Sikkerhed og certifisering for sundhedsteknologisk udstyr
|
|
|
- Bathsheba Campbell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sikkerhed og certifisering for sundhedsteknologisk udstyr Temadag på Sundhedsteknologiuddannelsens 6. semester Kim Dremstrup Nielsen, IST, AAU
2 Program Elsikkerhed, IEC mm. Lektor Kim Dremstrup Nielsen Sikkerhedsprocedurer på AS, Medikoteknisk chef Hans Henrik Pedersen, AS Certificeringsprocedurer i en medikoteknisk virksomhed Projektleder Lars Nilsson, Judex Datasystemer Sikkerhed i laboratorier, Lektor Michael Voigt Diskussion SMI - IST KDN/2002
3 Hazards by medical equipment Medical electrical equipment can present a range of hazards to the patient, the user, or to service personnel. 1 Mechanical Hazards Insecure fitting of controls to loose wheels on equipment trolleys. 2 Risk of fire or explosion Internal or external short circuits Many medical gases support combustion. 3 Absence of function The absence of function could threaten life. 4 Excessive or insufficient output E.g surgical diathermy units, anaestethic equipment etc. Calibration procedures are crucial. 5 Risk of exposure to spurious electric currents All electrical equipment may potentially expose people to the risk of unintentional exposure to electricity. In the case of medical electrical equipment the risk is potentially greater since patients are intentionally connected to such equipment.
4 Physiological effects of electricity Electrical Current can do following on human and animal tissue: AC can stimulate muscles and nerves DC and AC can burn skin and and other tissue depending on amplitude, frequency and duration DC can give electrochemical etching of skin underneath electrodes etc.
5 Physiological effects of electricity Electrical Current thus can have following effects on the human body: 1 Electrolysis 2 Burns 3 Muscle cramps 4 Respiratory arrest 5 Cardiac arrest 6 Ventricular fibrillation
6 Physiological effects of electricity Electrical Current thus can have following effects on the human body: 1 Electrolysis 2 Burns 3 Muscle cramps 4 Respiratory arrest 5 Cardiac arrest The movement of ions of opposite polarities in opposite directions through a medium is called electrolysis and can be made to occur be made to occur by passing DC currents through body tissues or fluids. If a DC current is passed through body tissues for a period of minutes, ulceration begins to occur. Such ulcers, while not normally fatal, can be painful and take long periods to heal. 6 Ventricular fibrillation
7 Physiological effects of electricity Electrical Current thus can have following effects on the human body: 1 Electrolysis 2 Burns 3 Muscle cramps 4 Respiratory arrest 5 Cardiac arrest 6 Ventricular fibrillation When an electric current passes through any substance having electrical resistance, heat is produced. The amount of heat depends on the power-dissipated (I2R). Whether or not the heat produces a burn depends on the current density. Human tissue is capable of carrying electric currents quite successfully. Skin normally has a fairly high electrical resistance while the moist tissue underneath the skin has a much lower resistance. Electrical burns often produce their most marked effects near to the skin, although it is fairly easy for internal electrical burns to be produced which if nor fatal can cause long lasting injury.
8 Physiological effects of electricity Electrical Current thus can have following effects on the human body: 1 Electrolysis 2 Burns 3 Muscle cramps 4 Respiratory arrest 5 Cardiac arrest When an electrical stimulus is applied to a motor nerve or muscle, the muscle does exactly what it is designed to do in the presence of such a stimulus i.e. it contracts. The prolonged involuntary contraction of muscles (tetanus) caused by external electrical stimulus is responsible for the phenomenon where a person who is holding an electrically live object can be unable to let go. 6 Ventricular fibrillation
9 Physiological effects of electricity Electrical Current thus can have following effects on the human body: 1 Electrolysis 2 Burns 3 Muscle cramps The muscles between the ribs (intercostal muscles) need to repeatedly contract and relax in order in order to facilitate breathing. Prolonged tetanus of these muscles can therefore prevent breathing. 4 Respiratory arrest 5 Cardiac arrest 6 Ventricular fibrillation
10 Physiological effects of electricity Electrical Current thus can have following effects on the human body: 1 Electrolysis 2 Burns 3 Muscle cramps 4 Respiratory arrest The heart is a muscular organ which needs to able to contract and relax repetitively in order to perform its function as a pump for the blood. Tetanus of the heart musculature will prevent the pumping process. 5 Cardiac arrest 6 Ventricular fibrillation
11 Physiological effects of electricity Electrical Current thus can have following effects on the human body: 1 Electrolysis 2 Burns 3 Muscle cramps 4 Respiratory arrest 5 Cardiac arrest 6 Ventricular fibrillation The ventricles of the heart are the chambers responsible for pumping blood out of the heart. When the heart is in ventricular fibrillation, the musculature of the ventricles undergoes irregular, uncoordinated twitching resulting in no net blood flow. The condition proves fatal if not corrected in a very short space of time. Ventricular fibrillation can be triggered by very small electrical stimuli. A current as low as 70mA flowing from hand to hand across the chest or 20microamps directly through the heart may be enough. It is for this reason that most deaths from electric shock are attributable to the occurrence of ventricular fibrillation.
12 Electrical Safety Exposition = Current x Time - Duration [msec] vs. Current[mA] 1. Below sensation (up til 1mA ) 2. Sensation but no risc (10mA over longer time can give pain) 3. Risk for muscle cramp 4. < 50% s risk for cardiac fibrillation(small burns can occur) 5. > 50 % s risk for cardiac fibrillation (paralysis of breathing and burns) 50 kg bodymass at 50 Hz
13 Electrical Safety Let-go Current NB! Largest sensitivity at 50Hz
14 Prevention of accidents Design of own electro medical equipment : Use the regulatives and the recommandations from the International Electrotechnical Commission IEC standards (IEC and substandards) Of the shelf / Bougth equipment: Must comply to these standards
15 Regulations in Denmark Stærkstrømsbekendtgørelsen af 1/5-1993, former stærkstrømsreglementet, generel part, and part: Elektromedicinske apparater afsnit 135, is a translation of: DS/EN A1 + A2 + A11 + A12 + A13 and corrections Which again is an adaptation to IEC and sub-standards Shall, Should and May
16 Classification of electro medical equipment Classes I,II and III Types B, BF, and CF
17 Class I product: Classification of electro medical equipment A product that is provided with a reliable protective earth such that all accessible metal parts can t become live in the event of a failure of Basic Insulation and therefore will provide protection against electric shock in the case of the failure of Basic Insulation. Class II product: A product without a protective earth and where Double or Reinforced Insulation (typically a plastic enclosure) is relied upon to provide the protection against electric shock. Class III product: For internally powered source, such as a battery.
18 Classification of electro medical equipment - Class I Class 1 equipment GROUNDING Class 1 equipment has a protective earth. The basic means of protection is the insulation between live parts and exposed conductive parts such as the metal enclosure. In the event of a fault which would otherwise cause an exposed conductive part to become live, the supplementary protection (i.e. protective earth) comes into effect. A large fault current flows from the mains part to earth via the protective earth conductor which causes a protective device (usually a fuse) in the mains circuit to dissconnect the equipment from the supply. Confusion can arise due to the use of plastic laminates for finishing equipment. A case that appears to be plastic does not necessarily indicate that the equipment is not class 1. There is no agreed symbol in use to indicate that equipment is class 1.
19 Classification of electro medical equipment Class II Class II equipment Double Insulation The method of protection against electric shock in the case of class II equipment is either double insulation or reinforced insulation. In double insulated equipment the basic protection is afforded by the first layer of insulation. If basic protection fails then supplementary protection is afforded by a second layer of insulation preventing contact with live parts. Class II medical electrical equipment should be fused at the equipment end of the supply lead in either mains conductor or in both conductors if the equipment has a functional earth.
20 Classification of electro medical equipment Class III Class III equipment is defined as that in which protection against electric shock relies on the fact that no voltages higher than safety extra low voltage (SELV) are present.selv is defined in turn in the relevent standard as a voltage not exceeding 25V ac or 60V dc. In practice such equipment is either battery operated or supplied by a SELV transformer. If battery operated equipment is capable of being operated when connected to the mains (for example, for battery charging) then it must be safety tested as either class 1 or class II equipment. Similarly, equipment powered from a SELV transformer should be tested in conjunction with the transformer as class 1 or class II equipment as appropriate. The standard relating to medical electrical equipment does not recognise class III equipment since limitation of voltage is not sufficient to ensure safety of the patient, but use: Internally Powered Equipment
21 Classification of electro medical equipment - Typing Type B Sufficient protection of patient, regarding leakage currents and grounding if applied (Type I) Type BF Type B equipment with FLOATING/ISOLATED patient connection Type CF Lower leakage currents than BF, but also floating patient connection
22 Leakage currents Causes of leakage currents If any conductor is raised to a potential above earth potential, then current is bound to flow from that conductor to earth. This is true even of conductors that are well insulated from earth, since there is no such thing as perfect insulation or infinite resistance. The amount of current that flows depends on: The voltage on the conductor The capacitive reactance between the conductor and earth The resistance between the conductor and earth The current which flows from or between conductors which are normally insulated from earth and each other are called leakage currents. Such currents must be limited by the design of the equipment to safe values.
23 Leakage currents For medical electrical equipment, several different leakage currents are defined according to the paths that the leakage currents flow through. Earth leakage current Enclosure leakage current Patient leakage current Patient auxilliary current
24 Earth leakage current Earth leakage current is the current which normally flows in the earth conductor of a protectively earthed piece of equipment. It is a fundamental safety requirement that in the event of a single fault occurring, such as the earth becoming open circuit, no hazard should exist. If the earth leakage current is low then the risk of electric shock in the event of a fault is reduced
25 Enclosure leakage current Enclosure leakage current is described as the current that flows from an exposed conductive part of the conductor to earth through a conductor other than the protective earth conductor. It is usual when testing medical electrical equipment to measure enclosure leakage current from points on the enclosure which are not protectively earthed. On many pieces of equipment no such points may exist. This is not a problem. The test included in the Figure 2. Enclosure leakage path test regimes to cover the eventuality where no such points do exist and ensure no hazard is created by them.
26 Patient leakage current Patient leakage current is the leakage current that flows through a patient connected to an applied part or parts. It can either flow from the applied parts via the patient to earth or from an external source of high potential via the patient and the applied parts to earth.
27 Patient auxilliary current The patient auxilliary current is defined as the current which normally flows between parts of the applied part through the patient which is not intended to produce a physiolgical effect, also called meassurement current.
28 Patient leakage current limits IEC 60601
29 Patient leakage current Type B BF CF Cond N SF N SF N SF Pat leak All currents in mikroamp (10E-6A) Also limits for ground leakage, capsulation leakage, measurement current
30 Grounding All type I equipments must have a ground lead In the supply wire. This ensures that current from e.g. broken mains leads inside the capsulation will go to ground and not to the subject.
31 Safety Transformers. In heterogeneous setups as often seen in labs: Use SAFETY TRANSFORMERS
32 Safety precautions Equipment must be safe Type B, BF og CF Connect equipment to a safe supply source Use safety transformers, only ONE source Use the equipment in a safe manner Remove lamps, coffe machines etc. Use common sense
33 Further reading Stærkstrømsbekendtgørelsen afs. 135 IEC and substandards Webster J.G., Medical Instrumentation, 3rd edt, Chapter 14 EL-sikkerhed, Råd om elektromedicinsk udstyr. Projektrapport 83.01, Dansk Sygehus Institut 1983
CHAPTER 2: ELECTRICAL SAFETY
 Contents: CHAPTER 2: ELECTRICAL SAFETY 2.1 Physiological Effects of Electricity 2.2 Macroshock and Microshock 2.3 Approaches Towards Protection Against Shock 2.4 Medical Safety Test 2.5 Medical Equipment:
Contents: CHAPTER 2: ELECTRICAL SAFETY 2.1 Physiological Effects of Electricity 2.2 Macroshock and Microshock 2.3 Approaches Towards Protection Against Shock 2.4 Medical Safety Test 2.5 Medical Equipment:
Electrical Safety in Hospitals
 Electrical Safety in Hospitals Safety in Clinical Environment Electrical hazards Electrical shocks (micro and macro) due to equipment failure, failure of power delivery systems, ground failures, burns,
Electrical Safety in Hospitals Safety in Clinical Environment Electrical hazards Electrical shocks (micro and macro) due to equipment failure, failure of power delivery systems, ground failures, burns,
INSPECTION OF MEDICAL DEVICES
 INSPECTION OF MEDICAL DEVICES Safety And Maintenance For Industrial Systems Sapienza Università di Roma, Ing. Silvia Ruggieri 1 Safe MD development Physiological effects of electricity and Consequences
INSPECTION OF MEDICAL DEVICES Safety And Maintenance For Industrial Systems Sapienza Università di Roma, Ing. Silvia Ruggieri 1 Safe MD development Physiological effects of electricity and Consequences
Definitions found in several locations:
 Definitions found in several locations: NFPA 70 - National Electric Code NFPA 70B Recommended Practice for Electrical Equipment Maintenance. NFPA 70E Electrical Safety in the Workplace OSHA 1910 Subpart
Definitions found in several locations: NFPA 70 - National Electric Code NFPA 70B Recommended Practice for Electrical Equipment Maintenance. NFPA 70E Electrical Safety in the Workplace OSHA 1910 Subpart
Please print or type all responses except where a signature is required. DESIGN PROJECT TITLE: SEMESTER AND COURSE REFERENCE NUMBER: STUDENT NAME:
 ENGR 196, 296, 396 PROJECT FORM (Circle the correct course number) Prior to signing up for an ENGR 196, 296, 396 hands on project, the student must acquire the signature of the faculty member who will
ENGR 196, 296, 396 PROJECT FORM (Circle the correct course number) Prior to signing up for an ENGR 196, 296, 396 hands on project, the student must acquire the signature of the faculty member who will
Rigel 601 CHECKBOX. Instruction Manual. 348A551 Issue 2.0. April Seaward Electronic Ltd. Issue 2.0
 Rigel 601 CHECKBOX Instruction Manual 348A551 Issue 2.0 April 2006 2006 Seaward Electronic Ltd. Issue 2.0 Limited Warranty & Limitation of Liability Rigel Medical guarantees this product for a period of
Rigel 601 CHECKBOX Instruction Manual 348A551 Issue 2.0 April 2006 2006 Seaward Electronic Ltd. Issue 2.0 Limited Warranty & Limitation of Liability Rigel Medical guarantees this product for a period of
Dealing with Electrical Hazards in the Workplace
 Dealing with Electrical Hazards in the Workplace Presented By: Tom Norwood Sr. Safety Specialist A SUBSIDIARY OF MEGGER TRAINING INSTITUTE, INC. Dallas, Texas Introduction Several hundred electrical fatalities
Dealing with Electrical Hazards in the Workplace Presented By: Tom Norwood Sr. Safety Specialist A SUBSIDIARY OF MEGGER TRAINING INSTITUTE, INC. Dallas, Texas Introduction Several hundred electrical fatalities
5 th year (Control department)
 Benha Faculty of Engineering Benha University 5 th year (Control department) Clinical Equipment Management(E527) Examiner: Dr.Waleed A.A Salem Final Written Examination 2012 / 2013 Time : Three Hours Answer
Benha Faculty of Engineering Benha University 5 th year (Control department) Clinical Equipment Management(E527) Examiner: Dr.Waleed A.A Salem Final Written Examination 2012 / 2013 Time : Three Hours Answer
Guidelines to the standard IEC60601
 EUROPEAN POWER SUPPLY MANUFACTURERS ASSOCIATION (Visit the EPSMA website at www.epsma.org) Medical Approvals for Power Supplies Guidelines to the standard IEC60601 Revision Date: 2009-09-12 This document
EUROPEAN POWER SUPPLY MANUFACTURERS ASSOCIATION (Visit the EPSMA website at www.epsma.org) Medical Approvals for Power Supplies Guidelines to the standard IEC60601 Revision Date: 2009-09-12 This document
Electrical Safety. Toolbox Talk
 Electrical Safety Toolbox Talk Establishing an Electrical Safety Program There are five objectives of an safety program: 1. Make personnel more aware of rules, responsibilities and procedures for working
Electrical Safety Toolbox Talk Establishing an Electrical Safety Program There are five objectives of an safety program: 1. Make personnel more aware of rules, responsibilities and procedures for working
This training session covers electrical safety for unqualified persons. Unqualified persons are machine operators, operators of powered industrial
 This training session covers electrical safety for unqualified persons. Unqualified persons are machine operators, operators of powered industrial trucks, construction workers, and others who are not qualified
This training session covers electrical safety for unqualified persons. Unqualified persons are machine operators, operators of powered industrial trucks, construction workers, and others who are not qualified
Leakage Current Testing Is it right for your application?
 Leakage Current Testing Is it right for your application? Introduction The Leakage Current test (LCT for short) is most often specified to be performed as a type test in a design or engineering laboratory
Leakage Current Testing Is it right for your application? Introduction The Leakage Current test (LCT for short) is most often specified to be performed as a type test in a design or engineering laboratory
Electrical Safety. Unqualified Worker
 Electrical Safety Unqualified Worker Session Objectives Understand the hazards of electricity Identify and avoid common electrical hazards Follow safe work practices around electrical equipment How Does
Electrical Safety Unqualified Worker Session Objectives Understand the hazards of electricity Identify and avoid common electrical hazards Follow safe work practices around electrical equipment How Does
Industrial Relations
 Industrial & Management Engineering Department Industrial Relations IM 111 Dr Yehia Youssef IM111 Lecture 7 1 Definitions Hazard: A hazard is anything that can cause harm to people. Examples are dangerous
Industrial & Management Engineering Department Industrial Relations IM 111 Dr Yehia Youssef IM111 Lecture 7 1 Definitions Hazard: A hazard is anything that can cause harm to people. Examples are dangerous
DX 3 RCDs. Technical data Nature and consequences of electrical risks Direct and indirect contact. Direct contacts
 RCDs Nature and consequences of electrical risks Direct and indirect contact All electrical risks for people are the result of direct or indirect contact. What are these contacts? And how can we protect
RCDs Nature and consequences of electrical risks Direct and indirect contact All electrical risks for people are the result of direct or indirect contact. What are these contacts? And how can we protect
Circuit model of medical equipment for electrical safety purposes
 Risk Analysis IX 507 Circuit model of medical equipment for electrical safety purposes E. Zennaro 1, C. Mazzetti 1, F. Fiamingo 2 & G. L. Amicucci 2 1 Department of Astronautics, Electrical and Energetics
Risk Analysis IX 507 Circuit model of medical equipment for electrical safety purposes E. Zennaro 1, C. Mazzetti 1, F. Fiamingo 2 & G. L. Amicucci 2 1 Department of Astronautics, Electrical and Energetics
Reference Number PDS 10 (RIC Standard: EP SP)
 Discipline Engineering Standard NSW Category Electrical Title Reference Number PDS 10 (RIC Standard: EP 00 00 00 08 SP) Document Control Status Date Prepared Reviewed Endorsed Approved Mar 05 Standards
Discipline Engineering Standard NSW Category Electrical Title Reference Number PDS 10 (RIC Standard: EP 00 00 00 08 SP) Document Control Status Date Prepared Reviewed Endorsed Approved Mar 05 Standards
REPORTING AND TREATMENT REQUIRED AS A RESULT OF AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT CS-OHS-5
 Form S1745 (Amd 7/97) CS ENERGY PROCEDURE FOR REPORTING AND TREATMENT REQUIRED AS A RESULT OF AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT CS-OHS-5 Responsible Officer: Authorised Person Approved : GM Production Contents 1.
Form S1745 (Amd 7/97) CS ENERGY PROCEDURE FOR REPORTING AND TREATMENT REQUIRED AS A RESULT OF AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT CS-OHS-5 Responsible Officer: Authorised Person Approved : GM Production Contents 1.
Respiration. Figure 22: Schematic representation of the respiratory system
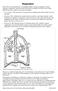 Respiration One of the seven characteristics of something which is living is respiration. Strictly speaking, respiration is the process that takes place at cellular level and is one of three different
Respiration One of the seven characteristics of something which is living is respiration. Strictly speaking, respiration is the process that takes place at cellular level and is one of three different
The definition of a competent person given in the Electricity at Work Regulations 1989 (EWR) is as follows:
 Electrical Safety Guidance Note 1 - General Guidance Competent Person The definition of a competent person given in the Electricity at Work Regulations 1989 (EWR) is as follows: "A person in the possession
Electrical Safety Guidance Note 1 - General Guidance Competent Person The definition of a competent person given in the Electricity at Work Regulations 1989 (EWR) is as follows: "A person in the possession
Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science. Electrical Safety. for Staff and Students in EECS Instructional Laboratories
 NEVER WORK ALONE Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science Electrical Safety for Staff and Students in EECS Instructional Laboratories If you will be working with energized circuits or equipment
NEVER WORK ALONE Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science Electrical Safety for Staff and Students in EECS Instructional Laboratories If you will be working with energized circuits or equipment
Background for the rules in the laboratory. Safety rules for work in the electrical laboratories. Working permission
 Krisztina Leban & Ewen Ritchie e mail: kle@et.aau.dk, aer@et.aau.dkaau Departmant of Energy Technology, Aalborg University 1 Topics Background for the rules in the laboratory Safety rules for work in the
Krisztina Leban & Ewen Ritchie e mail: kle@et.aau.dk, aer@et.aau.dkaau Departmant of Energy Technology, Aalborg University 1 Topics Background for the rules in the laboratory Safety rules for work in the
Key Comparison of Safety Requirements in Europe, North America and Australia for Electronic Products
 Key Comparison of Safety Requirements in Europe, North America and Australia for Electronic Products Mr. K.F. Siu 15 April, 2010 www.intertek.com 1 Presentation Agenda Standards For Audio/Video Product
Key Comparison of Safety Requirements in Europe, North America and Australia for Electronic Products Mr. K.F. Siu 15 April, 2010 www.intertek.com 1 Presentation Agenda Standards For Audio/Video Product
Electrical. OSHA Office of Training and Education 1
 Electrical OSHA Office of Training and Education 1 Introduction An average of one worker is electrocuted on the job every day There are four main types of electrical injuries: Electrocution (death due
Electrical OSHA Office of Training and Education 1 Introduction An average of one worker is electrocuted on the job every day There are four main types of electrical injuries: Electrocution (death due
Section 2 Safety, Tools and Equipment, Shop Practices Unit 4 General Safety Practices. Unit Objectives. Pressure Vessels and Piping (1 of 2)
 Section 2 Safety, Tools and Equipment, Shop Practices Unit 4 General Safety Practices Unit Objectives After studying this chapter, you should be able to: Describe proper procedures for working with pressurized
Section 2 Safety, Tools and Equipment, Shop Practices Unit 4 General Safety Practices Unit Objectives After studying this chapter, you should be able to: Describe proper procedures for working with pressurized
The best safeguard against accidents is a genuine safety culture - awareness and constant vigilance on the part of all those involved, and the
 The best safeguard against accidents is a genuine safety culture - awareness and constant vigilance on the part of all those involved, and the establishment of safety as a permanent and natural feature
The best safeguard against accidents is a genuine safety culture - awareness and constant vigilance on the part of all those involved, and the establishment of safety as a permanent and natural feature
Policies, Procedures, Guidelines and Protocols
 Policies, Procedures, Guidelines and Protocols Document Details Title Portable Electrical Equipment Management Policy Trust Ref No 701-29768 Local Ref (optional) Main points the document Responsibilities
Policies, Procedures, Guidelines and Protocols Document Details Title Portable Electrical Equipment Management Policy Trust Ref No 701-29768 Local Ref (optional) Main points the document Responsibilities
C&G Level 3 Award in the Periodic Inspection, Testing and Certification of Electrical Installations
 C&G 2395-01 Level 3 Award in the Periodic Inspection, Testing and Certification of Electrical Installations Test instruments and recommended testing sequence 1 Outcomes of this Session describe the different
C&G 2395-01 Level 3 Award in the Periodic Inspection, Testing and Certification of Electrical Installations Test instruments and recommended testing sequence 1 Outcomes of this Session describe the different
IMPORTANT SAFETY AND HEALTH INFORMATION
 IMPORTANT SAFETY AND HEALTH INFORMATION This document presents important safety warnings, instructions, and information intended to minimize hazards associated with the use of TASER International, Inc.
IMPORTANT SAFETY AND HEALTH INFORMATION This document presents important safety warnings, instructions, and information intended to minimize hazards associated with the use of TASER International, Inc.
Welding With Arc Welding Equipment
 Optional Information Name of School: Date of Inspection: Vocational Program/Course/Room: Signature of Inspector: Welding With Arc Welding Equipment Self Inspection Checklist Guidelines: This checklist
Optional Information Name of School: Date of Inspection: Vocational Program/Course/Room: Signature of Inspector: Welding With Arc Welding Equipment Self Inspection Checklist Guidelines: This checklist
ES18 Security Theory/Regulations Answer Schedule
 ES18 Security Theory/Regulations Answer Schedule Notes:1. means that the preceding statement/answer earns 1 mark. 2. This schedule sets out the expected answers to the examination questions. The marker
ES18 Security Theory/Regulations Answer Schedule Notes:1. means that the preceding statement/answer earns 1 mark. 2. This schedule sets out the expected answers to the examination questions. The marker
WHS-05 Electric Shock Response
 Table of Contents 1 Purpose... 3 2 Scope... 3 3 References... 3 4 Roles and Responsibilities... 3 5 Definitions... 4 6 Records... 4 7 Rescue and first aid... 4 8 Medical emergency response (Code Blue)...
Table of Contents 1 Purpose... 3 2 Scope... 3 3 References... 3 4 Roles and Responsibilities... 3 5 Definitions... 4 6 Records... 4 7 Rescue and first aid... 4 8 Medical emergency response (Code Blue)...
SAFETY QUALITY TECHNOLOGY. Guidance on Safe Isolation Procedures
 SAFETY QUALITY TECHNOLOGY Guidance on Safe Isolation Procedures Introduction Every year, people working on construction sites suffer electric shock and burn injuries some of which, tragically, are fatal.
SAFETY QUALITY TECHNOLOGY Guidance on Safe Isolation Procedures Introduction Every year, people working on construction sites suffer electric shock and burn injuries some of which, tragically, are fatal.
Electronics Lab Advanced Electrical Engineering Lab Course II Spring 2006
 Safety Instructions Electronics Lab Advanced Electrical Engineering Lab Course II Spring 2006 Instructor: H. Elgala, Dr. D. Knipp Ta http://www.faculty.iu-bremen.de/course/c300221a/ee_module_2 Purpose
Safety Instructions Electronics Lab Advanced Electrical Engineering Lab Course II Spring 2006 Instructor: H. Elgala, Dr. D. Knipp Ta http://www.faculty.iu-bremen.de/course/c300221a/ee_module_2 Purpose
QPEO2/037N Credit Value: 15 QCF Level: 2 GLH: 68 Maintaining electrical equipment/systems
 Performing Engineering Operations QPEO2/037N Credit Value: 15 QCF Level: 2 GLH: 68 Maintaining electrical equipment/systems Learner Name: 2013 Excellence, Achievement & Learning Ltd EAL Assessment Route
Performing Engineering Operations QPEO2/037N Credit Value: 15 QCF Level: 2 GLH: 68 Maintaining electrical equipment/systems Learner Name: 2013 Excellence, Achievement & Learning Ltd EAL Assessment Route
Guidance and history. Why MEIGaN? Medical Locations & Healthcare Electrics Part 1
 Medical Locations & Healthcare Electrics Part 1 Emergency Isolation Room Paediatric Isolation Room Paediatric HDU Medical Locations The risk, Earthing, IPS and UPS IEC 60364, MEIGaN and IET GN7 2015 Richard
Medical Locations & Healthcare Electrics Part 1 Emergency Isolation Room Paediatric Isolation Room Paediatric HDU Medical Locations The risk, Earthing, IPS and UPS IEC 60364, MEIGaN and IET GN7 2015 Richard
ECE Lab Safety. Module All Jan 2018
 ECE Lab Safety Module All Jan 2018 Agenda Lab Policies Electrical Safety Distribution Grounding Physiology CPR/AED Biological Safety Jewelry Lead Eye Safety Test online, 25 random multiple choice questions,
ECE Lab Safety Module All Jan 2018 Agenda Lab Policies Electrical Safety Distribution Grounding Physiology CPR/AED Biological Safety Jewelry Lead Eye Safety Test online, 25 random multiple choice questions,
Original Date of Issue: 04/09
 POLICIES AND PROCEDURES DEPARTMENT: Environmental Health and Safety SUBJECT: Electrical Safety Program Original Date of Issue: 04/09 Reviewed 12/2011 Revised 12/2011 BACKGROUND ELECTRIC SHOCK It is well
POLICIES AND PROCEDURES DEPARTMENT: Environmental Health and Safety SUBJECT: Electrical Safety Program Original Date of Issue: 04/09 Reviewed 12/2011 Revised 12/2011 BACKGROUND ELECTRIC SHOCK It is well
1.8 INDUSTRIAL PROCESS WEIGHING IN HAZARDOUS AREAS
 1.8 INDUSTRIAL PROCESS WEIGHING IN HAZARDOUS AREAS EXPLOSION PROTECTION In addition to the type approval and certification of industrial weighing systems concerned with accuracy, equipment that is also
1.8 INDUSTRIAL PROCESS WEIGHING IN HAZARDOUS AREAS EXPLOSION PROTECTION In addition to the type approval and certification of industrial weighing systems concerned with accuracy, equipment that is also
Spasticity / Dystonia
 Spasticity / Dystonia How can a pump help my movement disorder? This therapy, called intrathecal infusion, is a treatment for controlling some movement disorders. It uses a surgically implanted pump and
Spasticity / Dystonia How can a pump help my movement disorder? This therapy, called intrathecal infusion, is a treatment for controlling some movement disorders. It uses a surgically implanted pump and
SEGMENT NINE - Electricity
 71 SEGMENT NINE - Electricity After studying this segment you should have a greater understanding of the potential danger posed by electricity and the steps taken in the workplace to ensure that electrical
71 SEGMENT NINE - Electricity After studying this segment you should have a greater understanding of the potential danger posed by electricity and the steps taken in the workplace to ensure that electrical
Ground Fault Protection for Electrical Tools
 Hanover Risk Solutions Ground Fault Protection for Electrical Tools Effective electrical tool and equipment grounding are extremely important on construction sites. Injuries and deaths can result from
Hanover Risk Solutions Ground Fault Protection for Electrical Tools Effective electrical tool and equipment grounding are extremely important on construction sites. Injuries and deaths can result from
Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter(GFCI) Policy
 NewStar Netronics, LLC American Products for the World Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter(GFCI) Policy 3926 East 3 rd Street Tulsa, OK 74112 Phone (918)894-5006 Fax (918)836-9909 tech@newstarnetronics.com
NewStar Netronics, LLC American Products for the World Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter(GFCI) Policy 3926 East 3 rd Street Tulsa, OK 74112 Phone (918)894-5006 Fax (918)836-9909 tech@newstarnetronics.com
CS ENERGY PROCEDURE FOR ELECTRIC SHOCK TREATMENT AND REPORTING CS-OHS-05
 CS-OHS-05 10/04/2012 CS ENERGY PROCEDURE FOR ELECTRIC SHOCK TREATMENT AND REPORTING CS-OHS-05 Responsible Officer: Group Manager Health and Safety Responsible Executive: Executive General Manager Corporate
CS-OHS-05 10/04/2012 CS ENERGY PROCEDURE FOR ELECTRIC SHOCK TREATMENT AND REPORTING CS-OHS-05 Responsible Officer: Group Manager Health and Safety Responsible Executive: Executive General Manager Corporate
2018 NFPA 70E Significant Changes 7/27/2017. EFCOG Electrical Safety Task Group Workshop, July 2017
 Significant Changes EFCOG Electrical Safety Task Group Workshop, July 2017 Appreciation Thanks to: Paul Dobrowsky creating the base PPT program Chair, Dave Dini for leading the Committee through the process
Significant Changes EFCOG Electrical Safety Task Group Workshop, July 2017 Appreciation Thanks to: Paul Dobrowsky creating the base PPT program Chair, Dave Dini for leading the Committee through the process
Preview to the 2018 NFPA 70E, the Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace
 Preview to the 2018 NFPA 70E, the Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace Preview to the 2018 NFPA 70E, the Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace Technical Committee Members James Dollard,
Preview to the 2018 NFPA 70E, the Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace Preview to the 2018 NFPA 70E, the Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace Technical Committee Members James Dollard,
Med Aire Alternating Pressure Pump and Pad System
 User Manual Med Aire Alternating Pressure Pump and Pad System 14002E 14001E Symbols & Statements NOTE Indicates some tips or some information users should be aware of. CAUTION Indicates correct operating
User Manual Med Aire Alternating Pressure Pump and Pad System 14002E 14001E Symbols & Statements NOTE Indicates some tips or some information users should be aware of. CAUTION Indicates correct operating
SECTION 51 NFPA 70E POLICY. Health & Safety Policy and Procedures Manual
 SECTION 51 NFPA 70E POLICY Health & Safety Policy and 1. Protection Against Arc Flash A. Policy: An arc flash is a dangerous condition associated with the release of energy caused by an electric arc. An
SECTION 51 NFPA 70E POLICY Health & Safety Policy and 1. Protection Against Arc Flash A. Policy: An arc flash is a dangerous condition associated with the release of energy caused by an electric arc. An
! Warning, refer to accompanying documents.
 About this Manual To the best of our knowledge and at the time written, the information contained in this document is technically correct and the procedures accurate and adequate to operate this instrument
About this Manual To the best of our knowledge and at the time written, the information contained in this document is technically correct and the procedures accurate and adequate to operate this instrument
The Electricity at Work Regulations 1989
 Health and Safety The Electricity at Work Regulations 1989 Subtitle H6 Guidance on Regulations The Electricity at Work Regulations 1989 Subtitle H6 This new edition of HSR25 will help dutyholders meet
Health and Safety The Electricity at Work Regulations 1989 Subtitle H6 Guidance on Regulations The Electricity at Work Regulations 1989 Subtitle H6 This new edition of HSR25 will help dutyholders meet
Type Operating Instructions. 2/2-way solenoid valve 2/2-Wege Magnetventil Electrovanne 2/2 voies.
 2/2-way solenoid valve 2/2-Wege Magnetventil Electrovanne 2/2 voies We reserve the right to make technical changes without notice. Technische Änderungen vorbehalten. Sous réserve de modifications techniques.
2/2-way solenoid valve 2/2-Wege Magnetventil Electrovanne 2/2 voies We reserve the right to make technical changes without notice. Technische Änderungen vorbehalten. Sous réserve de modifications techniques.
LTB013EN. Operating Instruction Trimod Besta Level Switch types XA 5, XB 5 for use in potentially explosive atmospheres acc.
 LTB013EN Operating Instruction Trimod Besta Level Switch types XA 5, XB 5 for use in potentially explosive atmospheres acc. to IECEx scheme Subject to technical modification Bachofen AG Ackerstrasse 42
LTB013EN Operating Instruction Trimod Besta Level Switch types XA 5, XB 5 for use in potentially explosive atmospheres acc. to IECEx scheme Subject to technical modification Bachofen AG Ackerstrasse 42
AC1810 / AC1810-A TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS. Operating Pressure psi ( kgs/cm²) [AC1810] Displacement. Net Weight
![AC1810 / AC1810-A TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS. Operating Pressure psi ( kgs/cm²) [AC1810] Displacement. Net Weight AC1810 / AC1810-A TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS. Operating Pressure psi ( kgs/cm²) [AC1810] Displacement. Net Weight](/thumbs/83/88369739.jpg) Technical Specifications Operating Instructions Maintenance Information Troubleshooting Guide Parts Diagrams AC1810 / AC1810-A THE EVOLUTION OF PERFECTION CAUTION: Before attempting to use or service this
Technical Specifications Operating Instructions Maintenance Information Troubleshooting Guide Parts Diagrams AC1810 / AC1810-A THE EVOLUTION OF PERFECTION CAUTION: Before attempting to use or service this
Environmental Safety
 Environmental Safety Macroshock & Microshock! 2 Macroshock! 2 Microshock! 2 Preventative strategies!... 2 Explosions & Fire! 3 Anaesthetic Waste Gases! 3 Scavenging! 3 Breathing System Outlet!... 3 Types
Environmental Safety Macroshock & Microshock! 2 Macroshock! 2 Microshock! 2 Preventative strategies!... 2 Explosions & Fire! 3 Anaesthetic Waste Gases! 3 Scavenging! 3 Breathing System Outlet!... 3 Types
MANUAL DIRECT PURGE OPTION. UNION Instruments GmbH CWD2005 PLUS. General information, safety standards and regulations for direct purge option
 MANUAL DIRECT PURGE OPTION UNION Instruments GmbH CWD2005 PLUS General information, safety standards and regulations for direct purge option Version: V1.00 Stand: 24.03.2010 Union Instruments GmbH Zeppelinstr.
MANUAL DIRECT PURGE OPTION UNION Instruments GmbH CWD2005 PLUS General information, safety standards and regulations for direct purge option Version: V1.00 Stand: 24.03.2010 Union Instruments GmbH Zeppelinstr.
Translation Principles of testing and certification for insulating hose assemblies on cable cutting devices
 Translation Principles of testing and certification for insulating hose assemblies on cable cutting devices Status as of 2014-01 Principles of testing Insulating hose assemblies on cable cutting devices
Translation Principles of testing and certification for insulating hose assemblies on cable cutting devices Status as of 2014-01 Principles of testing Insulating hose assemblies on cable cutting devices
Maintaining electrical equipment/systems
 Unit 037 Maintaining electrical equipment/systems Level: 2 Credit value: 15 NDAQ number: 500/9514/6 Unit aim This unit covers the skills and knowledge needed to prove the competences required to cover
Unit 037 Maintaining electrical equipment/systems Level: 2 Credit value: 15 NDAQ number: 500/9514/6 Unit aim This unit covers the skills and knowledge needed to prove the competences required to cover
Course 115. Electrical Safety for Employees: Basic
 Electrical Safety for Employees: Basic This page intentionally blank OSHAcademy Course 115 Study Guide Electrical Safety Basic Copyright 2017 Geigle Safety Group, Inc. No portion of this text may be reprinted
Electrical Safety for Employees: Basic This page intentionally blank OSHAcademy Course 115 Study Guide Electrical Safety Basic Copyright 2017 Geigle Safety Group, Inc. No portion of this text may be reprinted
Verification Of Calibration for Direct-Reading Portable Gas Monitors
 U. S. Department of Labor Occupational Safety and Health Administration Directorate of Science, Technology and Medicine Office of Science and Technology Assessment Verification Of Calibration for Direct-Reading
U. S. Department of Labor Occupational Safety and Health Administration Directorate of Science, Technology and Medicine Office of Science and Technology Assessment Verification Of Calibration for Direct-Reading
Hazards and Risks Associated With the Use of Electricity in the Workplace
 Hazards and Risks Associated With the Use of Electricity in the Workplace A simple electrical circuit can be described by reference to three parameters: voltage, current and resistance. These three parameters
Hazards and Risks Associated With the Use of Electricity in the Workplace A simple electrical circuit can be described by reference to three parameters: voltage, current and resistance. These three parameters
Doc No: ELECTRIC Midland Engineering Co., Inc. Initial Issue Date 12/14/15 Safety Management System
 Revision Page 1 of PURPOSE The purpose is to eliminate unsafe conditions involving electrical equipment and tools, including faulty insulation, improper grounding, loose electrical connections, defective
Revision Page 1 of PURPOSE The purpose is to eliminate unsafe conditions involving electrical equipment and tools, including faulty insulation, improper grounding, loose electrical connections, defective
IEC April Authorized Sole Agent : PT. Wisma Niagatama Perkasa. Phone : (031) Fax. : (031)
 IEC 62271-200 April 2004 Authorized Sole Agent : PT. Wisma Niagatama Perkasa Phone : (031) 5041242 Fax. : (031) 5044580 IEC 62271-200 Introduction Scope This standard specifies requirements for factory-assembled
IEC 62271-200 April 2004 Authorized Sole Agent : PT. Wisma Niagatama Perkasa Phone : (031) 5041242 Fax. : (031) 5044580 IEC 62271-200 Introduction Scope This standard specifies requirements for factory-assembled
PLEASE READ CAREFULLY BEFORE INSTALLING OR USING MEGA POOL SAVER MPS 1100
 MPS-1100 User Manual Mega Pool Saver Ltd PLEASE READ CAREFULLY BEFORE INSTALLING OR USING MEGA POOL SAVER MPS 1100 For further up to date instructions on how to install Mega Pool Saver MPS 1100, please
MPS-1100 User Manual Mega Pool Saver Ltd PLEASE READ CAREFULLY BEFORE INSTALLING OR USING MEGA POOL SAVER MPS 1100 For further up to date instructions on how to install Mega Pool Saver MPS 1100, please
BGA158 Series CE Approved Class A Shutoff Gas Valve
 Installation Instructions BGA158 Issue Date August 24, 2011 BGA158 Series CE Approved Class A Shutoff Gas Valve Applications The BGA158 Series shutoff gas valve is an electrically operated gas valve that
Installation Instructions BGA158 Issue Date August 24, 2011 BGA158 Series CE Approved Class A Shutoff Gas Valve Applications The BGA158 Series shutoff gas valve is an electrically operated gas valve that
Inspection and Testing
 Chapter 16 Inspection and Testing 16.1 INTRODUCTION The Purpose of Inspection, Testing and Certification or Reporting The fundamental reason for inspecting and testing an electrical installation is to
Chapter 16 Inspection and Testing 16.1 INTRODUCTION The Purpose of Inspection, Testing and Certification or Reporting The fundamental reason for inspecting and testing an electrical installation is to
Conduction of Electrical Current to and Through the Human Body: A Review
 Conduction of Electrical Current to and Through the Human Body: A Review Raymond M. Fish, PhD, MD, FACEP, a and Leslie A. Geddes, MS, PhD, DSc b a Bioacoustics Research Lab & Department of Surgery, University
Conduction of Electrical Current to and Through the Human Body: A Review Raymond M. Fish, PhD, MD, FACEP, a and Leslie A. Geddes, MS, PhD, DSc b a Bioacoustics Research Lab & Department of Surgery, University
Covered Task 409OP Training Guide Inspecting Interference Bonds
 Directions This training guide is to be used by a Subject matter expert (SME) authorized Evaluator/Trainer and Trainee during on-thejob training (OJT) or prior to an evaluation as a resource. (S) Indicates
Directions This training guide is to be used by a Subject matter expert (SME) authorized Evaluator/Trainer and Trainee during on-thejob training (OJT) or prior to an evaluation as a resource. (S) Indicates
Type 0404 / /2-way solenoid valve 2/2-Wege-Magnetventil Électrovanne 2/2 voies Operating Instructions Bedienungsanleitung Manuel d utilisation
 Type 0404 / 5404 2/2-way solenoid valve 2/2-Wege-Magnetventil Électrovanne 2/2 voies Operating Instructions Bedienungsanleitung Manuel d utilisation 1 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS The operating instructions
Type 0404 / 5404 2/2-way solenoid valve 2/2-Wege-Magnetventil Électrovanne 2/2 voies Operating Instructions Bedienungsanleitung Manuel d utilisation 1 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS The operating instructions
Dr Morris Odell. Victorian Institute of Forensic Medicine VIFM
 TASERS and STUN GUNS Dr Morris Odell Victorian Institute of Forensic Medicine Intentional Electric Shock Devices Less than Lethal weapons Stun guns Tasers Cattle prods, Electric fences, Man traps Conducted
TASERS and STUN GUNS Dr Morris Odell Victorian Institute of Forensic Medicine Intentional Electric Shock Devices Less than Lethal weapons Stun guns Tasers Cattle prods, Electric fences, Man traps Conducted
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION
 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION IEC TS 61245 Edition 2.0 2015-03 Artificial pollution tests on high-voltage ceramic and glass insulators to be used on d.c. systems INTERNATIONAL ELECTROTECHNICAL COMMISSION ICS
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION IEC TS 61245 Edition 2.0 2015-03 Artificial pollution tests on high-voltage ceramic and glass insulators to be used on d.c. systems INTERNATIONAL ELECTROTECHNICAL COMMISSION ICS
* * Data Sheet and Operating Manual. Digital manometer ME01 ## # 87 # HL S#### Dust explosion protection Zone 22.
 *09005087* DB_BA_EN_ME01_S Rev.A 12/16 *09005087* d e v e l o p i n g s o l u t i o n s Data Sheet and Operating Manual ME01 Digital manometer Table of Contents ME01 ## # 87 # HL S#### Dust explosion protection
*09005087* DB_BA_EN_ME01_S Rev.A 12/16 *09005087* d e v e l o p i n g s o l u t i o n s Data Sheet and Operating Manual ME01 Digital manometer Table of Contents ME01 ## # 87 # HL S#### Dust explosion protection
Electrical Safety. Introduction
 Electrical Safety 1 Introduction There are four main types of electrical injuries: Electrocution (death due to electrical shock) Electrical shock Burns Falls Around 300 workers were electrocuted in 2008
Electrical Safety 1 Introduction There are four main types of electrical injuries: Electrocution (death due to electrical shock) Electrical shock Burns Falls Around 300 workers were electrocuted in 2008
Wing Union/Hammer Union Pressure Sensors. Datasheet. Models 435/437
 Wing Union/Hammer Union Pressure Sensors Models 435/437 0 psi to 5000 psi; 0 psi to 6000 psi; 0 psi to 10000 psi; 0 psi to 15000 psi; 0 psi to 20000 psi; 0 bar to 350 bar; 0 bar to 400 bar; 0 bar to 700
Wing Union/Hammer Union Pressure Sensors Models 435/437 0 psi to 5000 psi; 0 psi to 6000 psi; 0 psi to 10000 psi; 0 psi to 15000 psi; 0 psi to 20000 psi; 0 bar to 350 bar; 0 bar to 400 bar; 0 bar to 700
SEMEM3-65 Servicing anaesthetic and ventilation equipment
 Overview This unit identifies the competences you need to carry out servicing activities on anaesthetic and ventilation equipment, in accordance with approved procedures. You will be required to service
Overview This unit identifies the competences you need to carry out servicing activities on anaesthetic and ventilation equipment, in accordance with approved procedures. You will be required to service
IEC :2012 Risk Management Client Completion Form
 IEC 60601-1:2012 Risk Management Client Completion Form F 028c (2018-09-28) IEC 60601-1:2012 Medical electrical equipment: General requirements for basic safety and essential performance (Edition 3.1 Consolidated
IEC 60601-1:2012 Risk Management Client Completion Form F 028c (2018-09-28) IEC 60601-1:2012 Medical electrical equipment: General requirements for basic safety and essential performance (Edition 3.1 Consolidated
Hydrogen Cyanide OC 275/3. Target Audience:
 Hydrogen Cyanide OC 275/3 Target Audience: Agricultural and Factory Inspectors FCG Specialist Inspectors (Occ Hyg) Senior/Employment Medical Advisers Employment Nursing Advisers Date issued: 1990-11-22
Hydrogen Cyanide OC 275/3 Target Audience: Agricultural and Factory Inspectors FCG Specialist Inspectors (Occ Hyg) Senior/Employment Medical Advisers Employment Nursing Advisers Date issued: 1990-11-22
CIRCUIT BREAKER TESTING - JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS
 Title: Circuit Breaker Testing Purpose and Scope: Provide guidelines for testing of Circuit Breakers. Staffing Resources: Staff will have the minimum requirement of an Electrical Fitter/Mechanic Licence
Title: Circuit Breaker Testing Purpose and Scope: Provide guidelines for testing of Circuit Breakers. Staffing Resources: Staff will have the minimum requirement of an Electrical Fitter/Mechanic Licence
Welfare of Poultry at Slaughter
 Welfare of Poultry at Slaughter Regional approach of the implementation and enforcement of Regulation 1099/2009 Workshop organised by Regional Animal Welfare Centre (RAWC) for Balkan region Mohan Raj University
Welfare of Poultry at Slaughter Regional approach of the implementation and enforcement of Regulation 1099/2009 Workshop organised by Regional Animal Welfare Centre (RAWC) for Balkan region Mohan Raj University
Paradise Pump Series Operator s Manual
 Paradise Pump Series Operator s Manual P/N 12421-000 9/05 Paradise Pump Operator s Manual Important Before using the Paradise Pump Alternating Pressure Relief Systems, please read and understand this
Paradise Pump Series Operator s Manual P/N 12421-000 9/05 Paradise Pump Operator s Manual Important Before using the Paradise Pump Alternating Pressure Relief Systems, please read and understand this
BGA158, BGA171 and BGA110 Series Shutoff Gas Valve
 Installation Instructions BGA Series Issue Date October 3, 2017 BGA158, BGA171 and BGA110 Series Shutoff Gas Valve Applications The BGA Series shutoff gas valve is an electrically operated gas valve that
Installation Instructions BGA Series Issue Date October 3, 2017 BGA158, BGA171 and BGA110 Series Shutoff Gas Valve Applications The BGA Series shutoff gas valve is an electrically operated gas valve that
ELECTRICAL (COMPREHENSIVE) SAFETY PROGRAM REGULATORY STANDARD: OSHA - 29 CFR CFR , ,
 ELECTRICAL (COMPREHENSIVE) SAFETY PROGRAM REGULATORY STANDARD: OSHA - 29 CFR 1910.331 335-29 CFR 1926.302, 1926.416, 1926.417 BASIS: The National Safety Council estimates that there are at least 300 deaths
ELECTRICAL (COMPREHENSIVE) SAFETY PROGRAM REGULATORY STANDARD: OSHA - 29 CFR 1910.331 335-29 CFR 1926.302, 1926.416, 1926.417 BASIS: The National Safety Council estimates that there are at least 300 deaths
Frequently Asked Questions About AEDs updated 11/2/2015
 Frequently Asked Questions About AEDs updated 11/2/2015 What does AED stand for? AED stands for automated external defibrillator. What s an AED? An AED is a device used to administer an electric shock
Frequently Asked Questions About AEDs updated 11/2/2015 What does AED stand for? AED stands for automated external defibrillator. What s an AED? An AED is a device used to administer an electric shock
Automatic Valve Proving Control
 ISO 9001 Automatic Valve Proving Control 7 696 LDU11 UL recognized FM approved Features Performs leak test of the gas shut-off valves before start-up and/or immediately after burner shut-down No inlet
ISO 9001 Automatic Valve Proving Control 7 696 LDU11 UL recognized FM approved Features Performs leak test of the gas shut-off valves before start-up and/or immediately after burner shut-down No inlet
BGA158 Series CE Approved Class B Shutoff Gas Valve
 Installation Instructions BGA158 Issue Date March 22, 2016 BGA158 Series CE Approved Class B Shutoff Gas Valve Applications The BGA158 Series shutoff gas valve is an electrically operated shutoff valve
Installation Instructions BGA158 Issue Date March 22, 2016 BGA158 Series CE Approved Class B Shutoff Gas Valve Applications The BGA158 Series shutoff gas valve is an electrically operated shutoff valve
Supplementary Operator s Manual 42/24-14 EN Rev. 3
 Advance Optima Continuous Gas Analyzers AO2000 Series with Uras26, Magnos206, Caldos25, Caldos27 Designed per Category 3G for Measurement of Flammable Gases ( Safety Concept ) and Non-flammable Gases Supplementary
Advance Optima Continuous Gas Analyzers AO2000 Series with Uras26, Magnos206, Caldos25, Caldos27 Designed per Category 3G for Measurement of Flammable Gases ( Safety Concept ) and Non-flammable Gases Supplementary
PSSI 3 High Voltage Metal-Enclosed Switchgear
 1. SCOPE This Safety Instruction applies the principles established by the ScottishPower Safety Rules (Electrical and Mechanical) and Company Safety Instructions to achieve Safety from the System for personnel
1. SCOPE This Safety Instruction applies the principles established by the ScottishPower Safety Rules (Electrical and Mechanical) and Company Safety Instructions to achieve Safety from the System for personnel
Electrical Safety A HANDBOOK FOR EMERGENCY PERSONNEL
 Electrical Safety A HANDBOOK FOR EMERGENCY PERSONNEL Left to right: Robert Chandler, City of Charlottetown Firefighter; Grant Boswall, Power Line Technician; and Scott Lowther, Power Line Foreman. Electrical
Electrical Safety A HANDBOOK FOR EMERGENCY PERSONNEL Left to right: Robert Chandler, City of Charlottetown Firefighter; Grant Boswall, Power Line Technician; and Scott Lowther, Power Line Foreman. Electrical
Administrative Procedures Automated External Defibrillator (AED)
 Administrative Procedures Automated External Defibrillator (AED) PURPOSE: The purpose of these procedures is to give guidance to those employees of the Lynden School District who are trained and willing
Administrative Procedures Automated External Defibrillator (AED) PURPOSE: The purpose of these procedures is to give guidance to those employees of the Lynden School District who are trained and willing
Ultima. X Series Gas Monitor
 Ultima X Series Gas Monitor Safety Manual SIL 2 Certified " The Ultima X Series Gas Monitor is qualified as an SIL 2 device under IEC 61508 and must be installed, used, and maintained in accordance with
Ultima X Series Gas Monitor Safety Manual SIL 2 Certified " The Ultima X Series Gas Monitor is qualified as an SIL 2 device under IEC 61508 and must be installed, used, and maintained in accordance with
Point level switches for safety systems
 Point level switches for safety systems By: Bill Sholette Level Products Business Manager Northeast US - Endress+Hauser Point level switches are often used in applications designed to prevent accidents.
Point level switches for safety systems By: Bill Sholette Level Products Business Manager Northeast US - Endress+Hauser Point level switches are often used in applications designed to prevent accidents.
Arran LED Floodlight Luminaire
 Arran LED Floodlight Luminaire INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS Important: Please read these instructions carefully before installing or maintaining this equipment. Good electrical
Arran LED Floodlight Luminaire INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS Important: Please read these instructions carefully before installing or maintaining this equipment. Good electrical
Low Voltage Electricity System Safety Rules & Associated Safety Guidance
 Annex J To Loughborough University Facilities Management (FM) Health and Safety Policy Low Voltage Electricity System Safety Rules & Associated Safety Guidance 1. Introduction a. These Safety Rules are
Annex J To Loughborough University Facilities Management (FM) Health and Safety Policy Low Voltage Electricity System Safety Rules & Associated Safety Guidance 1. Introduction a. These Safety Rules are
2.017 Lab Rules and Safety Rm September 9, 2009 (Version 2) Dr. Harrison H. Chin
 2.017 Lab Rules and Safety Rm. 5-007 September 9, 2009 (Version 2) Dr. Harrison H. Chin LAB RULES 1. WORK SAFELY IN THE LAB 2. POWER TOOL USE IS RESTRICTED 3. DO NOT WORK WITH CHEMICALS ALONE 4. CLEAN
2.017 Lab Rules and Safety Rm. 5-007 September 9, 2009 (Version 2) Dr. Harrison H. Chin LAB RULES 1. WORK SAFELY IN THE LAB 2. POWER TOOL USE IS RESTRICTED 3. DO NOT WORK WITH CHEMICALS ALONE 4. CLEAN
Electrical. Version 1.0
 This document is intended to provide basic safety guidelines for the Physical Plant Department at Community College of Allegheny County. The information provided in this guide may vary by site. Version
This document is intended to provide basic safety guidelines for the Physical Plant Department at Community College of Allegheny County. The information provided in this guide may vary by site. Version
SEMEMI SQA Unit Code H2AP 04 Carrying out fault location on electrical equipment and circuits
 Carrying out fault location on electrical equipment and circuits Overview This unit identifies the competences you need to locate faults on electrical equipment and circuits, in accordance with approved
Carrying out fault location on electrical equipment and circuits Overview This unit identifies the competences you need to locate faults on electrical equipment and circuits, in accordance with approved
SDX Submersible Depth Transmitter User Manual
 SDX Submersible Depth Transmitter User Manual October 2007 USER INFORMATION Stevens makes no warranty as to the information furnished in these instructions and the reader assumes all risk in the use thereof.
SDX Submersible Depth Transmitter User Manual October 2007 USER INFORMATION Stevens makes no warranty as to the information furnished in these instructions and the reader assumes all risk in the use thereof.
Calibration Requirements for Direct Reading Confined Space Gas Detectors
 : Calibration Requirements for Direct Reading Confined Space Gas Detectors However, the definition of bump test has always been a little slippery. Some manufacturers differentiate between a bump test that
: Calibration Requirements for Direct Reading Confined Space Gas Detectors However, the definition of bump test has always been a little slippery. Some manufacturers differentiate between a bump test that
How Animals Survive (Circulation and Gas Exchange)
 How Animals Survive (Circulation and Gas Exchange) by Flourence Octaviano on February 16, 2018 lesson duration of 30 minutes under Earth and Life Science generated on February 16, 2018 at 12:45 am Tags:
How Animals Survive (Circulation and Gas Exchange) by Flourence Octaviano on February 16, 2018 lesson duration of 30 minutes under Earth and Life Science generated on February 16, 2018 at 12:45 am Tags:
PLANT/EQUIPMENT/ASSET HAZARD REPORT
 Asset Description: EL-08001-011 : Harrison 550 CNC Lathe Large Sale Type For what use is this asset being sold? Re-Use þ Spare Parts Scrap Note 1: Assets are sold only for the use indicated. Any other
Asset Description: EL-08001-011 : Harrison 550 CNC Lathe Large Sale Type For what use is this asset being sold? Re-Use þ Spare Parts Scrap Note 1: Assets are sold only for the use indicated. Any other
User s Guide Temperature Sensor Converter TSC-599
 User s Guide Temperature Sensor Converter TSC-599 ILX Lightwave Corporation 31950 Frontage Road Bozeman, MT, U.S.A. 59715 U.S. & Canada: 1-800-459-9459 International Inquiries: 406-556-2481 Fax 406-586-9405
User s Guide Temperature Sensor Converter TSC-599 ILX Lightwave Corporation 31950 Frontage Road Bozeman, MT, U.S.A. 59715 U.S. & Canada: 1-800-459-9459 International Inquiries: 406-556-2481 Fax 406-586-9405
