Electrical Safety in Hospitals
|
|
|
- Annis Fowler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Electrical Safety in Hospitals
2 Safety in Clinical Environment Electrical hazards Electrical shocks (micro and macro) due to equipment failure, failure of power delivery systems, ground failures, burns, fire, etc. Mechanical hazards mobility aids, transfer devices, prosthetic devices, mechanical assist devices, patient support devices Environmental hazards Solid wastes, noise, utilities (natural gas), building structures, etc. Biological hazards Infection control, viral outbreak, isolation, decontamination, sterilization, waste disposal issues Radiation hazards Use of radioactive materials, radiation devices (MRI, CT, PET), exposure control
3 Electrical Safety Many sources of energy, potentially hazardous substances, instruments and procedures Use of fire, compressed air, water, chemicals, drugs, microorganisms, waste, sound, electricity, radiation, natural and unnatural disaster, negligence, sources of radiation, etc. Medical procedures expose patients to increased risks of hazards due to skin and membranes being penetrated / altered 10,000 device related injuries in the US every year! Typically due to Improper use Inadequate training Lack of experience Improper (lack of) use of manuals Device failure
4 Physiological Effects of Electricity For electricity to have an effect on the human body: An electrical potential difference must be present The individual must be part of the electrical circuit, that is, a current must enter the body at one point and leave it at another. However, what causes the physiological effect is NOT voltage, but rather CURRENT. A high voltage (KV,(10 3 V)) applied over a large impedance (rough skin) may not cause much (any) damage A low voltage applied over very small impedances (heart tissue) may cause grave consequences (ventricular fibrillation) The magnitude of the current is simply the applied voltage divided by the total effective impedance the current faces; skin : largest. Electricity can have one of three effects: Electrical stimulation of excitable tissue (muscles, nerve) Resistive heating of tissue Electrical burns / tissue damage for direct current and high voltages
5 Physiological Effects of Electricity The real physiological effect depends on the actual path of the current Dry skin impedance:93 kω / cm 2 Electrode gel on skin: 10.8 kω / cm 2 Penetrated skin: 200 Ω / cm 2 Physiological effects of electricity. Threshold or estimated mean values are given for each effect in a 70 kg human for a 1 to 3 s exposure to 60 Hz current applied via copper wires grasped by the hands.
6 Physiological Effects of Electricity Threshold of perception: The minimal current that an individual can detect. For AC (with wet hands) can be as small as 0.5 ma at 60 Hz. For DC, 2 ~10 ma Let-go current: The maximal current at which the subject can voluntarily withdraw. 6 ~ 100 ma, at which involuntary muscle contractions, reflex withdrawals, secondary physical effects (falling, hitting head) may also occur Respiratory Paralysis / Pain / Fatigue At as low as 20 ma, involuntary contractions of respiratory muscles can cause asphyxiation / respiratory arrest, if the current is not interrupted. Strong involuntary contraction of other muscles can cause pain and fatigue Ventricular fibrillation 75 ~ 400 ma can cause heart muscles to contract uncontrollably, altering the normal propagation of the electrical activity of the heart. HR can raise up to 300 bpm, rapid, disorganized and too high to pump any meaningful amount of blood ventricular fibrillation. Normal rhythm can only return using a defibrillator Sustained myocardial contraction / Burns and physical injury At 1 ~6 A, the entire heart muscle contracts and heart stops beating. This will not cause irreversible tissue damage, however, as normal rhythm will return once the current is removed. At or after 10A, however, burns can occur, particularly at points of entry and exit.
7 Important Susceptibility Parameters Threshold and let-go current variability Distributions of perception thresholds and let-go currents These data depend on surface area of contact, moistened hand grasping AWG No. 8 copper wire, 70 kg human, 60Hz, 1~3 s. of exposure
8 Important Susceptibility Parameters Frequency Note that the minimal let-go current happens at the precise frequency of commercial power-line, 50-60Hz. Let-go current rises below 10 Hz and above several hundred Hz. Let-go current versus frequency Percentile values indicate variability of let-go current among individuals. Let-go currents for women are about twothirds the values for men.
9 Important Susceptibility Parameters Duration The longer the duration, the smaller the current at which ventricular fibrillation occurs Shock must occur long enough to coincide with the most vulnerable period occurring during the T wave. Weight Fibrillation threshold increases with body weight (from 50mA for 6kg dogs to 130 ma for 24 kg dogs. Fibrillation current versus shock duration. Thresholds for ventricular fibrillation in animals for 60 Hz AC current. Duration of current (0.2 to 5 s) and weight of animal body were varied.
10 Points of entry Important Susceptibility Parameters The magnitude of the current required to fibrillate the heart is far greater if the current is applied directly to heart; externally applied current loses much of its amplitude due to current distributions. Large, externally applied currents cause macroshock. If catheters are used, the natural protection provided by the skin 15 kω ~ 2 MΩ) is bypassed, greatly reducing the amount of current req d to cause fibrillation. Even smallest currents (80 ~ 600 μa), causing microshock, may result in fibrillation. Safety limit for microshocks is 10 μa. The precise point of entry, even externally is very important: If both points of entry and exit are on the same extremity, the risk of fibrillation is greatly reduced even at high currents (e.g. the current req d for fibrillation through Lead I (LA-RA) electrodes is higher than for Leads II (LL-RA) and III (LL-LA).
11 Important Susceptibility Parameters Points of entry Effect of entry points on current distribution(a) Macroshock, externally applied current spreads throughout the body. (b) Microshock, all the current applied through an intracardiac catheter flows through the heart.
12 Macroshock Most electrical devices have a metal cabinet, which constitutes a hazard, in case of an insulation failure or shortened component between the hot power lead and the chassis. There is then 115 ~ 230 V between the chassis and any other grounded object. The first line of defense available to patients is their skin. The outer layer provides 15 kωto 1 MΩdepending on the part of the body, moisture and sweat present, 1% of that of dry skin if skin is broken, Internal resistance of the body is 200Ωfor each limb, and 100Ωfor the trunk, thus internal body resistance between any two limbs is about 500Ω(somewhat higher for obese people due to high resistivity of the adipose tissue)! Any procedure that reduces or eliminates the skin resistance increases the risk of electrical shock, including biopotential electrode gel, electronic thermometers placed in ears, mouth, rectum, intravenous catheters, etc. A third wire, grounded to earth, can greatly reduce the effect of macroshock, as the resistance of that path would be much smaller then even that of internal body resistance!
13 Macroshock Hazards Direct faults between the hot conductor and the ground is not common, and technically speaking, ground connection is not necessary during normal operation. In fact, a ground fault will not be detected during normal operation of the device, only when someone touches it, the hazard becomes known. Therefore, ground wire in devices and receptacles must be periodically tested.
14 Macroshock Hazards
15 Microshock Hazards Small currents inevitably flow between adjacent insulated conductors at different potentials leakage currents which flow through stray capacitances, insulation, dust and moisture Leakage current flowing to the chassis flows safely to the ground, if a low-resistance ground wire is available.
16 Microshock Hazards If ground wire is broken, the chassis potential rises above the ground; a patient who has a grounded connection to the heart (e.g. through a catheter) receives a microshock if s/he touches the chassis. If there is a connection from the chassis to the patient s heart, and a connection to the ground anywhere in the body, this also causes microshock. Note that the hazard for microshock only exists if there is a direct connection to the heart. Otherwise, even the internal resistance of the body is high enough top prevent the microshocks.
17 Microshocks can also occur if different devices are not at the exact same ground potential. In fact, the microshock can occur even when a device that does not connected to the patient has a ground fault! A fairly common ground wire resistance of 0.1Ω can easily cause a a 500mV potential difference if initiated due to a, say 5A of ground fault. Microshock via Ground Potentials If the patient resistance is less then 50kΩ, this would cause an above safe current of 10µA
18 Microshock Via Ground Potentials
19 Safety Codes & Standards Limits on leakage current are instituted and regulated by the safety codes instituted in part by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), American National Standards Institute (ANSI), Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI), and Emergency Care Research Institute (ECRI).
20 Basic Approaches to Shock Protection There are two major ways to protect patients from shocks: Completely isolate and insulate patient from all sources of electric current Keep all conductive surfaces within reach of the patient at the same voltage Neither can be fully achieved some combination of these two Grounding system Isolated power-distribution system Ground-fault circuit interrupters (GFCI)
21 Grounding Systems Low resistance (0.15 Ω) ground that can carry currents up to the circuit-breaker ratings protects patients by keeping all conductive surfaces and receptacle grounds at the same potential. Protects patients from Macroshocks Microshocks Ground faults elsewhere (!) The difference between the receptacle grounds and other surface should be no more then 40 mv) All the receptacle grounds and conductive surfaces in the vicinity of the patient are connected to the patient-equipment grounding point. Each patientequipment grounding point is connected to the reference grounding point that makes a single connection to the building ground.
22 Isolated Power Systems A good equipotential grounding system cannot eliminate large current that may result from major ground-faults (which are rather rare). Isolated power systems can protect against such major (single) ground faults Provide considerable protection against macroshocks, particularly around wet conditions However, they are expensive! Used only at locations where flammable anesthetics are used. Additional minor protection against microshocks does not justify the high cost of these systems to be used everywhere in the clinical environment
23 Protection through Equipment Design Strain-relief devices for cords, where cord enters the equipment and between the cord and plug Reduction of leakage current through proper layout and insulation to minimize the capacitance between all hot conductors and the chassis Double insulation to prevent the contact of the patient with the chassis or any other conducting surface (outer case being insulating material, plastic knobs, etc.) Operation at low voltages; solid state devices operating at <10V are far less likely to cause macroshocks Electrical isolation in circuit design
24 Electrical Safety Analyzers Testing Electrical Appliances Leakage current in patient leads: Potentially most damaging leakage is the one with patient leads, since they typically have low impedance patient contacts Current should be restricted to 50μA for non-isolated leads and to 10 μa for isolated leads (used with catheters / electrodes that make connection to the heart) Leakage current between any pair of leads, or between a single lead and other patient connections should also be controlled Leakage in case of line voltage appearing on the patient should also be restricted.
CHAPTER 2: ELECTRICAL SAFETY
 Contents: CHAPTER 2: ELECTRICAL SAFETY 2.1 Physiological Effects of Electricity 2.2 Macroshock and Microshock 2.3 Approaches Towards Protection Against Shock 2.4 Medical Safety Test 2.5 Medical Equipment:
Contents: CHAPTER 2: ELECTRICAL SAFETY 2.1 Physiological Effects of Electricity 2.2 Macroshock and Microshock 2.3 Approaches Towards Protection Against Shock 2.4 Medical Safety Test 2.5 Medical Equipment:
INSPECTION OF MEDICAL DEVICES
 INSPECTION OF MEDICAL DEVICES Safety And Maintenance For Industrial Systems Sapienza Università di Roma, Ing. Silvia Ruggieri 1 Safe MD development Physiological effects of electricity and Consequences
INSPECTION OF MEDICAL DEVICES Safety And Maintenance For Industrial Systems Sapienza Università di Roma, Ing. Silvia Ruggieri 1 Safe MD development Physiological effects of electricity and Consequences
5 th year (Control department)
 Benha Faculty of Engineering Benha University 5 th year (Control department) Clinical Equipment Management(E527) Examiner: Dr.Waleed A.A Salem Final Written Examination 2012 / 2013 Time : Three Hours Answer
Benha Faculty of Engineering Benha University 5 th year (Control department) Clinical Equipment Management(E527) Examiner: Dr.Waleed A.A Salem Final Written Examination 2012 / 2013 Time : Three Hours Answer
Electrical Safety. Introduction
 Electrical Safety 1 Introduction There are four main types of electrical injuries: Electrocution (death due to electrical shock) Electrical shock Burns Falls Around 300 workers were electrocuted in 2008
Electrical Safety 1 Introduction There are four main types of electrical injuries: Electrocution (death due to electrical shock) Electrical shock Burns Falls Around 300 workers were electrocuted in 2008
Electrical. OSHA Office of Training and Education 1
 Electrical OSHA Office of Training and Education 1 Introduction An average of one worker is electrocuted on the job every day There are four main types of electrical injuries: Electrocution (death due
Electrical OSHA Office of Training and Education 1 Introduction An average of one worker is electrocuted on the job every day There are four main types of electrical injuries: Electrocution (death due
Electrical Safety. Unqualified Worker
 Electrical Safety Unqualified Worker Session Objectives Understand the hazards of electricity Identify and avoid common electrical hazards Follow safe work practices around electrical equipment How Does
Electrical Safety Unqualified Worker Session Objectives Understand the hazards of electricity Identify and avoid common electrical hazards Follow safe work practices around electrical equipment How Does
Electrical Safety. Toolbox Talk
 Electrical Safety Toolbox Talk Establishing an Electrical Safety Program There are five objectives of an safety program: 1. Make personnel more aware of rules, responsibilities and procedures for working
Electrical Safety Toolbox Talk Establishing an Electrical Safety Program There are five objectives of an safety program: 1. Make personnel more aware of rules, responsibilities and procedures for working
This training session covers electrical safety for unqualified persons. Unqualified persons are machine operators, operators of powered industrial
 This training session covers electrical safety for unqualified persons. Unqualified persons are machine operators, operators of powered industrial trucks, construction workers, and others who are not qualified
This training session covers electrical safety for unqualified persons. Unqualified persons are machine operators, operators of powered industrial trucks, construction workers, and others who are not qualified
Definitions found in several locations:
 Definitions found in several locations: NFPA 70 - National Electric Code NFPA 70B Recommended Practice for Electrical Equipment Maintenance. NFPA 70E Electrical Safety in the Workplace OSHA 1910 Subpart
Definitions found in several locations: NFPA 70 - National Electric Code NFPA 70B Recommended Practice for Electrical Equipment Maintenance. NFPA 70E Electrical Safety in the Workplace OSHA 1910 Subpart
REPORTING AND TREATMENT REQUIRED AS A RESULT OF AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT CS-OHS-5
 Form S1745 (Amd 7/97) CS ENERGY PROCEDURE FOR REPORTING AND TREATMENT REQUIRED AS A RESULT OF AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT CS-OHS-5 Responsible Officer: Authorised Person Approved : GM Production Contents 1.
Form S1745 (Amd 7/97) CS ENERGY PROCEDURE FOR REPORTING AND TREATMENT REQUIRED AS A RESULT OF AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT CS-OHS-5 Responsible Officer: Authorised Person Approved : GM Production Contents 1.
Sikkerhed og certifisering for sundhedsteknologisk udstyr
 Sikkerhed og certifisering for sundhedsteknologisk udstyr Temadag på Sundhedsteknologiuddannelsens 6. semester Kim Dremstrup Nielsen, IST, AAU Program 9.00-10.00 Elsikkerhed, IEC 60601 mm. Lektor Kim Dremstrup
Sikkerhed og certifisering for sundhedsteknologisk udstyr Temadag på Sundhedsteknologiuddannelsens 6. semester Kim Dremstrup Nielsen, IST, AAU Program 9.00-10.00 Elsikkerhed, IEC 60601 mm. Lektor Kim Dremstrup
Please print or type all responses except where a signature is required. DESIGN PROJECT TITLE: SEMESTER AND COURSE REFERENCE NUMBER: STUDENT NAME:
 ENGR 196, 296, 396 PROJECT FORM (Circle the correct course number) Prior to signing up for an ENGR 196, 296, 396 hands on project, the student must acquire the signature of the faculty member who will
ENGR 196, 296, 396 PROJECT FORM (Circle the correct course number) Prior to signing up for an ENGR 196, 296, 396 hands on project, the student must acquire the signature of the faculty member who will
Dealing with Electrical Hazards in the Workplace
 Dealing with Electrical Hazards in the Workplace Presented By: Tom Norwood Sr. Safety Specialist A SUBSIDIARY OF MEGGER TRAINING INSTITUTE, INC. Dallas, Texas Introduction Several hundred electrical fatalities
Dealing with Electrical Hazards in the Workplace Presented By: Tom Norwood Sr. Safety Specialist A SUBSIDIARY OF MEGGER TRAINING INSTITUTE, INC. Dallas, Texas Introduction Several hundred electrical fatalities
Circuit model of medical equipment for electrical safety purposes
 Risk Analysis IX 507 Circuit model of medical equipment for electrical safety purposes E. Zennaro 1, C. Mazzetti 1, F. Fiamingo 2 & G. L. Amicucci 2 1 Department of Astronautics, Electrical and Energetics
Risk Analysis IX 507 Circuit model of medical equipment for electrical safety purposes E. Zennaro 1, C. Mazzetti 1, F. Fiamingo 2 & G. L. Amicucci 2 1 Department of Astronautics, Electrical and Energetics
Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter(GFCI) Policy
 NewStar Netronics, LLC American Products for the World Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter(GFCI) Policy 3926 East 3 rd Street Tulsa, OK 74112 Phone (918)894-5006 Fax (918)836-9909 tech@newstarnetronics.com
NewStar Netronics, LLC American Products for the World Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter(GFCI) Policy 3926 East 3 rd Street Tulsa, OK 74112 Phone (918)894-5006 Fax (918)836-9909 tech@newstarnetronics.com
Ground Fault Protection for Electrical Tools
 Hanover Risk Solutions Ground Fault Protection for Electrical Tools Effective electrical tool and equipment grounding are extremely important on construction sites. Injuries and deaths can result from
Hanover Risk Solutions Ground Fault Protection for Electrical Tools Effective electrical tool and equipment grounding are extremely important on construction sites. Injuries and deaths can result from
GENERAL ELECTRICAL SAFETY
 GENERAL ELECTRICAL SAFETY Introduction Electricity has long been recognized as a serious workplace hazard. Many workers are unaware of the potential electrical hazards present in their work environment,
GENERAL ELECTRICAL SAFETY Introduction Electricity has long been recognized as a serious workplace hazard. Many workers are unaware of the potential electrical hazards present in their work environment,
The best safeguard against accidents is a genuine safety culture - awareness and constant vigilance on the part of all those involved, and the
 The best safeguard against accidents is a genuine safety culture - awareness and constant vigilance on the part of all those involved, and the establishment of safety as a permanent and natural feature
The best safeguard against accidents is a genuine safety culture - awareness and constant vigilance on the part of all those involved, and the establishment of safety as a permanent and natural feature
Reference Number PDS 10 (RIC Standard: EP SP)
 Discipline Engineering Standard NSW Category Electrical Title Reference Number PDS 10 (RIC Standard: EP 00 00 00 08 SP) Document Control Status Date Prepared Reviewed Endorsed Approved Mar 05 Standards
Discipline Engineering Standard NSW Category Electrical Title Reference Number PDS 10 (RIC Standard: EP 00 00 00 08 SP) Document Control Status Date Prepared Reviewed Endorsed Approved Mar 05 Standards
ECE Lab Safety. Module All Jan 2018
 ECE Lab Safety Module All Jan 2018 Agenda Lab Policies Electrical Safety Distribution Grounding Physiology CPR/AED Biological Safety Jewelry Lead Eye Safety Test online, 25 random multiple choice questions,
ECE Lab Safety Module All Jan 2018 Agenda Lab Policies Electrical Safety Distribution Grounding Physiology CPR/AED Biological Safety Jewelry Lead Eye Safety Test online, 25 random multiple choice questions,
DX 3 RCDs. Technical data Nature and consequences of electrical risks Direct and indirect contact. Direct contacts
 RCDs Nature and consequences of electrical risks Direct and indirect contact All electrical risks for people are the result of direct or indirect contact. What are these contacts? And how can we protect
RCDs Nature and consequences of electrical risks Direct and indirect contact All electrical risks for people are the result of direct or indirect contact. What are these contacts? And how can we protect
Industrial Relations
 Industrial & Management Engineering Department Industrial Relations IM 111 Dr Yehia Youssef IM111 Lecture 7 1 Definitions Hazard: A hazard is anything that can cause harm to people. Examples are dangerous
Industrial & Management Engineering Department Industrial Relations IM 111 Dr Yehia Youssef IM111 Lecture 7 1 Definitions Hazard: A hazard is anything that can cause harm to people. Examples are dangerous
Respiration. Figure 22: Schematic representation of the respiratory system
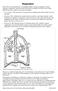 Respiration One of the seven characteristics of something which is living is respiration. Strictly speaking, respiration is the process that takes place at cellular level and is one of three different
Respiration One of the seven characteristics of something which is living is respiration. Strictly speaking, respiration is the process that takes place at cellular level and is one of three different
WHS-05 Electric Shock Response
 Table of Contents 1 Purpose... 3 2 Scope... 3 3 References... 3 4 Roles and Responsibilities... 3 5 Definitions... 4 6 Records... 4 7 Rescue and first aid... 4 8 Medical emergency response (Code Blue)...
Table of Contents 1 Purpose... 3 2 Scope... 3 3 References... 3 4 Roles and Responsibilities... 3 5 Definitions... 4 6 Records... 4 7 Rescue and first aid... 4 8 Medical emergency response (Code Blue)...
Med Aire Alternating Pressure Pump and Pad System
 User Manual Med Aire Alternating Pressure Pump and Pad System 14002E 14001E Symbols & Statements NOTE Indicates some tips or some information users should be aware of. CAUTION Indicates correct operating
User Manual Med Aire Alternating Pressure Pump and Pad System 14002E 14001E Symbols & Statements NOTE Indicates some tips or some information users should be aware of. CAUTION Indicates correct operating
Environmental Safety
 Environmental Safety Macroshock & Microshock! 2 Macroshock! 2 Microshock! 2 Preventative strategies!... 2 Explosions & Fire! 3 Anaesthetic Waste Gases! 3 Scavenging! 3 Breathing System Outlet!... 3 Types
Environmental Safety Macroshock & Microshock! 2 Macroshock! 2 Microshock! 2 Preventative strategies!... 2 Explosions & Fire! 3 Anaesthetic Waste Gases! 3 Scavenging! 3 Breathing System Outlet!... 3 Types
RESTORATION OF HEART RHYTHM DURING FIBRILLATION BY A CONDENSER DISCHARGE
 RESTORATION OF HEART RHYTHM DURING FIBRILLATION BY A CONDENSER DISCHARGE N. L. G U R V I C H A N D G. S. Y U N 1 E V h e M o s c o w I n s t i t u t e o f P h y s i o l o g y under L. S. Stem has investigated
RESTORATION OF HEART RHYTHM DURING FIBRILLATION BY A CONDENSER DISCHARGE N. L. G U R V I C H A N D G. S. Y U N 1 E V h e M o s c o w I n s t i t u t e o f P h y s i o l o g y under L. S. Stem has investigated
CS ENERGY PROCEDURE FOR ELECTRIC SHOCK TREATMENT AND REPORTING CS-OHS-05
 CS-OHS-05 10/04/2012 CS ENERGY PROCEDURE FOR ELECTRIC SHOCK TREATMENT AND REPORTING CS-OHS-05 Responsible Officer: Group Manager Health and Safety Responsible Executive: Executive General Manager Corporate
CS-OHS-05 10/04/2012 CS ENERGY PROCEDURE FOR ELECTRIC SHOCK TREATMENT AND REPORTING CS-OHS-05 Responsible Officer: Group Manager Health and Safety Responsible Executive: Executive General Manager Corporate
Guidance and history. Why MEIGaN? Medical Locations & Healthcare Electrics Part 1
 Medical Locations & Healthcare Electrics Part 1 Emergency Isolation Room Paediatric Isolation Room Paediatric HDU Medical Locations The risk, Earthing, IPS and UPS IEC 60364, MEIGaN and IET GN7 2015 Richard
Medical Locations & Healthcare Electrics Part 1 Emergency Isolation Room Paediatric Isolation Room Paediatric HDU Medical Locations The risk, Earthing, IPS and UPS IEC 60364, MEIGaN and IET GN7 2015 Richard
Codex Seven HACCP Principles. (Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment & Management)
 Codex Seven HACCP Principles (Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment & Management) Logic sequence for application of HACCP Assemble the HACCP team Describe product Identify intended use Construct a flow
Codex Seven HACCP Principles (Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment & Management) Logic sequence for application of HACCP Assemble the HACCP team Describe product Identify intended use Construct a flow
CIRCUIT BREAKER TESTING - JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS
 Title: Circuit Breaker Testing Purpose and Scope: Provide guidelines for testing of Circuit Breakers. Staffing Resources: Staff will have the minimum requirement of an Electrical Fitter/Mechanic Licence
Title: Circuit Breaker Testing Purpose and Scope: Provide guidelines for testing of Circuit Breakers. Staffing Resources: Staff will have the minimum requirement of an Electrical Fitter/Mechanic Licence
Why do I need to do an Arc-Flash Analysis?
 Why do I need to do an Arc-Flash Analysis? Presented By Tom Norwood for Alexander Nizov, P.E. Principal/Manager Electrical Engineering Division TRAINING INSTITUTE, INC. A SUBSIDIARY OF MEGGER Hazards Analysis
Why do I need to do an Arc-Flash Analysis? Presented By Tom Norwood for Alexander Nizov, P.E. Principal/Manager Electrical Engineering Division TRAINING INSTITUTE, INC. A SUBSIDIARY OF MEGGER Hazards Analysis
PLEASE READ CAREFULLY BEFORE INSTALLING OR USING MEGA POOL SAVER MPS 1100
 MPS-1100 User Manual Mega Pool Saver Ltd PLEASE READ CAREFULLY BEFORE INSTALLING OR USING MEGA POOL SAVER MPS 1100 For further up to date instructions on how to install Mega Pool Saver MPS 1100, please
MPS-1100 User Manual Mega Pool Saver Ltd PLEASE READ CAREFULLY BEFORE INSTALLING OR USING MEGA POOL SAVER MPS 1100 For further up to date instructions on how to install Mega Pool Saver MPS 1100, please
F-330 Instruction manual. Magic Glove Bio Skin Smoother High Frequency Ultrasound Galvanic
 F-330 Instruction manual Magic Glove Bio Skin Smoother High Frequency Ultrasound Galvanic Warning Never under any circumstances attempt to open or inspect the internal components or accessories of the
F-330 Instruction manual Magic Glove Bio Skin Smoother High Frequency Ultrasound Galvanic Warning Never under any circumstances attempt to open or inspect the internal components or accessories of the
PRODUCT SPECIFICATION
 MINI-FIT SR. SERIES 1.0 SCOPE This specification covers the 10.00 mm / (.394 in.) centerline tin and gold plated connector series, single and dual row versions in wire to wire and wire to printed circuit
MINI-FIT SR. SERIES 1.0 SCOPE This specification covers the 10.00 mm / (.394 in.) centerline tin and gold plated connector series, single and dual row versions in wire to wire and wire to printed circuit
Raymond Kirby Robotics Teaching Laboratory Introductory Notes
 School of Aerospace, Mechanical and Mechatronic Engineering Raymond Kirby Robotics Teaching Laboratory Introductory Notes The Raymond Kirby Robotics Teaching Laboratory previously known as the Mechatronics
School of Aerospace, Mechanical and Mechatronic Engineering Raymond Kirby Robotics Teaching Laboratory Introductory Notes The Raymond Kirby Robotics Teaching Laboratory previously known as the Mechatronics
AC1810 / AC1810-A TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS. Operating Pressure psi ( kgs/cm²) [AC1810] Displacement. Net Weight
![AC1810 / AC1810-A TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS. Operating Pressure psi ( kgs/cm²) [AC1810] Displacement. Net Weight AC1810 / AC1810-A TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS. Operating Pressure psi ( kgs/cm²) [AC1810] Displacement. Net Weight](/thumbs/83/88369739.jpg) Technical Specifications Operating Instructions Maintenance Information Troubleshooting Guide Parts Diagrams AC1810 / AC1810-A THE EVOLUTION OF PERFECTION CAUTION: Before attempting to use or service this
Technical Specifications Operating Instructions Maintenance Information Troubleshooting Guide Parts Diagrams AC1810 / AC1810-A THE EVOLUTION OF PERFECTION CAUTION: Before attempting to use or service this
Electrical Safety PPT-SM-ELECTSFTY V.A.0.0
 Electrical Safety 1 Electrical Safety OSHA s electrical safety standard covers Work on or near exposed energized equipment Proper use of electrical protective equipment Safe use of portable electric equipment
Electrical Safety 1 Electrical Safety OSHA s electrical safety standard covers Work on or near exposed energized equipment Proper use of electrical protective equipment Safe use of portable electric equipment
ES18 Security Theory/Regulations Answer Schedule
 ES18 Security Theory/Regulations Answer Schedule Notes:1. means that the preceding statement/answer earns 1 mark. 2. This schedule sets out the expected answers to the examination questions. The marker
ES18 Security Theory/Regulations Answer Schedule Notes:1. means that the preceding statement/answer earns 1 mark. 2. This schedule sets out the expected answers to the examination questions. The marker
Safety Issues in Healthcare Programs / Healthcare Employment
 Safety Issues in Healthcare Programs / Healthcare Employment Observing all safety procedures in place and recognizing the hazards that may be around you at all times will help to minimize accidents while
Safety Issues in Healthcare Programs / Healthcare Employment Observing all safety procedures in place and recognizing the hazards that may be around you at all times will help to minimize accidents while
10 Best Practices for Electrosurgical Unit Testing
 10 Best Practices for Electrosurgical Unit Testing Tips to quickly and effectively test electrosurgical devices to ensure performance and safety White Paper Let s start with the basics. Electrosurgical
10 Best Practices for Electrosurgical Unit Testing Tips to quickly and effectively test electrosurgical devices to ensure performance and safety White Paper Let s start with the basics. Electrosurgical
Original Date of Issue: 04/09
 POLICIES AND PROCEDURES DEPARTMENT: Environmental Health and Safety SUBJECT: Electrical Safety Program Original Date of Issue: 04/09 Reviewed 12/2011 Revised 12/2011 BACKGROUND ELECTRIC SHOCK It is well
POLICIES AND PROCEDURES DEPARTMENT: Environmental Health and Safety SUBJECT: Electrical Safety Program Original Date of Issue: 04/09 Reviewed 12/2011 Revised 12/2011 BACKGROUND ELECTRIC SHOCK It is well
Dr Morris Odell. Victorian Institute of Forensic Medicine VIFM
 TASERS and STUN GUNS Dr Morris Odell Victorian Institute of Forensic Medicine Intentional Electric Shock Devices Less than Lethal weapons Stun guns Tasers Cattle prods, Electric fences, Man traps Conducted
TASERS and STUN GUNS Dr Morris Odell Victorian Institute of Forensic Medicine Intentional Electric Shock Devices Less than Lethal weapons Stun guns Tasers Cattle prods, Electric fences, Man traps Conducted
Electronics Lab Advanced Electrical Engineering Lab Course II Spring 2006
 Safety Instructions Electronics Lab Advanced Electrical Engineering Lab Course II Spring 2006 Instructor: H. Elgala, Dr. D. Knipp Ta http://www.faculty.iu-bremen.de/course/c300221a/ee_module_2 Purpose
Safety Instructions Electronics Lab Advanced Electrical Engineering Lab Course II Spring 2006 Instructor: H. Elgala, Dr. D. Knipp Ta http://www.faculty.iu-bremen.de/course/c300221a/ee_module_2 Purpose
Fingertip Pulse Oximeter
 Instruction Manual Fingertip Pulse Oximeter Item # 40-810-000 Item # 40-811-000 Item # 40-812-000 Item # 40-813-000 Please read this guidebook completely before operating this unit. Limited Two-Year Warranty
Instruction Manual Fingertip Pulse Oximeter Item # 40-810-000 Item # 40-811-000 Item # 40-812-000 Item # 40-813-000 Please read this guidebook completely before operating this unit. Limited Two-Year Warranty
C&G 2395 Exam Paper April Section A - All questions carry equal marks. Answer all three questions. Show all calculations.
 C&G 2395 Exam Paper April 2013 Section A - All questions carry equal marks. Answer all three questions. Show all calculations. Q.1 The electrical installation in a small food retail outlet is scheduled
C&G 2395 Exam Paper April 2013 Section A - All questions carry equal marks. Answer all three questions. Show all calculations. Q.1 The electrical installation in a small food retail outlet is scheduled
BASIC KNOWLEDGE OF LABORATORY FIRST AID
 BASIC KNOWLEDGE OF LABORATORY FIRST AID RV: 02/02/2015 prevencio@uv.es Page 1 of 7 . General issues to be considered by the rescuer in the event of an accident are described below: - Proceed as follows:
BASIC KNOWLEDGE OF LABORATORY FIRST AID RV: 02/02/2015 prevencio@uv.es Page 1 of 7 . General issues to be considered by the rescuer in the event of an accident are described below: - Proceed as follows:
Electrical. Version 1.0
 This document is intended to provide basic safety guidelines for the Physical Plant Department at Community College of Allegheny County. The information provided in this guide may vary by site. Version
This document is intended to provide basic safety guidelines for the Physical Plant Department at Community College of Allegheny County. The information provided in this guide may vary by site. Version
LABORATORY SAFETY MANUAL
 SCHOOL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING & TELECOMMUNICATIONS LABORATORY SAFETY MANUAL FOR UNDERGRADUATE STUDENTS 2004 EE&T UG Safety Manual 1 Introduction School UG Laboratory Safety Manual The aim of this manual
SCHOOL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING & TELECOMMUNICATIONS LABORATORY SAFETY MANUAL FOR UNDERGRADUATE STUDENTS 2004 EE&T UG Safety Manual 1 Introduction School UG Laboratory Safety Manual The aim of this manual
Doc No: ELECTRIC Midland Engineering Co., Inc. Initial Issue Date 12/14/15 Safety Management System
 Revision Page 1 of PURPOSE The purpose is to eliminate unsafe conditions involving electrical equipment and tools, including faulty insulation, improper grounding, loose electrical connections, defective
Revision Page 1 of PURPOSE The purpose is to eliminate unsafe conditions involving electrical equipment and tools, including faulty insulation, improper grounding, loose electrical connections, defective
Hazards and Risks Associated With the Use of Electricity in the Workplace
 Hazards and Risks Associated With the Use of Electricity in the Workplace A simple electrical circuit can be described by reference to three parameters: voltage, current and resistance. These three parameters
Hazards and Risks Associated With the Use of Electricity in the Workplace A simple electrical circuit can be described by reference to three parameters: voltage, current and resistance. These three parameters
USER MANUAL SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS. For the most current manual revision, please visit our Website:
 USER MANUAL Model: PM4300 Series SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS For the most current manual revision, please visit our Website: www.precisionmedical.com 300 Held Drive Tel: (+001) 610-262-6090 Northampton, PA
USER MANUAL Model: PM4300 Series SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS For the most current manual revision, please visit our Website: www.precisionmedical.com 300 Held Drive Tel: (+001) 610-262-6090 Northampton, PA
Conduction of Electrical Current to and Through the Human Body: A Review
 Conduction of Electrical Current to and Through the Human Body: A Review Raymond M. Fish, PhD, MD, FACEP, a and Leslie A. Geddes, MS, PhD, DSc b a Bioacoustics Research Lab & Department of Surgery, University
Conduction of Electrical Current to and Through the Human Body: A Review Raymond M. Fish, PhD, MD, FACEP, a and Leslie A. Geddes, MS, PhD, DSc b a Bioacoustics Research Lab & Department of Surgery, University
FACULTY OF EDUCATION LOW RISK HEALTH AND SAFETY FORM FORM B
 FACULTY OF EDUCATION LOW RISK HEALTH AND SAFETY FORM FORM B Research Projects Date / / Faculty of Education Staff/Student No. Research Project Information Circle the appropriate research activity pertaining
FACULTY OF EDUCATION LOW RISK HEALTH AND SAFETY FORM FORM B Research Projects Date / / Faculty of Education Staff/Student No. Research Project Information Circle the appropriate research activity pertaining
GFCIs and Swimming Pools A Natural Fit
 GFCIs and Swimming Pools A Natural Fit Swimming Pool Triangle Most of us have seen or read something about the figure commonly known as the fire triangle (oxygen, heat, and fuel), which is a working model
GFCIs and Swimming Pools A Natural Fit Swimming Pool Triangle Most of us have seen or read something about the figure commonly known as the fire triangle (oxygen, heat, and fuel), which is a working model
Safe Schools: A Health and Safety Check
 Name of School: Optional Information Date of Inspection: Vocational Program/Course/Room: Signature of Inspector: Use of Electrical Equipment Self-Inspection Checklist Guidelines: This checklist covers
Name of School: Optional Information Date of Inspection: Vocational Program/Course/Room: Signature of Inspector: Use of Electrical Equipment Self-Inspection Checklist Guidelines: This checklist covers
Rigel 601 CHECKBOX. Instruction Manual. 348A551 Issue 2.0. April Seaward Electronic Ltd. Issue 2.0
 Rigel 601 CHECKBOX Instruction Manual 348A551 Issue 2.0 April 2006 2006 Seaward Electronic Ltd. Issue 2.0 Limited Warranty & Limitation of Liability Rigel Medical guarantees this product for a period of
Rigel 601 CHECKBOX Instruction Manual 348A551 Issue 2.0 April 2006 2006 Seaward Electronic Ltd. Issue 2.0 Limited Warranty & Limitation of Liability Rigel Medical guarantees this product for a period of
Northern Kentucky University Issue Date: 11/02/2018 Revised Date: Title: PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT PROCEDURE OBJECTIVE AND PURPOSE
 Northern Kentucky University Issue Date: 11/02/2018 Revised Date: Policy Link: Occupational Safety Policy Title: PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT PROCEDURE OBJECTIVE AND PURPOSE The objective of this procedure
Northern Kentucky University Issue Date: 11/02/2018 Revised Date: Policy Link: Occupational Safety Policy Title: PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT PROCEDURE OBJECTIVE AND PURPOSE The objective of this procedure
Figure Source:
 In the Fall of 2018, EPRI opened a test facility to the public so that they could witness testing at the EPRI swimming pool assessment infrastructure within EPRI s laboratory in Lenox, Massachusetts. Those
In the Fall of 2018, EPRI opened a test facility to the public so that they could witness testing at the EPRI swimming pool assessment infrastructure within EPRI s laboratory in Lenox, Massachusetts. Those
Bulletin Swimming pool, hot tub and spa installations Rules , , , , , and
 Bulletin 68-7-11 Swimming pool, hot tub and spa installations Rules 68-000, 68-056, 68-058, 68-064, 68-068, 68-302 and 68-404 Scope (1) Swimming pools - general (2) Grounding & bonding (a) Bonding for
Bulletin 68-7-11 Swimming pool, hot tub and spa installations Rules 68-000, 68-056, 68-058, 68-064, 68-068, 68-302 and 68-404 Scope (1) Swimming pools - general (2) Grounding & bonding (a) Bonding for
HEAT INJURIES. MANSCEN Safety Office
 HEAT INJURIES MANSCEN Safety Office OBJECTIVES 1. Know Individual risk factors. 2. Proper Acclimatization. 3. Know types of heat injuries, and first aid. 4. Be able to read and obtain WBGT index. A. INDIVIDUAL
HEAT INJURIES MANSCEN Safety Office OBJECTIVES 1. Know Individual risk factors. 2. Proper Acclimatization. 3. Know types of heat injuries, and first aid. 4. Be able to read and obtain WBGT index. A. INDIVIDUAL
Soft Tissue Injuries
 KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES Soft Tissue Injuries 1. List two signs of closed wounds. 2. List four purposes of bandaging. 3. Describe the best initial defence against infection of an open wound. 4. Describe how
KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES Soft Tissue Injuries 1. List two signs of closed wounds. 2. List four purposes of bandaging. 3. Describe the best initial defence against infection of an open wound. 4. Describe how
C&G 2395 Exam Paper June Section A-All questions carry equal marks. Answer all three questions. Show all calculations.
 C&G 2395 Exam Paper June 2013 Section A-All questions carry equal marks. Answer all three questions. Show all calculations. 1. The electrical installation in an industrial unit is scheduled for a periodic
C&G 2395 Exam Paper June 2013 Section A-All questions carry equal marks. Answer all three questions. Show all calculations. 1. The electrical installation in an industrial unit is scheduled for a periodic
Spasticity / Dystonia
 Spasticity / Dystonia How can a pump help my movement disorder? This therapy, called intrathecal infusion, is a treatment for controlling some movement disorders. It uses a surgically implanted pump and
Spasticity / Dystonia How can a pump help my movement disorder? This therapy, called intrathecal infusion, is a treatment for controlling some movement disorders. It uses a surgically implanted pump and
Overview. The user must follow the instructions below.
 Overview Thank you for purchasing i-pad. This product can be successfully and safely used for a long period if you familiarize yourself with the instructions and precautions by reading the user's manual
Overview Thank you for purchasing i-pad. This product can be successfully and safely used for a long period if you familiarize yourself with the instructions and precautions by reading the user's manual
29. Personal Protective Equipment
 29. Personal Protective Equipment This Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) procedure has been prepared to inform employees of potential hazards in the workplace and to identify the proper PPE to be used
29. Personal Protective Equipment This Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) procedure has been prepared to inform employees of potential hazards in the workplace and to identify the proper PPE to be used
PART I. GENERAL REQUIREMENTS FOR PERMANENTLY INSTALLED POOLS, STORABLE POOLS, OUTDOOR SPAS, OUTDOOR HOT TUBS, OR FOUNTAINS
 The overriding concern of Article 680 is to keep people and electricity separated. Some ways in which Article 680 accomplishes this include: References to other articles. Equipment Requirements. Any equipment
The overriding concern of Article 680 is to keep people and electricity separated. Some ways in which Article 680 accomplishes this include: References to other articles. Equipment Requirements. Any equipment
PLANT/EQUIPMENT/ASSET HAZARD REPORT
 Asset Description: EL-08001-011 : Harrison 550 CNC Lathe Large Sale Type For what use is this asset being sold? Re-Use þ Spare Parts Scrap Note 1: Assets are sold only for the use indicated. Any other
Asset Description: EL-08001-011 : Harrison 550 CNC Lathe Large Sale Type For what use is this asset being sold? Re-Use þ Spare Parts Scrap Note 1: Assets are sold only for the use indicated. Any other
Electrical Safety, Subpart K
 SHARP Instructor Training Guide Training Overview: Electrical Safety, Subpart K This guide is designed to assist the instructor with the presentation of the Electrical Safety training materials. Each numbered
SHARP Instructor Training Guide Training Overview: Electrical Safety, Subpart K This guide is designed to assist the instructor with the presentation of the Electrical Safety training materials. Each numbered
Course Title: Industrial Safety in Electronics Engineering Technology Number of Credits: 3 B.A. B.S. B.A.S A.A. A.S. Degree Type
 GENERAL INFORMATION Name: Diane King Phone #: 77021 Course Prefix/Number: ETI3704 Course Title: Industrial Safety in Electronics Engineering Technology Number of Credits: 3 B.A. B.S. B.A.S A.A. A.S. Degree
GENERAL INFORMATION Name: Diane King Phone #: 77021 Course Prefix/Number: ETI3704 Course Title: Industrial Safety in Electronics Engineering Technology Number of Credits: 3 B.A. B.S. B.A.S A.A. A.S. Degree
2.017 Lab Rules and Safety Rm September 9, 2009 (Version 2) Dr. Harrison H. Chin
 2.017 Lab Rules and Safety Rm. 5-007 September 9, 2009 (Version 2) Dr. Harrison H. Chin LAB RULES 1. WORK SAFELY IN THE LAB 2. POWER TOOL USE IS RESTRICTED 3. DO NOT WORK WITH CHEMICALS ALONE 4. CLEAN
2.017 Lab Rules and Safety Rm. 5-007 September 9, 2009 (Version 2) Dr. Harrison H. Chin LAB RULES 1. WORK SAFELY IN THE LAB 2. POWER TOOL USE IS RESTRICTED 3. DO NOT WORK WITH CHEMICALS ALONE 4. CLEAN
11/2/2017. Course Objectives. Overview
 Course Objectives The objective of this CBT module is to insure that personnel receive basic training in electrical safety. Every employee's work involves electricity. This may vary from typical electrical
Course Objectives The objective of this CBT module is to insure that personnel receive basic training in electrical safety. Every employee's work involves electricity. This may vary from typical electrical
Hypothermia. Hypothermia. By: Louis Durkin MD 1 Credit Course Approved by NJ OEMS For EMT-Basic Only
 Hypothermia By: Louis Durkin MD 1 Credit Course Approved by NJ OEMS For EMT-Basic Only Objectives Explain the basic physiology of thermoregulation Define the basic metabolic rate Explain common measurements
Hypothermia By: Louis Durkin MD 1 Credit Course Approved by NJ OEMS For EMT-Basic Only Objectives Explain the basic physiology of thermoregulation Define the basic metabolic rate Explain common measurements
REFERENCE SPECIFICATION
 1 / 8 1. Notification Items 1.1 Law and the regulation which are applied 1 Ozone depleting substances specified by Montreal Protocol have not been used in the manufacturing process of the material used
1 / 8 1. Notification Items 1.1 Law and the regulation which are applied 1 Ozone depleting substances specified by Montreal Protocol have not been used in the manufacturing process of the material used
Analysis of Pressure Rise During Internal Arc Faults in Switchgear
 Analysis of Pressure Rise During Internal Arc Faults in Switchgear ASANUMA, Gaku ONCHI, Toshiyuki TOYAMA, Kentaro ABSTRACT Switchgear include devices that play an important role in operations such as electric
Analysis of Pressure Rise During Internal Arc Faults in Switchgear ASANUMA, Gaku ONCHI, Toshiyuki TOYAMA, Kentaro ABSTRACT Switchgear include devices that play an important role in operations such as electric
Engineering Technical Report 128. Risk Assessment for BT Operators Working In a ROEP Zone. Draft for Approval
 Engineering Technical Report 128 2006 Risk Assessment for BT Operators Working In a ROEP Zone Draft for Approval 2006 Energy Networks Association All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be
Engineering Technical Report 128 2006 Risk Assessment for BT Operators Working In a ROEP Zone Draft for Approval 2006 Energy Networks Association All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be
Key Comparison of Safety Requirements in Europe, North America and Australia for Electronic Products
 Key Comparison of Safety Requirements in Europe, North America and Australia for Electronic Products Mr. K.F. Siu 15 April, 2010 www.intertek.com 1 Presentation Agenda Standards For Audio/Video Product
Key Comparison of Safety Requirements in Europe, North America and Australia for Electronic Products Mr. K.F. Siu 15 April, 2010 www.intertek.com 1 Presentation Agenda Standards For Audio/Video Product
NovelBright LED Illuminator
 NovelBright LED Illuminator Instruction Manual version NS01_11 Instruction Manual This LED illuminator is suitable for research use only. It must be used by specialized personnel that know the health risks
NovelBright LED Illuminator Instruction Manual version NS01_11 Instruction Manual This LED illuminator is suitable for research use only. It must be used by specialized personnel that know the health risks
Covered Task 409OP Training Guide Inspecting Interference Bonds
 Directions This training guide is to be used by a Subject matter expert (SME) authorized Evaluator/Trainer and Trainee during on-thejob training (OJT) or prior to an evaluation as a resource. (S) Indicates
Directions This training guide is to be used by a Subject matter expert (SME) authorized Evaluator/Trainer and Trainee during on-thejob training (OJT) or prior to an evaluation as a resource. (S) Indicates
Smart JVA Module WARNING. For use with AquaLink RS systems with rev R firmware or newer.
 INstallation and OPERATION Manual Smart JVA Module For use with AquaLink RS systems with rev R firmware or newer. H0370200 Rev C FOR YOUR SAFETY - This product must be installed and serviced by a contractor
INstallation and OPERATION Manual Smart JVA Module For use with AquaLink RS systems with rev R firmware or newer. H0370200 Rev C FOR YOUR SAFETY - This product must be installed and serviced by a contractor
77-I0PN230 Rev. A. Model 1030 User Manual
 77I0PN230 Rev. A TABLE OF CONTENTS FUNCTION...2 TREATMENT...3 INDICATIONS FOR USE...4 CONTRAINDICATIONS...4 CLEANING...4 MAINTENANCE...4 CLASSIFICATION & SYMBOLS...4 DISINFECTION / STERILIZATION...4 SAFETY
77I0PN230 Rev. A TABLE OF CONTENTS FUNCTION...2 TREATMENT...3 INDICATIONS FOR USE...4 CONTRAINDICATIONS...4 CLEANING...4 MAINTENANCE...4 CLASSIFICATION & SYMBOLS...4 DISINFECTION / STERILIZATION...4 SAFETY
This presentation provides an overview of modern methods for minimizing the arc-flash hazard.
 Electricity is all around us. An uncontrolled release of electric energy is extremely dangerous, posing a threat to human life, causing equipment damage, and jeopardizing the manufacturing process that
Electricity is all around us. An uncontrolled release of electric energy is extremely dangerous, posing a threat to human life, causing equipment damage, and jeopardizing the manufacturing process that
WORK ENVIRONMENT SAFETY. Body Mechanics. Electrical Safety. Employee. Safety. Fall. Needlestick Prevention. Safety
 WORK ENVIRONMENT SAFETY Electrical Safety Employee Safety Body Mechanics Fall Safety Needlestick Prevention Rev.: bw/january 2016 COMMON INJURIES AND ACCIDENTS Slips, trips and falls Back injuries Ergonomic
WORK ENVIRONMENT SAFETY Electrical Safety Employee Safety Body Mechanics Fall Safety Needlestick Prevention Rev.: bw/january 2016 COMMON INJURIES AND ACCIDENTS Slips, trips and falls Back injuries Ergonomic
Saline C 6.0 Junction Box
 ISHCSJBOX RevA Saline C 6.0 Junction Box Junction Box for Saline C 6.0 Commercial Salt Chlorine Generator Owner s Manual Contents Description...3 Installation...4 Operation...7 Maintenance...8 Parts Guide...9
ISHCSJBOX RevA Saline C 6.0 Junction Box Junction Box for Saline C 6.0 Commercial Salt Chlorine Generator Owner s Manual Contents Description...3 Installation...4 Operation...7 Maintenance...8 Parts Guide...9
Level MEASUREMENT 1/2016
 Level MEASUREMENT 1/2016 AGENDA 2 A. Introduction B. Float method C. Displacer method D. Hydrostatic pressure method E. Capacitance method G. Ultrasonic method H. Radar method I. Laser method J. Level
Level MEASUREMENT 1/2016 AGENDA 2 A. Introduction B. Float method C. Displacer method D. Hydrostatic pressure method E. Capacitance method G. Ultrasonic method H. Radar method I. Laser method J. Level
Check with local zoning official for property line distance requirements.
 RESIDENTIAL POOL PLAN SUBMITTAL GUIDELINES The following guidelines are intended to assist municipal residents with the permit acquisition process with regard to pools, spas and hot tubs for single family
RESIDENTIAL POOL PLAN SUBMITTAL GUIDELINES The following guidelines are intended to assist municipal residents with the permit acquisition process with regard to pools, spas and hot tubs for single family
PLANT/EQUIPMENT/ASSET HAZARD REPORT
 Asset Description: EL-09100-060 : Gantry hoist system Sale Type For what use is this asset being sold? Re-Use Spare Parts Scrap Note 1: Assets are sold only for the use indicated. Any other use is at the
Asset Description: EL-09100-060 : Gantry hoist system Sale Type For what use is this asset being sold? Re-Use Spare Parts Scrap Note 1: Assets are sold only for the use indicated. Any other use is at the
Technical Data. General specifications. Rated operating distance s n 2 mm
 0102 Model Number Features 2 mm flush Usable up to SIL 2 acc. to IEC 61508 Technical Data specifications Switching function Normally closed (NC) Output type NAMUR Rated operating distance s n 2 mm Installation
0102 Model Number Features 2 mm flush Usable up to SIL 2 acc. to IEC 61508 Technical Data specifications Switching function Normally closed (NC) Output type NAMUR Rated operating distance s n 2 mm Installation
Common Sense Approach to OSHA Safety Procedures. Course Instructor: Kaleb Brashear Course id #:3 Credits: 2 hours
 Common Sense Approach to OSHA Safety Procedures Course Instructor: Kaleb Brashear Course id #:3 Credits: 2 hours Outline I. Intro II. What is OSHA? A. Definition of OSHA B. OSHA s role III. History of
Common Sense Approach to OSHA Safety Procedures Course Instructor: Kaleb Brashear Course id #:3 Credits: 2 hours Outline I. Intro II. What is OSHA? A. Definition of OSHA B. OSHA s role III. History of
Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science. Electrical Safety. for Staff and Students in EECS Instructional Laboratories
 NEVER WORK ALONE Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science Electrical Safety for Staff and Students in EECS Instructional Laboratories If you will be working with energized circuits or equipment
NEVER WORK ALONE Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science Electrical Safety for Staff and Students in EECS Instructional Laboratories If you will be working with energized circuits or equipment
Faculty/School: Pharmacy Initial Issue Date: Oct 2016
 Use this form to assist you to complete risk assessments for hazardous activities and processes. Any serious or ongoing hazards should be reported via RiskWare to ensure that appropriate corrective actions
Use this form to assist you to complete risk assessments for hazardous activities and processes. Any serious or ongoing hazards should be reported via RiskWare to ensure that appropriate corrective actions
Technical Data. General specifications. Rated operating distance s n 5 mm
 0102 Model Number Features 5 mm flush Usable up to SIL 2 acc. to IEC 61508 Accessories EXG-18 Quick mounting bracket with dead stop BF 18 Mounting flange, 18 mm Technical Data specifications Switching
0102 Model Number Features 5 mm flush Usable up to SIL 2 acc. to IEC 61508 Accessories EXG-18 Quick mounting bracket with dead stop BF 18 Mounting flange, 18 mm Technical Data specifications Switching
Laboratory Personal Protective Equipment & Hazard Assessment Tool
 Laboratory Personal Protective Equipment & Hazard Assessment Tool This form must be completed by the person in charge of the laboratory, with the guidance of the Chemical Hygiene Officer to conduct a laboratory
Laboratory Personal Protective Equipment & Hazard Assessment Tool This form must be completed by the person in charge of the laboratory, with the guidance of the Chemical Hygiene Officer to conduct a laboratory
OSHAcademy Course 715 Study Guide. Electrical Safety Basics
 Electrical Safety Basics Electrical Safety Basics Copyright 2013 Geigle Safety Group, Inc. No portion of this text may be reprinted for other than personal use. Any commercial use of this document is strictly
Electrical Safety Basics Electrical Safety Basics Copyright 2013 Geigle Safety Group, Inc. No portion of this text may be reprinted for other than personal use. Any commercial use of this document is strictly
#11581 SAFELY ON YOUR FEET
 C a p t i o n e d M e d i a P r o g r a m VOICE (800) 237-6213 TTY (800) 237-6819 FAX (800) 538-5636 E-MAIL info@captionedmedia.org WEB www.captionedmedia.org #11581 SAFELY ON YOUR FEET AURORA PICTURES,
C a p t i o n e d M e d i a P r o g r a m VOICE (800) 237-6213 TTY (800) 237-6819 FAX (800) 538-5636 E-MAIL info@captionedmedia.org WEB www.captionedmedia.org #11581 SAFELY ON YOUR FEET AURORA PICTURES,
Arc Flash. Safety 21
 Arc Flash Safety 21 Arc Flash Introduction Electrical Hazards Safety Planning De-Energizing Equipment Working Hot Summary Introduction Most people don t think about electricity very much, which is surprising
Arc Flash Safety 21 Arc Flash Introduction Electrical Hazards Safety Planning De-Energizing Equipment Working Hot Summary Introduction Most people don t think about electricity very much, which is surprising
4 Staff Selection, Appraisal and Development. To prevent harm by identifying and controlling potential hazards.
 OTAGO POLYTECHNIC MANAGEMENT POLICY Number: MP0403.04 Title: Hazard Management ITPNZ Standard: 4 Staff Selection, Appraisal and Development Chief Executive Approval: Approval Date: 17 Apr 12 Effective
OTAGO POLYTECHNIC MANAGEMENT POLICY Number: MP0403.04 Title: Hazard Management ITPNZ Standard: 4 Staff Selection, Appraisal and Development Chief Executive Approval: Approval Date: 17 Apr 12 Effective
PRODUCT SPECIFICATION FOR APPROVAL
 FARNELL INST UK Issue : Date of issue : Mar 08,2010 Classification: New Change PRODUCT FOR APPROVAL Product Description : Product Part Number : (Panasonic Part Number : ) Country of Origin : Malaysia (It
FARNELL INST UK Issue : Date of issue : Mar 08,2010 Classification: New Change PRODUCT FOR APPROVAL Product Description : Product Part Number : (Panasonic Part Number : ) Country of Origin : Malaysia (It
C&G Level 3 Award in the Periodic Inspection, Testing and Certification of Electrical Installations
 C&G 2395-01 Level 3 Award in the Periodic Inspection, Testing and Certification of Electrical Installations Test instruments and recommended testing sequence 1 Outcomes of this Session describe the different
C&G 2395-01 Level 3 Award in the Periodic Inspection, Testing and Certification of Electrical Installations Test instruments and recommended testing sequence 1 Outcomes of this Session describe the different
Chapter 2. Welding Safety Delmar, Cengage Learning
 Chapter 2 Welding Safety Objectives After completing this chapter, you will be able to: Explain how to work safely Identify each degree of burn and describe how to provide first aid List the types of protective
Chapter 2 Welding Safety Objectives After completing this chapter, you will be able to: Explain how to work safely Identify each degree of burn and describe how to provide first aid List the types of protective
