An Investigation of Atmospheric Stability and Its Impact on Scatterometer Winds Across the Gulf Stream
|
|
|
- Angel Porter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 An Investigation of Atmospheric Stability and Its Impact on Scatterometer Winds Across the Gulf Stream Jim Edson University of Connecticut Doug Vandemark & Amanda Plagge University of New Hampshire
2 CLIMODE Deployments and Cruises November 2005: Mooring & Profiler Deployment Cruise January 18-30, 2006: Pilot Experiment, ASIS/FILIS Deployment October 2006: Mooring Turnaround Cruise February-March 2007: 6week Main Experiment, ASIS/FILIS Deployments, Microstructure, Surveys. November 2007: Mooring Recovery Cruise
3 CLIMODE Deployments and Cruises November 2005: Mooring & Profiler Deployment Cruise January 18-30, 2006: Pilot Experiment, ASIS/FILIS Deployment October 2006: Mooring Turnaround Cruise February-March 2007: 6week Main Experiment, ASIS/FILIS Deployments, Microstructure, Surveys. February 2007: Mooring Recovery Cruise
4 The Gulf Stream Co l d A ir O ak utbre L s 14oC 22oC Cold air outbreaks drive extremely active convection over the region. The net winter heat loss in this region is 400 W/m2.
5 CLIMODE Platforms
6 Sensor Packages R/V Atlantis and Knorr 2-3 DCFS (Sonic/MotionPak/Licor) IR and Solar Radiometers IR SST RH/T/P Sensors ShipSystem (Precip, Tsea, Salinity, ADCP) ASIS DCFS (Sonic/MotionPak/Licor) IR and Solar Radiometers RH/T/P Sensors 6 Wave Wires Subsurface (Tsea, Salinity, ADCP, Nortek) Discus Low Power DCFS (Sonic/MotionPakIII) Redundant IR and Solar Radiometers Redundant U/RH/T/P Sensors (ASIMET) Subsurface (T/S, Nortek, VACM)
7
8 Moving Platform vs. Fixed Tower Uncorrected ~530 m
9 Moving Platform vs. Fixed Tower Corrected ~530 m
10 Bulk Aerodynamic Method Latent Heat Flux: ρ Lv <wq> ρ LvCE U Q Sensible Heat Flux: ρ cp <wθ> ρ cpch U Θ Momentum Flux: -ρ<uw> -ρ CD U 2 Direct Covariance Bulk Aerodynamic
11 Drag Coefficient Formulas Semi-empirical uw κ C D ( z / z0, z / L) = = 2 U ln( z / zo ) ψ m ( z / L) 2 Atmospheric Stability 2 κ uw C DN ( z / z0 ) = = 2 ln( z / z ) U o N Empirical 103 C DN (U10 N ) = TOGA-COARE 4.0 Surface Roughness U10 N 11 ms U10 N 11 U10 N 25 ms -1 Wind Speed Dependent Large & Pond (1981)
12 Drag Coefficient Formulas Semi-empirical uw κ C D ( z / z0, z / L) = = 2 U ln( z / zo ) ψ m ( z / L) 2 Atmospheric Stability 2 κ uw C DN ( z / z0 ) = = 2 ln( z / z ) U o N TOGA-COARE 4.0 Surface Roughness COARE parameterizes the roughness length as: ν u*2 zo = α + β (U10 ) u* g Charnock Parameter
13 MBL/CBLAST/CLIMODE Drag Coefficients ν u*2 zo = α + β (U10 ) u* g
14 Wave Age Dependent Drag u* / c p = U10 N 0.007
15 Wave Age Dependent Drag β = A(c p / u* ) B plus u* / c p = U equals ECMWF
16 Flux Time Series
17 Summary A wind speed dependent drag coefficient give good results over a wind range of sea-states/wave-ages. This requires a wind speed dependent Charnock variable Numerous investigations have shown that the Charnock variable is dependent on wave-age. However, these findings can be reconciled since observed wave ages over the coastal and open ocean are clearly associated with wind ranges.
18 QuikSCAT Wind Speeds
19 QuikSCAT vs. Buoy Wind Direction
20 QuikSCAT vs. Buoy Wind Speeds
21 Atmospheric Forcing Sikora et al. (1995) PO.DAAC
22 Stability Effects Near SST Fronts Boundary Layer Adjustment Baroclinic adjustment to horizontal temperature gradients. Acceleration/deceleration of surface winds. Surface Layer Adjustment QuikSCAT measures surface roughness/stress Surface stress is proportional to neutral winds, UN UN < U in unstable conditions UN > U in stable conditions Mesoscale Adjustment to SST fronts Combination of both?
23 QuikSCAT vs. Buoy Wind Speeds Surface Layer Adjustment U10 U10 U(z) = u*/κ[ln(z/zo) ψm(z/l)]
24 QuikSCAT vs. Buoy Wind Speeds Surface Layer Adjustment U10 U10 U(z) = u*/κ[ln(z/zo) ψm(z/l)] U10N U10N UN(z) = u*/κ[ln(z/zo)]
25 QuikSCAT vs. Buoy Wind Speeds Surface Layer Adjustment U10 U10 U(z) = u*/κ[ln(z/zo) ψm(z/l)] U10N U10N UN(z) = u*/κ[ln(z/zo)]
26 QuikSCAT vs. Buoy Wind Speeds Surface Layer Adjustment Larger than measured Smaller than measured U(z) = u*/κ[ln(z/zo) ψm(z/l)] UN(z) = u*/κ[ln(z/zo)]
27 QuikSCAT vs. Buoy Wind Speeds Surface Layer Adjustment Baroclinicity? U(z) = u*/κ[ln(z/zo) ψm(z/l)] UN(z) = u*/κ[ln(z/zo)]
28 QuikSCAT vs. Buoy Wind Speeds Boundary Layer (Baroclinic) Adjustment
29 Coupling Coefficients O Neill et al. (submitted)
30 30 Day Perturbations Courtesy of JHU/APL
31 QuikSCAT vs. Buoy Wind Speeds Boundary Layer (Baroclinic) Adjustment O Neill et al. (submitted)
32 QuikSCAT vs. Buoy Wind Speeds Boundary Layer (Baroclinic) Adjustment O Neill et al. (submitted)
33 QuikSCAT vs. Buoy Wind Speeds Boundary Layer (Baroclinic) Adjustment No obvious trend in perturbations when computed versus sea-air virtual temperature difference.
34 QuikSCAT vs. Buoy Wind Speeds Boundary Layer (Baroclinic) Adjustment However, it becomes more obvious when you only look at cold/cool air advection. JHU/APL
35 QuikSCAT vs. Buoy Wind Speeds Boundary Layer (Baroclinic) Adjustment However, it becomes more obvious when you only look at cold/cool air advection. JHU/APL
36 Summary A wind speed dependent drag coefficient give good results over a wind range of sea-states/wave-ages. This requires a wind speed dependent Charnock variable Numerous investigations have shown that the Charnock variable is dependent on wave-age. However, these findings can be reconciled since observed wave ages over the coastal and open ocean are clearly associated with wind ranges. Some of the variability in the QuikSCAT winds is due to adjustment of the neutral wind to changes in stratification and not changes in the actual wind speeds. This variability obeys MO-Similarity in the mean. This effect enhances the gradient in neutral winds but not actual. Significant variability in the QuikSCAT winds is not explained by this effect The one-buoy approximation of the coupling coefficients is in reasonably good agreement with previous studies. This includes the neutral wind, measured wind, and directly measured stress. The physical processes responsible for this correlation is Compare stress!
37 Thanks to NSF and NASA for supporting this research.
38 QuikSCAT vs. Buoy Wind Speeds Surface Layer Adjustment U10 U10 U(z) = u*/κ[ln(z/zo) ψm(z/l)] U10N U10N UN(z) = u*/κ[ln(z/zo)]
On the Interpretation of Scatterometer Winds near Sea Surface Temperature Fronts
 On the Interpretation of Scatterometer Winds near Sea Surface Temperature Fronts Jim Edson University of Connecticut Amanda Plagge & Doug Vandemark University of New Hampshire IOVWST Meeting Utrecht, NL
On the Interpretation of Scatterometer Winds near Sea Surface Temperature Fronts Jim Edson University of Connecticut Amanda Plagge & Doug Vandemark University of New Hampshire IOVWST Meeting Utrecht, NL
Wind Stress Working Group 2015 IOVWST Meeting Portland, OR
 Wind Stress Working Group 2015 IOVWST Meeting Portland, OR Summary of Research Topics, Objectives and Questions James B. Edson University of Connecticut SPURS Mooring, Farrar, WHOI Background Motivation
Wind Stress Working Group 2015 IOVWST Meeting Portland, OR Summary of Research Topics, Objectives and Questions James B. Edson University of Connecticut SPURS Mooring, Farrar, WHOI Background Motivation
Field assessment of ocean wind stress derived from active and passive microwave sensors
 Field assessment of ocean wind stress derived from active and passive microwave sensors Doug Vandemark, Marc Emond (UNH) Jim Edson (UCONN) Bertrand Chapron (IFREMER) Motivations Are there 1 st or 2 nd
Field assessment of ocean wind stress derived from active and passive microwave sensors Doug Vandemark, Marc Emond (UNH) Jim Edson (UCONN) Bertrand Chapron (IFREMER) Motivations Are there 1 st or 2 nd
Review of Equivalent Neutral Winds and Stress
 Review of Equivalent Neutral Winds and Stress Mark A. Bourassa Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies, Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Institute & Department of Earth, Ocean and Atmospheric Science
Review of Equivalent Neutral Winds and Stress Mark A. Bourassa Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies, Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Institute & Department of Earth, Ocean and Atmospheric Science
Conditions for Offshore Wind Energy Use
 Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg Institute of Physics Energy Meteorology Group Detlev Heinemann Conditions for Offshore Wind Energy Use Detlev Heinemann ForWind Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg
Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg Institute of Physics Energy Meteorology Group Detlev Heinemann Conditions for Offshore Wind Energy Use Detlev Heinemann ForWind Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg
Dynamics and variability of surface wind speed and divergence over mid-latitude ocean fronts
 Dynamics and variability of surface wind speed and divergence over mid-latitude ocean fronts Larry O Neill 1, Tracy Haack 2, and Simon de Szoeke 1 1 Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR 2 Naval Research
Dynamics and variability of surface wind speed and divergence over mid-latitude ocean fronts Larry O Neill 1, Tracy Haack 2, and Simon de Szoeke 1 1 Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR 2 Naval Research
Surface Fluxes and Wind-Wave Interactions in Weak Wind Conditions
 Surface Fluxes and Wind-Wave Interactions in Weak Wind Conditions Jielun Sun Microscale and Mesoscale Meteorology National Center for Atmospheric Research phone: (303) 497-8994 fax: (303) 497-8171 email:
Surface Fluxes and Wind-Wave Interactions in Weak Wind Conditions Jielun Sun Microscale and Mesoscale Meteorology National Center for Atmospheric Research phone: (303) 497-8994 fax: (303) 497-8171 email:
Constraining a global, eddying, ocean and sea ice model with scatterometer data
 Constraining a global, eddying, ocean and sea ice model with scatterometer data D. Menemenlis, H. Zhang, D. Moroni, and S. Hristova-Veleva IOVWST, Utrecht, Netherlands, 13 June 2012 QuikSCAT GRACE =? Jason
Constraining a global, eddying, ocean and sea ice model with scatterometer data D. Menemenlis, H. Zhang, D. Moroni, and S. Hristova-Veleva IOVWST, Utrecht, Netherlands, 13 June 2012 QuikSCAT GRACE =? Jason
Air-Sea Interaction Spar Buoy Systems
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Distribution approved for public release; distribution is unlimited Air-Sea Interaction Spar Buoy Systems Hans C. Graber CSTARS - University of Miami 11811 SW 168 th Street, Miami,
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Distribution approved for public release; distribution is unlimited Air-Sea Interaction Spar Buoy Systems Hans C. Graber CSTARS - University of Miami 11811 SW 168 th Street, Miami,
Importance of thermal effects and sea surface roughness for offshore wind resource assessment
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 09, 2018 Importance of thermal effects and sea surface roughness for offshore wind resource assessment Lange, B.; Larsen, Søren Ejling; Højstrup, Jørgen; Barthelmie,
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 09, 2018 Importance of thermal effects and sea surface roughness for offshore wind resource assessment Lange, B.; Larsen, Søren Ejling; Højstrup, Jørgen; Barthelmie,
The Air-Sea Interaction. Masanori Konda Kyoto University
 2 The Air-Sea Interaction Masanori Konda Kyoto University 2.1 Feedback between Ocean and Atmosphere Heat and momentum exchange between the ocean and atmosphere Atmospheric circulation Condensation heat
2 The Air-Sea Interaction Masanori Konda Kyoto University 2.1 Feedback between Ocean and Atmosphere Heat and momentum exchange between the ocean and atmosphere Atmospheric circulation Condensation heat
Lecture 7. More on BL wind profiles and turbulent eddy structures. In this lecture
 Lecture 7. More on BL wind profiles and turbulent eddy structures In this lecture Stability and baroclinicity effects on PBL wind and temperature profiles Large-eddy structures and entrainment in shear-driven
Lecture 7. More on BL wind profiles and turbulent eddy structures In this lecture Stability and baroclinicity effects on PBL wind and temperature profiles Large-eddy structures and entrainment in shear-driven
2.5 SHIPBOARD TURBULENCE MEASUREMENTS OF THE MARINE ATMOSPHERIC BOUNDARY LAYER FROM HIRES EXPERIMENT
 2.5 SHIPBOARD TURBULENCE MEASUREMENTS OF THE MARINE ATMOSPHERIC BOUNDARY LAYER FROM HIRES EXPERIMENT John Kalogiros 1*, Q. Wang 2, R. J. Lind 2, T. Herbers 2, and J. Cook 2 1 National Observatory of Athens,
2.5 SHIPBOARD TURBULENCE MEASUREMENTS OF THE MARINE ATMOSPHERIC BOUNDARY LAYER FROM HIRES EXPERIMENT John Kalogiros 1*, Q. Wang 2, R. J. Lind 2, T. Herbers 2, and J. Cook 2 1 National Observatory of Athens,
RECTIFICATION OF THE MADDEN-JULIAN OSCILLATION INTO THE ENSO CYCLE
 RECTIFICATION OF THE MADDEN-JULIAN OSCILLATION INTO THE ENSO CYCLE By William S. Kessler and Richard Kleeman Journal of Climate Vol.13, 1999 SWAP, May 2009, Split, Croatia Maristella Berta What does give
RECTIFICATION OF THE MADDEN-JULIAN OSCILLATION INTO THE ENSO CYCLE By William S. Kessler and Richard Kleeman Journal of Climate Vol.13, 1999 SWAP, May 2009, Split, Croatia Maristella Berta What does give
Parameterizations (fluxes, convection)
 Parameterizations (fluxes, convection) Heinke Schlünzen Meteorological Institute, University of Hamburg New resolutions - new challenges What is the current status? Surface fluxes Convection Towards improving
Parameterizations (fluxes, convection) Heinke Schlünzen Meteorological Institute, University of Hamburg New resolutions - new challenges What is the current status? Surface fluxes Convection Towards improving
CHAPTER 4. Marine Boundary Layer characteristics
 76 CHAPTER 4 Marine Boundary Layer characteristics The surface boundary layer over oceans play an important role in the exchange of energy, mass and momentum across the water surface, which influences
76 CHAPTER 4 Marine Boundary Layer characteristics The surface boundary layer over oceans play an important role in the exchange of energy, mass and momentum across the water surface, which influences
Flow modelling hills complex terrain and other issues
 Flow modelling hills, complex terrain and other issues Modelling approaches sorted after complexity Rules of thumbs Codes and standards Linear model, 1 st order turbulence closure LINCOM/Wasp Reynolds-averaged
Flow modelling hills, complex terrain and other issues Modelling approaches sorted after complexity Rules of thumbs Codes and standards Linear model, 1 st order turbulence closure LINCOM/Wasp Reynolds-averaged
Kathleen Dohan. Wind-Driven Surface Currents. Earth and Space Research, Seattle, WA
 Updates to OSCAR and challenges with capturing the wind-driven currents. Wind-Driven Surface Currents Kathleen Dohan Earth and Space Research, Seattle, WA ENSO OSCAR Surface currents from satellite fields
Updates to OSCAR and challenges with capturing the wind-driven currents. Wind-Driven Surface Currents Kathleen Dohan Earth and Space Research, Seattle, WA ENSO OSCAR Surface currents from satellite fields
Gravity waves in stable atmospheric boundary layers
 Gravity waves in stable atmospheric boundary layers Carmen J. Nappo CJN Research Meteorology Knoxville, Tennessee 37919, USA Abstract Gravity waves permeate the stable atmospheric planetary boundary layer,
Gravity waves in stable atmospheric boundary layers Carmen J. Nappo CJN Research Meteorology Knoxville, Tennessee 37919, USA Abstract Gravity waves permeate the stable atmospheric planetary boundary layer,
A new mechanism of oceanatmosphere coupling in midlatitudes
 A new mechanism of oceanatmosphere coupling in midlatitudes Arnaud Czaja & Nicholas Blunt Imperial College, London Grantham Institute for Climate Change 1. Motivation Two key questions By which mechanism(s)
A new mechanism of oceanatmosphere coupling in midlatitudes Arnaud Czaja & Nicholas Blunt Imperial College, London Grantham Institute for Climate Change 1. Motivation Two key questions By which mechanism(s)
Mesoscale air-sea interaction and feedback in the western Arabian Sea
 Mesoscale air-sea interaction and feedback in the western Arabian Sea Hyodae Seo (Univ. of Hawaii) Raghu Murtugudde (UMD) Markus Jochum (NCAR) Art Miller (SIO) AMS Air-Sea Interaction Workshop Phoenix,
Mesoscale air-sea interaction and feedback in the western Arabian Sea Hyodae Seo (Univ. of Hawaii) Raghu Murtugudde (UMD) Markus Jochum (NCAR) Art Miller (SIO) AMS Air-Sea Interaction Workshop Phoenix,
Estimating atmospheric stability from observations and correcting wind shear models accordingly
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Estimating atmospheric stability from observations and correcting wind shear models accordingly To cite this article: M C Holtslag et al 2014 J. Phys.:
Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Estimating atmospheric stability from observations and correcting wind shear models accordingly To cite this article: M C Holtslag et al 2014 J. Phys.:
Development of a Regional Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere Model
 2.2 Development of a Regional Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere Model Hyodae Seo, Arthur J. Miller, John O. Roads, and Masao Kanamitsu Scripps Institution of Oceanography 6th Conference on Coastal Atmospheric and
2.2 Development of a Regional Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere Model Hyodae Seo, Arthur J. Miller, John O. Roads, and Masao Kanamitsu Scripps Institution of Oceanography 6th Conference on Coastal Atmospheric and
Goal: Develop quantitative understanding of ENSO genesis, evolution, and impacts
 The Delayed Oscillator Zebiak and Cane (1987) Model Other Theories Theory of ENSO teleconnections Goal: Develop quantitative understanding of ENSO genesis, evolution, and impacts The delayed oscillator
The Delayed Oscillator Zebiak and Cane (1987) Model Other Theories Theory of ENSO teleconnections Goal: Develop quantitative understanding of ENSO genesis, evolution, and impacts The delayed oscillator
= y y. In meteorological parlance, terms such as the above are known as
 Mesoscale Meteorology: The Planetary Boundary Layer 8 March 017 Introduction The planetary boundary layer, sometimes referred to as the atmospheric boundary layer, is a layer of finite depth over which
Mesoscale Meteorology: The Planetary Boundary Layer 8 March 017 Introduction The planetary boundary layer, sometimes referred to as the atmospheric boundary layer, is a layer of finite depth over which
11.4 WIND STRESS AND WIND WAVE OBSERVATIONS IN THE PRESENCE OF SWELL 2. METHODS
 11.4 WIND STRESS AND WIND WAVE OBSERVATIONS IN THE PRESENCE OF SWELL Douglas Vandemark 1*, W. M. Drennan 2, J. Sun, 3 J. R. French 4 and Hans Graber 2 1 NASA/GSFC, Wallops Island, VA 2 Univ. of Miami,
11.4 WIND STRESS AND WIND WAVE OBSERVATIONS IN THE PRESENCE OF SWELL Douglas Vandemark 1*, W. M. Drennan 2, J. Sun, 3 J. R. French 4 and Hans Graber 2 1 NASA/GSFC, Wallops Island, VA 2 Univ. of Miami,
The Influence of Ocean Surface Waves on Offshore Wind Turbine Aerodynamics. Ali Al Sam
 The Influence of Ocean Surface Waves on Offshore Wind Turbine Aerodynamics Ali Al Sam What I m going to wear today? Do I need to leave early to get to work? Taking buss or riding bike? Where will we drink
The Influence of Ocean Surface Waves on Offshore Wind Turbine Aerodynamics Ali Al Sam What I m going to wear today? Do I need to leave early to get to work? Taking buss or riding bike? Where will we drink
The relevance of ocean surface current in the ECMWF analysis and forecast system. Hans Hersbach Jean-Raymond Bidlot
 The relevance of ocean surface current in the ECMWF analysis and forecast system Hans Hersbach Jean-Raymond Bidlot European Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasts, Reading, U.K. hans.hersbach@ecmwf.int
The relevance of ocean surface current in the ECMWF analysis and forecast system Hans Hersbach Jean-Raymond Bidlot European Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasts, Reading, U.K. hans.hersbach@ecmwf.int
Atmospheric dynamics and meteorology
 Atmospheric dynamics and meteorology B. Legras, http://www.lmd.ens.fr/legras II Potential vorticity, tropopause and baroclinic instability (supposed to be known: notions on the conservation of potential
Atmospheric dynamics and meteorology B. Legras, http://www.lmd.ens.fr/legras II Potential vorticity, tropopause and baroclinic instability (supposed to be known: notions on the conservation of potential
Wind: Small Scale and Local Systems Chapter 9 Part 1
 Wind: Small Scale and Local Systems Chapter 9 Part 1 Atmospheric scales of motion Scales of atmospheric circulations range from meters or less to thousands of kilometers- millions of meters Time scales
Wind: Small Scale and Local Systems Chapter 9 Part 1 Atmospheric scales of motion Scales of atmospheric circulations range from meters or less to thousands of kilometers- millions of meters Time scales
The Cross-Calibrated Multi-Platform (CCMP) Ocean Vector Wind Analysis (V2.0)
 The Cross-Calibrated Multi-Platform (CCMP) Ocean Vector Wind Analysis (V2.0) Carl A. Mears, L. Ricciardulli, J. Scott and F. J. Wentz Remote Sensing Systems Ross Hoffman, S. Mark Leidner Robert Atlas Atmospheric
The Cross-Calibrated Multi-Platform (CCMP) Ocean Vector Wind Analysis (V2.0) Carl A. Mears, L. Ricciardulli, J. Scott and F. J. Wentz Remote Sensing Systems Ross Hoffman, S. Mark Leidner Robert Atlas Atmospheric
Determination of the Spatial Variation of the Atmosphere and Ocean Wave Fields in Extremely Light Wind Regimes
 Determination of the Spatial Variation of the Atmosphere and Ocean Wave Fields in Extremely Light Wind Regimes Gennaro H. Crescenti U.S. Dept. Commerce / NOAA Air Resources Laboratory Field Research Division
Determination of the Spatial Variation of the Atmosphere and Ocean Wave Fields in Extremely Light Wind Regimes Gennaro H. Crescenti U.S. Dept. Commerce / NOAA Air Resources Laboratory Field Research Division
Goals. Unconditional stability Conditional stability Buoyancy Buoyancy waves
 Stability and waves Goals Unconditional stability Conditional stability Buoyancy Buoyancy waves Moist adiabatic lapse rate Archimedes principle A body immersed in a fluid is buoyed up by a force equal
Stability and waves Goals Unconditional stability Conditional stability Buoyancy Buoyancy waves Moist adiabatic lapse rate Archimedes principle A body immersed in a fluid is buoyed up by a force equal
Climate-Quality Intercalibration of Scatterometer Missions
 Climate-Quality Intercalibration of Scatterometer Missions Lucrezia Ricciardulli and Frank Wentz Remote Sensing Systems, Santa Rosa, California IOVWST meeting Sapporo, Japan, May 2016 Photo Courtesy: 1
Climate-Quality Intercalibration of Scatterometer Missions Lucrezia Ricciardulli and Frank Wentz Remote Sensing Systems, Santa Rosa, California IOVWST meeting Sapporo, Japan, May 2016 Photo Courtesy: 1
Geophysical Fluid Dynamics of the Earth. Jeffrey B. Weiss University of Colorado, Boulder
 Geophysical Fluid Dynamics of the Earth Jeffrey B. Weiss University of Colorado, Boulder The Earth is a spinning sphere Coriolis force depends on latitude solar flux depends on latitude Michael Ritter,
Geophysical Fluid Dynamics of the Earth Jeffrey B. Weiss University of Colorado, Boulder The Earth is a spinning sphere Coriolis force depends on latitude solar flux depends on latitude Michael Ritter,
Super-parameterization of boundary layer roll vortices in tropical cyclone models
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Super-parameterization of boundary layer roll vortices in tropical cyclone models PI Isaac Ginis Graduate School of Oceanography
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Super-parameterization of boundary layer roll vortices in tropical cyclone models PI Isaac Ginis Graduate School of Oceanography
Importance of thermal effects and sea surface roughness for offshore wind resource assessment
 Importance of thermal effects and sea surface roughness for offshore wind resource assessment Bernhard Lange (1), Søren E. Larsen (2), Jørgen Højstrup (2), Rebecca Barthelmie (2) (1) University of Oldenburg,
Importance of thermal effects and sea surface roughness for offshore wind resource assessment Bernhard Lange (1), Søren E. Larsen (2), Jørgen Højstrup (2), Rebecca Barthelmie (2) (1) University of Oldenburg,
Atmospheric Forcing and the Structure and Evolution of the Upper Ocean in the Bay of Bengal
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Atmospheric Forcing and the Structure and Evolution of the Upper Ocean in the Bay of Bengal J. Thomas Farrar and Robert
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Atmospheric Forcing and the Structure and Evolution of the Upper Ocean in the Bay of Bengal J. Thomas Farrar and Robert
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF THE SURFACE MARINE ATMOSPHERIC BOUNDARY LAYER OVER AEGEAN SEA, GREECE
 CEST213 Athens, Greece Ref no: XXX EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF THE SURFACE MARINE ATMOSPHERIC BOUNDARY LAYER OVER AEGEAN SEA, GREECE KOSTOPOULOS* V. E. and HELMIS* C. G. *Department of Environmental Physics
CEST213 Athens, Greece Ref no: XXX EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF THE SURFACE MARINE ATMOSPHERIC BOUNDARY LAYER OVER AEGEAN SEA, GREECE KOSTOPOULOS* V. E. and HELMIS* C. G. *Department of Environmental Physics
Wind shear and its effect on wind turbine noise assessment Report by David McLaughlin MIOA, of SgurrEnergy
 Wind shear and its effect on wind turbine noise assessment Report by David McLaughlin MIOA, of SgurrEnergy Motivation Wind shear is widely misunderstood in the context of noise assessments. Bowdler et
Wind shear and its effect on wind turbine noise assessment Report by David McLaughlin MIOA, of SgurrEnergy Motivation Wind shear is widely misunderstood in the context of noise assessments. Bowdler et
Scales of Atmospheric Motion Scale Length Scale (m) Time Scale (sec) Systems/Importance Molecular (neglected)
 Supplement Wind, Fetch and Waves Scales of Atmospheric Motion Scale Length Scale (m) Time Scale (sec) Systems/Importance Molecular 10-7 - 10-2 10-1 (neglected) Coriolis not important Turbulent 10-2 10
Supplement Wind, Fetch and Waves Scales of Atmospheric Motion Scale Length Scale (m) Time Scale (sec) Systems/Importance Molecular 10-7 - 10-2 10-1 (neglected) Coriolis not important Turbulent 10-2 10
Impact of fine-scale wind stress curl structures on coastal upwelling dynamics : The Benguela system as a case of study.
 IOVWST Meeting May 21, 2015, Portland (OR) Impact of fine-scale wind stress curl structures on coastal upwelling dynamics : The Benguela system as a case of study. Fabien Desbiolles1,2, Bruno Blanke1,
IOVWST Meeting May 21, 2015, Portland (OR) Impact of fine-scale wind stress curl structures on coastal upwelling dynamics : The Benguela system as a case of study. Fabien Desbiolles1,2, Bruno Blanke1,
Scott Denning CSU CMMAP 1
 Thermodynamics, Buoyancy, and Vertical Motion Temperature, Pressure, and Density Buoyancy and Static Stability Adiabatic Lapse Rates Dry and Moist Convective Motions Present Atmospheric Composition What
Thermodynamics, Buoyancy, and Vertical Motion Temperature, Pressure, and Density Buoyancy and Static Stability Adiabatic Lapse Rates Dry and Moist Convective Motions Present Atmospheric Composition What
Jackie May* Mark Bourassa. * Current affilitation: QinetiQ-NA
 Jackie May* Mark Bourassa * Current affilitation: QinetiQ-NA Background/Motivation In situ observations (ships and buoys) are used to validate satellite observations Problems with comparing data Sparseness
Jackie May* Mark Bourassa * Current affilitation: QinetiQ-NA Background/Motivation In situ observations (ships and buoys) are used to validate satellite observations Problems with comparing data Sparseness
Global Ocean Wind Power Sensitivity to Surface Layer Stability
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1029/, Global Ocean Wind Power Sensitivity to Surface Layer Stability S. B. Capps Department of Earth System Science, University of California, Irvine,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1029/, Global Ocean Wind Power Sensitivity to Surface Layer Stability S. B. Capps Department of Earth System Science, University of California, Irvine,
Observations of Velocity Fields Under Moderately Forced Wind Waves
 Observations of Velocity Fields Under Moderately Forced Wind Waves Timothy P. Stanton Oceanography Department, Code OC/ST Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943-5000 phone: (831) 656 3144 fax: (831)
Observations of Velocity Fields Under Moderately Forced Wind Waves Timothy P. Stanton Oceanography Department, Code OC/ST Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943-5000 phone: (831) 656 3144 fax: (831)
Indian Ocean Seasonal Cycle Jérôme Vialard (IRD) LOCEAN Paris France From Schott & McCreary (Prog. Oc.
 Indian Ocean Seasonal Cycle Jérôme Vialard (IRD) LOCEAN Paris France jerome.vialard@ird.fr From Schott & McCreary (Prog. Oc. 2001) Outline The monsoon cycle The basin-scale dynamical response Thermocline
Indian Ocean Seasonal Cycle Jérôme Vialard (IRD) LOCEAN Paris France jerome.vialard@ird.fr From Schott & McCreary (Prog. Oc. 2001) Outline The monsoon cycle The basin-scale dynamical response Thermocline
Lifting satellite winds from 10 m to hub-height
 Lifting satellite winds from 10 m to hub-height Hasager, C.B., Badger, M., Peña, A., Hahmann, A., Volker, P. 23 May 2016 VindkraftNet meeting, DONG Energy, Skærbæk Motivation We have: Satellite wind maps
Lifting satellite winds from 10 m to hub-height Hasager, C.B., Badger, M., Peña, A., Hahmann, A., Volker, P. 23 May 2016 VindkraftNet meeting, DONG Energy, Skærbæk Motivation We have: Satellite wind maps
CHANGE OF THE BRIGHTNESS TEMPERATURE IN THE MICROWAVE REGION DUE TO THE RELATIVE WIND DIRECTION
 JP4.12 CHANGE OF THE BRIGHTNESS TEMPERATURE IN THE MICROWAVE REGION DUE TO THE RELATIVE WIND DIRECTION Masanori Konda* Department of Geophysics, Graduate School of Science, Kyoto University, Japan Akira
JP4.12 CHANGE OF THE BRIGHTNESS TEMPERATURE IN THE MICROWAVE REGION DUE TO THE RELATIVE WIND DIRECTION Masanori Konda* Department of Geophysics, Graduate School of Science, Kyoto University, Japan Akira
Modelling atmospheric stability with CFD: The importance of tall profiles
 ENERGY Modelling atmospheric stability with CFD: The importance of tall profiles VindKraftNet Seminar on Profiles Jean-François Corbett, Global Head of CFD Service 1 SAFER, SMARTER, GREENER DNV GL CFD
ENERGY Modelling atmospheric stability with CFD: The importance of tall profiles VindKraftNet Seminar on Profiles Jean-François Corbett, Global Head of CFD Service 1 SAFER, SMARTER, GREENER DNV GL CFD
A simple 1D numerical model for operational nowcasting of sea breeze at the HKIA
 A simple 1D numerical model for operational nowcasting of sea breeze at the HKIA Julian S.Y Tang, P. Cheung WSN16, 25-29 July 2016 Presented by P. CHEUNG Sea breeze at HKIA Mostly westerlies in background
A simple 1D numerical model for operational nowcasting of sea breeze at the HKIA Julian S.Y Tang, P. Cheung WSN16, 25-29 July 2016 Presented by P. CHEUNG Sea breeze at HKIA Mostly westerlies in background
Figure 1 Lake Ontario Offshore Study Area near East Toronto
 Wind Energy Resource Assessment and Forecasting for Sites on the Great Lakes Peter Taylor1,2, Jim Salmon2, Jack Simpson3, Wensong Weng1, Matthew Corkum1 and Hong Liu1 1 CRESS, York niversity, 2 Zephyr
Wind Energy Resource Assessment and Forecasting for Sites on the Great Lakes Peter Taylor1,2, Jim Salmon2, Jack Simpson3, Wensong Weng1, Matthew Corkum1 and Hong Liu1 1 CRESS, York niversity, 2 Zephyr
Investigation on Deep-Array Wake Losses Under Stable Atmospheric Conditions
 Investigation on Deep-Array Wake Losses Under Stable Atmospheric Conditions Yavor Hristov, Mark Zagar, Seonghyeon Hahn, Gregory Oxley Plant Siting and Forecasting Vestas Wind Systems A/S Introduction Introduction
Investigation on Deep-Array Wake Losses Under Stable Atmospheric Conditions Yavor Hristov, Mark Zagar, Seonghyeon Hahn, Gregory Oxley Plant Siting and Forecasting Vestas Wind Systems A/S Introduction Introduction
Surface Wind Speed Distributions: Implications for Climate and Wind Power
 Surface Wind Speed Distributions: Implications for Climate and Wind Power Scott B. Capps and Charles S. Zender Department of Earth System Science University of California, Irvine Thanks: W. Liu (JPL),
Surface Wind Speed Distributions: Implications for Climate and Wind Power Scott B. Capps and Charles S. Zender Department of Earth System Science University of California, Irvine Thanks: W. Liu (JPL),
Impacts of diffusion in stable boundary layers and orographic drag
 Impacts of diffusion in stable boundary layers and orographic drag Irina Sandu Thanks: Anton Beljaars, Ted Shepherd, Ayrton Zadra, Felix Pithan, Alessio Bozzo, Peter Bechtold 1 Outline Context: drag and
Impacts of diffusion in stable boundary layers and orographic drag Irina Sandu Thanks: Anton Beljaars, Ted Shepherd, Ayrton Zadra, Felix Pithan, Alessio Bozzo, Peter Bechtold 1 Outline Context: drag and
Chapter 2. Turbulence and the Planetary Boundary Layer
 Chapter 2. Turbulence and the Planetary Boundary Layer In the chapter we will first have a qualitative overview of the PBL then learn the concept of Reynolds averaging and derive the Reynolds averaged
Chapter 2. Turbulence and the Planetary Boundary Layer In the chapter we will first have a qualitative overview of the PBL then learn the concept of Reynolds averaging and derive the Reynolds averaged
Thermodynamic Boundary Layer profiles
 Thermodynamic Boundary Layer profiles Model and Aircraft data from the VOCALS 2008 Stratocumulus field campaign Paul Barrett July 2009 2 nd VOCALS MEETING Seattle, July 2009 Thermodynamics vl BEGIN ANALYSIS
Thermodynamic Boundary Layer profiles Model and Aircraft data from the VOCALS 2008 Stratocumulus field campaign Paul Barrett July 2009 2 nd VOCALS MEETING Seattle, July 2009 Thermodynamics vl BEGIN ANALYSIS
An Extreme Oceanic & Atmospheric Event in the South Pacific & Western Antarctica Associated With the El Niño
 An Extreme Oceanic & Atmospheric Event in the South Pacific & Western Antarctica Associated With the 2009-10 El Niño Tong Lee*, Carmen Böning, Will Hobbs, Josh Willis, Daria Halkides, Ichiro Fukumori,
An Extreme Oceanic & Atmospheric Event in the South Pacific & Western Antarctica Associated With the 2009-10 El Niño Tong Lee*, Carmen Böning, Will Hobbs, Josh Willis, Daria Halkides, Ichiro Fukumori,
TRIAXYS Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler Comparison Study
 TRIAXYS Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler Comparison Study By Randolph Kashino, Axys Technologies Inc. Tony Ethier, Axys Technologies Inc. Reo Phillips, Axys Technologies Inc. February 2 Figure 1. Nortek
TRIAXYS Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler Comparison Study By Randolph Kashino, Axys Technologies Inc. Tony Ethier, Axys Technologies Inc. Reo Phillips, Axys Technologies Inc. February 2 Figure 1. Nortek
SST contour interval 1K wind speed m/s. Imprint of ocean mesoscale on extratropical atmosphere warm SST associated with high wind speed
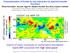 Characterization of frontal air-sea interaction by spectral transfer functions Niklas Schneider 1, Bunmei Taguchi 2, Masami Nonaka 2 and Akira Kuwano-Yoshida 2 1 International Pacific Research Center,
Characterization of frontal air-sea interaction by spectral transfer functions Niklas Schneider 1, Bunmei Taguchi 2, Masami Nonaka 2 and Akira Kuwano-Yoshida 2 1 International Pacific Research Center,
A Correction for Land Contamination of Atmospheric Variables near Land Sea Boundaries*
 APRIL 2007 K A R A E T A L. 803 A Correction for Land Contamination of Atmospheric Variables near Land Sea Boundaries* A. BIROL KARA, ALAN J. WALLCRAFT, AND HARLEY E. HURLBURT Oceanography Division, Naval
APRIL 2007 K A R A E T A L. 803 A Correction for Land Contamination of Atmospheric Variables near Land Sea Boundaries* A. BIROL KARA, ALAN J. WALLCRAFT, AND HARLEY E. HURLBURT Oceanography Division, Naval
Atmospheric Stability Affects Wind Turbine Performance and Wake Effect
 Atmospheric Stability Affects Wind Turbine Performance and Wake Effect Hong Liu, John Liu*, Gus DiMaria and Jon Fournier CanWEA Annual Conference and Exhibition, October 23-25, 2018, Calgary, AB *York
Atmospheric Stability Affects Wind Turbine Performance and Wake Effect Hong Liu, John Liu*, Gus DiMaria and Jon Fournier CanWEA Annual Conference and Exhibition, October 23-25, 2018, Calgary, AB *York
P3.1 CONTRIBUTIONS FROM CALIFORNIA COASTAL-ZONE SURFACE FLUXES TO HEAVY COASTAL PRECIPITATION: A CASE STUDY FROM AN EL NIÑO YEAR
 Symposium on Observing and Understanding the Variability of Water in Weather and Climate, 9-13 February, Long Beach, CA P3.1 CONTRIBUTIONS FROM CALIFORNIA COASTAL-ZONE SURFACE FLUXES TO HEAVY COASTAL PRECIPITATION:
Symposium on Observing and Understanding the Variability of Water in Weather and Climate, 9-13 February, Long Beach, CA P3.1 CONTRIBUTIONS FROM CALIFORNIA COASTAL-ZONE SURFACE FLUXES TO HEAVY COASTAL PRECIPITATION:
Module 8 Ocean Circulation and Surface Processes 8.1 Introduction Winds are produced in response to radiative heating of the atmosphere.
 Module 8 Ocean Circulation and Surface Processes 8.1 Introduction Winds are produced in response to radiative heating of the atmosphere. These winds constitute an important forcing for ocean currents,
Module 8 Ocean Circulation and Surface Processes 8.1 Introduction Winds are produced in response to radiative heating of the atmosphere. These winds constitute an important forcing for ocean currents,
Development of SAR-Derived Ocean Surface Winds at NOAA/NESDIS
 Development of SAR-Derived Ocean Surface Winds at NOAA/NESDIS Pablo Clemente-Colón, William G. Pichel, NOAA/NESDIS Frank M. Monaldo, Donald R. Thompson The Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory
Development of SAR-Derived Ocean Surface Winds at NOAA/NESDIS Pablo Clemente-Colón, William G. Pichel, NOAA/NESDIS Frank M. Monaldo, Donald R. Thompson The Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory
METCRAX II An upcoming field investigation of downslopewindstorm-type
 METCRAX II An upcoming field investigation of downslopewindstorm-type flows on the inner sidewall of Arizona's Meteor Crater C. David Whiteman, Sebastian W. Hoch, Rich Rotunno, Ron Calhoun, Manuela Lehner,
METCRAX II An upcoming field investigation of downslopewindstorm-type flows on the inner sidewall of Arizona's Meteor Crater C. David Whiteman, Sebastian W. Hoch, Rich Rotunno, Ron Calhoun, Manuela Lehner,
Air-water flux reconciliation between the atmospheric CO 2 profile and mass balance techniques
 1 Air-water flux reconciliation between the atmospheric CO 2 profile and mass balance techniques Wade R. McGillis 1,2, John W. H. Dacey 3, Jonathan D. Ware 3, David T. Ho 1, Jonathan T. Bent 1, William
1 Air-water flux reconciliation between the atmospheric CO 2 profile and mass balance techniques Wade R. McGillis 1,2, John W. H. Dacey 3, Jonathan D. Ware 3, David T. Ho 1, Jonathan T. Bent 1, William
Application for Consent to Conduct Marine Scientific Research. F Internal Waves in Straits (IWISE) Institution Contact Information Director
 1. General Information 1.1 Reference ID: Application for Consent to Conduct Marine Scientific Research Application number: Project name: F2010-111 Internal Waves in Straits (IWISE) 1.2 Sponsoring institution(s):
1. General Information 1.1 Reference ID: Application for Consent to Conduct Marine Scientific Research Application number: Project name: F2010-111 Internal Waves in Straits (IWISE) 1.2 Sponsoring institution(s):
Ocean Circulation. Si Hui Lee and Frances Wen. You can access ME at
 Ocean Circulation Si Hui Lee and Frances Wen You can access ME at http://tinyurl.com/oceancirculation Earth - the blue planet - 71% area covered by the oceans - 3/4 of ocean area between 3000-6000m deep
Ocean Circulation Si Hui Lee and Frances Wen You can access ME at http://tinyurl.com/oceancirculation Earth - the blue planet - 71% area covered by the oceans - 3/4 of ocean area between 3000-6000m deep
IOVWST Wind Stress Working Group May 29, 2014
 IOVWST Wind Stress Working Group May 29, 2014 1. Introduction The Ocean Vector Wind (OVW) Wind Stress Working Group (WSWG) is a subgroup of the International OVW Science Team (IOVWST). Formation of the
IOVWST Wind Stress Working Group May 29, 2014 1. Introduction The Ocean Vector Wind (OVW) Wind Stress Working Group (WSWG) is a subgroup of the International OVW Science Team (IOVWST). Formation of the
Monitoring Conditions Offshore with Satellites
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 15, 2017 Monitoring Conditions Offshore with Satellites Karagali, Ioanna; Hasager, Charlotte Bay; Badger, Merete; Bingöl, Ferhat; Ejsing Jørgensen, Hans Publication
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 15, 2017 Monitoring Conditions Offshore with Satellites Karagali, Ioanna; Hasager, Charlotte Bay; Badger, Merete; Bingöl, Ferhat; Ejsing Jørgensen, Hans Publication
UNDERSTANDING NEAR-SURFACE AND IN-CLOUD TURBULENT FLUXES IN THE COASTAL STRATOCUMULUS-TOPPED BOUNDARY LAYERS
 UNDERSTANDING NEAR-SURFACE AND IN-CLOUD TURBULENT FLUXES IN THE COASTAL STRATOCUMULUS-TOPPED BOUNDARY LAYERS FINAL TECHNICAL REPORT BY IOANNIS KALOGIROS OCTOBER 2004 NAVAL POSTGRADUATE SCHOOL, CA, USA
UNDERSTANDING NEAR-SURFACE AND IN-CLOUD TURBULENT FLUXES IN THE COASTAL STRATOCUMULUS-TOPPED BOUNDARY LAYERS FINAL TECHNICAL REPORT BY IOANNIS KALOGIROS OCTOBER 2004 NAVAL POSTGRADUATE SCHOOL, CA, USA
NSF's Ocean Observatories Initiative: Building Research Infrastructure for the Pacific Northwest and the Broader Community
 Agenda Item B.3.b Supplemental OOI PowerPoint April 2013 Ocean Observatories Initiative NSF's Ocean Observatories Initiative: Building Research Infrastructure for the Pacific Northwest and the Broader
Agenda Item B.3.b Supplemental OOI PowerPoint April 2013 Ocean Observatories Initiative NSF's Ocean Observatories Initiative: Building Research Infrastructure for the Pacific Northwest and the Broader
PHSC 3033: Meteorology Stability
 PHSC 3033: Meteorology Stability Equilibrium and Stability Equilibrium s 2 States: Stable Unstable Perturbed from its initial state, an object can either tend to return to equilibrium (A. stable) or deviate
PHSC 3033: Meteorology Stability Equilibrium and Stability Equilibrium s 2 States: Stable Unstable Perturbed from its initial state, an object can either tend to return to equilibrium (A. stable) or deviate
Sediment transport. Sediment transport. Boundary layer stress. τ : This lecture
 Sediment transport GEO3-4306: oastal Morphodynamics Sediment transport This lecture background modes of sediment transport cross-shore transport longshore transport sediment balance oundary layer stress
Sediment transport GEO3-4306: oastal Morphodynamics Sediment transport This lecture background modes of sediment transport cross-shore transport longshore transport sediment balance oundary layer stress
Regional coupled modeling of eddy-wind interaction in the California Current System Eddy kinetic energy and Ekman pumping
 Regional coupled modeling of eddy-wind interaction in the California Current System Eddy kinetic energy and Ekman pumping Hyodae Seo Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Art Miller & Joel Norris Scripps
Regional coupled modeling of eddy-wind interaction in the California Current System Eddy kinetic energy and Ekman pumping Hyodae Seo Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Art Miller & Joel Norris Scripps
Air Pollution Dispersion
 Air Pollution Dispersion Dispersion Processes Convective Dispersion Air Parcel Dynamics Adiabatic Process Lapse Rate Equilibrium and Stability Atmospheric Stability Stability and Dispersion Temperature
Air Pollution Dispersion Dispersion Processes Convective Dispersion Air Parcel Dynamics Adiabatic Process Lapse Rate Equilibrium and Stability Atmospheric Stability Stability and Dispersion Temperature
Wind Project Siting & Resource Assessment
 Wind Project Siting & Resource Assessment David DeLuca, Project Manager AWS Truewind, LLC 463 New Karner Road Albany, NY 12205 ddeluca@awstruewind.com www.awstruewind.com AWS Truewind - Overview Industry
Wind Project Siting & Resource Assessment David DeLuca, Project Manager AWS Truewind, LLC 463 New Karner Road Albany, NY 12205 ddeluca@awstruewind.com www.awstruewind.com AWS Truewind - Overview Industry
Mooring Modifications for the Reduction of Losses to Vandalism
 Mooring Modifications for the Reduction of Losses to Vandalism H. Paul Freitag Chris Meinig Andrew J. Shepherd Pacific Marine Environmental Laboratory Seattle, Washington, USA Linda D. Stratton JISAO/University
Mooring Modifications for the Reduction of Losses to Vandalism H. Paul Freitag Chris Meinig Andrew J. Shepherd Pacific Marine Environmental Laboratory Seattle, Washington, USA Linda D. Stratton JISAO/University
State Estimation of the California Current System Using 4DVar Ocean Data Assimilation
 State Estimation of the California Current System Using 4DVar Ocean Data Assimilation Hajoon Song, Arthur J. Miller and Bruce Cornuelle Scripps Institution of Oceanography, UCSD International Workshop
State Estimation of the California Current System Using 4DVar Ocean Data Assimilation Hajoon Song, Arthur J. Miller and Bruce Cornuelle Scripps Institution of Oceanography, UCSD International Workshop
DUE TO EXTERNAL FORCES
 17B.6 DNS ON GROWTH OF A VERTICAL VORTEX IN CONVECTION DUE TO EXTERNAL FORCES Ryota Iijima* and Tetsuro Tamura Tokyo Institute of Technology, Yokohama, Japan 1. INTRODUCTION Various types of vertical vortices,
17B.6 DNS ON GROWTH OF A VERTICAL VORTEX IN CONVECTION DUE TO EXTERNAL FORCES Ryota Iijima* and Tetsuro Tamura Tokyo Institute of Technology, Yokohama, Japan 1. INTRODUCTION Various types of vertical vortices,
Meteorology & Air Pollution. Dr. Wesam Al Madhoun
 Meteorology & Air Pollution Dr. Wesam Al Madhoun Dispersion = Advection (Transport) + Dilution (Diffusion) Source Transport Receptor Re-entrainment Fick s law of diffusion J= - D * D C/Dx Where, J= Mass
Meteorology & Air Pollution Dr. Wesam Al Madhoun Dispersion = Advection (Transport) + Dilution (Diffusion) Source Transport Receptor Re-entrainment Fick s law of diffusion J= - D * D C/Dx Where, J= Mass
Alongshore wind stress (out of the page) Kawase/Ocean 420/Winter 2006 Upwelling 1. Coastal upwelling circulation
 Kawase/Ocean 420/Winter 2006 Upwelling 1 Coastal upwelling circulation We found that in the northern hemisphere, the transport in the surface Ekman layer is to the right of the wind. At the bottom, there
Kawase/Ocean 420/Winter 2006 Upwelling 1 Coastal upwelling circulation We found that in the northern hemisphere, the transport in the surface Ekman layer is to the right of the wind. At the bottom, there
OAFlux: global, 0.25, daily
 Including ASCAT in OAFlux Global Vector Wind Analysis (1987 present) with programming support from Dr. Xiangze Jin July 1987 OAFlux: global, 0.25, daily QuikSCAT AMSRE SSMI (F08, F10, F11, F13, F14, F15,
Including ASCAT in OAFlux Global Vector Wind Analysis (1987 present) with programming support from Dr. Xiangze Jin July 1987 OAFlux: global, 0.25, daily QuikSCAT AMSRE SSMI (F08, F10, F11, F13, F14, F15,
Local Winds. Please read Ahrens Chapter 10
 Local Winds Please read Ahrens Chapter 10 Scales of Motion Microscale: meters Turbulent eddies Formed by mechanical disturbance or convection Lifetimes of minutes Mesoscale: km s to 100 s of km s Local
Local Winds Please read Ahrens Chapter 10 Scales of Motion Microscale: meters Turbulent eddies Formed by mechanical disturbance or convection Lifetimes of minutes Mesoscale: km s to 100 s of km s Local
Exploring wave-turbulence interaction through LES modeling
 Exploring wave-turbulence interaction through LES modeling Mireia Udina 1 Jielun Sun 2 M. Rosa Soler 1 Branko Kosović 2 1. Dept. Astronomia i Meteorologia Universitat de Barcelona, Barcelona, Catalunya
Exploring wave-turbulence interaction through LES modeling Mireia Udina 1 Jielun Sun 2 M. Rosa Soler 1 Branko Kosović 2 1. Dept. Astronomia i Meteorologia Universitat de Barcelona, Barcelona, Catalunya
Observed directional characteristics of the wind, wind stress, and surface waves on the open ocean
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 99, NO. C11, PAGES 22,589 22,596, NOVEMBER 15, 1994 Observed directional characteristics of the wind, wind stress, and surface waves on the open ocean Karl F. Rieder
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 99, NO. C11, PAGES 22,589 22,596, NOVEMBER 15, 1994 Observed directional characteristics of the wind, wind stress, and surface waves on the open ocean Karl F. Rieder
Observations and Modeling of Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction over the California Current System
 Observations and Modeling of Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction over the California Current System Cape Blanco Dudley Chelton 1, Xin Jin 2, Jim McWilliams 2 & Tracy Haack 3 1 Oregon State University
Observations and Modeling of Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction over the California Current System Cape Blanco Dudley Chelton 1, Xin Jin 2, Jim McWilliams 2 & Tracy Haack 3 1 Oregon State University
Flight Corridor. The speed-altitude band where flight sustained by aerodynamic forces is technically possible is called the flight corridor.
 Flight Corridor The speed-altitude band where flight sustained by aerodynamic forces is technically possible is called the flight corridor. The subsonic Boeing 747 and supersonic Concorde have flight corridors
Flight Corridor The speed-altitude band where flight sustained by aerodynamic forces is technically possible is called the flight corridor. The subsonic Boeing 747 and supersonic Concorde have flight corridors
Evaluating the impact of ocean gravity wave variability on Aquarius satellite measurements. D. Vandemark, H. Feng Univ. of New Hampshire/EOS
 Evaluating the impact of ocean gravity wave variability on Aquarius satellite measurements D. Vandemark, H. Feng Univ. of New Hampshire/EOS Global Wave model fields, Aquarius L2_wwav files*, Day 240-271
Evaluating the impact of ocean gravity wave variability on Aquarius satellite measurements D. Vandemark, H. Feng Univ. of New Hampshire/EOS Global Wave model fields, Aquarius L2_wwav files*, Day 240-271
SIO 210 Introduction to Physical Oceanography Mid-term examination November 4, 2013; 50 minutes
 SIO 210 Introduction to Physical Oceanography Mid-term examination November 4, 2013; 50 minutes Closed book; one sheet of your own notes is allowed. A calculator is allowed. (100 total points.) Possibly
SIO 210 Introduction to Physical Oceanography Mid-term examination November 4, 2013; 50 minutes Closed book; one sheet of your own notes is allowed. A calculator is allowed. (100 total points.) Possibly
Observed Roughness Lengths for Momentum and Temperature on a Melting Glacier Surface
 5 Observed Roughness Lengths for Momentum and Temperature on a Melting Glacier Surface The roughness lengths for momentum and temperature are calculated on a melting glacier surface. Data from a five level
5 Observed Roughness Lengths for Momentum and Temperature on a Melting Glacier Surface The roughness lengths for momentum and temperature are calculated on a melting glacier surface. Data from a five level
Reference wind speed anomaly over the Dutch part of the North Sea
 Reference wind speed anomaly over the Dutch part of the North Sea A.J. Brand This report has been presented at the European Offshore Wind 2009 Conference, Stockholm, 4-6 September, 2009 ECN-M--09-28 2
Reference wind speed anomaly over the Dutch part of the North Sea A.J. Brand This report has been presented at the European Offshore Wind 2009 Conference, Stockholm, 4-6 September, 2009 ECN-M--09-28 2
The Use of Bulk and Profile Methods for Determining Surface Heat Fluxes in the Presence of Glacier Winds
 3 The Use of Bulk and Profile Methods for Determining Surface Heat Fluxes in the Presence of Glacier Winds A -D second-order closure model and in situ observations on a melting glacier surface are used
3 The Use of Bulk and Profile Methods for Determining Surface Heat Fluxes in the Presence of Glacier Winds A -D second-order closure model and in situ observations on a melting glacier surface are used
A. Bentamy 1, S. A. Grodsky2, D.C. Fillon1, J.F. Piollé1 (1) Laboratoire d Océanographie Spatiale / IFREMER (2) Univ. Of Maryland
 Calibration and Validation of Multi-Satellite scatterometer winds A. Bentamy 1, S. A. Grodsky2, D.C. Fillon1, J.F. Piollé1 (1) Laboratoire d Océanographie Spatiale / IFREMER (2) Univ. Of Maryland Topics
Calibration and Validation of Multi-Satellite scatterometer winds A. Bentamy 1, S. A. Grodsky2, D.C. Fillon1, J.F. Piollé1 (1) Laboratoire d Océanographie Spatiale / IFREMER (2) Univ. Of Maryland Topics
Derivation of Turbulent Flux Profiles and Roughness Lengths from Katabatic Flow Dynamics
 Derivation of Turbulent Flux Profiles and Roughness Lengths from Katabatic Flow Dynamics The dynamics of katabatic flows are used to determine the vertical momentum flux profiles and surface roughness
Derivation of Turbulent Flux Profiles and Roughness Lengths from Katabatic Flow Dynamics The dynamics of katabatic flows are used to determine the vertical momentum flux profiles and surface roughness
MET Lecture 8 Atmospheric Stability
 MET 4300 Lecture 8 Atmospheric Stability Stability Concept Stable: Ball returns to original position Neutral: Ball stays wherever it is placed Unstable: Displacement grows with time. Atmospheric Stability
MET 4300 Lecture 8 Atmospheric Stability Stability Concept Stable: Ball returns to original position Neutral: Ball stays wherever it is placed Unstable: Displacement grows with time. Atmospheric Stability
The Evolution of Vertical Spatial Coherence with Range from Source
 The Evolution of Vertical Spatial Coherence with Range from Source Peter H. Dahl Applied Physics Laboratory and Mechanical Engineering Dept. University of Washington Research sponsored by U.S. Office of
The Evolution of Vertical Spatial Coherence with Range from Source Peter H. Dahl Applied Physics Laboratory and Mechanical Engineering Dept. University of Washington Research sponsored by U.S. Office of
Atmospheric & Ocean Circulation-
 Atmospheric & Ocean Circulation- Overview: Atmosphere & Climate Atmospheric layers Heating at different latitudes Atmospheric convection cells (Hadley, Ferrel, Polar) Coriolis Force Generation of winds
Atmospheric & Ocean Circulation- Overview: Atmosphere & Climate Atmospheric layers Heating at different latitudes Atmospheric convection cells (Hadley, Ferrel, Polar) Coriolis Force Generation of winds
ATMS 310 Tropical Dynamics
 ATMS 310 Tropical Dynamics Introduction Throughout the semester we have focused on mid-latitude dynamics. This is not to say that the dynamics of other parts of the world, such as the tropics, are any
ATMS 310 Tropical Dynamics Introduction Throughout the semester we have focused on mid-latitude dynamics. This is not to say that the dynamics of other parts of the world, such as the tropics, are any
