The Scientific Bulletin of VALAHIA University MATERIALS and MECHANICS Nr. 5 (year 8) 2010
|
|
|
- Toby Leonard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 STATISTIC PROCESSING OF MEASUREMENTS DONE WITH CALORCRO EQUIPMENT FOR ASSESSING THE GAIT ENERGETIC EXPENDITURE AT HEALTHY SUBJECTS AND PATIENTS SUFFERING FROM OSTEOARTHRITIS OF LOWER LIMBS G. CAPRIS 1), S. MIU 2), S. CONSTANTIN 1), D. BUCUR 2), S. POPESCU 3) 1) National Institute of Research and Development in Mechatronics and Measurement Technique, Bucharest, Romania; 2) Fine Mechanics and Mechatronics Faculty, Politehnica University of Bucharest, Romania; 3) National Institute for Rehabilitation, Physical Medicine and Balnealclimatology, Bucharest, Romania. Abstarct. Based on the endeavour of using movement as an efficient treatment, the CALORCRO project has as an aim to promote physical effort as a part of osteoarthritis treatment in Romanian clinics. The project partners worked out both a method to evaluate the gait energetic expenditure and a portable computerized equipment to measure the gait parameters. The newness of both method and equipment consists in the concept of merging the advantages of the two existing systems: pedometer and treadmill with embedded force platforms, in order to evaluate the gait energetic expenditure. The objective of this study was to find the altering degree of some gait kinematic parameters and of the gait energetic expenditure (total expended power) of the subjects suffering from osteoarthritis of the lower limbs compared to healthy subjects, using the CALORCRO device. 1. MATERIALS AND METHODS 1.1. Sample. We studied 8 healthy women with the following characteristics: mean age 44.67±13 years, mean body weight 74.47±11 kg, mean lower limb length 94.85±4.2 cm and also a second group of 9 patients with osteoarthritis (ankle 2 patients, knee 4 patients, hip 3 patients), who have the following characteristics: mean age 67.11±7.82 years, mean body weight 82.73±17.05 kg, mean lower limb length 82.67±3.27 cm. The healthy subjects were selected from persons who never suffered from diseases that affect the locomotion system Equipment and procedure. Each subject performed three trials of 20 m normal gait on a horizontal surface and was equipped with the portable device CALORCRO, consisting of two overshoe supports carrying force sensors, two signal conditioning blocs, a data acquisition, processing and displaying system. The gait energetic expenditure calculation algorythm is based on the assessment of the internal and external work, using as input data the vertical ground reaction forces (VGRF) of each foot, the coordinates of the force sensors in the sensor supports and anthropometric data of the subject. The algorythm was verified through com-paring our results with those existing in other similar works 1, 2, 3 and also by simultanously testing several healthy subjects equipped both with our device and with the portable device Cosmed K4b 2, (indirect calorimetry). The validation of the measured values of the healthy subjects VGRF and their graphical display in time was achieved by comparing these with those given by the PEDAR- NOVEL equipment. In order to accomplish this the CALORCRO software comprises o function that aquires data files *.fgt* of the PEDAR-NOVEL equipment. The working procedure of the CALORCRO device consists of instruc-ting the subject, mounting equipment, recording the gait trial, printing the Gait Analysis Report (GAR) Studied variables 1) Gait speed (V) (m/s) as ratio of walked distance and its duration, 2) Step length (cm) as ratio of walked distance and number of recorded steps; 3) Time parameters of gait: stride duration (s), stance phase duration (s) balance phase duration (s); 4) VGRF (N) as a sum of the forces measured by each sensor with a 100 Hz sampling frequency; 5) Vertical speed (VS) of the body Center of Mass (COM) as time integral of the VGRF divided by body mass; 6) Vertical displacement of COM as a time integral of VS; 7) External vertical power (EVP) (W) as a ratio of the total positive work of VGRF of both feet during a step and step duration [2], [3]; 8) External power of forwardly oriented movement (EFP) (W) as a ratio of total positive work of the projection of the GRF in the gait direction of both feet during a step and step duration. 9) Internal power (IP) (W) evaluated with Minetti s relationship [5]; 10) R1 [W/(kg.m/s)] ratio of the EVP (W) and body weight (BW)xV; 11) R2 [W/(kg.m/s)] ratio of total expended power (EVP+EFP+IP) and (BWxV) Statistics For each healthy subject and each patient, mean values and standard deviations were computed for several parameters: gait speed, step length, stride duration, 129
2 duration of left stance relative to step duration, duration of right stance relative to step duration, R1 ratio of the EVP (W) and (BWx V), R2 ratio of total expended power and (BWxV). In order to establish which of the variables (shown at 2.3) can discriminate a healthy subject from a sick one, sensitivity (Se) and specificity (Sp) of these variables were evaluated for both the group of healthy people and the group of the patients. Sensitivity is the probability of calling an actually sick person as sick, and specificity is defined as the probability of calling an actually healthy person as healthy. We tried to analyze the relevance of our test using the ROC method (Receiver Operating Characteristic). The ROC curve is a graphical plot of the sensitivity vs. (1- specificity), for the binary system of healthy and sick people. The two coordinates have a maximum value equal to 1. The shape of the curve itself depends on the threshold of that test. The classifier s best accuracy occurs at a threshold greater than In order to get a quick interpretation of the ROC curve one uses the value of the area under the curve (AUC). This single scalar value represents the expected performance. Since the AUC is a portion of the area of the unit square, its value will always be between 0 and 1.0. However, because random guessing produces the diagonal line between (0, 0) and (1, 1), which has an area of 0.5, no realistic classifier should have an AUC less than 0.5. The AUC has an important statistical property: the AUC of a classifier is equivalent to the probability that the classifier will rank a randomly chosen sick person higher than a randomly chosen healthy person. The data registered during the tests performed by the two groups of subjects (sick and healthy people)were worked out and shown in the tables I and II. ROC curves for each of the variables were plotted: walking speed (m/s), step length (m), step frequency (Hz), single support phase duration for each foot (left foot and right foot) relative to the step duration (%), rate between the vertical external power and the product: subject s weight x advance speed - R1 (W/(kg.m/s)), the rate the total external power and the product: subject s weight x advance speed R2 (W/(kg. m/s)), (fig.1, fi g. 2 and fi g. 3). Table I: Gait variables for healthy subjects (mean values) Healthy Speed Step Stride Right foot Left foot R1 R2 subjects length frequency stance stance (m/s) (cm) (Hz) (%) (%) W/(Kg.m/s) W/(Kg.m/s) I 1,460 73,500 1,145 58,820 57,137 0,417 2,063 II 1,133 61,070 0,994 60,050 56,093 0,738 1,914 III 1,043 59,385 0,984 60,065 55,633 0,679 1,612 IV 1,257 54,323 1,146 58,483 57,937 0,551 1,711 V 1,280 63,000 1,080 57,893 53,240 0,822 1,963 VI 1,200 63,676 0,878 58,231 55,404 0,685 1,797 VII 1,400 68,858 0,849 58,118 54,630 0,461 1,824 VIII 1,670 75,716 1,140 57,524 53,778 0,350 2,026 Table II: Gait variables for patients (mean values) Patients Speed Step Stride Right foot Left foot R1 R2 length frequency stance stance (m/s) (cm) (Hz) (%) (%) W/(Kg.m/s) W/(Kg.m/s) I 1,063 62,557 0,851 60,284 55,507 1,271 2,298 II 0,794 55,114 0,712 57,756 58,201 1,278 ~ III 0,328 26,480 0,612 69,184 64,572 4,200 ~ IV 0,854 53,363 0,830 62,646 59,836 1,414 ~ V 0,362 34,060 0,554 64,800 64,344 3,384 ~ VI 0,683 44,125 0,786 61,565 59,685 0,766 1,483 VII 0,821 50,673 0,829 64,226 61,420 0,732 1,569 VIII 0,848 52,918 0,808 61,473 61,949 1,532 2,382 IX 0,677 51,153 0,697 62,710 62,840 1,264 ~ 130
3 Se Se Se The Scientific Bulletin of VALAHIA University MATERIALS and MECHANICS Nr. 5 (year 8) ,00 0,90 0,80 0,70 0,60 0,50 0,40 0,30 0,20 0,10 0,00 walking speed step length stride frequency 0,00 0,10 0,20 0,30 0,40 0,50 0,60 0,70 0,80 0,90 1,00 1-Sp Fig. 1: ROC curves for: speed, step length, stride frequency. AUC for speed: 0,993; AUC for step length: 0,951; AUC for stride frequency: 1,00 0,90 0,80 0,70 0,60 0,50 0,40 right foot stance 0,30 left foot stance 0,20 0,10 0,00 0,00 0,10 0,20 0,30 0,40 0,50 0,60 0,70 0,80 0,90 1,00 1-Sp Fig. 2: ROC curves for duration of right/left foot stance relative to step duration. AUC for right stance: 0,883; AUC for left stance: 0,994 1,00 0,90 0,80 0,70 0,60 0,50 0,40 0,30 0,20 0,10 0,00 external vertical power / BWxV total expended power / BWxV 0,00 0,10 0,20 0,30 0,40 0,50 0,60 0,70 0,80 0,90 1,00 1-Sp Fig. 3: ROC curves for R1 and R2. AUC for R1: 0,937; AUC for R2: 0,
4 Most of the curves plotted are characterized by an AUC greater than so that one can assume that the analysis of the following variables: walking speed (m/s), step length (m), step frequency (Hz), single support phase duration for each foot (left foot and right foot) relative to the step duration (%), rate between the vertical external power and the product: subject s weight x advance speed (W/(kg.m/s)), allow a good identification of the subjects suffering from osteoarthritis. The parameter represented by the total external power and the product of the subject s weight and advance speed (W/(kg.m/s)) resulted in an AUC of only 0.5 and does not lead to a proper threshold that is able to positively allow an osteoarthritis diagnosis. 2. RESULTS Gait Analysis Report (GAR) was printed of each gait trial (fig.4). The gait variables as mean values and their standard deviations were assessed for patients and healthy subjects; based on ROC curves, under ROC curve areas (AUC) and cutoff values were also assesssed (table III). The external power of the forwardly oriented movement (EFP) couldn t be assessed for all the patients, as the VGRF curve had a shape showing no heel strike and no toe off action due to their disease. This impeded us to assess the EFP using EFP algorythm. 3. DISCUSSION 3.1. Equipment and procedure The CALORCRO equipment and the assessing method used by us have several advantages in gait analysis of ambulatory patients suffering from osteoarthritis at lower limbs. The overshoe sensor supports do not disturb normal gait, measurements are quickly and noninvasively achieved and results include both main kinematic gait variables and the energetic expenditure. The assessing method allows the numerical evaluation of gait disturbances in clinical practice. 3.2 Gait disturbances of patients suffering from osteoarthritis of lower limbs Analysis of the data recordings, graphs in GAR (fig.4) and statistical analysis of the studied variables brought about the following results: Patients in the initial disease stage, with painful decompensation have a shorter stance phase on the ill limb. If the functional decompensation prevailed the pain, the stance phases on both limbs are almost equal with those of healthy subjects. Patients in an advanced phase of disease show a much longer stance phase on both feet, compared to the healthy subjects. Depending on how severe the illness is, the patients VGRF curve shapes differ from the ones of healthy subjects, due to many irregularities, such as no heel strike and no toe off parts.the maximum force corresponding to the ill limb stance is smaller compared to the one of the healthy limb, as patients avoid pressing the ill joint. The vertical COM speed (VS) has an irregular variation. The mean values of the total expended power of the healthy subjects are similar with those found by other researchers [4]. The patients gait parameters differ from those of the healthy subjects in the following aspects: slower gait speed, shorter step length, smaller stride frequency, longer stance duration and greater values of R1 ratio of EVP/(BWxV). The decrease of gait speed, step length, stride frequency shows that the patients suffering from lower limb osteoarthritis tend to slow down the limb movement, behaviour similar to the bradykinesia specific to the patients suffering from fibromyalgia [6]. This is accompanied by an increase of the stance duration and a decrease of the balance period, relative to the step duration. The alteration of the EVP consumed during the gait process proved to be another significant criterion in diagnosing patients with lower limbs osteoarthritis (table III). The statistical analysis of R2, that is the ratio of total expended power and (BWxV) showed that this parameter cannot discriminate the patients from the healthy subjects for the following reasons: Patients suffering from an incipient lower limb osteoarthritis, who build a correct shape of the VGRF curve while walking, tend to combine an increase of the EVP with a decrease of both EFP and IP because they slow down the gait speed and decrease the stride frequency. Patients suffering from lower limb osteoarthritis in an advanced stage of evolution show an increase of the EVP accompanied by a decrease of the IP, due to the diminution of the stride frequency. The abnormal shape of the VGRF curve while walking hindered us to apply the algorythm for assessing the EFP of these patients. The discrimination accuracy between the patients group and the healthy group is measured by the area (AUC) under the ROC curves (table III). The gait speed test and the stride frequency test make an excelent separation of the osteoarthritis patients and the step length working out this as well. The test R1 ratio of EVP/(BWxV) is a good test, but the test R2 ratio of (EVP+EFP+IP)/(BWxV) is completely irrelevant, according to this analysis. 4. CONCLUSIONS The gait parameters that differentiate patients suffering from lower limb osteoarthritis and healthy subjects were showed by the ROC analysis (table III). Those who generate an AUC value greater than , are the following: gait speed, stride frequency, step length, ratio R1 of the EVP and (BWx V), stance relative to step duration. 132
5 Total expended power is not a relevant parameter as the human body has the natural tendency to conserve it s whole energy. As the total expended power is a sum of three power parameters (EVP, EFP, IP) the increase of one parameter (EVP) is accompanied by the decrease of the remaining, in order to conserve the body energy. This study confirms that both kinematic and energy analysis are useful in evaluating both lower limb osteoarthritis stage of evolution and monitoring the treatment effects. Acknowledgments: This study was supported by CEEX Programms, PNCDI 2, Romania: CALORCRO and SIMSANO Projects. REFERENCES: [1] Pontzer H. A new model predicting locomotor cost from limb lengh via force production. J.Exp.Biology, 2005, 208: [2] Donelan JM, Kram R, Kuo AD. Simultaneous, positive and negative external mechanical work in human walking. J.Biomechanics, 2002, 35: [3] Griffin TM, Roberts TJ, Kram R. Metabolic cost of generating muscular force in human walking:insights from load-carrying and speed experiments.j.appl.physiol, 2003, 95: [4] Browning RC, Kram R. Energetic cost and preferred speed of walking in obese vs. normal weight women. J.Obesity Research, 2005, vol.13, No5: [5] Minetti AE, Saibene F. Mechanical work rate minimization and freely chosen stride frequency of human walking: a mathematical model. J Exp.Biol.170, 1992, [6] Auvinet B, Bilekot R, Alix AS, Chaleil D, Barrey E. Gait disorders in patients with fibromyalgia. J.Joint Bone Spine 73, 2006, [7] Fawcett T. An introduction to ROC analysis. J.Pattern Recognition Letters 27, 2006, Gait parameter Table III: Statistical analysis of the gait parameterts of patients suffering from lower limb osteoarthritis and healthy subjects Subjects Patients Healthy subjects Sensitivity and specificity of gait parameters AUC Discrimination Cutoff Walking speed (m/s) 0.714± ± excellent Stride frequency (Hz) 0.742± ± ,965 excellent Step length (cm) 47.82± ±6.78 0,951 excellent R1 ratio of external vertical power/ (BWx V) [W/(kg.m/s)] R2 ratio of total expended power / (BWxV) [W/kg.m/s] Duration of left foot stance relative to step duration (%) Duration of right foot stance relative to step duration (%) 1.76± ± ,937 good ±0.409 (4 patients) 1.864± ,500 fail ± ± excellent ± ±0.89 0,889 excellent
6 Fig. 4. Gait Analysis Raport (GAR) for a healthy subject 134
Portable Apparatus for Gait Analysis Based on Tactile Force Sensors
 Portable Apparatus for Gait Analysis Based on Tactile Force Sensors Dr. eng. Georgeta CAPRIS, eng. Steluţa CONSTANTIN, eng. Anghel CONSTANTIN INCDMTM ABSTRACT: This article presents the authors experience
Portable Apparatus for Gait Analysis Based on Tactile Force Sensors Dr. eng. Georgeta CAPRIS, eng. Steluţa CONSTANTIN, eng. Anghel CONSTANTIN INCDMTM ABSTRACT: This article presents the authors experience
An investigation of kinematic and kinetic variables for the description of prosthetic gait using the ENOCH system
 An investigation of kinematic and kinetic variables for the description of prosthetic gait using the ENOCH system K. OBERG and H. LANSHAMMAR* Amputee Training and Research Unit, University Hospital, Fack,
An investigation of kinematic and kinetic variables for the description of prosthetic gait using the ENOCH system K. OBERG and H. LANSHAMMAR* Amputee Training and Research Unit, University Hospital, Fack,
Gait Analyser. Description of Walking Performance
 Gait Analyser Description of Walking Performance This brochure will help you to understand clearly the parameters described in the report of the Gait Analyser, provide you with tips to implement the walking
Gait Analyser Description of Walking Performance This brochure will help you to understand clearly the parameters described in the report of the Gait Analyser, provide you with tips to implement the walking
Efficient Variability: Linking Fractal Walking Patterns with Metabolic Energy Savings
 Efficient Variability: Linking Fractal Walking Patterns with Metabolic Energy Savings Project Description Decades of research in biomechanics, neuroscience, and biology have produced two theories on why
Efficient Variability: Linking Fractal Walking Patterns with Metabolic Energy Savings Project Description Decades of research in biomechanics, neuroscience, and biology have produced two theories on why
Normal and Abnormal Gait
 Normal and Abnormal Gait Adrielle Fry, MD EvergreenHealth, Division of Sport and Spine University of Washington Board Review Course March 6, 2017 What are we going to cover? Definitions and key concepts
Normal and Abnormal Gait Adrielle Fry, MD EvergreenHealth, Division of Sport and Spine University of Washington Board Review Course March 6, 2017 What are we going to cover? Definitions and key concepts
ASSESMENT Introduction REPORTS Running Reports Walking Reports Written Report
 ASSESMENT REPORTS Introduction Left panel Avatar Playback Right Panel Patient Gait Parameters Report Tab Click on parameter to view avatar at that point in time 2 Introduction Software will compare gait
ASSESMENT REPORTS Introduction Left panel Avatar Playback Right Panel Patient Gait Parameters Report Tab Click on parameter to view avatar at that point in time 2 Introduction Software will compare gait
In memory of Dr. Kevin P. Granata, my graduate advisor, who was killed protecting others on the morning of April 16, 2007.
 Acknowledgement In memory of Dr. Kevin P. Granata, my graduate advisor, who was killed protecting others on the morning of April 16, 2007. There are many others without whom I could not have completed
Acknowledgement In memory of Dr. Kevin P. Granata, my graduate advisor, who was killed protecting others on the morning of April 16, 2007. There are many others without whom I could not have completed
Analysis of Foot Pressure Variation with Change in Stride Length
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-853, p-issn: 2279-861.Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. IV (Oct. 214), PP 46-51 Dr. Charudatta V. Shinde, M.S. MCh ( Orthopaedics ), Dr. Weijie
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-853, p-issn: 2279-861.Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. IV (Oct. 214), PP 46-51 Dr. Charudatta V. Shinde, M.S. MCh ( Orthopaedics ), Dr. Weijie
THE INFLUENCE OF SLOW RECOVERY INSOLE ON PLANTAR PRESSURE AND CONTACT AREA DURING WALKING
 March 12, 2015 5:39:44pm WSPC/170-JMMB 1540005 ISSN: 0219-51942nd Reading Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology Vol. 15, No. 2 (2015) 1540005 (6 pages) c World Scientific Publishing Company DOI:
March 12, 2015 5:39:44pm WSPC/170-JMMB 1540005 ISSN: 0219-51942nd Reading Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology Vol. 15, No. 2 (2015) 1540005 (6 pages) c World Scientific Publishing Company DOI:
SPRINTING CHARACTERISTICS OF WOMEN S 100 METER FINALS AT THE IAAF WORLD CHAMPIONSHOPS DAEGU 2011
 9:30-9:45 am Sang-Kyoon Park. Sprinting characteristics of women's 100 meter finals at the IAAF world championships Daegu 2011. (228) SPRINTING CHARACTERISTICS OF WOMEN S 100 METER FINALS AT THE IAAF WORLD
9:30-9:45 am Sang-Kyoon Park. Sprinting characteristics of women's 100 meter finals at the IAAF world championships Daegu 2011. (228) SPRINTING CHARACTERISTICS OF WOMEN S 100 METER FINALS AT THE IAAF WORLD
Ambulatory monitoring of gait quality with wearable inertial sensors
 Ambulatory monitoring of gait quality with wearable inertial sensors Dr. Philippe Terrier, PhD June 2016 Summary 1. Why? Reasons for measuring gait in real life conditions 2. What? Real-life assessment
Ambulatory monitoring of gait quality with wearable inertial sensors Dr. Philippe Terrier, PhD June 2016 Summary 1. Why? Reasons for measuring gait in real life conditions 2. What? Real-life assessment
-Elastic strain energy (duty factor decreases at higher speeds). Higher forces act on feet. More tendon stretch. More energy stored in tendon.
 As velocity increases ( ) (i.e. increasing Froude number v 2 / gl) the component of the energy cost of transport associated with: -Internal kinetic energy (limbs accelerated to higher angular velocity).
As velocity increases ( ) (i.e. increasing Froude number v 2 / gl) the component of the energy cost of transport associated with: -Internal kinetic energy (limbs accelerated to higher angular velocity).
INTERACTION OF STEP LENGTH AND STEP RATE DURING SPRINT RUNNING
 INTERACTION OF STEP LENGTH AND STEP RATE DURING SPRINT RUNNING Joseph P. Hunter 1, Robert N. Marshall 1,, and Peter J. McNair 3 1 Department of Sport and Exercise Science, The University of Auckland, Auckland,
INTERACTION OF STEP LENGTH AND STEP RATE DURING SPRINT RUNNING Joseph P. Hunter 1, Robert N. Marshall 1,, and Peter J. McNair 3 1 Department of Sport and Exercise Science, The University of Auckland, Auckland,
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF EXOSKELETON FOR ANKLE AND KNEE JOINT
 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF EXOSKELETON FOR ANKLE AND KNEE JOINT PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S0925 COLLEGE : NEW HORIZON COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, BANGALORE BRANCH : MECHANICAL ENGINEERING GUIDES : DR GANESHA PRASAD
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF EXOSKELETON FOR ANKLE AND KNEE JOINT PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S0925 COLLEGE : NEW HORIZON COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, BANGALORE BRANCH : MECHANICAL ENGINEERING GUIDES : DR GANESHA PRASAD
SPECIFIC METHODS OF HIP IMPLANT NON-INVASIVE ASSESSMENT
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol. 9 (58) No. 2 - Special Issue 2016 Series I: Engineering Sciences SPECIFIC METHODS OF HIP IMPLANT NON-INVASIVE ASSESSMENT A. SUCIU 1 D. COTOROS 1 A.
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol. 9 (58) No. 2 - Special Issue 2016 Series I: Engineering Sciences SPECIFIC METHODS OF HIP IMPLANT NON-INVASIVE ASSESSMENT A. SUCIU 1 D. COTOROS 1 A.
Equine Cannon Angle System
 Equine Cannon System How to interpret the results December 2010 Page 1 of 14 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 The Sagittal Plane... 4 The Coronal Plane... 5 Results Format... 6 How to Interpret the
Equine Cannon System How to interpret the results December 2010 Page 1 of 14 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 The Sagittal Plane... 4 The Coronal Plane... 5 Results Format... 6 How to Interpret the
Spasticity in gait. Wessex ACPIN Spasticity Presentation Alison Clarke
 Spasticity in gait Clinicians recognise spasticity but the elements of spasticity contributing to gait patterns are often difficult to identify: Variability of muscle tone Observation/recording General
Spasticity in gait Clinicians recognise spasticity but the elements of spasticity contributing to gait patterns are often difficult to identify: Variability of muscle tone Observation/recording General
Using GPOPS-II to optimize sum of squared torques of a double pendulum as a prosthesis leg. Abstract
 Using GPOPS-II to optimize sum of squared torques of a double pendulum as a prosthesis leg Abstract Milad Zarei MCE 593 Prosthesis Design & Control A two-dimensional, two links pendulum is developed to
Using GPOPS-II to optimize sum of squared torques of a double pendulum as a prosthesis leg Abstract Milad Zarei MCE 593 Prosthesis Design & Control A two-dimensional, two links pendulum is developed to
COMPARISON STUDY BETWEEN THE EFFICIENY OF THE START TECHNIQUES IN THE ROMANIAN COMPETITIVE SWIMMING
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series IX: Sciences of Human Kinetics Vol. 6 (55) No. 1 2013 COMPARISON STUDY BETWEEN THE EFFICIENY OF THE START TECHNIQUES IN THE ROMANIAN COMPETITIVE
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series IX: Sciences of Human Kinetics Vol. 6 (55) No. 1 2013 COMPARISON STUDY BETWEEN THE EFFICIENY OF THE START TECHNIQUES IN THE ROMANIAN COMPETITIVE
Walking and Running BACKGROUND REVIEW. Planar Pendulum. BIO-39 October 30, From Oct. 25, Equation of motion (for small θ) Solution is
 Walking and Running BIO-39 October 30, 2018 BACKGROUND REVIEW From Oct. 25, 2018 Planar Pendulum Equation of motion (for small θ) 2 d g 0 2 dt Solution is Where: g is acceleration due to gravity l is pendulum
Walking and Running BIO-39 October 30, 2018 BACKGROUND REVIEW From Oct. 25, 2018 Planar Pendulum Equation of motion (for small θ) 2 d g 0 2 dt Solution is Where: g is acceleration due to gravity l is pendulum
A COMPARISON OF SELECTED BIOMECHANICAL PARAMETERS OF FRONT ROW SPIKE BETWEEN SHORT SET AND HIGH SET BALL
 A COMPARISON OF SELECTED BIOMECHANICAL PARAMETERS OF FRONT ROW SPIKE BETWEEN SHORT SET AND HIGH SET BALL PAPAN MONDAL a AND SUDARSAN BHOWMICK b,* a Assistant Professor, Department of Physical Education,
A COMPARISON OF SELECTED BIOMECHANICAL PARAMETERS OF FRONT ROW SPIKE BETWEEN SHORT SET AND HIGH SET BALL PAPAN MONDAL a AND SUDARSAN BHOWMICK b,* a Assistant Professor, Department of Physical Education,
Using sensory feedback to improve locomotion performance of the salamander robot in different environments
 Using sensory feedback to improve locomotion performance of the salamander robot in different environments João Lourenço Silvério Assistant: Jérémie Knüsel Structure of the presentation: I. Overview II.
Using sensory feedback to improve locomotion performance of the salamander robot in different environments João Lourenço Silvério Assistant: Jérémie Knüsel Structure of the presentation: I. Overview II.
The Starting Point. Prosthetic Alignment in the Transtibial Amputee. Outline. COM Motion in the Coronal Plane
 Prosthetic Alignment in the Transtibial Amputee The Starting Point David C. Morgenroth, MD, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine University of Washington VAPSHCS Outline COM Motion in the Coronal Plane
Prosthetic Alignment in the Transtibial Amputee The Starting Point David C. Morgenroth, MD, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine University of Washington VAPSHCS Outline COM Motion in the Coronal Plane
CHAPTER IV FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF THE KNEE JOINT WITHOUT A MEDICAL IMPLANT
 39 CHAPTER IV FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF THE KNEE JOINT WITHOUT A MEDICAL IMPLANT 4.1 Modeling in Biomechanics The human body, apart of all its other functions is a mechanical mechanism and a structure,
39 CHAPTER IV FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF THE KNEE JOINT WITHOUT A MEDICAL IMPLANT 4.1 Modeling in Biomechanics The human body, apart of all its other functions is a mechanical mechanism and a structure,
Figure 1 betois (bending torsion insole system) system with five measuring points and A/D- converter.
 Bending and Torsional Moments - A new measuring system for gait analysis Nora Dawin & Annette Kerkhoff & Klaus Peikenkamp, University of Applied Sciences Münster, Germany Abstract The Laboratory of Biomechanics
Bending and Torsional Moments - A new measuring system for gait analysis Nora Dawin & Annette Kerkhoff & Klaus Peikenkamp, University of Applied Sciences Münster, Germany Abstract The Laboratory of Biomechanics
Internet Technology Fundamentals. To use a passing score at the percentiles listed below:
 Internet Technology Fundamentals To use a passing score at the percentiles listed below: PASS candidates with this score or HIGHER: 2.90 High Scores Medium Scores Low Scores Percentile Rank Proficiency
Internet Technology Fundamentals To use a passing score at the percentiles listed below: PASS candidates with this score or HIGHER: 2.90 High Scores Medium Scores Low Scores Percentile Rank Proficiency
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Gait Posture. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2009 May 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Gait Posture. 2008 May ; 27(4): 710 714. Two simple methods for determining gait events during treadmill and overground walking using
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Gait Posture. 2008 May ; 27(4): 710 714. Two simple methods for determining gait events during treadmill and overground walking using
Sensitivity of toe clearance to leg joint angles during extensive practice of obstacle crossing: Effects of vision and task goal
 Sensitivity of toe clearance to leg joint angles during extensive practice of obstacle crossing: Effects of vision and task goal Sérgio Tosi Rodrigues 1, Valéria Duarte Garcia 1,2, Arturo Forner- Cordero
Sensitivity of toe clearance to leg joint angles during extensive practice of obstacle crossing: Effects of vision and task goal Sérgio Tosi Rodrigues 1, Valéria Duarte Garcia 1,2, Arturo Forner- Cordero
The overarching aim of the work presented in this thesis was to assess and
 CHAPTER 7 EPILOGUE Chapter 7 The overarching aim of the work presented in this thesis was to assess and understand the effort for balance control in terms of the metabolic cost of walking in able-bodied
CHAPTER 7 EPILOGUE Chapter 7 The overarching aim of the work presented in this thesis was to assess and understand the effort for balance control in terms of the metabolic cost of walking in able-bodied
EXSC 408L Fall '03 Problem Set #2 Linear Motion. Linear Motion
 Problems: 1. Once you have recorded the calibration frame for a data collection, why is it important to make sure the camera does not shut off? hat happens if the camera automatically shuts off after being
Problems: 1. Once you have recorded the calibration frame for a data collection, why is it important to make sure the camera does not shut off? hat happens if the camera automatically shuts off after being
Mechanical energy fluctuations during hill walking: the effects of slope on inverted pendulum exchange
 4895 The Journal of Experimental Biology 209, 4895-4900 Published by The Company of Biologists 2006 doi:10.1242/jeb.02584 Mechanical energy fluctuations during hill walking: the effects of slope on inverted
4895 The Journal of Experimental Biology 209, 4895-4900 Published by The Company of Biologists 2006 doi:10.1242/jeb.02584 Mechanical energy fluctuations during hill walking: the effects of slope on inverted
RUNNING SHOE STIFFNESS: THE EFFECT ON WALKING GAIT
 RUNNING SHOE STIFFNESS: THE EFFECT ON WALKING GAIT Stephen N Stanley, Peter J M c Nair, Angela G Walker, & Robert N Marshall Auckland Institute of Technology, Auckland, New Zealand University of Auckland,
RUNNING SHOE STIFFNESS: THE EFFECT ON WALKING GAIT Stephen N Stanley, Peter J M c Nair, Angela G Walker, & Robert N Marshall Auckland Institute of Technology, Auckland, New Zealand University of Auckland,
ROSE-HULMAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Mechanical Engineering. Mini-project 3 Tennis ball launcher
 Mini-project 3 Tennis ball launcher Mini-Project 3 requires you to use MATLAB to model the trajectory of a tennis ball being shot from a tennis ball launcher to a player. The tennis ball trajectory model
Mini-project 3 Tennis ball launcher Mini-Project 3 requires you to use MATLAB to model the trajectory of a tennis ball being shot from a tennis ball launcher to a player. The tennis ball trajectory model
Saturday, 15 July 2006 SAP-30: 10:45-11:15 CHANGE OF SPEED IN SIMULATED CROSS-COUNTRY SKI RACING: A KINEMATIC ANALYSIS
 CHANGE OF SPEED IN SIMULATED CROSS-COUNTRY SKI RACING: A KINEMATIC ANALYSIS M. Barberis (1,2), A. Rouard (2), N. Messenger (1). School of Sport and Exercise Sciences, University of Leeds, Leeds, UK (1)
CHANGE OF SPEED IN SIMULATED CROSS-COUNTRY SKI RACING: A KINEMATIC ANALYSIS M. Barberis (1,2), A. Rouard (2), N. Messenger (1). School of Sport and Exercise Sciences, University of Leeds, Leeds, UK (1)
Normal and Pathological Gait
 Normal and Pathological Gait Introduction Human gait locomotion Bipedal, biphasic forward propulsion of centre of gravity of the human body, in which there are alternate sinuous movements of different
Normal and Pathological Gait Introduction Human gait locomotion Bipedal, biphasic forward propulsion of centre of gravity of the human body, in which there are alternate sinuous movements of different
The effects of a suspended-load backpack on gait
 Industrial and Manufacturing Systems Engineering Publications Industrial and Manufacturing Systems Engineering 2009 The effects of a suspended-load backpack on gait Xu Xu North Carolina State University
Industrial and Manufacturing Systems Engineering Publications Industrial and Manufacturing Systems Engineering 2009 The effects of a suspended-load backpack on gait Xu Xu North Carolina State University
Colin Jackson's Hurdle Clearance Technique
 Colin Jackson's Hurdle Clearance Technique By Milan Čoh, Biomechanical Laboratory, Faculty of Sport, University of Ljubljana, Slovenia INTRODUCTION Colin Jackson is, uncontestedly, one of the greatest
Colin Jackson's Hurdle Clearance Technique By Milan Čoh, Biomechanical Laboratory, Faculty of Sport, University of Ljubljana, Slovenia INTRODUCTION Colin Jackson is, uncontestedly, one of the greatest
Gait Analysis by High School Students
 Gait Analysis by High School Students André Heck 1 and Caroline van Dongen 2 1 AMSTEL Institute, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, heck@science.uva.nl 2 St. Antoniuscollege, Gouda, The
Gait Analysis by High School Students André Heck 1 and Caroline van Dongen 2 1 AMSTEL Institute, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, heck@science.uva.nl 2 St. Antoniuscollege, Gouda, The
Analysis of Gait Characteristics Changes in Normal Walking and Fast Walking Of the Elderly People
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 08, Issue 7 (July. 2018), V (V) 34-41 www.iosrjen.org Analysis of Gait Characteristics Changes in and Of the Elderly
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 08, Issue 7 (July. 2018), V (V) 34-41 www.iosrjen.org Analysis of Gait Characteristics Changes in and Of the Elderly
Stride Frequency, Body Fat Percentage, and the Amount of Knee Flexion Affect the Race Time of Male Cross Country Runners
 Stride Frequency, Body Fat Percentage, and the Amount of Knee Flexion Affect the Race Time of Male Cross Country Runners Vineel Mallavarapu 1 and Kevin Finn 2 1 Cedar Falls High School, Cedar Falls, IA
Stride Frequency, Body Fat Percentage, and the Amount of Knee Flexion Affect the Race Time of Male Cross Country Runners Vineel Mallavarapu 1 and Kevin Finn 2 1 Cedar Falls High School, Cedar Falls, IA
Artifacts Due to Filtering Mismatch in Drop Landing Moment Data
 Camenga et al. UW-L Journal of Undergraduate Research XVI (213) Artifacts Due to Filtering Mismatch in Drop Landing Moment Data Elizabeth T. Camenga, Casey J. Rutten, Brendan D. Gould, Jillian T. Asmus,
Camenga et al. UW-L Journal of Undergraduate Research XVI (213) Artifacts Due to Filtering Mismatch in Drop Landing Moment Data Elizabeth T. Camenga, Casey J. Rutten, Brendan D. Gould, Jillian T. Asmus,
Chapter 11 Waves. Waves transport energy without transporting matter. The intensity is the average power per unit area. It is measured in W/m 2.
 Chapter 11 Waves Energy can be transported by particles or waves A wave is characterized as some sort of disturbance that travels away from a source. The key difference between particles and waves is a
Chapter 11 Waves Energy can be transported by particles or waves A wave is characterized as some sort of disturbance that travels away from a source. The key difference between particles and waves is a
Combining effects in human walking: load, speed and gradient
 Combining effects in human walking: load, speed and gradient Leonardo Peyré-Tartaruga, Ph.D. Laboratório de Pesquisa do Exercício, Ufrgs, Porto Alegre, Brazil Laboratorio di Fisiomeccanica della Locomozione,
Combining effects in human walking: load, speed and gradient Leonardo Peyré-Tartaruga, Ph.D. Laboratório de Pesquisa do Exercício, Ufrgs, Porto Alegre, Brazil Laboratorio di Fisiomeccanica della Locomozione,
Inertial compensation for belt acceleration in an instrumented treadmill
 Inertial compensation for belt acceleration in an instrumented treadmill Sandra K. Hnat, Antonie J. van den Bogert Department of Mechanical Engineering, Cleveland State University Cleveland, OH 44115,
Inertial compensation for belt acceleration in an instrumented treadmill Sandra K. Hnat, Antonie J. van den Bogert Department of Mechanical Engineering, Cleveland State University Cleveland, OH 44115,
A New Approach to Modeling Vertical Stiffness in Heel-Toe Distance Runners
 Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Faculty Publications 2003-12-01 A New Approach to Modeling Vertical Stiffness in Heel-Toe Distance Runners Iain Hunter iain_hunter@byu.edu Follow this and
Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Faculty Publications 2003-12-01 A New Approach to Modeling Vertical Stiffness in Heel-Toe Distance Runners Iain Hunter iain_hunter@byu.edu Follow this and
Supplementary Figure S1
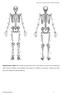 Supplementary Figure S1: Anterior and posterior views of the marker set used in the running gait trials. Forty-six markers were attached to the subject (15 markers on each leg, 4 markers on each arm, and
Supplementary Figure S1: Anterior and posterior views of the marker set used in the running gait trials. Forty-six markers were attached to the subject (15 markers on each leg, 4 markers on each arm, and
Shoe-shaped Interface for Inducing a Walking Cycle
 Shoe-shaped Interface for Inducing a Walking Cycle Junji Watanabe*, Hideyuki Ando**, Taro Maeda** * Graduate School of Information Science and Technology, The University of Tokyo 7-3-1, Hongo, Bunkyo-ku,
Shoe-shaped Interface for Inducing a Walking Cycle Junji Watanabe*, Hideyuki Ando**, Taro Maeda** * Graduate School of Information Science and Technology, The University of Tokyo 7-3-1, Hongo, Bunkyo-ku,
KINEMATIC QUANTIFICATION OF GAIT SYMMETRY BASED ON BILATERAL CYCLOGRAMS
 KINEMATIC QUANTIFICATION OF GAIT SYMMETRY BASED ON BILATERAL CYCLOGRAMS Ambarish Goswami Honda Research Institute Mountain View, California, USA agoswami@honda-ri.com Abstract Symmetry is considered to
KINEMATIC QUANTIFICATION OF GAIT SYMMETRY BASED ON BILATERAL CYCLOGRAMS Ambarish Goswami Honda Research Institute Mountain View, California, USA agoswami@honda-ri.com Abstract Symmetry is considered to
Biomechanical analysis of the medalists in the 10,000 metres at the 2007 World Championships in Athletics
 STUDY Biomechanical analysis of the medalists in the 10,000 metres at the 2007 World Championships in Athletics by IAAF 23:3; 61-66, 2008 By Yasushi Enomoto, Hirosuke Kadono, Yuta Suzuki, Tetsu Chiba,
STUDY Biomechanical analysis of the medalists in the 10,000 metres at the 2007 World Championships in Athletics by IAAF 23:3; 61-66, 2008 By Yasushi Enomoto, Hirosuke Kadono, Yuta Suzuki, Tetsu Chiba,
Equation 1: F spring = kx. Where F is the force of the spring, k is the spring constant and x is the displacement of the spring. Equation 2: F = mg
 1 Introduction Relationship between Spring Constant and Length of Bungee Cord In this experiment, we aimed to model the behavior of the bungee cord that will be used in the Bungee Challenge. Specifically,
1 Introduction Relationship between Spring Constant and Length of Bungee Cord In this experiment, we aimed to model the behavior of the bungee cord that will be used in the Bungee Challenge. Specifically,
Equine Results Interpretation Guide For Cannon Angles May 2013
 Equine Results Interpretation Guide For Cannon Angles May 2013 Page 1 of 20 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Options for all plots... 7 3. Tables of data... 8 4. Gaits... 10 5. Walk... 10 6. Trot...
Equine Results Interpretation Guide For Cannon Angles May 2013 Page 1 of 20 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Options for all plots... 7 3. Tables of data... 8 4. Gaits... 10 5. Walk... 10 6. Trot...
Coaching the Triple Jump Boo Schexnayder
 I. Understanding the Event A. The Run and Its Purpose B. Hip Undulation and the Phases C. Making the Connection II. III. IV. The Approach Run A. Phases B. Technical Features 1. Posture 2. Progressive Body
I. Understanding the Event A. The Run and Its Purpose B. Hip Undulation and the Phases C. Making the Connection II. III. IV. The Approach Run A. Phases B. Technical Features 1. Posture 2. Progressive Body
Joint Torque Evaluation of Lower Limbs in Bicycle Pedaling
 11th conference of the International Sports Engineering Association, ISEA 216 Delft University of Technology; July 12 th Joint Torque Evaluation of Lower Limbs in Bicycle Pedaling Hiroki Yamazaki Akihiro
11th conference of the International Sports Engineering Association, ISEA 216 Delft University of Technology; July 12 th Joint Torque Evaluation of Lower Limbs in Bicycle Pedaling Hiroki Yamazaki Akihiro
Load dynamics of joints in Nordic walking
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 11 (2011) 544 551 5 th Asia-Pacific Congress on Sports Technology (APCST) Load dynamics of joints in Nordic walking Takayuki Koizumi a*, Nobutaka
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 11 (2011) 544 551 5 th Asia-Pacific Congress on Sports Technology (APCST) Load dynamics of joints in Nordic walking Takayuki Koizumi a*, Nobutaka
LocoMorph Deliverable 4.4 part 2.4
 LocoMorph Deliverable 4.4 part 2.4 Kinematics in healthy and morphosed long-tailed lizards (Takydromus sexlineatus): comparison of a simulation model with experimental animal data. Aim D Août K, Karakasiliotis
LocoMorph Deliverable 4.4 part 2.4 Kinematics in healthy and morphosed long-tailed lizards (Takydromus sexlineatus): comparison of a simulation model with experimental animal data. Aim D Août K, Karakasiliotis
Energetics Study of Mechanically Coupled Human Walking. Honors Undergraduate Thesis. the Undergraduate School of The Ohio State University
 Energetics Study of Mechanically Coupled Human Walking Honors Undergraduate Thesis Presented in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree Bachelor of Science in the Undergraduate School of
Energetics Study of Mechanically Coupled Human Walking Honors Undergraduate Thesis Presented in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree Bachelor of Science in the Undergraduate School of
Is lung capacity affected by smoking, sport, height or gender. Table of contents
 Sample project This Maths Studies project has been graded by a moderator. As you read through it, you will see comments from the moderator in boxes like this: At the end of the sample project is a summary
Sample project This Maths Studies project has been graded by a moderator. As you read through it, you will see comments from the moderator in boxes like this: At the end of the sample project is a summary
How Do You Swing? You should be working with new lab partners starting with this lab.
 You should be working with new lab partners starting with this lab. Exploration: Swinging your arms and legs back and forth Discuss and try out the following questions within your lab group. After you
You should be working with new lab partners starting with this lab. Exploration: Swinging your arms and legs back and forth Discuss and try out the following questions within your lab group. After you
GAIT RECOVERY IN HEALTHY SUBJECTS: PERTURBATIONS TO THE KNEE MOTION WITH A SMART KNEE BRACE. by Mehmet Temel
 GAIT RECOVERY IN HEALTHY SUBJECTS: PERTURBATIONS TO THE KNEE MOTION WITH A SMART KNEE BRACE by Mehmet Temel A thesis submitted to the Faculty of the University of Delaware in partial fulfillment of the
GAIT RECOVERY IN HEALTHY SUBJECTS: PERTURBATIONS TO THE KNEE MOTION WITH A SMART KNEE BRACE by Mehmet Temel A thesis submitted to the Faculty of the University of Delaware in partial fulfillment of the
The effect of different backpack loading systems on trunk forward lean angle during walking among college students
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Sports and Exercise Science, 2012, 1 (1):1-5 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN: 2278 005X The effect of different
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Sports and Exercise Science, 2012, 1 (1):1-5 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN: 2278 005X The effect of different
SCHEINWORKS Measuring and Analysis Systems by
 Pressure Measurement Systems for standing and walking analysis Germany since 1879 Pressure Measurement Systems for standing and walking analysis Documentation of Gait image Stance Symmetry of all parameters
Pressure Measurement Systems for standing and walking analysis Germany since 1879 Pressure Measurement Systems for standing and walking analysis Documentation of Gait image Stance Symmetry of all parameters
The Math and Science of Bowling
 The Report (100 : The Math and Science of Bowling 1. For this project, you will need to collect some data at the bowling alley. You will be on a team with one other student. Each student will bowl a minimum
The Report (100 : The Math and Science of Bowling 1. For this project, you will need to collect some data at the bowling alley. You will be on a team with one other student. Each student will bowl a minimum
A Nomogram Of Performances In Endurance Running Based On Logarithmic Model Of Péronnet-Thibault
 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn: 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-6, Issue-9, pp-78-85 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access A Nomogram Of Performances In Endurance Running
American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn: 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-6, Issue-9, pp-78-85 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access A Nomogram Of Performances In Endurance Running
10/22/15. Walking vs Running. Normal Running Mechanics. Treadmill vs. Overground Are they the same? Importance of Gait Analysis.
 2 angle (deg) 1/22/1 Normal Running Mechanics Walking vs Running Irene Davis, PhD, PT, FACSM, FAPTA, FASB Director, Spaulding National Running Center Walking Periods of DOUBLE SUPPORT Running Periods of
2 angle (deg) 1/22/1 Normal Running Mechanics Walking vs Running Irene Davis, PhD, PT, FACSM, FAPTA, FASB Director, Spaulding National Running Center Walking Periods of DOUBLE SUPPORT Running Periods of
by Michael Young Human Performance Consulting
 by Michael Young Human Performance Consulting The high performance division of USATF commissioned research to determine what variables were most critical to success in the shot put The objective of the
by Michael Young Human Performance Consulting The high performance division of USATF commissioned research to determine what variables were most critical to success in the shot put The objective of the
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 112 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 112 (2015 ) 540 545 7th Asia-Pacific Congress on Sports Technology, APCST 2015 Movement variability of professional pool billiards
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 112 (2015 ) 540 545 7th Asia-Pacific Congress on Sports Technology, APCST 2015 Movement variability of professional pool billiards
2600T Series Pressure Transmitters Plugged Impulse Line Detection Diagnostic. Pressure Measurement Engineered solutions for all applications
 Application Description AG/266PILD-EN Rev. C 2600T Series Pressure Transmitters Plugged Impulse Line Detection Diagnostic Pressure Measurement Engineered solutions for all applications Increase plant productivity
Application Description AG/266PILD-EN Rev. C 2600T Series Pressure Transmitters Plugged Impulse Line Detection Diagnostic Pressure Measurement Engineered solutions for all applications Increase plant productivity
PHASE 1 WIND STUDIES REPORT
 PHASE 1 WIND STUDIES REPORT ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES AND PRELIMINARY DESIGN FOR A SUICIDE DETERRENT SYSTEM Contract 2006-B-17 24 MAY 2007 Golden Gate Bridge Highway and Transportation District Introduction
PHASE 1 WIND STUDIES REPORT ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES AND PRELIMINARY DESIGN FOR A SUICIDE DETERRENT SYSTEM Contract 2006-B-17 24 MAY 2007 Golden Gate Bridge Highway and Transportation District Introduction
The three steps for biomechanical assessment are the following: > Periodically verify the results and the efficacy of treatment
 ENG After having carried out and saved a test, two reports are immediately available: > Gait/Run report: specific report for gait or running tests, with average values, standard deviation and variability
ENG After having carried out and saved a test, two reports are immediately available: > Gait/Run report: specific report for gait or running tests, with average values, standard deviation and variability
Chapter 11 Waves. Waves transport energy without transporting matter. The intensity is the average power per unit area. It is measured in W/m 2.
 Energy can be transported by particles or waves: Chapter 11 Waves A wave is characterized as some sort of disturbance that travels away from a source. The key difference between particles and waves is
Energy can be transported by particles or waves: Chapter 11 Waves A wave is characterized as some sort of disturbance that travels away from a source. The key difference between particles and waves is
Analysis of Backward Falls Caused by Accelerated Floor Movements Using a Dummy
 Original Article Analysis of Backward Falls Caused by Accelerated Floor Movements Using a Dummy Hisao NAGATA 1 * and Hisato OHNO 2 1 National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health, 1 4 6 Umezono,
Original Article Analysis of Backward Falls Caused by Accelerated Floor Movements Using a Dummy Hisao NAGATA 1 * and Hisato OHNO 2 1 National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health, 1 4 6 Umezono,
Phys 201A. Lab 6 - Motion with Constant acceleration Kinematic Equations
 Phys 201A Lab 6 - Motion with Constant acceleration Kinematic Equations Problems: It would be good to list your four kinematic equations below for ready reference. Kinematic equations 1) An amateur bowler
Phys 201A Lab 6 - Motion with Constant acceleration Kinematic Equations Problems: It would be good to list your four kinematic equations below for ready reference. Kinematic equations 1) An amateur bowler
RESEARCH ON THE CHANGES OF THE RESCUERS HEART RATE DURING TRAINING
 RESEARCH ON THE CHANGES OF THE RESCUERS HEART RATE DURING TRAINING Daniel Pupazan, Phd. Eng.,INCD INSEMEX Petrosani Artur George Gaman, Phd. Eng.,INCD INSEMEX Petrosani Cosmin Ilie, Phd. Eng., INCD INSEMEX
RESEARCH ON THE CHANGES OF THE RESCUERS HEART RATE DURING TRAINING Daniel Pupazan, Phd. Eng.,INCD INSEMEX Petrosani Artur George Gaman, Phd. Eng.,INCD INSEMEX Petrosani Cosmin Ilie, Phd. Eng., INCD INSEMEX
ACTIVITY MONITORING SYSTEM
 ACTIVITY MONITORING SYSTEM Hardik Shah 1, Mohit Srivastava 2, Sankarshan Shukla 3, Dr. Mita Paunwala 4 Student, Electronics and Communication, CKPCET, Surat, Gujarat, India 1 Student, Electronics and Communication,
ACTIVITY MONITORING SYSTEM Hardik Shah 1, Mohit Srivastava 2, Sankarshan Shukla 3, Dr. Mita Paunwala 4 Student, Electronics and Communication, CKPCET, Surat, Gujarat, India 1 Student, Electronics and Communication,
What is the optimal design of a rocker shoe
 What is the optimal design of a rocker shoe University of Salford School of Health, Sport and Rehabilitation Sciences Deutsche Sporthochschule Köln J Chapman, S Preece, C Nester, B Braunstein, P Bruggerman
What is the optimal design of a rocker shoe University of Salford School of Health, Sport and Rehabilitation Sciences Deutsche Sporthochschule Köln J Chapman, S Preece, C Nester, B Braunstein, P Bruggerman
Simulation-based design to reduce metabolic cost
 Simulation-based design to reduce metabolic cost Overview: Lecture + Hands On Exercise 1. Generating and evaluating a muscledriven simulation of walking 2. Metabolics 101 3. Designing and evaluating devices
Simulation-based design to reduce metabolic cost Overview: Lecture + Hands On Exercise 1. Generating and evaluating a muscledriven simulation of walking 2. Metabolics 101 3. Designing and evaluating devices
IAC-13-A1.6.1 THE ANALYSIS OF THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN MOTION RESTRAINTS CAUSED BY PRESSURIZED SUITS AND RISK OF FALLING
 IAC-13-A1.6.1 THE ANALYSIS OF THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN MOTION RESTRAINTS CAUSED BY PRESSURIZED SUITS AND RISK OF FALLING Yasuhiro Akiyama Nagoya University, Japan, akiyama-yasuhiro@mech.nagoya-u.ac.jp
IAC-13-A1.6.1 THE ANALYSIS OF THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN MOTION RESTRAINTS CAUSED BY PRESSURIZED SUITS AND RISK OF FALLING Yasuhiro Akiyama Nagoya University, Japan, akiyama-yasuhiro@mech.nagoya-u.ac.jp
Calculation of Trail Usage from Counter Data
 1. Introduction 1 Calculation of Trail Usage from Counter Data 1/17/17 Stephen Martin, Ph.D. Automatic counters are used on trails to measure how many people are using the trail. A fundamental question
1. Introduction 1 Calculation of Trail Usage from Counter Data 1/17/17 Stephen Martin, Ph.D. Automatic counters are used on trails to measure how many people are using the trail. A fundamental question
Do Thigh Circumference and Mass Changes Associated With Obesity Alter Walking Biomechanics?
 University of Tennessee, Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange Masters Theses Graduate School 5-2011 Do Thigh Circumference and Mass Changes Associated With Obesity Alter Walking Biomechanics?
University of Tennessee, Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange Masters Theses Graduate School 5-2011 Do Thigh Circumference and Mass Changes Associated With Obesity Alter Walking Biomechanics?
Neurorehabil Neural Repair Oct 23. [Epub ahead of print]
![Neurorehabil Neural Repair Oct 23. [Epub ahead of print] Neurorehabil Neural Repair Oct 23. [Epub ahead of print]](/thumbs/86/94477916.jpg) APPENDICE Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2009 Oct 23. [Epub ahead of print] Segmental Muscle Vibration Improves Walking in Chronic Stroke Patients With Foot Drop: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Paoloni M,
APPENDICE Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2009 Oct 23. [Epub ahead of print] Segmental Muscle Vibration Improves Walking in Chronic Stroke Patients With Foot Drop: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Paoloni M,
Analysis of ankle kinetics and energy consumption with an advanced microprocessor controlled ankle foot prosthesis.
 Analysis of ankle kinetics and energy consumption with an advanced microprocessor controlled ankle foot prosthesis. D.Moser, N.Stech, J.McCarthy, G.Harris, S.Zahedi, A.McDougall Summary This study reports
Analysis of ankle kinetics and energy consumption with an advanced microprocessor controlled ankle foot prosthesis. D.Moser, N.Stech, J.McCarthy, G.Harris, S.Zahedi, A.McDougall Summary This study reports
RESEARCH ARTICLE Energetically optimal stride frequency in running: the effects of incline and decline
 289 The Journal of Experimental Biology 214, 289-295 211. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd doi:1.1242/jeb.53157 RESEARCH ARTICLE Energetically optimal stride frequency in running: the effects
289 The Journal of Experimental Biology 214, 289-295 211. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd doi:1.1242/jeb.53157 RESEARCH ARTICLE Energetically optimal stride frequency in running: the effects
GROUND REACTION FORCE DOMINANT VERSUS NON-DOMINANT SINGLE LEG STEP OFF
 GROUND REACTION FORCE DOMINANT VERSUS NON-DOMINANT SINGLE LEG STEP OFF Sara Gharabaghli, Rebecca Krogstad, Sara Lynch, Sofia Saavedra, and Tamara Wright California State University, San Marcos, San Marcos,
GROUND REACTION FORCE DOMINANT VERSUS NON-DOMINANT SINGLE LEG STEP OFF Sara Gharabaghli, Rebecca Krogstad, Sara Lynch, Sofia Saavedra, and Tamara Wright California State University, San Marcos, San Marcos,
Use of Ground Reaction Force Parameters in Predicting Peak Tibia! Accelerations in Running
 TECHNICAL NOTES JOURNAL OF APPLIED BIOMECHANICS, 1993,9,306-314 O 1993 by Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. Use of Ground Reaction Force Parameters in Predicting Peak Tibia! Accelerations in Running Ewald
TECHNICAL NOTES JOURNAL OF APPLIED BIOMECHANICS, 1993,9,306-314 O 1993 by Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. Use of Ground Reaction Force Parameters in Predicting Peak Tibia! Accelerations in Running Ewald
Simultaneous positive and negative external mechanical work in human walking
 Journal of Biomechanics 35 (2002) 117 124 Simultaneous positive and negative external mechanical work in human walking J.Maxwell Donelan a, *, Rodger Kram a, Arthur D. Kuo b a Locomotion Laboratory, Department
Journal of Biomechanics 35 (2002) 117 124 Simultaneous positive and negative external mechanical work in human walking J.Maxwell Donelan a, *, Rodger Kram a, Arthur D. Kuo b a Locomotion Laboratory, Department
1 INEGI Instituto de Engenharia Mecânica e Gestão Industrial, Porto, Portugal, FEUP Faculdade de Engenharia,
 REGISTRATION BETWEEN DATA FROM VISUAL SENSORS AND FORCE PLATFORM IN GAIT EVENT DETECTION Sousa, Daniela Sofia S., Tavares, João Manuel R. S., Correia, Miguel V., Mendes, Emília, Veloso, António 4, Silva,
REGISTRATION BETWEEN DATA FROM VISUAL SENSORS AND FORCE PLATFORM IN GAIT EVENT DETECTION Sousa, Daniela Sofia S., Tavares, João Manuel R. S., Correia, Miguel V., Mendes, Emília, Veloso, António 4, Silva,
The Effect of a Seven Week Exercise Program on Golf Swing Performance and Musculoskeletal Screening Scores
 The Effect of a Seven Week Exercise Program on Golf Swing Performance and Musculoskeletal Screening Scores 2017 Mico Hannes Olivier Bachelor of Sport Science Faculty of Health Sciences and Medicine Bond
The Effect of a Seven Week Exercise Program on Golf Swing Performance and Musculoskeletal Screening Scores 2017 Mico Hannes Olivier Bachelor of Sport Science Faculty of Health Sciences and Medicine Bond
Diabetes and Orthoses. Rob Bradbury Talar Made
 Diabetes and Orthoses Rob Bradbury Talar Made Diabetes High prevalence disease 4-6% in UK (over 2.5 mill diagnosed and a further 0.5 ) 6+% in USA 40% in some parts of Middle East (may be higher in Indian
Diabetes and Orthoses Rob Bradbury Talar Made Diabetes High prevalence disease 4-6% in UK (over 2.5 mill diagnosed and a further 0.5 ) 6+% in USA 40% in some parts of Middle East (may be higher in Indian
Putting Report Details: Key and Diagrams: This section provides a visual diagram of the. information is saved in the client s database
 Quintic Putting Report Information Guide Putting Report Details: Enter personal details of the client or individual who is being analysed; name, email address, date, mass, height and handicap. This information
Quintic Putting Report Information Guide Putting Report Details: Enter personal details of the client or individual who is being analysed; name, email address, date, mass, height and handicap. This information
GAIT ANALYSIS OF SUBJECTS WITH ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT RUPTURE USING MEDILOGIC SOLE PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION MEASUREMENT SYSTEM
 GAIT ANALYSIS OF SUBJECTS WITH ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT RUPTURE USING MEDILOGIC SOLE PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION MEASUREMENT SYSTEM D. Höftberger 1, A. Kozek 1, J. Langer 1, J. Obergruber 1 1 Fachhochschule
GAIT ANALYSIS OF SUBJECTS WITH ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT RUPTURE USING MEDILOGIC SOLE PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION MEASUREMENT SYSTEM D. Höftberger 1, A. Kozek 1, J. Langer 1, J. Obergruber 1 1 Fachhochschule
E. Agu, M. Kasperski Ruhr-University Bochum Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Sciences
 EACWE 5 Florence, Italy 19 th 23 rd July 29 Flying Sphere image Museo Ideale L. Da Vinci Chasing gust fronts - wind measurements at the airport Munich, Germany E. Agu, M. Kasperski Ruhr-University Bochum
EACWE 5 Florence, Italy 19 th 23 rd July 29 Flying Sphere image Museo Ideale L. Da Vinci Chasing gust fronts - wind measurements at the airport Munich, Germany E. Agu, M. Kasperski Ruhr-University Bochum
GEA FOR ADVANCED STRUCTURAL DYNAMIC ANALYSIS
 SMART SOLUTIONS FOR VIBRATION MONITORING GEA FOR ADVANCED STRUCTURAL DYNAMIC ANALYSIS ANALYSIS OF CIVIL STRUCTURES - EXPO MERLATA PEDESTRIAN BRIDGE ABSTRACT Civil structures and in particular bridges and
SMART SOLUTIONS FOR VIBRATION MONITORING GEA FOR ADVANCED STRUCTURAL DYNAMIC ANALYSIS ANALYSIS OF CIVIL STRUCTURES - EXPO MERLATA PEDESTRIAN BRIDGE ABSTRACT Civil structures and in particular bridges and
Steeplechase Hurdle Economy, Mechanics, and Performance
 Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Theses and Dissertations 2013-06-27 Steeplechase Hurdle Economy, Mechanics, and Performance Sarah Ingebretsen Brigham Young University - Provo Follow this
Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Theses and Dissertations 2013-06-27 Steeplechase Hurdle Economy, Mechanics, and Performance Sarah Ingebretsen Brigham Young University - Provo Follow this
Continuous sweep versus discrete step protocols for studying effects of wearable robot assistance magnitude
 Malcolm et al. Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation (2017) 14:72 DOI 10.1186/s12984-017-0278-2 RESEARCH Continuous sweep versus discrete step protocols for studying effects of wearable robot
Malcolm et al. Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation (2017) 14:72 DOI 10.1186/s12984-017-0278-2 RESEARCH Continuous sweep versus discrete step protocols for studying effects of wearable robot
Comparison of gait properties during level walking and stair ascent and descent with varying loads
 Vol.2, No.12, 1372-1376 (2010) doi:10.4236/health.2010.212203 Health Comparison of gait properties during level walking and stair ascent and descent with varying loads Tomohiro Demura 1*, Shin-ich Demura
Vol.2, No.12, 1372-1376 (2010) doi:10.4236/health.2010.212203 Health Comparison of gait properties during level walking and stair ascent and descent with varying loads Tomohiro Demura 1*, Shin-ich Demura
Complex movement patterns of a bipedal walk
 1 Complex movement patterns of a bipedal walk Objectives After completing this lesson, you will be able to: Describe the complex movement patterns of a bipedal walk. Describe the biomechanics of walking
1 Complex movement patterns of a bipedal walk Objectives After completing this lesson, you will be able to: Describe the complex movement patterns of a bipedal walk. Describe the biomechanics of walking
Experiment P18: Buoyant Force (Force Sensor)
 PASCO scientific Physics Lab Manual: P18-1 Experiment P18: (Force Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file Newton's Laws 45 m 300/500/700 P18 P18_BUOY.SWS EQUIPMENT NEEDED CONSUMABLES
PASCO scientific Physics Lab Manual: P18-1 Experiment P18: (Force Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file Newton's Laws 45 m 300/500/700 P18 P18_BUOY.SWS EQUIPMENT NEEDED CONSUMABLES
EEC 686/785 Modeling & Performance Evaluation of Computer Systems. Lecture 6. Wenbing Zhao. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 EEC 686/785 Modeling & Performance Evaluation of Computer Systems Lecture 6 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Cleveland State University wenbing@ieee.org Outline 2 Review of lecture 5 The
EEC 686/785 Modeling & Performance Evaluation of Computer Systems Lecture 6 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Cleveland State University wenbing@ieee.org Outline 2 Review of lecture 5 The
Advanced Test Equipment Rentals ATEC (2832) OMS 600
 Established 1981 Advanced Test Equipment Rentals www.atecorp.com 800-404-ATEC (2832) OMS 600 Continuous partial discharge monitoring system for power generators and electrical motors Condition monitoring
Established 1981 Advanced Test Equipment Rentals www.atecorp.com 800-404-ATEC (2832) OMS 600 Continuous partial discharge monitoring system for power generators and electrical motors Condition monitoring
siot-shoe: A Smart IoT-shoe for Gait Assistance (Miami University)
 siot-shoe: A Smart IoT-shoe for Gait Assistance (Miami University) Abstract Mark Sullivan, Casey Knox, Juan Ding Gait analysis through the Internet of Things (IoT) is able to provide an overall assessment
siot-shoe: A Smart IoT-shoe for Gait Assistance (Miami University) Abstract Mark Sullivan, Casey Knox, Juan Ding Gait analysis through the Internet of Things (IoT) is able to provide an overall assessment
