PRESSURE AREA CARE LEARNER INFORMATION PACK AND WORKBOOK. Name. Worcestershire Health and Care. Worcestershire Acute Hospitals NHS Trust
|
|
|
- Imogene Patterson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PRESSURE AREA CARE LEARNER INFORMATION PACK AND WORKBOOK Name Worcestershire Acute Hospitals NHS Trust Worcestershire Health and Care Redditch and Bromsgrove Clinical Commissioning Group South Worcestershire Clinical Commissioning Group Wyre Forest Clinical Commissioning Group
2 Contents Section 1 Normal structure and function of the skin Page 3 Section 2 How pressure ulcers develop Page 6 Section 3 The importance of risk assessment Page 7 Section 4 Skin Inspection Page 10 Section 5 Prevention Page 10 Section 6 Repositioning Page 12 Section 7 Management of pressure damage Page 14 Section 8 Encouraging personal engagement Page 15 Introduction Pressure ulcers (also known as pressure sores) are a common problem, which can severely affect the quality of life for individuals. However with good care, most can be avoided, by removing the causes of pressure damage. This workbook will enable you to undertake pressure area care for individuals, following the individual s care plan and risk assessment, as well as relevant protocols and procedures within your work area. The aim is to maintain healthy skin and thus prevent breakdown and the development of pressure sores. You will learn about the risk factors that make an individual more likely to develop pressure ulcers, changes in skin condition to look out for and how to position individuals to reduce pressure. You will learn the 5 elements of care that can be bundled together to prevent pressure ulcers developing. SSKIN: Surface Skin Inspection Keep Moving Incontinence Nutrition Throughout the workbook, you will have the opportunity to demonstrate your learning through activities and questions. 2
3 1. The normal structure and function of the skin The skin is an amazing organ. Measuring around 2 square meters and accounting for up to 15% of your body weight, it is the largest and heaviest organ of your body. It is made up of three layers: The epidermis this is the thin outer layer of the skin that you can see when you look at yourself. It is only about 0.04mm thick and does not have its own network of blood vessels, so that it has to get its nutrients from the underlying dermal layer. Every 4 weeks the epidermis completely renews itself as the outer cells are worn away and replaced with new ones from underneath. The dermis this lies beneath the epidermis, it is about 0.5mm thick and is the active part of the skin. It contains blood vessels, nerves, hair follicles, sebaceous (oil) and sweat glands and lymphatics. The dermis contains collagen, fat and elastin fibres which give the skin its strength and flexibility. Subcutaneous fat layer this layer of subcutaneous fat lies under the dermis. It also contains blood vessels and connective tissue. It forms a protective layer over the underlying organs and structures and also acts as an energy source for the body and provides insulation from changes in the outside temperature. 3
4 The skin has several different functions, but its main job is to protect the body. It does this by: Regulating temperature when the outside temperature rises, the body is cooled by the production and evaporation of sweat from the skin. Blood vessels in the skin dilate to increase blood flow near the surface of the skin (that s why you go red when you get hot) so that heat can be radiated away from the body. When the outside temperature falls, the skin tries to insulate the body by forming goose bumps, this makes the hairs stand up trapping warm air near the body and the blood vessels contract to limit the heat lost at its surface. Forming a physical barrier the skin helps to shield the body from mechanical, thermal or chemical damage. It also protects you from UV radiation, bacterial invasion and stops you becoming dehydrated. Providing sensation nerve endings within the skin can detect changes in temperature and pressure. They can also detect vibration and pain. Excreting waste products the skin is one way in which the body gets rid of excess heat, water, salts and toxic organic compounds. The skin is considered to be an organ because one of its important functions is to help in the production of Vitamin D. When your skin is exposed to sunlight, the UV rays produce Vitamin D which is needed to form healthy bones. The appearance of the skin is important because if damaged or abnormal in any way, it can affect an individual s body image and quality of life. Finally skin plays a part in communicating with others. Like body language, changes in skin colour (e.g. blushing), facial expression and body odour can all give clues as to how an individual is really feeling. Sometimes this may be at odds with what the individual is actually saying. 4
5 ACTIVITY 1 1. What are the 3 layers of the skin? Briefly describe each one 2. Name four functions of the skin 3. Why is the skin considered to be an organ? 5
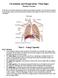
6 2. How pressure ulcers develop Pressure ulcers, often called bed sores, can be a problem for any individual in any care setting. They develop when unrelieved pressure prevents the blood being supplied to the cells and if the pressure is not removed, the damage will spread. The severity of the damage can range from reddening of the skin to large cavity wounds with damage to muscles and even bones. Damage may be caused by: prolonged periods of inactivity (lying or sitting in bed or in a chair for hours without moving) high pressure for relatively short periods of time (e.g, a commode for 20 minutes or poor handling when being moved) pressure from equipment being used to monitor or treat an individual (e.g. catheters, heart monitors or bandages) The most common sites for pressure ulcers to develop are: The sacrum (the curved triangular bone just above the buttocks) accounts for around 30% of all pressure ulcers The heels accounts for around 25-30% of all pressure ulcers The bottom accounts for around 10% of all pressure ulcers The remaining 30% of pressure ulcers recorded generally occur over bony prominences such as the shoulders, ankles and elbows (see diagram below). figure 1 6
7 ACTIVITY 2 List where you think the pressure areas would be on a person lying in bed on their back 3. The importance of using pressure damage risk assessment tools Individuals who are immobile spend a long time in a bed, or wheelchair, or who spend a long time sitting each day are particularly prone to developing pressure ulcers. However some individuals are more at risk of developing pressure ulcers than others, and a number of factors have been identified as being important in predicting who is most at risk. There are several risk assessment This starts with the risk assessment tool that you will have been introduced to in your training. Internal (Intrinsic) risk factors these are factors to do with the individual and what makes them at risk. These include: Age those over 65, neonates and very young children are at highest risk. Health if the individual is unwell, they are at increased risk. Acute illness can cause changes in the body s normal functioning e.g. raised temperature, low blood pressure, constriction of the blood vessels. Chronic or terminal illness may result in reduced mobility or poor circulation. Certain medications can also increase the risk, e.g. by increasing sedation. Level of consciousness if the individual is lethargic or becomes unconscious, he or she will not be able to change position to reduce pressure e.g. following acute illness or surgery. Weight Underweight and overweight individuals are at risk of developing pressure ulcers: underweight as the bony areas on the body become more prominent and overweight because there is more weight on the pressure points and the blood supply has further to travel through the fat layer to the dermis. Nutritional status those who are malnourished or dehydrated are at most risk. Poor nutrition can affect the elasticity of the skin and it s ability to fight infection. Previous history individuals who have suffered from pressure damage in the past are more likely to develop pressure sores. 7
8 Mobility patients who have reduced mobility or are immobile are most at risk, because they are less able to relieve pressure by moving position. Sensory functioning individuals with sensory impairment (e.g. those unable to sense pain due to nerve damage or spinal injury) may not receive the stimulus to move to relieve pressure and are at greater risk. Urinary or bowel incontinence/leg ulcer moisture Vascular disease individuals with poor circulation due to damaged or partially blocked blood vessels are at increased risk of pressure damage. This is due to reduced blood volume and reduced flow of blood in the arteries and capillaries supplying the skin and underlying tissues. Extrinsic risk factors - these are factors to do with the surrounding environment and the things that can cause the damage e.g. Amount of pressure e.g. from a bandage that has been applied too tightly Type of pressure e.g. from being moved across a bed Duration of pressure e.g. how long the individual remains in the same position Level of care available e.g. staffing levels may mean that the individual can be moved every 2 hours or only 4 times per day Type of mattress using low pressure foam mattresses may reduce the risk Design of seat or wheelchair Education showing individuals how to sit correctly and explaining why frequent repositioning is important can reduce the risk External influences upon the skin such as urine, faeces, starch from sheets, perfumes etc Risk assessment tools, combined with clinical judgment of the h staff are used to formulate the individual s care plan to prevent pressure ulcers developing and to treat or manage any already present. The level of risk will be indicated on page 3 of the Think SSKIN pressure sore prevention guide 8
9 ACTIVITY 3 Mr. Brown is 67, weighs more than he should (15 stone and he is 5ft 7ins), he has a history of high blood pressure and is recovering from a hip replacement operation which has limited his mobility. 1. What are the factors that put Mr. Brown at risk of developing pressure ulcers? Mrs. Smith is 75; she is in the terminal stages of breast cancer and is confined to bed. She finds it difficult to eat, and needs diamorphine to help control the pain. Unfortunately this medication makes her very drowsy and she spends much of the day drifting in and out of consciousness. 2. What are the factors that put Mrs. Smith at risk of developing pressure ulcers? 3. Do you think Mr Brown or Mrs Smith is more at risk and why? 9
10 4. Skin Inspection: Check the skin regularly as this will help to prevention pressure ulcers through early detection of redness. Check when washing or dressing a person to make it part of a daily routine. Keep Moving: Getting individuals moving so that they can change position by themselves Making sure that individuals are regularly repositioned to relieve pressure over bony prominences when sitting in a chair or lying on a bed. Keeping time spent on the damaged area to a minimum Moving and handling individuals with great care to prevent friction, abrasion or stretching of the skin Incontinence: Keeping the skin clean and dry, using soap and water or prescribed skin cleansers not baby wipes. Ensuring any prescribed creams or barrier creams are applied as directed. Nutrition and Hydration: Making sure each individual has access to a drink to keep the skin hydrated and adequate nutrition to maintain healthy skin Finally educate individuals on how to avoid damage by involving them in their care and implementing the SSKIN bundle 5. Prevention Two important aspects of your job in preventing pressure damage will be skin inspection and repositioning. Skin inspection this is the best way of identifying whether pressure damage could become a problem. Ideally the individual should inspect their own skin regularly for any changes, but this is not always possible and you may have to carry out the inspection for them. This will involve checking the skin over bony prominences (e.g. the heels, sacrum, buttocks) and any other areas likely to be affected by pressure. The signs of early pressure damage that you should look out for are: Redness Non-blanching redness of the skin (erythema) does not go white (blanch) if you apply light finger pressure. (see figure 2). On pigmented skin, redness will not be seen; a blue/purple tone may be seen as the indicator of pressure damage. Other signs to look and feel for are, the skin may also feel warm to the touch, show signs of oedema (swelling) or become hard. 10
11 Figure 2: Blisters blisters over a bony areas indicate that the epidermis has become separated from the underlying dermis. Discolouration in the early stages the skin usually becomes red. However watch out for other discolouration which may indicate that significant damage has already occurred. If the skin appears more blue, purple or black, it could mean that there is more extensive damage below the surface of the skin. In particular if the skin is black with a hard or leathery covering it indicates that tissue necrosis (death) has occurred and the individual has a severe pressure ulcer. It is more difficult to see early signs of pressure damage in dark or heavily pigmented skin, which may appear purple or blue rather than red. Figure 3: 11
12 6. Repositioning If possible the individual should be encouraged to reposition themselves whenever they begin to feel uncomfortable. However if this is not possible, or practical, you will have to carry out regular manual repositioning. Frequency - the starting point for any effective turning regime should be every 2 hours. If there is no marking of the skin during this time you can increase time slowly to determine the maximum amount of time an individual can be left for. This is particularly helpful at night to enable people to have longer between turns. Support surfaces it is important to choose an appropriate support surface when repositioning individuals. Community nurses or OT s will undertake this assessment for you. Please visit link page on reacttoredskin website. Mattresses Foam and alternating air matresses can be used with people at risk of developing pressure ulcers. Seating selecting appropriate seating should be left to a trained assessor such as a physiotherapist or occupational therapist. They should ensure that the entire chair and cushion ensure correct weight distribution, postural alignment and support for the feet. Heel protectors the heels are at high risk of developing pressure sores, because there is very little soft tissue protecting the bone. The risk is even greater if the individual suffers from swelling of the lower leg due to circulatory problems. To reduce the risk an inflatable heel protector should be used when the individual is in bed or sitting with their feet on a footstool. If an inflatable heel protector is not available, foam heel lift protectors or pillows may be used instead. The community nurse will plan which heel protector is to be used by the individual. Other aids there are many aids available claiming to help reduce the risk of pressure ulcers. However none of these have been scientifically proven to help and indeed some may even make things worse. In particular you should not use: Ring cushions or other doughnut shaped devices Synthetic sheepskins Water-filled gloves The community nurses or therapists will need to be alerted if any of the equipment looks like it is not functioning. For example an air mattress that is alarming or deflated, a foam mattress that is ripped/torn or dipped in the centre. You may be asked to reinflate static air equipment (Repose). This may include a mattress, cushion or foot protectors. The hand held pump will be provided with the equipment. Ask for training if you are unsure. Alternative positions there are many repositioning alternatives. If possible get the individual to stand. If this is not possible one of the most popular alternative positions is the sideways 30 degree tilt. The body is positioned using pillows to reduce pressure over the bony prominences.. The advantages are that repositioning can be carried out regularly with minimal disturbance to the patient and less risk of back injury for the carer. 12
13 ACTIVITY 4 1. List 5 things you can do to help prevent pressure damage 2. What are the three most common early signs of pressure damage? 13
14 7.Management of Existing Pressure Ulcer Damage There are two main areas of concern for Health & Safety when carrying out pressure area care: a) Infection control It is very important to prevent any areas with pressure damage becoming infected. Not only will infection delay healing of the wound, but it could lead to more serious systemic (whole body) infections such as septicaemia (bacterial infection of the bloodstream). Such systemic infections can be fatal in vulnerable patients such as neonates (newborn infants) and the elderly. You can help to prevent the spread of infection by taking standard precautions including: Washing your hands thoroughly before and after carrying out pressure area care Wearing disposable gloves and aprons Wearing a new pair of gloves for each patient and washing your hands thoroughly between individuals. Making sure the pressure ulcer is covered with a dressing to minimize the risk of airborne cross-infection. Contact a trained nurse if the dressing has come off. b) Moving and handling Moving and handling injuries are unfortunately fairly common in any care setting. There is a risk both to the carer and the service user. To reduce the risk of moving and handling injuries when carrying out pressure area care, you should carefully follow the procedures specified by your workplace. These should include: Using correct techniques for lifting, carrying, moving, setting down and repositioning individuals. Checking your position and posture throughout the move Using hoists or other technical moving and handling aidswherever possible particularly a slide sheet to prevent shearing on the skin. Taking particular care when moving vulnerable individualsacross a bed or cushion to prevent abrasion of the skin due to friction between the skin and the mattress or cushion. Any abrasion can make superficial pressure ulcers worse especially if the individual s skin is moist or wet due to sweating or incontinence. 14
15 8. How to encourage individuals to be involved in their own pressure area care. Some individuals may only be at risk of developing pressure damage for a short while e.g. whilst they recover from an acute illness or surgery. For others, there may be a constant risk of pressure damage due to loss of mobility or an illness It is important that you encourage individuals to be involved in their own pressure area care where possible. You can do this by: Explaining the importance of pressure area care Educating them on the signs of pressure damage to look out for Making sure they know what to do if they suspect pressure damage. Contact the carer or community nurse direct Getting them to regularly check the condition of their skin If possible reminding them to frequently reposition themselves Stressing the need for them to maintain a high standard of hygiene to keep skin clean and dry Explaining the importance of eating a healthy diet and drinking enough water Helping them to become mobile again as soon as possible e.g. by using mobility aids or exercise How can you make a difference? Be aware of how to prevent pressure ulcers. Know the signs to look and feel for. Encourage mobility for all individuals. Report any early signs for a more in-depth assessment. Provide individuals with information on prevention and help them to understand it. Working together as a team of carers with the individual at risk is the best way to prevent pressure ulcers occurring. Pressure ulcer prevention is everyone s business and by working together and knowing when to ask for additional support, the development of pressure ulcers will become a rare event. 15
16 For additional information about the prevention of pressure ulcers you can use one of the following resource websites: Information contained within this booklet has been approved by: Worcestershire Acute Hospitals NHS Trust Worcestershire Health and Care Redditch and Bromsgrove Clinical Commissioning Group South Worcestershire Clinical Commissioning Group Wyre Forest Clinical Commissioning Group 16
17 17
18 18
PRESSURE AREA CARE LEARNER INFORMATION PACK AND WORKBOOK. Name. North Warwickshire Clinical Commissioning Group. South Warwickshire
 PRESSURE AREA CARE LEARNER INFORMATION PACK AND WORKBOOK Name North Warwickshire Clinical Commissioning Group South Warwickshire Clinical Commissioning Group South Warwickshire Introduction Pressure ulcers
PRESSURE AREA CARE LEARNER INFORMATION PACK AND WORKBOOK Name North Warwickshire Clinical Commissioning Group South Warwickshire Clinical Commissioning Group South Warwickshire Introduction Pressure ulcers
Pressure area prevention and care
 Birmingham Community Healthcare NHS Trust Think... S S K I N 2014 Pressure area prevention and care Learner information pack and workbook Name... Date completed... Marked by... Marks... / Introduction
Birmingham Community Healthcare NHS Trust Think... S S K I N 2014 Pressure area prevention and care Learner information pack and workbook Name... Date completed... Marked by... Marks... / Introduction
Staying healthy How to prevent pressure ulcers. Including: fluid intake, nutrition, skincare, and the prevention of falls.
 Staying healthy How to prevent pressure ulcers Including: fluid intake, nutrition, skincare, and the prevention of falls. Staying healthy: How to prevent pressure ulcers Introduction Torbay and South Devon
Staying healthy How to prevent pressure ulcers Including: fluid intake, nutrition, skincare, and the prevention of falls. Staying healthy: How to prevent pressure ulcers Introduction Torbay and South Devon
Pressure. There are a number of factors that put you at risk. Limited mobility can place extended pressure on an area of your body.
 Pressure Preventing pressure sores is a daily concern for individuals who have a spinal cord injury (SCI). You want to stay healthy and avoid this serious skin problem in order to be free to do whatever
Pressure Preventing pressure sores is a daily concern for individuals who have a spinal cord injury (SCI). You want to stay healthy and avoid this serious skin problem in order to be free to do whatever
Pressure Ulcers ecourse
 Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 5.2: Repositioning & Support Surfaces Handout 2015 Steppingstones Partnership, Inc. / Learning Nurse: All Rights Reserved See: Terms of Use at LearningNurse.org for acceptable
Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 5.2: Repositioning & Support Surfaces Handout 2015 Steppingstones Partnership, Inc. / Learning Nurse: All Rights Reserved See: Terms of Use at LearningNurse.org for acceptable
Pressure Area Management in Critical Care
 Academic Department of Critical Care Queen Alexandra Hospital Portsmouth Pressure Area Management in Critical Care Aim: Scope: To provide guidance on pressure area management for Critical Care patients.
Academic Department of Critical Care Queen Alexandra Hospital Portsmouth Pressure Area Management in Critical Care Aim: Scope: To provide guidance on pressure area management for Critical Care patients.
Abduction- Where the legs rotate outward from the pelvis. Often caused by too wide or short of a seat or too deep an ischial well.
 Abduction- Where the legs rotate outward from the pelvis. Often caused by too wide or short of a seat or too deep an ischial well. Larger patients often have an issue here due to tissue. Leg troughs, thigh
Abduction- Where the legs rotate outward from the pelvis. Often caused by too wide or short of a seat or too deep an ischial well. Larger patients often have an issue here due to tissue. Leg troughs, thigh
Soft Tissue Injuries
 KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES Soft Tissue Injuries 1. List two signs of closed wounds. 2. List four purposes of bandaging. 3. Describe the best initial defence against infection of an open wound. 4. Describe how
KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES Soft Tissue Injuries 1. List two signs of closed wounds. 2. List four purposes of bandaging. 3. Describe the best initial defence against infection of an open wound. 4. Describe how
Intelli-Gel Cushions. cushions. kirton-healthcare.co.uk
 Cushions kirton-healthcare.co.uk 3 What is a Pressure Ulcer? A pressure ulcer is an injury to the skin and tissue under it. Sitting or lying in the same position will begin to cut off the flow of blood
Cushions kirton-healthcare.co.uk 3 What is a Pressure Ulcer? A pressure ulcer is an injury to the skin and tissue under it. Sitting or lying in the same position will begin to cut off the flow of blood
CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse: Module 5.2 Quiz II page 1
 CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse: Module 5.2 Quiz II 1. What factors determine how often we should reposition an individual? a. Staff availability b. Patient health condition c. Skin condition d. Support
CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse: Module 5.2 Quiz II 1. What factors determine how often we should reposition an individual? a. Staff availability b. Patient health condition c. Skin condition d. Support
Changing positions. 1. Turn the patient often (at least every two hours or so).
 Changing positions If a patient must spend a lot of time in bed, changing positions and keeping his body aligned is important. It can help: exercise his joints him breathe better improve blood flow prevent
Changing positions If a patient must spend a lot of time in bed, changing positions and keeping his body aligned is important. It can help: exercise his joints him breathe better improve blood flow prevent
Harvest Healthcare Clinical Evidence. P161M - Viscoflex Mattress P161MOE - Viscoflex Evolutive Mattress
 Harvest Healthcare Clinical Evidence P161M - Viscoflex Mattress P161MOE - Viscoflex Evolutive Mattress 2 PRESSURE ULCERS AN INTRODUCTION Definition Pressure Ulcer: Pressure ulcers (also known as pressure
Harvest Healthcare Clinical Evidence P161M - Viscoflex Mattress P161MOE - Viscoflex Evolutive Mattress 2 PRESSURE ULCERS AN INTRODUCTION Definition Pressure Ulcer: Pressure ulcers (also known as pressure
Staying Warm in the Winter
 Staying Warm in the Winter When winter arrives it doesn t mean an end to enjoying the outdoors. Staying active during the winter months is essential! Instead, it s important to keep warm while working
Staying Warm in the Winter When winter arrives it doesn t mean an end to enjoying the outdoors. Staying active during the winter months is essential! Instead, it s important to keep warm while working
AIRCARE INTERNATIONAL Unit 3, Shannonside Business Park, Birdhill, Co. Tipperary,Ireland Tel : +353 (0) Fax : +353 (0)
 Introduction Pressure ulcers are common and costly, posing a serious health concern impacting cost of care, reimbursement and quality of life, while affecting patients, healthcare workers and healthcare
Introduction Pressure ulcers are common and costly, posing a serious health concern impacting cost of care, reimbursement and quality of life, while affecting patients, healthcare workers and healthcare
Cold and Heat Emergencies Video Cold & Heat Emergencies
 CHAPTER 20 Cold and Heat Emergencies Video Cold & Heat Emergencies Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the different types of cold and heat emergencies and what you can do to prevent them. 2. Explain factors
CHAPTER 20 Cold and Heat Emergencies Video Cold & Heat Emergencies Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the different types of cold and heat emergencies and what you can do to prevent them. 2. Explain factors
Soft Tissue Trauma. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Recognize and manage various types of soft tissue injuries. State function of skin
 Soft Tissue Trauma Lesson Goal Recognize and manage various types of soft tissue injuries Lesson Objectives State function of skin List and describe 3 layers of skin Explain why BSI is a critical safety
Soft Tissue Trauma Lesson Goal Recognize and manage various types of soft tissue injuries Lesson Objectives State function of skin List and describe 3 layers of skin Explain why BSI is a critical safety
What is a wound? An injury to the skin and some times other deeper soft tissues. Types:
 1 Dr. Samer Sara What is a wound? An injury to the skin and some times other deeper soft tissues. Types: Open wounds: Skin is torn or cut, often leads to bleeding. Closed wounds: Skin is not affected and
1 Dr. Samer Sara What is a wound? An injury to the skin and some times other deeper soft tissues. Types: Open wounds: Skin is torn or cut, often leads to bleeding. Closed wounds: Skin is not affected and
wheelchair user guide motivation quality of life
 quality of life Sri Lanka 104 Havelock Road Colombo 5 Sri Lanka Tel: +94 11 5378 230 to 3 Fax: +94 11 2589 334 email: info@.org.uk website: www.worldmade.info wheelchair user guide checking for pressure
quality of life Sri Lanka 104 Havelock Road Colombo 5 Sri Lanka Tel: +94 11 5378 230 to 3 Fax: +94 11 2589 334 email: info@.org.uk website: www.worldmade.info wheelchair user guide checking for pressure
Heat Stress Prevention Written Program Laredo ISD Safety/Risk/Emergency Management Department
 Heat Stress Prevention Written Program Laredo ISD Safety/Risk/Emergency Management Department HEAT STRESSS PROGRAM 2016 LJP/ 1 1.0 Purpose This Heat Stress Prevention Program has been developed to provide
Heat Stress Prevention Written Program Laredo ISD Safety/Risk/Emergency Management Department HEAT STRESSS PROGRAM 2016 LJP/ 1 1.0 Purpose This Heat Stress Prevention Program has been developed to provide
BASIC KNOWLEDGE OF LABORATORY FIRST AID
 BASIC KNOWLEDGE OF LABORATORY FIRST AID RV: 02/02/2015 prevencio@uv.es Page 1 of 7 . General issues to be considered by the rescuer in the event of an accident are described below: - Proceed as follows:
BASIC KNOWLEDGE OF LABORATORY FIRST AID RV: 02/02/2015 prevencio@uv.es Page 1 of 7 . General issues to be considered by the rescuer in the event of an accident are described below: - Proceed as follows:
Frequency of Occurrence
 Pressure Relief Wound Care Foot Drop BACKGROUND Bedfast patients are at very high risk of developing pressure ulcers on the feet and ankles. A shallow injury or pressure ulcer can become a deep stage IV
Pressure Relief Wound Care Foot Drop BACKGROUND Bedfast patients are at very high risk of developing pressure ulcers on the feet and ankles. A shallow injury or pressure ulcer can become a deep stage IV
'First Aid' Results For JOE BLOGGS. First Aid. Summary
 'First Aid' Results For JOE BLOGGS First Aid Summary Name First Aid Test Language English Started - Finished 08th Apr 2016 13:52:48-08th Apr 2016 13:54:32 Time Available00:15:00 ( time taken 00:01:30 )
'First Aid' Results For JOE BLOGGS First Aid Summary Name First Aid Test Language English Started - Finished 08th Apr 2016 13:52:48-08th Apr 2016 13:54:32 Time Available00:15:00 ( time taken 00:01:30 )
UKA Medical Advice. Hot Weather
 UKA Medical Advice Hot Weather Author: Dr Natasha Beach, UKA Medical Advisor (runbritain) June 2018 Warm or Hot Weather While the United Kingdom and Ireland are not famed for their seasonally high temperatures,
UKA Medical Advice Hot Weather Author: Dr Natasha Beach, UKA Medical Advisor (runbritain) June 2018 Warm or Hot Weather While the United Kingdom and Ireland are not famed for their seasonally high temperatures,
Interface Pressure Testing as an Alternating Pressure Surface
 as an Alternating Introduction Pressure injuries are common and costly, posing a serious health concern impacting cost of care, reimbursement and quality of life, while affecting patients, healthcare workers
as an Alternating Introduction Pressure injuries are common and costly, posing a serious health concern impacting cost of care, reimbursement and quality of life, while affecting patients, healthcare workers
LIFECOMFORT ACTIVE AIR
 LIFECOMFORT ACTIVE AIR Dynamic Alternating Air es for Pressure Care aspire for... Prevention & Therapy of Pressure Injuries www.aspirecare.com.au LIFECOMFORT ACTIVE AIR MATTRESS RANGE Pressure Injury prevention
LIFECOMFORT ACTIVE AIR Dynamic Alternating Air es for Pressure Care aspire for... Prevention & Therapy of Pressure Injuries www.aspirecare.com.au LIFECOMFORT ACTIVE AIR MATTRESS RANGE Pressure Injury prevention
Circulation and Respiration: Vital Signs Student Version
 Circulation and Respiration: Vital Signs Student Version In this lab, you will learn about the circulatory and respiratory systems. You will test the capacity of your lungs, measure your blood pressure
Circulation and Respiration: Vital Signs Student Version In this lab, you will learn about the circulatory and respiratory systems. You will test the capacity of your lungs, measure your blood pressure
INTERFACE PRESSURE MAPPING
 INTERFACE PRESSURE MAPPING Protocol and Interpretation Interface Pressure Mapping (IPM) using the XSENSOR System is a very effective tool for comparing and evaluating the effectiveness of pressure distribution
INTERFACE PRESSURE MAPPING Protocol and Interpretation Interface Pressure Mapping (IPM) using the XSENSOR System is a very effective tool for comparing and evaluating the effectiveness of pressure distribution
First Aid - immediate care that is given to the victim of an injury or illness until experts can take over - Oftentimes, it s the difference between
 First Aid First Aid - immediate care that is given to the victim of an injury or illness until experts can take over - Oftentimes, it s the difference between life and death or recovery vs permanent disability
First Aid First Aid - immediate care that is given to the victim of an injury or illness until experts can take over - Oftentimes, it s the difference between life and death or recovery vs permanent disability
Guidelines on Working in Cold Conditions Re-endorsed by Annual Conference 2017
 Guidelines on Working in Cold Conditions Re-endorsed by Annual Conference 2017 What is cold? Cold is experienced when the body is in circumstances that deplete the body s heat and potentially reduce its
Guidelines on Working in Cold Conditions Re-endorsed by Annual Conference 2017 What is cold? Cold is experienced when the body is in circumstances that deplete the body s heat and potentially reduce its
Evaluation copy. Effect of Vascularity on Skin Temperature Recovery. Computer
 Effect of Vascularity on Skin Temperature Recovery Computer 2 Homeostasis refers to the body s ability to maintain internal conditions (e.g., temperature, ph, hydration) within the narrow limits that are
Effect of Vascularity on Skin Temperature Recovery Computer 2 Homeostasis refers to the body s ability to maintain internal conditions (e.g., temperature, ph, hydration) within the narrow limits that are
Principles of Providing First Aid
 First Aid Principles of Providing First Aid Immediate care that is provided to the victim of injury or illness to minimize the adverse effects until experts take over. Proper first aid can mean the difference
First Aid Principles of Providing First Aid Immediate care that is provided to the victim of injury or illness to minimize the adverse effects until experts take over. Proper first aid can mean the difference
Program B-4 Evaluating Physical Development and Nutrition
 Program B-4 Evaluating Physical Development and Nutrition 31 32 I. The Importance of Body Measurement Body measurements are one way we measure a student's physical development. We can evaluate health,
Program B-4 Evaluating Physical Development and Nutrition 31 32 I. The Importance of Body Measurement Body measurements are one way we measure a student's physical development. We can evaluate health,
LESSON 8: COLD WEATHER INJURIES
 LESSON 8: COLD WEATHER INJURIES dehydration frostbite hypothermia insulate precipitation subcutaneous superficial CLOTHING When in cold weather, you should wear several layers of loose clothing and dress
LESSON 8: COLD WEATHER INJURIES dehydration frostbite hypothermia insulate precipitation subcutaneous superficial CLOTHING When in cold weather, you should wear several layers of loose clothing and dress
GUIDELINES ON WORKING IN COLD CONDITIONS
 GUIDELINES ON WORKING IN COLD CONDITIONS Re-Endorsed by Annual Conference 2017 NSW Nurses and Midwives' Association 50 O Dea Avenue Waterloo NSW 2017 P 02 8595 1234 (metro) 1300 367 962 (regional) www.nswnma.asn.au
GUIDELINES ON WORKING IN COLD CONDITIONS Re-Endorsed by Annual Conference 2017 NSW Nurses and Midwives' Association 50 O Dea Avenue Waterloo NSW 2017 P 02 8595 1234 (metro) 1300 367 962 (regional) www.nswnma.asn.au
Guide to Cold Stress at Work
 Guide to Cold Stress at Work WCB Website: www.wcb.pe.ca Toll free in Atlantic Canada: 1-800-237-5049 Revised: Jan/06 Cold Stress at Work Working in the cold is part of the job for many Prince Edward Islanders.
Guide to Cold Stress at Work WCB Website: www.wcb.pe.ca Toll free in Atlantic Canada: 1-800-237-5049 Revised: Jan/06 Cold Stress at Work Working in the cold is part of the job for many Prince Edward Islanders.
Managers and supervisors. 28/06/2016 Version number: v0
 Managers and supervisors Introduction The Ministry of Labour (MOL) in UAE issues a Decree every year concerning the mid-day break during the summer months for those working under the sun: 15 June-15 September
Managers and supervisors Introduction The Ministry of Labour (MOL) in UAE issues a Decree every year concerning the mid-day break during the summer months for those working under the sun: 15 June-15 September
Chair exercises Sally Ann Belward, Falls Clinical Lead Physiotherapist
 Chair exercises Sally Ann Belward, Falls Clinical Lead Physiotherapist Exercise safety Exercise should be comfortable and fun Ensure participants are sat on a sturdy chair, have comfortable clothing and
Chair exercises Sally Ann Belward, Falls Clinical Lead Physiotherapist Exercise safety Exercise should be comfortable and fun Ensure participants are sat on a sturdy chair, have comfortable clothing and
Cushions for pressure relief in the seated position
 Cushions for pressure relief in the seated position Name Size in cm. Item no. About the device Application Seat 42 x 42 x 5 70008 Seat cushion, extra strong. Pressure distribution for the mitigation of
Cushions for pressure relief in the seated position Name Size in cm. Item no. About the device Application Seat 42 x 42 x 5 70008 Seat cushion, extra strong. Pressure distribution for the mitigation of
 EXTERNAL BLEEDING Definition: This is where the blood vessels and the skin are cut and blood is escaping the body. Causes: Damage to the skin caused by trauma. Can be a laceration (clean cut), abrasion,
EXTERNAL BLEEDING Definition: This is where the blood vessels and the skin are cut and blood is escaping the body. Causes: Damage to the skin caused by trauma. Can be a laceration (clean cut), abrasion,
HOW-TO CONDUCT A WEEKLY SAFETY MEETING
 HOW-TO CONDUCT A WEEKLY SAFETY MEETING 1. Hold the meeting on the job, preferably where everyone can sit and relax. 2. Hold the meeting at the beginning of the shift, right after lunch, or after a break.
HOW-TO CONDUCT A WEEKLY SAFETY MEETING 1. Hold the meeting on the job, preferably where everyone can sit and relax. 2. Hold the meeting at the beginning of the shift, right after lunch, or after a break.
set up the work area to meet legal, hygiene, organisation procedures and manufacturers instructions
 Unit 747 Provide Body Wrapping and Flotation Treatments Guided Learning Hours: 59 Learning Outcome Assessment Criteria 1. Be able to maintain safe and effective 1methods of working when providing body
Unit 747 Provide Body Wrapping and Flotation Treatments Guided Learning Hours: 59 Learning Outcome Assessment Criteria 1. Be able to maintain safe and effective 1methods of working when providing body
COMMUNITY RESPONSE TO MEDICAL EMERGENCIES:
 COMMUNITY RESPONSE TO MEDICAL EMERGENCIES: For any on-campus emergency, dial x456 from an on campus phone or From a cell phone dial 508-494-9010. A medical emergency can occur anywhere on campus. The reaction
COMMUNITY RESPONSE TO MEDICAL EMERGENCIES: For any on-campus emergency, dial x456 from an on campus phone or From a cell phone dial 508-494-9010. A medical emergency can occur anywhere on campus. The reaction
INSTRUCTION MANUAL. Automatic Blood Pressure Monitor with Fit Cuff. =Fit Cuff=!"#$% IA1B. Model
 IA1B INSTRUCTION MANUAL Automatic Blood Pressure Monitor with Fit Cuff =Fit Cuff=!"#$% Model IA1B Contents Introduction... 2 Notes on Safety... 3 Know Your Unit... 5 Quick Reference Guide... 7 Initial
IA1B INSTRUCTION MANUAL Automatic Blood Pressure Monitor with Fit Cuff =Fit Cuff=!"#$% Model IA1B Contents Introduction... 2 Notes on Safety... 3 Know Your Unit... 5 Quick Reference Guide... 7 Initial
Caring for a balloon retained gastrostomy tube (Pexact or RIG tube) GI Unit Patient Information Leaflet
 Caring for a balloon retained gastrostomy tube (Pexact or RIG tube) GI Unit Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is about caring for a balloon retained gastrostomy tube. It includes information
Caring for a balloon retained gastrostomy tube (Pexact or RIG tube) GI Unit Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is about caring for a balloon retained gastrostomy tube. It includes information
ALFRED HYPERBARIC SERVICE. Service and Care. Information for Patients
 ALFRED HYPERBARIC SERVICE Service and Care Information for Patients ALFRED HEALTH Alfred Hyperbaric Service The Alfred Commercial Road Melbourne, VIC 3004 Phone (03) 9076 2269 Fax (03) 9076 3052 This booklet
ALFRED HYPERBARIC SERVICE Service and Care Information for Patients ALFRED HEALTH Alfred Hyperbaric Service The Alfred Commercial Road Melbourne, VIC 3004 Phone (03) 9076 2269 Fax (03) 9076 3052 This booklet
GUIDELINE for MSD Hazard Control Measures
 APPENDIX C GUIDELINE for MSD Hazard Control Measures This MSD Control Measures guideline document will help you eliminate or reduce musculoskeletal disorder hazards identified by the MSD Hazard ID Form.
APPENDIX C GUIDELINE for MSD Hazard Control Measures This MSD Control Measures guideline document will help you eliminate or reduce musculoskeletal disorder hazards identified by the MSD Hazard ID Form.
Nina Elisabeth N Storvik Theres Arulf
 Nina Elisabeth N Storvik Theres Arulf 1 Program Accident scene command and initial assessment Patient examination ABCDE -approach CPR Recovery position Bleedings Hypothermia - Frostbite Fractures Burns
Nina Elisabeth N Storvik Theres Arulf 1 Program Accident scene command and initial assessment Patient examination ABCDE -approach CPR Recovery position Bleedings Hypothermia - Frostbite Fractures Burns
EXPOSURE TO THE COLD. November 6, 2013
 EXPOSURE TO THE COLD November 6, 2013 WHAT IS COLD STRESS Cold stress is the transfer of body heat out to a colder environment When you are exposed to a cold environment, most of your body's energy is
EXPOSURE TO THE COLD November 6, 2013 WHAT IS COLD STRESS Cold stress is the transfer of body heat out to a colder environment When you are exposed to a cold environment, most of your body's energy is
Getting Back To Life: How To Care For Yourself After Back Surgery
 Getting Back To Life: How To Care For Yourself After Back Surgery How To Put On Your Back Brace Freedom 631 LSO Spinal Orthosis Apply the brace while sitting up on the side of the bed.** Open up the brace
Getting Back To Life: How To Care For Yourself After Back Surgery How To Put On Your Back Brace Freedom 631 LSO Spinal Orthosis Apply the brace while sitting up on the side of the bed.** Open up the brace
Safety Services Guidance. Hand Arm Vibration
 Hand Arm Vibration Key word(s): Vibration, exposure action value, exposure action limit, machinery, hand held power tools, trigger times, maintenance, surveillance Target audience: Managers, staff who
Hand Arm Vibration Key word(s): Vibration, exposure action value, exposure action limit, machinery, hand held power tools, trigger times, maintenance, surveillance Target audience: Managers, staff who
Adult Pressure Care. Star Cushion. High Performance Air Cell Cushions
 Adult Pressure Care Star Cushion High Performance Air Cell Cushions Welcome to Star Cushion Solutions for: Pressure ulcers - Prevention and Therapy, Positioning - Symmetry and Stability. It can take only
Adult Pressure Care Star Cushion High Performance Air Cell Cushions Welcome to Star Cushion Solutions for: Pressure ulcers - Prevention and Therapy, Positioning - Symmetry and Stability. It can take only
Hand Safety. 1 Copyright 2014 by PEC Safety Management, Inc. PPT-SM-HNDSFTY 2014
 Hand Safety 1 Copyright by PEC Safety Management, Inc. Hand Safety One-third of all oil and gas industry accidents are hand injuries Companies should use engineering and work practice controls to protect
Hand Safety 1 Copyright by PEC Safety Management, Inc. Hand Safety One-third of all oil and gas industry accidents are hand injuries Companies should use engineering and work practice controls to protect
"HAND, WRIST AND FINGER SAFETY"
 PRESENTER'S GUIDE "HAND, WRIST AND FINGER SAFETY" Part of the "SAFETY MEETING KIT" Series Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today...and Tomorrow OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM
PRESENTER'S GUIDE "HAND, WRIST AND FINGER SAFETY" Part of the "SAFETY MEETING KIT" Series Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today...and Tomorrow OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM
ALPHAXCELL. Active pressure relieving mattress overlay system for medium risk patients in all environments
 ALPHAXCELL Active pressure relieving mattress overlay system for medium risk patients in all environments TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION AlphaXcell Order Code AXL30 (Complete System) Pump Model (UK) ALX01 Model
ALPHAXCELL Active pressure relieving mattress overlay system for medium risk patients in all environments TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION AlphaXcell Order Code AXL30 (Complete System) Pump Model (UK) ALX01 Model
FIRST AID. Study Topics. At a minimum, the following topics are to be studied for the first aid exam.
 FIRST AID Study Topics At a minimum, the following topics are to be studied for the first aid exam. TOPIC Avoid getting air in stomach during rescue breathing Burns Kinds of Burns & Care Calling for Help
FIRST AID Study Topics At a minimum, the following topics are to be studied for the first aid exam. TOPIC Avoid getting air in stomach during rescue breathing Burns Kinds of Burns & Care Calling for Help
HEAT INJURIES. MANSCEN Safety Office
 HEAT INJURIES MANSCEN Safety Office OBJECTIVES 1. Know Individual risk factors. 2. Proper Acclimatization. 3. Know types of heat injuries, and first aid. 4. Be able to read and obtain WBGT index. A. INDIVIDUAL
HEAT INJURIES MANSCEN Safety Office OBJECTIVES 1. Know Individual risk factors. 2. Proper Acclimatization. 3. Know types of heat injuries, and first aid. 4. Be able to read and obtain WBGT index. A. INDIVIDUAL
HEAT ILLNESS PREVENTION PLAN
 www.westhillscollege.com HEAT ILLNESS PREVENTION PLAN October, 2008 Status: Last Revised July, 2008 Approved WHCCD Risk Management Committee 10/10/08 WHCCD Board of Trustees approval 12/16/08 HEAT ILLNESS
www.westhillscollege.com HEAT ILLNESS PREVENTION PLAN October, 2008 Status: Last Revised July, 2008 Approved WHCCD Risk Management Committee 10/10/08 WHCCD Board of Trustees approval 12/16/08 HEAT ILLNESS
Chapter 8 - POSTURE. The following guidelines can be used to develop good postural habits. ! 2010 High Performance Golf
 Chapter 8 - POSTURE Posture is the habitual position that people hold themselves in, whether they are sitting, standing, active or sedentary. The aim of good posture is to maintain the natural curves of
Chapter 8 - POSTURE Posture is the habitual position that people hold themselves in, whether they are sitting, standing, active or sedentary. The aim of good posture is to maintain the natural curves of
19. HEAT STRESS ON THE FARM
 19. HEAT STRESS ON THE FARM THE HAZARD Every farmer and farm workers must be familiar with and learn how to deal with the condition of heat stress. However, heat stress is generally not desirable, and
19. HEAT STRESS ON THE FARM THE HAZARD Every farmer and farm workers must be familiar with and learn how to deal with the condition of heat stress. However, heat stress is generally not desirable, and
General Purpose Slings Instruction & Safety Manual
 General Purpose Slings Instruction & Safety Manual Please read this manual before operation, for maintenance instructions and safe usage The enabling power of applied knowledge General Purpose Slings Instruction
General Purpose Slings Instruction & Safety Manual Please read this manual before operation, for maintenance instructions and safe usage The enabling power of applied knowledge General Purpose Slings Instruction
Cold Weather Injuries 1.0 Contact Hours Presented by: CEU Professor
 Cold Weather Injuries 1.0 Contact Hours Presented by: CEU Professor 7 www.ceuprofessoronline.com Copyright 8 2007 The Magellan Group, LLC All Rights Reserved. Reproduction and distribution of these materials
Cold Weather Injuries 1.0 Contact Hours Presented by: CEU Professor 7 www.ceuprofessoronline.com Copyright 8 2007 The Magellan Group, LLC All Rights Reserved. Reproduction and distribution of these materials
Viral Haemorrhagic Fever (VHF) - The correct order for donning and the safe order for removal and disposal of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
 Viral Haemorrhagic Fever (VHF) - The correct order for donning and the safe order for removal and disposal of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) An educational resource for healthcare workers in NHS Scotland
Viral Haemorrhagic Fever (VHF) - The correct order for donning and the safe order for removal and disposal of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) An educational resource for healthcare workers in NHS Scotland
... Participant Guide
 ... Participant Guide Welcome! Congratulations on taking the first step to a healthier you! We hope this program will help you make physical activity a regular part of your everyday life. Why walk? We
... Participant Guide Welcome! Congratulations on taking the first step to a healthier you! We hope this program will help you make physical activity a regular part of your everyday life. Why walk? We
FIRST AID (CPR) Yerevan Dc. Anna Toplaghaltsyan
 FIRST AID (CPR) Yerevan 2018 Dc. Anna Toplaghaltsyan First aid is The assistance given to any person suffering a sudden illness or injury, with care provided to preserve life, prevent the condition from
FIRST AID (CPR) Yerevan 2018 Dc. Anna Toplaghaltsyan First aid is The assistance given to any person suffering a sudden illness or injury, with care provided to preserve life, prevent the condition from
Chapter 2. Lesson 8. Cold Weather Injuries. What You Will Learn to Do. Linked Core Abilities. Skills and Knowledge You Will Gain along the Way
 Lesson 8 Cold Weather Injuries Key Terms dehydration frostbite hypothermia insulate precipitation subcutaneous superficial What You Will Learn to Do Determine first aid treatment for cold weather injuries
Lesson 8 Cold Weather Injuries Key Terms dehydration frostbite hypothermia insulate precipitation subcutaneous superficial What You Will Learn to Do Determine first aid treatment for cold weather injuries
Invacare Therapeutic Support Surfaces Catalog
 Catalog Patients immobilized and unable to move can suffer serious destruction of the skin and soft body tissue in as little as one hour. This often results in the formation of a pressure ulcer. A pressure
Catalog Patients immobilized and unable to move can suffer serious destruction of the skin and soft body tissue in as little as one hour. This often results in the formation of a pressure ulcer. A pressure
NHS Training for Physiotherapy Support Workers. Workbook 16 Gait re-education
 NHS Training for Physiotherapy Support Workers Workbook 16 Gait re-education Contents Workbook 16 Gait re-education 1 16.1 Aim 3 16.2 Learning outcomes 3 16.3 Preparation for walking assessment and walking
NHS Training for Physiotherapy Support Workers Workbook 16 Gait re-education Contents Workbook 16 Gait re-education 1 16.1 Aim 3 16.2 Learning outcomes 3 16.3 Preparation for walking assessment and walking
Open Zen Community: Postures for People with Chronic Pain CHAIR POSTURES
 Open Zen Community: Postures for People with Chronic Pain CHAIR POSTURES This is a traditional chair-sitting posture in which the practitioner sits forward in the chair, feet flat on the floor, with hands
Open Zen Community: Postures for People with Chronic Pain CHAIR POSTURES This is a traditional chair-sitting posture in which the practitioner sits forward in the chair, feet flat on the floor, with hands
Lebanese Red Cross - Emergency Medical Services First Aid Training course Skills Summary Adult Airways Obstruction
 s Summary Adult Airways Obstruction Choking is recognized Rescuer asks if victim can speak, cough or breathe Rescuer encourages victim to cough in case of a partial obstruction 1 Adult Airway Obsturction
s Summary Adult Airways Obstruction Choking is recognized Rescuer asks if victim can speak, cough or breathe Rescuer encourages victim to cough in case of a partial obstruction 1 Adult Airway Obsturction
To keep the body in good health is a duty otherwise we shall not be able to keep our mind strong and clear. - Guatama Buddha
 To keep the body in good health is a duty otherwise we shall not be able to keep our mind strong and clear. - Guatama Buddha Desk Stretches Why Stretch? Stretching allows the muscle to release tension.
To keep the body in good health is a duty otherwise we shall not be able to keep our mind strong and clear. - Guatama Buddha Desk Stretches Why Stretch? Stretching allows the muscle to release tension.
LUNA V. User Manual. Warning
 LUNA V User Manual Warning Dear user Thanks for using our company's products, in order to fully make use of the products, we sincerely suggests follow: Please read this instructionin detail, and keep it
LUNA V User Manual Warning Dear user Thanks for using our company's products, in order to fully make use of the products, we sincerely suggests follow: Please read this instructionin detail, and keep it
First Aid Handbook. Contents
 First Aid Handbook Contents Bleeding Cuts or Wounds... 2 Hands-Only CPR for Adults... 3 Thermal Burns Treatment... 4 For All Burns... 4 For First-Degree Burns (Affecting Top Layer of Skin)... 4 For Second-Degree
First Aid Handbook Contents Bleeding Cuts or Wounds... 2 Hands-Only CPR for Adults... 3 Thermal Burns Treatment... 4 For All Burns... 4 For First-Degree Burns (Affecting Top Layer of Skin)... 4 For Second-Degree
Cobi Positioning Cushions
 Cobi Positioning Cushions For specific positioning needs Ideally used for User manual - Bariatric users. - Paresis. - Sclerosis patients. - Brain damage. - Dementia. - Neurological patients. - Pain patients.
Cobi Positioning Cushions For specific positioning needs Ideally used for User manual - Bariatric users. - Paresis. - Sclerosis patients. - Brain damage. - Dementia. - Neurological patients. - Pain patients.
Loading your garment onto the applicator. Helpful tips. Please ensure that your garment is not inside out before you begin.
 Loading your garment onto the applicator (Step 1) Position the applicator with the elongated hole facing you. Please ensure that your garment is not inside out before you begin. (Step 2) Ensure that the
Loading your garment onto the applicator (Step 1) Position the applicator with the elongated hole facing you. Please ensure that your garment is not inside out before you begin. (Step 2) Ensure that the
Dynamic pressure system for pressure relief
 Dynamic pressure system for pressure relief Foreword/Content Optimal use of the right products. In this issue you will find an overview of our core assortment of dynamic alternating pressure relief systems
Dynamic pressure system for pressure relief Foreword/Content Optimal use of the right products. In this issue you will find an overview of our core assortment of dynamic alternating pressure relief systems
EXTREME HEAT. Extreme Heat Related Terms. Heat Wave - Prolonged period of excessive heat, often combined with excessive humidity.
 Residents of southeast Louisiana are typically accustomed to dealing with warm, humid weather. But extreme and prolonged heat and humidity conditions can result in serious medical emergencies, even for
Residents of southeast Louisiana are typically accustomed to dealing with warm, humid weather. But extreme and prolonged heat and humidity conditions can result in serious medical emergencies, even for
July Safety Topic: Grain Bin Safety & Heat Exhaustion
 July Safety Topic: Grain Bin Safety & Heat Exhaustion MONTICELLO, IA At Innovative Ag Services, we take safety very seriously. Safety is not something that is talked about once a year and then forgotten.
July Safety Topic: Grain Bin Safety & Heat Exhaustion MONTICELLO, IA At Innovative Ag Services, we take safety very seriously. Safety is not something that is talked about once a year and then forgotten.
Integumentary System EQS 110
 Integumentary System EQS 110 Table of Contents Click on the different sections of the table of contents to jump through this document Functions of the Integument... 3 Anatomy of the Skin... 3 Epidermis...
Integumentary System EQS 110 Table of Contents Click on the different sections of the table of contents to jump through this document Functions of the Integument... 3 Anatomy of the Skin... 3 Epidermis...
HEAT STRESS Prevention Program
 HEAT STRESS Prevention Program FACTS Although heat-related illness and death are readily preventable, the CDC reports an annual average of 600 Heat related deaths and over 7,000 Heat related illnesses
HEAT STRESS Prevention Program FACTS Although heat-related illness and death are readily preventable, the CDC reports an annual average of 600 Heat related deaths and over 7,000 Heat related illnesses
Chapter 2. Welding Safety Delmar, Cengage Learning
 Chapter 2 Welding Safety Objectives After completing this chapter, you will be able to: Explain how to work safely Identify each degree of burn and describe how to provide first aid List the types of protective
Chapter 2 Welding Safety Objectives After completing this chapter, you will be able to: Explain how to work safely Identify each degree of burn and describe how to provide first aid List the types of protective
Universal Precautions
 First Aid Safety First Aid is a matter of Personal Choice. The Company does not require employees to provide first aid for fellow employees. We have a medical provider close by to provide these services.
First Aid Safety First Aid is a matter of Personal Choice. The Company does not require employees to provide first aid for fellow employees. We have a medical provider close by to provide these services.
Top 10 Yoga Exercises to relieve Sciatica
 Top 10 Yoga Exercises to relieve Sciatica This is due to compression and inflammation of the spinal nerves. A sharp pain radiates from the lower back to to the leg and foot in a pattern determined by the
Top 10 Yoga Exercises to relieve Sciatica This is due to compression and inflammation of the spinal nerves. A sharp pain radiates from the lower back to to the leg and foot in a pattern determined by the
Do your share as a good citizen in your school, community, country, and the world
 Lesson 3 Controlling Bleeding What You Will Learn to Do Determine first aid procedures for bleeding victim Linked Core Abilities Do your share as a good citizen in your school, community, country, and
Lesson 3 Controlling Bleeding What You Will Learn to Do Determine first aid procedures for bleeding victim Linked Core Abilities Do your share as a good citizen in your school, community, country, and
Cold Weather Emergencies
 Cold Weather Emergencies Introduction Medical emergencies can result from exposure to heat or cold. Certain populations are at higher risk for heat and cold emergencies. Children Older people People with
Cold Weather Emergencies Introduction Medical emergencies can result from exposure to heat or cold. Certain populations are at higher risk for heat and cold emergencies. Children Older people People with
WVWCI BIGGEST LOSER WEEK 3: WALKING BASICS DRESS FOR SUCCESS
 DRESS FOR SUCCESS Make sure you dress appropriately for walking. The following items will help you judge what to wear: Wear shoes with proper arch support, a firm heel, and thick, flexible soles that will
DRESS FOR SUCCESS Make sure you dress appropriately for walking. The following items will help you judge what to wear: Wear shoes with proper arch support, a firm heel, and thick, flexible soles that will
Colic Fact Sheet One hell of a belly ache
 Colic Fact Sheet One hell of a belly ache No other word strikes fear in the hearts and minds of horse owners more than the word Colic - it can affect any horse at any time for a multitude of reason. Sadly,
Colic Fact Sheet One hell of a belly ache No other word strikes fear in the hearts and minds of horse owners more than the word Colic - it can affect any horse at any time for a multitude of reason. Sadly,
Autom ate d t u r n i n g at yo u r f i n g e r t i ps
 pioneering simplicity Autom ate d t u r n i n g at yo u r f i n g e r t i ps l ateral turning system frontiermedical group Lateral turning system Regular manual turning of patients can be intrusive, particularly
pioneering simplicity Autom ate d t u r n i n g at yo u r f i n g e r t i ps l ateral turning system frontiermedical group Lateral turning system Regular manual turning of patients can be intrusive, particularly
T H E H U M A N B R A I N
 1 W O R D S allow = let area = place balance =to spread your weight so that you do not fall breathe = to take air into your lungs and send it out again cell = the smallest part of a living thing that can
1 W O R D S allow = let area = place balance =to spread your weight so that you do not fall breathe = to take air into your lungs and send it out again cell = the smallest part of a living thing that can
Manual Handling Procedure
 Manual Handling Procedure Table of Contents 1 Purpose... 3 2 Scope... 3 3 Definitions... 3 4 Responsibilities... 3 4.1 Managers And Supervisors... 3 4.2 Workers (Employees, Contractors And Visitors)...
Manual Handling Procedure Table of Contents 1 Purpose... 3 2 Scope... 3 3 Definitions... 3 4 Responsibilities... 3 4.1 Managers And Supervisors... 3 4.2 Workers (Employees, Contractors And Visitors)...
PRESSURE REDISTRIBUTION SYSTEM. with people in mind
 ALPHA RESPONSE PRESSURE REDISTRIBUTION SYSTEM with people in mind introduction superior Features For over 0 years the Alpha range of pressure redistributing mattresses has been proven to offer patients,
ALPHA RESPONSE PRESSURE REDISTRIBUTION SYSTEM with people in mind introduction superior Features For over 0 years the Alpha range of pressure redistributing mattresses has been proven to offer patients,
Soteria Strains. Safe Patient Handling and Mobility Program Guide
 Soteria Strains Safe Patient Handling and Mobility Program Guide Section 4 Special Considerations Section 4.1 - Emergency Situations V1.0 edited July 20, 2015 A provincial strategy for healthcare workplace
Soteria Strains Safe Patient Handling and Mobility Program Guide Section 4 Special Considerations Section 4.1 - Emergency Situations V1.0 edited July 20, 2015 A provincial strategy for healthcare workplace
Contents Introduction Wear Supportive Footwear Do Heat Therapy Do Cold Therapy Perform Restorative Exercises...
 Contents Introduction... 3 1. Wear Supportive Footwear... 5 2. Do Heat Therapy... 6 3. Do Cold Therapy... 7 4. Perform Restorative Exercises... 7 5. Maintain Your Optimum BMI... 8 6. Wear Arch Support
Contents Introduction... 3 1. Wear Supportive Footwear... 5 2. Do Heat Therapy... 6 3. Do Cold Therapy... 7 4. Perform Restorative Exercises... 7 5. Maintain Your Optimum BMI... 8 6. Wear Arch Support
What is FIRST AID? What is MEDICAL AID?
 What is FIRST AID? Name: _ First Aid is the first emergency help given to someone who is hurt or suddenly sick, using stuff that is readily available. What can you do as a First Aider Wolf Cub? 1. 2. 3.
What is FIRST AID? Name: _ First Aid is the first emergency help given to someone who is hurt or suddenly sick, using stuff that is readily available. What can you do as a First Aider Wolf Cub? 1. 2. 3.
California State University Bakersfield Heat Illness Prevention Policy. Revised November 2017
 California State University Bakersfield Heat Illness Prevention Policy Revised November 2017 THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK 1 Contents 1.0 Policy... 3 2.0 Authority... 3 3.0 Scope... 3 4.0 Definitions...
California State University Bakersfield Heat Illness Prevention Policy Revised November 2017 THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK 1 Contents 1.0 Policy... 3 2.0 Authority... 3 3.0 Scope... 3 4.0 Definitions...
Paradise Pump Series Operator s Manual
 Paradise Pump Series Operator s Manual P/N 12421-000 9/05 Paradise Pump Operator s Manual Important Before using the Paradise Pump Alternating Pressure Relief Systems, please read and understand this
Paradise Pump Series Operator s Manual P/N 12421-000 9/05 Paradise Pump Operator s Manual Important Before using the Paradise Pump Alternating Pressure Relief Systems, please read and understand this
English Español Português Italiano Deutch Français INSTRUCTION MANUAL FOR DIGITAL BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR MODEL CH-656C. - Eng 1 -
 English Español Português Italiano Deutch Français INSTRUCTION MANUAL FOR DIGITAL BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR MODEL CH-656C M - Eng 1 - CLEANING METHOD OF CUFF After cleaning the cuff with a neutral detergent,
English Español Português Italiano Deutch Français INSTRUCTION MANUAL FOR DIGITAL BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR MODEL CH-656C M - Eng 1 - CLEANING METHOD OF CUFF After cleaning the cuff with a neutral detergent,
Walking is the best possible exercise.
 Walking Best, safest, and most natural form of exercise Effective form of exercise for all ages Effective form of exercise for all states and levels of health Increases sense of well-being Walking is the
Walking Best, safest, and most natural form of exercise Effective form of exercise for all ages Effective form of exercise for all states and levels of health Increases sense of well-being Walking is the
HEAT MANAGEMENT PROCEDURE
 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. OBJECTIVE... 2 2. SCOPE... 2 3. DEFINITIONS... 2 4. RESPONSIBILITIES... 2 5. HAZARD AND RISK ASSESSMENT... 2 5.1 HEAT RELATED ILLNESS... 3 5.1.1 Risk Factors... 3 5.1.2 Controls...
TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. OBJECTIVE... 2 2. SCOPE... 2 3. DEFINITIONS... 2 4. RESPONSIBILITIES... 2 5. HAZARD AND RISK ASSESSMENT... 2 5.1 HEAT RELATED ILLNESS... 3 5.1.1 Risk Factors... 3 5.1.2 Controls...
Control of Vibration at Work
 Control of Vibration at Work 1) POLICY University of Glasgow will put in place measures to protect employees from the risks of Hand Arm Vibration Syndrome (HAVS) and Whole Body Vibration. These measures
Control of Vibration at Work 1) POLICY University of Glasgow will put in place measures to protect employees from the risks of Hand Arm Vibration Syndrome (HAVS) and Whole Body Vibration. These measures
A designated area will have been assigned for all blood specimens to be taken. All blood should then be taken in that area only.
 Venepuncture No: 008D 1. Introduction Blood sampling is a necessary requirement to assess the biochemical and haematological profile of subjects who enter clinical research studies. Risks to the subject
Venepuncture No: 008D 1. Introduction Blood sampling is a necessary requirement to assess the biochemical and haematological profile of subjects who enter clinical research studies. Risks to the subject
