In the Belly of the Whale
|
|
|
- Alban McDaniel
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Timeframe 1-2 Fifty minute class periods Target Audience Grades 4th- 6th Suggested Materials Comb Small sieve Straws Small plastic beads, rice, black pepper Container for water (3 stations for each group) Station cards Description Students work in cooperative groups and participate in a hands-on activity that simulates the feeding methods of the humpback, right, and gray whales. Students collect data and construct a bar graph to compare the feeding styles of these three baleen whales, and share findings with the class. Objectives Students will: Understand the different feeding strategies used by whales Describe the feeding behavior of three species of baleen whales Develop a prediction Collect and graph mock data Essential Questions How are the feeding methods of baleen whales similar and different? Why do baleen whales use different feeding strategies? Background Information Whales are very large mammals that consume large amounts of food each day. The more aggressive predators are the Toothed Whales (Odontoceti) and they eat larger fish and other aquatic life such as squid and seals. Even though these larger whales do have teeth, most of them don t use them to tear apart their food. They use the teeth for the killing process only. Then they end up swallowing their prey whole. Contact: SMILE Program smileprogram@oregonstate.edu Baleen whales have a type of filtering system in their jaw. This allows them to catch a great deal that is in the water, keep what is food, and then to filter out the rest. Generally, they will eat smaller sized prey, such as zooplankton, krill, amphipods and smaller fish. On average, a whale will eat 4% of its body weight as long as there is enough food readily available. Baleen whales can be gulpers, skimmers, and suckers.
2 Gulpers are whales that have throat grooves that expand when they are feeding and their mouths are filled with water. Their feeding behavior is also sometimes referred to as lunging, as they propel through the water to gather food. The water is gulped then forced through the baleen, filtering out krill and small fish. This baleen will be tougher than skimmers but not as thick and tough as sucking baleen. Gulpers include whales such as the Humpback Whale and the Blue Whale. Skimmers include the Right Whale. These whales often feed near the surface, with their mouths open to filter out small organisms called copepods and krill for food. Blue whale baleen will be feathery, as these whales are only filtering krill or copepods from the water. Suckers include the Gray Whale family. When feeding, gray whales roll on their sides with their mouths parallel to the ocean floor. They pull their huge tongues into the back of their mouths, sucking huge amounts of mud, and everything in the mud, into their mouths. The mouthful of mud and water is pushed through the baleen to filter out the amphipods. Baleen for this method of feeding will be tough, thick, and durable, as these whales must filter mud and sand. Preparation Fill the three containers with water. Use the permanent marker to label three paper towels with the name of each whale group: gulper (bubble-netters), lunge feeder, and sucker. Sprinkle small beads and pepper in the bowls of water and add rice grains to sink to the bottom. These items will represent whale food items such as zooplankton and small fish. Put out station signs at each bowl. Next Generation Science Standards PERFORMANCE EXPECTATIONS: MS-LS2-1. Analyze and interpret data to provide evidence for the effects of resource availability on organisms and populations of organisms in an ecosystem. DISCIPLINARY CORE IDEAS: LS2.A.: Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems LS2.C.: Ecosystem Dynamics, Functioning and Resiliance SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING PRACTICES: Developing and Using Models Analyzing and Interpreting Data CROSSCUTTING CONCEPTS: Structure and Function Systems and Systems Models Energy and Matter Activity Introduction Show students the following video clips of the different types of feeding strategies of Gray, Humpback, and Right whales. Discuss: what did you see? What did you wonder about it? What do you wonder? Discuss the different feeding strategies and which whales use them. Right whales feed by skimming the ocean surface with their mouths open. They use the filter-like baleen structures in their mouths to catch food items such as small crustaceans or fish. Right whale feeding video: Gray whales are a sucker species. They have expandable throat pouches that can hold larger volumes of seawater and prey. Gray whale feeding video: Humpback whales are a gulper species. Many humpbacks feed cooperativelyin groups by using a strategy called bubblenetting. Humpback whale feeding video:
3 z00g0rxesp0 Activity: 1. Divide students into groups of three. Tell them that they will test out the different feeding strategies of the three whales in each of the containers. Have them read the station cards and review the equipment available. Ask them to make predictions: which feeding strategies will be the most efficient at collecting the beads or the rice, pepper (plankton and fish)? 2. Direct students to collect the beads, pepper and rice using the different utensils. Give them 15 seconds per utensil. Have students discuss which utensil worked the best on which food type and identify which whale would use this method of feeding. Have them save paper towels with food until the end of the activity. 3. Once students have tested all feeding strategies, have them place all three labeled paper towels next to each other and examine them closely. What general observations can they make from this rough comparison? 4. Count the simulated prey items on each paper towel. Record the data in the table. 5. Have students create a graphical representation of their findings. 6. Have each group report (either in writing or orally) on their most successful method of feeding and which whale it represents. Have students include their predication, how accurate were they? 7. Have students compare their findings with those of their fellow student-scientists. Did others have similar or dissimilar results? Wrap Up Which feeding style captured the most prey? Can you explain why? Which feeding style captured the least prey? Can you explain why? What was realistic and not realistic about this simulation? Why might whales have different feeding strategies? Is one strategy better than another? Extension Have students research and report on one of the whales that they learned about (or another species of whale).
4 This project is supported by the Regional Class Research Vessel Program in the College of Earth, Ocean, and Atmospheric Sciences at Oregon State University. Resources Marine Mammal Institute: pdf Whale Feast Feeding Discovery Lab: Whale%20Feast%20Feeding%20Discovery%20Lab.pdf
5 Station 1 Discovery Card Humpback Whales Humpbacks feed on herring and on swarms of small shrimp-like animals, called krill, by lunging. They have an interesting manner of feeding called bubble-net feeding. They blow curtains of bubbles, to trap their food. An individual whale can make a bubble-net, or a team of up to 20 hump- backs working together can make huge nets to encircle the fish. The humpbacks are believed to use their long, white flippers to herd fish. They then open their mouths and swim up through the bubble net to gulp up the fish. Simulate the feeding of the humpback whale by using the plastic pocket combs to represent their baleen and drinking straws to represent their blowholes. Use the drinking straws to gently blow bubbles into the water near the outer edges of the container. Station 2 Discovery Card Gray Whales Gray whales are filter feeders, sifting their food through baleen plates. But unlike any other species of whale, grey whales strain the sediment of the sea floor for food. Individuals roll onto their sides after diving to the bottom and take large amounts of sediment into their mouth. As the whale rises to the surface, it strains the contents of the mouth through the baleen, leaving a trail of mud and sand behind it. Gray whales eat tiny amphipods, shrimp-like animals that live inside that sediment among other tiny animals scraped up from the floor. Simulate Gray whale feeding by using a comb to represent baleen that scrapes food up from the bottom and lets the water run it through leaving prey items. Station 3 Discovery Card Right Whales The Right whale diet consists almost exclusively of krill, a type of plankton. When these whales hunt for food they swim towards large schools of krill with their mouth open and engulf both their prey along with the surrounding water. They then push the water out of their mouth with their tongue while keeping the krill trapped inside their baleen bristles. Simulate Right whale feeding by running a small sieve across the top of the water to represent the open mouth of the whale capturing its prey.
6 Student Activity Handout
Breathing, Feeding, & Moving in Water
 Breathing, Feeding, & Moving in Water Overview Students will learn about whale adaptations for breathing, feeding, and moving in water. Before Your Visit: Students will read and discuss a text about whale
Breathing, Feeding, & Moving in Water Overview Students will learn about whale adaptations for breathing, feeding, and moving in water. Before Your Visit: Students will read and discuss a text about whale
Breathing, Feeding, & Moving in Water
 Breathing, Feeding, & Moving in Water Overview Students will learn about whale adaptations for,, and in water. Before Your Visit: Students will read or listen to a text about whale adaptations to life
Breathing, Feeding, & Moving in Water Overview Students will learn about whale adaptations for,, and in water. Before Your Visit: Students will read or listen to a text about whale adaptations to life
Breathing, Feeding, & Moving in Water
 Breathing, Feeding, & Moving in Water Activities for Overview Students will learn about whale adaptations for,, and in water. Before Your Visit: Students will read or listen to a text about whale adaptations
Breathing, Feeding, & Moving in Water Activities for Overview Students will learn about whale adaptations for,, and in water. Before Your Visit: Students will read or listen to a text about whale adaptations
WhaleWorks: Student Booklet
 2009 SMILE Winter Teacher Workshop High School Club Activities : Student Booklet STATION A: Good Vibrations At this station, you will be using tuning forks to experiment how sound travels through, air,
2009 SMILE Winter Teacher Workshop High School Club Activities : Student Booklet STATION A: Good Vibrations At this station, you will be using tuning forks to experiment how sound travels through, air,
MARINE MAMMALS. Species: Feeding: Breathing adaptations? Seasonality: What species can be commonly seen locally? baleen or teeth?
 MARINE MAMMALS The order Cetacea, which includes whales, dolphins, and porpoises is divided into two suborders: Mysticeti and Odontoceti. For the suborders below, list the species commonly sighted in Virginia
MARINE MAMMALS The order Cetacea, which includes whales, dolphins, and porpoises is divided into two suborders: Mysticeti and Odontoceti. For the suborders below, list the species commonly sighted in Virginia
Cetaceans (Toothed & Baleen Whales)
 Cetaceans (Toothed & Baleen Whales) By: Christa Jewett, Instructor For since the creation of the world God s invisible qualities His eternal power and divine nature have been clearly seen, being understood
Cetaceans (Toothed & Baleen Whales) By: Christa Jewett, Instructor For since the creation of the world God s invisible qualities His eternal power and divine nature have been clearly seen, being understood
Whales. Visit for thousands of books and materials. A Reading A Z Level O Leveled Reader Word Count: 1,106
 LEVELED READER O Written by Vic Moors www.readinga-z.com Whales A Reading A Z Level O Leveled Reader Word Count: 1,106 Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials. Written by Vic Moors
LEVELED READER O Written by Vic Moors www.readinga-z.com Whales A Reading A Z Level O Leveled Reader Word Count: 1,106 Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials. Written by Vic Moors
Marine predators and prey
 Science Unit: Lesson 5: Beluga Whale Marine predators and prey School Year: 2015/2016 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Notes: Champlain Heights Annex, Vancouver School District
Science Unit: Lesson 5: Beluga Whale Marine predators and prey School Year: 2015/2016 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Notes: Champlain Heights Annex, Vancouver School District
Lesson 11: Introduction to Right Whales
 Cetaceans 4 th Grade Curriculum Lesson 11: Introduction to Right Whales Page 11-1 Lesson 11: Introduction to Right Whales Objectives: Students will learn about North Atlantic right whale life histories.
Cetaceans 4 th Grade Curriculum Lesson 11: Introduction to Right Whales Page 11-1 Lesson 11: Introduction to Right Whales Objectives: Students will learn about North Atlantic right whale life histories.
Dissecting data. Amanda Bromilow Virginia Institute of Marine Science. Grade Level Middle School. Subject area Life, Environmental, or Marine Science
 Dissecting data Amanda Bromilow Virginia Institute of Marine Science Grade Level Middle School Subject area Life, Environmental, or Marine Science This work is sponsored by the National Estuarine Research
Dissecting data Amanda Bromilow Virginia Institute of Marine Science Grade Level Middle School Subject area Life, Environmental, or Marine Science This work is sponsored by the National Estuarine Research
Zooplankton Migration Patterns at Scotton Landing: Behavioral Adaptations written by Lauren Zodl, University of Delaware
 Zooplankton Migration Patterns at Scotton Landing: Behavioral Adaptations written by Lauren Zodl, University of Delaware Summary: Zooplankton have evolved specific migration patterns that increase their
Zooplankton Migration Patterns at Scotton Landing: Behavioral Adaptations written by Lauren Zodl, University of Delaware Summary: Zooplankton have evolved specific migration patterns that increase their
Wyland Transparencies
 Table of Contents Introduction...3 How to Use This ook...4 Cross-Curricular Activities...5 Standards and enchmarks...6 Wyland: Artist of the Sea...7 Wylie Whale s Wonderful Journey...9 Wylie s Journey
Table of Contents Introduction...3 How to Use This ook...4 Cross-Curricular Activities...5 Standards and enchmarks...6 Wyland: Artist of the Sea...7 Wylie Whale s Wonderful Journey...9 Wylie s Journey
Barnacles attach to hard surfaces and use their legs to catch tiny particles of food, including plankton from the water around them.
 Food Web Resources - Food Chain Cards Barnacles attach to hard surfaces and use their legs to catch tiny particles of food, including plankton from the water around them Barnacle Edible crabs use their
Food Web Resources - Food Chain Cards Barnacles attach to hard surfaces and use their legs to catch tiny particles of food, including plankton from the water around them Barnacle Edible crabs use their
The Great Barrier Reef
 The Great Barrier Reef The Great Barrier Reef Where are the most biologically diverse places on the planet? If I asked you this question, you might guess the Amazon rainforest in Brazil or the jungles
The Great Barrier Reef The Great Barrier Reef Where are the most biologically diverse places on the planet? If I asked you this question, you might guess the Amazon rainforest in Brazil or the jungles
The Pelagic Zone.! The open ocean is called the pelagic zone.!
 The Open Ocean The Pelagic Zone! The open ocean is called the pelagic zone.! Epipelagic! We will focus on the top 200 m or 650 feet called the epipelagic zone.!! The photic zone is to a depth where light
The Open Ocean The Pelagic Zone! The open ocean is called the pelagic zone.! Epipelagic! We will focus on the top 200 m or 650 feet called the epipelagic zone.!! The photic zone is to a depth where light
Grade 4 English Language Arts/Literacy End of Year M/L Informational Text Set 2017 Released Items
 Partnership for Assessment of Readiness for College and Careers Grade 4 English Language Arts/Literacy End of Year M/L Informational Text Set 2017 Released Items 2017 Released Items: Grade 4 End of Year
Partnership for Assessment of Readiness for College and Careers Grade 4 English Language Arts/Literacy End of Year M/L Informational Text Set 2017 Released Items 2017 Released Items: Grade 4 End of Year
Ocean Current Worksheet
 Ocean Current Worksheet Temperature Affects and Surface Currents: Surface waters of the Earth s oceans are forced to move, primarily by winds. Where winds blow in the same direction for a long period of
Ocean Current Worksheet Temperature Affects and Surface Currents: Surface waters of the Earth s oceans are forced to move, primarily by winds. Where winds blow in the same direction for a long period of
WHALES. & Whale Sharks
 WHALES & Whale Sharks Introduction Today we are going to learn about the biggest mammals of the ocean and one animal that is commonly mistaken for a whale but is actually a fish. Whale is the common name
WHALES & Whale Sharks Introduction Today we are going to learn about the biggest mammals of the ocean and one animal that is commonly mistaken for a whale but is actually a fish. Whale is the common name
Wendy s Whale Watching Trip by Wally Gutierrez
 Wendy s Whale Watching Trip by Wally Gutierrez How will we know when whales are close? Will we hear them? asked Wendy. She was whale watching for the very first time. The thought of seeing a whale up close
Wendy s Whale Watching Trip by Wally Gutierrez How will we know when whales are close? Will we hear them? asked Wendy. She was whale watching for the very first time. The thought of seeing a whale up close
Lesson 3: Which fish should I eat?
 Lesson 3: Which fish should I eat? Objectives: Students will know how to answer the question, Are some fish less harmful to eat from the Hudson River than others? and be able to provide evidence to support
Lesson 3: Which fish should I eat? Objectives: Students will know how to answer the question, Are some fish less harmful to eat from the Hudson River than others? and be able to provide evidence to support
food chain checkers Lesson Plans and Activities for the Classroom
 Lesson Plans and Activities for the Classroom www.windows.ucar.edu food chain checkers Summary Source Grade Level 5-9 Time Student Learning Outcomes National Standards Students play a game that models
Lesson Plans and Activities for the Classroom www.windows.ucar.edu food chain checkers Summary Source Grade Level 5-9 Time Student Learning Outcomes National Standards Students play a game that models
Dinner Dilemma [Grades 3-5]
![Dinner Dilemma [Grades 3-5] Dinner Dilemma [Grades 3-5]](/thumbs/93/112477039.jpg) Dinner Dilemma [Grades 3-5] Georgia Standards of Excellence Addressed: S4L1. Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information about the roles of organisms and the flow of energy within an ecosystem. a. Develop
Dinner Dilemma [Grades 3-5] Georgia Standards of Excellence Addressed: S4L1. Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information about the roles of organisms and the flow of energy within an ecosystem. a. Develop
Orca Comprehension. Name:
 Whales Name: There are two main types of whale, toothed and baleen. Baleen whales are generally larger than toothed whales and tend to be solitary mammals this means they mainly travel alone. Toothed whales
Whales Name: There are two main types of whale, toothed and baleen. Baleen whales are generally larger than toothed whales and tend to be solitary mammals this means they mainly travel alone. Toothed whales
Lesson 10: Oyster Reefs and Their Inhabitants
 Lesson 10: Oyster Reefs and Their Inhabitants Focus Question: What animals use oyster reefs for habitats? Objective: observe properties of animals found within a bag of oysters; Infer about the quality
Lesson 10: Oyster Reefs and Their Inhabitants Focus Question: What animals use oyster reefs for habitats? Objective: observe properties of animals found within a bag of oysters; Infer about the quality
Seventh Grade. Maui Ocean Center Learning Worksheet. Name: Our mission is to foster understanding, wonder and respect for Hawai i s Marine Life.
 Name: Maui Ocean Center Learning Worksheet Seventh Grade Our mission is to foster understanding, wonder and respect for Hawai i s Marine Life. Based on benchmarks SC.6.3.1, SC. 7.3.1, SC. 7.3.2, SC. 7.5.4
Name: Maui Ocean Center Learning Worksheet Seventh Grade Our mission is to foster understanding, wonder and respect for Hawai i s Marine Life. Based on benchmarks SC.6.3.1, SC. 7.3.1, SC. 7.3.2, SC. 7.5.4
Temperature Main thermocline is present in the mesopelagic Relatively constant at the ocean depths, below 1000m About 35 F = 2 C
 Number of species Marine ecosystems 6: Deep Sea Delimited by the photic zone (200m) and the bottom of the ocean Mesopelagic Ocean depths 200-1000m Below 1000m Unique features Lack of primary production
Number of species Marine ecosystems 6: Deep Sea Delimited by the photic zone (200m) and the bottom of the ocean Mesopelagic Ocean depths 200-1000m Below 1000m Unique features Lack of primary production
Oh, the tension (1 Hour)
 Oh, the tension (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 2 Grade Range: K-2 OVERVIEW In this activity, students carefully add drops of liquids to the surface of a penny to help them understand the
Oh, the tension (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 2 Grade Range: K-2 OVERVIEW In this activity, students carefully add drops of liquids to the surface of a penny to help them understand the
E D U C ATIO N A L A C TIVIT Y G UID E
 E D U C ATIO N A L A C TIVIT Y G UID E An Amazing Journey Across Our Planet Starting April 22, 2009 the 40 th anniversary of Earth Day you and your students are invited to share an unforgettable true-life
E D U C ATIO N A L A C TIVIT Y G UID E An Amazing Journey Across Our Planet Starting April 22, 2009 the 40 th anniversary of Earth Day you and your students are invited to share an unforgettable true-life
Whales are warm-blooded mammals that live in the sea, breathe air, and nurse their young with mother's milk. They are often called marine mammals
 EDUCATION RESOURCES: Facts about whales, dolphins and porpoises What is a whale? Whales are warm-blooded mammals that live in the sea, breathe air, and nurse their young with mother's milk. They are often
EDUCATION RESOURCES: Facts about whales, dolphins and porpoises What is a whale? Whales are warm-blooded mammals that live in the sea, breathe air, and nurse their young with mother's milk. They are often
ZOOPLANKTON. Zooplankton: 2. Crustaceans Copepods. Diverse -- protozoans and others
 ZOOPLANKTON Diverse -- protozoans and others Nutrition modes: Herbivores (graze on phytoplankton) Carnivores (predators) Radiolaria Foraminifera Zooplankton: 1. Protozoans: Foraminifera and Radiolarians
ZOOPLANKTON Diverse -- protozoans and others Nutrition modes: Herbivores (graze on phytoplankton) Carnivores (predators) Radiolaria Foraminifera Zooplankton: 1. Protozoans: Foraminifera and Radiolarians
Ocean. T he ocean covers about 71 percent of the earth. The shallow part of the ocean. 1 Photocopy pages Cut out all the pieces
 Flip open the pages of this mini-book to shed light on the layers of the ocean. Habitat Hallmarks T he ocean covers about 71 percent of the earth. The shallow part of the ocean lies above the continental
Flip open the pages of this mini-book to shed light on the layers of the ocean. Habitat Hallmarks T he ocean covers about 71 percent of the earth. The shallow part of the ocean lies above the continental
ORCA s Whale Education Month Lesson Pack 2: Marine Litter
 ORCA s Whale Education Month Lesson Pack 2: Marine Litter Photo Credit: Colin Kilpatrick Learn more about one of the biggest threats facing our wildlife today marine litter. Your students will investigate
ORCA s Whale Education Month Lesson Pack 2: Marine Litter Photo Credit: Colin Kilpatrick Learn more about one of the biggest threats facing our wildlife today marine litter. Your students will investigate
Marine Ecosystems. Aquatic Ecosystems Section 2
 Marine Ecosystems Marine ecosystems are located mainly in coastal areas and in the open ocean. Organisms that live in coastal areas adapt to changes in water level and salinity. Organisms that live in
Marine Ecosystems Marine ecosystems are located mainly in coastal areas and in the open ocean. Organisms that live in coastal areas adapt to changes in water level and salinity. Organisms that live in
2010 Teacher Created Resources, Inc.
 Editor Erica N. Russikoff, M.A. Illustrator Clint McKnight Cover Artist Brenda DiAntonis Editor in Chief Ina Massler Levin, M.A. Creative Director Karen J. Goldfluss, M.S. Ed. Art Coordinator Renée Christine
Editor Erica N. Russikoff, M.A. Illustrator Clint McKnight Cover Artist Brenda DiAntonis Editor in Chief Ina Massler Levin, M.A. Creative Director Karen J. Goldfluss, M.S. Ed. Art Coordinator Renée Christine
This article is provided courtesy of the American Museum of Natural History.
 Long Term Monitoring of the Hudson River Long-Term Monitoring of the Hudson River This article is provided courtesy of the American Museum of Natural History. A puzzling reversal In 2005, 14 years after
Long Term Monitoring of the Hudson River Long-Term Monitoring of the Hudson River This article is provided courtesy of the American Museum of Natural History. A puzzling reversal In 2005, 14 years after
Prior Knowledge: Students should have an understanding that plants and animals compete for resources such as food, space, water, air and shelter.
 Science Lesson Plan Form Teacher: 4 th Grade Lesson: Predator/Prey SPI: 2.1 Science Goal: Recognize the impact of predation and competition on an ecosystem. What is the big idea of this standard? All life
Science Lesson Plan Form Teacher: 4 th Grade Lesson: Predator/Prey SPI: 2.1 Science Goal: Recognize the impact of predation and competition on an ecosystem. What is the big idea of this standard? All life
;DG:HIH Plankton
 or coral reefs near the shore of the ocean it is easy for us to see the various parts of an ecosystem, especially because the near-shore ecosystems tend to be particularly productive and have a high level
or coral reefs near the shore of the ocean it is easy for us to see the various parts of an ecosystem, especially because the near-shore ecosystems tend to be particularly productive and have a high level
Build Your Own Zooplankton
 Build Your Own Zooplankton Grade Level: This specific lesson is geared towards grades 9-12, but it can be modified for older or younger students. Lesson Summary: Students will use their knowledge of zooplankton
Build Your Own Zooplankton Grade Level: This specific lesson is geared towards grades 9-12, but it can be modified for older or younger students. Lesson Summary: Students will use their knowledge of zooplankton
Oceanic Zone. Open ocean past the continental shelf. Water can be very deep. Nutrients are scarce. Fewer organisms live in this zone
 Oceanic Zone Oceanic Zone Open ocean past the continental shelf Water can be very deep Nutrients are scarce Fewer organisms live in this zone Includes photic and aphotic zones Photic Zone Top 200m of
Oceanic Zone Oceanic Zone Open ocean past the continental shelf Water can be very deep Nutrients are scarce Fewer organisms live in this zone Includes photic and aphotic zones Photic Zone Top 200m of
Our Council s Own: Oceanography Cadette/Senior/Ambassador Badge
 Our Council s Own: Oceanography Cadette/Senior/Ambassador Badge Oceanography: The science that deals with oceans, the delimitation of their extent and depth, the physics and chemistry of their water, marine
Our Council s Own: Oceanography Cadette/Senior/Ambassador Badge Oceanography: The science that deals with oceans, the delimitation of their extent and depth, the physics and chemistry of their water, marine
Subject-Verb Agreement
 Name The Midnight Ride Subject-Verb greement The subject and verb in a sentence must agree, or work together. singular subject needs a singular verb. plural subject needs a plural verb. Use the following
Name The Midnight Ride Subject-Verb greement The subject and verb in a sentence must agree, or work together. singular subject needs a singular verb. plural subject needs a plural verb. Use the following
Lesson 2 Adaptations. Performance Objectives Students will:
 Lesson 2 Adaptations Overview The class will engage in a lab demonstrating the ways in which whales benefit from being so large. Students will create an imaginary creature with adaptations to survive in
Lesson 2 Adaptations Overview The class will engage in a lab demonstrating the ways in which whales benefit from being so large. Students will create an imaginary creature with adaptations to survive in
OIMB GK12 CURRICULUM. Beach Hopper Introduction and Jumping Experiment
 OIMB GK12 CURRICULUM 2 nd grade 1 hour (or broken into two lessons) Beach Hopper Introduction and Jumping Experiment Oregon Science Content Standards: 2.1 Structure and Function: Living and non-living
OIMB GK12 CURRICULUM 2 nd grade 1 hour (or broken into two lessons) Beach Hopper Introduction and Jumping Experiment Oregon Science Content Standards: 2.1 Structure and Function: Living and non-living
6 Producers and Consumers
 6 Producers and Consumers In k e l p f o r e s t s or coral reefs near the shore of the ocean it is easy for us to see the various parts of an ecosystem, especially because the near-shore ecosystems tend
6 Producers and Consumers In k e l p f o r e s t s or coral reefs near the shore of the ocean it is easy for us to see the various parts of an ecosystem, especially because the near-shore ecosystems tend
Where the Wind Blows. Credits: Elizabeth Gall & Laura Moribe, University of Tennessee Extension. Background. Introduction and Opening Questions
 Where the Wind Blows W 336-F Credits: Elizabeth Gall & Laura Moribe, University of Tennessee Extension Skill Level 5th & 6th grade Learner Outcomes Youth will be able to list two factors that cause ocean
Where the Wind Blows W 336-F Credits: Elizabeth Gall & Laura Moribe, University of Tennessee Extension Skill Level 5th & 6th grade Learner Outcomes Youth will be able to list two factors that cause ocean
Have You Wondered? College of Marine Sciences, Shanghai Ocean University
 Have You Wondered? 1. What role sponges play in marine ecosystems? 2. Why some animals are radially symmetrical? 3. If all gelatinous animals are jellyfishes? 4. What flatworms are? 5. What a lophophorate
Have You Wondered? 1. What role sponges play in marine ecosystems? 2. Why some animals are radially symmetrical? 3. If all gelatinous animals are jellyfishes? 4. What flatworms are? 5. What a lophophorate
Hudson River Food Webs
 Name Date Part 1: Introduction to the In part one, you will learn about food chains in one of the major environments in the Hudson River: marsh, brackish channel, freshwater channel, or freshwater shallows.
Name Date Part 1: Introduction to the In part one, you will learn about food chains in one of the major environments in the Hudson River: marsh, brackish channel, freshwater channel, or freshwater shallows.
Origin and Importance! ! Fish were the first vertebrates to appear on Earth about 500 million years ago.
 2/9/14 Origin and Importance Evolution Marine Fish Fish were the first vertebrates to appear on Earth about 500 million years ago. Fish are the most economically important organism and are a vital source
2/9/14 Origin and Importance Evolution Marine Fish Fish were the first vertebrates to appear on Earth about 500 million years ago. Fish are the most economically important organism and are a vital source
WHALE EXPLORATION. Use your imagination to take yourself on a virtual field trip with Ocean Connectors!
 WHALE EXPLORATION Use your imagination to take yourself on a virtual field trip with Ocean Connectors! This is the boat we will be boarding today! It is called the Marietta. It is 90 feet long. This is
WHALE EXPLORATION Use your imagination to take yourself on a virtual field trip with Ocean Connectors! This is the boat we will be boarding today! It is called the Marietta. It is 90 feet long. This is
LEVEL M TABE 11 & 12 READING OTT. Whale Watching. Read the passage. Then answer questions 1 through 7.
 Read the passage. Then answer questions 1 through 7. Whale Watching Across the blue, rolling waves, a dark hump rises from the sea. It slides out of sight as an enormous tail lifts and falls. As it does,
Read the passage. Then answer questions 1 through 7. Whale Watching Across the blue, rolling waves, a dark hump rises from the sea. It slides out of sight as an enormous tail lifts and falls. As it does,
2016 West Coast Entanglement Summary
 March 2017 2016 West Coast Entanglement Summary Overview of Entanglement Data west coast region MMHSRP Permit #18786 In 2016, 71 separate cases of entangled whales were reported off the coasts of Washington,
March 2017 2016 West Coast Entanglement Summary Overview of Entanglement Data west coast region MMHSRP Permit #18786 In 2016, 71 separate cases of entangled whales were reported off the coasts of Washington,
6 Producers and Consumers IN KELP FORESTS or coral reefs near the shore of the ocean it is easy for us to see
 6 Producers and Consumers IN KELP FORESTS or coral reefs near the shore of the ocean it is easy for us to see the various parts of an ecosystem, especially because the near-shore ecosystems tend to be
6 Producers and Consumers IN KELP FORESTS or coral reefs near the shore of the ocean it is easy for us to see the various parts of an ecosystem, especially because the near-shore ecosystems tend to be
Nekton and Benthos. Nekton DISCUSSION:
 Equipment for general class use: Nekton and Benthos a set of videos from selected sources a set of well labeled specimens in phylogenetic order DISCUSSION: Nekton Nekton is a term that applies to those
Equipment for general class use: Nekton and Benthos a set of videos from selected sources a set of well labeled specimens in phylogenetic order DISCUSSION: Nekton Nekton is a term that applies to those
Ecological interactions between forage fish, rorquals, and fisheries in Haida Gwaii
 Ecological interactions between forage fish, rorquals, and fisheries in Haida Gwaii Szymon Surma MSc candidate UBC Fisheries Centre The problem rorquals: lunge-feeding baleen whales eat large quantities
Ecological interactions between forage fish, rorquals, and fisheries in Haida Gwaii Szymon Surma MSc candidate UBC Fisheries Centre The problem rorquals: lunge-feeding baleen whales eat large quantities
PARCC Research Simulation Task Grade 4 Reading Lesson 8: Practice Completing the Research Simulation Task
 Rationale Goal Task Foci Objectives Materials Procedures PARCC Research Simulation Task Grade 4 Reading Lesson 8: Practice Completing the Research Simulation Task This lesson provides students with practice
Rationale Goal Task Foci Objectives Materials Procedures PARCC Research Simulation Task Grade 4 Reading Lesson 8: Practice Completing the Research Simulation Task This lesson provides students with practice
 Kingdom: Animalia Phylum:Mollusca Classes: Bivalva, Gastropoda, Cephalopoda http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0a7j5prl8hc&feature=related http://www2.beavercreek.k12.oh.us/videos/45/pgr45_700k.asf What is
Kingdom: Animalia Phylum:Mollusca Classes: Bivalva, Gastropoda, Cephalopoda http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0a7j5prl8hc&feature=related http://www2.beavercreek.k12.oh.us/videos/45/pgr45_700k.asf What is
Characters. Photographs by Peg & Datiz, Student Conservationists. Illustrations by George Carrara. Written by Yein Suh
 Written by Yein Suh Photographs by Peg & Datiz, Student Conservationists Illustrations by George Carrara 1 Characters 2 Ms. Lee teaches her class about the Arctic Circle. It is an area around the North
Written by Yein Suh Photographs by Peg & Datiz, Student Conservationists Illustrations by George Carrara 1 Characters 2 Ms. Lee teaches her class about the Arctic Circle. It is an area around the North
Vertical Migration and the Lake Superior Food Chain
 + Vertical Migration and the Lake Superior Food Chain Grade Level: 3-5 Activity Duration: 45 min 1hr Overview: I. Set Up II. Introduction what s in the lake III. What are you? IV. Lake Superior food chain
+ Vertical Migration and the Lake Superior Food Chain Grade Level: 3-5 Activity Duration: 45 min 1hr Overview: I. Set Up II. Introduction what s in the lake III. What are you? IV. Lake Superior food chain
Physeter catodon Linnaeus, 1758 PHYS Phys 1 SPW
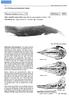 click for previous page 68 Marine Mammals of the World 2.4.2 FAO Species Identification Sheets Physeter catodon Linnaeus, 1758 PHYS Phys 1 SPW Other scientific names still in use: Physeter macrocephalus
click for previous page 68 Marine Mammals of the World 2.4.2 FAO Species Identification Sheets Physeter catodon Linnaeus, 1758 PHYS Phys 1 SPW Other scientific names still in use: Physeter macrocephalus
Polar Animals. Polar Bears
 Some animals live in very hot places, e.g. snakes and camels live in deserts. Other animals live in extremely cold places, like the Arctic or Antarctic. Polar Bears Polar bears live in the ice and snow
Some animals live in very hot places, e.g. snakes and camels live in deserts. Other animals live in extremely cold places, like the Arctic or Antarctic. Polar Bears Polar bears live in the ice and snow
F I E L D T R I P CHAPERONE GUIDE
 Need FONT 3rd GRADE F I E L D T R I P CHAPERONE GUIDE Chaperones: Use this guide to move your group through the Aquarium s galleries. The background information, guided questions, and activities will keep
Need FONT 3rd GRADE F I E L D T R I P CHAPERONE GUIDE Chaperones: Use this guide to move your group through the Aquarium s galleries. The background information, guided questions, and activities will keep
Whale Sharks: Giant Fish. Whale Sharks: Giant Fish A Reading A Z Level R Leveled Book Word Count: 968 LEVELED BOOK R
 Whale Sharks: Giant Fish A Reading A Z Level R Leveled Book Word Count: 968 LEVELED BOOK R Whale Sharks: Giant Fish Connections Writing Whale sharks do not use their teeth for eating. Write a poem describing
Whale Sharks: Giant Fish A Reading A Z Level R Leveled Book Word Count: 968 LEVELED BOOK R Whale Sharks: Giant Fish Connections Writing Whale sharks do not use their teeth for eating. Write a poem describing
Beaver Fever. Adapted From: Oh Deer, Project Wild K-12 Activity Guide, Project WILD, p
 Beaver Fever Carrying Capacity Adapted From: Oh Deer, Project Wild K-12 Activity Guide, Project WILD, p. 36-40 Grade Level: Basic or intermediate Duration: Approximately 30 to 45 minutes depending on discussion.
Beaver Fever Carrying Capacity Adapted From: Oh Deer, Project Wild K-12 Activity Guide, Project WILD, p. 36-40 Grade Level: Basic or intermediate Duration: Approximately 30 to 45 minutes depending on discussion.
Nevada Academic Content Standards Science
 Animal Homes Students will understand that all animals live in a habitat and identify the four basic resources all animals need in their habitat to survive: food, water, shelter, and space. Grade Level:
Animal Homes Students will understand that all animals live in a habitat and identify the four basic resources all animals need in their habitat to survive: food, water, shelter, and space. Grade Level:
Predator Prey Lab Exercise L2
 Predator Prey Lab Exercise L2 Name Date Objective: To compare predator and prey populations over time in a small ecosystem. Introduction: In 1970 the deer population of a small island forest preserve was
Predator Prey Lab Exercise L2 Name Date Objective: To compare predator and prey populations over time in a small ecosystem. Introduction: In 1970 the deer population of a small island forest preserve was
TEACHER BACKGROUND - Creatures of the Deep Sea FOR SEA Institute of Marine Science 2001 J. A. Kolb
 Pacific Viperfish The Pacific viperfish feeds on lanternfish and squid. It has a very large mouth and fang-like teeth. Once the viperfish catches something, it won't get away. Its size ranges from 22-30
Pacific Viperfish The Pacific viperfish feeds on lanternfish and squid. It has a very large mouth and fang-like teeth. Once the viperfish catches something, it won't get away. Its size ranges from 22-30
Freaky very odd, strange or eccentric
 Fall 2016 Freaky Fish of Pennsylvania Fall is when many people enjoy celebrating Halloween. We decorate our homes with all things creepy, freaky and spooky. Often, when we think of creepy creatures, we
Fall 2016 Freaky Fish of Pennsylvania Fall is when many people enjoy celebrating Halloween. We decorate our homes with all things creepy, freaky and spooky. Often, when we think of creepy creatures, we
Third Grade Animal Adaptation Reports. By: Ms. Ainsworth s class
 Third Grade Animal Adaptation Reports By: Ms. Ainsworth s class Great White Shark The great white shark has some adaptations. One is it could blend in the bottom of the ocean because its back helps it
Third Grade Animal Adaptation Reports By: Ms. Ainsworth s class Great White Shark The great white shark has some adaptations. One is it could blend in the bottom of the ocean because its back helps it
Fine-Scale Survey of Right and Humpback Whale Prey Abundance and Distribution
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Fine-Scale Survey of Right and Humpback Whale Prey Abundance and Distribution Joseph D. Warren School of Marine and Atmospheric
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Fine-Scale Survey of Right and Humpback Whale Prey Abundance and Distribution Joseph D. Warren School of Marine and Atmospheric
OIMB GK12 CURRICULUM. LIGHT IN THE DEEP SEA Adapted from NOAA s All That Glitters
 5th Grade 60 minutes LIGHT IN THE DEEP SEA Adapted from NOAA s All That Glitters Oregon Science Content Standards: 5.2 Interaction and Change: Force, energy, matter, and organisms interact within living
5th Grade 60 minutes LIGHT IN THE DEEP SEA Adapted from NOAA s All That Glitters Oregon Science Content Standards: 5.2 Interaction and Change: Force, energy, matter, and organisms interact within living
Search for the missing sea otters
 Search for the missing sea otters Objectives: Based on a real study of sea otter declines Apply your knowledge of basic concepts of population and community ecology Interpret data from graphs and tables
Search for the missing sea otters Objectives: Based on a real study of sea otter declines Apply your knowledge of basic concepts of population and community ecology Interpret data from graphs and tables
UNIT 5B. WATER QUALITY AND QUANTITY
 UNIT 5B. WATER QUALITY AND QUANTITY ACTIVITY TIME LEVEL Water Temperature & Comfort 45 minutes Introductory Fish & Water Temperature Chart Analysis 60-90 minutes Introductory Goldfish Lab Activity 30-45
UNIT 5B. WATER QUALITY AND QUANTITY ACTIVITY TIME LEVEL Water Temperature & Comfort 45 minutes Introductory Fish & Water Temperature Chart Analysis 60-90 minutes Introductory Goldfish Lab Activity 30-45
Table Description of 15 shark species. Shark Number. Common: Scientific: Common: Scientific:
 Table 1.12. Description of 15 shark species Shark Number Description 1 This is the second-largest fish, reaching 11.7 meters (m) in length. It is an openocean plankton feeder considered harmless to humans.
Table 1.12. Description of 15 shark species Shark Number Description 1 This is the second-largest fish, reaching 11.7 meters (m) in length. It is an openocean plankton feeder considered harmless to humans.
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore W HALE TALES Research biologist reveals blue whales' striking characteristics
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore W HALE TALES Research biologist reveals blue whales' striking characteristics
Videoconferencing pre/post materials
 Dear Teacher, Videoconferencing pre/post materials We are looking forward to our interactive videoconference with you and your students. During the program your students will have the opportunity to explore
Dear Teacher, Videoconferencing pre/post materials We are looking forward to our interactive videoconference with you and your students. During the program your students will have the opportunity to explore
Inuit Insight on Fear of Killer Whales. New Trick in New Jersey [March 2012] If you drive 25 mi/day or less you better read this...
![Inuit Insight on Fear of Killer Whales. New Trick in New Jersey [March 2012] If you drive 25 mi/day or less you better read this... Inuit Insight on Fear of Killer Whales. New Trick in New Jersey [March 2012] If you drive 25 mi/day or less you better read this...](/thumbs/96/126606377.jpg) New Trick in New Jersey [March 2012] If you drive 25 mi/day or less you better read this... Insurance.Comparisons.org skip to main content earth space tech and gadgets animals history adventure human brain
New Trick in New Jersey [March 2012] If you drive 25 mi/day or less you better read this... Insurance.Comparisons.org skip to main content earth space tech and gadgets animals history adventure human brain
ALL THAT GLITTERS Overview An activity highlighting what happens to light and colors in the deep sea.
 RAINY DAY KITS FOR ENVIRONMENTAL EDUCATION This Lesson Generously Contributed by: ALL THAT GLITTERS Overview An activity highlighting what happens to light and colors in the deep sea. Key Concepts Students
RAINY DAY KITS FOR ENVIRONMENTAL EDUCATION This Lesson Generously Contributed by: ALL THAT GLITTERS Overview An activity highlighting what happens to light and colors in the deep sea. Key Concepts Students
Marine Animals. II. The Chordates. OCN 201 Biology Lecture 7
 Marine Animals II. The Chordates OCN 201 Biology Lecture 7 The Animal Family Tree Chordates Arthropods Segmented Worms Mollusks mouth first anus first Echinoderms Cnidarians Round Worms Ctenophores Flatworms
Marine Animals II. The Chordates OCN 201 Biology Lecture 7 The Animal Family Tree Chordates Arthropods Segmented Worms Mollusks mouth first anus first Echinoderms Cnidarians Round Worms Ctenophores Flatworms
Kelp Forest Conservation Food web activity
 Kelp Forest Conservation Food web activity Activity Steps Cut out the kelp forest food web organisms cards. Have students form small groups. Pass out one food web organism and to each group. Using a blank
Kelp Forest Conservation Food web activity Activity Steps Cut out the kelp forest food web organisms cards. Have students form small groups. Pass out one food web organism and to each group. Using a blank
WDC Ethogram- Humpback Whale Behavior 2013
 - Humpback Whale Behavior List of Behaviors Feeding Behaviors General Behaviors Surface Display Behaviors Interactive Behaviors Bubble Cloud Dive Breach Spy Hopping Bubble Net High Fluking Dive Full Breach
- Humpback Whale Behavior List of Behaviors Feeding Behaviors General Behaviors Surface Display Behaviors Interactive Behaviors Bubble Cloud Dive Breach Spy Hopping Bubble Net High Fluking Dive Full Breach
Chapter 7. Marine Animals Without a Backbone
 Chapter 7 Marine Animals Without a Backbone Molluscs Characteristics of Phylum: More than 200,000 species Name means "soft body" Basic body plan head, muscular foot and visceral mass in most species Mantle-
Chapter 7 Marine Animals Without a Backbone Molluscs Characteristics of Phylum: More than 200,000 species Name means "soft body" Basic body plan head, muscular foot and visceral mass in most species Mantle-
Stonefly. Gilled Snails
 Mid-Michigan Macroinvertebrates Identification Guide & Descriptions Mayfly Nymphs have 3 tail filaments occasionally 2 tail filaments never paddle or fan-like Feathery gills line the sides of the abdomen
Mid-Michigan Macroinvertebrates Identification Guide & Descriptions Mayfly Nymphs have 3 tail filaments occasionally 2 tail filaments never paddle or fan-like Feathery gills line the sides of the abdomen
UTAH LAKE JUNE SUCKER
 UTAH LAKE JUNE SUCKER PROCEDURE: Activity Game: UTAH LAKE JUNE SUCKER GAME Instructions: 1. Hand out one Utah Lake Card per student. 2. Select one area of the gym to be Utah Lake and another to be Provo
UTAH LAKE JUNE SUCKER PROCEDURE: Activity Game: UTAH LAKE JUNE SUCKER GAME Instructions: 1. Hand out one Utah Lake Card per student. 2. Select one area of the gym to be Utah Lake and another to be Provo
Oh Deer! Objectives. Background. Method. Materials
 Oh Deer! Objectives Students will (1) identify and describe food, water, and shelter as three essential components of habitat; (2) describe factors that influence carrying capacity; (3) define limiting
Oh Deer! Objectives Students will (1) identify and describe food, water, and shelter as three essential components of habitat; (2) describe factors that influence carrying capacity; (3) define limiting
b. Graphs provide a means of quickly comparing data sets. Concepts: a. A graph can be used to identify statistical trends
 Baseball Bat Testing: Subjects: Topics: data. Math/Science Gathering and organizing data from an experiment Creating graphical representations of experimental data Analyzing and interpreting graphical
Baseball Bat Testing: Subjects: Topics: data. Math/Science Gathering and organizing data from an experiment Creating graphical representations of experimental data Analyzing and interpreting graphical
Well, Well, Well. BACKGROUND Seasonal upwelling is a very important process in the coastal ocean of the Pacific Northwest.
 Well, Well, Well SUMMARY In this activity students investigate the relationship between winds, surface currents, sea surface temperature and upwelling and downwelling off the coast of OR and WA. Students
Well, Well, Well SUMMARY In this activity students investigate the relationship between winds, surface currents, sea surface temperature and upwelling and downwelling off the coast of OR and WA. Students
MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH. Adventures Aboard The Land SHARC (Science Hands-On And Related Careers) On-Site Package
 MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH MIDDLE SCHOOL PROGRAM Adventures Aboard The Land SHARC (Science Hands-On And Related Careers) On-Site Package MAST Academy Maritime and Science Technology High School Miami-Dade County
MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH MIDDLE SCHOOL PROGRAM Adventures Aboard The Land SHARC (Science Hands-On And Related Careers) On-Site Package MAST Academy Maritime and Science Technology High School Miami-Dade County
Debra J. Housel, M.S. Ed. Author
 Editor Eric Migliaccio Managing Editor Ina Massler Levin, M.A. Editor-in-Chief Sharon Coan, M.S. Ed. Illustrator Bruce Hedges Cover Artist Brenda DiAntonis Art Coordinator Kevin Barnes Art Director CJae
Editor Eric Migliaccio Managing Editor Ina Massler Levin, M.A. Editor-in-Chief Sharon Coan, M.S. Ed. Illustrator Bruce Hedges Cover Artist Brenda DiAntonis Art Coordinator Kevin Barnes Art Director CJae
Bainbridge Island School District Life Science UNIT 2 - Southern Resident Orcas Grade 4
 Bainbridge Island School District Life Science UNIT 2 - Southern Resident Orcas Grade 4 Unit created by Laurie Spickard, curriculum specialist Essential question for the unit Why are the Southern Resident
Bainbridge Island School District Life Science UNIT 2 - Southern Resident Orcas Grade 4 Unit created by Laurie Spickard, curriculum specialist Essential question for the unit Why are the Southern Resident
JadEco, LLC PO BOX 445 Shannon, IL 61078
 Introduction: With the assistance of Lake Holiday staff and volunteers, we were able to conduct an AC electrofishing survey on May 8, 27. Water temperatures were 2.3 C (8.5 F) and water clarity was decent
Introduction: With the assistance of Lake Holiday staff and volunteers, we were able to conduct an AC electrofishing survey on May 8, 27. Water temperatures were 2.3 C (8.5 F) and water clarity was decent
OCEAN AWARE: PART 1. Meeting Plan A N I N S T A N T M E E T I N G F O R B R O W N I E S F R O M T H E B C P R O G R A M C O M M I T T E E
 BRITISH COLUMBIA COUNCIL OCEAN AWARE: PART 1 A N I N S T A N T M E E T I N G F O R B R O W N I E S F R O M T H E B C P R O G R A M C O M M I T T E E The ocean is an amazing place, something that everyone
BRITISH COLUMBIA COUNCIL OCEAN AWARE: PART 1 A N I N S T A N T M E E T I N G F O R B R O W N I E S F R O M T H E B C P R O G R A M C O M M I T T E E The ocean is an amazing place, something that everyone
Animals of the Pelagic Environment. Making a living--adaptations Staying Above the Seafloor. Adaptations
 Animals of the Pelagic Environment Making a living--adaptations Staying Above the Seafloor Eating Gas Containers Floaters Swimmers (nekton) Mobility Speed Temperature Group Behavior Reproduction Schooling
Animals of the Pelagic Environment Making a living--adaptations Staying Above the Seafloor Eating Gas Containers Floaters Swimmers (nekton) Mobility Speed Temperature Group Behavior Reproduction Schooling
The Great Shark Escape
 The Magic School Bus A Science Chapter Book #7 The Great Shark Escape Lapbook by Amy Yee. Yee Shall Know http:///www.yeeshallknow.com Lapbook Basics Follow the instructions in the following page(s) to
The Magic School Bus A Science Chapter Book #7 The Great Shark Escape Lapbook by Amy Yee. Yee Shall Know http:///www.yeeshallknow.com Lapbook Basics Follow the instructions in the following page(s) to
CARTESIAN DIVER (1 Hour)
 (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 2 Grade Range: K-2 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will build a Cartesian diver and discover how compression and changes in density cause the diver to mysteriously
(1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 2 Grade Range: K-2 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will build a Cartesian diver and discover how compression and changes in density cause the diver to mysteriously
"Oh! Deer! & Limiting Factors" adapted from Project Wild Mr. Mark Musselman Audubon at the Francis Beidler Forest
 "Oh! Deer! & Limiting Factors" adapted from Project Wild Mr. Mark Musselman Audubon at the Francis Beidler Forest Overview: Student act out the parts of a deer herd looking for food, water, and shelter.
"Oh! Deer! & Limiting Factors" adapted from Project Wild Mr. Mark Musselman Audubon at the Francis Beidler Forest Overview: Student act out the parts of a deer herd looking for food, water, and shelter.
Edible Trawl. Yes, you can eat this experiment!
 Edible Trawl Yes, you can eat this experiment! Next Generation Science Standards In this lesson, students will learn how the selection of sampling gear depends on the questions being asked. Students will
Edible Trawl Yes, you can eat this experiment! Next Generation Science Standards In this lesson, students will learn how the selection of sampling gear depends on the questions being asked. Students will
HUNGRY, HUNGRY HIPPOS Learn about the 3rd largest mammal in the world. He weighs over 5,000 pounds and only eats plants!
 HUNGRY, HUNGRY HIPPOS Learn about the 3rd largest mammal in the world. He weighs over 5,000 pounds and only eats plants! Grade(s): 2-4 Objectives (grade dependent): Student(s) will be able to: use place
HUNGRY, HUNGRY HIPPOS Learn about the 3rd largest mammal in the world. He weighs over 5,000 pounds and only eats plants! Grade(s): 2-4 Objectives (grade dependent): Student(s) will be able to: use place
OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY EXTENSION
 April OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY EXTENSION Cloverbud Investigators: Career Detectives Background: Dolphins can t talk underwater or can they? Dolphins are mammals that spend their whole life in water and while
April OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY EXTENSION Cloverbud Investigators: Career Detectives Background: Dolphins can t talk underwater or can they? Dolphins are mammals that spend their whole life in water and while
Lake Habitat. Cachuma Lake DISCOVERY BOOK Cachuma Lake Discovery Book V1, Santa Barbara County Parks
 Habitat Cachuma DISCOVERY BOOK 3.0 Habitat From land, a lake looks like one big pool. Under the surface of the water, lakes can have different habitats, just as the land does. We say that the lake is heterogeneous,
Habitat Cachuma DISCOVERY BOOK 3.0 Habitat From land, a lake looks like one big pool. Under the surface of the water, lakes can have different habitats, just as the land does. We say that the lake is heterogeneous,
A DAY AT THE WHITNEY LAB The Whitney Laboratory for Marine Bioscience An Institute for Marine Research and Biotechnology
 A DAY AT THE WHITNEY LAB The Whitney Laboratory for Marine Bioscience An Institute for Marine Research and Biotechnology STUDENT NAME: What s For Lunch? The Mission In this activity, you will make an educated
A DAY AT THE WHITNEY LAB The Whitney Laboratory for Marine Bioscience An Institute for Marine Research and Biotechnology STUDENT NAME: What s For Lunch? The Mission In this activity, you will make an educated
