ROAD ACCIDENT SEVERITY ANALYSIS FOR HYDERABAD CITY
|
|
|
- Hector Higgins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ROAD ACCIDENT SEVERITY ANALYSIS FOR HYDERABAD CITY S. Ghanshyam Singh 1, T. Saikrishna Bharadwaj 2, Mohammad Ibrahim 3, Arumulla Raju 4 1 Assistant Professor of Civil Engineering,CMR Institute of Technology, Hyderabad, Telangana, (India) 2 PG Student, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Mallareddy Institute of Technology and Science, Hyderabad, Telangana, (India) 3,4 PG Student, Dept. of Civil Engineering, University College of Engineering Osmania University, Hyderabad, Telangana, ( India) ABSTRACT Understanding the underlying relationship between the crash injury severity and factors such as driver s characteristics, vehicle type and roadway conditions are very important for improving traffic safety. Many transportation agencies use accident frequencies, and statistical models of accident frequencies, as a basis for prioritizing highway safety improvements. However, the use of accident severities in safety programming has often been limited to the vocational assessment of accident fatalities, with little or no emphasis being placed on the full severity distribution of accidents (property damage only, possible injury) which is needed to fully assess the benefits of competing safety-improvement projects. In the thesis we demonstrate a modeling approach that can be used to better understand the injury-severity distributions of accidents on highway segments, and the effect that traffic characteristics. The approach we use allows for the possibility that estimated model parameters can vary randomly across road segments to account for unobserved effects potentially relating to roadway characteristics, environmental factors, and driver behavior. Using severity data for Hyderabad city, a mixed logit model is estimated. Estimation findings indicate that volume-related variables, while roadway characteristics such as the number of horizontal curves, number of grade breaks per km and pavement friction are best modeled for severity as fixed parameters. It was observed that rear end and swipe is significant for non-fatal accidents. Our results show that the mixed logit model has considerable promise as a methodological tool in accident analysis. I. INTRODUCTION India is undergoing major economic and demographic transition coupled with increasing urbanization and motorization. Among the top ten causes of mortality in the country, Road Traffic Accident was the tenth cause two decades back, but with the increasing urban expanse and lifestyle changes, it is projected that road traffic accidents will occupy the fifth position in the list of major killers and third position among causes of disease burden in 2020.In India, 11% of deaths due to non communicable diseases are due to injuries and 78% of injury 61 P a g e
2 deaths are due to road traffic accidents. It is the leading cause of mortality for young adults of less than 45 years and a major burden of disease across all age groups. Many metropolitan cities, including Hyderabad, India increase number of road accidents is imposing considerable social and economic burdens on the victims, and various direct and indirect costs. Road accidents are essentially caused by improper interactions between vehicles, and other road users or roadway features. The situation that leads to improper interactions could be the result of the complex interplay of a number of factors such as pavement characteristics, geometric features, traffic characteristics, road users, behavior, vehicle design, driver s characteristics and environmental aspects. Thus, the whole system of accident occurrence is a complex phenomenon. 1.1 Need for the study In India, the traffic is highly heterogeneous in nature, ranging from pedestrians, animal drawn carts, cycle rickshaw, handcarts, to motorized vehicles, like motor cycles, three wheelers, motor cars, buses, trucks, multi axle as well as over sized vehicles. Analysis of traffic data indicated that drivers fault is responsible for a majority of the accidents and fatalities; where as human factor is a major contributor to the accidents As per recorded data in year 2011, about accidents have occurred and persons were killed in Andhra Pradesh state. In Hyderabad, approximately 9000 no of accidents occurred in the year On average, more than 2300 people are killed and about 6854 injured in traffic accidents annually. Hyderabad fatality rate has consistently been within the highest range in the nation in the last decade(sixth rank). 1.2 Objective of study a. Identify and quantify the main contributing factors to the severity of road accidents in Hyderabad including human and roadway and environmental factors. b. Identify policies and countermeasures to the major safety factor problems in Hyderabad. c. Estimate the safety benefit of implementing proposed policies and countermeasures. II. LITERATURE REVIEW a) Timothy R. NeumanC. Glennon (TRR 923) have developed linear regression equation for the analysis for highway curves. They have found that the accident rate increases as the degree of curvature increases and decreases as the length of the curve shoulder width, and road width increases. b) Kadiyali.L.R etal., (1984) developed an accident model based on population and motor vehicle by using regression technique. The collected accident data for 20 years ( ), population and number of motor vehicles India. Based on the past trend a regression equation is developed based on number of deaths per 10,000 vehicles (D) and number of motor vehicles per 1000 population (V) and is follows i. D= V Where, D= number of deaths per vehicles V= number of vehicles per 1000 population. Assuming that the lane width, shoulder width and shoulder type have significant affect on safety. 62 P a g e
3 c) Charles V. Zegeer and John A. Deacon (1992) developed a model. The research quantifies the effect of lane width, shoulder width and shoulder type on highway crash experience. The model, which is applicable to two-lane, rural highways is as follows: AR = (0.8907) L (0.9562) S (1.0026) LS (0.9403) P (1.0040) LP Where, AR = number of Run-off-Road and Opposite Direction accidents per million vehicle miles L = lane width in feet S = shoulder width in feet (including stabilized and unstabilized components) P = width in feet of stabilized component of shoulder (0 < P < S). d) Matthew G. Karlaftis and Ioannis Golias (2002) have developed a relationship between rural road geometric characteristics, accident rates and their prediction, using a rigorous non-parametric statistical methodology known as hierarchical tree-based regression. e) Srinivas Rao and Madhu (2005) laid emphasis on accident studies conducted national highway-5 from Anakapalli to Vishakhapatnam stretch of nearly 40km. From their studies they found that most of the accident on this stretch was due to the inadequate sign boards to guide the road user to perceive the situation and act upon it. f) Dahee Hong etal (2005) have developed a regression modal for two lane and is given by i. Y= *X X2 Where, Y: Number of Accident (accident/km), X1: Number of Intersections (unit/km) X2: Number of Pedestrian Traffic Signals (unit/km).for this the R square value is g) Archana (2008) submitted her desertion work by conducting studies at kerala and showed the percentage of vehicles vs. number of years, number of years vs number of accidents and timely variation of accidents. h) Kishore Babu (2009) conducted studies on NH7 from nizamabab to Mahbubnagar. From his studies he forum that more number of accidents occur near village. Due to the inadequate signs and markings. Numbers of accidents occur near minor road junctions. III. METHODOLOGY 63 P a g e
4 Figure 1 Methodology Adopted for the Study IV. DATA COLLECTION 4.1 Study Area Description The accident data was collected by Hyderabad city from the records kept by the state police department for five year period and also from Accident Deaths and Suicides in India 2011, published by the National Crime Records Bureau, Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India, and New Delhi. Further accident data for north, east, west, south and central zones were collected for five year period from the respective police department of all zones. The accident data details collected include time, number of vehicles involved, severity, hourly & pedestrian involvement etc. The zonal description and the police station limits are obtained thorough of TS police. The population details are also collected. Figure. Shows study area and its zone limits 64 P a g e
5 Figure 2 Police Zones Limits of Hyderabad city 4.2 Accident data It was assumed that knowledge of the circumstances and severity of accidents would be essential in their modeling since the causes of, and countermeasures to help prevent, different accident types may be very different. For example, causes and countermeasures for a slight pedestrian accident would certainly be different to a major head-on vehicle accident. The following data were therefore identified and proposed for collection from files at individual police stations. 1. Zone and Place 2. Time of day of collision and Day, Month and year 3. Overall accident severity (classified as that of the Fatal, Non Fatal & Serious) 4. Number and types of vehicles involved and Number, severity (fatal, non fatal & serious) 5. Vehicle type in which (or by which) the casualty was injured 6. Collision pattern: vehicle man oeuvres prior to crash: text and diagram. This is especially important for junction accidents. Sketches were to be encouraged and collected separately if the appropriate movements could not be entered into a spreadsheet as compass directions for example. Collision type (e.g. head on, rear-end, swipe etc.) 4.3 Road environment inventory/survey data The nature of the road environment is known to have a major influence on the occurrence of accidents. The starting point for the collection of road feature data was to produce lists of various parameters which had been found to have a significant influence on road safety from existing research. These studies have been summarized in the literature review in Appendix A. Although a large number of variables can be collected during a physical survey of the road and it is desirable to measure as many variables as possible, this must be balanced against what is practical and feasible given time and budgetary constraints. From the significant variables highlighted in the literature review, a consideration of how variables are collated, the following data were identified for collection: - 1. Road reference and Carriageway surface condition 65 P a g e
6 2. Median type, presence of gaps in the median and the nature (type, width, condition) of the shoulder. 3. Number of lanes and their widths and Whether or not curves are super-elevated 4. The presence of a slick surface and quality of a footpath 5. The presence, quality of road signs and road markings 6. The degree of side friction imposed by pedestrians, shop fronts, parked vehicles, bus stops on passing traffic and The nature of the off-road environment (embankment or flat; rural or urban; residential or industrial; drains, barriers or kerbs; etc) 4.4 Accident Data Collection from Secondary Sources In India, police men are responsible for recording road accidents. The accident data was collected from concern police stations. Data consisting details of accidents for five zones of Hyderabad city from year 2001 to 2011are collected. Accident details includes date, day of occurrence, time of accident, type of area, nature of accident, vehicles involved, classification of accident, number of deaths, number of injured, type of maneuver, responsibility of driver, cause of accident etc. Table 1 indicates the road accident data for Hyderabad City. Table 1 Road Accident Data for Hyderabad City Year Population (P) Vehicles (N) Fatalities (F) Injuries (I) Accidents (C) P a g e
7 V. RESULTS & ANALYSIS 5.1 Accident Data Analysis for Hyderabad City Yearly Variation of Accidents During 2009 to 2011 numbers of accidents registered in various zones of Hyderabad city police station wise are represented in Table 5.1. The total distance covered is 650sq.kilometers. A total 6649 accidents were recorded during 2009 to 2011, in these 85 were fatal accidents and 6537 were non-fatal accidents. More number of accidents occurred in west zone of police station region than remaining police station regions. The police station wise distributions of accidents are presented in table 2. Table2: Police station wise accidents occurred Police Station Limits Zone wise F NF F NF F NF Central Zone North Zone East Zone West Zone South Zone Hyderabad Nature of Accident Occurred The rear end collision and head on collision are more due to misjudgment of speeds between following and opposing vehicles, as show in Table 3 and presented graphically in Figure: 3 Table 3: Nature of accidents occurred NO.OF NATURE OF ACCIDENT ACCIDENTS Head on collision 852 Rear end collision 542 Swipe collision P a g e
8 Figure 3 Composition of Nature of Accidents Time Wise Distribution of Accidents The time of occurrence of accidents is categorized into hourly blocks indicating that the accidents are distributed throughout the day. It is seen that the accidents occurred during day and night are in equal proportion. From Table 4 it is observed that accidents are occurring during 19:00 to 20:00 and 16:00 to 17:00 hours and presented graphically in Figure 4 Table 4: Time wise distribution of accidents HOUR OF THE DAY HOUR OF THE DAY NO OF ACCIDENTS 0:00-1: :00-13: :00-2: :00-14: :00-3: :00-15: :00-4: :00-16: :00-5: :00-17: :00-6: :00-18: :00-7: :00-19: :00-8: :00-20: :00-9: :00-21: :00-10: :00-22: :00-11: :00:00-23: :00-12: :00-24:00 75 NO OF ACCIDENTS 68 P a g e
9 ts Figure 4 Time wise distribution of accident 5.2 Analysis of Road Accidents Using SPSS Analysis for type of collision The logistic Regression is used for development of models based on severity which is given by е β 0 +β 1 x 1 y = е β 0 +β 1 x 1 Where y = Dependent Variable x = Odd against even Fatal and Non Fatal a) Head on collision:- Odd ratio is determined where n11, n12, n21 & n22 are.. n 11 = 2; n 1 2 = 101; n 21 = 85; n 22 = 5395 Odds ratio = n 11 x n 22 = 2 x 5395 = = = n 12 x n 21 = 85 x Odds ratio = exp (β 1 ) where exp (β 1 ) = β 1 = log (1.256) = P a g e
10 Confidence Interval = Exp {β 1 } ± Ƶ 1 - δ x SE (β 1 ) SE (β 1 ) = = = Confidence Interval = exp {β 1 } ± Ƶ 1 - δ x SE (β 1 ) = exp {(0.0928) ± (1.96) x (0.7223)} = exp {( ) ± ( )} = exp {1.514, } = ( , ) The Odds Ratio between Head on accident and Severity of the accident is computed and found to be which indicates that the Odds against even is around 100 percent Severity. We have also computed the Confidence internal of Severity of accident and found that the interval is (4.54, 0.268) indicating that the confidence interval values is skewed towards right side the normal curve. b) Rear end collision type:- n 11 = 81; n 1 2 =5357; n 21 = 6; n 22 =139 Odds ratio = n 11 x n 22 = 81 x139 = = n 12 x n 21 = 5357 x6 Odds ratio = exp (β 1 ) where exp (β 1 ) = β 1 = log ( ) = Confidence Interval = Exp {β 1 } ± Ƶ 1 - δ x SE (β 1 ) SE (β 1 ) = = = 0.43 Confidence Interval =exp {β 1 } ± Ƶ 1 - δ x SE (β 1 ) = exp {(-0.455) ± (1.96) x (0.43)} = exp { ( ) ± (0.8428)} 70 P a g e
11 = exp {0.3878, } = (1.473, ) From the above analysis of Rear end Severity it is observed that accidents are very less in occurrence with an Odds Ratio (-0.455). This is observed in during Also with respect to Confidence Interval (CI) the distribution is not much skewed. c) Swipe end collision type n 11 = 4; n 1 2 =38; n 21 =83; n 22 =5458 odds ratio = n 11 x n 22 = 4 x 5458 = 6.92 =n 12 x n 21 = 38 x 83 Odds ratio = exp (β 1 ) where exp (β 1 ) = 6.92 β 1 = log (6.92) = Confidence Interval = Exp {β 1 } ± Ƶ 1 - δ x SE (β 1 ) SE (β 1 ) = = = Confidence Interval = exp {β 1 } ± Ƶ 1 - δ x SE (β 1 ) = exp {(0.840) ± (1.96) x (0.537)} = exp { (0.840) ± (1.052)} = exp {1.892, } = (6.632, ) From the above calculations it is observed that the Severity of Swipe end accidents is assumed 84 percent during indicating there are good amount of Swipe end accidents taken place. With respect to the Confidence Interval (CI) the Swipe end accidents are skewed towards right side of the normal curve.a Cross Tabulation between Severity of accident and the type of collision is shown in table 5 and its chi-square test results are shown in table 6 71 P a g e
12 Table 5 Cross tabulation between Severity & Types of Collision Head on Rear end yes no yes no Severity Fatal non fatal Count Expected Count Count Expected Count Count Expected Count Severity fatal non fatal Count Expected Count Count Expected Count Count Expected Count Severity fatal non fatal Swipe yes no Count Expected Count Count Expected Count Count Expected Count Table 6 Pearson Chi-Square Tests Results for severity & type of collision Type of Collision Value df Head on Severity.101 a Asymp. Sig. (2-sided) Exact Sig. (2-sided) Not significant Exact Sig. (1-sided) Rear end on Severity a 1.11 Significant Swipe on Severity a Significant 72 P a g e
13 VI. CONCLUSIONS The following conclusions can be drawn based on the present data It is observed that among all categories of vehicles, buses comprised the single highest number of involvement in accidents. This suggests that some more studies should be undertaken in the future to investigate the possible causes of involvement of buses in accidents in order to find appropriate remedial measures. This would in turn help to improve the overall road safety situation in Hyderabad City More number of accidents is occurred in central zone compare to the other four zones. Heavy vehicles and were major cause of accidents. Inadequate shoulder width forcing the heavy vehicles to come on to the carriage way there by conflicting with the traffic. More number of non fatal accidents are occurred in the city because of reduction in the journey speed. Most of accidents occurred during day time. More number of accidents occurred due to the driver s fault Highest numbers of accidents have occurred Arterial roads. Swipe & Rear end accidents are more significant for non fatal accidents occurrence in the city. Swipe end, Rear end and Head on collision is evaluated using the logistic regression. Odds against Fatal to Non Fatal were evaluated and found those rear end swipes are significant for non fatal accidents. REFERENCES 1. Accidental Deaths and Suicides in India 1996, 1997 and 1998, published by the National Motor transport statistics of India. Ministry of surface transport. New Delhi. ( ). 2. Clark,W.C., Greenberg, D.B., (1971) Effect of stress, knowledge of results, and proactive inhibition on verbal recognition memory (d_) and response criterion (Lx). J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 17, Andreassen, D. linking (1985) Deaths with vehicles and population. Traffic Engineering & Control 26(11): pp Dinesh Mohan. (1985) an analysis of road traffic fatalities in Delhi, India. Accident Analysis & Prevention 17(1): pp Baviskar, S.B, (1999) Road accidents in Nashik Municipal Corporation Area: A Case Study, Indian Journal of Transport Management, vol. 23(9), pp Al-Ghamdi, A.S. (2002) Using Logistic Regression to Estimate the Influence of Accident Factors on Accident Severity, Accident Analysis and Prevention, Vol. 34, Dissanayake, S., Lu, J., Analysis of severity of young driver crashes, sequential binary logistic regression modeling. Journal of the Transportation Research Board 1784, Beede, K.E., Kass, S.J., (2006) Engrossed in conversation: the impact of cell phones on simulated driving performance in Accident Analysis Prevention 38, Chang, H., Yeh, T., Risk factors to driver fatalities in single-vehicle crashes: comparisons between non-motorcycle drivers and motorcyclists. Journal of Transportation Engineering 132(3), Crime Records Bureau, Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India, New Delhi. 73 P a g e
Development of Models for Crash Prediction and Collision Estimation- A Case Study for Hyderabad City
 Development of Models for Crash Prediction and Collision Estimation- A Case Study for Hyderabad City V. Niveditha, A. Ramesh 2 and M. Kumar 3 Received: 27.10. 2015 Accepted: 15.02.2016 Abstract Road traffic
Development of Models for Crash Prediction and Collision Estimation- A Case Study for Hyderabad City V. Niveditha, A. Ramesh 2 and M. Kumar 3 Received: 27.10. 2015 Accepted: 15.02.2016 Abstract Road traffic
ANALYSIS OF ACCIDENT SURVEY ON PEDESTRIANS ON NATIONAL HIGHWAY 16 USING STATISTICAL METHODS
 ANALYSIS OF ACCIDENT SURVEY ON PEDESTRIANS ON NATIONAL HIGHWAY 16 USING STATISTICAL METHODS K.SWETHA Assistant Professor Civil Department, Sai Ganapati Engineering College, JNTUK, Visakhapatnam, India,
ANALYSIS OF ACCIDENT SURVEY ON PEDESTRIANS ON NATIONAL HIGHWAY 16 USING STATISTICAL METHODS K.SWETHA Assistant Professor Civil Department, Sai Ganapati Engineering College, JNTUK, Visakhapatnam, India,
Chapter 5 DATA COLLECTION FOR TRANSPORTATION SAFETY STUDIES
 Chapter 5 DATA COLLECTION FOR TRANSPORTATION SAFETY STUDIES 5.1 PURPOSE (1) The purpose of the Traffic Safety Studies chapter is to provide guidance on the data collection requirements for conducting a
Chapter 5 DATA COLLECTION FOR TRANSPORTATION SAFETY STUDIES 5.1 PURPOSE (1) The purpose of the Traffic Safety Studies chapter is to provide guidance on the data collection requirements for conducting a
INTERSECTION SAFETY RESEARCH IN CRACOW UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
 12 Marian TRACZ, Andrzej TARKO, Stanislaw GACA Cracow University of Technology INTERSECTION SAFETY RESEARCH IN CRACOW UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY 1. Trends in traffic safety in Poland Research activity in
12 Marian TRACZ, Andrzej TARKO, Stanislaw GACA Cracow University of Technology INTERSECTION SAFETY RESEARCH IN CRACOW UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY 1. Trends in traffic safety in Poland Research activity in
STUDY AND ANALYSIS OF ACCIDENTS ON NH 71-A
 STUDY AND ANALYSIS OF ACCIDENTS ON NH 71-A SARANSH Department of Civil Engineering Institute of technology and science Bhiwani S.S KAZAL Department of Civil Engineering. Institute of technology and science
STUDY AND ANALYSIS OF ACCIDENTS ON NH 71-A SARANSH Department of Civil Engineering Institute of technology and science Bhiwani S.S KAZAL Department of Civil Engineering. Institute of technology and science
IDENTIFICATION OF BLACKSPOT REGION ALONG ANANDAPURAM TO ANAKAPALLI STRECH VIA SH-38
 IDENTIFICATION OF BLACKSPOT REGION ALONG ANANDAPURAM TO ANAKAPALLI STRECH VIA SH-38 S.Naveen Kumar 1,O.Ganesh Kumar 2,K.Swetha 3 1,2,3 Assistant Professor,Department of Civil Engineering, Sai Ganapathi
IDENTIFICATION OF BLACKSPOT REGION ALONG ANANDAPURAM TO ANAKAPALLI STRECH VIA SH-38 S.Naveen Kumar 1,O.Ganesh Kumar 2,K.Swetha 3 1,2,3 Assistant Professor,Department of Civil Engineering, Sai Ganapathi
4/27/2016. Introduction
 EVALUATING THE SAFETY EFFECTS OF INTERSECTION SAFETY DEVICES AND MOBILE PHOTO ENFORCEMENT AT THE CITY OF EDMONTON Karim El Basyouny PhD., Laura Contini M.Sc. & Ran Li, M.Sc. City of Edmonton Office of
EVALUATING THE SAFETY EFFECTS OF INTERSECTION SAFETY DEVICES AND MOBILE PHOTO ENFORCEMENT AT THE CITY OF EDMONTON Karim El Basyouny PhD., Laura Contini M.Sc. & Ran Li, M.Sc. City of Edmonton Office of
1. Introduction. 2. Survey Method. Volume 6 Issue 5, May Licensed Under Creative Commons Attribution CC BY
 A Study on Performance of an Urban Arterial Corridor Guggilla Raju 1, Rontala Ashwini 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, GCET 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering,
A Study on Performance of an Urban Arterial Corridor Guggilla Raju 1, Rontala Ashwini 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, GCET 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering,
SAFETY EVALUATION OF AN UNCONTROLLED
 SAFETY EVALUATION OF AN UNCONTROLLED INTERSECTION USING SURROGATE SAFETY MEASURES By S. Shekhar Babu Research scholar (Ext) IITB Asso Prof CME Pune Prof. P. Vedagiri Asst Prof Dept of civil Engg IIT Bombay
SAFETY EVALUATION OF AN UNCONTROLLED INTERSECTION USING SURROGATE SAFETY MEASURES By S. Shekhar Babu Research scholar (Ext) IITB Asso Prof CME Pune Prof. P. Vedagiri Asst Prof Dept of civil Engg IIT Bombay
Planning and Design of Proposed ByPass Road connecting Kalawad Road to Gondal Road, Rajkot - Using Autodesk Civil 3D Software.
 Planning and Design of Proposed ByPass Road connecting Kalawad Road to Gondal Road, Rajkot - Using Autodesk Civil 3D Software. 1 Harshil S. Shah, 2 P.A.Shinkar 1 M.E. Student(Transportation Engineering),
Planning and Design of Proposed ByPass Road connecting Kalawad Road to Gondal Road, Rajkot - Using Autodesk Civil 3D Software. 1 Harshil S. Shah, 2 P.A.Shinkar 1 M.E. Student(Transportation Engineering),
ARE SIGNALIZED INTERSECTIONS WITH CROSSWALKS SAFER IN INDIA? A STUDY BASED ON SAFETY ANALYSIS USING VIDEO DATA
 ARE SIGNALIZED INTERSECTIONS WITH CROSSWALKS SAFER IN INDIA? A STUDY BASED ON SAFETY ANALYSIS USING VIDEO DATA By Marisamynathan S Research Scholar & Dr. P. Vedagiri Associate Professor Indian Institute
ARE SIGNALIZED INTERSECTIONS WITH CROSSWALKS SAFER IN INDIA? A STUDY BASED ON SAFETY ANALYSIS USING VIDEO DATA By Marisamynathan S Research Scholar & Dr. P. Vedagiri Associate Professor Indian Institute
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET), ISSN (Print), AND TECHNOLOGY (IJCIET)
 INTERNATIONAL ISSN 0976 6316(Online), Volume JOURNAL 5, Issue 6, June (2014), OF pp. 16-24 CIVIL IAEME ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (IJCIET) ISSN 0976 6308 (Print) ISSN 0976 6316(Online) Volume 5, Issue
INTERNATIONAL ISSN 0976 6316(Online), Volume JOURNAL 5, Issue 6, June (2014), OF pp. 16-24 CIVIL IAEME ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (IJCIET) ISSN 0976 6308 (Print) ISSN 0976 6316(Online) Volume 5, Issue
Road Crash Analysis and Alleviation Measures
 Road Crash Analysis and Alleviation Measures R. Nirmala #1 1 Department of Civil Engineering, Sathyabama University, Chennai-119, India 1 nirmala.civil@sathyabamauniversity.ac.in Abstract Now-a days there
Road Crash Analysis and Alleviation Measures R. Nirmala #1 1 Department of Civil Engineering, Sathyabama University, Chennai-119, India 1 nirmala.civil@sathyabamauniversity.ac.in Abstract Now-a days there
Introduction 4/28/ th International Conference on Urban Traffic Safety April 25-28, 2016 EDMONTON, ALBERTA, CANADA
 4/28/2016 EVALUATING THE SAFETY EFFECTS OF INTERSECTION SAFETY DEVICES AND MOBILE PHOTO ENFORCEMENT AT THE CITY OF EDMONTON Karim El Basyouny PhD., Laura Contini M.Sc. & Ran Li, M.Sc. City of Edmonton
4/28/2016 EVALUATING THE SAFETY EFFECTS OF INTERSECTION SAFETY DEVICES AND MOBILE PHOTO ENFORCEMENT AT THE CITY OF EDMONTON Karim El Basyouny PhD., Laura Contini M.Sc. & Ran Li, M.Sc. City of Edmonton
ENGINEERING DESIGN STANDARDS TO ENSURE ROAD SAFETY: EXPERIENCES FROM INDIA
 ENGINEERING DESIGN STANDARDS TO ENSURE ROAD SAFETY: EXPERIENCES FROM INDIA Atul Kumar 1 ABSTRACT The primary goal of designing roads with adequate standards is to achieve a safer transport facility for
ENGINEERING DESIGN STANDARDS TO ENSURE ROAD SAFETY: EXPERIENCES FROM INDIA Atul Kumar 1 ABSTRACT The primary goal of designing roads with adequate standards is to achieve a safer transport facility for
Identification and Improvement of Accident Black Spots on N.H.- 3 District Una, Himachal Pradesh A Case Study
 Identification and Improvement of Accident Black Spots on N.H.- 3 District Una, Himachal Pradesh A Case Study Vivek Assist. Professor, Civil Engineering, Lovely Professional University Phagwara, India
Identification and Improvement of Accident Black Spots on N.H.- 3 District Una, Himachal Pradesh A Case Study Vivek Assist. Professor, Civil Engineering, Lovely Professional University Phagwara, India
VRU Safety & Traffic Calming Measures in Urban & Rural Areas
 VRU Safety & Traffic Calming Measures in Urban & Rural Areas 2 What is Traffic Calming? Road engineering approaches aimed at bringing the design of the road in accordance with the desired speeds of the
VRU Safety & Traffic Calming Measures in Urban & Rural Areas 2 What is Traffic Calming? Road engineering approaches aimed at bringing the design of the road in accordance with the desired speeds of the
BUILDING CHINARAP. Zhang Tiejun Research Institute of Highway (RIOH) Beijing, China
 BUILDING CHINARAP Zhang Tiejun Research Institute of Highway (RIOH) Beijing, China E-mail: tj.zhang@rioh.cn Greg Smith International Road Assessment Programme (irap) Beijing, China E-mail: greg.smith@irap.org
BUILDING CHINARAP Zhang Tiejun Research Institute of Highway (RIOH) Beijing, China E-mail: tj.zhang@rioh.cn Greg Smith International Road Assessment Programme (irap) Beijing, China E-mail: greg.smith@irap.org
A STUDY ON GAP-ACCEPTANCE OF UNSIGNALIZED INTERSECTION UNDER MIXED TRAFFIC CONDITIONS
 A STUDY ON GAP-ACCEPTANCE OF UNSIGNALIZED INTERSECTION UNDER MIXED TRAFFIC CONDITIONS S.Siva Gowri Prasad 1, Ramesh Surisetty 2, Suresh Kumar ch 3 1 Assistant professor, Department, of Civil Engineering,
A STUDY ON GAP-ACCEPTANCE OF UNSIGNALIZED INTERSECTION UNDER MIXED TRAFFIC CONDITIONS S.Siva Gowri Prasad 1, Ramesh Surisetty 2, Suresh Kumar ch 3 1 Assistant professor, Department, of Civil Engineering,
International Journal of Advance Research in Engineering, Science & Technology
 Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.542 International Journal of Advance Research in Engineering, Science & Technology e-issn: 2393-9877, p-issn: 2394-2444 Volume 4, Issue 4, April-2017 Planning & Design Of New By-pass
Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.542 International Journal of Advance Research in Engineering, Science & Technology e-issn: 2393-9877, p-issn: 2394-2444 Volume 4, Issue 4, April-2017 Planning & Design Of New By-pass
ANALYSIS OF SIDE FRICTION ON URBAN ARTERIALS
 Transport and Telecommunication Vol. 19, no. 1, 18 Transport and Telecommunication, 18, volume 19, no. 1, 21 Transport and Telecommunication Institute, Lomonosova 1, Riga, LV-119, Latvia DOI 1.2478/ttj-18-3
Transport and Telecommunication Vol. 19, no. 1, 18 Transport and Telecommunication, 18, volume 19, no. 1, 21 Transport and Telecommunication Institute, Lomonosova 1, Riga, LV-119, Latvia DOI 1.2478/ttj-18-3
Pedestrian Safety in Cities
 Pedestrian Safety in Cities Priorities for India Geetam Tiwari MoUD Chair Professor, Coordinator, TRIPP Indian Institute of Technology Delhi, India URBAN MOBILITY INDIA 2013 IIT Delhi 2013 RTI in Urban
Pedestrian Safety in Cities Priorities for India Geetam Tiwari MoUD Chair Professor, Coordinator, TRIPP Indian Institute of Technology Delhi, India URBAN MOBILITY INDIA 2013 IIT Delhi 2013 RTI in Urban
ROAD SAFETY AUDIT OF A RURAL ROAD
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 8, Issue 4, April 2017, pp. 752-761, Article ID: IJCIET_08_04_087 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=8&itype=4
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 8, Issue 4, April 2017, pp. 752-761, Article ID: IJCIET_08_04_087 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=8&itype=4
Road Accident Analysis and Identify the black spot location On State Highway-5 (Halol-Godhra Section)
 Road Accident Analysis and Identify the black spot location On State Highway-5 (Halol-Godhra Section) 1 Shah Dhruvit, 2 Shah Pranay M. 1 M.E civil(transportation), 2 M.E civil, P.h.d.(pursuing) 1 Tatva
Road Accident Analysis and Identify the black spot location On State Highway-5 (Halol-Godhra Section) 1 Shah Dhruvit, 2 Shah Pranay M. 1 M.E civil(transportation), 2 M.E civil, P.h.d.(pursuing) 1 Tatva
Analysis of Causal Factors of Accidents near Mahipalpur Junction on NH-8 in Delhi
 Analysis of Causal Factors of Accidents near Mahipalpur Junction on NH-8 in Delhi Nirpinder Jain 1, Bharat Bhushan Jindal 2 1, 2 (Research Scholar, IK Gujral Punjab Technical University, Kapurthala, Punjab,
Analysis of Causal Factors of Accidents near Mahipalpur Junction on NH-8 in Delhi Nirpinder Jain 1, Bharat Bhushan Jindal 2 1, 2 (Research Scholar, IK Gujral Punjab Technical University, Kapurthala, Punjab,
Title of the proposed project Development of a Toolbox for Evaluation and Identification of Urban Road Safety Improvement Measures
 Centre of Excellence (CoE) in Urban Transport Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Madras Title of the proposed project Development of a Toolbox for Evaluation and Identification of Urban Road Safety Improvement
Centre of Excellence (CoE) in Urban Transport Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Madras Title of the proposed project Development of a Toolbox for Evaluation and Identification of Urban Road Safety Improvement
UG Student, Department of Civil Engineering, MITS, Ernakulam 5. Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, MITS, Ernakulam
 BLACK SPOT IDENTIFICATION USING ACCIDENT SEVERITY INDEX METHOD M Mohammed Fayaz 1, Mrudula S P 2, Sarah Jaison George 3, Sherin P Yoyak 4, Serin Sara Roy 5 1,2,3,4 UG Student, Department of Civil Engineering,
BLACK SPOT IDENTIFICATION USING ACCIDENT SEVERITY INDEX METHOD M Mohammed Fayaz 1, Mrudula S P 2, Sarah Jaison George 3, Sherin P Yoyak 4, Serin Sara Roy 5 1,2,3,4 UG Student, Department of Civil Engineering,
Potential Factors Affecting Roadway Departure Crashes in Oahu, Hawaii
 Potential Factors Affecting Roadway Departure Crashes in Oahu, Hawaii Pasha Hashemi (1), Adrian Ricardo Archilla(2) (1)Graduate Research Assistant, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University
Potential Factors Affecting Roadway Departure Crashes in Oahu, Hawaii Pasha Hashemi (1), Adrian Ricardo Archilla(2) (1)Graduate Research Assistant, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University
Analyses and statistics on the frequency and the incidence of traffic accidents within Dolj County
 UNIVERSITY OF PITESTI SCIENTIFIC BULLETIN Faculty of Mechanics and Technology AUTOMOTIVE series, year XXIV, no. 28 Analyses and statistics on the frequency and the incidence of traffic accidents within
UNIVERSITY OF PITESTI SCIENTIFIC BULLETIN Faculty of Mechanics and Technology AUTOMOTIVE series, year XXIV, no. 28 Analyses and statistics on the frequency and the incidence of traffic accidents within
Impact of Work Zone on Traffic Accident Characteristics of Kochi
 Impact of Work Zone on Traffic Accident Characteristics of Kochi Chinnu Gopakumar M Tech Student, Civil Department, TocH Institute of Science and Technology, Ernakulam, India Aby Varghese Assistant Professor,
Impact of Work Zone on Traffic Accident Characteristics of Kochi Chinnu Gopakumar M Tech Student, Civil Department, TocH Institute of Science and Technology, Ernakulam, India Aby Varghese Assistant Professor,
Title: Modeling Crossing Behavior of Drivers and Pedestrians at Uncontrolled Intersections and Mid-block Crossings
 Title: Modeling Crossing Behavior of Drivers and Pedestrians at Uncontrolled Intersections and Mid-block Crossings Objectives The goal of this study is to advance the state of the art in understanding
Title: Modeling Crossing Behavior of Drivers and Pedestrians at Uncontrolled Intersections and Mid-block Crossings Objectives The goal of this study is to advance the state of the art in understanding
Road Safety Analysis A Case Study of National Highway 1-A in India. Authors
 Road Safety Analysis A Case Study of National Highway 1-A in India Authors M. S. Mir & F. A. Mir (Civil Engineering Department, NIT Srinagar India) Presentation by Mohammad Shafi Mir INTRODUCTION Road
Road Safety Analysis A Case Study of National Highway 1-A in India Authors M. S. Mir & F. A. Mir (Civil Engineering Department, NIT Srinagar India) Presentation by Mohammad Shafi Mir INTRODUCTION Road
Characteristics of Traffic Accidents in Highway Work Zones
 Characteristics of Traffic Accidents in Highway Work Zones A DETAILED ANALYSIS OF WORK ZONE ACCIDENTS REPORTED ON NEW YORK STATE DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION CONSTRUCTION PROJECTS ESTABLISHED THE PREDOMINANT
Characteristics of Traffic Accidents in Highway Work Zones A DETAILED ANALYSIS OF WORK ZONE ACCIDENTS REPORTED ON NEW YORK STATE DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION CONSTRUCTION PROJECTS ESTABLISHED THE PREDOMINANT
CAPACITY ESTIMATION OF URBAN ROAD IN BAGHDAD CITY: A CASE STUDY OF PALESTINE ARTERIAL ROAD
 VOL. 13, NO. 21, NOVEMBER 218 ISSN 1819-668 26-218 Asian Research Publishing Network (ARPN). All rights reserved. CAPACITY ESTIMATION OF URBAN ROAD IN BAGHDAD CITY: A CASE STUDY OF PALESTINE ARTERIAL ROAD
VOL. 13, NO. 21, NOVEMBER 218 ISSN 1819-668 26-218 Asian Research Publishing Network (ARPN). All rights reserved. CAPACITY ESTIMATION OF URBAN ROAD IN BAGHDAD CITY: A CASE STUDY OF PALESTINE ARTERIAL ROAD
Safety Performance of Two-Way Stop-Controlled Expressway Intersections
 Safety Performance of Two-Way Stop-Controlled Expressway Intersections UNDERSTANDING THE SAFETY PERFORMANCE OF TWO-WAY STOP- CONTROLLED RURAL EXPRESSWAY INTERSECTIONS WILL HELP CORRIDOR PLANNERS AND DESIGNERS
Safety Performance of Two-Way Stop-Controlled Expressway Intersections UNDERSTANDING THE SAFETY PERFORMANCE OF TWO-WAY STOP- CONTROLLED RURAL EXPRESSWAY INTERSECTIONS WILL HELP CORRIDOR PLANNERS AND DESIGNERS
WHY AND WHEN PEDESTRIANS WALK ON CARRIAGEWAY IN PRESENCE OF FOOTPATH? A BEHAVIORAL ANALYSIS IN MIXED TRAFFIC SCENARIO OF INDIA.
 WHY AND WHEN PEDESTRIANS WALK ON CARRIAGEWAY IN PRESENCE OF FOOTPATH? A BEHAVIORAL ANALYSIS IN MIXED TRAFFIC SCENARIO OF INDIA. Sobhana Patnaik, Mukti Advani, Purnima Parida. There are reasons for walking
WHY AND WHEN PEDESTRIANS WALK ON CARRIAGEWAY IN PRESENCE OF FOOTPATH? A BEHAVIORAL ANALYSIS IN MIXED TRAFFIC SCENARIO OF INDIA. Sobhana Patnaik, Mukti Advani, Purnima Parida. There are reasons for walking
A Traffic Operations Method for Assessing Automobile and Bicycle Shared Roadways
 A Traffic Operations Method for Assessing Automobile and Bicycle Shared Roadways A Thesis Proposal By James A. Robertson Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
A Traffic Operations Method for Assessing Automobile and Bicycle Shared Roadways A Thesis Proposal By James A. Robertson Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
Relationship of Road Lane Width to Safety for Urban and Suburban Arterials
 Relationship of Road Lane Width to Safety for Urban and Suburban Arterials Phd. Alma AFEZOLLI Polytechnic University of Tirana Construction and Infrastructure Department of Civil Engineering Faculty Tirana,
Relationship of Road Lane Width to Safety for Urban and Suburban Arterials Phd. Alma AFEZOLLI Polytechnic University of Tirana Construction and Infrastructure Department of Civil Engineering Faculty Tirana,
Identification of Accidental Locations on NH-10 Highways
 Volume-5, Issue-3, June-2015 International Journal of Engineering and Management Research Page Number: 732-737 Identification of Accidental Locations on NH-10 Highways Rina 1, S.S Kajal 2 1 Student, Civil
Volume-5, Issue-3, June-2015 International Journal of Engineering and Management Research Page Number: 732-737 Identification of Accidental Locations on NH-10 Highways Rina 1, S.S Kajal 2 1 Student, Civil
Crash Patterns in Western Australia. Kidd B., Main Roads Western Australia Willett P., Traffic Research Services
 Crash Patterns in Western Australia Kidd B., Main Roads Western Australia Willett P., Traffic Research Services Abstract Examination of crash patterns is one way of identifying key factors on which focus
Crash Patterns in Western Australia Kidd B., Main Roads Western Australia Willett P., Traffic Research Services Abstract Examination of crash patterns is one way of identifying key factors on which focus
1.3.4 CHARACTERISTICS OF CLASSIFICATIONS
 Geometric Design Guide for Canadian Roads 1.3.4 CHARACTERISTICS OF CLASSIFICATIONS The principal characteristics of each of the six groups of road classifications are described by the following figure
Geometric Design Guide for Canadian Roads 1.3.4 CHARACTERISTICS OF CLASSIFICATIONS The principal characteristics of each of the six groups of road classifications are described by the following figure
INFLUENCE OF TRAFFIC FLOW SEPARATION DEVICES ON ROAD SAFETY IN BRAZIL S MULTILANE HIGHWAYS
 INFLUENCE OF TRAFFIC FLOW SEPARATION DEVICES ON ROAD SAFETY IN BRAZIL S MULTILANE HIGHWAYS Gabriel Andrade Lanzaro Universidade de Brasília Departamento de Engenharia Civil e Ambiental, Faculdade de Tecnologia,
INFLUENCE OF TRAFFIC FLOW SEPARATION DEVICES ON ROAD SAFETY IN BRAZIL S MULTILANE HIGHWAYS Gabriel Andrade Lanzaro Universidade de Brasília Departamento de Engenharia Civil e Ambiental, Faculdade de Tecnologia,
Analysis Of Road Accidents National Highway-5
 Volume: 2 Issue: 2 Apr,206,ISSN_NO: 2320-723X Analysis Of Road Accidents National Highway-5 Dr.A.S.kanagalakshmi*, M.dinesh**, M.saikrishna raju**, Jishar jaffry**, Syed Ashish basha** *professor, Dept
Volume: 2 Issue: 2 Apr,206,ISSN_NO: 2320-723X Analysis Of Road Accidents National Highway-5 Dr.A.S.kanagalakshmi*, M.dinesh**, M.saikrishna raju**, Jishar jaffry**, Syed Ashish basha** *professor, Dept
People killed and injured per million hours spent travelling, Motorcyclist Cyclist Driver Car / van passenger
 Cyclists CRASH FACTSHEET 27 CRASH STATISTICS FOR THE YEAR ENDED 31 DEC 26 Prepared by Strategy and Sustainability, Ministry of Transport Cyclists have a number of risk factors that do not affect car drivers.
Cyclists CRASH FACTSHEET 27 CRASH STATISTICS FOR THE YEAR ENDED 31 DEC 26 Prepared by Strategy and Sustainability, Ministry of Transport Cyclists have a number of risk factors that do not affect car drivers.
Post impact trajectory of vehicles at rural intersections
 Post impact trajectory of vehicles at rural intersections Doecke SD., Woolley JE. and Mackenzie JR. Centre for Automotive Safety Research Abstract This report describes the path of vehicles after a collision
Post impact trajectory of vehicles at rural intersections Doecke SD., Woolley JE. and Mackenzie JR. Centre for Automotive Safety Research Abstract This report describes the path of vehicles after a collision
Safety and Design Alternatives for Two-Way Stop-Controlled Expressway Intersections
 Safety and Design Alternatives for Two-Way Stop-Controlled Expressway Intersections Thomas H. Maze Center for Transportation Research and Education Iowa State University 2901 South Loop Drive, Suite 3100
Safety and Design Alternatives for Two-Way Stop-Controlled Expressway Intersections Thomas H. Maze Center for Transportation Research and Education Iowa State University 2901 South Loop Drive, Suite 3100
A study on Nh-11 to find out the causes and High accident Zone between Jaipur to Sikar
 A study on Nh-11 to find out the causes and High accident Zone between Jaipur to Sikar Shelendra Kumar 1, Hemant Kumar Agrawal 2 Assistant Professor Civil engineering department Sobhasaria engineering
A study on Nh-11 to find out the causes and High accident Zone between Jaipur to Sikar Shelendra Kumar 1, Hemant Kumar Agrawal 2 Assistant Professor Civil engineering department Sobhasaria engineering
Road Accidental Analysis: A Case Study of Rajasthan State, India
 IOSR Journal Of Humanities And Social Science (IOSR-JHSS) Volume 19, Issue 5, Ver. V (May. 2014), PP 34-40 e-issn: 2279-0837, p-issn: 2279-0845. Road Accidental Analysis: A Case Study of Rajasthan State,
IOSR Journal Of Humanities And Social Science (IOSR-JHSS) Volume 19, Issue 5, Ver. V (May. 2014), PP 34-40 e-issn: 2279-0837, p-issn: 2279-0845. Road Accidental Analysis: A Case Study of Rajasthan State,
Truck Climbing Lane Traffic Justification Report
 ROUTE 7 (HARRY BYRD HIGHWAY) WESTBOUND FROM WEST MARKET STREET TO ROUTE 9 (CHARLES TOWN PIKE) Truck Climbing Lane Traffic Justification Report Project No. 6007-053-133, P 101 Ι UPC No. 58599 Prepared by:
ROUTE 7 (HARRY BYRD HIGHWAY) WESTBOUND FROM WEST MARKET STREET TO ROUTE 9 (CHARLES TOWN PIKE) Truck Climbing Lane Traffic Justification Report Project No. 6007-053-133, P 101 Ι UPC No. 58599 Prepared by:
Accident data analysis using Statistical methods A case study of Indian Highway
 Accident data analysis using Statistical methods A case study of Indian Highway Rahul Badgujar 1, Priyam Mishra 2, Mayank Chandra 3, Sayali Sandbhor 4, Humera Khanum 5 1,2,3 Undergraduate scholars, Department
Accident data analysis using Statistical methods A case study of Indian Highway Rahul Badgujar 1, Priyam Mishra 2, Mayank Chandra 3, Sayali Sandbhor 4, Humera Khanum 5 1,2,3 Undergraduate scholars, Department
THE DEVELOPMENT OF MALAYSIAN HIGHWAY RAIL LEVEL CROSSING SAFETY SYSTEMS: A PROPOSED RESEARCH FRAMEWORK. Siti Zaharah Ishak
 THE DEVELOPMENT OF MALAYSIAN HIGHWAY RAIL LEVEL CROSSING SAFETY SYSTEMS: A PROPOSED RESEARCH FRAMEWORK Siti Zaharah Ishak Transport System Centre, School of Natural & Built Environments, University Of
THE DEVELOPMENT OF MALAYSIAN HIGHWAY RAIL LEVEL CROSSING SAFETY SYSTEMS: A PROPOSED RESEARCH FRAMEWORK Siti Zaharah Ishak Transport System Centre, School of Natural & Built Environments, University Of
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW
 CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW 2.1 Introduction This chapter presents some background information of the available literature related to the development of accident rates, accident models and accident statistic
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW 2.1 Introduction This chapter presents some background information of the available literature related to the development of accident rates, accident models and accident statistic
BLACK SPOTS MANAGEMENT - SLOVENIAN EXPERIENCE
 BLACK SPOTS MANAGEMENT - SLOVENIAN EXPERIENCE PhD Marko Renčelj, Assoc. Prof. Matjaž Šraml, University of Maribor, Faculty for Civil Engineering X International Symposium "ROAD ACCIDENTS PREVENTION 2010"
BLACK SPOTS MANAGEMENT - SLOVENIAN EXPERIENCE PhD Marko Renčelj, Assoc. Prof. Matjaž Šraml, University of Maribor, Faculty for Civil Engineering X International Symposium "ROAD ACCIDENTS PREVENTION 2010"
Controlling Traffic by Designing Signal at Intersection of Vidisha Sachin Jat 1 Mr. S.S. Goliya 2 Sachin Nagayach 3 Rohit Gurjar 3
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 05, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Controlling Traffic by Designing Signal at Intersection of Vidisha Sachin Jat 1 Mr. S.S.
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 05, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Controlling Traffic by Designing Signal at Intersection of Vidisha Sachin Jat 1 Mr. S.S.
OVERVIEW OF CURRENT ROAD SAFETY SITUATION IN MALAYSIA
 OVERVIEW OF CURRENT ROAD SAFETY SITUATION IN MALAYSIA Mohamad Nizam Mustafa Highway Planning Unit Road Safety Section Ministry of Works Jalan Sultan Salahuddin 50580 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia ABSTRACT Road
OVERVIEW OF CURRENT ROAD SAFETY SITUATION IN MALAYSIA Mohamad Nizam Mustafa Highway Planning Unit Road Safety Section Ministry of Works Jalan Sultan Salahuddin 50580 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia ABSTRACT Road
Napier City road trauma for Napier City. Road casualties Estimated social cost of crashes* Major road safety issues.
 ISSN 1176-841X July 25 Land Transport New Zealand has prepared this road safety issues report. It is based on reported crash data and trends for the 2 24 period. The intent of the report is to highlight
ISSN 1176-841X July 25 Land Transport New Zealand has prepared this road safety issues report. It is based on reported crash data and trends for the 2 24 period. The intent of the report is to highlight
IJRASET: All Rights are Reserved
 Study on Road Accidents and Safety Measures along Selected Roads in Tiruchirappalli, India Dr. G. Nagasubramaniyan 1, N. Satyanarayan 2 1 Associate Professor, Dept. of Humanities and Social Sciences, National
Study on Road Accidents and Safety Measures along Selected Roads in Tiruchirappalli, India Dr. G. Nagasubramaniyan 1, N. Satyanarayan 2 1 Associate Professor, Dept. of Humanities and Social Sciences, National
Pedestrian Accident Prediction Model for Rural Road
 Pedestrian Accident Prediction Model for Rural Road A.K.Sharma Civil Engineering Department RCOEM Nagpur, India sharmaakrkn@yahoo.co.in V.S.Landge Civil Engineering Department VNIT Nagpur, India vslandge@rediffmail.com
Pedestrian Accident Prediction Model for Rural Road A.K.Sharma Civil Engineering Department RCOEM Nagpur, India sharmaakrkn@yahoo.co.in V.S.Landge Civil Engineering Department VNIT Nagpur, India vslandge@rediffmail.com
Deaths/injuries in motor vehicle crashes per million hours spent travelling, July 2007 June 2011 (All ages) Mode of travel
 Cyclists CRASH STATISTICS FOR THE YEAR ENDED 31 DECEMBER 211 Prepared by the Ministry of Transport CRASH FACTSHEET 212 Cyclists have a number of risk factors that do not affect car drivers. The main risk
Cyclists CRASH STATISTICS FOR THE YEAR ENDED 31 DECEMBER 211 Prepared by the Ministry of Transport CRASH FACTSHEET 212 Cyclists have a number of risk factors that do not affect car drivers. The main risk
(HIGHWAY GEOMETRIC DESIGN -1)
 LECTURE HOUR-19 TE-1(10CV56) UNIT-3 (HIGHWAY GEOMETRIC DESIGN -1) Width of carriage way: Width of the carriage way or the width of the pavement depends on the width of the traffic lane and number of lanes.
LECTURE HOUR-19 TE-1(10CV56) UNIT-3 (HIGHWAY GEOMETRIC DESIGN -1) Width of carriage way: Width of the carriage way or the width of the pavement depends on the width of the traffic lane and number of lanes.
20 meters beyond the circulating part of the roundabout. Includes pedestrian and
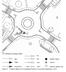 Table A1 Roundabout segments Roundabout segment Entry lane Segment 1 Segment 2 Circulatory road Segment 3 Description 20 100 meters off the roundabout. Oncoming traffic, queues associated with congestion.
Table A1 Roundabout segments Roundabout segment Entry lane Segment 1 Segment 2 Circulatory road Segment 3 Description 20 100 meters off the roundabout. Oncoming traffic, queues associated with congestion.
For Information Only. Pedestrian Collisions (2011 to 2015) Resolution. Presented: Monday, Apr 18, Report Date Tuesday, Apr 05, 2016
 Presented To: Operations Committee For Information Only Pedestrian Collisions (0 to 0) Presented: Monday, Apr 8, 06 Report Date Tuesday, Apr 0, 06 Type: Correspondence for Information Only Resolution For
Presented To: Operations Committee For Information Only Pedestrian Collisions (0 to 0) Presented: Monday, Apr 8, 06 Report Date Tuesday, Apr 0, 06 Type: Correspondence for Information Only Resolution For
Pedestrian Level of Service at Intersections in Bhopal City
 Pedestrian Level of Service at Intersections in Bhopal City 1 Rakesh Wahane 1 M.E. Student 1 Department of Civil Engineering 1 Samrat Ashok Technological Institute Vidisha MP 464001 Abstract - This study
Pedestrian Level of Service at Intersections in Bhopal City 1 Rakesh Wahane 1 M.E. Student 1 Department of Civil Engineering 1 Samrat Ashok Technological Institute Vidisha MP 464001 Abstract - This study
Introduction Methodology Study area and data collection Results and recommendation Conclusion References
 Introduction Methodology Study area and data collection Results and recommendation Conclusion References It is formal procedure for assessing accident potential and safety performance in the provision
Introduction Methodology Study area and data collection Results and recommendation Conclusion References It is formal procedure for assessing accident potential and safety performance in the provision
SCHOOL CROSSING PROTECTION CRITERIA
 CITY OF MADISON TRAFFIC ENGINEERING SCHOOL CROSSING PROTECTION CRITERIA January 2016 Adopted as Policy on August 31, 1976, by Common Council by Amended Resolution #29,540 Amended on September 14, 1976,
CITY OF MADISON TRAFFIC ENGINEERING SCHOOL CROSSING PROTECTION CRITERIA January 2016 Adopted as Policy on August 31, 1976, by Common Council by Amended Resolution #29,540 Amended on September 14, 1976,
Lessons Learned from the Minnesota County Road Safety Plans. Richard Storm CH2M HILL
 Lessons Learned from the Minnesota County Road Safety Plans Richard Storm CH2M HILL May 21, 2014 Overview of the MN CRSP: Why Prepare Safety Plans for Local Systems? MAP-21: Requires states to address
Lessons Learned from the Minnesota County Road Safety Plans Richard Storm CH2M HILL May 21, 2014 Overview of the MN CRSP: Why Prepare Safety Plans for Local Systems? MAP-21: Requires states to address
Delay analysis due to Road side activities at Urban Arterial Road of Rajkot city
 Delay analysis due to Road side activities at Urban Arterial Road of Rajkot city Rita Bhanushali 1, Prashant Lakkad 2, Mayank Kanani 3 1Final year M.E Student, Civil Engineering Department, Atmiya Institute
Delay analysis due to Road side activities at Urban Arterial Road of Rajkot city Rita Bhanushali 1, Prashant Lakkad 2, Mayank Kanani 3 1Final year M.E Student, Civil Engineering Department, Atmiya Institute
DOT HS September Crash Factors in Intersection-Related Crashes: An On-Scene Perspective
 DOT HS 811 366 September 2010 Crash Factors in Intersection-Related Crashes: An On-Scene Perspective DISCLAIMER This publication is distributed by the U.S. Department of Transportation, National Highway
DOT HS 811 366 September 2010 Crash Factors in Intersection-Related Crashes: An On-Scene Perspective DISCLAIMER This publication is distributed by the U.S. Department of Transportation, National Highway
SCHOOL CROSSING PROTECTION CRITERIA
 CITY OF MADISON TRAFFIC ENGINEERING SCHOOL CROSSING PROTECTION CRITERIA AUGUST 1990 Adopted as Policy on August 31, 1976, by Common Council by Amended Resolution #29,540 Amended on September 14, 1976,
CITY OF MADISON TRAFFIC ENGINEERING SCHOOL CROSSING PROTECTION CRITERIA AUGUST 1990 Adopted as Policy on August 31, 1976, by Common Council by Amended Resolution #29,540 Amended on September 14, 1976,
Double Pair Comparisons PART III AGE & GENDER. Age and Crash Risk. Subject & control groups Relative risk or rate. Relative Accident Involvement Ratio
 Double Pair Comparisons PART III AGE & GENDER Subject & control groups Relative risk or rate Ratio of subject to control Relative Accident Involvement Ratio Age and Crash Risk RAIR = % at-fault % not at-fault
Double Pair Comparisons PART III AGE & GENDER Subject & control groups Relative risk or rate Ratio of subject to control Relative Accident Involvement Ratio Age and Crash Risk RAIR = % at-fault % not at-fault
the Ministry of Transport is attributed as the source of the material
 Cyclists 2015 Disclaimer All reasonable endeavours are made to ensure the accuracy of the information in this report. However, the information is provided without warranties of any kind including accuracy,
Cyclists 2015 Disclaimer All reasonable endeavours are made to ensure the accuracy of the information in this report. However, the information is provided without warranties of any kind including accuracy,
Estimation of accident rate at blockspots
 2017; 3(5): 786-792 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2017; 3(5): 786-792 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 21-03-2017 Accepted: 22-04-2017 M Anvesh Kumar Assistant
2017; 3(5): 786-792 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2017; 3(5): 786-792 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 21-03-2017 Accepted: 22-04-2017 M Anvesh Kumar Assistant
Road Markings. Lecture Notes in Transportation Systems Engineering. Prof. Tom V. Mathew
 Road Markings Lecture Notes in Transportation Systems Engineering Prof. Tom V. Mathew 1 Overview The essential purpose of road markings is to guide and control traffic on a highway. They supplement the
Road Markings Lecture Notes in Transportation Systems Engineering Prof. Tom V. Mathew 1 Overview The essential purpose of road markings is to guide and control traffic on a highway. They supplement the
Overhead Pedestrian Crossings Economic Evaluation through Vehicle Operating Cost and Travel Time Savings
 OUSL Journal (2014) Vol 7, (pp77-94) Overhead Pedestrian Crossings Economic Evaluation through Vehicle Operating Cost and Travel Time Savings K. M. G. N. S. Kumara, V. K. M. Pinnagoda and K. S. Weerasekera
OUSL Journal (2014) Vol 7, (pp77-94) Overhead Pedestrian Crossings Economic Evaluation through Vehicle Operating Cost and Travel Time Savings K. M. G. N. S. Kumara, V. K. M. Pinnagoda and K. S. Weerasekera
Prediction model of cyclist s accident probability in the City of Malang
 MATEC Web of Conferences 8, 04003 (208) ISTSDC 207 https://doi.org/0.05/matecconf/208804003 Prediction model of cyclist s accident probability in the City of Malang Imma Widyawati Agustin,*, Muhammad Zainul
MATEC Web of Conferences 8, 04003 (208) ISTSDC 207 https://doi.org/0.05/matecconf/208804003 Prediction model of cyclist s accident probability in the City of Malang Imma Widyawati Agustin,*, Muhammad Zainul
The Impact of Narrow Lane on Safety of the Arterial Roads. Hyeonsup Lim
 The Impact of Narrow Lane on Safety of the Arterial Roads Hyeonsup Lim What do we know about Narrow Lane? AASHTO Green book, lane widths may vary from 10 to 12 feet for rural and urban arterials. NCHRP
The Impact of Narrow Lane on Safety of the Arterial Roads Hyeonsup Lim What do we know about Narrow Lane? AASHTO Green book, lane widths may vary from 10 to 12 feet for rural and urban arterials. NCHRP
The Corporation of the City of Sarnia. School Crossing Guard Warrant Policy
 The Corporation of the City of Sarnia School Crossing Guard Warrant Policy Table of Contents Overview And Description... 2 Role of the School Crossing Guard... 2 Definition of a Designated School Crossing...
The Corporation of the City of Sarnia School Crossing Guard Warrant Policy Table of Contents Overview And Description... 2 Role of the School Crossing Guard... 2 Definition of a Designated School Crossing...
appendix b BLOS: Bicycle Level of Service B.1 Background B.2 Bicycle Level of Service Model Winston-Salem Urban Area
 appendix b BLOS: B.1 Background Winston-Salem Urban Area Bicycle Level of Service Level of Service (LOS) is a framework that transportation professionals use to describe existing conditions (or suitability)
appendix b BLOS: B.1 Background Winston-Salem Urban Area Bicycle Level of Service Level of Service (LOS) is a framework that transportation professionals use to describe existing conditions (or suitability)
Identification and Improvement of Accidents black Spots for Mixed Traffic Streets in Developed Cities-A Case Study
 Identification and Improvement of Accidents black Spots for Mixed Traffic Streets in Developed Cities-A Case Study M.Subbareddy 1, K.S.B.Prasad 2 Department of Civil Engineering, GMRInstitute of Technology,
Identification and Improvement of Accidents black Spots for Mixed Traffic Streets in Developed Cities-A Case Study M.Subbareddy 1, K.S.B.Prasad 2 Department of Civil Engineering, GMRInstitute of Technology,
Designing for Pedestrians: An Engineering Symposium. Rutgers University March 21, 2013
 Designing for Pedestrians: An Engineering Symposium Rutgers University March 21, 2013 The Problem 2 Pedestrian Fatalities Pedestrian Fatalities by Year in US (1994-2010) 6000 5000 4000 3000 2000 1000 0
Designing for Pedestrians: An Engineering Symposium Rutgers University March 21, 2013 The Problem 2 Pedestrian Fatalities Pedestrian Fatalities by Year in US (1994-2010) 6000 5000 4000 3000 2000 1000 0
Traffic Improvement for Urban Road Intersection, Surat
 Traffic Improvement for Urban Road Intersection, Surat Sharukh Marfani 1, Dharmkumar Shihora 2, Chirag Kanthariya 3, Harshal Kansara 4 1Assistant Professor, Civil Engineering Department, F.E.T.R, Bardoli,
Traffic Improvement for Urban Road Intersection, Surat Sharukh Marfani 1, Dharmkumar Shihora 2, Chirag Kanthariya 3, Harshal Kansara 4 1Assistant Professor, Civil Engineering Department, F.E.T.R, Bardoli,
Safety Impacts: Presentation Overview
 Safety Impacts: Presentation Overview The #1 Theme How Access Management Improves Safety Conflict Points The Science of Access Management By Treatment Studies Themes for Texas Access Management Improve
Safety Impacts: Presentation Overview The #1 Theme How Access Management Improves Safety Conflict Points The Science of Access Management By Treatment Studies Themes for Texas Access Management Improve
HSIS. Association of Selected Intersection Factors With Red-Light-Running Crashes. State Databases Used SUMMARY REPORT
 HSIS HIGHWAY SAFETY INFORMATION SYSTEM The Highway Safety Information Systems (HSIS) is a multi-state safety data base that contains accident, roadway inventory, and traffic volume data for a select group
HSIS HIGHWAY SAFETY INFORMATION SYSTEM The Highway Safety Information Systems (HSIS) is a multi-state safety data base that contains accident, roadway inventory, and traffic volume data for a select group
An Analysis of the Travel Conditions on the U. S. 52 Bypass. Bypass in Lafayette, Indiana.
 An Analysis of the Travel Conditions on the U. S. 52 Bypass in Lafayette, Indiana T. B. T readway Research Assistant J. C. O ppenlander Research Engineer Joint Highway Research Project Purdue University
An Analysis of the Travel Conditions on the U. S. 52 Bypass in Lafayette, Indiana T. B. T readway Research Assistant J. C. O ppenlander Research Engineer Joint Highway Research Project Purdue University
A location model for pedestrian crossings in arterial streets
 A location model for pedestrian crossings in arterial streets B. Amini¹ & H. Ghahramani² ¹Department of Civil Engineering, International University of Imam Khomeini, Iran ²Iran University of Science and
A location model for pedestrian crossings in arterial streets B. Amini¹ & H. Ghahramani² ¹Department of Civil Engineering, International University of Imam Khomeini, Iran ²Iran University of Science and
PLANNING FOR SUSTAINABLE PEDESTRIAN INFRASTRUCTURE NALIN SINHA INITIATIVE FOR TRANSPORTATION & DEVELOPMENT PROG. (ITD), DELHI
 PLANNING FOR SUSTAINABLE PEDESTRIAN INFRASTRUCTURE NALIN SINHA INITIATIVE FOR TRANSPORTATION & DEVELOPMENT PROG. (ITD), DELHI India s Road Network 5 million kms: Total road length 2.6 mn kms: Surfaced
PLANNING FOR SUSTAINABLE PEDESTRIAN INFRASTRUCTURE NALIN SINHA INITIATIVE FOR TRANSPORTATION & DEVELOPMENT PROG. (ITD), DELHI India s Road Network 5 million kms: Total road length 2.6 mn kms: Surfaced
Analysis of Unsignalized Intersection
 International Journal of Constructive Research in Civil Engineering (IJCRCE) Volume 2, Issue 1, 2016, PP 30-36 ISSN 2454-8693 (Online) www.arcjournals.org Analysis of Unsignalized Intersection B.Ramkumar
International Journal of Constructive Research in Civil Engineering (IJCRCE) Volume 2, Issue 1, 2016, PP 30-36 ISSN 2454-8693 (Online) www.arcjournals.org Analysis of Unsignalized Intersection B.Ramkumar
Bicycle - Motor Vehicle Collisions on Controlled Access Highways in Arizona
 Bicycle - Motor Vehicle Collisions on Controlled Access Highways in Arizona Analysis from January 1, 1991 to June 30, 2002 Richard C. Moeur, PE Traffic Design Manager, Northern Region Michelle N. Bina
Bicycle - Motor Vehicle Collisions on Controlled Access Highways in Arizona Analysis from January 1, 1991 to June 30, 2002 Richard C. Moeur, PE Traffic Design Manager, Northern Region Michelle N. Bina
ROAD ACCIDENTS AND SAFETY STUDY OF RAJSHAHI CITY IN BANGLADESH
 Proceedings of the 4 th International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 218), 9~11 February 218, KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh (ISBN-978-984-4-52-6) ROAD ACCIDENTS AND SAFETY
Proceedings of the 4 th International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 218), 9~11 February 218, KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh (ISBN-978-984-4-52-6) ROAD ACCIDENTS AND SAFETY
Field and Analytical Investigation of Accidents Data on the Egyptian Road Network
 J. Civil Eng. Architect. Res. Vol. 4, No. 2, 2017, pp. 1923-1930 Received: January 23, 2016; Published: February 25, 2017 Journal of Civil Engineering and Architecture Research Field and Analytical Investigation
J. Civil Eng. Architect. Res. Vol. 4, No. 2, 2017, pp. 1923-1930 Received: January 23, 2016; Published: February 25, 2017 Journal of Civil Engineering and Architecture Research Field and Analytical Investigation
Fatal Head-On Crashes on. Rural Two-Lane Two-Way Highways in Minnesota
 Fatal Head-On on Rural Two-Lane Two-Way Highways in Minnesota A Report Submitted to the Minnesota Department of Transportation By Derek Leuer, PE Office of Traffic, Safety, and Technology Minnesota Department
Fatal Head-On on Rural Two-Lane Two-Way Highways in Minnesota A Report Submitted to the Minnesota Department of Transportation By Derek Leuer, PE Office of Traffic, Safety, and Technology Minnesota Department
Analysis of Signalized Intersection Crashes Nasima Bhuiyan, EmelindaM. Parentela and Venkata S. Inapuri
 Analysis of Signalized Intersection Crashes Nasima Bhuiyan, EmelindaM. arentela and Venkata S. Inapuri Abstract The goals of providing high levels of mobility and intersection efficiency while simultaneously
Analysis of Signalized Intersection Crashes Nasima Bhuiyan, EmelindaM. arentela and Venkata S. Inapuri Abstract The goals of providing high levels of mobility and intersection efficiency while simultaneously
Effects of Traffic Condition (v/c) on Safety at Freeway Facility Sections
 Effects of Traffic Condition (v/c) on Safety at Freeway Facility Sections JAENAM CHANG Engineer, Korea Engineering Consultants Corp., Korea CHEOL OH Graduate Student Researcher, University of California,
Effects of Traffic Condition (v/c) on Safety at Freeway Facility Sections JAENAM CHANG Engineer, Korea Engineering Consultants Corp., Korea CHEOL OH Graduate Student Researcher, University of California,
A Silent Tsunami on Indian Road: A Comprehensive Analysis of Epidemiological Aspects of Road Traffic Accidents
 . British Journal of Medicine & Medical Research British Journal of Medicine & Medical Research 1(1): 14-23, 2011 SCIENCEDOMAIN international www.sciencedomain.org A Silent Tsunami on Indian Road: A Comprehensive
. British Journal of Medicine & Medical Research British Journal of Medicine & Medical Research 1(1): 14-23, 2011 SCIENCEDOMAIN international www.sciencedomain.org A Silent Tsunami on Indian Road: A Comprehensive
1 Monash University Accident Research Centre, Monash University, Victoria, RACV, 550 Princes Highway Noble Park, Victoria, 3174.
 Roadside Environment Safety: a statistical analysis of collisions with fixed roadside objects in Victoria Amanda Delaney 1, Stuart Newstead 1, Bruce Corben 1, Jim Langford 1 and Peter Daly 2 1 Monash University
Roadside Environment Safety: a statistical analysis of collisions with fixed roadside objects in Victoria Amanda Delaney 1, Stuart Newstead 1, Bruce Corben 1, Jim Langford 1 and Peter Daly 2 1 Monash University
Effects of Automated Speed Enforcement in Montgomery County, Maryland, on Vehicle Speeds, Public Opinion, and Crashes
 Effects of Automated Speed Enforcement in Montgomery County, Maryland, on Vehicle Speeds, Public Opinion, and Crashes August 2015 Wen Hu Insurance Institute for Highway Safety Anne T. McCartt Insurance
Effects of Automated Speed Enforcement in Montgomery County, Maryland, on Vehicle Speeds, Public Opinion, and Crashes August 2015 Wen Hu Insurance Institute for Highway Safety Anne T. McCartt Insurance
THE DEVELOPMENTOF A PREDICTION MODEL OF THE PASSENGER CAR EQUIVALENT VALUES AT DIFFERENT LOCATIONS
 THE DEVELOPMENTOF A PREDICTION MODEL OF THE PASSENGER CAR EQUIVALENT VALUES AT DIFFERENT LOCATIONS Nurul Hidayati 1, Ronghui Liu 2 and Frank Montgomery 2 1 Civil Engineering, Postgraduate Program Department,
THE DEVELOPMENTOF A PREDICTION MODEL OF THE PASSENGER CAR EQUIVALENT VALUES AT DIFFERENT LOCATIONS Nurul Hidayati 1, Ronghui Liu 2 and Frank Montgomery 2 1 Civil Engineering, Postgraduate Program Department,
International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology. (A High Impact Factor, Monthly, Peer Reviewed Journal)
 A Preliminary Study on Possible Alternate Roadways to Reduce Traffic Hazards at Velachery Township in Chennai Traffic Flow Minimization- a Prelimary Study Deepak R, Gangha G Department of Civil Engineering,
A Preliminary Study on Possible Alternate Roadways to Reduce Traffic Hazards at Velachery Township in Chennai Traffic Flow Minimization- a Prelimary Study Deepak R, Gangha G Department of Civil Engineering,
Assessing Level of Service for Highways in a New Metropolitan City
 Assessing Level of Service for Highways in a New Metropolitan City Ganesh Pawar Civil Engineering Department G. H. Raisoni College of Engineering Nagpur, India,4416 Dr. Bhalachandra Khode Civil Engineering
Assessing Level of Service for Highways in a New Metropolitan City Ganesh Pawar Civil Engineering Department G. H. Raisoni College of Engineering Nagpur, India,4416 Dr. Bhalachandra Khode Civil Engineering
Geometric designs for Safe Highways. Dr. Manoj M. Asst. Professor Department of Civil Engineering IIT Delhi
 Geometric designs for Safe Highways Dr. Manoj M. Asst. Professor Department of Civil Engineering IIT Delhi WORKSHOP-CUM-TRAINING PROGRAMME ON ROAD SAFETY 17th 21st September 2018 Outline Introduction Cross
Geometric designs for Safe Highways Dr. Manoj M. Asst. Professor Department of Civil Engineering IIT Delhi WORKSHOP-CUM-TRAINING PROGRAMME ON ROAD SAFETY 17th 21st September 2018 Outline Introduction Cross
