is an innovation in the field of prosthetic feet. It is
empower Reclaim your power. Information for technicians empower Ottobock 1 empower Powered propulsion for more freedom in life The empower Ankle is an innovation in the field of prosthetic feet. It is
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN TAEKWONDO ROUNDHOUSE KICK EXECUTED BY THE FRONT AND BACK LEG - A BIOMECHANICAL STUDY
 268 Isas 2000! Hong Kong DIFFERENCE BETWEEN TAEKWONDO ROUNDHOUSE KICK EXECUTED BY THE FRONT AND BACK LEG - A BIOMECHANICAL STUDY Pui-Wah Kong, Tze-Chung Luk and Youlian Hong The Chinese University of Hong
268 Isas 2000! Hong Kong DIFFERENCE BETWEEN TAEKWONDO ROUNDHOUSE KICK EXECUTED BY THE FRONT AND BACK LEG - A BIOMECHANICAL STUDY Pui-Wah Kong, Tze-Chung Luk and Youlian Hong The Chinese University of Hong
JOHN SHORTT :14. Personal Bicycle Fitting Report RIDER SITE BIKE FITTER SUMMARY OF SESSION. John Shortt Age: 57 Male
 Personal Bicycle Fitting Report JOHN SHORTT 2014-04-30 11:14 RIDER John Shortt Age: 57 Male john.shortt@cycle.ie BIKE MAKE/MODEL: BMC, Road Racer SL02 SIZE: 54 YEAR: 2012 TYPE: Road SITE Bike Fit Studio
Personal Bicycle Fitting Report JOHN SHORTT 2014-04-30 11:14 RIDER John Shortt Age: 57 Male john.shortt@cycle.ie BIKE MAKE/MODEL: BMC, Road Racer SL02 SIZE: 54 YEAR: 2012 TYPE: Road SITE Bike Fit Studio
Simulation-based design to reduce metabolic cost
 Simulation-based design to reduce metabolic cost Overview: Lecture + Hands On Exercise 1. Generating and evaluating a muscledriven simulation of walking 2. Metabolics 101 3. Designing and evaluating devices
Simulation-based design to reduce metabolic cost Overview: Lecture + Hands On Exercise 1. Generating and evaluating a muscledriven simulation of walking 2. Metabolics 101 3. Designing and evaluating devices
REPORT. A comparative study of the mechanical and biomechanical behaviour of natural turf and hybrid turf for the practise of sports
 REPORT A comparative study of the mechanical and biomechanical behaviour of natural turf and hybrid turf for the practise of sports Addressed to: PSF - PALAU TURF Date: May 2015 Table of Contents SHEET
REPORT A comparative study of the mechanical and biomechanical behaviour of natural turf and hybrid turf for the practise of sports Addressed to: PSF - PALAU TURF Date: May 2015 Table of Contents SHEET
SCHEINWORKS Measuring and Analysis Systems by
 Pressure Measurement Systems for standing and walking analysis Germany since 1879 Pressure Measurement Systems for standing and walking analysis Documentation of Gait image Stance Symmetry of all parameters
Pressure Measurement Systems for standing and walking analysis Germany since 1879 Pressure Measurement Systems for standing and walking analysis Documentation of Gait image Stance Symmetry of all parameters
MANUAL POSITION SIMULATOR
 Introduction The Position Simulator has been developed to round off the Bikefitting.com Standard analysis. This device is very unique because you can determine exactly the right seat-angle. The measurement
Introduction The Position Simulator has been developed to round off the Bikefitting.com Standard analysis. This device is very unique because you can determine exactly the right seat-angle. The measurement
Computer Aided Drafting, Design and Manufacturing Volume 26, Number 2, June 2016, Page 53. The design of exoskeleton lower limbs rehabilitation robot
 Computer Aided Drafting, Design and Manufacturing Volume 26, Number 2, June 2016, Page 53 CADDM The design of exoskeleton lower limbs rehabilitation robot Zhao Xiayun 1, Wang Zhengxing 2, Liu Zhengyu 1,3,
Computer Aided Drafting, Design and Manufacturing Volume 26, Number 2, June 2016, Page 53 CADDM The design of exoskeleton lower limbs rehabilitation robot Zhao Xiayun 1, Wang Zhengxing 2, Liu Zhengyu 1,3,
Normal and Abnormal Gait
 Normal and Abnormal Gait Adrielle Fry, MD EvergreenHealth, Division of Sport and Spine University of Washington Board Review Course March 6, 2017 What are we going to cover? Definitions and key concepts
Normal and Abnormal Gait Adrielle Fry, MD EvergreenHealth, Division of Sport and Spine University of Washington Board Review Course March 6, 2017 What are we going to cover? Definitions and key concepts
Element DS. Product Manual
 Element DS Product Manual Instructions The Element DS is designed to be maintenance free. The foot is water resistant; however, if the foot is submerged in water, the foot and foot shell should be rinsed
Element DS Product Manual Instructions The Element DS is designed to be maintenance free. The foot is water resistant; however, if the foot is submerged in water, the foot and foot shell should be rinsed
Empower. Reclaim your power. Information for technicians. Empower Ottobock 1
 Empower Reclaim your power. Information for technicians Empower Ottobock 1 Empower Powered propulsion for more freedom in life The Empower is an innovation in the field of prosthetic feet. It is equipped
Empower Reclaim your power. Information for technicians Empower Ottobock 1 Empower Powered propulsion for more freedom in life The Empower is an innovation in the field of prosthetic feet. It is equipped
Analysis of Backward Falls Caused by Accelerated Floor Movements Using a Dummy
 Original Article Analysis of Backward Falls Caused by Accelerated Floor Movements Using a Dummy Hisao NAGATA 1 * and Hisato OHNO 2 1 National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health, 1 4 6 Umezono,
Original Article Analysis of Backward Falls Caused by Accelerated Floor Movements Using a Dummy Hisao NAGATA 1 * and Hisato OHNO 2 1 National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health, 1 4 6 Umezono,
Ankle biomechanics demonstrates excessive and prolonged time to peak rearfoot eversion (see Foot Complex graph). We would not necessarily expect
 Case Study #1 The first case study is a runner presenting with bilateral shin splints with pain and tenderness along the medial aspect of the tibia. The symptoms have increased significantly over the last
Case Study #1 The first case study is a runner presenting with bilateral shin splints with pain and tenderness along the medial aspect of the tibia. The symptoms have increased significantly over the last
Kinterra Instructions for Use Product Number: ROM-00-XXXXX-XX
 Kinterra Instructions for Use Product Number: ROM-00-XXXXX-XX Introduction Patient Selection Assembly Alignment The Kinterra foot/ankle system combines hydraulics and carbon fiber, to provide low to moderate
Kinterra Instructions for Use Product Number: ROM-00-XXXXX-XX Introduction Patient Selection Assembly Alignment The Kinterra foot/ankle system combines hydraulics and carbon fiber, to provide low to moderate
A Musculoskeletal Driven Forward Dynamics Simulation of Swing Phase of Transfemoral Amputee Gait
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 4(2): 187-196, 2010 ISSN 1991-8178 A Musculoskeletal Driven Forward Dynamics Simulation of Swing Phase of Transfemoral Amputee Gait 1 2 3 4 5 Y. Dabiri,
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 4(2): 187-196, 2010 ISSN 1991-8178 A Musculoskeletal Driven Forward Dynamics Simulation of Swing Phase of Transfemoral Amputee Gait 1 2 3 4 5 Y. Dabiri,
Evaluation of gait symmetry in poliomyelitis subjects : Comparison of a
 Evaluation of gait symmetry in poliomyelitis subjects : Comparison of a conventional knee ankle foot orthosis (KAFO) and a new powered KAFO. Arazpour, M, Ahmadi, F, Bahramizadeh, M, Samadiam, M, Mousavi,
Evaluation of gait symmetry in poliomyelitis subjects : Comparison of a conventional knee ankle foot orthosis (KAFO) and a new powered KAFO. Arazpour, M, Ahmadi, F, Bahramizadeh, M, Samadiam, M, Mousavi,
A SEX COMPARISON OF RELEASE TORQUES DURING A SELF RELEASE TEST OF SKI BINDINGS ADJUSTED TO THE ISO STANDARD
 A SEX COMPARISON OF RELEASE TORQUES DURING A SELF RELEASE TEST OF SKI BINDINGS ADJUSTED TO THE ISO 11088 STANDARD Markus Posch, Robert Eberle, Gerhard Ruedl ISSS 2015 San Vito INTRODUCTION Female recreational
A SEX COMPARISON OF RELEASE TORQUES DURING A SELF RELEASE TEST OF SKI BINDINGS ADJUSTED TO THE ISO 11088 STANDARD Markus Posch, Robert Eberle, Gerhard Ruedl ISSS 2015 San Vito INTRODUCTION Female recreational
PREVIEW ONLY SWIMMING FAST SWIMMING IN AUSTRALIA PHYSIOTHERAPY ASSESSMENT OF SWIMMERS. Cameron Elliott. These notes are a preview. Slides are limited.
 Be sure to convert to your own time zone at Cameron Elliott B.App.Sc (Physio) PHYSIOTHERAPY ASSESSMENT OF SWIMMERS Cameron Elliott SWIMMING IN AUSTRALIA Over 160,000 adults participate in organised swimming
Be sure to convert to your own time zone at Cameron Elliott B.App.Sc (Physio) PHYSIOTHERAPY ASSESSMENT OF SWIMMERS Cameron Elliott SWIMMING IN AUSTRALIA Over 160,000 adults participate in organised swimming
Kinetic chain checkpoints
 Kinetic chain checkpoints Observations: Foot/ankle Knee Lumbo-Pelvic-Hip-Complex (LPHC) Shoulder and Cervical Spine (upper body) Each joint region has a specific and optimal motion based on its structure
Kinetic chain checkpoints Observations: Foot/ankle Knee Lumbo-Pelvic-Hip-Complex (LPHC) Shoulder and Cervical Spine (upper body) Each joint region has a specific and optimal motion based on its structure
KINEMATIC ANALYSIS OF SHOT PUT IN ELITE ATHLETES A CASE STUDY
 KINEMATIC ANALYSIS OF SHOT PUT IN ELITE ATHLETES A CASE STUDY Weimin Liu and Mingxuan Wang Jiangsu Research Institute of Sports Science, Nanjing, People's Republic of China This paper presented the application
KINEMATIC ANALYSIS OF SHOT PUT IN ELITE ATHLETES A CASE STUDY Weimin Liu and Mingxuan Wang Jiangsu Research Institute of Sports Science, Nanjing, People's Republic of China This paper presented the application
RUNNING SHOE STIFFNESS: THE EFFECT ON WALKING GAIT
 RUNNING SHOE STIFFNESS: THE EFFECT ON WALKING GAIT Stephen N Stanley, Peter J M c Nair, Angela G Walker, & Robert N Marshall Auckland Institute of Technology, Auckland, New Zealand University of Auckland,
RUNNING SHOE STIFFNESS: THE EFFECT ON WALKING GAIT Stephen N Stanley, Peter J M c Nair, Angela G Walker, & Robert N Marshall Auckland Institute of Technology, Auckland, New Zealand University of Auckland,
Artifacts Due to Filtering Mismatch in Drop Landing Moment Data
 Camenga et al. UW-L Journal of Undergraduate Research XVI (213) Artifacts Due to Filtering Mismatch in Drop Landing Moment Data Elizabeth T. Camenga, Casey J. Rutten, Brendan D. Gould, Jillian T. Asmus,
Camenga et al. UW-L Journal of Undergraduate Research XVI (213) Artifacts Due to Filtering Mismatch in Drop Landing Moment Data Elizabeth T. Camenga, Casey J. Rutten, Brendan D. Gould, Jillian T. Asmus,
KEVIN BATCHELOR :01 SITE FITTER
 Personal Bicycle Fitting Report KEVIN BATCHELOR 2014-05-30 15:01 RIDER Kevin Batchelor Age: 32 Male Blank@Blank.com BIKE MAKE/MODEL: Mosaic, RT-1 SIZE: Custom YEAR: 2013 TYPE: Road SITE Retul HQ 5445 Conestoga
Personal Bicycle Fitting Report KEVIN BATCHELOR 2014-05-30 15:01 RIDER Kevin Batchelor Age: 32 Male Blank@Blank.com BIKE MAKE/MODEL: Mosaic, RT-1 SIZE: Custom YEAR: 2013 TYPE: Road SITE Retul HQ 5445 Conestoga
SYMBIONIC LEG 3 INTRODUCTION KEY FEATURES ÖSSUR DYNAMIC SOLUTIONS
 INTRODUCTION Featuring the latest advances in Bionic Technology by Össur, SYMBIONIC LEG 3 is the next generation of integrated prosthetic devices that combines a microprocessor knee and powered microprocessor
INTRODUCTION Featuring the latest advances in Bionic Technology by Össur, SYMBIONIC LEG 3 is the next generation of integrated prosthetic devices that combines a microprocessor knee and powered microprocessor
Aeris Performance 2. Product Manual
 Aeris Performance 2 Product Manual Instructions The Aeris Performance 2 is designed to be maintenance free. The foot is water resistant; however, if the foot is submerged in water, the foot and foot shell
Aeris Performance 2 Product Manual Instructions The Aeris Performance 2 is designed to be maintenance free. The foot is water resistant; however, if the foot is submerged in water, the foot and foot shell
Analysis of Gait Characteristics Changes in Normal Walking and Fast Walking Of the Elderly People
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 08, Issue 7 (July. 2018), V (V) 34-41 www.iosrjen.org Analysis of Gait Characteristics Changes in and Of the Elderly
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 08, Issue 7 (July. 2018), V (V) 34-41 www.iosrjen.org Analysis of Gait Characteristics Changes in and Of the Elderly
COMPARISON OF BIOMECHANICAL DATA OF A SPRINT CYCLIST IN THE VELODROME AND IN THE LABORATORY
 COMPARISON OF BIOMECHANICAL DATA OF A SPRINT CYCLIST IN THE VELODROME AND IN THE LABORATORY Louise Burnie 1,2, Paul Barratt 3, Keith Davids 1, Paul Worsfold 2,4, Jon Wheat 1 Centre for Sports Engineering
COMPARISON OF BIOMECHANICAL DATA OF A SPRINT CYCLIST IN THE VELODROME AND IN THE LABORATORY Louise Burnie 1,2, Paul Barratt 3, Keith Davids 1, Paul Worsfold 2,4, Jon Wheat 1 Centre for Sports Engineering
Can Asymmetric Running Patterns Be Predicted By Assessment of Asymmetric Standing Posture? A Case Study in Elite College Runners
 REVIEW ARTICLE Can Asymmetric Running Patterns Be Predicted By Assessment of Asymmetric Standing Posture? A Case Study in Elite College Runners Paige E. Skorseth; Patrick T. Knott, PhD, PA-C Abstract Objective:
REVIEW ARTICLE Can Asymmetric Running Patterns Be Predicted By Assessment of Asymmetric Standing Posture? A Case Study in Elite College Runners Paige E. Skorseth; Patrick T. Knott, PhD, PA-C Abstract Objective:
The Influence of Load Carrying Modes on Gait variables of Healthy Indian Women
 The Influence of Load Carrying Modes on Gait variables of Healthy Indian Women *Guha Thakurta A, Iqbal R and De A National Institute of Industrial Engineering, Powai, Vihar Lake, Mumbai-400087, India,
The Influence of Load Carrying Modes on Gait variables of Healthy Indian Women *Guha Thakurta A, Iqbal R and De A National Institute of Industrial Engineering, Powai, Vihar Lake, Mumbai-400087, India,
The influence of lower-limb prostheses technology on Paracanoeing timetrial
 The influence of lower-limb prostheses technology on Paracanoeing timetrial performance. Shelley Ellis 1*, Andrew Callaway 1, Bryce Dyer 2 1 Department of Sport & Physical Activity, Bournemouth University,
The influence of lower-limb prostheses technology on Paracanoeing timetrial performance. Shelley Ellis 1*, Andrew Callaway 1, Bryce Dyer 2 1 Department of Sport & Physical Activity, Bournemouth University,
STRESS ANALYSIS OF BICYCLE PADDLE AND OPTIMIZED BY FINITE ELEMENT METHOD. S. Abeygunasekara 1, T. M. M. Amarasekara 2
 - 96 - STRESS ANALYSIS OF BICYCLE PADDLE AND OPTIMIZED BY FINITE ELEMENT METHOD S. Abeygunasekara 1, T. M. M. Amarasekara 2 1 Faculty of Engineering & Technology, Colombo International Nautical Engineering
- 96 - STRESS ANALYSIS OF BICYCLE PADDLE AND OPTIMIZED BY FINITE ELEMENT METHOD S. Abeygunasekara 1, T. M. M. Amarasekara 2 1 Faculty of Engineering & Technology, Colombo International Nautical Engineering
Biomechanics and Models of Locomotion
 Physics-Based Models for People Tracking: Biomechanics and Models of Locomotion Marcus Brubaker 1 Leonid Sigal 1,2 David J Fleet 1 1 University of Toronto 2 Disney Research, Pittsburgh Biomechanics Biomechanics
Physics-Based Models for People Tracking: Biomechanics and Models of Locomotion Marcus Brubaker 1 Leonid Sigal 1,2 David J Fleet 1 1 University of Toronto 2 Disney Research, Pittsburgh Biomechanics Biomechanics
PURPOSE. METHODS Design
 7 Murrary, M.P.; Sepic, S.B.; Gardner, G.M.; and Mollinger, L.A., "Gait patterns of above-knee amputees using constant-friction knee components," Bull Prosthet Res, 17(2):35-45, 1980. 8 Godfrey, C.M.;
7 Murrary, M.P.; Sepic, S.B.; Gardner, G.M.; and Mollinger, L.A., "Gait patterns of above-knee amputees using constant-friction knee components," Bull Prosthet Res, 17(2):35-45, 1980. 8 Godfrey, C.M.;
Motion Analysis on Backward Walking: Kinetics, Kinematics, and Electromyography
 Motion Analysis on Backward Walking: Kinetics, Kinematics, and Electromyography Min Hyeon Lee The Graduate School Yonsei University Department of Biomedical Engineering Motion Analysis on Backward Walking:
Motion Analysis on Backward Walking: Kinetics, Kinematics, and Electromyography Min Hyeon Lee The Graduate School Yonsei University Department of Biomedical Engineering Motion Analysis on Backward Walking:
3 people 3 unique lifestyles 3 advanced foot solutions
 3 people 3 unique lifestyles 3 advanced foot solutions Reclaim your life Information for practitioners Shelby Hans Intelligent feet are made for more than just walking Today s advanced microprocessor controlled
3 people 3 unique lifestyles 3 advanced foot solutions Reclaim your life Information for practitioners Shelby Hans Intelligent feet are made for more than just walking Today s advanced microprocessor controlled
INTRODUCTION TO GAIT ANALYSIS DATA
 INTRODUCTION TO GAIT ANALYSIS DATA 1. Phases of gait a. Stance (% gc) i. Loading response (10%) ii. Mid- and terminal stance (%) iii. Pre-swing (10%) b. Swing (% gc) i. Initial swing ii. Mid-swing iii.
INTRODUCTION TO GAIT ANALYSIS DATA 1. Phases of gait a. Stance (% gc) i. Loading response (10%) ii. Mid- and terminal stance (%) iii. Pre-swing (10%) b. Swing (% gc) i. Initial swing ii. Mid-swing iii.
Transformation of nonfunctional spinal circuits into functional states after the loss of brain input
 Transformation of nonfunctional spinal circuits into functional states after the loss of brain input G. Courtine, Y. P. Gerasimenko, R. van den Brand, A. Yew, P. Musienko, H. Zhong, B. Song, Y. Ao, R.
Transformation of nonfunctional spinal circuits into functional states after the loss of brain input G. Courtine, Y. P. Gerasimenko, R. van den Brand, A. Yew, P. Musienko, H. Zhong, B. Song, Y. Ao, R.
Using GPOPS-II to optimize sum of squared torques of a double pendulum as a prosthesis leg. Abstract
 Using GPOPS-II to optimize sum of squared torques of a double pendulum as a prosthesis leg Abstract Milad Zarei MCE 593 Prosthesis Design & Control A two-dimensional, two links pendulum is developed to
Using GPOPS-II to optimize sum of squared torques of a double pendulum as a prosthesis leg Abstract Milad Zarei MCE 593 Prosthesis Design & Control A two-dimensional, two links pendulum is developed to
Kintrol Instructions for Use Product Number: VS4
 Kintrol Instructions for Use Product Number: VS4 Introduction The Kintrol foot/ankle combines hydraulics and fiberglass to provide K2 ambulators an exceptionally normal walking gait regardless of surface
Kintrol Instructions for Use Product Number: VS4 Introduction The Kintrol foot/ankle combines hydraulics and fiberglass to provide K2 ambulators an exceptionally normal walking gait regardless of surface
KICKBIKE Your key to optimum sports performance
 KICKBIKE Your key to optimum sports performance Efficient Running is essential to optimum performance of most sports we play. Whether we want to maximize our speed, maximize our endurance, or both, an
KICKBIKE Your key to optimum sports performance Efficient Running is essential to optimum performance of most sports we play. Whether we want to maximize our speed, maximize our endurance, or both, an
Life Without Limitations
 Mobility Grades Product Selection Life Without Limitations Presenter: Matt Henderson Ossur Asia Pacific Agenda What is missing? K Level Review Required features for given K Levels A Look at Specific Products
Mobility Grades Product Selection Life Without Limitations Presenter: Matt Henderson Ossur Asia Pacific Agenda What is missing? K Level Review Required features for given K Levels A Look at Specific Products
Walking with coffee: when and why coffee spills
 Walking with coffee: when and why coffee spills Hans C. Mayer and Rouslan Krechetnikov Department of Mechanical Engineering University of California at Santa Barbara February 20-24, 2012 Page 1/25 Motivation
Walking with coffee: when and why coffee spills Hans C. Mayer and Rouslan Krechetnikov Department of Mechanical Engineering University of California at Santa Barbara February 20-24, 2012 Page 1/25 Motivation
Stress Analysis of Four-Bar Linkage Transfemoral Prosthetic in Gait Cycle
 Stress Analysis of Four-Bar Linkage Transfemoral Prosthetic in Gait Cycle Sugiyanto 1, B.P. Alhakim, B. Setiana 2, R. Ismail 3 and M. Tauviqirrahman 4 * Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of
Stress Analysis of Four-Bar Linkage Transfemoral Prosthetic in Gait Cycle Sugiyanto 1, B.P. Alhakim, B. Setiana 2, R. Ismail 3 and M. Tauviqirrahman 4 * Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of
DEVELOPMENT OF REAL-TIME EMG SONIFICATION SYSTEM FOR GAIT
 The 24 th International Conference on Auditory Display (ICAD 218) June 1-15, 218, Michigan Technological University DEVELOPMENT OF REAL-TIME EMG SONIFICATION SYSTEM FOR GAIT ABSTRACT We developed a system
The 24 th International Conference on Auditory Display (ICAD 218) June 1-15, 218, Michigan Technological University DEVELOPMENT OF REAL-TIME EMG SONIFICATION SYSTEM FOR GAIT ABSTRACT We developed a system
C-Brace Orthotronic Mobility System
 C-Brace Orthotronic Mobility System You ll always remember your first step Information for practitioners C-Brace Orthotics reinvented Until now, you and your patients with conditions like incomplete spinal
C-Brace Orthotronic Mobility System You ll always remember your first step Information for practitioners C-Brace Orthotics reinvented Until now, you and your patients with conditions like incomplete spinal
Figure 1 betois (bending torsion insole system) system with five measuring points and A/D- converter.
 Bending and Torsional Moments - A new measuring system for gait analysis Nora Dawin & Annette Kerkhoff & Klaus Peikenkamp, University of Applied Sciences Münster, Germany Abstract The Laboratory of Biomechanics
Bending and Torsional Moments - A new measuring system for gait analysis Nora Dawin & Annette Kerkhoff & Klaus Peikenkamp, University of Applied Sciences Münster, Germany Abstract The Laboratory of Biomechanics
Influence of speed on gait parameters and on symmetry in transtibial
 Prosthetics and Orthotics International, 1996, 20, 153-158 Influence of speed on gait parameters and on symmetry in transtibial amputees E. ISAKOV*, H. BURGER**, J. KRAJNIK**, M. GREGORIC** and C. MARINCEK**
Prosthetics and Orthotics International, 1996, 20, 153-158 Influence of speed on gait parameters and on symmetry in transtibial amputees E. ISAKOV*, H. BURGER**, J. KRAJNIK**, M. GREGORIC** and C. MARINCEK**
Gait analysis for the development of the biped robot foot structure
 Preprints of the 9th World Congress The International Federation of Automatic Control Cape Town, South Africa. August 4-9, 4 Gait analysis for the development of the biped robot foot structure Yusuke OGAWA
Preprints of the 9th World Congress The International Federation of Automatic Control Cape Town, South Africa. August 4-9, 4 Gait analysis for the development of the biped robot foot structure Yusuke OGAWA
Influence of Synchronized Dead Point Elimination Crank on Cyclist Muscle Fatigue
 Influence of Synchronized Dead Point Elimination Crank on Cyclist Muscle Fatigue Khadijah Akmal Abdul Aziz 1,*, Ahmad Faizal S 1., Norasmadi Abdul Rahim 1, Mohd. Hanafi Mat Som 1, and Hamzah Sakeran 1
Influence of Synchronized Dead Point Elimination Crank on Cyclist Muscle Fatigue Khadijah Akmal Abdul Aziz 1,*, Ahmad Faizal S 1., Norasmadi Abdul Rahim 1, Mohd. Hanafi Mat Som 1, and Hamzah Sakeran 1
Rehabilitation of Non-operative Hamstring Injuries
 Rehabilitation of Non-operative Hamstring Injuries 12 th Annual Colorado University Sports Medicine Fall Symposium Robert A. Panariello MS, PT, ATC, CSCS Founding Partner, Chief Clinical Officer Professional
Rehabilitation of Non-operative Hamstring Injuries 12 th Annual Colorado University Sports Medicine Fall Symposium Robert A. Panariello MS, PT, ATC, CSCS Founding Partner, Chief Clinical Officer Professional
G-EOL. Discover the simplicity of gait therapy intended for daily use
 G-EOL Discover the simplicity of gait therapy intended for daily use Reha Technology a passion for robotic-assisted gait therapy For over 10 years, Reha Technology has been successfully developing innovative,
G-EOL Discover the simplicity of gait therapy intended for daily use Reha Technology a passion for robotic-assisted gait therapy For over 10 years, Reha Technology has been successfully developing innovative,
A New Approach to Modeling Vertical Stiffness in Heel-Toe Distance Runners
 Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Faculty Publications 2003-12-01 A New Approach to Modeling Vertical Stiffness in Heel-Toe Distance Runners Iain Hunter iain_hunter@byu.edu Follow this and
Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Faculty Publications 2003-12-01 A New Approach to Modeling Vertical Stiffness in Heel-Toe Distance Runners Iain Hunter iain_hunter@byu.edu Follow this and
Wind turbine Varying blade length with wind speed
 IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, PP 01-05 www.iosrjournals.org Wind turbine Varying blade length with wind speed Mohammed Ashique
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, PP 01-05 www.iosrjournals.org Wind turbine Varying blade length with wind speed Mohammed Ashique
The importance of physical activity throughout an individual's life is indisputable. As healthcare
 What to Expect When They re Expecting: A Look at Biomechanical Changes in Walking/Running During Pregnancy Jennifer Bruer-Vandeweert, Megan Hotchkiss, Jamie Kronenberg, Kristin Olson Dr. Rumit Singh Kakar,
What to Expect When They re Expecting: A Look at Biomechanical Changes in Walking/Running During Pregnancy Jennifer Bruer-Vandeweert, Megan Hotchkiss, Jamie Kronenberg, Kristin Olson Dr. Rumit Singh Kakar,
Meridium. Reclaim your way. Information for clinicians
 Meridium Reclaim your way. Information for clinicians Reclaim your way. With the development of the individualised Meridium prosthetic foot, Ottobock has incorporated the latest technology to achieve a
Meridium Reclaim your way. Information for clinicians Reclaim your way. With the development of the individualised Meridium prosthetic foot, Ottobock has incorporated the latest technology to achieve a
Training Program. Definitions. Preparation for Training
 Training Program The attached 8 week program is designed for EXPERIENCED cyclists aiming for the Grafton to Inverell Cycle Classic 228km ride. It can be used as a guide to assist you prepare for the event
Training Program The attached 8 week program is designed for EXPERIENCED cyclists aiming for the Grafton to Inverell Cycle Classic 228km ride. It can be used as a guide to assist you prepare for the event
MECHANICAL MUSCLE PROPERTIES AND INTERMUSCULAR COORDINATION IN MAXIMAL AND SUBMAXIMAL CYCLING: THEORETICAL AND PRACTICAL IMPLICATIONS
 MECHANICAL MUSCLE PROPERTIES AND INTERMUSCULAR COORDINATION IN MAXIMAL AND SUBMAXIMAL CYCLING: THEORETICAL AND PRACTICAL IMPLICATIONS A thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy By Paul Richard
MECHANICAL MUSCLE PROPERTIES AND INTERMUSCULAR COORDINATION IN MAXIMAL AND SUBMAXIMAL CYCLING: THEORETICAL AND PRACTICAL IMPLICATIONS A thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy By Paul Richard
Aerodynamic Measures for the Vortex-induced Vibration of π-shape Composite Girder in Cable-stayed Bridge
 Aerodynamic Measures for the Vortex-induced Vibration of π-shape Composite Girder in Cable-stayed Bridge *Feng Wang 1), Jialing Song 2), Tuo Wu 3), and Muxiong Wei 4) 1), 2, 3), 4) Highway School, Chang
Aerodynamic Measures for the Vortex-induced Vibration of π-shape Composite Girder in Cable-stayed Bridge *Feng Wang 1), Jialing Song 2), Tuo Wu 3), and Muxiong Wei 4) 1), 2, 3), 4) Highway School, Chang
