(51) Int Cl.: A61B 5/00 ( ) A61B 5/022 ( )
|
|
|
- Shannon Hopkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (19) TEPZZ _9_77_B_T (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: Bulletin 2013/21 (51) Int Cl.: A61B 5/00 ( ) A61B 5/022 ( ) (21) Application number: (22) Date of filing: (54) Portable device for measuring blood pressure and method therefor Tragbare Vorrichtung zum Messen des Blutdrucks und Verfahren dafür Dispositif portable pour mesurer la pression artérielle et procédé correspondant (84) Designated Contracting States: AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO SE SI SK SM TR (30) Priority: KR (43) Date of publication of application: Bulletin 2010/22 (73) Proprietor: Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. Suwon-si, Gyeonggi-do, (KR) (72) Inventor: Cho, Jae-Geol , Gyeonggi-do (KR) (74) Representative: Grünecker, Kinkeldey, Stockmair & Schwanhäusser Leopoldstrasse München (DE) (56) References cited: EP-A EP-A US-A EP B1 Note: Within nine months of the publication of the mention of the grant of the European patent in the European Patent Bulletin, any person may give notice to the European Patent Office of opposition to that patent, in accordance with the Implementing Regulations. Notice of opposition shall not be deemed to have been filed until the opposition fee has been paid. (Art. 99(1) European Patent Convention). Printed by Jouve, PARIS (FR)
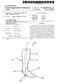
2 Description BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 5 1. Field of the Invention 10 [0001] The present invention relates generally to a portable device for measuring blood pressure and a method therefor. More particularly, the present invention relates to a portable device for measuring wrist or finger arterial pressure corresponding to brachial arterial pressure and a method therefor. 2. Description of the Related Art [0002] Blood pressure is one of the most useful vital signs for human health care. Clinically, blood pressure provides an index by which abnormalities of the circulatory system, including the heart and blood vessels, can be diagnosed. Blood pressure outside a normal range requires consistent care. Arterial pressure changes with cardiac pulsation. The peak pressure the arteries feel when the ventricles are contracting and pushing the blood out into the arteries is called systolic pressure. Even when the ventricles are relaxing and filling back up with blood, the elasticity of the walls of the arteries maintains some blood pressure, and thus the blood pressure does not drop to zero. This lower level of blood pressure is called diastolic pressure. [0003] Nervousness often results in a high blood pressure measurement when a person visits a clinic. Since blood pressure varies with a variety of factors, it is difficult to get an accurate blood pressure measurement at one time. Hence, a home-use electronic blood pressure monitor is necessary to enable users to constantly measure their blood pressures at their homes. The most widely used automatic electronic blood pressure monitor operates by volume oscillometry. The volume oscillometry scheme measures blood pressure based on oscillations that are generated by raising or dropping pressure to the arteries with use of a cuff. In this measuring method, the cuff pressure at which the pulse arising from cardiac pulsation has a maximum amplitude that is estimated to be a mean blood pressure. Herein, the systolic and diastolic pressures are estimated to be cuff pressures having 45 to 57% and 74 to 82% of the maximum amplitude, respectively. [0004] FIG. 1 is a graph illustrating blood pressure measurements based on oscillation pressures of a cuff. Referring to FIG. 1, the ratio of a systolic amplitude to a maximum amplitude and the ratio of a diastolic amplitude to the maximum amplitude are called characteristic ratios, which vary with individuals. It is known that the characteristic ratios are greatly affected by cuff characteristics, the characteristics of artery vessels, the shape and amplitude of arterial pressure waves, etc. [0005] At present, most blood pressure monitors measure blood pressure in an upper arm at heart level. For measurement convenience, products for measuring blood pressure in a wrist or a finger using a cuff have been developed and commercialized. [0006] Such a wrist- or finger-type blood pressure monitor is smaller than the upper arm-type monitor. Due to the small size, the wrist- or finger-type blood pressure monitor is portable and obviates the need to take off a portion of a patient s clothing for pressure measuring, thus allowing blood pressure measuring at any time. However, because a wrist or finger arterial signal is weaker than a brachial arterial signal, it basically has a low Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR). Therefore, the wrist- or finger-type blood pressure monitor is less accurate than the upper arm-type one. [0007] Blood pressure may differ at different artery positions due to a plurality of factors. Hence, the wrist- or fingertype blood pressure monitor may give a different blood pressure measurement from that of the upper arm-type one. As a consequence, blood pressure measurements of the wrist- or finger-type blood pressure monitor may be less reliable to users. [0008] A conventional wrist- or finger-type blood pressure monitor measures an arterial pressure by oscillometry, like the upper arm-type blood pressure monitor. If the blood pressure monitor is precise and the brachial arterial pressure is equal to the wrist- or finger arterial pressure, a pressure at the upper arm should be equal to a pressure at the wrist or finger which is leveled at the heart height. [0009] However, the brachial arterial pressure is different from the wrist or finger arterial pressure due to the characteristics of blood flow, and the differences between individuals. [0010] That is, a measured wrist or finger arterial pressure of a user may be higher or lower than a measured brachial arterial pressure for the same individual. [0011] FIG. 2 illustrates characteristics of blood pressure and waveform changes with respect to the positions of arteries. In FIG. 2, pulse pressure changes with respect to the distances of the arteries to an aorta are shown, as well as pulse pressure changes that vary with age. That is, the difference between systolic and diastolic pressures increases at an artery more remote from an aorta at younger ages due to the overlap of reflective waves. At older ages, the difference is zero or may increase. Even individuals of the same age may differ in the systolic-diastolic difference. 2
3 Therefore, when a user familiar with the upper arm-type blood pressure monitor popular in clinics uses the wrist- or finger-type blood pressure monitor, for use convenience or portability, he may be confused with blood pressure measurements. 5 SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION [0012] The present invention has been made to address at least the above problems and/or disadvantages, and to provide at least the advantages described below. [0013] An aspect of an embodiment of the present invention provides a portable blood pressure measuring apparatus for giving a user a wrist or finger arterial pressure compensated to correspond to a brachial arterial pressure that differs in individuals, and a method therefor. [0014] In accordance with an aspect of an embodiment of the present invention, there is provided a portable blood pressure measuring apparatus in which a blood pressure measurer measures a blood pressure being an arterial pressure at a wrist or a finger, a Pulse Wave Velocity (PWV) measurer measures a PWV, a controller controls compensation of the blood pressure using the PWV so that the blood pressure being an arterial pressure at a wrist or finger corresponds to a brachial blood pressure as defined in claim 1, and a display displays the compensated blood pressure. [0015] In accordance with another aspect of an embodiment of the present invention, there is provided a portable blood pressure measuring method as defined in claim 6 in which a blood pressure being an arterial pressure at a wrist or a finger is measured in blood pressure measuring mode, a PWV is measured, the blood pressure is compensated using the PWV so that the blood pressure being an arterial pressure at a wrist or finger corresponds to a brachial blood pressure, and the compensated blood pressure is displayed. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS 25 [0016] The above and other aspects, features and advantages of certain embodiments of the present invention will be more apparent from the following detailed description taken in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, in which: FIG. 1 is a graph illustrating blood pressure measurements based on oscillation pressures of a cuff; FIG. 2 illustrates characteristics of blood pressure and waveform changes with respect to the positions of arteries; FIG. 3 illustrates measuring of a Pulse Wave Velocity (PWV) using an ElectroCardioGram (ECG) signal and a PhotoPlethysnoGraphy (PPG) signal; FIGs. 4A, 4B and 4C illustrate pulse wave overlap characteristics according to PWVs; FIG. 5 is a graph illustrating a relationship between PWV and radial and brachial blood pressures; FIG. 6A is a graph illustrating a relationship between PWV and radial-brachial systolic pressure difference; Fig. 6B is a graph illustrating a relationship between PWV and radial-brachial diastolic pressure difference; Fig. 6C illustrate when the positions of the wrists is lower than the heart level; Fig. 6D illustrate when the positions of the wrists is same the heart level; Fig. 6E illustrate when the positions of the wrists is same the heart level; Fig. 7 is a block diagram of a portable blood pressure measuring apparatus according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention; Fig. 8 illustrates a portable blood pressure measuring apparatus according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention; Fig. 9 illustrates a portable blood pressure measuring apparatus according to another exemplary embodiment of the present invention; Fig. 10 is a flowchart illustrating an operation for measuring blood pressure in a portable blood pressure measuring apparatus according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention; and FIGs. 11A and 11B are graphs illustrating blood pressures measured by a portable blood pressure measuring apparatus according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention. 50 DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF EMBODIMENTS OF THE INVENTION 55 [0017] The matters defined in the description such as a detailed construction and elements are provided to assist in a comprehensive understanding of the embodiments of the invention. Accordingly, those of ordinary skill in the art will recognize that various changes and modifications of the embodiments described herein can be made without departing from the scope and spirit of the invention. Also, descriptions of well-known functions and constructions are omitted for clarity and conciseness. Throughout the drawings, the same drawing reference numerals will be understood to refer to the same elements, features and structures. [0018] To calculate the difference between brachial blood pressure and radial blood pressure, information by which 3
4 to measure or estimate an individual deviation is necessary in a conventional blood pressure measuring method. The information may be the velocity of pulse waves from which blood pressure is measured. Accordingly, Pulse Wave Velocity (PWW) is used to compensate for an individual radial-brachial pressure difference in accordance with the present invention. [0019] FIG. 3 illustrates measuring of a PWV using an ElectroCardioGram (ECG) signal and a PhotoPlethysnoGraphy (PPG) signal. Referring to FIG. 3, the time difference between an R-peak of the ECG signal and start of a PPG signal measured by an optical sensor in a portable blood pressure measuring apparatus carried around a wrist or a finger, namely a Pulse Transit Time (PTT) is the time taken for the PPG signal to reach a measurement spot as the ventricles are contracted. A PWV is calculated by dividing the distance between the heart and the measurement spot of the PPG signal by the PTT. The PWV is widely used as an arterial stiffness index. [0020] FIGs. 4A, 4B and 4C illustrate pulse wave overlap characteristics according to PWVs. A PPG signal generated from ventricular contraction causes a reflective wave at an aortic bifurcation or an aortic termination. As illustrated in FIG. 4A, the magnitude and shape of a PPG signal at a certain spot on an artery are determined by the overlap between the original PPG signal and a reflective wave. [0021] Referring to FIG. 4B, if the PWV is low, the overlap between the reflective wave and the PPG signal does not increase the maximum pressure of the PPG signal. On the other hand, when the PWV is high, as illustrated in FIG. 4C, if the overlap between the reflective wave and the PPG signal increases the maximum pressure of the overlapped wave, that is, the systolic pressure is above the maximum pressure of the original PPG signal, the increase of the PWV also increases the systolic pressure due to the overlap. [0022] The overlap of the PPG signal also depends on the distance from a spot where the reflective wave is generated, as well as the PWV. [0023] If a PPG signal measured at a wrist or a finger near the aortic termination where a reflective wave is created is different from a PPG signal measured at the brachial aorta relatively far from the aortic termination, in terms of magnitude and shape, this difference is caused by a difference in overlap time, as described above. [0024] When the PWV is low, for example, when a wave having the shape illustrated in FIG. 4C is formed at the wrist aorta and a wave having the shape illustrated in FIG. 4B is formed at the brachial aorta, the systolic pressure changes as much as the difference between the maximum pressures illustrated in FIGs. 4B and 4C. [0025] When the PWV increases, the maximum pressure of the wrist or finger aorta increases due to wave overlap. As a consequence, the maximum pressure difference between the wrist or finger aorta and the brachial aorta increases. [0026] If arteriosclerosis causes an extremely high PWV, the waves of the wrist or finger and brachial aortas have the shape illustrated in FIG. 4C. In this case, the maximum pressure difference between the wrist or finger aorta and the brachial aorta may drop. [0027] In general, the difference between the radial or finger artery pressure and the brachial pressure measured at the same height (i.e. the height measured from the heart level) tends to increase as the PWV is higher. [0028] FIG. 5 is a graph illustrating a relationship between PWVs and radial and brachial blood pressures. The graph shows results of a test that was performed to verify the trend that the difference between the radial pressure and the brachial pressure increases with the PWV [0029] Blood pressures of six persons were measured at heart level using a cuff-based upper arm blood pressure monitor (A&D, UA-767) and a cuff-based wrist blood pressure monitor (Citizen, CH-656C). For each person at the same position, a PWV is measured from the ECG signals of both hands and a PPG signal of a finger measured by a transmissive optical sensor. The PWV and the mean difference between the radial pressure and the brachial pressure were plotted as a graph. As expected, the graph indicates that the difference between the radial pressure and the brachial pressure increases with the PWV. [0030] To find out whether the characteristics illustrated in FIG. 5 also apply to a wider range of PWVs and a wider range of blood pressures, as illustrated in Fig. 6C, 6D and 6E the positions of the wrists of the six persons were changed with respect to the heart level, thereby causing an about -30 to 40mm Hg-difference between the radial pressure and the brachial pressure. In the case illustrated in FIG. 6, it is revealed that both the systolic and diastolic pressure differences between the radial pressure and the brachial pressure have a correlation coefficient of about 0.9. [0031] The operation of the portable blood pressure measuring apparatus based on the relationship between the PWV and the radial-brachial difference is described in detail with reference to FIGs. 7 to 10. [0032] FIG. 7 is a block diagram of a portable blood pressure measuring apparatus according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, FIG. 8 illustrates a portable blood pressure measuring apparatus according to embodiment of the present invention, FIG. 9 illustrates a portable blood pressure measuring apparatus according to another preferred embodiment of the present invention, and FIG. 10 is a flowchart illustrating an operation for measuring blood pressure in a portable blood pressure measuring apparatus according to an preferred embodiment of the present invention. [0033] Referring to FIG. 7, a pressure measurer 720 measures a wrist or finger and provides the pressure measurement to a controller 710. Also provided are display 750, memory 740 and keypad 760. [0034] A PWV measurer 730 measures a PWV, including an ECG electrode portion 731 and an optical sensor
5 [0035] The ECG electrode portion 731 includes at least two electrodes. It is assumed that the ECG electrode portion 731 includes three electrodes in accordance with the exemplary embodiment of the present invention. Two of the three electrodes are provided inside a cuff of the portable blood pressure measuring apparatus and the other electrode is provided outside the cuff. Alternatively, one of the three electrodes is inside the cuff, while the other two electrodes are positioned outside the cuff. [0036] The optical sensor 732 includes a light source and a light receiving device. The optical sensor 732 may reside in the cuff or in an additional device attached to a finger. [0037] The structure of the PWV measurer 730 will be described in detail with reference to FIGs. 8 and 9. FIG. 8 illustrates a wrist-type blood pressure measuring apparatus. Three electrodes 731 a, 731b and 731c for measuring an EGC signal are added to a conventional blood pressure monitor cuff 770. An optical sensor 732 for measuring a PPG signal is provided inside a cuff 770 that contacts a wrist aorta portion or is provided in an additional device 800 that wraps around a finger. [0038] As illustrated in FIG. 8, regarding ECG electrodes, two ECG electrodes (e.g. a (-) electrode 731a and a GND electrode 731b) are provided at a portion that contacts with an arm around which the cuff 770 is wrapped, and one ECG electrode (e.g. a positive (+) electrode 731c) is provided on a display 750 or outside the cuff 770. Alternatively, the electrode 731c may be positioned inside the cuff 770 and the two electrodes 731a and 731b may be positioned outside the cuff 770. [0039] When blood pressure is measured, the ECG electrodes within the cuff 770 are brought into contact with the arm around which the cuff 770 is wrapped. Therefore, an ECG is measured by contacting a finger from the hand of the arm without the cuff 770. [0040] As illustrated in FIG. 8, pulse waves by which to measure the PWV may be measured by adding a transmissive optical sensor 732a and 732b to the additional device 800 installed to the finger or a reflective optical sensor (a light source 732c and a light receiving device 732d) inside the cuff 770. Especially when a PPG signal is measured at the wrist aorta, it is preferable to dispose the light source 732c and the light receiving device 732d such that the aorta is positioned between the light source 732c and the light receiving devices 732d. [0041] FIG. 9 illustrates a finger-type blood pressure measuring apparatus. Like the writs-type blood pressure measuring apparatus, the finger-type blood pressure measuring apparatus preferably additionally has ECG electrodes 730 inside and outside the cuff 770 in order to measure the PWV Since the finger aorta is small, oscillation may be measured by use of optical sensors 732a and 732b instead of pressure oscillation of the cuff 770. In this case, the optical sensors 732a and 732b are added inside the cuff 770 to apply the oscillometry method, compared to the wrist-type blood pressure measuring apparatus. The PWV may be measured using the optical sensors 732a and 732b. [0042] However, since the PWV changes when pressure is applied to arterial vessels by pressing the cuff 770, it is preferred that a transmissive or reflective optical sensor is additionally provided in an additional device 800 attached to the tip of the finger, besides the optical sensor within the cuff. [0043] The controller 710 providers overall control to the portable blood pressure measuring apparatus. Upon receipt of a wrist or finger pressure value measured by the pressure measurer 720, the controller 710 controls compensation of the received wrist or finger pressure value using the PWV received from the PWV measurer 730 by an equation for compensating the wrist or finger pressure to correspond to a brachial pressure. [0044] The controller 720 controls the compensated wrist or finger pressure to be displayed on the display 750. [0045] The memory 740 stores the compensation equation which has been selected from among the following compensation equations: where P brachial is a brachial blood pressure P wrist or finger is a blood pressure measured at the wrist or finger, PWV is a PWV, and a, b, c, d and e are empirical constants for compensating the wrist or finger pressure value. [0046] The compensation equation can also be empirically selected by a developer of the portable blood pressure measuring apparatus. The developer determines the correlation coefficients between wrist or finger and brachial pressure difference and the PWV for both systolic and diastolic pressures, selects an equation that approximates the wrist or 5
6 finger pressure to the brachial pressure from among the equations as described above, and stores the equation in the memory 740. Alternatively, the developer derives more than the above compensation equations by performing testing based on an equation P brachial = f(p wrist or finger, PWV), pursuant to the relationship between PWV and wrist or finger -brachial pressure difference illustrated in FIG. 6. [0047] In accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, the memory 740 stores all of equations 1 through 3 so that only a user-selected equation is used in pressure measuring mode, and the memory 740 preferably also stores the compensated radial pressure. [0048] The display 750 displays the wrist or finger pressure compensated to correspond to the brachial pressure in the pressure measuring mode. The keypad 760 includes function keys by which functions of the portable blood pressure measuring apparatus are set. [0049] A blood pressure measuring operation of the portable blood pressure measuring apparatus illustrated in FIGs. 7, 8 and 9 is described in detail with reference to FIG. 10. [0050] FIG. 10 is a flowchart illustrating an operation for measuring blood pressure in a portable blood pressure measuring apparatus according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention. [0051] Referring to FIG. 10, upon selection of pressure measuring mode by key input of the keypad 760, the controller 740 senses the pressure measuring mode and transitions the portable blood pressure measuring apparatus to a pressure measuring mode in step [0052] The pressure measurer 720 measures a wrist or finger pressure by the oscillation of the cuff and transmits the wrist or finger pressure to the controller 740 in the pressure measuring mode in step [0053] In step 1003, the PWV measurer 730 measures a PWV through the ECG electrode portion 731 and the optical sensor 732 and provides the PWV to the controller 740. [0054] Upon receipt of the wrist or finger pressure and the PWV, the controller 740 compensates the wrist or finger pressure to correspond to a brachial pressure utilizing the compensation equation stored in the memory 740, in step [0055] In step 1005, the controller 740 displays the compensated wrist or finger pressure on the display 750. [0056] FIGs. 11A and 11B are graphs illustrating blood pressures measured by a portable blood pressure measuring apparatus according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention. In FIG. 11, in the case of an about -30 to 40mm Hg difference between the radial pressure and the brachial pressure as illustrated in FIG. 6, the pressure difference is decreased by the procedure of FIG. 10. The compensation equation used herein is equation 1. [0057] As is apparent from the above description, the portable blood pressure measuring apparatus and method of the present invention effectively eliminate the difference between a radial pressure and a brachial pressure for individuals using a PWV. Therefore, the radial pressure is compensated to correspond to the brachial pressure, for the user. Since consistency is secured between an upper arm blood pressure monitor used in a clinic and a wrist-type or finger-type blood pressure monitor, instant blood pressure measurement and management is obtained. [0058] Embodiments of the present invention can also be embodied as computer-readable codes on a computer-readable recording medium. The computer-readable recording medium includes data storage devices that store data for subsequent use by a computer system. Examples of the computer-readable recording medium include, but are not limited to, Read-Only Memory (ROM), Random-Access Memory (RAM), CD-ROMs, magnetic tapes, floppy disks, optical data storage devices, and carrier waves (such as data transmission through the Internet via wired or wireless transmission paths). The computer-readable recording medium can also be distributed over network-coupled computer systems so that the computer-readable code is stored and executed in a distributed fashion. Also, function programs, codes, and code segments for accomplishing the present invention can be easily construed as within the scope of the invention by programmers skilled in the art to which the present invention pertains. 45 Claims 1. A portable blood pressure measuring apparatus comprising: a blood pressure measurer (720) for measuring a radial blood pressure, wherein the radial blood pressure is an arterial pressure measured at a wrist or a finger; a Pulse Wave Velocity (PWV) measurer (730) for measuring a PWV; a controller (710) for controlling compensation of the radial blood pressure using the measured PWV so that the radial blood pressure corresponds to a brachial blood pressure; and a display (750) for displaying the compensated radial blood pressure; wherein the controller (710) controls the compensation of the radial blood pressure using one of the following equations, 6
7 5 10 where P brachial is a brachial blood pressure measurement, P radial is a radial blood pressure measurement, PWV is a PWV, and a, b, c, d and e are empirical constants for compensating the radial blood pressure measurement The portable blood pressure measuring apparatus of claim 1, wherein the PWV measurer (730) includes an ElectroCardioGram (ECG) electrode portion (731) for measuring an ECG signal and an optical sensor (732) for measuring a PhotoPlethysnoGraphy signal The portable blood pressure measuring apparatus of claim 2, wherein the ECG electrode portion (731) includes at least two electrodes, at least one of the electrodes positioned inside a cuff (770) of the portable blood pressure measuring apparatus and at least another one of the electrodes positioned outside the cuff (770). 4. The portable blood pressure measuring apparatus of claim 2, wherein the optical sensor (732) includes a light source (732c) and a light receiving device (732d) and is provided inside a cuff (770) of the portable blood pressure measuring apparatus or at an additional device attached to the finger. 5. The portable blood pressure measuring apparatus of claim 1, further comprising a memory (740) for pre-storing the selected one of <equation 1 >, <equation 2>, and <equation 3>. 6. A portable blood pressure measuring method comprising: measuring a radial blood pressure being an arterial pressure at a wrist or a finger in blood pressure measuring mode; measuring a Pulse Wave Velocity (PWV); compensating the radial blood pressure using the PWV so that the radial blood pressure corresponds to a brachial blood pressure; and displaying the compensated radial blood pressure; wherein the compensation comprises compensating the radial blood pressure using one of the following equations, where P brachial is a brachial blood pressure measurement, P radial is a radial blood pressure measurement, PWV is a PWV, and a, b, c, d and e are empirical constants for compensating the radial blood pressure measurement. 7. The portable blood pressure measuring method of claim 6, wherein the PWV measuring comprises measuring the PWV using an ElectroCardioGram (ECG) signal and a PhotoPlethysnoGraphy signal The portable blood pressure measuring method of claim 6, wherein the selected one of <equation 1 >, <equation 2>, and <equation 3> is pre-stored. 7
8 Patentansprüche 1. Tragbares Blutdruckmessgerät, umfassend: 5 10 einen Blutdruckmesser (720) zum Messen eines Radialblutdrucks, wobei der Radialblutdruck ein an einem Handgelenk bzw. einer Handwurzel oder einem Finger gemessener Arterialdruck ist; einen PWV-Messer (Pulse Wave Velocity PWV, Pulswellengeschwindigkeit) (730) zum Messen einer PWV; eine Steuerung (710) zum Steuern eines Ausgleiches des Radialblutdrucks unter Verwendung der gemessenen PWV derart, dass der Radialblutdruck einem Brachialblutdruck entspricht; und eine Anzeige (750) zum Anzeigen des ausgeglichenen Radialblutdrucks; wobei die Steuerung (710) den Ausgleich des Radialblutdrucks unter Verwendung von einer der nachfolgenden Gleichungen steuert: wobei P brachial eine Brachialblutdruckmessung ist, P radial eine Radialblutdruckmessung ist, PWV eine PWV ist und a, b, c, d und e empirische Konstanten zum Ausgleichen der Radialblutdruckmessung sind Tragbares Blutdruckmessgerät nach Anspruch 1, wobei der PWV-Messer (730) einen ElectroCardioGram-Elektrodenabschnitt (ElectroCardioGram ECG, Elektrokardiogramm) (731) zum Messen eines ECG-Signals und einen optischen Sensor (732) zum Messen eines PhotoPlethysnoGraphy-Signals beinhaltet Tragbares Blutdruckmessgerät nach Anspruch 2, wobei der ECG-Elektrodenabschnitt (731) wenigstens zwei Elektroden beinhaltet, wobei wenigstens eine der Elektroden innerhalb einer Manschette (770) des tragbaren Blutdruckmessgerätes positioniert ist und wenigstens eine weitere der Elektroden außerhalb der Manschette (770) positioniert ist Tragbares Blutdruckmessgerät nach Anspruch 2, wobei der optische Sensor (732) eine Lichtquelle (732c) und eine Lichtempfangsvorrichtung (732d) beinhaltet und innerhalb einer Manschette (770) des tragbaren Blutdruckmessgerätes oder an einer an dem Finger angebrachten zusätzlichen Vorrichtung vorgesehen ist. 5. Tragbares Blutdruckmessgerät nach Anspruch 1, des Weiteren umfassend einen Speicher (740) zum Vorabspeichern der ausgewählten von <Gleichung 1 >, <Gleichung 2> und <Gleichung 3> Tragbares Blutdruckmessverfahren, umfassend: Messen eines Radialblutdrucks, der ein Arterialdruck an einem Handgelenk bzw. einer Handwurzel oder einem Finger im Blutdruckmessmodus ist; Messen einer Pulswellengeschwindigkeit (Pulse Wave Velocity PWV); Ausgleichen des Radialblutdrucks unter Verwendung der PWV derart, dass der Radialblutdruck einem Brachialblutdruck entspricht; und Anzeigen des ausgeglichenen Radialblutdrucks; wobei der Ausgleich ein Ausgleichen des Radialblutdrucks unter Verwendung von einer der nachfolgenden Gleichungen beinhaltet: 8
9 5 10 wobei P brachial eine Brachialblutdruckmessung ist, P radial eine Radialblutdruckmessung ist, PWV eine PWV ist und a, b, c, d und e empirische Konstanten zum Ausgleichen der Radialblutdruckmessung sind Tragbares Blutdruckmessverfahren nach Anspruch 6, wobei das Messen der PWV ein Messen der PWV unter Verwendung eines ElectroCardioGram-Signals (ElectroCardioGram ECG, Elektrokardiogramm) und eines Photo- PlethysnoGraphy-Signals umfasst Tragbares Blutdruckmessverfahren nach Anspruch 6, wobei die ausgewählte von <Gleichung 1 >, <Gleichung 2> und <Gleichung 3> vorab gespeichert wird. Revendications Appareil portable de mesure de la pression sanguine comprenant : un dispositif de mesure de pression sanguine (720) pour mesurer une pression sanguine radiale, dans lequel la pression sanguine radiale est une pression artérielle mesurée au poignet ou à un doigt ; - un dispositif de mesure (730) de la vitesse du pouls (PWV) pour mesurer la PWV ; - un dispositif de commande (710) pour commander une compensation de la pression sanguine radiale en utilisant la PWV mesurée de sorte que la pression sanguine radiale corresponde à une pression sanguine brachiale ; et - un afficheur (750) pour afficher la pression sanguine radiale compensée ; - dans lequel le dispositif de commande (710) commande la compensation de la pression sanguine radiale en utilisant une des équations suivantes : dans lesquelles P brachial est une mesure de la pression sanguine brachiale, P radial est une mesure de la pression sanguine radiale, PWV est une PWV et a, b, c, d et e sont des constantes empiriques pour compenser la mesure de la pression sanguine radiale. 2. Appareil portable de mesure de la pression sanguine selon la revendication 1, dans lequel le dispositif de mesure de PWV (730) comprend une partie d électrode (731) d électrocardiogramme (ECG) pour mesurer un signal ECG et un capteur optique (732) pour mesurer un signal de photopléthysmographie. 3. Appareil portable de mesure de la pression sanguine selon la revendication 2, dans lequel la partie d électrode ECG (731) comprend au moins deux électrodes, au moins une des électrodes positionnée à l intérieur d un brassard (770) de l appareil portable de mesure de la pression sanguine et au moins une autre des électrodes positionnée 9
10 à l extérieur du brassard (770) Appareil portable de mesure de la pression sanguine selon la revendication 2, dans lequel le capteur optique (732) comprend une source de lumière (732c) et un dispositif de réception de lumière (732d) et est disposé à l intérieur d un brassard (770) de l appareil portable de mesure de la pression sanguine ou au niveau d un dispositif supplémentaire attaché au doigt Appareil portable de mesure de la pression sanguine selon la revendication 1, comprenant en outre une mémoire (740) pour pré-stocker l équation sélectionnée parmi <équation 1>, <équation 2> et <équation 3>. 6. Procédé portable de mesure de la pression sanguine, comprenant les étapes consistant à : mesurer une pression sanguine radiale qui est une pression artérielle au poignet ou à un doigt en mode de mesure de pression sanguine ; - mesurer une vitesse du pouls (PWV) ; - compenser la pression sanguine radiale en utilisant la PWV mesurée de sorte que la pression sanguine radiale corresponde à une pression sanguine brachiale ; et - afficher la pression sanguine radiale compensée ; - pour lequel la compensation comprend de compenser la pression sanguine radiale en utilisant une des équations suivantes : dans lesquelles P brachial est une mesure de la pression sanguine brachiale, P radial est une mesure de la pression sanguine radiale, PWV est une PWV et a, b, c, d et e sont des constantes empiriques pour compenser la mesure de la pression sanguine radiale Procédé portable de mesure de la pression sanguine selon la revendication 6, pour lequel la mesure de la PWV comprend de mesurer la PWV en utilisant un signal d électrocardiogramme (ECG) et un signal de photopléthysmographie. 8. Procédé portable de mesure de la pression sanguine selon la revendication 6, pour lequel l équation sélectionnée parmi <équation 1>, <équation 2> et <équation 3> est pré-stockée
11 11
12 12
13 13
14 14
15 15
16 16
17 17
18 18
19 19
20 20
TEPZZ 9_ 9 A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2015/36
 (19) TEPZZ 9_ 9 A_T (11) EP 2 913 293 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 02.09.2015 Bulletin 2015/36 (51) Int Cl.: B66D 1/38 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 15250003.9 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 9_ 9 A_T (11) EP 2 913 293 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 02.09.2015 Bulletin 2015/36 (51) Int Cl.: B66D 1/38 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 15250003.9 (22)
TEPZZ 69Z 85A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
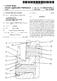
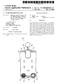
 (19) TEPZZ 69Z 8A T (11) EP 2 690 28 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.01.14 Bulletin 14/0 (21) Application number: 13177476.2 (1) Int Cl.: F03D 7/02 (06.01) F03D 7/00 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ 69Z 8A T (11) EP 2 690 28 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.01.14 Bulletin 14/0 (21) Application number: 13177476.2 (1) Int Cl.: F03D 7/02 (06.01) F03D 7/00 (06.01)
TEPZZ 54Z549A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ 54Z549A_T (11) EP 2 540 549 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 02.01.2013 Bulletin 2013/01 (21) Application number: 11747089.8
(19) TEPZZ 54Z549A_T (11) EP 2 540 549 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 02.01.2013 Bulletin 2013/01 (21) Application number: 11747089.8
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (11) EP 2 481 666 A1 (43) Date of publication: 01.08.2012 Bulletin 2012/31 (21) Application number: 10826779.0 (22) Date
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (11) EP 2 481 666 A1 (43) Date of publication: 01.08.2012 Bulletin 2012/31 (21) Application number: 10826779.0 (22) Date
TEPZZ _ Z684A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: A01D 34/82 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ _ Z684A_T (11) EP 3 1 684 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 2.01.17 Bulletin 17/04 (1) Int Cl.: A01D 34/82 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1617949.9 (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ _ Z684A_T (11) EP 3 1 684 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 2.01.17 Bulletin 17/04 (1) Int Cl.: A01D 34/82 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1617949.9 (22) Date of
TEPZZ 6Z4795A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2013/25
 (19) TEPZZ 6Z479A T (11) EP 2 604 79 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 19.06.2013 Bulletin 2013/2 (1) Int Cl.: F01D /18 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 12194748. (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ 6Z479A T (11) EP 2 604 79 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 19.06.2013 Bulletin 2013/2 (1) Int Cl.: F01D /18 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 12194748. (22) Date
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2013/48
 (19) TEPZZ 66654 A_T (11) EP 2 666 543 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 27.11.2013 Bulletin 2013/48 (51) Int Cl.: B02C 13/286 (2006.01) B02C 13/18 (2006.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ 66654 A_T (11) EP 2 666 543 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 27.11.2013 Bulletin 2013/48 (51) Int Cl.: B02C 13/286 (2006.01) B02C 13/18 (2006.01) (21) Application
*EP A2* EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2003/34
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP00133679A2* (11) EP 1 336 79 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 20.08.2003 Bulletin 2003/34
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP00133679A2* (11) EP 1 336 79 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 20.08.2003 Bulletin 2003/34
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 55475 A_T (11) EP 2 554 752 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 06.02.2013 Bulletin 2013/06 (21) Application number: 11176100.3 (51) Int Cl.: E02D 7/06 (2006.01) E02D
(19) TEPZZ 55475 A_T (11) EP 2 554 752 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 06.02.2013 Bulletin 2013/06 (21) Application number: 11176100.3 (51) Int Cl.: E02D 7/06 (2006.01) E02D
TEPZZ _ 5778A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ _ 778A_T (11) EP 3 13 778 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 01.03.2017 Bulletin 2017/09 (21) Application number: 1183169.0 (1) Int Cl.: C21D 9/6 (2006.01) F27B 9/04
(19) TEPZZ _ 778A_T (11) EP 3 13 778 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 01.03.2017 Bulletin 2017/09 (21) Application number: 1183169.0 (1) Int Cl.: C21D 9/6 (2006.01) F27B 9/04
(51) Int Cl.: A61B 1/00 ( )
 (19) (11) EP 1 726 248 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 22.12. Bulletin /1 (21) Application number: 07790.4 (22) Date of filing: 1.03.0
(19) (11) EP 1 726 248 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 22.12. Bulletin /1 (21) Application number: 07790.4 (22) Date of filing: 1.03.0
(51) Int Cl.: B64C 39/02 ( ) A63H 29/16 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ Z64 7A_T (11) EP 3 06 427 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 17.08.16 Bulletin 16/33 (1) Int Cl.: B64C 39/02 (06.01) A63H 29/16 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1389.2
(19) TEPZZ Z64 7A_T (11) EP 3 06 427 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 17.08.16 Bulletin 16/33 (1) Int Cl.: B64C 39/02 (06.01) A63H 29/16 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1389.2
TEPZZ 7_687ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2014/15
 (19) TEPZZ 7_687ZA_T (11) EP 2 716 870 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 09.04.2014 Bulletin 2014/15 (51) Int Cl.: F01D 5/20 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 13187418.2 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 7_687ZA_T (11) EP 2 716 870 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 09.04.2014 Bulletin 2014/15 (51) Int Cl.: F01D 5/20 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 13187418.2 (22)
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY DIVISION NEWPORT OFFICE OF COUNSEL PHONE: FAX: DSN:
 IMAVSBA WARFARE CENTERS NEWPORT DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFARE CENTER DIVISION NEWPORT OFFICE OF COUNSEL PHONE: 401 832-3653 FAX: 401 832-4432 DSN: 432-3653 Attorney Docket No. 85031 Date:
IMAVSBA WARFARE CENTERS NEWPORT DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFARE CENTER DIVISION NEWPORT OFFICE OF COUNSEL PHONE: 401 832-3653 FAX: 401 832-4432 DSN: 432-3653 Attorney Docket No. 85031 Date:
(51) Int Cl.: E04H 4/12 ( ) F16L 41/00 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 4ZZ4B_T (11) EP 2 40 04 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 08.03.2017 Bulletin 2017/10 (1) Int Cl.: E04H 4/12 (2006.01) F16L
(19) TEPZZ 4ZZ4B_T (11) EP 2 40 04 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 08.03.2017 Bulletin 2017/10 (1) Int Cl.: E04H 4/12 (2006.01) F16L
TEPZZ 5_84 8A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ 5_84 8A_T (11) EP 2 518 438 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 31.10.2012 Bulletin 2012/44 (21) Application number: 10839590.6
(19) TEPZZ 5_84 8A_T (11) EP 2 518 438 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 31.10.2012 Bulletin 2012/44 (21) Application number: 10839590.6
(51) Int Cl. 7 : G01L 11/02, G01L 1/24
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP00991B1* (11) EP 1 099 1 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP00991B1* (11) EP 1 099 1 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the
(51) Int Cl.: A61M 1/34 ( ) A61M 1/16 ( ) (56) References cited:
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (11) EP 1 17 917 B1 (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 12.12.07 Bulletin 07/0 (1) Int Cl.: A61M 1/34 (06.01) A61M 1/16 (06.01) (21)
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (11) EP 1 17 917 B1 (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 12.12.07 Bulletin 07/0 (1) Int Cl.: A61M 1/34 (06.01) A61M 1/16 (06.01) (21)
Boom for a load handling machine.
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository Boom for a load handling machine This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an author. Citation: NURSE, A.D....et
Loughborough University Institutional Repository Boom for a load handling machine This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an author. Citation: NURSE, A.D....et
(51) Int Cl.: A63B 57/00 ( ) A63B 47/00 ( )
 (19) (11) EP 1 608 442 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 01.10.2008 Bulletin 2008/40 (21) Application number: 04724071.8 (22) Date of
(19) (11) EP 1 608 442 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 01.10.2008 Bulletin 2008/40 (21) Application number: 04724071.8 (22) Date of
(51) Int Cl.: F17C 9/02 ( )
 (19) (11) EP 0 911 572 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 05.09.2007 Bulletin 2007/36 (51) Int Cl.: F17C 9/02 (2006.01) (21) Application
(19) (11) EP 0 911 572 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 05.09.2007 Bulletin 2007/36 (51) Int Cl.: F17C 9/02 (2006.01) (21) Application
(51) Int Cl.: F16L 1/16 ( ) F16L 1/23 ( ) F16L 1/18 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 689_7 B_T (11) EP 2 689 173 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 28.09.2016 Bulletin 2016/39 (21) Application number: 12712241.4
(19) TEPZZ 689_7 B_T (11) EP 2 689 173 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 28.09.2016 Bulletin 2016/39 (21) Application number: 12712241.4
(51) Int Cl.: B62M 25/04 ( )
 (19) (11) EP 2 06 298 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 28.09.2011 Bulletin 2011/39 (1) Int Cl.: B62M 2/04 (2006.01) (21) Application
(19) (11) EP 2 06 298 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 28.09.2011 Bulletin 2011/39 (1) Int Cl.: B62M 2/04 (2006.01) (21) Application
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY DIVISION NEWPORT OFFICE OF COUNSEL PHONE: FAX: DSN:
 M/W/SEA WARFARE CENTERS NEWPORT DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFARE CENTER DIVISION NEWPORT OFFICE OF COUNSEL PHONE: 401 832-3653 FAX: 401 832-4432 DSN: 432-3653 Attorney Docket No. 99558 Date:
M/W/SEA WARFARE CENTERS NEWPORT DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFARE CENTER DIVISION NEWPORT OFFICE OF COUNSEL PHONE: 401 832-3653 FAX: 401 832-4432 DSN: 432-3653 Attorney Docket No. 99558 Date:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090235422A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0235422 A1 Lueking (43) Pub. Date: (54) APPARATUS AND METHODS FOR HOLDING Publication Classification SHN GUARDS
(19) United States US 20090235422A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0235422 A1 Lueking (43) Pub. Date: (54) APPARATUS AND METHODS FOR HOLDING Publication Classification SHN GUARDS
(10) Patent No.: US 7,331,117 B2
 111111 1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US007331117B2 (12) United States Patent Lau et al. (10) Patent No.: US 7,331,117 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19,2008 (54) CALCANEAL
111111 1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US007331117B2 (12) United States Patent Lau et al. (10) Patent No.: US 7,331,117 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19,2008 (54) CALCANEAL
PHY100 s Lab: The Relationship Between Liquid Pressure and Depth as it applies to Blood Pressure. Course & Sec:
 PHY100 s Lab: The Relationship Between Liquid Pressure and Depth as it applies to Blood Pressure Name: Lab Partner: Course & Sec: Date: Disclaimer: The procedures in this lab are not according to proper
PHY100 s Lab: The Relationship Between Liquid Pressure and Depth as it applies to Blood Pressure Name: Lab Partner: Course & Sec: Date: Disclaimer: The procedures in this lab are not according to proper
FIREARMS IN THE EU September respondents. EU Member States PUBLIC PERCEPTIONS OF FIREARMS
 FIREARMS IN THE EU The disruption of illicit manufacturing and trafficking in firearms is one of the EU s law enforcement priorities for 2014-17 PUBLIC PERCEPTIONS OF FIREARMS Source: Flash Eurobarometer
FIREARMS IN THE EU The disruption of illicit manufacturing and trafficking in firearms is one of the EU s law enforcement priorities for 2014-17 PUBLIC PERCEPTIONS OF FIREARMS Source: Flash Eurobarometer
The below identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
 DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY OFFICE OF COUNSEL NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFARE CENTER DIVISION 1176 HOWELL STREET NEWPORT Rl 02841-1708 IN REPLY REFER TO Attorney Docket No. 300170 20 March 2018 The below identified
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY OFFICE OF COUNSEL NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFARE CENTER DIVISION 1176 HOWELL STREET NEWPORT Rl 02841-1708 IN REPLY REFER TO Attorney Docket No. 300170 20 March 2018 The below identified
(51) Int Cl.: F03D 1/06 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 68Z 4B_T (11) EP 2 368 034 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 28.06.17 Bulletin 17/26 (21) Application number: 09737464.9 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 68Z 4B_T (11) EP 2 368 034 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 28.06.17 Bulletin 17/26 (21) Application number: 09737464.9 (22)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,524,267 B1
 USOO6524267B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,524,267 B1 Gremel et al. 45) Date of Patent: Feb. 25, 2003 9 (54) VENOUS FILTER FOR ASSISTED VENOUS (56) References Cited RETUR N U.S. PATENT
USOO6524267B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,524,267 B1 Gremel et al. 45) Date of Patent: Feb. 25, 2003 9 (54) VENOUS FILTER FOR ASSISTED VENOUS (56) References Cited RETUR N U.S. PATENT
1. Annex 1: Indicators
 1. Annex 1: Indicators 1.1 Input indicators 1. Financial envelope of AGN operating agreements over 7 years, in * Euro 613 740 613 740 572 773 553 605 553 605 638 904 638 904 *Reported budget outcome 2.
1. Annex 1: Indicators 1.1 Input indicators 1. Financial envelope of AGN operating agreements over 7 years, in * Euro 613 740 613 740 572 773 553 605 553 605 638 904 638 904 *Reported budget outcome 2.
NOTICE. The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
 Serial Number 09/113.010 Filing Date 26 June 1998 Inventor Daniel M. Glenning Michael Visich NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be
Serial Number 09/113.010 Filing Date 26 June 1998 Inventor Daniel M. Glenning Michael Visich NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,834,776 B1
 USOO6834776B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,834,776 B1 Corvese (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 28, 2004 (54) TENNIS BALL RETRIEVING DEVICE 5,125,654 A 6/1992 Bruno... 473/460 (75) Inventor:
USOO6834776B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,834,776 B1 Corvese (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 28, 2004 (54) TENNIS BALL RETRIEVING DEVICE 5,125,654 A 6/1992 Bruno... 473/460 (75) Inventor:
NOTICE. The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
 Serial Number 09/515.214 Filing Date 28 February 2000 Inventor Robert J. Obara NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
Serial Number 09/515.214 Filing Date 28 February 2000 Inventor Robert J. Obara NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
(51) Int Cl.: F02M 21/02 ( ) F02D 19/06 ( ) F02D 19/02 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 9 7 7B_T (11) EP 2 92 727 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 22.11.17 Bulletin 17/47 (1) Int Cl.: F02M 21/02 (06.01) F02D 19/06
(19) TEPZZ 9 7 7B_T (11) EP 2 92 727 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 22.11.17 Bulletin 17/47 (1) Int Cl.: F02M 21/02 (06.01) F02D 19/06
3.940,144 2/1976 Dickie... is strap is secured to the waist belt while the other end of the
 USOO61296.38A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Davis (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 10, 2000 54 GOLF SWING TRAININGAPPARATUS 5,303,927 4/1994 Perry et al.... 473/215 5,704,856 1/1998 Morse... 473/422
USOO61296.38A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Davis (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 10, 2000 54 GOLF SWING TRAININGAPPARATUS 5,303,927 4/1994 Perry et al.... 473/215 5,704,856 1/1998 Morse... 473/422
Module No GETTING ACQUAINTED GENERAL GUIDE TIMEKEEPING
 Module No. 2196 2196-1 GETTING ACQUAINTED Congratulations upon your selection of this CASIO Pressure Monitor Watch (BP-1B, Module No. 2196). To get the most out of your purchase, be sure to carefully read
Module No. 2196 2196-1 GETTING ACQUAINTED Congratulations upon your selection of this CASIO Pressure Monitor Watch (BP-1B, Module No. 2196). To get the most out of your purchase, be sure to carefully read
(51) Int Cl.: B63C 1/06 ( ) B63C 1/02 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 498 9B_T (11) EP 2 349 829 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 20.02.2013 Bulletin 2013/08 (21) Application number: 09760263.
(19) TEPZZ 498 9B_T (11) EP 2 349 829 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 20.02.2013 Bulletin 2013/08 (21) Application number: 09760263.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050272546A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0272546A1 Reiter (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 8, 2005 (54) RIVETED SPROCKETASSEMBLY (75) Inventor: Markus Reiter,
(19) United States US 20050272546A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0272546A1 Reiter (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 8, 2005 (54) RIVETED SPROCKETASSEMBLY (75) Inventor: Markus Reiter,
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Yang USOO58394.71A 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: 5,839,471 Nov. 24, 1998 54). SEALING MEMBER FOR AWALVE 76 Inventor: Tsai Chen Yang, No. 15-11, Tou Ren Lane, Tou Ren
United States Patent (19) Yang USOO58394.71A 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: 5,839,471 Nov. 24, 1998 54). SEALING MEMBER FOR AWALVE 76 Inventor: Tsai Chen Yang, No. 15-11, Tou Ren Lane, Tou Ren
Circulation and Respiration: Vital Signs Student Version
 Circulation and Respiration: Vital Signs Student Version In this lab, you will learn about the circulatory and respiratory systems. You will test the capacity of your lungs, measure your blood pressure
Circulation and Respiration: Vital Signs Student Version In this lab, you will learn about the circulatory and respiratory systems. You will test the capacity of your lungs, measure your blood pressure
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 2004O126242A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0126242 A1 Howard et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 1, 2004 (54) BOAT PROPELLER AND GUARD DEVICE (52) U.S. Cl....
US 2004O126242A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0126242 A1 Howard et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 1, 2004 (54) BOAT PROPELLER AND GUARD DEVICE (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,055,842 B1. Lin (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 6, (54) FOLDING ELECTRIC BICYCLE 6,883,817 B1 4/2005 Chu...
 United States Patent US007055842B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: Lin (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 6, 2006 (54) FOLDING ELECTRIC BICYCLE 6,883,817 B1 4/2005 Chu... 280,278 2002/0175491 A1* 11/2002 Clark... 280/288.4
United States Patent US007055842B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: Lin (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 6, 2006 (54) FOLDING ELECTRIC BICYCLE 6,883,817 B1 4/2005 Chu... 280,278 2002/0175491 A1* 11/2002 Clark... 280/288.4
(51) Int Cl.: A61M 1/14 ( ) A61M 1/36 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 6_6 7B_T (11) EP 2 616 117 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 09.12. Bulletin /0 (21) Application number: 117342.0 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ 6_6 7B_T (11) EP 2 616 117 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 09.12. Bulletin /0 (21) Application number: 117342.0 (22) Date
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060049223A1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0049223 A1 Mora et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2006 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) SCORECARD HOLDER FOR GOLF Inventors:
(19) United States US 20060049223A1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0049223 A1 Mora et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2006 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) SCORECARD HOLDER FOR GOLF Inventors:
E2IB (7/02 ( ) (52) U.S. Cl /19: 464/155 (58) Field of Classification Search / , 175/325.6
 US007 186182B2 (12) United States Patent Wenzel et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,186,182 B2 Mar. 6, 2007 (54) DRIVE LINE FOR DOWN HOLE MUD MOTOR (76) Inventors: William R. Wenzel, 1738
US007 186182B2 (12) United States Patent Wenzel et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,186,182 B2 Mar. 6, 2007 (54) DRIVE LINE FOR DOWN HOLE MUD MOTOR (76) Inventors: William R. Wenzel, 1738
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO8352206B2 () Patent No.: Buess (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 8, 2013 (54) METHOD FOR THE SIGNAL (56) References Cited LINEARIZATION OF A GAS SENSOR OUTPUT SIGNAL U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent USOO8352206B2 () Patent No.: Buess (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 8, 2013 (54) METHOD FOR THE SIGNAL (56) References Cited LINEARIZATION OF A GAS SENSOR OUTPUT SIGNAL U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
TEPZZ Z984B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION. (51) Int Cl.: A61M 25/10 ( ) A61B 1/015 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ Z984B_T (11) EP 2 3 984 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 28..1 Bulletin 1/44 (21) Application number: 09787498.6 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ Z984B_T (11) EP 2 3 984 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 28..1 Bulletin 1/44 (21) Application number: 09787498.6 (22) Date
TEPZZ 7 Z67A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 7 Z67A_T (11) EP 2 711 067 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.03.14 Bulletin 14/13 (21) Application number: 12188.1 (1) Int Cl.: B01D 3/60 (06.01) B01D 3/92 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ 7 Z67A_T (11) EP 2 711 067 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.03.14 Bulletin 14/13 (21) Application number: 12188.1 (1) Int Cl.: B01D 3/60 (06.01) B01D 3/92 (06.01)
Update of trade weights data underlying the EERs and HCIs
 August 2017 Update of trade weights data underlying the EERs and HCIs The trade weights underlying the calculation of the effective exchange rates (EERs) of the euro and the harmonised competitiveness
August 2017 Update of trade weights data underlying the EERs and HCIs The trade weights underlying the calculation of the effective exchange rates (EERs) of the euro and the harmonised competitiveness
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,923,737 B1
 USOO6923737B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,923,737 B1 Walker (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 2, 2005 (54) BASEBALL SWING TRAINING APPARATUS 3,115,129 A 12/1963 Merriman... 124/5 3,115,342
USOO6923737B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,923,737 B1 Walker (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 2, 2005 (54) BASEBALL SWING TRAINING APPARATUS 3,115,129 A 12/1963 Merriman... 124/5 3,115,342
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 200701.23374A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/01233.74 A1 Jones (43) Pub. Date: May 31, 2007 (54) BASKETBALL GOAL RIM LOCK Publication Classification (76)
US 200701.23374A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/01233.74 A1 Jones (43) Pub. Date: May 31, 2007 (54) BASKETBALL GOAL RIM LOCK Publication Classification (76)
(51) Int Cl.: A61G 7/00 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ_985 7 B_T (11) EP 1 985 273 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 30.07.2014 Bulletin 2014/31 (51) Int Cl.: A61G 7/00 (2006.01)
(19) TEPZZ_985 7 B_T (11) EP 1 985 273 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 30.07.2014 Bulletin 2014/31 (51) Int Cl.: A61G 7/00 (2006.01)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0176367 A1 PENNINGTON et al. US 201701.76367A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 22, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) APPARATUS TO MEASURE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0176367 A1 PENNINGTON et al. US 201701.76367A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 22, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) APPARATUS TO MEASURE
Deliverable D3.2 Assembly of Basic Fact Sheets 2010
 Road Safety Data, Collection, Transfer and Analysis Deliverable D3.2 Assembly of Basic Fact Sheets 2010 Please refer to this report as follows: Broughton, J and Knowles, J (2011) Assembly of Basic Fact
Road Safety Data, Collection, Transfer and Analysis Deliverable D3.2 Assembly of Basic Fact Sheets 2010 Please refer to this report as follows: Broughton, J and Knowles, J (2011) Assembly of Basic Fact
MANUAL BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR BPM 168B Contents Blood Pressure Monitor Intended Use What is blood pressure?
 MANUAL BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR BPM 168B Contents 01... Blood Pressure Monitor Intended Use 02... 1. What is blood pressure? 02... 2. Why is it useful measure blood pressure at home?... A. WHO blood pressure
MANUAL BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR BPM 168B Contents 01... Blood Pressure Monitor Intended Use 02... 1. What is blood pressure? 02... 2. Why is it useful measure blood pressure at home?... A. WHO blood pressure
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,893,786 Stevens 45 Date of Patent: Apr. 13, 1999
 III IIII USOO589.3786A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Stevens 45 Date of Patent: Apr. 13, 1999 54 AUTOMATIC TELESCOPING BOUYANT 5,582,127 12/1996 Willis et al.... 116/210 IDENTIFICATION DEVICE
III IIII USOO589.3786A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Stevens 45 Date of Patent: Apr. 13, 1999 54 AUTOMATIC TELESCOPING BOUYANT 5,582,127 12/1996 Willis et al.... 116/210 IDENTIFICATION DEVICE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 US 2013 0186486A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0186486A1 Ding (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 25, 2013 (54) SYSTEM FOR AND METHOD OF (52) U.S. Cl. MONITORING FLOW
US 2013 0186486A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0186486A1 Ding (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 25, 2013 (54) SYSTEM FOR AND METHOD OF (52) U.S. Cl. MONITORING FLOW
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060289584A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0289584A1 Lu (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 28, 2006 (54) PROTECTIVE BAG HAVING INNER PAD FOR SURFBOARD (76) Inventor:
(19) United States US 20060289584A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0289584A1 Lu (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 28, 2006 (54) PROTECTIVE BAG HAVING INNER PAD FOR SURFBOARD (76) Inventor:
BLOOD PRESSURE SENSOR 0377i
 BLOOD PRESSURE SENSOR 0377i USER S GUIDE CENTRE FOR MICROCOMPUTER APPLICATIONS http://www.cma-science.nl Short description The Blood Pressure sensor 0377i is used to measure arterial blood pressure in
BLOOD PRESSURE SENSOR 0377i USER S GUIDE CENTRE FOR MICROCOMPUTER APPLICATIONS http://www.cma-science.nl Short description The Blood Pressure sensor 0377i is used to measure arterial blood pressure in
BLOOD PRESSURE SENSOR BT17i USER S GUIDE
 BLOOD PRESSURE SENSOR BT17i USER S GUIDE CENTRE FOR MICROCOMPUTER APPLICATIONS http://www.cma-science.nl Short description The Blood Pressure sensor BT17i allows measuring arterial blood pressure. The
BLOOD PRESSURE SENSOR BT17i USER S GUIDE CENTRE FOR MICROCOMPUTER APPLICATIONS http://www.cma-science.nl Short description The Blood Pressure sensor BT17i allows measuring arterial blood pressure. The
Information on the implementation of Commission Regulation (EC) No 504/2008 on the identification of equidae
 Information on the implementation of Commission Regulation (EC) No 504/2008 on the identification of equidae report based on MSs' information Unit G2 Animal health Directorate-General for European Commission,
Information on the implementation of Commission Regulation (EC) No 504/2008 on the identification of equidae report based on MSs' information Unit G2 Animal health Directorate-General for European Commission,
58) Field of searby 36, so asso's "... includes a pair of Support Straps connected at opposed ends
 USOO6113460A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: McKeown (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 5, 2000 54) COMBINATION WOMENS GARMENT AND 2,428,175 8/1947 Norton... 450/31 BREAST SUPPORT 3,527,231 9/1970 Catanese
USOO6113460A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: McKeown (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 5, 2000 54) COMBINATION WOMENS GARMENT AND 2,428,175 8/1947 Norton... 450/31 BREAST SUPPORT 3,527,231 9/1970 Catanese
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Beyl 54 (76) 21) 22 (51) (52) (58) (56) ARROWHEAD WITH REFILLABLE CARTRIDGES FOR HIGH IMPACT ARROWS Inventor: James A. Beyl, 633 E. Lamme, Bozeman, Mont. 59715 Appl. No.: 836,546
United States Patent (19) Beyl 54 (76) 21) 22 (51) (52) (58) (56) ARROWHEAD WITH REFILLABLE CARTRIDGES FOR HIGH IMPACT ARROWS Inventor: James A. Beyl, 633 E. Lamme, Bozeman, Mont. 59715 Appl. No.: 836,546
exercising facility (14), when the arms of the person are to
 USOO5906563A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,906,563 Pittari (45) Date of Patent: May 25, 1999 54) DUAL EXERCISE BIKE 5,284.462 2/1994 Olschansky et al.... 482/64 5,342,262 8/1994 Hansen......
USOO5906563A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,906,563 Pittari (45) Date of Patent: May 25, 1999 54) DUAL EXERCISE BIKE 5,284.462 2/1994 Olschansky et al.... 482/64 5,342,262 8/1994 Hansen......
Life Domain: Education and Vocational Training Goal Dimension: Objective Living Conditions
 Life Domain: Education and Vocational Training Goal Dimension: Objective Living Conditions Measurement Dimension: Educational Performance Subdimension: Pupil literacy Indicator: F1211 Reading Literacy
Life Domain: Education and Vocational Training Goal Dimension: Objective Living Conditions Measurement Dimension: Educational Performance Subdimension: Pupil literacy Indicator: F1211 Reading Literacy
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,598,456 B2
 USOO6598456 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Potts (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 29, 2003 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEMS FOR CONTROL 4,648,490 A * 3/1987 Bergloff... 188/297 OF ACCELERATION PULSES GENERATED
USOO6598456 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Potts (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 29, 2003 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEMS FOR CONTROL 4,648,490 A * 3/1987 Bergloff... 188/297 OF ACCELERATION PULSES GENERATED
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,780,559 B2
 USOO7780559B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 7,780,559 B2 Zbikowski et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, 20 (54) CHAIN TRANSMISSION (58) Field of Classification Search... 474/212, 474/213,
USOO7780559B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 7,780,559 B2 Zbikowski et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, 20 (54) CHAIN TRANSMISSION (58) Field of Classification Search... 474/212, 474/213,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0066794 A1 Durfee US 2008 OO66794A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) AUTOMATIC HUNTING BLIND Inventor:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0066794 A1 Durfee US 2008 OO66794A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) AUTOMATIC HUNTING BLIND Inventor:
AC EE 44 III. Nice. Ab-Say AAA K. United States Patent (19) Adams. Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Nydegger & Associates 57 ABSTRACT
 United States Patent (19) Adams 54 76) 21 22) 51 (52) (58) 56 CONTANER STORAGE SYSTEM Inventor: Kathleen Adams, 3550 Marlesta Dr. San Diego, Calif. 92111 Appl. No.: 587,456 Filed: Jan. 11, 1996 Int. C....
United States Patent (19) Adams 54 76) 21 22) 51 (52) (58) 56 CONTANER STORAGE SYSTEM Inventor: Kathleen Adams, 3550 Marlesta Dr. San Diego, Calif. 92111 Appl. No.: 587,456 Filed: Jan. 11, 1996 Int. C....
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,984,723 B2
 US007.984723B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,984,723 B2 Seivert et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 26, 2011 (54) SELF-STANDING WALKING CANE D113,865 S * 3/1939 Fletcher... D3/7 D138,330
US007.984723B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,984,723 B2 Seivert et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 26, 2011 (54) SELF-STANDING WALKING CANE D113,865 S * 3/1939 Fletcher... D3/7 D138,330
Safety culture in professional road transport in Norway and Greece
 Safety culture in professional road transport in Norway and Greece Tor-Olav Nævestad 1, Ross O. Phillips 1, Alexandra Laiou 2, George Yannis 2 1 Institute of Transport Economics, Norway 2 National Technical
Safety culture in professional road transport in Norway and Greece Tor-Olav Nævestad 1, Ross O. Phillips 1, Alexandra Laiou 2, George Yannis 2 1 Institute of Transport Economics, Norway 2 National Technical
The below identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
 DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFARE CENTER DIVISION NEWPORT OFFICE OF COUNSEL PHONE: (401) 832-3653 FAX: (401) 832-4432 NEWPORT DSN: 432-3653 Attorney Docket No. 96811 Date: 14 May 2008 The below
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFARE CENTER DIVISION NEWPORT OFFICE OF COUNSEL PHONE: (401) 832-3653 FAX: (401) 832-4432 NEWPORT DSN: 432-3653 Attorney Docket No. 96811 Date: 14 May 2008 The below
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,867,058 B2
 US007867058E32 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,867,058 B2 Sweeney (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 11, 2011 (54) SPORTS BRA 2,624,881 A * 1/1953 Lee... 450,89 6,176,761 B1* 1/2001 Underhill......
US007867058E32 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,867,058 B2 Sweeney (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 11, 2011 (54) SPORTS BRA 2,624,881 A * 1/1953 Lee... 450,89 6,176,761 B1* 1/2001 Underhill......
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,880,421 B2. Watanabe et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 19, 2005
 USOO688.0421B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,880,421 B2 Watanabe et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 19, 2005 (54) ROLLED BALL SCREW AND METHOD FOR (56) References Cited ROLLING BALL SCREW
USOO688.0421B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,880,421 B2 Watanabe et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 19, 2005 (54) ROLLED BALL SCREW AND METHOD FOR (56) References Cited ROLLING BALL SCREW
PART 5 - OPTIONS CONTENTS 5.1 SYSTEM EXPANSION 5-3
 PART 5 - OPTIONS CONTENTS Para Page 5.1 SYSTEM EXPANSION 5-3 5.2 SENSORS 5-3 5.2.1 Trim Angle Sensor 5-3 5.2.2 Mast Rotation Sensor 5-3 5.2.3 Heel Angle Sensor 5-3 5.2.4 Barometric Pressure Sensor 5-3
PART 5 - OPTIONS CONTENTS Para Page 5.1 SYSTEM EXPANSION 5-3 5.2 SENSORS 5-3 5.2.1 Trim Angle Sensor 5-3 5.2.2 Mast Rotation Sensor 5-3 5.2.3 Heel Angle Sensor 5-3 5.2.4 Barometric Pressure Sensor 5-3
United States Patent (19) Condo et al.
 United States Patent (19) Condo et al. 54 BOXING TRAINING APPARATUS 75 Inventors: Girolamao Condo; Luigi Trocola, both of Eislingen, Fed. Rep. of Germany 73) Assignee: Petra Condo, Eislingen, Fed. Rep.
United States Patent (19) Condo et al. 54 BOXING TRAINING APPARATUS 75 Inventors: Girolamao Condo; Luigi Trocola, both of Eislingen, Fed. Rep. of Germany 73) Assignee: Petra Condo, Eislingen, Fed. Rep.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 20010O38536A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0038536A1 Wiggerman et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 8, 2001 (54) COMBINATION MARINE ACCESSORY Related U.S. Application
US 20010O38536A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0038536A1 Wiggerman et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 8, 2001 (54) COMBINATION MARINE ACCESSORY Related U.S. Application
Kroger Wrist Blood Pressure Monitor Manual Wordpress
 We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with kroger wrist blood pressure
We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with kroger wrist blood pressure
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,641,487 B1
 USOO6641487B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,641,487 B1 Hamburger (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 2003 (54) ADJUSTABLY WEIGHTED GOLF CLUB 4,872,684. A 10/1989 Dippel PUTTER HEAD WITH REMOVABLE
USOO6641487B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,641,487 B1 Hamburger (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 2003 (54) ADJUSTABLY WEIGHTED GOLF CLUB 4,872,684. A 10/1989 Dippel PUTTER HEAD WITH REMOVABLE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,757,647 B1
 US008757647B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,757,647 B1 Su (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 24, 2014 (54) ASSEMBLING STRUCTURE OF SUPPORT (56) References Cited (71) (72) (*) (21) (22) (60) (51)
US008757647B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,757,647 B1 Su (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 24, 2014 (54) ASSEMBLING STRUCTURE OF SUPPORT (56) References Cited (71) (72) (*) (21) (22) (60) (51)
AI TKA '[ Attorney Docket No Date: 28 June 2007
 AI TKA '[ DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFARE CENTER DPVSION NEWPORT OFFICE OF COUNSEL PHONE: (401) 832-3653 FAX: (401) 832-4432 NEWPORT DSN: 432-3653 Attorney Docket No. 84854 Date: 28 June
AI TKA '[ DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFARE CENTER DPVSION NEWPORT OFFICE OF COUNSEL PHONE: (401) 832-3653 FAX: (401) 832-4432 NEWPORT DSN: 432-3653 Attorney Docket No. 84854 Date: 28 June
Posting of workers in the European Union and EFTA countries : Report on A1 portable documents issued in 2010 and 2011
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION Employment, Social Affairs and Inclusion DG Analysis, Evaluation, External Relations Employment Analysis Posting of workers in the European Union and EFTA countries : Report on A1 portable
EUROPEAN COMMISSION Employment, Social Affairs and Inclusion DG Analysis, Evaluation, External Relations Employment Analysis Posting of workers in the European Union and EFTA countries : Report on A1 portable
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 20060227285A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Huang (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 12, 2006 (54) DIVING MASK Publication Classification (76) Inventor: Shao-Yin Huang, Taipei
US 20060227285A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Huang (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 12, 2006 (54) DIVING MASK Publication Classification (76) Inventor: Shao-Yin Huang, Taipei
Unprotected road users left behind in efforts to reduce road deaths 5 th PIN Conference 21 June Henk Stipdonk, SWOV
 Unprotected road users left behind in efforts to reduce road deaths 5 th PIN Conference 21 June 2011 Henk Stipdonk, SWOV Reduction in road deaths since 2001 44% of all deaths are unprotected road users,
Unprotected road users left behind in efforts to reduce road deaths 5 th PIN Conference 21 June 2011 Henk Stipdonk, SWOV Reduction in road deaths since 2001 44% of all deaths are unprotected road users,
USOO6O76829A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,076,829 Oblack (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 20, 2000
 USOO6O76829A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,076,829 Oblack (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 20, 2000 54) BALL THROWINGAPPARATUS AND 3,428,036 2/1969 Parker. METHOD 3,589,349 6/1971 Parker. 3.841,292
USOO6O76829A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,076,829 Oblack (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 20, 2000 54) BALL THROWINGAPPARATUS AND 3,428,036 2/1969 Parker. METHOD 3,589,349 6/1971 Parker. 3.841,292
Country
 Life Domain: Income, Standard of Living, and Consumption Patterns Goal Dimension: Disparities, Inequalities, and Social Exclusion Measurement Dimension: Subdimension: Indicator: Definition: Population:
Life Domain: Income, Standard of Living, and Consumption Patterns Goal Dimension: Disparities, Inequalities, and Social Exclusion Measurement Dimension: Subdimension: Indicator: Definition: Population:
Lightweight portable training device to simulate kayaking
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Lightweight portable training device to simulate kayaking 12-7-2010 Ronald Eaglin University of Central Florida Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Lightweight portable training device to simulate kayaking 12-7-2010 Ronald Eaglin University of Central Florida Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 201400.07860A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0007860 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 9, 2014 (54) SMOKELESS PORTABLE ROASTER (57) ABSTRACT (76) Inventor: Chien-Chang
(19) United States US 201400.07860A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0007860 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 9, 2014 (54) SMOKELESS PORTABLE ROASTER (57) ABSTRACT (76) Inventor: Chien-Chang
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7353986B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,353.986 B2 Sugai (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 8, 2008 (54) ELECTRONIC PEDOMETER 5,117.444 A * 5/1992 Sutton et al.... 377,242 6.254,513 B1 7/2001
(12) United States Patent USOO7353986B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,353.986 B2 Sugai (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 8, 2008 (54) ELECTRONIC PEDOMETER 5,117.444 A * 5/1992 Sutton et al.... 377,242 6.254,513 B1 7/2001
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090005197A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0005197 A1 Mayer (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 1, 2009 (54) HOCKEY STICK HAVING AN ANGLED (52) U.S. Cl.... 473/560;
(19) United States US 20090005197A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0005197 A1 Mayer (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 1, 2009 (54) HOCKEY STICK HAVING AN ANGLED (52) U.S. Cl.... 473/560;
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent WOf USOO6273279B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 14, 2001 (54) GOLF TOWEL HOLDER (76) Inventor: Jerrold M. Wolf, 1036 E. Melody La., Fullerton, CA (US) 92831 (*) Notice:
(12) United States Patent WOf USOO6273279B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 14, 2001 (54) GOLF TOWEL HOLDER (76) Inventor: Jerrold M. Wolf, 1036 E. Melody La., Fullerton, CA (US) 92831 (*) Notice:
(12) United States Patent
 US008807568B1 (12) United States Patent Ruder (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 19, 2014 (54) BALL GAME (71) Applicant: Christofer Joseph Ruder, Chicago, IL (US) (72) Inventor: Christofer Joseph
US008807568B1 (12) United States Patent Ruder (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 19, 2014 (54) BALL GAME (71) Applicant: Christofer Joseph Ruder, Chicago, IL (US) (72) Inventor: Christofer Joseph
DISCLAIMER. Government. Neither the United States Government nor any agency thereof, nor any of their
 S-76,491 03 r3 0 m 0 X u a r3 I (v 0 2 I W CI +,.rl k 3. W E c 6) X A MEANS FOR POSITIVELY SEATING A.PIEZOCERAMIC ELEMENT IN A PIEZOELECTRIC VALVE DURING INLET GAS INJECTION Kenneth E. Wright DISCLAIMER
S-76,491 03 r3 0 m 0 X u a r3 I (v 0 2 I W CI +,.rl k 3. W E c 6) X A MEANS FOR POSITIVELY SEATING A.PIEZOCERAMIC ELEMENT IN A PIEZOELECTRIC VALVE DURING INLET GAS INJECTION Kenneth E. Wright DISCLAIMER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014036O734A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0360734 A1 DOane et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 11, 2014 (54) PACKER SETTING MECHANISM (71) Applicants: James
(19) United States US 2014036O734A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0360734 A1 DOane et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 11, 2014 (54) PACKER SETTING MECHANISM (71) Applicants: James
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,393,587 B2
 US008393.587B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,393,587 B2 Hoernig (45) Date of Patent: *Mar. 12, 2013 (54) BATH FIXTURE MOUNTING SYSTEM (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Victor Hoernig,
US008393.587B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,393,587 B2 Hoernig (45) Date of Patent: *Mar. 12, 2013 (54) BATH FIXTURE MOUNTING SYSTEM (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Victor Hoernig,
The UPOV Convention: an International Standard
 EU Plant Variety Rights in the 21 st Century Conference on the outcome of the evaluation of the Community Plant Variety Rights Regime The UPOV Convention: an International Standard Peter Button (Vice Secretary-General,
EU Plant Variety Rights in the 21 st Century Conference on the outcome of the evaluation of the Community Plant Variety Rights Regime The UPOV Convention: an International Standard Peter Button (Vice Secretary-General,
United States Patent (19) Lotta
 United States Patent (19) Lotta 54 SEATING UNIT FORA BATHTUB, SHOWER STALL OR THE LIKE 76 Inventor: Russell P. Lotta, 1632 Regina La., Rockford, Ill. 61102 21 Appl. No.: 790,401 22 Filed: Apr. 25, 1977
United States Patent (19) Lotta 54 SEATING UNIT FORA BATHTUB, SHOWER STALL OR THE LIKE 76 Inventor: Russell P. Lotta, 1632 Regina La., Rockford, Ill. 61102 21 Appl. No.: 790,401 22 Filed: Apr. 25, 1977
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Fujikawa 54 HYDRAULIC CONTROL SYSTEM FOR A ROCK DRILL (75) Inventor: Kozo Fujikawa, Hiroshima, Japan 73) Assignee: Toyo Kogyo Co., Ltd., Hiroshima, Japan 21 Appl. No.: 194,391
United States Patent (19) Fujikawa 54 HYDRAULIC CONTROL SYSTEM FOR A ROCK DRILL (75) Inventor: Kozo Fujikawa, Hiroshima, Japan 73) Assignee: Toyo Kogyo Co., Ltd., Hiroshima, Japan 21 Appl. No.: 194,391
