Many elite cyclists therefore try to optimise their position for drag by means of field tests or wind tunnel tests. More recently, also Computational
|
|
|
- Duane Henry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Seventh International Colloquium on Bluff Body Aerodynamics and Applications (BBAA7) Shanghai, China; September 2-6, 2012 RANS and LES simulations of the interference drag of two cyclists B. Blocken a, T. Defraeye b,c, E. Koninckx d, J. Carmeliet e,f, P. Hespel g a Building Physics and Services, Eindhoven University of Technology, P.O. Box 513, 5600 MB Eindhoven, The Netherlands, b.j.e.blocken@tue.nl b Division of Building Physics, Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, Kasteelpark Arenberg 40, Leuven, Belgium c Division of Mechatronics, Biostatistics and Sensors, Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, Willem de Croylaan 42, Leuven, Belgium d Flemish Cycling Federation, Globelaan 49/2, 1190 Brussels, Belgium e Chair of Building Physics, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich (ETHZ), Wolfgang- Pauli-Strasse 15, 8093 Zürich, Switzerland f Laboratory for Building Science and Technology, Empa, Überlandstrasse 129, 8600 Dübendorf, Switzerland g Research Centre for Exercise and Health, Department of Biomedical Kinesiology, Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, Tervuursevest 101, 3001 Heverlee, Belgium ABSTRACT: This paper presents a numerical study of the interference drag of two cyclists in dropped position and in time-trial position. The study is based on 3D laser scanning of the cyclist geometry and on high-resolution grid generation, where the centre of the wall-adjacent cell is at about 15 micrometer from the body surface, resulting in y* values well below 5. The cell size in the wake is about 0.03 m. Both the Reynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) approach with closure provided by the standard k-ε model and Large Eddy Simulations (LES) are performed. For LES, the time step is 3x10-4 s based on the CFL number. The interference drag is evaluated for inter-cyclist spacing varying from d = 0.01 to d = 1 m. Although the RANS and LES approach provided similarly accurate results for pressure coefficients and aerodynamic drag of a single cyclist, the results of both approaches for the interference drag are quite different. Compared to a single cyclist, the drag reduction for the dropped position with d = 0.01 m and with RANS is 2% for the first cyclist and 26% for the second one, while with LES it is 3% and 34%, respectively. For the time-trial position with d = 0.01 m, the reductions with RANS are 3% for the first cyclist and 16% for the second one, while with LES these values are 2% and 36%, respectively. Additional wind tunnel experiments with two cyclists are scheduled for further validation studies. Additional analysis of the CFD results will be performed to analyze the reasons for the large differences between RANS and LES results. KEYWORDS: Cyclist aerodynamics, drag resistance, Computational Fluid Dynamics. 1. INTRODUCTION At racing speeds (± 50 km/h in time trails), the aerodynamic resistance experienced by a cyclist, also called drag, is about 90% of his/her total resistance (Grappe et al. 1997, Kyle and Burke 1984). The major part is caused by form drag, related to the position of the cyclist on the bicycle. 1666
2 Many elite cyclists therefore try to optimise their position for drag by means of field tests or wind tunnel tests. More recently, also Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) has been applied in cycling (Hanna 2002, Lukes et al. 2004, Defraeye et al. 2010a, 2010b). Most studies were performed by solving the steady Reynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) equations. Most studies have also employed wall-function modelling for the near-wall region. Recent studies however have explicitly resolved the boundary layer by low-reynolds number modelling (LRNM) (Defraeye et al. 2010a, 2010b). These CFD simulations were validated with detailed wind tunnel measurements on a full-scale (real) cyclist (Defraeye et al. 2010a) and a ½ scale model (Defraeye et al. 2010b). The study by Defraeye et al. (2010a) compared CFD simulations with drag measurements on a full-scale cyclist and indicated that, for the dropped position, Large Eddy Simulation (LES) yields a deviation in the drag area of 3%, while steady RANS with the standard k-ε model yields a deviation of 7% compared to the measurements. However, for the reduced-scale (1:2) model (upright position), steady RANS with the standard k-ε model provided a deviation in the drag area of only 4% compared to 6% with LES (Defraeye et al. 2010b). These results indicate that the RANS and LES results for the aerodynamic drag are very close. Therefore, they might suggest that further studies in cyclist aerodynamics can be conducted with steady RANS and the standard k-ε model, and that more time-consuming and intrinsically more accurate simulations with LES would not be necessary. To analyze the validity of this hypothesis, this paper provides results of a numerical study with both RANS and LES of the interference drag of two cyclists, riding one behind the other, in still air (zero wind speed). 2. CFD SIMULATIONS: COMPUTATIONAL PARAMETERS AND SETTINGS A digital model of the cyclist was obtained for the dropped position and the time-trial position using a high-resolution 3D laser scanning system (K-Scan, Nikon Metrology, Belgium), capturing the specific body characteristics of the cyclist. For meshing purposes, surface details were smoothed out to some extent and the bicycle was not included in the computational model. Two of these virtual cyclists were placed in a computational domain, one behind the other, with a spacing d varying from d = 0.01 m to 1m, including: 0.01 m, 0.25 m, 0.5 m and 1 m (Figs. 1 and 2). The size of the computational domain, for the two cyclists with d = 0.01 m, is L x W x H = 21 m x 6 m x 7 m. For the other distances, the length of the domain is increased with the spacing d. The grid is a hybrid grid, consisting of very small prismatic cells in the boundary-layer region near the cyclist s surface, with the first computational cell at only 15 m from the body surface. This high resolution is needed because low-reynolds number modelling requires the y * values of the wall-adjacent cells to be about 1 and certainly lower than 5 (Casey and Wintergerste 2000). Further away from the surface, tetrahedral cells have been used, with an average cell size in the wake region of about 0.03 m. The resulting grids for a single cyclist contain about 7.7x10 6 cells, while the grids for the two cyclists contain about 12.0x10 6 cells. The grids are based on gridsensitivity analysis according to best practice guidelines in CFD (Casey and Wintergerste 2000, Franke et al. 2007, Tominaga et al. 2008). The grid discretisation error was estimated by means of Richardson extrapolation and was about 3% for the drag force of the single cyclist. At the inlet, a uniform inlet velocity of 15 m/s is imposed, with zero turbulence intensity, which represents the relative air movement around the cyclists due to the cycling speed in still air 1667
3 The Seventh International Colloquium on Bluff Body Aerodynamics and Applications (BBAA7) Shanghai, China; September 2-6, 2012 (zero wind speed). For the side and top boundaries, a slip-wall boundary (symmetry) was used. Slip walls assume that the normal velocity component and the normal gradients at the boundary are zero, resulting in flow parallel to the boundary. At the outlet of the computational domain, ambient static pressure was imposed. Two approaches are used: (1) 3D steady RANS with the standard k- turbulence model (Launder and Spalding 1972) and with low-reynolds number modelling (LRNM), for which the one-equation Wolfshtein model (Wolfshtein 1969) is used in this study. Second-order discretisation schemes are used throughout. The SIMPLE algorithm is used for pressure-velocity coupling. Pressure interpolation is second order. (2) 3D LES simulations with the dynamic Smagorinsky subgrid-scale model (Kim 2004) with LRNM. Second-order discretisation schemes are used except for momentum, for which a central differencing scheme is used. Second-order implicit time stepping is used, and 20 iterations per time step were found to be sufficient to have convergence within a time step. The temporal discretisation is related to the spatial discretisation by the CFL (Courant-Friedrichs-Lewy) number: CFL = uδt/d, where u is the characteristic velocity in the cell, t is the time step and d is the characteristic cell dimension. Time steps resulting in CFL numbers of 1 are suggested in the wake region (Spalart 2001). For the simulations, the choice of the time step and averaging period was also based on a sensitivity analysis. A time step of 3x10-4 s was chosen, resulting in CFL numbers below about 5 in the majority of the domain, with maximal values that do not exceed 10, and values of about 0.5 in the wake. A dimensionless simulation time of about 2 flow-through-times was found to be sufficient to obtain stationary, i.e. stable averaged, values for drag and surface pressures, where the flowthrough-time is defined as: t FT = UT/L D, where U is the free-stream (approach flow) wind speed (15 m/s), T is the averaging period (2.8 s) and L D is the length of the computational domain (21 m). The simulations were performed with the commercial CFD code Fluent 6.3, which uses the control volume method. Figure 1. Two cyclists in dropped position at a variable spacing d. 1668
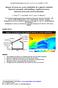
4 Figure 2. Two cyclists in time-trial position at a variable spacing d. 3. CFD SIMULATIONS: RESULTS Figure 3 shows an instantaneous image of the velocity contours in a vertical centreplane for the two cyclists in dropped position and with spacing d = 0.01 m. The low-velocity stagnation regions directly upstream of every cyclist can be observed, as well as the turbulent low-velocity wake of the first cyclist that partly engulfs the second cyclist. In this vertical centreplane and in this dropped cyclist position, flow separation is observed at the top of the helmets. The figure also shows the very dense grid resolution on the cyclist bodies and helmets. Figure 3. Instantaneous velocity contours in vertical centreplane for two cyclists in dropped position at distance d = 0.01 m. 1669
5 The Seventh International Colloquium on Bluff Body Aerodynamics and Applications (BBAA7) Shanghai, China; September 2-6, 2012 The results of the simulations are reported in Figures 4 and 5, in terms of drag reduction (DR) for the two cyclists, with respect to a single cyclist, and as a function of the inter-cyclist spacing d. Figure 4 shows the drag reduction for the first and for the second cyclist in dropped position, as obtained with RANS and with LES. It is noteworthy that there is also a drag reduction for the first cyclist due to the proximity of the second cyclist behind him/her, although this drag reduction is limited and it rapidly disappears with increasing inter-cyclist spacing. The intrinsically more accurate LES simulations indicate a larger drag reduction for both cyclists compared to RANS. For d = 0.01 m, LES indicates a reduction of 3% for the first cyclist and 34% for the second cyclist, while RANS indicates 2% for the first cyclist and 26% for the second one. Both approaches indicate a near-linear decrease of the drag reduction with increasing inter-cyclist spacing, although this decrease is more pronounced according to the LES results. At a distance of 1 m, the drag reduction for the second cyclist is still 28% (LES), while that for the first cyclist has become negligible. Figure 4. Drag reduction of two cyclists, with respect to a single cyclist, in dropped position at a variable spacing d, as obtained by RANS and LES simulations. 1670
6 Figure 5 shows the drag reduction for the first and for the second cyclist in time-trial position, as obtained with RANS and with LES. Also here, the drag reduction for the first cyclist due to the proximity of the second cyclist is clearly present. As opposed to the results for the dropped position, the results for the time-trial position show a very large difference between RANS and LES results for the second cyclist, more than a factor 2, while the differences in results for the first cyclist are negligible. For d = 0.01 m, LES indicates a reduction of 2% for the first cyclist and 36% for the second cyclist, while RANS indicates 3% for the first cyclist and 16% for the second one. Both approaches indicate a near-linear decrease of the drag reduction with increasing intercyclist spacing, which is most pronounced for the second cyclist with LES. At a distance of 1 m, the drag reduction for the second cyclist is still 30% (LES), while that for the first cyclist has become negligible. Figure 5. Drag reduction of two cyclists, with respect to a single cyclist, in time-trial position at a variable spacing d, as obtained by RANS and LES simulations. 1671
7 The Seventh International Colloquium on Bluff Body Aerodynamics and Applications (BBAA7) Shanghai, China; September 2-6, DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSIONS The interference drag (drag reduction) experienced by a second cyclist due to a cyclist in front of him/her is well-known. The fact that the first cyclist also experiences a drag reduction by the presence of the second one however, is less known, although there are some previous studies that suggest drag reduction of an upstream body by its downstream counterpart (e.g. Iniguez-de-la Torre and Iniguez 2009). The reason for the drag reduction of the first cyclist by the second one is the overpressure region in front of this second cyclist. This overpressure region merges with the underpressure region (wake) behind the first cyclist, thereby reducing the underpressure in this region and reducing the drag force. This effect is more pronounced as the cyclists ride closer behind each other. Previous numerical studies on the aerodynamics of a single cyclist riding in still air (Defraeye et al. 2010a, 2010b) have shown that the RANS and LES approach provided similarly accurate results for pressure coefficients and aerodynamic drag. In particular, the study by Defraeye et al. (2010a) compared CFD simulations with drag measurements on a full-scale cyclist and indicated that, for the dropped position, Large Eddy Simulation (LES) yields a deviation in the drag area of 3%, while steady RANS with the standard k-ε model yields a deviation of 7%. However, for the reduced-scale (1:2) model (upright position), steady RANS with the standard k-ε model provided a deviation in the drag area of only 4% compared to 6% with LES (Defraeye et al. 2010b). These results might suggest that further studies can be conducted with steady RANS and the standard k- ε model, and that more time-consuming and intrinsically more accurate simulations with LES would not be necessary. However, the comparison of RANS and LES simulations of the interference drag of two cyclists show large to very large differences between both approaches. Compared to a single cyclist, the drag reduction for the dropped position with d = 0.01 m and with RANS is 2% for the first cyclist and 26% for the second one, while with LES it is 3% and 34%, respectively. For the time-trial position with d = 0.01 m, the reductions with RANS are 3% for the first cyclist and 16% for the second one, while with LES these values are 2% and 36%, respectively. Hereby not only the differences between RANS and LES is remarkable, but also the fact that this difference is much larger for the time-trial position than for the dropped position. Additional wind tunnel experiments with two cyclists are scheduled for further validation studies. Also, additional analysis of the CFD results will be performed to analyze the reasons for these large differences between RANS and LES results. 5. REFERENCES Casey, M., Wintergerste, T., Best Practice Guidelines. ERCOFTAC Special Interest Group on Quality and Trust in Industrial CFD, ERCOFTAC. Defraeye, T., Blocken, B., Koninckx, E., Hespel, P., Carmeliet J., 2010a. Aerodynamic study of different cyclist positions: CFD analysis and full-scale wind-tunnel tests. Journal of Biomechanics 43(7): Defraeye, T., Blocken, B., Koninckx, E., Hespel, P., Carmeliet J., 2010b. Computational Fluid Dynamics analysis of cyclist aerodynamics: Performance of different turbulence-modelling and boundary-layer modelling approaches. Journal of Biomechanics 43(12): Franke, J., Hellsten, A., Schlünzen H., Carissimo, B., Best practice guideline for the CFD simulation of flows in the urban environment, COST Action 732. Grappe, G., Candau, R., Belli, A., Rouillon, J.D., Aerodynamic drag in field cycling with special reference to the Obree s position. Ergonomics 40 (12),
8 Hanna, R.K., Can CFD make a performance difference in sport?. In: Ujihashi, S., Haake, S.J. (Eds.), The Engineering of Sport 4. Blackwell Science, Oxford, pp Iniguez-de-la Torre, A., Iniguez, J., Aerodynamics of a cycling team in a time trial: does the cyclist at the front benefit? European Journal of Physics 30, Kim, S.-E., Large eddy simulation using unstructured meshes and dynamic subgrid-scale turbulence models. In: Proceedings of the 34th AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference and Exhibit, Technical Report AIAA Port- land, Oregon. Kyle, C.R., Burke, E.R., Improving the racing bicycle. Mechanical Engineering 106 (9), Launder, B.E., Spalding, D.B., Lectures in Mathematical Models of Turbulence, Academic Press, London, England. Lukes, R.A., Hart, J.H., Chin, S.B., Haake, S.J., The aerodynamics of mountain bicycles: The role of computational fluid dynamics. In: Hubbard, M., Mehta, R.D., Pallis, J.M. (Eds.), The Engineering of Sport 5. International Sports Engineering Association, Sheffield. Spalart, P.R., Young person s guide to Detached-Eddy Simulation grids. NASA Contractor Report CR NASA, Virginia. Tominaga, Y., Mochida A., Yoshie, R., Kataoka, H., Nozu, T., Yoshikawa, M., Shirasawa, T., AIJ guidelines for practical applications of CFD to pedestrian wind environment around buildings, Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics 96(10-11), Wolfshtein, M., The velocity and temperature distribution in one-dimensional flow with turbulence augmentation and pressure gradient. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer 12 (3),
Cyclist drag in team pursuit: influence of cyclist sequence, stature, and arm
 Cyclist drag in team pursuit: influence of cyclist sequence, stature, and arm spacing Thijs Defraeye a,*, Bert Blocken b, Erwin Koninckx c,d, Peter Hespel d, Pieter Verboven a, Bart Nicolai a, Jan Carmeliet
Cyclist drag in team pursuit: influence of cyclist sequence, stature, and arm spacing Thijs Defraeye a,*, Bert Blocken b, Erwin Koninckx c,d, Peter Hespel d, Pieter Verboven a, Bart Nicolai a, Jan Carmeliet
a high-rise (78 m) building in the city of Antwerp. CFD simulations are performed for the building with and without second-skin facade concept impleme
 The Seventh International Colloquium on Bluff Body Aerodynamics and Applications (BBAA7) Shanghai, China; September 2-6, 2012 CFD analysis of wind comfort on high-rise building balconies: validation and
The Seventh International Colloquium on Bluff Body Aerodynamics and Applications (BBAA7) Shanghai, China; September 2-6, 2012 CFD analysis of wind comfort on high-rise building balconies: validation and
CFD simulations of the aerodynamic drag of two drafting cyclists
 Accepted for publication in Computers & Fluids on November 21, 2012 CFD simulations of the aerodynamic drag of two drafting cyclists Bert Blocken a,, Thijs Defraeye b, Erwin Koninckx c, Jan Carmeliet d,e,
Accepted for publication in Computers & Fluids on November 21, 2012 CFD simulations of the aerodynamic drag of two drafting cyclists Bert Blocken a,, Thijs Defraeye b, Erwin Koninckx c, Jan Carmeliet d,e,
Aerodynamic study of different cyclist positions: CFD analysis and fullscale wind-tunnel tests
 Accepted for publication in Journal of Biomechanics (Jan. 27, 2010) Aerodynamic study of different cyclist positions: CFD analysis and fullscale wind-tunnel tests Thijs Defraeye a, *, Bert Blocken b, Erwin
Accepted for publication in Journal of Biomechanics (Jan. 27, 2010) Aerodynamic study of different cyclist positions: CFD analysis and fullscale wind-tunnel tests Thijs Defraeye a, *, Bert Blocken b, Erwin
Numerical analysis of surface pressure coefficients for a building with balconies
 Numerical analysis of surface pressure coefficients for a building with balconies Montazeri H., Blocken B. Building Physics and Services, Eindhoven University of Technology, P.O. box 513, 5600 MB Eindhoven,
Numerical analysis of surface pressure coefficients for a building with balconies Montazeri H., Blocken B. Building Physics and Services, Eindhoven University of Technology, P.O. box 513, 5600 MB Eindhoven,
Improving pedestrian wind comfort around a high rise building in an urban area: a case study by CFD simulations and on-site measurements
 Improving pedestrian wind comfort around a high rise building in an urban area: a case study by CFD simulations and on-site measurements WD Janssen, B Blocken, and T van Hooff Unit Building Physics and
Improving pedestrian wind comfort around a high rise building in an urban area: a case study by CFD simulations and on-site measurements WD Janssen, B Blocken, and T van Hooff Unit Building Physics and
Computational evaluation of pedestrian wind comfort and wind safety around a high-rise building in an urban area
 International Environmental Modelling and Software Society (iemss) 7th Intl. Congress on Env. Modelling and Software, San Diego, CA, USA, Daniel P. Ames, Nigel W.T. Quinn and Andrea E. Rizzoli (Eds.) http://www.iemss.org/society/index.php/iemss-2014-proceedings
International Environmental Modelling and Software Society (iemss) 7th Intl. Congress on Env. Modelling and Software, San Diego, CA, USA, Daniel P. Ames, Nigel W.T. Quinn and Andrea E. Rizzoli (Eds.) http://www.iemss.org/society/index.php/iemss-2014-proceedings
Effect of Diameter on the Aerodynamics of Sepaktakraw Balls, A Computational Study
 ISSN 1750-9823 (print) International Journal of Sports Science and Engineering Vol. 03 (2009) No. 01, pp. 017-021 Effect of Diameter on the Aerodynamics of Sepaktakraw Balls, A Computational Study Zahari
ISSN 1750-9823 (print) International Journal of Sports Science and Engineering Vol. 03 (2009) No. 01, pp. 017-021 Effect of Diameter on the Aerodynamics of Sepaktakraw Balls, A Computational Study Zahari
COMPARISONS OF COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS AND
 The Seventh Asia-Pacific Conference on Wind Engineering, November 8-12, 2009, Taipei, Taiwan COMPARISONS OF COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS AND WIND TUNNEL EXPERIMENTS FOR PEDESTRIAN WIND ENVIRONMENTS Chin-Hsien
The Seventh Asia-Pacific Conference on Wind Engineering, November 8-12, 2009, Taipei, Taiwan COMPARISONS OF COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS AND WIND TUNNEL EXPERIMENTS FOR PEDESTRIAN WIND ENVIRONMENTS Chin-Hsien
Development of a low- cost 3D scan system with CFD for assessing aerodynamics in cycling June 2017
 Development and validation of a low- cost system for assessing aerodynamics in cycling using computational fluid dynamics Felix A.J. Wolbert Sports Technology, Aalborg University, Denmark Abstract Introduction:
Development and validation of a low- cost system for assessing aerodynamics in cycling using computational fluid dynamics Felix A.J. Wolbert Sports Technology, Aalborg University, Denmark Abstract Introduction:
Surrounding buildings and wind pressure distribution on a high rise building
 Surrounding buildings and wind pressure distribution on a high rise building Conference or Workshop Item Accepted Version Luo, Z. (2008) Surrounding buildings and wind pressure distribution on a high rise
Surrounding buildings and wind pressure distribution on a high rise building Conference or Workshop Item Accepted Version Luo, Z. (2008) Surrounding buildings and wind pressure distribution on a high rise
Aerodynamic study of a cyclist s moving legs using an innovative approach
 Aerodynamic study of a cyclist s moving legs using an innovative approach Francesco Pozzetti 30 September 2017 Abstract During a period of four weeks in September, I completed a research project in fluid
Aerodynamic study of a cyclist s moving legs using an innovative approach Francesco Pozzetti 30 September 2017 Abstract During a period of four weeks in September, I completed a research project in fluid
Pedestrian wind comfort around buildings: comparison of wind comfort criteria based on whole-flow field data for a complex case study
 Accepted for publication in Building and Environment, October 25, 2012 Pedestrian wind comfort around buildings: comparison of wind comfort criteria based on whole-flow field data for a complex case study
Accepted for publication in Building and Environment, October 25, 2012 Pedestrian wind comfort around buildings: comparison of wind comfort criteria based on whole-flow field data for a complex case study
Computational Analysis of the S Airfoil Aerodynamic Performance
 Computational Analysis of the 245-3S Airfoil Aerodynamic Performance Luis Velazquez-Araque and Jiří Nožička 2 Department of Mechanical Engineering National University of Táchira, San Cristóbal 5, Venezuela
Computational Analysis of the 245-3S Airfoil Aerodynamic Performance Luis Velazquez-Araque and Jiří Nožička 2 Department of Mechanical Engineering National University of Táchira, San Cristóbal 5, Venezuela
Welke daalhouding is het meest aerodynamisch?
 Welke daalhouding is het meest aerodynamisch? Bert Blocken a,b a Faculteit Bouwkunde, Technische Universiteit Eindhoven, Nederland b Departement Burgerlijke Bouwkunde, KU Leuven, België Welke daalhouding
Welke daalhouding is het meest aerodynamisch? Bert Blocken a,b a Faculteit Bouwkunde, Technische Universiteit Eindhoven, Nederland b Departement Burgerlijke Bouwkunde, KU Leuven, België Welke daalhouding
Modelling the Output of a Flat-Roof Mounted Wind Turbine with an Edge Mounted Lip
 Modelling the Output of a Flat-Roof Mounted Wind Turbine with an Edge Mounted Lip S. J. Wylie 1, S. J. Watson 1, D. G. Infield 2 1 Centre for Renewable Energy Systems Technology, Department of Electronic
Modelling the Output of a Flat-Roof Mounted Wind Turbine with an Edge Mounted Lip S. J. Wylie 1, S. J. Watson 1, D. G. Infield 2 1 Centre for Renewable Energy Systems Technology, Department of Electronic
OPTIMIZING THE LENGTH OF AIR SUPPLY DUCT IN CROSS CONNECTIONS OF GOTTHARD BASE TUNNEL. Rehan Yousaf 1, Oliver Scherer 1
 OPTIMIZING THE LENGTH OF AIR SUPPLY DUCT IN CROSS CONNECTIONS OF GOTTHARD BASE TUNNEL Rehan Yousaf 1, Oliver Scherer 1 1 Pöyry Infra Ltd, Zürich, Switzerland ABSTRACT Gotthard Base Tunnel with its 57 km
OPTIMIZING THE LENGTH OF AIR SUPPLY DUCT IN CROSS CONNECTIONS OF GOTTHARD BASE TUNNEL Rehan Yousaf 1, Oliver Scherer 1 1 Pöyry Infra Ltd, Zürich, Switzerland ABSTRACT Gotthard Base Tunnel with its 57 km
Wind tunnel test and numerical simulation of wind pressure on a high-rise building
 Journal of Chongqing University (English Edition) [ISSN 1671-8224] Vol. 9 No. 1 March 2010 Article ID: 1671-8224(2010)01-0047-07 To cite this article: AL ZOUBI Feras, LI Zheng-liang, WEI Qi-ke, SUN Yi.
Journal of Chongqing University (English Edition) [ISSN 1671-8224] Vol. 9 No. 1 March 2010 Article ID: 1671-8224(2010)01-0047-07 To cite this article: AL ZOUBI Feras, LI Zheng-liang, WEI Qi-ke, SUN Yi.
RESEARCH ON MEASUREMENT AND SIMULATION OF THE WIND ENVIRON- MENT AROUND BUILDINGS IN CAMPUS
 Eleventh International IBPSA Conference Glasgow, Scotland July 27-30, 2009 RESEARCH ON MEASUREMENT AND SIMULATION OF THE WIND ENVIRON- MENT AROUND BUILDINGS IN CAMPUS Bing Wang 1, Borong Lin 1,* 1Deparment
Eleventh International IBPSA Conference Glasgow, Scotland July 27-30, 2009 RESEARCH ON MEASUREMENT AND SIMULATION OF THE WIND ENVIRON- MENT AROUND BUILDINGS IN CAMPUS Bing Wang 1, Borong Lin 1,* 1Deparment
Measurement and simulation of the flow field around a triangular lattice meteorological mast
 Measurement and simulation of the flow field around a triangular lattice meteorological mast Matthew Stickland 1, Thomas Scanlon 1, Sylvie Fabre 1, Andrew Oldroyd 2 and Detlef Kindler 3 1. Department of
Measurement and simulation of the flow field around a triangular lattice meteorological mast Matthew Stickland 1, Thomas Scanlon 1, Sylvie Fabre 1, Andrew Oldroyd 2 and Detlef Kindler 3 1. Department of
Wind tunnel effects on wingtip vortices
 48th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting Including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition 4-7 January 2010, Orlando, Florida AIAA 2010-325 Wind tunnel effects on wingtip vortices Xin Huang 1, Hirofumi
48th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting Including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition 4-7 January 2010, Orlando, Florida AIAA 2010-325 Wind tunnel effects on wingtip vortices Xin Huang 1, Hirofumi
AIRFLOW GENERATION IN A TUNNEL USING A SACCARDO VENTILATION SYSTEM AGAINST THE BUOYANCY EFFECT PRODUCED BY A FIRE
 - 247 - AIRFLOW GENERATION IN A TUNNEL USING A SACCARDO VENTILATION SYSTEM AGAINST THE BUOYANCY EFFECT PRODUCED BY A FIRE J D Castro a, C W Pope a and R D Matthews b a Mott MacDonald Ltd, St Anne House,
- 247 - AIRFLOW GENERATION IN A TUNNEL USING A SACCARDO VENTILATION SYSTEM AGAINST THE BUOYANCY EFFECT PRODUCED BY A FIRE J D Castro a, C W Pope a and R D Matthews b a Mott MacDonald Ltd, St Anne House,
Simulation of Flow Field Past Symmetrical Aerofoil Baffles Using Computational Fluid Dynamics Method
 Proceedings of the 4 th International Conference of Fluid Flow, Heat and Mass Transfer (FFHMT'17) Toronto, Canada August 21 23, 2017 Paper No. 120 DOI: 10.11159/ffhmt17.120 Simulation of Flow Field Past
Proceedings of the 4 th International Conference of Fluid Flow, Heat and Mass Transfer (FFHMT'17) Toronto, Canada August 21 23, 2017 Paper No. 120 DOI: 10.11159/ffhmt17.120 Simulation of Flow Field Past
AERODYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS OF NACA 0012 AIRFOIL SECTION AT DIFFERENT ANGLES OF ATTACK
 AERODYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS OF NACA 0012 AIRFOIL SECTION AT DIFFERENT ANGLES OF ATTACK SUPREETH NARASIMHAMURTHY GRADUATE STUDENT 1327291 Table of Contents 1) Introduction...1 2) Methodology.3 3) Results...5
AERODYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS OF NACA 0012 AIRFOIL SECTION AT DIFFERENT ANGLES OF ATTACK SUPREETH NARASIMHAMURTHY GRADUATE STUDENT 1327291 Table of Contents 1) Introduction...1 2) Methodology.3 3) Results...5
Influence of rounding corners on unsteady flow and heat transfer around a square cylinder
 Influence of rounding corners on unsteady flow and heat transfer around a square cylinder S. K. Singh Deptt. of Mech. Engg., M. B. M. Engg. College / J. N. V. University, Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India Abstract
Influence of rounding corners on unsteady flow and heat transfer around a square cylinder S. K. Singh Deptt. of Mech. Engg., M. B. M. Engg. College / J. N. V. University, Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India Abstract
COMPUTATIONAL FLOW MODEL OF WESTFALL'S LEADING TAB FLOW CONDITIONER AGM-09-R-08 Rev. B. By Kimbal A. Hall, PE
 COMPUTATIONAL FLOW MODEL OF WESTFALL'S LEADING TAB FLOW CONDITIONER AGM-09-R-08 Rev. B By Kimbal A. Hall, PE Submitted to: WESTFALL MANUFACTURING COMPANY September 2009 ALDEN RESEARCH LABORATORY, INC.
COMPUTATIONAL FLOW MODEL OF WESTFALL'S LEADING TAB FLOW CONDITIONER AGM-09-R-08 Rev. B By Kimbal A. Hall, PE Submitted to: WESTFALL MANUFACTURING COMPANY September 2009 ALDEN RESEARCH LABORATORY, INC.
Windsimulaties op de meteorologische microschaal
 Windsimulaties op de meteorologische microschaal dr.ir. Twan van Hooff prof.dr.ir. Bert Blocken Building Physics Section KU Leuven Unit Building Physics and Services TU/e 2015 Twan van Hooff All Rights
Windsimulaties op de meteorologische microschaal dr.ir. Twan van Hooff prof.dr.ir. Bert Blocken Building Physics Section KU Leuven Unit Building Physics and Services TU/e 2015 Twan van Hooff All Rights
PERFORMANCE OF A FLAPPED DUCT EXHAUSTING INTO A COMPRESSIBLE EXTERNAL FLOW
 24 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES PERFORMANCE OF A FLAPPED DUCT EXHAUSTING INTO A COMPRESSIBLE EXTERNAL FLOW P. R. Pratt, J. K. Watterson, E. Benard, S. Hall School of Aeronautical
24 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES PERFORMANCE OF A FLAPPED DUCT EXHAUSTING INTO A COMPRESSIBLE EXTERNAL FLOW P. R. Pratt, J. K. Watterson, E. Benard, S. Hall School of Aeronautical
Aerodynamic Performance of 160km Box Car
 Aerodynamic Performance of 16km Box Car *Tianyun Dong 1) and Xifeng Liang 2) 1), 2) Key Laboratory of Traffic Safety on Track of Ministry of Education, School of Traffic & Transportation Engineering, Central
Aerodynamic Performance of 16km Box Car *Tianyun Dong 1) and Xifeng Liang 2) 1), 2) Key Laboratory of Traffic Safety on Track of Ministry of Education, School of Traffic & Transportation Engineering, Central
Numerical investigation on the effect of overhang roof around rural house
 Numerical investigation on the effect of overhang roof around rural house *Taksiah A. Majid 1), Shaharudin Shah Zaini 2), Mohd Azmi Ismail 3), Siti Noratikah Che Deraman 4) and Jing Lin Poon 5) 1), 2),
Numerical investigation on the effect of overhang roof around rural house *Taksiah A. Majid 1), Shaharudin Shah Zaini 2), Mohd Azmi Ismail 3), Siti Noratikah Che Deraman 4) and Jing Lin Poon 5) 1), 2),
CFD Analysis ofwind Turbine Airfoil at Various Angles of Attack
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 13, Issue 4 Ver. II (Jul. - Aug. 2016), PP 18-24 www.iosrjournals.org CFD Analysis ofwind Turbine
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 13, Issue 4 Ver. II (Jul. - Aug. 2016), PP 18-24 www.iosrjournals.org CFD Analysis ofwind Turbine
Investigation on 3-D Wing of commercial Aeroplane with Aerofoil NACA 2415 Using CFD Fluent
 Investigation on 3-D of commercial Aeroplane with Aerofoil NACA 2415 Using CFD Fluent Rohit Jain 1, Mr. Sandeep Jain 2, Mr. Lokesh Bajpai 3 1PG Student, 2 Associate Professor, 3 Professor & Head 1 2 3
Investigation on 3-D of commercial Aeroplane with Aerofoil NACA 2415 Using CFD Fluent Rohit Jain 1, Mr. Sandeep Jain 2, Mr. Lokesh Bajpai 3 1PG Student, 2 Associate Professor, 3 Professor & Head 1 2 3
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF ACTIVE FLOW CONTROL BASED ON STREAMWISE VORTICES FOR A BLUNT TRAILING EDGE AIRFOIL
 BBAA VI International Colloquium on: Bluff Bodies Aerodynamics & Applications Milano, Italy, July, 20-24 2008 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF ACTIVE FLOW CONTROL BASED ON STREAMWISE VORTICES FOR A BLUNT TRAILING
BBAA VI International Colloquium on: Bluff Bodies Aerodynamics & Applications Milano, Italy, July, 20-24 2008 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF ACTIVE FLOW CONTROL BASED ON STREAMWISE VORTICES FOR A BLUNT TRAILING
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 112 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 112 (2015 ) 418 423 7th Asia-Pacific Congress on Sports Technology, APCST 2015 Comparison of the aerodynamic performance of
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 112 (2015 ) 418 423 7th Asia-Pacific Congress on Sports Technology, APCST 2015 Comparison of the aerodynamic performance of
OPTIMIZATION OF SINGLE STAGE AXIAL FLOW COMPRESSOR FOR DIFFERENT ROTATIONAL SPEED USING CFD
 http:// OPTIMIZATION OF SINGLE STAGE AXIAL FLOW COMPRESSOR FOR DIFFERENT ROTATIONAL SPEED USING CFD Anand Kumar S malipatil 1, Anantharaja M.H 2 1,2 Department of Thermal Power Engineering, VTU-RO Gulbarga,
http:// OPTIMIZATION OF SINGLE STAGE AXIAL FLOW COMPRESSOR FOR DIFFERENT ROTATIONAL SPEED USING CFD Anand Kumar S malipatil 1, Anantharaja M.H 2 1,2 Department of Thermal Power Engineering, VTU-RO Gulbarga,
Validating CFD Simulation Results: Wind flow around a surface mounted cube in a turbulent channel flow
 Validating CFD Simulation Results: Wind flow around a surface mounted cube in a turbulent channel flow ISLAM ABOHELA 1, NEVEEN HAMZA 1, STEVEN DUDEK 1 1 School of Architecture, Planning and Landscape,
Validating CFD Simulation Results: Wind flow around a surface mounted cube in a turbulent channel flow ISLAM ABOHELA 1, NEVEEN HAMZA 1, STEVEN DUDEK 1 1 School of Architecture, Planning and Landscape,
Experimental Investigation Of Flow Past A Rough Surfaced Cylinder
 (AET- 29th March 214) RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Experimental Investigation Of Flow Past A Rough Surfaced Cylinder Monalisa Mallick 1, A. Kumar 2 1 (Department of Civil Engineering, National Institute
(AET- 29th March 214) RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Experimental Investigation Of Flow Past A Rough Surfaced Cylinder Monalisa Mallick 1, A. Kumar 2 1 (Department of Civil Engineering, National Institute
Numerical Simulation And Aerodynamic Performance Comparison Between Seagull Aerofoil and NACA 4412 Aerofoil under Low-Reynolds 1
 Advances in Natural Science Vol. 3, No. 2, 2010, pp. 244-20 www.cscanada.net ISSN 171-7862 [PRINT] ISSN 171-7870 [ONLINE] www.cscanada.org *The 3rd International Conference of Bionic Engineering* Numerical
Advances in Natural Science Vol. 3, No. 2, 2010, pp. 244-20 www.cscanada.net ISSN 171-7862 [PRINT] ISSN 171-7870 [ONLINE] www.cscanada.org *The 3rd International Conference of Bionic Engineering* Numerical
CFD SIMULATIONS OF GAS DISPERSION IN VENTILATED ROOMS
 CFD SIMULATIONS OF GAS DISPERSION IN VENTILATED ROOMS T. Gélain, C. Prévost Institut de Radioprotection et de Sûreté Nucléaire (IRSN), Saclay, France Abstract In order to better understand the risks due
CFD SIMULATIONS OF GAS DISPERSION IN VENTILATED ROOMS T. Gélain, C. Prévost Institut de Radioprotection et de Sûreté Nucléaire (IRSN), Saclay, France Abstract In order to better understand the risks due
Aerodynamic Analysis of Blended Winglet for Low Speed Aircraft
 , July 1-3, 2015, London, U.K. Aerodynamic Analysis of Blended Winglet for Low Speed Aircraft Pooja Pragati, Sudarsan Baskar Abstract This paper provides a practical design of a new concept of massive
, July 1-3, 2015, London, U.K. Aerodynamic Analysis of Blended Winglet for Low Speed Aircraft Pooja Pragati, Sudarsan Baskar Abstract This paper provides a practical design of a new concept of massive
Cross Comparisons of CFD Prediction for Wind Environment at Pedestrian Level around Buildings
 Cross Comparisons of CFD Prediction for Wind Environment at Pedestrian Level around Buildings Part Comparison of Results for Flow-field around a High-rise Building Located in Surrounding City Blocks Ryuichiro
Cross Comparisons of CFD Prediction for Wind Environment at Pedestrian Level around Buildings Part Comparison of Results for Flow-field around a High-rise Building Located in Surrounding City Blocks Ryuichiro
A COMPUTATIONAL STUDY ON THE DESIGN OF AIRFOILS FOR A FIXED WING MAV AND THE AERODYNAMIC CHARACTERISTIC OF THE VEHICLE
 28 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES A COMPUTATIONAL STUDY ON THE DESIGN OF AIRFOILS FOR A FIXED WING MAV AND THE AERODYNAMIC CHARACTERISTIC OF THE VEHICLE Jung-Hyun Kim*, Kyu-Hong
28 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES A COMPUTATIONAL STUDY ON THE DESIGN OF AIRFOILS FOR A FIXED WING MAV AND THE AERODYNAMIC CHARACTERISTIC OF THE VEHICLE Jung-Hyun Kim*, Kyu-Hong
WIND FLOW CHARACTERISTICS AROUND ROOFTOP SOLAR ARRAY - A NUMERICAL STUDY
 The Eighth Asia-Pacific Conference on Wind Engineering, December 10 14, 2013, Chennai, India WIND FLOW CHARACTERISTICS AROUND ROOFTOP SOLAR ARRAY - A NUMERICAL STUDY D.Ghosh 1, A. K. Mittal 2, S. Behera
The Eighth Asia-Pacific Conference on Wind Engineering, December 10 14, 2013, Chennai, India WIND FLOW CHARACTERISTICS AROUND ROOFTOP SOLAR ARRAY - A NUMERICAL STUDY D.Ghosh 1, A. K. Mittal 2, S. Behera
CYCLE ANALYSIS OF LINEAR COMPRESSORS USING THREE- DIMENSIONAL CFD
 CYCLE ANALYSIS OF LINEAR COMPRESSORS USING THREE- DIMENSIONAL CFD I. Y. An and Y. L. Lee Department of Mechanical Engineering, Kongju National University, Korea E-Mail: ylee@kongju.ac.kr ABSTRACT In order
CYCLE ANALYSIS OF LINEAR COMPRESSORS USING THREE- DIMENSIONAL CFD I. Y. An and Y. L. Lee Department of Mechanical Engineering, Kongju National University, Korea E-Mail: ylee@kongju.ac.kr ABSTRACT In order
Full scale measurements and simulations of the wind speed in the close proximity of the building skin
 Full scale measurements and simulations of the wind speed in the close proximity of the building skin Radoslav Ponechal 1,* and Peter Juras 1 1 University of Zilina, Faculty of Civil Engineering, Department
Full scale measurements and simulations of the wind speed in the close proximity of the building skin Radoslav Ponechal 1,* and Peter Juras 1 1 University of Zilina, Faculty of Civil Engineering, Department
FLOW CONSIDERATIONS IN INDUSTRIAL SILENCER DESIGN
 FLOW CONSIDERATIONS IN INDUSTRIAL SILENCER DESIGN George Feng, Kinetics Noise Control, Inc., 3570 Nashua Drive, Mississauga, Ontario Vadim Akishin, Kinetics Noise Control, Inc., 3570 Nashua Drive, Mississauga,
FLOW CONSIDERATIONS IN INDUSTRIAL SILENCER DESIGN George Feng, Kinetics Noise Control, Inc., 3570 Nashua Drive, Mississauga, Ontario Vadim Akishin, Kinetics Noise Control, Inc., 3570 Nashua Drive, Mississauga,
AIRFLOW AND TEMPERATURE FIELD CALCULATIONS FOR WINTER SPORTS FACILITIES
 AIRFLOW AND TEMPERATURE FIELD CALCULATIONS FOR WINTER SPORTS FACILITIES Andrea Frisque* Stantec Consulting, Vancouver BC V6B6A3, Canada Rowan, Williams, Davies & Irwin (RWDI), Vancouver, BC, V5Z 1K5, Canada**
AIRFLOW AND TEMPERATURE FIELD CALCULATIONS FOR WINTER SPORTS FACILITIES Andrea Frisque* Stantec Consulting, Vancouver BC V6B6A3, Canada Rowan, Williams, Davies & Irwin (RWDI), Vancouver, BC, V5Z 1K5, Canada**
Validation of Wind Loads on a Slender Vessel using CFD
 Validation of Wind Loads on a Slender Vessel using CFD Jonathan W. Vogt *, Marco Bovio, and Benoit Mallol * Damen Shipyards, Singapore, Damen Shipyards, Gorinchem/Netherlands, NUMECA International, Brussels/Belgium
Validation of Wind Loads on a Slender Vessel using CFD Jonathan W. Vogt *, Marco Bovio, and Benoit Mallol * Damen Shipyards, Singapore, Damen Shipyards, Gorinchem/Netherlands, NUMECA International, Brussels/Belgium
CFD ANALYSIS AND COMPARISON USING ANSYS AND STAR-CCM+ OF MODEL AEROFOIL SELIG 1223
 International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 8, Issue 11, November 2017, pp. 312 318, Article ID: IJMET_08_11_034 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=8&itype=11
International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 8, Issue 11, November 2017, pp. 312 318, Article ID: IJMET_08_11_034 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=8&itype=11
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 147 (2016 ) 74 80
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 147 (2016 ) 74 80 11th conference of the International Sports Engineering Association, ISEA 2016 Comparison of the aerodynamic
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 147 (2016 ) 74 80 11th conference of the International Sports Engineering Association, ISEA 2016 Comparison of the aerodynamic
URBAN ENERGY AND MICROCLIMATE: WIND TUNNEL EXPERIMENTS AND MULTISCALE MODELING
 URBAN ENERGY AND MICROCLIMATE: WIND TUNNEL EXPERIMENTS AND MULTISCALE MODELING Jan Carmeliet 1,2, Jonas Allegrini 1,2, Peter Moonen 1,2, Saba Saneinejad 1, Viktor Dorer 2 1 ETHZ, Chair of Building Physics,
URBAN ENERGY AND MICROCLIMATE: WIND TUNNEL EXPERIMENTS AND MULTISCALE MODELING Jan Carmeliet 1,2, Jonas Allegrini 1,2, Peter Moonen 1,2, Saba Saneinejad 1, Viktor Dorer 2 1 ETHZ, Chair of Building Physics,
Wind Flow Model of Area Surrounding the Case Western Reserve University Wind Turbine
 Wind Flow Model of Area Surrounding the Case Western Reserve University Wind Turbine Matheus C. Fernandes 1, David H. Matthiesen PhD *2 1 Case Western Reserve University Dept. of Mechanical Engineering,
Wind Flow Model of Area Surrounding the Case Western Reserve University Wind Turbine Matheus C. Fernandes 1, David H. Matthiesen PhD *2 1 Case Western Reserve University Dept. of Mechanical Engineering,
CFD DESIGN STUDY OF A CIRCULATION CONTROL INLET GUIDE VANE OF AN AEROFOIL
 Int. J. Mech. Eng. & Rob. Res. 2012 Manjunath Ichchangi and Manjunath H, 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2278 0149 www.ijmerr.com Vol. 1, No. 3, October 2012 2012 IJMERR. All Rights Reserved CFD DESIGN STUDY
Int. J. Mech. Eng. & Rob. Res. 2012 Manjunath Ichchangi and Manjunath H, 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2278 0149 www.ijmerr.com Vol. 1, No. 3, October 2012 2012 IJMERR. All Rights Reserved CFD DESIGN STUDY
Impact of eaves on cross-ventilation of a generic isolated leeward sawtooth roof building: windward eaves, leeward eaves and eaves inclination
 Accepted for publication in Building and Environment on May 11, 2015 Impact of eaves on cross-ventilation of a generic isolated leeward sawtooth roof building: windward eaves, leeward eaves and eaves inclination
Accepted for publication in Building and Environment on May 11, 2015 Impact of eaves on cross-ventilation of a generic isolated leeward sawtooth roof building: windward eaves, leeward eaves and eaves inclination
Determination of the wind pressure distribution on the facade of the triangularly shaped high-rise building structure
 Determination of the wind pressure distribution on the facade of the triangularly shaped high-rise building structure Norbert Jendzelovsky 1,*, Roland Antal 1 and Lenka Konecna 1 1 STU in Bratislava, Faculty
Determination of the wind pressure distribution on the facade of the triangularly shaped high-rise building structure Norbert Jendzelovsky 1,*, Roland Antal 1 and Lenka Konecna 1 1 STU in Bratislava, Faculty
Influence of wing span on the aerodynamics of wings in ground effect
 Influence of wing span on the aerodynamics of wings in ground effect Sammy Diasinos 1, Tracie J Barber 2 and Graham Doig 2 Abstract A computational fluid dynamics study of the influence of wing span has
Influence of wing span on the aerodynamics of wings in ground effect Sammy Diasinos 1, Tracie J Barber 2 and Graham Doig 2 Abstract A computational fluid dynamics study of the influence of wing span has
APPLICATION OF COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (CFD) IN WIND ANALYSIS OF TALL BUILDINGS. Damith Mohotti, Priyan Mendis, Tuan Ngo
 APPLICATION OF COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (CFD) IN WIND ANALYSIS OF TALL BUILDINGS Damith Mohotti, Priyan Mendis, Tuan Ngo Department of Infrastructures Engineering, The University of Melbourne, Victoria,
APPLICATION OF COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (CFD) IN WIND ANALYSIS OF TALL BUILDINGS Damith Mohotti, Priyan Mendis, Tuan Ngo Department of Infrastructures Engineering, The University of Melbourne, Victoria,
Smooth hill validation in FUROW s wind resource module using OpenFOAM
 in for Wind flow Numerical Smooth hill validation in s wind resource module using 5 th Symposium on in Wind Energy (SOWE 2017), Javier Magdalena Saiz, José Marín Palacios, Jesús Matesanz García and Laura
in for Wind flow Numerical Smooth hill validation in s wind resource module using 5 th Symposium on in Wind Energy (SOWE 2017), Javier Magdalena Saiz, José Marín Palacios, Jesús Matesanz García and Laura
Dhruvin V Shah 1, Arpit N Patel 2, Darshan N Panchal 3, Arnab J Ganguly 4
 CFD Analysis of Reverse Swing of Cricket Ball Dhruvin V Shah 1, Arpit N Patel 2, Darshan N Panchal 3, Arnab J Ganguly 4 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Aeronautical Engineering, SVIT-Vasad dhruvinshah.aero@svitvasad.ac.in
CFD Analysis of Reverse Swing of Cricket Ball Dhruvin V Shah 1, Arpit N Patel 2, Darshan N Panchal 3, Arnab J Ganguly 4 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Aeronautical Engineering, SVIT-Vasad dhruvinshah.aero@svitvasad.ac.in
Centre for Offshore Renewable Energy Engineering, School of Energy, Environment and Agrifood, Cranfield University, Cranfield, MK43 0AL, UK 2
 Fluid Structure Interaction Modelling of A Novel 10MW Vertical-Axis Wind Turbine Rotor Based on Computational Fluid Dynamics and Finite Element Analysis Lin Wang 1*, Athanasios Kolios 1, Pierre-Luc Delafin
Fluid Structure Interaction Modelling of A Novel 10MW Vertical-Axis Wind Turbine Rotor Based on Computational Fluid Dynamics and Finite Element Analysis Lin Wang 1*, Athanasios Kolios 1, Pierre-Luc Delafin
3D-simulation of the turbulent wake behind a wind turbine
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series 3D-simulation of the turbulent wake behind a wind turbine To cite this article: Steffen Wußow et al 2007 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 75 012033 View the article online for
Journal of Physics: Conference Series 3D-simulation of the turbulent wake behind a wind turbine To cite this article: Steffen Wußow et al 2007 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 75 012033 View the article online for
Effect of Co-Flow Jet over an Airfoil: Numerical Approach
 Contemporary Engineering Sciences, Vol. 7, 2014, no. 17, 845-851 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ces.2014.4655 Effect of Co-Flow Jet over an Airfoil: Numerical Approach Md. Riajun
Contemporary Engineering Sciences, Vol. 7, 2014, no. 17, 845-851 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ces.2014.4655 Effect of Co-Flow Jet over an Airfoil: Numerical Approach Md. Riajun
Development of virtual 3D human manikin with integrated breathing functionality
 SAT-9.2-2-HT-06 Development of virtual 3D human manikin with integrated breathing functionality Martin Ivanov Development of virtual 3D human manikin with integrated breathing functionality: The presented
SAT-9.2-2-HT-06 Development of virtual 3D human manikin with integrated breathing functionality Martin Ivanov Development of virtual 3D human manikin with integrated breathing functionality: The presented
Numerical simulation and analysis of aerodynamic drag on a subsonic train in evacuated tube transportation
 Journal of Modern Transportation Volume 20, Number 1, March 2012, Page 44-48 Journal homepage: jmt.swjtu.edu.cn DOI: 10.1007/BF03325776 1 Numerical simulation and analysis of aerodynamic drag on a subsonic
Journal of Modern Transportation Volume 20, Number 1, March 2012, Page 44-48 Journal homepage: jmt.swjtu.edu.cn DOI: 10.1007/BF03325776 1 Numerical simulation and analysis of aerodynamic drag on a subsonic
Numerical Investigation of Multi Airfoil Effect on Performance Increase of Wind Turbine
 International Journal of Engineering & Applied Sciences (IJEAS) International Journal of Engineering Applied Sciences (IJEAS) Vol.9, Issue 3 (2017) 75-86 Vol.x, Issue x(201x)x-xx http://dx.doi.org/10.24107/ijeas.332075
International Journal of Engineering & Applied Sciences (IJEAS) International Journal of Engineering Applied Sciences (IJEAS) Vol.9, Issue 3 (2017) 75-86 Vol.x, Issue x(201x)x-xx http://dx.doi.org/10.24107/ijeas.332075
The evolution of the application of CFD on pedestrian wind comfort in engineering practice, a validation study
 EACWE 5 Florence, Italy 19 th 23 rd July 2009 Flying Sphere image Museo Ideale L. Da Vinci The evolution of the application of CFD on pedestrian wind comfort in engineering practice, a validation study
EACWE 5 Florence, Italy 19 th 23 rd July 2009 Flying Sphere image Museo Ideale L. Da Vinci The evolution of the application of CFD on pedestrian wind comfort in engineering practice, a validation study
MODELING AND SIMULATION OF VALVE COEFFICIENTS AND CAVITATION CHARACTERISTICS IN A BALL VALVE
 Proceedings of the 37 th International & 4 th National Conference on Fluid Mechanics and Fluid Power FMFP2010 December 16-18, 2010, IIT Madras, Chennai, India FMFP2010 341 MODELING AND SIMULATION OF VALVE
Proceedings of the 37 th International & 4 th National Conference on Fluid Mechanics and Fluid Power FMFP2010 December 16-18, 2010, IIT Madras, Chennai, India FMFP2010 341 MODELING AND SIMULATION OF VALVE
CFD ANALYSIS OF FLOW AROUND AEROFOIL FOR DIFFERENT ANGLE OF ATTACKS
 www.mechieprojects.com CFD ANALYSIS OF FLOW AROUND AEROFOIL FOR DIFFERENT ANGLE OF ATTACKS PRESENTATION OUTLINE AIM INTRODUCTION LITERATURE SURVEY CFD ANALYSIS OF AEROFOIL RESULTS CONCLUSIONS www.mechieprojects.com
www.mechieprojects.com CFD ANALYSIS OF FLOW AROUND AEROFOIL FOR DIFFERENT ANGLE OF ATTACKS PRESENTATION OUTLINE AIM INTRODUCTION LITERATURE SURVEY CFD ANALYSIS OF AEROFOIL RESULTS CONCLUSIONS www.mechieprojects.com
THE 22nd CHESAPEAKE SAILING YACHT SYMPOSIUM ANNAPOLIS, MARYLAND, MARCH 2016
 THE 22nd CHESAPEAKE SAILING YACHT SYMPOSIUM ANNAPOLIS, MARYLAND, MARCH 2016 A Comparison of RANS and LES for Upwind Sailing Aerodynamics Stefano Nava, University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand John
THE 22nd CHESAPEAKE SAILING YACHT SYMPOSIUM ANNAPOLIS, MARYLAND, MARCH 2016 A Comparison of RANS and LES for Upwind Sailing Aerodynamics Stefano Nava, University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand John
Numerical and Experimental Investigation of the Possibility of Forming the Wake Flow of Large Ships by Using the Vortex Generators
 Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 2011 Numerical and Experimental Investigation of the Possibility of Forming the Wake Flow of Large Ships by Using the
Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 2011 Numerical and Experimental Investigation of the Possibility of Forming the Wake Flow of Large Ships by Using the
New Technologies applied to the design and optimization of tunnel ventilation systems
 New Technologies applied to the design and optimization of tunnel ventilation systems Ing. Justo Suárez Area Manager - ZITRON Dot. Ing. Massimiliano Bringiotti Managing Director - GEOTUNNEL Ing. Ana Belén
New Technologies applied to the design and optimization of tunnel ventilation systems Ing. Justo Suárez Area Manager - ZITRON Dot. Ing. Massimiliano Bringiotti Managing Director - GEOTUNNEL Ing. Ana Belén
Predicting the Suction Gas Superheating in Reciprocating Compressors
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2014 Predicting the Suction Gas Superheating in Reciprocating Compressors Jonatas Ferreira
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2014 Predicting the Suction Gas Superheating in Reciprocating Compressors Jonatas Ferreira
Unsteady Aerodynamics of Tandem Airfoils Pitching in Phase
 Unsteady Aerodynamics of Tandem Airfoils Pitching in Phase Ravindra A Shirsath and Rinku Mukherjee Abstract This paper presents the results of a numerical simulation of unsteady, incompressible and viscous
Unsteady Aerodynamics of Tandem Airfoils Pitching in Phase Ravindra A Shirsath and Rinku Mukherjee Abstract This paper presents the results of a numerical simulation of unsteady, incompressible and viscous
Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Review 9 (5) (2016) Research Article. CFD Simulations of Flow Around Octagonal Shaped Structures
 Jestr Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Review 9 (5) (2016) 72-76 Research Article JOURNAL OF Engineering Science and Technology Review www.jestr.org CFD Simulations of Flow Around Octagonal
Jestr Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Review 9 (5) (2016) 72-76 Research Article JOURNAL OF Engineering Science and Technology Review www.jestr.org CFD Simulations of Flow Around Octagonal
Numerical simulation of aerodynamic performance for two dimensional wind turbine airfoils
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 31 (2012) 80 86 International Conference on Advances in Computational Modeling and Simulation Numerical simulation of aerodynamic performance
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 31 (2012) 80 86 International Conference on Advances in Computational Modeling and Simulation Numerical simulation of aerodynamic performance
Numerical Computations of Wind Turbine Wakes Using Full Rotor Modeling
 2012 2nd International Conference on Power and Energy Systems (ICPES 2012) IPCSIT vol. 56 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore DOI: 10.7763/IPCSIT.2012.V56.21 Numerical Computations of Wind Turbine Wakes
2012 2nd International Conference on Power and Energy Systems (ICPES 2012) IPCSIT vol. 56 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore DOI: 10.7763/IPCSIT.2012.V56.21 Numerical Computations of Wind Turbine Wakes
CFD Study of Solid Wind Tunnel Wall Effects on Wing Characteristics
 Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 9(45), DOI :10.17485/ijst/2016/v9i45/104585, December 2016 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 CFD Study of Solid Wind Tunnel Wall Effects on
Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 9(45), DOI :10.17485/ijst/2016/v9i45/104585, December 2016 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 CFD Study of Solid Wind Tunnel Wall Effects on
AIRFOIL PROFILE OPTIMIZATION OF AN AIR SUCTION EQUIPMENT WITH AN AIR DUCT
 THERMAL SCIENCE, Year 2015, Vol. 19, No. 4, pp. 1217-1222 1217 AIRFOIL PROFILE OPTIMIZATION OF AN AIR SUCTION EQUIPMENT WITH AN AIR DUCT by Li QIU a,b, Rui WANG a,*, Xiao-Dong CHEN b, and De-Peng WANG
THERMAL SCIENCE, Year 2015, Vol. 19, No. 4, pp. 1217-1222 1217 AIRFOIL PROFILE OPTIMIZATION OF AN AIR SUCTION EQUIPMENT WITH AN AIR DUCT by Li QIU a,b, Rui WANG a,*, Xiao-Dong CHEN b, and De-Peng WANG
ANALYSIS OF AERODYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS OF A SUPERCRITICAL AIRFOIL FOR LOW SPEED AIRCRAFT
 ANALYSIS OF AERODYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS OF A SUPERCRITICAL AIRFOIL FOR LOW SPEED AIRCRAFT P.Sethunathan 1, M.Niventhran 2, V.Siva 2, R.Sadhan Kumar 2 1 Asst.Professor, Department of Aeronautical Engineering,
ANALYSIS OF AERODYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS OF A SUPERCRITICAL AIRFOIL FOR LOW SPEED AIRCRAFT P.Sethunathan 1, M.Niventhran 2, V.Siva 2, R.Sadhan Kumar 2 1 Asst.Professor, Department of Aeronautical Engineering,
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF STATIC INTERFERENCE EFFECTS FOR SINGLE BUILDINGS GROUP
 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF STATIC INTERFERENCE EFFECTS FOR SINGLE BUILDINGS GROUP Xing-qian Peng, Chun-hui Zhang 2 and Chang-gui Qiao 2 Professor, College of Civil Engineering, Huaqiao University, Quanzhou,
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF STATIC INTERFERENCE EFFECTS FOR SINGLE BUILDINGS GROUP Xing-qian Peng, Chun-hui Zhang 2 and Chang-gui Qiao 2 Professor, College of Civil Engineering, Huaqiao University, Quanzhou,
Study on Fire Plume in Large Spaces Using Ground Heating
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 11 (2011) 226 232 The 5 th Conference on Performance-based Fire and Fire Protection Engineering Study on Fire Plume in Large Spaces Using
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 11 (2011) 226 232 The 5 th Conference on Performance-based Fire and Fire Protection Engineering Study on Fire Plume in Large Spaces Using
Steady Analysis of NACA Flush Inlet at High Subsonic and Supersonic Speeds
 , July 1-3, 2015, London, U.K. Steady Analysis of NACA Flush Inlet at High Subsonic and Supersonic Speeds Taimur A. Shams 1, Masud J 2 Abstract Essence of this research is to report computational analysis
, July 1-3, 2015, London, U.K. Steady Analysis of NACA Flush Inlet at High Subsonic and Supersonic Speeds Taimur A. Shams 1, Masud J 2 Abstract Essence of this research is to report computational analysis
Computational Analysis of Blunt Trailing Edge NACA 0012 Airfoil
 Computational Analysis of Blunt Trailing Edge NACA 2 Airfoil Anusha K Department of Aerospace Engineering Madras Institute of Technology, India anusugan7@gmail.com Abstract Blunt trailing edge airfoil
Computational Analysis of Blunt Trailing Edge NACA 2 Airfoil Anusha K Department of Aerospace Engineering Madras Institute of Technology, India anusugan7@gmail.com Abstract Blunt trailing edge airfoil
High Swept-back Delta Wing Flow
 Advanced Materials Research Submitted: 2014-06-25 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vol. 1016, pp 377-382 Accepted: 2014-06-25 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.1016.377 Online: 2014-08-28 2014 Trans Tech Publications,
Advanced Materials Research Submitted: 2014-06-25 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vol. 1016, pp 377-382 Accepted: 2014-06-25 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.1016.377 Online: 2014-08-28 2014 Trans Tech Publications,
High fidelity gust simulations around a transonic airfoil
 High fidelity gust simulations around a transonic airfoil AEROGUST Workshop 27 th - 28 th April 2017, University of Liverpool Presented by B. Tartinville (Numeca) Outline of the presentation 1Objectives
High fidelity gust simulations around a transonic airfoil AEROGUST Workshop 27 th - 28 th April 2017, University of Liverpool Presented by B. Tartinville (Numeca) Outline of the presentation 1Objectives
COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF AIRFOIL NACA0015
 International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 8, Issue 2, February 2017, pp. 210 219 Article ID: IJMET_08_02_026 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=8&itype=2
International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 8, Issue 2, February 2017, pp. 210 219 Article ID: IJMET_08_02_026 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=8&itype=2
Single Phase Pressure Drop and Flow Distribution in Brazed Plate Heat Exchangers
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2016 Single Phase Pressure Drop and Flow Distribution in Brazed Plate Heat Exchangers
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2016 Single Phase Pressure Drop and Flow Distribution in Brazed Plate Heat Exchangers
Effects of seam and surface texture on tennis balls aerodynamics
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 34 (2012 ) 140 145 9 th Conference of the International Sports Engineering Association (ISEA) Effects of seam and surface texture on tennis
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 34 (2012 ) 140 145 9 th Conference of the International Sports Engineering Association (ISEA) Effects of seam and surface texture on tennis
Analysis on Turbulent Flows using Large-eddy Simulation on the Seaside Complex Terrain
 Analysis on Turbulent Flows using Large-eddy Simulation on the Seaside Complex Terrain Takeshi Kamio, Makoto Iida, Chuichi Arakawa The University of Tokyo, Japan Outline Backgrounds and Purposes Complex
Analysis on Turbulent Flows using Large-eddy Simulation on the Seaside Complex Terrain Takeshi Kamio, Makoto Iida, Chuichi Arakawa The University of Tokyo, Japan Outline Backgrounds and Purposes Complex
Aerodynamic Shape Design of the Bow Network Monitoring Equipment of High-speed Train
 2017 2nd International Conference on Industrial Aerodynamics (ICIA 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-481-3 Aerodynamic Shape Design of the Bow Network Monitoring Equipment of High-speed Train Wang Zhe and Ji Peng
2017 2nd International Conference on Industrial Aerodynamics (ICIA 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-481-3 Aerodynamic Shape Design of the Bow Network Monitoring Equipment of High-speed Train Wang Zhe and Ji Peng
Computational Analysis of Cavity Effect over Aircraft Wing
 World Engineering & Applied Sciences Journal 8 (): 104-110, 017 ISSN 079-04 IDOSI Publications, 017 DOI: 10.589/idosi.weasj.017.104.110 Computational Analysis of Cavity Effect over Aircraft Wing 1 P. Booma
World Engineering & Applied Sciences Journal 8 (): 104-110, 017 ISSN 079-04 IDOSI Publications, 017 DOI: 10.589/idosi.weasj.017.104.110 Computational Analysis of Cavity Effect over Aircraft Wing 1 P. Booma
ISOLATION OF NON-HYDROSTATIC REGIONS WITHIN A BASIN
 ISOLATION OF NON-HYDROSTATIC REGIONS WITHIN A BASIN Bridget M. Wadzuk 1 (Member, ASCE) and Ben R. Hodges 2 (Member, ASCE) ABSTRACT Modeling of dynamic pressure appears necessary to achieve a more robust
ISOLATION OF NON-HYDROSTATIC REGIONS WITHIN A BASIN Bridget M. Wadzuk 1 (Member, ASCE) and Ben R. Hodges 2 (Member, ASCE) ABSTRACT Modeling of dynamic pressure appears necessary to achieve a more robust
Flow Field Phenomena about Lift and Downforce Generating Cambered Aerofoils in Ground Effect
 16 th Australasian Fluid Mechanics Conference Crown Plaza, Gold Coast, Australia 2-7 December 2007 Flow Field Phenomena about Lift and Downforce Generating Cambered Aerofoils in Ground Effect J.W. Vogt,
16 th Australasian Fluid Mechanics Conference Crown Plaza, Gold Coast, Australia 2-7 December 2007 Flow Field Phenomena about Lift and Downforce Generating Cambered Aerofoils in Ground Effect J.W. Vogt,
Experimental and Theoretical Investigation for the Improvement of the Aerodynamic Characteristic of NACA 0012 airfoil
 International Journal of Mining, Metallurgy & Mechanical Engineering (IJMMME) Volume 2, Issue 1 (214) ISSN 232 46 (Online) Experimental and Theoretical Investigation for the Improvement of the Aerodynamic
International Journal of Mining, Metallurgy & Mechanical Engineering (IJMMME) Volume 2, Issue 1 (214) ISSN 232 46 (Online) Experimental and Theoretical Investigation for the Improvement of the Aerodynamic
STUDY OF THE INFLUENCE OF A GAP BETWEEN THE WING AND SLOTTED FLAP ON THE AERODYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS OF ULTRA-LIGHT AIRCRAFT WING AIRFOIL
 Review of the Air Force Academy No 3 (30) 2015 STUDY OF THE INFLUENCE OF A GAP BETWEEN THE WING AND SLOTTED FLAP ON THE AERODYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS OF ULTRA-LIGHT AIRCRAFT WING AIRFOIL 1. INTRODUCTION
Review of the Air Force Academy No 3 (30) 2015 STUDY OF THE INFLUENCE OF A GAP BETWEEN THE WING AND SLOTTED FLAP ON THE AERODYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS OF ULTRA-LIGHT AIRCRAFT WING AIRFOIL 1. INTRODUCTION
Numerical Investigation of Flow Around Two Cylinders using Large-Eddy Simulation
 Numerical Investigation of Flow Around Two Cylinders using Large-Eddy Simulation Baraal Qays Mahdi M. Sc. Student, Mechanical Engineering, Department of Mechanical Engineering. Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia,
Numerical Investigation of Flow Around Two Cylinders using Large-Eddy Simulation Baraal Qays Mahdi M. Sc. Student, Mechanical Engineering, Department of Mechanical Engineering. Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia,
Workshop 1: Bubbly Flow in a Rectangular Bubble Column. Multiphase Flow Modeling In ANSYS CFX Release ANSYS, Inc. WS1-1 Release 14.
 Workshop 1: Bubbly Flow in a Rectangular Bubble Column 14. 5 Release Multiphase Flow Modeling In ANSYS CFX 2013 ANSYS, Inc. WS1-1 Release 14.5 Introduction This workshop models the dispersion of air bubbles
Workshop 1: Bubbly Flow in a Rectangular Bubble Column 14. 5 Release Multiphase Flow Modeling In ANSYS CFX 2013 ANSYS, Inc. WS1-1 Release 14.5 Introduction This workshop models the dispersion of air bubbles
Computational Investigation of Airfoils with Miniature Trailing Edge Control Surfaces
 AIAA-24-5 Computational Investigation of Airfoils with Miniature Trailing Edge Control Surfaces Hak-Tae Lee, Ilan M. Kroo Stanford University, Stanford, CA 9435 Abstract Miniature trailing edge effectors
AIAA-24-5 Computational Investigation of Airfoils with Miniature Trailing Edge Control Surfaces Hak-Tae Lee, Ilan M. Kroo Stanford University, Stanford, CA 9435 Abstract Miniature trailing edge effectors
An Investigation on the Performance Characteristics of a Centrifugal Compressor
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 10, Issue 11 (November 2014), PP.77-83 An Investigation on the Performance Characteristics
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 10, Issue 11 (November 2014), PP.77-83 An Investigation on the Performance Characteristics
The application of laser diagnostics to cycling aerodynamics T. N.
 161 7th Australian Conference on Laser Diagnostics in Fluid Mechanics and Combustion Melbourne, Australia 9-11 December 2015 The application of laser diagnostics to cycling aerodynamics T. N. T.N. Crouch
161 7th Australian Conference on Laser Diagnostics in Fluid Mechanics and Combustion Melbourne, Australia 9-11 December 2015 The application of laser diagnostics to cycling aerodynamics T. N. T.N. Crouch
