Eudistylia vancouveri
|
|
|
- Doris Sutton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
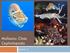
1 Eudistylia vancouveri A feather-duster worm Phylum: Annelida Class: Polychaeta Order: Canalipalpata, Sabellida Family: Sabellidae, Sabellinae Taxonomy: Eudistylia polymorpha was originally described as Sabella vancouveri and later re-described and figured by Johnson (1901) as Bispira polymorpha, when Eudistylia was differentiated by characters of thoracic notosetae which were later deemed insignificant at the genus level and the two genera were synonymized to Eudistylia (Fauvel 1927 and Johansson 1927 in Banse 1979). Since then, several species have been synonymized with E. polymorpha including Sabella vancouveri and S. columbiana, E. abbreviata, E. gigantea, E. plumosa and E. tenella (Banse 1979). Description Size: One of the largest sabellids. Individuals range in size from mm in length and mm in width, where the tube is up to 10 mm diameter (Hartman 1969; Kozloff 1974). This description is based on illustrated and dissected specimens (Fig. 1). Color: Crown of tentacles dark red and green and radially striped (5 8 stripes) (Hartman 1969; Kozloff 1974). Hartman (1969) reports tentacles that were dark red and orange or yellow in California, but this description may refer to E. polymorpha, in part (see possible misidentifications). Some tentacles are white-tipped. The illustrated specimen (Fig. 1) had a buff colored body with light green markings and white spots. The tube is buff or grey in color. General Morphology: A robust worm with a short tentacular crown that is brilliantly colored (Hartman 1969). Worms can be recognized in large groups called hummocks where tubes are built upon each other and resemble shrubs (e.g. Fig. 3). Body: Body divided into thoracic and abdominal regions where abdomen gradually tapers posteriorly. Anterior: Prostomium or head is reduced and indistinguishable (Figs. 4, 5). Trunk: Thorax of eight segments and abdomen of many segments. Thoracic collar with four lobes (Fig. 4) that are visible on the ventral side with no long thoracic membrane. Collar is used to build the tube by incorporating sand grains with exuded mucus and attaching a rope to the tube anterior. Posterior: Worm body tapers toward posterior to slender yet broad pygidium (Fig. 1). Parapodia: Biramous, (Figs. 1, 6) except for first or collar segment, which has only notopodia (Hartman 1969). In thoracic setigers (setigers 2 8), the notopodia have bundles of long and slender setae (Figs. 7b, c). The neuropodia on setigers 2 8 have pairs of short uncini (hooks) (Fig. 7a) encased in zipper-like, raised ridges called tori (Fig. 6). This arrangement is reversed in the abdomen, where the notopodia contain hooks in the abdominal segments and the neuropodia have long spines (Fig. 6). Setae (chaetae): Thoracic notosetae of two kinds (genus Eudistylia): one long, slender and bilimbate (Fig. 7b) and the other spatulate and not scimitar-like (Fig. 7c). Abdominal notosetae are short avicular uncini (Fig. 7e). Thoracic neurosetae in torus, pennoned or flagged and acivular hooks or uncini arranged in a long row of about 20 pairs (Fig. 7a). Abdominal neurosetae long and pointed (Fig. 7d). Eyes/Eyespots: Anterior eyespots lacking however, eyespots are present on radiole ribs where each radiole has 5 7 black eyes in a row (Hartman 1969) (Fig. 2) on the dorsalmost radiole pair (Blake and Ruff 2007). Anterior Appendages: Anterior crown of tentacles made up of two equal parts
2 A publication of the University of Oregon Libraries and the Oregon Institute of Marine Biology Individual species: and full 3rd edition: corrections to
3 composed of many radioles (Fig. 1). Radioles, also called cirri or tentacles, are branches or pinnules (Fig. 2) and dark eyespots along the lower edge, especially near radiole bases (Fig. 2). Bases are spiraled twice (genus Eudistylia). Crown conceals mouth and head and edges are smooth and not incised (Hartman 1969) (Fig. 5). Branchiae: Blood within branchiae is green in color due to the respiratory pigment chlorocruorin (Abbott and Reish 1980; Terwilliger et al. 1975). Branchial base without groove dorsally (Blake and Ruff 2007). Burrow/Tube: Tube is long, cylindrical, flexible, permanent, tough, leathery and membranous. It is made of mucus and cemented sediment and is not calcareous and without operculum. Worm can completely withdraw into tube. Pharynx: Genitalia: Nephridia: Possible Misidentifications Characteristics of the family Sabellidae are the tentacular crown of bipinnate radioles, lack of gills on the body segments and setal types reversed from thoracic to abdominal regions (see parapodia). These characters they share with the Serpulidae, however, sabellids are distinct from serpulids by having a leathery tube of mucus and sand which lacks an operculum or trap door. Serpulids, on the other hand, have a calcareous tube and a staked operculum resembling a golf tee (O Donoghue 1924). Other tube worms include the Terebellidae, which have soft cirri that cannot be completely retracted into the tube (as sabellids can). Terebellids sometimes have gills on their anterior segments (see Thelepus crispus and Pista pacifica), and their setal types are not inverted (Blake 1975). A family with an easily confusing name is the Sabellaridae, which builds sand tubes. These have 2 3 rows of paleae (flattened setae) forming highly modified cephalic structures, but not crowns. Their bodies are individual branches of the crown and are single and undivided with forked, simple side clearly defined into thorax, abdomen and long caudal region. Within the family Sabellidae, there are two subfamilies represented locally, Fabriciinae and Sabellinae. The subfamily Fabriciinae differs from the Sabellinae in its small size and in its temporary fragile mucus tubes. Several northwest genera exist, including: Chone species are tiny worms with a membrane partly uniting its radioles and a thoracic collar which is complete and not lobed. Local species have 15 or fewer pairs of radioles. Fabricia species have few segments and sparse radioles and individuals are quite small. Amphicorina has 7 8 abdominal segments, not three. The subfamily Sabellinae (to which E. vancouveri belongs) is noted for its avicular uncini in the thoracic neuropodia, and for its permanent, tough and leathery tubes. Other genera of the sub-family include: Schizobranchia (=split branch) species are common from central California to Puget Sound (Blake and Ruff 2007). This small worm occurs in great masses on floats. Its radioles are branched, not single and it is often tan colored with a bright red crown (not striped) (Kozloff 1974). Schizobranchia insignis (Bush, 1905) often occurs with and is intermixed in clumps with Eudistylia vancouveri (Blake and Ruff 2007). Megalomma species usually occurs in deep water and are rare intertidally. The composite eyes which characterize this genus are spiraled around the radiole ends (Blake 1975). Pseudopotamilla includes three local species of small, rare tube worms which share with Eudistylia the simple pinnate crown of radioles, but the bases of whose two crowns of tentacles are curved into semicircles and are not spiraled. Sabella species bear two lobes on the thoracic collar, rather than four in Eudistylia vancouveri. All members of this genus have spiraled fascicles on their
4 abdominal setae (Knight-Jones and Perkins 1998). Brispira species are found in membranous tubes on rocky bottoms. This genus was revised in 1998 (Knight-Jones and Perkins) and now includes Brispira (=Sabella) crassicornis which has paired eyespots in deep red bands on its radioles (Blake 1975). Myxicola species have a thick, transparent mucus sheath or gelatinous tube covering its body and its radioles are joined by a web for most of their length (Fitzhugh 1989). Eudistylia vancouveri and E. polymorpha, may in fact be the same species (Ricketts and Calvin 1971) and some believe that hybridization occurs (Blake and Ruff 2007). There are two obvious differences between them: E. polymorpha does not have striped radioles, they are a solid dark red with orange tips and the dorsal edge of the crown of radioles in not entire (Fig. 5), but is instead notched. Eudistylia vancouveri is slightly larger than E. polymorpha and the latter is much less likely to be found in large clumps and is the more common species in California (Kozloff 1993). Eudistylia polymorpha is also recognizable by a deep cleft or groove, which serves in excretory and gametic transport out of the tube, on each side and at the base of the two spiraled cirri (Blake and Ruff 2007). This groove is ventral and becomes dorsal anteriorly (Kozloff 1993). Ecological Information Range: Type locality is Vancouver Island, B.C. (Hartman 1969). NE Pacific range from Alaska to central California. Local Distribution: In Coos Bay on floating docks or in hummocks. Several hummocks occur just northwest of the OIMB beach. Habitat: Wharfs, floats, sandy and silty mudflats, as well as vertical rock faces in heavy surf (Kozloff 1974). Salinity: Found at salinities of >30, in areas of heavy flushing of water. This species doesn t tolerate reduced salinity (Ricketts and Calvin 1971). Temperature: Cold to temperate. Tidal Level: Collected on floats just below water surface, intertidal (Hartman 1969). Associates: Associates include the copepod, Gastrodelphys dalesi (at Tomales Point, California), but worm tubes form a complex microhabitat in which many animals and plants survive. Tube hummocks of Eudistylia vancouveri are often interspersed with another sabellid, Schizobranchia insignis (Blake and Ruff 2007). Abundance: Gregarious and can be the principal sabellid in rocky habitats (e.g. Puget Sound, Kozloff 1974). Individuals grow in large clumps, in shrub-like masses called hummocks (Ricketts and Calvin 1971) (Fig. 3). Life-History Information Reproduction: Developmental modes among sabellids are highly variable from brooded lecithotrophy, to direct development, and planktonic larvae that are either planktotrophic or lecithotrophic (Crumrine 2001). Eudistylia vancouveri are sexual and dioecious although asexual reproduction with some regeneration is also possible. Males, with white sperm, and females, with green eggs, are free spawners and gametes are released through abdominal nephridial pores and into a ventral shallow groove (Fig. 4) and out of tube. Spawning has been observed from late February to July (Washington, Fernald et al. 1987). The development of Eudistylia vancouveri is not known. Larva: There are only two local sabellid species with described larvae and those are Demonax media and Chone infundibuliformis (Crumrine 2001). Juvenile: Longevity: Growth Rate: Food: A filter feeder. Plankton particles are trapped by funnel of pinnules and driven by beating cilia, carried down to radiole base where they are sorted and ingested. Predators: This species is frequently used by humans for fish bait. Behavior: Individuals can retract fully extended tentacular crown rapidly and does so in response to even slight disturbance, such as a passing shadow. The ability to retract is due to large nerve fibers that allow A publication of the University of Oregon Libraries and the Oregon Institute of Marine Biology Individual species: and full 3rd edition: corrections to oimbref@uoregon.edu
5 the worm to withdraw completely into its tube at rates up to 7 m/s (Eudistylia polymorpha, Abbot and Reish 1980). Bibliography 1. ABBOTT, D. P., and D. J. REISH Polychaeta: the marine annelid worms, p In: Intertidal invertebrates of California. R. H. Morris, D. P. Abbott, and E. C. Haderlie (eds.). Stanford University Press, Stanford, CA. 2. BANSE, K Sabellidae (Polychaeta) principally from the northeast Pacific Ocean. Journal of the Fisheries Research Board of Canada. 36: BLAKE, J. A The Larval development of Polychaeta from the northern California coast. III. eighteen species of Errantia. Ophelia. 14: BLAKE, J. A., and E. R. RUFF Polychaeta, p In: Light and Smith manual: intertidal invertebrates from central California to Oregon. J. Carlton (ed.). University of California Press, Berkeley, CA. 5. CRUMRINE, L Polychaeta, p In: Identification guide to larval marine invertebrates of the Pacific Northwest. A. Shanks (ed.). Oregon State University Press, Corvallis, OR. 6. FERNALD, R. L., C. O. HERMANS, T. C. LACALLI, W. H. WILSON, JR, and S. A. WOODIN Phylum Annelida, Class Polychaeta, p In: Reproduction and development of marine invertebrates of the northern Pacific coast. M. F. Strathmann (ed.). University of Washington Press, Seattle, WA. 7. FITZHUGH, K Systematic revision of the Sabellidae- Caobangiidae-Sabellongidae complex (Annelida, Polychaeta). Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History. 192: HARTMAN, O Atlas of the sedentariate polychaetous annelids from California. Allan Hancock Foundation, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA. 9. JOHNSON, H. P The Polychaeta of the Puget Sound region. Proceedings of the Boston Society of Natural History. 29: KNIGHT-JONES, P., and T. H. PERKINS A revision of Sabella, Bispira and Stylomma (Polychaeta : Sabellidae). Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 123: KOZLOFF, E. N Keys to the marine invertebrates of Puget Sound, the San Juan Archipelago, and adjacent regions. University of Washington Press, Seattle. 12. KOZLOFF, E.N Seashore life of the northern Pacific coast: an illustrated guide to northern California, Oregon, Washington, and British Columbia. University of Washington Press, Seattle, WA 13. O'DONOGHUE, C. H A note on the polychaetous annelid Eudistylia gigantea Bush. Contributions to Canadian Biology. 1: RICKETTS, E. F., and J. CALVIN Between Pacific tides. Stanford University Press, Stanford, California. 15. TERWILLIGER, R. C., R. L. GARLICK, N. B. TERWILLIGER, and D. P. BLAIR Molecular weight of Eudistylia vancouveri chlorocruorin and its subunits. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 400:
Thelepus crispus. A terebellid worm
 Thelepus crispus A terebellid worm Phylum: Annelida Class: Polychaeta Order: Terebellida Family: Terebellidae Description Size: Individuals range in size from 70 280 mm in length (Hartman 1969). The greatest
Thelepus crispus A terebellid worm Phylum: Annelida Class: Polychaeta Order: Terebellida Family: Terebellidae Description Size: Individuals range in size from 70 280 mm in length (Hartman 1969). The greatest
Eteone lighti. A paddleworm
 Eteone lighti A paddleworm Phylum: Annelida Class: Polychaeta Order: Phyllodocida Family: Phyllodocidae Taxonomy: The genus Eteone was revised into three genera (Eteone, Hypereteone, Mysta) by Wilson (1988)
Eteone lighti A paddleworm Phylum: Annelida Class: Polychaeta Order: Phyllodocida Family: Phyllodocidae Taxonomy: The genus Eteone was revised into three genera (Eteone, Hypereteone, Mysta) by Wilson (1988)
Eteone pacifica. A paddleworm
 Eteone pacifica A paddleworm Phylum: Annelida Class: Polychaeta Order: Phyllodocida Family: Phyllodocidae Taxonomy: Treadwell described this species as Eteone maculata in 1922. This name was replaced by
Eteone pacifica A paddleworm Phylum: Annelida Class: Polychaeta Order: Phyllodocida Family: Phyllodocidae Taxonomy: Treadwell described this species as Eteone maculata in 1922. This name was replaced by
Leitoscoloplos pugettensis
 Leitoscoloplos pugettensis A burrowing polychaete worm Phylum: Annelida Class: Polychaeta Order: Orbiniida Family: Orbiniidae Taxonomy In 1957 Pettibone determined that H. elongatus was a homonym a different
Leitoscoloplos pugettensis A burrowing polychaete worm Phylum: Annelida Class: Polychaeta Order: Orbiniida Family: Orbiniidae Taxonomy In 1957 Pettibone determined that H. elongatus was a homonym a different
Nereis vexillosa. The large mussel worm. Taxonomy: One may find several subjective synonyms for Nereis vexillosa, but none are widely used currently.
 Nereis vexillosa The large mussel worm Phylum: Annelida Class: Polychaeta Order: Phyllodocida Family: Nereidae Taxonomy: One may find several subjective synonyms for Nereis vexillosa, but none are widely
Nereis vexillosa The large mussel worm Phylum: Annelida Class: Polychaeta Order: Phyllodocida Family: Nereidae Taxonomy: One may find several subjective synonyms for Nereis vexillosa, but none are widely
Polychaete Key for Chesapeake Bay and Coastal Virginia
 Polychaete Key for Chesapeake Bay and Coastal Virginia Compiled (with some portions written) and illustrated by Aaron Bartholomew Thanks to the following people for their help on the key: Robert Diaz,
Polychaete Key for Chesapeake Bay and Coastal Virginia Compiled (with some portions written) and illustrated by Aaron Bartholomew Thanks to the following people for their help on the key: Robert Diaz,
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. CHAPTER 17. Annelids 17-1
 CHAPTER 17 Annelids 17-1 Characteristics of the Phylum Annelida Diversity Exhibit segmentation or metamerism Bodies composed of repeated units Each unit contains components of most MAJOR organ systems
CHAPTER 17 Annelids 17-1 Characteristics of the Phylum Annelida Diversity Exhibit segmentation or metamerism Bodies composed of repeated units Each unit contains components of most MAJOR organ systems
PHYLUM: PLATHYHELMINTHES
 PHYLUM: PLATHYHELMINTHES FLATWORMS Free living (living independently i.e. not attached) Bilaterally symmetrical with a definite front and back, and with left and right sides. Mobile creeping animals. Concentration
PHYLUM: PLATHYHELMINTHES FLATWORMS Free living (living independently i.e. not attached) Bilaterally symmetrical with a definite front and back, and with left and right sides. Mobile creeping animals. Concentration
 Kingdom: Animalia Phylum:Mollusca Classes: Bivalva, Gastropoda, Cephalopoda http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0a7j5prl8hc&feature=related http://www2.beavercreek.k12.oh.us/videos/45/pgr45_700k.asf What is
Kingdom: Animalia Phylum:Mollusca Classes: Bivalva, Gastropoda, Cephalopoda http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0a7j5prl8hc&feature=related http://www2.beavercreek.k12.oh.us/videos/45/pgr45_700k.asf What is
Lumbricus terrestris - preserved specimens for dissection
 Lumbricus terrestris - preserved specimens for dissection External Anatomy: Prostomium (observe under dissecting microscope for external sensory organs), peristomium, clitellum, setae (dissecting microscope),
Lumbricus terrestris - preserved specimens for dissection External Anatomy: Prostomium (observe under dissecting microscope for external sensory organs), peristomium, clitellum, setae (dissecting microscope),
Each unit contains components of most organ systems. Increased burrowing efficiency by permitting movement of segments
 CHAPTER 17 Annelids Characteristics of the Phylum Annelida Diversity Exhibit segmentation or Bodies composed of units Each unit contains components of most organ systems Increased burrowing efficiency
CHAPTER 17 Annelids Characteristics of the Phylum Annelida Diversity Exhibit segmentation or Bodies composed of units Each unit contains components of most organ systems Increased burrowing efficiency
Species of Fabriciola Friedrich, 1939 (Polychaeta: Sabellidae: Fabriciinae), from the California Coast!
 Pacific Science (1992), vol. 46, no. 1: 68-76 1992 by University of Hawaii Press. All rights reserved Species of Fabriciola Friedrich, 1939 (Polychaeta: Sabellidae: Fabriciinae), from the California Coast!
Pacific Science (1992), vol. 46, no. 1: 68-76 1992 by University of Hawaii Press. All rights reserved Species of Fabriciola Friedrich, 1939 (Polychaeta: Sabellidae: Fabriciinae), from the California Coast!
Manual and then a copy of Ricketts and Calvin, Between Pacific Tides. By this
 An Identification Guide to the Larval Marine Invertebrates of the Pacific Northwest Edited OREGON INSTITUTE OF MARINE BIOLOGY Oregon State University Press Corvallis Dedication This volume is dedicated
An Identification Guide to the Larval Marine Invertebrates of the Pacific Northwest Edited OREGON INSTITUTE OF MARINE BIOLOGY Oregon State University Press Corvallis Dedication This volume is dedicated
-8- spinous. nape caudal fin. body depth. pectoral fin. anus. total length Fig. 4
 click for previous page -8-1.3 Illustrated Glossary of Technical Terms and Measurements External Morphology and Measurements spinous dorsal fin soft nape caudal fin interorbital body depth snout lateral
click for previous page -8-1.3 Illustrated Glossary of Technical Terms and Measurements External Morphology and Measurements spinous dorsal fin soft nape caudal fin interorbital body depth snout lateral
Slide 1. Slide 1. Next. 5:30:08 AM
 Slide 1 Slide 1 http://www3.utep.edu/leb/mosquito/larvslide1.htm10/27/2004 5:30:08 AM Slide 1 Slide 2 Recognition that the specimens are mosquito larvae is a prerequisite to identification of the genera.
Slide 1 Slide 1 http://www3.utep.edu/leb/mosquito/larvslide1.htm10/27/2004 5:30:08 AM Slide 1 Slide 2 Recognition that the specimens are mosquito larvae is a prerequisite to identification of the genera.
Coelomate Worms: Sipunculans, Pogonophorans, Echiurans and Vestimenifera
 Coelomate Worms Coelomate Worms: Sipunculans, Pogonophorans, Echiurans and Vestimenifera Ectoderm Mesoderm Dt Endoderm Coelom Often dismissed as minor or lesser Comprise less than 600 species total Never
Coelomate Worms Coelomate Worms: Sipunculans, Pogonophorans, Echiurans and Vestimenifera Ectoderm Mesoderm Dt Endoderm Coelom Often dismissed as minor or lesser Comprise less than 600 species total Never
Anthopleura artemisia
 Anthopleura artemisia Buried anemone, moonglow anemone Phylum: Cnidaria Class: Anthozoa, Hexacorallia Order: Actiniaria, Nynantheae, Thenaria Family: Endomyaria, Actiniidae Taxonomy: Anthopleura artemisia
Anthopleura artemisia Buried anemone, moonglow anemone Phylum: Cnidaria Class: Anthozoa, Hexacorallia Order: Actiniaria, Nynantheae, Thenaria Family: Endomyaria, Actiniidae Taxonomy: Anthopleura artemisia
 Echinoderms Name Means: Echino- Spiny Derm- Skin About 7,000 species No Head! No Brain! No ventral, dorsal, posterior, or anterior sides! Do have oral (mouth) and aboral sides. Symmetry: Larvae are
Echinoderms Name Means: Echino- Spiny Derm- Skin About 7,000 species No Head! No Brain! No ventral, dorsal, posterior, or anterior sides! Do have oral (mouth) and aboral sides. Symmetry: Larvae are
A brief examination of the development of Phoronis sp. Phoronida is a small phylum associated with the lophophorates. The phylum
 A brief examination of the development of Phoronis sp Holly Keamrnerer Embryology Spring 2007 Introduction Phoronida is a small phylum associated with the lophophorates. The phylum consists of two genera
A brief examination of the development of Phoronis sp Holly Keamrnerer Embryology Spring 2007 Introduction Phoronida is a small phylum associated with the lophophorates. The phylum consists of two genera
Unit 18.2: Mollusks and Annelids
 Unit 18.2: Mollusks and Annelids Lesson Objectives Describe invertebrates in the phylum Mollusca. Summarize the characteristics of annelids. Vocabulary Annelida deposit feeder gills heart mantle Mollusca
Unit 18.2: Mollusks and Annelids Lesson Objectives Describe invertebrates in the phylum Mollusca. Summarize the characteristics of annelids. Vocabulary Annelida deposit feeder gills heart mantle Mollusca
What is an insect? An insect is an invertebrate (an animal with no spine) that has three pairs of legs and three
 What is an insect? An insect is an invertebrate (an animal with no spine) that has three pairs of legs and three Small minnow mayfly body divisions. The mouth, antennae, and eyes are located on the head;
What is an insect? An insect is an invertebrate (an animal with no spine) that has three pairs of legs and three Small minnow mayfly body divisions. The mouth, antennae, and eyes are located on the head;
Chapter 12 Part 2. The Worms Platyhelminthes, Nematoda & Annelida
 Chapter 12 Part 2 The Worms Platyhelminthes, Nematoda & Annelida Phylum: Platyhelminthes Examples: Flatworms, Planaria sp., tapeworms and blood flukes Acoelomate, Invertebrate, Simplest critter w/ bilateral
Chapter 12 Part 2 The Worms Platyhelminthes, Nematoda & Annelida Phylum: Platyhelminthes Examples: Flatworms, Planaria sp., tapeworms and blood flukes Acoelomate, Invertebrate, Simplest critter w/ bilateral
ON THE OCCURRENCE OF ARENICOLA BRASILIENSIS NONATO (FAMILY : ARENICOLIDAE, POLYCHAETA) IN INDIAN WATERS*
 /. Mar. biol. Ass. India, 1963, 5 (1): 8-1 ON THE OCCURRENCE OF ARENICOLA BRASILIENSIS NONATO (FAMILY : ARENICOLIDAE, POLYCHAETA) IN INDIAN WATERS* By P. R. S. TAMPI AND K. RANGARAJAN Central Marine Fisheries
/. Mar. biol. Ass. India, 1963, 5 (1): 8-1 ON THE OCCURRENCE OF ARENICOLA BRASILIENSIS NONATO (FAMILY : ARENICOLIDAE, POLYCHAETA) IN INDIAN WATERS* By P. R. S. TAMPI AND K. RANGARAJAN Central Marine Fisheries
ZOOLOGY SEGMENTED WORMS (Phylum Annelida)
 ZOOLOGY SEGMENTED WORMS (Phylum Annelida) I. Compared and Contrasted to Phylum Mollusca. A. They are like the molluscs in that they 1. are eucoelomate animals. 2. have specialized sense organs. 3. have
ZOOLOGY SEGMENTED WORMS (Phylum Annelida) I. Compared and Contrasted to Phylum Mollusca. A. They are like the molluscs in that they 1. are eucoelomate animals. 2. have specialized sense organs. 3. have
 OCTOPUS Found throughout the world in tropical, warm and cold temperate waters - the octopus is a bottom dweller, spending much of its life in hiding, usually in a hole among rocks. All octopus species
OCTOPUS Found throughout the world in tropical, warm and cold temperate waters - the octopus is a bottom dweller, spending much of its life in hiding, usually in a hole among rocks. All octopus species
Echinoderms. Phylum Echinodermata
 Echinoderms Phylum Echinodermata spiny skinned or hedgehog skin sea stars (starfish), sea urchins, sea cucumbers 6000 species radial symmetry in 2 o development bilateral symmetry in larva http://www.biologyreference.com/dn-ep/echinoderm.html
Echinoderms Phylum Echinodermata spiny skinned or hedgehog skin sea stars (starfish), sea urchins, sea cucumbers 6000 species radial symmetry in 2 o development bilateral symmetry in larva http://www.biologyreference.com/dn-ep/echinoderm.html
Ocean Series Coral Reefs
 Ocean Series Coral Reefs Coral is part of the animal kingdom, a member of the scientific phylum Cnidaria along with other marine creatures including sea jellies. Sea jellies have a soft gelatinous body
Ocean Series Coral Reefs Coral is part of the animal kingdom, a member of the scientific phylum Cnidaria along with other marine creatures including sea jellies. Sea jellies have a soft gelatinous body
Chapter 7. Marine Animals Without a Backbone
 Chapter 7 Marine Animals Without a Backbone Molluscs Characteristics of Phylum: More than 200,000 species Name means "soft body" Basic body plan head, muscular foot and visceral mass in most species Mantle-
Chapter 7 Marine Animals Without a Backbone Molluscs Characteristics of Phylum: More than 200,000 species Name means "soft body" Basic body plan head, muscular foot and visceral mass in most species Mantle-
Mollusks Soft-bodied Invertebrates
 Mollusks Soft-bodied Invertebrates Phylum Mollusca Very diverse - more species of molluscs than any other group in the ocean. Phylum includes: Bivalves (2 shells); ex. Clam Gastropods (1 shell, coiled);
Mollusks Soft-bodied Invertebrates Phylum Mollusca Very diverse - more species of molluscs than any other group in the ocean. Phylum includes: Bivalves (2 shells); ex. Clam Gastropods (1 shell, coiled);
LIBRARY. Class\ V"^ A *Ii:T_
 LIBRARY Class\ V"^ A *Ii:T_ ^ Publications OP FIELD MUSEUM OF NATURAL HISTORY ZOOLOGICAL SERIES Volume X Chicago, U. S. A. 1909-1923 7/,3 ^Issued September 18, 19 12. 69 NEW SPECIES OF FISHES FROM
LIBRARY Class\ V"^ A *Ii:T_ ^ Publications OP FIELD MUSEUM OF NATURAL HISTORY ZOOLOGICAL SERIES Volume X Chicago, U. S. A. 1909-1923 7/,3 ^Issued September 18, 19 12. 69 NEW SPECIES OF FISHES FROM
Chapter 35. Table of Contents. Section 1 Mollusca. Section 2 Annelida. Mollusks and Annelids
 Mollusks and Annelids Table of Contents Section 1 Mollusca Section 2 Annelida Section 1 Mollusca Objectives Describe the key characteristics of mollusks. Describe the body plan of mollusks. Name the characteristics
Mollusks and Annelids Table of Contents Section 1 Mollusca Section 2 Annelida Section 1 Mollusca Objectives Describe the key characteristics of mollusks. Describe the body plan of mollusks. Name the characteristics
click for previous page D E
 click for previous page D E DREP FAO SPECIES IDENTIFICATION SHEETS 1974 FISHING AREAS 57, 71 (E Ind. Ocean) (W Cent. Pacific) DREPANIDAE Sicklefishes (placed by some authors, together with the Platacidae,
click for previous page D E DREP FAO SPECIES IDENTIFICATION SHEETS 1974 FISHING AREAS 57, 71 (E Ind. Ocean) (W Cent. Pacific) DREPANIDAE Sicklefishes (placed by some authors, together with the Platacidae,
Spiny skinned animals with radial symmetrical body plan. Rays emanating from a common center. Internal skeleton of hardened plates of calcium
 Echinodermata Spiny skinned animals with radial symmetrical body plan. Rays emanating from a common center. Internal skeleton of hardened plates of calcium carbonate. Water vascular system and tube feet
Echinodermata Spiny skinned animals with radial symmetrical body plan. Rays emanating from a common center. Internal skeleton of hardened plates of calcium carbonate. Water vascular system and tube feet
Bivalves: Mollusks that Matter
 Objective Bivalves: Mollusks that Matter Version 6/05 Students will understand the anatomy and physiology of mussels, and understand why they may pose health risks to humans. National Science Education
Objective Bivalves: Mollusks that Matter Version 6/05 Students will understand the anatomy and physiology of mussels, and understand why they may pose health risks to humans. National Science Education
Phylum Mollusca. Soft-bodied animals. Internal or external shell. Include snails, slugs, clams, squids and octopi
 Phylum Mollusca Soft-bodied animals Internal or external shell Include snails, slugs, clams, squids and octopi Trochophore: free-swimming larval stage of an aquatic mollusk True coeloms Have complex organ
Phylum Mollusca Soft-bodied animals Internal or external shell Include snails, slugs, clams, squids and octopi Trochophore: free-swimming larval stage of an aquatic mollusk True coeloms Have complex organ
- 7 - DESCRIPTION OF SPECIES
 I - 7 - DESCRIPTION OF SPECIES./' Anguilla bicolor McClelland ' Level-finned eel (Figs.i & 2) Length of head 6-8 times in length of body; Diameter of eye 8-10 times, Inter-orbital length 2-2.5 times, Gape
I - 7 - DESCRIPTION OF SPECIES./' Anguilla bicolor McClelland ' Level-finned eel (Figs.i & 2) Length of head 6-8 times in length of body; Diameter of eye 8-10 times, Inter-orbital length 2-2.5 times, Gape
Crayfish Dissection. Materials:gloves, preserved crayfish, paper towel, dissecting pan, scissors, forceps, dissecting. Background: LME-305
 Living Science LME-305 Crayfish Dissection Materials:gloves, preserved crayfish, paper towel, dissecting pan, scissors, forceps, dissecting needle, dissecting pins, and pen or pencil Background: Like all
Living Science LME-305 Crayfish Dissection Materials:gloves, preserved crayfish, paper towel, dissecting pan, scissors, forceps, dissecting needle, dissecting pins, and pen or pencil Background: Like all
27-4 Mollusks. Slide 1 of 43. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 1 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What Is a Mollusk? Mollusks are soft-bodied animals that usually have an internal or external shell. Mollusks include snails, slugs, clams, squids, octopi... They are group together
1 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What Is a Mollusk? Mollusks are soft-bodied animals that usually have an internal or external shell. Mollusks include snails, slugs, clams, squids, octopi... They are group together
a. Kingdom: b. Phylum: c. Class: d. Order: e. Family: f. Genus: g. Species:
 Pre-lab Discussion: The earthworm belongs to a group of animals called annelids (segmented worms). The body of an annelid is usually divided internally and externally into well-defined segments, which
Pre-lab Discussion: The earthworm belongs to a group of animals called annelids (segmented worms). The body of an annelid is usually divided internally and externally into well-defined segments, which
2 Mollusks and Annelid Worms
 CHAPTER 15 2 Mollusks and Annelid Worms SECTION Invertebrates BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the four features of mollusks? What are
CHAPTER 15 2 Mollusks and Annelid Worms SECTION Invertebrates BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the four features of mollusks? What are
Title: May 31 2:42 PM (1 of 23) Phylum Mollusca
 Title: May 31 2:42 PM (1 of 23) Phylum Mollusca Title: May 31 3:25 PM (2 of 23) often referred to as mollusks second largest phylum has 7 classes only looking at 4 bilateral symmetry, true body cavity
Title: May 31 2:42 PM (1 of 23) Phylum Mollusca Title: May 31 3:25 PM (2 of 23) often referred to as mollusks second largest phylum has 7 classes only looking at 4 bilateral symmetry, true body cavity
Phylum: Porifera (sponges)
 Phylum: Porifera (sponges) (8,761 known species) General Description: Simplest animals, multicellular No organs or body systems Skeleton composed of spongin (soft) and spicules (hard) Symmetry: Asymmetrical
Phylum: Porifera (sponges) (8,761 known species) General Description: Simplest animals, multicellular No organs or body systems Skeleton composed of spongin (soft) and spicules (hard) Symmetry: Asymmetrical
NATIONAL BIORESOURCE DEVELOPMENT BOARD Dept. of Biotechnology Government of India, New Delhi
 NATIONAL BIORESOURCE DEVELOPMENT BOARD Dept. of Biotechnology Government of India, New Delhi MARINE BIORESOURCES FORMS DATA ENTRY: Form- 1(general) For office use: Fauna: Flora Microorganisms General Category:
NATIONAL BIORESOURCE DEVELOPMENT BOARD Dept. of Biotechnology Government of India, New Delhi MARINE BIORESOURCES FORMS DATA ENTRY: Form- 1(general) For office use: Fauna: Flora Microorganisms General Category:
Protostomes vs Deuterostomes. Phylum Mollusca
 Protostomes vs Deuterostomes Animals that have a true coelom and complete digestive system can be divided into two main groups. This division is based on the way their embryos develop and the way in which
Protostomes vs Deuterostomes Animals that have a true coelom and complete digestive system can be divided into two main groups. This division is based on the way their embryos develop and the way in which
Mollusks and Annelids. Chapter 23+
 Mollusks and Annelids Chapter 23+ 1 Annelids and Mollusks Coelomates Trochophore larvae Bilateral symmetry More complex organ systems 2 Moving On Up 3 Coelom Coelomates Evolutionary milestone True body
Mollusks and Annelids Chapter 23+ 1 Annelids and Mollusks Coelomates Trochophore larvae Bilateral symmetry More complex organ systems 2 Moving On Up 3 Coelom Coelomates Evolutionary milestone True body
Phylum Mollusca. Includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids.
 Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids. Bivalves Nautilus Characteristics Soft-bodied invertebrate Covered with protective mantle that may or may
Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids. Bivalves Nautilus Characteristics Soft-bodied invertebrate Covered with protective mantle that may or may
Tips for Identifying Common Fish Species in the Bush River
 Tips for Identifying Common Fish Species in the Bush River Juvenile Largemouth bass Spot Threadfin shad Juvenile White perch The Herrings (Family Clupeidae) Alewife American shad Blueback herring Atlantic
Tips for Identifying Common Fish Species in the Bush River Juvenile Largemouth bass Spot Threadfin shad Juvenile White perch The Herrings (Family Clupeidae) Alewife American shad Blueback herring Atlantic
SPECIES FACT SHEET. Common Name: Siuslaw Sand Tiger Beetle or Siuslaw Hairy-necked Tiger Beetle
 SPECIES FACT SHEET Common Name: Siuslaw Sand Tiger Beetle or Siuslaw Hairy-necked Tiger Beetle Scientific Name: Cicindela hirticollis siuslawensis (Graves, Krejci, and Graves 1988) Phylum: Arthropoda Class:
SPECIES FACT SHEET Common Name: Siuslaw Sand Tiger Beetle or Siuslaw Hairy-necked Tiger Beetle Scientific Name: Cicindela hirticollis siuslawensis (Graves, Krejci, and Graves 1988) Phylum: Arthropoda Class:
Northwest Ferns. by Gayle Hammond
 Northwest Ferns by Gayle Hammond Content: General Parts Sword Fern Bracken Fern Licorice Fern Lady Fern Deer Fern Giant Chain Fern Spreading Wood Fern Coastal Wood Fern Maiden Fern Shasta Fern Oak Fern
Northwest Ferns by Gayle Hammond Content: General Parts Sword Fern Bracken Fern Licorice Fern Lady Fern Deer Fern Giant Chain Fern Spreading Wood Fern Coastal Wood Fern Maiden Fern Shasta Fern Oak Fern
Salamanders of Idaho. Ambystomatidae Mole Salamanders Long-toed Salamander Barred Tiger Salamander. Dicamptodontidae Idaho Giant Salamander
 Salamanders of Idaho Ambystomatidae Mole Salamanders Long-toed Salamander Barred Tiger Salamander Dicamptodontidae Idaho Giant Salamander Plethodontidae Lungless Salamanders Coeur d Alene Salamander Salamandridae
Salamanders of Idaho Ambystomatidae Mole Salamanders Long-toed Salamander Barred Tiger Salamander Dicamptodontidae Idaho Giant Salamander Plethodontidae Lungless Salamanders Coeur d Alene Salamander Salamandridae
Making the Most of Your Monitoring Using Macroinvertebrates
 Making the Most of Your Monitoring Using Macroinvertebrates Benthic Macroinvertebrates What are they? Why are they important? Provide food for fish and other organisms Feed on algae, organic matter, and
Making the Most of Your Monitoring Using Macroinvertebrates Benthic Macroinvertebrates What are they? Why are they important? Provide food for fish and other organisms Feed on algae, organic matter, and
FAO SPECIES IDENTIFICATION SHEETS FISTULARIIDAE. Cornetfishes, flutemouths
 click for previous page FIST 1982 FAO SPECIES IDENTIFICATION SHEETS FISHING AREA 51 (W. Indian Ocean) FISTULARIIDAE Cornetfishes, flutemouths Body elongate and depressed. Mouth small, at end of a long
click for previous page FIST 1982 FAO SPECIES IDENTIFICATION SHEETS FISHING AREA 51 (W. Indian Ocean) FISTULARIIDAE Cornetfishes, flutemouths Body elongate and depressed. Mouth small, at end of a long
ANNELID LAB. Phylum Annelida
 ANNELID LAB Phylum Annelida Class Oligochaeta 1. Lumbricus terrestris preserved specimen for dissection 2. Lumbricus terrestris cross section slides 3. Lumbricus terrestris longitudinal, whole animal slides
ANNELID LAB Phylum Annelida Class Oligochaeta 1. Lumbricus terrestris preserved specimen for dissection 2. Lumbricus terrestris cross section slides 3. Lumbricus terrestris longitudinal, whole animal slides
CHAPTER 22. Echinoderms 22-1
 CHAPTER 22 Echinoderms 22-1 Phylum Echinodermata: Diversity and Characteristics Characteristics All members have a calcareous skeleton Spiny endoskeleton consists of plates Unique water-vascular system
CHAPTER 22 Echinoderms 22-1 Phylum Echinodermata: Diversity and Characteristics Characteristics All members have a calcareous skeleton Spiny endoskeleton consists of plates Unique water-vascular system
Apogon abrogramma Fraser and Lachner, 1985
 Apogon abrogramma Fraser and Lachner, 1985 English Name: Faintstripe cardinalfish Family: APOGONIDAE Local Name: Ehrongu boadhi Order: Perciformes Size: Common to 7cm; max. 10cm Specimen: MRS/0203/88 Distinctive
Apogon abrogramma Fraser and Lachner, 1985 English Name: Faintstripe cardinalfish Family: APOGONIDAE Local Name: Ehrongu boadhi Order: Perciformes Size: Common to 7cm; max. 10cm Specimen: MRS/0203/88 Distinctive
PHYLUM: PLATHYHELMINTHES
 PHYLUM: PLATHYHELMINTHES FLATWORMS CHARACTERISTICS Free living (living independently i.e. not attached) Bilaterally symmetrical with a definite front and back, and with left and right sides. Mobile creeping
PHYLUM: PLATHYHELMINTHES FLATWORMS CHARACTERISTICS Free living (living independently i.e. not attached) Bilaterally symmetrical with a definite front and back, and with left and right sides. Mobile creeping
FAO SPECIES IDENTIFICATION SHEETS KUHLIIDAE * Flagtails, daras
 click for previous page KUH 1983 FAO SPECIES IDENTIFICATION SHEETS FISHING AREA 51 (W. Indian Ocean) KUHLIIDAE * Flagtails, daras Body oblong, compressed. Maxilla mostly exposed, without supramaxilla;
click for previous page KUH 1983 FAO SPECIES IDENTIFICATION SHEETS FISHING AREA 51 (W. Indian Ocean) KUHLIIDAE * Flagtails, daras Body oblong, compressed. Maxilla mostly exposed, without supramaxilla;
click for previous page 245 General Remarks STOMATOPODS by M. Tavares, Universidade Santa Úrsula, Brazil
 click for previous page 245 General Remarks STOMATOPODS by M. Tavares, Universidade Santa Úrsula, Brazil 246 Stomatopods TECHNICAL TERMS AND MEASUREMENTS antennule eye carapace thoracic stomites 5 6 7
click for previous page 245 General Remarks STOMATOPODS by M. Tavares, Universidade Santa Úrsula, Brazil 246 Stomatopods TECHNICAL TERMS AND MEASUREMENTS antennule eye carapace thoracic stomites 5 6 7
oxfitates AMiiiui?can JMllselIm Threadfin from New Guinea BY J. T. NICHOLS A New Blenny from Bali and a New
 AMiiiui?can JMllselIm oxfitates PUBLISHED BY THE AMERICAN MUSEUM OF NATURAL HISTORY CENTRAL PARK WEST AT 79TH STREET, NEW YORK 24, N.Y. NUMBER i68o JUNE 30, 1954 A New Blenny from Bali and a New Threadfin
AMiiiui?can JMllselIm oxfitates PUBLISHED BY THE AMERICAN MUSEUM OF NATURAL HISTORY CENTRAL PARK WEST AT 79TH STREET, NEW YORK 24, N.Y. NUMBER i68o JUNE 30, 1954 A New Blenny from Bali and a New Threadfin
Which fish is for which state?
 By Jacob Buhrle Which fish is for which state? Oregon Chinook Salmon Florida Sailfish (saltwater) Largemouth Bass (freshwater) Eat or be Eaten: Chinook Salmon They feed on terrestrial and aquatic insects,
By Jacob Buhrle Which fish is for which state? Oregon Chinook Salmon Florida Sailfish (saltwater) Largemouth Bass (freshwater) Eat or be Eaten: Chinook Salmon They feed on terrestrial and aquatic insects,
Perch Dissection Lab
 Perch Dissection Lab Introduction: The fish in the class Osteichthyes have bony skeletons. There are three groups of the bony fish - -- ray-finned fish, lobe-finned fish, and the lung fish. The perch is
Perch Dissection Lab Introduction: The fish in the class Osteichthyes have bony skeletons. There are three groups of the bony fish - -- ray-finned fish, lobe-finned fish, and the lung fish. The perch is
Stonefly. Gilled Snails
 Mid-Michigan Macroinvertebrates Identification Guide & Descriptions Mayfly Nymphs have 3 tail filaments occasionally 2 tail filaments never paddle or fan-like Feathery gills line the sides of the abdomen
Mid-Michigan Macroinvertebrates Identification Guide & Descriptions Mayfly Nymphs have 3 tail filaments occasionally 2 tail filaments never paddle or fan-like Feathery gills line the sides of the abdomen
Phylum Mollusca (soft bodied)
 Phylum Mollusca (soft bodied) Most described species in the animal kingdom next to Phylum Arthropoda ~100,000 species... Marine, freshwater and terrestrial. 35,000 fossil species. Most diverse group of
Phylum Mollusca (soft bodied) Most described species in the animal kingdom next to Phylum Arthropoda ~100,000 species... Marine, freshwater and terrestrial. 35,000 fossil species. Most diverse group of
Field Identification of Tunas from Indian Waters
 3 Field from Indian Waters Subal Kumar Roul and Retheesh T. B. Pelagic Fisheries Division The Family Scombridae is one of the largest and most economically important fish family which comprises of most
3 Field from Indian Waters Subal Kumar Roul and Retheesh T. B. Pelagic Fisheries Division The Family Scombridae is one of the largest and most economically important fish family which comprises of most
Chapter 28 Mollusks & Annelids. BIOLOGY II Miss. Loulousis
 Chapter 28 Mollusks & Annelids BIOLOGY II Miss. Loulousis Mollusks have a true coelom Snails, slugs, oysters, clams, scallops, octopuses, and squids are all mollusks Annelid earthworm next section Mollusks
Chapter 28 Mollusks & Annelids BIOLOGY II Miss. Loulousis Mollusks have a true coelom Snails, slugs, oysters, clams, scallops, octopuses, and squids are all mollusks Annelid earthworm next section Mollusks
2. SYSTEMATIC CATALOGUE
 click for previous page 15 2. SYSTEMATIC CATALOGUE 2.1 General Aids to Identification 2.1.1 Diagnostic Features of the Family Caesionidae Oblong to fusiform, moderately compressed, medium-sized to small
click for previous page 15 2. SYSTEMATIC CATALOGUE 2.1 General Aids to Identification 2.1.1 Diagnostic Features of the Family Caesionidae Oblong to fusiform, moderately compressed, medium-sized to small
NATIONAL BIORESOURCE DEVELOPMENT BOARD Dept. of Biotechnology Government of India, New Delhi
 NATIONAL BIORESOURCE DEVELOPMENT BOARD Dept. of Biotechnology Government of India, New Delhi For office use: MARINE BIORESOURCES FORMS DATA ENTRY: Form- 1(general ) (please answer only relevant fields;
NATIONAL BIORESOURCE DEVELOPMENT BOARD Dept. of Biotechnology Government of India, New Delhi For office use: MARINE BIORESOURCES FORMS DATA ENTRY: Form- 1(general ) (please answer only relevant fields;
Bivalved molluscs filter feeders
 Class Bivalvia Bivalved molluscs have two shells (valves). Mussels, clams, oysters, scallops, shipworms. Mostly sessile filter feeders. No head or radula. Class Bivalvia Part of the mantle is modified
Class Bivalvia Bivalved molluscs have two shells (valves). Mussels, clams, oysters, scallops, shipworms. Mostly sessile filter feeders. No head or radula. Class Bivalvia Part of the mantle is modified
NATIONAL BIORESOURCE DEVELOPMENT BOARD Dept. of Biotechnology Government of India, New Delhi
 NATIONAL BIORESOURCE DEVELOPMENT BOARD Dept. of Biotechnology Government of India, New Delhi For office use: MARINE BIORESOURCES FORMS DATA ENTRY: Form- 1(general ) Ref. No.: (please answer only relevant
NATIONAL BIORESOURCE DEVELOPMENT BOARD Dept. of Biotechnology Government of India, New Delhi For office use: MARINE BIORESOURCES FORMS DATA ENTRY: Form- 1(general ) Ref. No.: (please answer only relevant
CHAPTER 11 STUDY GUIDE 11.1 Dividing Up the Body A. A spacious, fluid-filled coelom provides an efficient hydrostatic skeleton. B. When septa divided
 CHAPTER 11 STUDY GUIDE 11.1 Dividing Up the Body A. A spacious, fluid-filled coelom provides an efficient hydrostatic skeleton. B. When septa divided this coelom into a series of compartments, metamerism
CHAPTER 11 STUDY GUIDE 11.1 Dividing Up the Body A. A spacious, fluid-filled coelom provides an efficient hydrostatic skeleton. B. When septa divided this coelom into a series of compartments, metamerism
NATIONAL BIORESOURCE DEVELOPMENT BOARD Dept. of Biotechnology Government of India, New Delhi
 NATIONAL BIORESOURCE DEVELOPMENT BOARD Dept. of Biotechnology Government of India, New Delhi For office use only MARINE BIORESOURCES FORMS DATA ENTRY: Form- 1(general ) Ref. No.: (please answer only relevant
NATIONAL BIORESOURCE DEVELOPMENT BOARD Dept. of Biotechnology Government of India, New Delhi For office use only MARINE BIORESOURCES FORMS DATA ENTRY: Form- 1(general ) Ref. No.: (please answer only relevant
Asian Swamp Eel Monopterus albus
 Asian Swamp Eel Monopterus albus Significant adverse impacts have yet to be documented, but due to its predatory nature, the Asian swamp eel appears to have the potential for adverse environmental impacts
Asian Swamp Eel Monopterus albus Significant adverse impacts have yet to be documented, but due to its predatory nature, the Asian swamp eel appears to have the potential for adverse environmental impacts
INDICATOR BENTHIC MACROINVERTEBRATE SPECIES AND THEIR CHARACTERISTICS
 Coelenterata (Hydras) Turbellaria (Flatworms) A tube with tentacles Reproduces asexually by budding Movement: sessile, attached or fixed, not free moving Colour: clear to whitish Flattened shape Distinct
Coelenterata (Hydras) Turbellaria (Flatworms) A tube with tentacles Reproduces asexually by budding Movement: sessile, attached or fixed, not free moving Colour: clear to whitish Flattened shape Distinct
Topic Page: Annelida. Annelid Charact erist ics.
 Topic Page: Annelida Definition: annelid from Philip's Encyclopedia Any member of the Annelida phylum of segmented worms. All have encircling grooves usually corresponding to internal partitions of the
Topic Page: Annelida Definition: annelid from Philip's Encyclopedia Any member of the Annelida phylum of segmented worms. All have encircling grooves usually corresponding to internal partitions of the
Chapter 29 Echinoderms and Invertebrate Chordates. Section Echinoderms. I. What Is An Echinoderm? 11/1/2010. Biology II Mrs.
 Chapter 29 Echinoderms and Invertebrate Chordates Section 29.1 - Echinoderms Biology II Mrs. Michaelsen I. What Is An Echinoderm? A. Move by means of hydraulic, suction cuptipped appendages. B. Skin covered
Chapter 29 Echinoderms and Invertebrate Chordates Section 29.1 - Echinoderms Biology II Mrs. Michaelsen I. What Is An Echinoderm? A. Move by means of hydraulic, suction cuptipped appendages. B. Skin covered
Haemulon chrysargyreum Günther, 1859
 click for previous page 1538 Bony Fishes Haemulon chrysargyreum Günther, 1859 Frequent synonyms / misidentifications: Brachygenys chrysargyreus (Günther, 1859 ) / None. FAO names: En - Smallmouth grunt;
click for previous page 1538 Bony Fishes Haemulon chrysargyreum Günther, 1859 Frequent synonyms / misidentifications: Brachygenys chrysargyreus (Günther, 1859 ) / None. FAO names: En - Smallmouth grunt;
Phascolosoma agassizi
 Phascolosoma agassizi Pacific peanut worm Phylum: Annelida Class: Phascolosomatida Order: Phascolosomaformes Family: Phasoclosomatidae Taxonomy: The evolutionary origins of sipunculans, recently considered
Phascolosoma agassizi Pacific peanut worm Phylum: Annelida Class: Phascolosomatida Order: Phascolosomaformes Family: Phasoclosomatidae Taxonomy: The evolutionary origins of sipunculans, recently considered
TWO NEW SPECIES OF COPEPODS JAPANESE FISHES. Author(s) Yamaguti, Satyu; Yamasu, Terufumi.
 Title TWO NEW SPECIES OF COPEPODS JAPANESE FISHES PARASIT Author(s) Yamaguti, Satyu; Yamasu, Terufumi Citation PUBLICATIONS OF THE SETO MARINE BIO LABORATORY (1960), 8(1): 137-140 Issue Date 1960-05-30
Title TWO NEW SPECIES OF COPEPODS JAPANESE FISHES PARASIT Author(s) Yamaguti, Satyu; Yamasu, Terufumi Citation PUBLICATIONS OF THE SETO MARINE BIO LABORATORY (1960), 8(1): 137-140 Issue Date 1960-05-30
British Columbia Lingcod Egg Mass Survey Photo by LEMS volunteer: Jackie Hildering
 British Columbia Lingcod Egg Mass Survey 2010 Photo by LEMS volunteer: Jackie Hildering Kevin Kaufman & Jeff Marliave Vancouver Aquarium August, 2010 Introduction This year marked the 17 th anniversary
British Columbia Lingcod Egg Mass Survey 2010 Photo by LEMS volunteer: Jackie Hildering Kevin Kaufman & Jeff Marliave Vancouver Aquarium August, 2010 Introduction This year marked the 17 th anniversary
Invertebrates. Sponges: Porifera pore bearer 10/3/13
 Animals without backbones We ll cover characteristics of major phyla and some to class level (KPCOFGS) We ll also cover some natural history Refer to your notes that I posted on-line! Invertebrates Levels
Animals without backbones We ll cover characteristics of major phyla and some to class level (KPCOFGS) We ll also cover some natural history Refer to your notes that I posted on-line! Invertebrates Levels
Name Date Period. Mollusk Review TORSION HEMOLYMPH SESSILE TROCHOPHORE ADDUCTOR KIDNEY HEMOCOEL MANTLE CHROMATOPHORES VISCERAL MASS
 Name Date Period Mollusk Review MOLLUSK VOCABULARY: Match the word with its definition. TORSION HEMOLYMPH SESSILE TROCHOPHORE ADDUCTOR KIDNEY HEMOCOEL MANTLE CHROMATOPHORES VISCERAL MASS Free-swimming
Name Date Period Mollusk Review MOLLUSK VOCABULARY: Match the word with its definition. TORSION HEMOLYMPH SESSILE TROCHOPHORE ADDUCTOR KIDNEY HEMOCOEL MANTLE CHROMATOPHORES VISCERAL MASS Free-swimming
FAO SPECIES IDENTIFICATION SHEETS SYNODONTIDAE. Lizardfishes
 click for previous page SYNOD 1474 FAO SPECIES IDENTIFICATION SHEETS FISHING AREAS 57,71 (E Ind. Ocean) (W Cent. Pacific) SYNODONTIDAE Lizardfishes Body elongate, usually cylindrical and with adipose fin.
click for previous page SYNOD 1474 FAO SPECIES IDENTIFICATION SHEETS FISHING AREAS 57,71 (E Ind. Ocean) (W Cent. Pacific) SYNODONTIDAE Lizardfishes Body elongate, usually cylindrical and with adipose fin.
Chapter 30 Nonvertebrate Chordates, Fishes, and Amphibians Name
 Chapter 30 Nonvertebrate Chordates, Fishes, and Amphibians Name Lab Dissecting a Perch Background Information Fish are the largest group of vertebrates found in fresh and salt water. In fact, over 25,000
Chapter 30 Nonvertebrate Chordates, Fishes, and Amphibians Name Lab Dissecting a Perch Background Information Fish are the largest group of vertebrates found in fresh and salt water. In fact, over 25,000
An Unwelcome Newcomer
 An Unwelcome Newcomer An Unwelcome Newcomer This article is provided courtesy of the American Museum of Natural History. million eggs each year. Then Invasion of the Zebra Mussels the young mussels float
An Unwelcome Newcomer An Unwelcome Newcomer This article is provided courtesy of the American Museum of Natural History. million eggs each year. Then Invasion of the Zebra Mussels the young mussels float
THEJ FIRST ZOEA OF PORCELLANA. By W K. BROOKS and E. B. WILSON. With Plate* VI and VII.
 7 "83?* {Jn-fJatoj 11 "T THEJ FIRST ZOEA OF PORCELLANA. By W K BROOKS and E. B. WILSON. With Plate* VI and VII. 7z O THE FIRST ZOEA OF PORCELLANA. By W K. BROOKS and E. B. WILSON. With Plates VI and VII.
7 "83?* {Jn-fJatoj 11 "T THEJ FIRST ZOEA OF PORCELLANA. By W K BROOKS and E. B. WILSON. With Plate* VI and VII. 7z O THE FIRST ZOEA OF PORCELLANA. By W K. BROOKS and E. B. WILSON. With Plates VI and VII.
Phylum Platyhelminthes. You will need: five colours of pencil crayon or pen (preferably blue, green, red, orange and purple)
 Phylum Platyhelminthes You will need: five colours of pencil crayon or pen (preferably blue, green, red, orange and purple) Phylum Platyhelminthes bilaterally symmetrical have all 3 embryonic germ layers:
Phylum Platyhelminthes You will need: five colours of pencil crayon or pen (preferably blue, green, red, orange and purple) Phylum Platyhelminthes bilaterally symmetrical have all 3 embryonic germ layers:
Mollusca: Class Cephalopoda. Lecture 11
 Mollusca: Class Cephalopoda Lecture 11 Cephalophod Characteristics Characteristics of class All marine Most 6-70 cm up to 20m Architeuthis Shell divided by septa, chambers connected by siphuncle Closed
Mollusca: Class Cephalopoda Lecture 11 Cephalophod Characteristics Characteristics of class All marine Most 6-70 cm up to 20m Architeuthis Shell divided by septa, chambers connected by siphuncle Closed
Handbook for the identification of yellowfin and bigeye tunas in fresh, but less than ideal condition
 0 WCPFC SC1 FT IP 1 1st Meeting of the Scientific Committee of the Western and Central Pacific Fisheries Commission WCPFC SC1 Noumea, New Caledonia 8 19 August 2005 Handbook for the identification of yellowfin
0 WCPFC SC1 FT IP 1 1st Meeting of the Scientific Committee of the Western and Central Pacific Fisheries Commission WCPFC SC1 Noumea, New Caledonia 8 19 August 2005 Handbook for the identification of yellowfin
Fish Dissection. Background
 Fish Dissection The Fish Dissection program at Hatfield Marine Science Center is a 50-minute hands-on program for 4th through 12th grade students. Students will work in small groups as they examine a variety
Fish Dissection The Fish Dissection program at Hatfield Marine Science Center is a 50-minute hands-on program for 4th through 12th grade students. Students will work in small groups as they examine a variety
Polychaete Key for Chesapeake Bay and Coastal Virginia
 Polychaete Key for Chesapeake Bay and Coastal Virginia Compiled (with some portions written) and illustrated by Aaron Bartholomew Thanks to the following people for their help on the key: Robert Diaz,
Polychaete Key for Chesapeake Bay and Coastal Virginia Compiled (with some portions written) and illustrated by Aaron Bartholomew Thanks to the following people for their help on the key: Robert Diaz,
30 a. Allothunnus fallai Fig b.
 click for previous page - 18-30 a. Jaw teeth tiny, 40 to 55 on each side of upper and lower jaws; gillrakers fine and numerous, total of 70 to 80 on first arch; body elongate; distance from snout to second
click for previous page - 18-30 a. Jaw teeth tiny, 40 to 55 on each side of upper and lower jaws; gillrakers fine and numerous, total of 70 to 80 on first arch; body elongate; distance from snout to second
1. Animals are (diploid) with tissues arranged into organs and organ systems. 3. Animals require for aerobic respiration.
 Chapter 25 Animals: The Invertebrates I. Overview of the Animal Kingdom A. General Characteristics of Animals 1. Animals are (diploid) with tissues arranged into organs and organ systems. 2. Animals are.
Chapter 25 Animals: The Invertebrates I. Overview of the Animal Kingdom A. General Characteristics of Animals 1. Animals are (diploid) with tissues arranged into organs and organ systems. 2. Animals are.
ARTHROPODS JOINTED-LEGS ARTHROPODS ARE THE LARGEST GROUP OF ANIMALS!
 ARTHROPODS JOINTED-LEGS ARTHROPODS ARE THE LARGEST GROUP OF ANIMALS! WHO S WHO? SHRIMP ISOPOD SPIDER CRAB BARNACLE LOBSTER BASIC CHARACTERISTICS BILATERAL SYMMETRY SEGMENTED ANIMALS JOINTED BODY & PARTS
ARTHROPODS JOINTED-LEGS ARTHROPODS ARE THE LARGEST GROUP OF ANIMALS! WHO S WHO? SHRIMP ISOPOD SPIDER CRAB BARNACLE LOBSTER BASIC CHARACTERISTICS BILATERAL SYMMETRY SEGMENTED ANIMALS JOINTED BODY & PARTS
Biology and Ecological Impacts of the European Green Crab, Carcinus maenas, on the Pacific Coast of Canada
 Biology and Ecological Impacts of the European Green Crab, Carcinus maenas, on the Pacific Coast of Canada G.E. Gillespie and T.W. Therriault Fisheries and Oceans Canada Pacific Biological Station Green
Biology and Ecological Impacts of the European Green Crab, Carcinus maenas, on the Pacific Coast of Canada G.E. Gillespie and T.W. Therriault Fisheries and Oceans Canada Pacific Biological Station Green
ADVANCED INVERTEBRATES HAVE COMPLEX BODIES AND INTERNAL SYSTEMS
 ADVANCED INVERTEBRATES HAVE COMPLEX BODIES AND INTERNAL SYSTEMS Arthropoda Most successful phylum on Earth Exoskeleton chitin Striated muscle Articulation Crayfish, lobsters, shrimp, crabs Echinodermata
ADVANCED INVERTEBRATES HAVE COMPLEX BODIES AND INTERNAL SYSTEMS Arthropoda Most successful phylum on Earth Exoskeleton chitin Striated muscle Articulation Crayfish, lobsters, shrimp, crabs Echinodermata
Green Sturgeon Feeding Observations in Humboldt Bay, California
 Green Sturgeon Feeding Observations in Humboldt Bay, California Matt Goldsworthy 1, Bill Pinnix, Miles Barker 1, Liz Perkins 1, Aaron David, Jeffrey Jahn 1 Introduction Understanding the distribution,
Green Sturgeon Feeding Observations in Humboldt Bay, California Matt Goldsworthy 1, Bill Pinnix, Miles Barker 1, Liz Perkins 1, Aaron David, Jeffrey Jahn 1 Introduction Understanding the distribution,
The Animal Kingdom. Animal Kingdom. Characteristics of All Animals. Major Characteristics Used To Classify Animals
 The Animal Kingdom Animal Kingdom Phylums: 1. Sponges 2. Cnidaria Jelly Fish, Hydra 3. Flatworms Flukes, Tapeworms 4. Roundworms- Hookworms 5. Segmented Worms- Earthworms 6. Rotifera- Rotifers 7. Mullusca
The Animal Kingdom Animal Kingdom Phylums: 1. Sponges 2. Cnidaria Jelly Fish, Hydra 3. Flatworms Flukes, Tapeworms 4. Roundworms- Hookworms 5. Segmented Worms- Earthworms 6. Rotifera- Rotifers 7. Mullusca
Microbrotula randalli Cohen and Wourms, Samoa and Vanuatu at 30 to 38 m near reef-sand interface. Rare.
 click for previous page Ophidiiform Fishes of the World 107 Diagnosis and description: Body completely covered with small imbricate scales; head partly naked; snout depressed; eyes small, more than 6 times
click for previous page Ophidiiform Fishes of the World 107 Diagnosis and description: Body completely covered with small imbricate scales; head partly naked; snout depressed; eyes small, more than 6 times
Symmetry. Asymmetrical- no shape. Radial- same in half when cut any angle. Bilateral- having a distinct right and left side
 Symmetry Asymmetrical- no shape Radial- same in half when cut any angle Bilateral- having a distinct right and left side Invertebrates 95% of Animals No Backbone The simplest animals and they do not have
Symmetry Asymmetrical- no shape Radial- same in half when cut any angle Bilateral- having a distinct right and left side Invertebrates 95% of Animals No Backbone The simplest animals and they do not have
Student Handout #2 Using Abiotic and Biotic Parameters to Monitor Water Quality: A Field Experiment
 Student Handout #2 Using Abiotic and iotic Parameters to Monitor Water Quality: A Field Experiment Group One Taxa Pollution sensitive organisms found in good quality water, index value is 3. The order
Student Handout #2 Using Abiotic and iotic Parameters to Monitor Water Quality: A Field Experiment Group One Taxa Pollution sensitive organisms found in good quality water, index value is 3. The order
