Determinants of Traffic Fatalities and Injuries in Wolaita Zone, Ethiopia
|
|
|
- Kerrie McLaughlin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Determinants of Traffic Fatalities and Injuries in Wolaita Zone, Ethiopia Bereket Tessema Zewude (MSc.) 1* Kidus Meskele Ashine ( Ass. Professor) 2 1.Wolaita Sodo University, College of Natural and Computational Sciences, Wolaita Sodo, Ethiopia, P.O. Box Wolaita Sodo University, School of Law, Wolaita Sodo, Ethiopia, P.O. Box 138 Abstract Road traffic accidents are a major public health concern. In developing countries road traffic accidents are among the leading cause of death and injury. Ethiopia experiences the highest rate of such accidents in Sub- Saharan Africa. Out of all the accidents registered in Ethiopia, Addis Ababa accounts for 60% on average especially in Wolaita zone more 25% on average. The objective of this study is to identify factors that contribute to the occurrence of road traffic accidents leading to human injuries and death. For study purpose we employed ordinal logistic regression models to identify factors influencing traffic fatalities and injuries. Stratified sampling with proportional allocation and simple random sampling technique are used to select samples from recorded frame. The result of ordinal logistic regression analyses shows that drivers aged years caused the largest number of accidents. Low educational background of drivers, absence and poor lighting along roads, wet surface and asphalt surface, morning and evening hours, places like offices, residential and commercial neighborhoods, automobiles and small taxis/bajaj s were found to be associated with fatalities and serious injuries. We conclude that for effective and safe traffic management, the concerned transportation authorities can consider the above mentioned predictors as potential causes of accidents in their order of importance in order to take preventive measures. Keywords: Fatalities, injuries, odds ratio, ordinal logistic regression, traffic accident. Wolaita zone, Ethiopia Introduction Road traffic accident is defined as any vehicle accident occurring on a public highway. It includes collisions between vehicles and animals, vehicles and pedestrians, vehicles and fixed objects or vehicles and vehicles. Road traffic deaths accounted for 23% of all injury deaths worldwide in It has also been estimated that nearly 1.2 million people, male-to-female ratio being 2.34 to 1, are killed and million people are injured or disabled each year in road traffic accidents. On average 3,300 road users are killed and about 100,000 are injured and/or disabled each day in traffic (WHO, 2004). Road traffic injures are growing as the vehicle use of developing countries rises. By 2020, road traffic injures are expected to be the third leading cause of death and disability worldwide, by some calculations matching the toll of AIDS. Residents of developing countries are at much higher risk of road traffic injures than are residents of high-income countries. They are also at greater risk of death when a crash occurs. Developing countries also have inadequate trauma systems and are often unable to care for crash victims. Unless action is taken to improve road safety systems, poor countries will continue to bear the heavy toll of road traffic injuries (Lauren and Hill, 2005). The World Health Report (WHO, 2004) shows that of the 1.2 million people killed in road crashes worldwide, 85% are in developing countries. Sub-Saharan Africa alone with only 4% of the global vehicle registered accounts for 10% of the road fatalities, and the economic, social and health consequences are grave. Conversely, the high-income nations, with 60% of the total global vehicle fleet contribute only 14% of the annual road deaths. Human error, road environment and vehicle factors are reported by the traffic police as the main causes of road crashes. Two countries, South Africa and Nigeria, account for most of the reported deaths in Sub-Saharan Africa. The South Africa figure of over 9,000 has been consistent over time, while Nigeria with 6,185 deaths has declined from a high of over 9,200 in the early 1990s. Ethiopia, Kenya, Uganda, Tanzania and Ghana are the other countries that experience high number of road deaths (WHO, 2004). Out of all the accidents registered in Ethiopia, Addis Ababa accounts for 60% on average. This is partly because the city has only five outlets that connect it all regions of the country. In addition to this about 77% of vehicles in Ethiopia are registered here. Thus Wolaita zone, having a great concentration of vehicles and traffic, takes the lion s share in car accidents. Statistical data from the Wolaita zone Traffic. According to Tewolde (2007), the highest mean number of injuries per accident took place in residential areas by drivers in the age group of who have elementary school level of education. Therefore, in our case we tried to identify factors that contribute to the occurrence of road traffic accidents leading to human injuries and death. Data and Methodology Source of Data In Wolaita zone road traffic accidents are recorded by traffic department on daily basis. The data provide information on accidents that occur within 365 consecutive days. From the collected data we will registered as 38
2 slight injury, serious injury and fatal, respectively. A pilot sample was used in order to determine and estimate the required sample size. From the total record pilot samples were taken as slight injury, serious injury and fatal. This means the data have three strata: slight injury, serious injury and fatal. Stratified sampling with proportional allocation and simple random sampling technique was used to select samples from recorded frame for each stratum. Data Collection According to the definition of the Traffic Police, a road traffic accident is considered to be any event of human injury and/or death as a consequence of a physical collision between a responsible party (motor vehicle including motorcycle, car, van or truck, and bicycle) and an injured/damaged party (motor vehicle, bicycle/ bike, pedestrian, or any physical object, e.g., building or tree). In cases when the crash involves a motor vehicle and/or bicycle with pedestrians, the information about the driver/rider of the motor vehicle/bicycle (age, sex, alcohol consumption, speed, type of motor vehicle) is recorded at Wolaita zone traffic department regardless of the responsible party. When the accident involves two motor vehicles the record is made only for the responsible party. Variables included in the study The response variable is level of injury severity of road traffic accident involving humans. In this study the response is an ordered variable categorized into three: slight injury, serious injury and death. Slight injury assumes the lowest order one while serious injury and death have orders two and three, respectively. Predictor factors considered as determinants of traffic accidents involving human injuries are grouped into human, vehicle, road, environmental, and other factors. Human factors are sex of driver, age of driver, driving experience, vehicle ownership status and driver educational background. Vehicle factors are driving direction at the time of accident, vehicle type, and vehicle age. Environmental factors are atmospheric condition, light condition, day of accident, time of accident, and road condition. Road factors are place of accident, road situation, road junction, road class, and surface/pavement roughness. Other factors include reason for accident and accident type. Methodology Both ordinal logistic regression as well as cumulative logit model were used. For ordinal logistic regression response variable can take the three levels of injury as indicated above, and these are ordered depending on the level of severity as slight injury, serious injury and death the lowest, middle and highest orders being slight injury, serious injury and death, respectively. When the response variable denoted Y, is ordinal, the categories can be ordered in a natural way. One way to take account of ordering is the use of cumulative probabilities and cumulative odds. In general considering k ordered categories, these quantities defined are defined by: Currently, the most popular model for ordinal response uses logits of cumulative probabilities, often called cumulative logits. The cumulative logistic model for ordinal data is described below. Cumulative Logit Models A cumulative logit model is one of the most commonly used models for the analysis of ordinal categorical data and belongs to the class of generalized linear models. It is generalization of a binary logistic regression model when the response variable has more than two ordinal categories. It is also the cumulative logit model is used when the response of an individual unit is restricted to one of a finite number of ordinal values. In cumulative logit model, the effect of is the same for all i, often referred to as a proportional odds model (McCullagh and Nelder, 1989). In other words, the model assumes that the effect of each independent variable is the same for each cumulative probability. This model provides a single odds ratio (OR) estimate for all response categories, which can be obtained by exponentiation of the coefficient. The estimate is quite convenient in terms of the model s ease of interpretation and parsimony. The proportional odds model is used to estimate the odds of being at or below a particular level of the response variable. If there are i levels of ordinal outcomes, the model makes k-1 predictions, each estimating the cumulative probabilities at or below the i th level of outcome variable. This 39
3 model can estimate the odds of being at or beyond a particular level of the response variable as well, because below and beyond a particular category are just two complementary directions. The model s threshold varies for each of the equations and satisfies the conditions, where are cut points, usually nuisance parameters of little interest. A model can simultaneously describe the effect of an explanatory variable on all cumulative probabilities for y. the model is defined by: When this means that the corresponding independent variable is more likely to have higher values of y. Also the parameterization of this model is in accord with the usual formulation, in sense that a positive corresponds to a positive association ( a higher x tending to occur with higher y) in other words If ( odds greater than one) in this study this means increased likelihood of accident can be fatal/serious injury. Table 2. Parameter estimates of the ordinal logistic model Variables estimates S.E Wald Df sig odds-ratio Threshold [ severity level=1] [severity level=2] Age of driver * * * (ref.) Driving experience * 1 year * years * years *.56 >5years (ref.) Educational background * Elementary school * 5.79 Junior school * 4.18 Secondary school * 2.11 Above secondary school(ref.) Vehicle type * Automobile * 4.26 Bajaj * 4.48 Minibuses * 2.58 Cargo Buses * 3.35 Other vehicles(ref.) Atmospheric condition * Good condition * 5.93 Rainy(ref.) Light condition * Day light *.06 Dark but lighted *.07 Dark(ref.) Time of accident * Morning * 4.05 Day * 3.85 Evening * 5.99 Night(ref.) Road condition * Dry *.153 Wet(ref.) Road surface roughness * Asphalt * 5.75 Not asphalted(ref.) Road junction * No junction * 1.93 Junction(ref.) Place of accident * Office * 4.71 Residential * Commercial * 5.75 Religion centers * 3.25 Recreation * 2.78 School(ref.) Accident type * Crashing with pedestrian * 4.48 Crashing with another vehicles * 4.95 Others * 5.75 Cashing with objects(ref.) *Significant at 5% level of significance. 40
4 Results and Discussion The results of the ordinal logistic regression analysis in Table 2, shows that age of drivers is a significant indicator of fatal and serious injuries. The odds-ratio of accidents causing fatal/serious injury is higher in the case of young drivers (18-30 years and years) compared with the elderly drivers (aged above 51 years). As compared to those with driving experience of more than 5 years, the odds-ratio of causing fatal/serious injury for drivers with driving experience of utmost one year, 1-2 years and 2-5 years were lower by a factor of 0.22, 0.29, and 0.56 times, respectively. Drivers with elementary, junior secondary and secondary level of education are about 5.75, 4.18, and 2.11 times more likely to get involved in fatal/serious injuries as compared to those with above secondary school level of education, respectively. The odds-ratio of traffic accidents causing fatal/serious injury is higher for drivers with automobile (4.26 times), buses(3.35 times), Bajaj (4.48 times), and taxis or minibuses(2.58 times) as compared to the reference category other vehicles. The odds-ratio of accidents causing fatal/serious injury is higher during a clear condition as compared with a rainy condition. There is a significant relationship between light condition and severity level of accidents. The odds-ratio of traffic accidents causing fatal/serious injury is higher in a dark condition as compared to daylight and dark-lighted conditions. The odds of traffic accidents causing fatal /serious injury are higher in the morning, day and evening as compared to accidents at night. Regarding road condition, the likelihood of fatal/serious injury is higher on wet roads as compared to dry condition. Fatal and serious injury is about 5.75 times more likely to take place on asphalt roads compared to those driving on not asphalted roads. Accidents causing fatal/serious injuries at roads without junction are 1.93 times higher as compared to accidents at junction roads. Human Factors: While the actions of people might be influenced by subconscious motives and subliminal cues, they are also the most adaptive elements in the traffic system. They can create risk situations as well as respond to ever changing new demands of the traffic environment. The findings of the study show that accident rates of young drivers are more than the rest of the examinees. This may be related to reckless driving, psycho-biological immaturity, an excessive belief in one s own abilities, lack of experience, driving culture, and lifestyle induced risky type of exposure such as night driving. Drivers who have more than 5 years of experience cause fatal/serious injury than those who have less driving experience. This could be due to overconfidence and carelessness. The highest risk group for accident is drivers with primary school educational level. The risk of accident decreases a bit among junior high school graduates. Drivers with above secondary school level of education have the least involvement in accidents. This indicates that education is a considerable factor to prevent road traffic accidents. Thus, it can be said that understanding, interpreting and obeying the regulations are parallel to education and behaving more logical. Vehicle Factors: Vehicle type was found to be an important factor which affects human injury/fatality caused by traffic accidents. Even if buses and taxies/ minibuses play an essential role in public transportation, our results showed that these vehicles (in addition to automobiles, cargo vehicles and buses) pose a significantly greater fatal/serious injury risk to pedestrians. Note that cargo vehicles have larger mass, greater momentum and longer stopping distance. For any given speed, the greater the mass of the vehicle, the greater would be its force of impact at collision with the pedestrians leading to higher injury severities. Furthermore, it is possible that drivers of small vehicles but high speedy are more likely to weave around in traffic, change lanes, dart ahead of others or even take corners and curves faster. This finding seemed to be in accordance with other studies (Tewolde, 2007). Environmental Factors: Most of the accidents occurred in good conditions. Poor light conditions contributed to causing fatal/serious injuries, which indicates that poor light conditions could increase the probability of causing fatalities when a crash occurs. This is possibly due to poor visibility at night in the absence of street light is limited by the range of headlights and glare from oncoming vehicles headlights. In addition, drivers are also unable to distinguish pedestrians from the shaded surroundings due to their darker outfits. All these can lead to drivers braking later or taking less effective avoidance maneuvers leading to increased risk of crash and serious injury. This finding is consistent with other studies (Luma and Sivak, 1992). Traffic accidents causing fatal/serious injury are higher in the morning, during the day, and in the evening as compared to accidents during the night. This indicates that in the morning (the beginning of the working day) and evening (the end of the working day) the roads are typically busy with traffic volume, and during daytime, there are increased activities such as commercial activities and work related (office) activities, etc. So this situation gives rise to increase in the number of accidents. In terms of road surface condition, this study found out that wet surface condition resulted in a higher likelihood of fatal/serious injury than dry surface. This could be because on wet road surfaces it is difficult to stop vehicles easily. This implies that the possibility of death/serious injury will be high. Road factors: The environment with its road network creates the framework for the behavior of traffic and exposes those who are on the network to various accident risks. Traffic environment can support and promote safe behavior, but it can also encourage or lead to risky behavior. The findings of the study show that the majority of the fatal/serious injuries have occurred on asphalt roads. This finding is consistent with previous 41
5 studies (Yayeh, 2003). This is due to the fact that asphalt roads increase vehicular speed. Therefore, if a crash happens, a pedestrian is more likely to suffer from more severe injury due to the higher impact speed. The findings of this study show that traffic accidents causing fatal/serious injuries at no-junction roads are higher as compared to accidents at junction roads. This finding is consistent with the study by Singh et al. (1998). This could be due to the reason that at junction not only drivers but also pedestrians are more careful and also there may be traffic lights at junctions. Most accidents took place around offices, residential and commercial neighborhoods. It should be noted that these places are typically busy with traffic volume giving rise to increase in the number of accidents. A study by Tewolde (2007) also reported the same result. The findings of this study also show that the odds of accident being fatal/serious injury due to crashing with pedestrians, and crashing with another vehicle were higher as compared to crashing with objects. As expected, the serious injury risk significantly increased for pedestrians who tended to cross a road without proper right of way. Since drivers do not expect pedestrians at locations not designated for pedestrians, they might fail to detect the pedestrian in time and take evasive actions accordingly. This might result in higher impact speed during collision leading to greater injury risk. Negligent crossing behavior has been reported to be a major cause of pedestrian collision and injury by Yayeh (2003). Conclusion Drivers with driving experience of more than 5 years are significantly exposed to traffic accidents causing fatal/serious injury. Drivers aged years and aged year, drivers with lower educational background, no-junction roads, absence of lighting, wet surface and asphalt surface are highly associated with fatal/serious injuries. Accidents occurring in the morning and evening and accidents that occur in office areas, residential and commercial neighborhoods are more likely to result in fatal/serious injuries. Automobiles and taxis/bajaj create fatal or serious injury. References Lauren, P. and Hill, S. (2005). Road traffic Injuries-Can we avoid global epidemic? McCullagh, P. and Nelder, J.A. (1989). Generalized Linear Models (2nd Ed.), Chapman and Hall, New York. Singh, S.K. and Misra, A. (1998). Road accident analysis: A case Study of Patna City. Urban Transport Journal 2(2): Tewolde, M. (2007). Analysis on traffic accidents involving human injuries in the case of Addis Ababa. (Unpublished M.Sc. Thesis), Department of Statistics, Addis Ababa University. World Health Organization and the World Bank (2004). World report on road traffic injury prevention. Yayeh, A. (2003). The extent, variations and causes of road traffic accidents in Bahir Dar (Unpublished M.A. Thesis), Department of Geography, Addis Ababa University. 42
Crash Patterns in Western Australia. Kidd B., Main Roads Western Australia Willett P., Traffic Research Services
 Crash Patterns in Western Australia Kidd B., Main Roads Western Australia Willett P., Traffic Research Services Abstract Examination of crash patterns is one way of identifying key factors on which focus
Crash Patterns in Western Australia Kidd B., Main Roads Western Australia Willett P., Traffic Research Services Abstract Examination of crash patterns is one way of identifying key factors on which focus
Prediction model of cyclist s accident probability in the City of Malang
 MATEC Web of Conferences 8, 04003 (208) ISTSDC 207 https://doi.org/0.05/matecconf/208804003 Prediction model of cyclist s accident probability in the City of Malang Imma Widyawati Agustin,*, Muhammad Zainul
MATEC Web of Conferences 8, 04003 (208) ISTSDC 207 https://doi.org/0.05/matecconf/208804003 Prediction model of cyclist s accident probability in the City of Malang Imma Widyawati Agustin,*, Muhammad Zainul
People killed and injured per million hours spent travelling, Motorcyclist Cyclist Driver Car / van passenger
 Cyclists CRASH FACTSHEET 27 CRASH STATISTICS FOR THE YEAR ENDED 31 DEC 26 Prepared by Strategy and Sustainability, Ministry of Transport Cyclists have a number of risk factors that do not affect car drivers.
Cyclists CRASH FACTSHEET 27 CRASH STATISTICS FOR THE YEAR ENDED 31 DEC 26 Prepared by Strategy and Sustainability, Ministry of Transport Cyclists have a number of risk factors that do not affect car drivers.
Deaths/injuries in motor vehicle crashes per million hours spent travelling, July 2007 June 2011 (All ages) Mode of travel
 Cyclists CRASH STATISTICS FOR THE YEAR ENDED 31 DECEMBER 211 Prepared by the Ministry of Transport CRASH FACTSHEET 212 Cyclists have a number of risk factors that do not affect car drivers. The main risk
Cyclists CRASH STATISTICS FOR THE YEAR ENDED 31 DECEMBER 211 Prepared by the Ministry of Transport CRASH FACTSHEET 212 Cyclists have a number of risk factors that do not affect car drivers. The main risk
Road design and Safety philosophy, 1 st Draft
 Head Office SWEDEN www.vv.se Textphone: +46 243-750 90 Roger Johansson International Secretariat roger.johansson@vv.se Direct: +46 243 75880 Mobile: +46 70 6327373 Date: 2006-08-17 Reference: Road design
Head Office SWEDEN www.vv.se Textphone: +46 243-750 90 Roger Johansson International Secretariat roger.johansson@vv.se Direct: +46 243 75880 Mobile: +46 70 6327373 Date: 2006-08-17 Reference: Road design
SAVE THE NATION ASSOCIATION (SNA)
 SAVE THE NATION ASSOCIATION (SNA) A DRAFT DOCUMENT FOR BRASILLIA DECLARATION ON ROAD SAFETY CONTACT PERSONS: MESGANAW BIMREW, EXECUTIVE DIRECTOR CELL PHONE: +251920717744, EMAIL: mesganaw21@yahoo.com SEIFU
SAVE THE NATION ASSOCIATION (SNA) A DRAFT DOCUMENT FOR BRASILLIA DECLARATION ON ROAD SAFETY CONTACT PERSONS: MESGANAW BIMREW, EXECUTIVE DIRECTOR CELL PHONE: +251920717744, EMAIL: mesganaw21@yahoo.com SEIFU
2014 QUICK FACTS ILLINOIS CRASH INFORMATION. Illinois Emergency Medical Services for Children February 2016 Edition
 2014 QUICK FACTS ILLINOIS CRASH INFORMATION February 2016 Edition Illinois Emergency Medical Services for Children www.luhs.org/emsc Illinois Emergency Medical Services for Children TABLE OF CONTENTS
2014 QUICK FACTS ILLINOIS CRASH INFORMATION February 2016 Edition Illinois Emergency Medical Services for Children www.luhs.org/emsc Illinois Emergency Medical Services for Children TABLE OF CONTENTS
2012 QUICK FACTS ILLINOIS CRASH INFORMATION. Illinois Emergency Medical Services for Children September 2014 Edition
 2012 QUICK FACTS ILLINOIS CRASH INFORMATION September 2014 Edition Illinois Emergency Medical Services for Children www.luhs.org/emsc Illinois Emergency Medical Services for Children TABLE OF CONTENTS
2012 QUICK FACTS ILLINOIS CRASH INFORMATION September 2014 Edition Illinois Emergency Medical Services for Children www.luhs.org/emsc Illinois Emergency Medical Services for Children TABLE OF CONTENTS
Children s expectations and beliefs toward the relative safety of riding bicycles at night
 Children s expectations and beliefs toward the relative safety of riding bicycles at night William J. Vigilante, Jr. a and Raymond W. Lim b a Robson Forensic Inc., Lancaster, PA b Psychology Department,
Children s expectations and beliefs toward the relative safety of riding bicycles at night William J. Vigilante, Jr. a and Raymond W. Lim b a Robson Forensic Inc., Lancaster, PA b Psychology Department,
A preliminary analysis of in-depth accident data for powered two-wheelers and bicycles in Europe
 International Research Council on Biomechanics of Injury IRCOBI 2018 Athens, Greece, 12 September 2018 A preliminary analysis of in-depth accident data for powered two-wheelers and bicycles in Europe Ziakopoulos
International Research Council on Biomechanics of Injury IRCOBI 2018 Athens, Greece, 12 September 2018 A preliminary analysis of in-depth accident data for powered two-wheelers and bicycles in Europe Ziakopoulos
Post impact trajectory of vehicles at rural intersections
 Post impact trajectory of vehicles at rural intersections Doecke SD., Woolley JE. and Mackenzie JR. Centre for Automotive Safety Research Abstract This report describes the path of vehicles after a collision
Post impact trajectory of vehicles at rural intersections Doecke SD., Woolley JE. and Mackenzie JR. Centre for Automotive Safety Research Abstract This report describes the path of vehicles after a collision
MTCF. Michigan Traffic Crash Facts FACT SHEETS
 FACT SHEETS This page left intentionally blank GENERAL FACTS The driver, the roadway, and the motor vehicle contribute in some measure to every crash. A preponderance of evidence, however, points to driver
FACT SHEETS This page left intentionally blank GENERAL FACTS The driver, the roadway, and the motor vehicle contribute in some measure to every crash. A preponderance of evidence, however, points to driver
MTCF. Michigan Traffic Crash Facts FACT SHEETS
 FACT SHEETS This page left intentionally blank GENERAL FACTS The driver, the roadway, and the motor vehicle contribute in some measure to every crash. A preponderance of evidence, however, points to driver
FACT SHEETS This page left intentionally blank GENERAL FACTS The driver, the roadway, and the motor vehicle contribute in some measure to every crash. A preponderance of evidence, however, points to driver
TRAFFIC CRASHES involving BICYCLISTS
 The Office of the Chief of Police in Berlin BERLIN TRAFFIC CRASHES involving BICYCLISTS A special research project concerning bicycle crashes in West Berlin in the years 1981 through 1985 Police Analyst
The Office of the Chief of Police in Berlin BERLIN TRAFFIC CRASHES involving BICYCLISTS A special research project concerning bicycle crashes in West Berlin in the years 1981 through 1985 Police Analyst
the Ministry of Transport is attributed as the source of the material
 Cyclists 2015 Disclaimer All reasonable endeavours are made to ensure the accuracy of the information in this report. However, the information is provided without warranties of any kind including accuracy,
Cyclists 2015 Disclaimer All reasonable endeavours are made to ensure the accuracy of the information in this report. However, the information is provided without warranties of any kind including accuracy,
Film Guide for Educators. Designing for Safety
 Film Guide for Educators Designing for Safety Designing For Safety Key Concepts Speeding While Driving Speeding is the number one cause of injuries and deaths from driving. The main reasons are because
Film Guide for Educators Designing for Safety Designing For Safety Key Concepts Speeding While Driving Speeding is the number one cause of injuries and deaths from driving. The main reasons are because
Relative Vulnerability Matrix for Evaluating Multimodal Traffic Safety. O. Grembek 1
 337 Relative Vulnerability Matrix for Evaluating Multimodal Traffic Safety O. Grembek 1 1 Safe Transportation Research and Education Center, Institute of Transportation Studies, University of California,
337 Relative Vulnerability Matrix for Evaluating Multimodal Traffic Safety O. Grembek 1 1 Safe Transportation Research and Education Center, Institute of Transportation Studies, University of California,
ADVANCES IN TRANSPORTATION STUDIES An International Journal
 ADVANCES IN TRANSPORTATION STUDIES An International Journal Editor in Chief Andrea Benedetto Section A & B Contents Vol. XV July 2008 Section A A. Persson 5 Road traffic accidents in Ethiopia: magnitude,
ADVANCES IN TRANSPORTATION STUDIES An International Journal Editor in Chief Andrea Benedetto Section A & B Contents Vol. XV July 2008 Section A A. Persson 5 Road traffic accidents in Ethiopia: magnitude,
Alberta. Traffic Collision Statistics. Office of Traffic Safety Transportation Services Division May 2017
 Traffic Collision Statistics Office of Traffic Safety Transportation Services Division May 217 This page was intentionally left blank. 2 Table of Contents Traffic Collisions... 4 Traffic Collision Rates...
Traffic Collision Statistics Office of Traffic Safety Transportation Services Division May 217 This page was intentionally left blank. 2 Table of Contents Traffic Collisions... 4 Traffic Collision Rates...
Analysis and Countermeasure Research on the Death Rate of the Vulnerable Road Users in Traffic Accidents. Ying MEI
 2nd Annual International Conference on Social Science and Contemporary Humanity Development (SSCHD 2016) Analysis and Countermeasure Research on the Death Rate of the Vulnerable Road Users in Traffic Accidents
2nd Annual International Conference on Social Science and Contemporary Humanity Development (SSCHD 2016) Analysis and Countermeasure Research on the Death Rate of the Vulnerable Road Users in Traffic Accidents
SECTION 1. The current state of global road safety
 SECTION 1 The current state of global road safety The number of road traffic deaths each year has not increased but remains unacceptably high at 1.24 million per year. Many countries have successfully
SECTION 1 The current state of global road safety The number of road traffic deaths each year has not increased but remains unacceptably high at 1.24 million per year. Many countries have successfully
EUROPEAN TRANSPORT CONFERENCE 2006 ROAD SAFETY IN LONDON PAST SUCCESSES AND FUTURE INNOVATIONS
 EUROPEAN TRANSPORT CONFERENCE 26 ROAD SAFETY IN LONDON PAST SUCCESSES AND FUTURE INNOVATIONS Mr Chris Lines Head of the London Road Safety Unit, Transport for London 1. PAST SUCCESSES Road safety is a
EUROPEAN TRANSPORT CONFERENCE 26 ROAD SAFETY IN LONDON PAST SUCCESSES AND FUTURE INNOVATIONS Mr Chris Lines Head of the London Road Safety Unit, Transport for London 1. PAST SUCCESSES Road safety is a
ESTIMATION OF THE EFFECT OF AUTONOMOUS EMERGENCY BRAKING SYSTEMS FOR PEDESTRIANS ON REDUCTION IN THE NUMBER OF PEDESTRIAN VICTIMS
 ESTIMATION OF THE EFFECT OF AUTONOMOUS EMERGENCY BRAKING SYSTEMS FOR PEDESTRIANS ON REDUCTION IN THE NUMBER OF PEDESTRIAN VICTIMS Toshiyuki, Yanaoka Yukou, Takahashi Honda R&D Co.,Ltd. Automobile R&D Center
ESTIMATION OF THE EFFECT OF AUTONOMOUS EMERGENCY BRAKING SYSTEMS FOR PEDESTRIANS ON REDUCTION IN THE NUMBER OF PEDESTRIAN VICTIMS Toshiyuki, Yanaoka Yukou, Takahashi Honda R&D Co.,Ltd. Automobile R&D Center
Pedestrian Accidents in Utah
 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1325 69 Pedestrian Accidents in Utah ERIC YUAN-CHIN CHENG The objectives are to investigate the trend of Utah's pedestrian accident rate and to analyze and discuss some of
TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1325 69 Pedestrian Accidents in Utah ERIC YUAN-CHIN CHENG The objectives are to investigate the trend of Utah's pedestrian accident rate and to analyze and discuss some of
Road safety management and speed management
 Road safety management and speed management WP5-Responsible: ERDF PP6 - AMZS Branka Leskovšek, Robert Štaba 6.6.2013 Automobile Association of Slovenia (AMZS) Association of Automobile and Touring Clubs
Road safety management and speed management WP5-Responsible: ERDF PP6 - AMZS Branka Leskovšek, Robert Štaba 6.6.2013 Automobile Association of Slovenia (AMZS) Association of Automobile and Touring Clubs
DOI /HORIZONS.B P23 UDC : (497.11) PEDESTRIAN CROSSING BEHAVIOUR AT UNSIGNALIZED CROSSINGS 1
 DOI 10.20544/HORIZONS.B.03.1.16.P23 UDC 656.142.054:159.922(497.11) PEDESTRIAN CROSSING BEHAVIOUR AT UNSIGNALIZED CROSSINGS 1 JelenaMitrovićSimić 1, Valentina Basarić, VukBogdanović Department of Traffic
DOI 10.20544/HORIZONS.B.03.1.16.P23 UDC 656.142.054:159.922(497.11) PEDESTRIAN CROSSING BEHAVIOUR AT UNSIGNALIZED CROSSINGS 1 JelenaMitrovićSimić 1, Valentina Basarić, VukBogdanović Department of Traffic
Empirical Analysis of Speeding Behaviour and Determining. Speed Limits for Bicycles. Abstract
 Empirical Analysis of Speeding Behaviour and Determining Speed Limits for Bicycles Cheng, Qiangwei Li, Bo Gao and Manquan Guan Department of Traffic Management Engineering, Zhejiang Police College, Hangzhou,
Empirical Analysis of Speeding Behaviour and Determining Speed Limits for Bicycles Cheng, Qiangwei Li, Bo Gao and Manquan Guan Department of Traffic Management Engineering, Zhejiang Police College, Hangzhou,
North Carolina. Bicycle Crash Facts Prepared for
 North Carolina Bicycle Crash Facts 2006-2010 Prepared for The North Carolina Department of Transportation Division of Bicycle and Pedestrian Transportation Prepared by The University of North Carolina
North Carolina Bicycle Crash Facts 2006-2010 Prepared for The North Carolina Department of Transportation Division of Bicycle and Pedestrian Transportation Prepared by The University of North Carolina
Pedestrian Accidents in Kentucky
 Transportation Kentucky Transportation Center Research Report University of Kentucky Year 1976 Pedestrian Accidents in Kentucky Charles V. Zegeer Robert C. Deen Kentucky Department of Transportation Kentucky
Transportation Kentucky Transportation Center Research Report University of Kentucky Year 1976 Pedestrian Accidents in Kentucky Charles V. Zegeer Robert C. Deen Kentucky Department of Transportation Kentucky
Road Accident Analysis and Identify the black spot location On State Highway-5 (Halol-Godhra Section)
 Road Accident Analysis and Identify the black spot location On State Highway-5 (Halol-Godhra Section) 1 Shah Dhruvit, 2 Shah Pranay M. 1 M.E civil(transportation), 2 M.E civil, P.h.d.(pursuing) 1 Tatva
Road Accident Analysis and Identify the black spot location On State Highway-5 (Halol-Godhra Section) 1 Shah Dhruvit, 2 Shah Pranay M. 1 M.E civil(transportation), 2 M.E civil, P.h.d.(pursuing) 1 Tatva
Safety and Active Transport. Dr. Maureen Carew, Medical Officer of Health Renfrew County and District Health Unit May 30, 2014
 Safety and Active Transport Dr. Maureen Carew, Medical Officer of Health Renfrew County and District Health Unit May 30, 2014 Active Transport Vision Increase levels of walking and cycling Reduce vehicle
Safety and Active Transport Dr. Maureen Carew, Medical Officer of Health Renfrew County and District Health Unit May 30, 2014 Active Transport Vision Increase levels of walking and cycling Reduce vehicle
Transportation Issues Poll for New York City
 2016-17 Transportation Issues Poll for New York City 82% support Vision Zero and reducing traffic deaths 72% on average, support more street space for children to play, protected bike lanes and other safety
2016-17 Transportation Issues Poll for New York City 82% support Vision Zero and reducing traffic deaths 72% on average, support more street space for children to play, protected bike lanes and other safety
Automated Proactive Road Safety Analysis
 Transportation Research At McGill Seminar Nicolas Saunier nicolas.saunier@polymtl.ca November 25 th 2010 Outline 1 2 for 3 using Video Data 4 Using Microscopic Data 5 A World Health Issue Over 1.2 million
Transportation Research At McGill Seminar Nicolas Saunier nicolas.saunier@polymtl.ca November 25 th 2010 Outline 1 2 for 3 using Video Data 4 Using Microscopic Data 5 A World Health Issue Over 1.2 million
road safety issues 2001 road toll for Gisborne district July 2002 Road user casualties Estimated social cost of crashes*
 GISBORNE DISTRICT road safety issues July 22 The Land Transport Safety Authority (LTSA) has prepared this Road Safety Issues Report. It is based on reported crash data and trends for the 1997 21 period.
GISBORNE DISTRICT road safety issues July 22 The Land Transport Safety Authority (LTSA) has prepared this Road Safety Issues Report. It is based on reported crash data and trends for the 1997 21 period.
WILMAPCO Public Opinion Survey Summary of Results
 Wilmington Area Planning Council WILMAPCO Public Opinion Survey Summary of Results Prepared by: 2955 Valmont Road, Suite 300 Boulder, Colorado 80301 t: 303-444-7863 f: 303-444-1145 www.n-r-c.com Table
Wilmington Area Planning Council WILMAPCO Public Opinion Survey Summary of Results Prepared by: 2955 Valmont Road, Suite 300 Boulder, Colorado 80301 t: 303-444-7863 f: 303-444-1145 www.n-r-c.com Table
ITARDA INFORMATION. No.128. Special feature
 ITARDA INFORMATION No.128 Special feature Special feature Accidents when four-wheel vehicles are reversing ~ Drivers must thoroughly check behind them, especially in parking lots! ~ Introduction You may
ITARDA INFORMATION No.128 Special feature Special feature Accidents when four-wheel vehicles are reversing ~ Drivers must thoroughly check behind them, especially in parking lots! ~ Introduction You may
Napier City road trauma for Napier City. Road casualties Estimated social cost of crashes* Major road safety issues.
 ISSN 1176-841X July 25 Land Transport New Zealand has prepared this road safety issues report. It is based on reported crash data and trends for the 2 24 period. The intent of the report is to highlight
ISSN 1176-841X July 25 Land Transport New Zealand has prepared this road safety issues report. It is based on reported crash data and trends for the 2 24 period. The intent of the report is to highlight
SAFETY EVALUATION OF AN UNCONTROLLED
 SAFETY EVALUATION OF AN UNCONTROLLED INTERSECTION USING SURROGATE SAFETY MEASURES By S. Shekhar Babu Research scholar (Ext) IITB Asso Prof CME Pune Prof. P. Vedagiri Asst Prof Dept of civil Engg IIT Bombay
SAFETY EVALUATION OF AN UNCONTROLLED INTERSECTION USING SURROGATE SAFETY MEASURES By S. Shekhar Babu Research scholar (Ext) IITB Asso Prof CME Pune Prof. P. Vedagiri Asst Prof Dept of civil Engg IIT Bombay
Analyses and statistics on the frequency and the incidence of traffic accidents within Dolj County
 UNIVERSITY OF PITESTI SCIENTIFIC BULLETIN Faculty of Mechanics and Technology AUTOMOTIVE series, year XXIV, no. 28 Analyses and statistics on the frequency and the incidence of traffic accidents within
UNIVERSITY OF PITESTI SCIENTIFIC BULLETIN Faculty of Mechanics and Technology AUTOMOTIVE series, year XXIV, no. 28 Analyses and statistics on the frequency and the incidence of traffic accidents within
Planning Daily Work Trip under Congested Abuja Keffi Road Corridor
 ISBN 978-93-84468-19-4 Proceedings of International Conference on Transportation and Civil Engineering (ICTCE'15) London, March 21-22, 2015, pp. 43-47 Planning Daily Work Trip under Congested Abuja Keffi
ISBN 978-93-84468-19-4 Proceedings of International Conference on Transportation and Civil Engineering (ICTCE'15) London, March 21-22, 2015, pp. 43-47 Planning Daily Work Trip under Congested Abuja Keffi
The automobile is a complex system in which humans play an important role. Driving is
 FRONT BRAKE LIGHT Emily Gates DEA 325 Homework #3 November 29, 2007 The automobile is a complex system in which humans play an important role. Driving is largely a visual task 1 - when vision is obstructed,
FRONT BRAKE LIGHT Emily Gates DEA 325 Homework #3 November 29, 2007 The automobile is a complex system in which humans play an important role. Driving is largely a visual task 1 - when vision is obstructed,
Relationship Between Child Pedestrian Accidents and City Planning in Zarqa, Jordan
 112 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1281 Relationship Between Child Pedestrian Accidents and City Planning in Zarqa, Jordan ADU H. AL-BALBISSI, MOHAMED T. ABOUL-ELA, AND SABAH SAMMOUR The relationship between
112 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1281 Relationship Between Child Pedestrian Accidents and City Planning in Zarqa, Jordan ADU H. AL-BALBISSI, MOHAMED T. ABOUL-ELA, AND SABAH SAMMOUR The relationship between
1 Monash University Accident Research Centre, Monash University, Victoria, RACV, 550 Princes Highway Noble Park, Victoria, 3174.
 Roadside Environment Safety: a statistical analysis of collisions with fixed roadside objects in Victoria Amanda Delaney 1, Stuart Newstead 1, Bruce Corben 1, Jim Langford 1 and Peter Daly 2 1 Monash University
Roadside Environment Safety: a statistical analysis of collisions with fixed roadside objects in Victoria Amanda Delaney 1, Stuart Newstead 1, Bruce Corben 1, Jim Langford 1 and Peter Daly 2 1 Monash University
Maine Highway Safety Facts 2016
 Maine Highway Safety Facts 216 216 MAINE HIGHWAY SAFETY FACTS The Bureau of Highway Safety and the Maine Department of Transportation are pleased to present the 216 edition of Maine Highway Safety Facts.
Maine Highway Safety Facts 216 216 MAINE HIGHWAY SAFETY FACTS The Bureau of Highway Safety and the Maine Department of Transportation are pleased to present the 216 edition of Maine Highway Safety Facts.
VISIONZEROPHL.COM #VISIONZEROPHL
 What is Vision Zero? What is Vision Zero? A policy that states clearly that traffic deaths are preventable and unacceptable. CORE PRINCIPLES: Human life takes priority over mobility; Human error is inevitable
What is Vision Zero? What is Vision Zero? A policy that states clearly that traffic deaths are preventable and unacceptable. CORE PRINCIPLES: Human life takes priority over mobility; Human error is inevitable
Effects of Human and External Factors on Traffic Accidents
 BULETINUL UniversităŃii Petrol Gaze din Ploieşti Vol. LXI No. 1/009 9-17 Seria Matematică - Informatică - Fizică Effects of Human and External Factors on Traffic Accidents Murat Sari *, Özcan Mutlu **,
BULETINUL UniversităŃii Petrol Gaze din Ploieşti Vol. LXI No. 1/009 9-17 Seria Matematică - Informatică - Fizică Effects of Human and External Factors on Traffic Accidents Murat Sari *, Özcan Mutlu **,
Targeting collisions resulting in killed or serious injury (KSI) victims
 Targeting collisions resulting in killed or serious injury (KSI) victims Superintendent Steve Lyne Dorset Police @SuptSteveLyne Why important? 1.25m deaths a year globally (WHO, 2015) ¾ deaths are male
Targeting collisions resulting in killed or serious injury (KSI) victims Superintendent Steve Lyne Dorset Police @SuptSteveLyne Why important? 1.25m deaths a year globally (WHO, 2015) ¾ deaths are male
Determining bicycle infrastructure preferences A case study of Dublin
 *Manuscript Click here to view linked References 1 Determining bicycle infrastructure preferences A case study of Dublin Brian Caulfield 1, Elaine Brick 2, Orla Thérèse McCarthy 1 1 Department of Civil,
*Manuscript Click here to view linked References 1 Determining bicycle infrastructure preferences A case study of Dublin Brian Caulfield 1, Elaine Brick 2, Orla Thérèse McCarthy 1 1 Department of Civil,
Merseyside Road Safety Partnership s Annual Road Traffic Casualties Report 2015
 Merseyside Road Safety Partnership s Annual Road Traffic Casualties Report 2015 Contents 1. Overview of KSI s 2 2. Cyclists 4 3. Motorcyclists 8 4. Senior Road Users 10 5. Pedestrians 14 6. Car Drivers
Merseyside Road Safety Partnership s Annual Road Traffic Casualties Report 2015 Contents 1. Overview of KSI s 2 2. Cyclists 4 3. Motorcyclists 8 4. Senior Road Users 10 5. Pedestrians 14 6. Car Drivers
DEVELOPMENT OF A SET OF TRIP GENERATION MODELS FOR TRAVEL DEMAND ESTIMATION IN THE COLOMBO METROPOLITAN REGION
 DEVELOPMENT OF A SET OF TRIP GENERATION MODELS FOR TRAVEL DEMAND ESTIMATION IN THE COLOMBO METROPOLITAN REGION Ravindra Wijesundera and Amal S. Kumarage Dept. of Civil Engineering, University of Moratuwa
DEVELOPMENT OF A SET OF TRIP GENERATION MODELS FOR TRAVEL DEMAND ESTIMATION IN THE COLOMBO METROPOLITAN REGION Ravindra Wijesundera and Amal S. Kumarage Dept. of Civil Engineering, University of Moratuwa
INTERSECTION SAFETY RESEARCH IN CRACOW UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
 12 Marian TRACZ, Andrzej TARKO, Stanislaw GACA Cracow University of Technology INTERSECTION SAFETY RESEARCH IN CRACOW UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY 1. Trends in traffic safety in Poland Research activity in
12 Marian TRACZ, Andrzej TARKO, Stanislaw GACA Cracow University of Technology INTERSECTION SAFETY RESEARCH IN CRACOW UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY 1. Trends in traffic safety in Poland Research activity in
Bicycle - Motor Vehicle Collisions on Controlled Access Highways in Arizona
 Bicycle - Motor Vehicle Collisions on Controlled Access Highways in Arizona Analysis from January 1, 1991 to June 30, 2002 Richard C. Moeur, PE Traffic Design Manager, Northern Region Michelle N. Bina
Bicycle - Motor Vehicle Collisions on Controlled Access Highways in Arizona Analysis from January 1, 1991 to June 30, 2002 Richard C. Moeur, PE Traffic Design Manager, Northern Region Michelle N. Bina
EFFICIENCY OF TRIPLE LEFT-TURN LANES AT SIGNALIZED INTERSECTIONS
 EFFICIENCY OF TRIPLE LEFT-TURN LANES AT SIGNALIZED INTERSECTIONS Khaled Shaaban, Ph.D., P.E., PTOE (a) (a) Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Qatar University (a) kshaaban@qu.edu.qa
EFFICIENCY OF TRIPLE LEFT-TURN LANES AT SIGNALIZED INTERSECTIONS Khaled Shaaban, Ph.D., P.E., PTOE (a) (a) Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Qatar University (a) kshaaban@qu.edu.qa
Anatomy of Injury Severity and Fatality in Indonesian Traffic Accidents
 412 J. Eng. Technol. Sci., Vol. 49, No. 3, 2017, 412-422 Anatomy of Injury Severity and Fatality in Indonesian Traffic Accidents Sigit Puji Santosa 1*, Andi Isra Mahyuddin 1 & Febrianto Guntur Sunoto 2
412 J. Eng. Technol. Sci., Vol. 49, No. 3, 2017, 412-422 Anatomy of Injury Severity and Fatality in Indonesian Traffic Accidents Sigit Puji Santosa 1*, Andi Isra Mahyuddin 1 & Febrianto Guntur Sunoto 2
Evaluation of shared use of bicycles and pedestrians in Japan
 Urban Transport XIV 47 Evaluation of shared use of bicycles and pedestrians in Japan P. Zhe 1, H. Yamanaka 2 & K. Kakihara 1 1 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Graduate School of Advanced
Urban Transport XIV 47 Evaluation of shared use of bicycles and pedestrians in Japan P. Zhe 1, H. Yamanaka 2 & K. Kakihara 1 1 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Graduate School of Advanced
Copy of my report. Why am I giving this talk. Overview. State highway network
 Road Surface characteristics and traffic accident rates on New Zealand s state highway network Robert Davies Statistics Research Associates http://www.statsresearch.co.nz Copy of my report There is a copy
Road Surface characteristics and traffic accident rates on New Zealand s state highway network Robert Davies Statistics Research Associates http://www.statsresearch.co.nz Copy of my report There is a copy
Private sector, government (and civil society) partnership to improve road safety: A city-based approach
 Private sector, government (and civil society) partnership to improve road safety: A city-based approach CODATU XV Addis Ababa. October 25, 2012 Ryan Duly Global Road Safety Partnership Some background
Private sector, government (and civil society) partnership to improve road safety: A city-based approach CODATU XV Addis Ababa. October 25, 2012 Ryan Duly Global Road Safety Partnership Some background
MRI-2: Integrated Simulation and Safety
 MRI-2: Integrated Simulation and Safety Year 3 2 nd Quarterly Report Submitted by: Dr. Essam Radwan, P.E. (PI), Ahmed.Radwan@ucf.edu Dr. Hatem Abou-Senna, P.E., habousenna@ucf.edu Dr. Mohamed Abdel-Aty,
MRI-2: Integrated Simulation and Safety Year 3 2 nd Quarterly Report Submitted by: Dr. Essam Radwan, P.E. (PI), Ahmed.Radwan@ucf.edu Dr. Hatem Abou-Senna, P.E., habousenna@ucf.edu Dr. Mohamed Abdel-Aty,
Discerning Pedestrian Accidents in Dhaka-Barisal National Highway in Bangladesh
 Discerning Pedestrian Accidents in Dhaka-Barisal National Highway in Bangladesh 1 Fayaz Uddin, 2 Dr. Farzana Rahman, 3 Md. Mostafizur Rahman, 4 Md. Ariful Islam 1 Bangladesh University of Science and Technology
Discerning Pedestrian Accidents in Dhaka-Barisal National Highway in Bangladesh 1 Fayaz Uddin, 2 Dr. Farzana Rahman, 3 Md. Mostafizur Rahman, 4 Md. Ariful Islam 1 Bangladesh University of Science and Technology
Complete Streets: Building Momentum in Connecticut
 Complete Streets: Building Momentum in Connecticut Tri-State Transportation Campaign, 2012 What are Complete Streets? Complete Streets are safe, comfortable, and convenient for travel for everyone, regardless
Complete Streets: Building Momentum in Connecticut Tri-State Transportation Campaign, 2012 What are Complete Streets? Complete Streets are safe, comfortable, and convenient for travel for everyone, regardless
Strategies for Sharing the Road with Other Users
 Idaho Driver Education and Training Strategies for Sharing the Road with Other Users M15-1 Sharing the Road Introduction Idaho law requires motorists to operate their vehicles in a careful and prudent
Idaho Driver Education and Training Strategies for Sharing the Road with Other Users M15-1 Sharing the Road Introduction Idaho law requires motorists to operate their vehicles in a careful and prudent
Cycling and risk. Cycle facilities and risk management
 Cycling and risk Cycle facilities and risk management Failure to recognize possibilities is the most dangerous and common mistake one can make. Mae Jemison, astronaut 6/11/2010 York Regional Council Cycling
Cycling and risk Cycle facilities and risk management Failure to recognize possibilities is the most dangerous and common mistake one can make. Mae Jemison, astronaut 6/11/2010 York Regional Council Cycling
ROAD SAFETY AND POVERTY
 ROAD SAFETY AND POVERTY BY J. M Y. AMEGASHIE FCILT TECHNICAL DIRECTOR GRSP GHANA TABLE 1: ANNUAL DISTRIBUTION OF FATALITIES BY ROAD USER CLASS ROAD USER CLASS Year PED CAR HGV BUS/MI NI BUS M/CYCLE PICK-
ROAD SAFETY AND POVERTY BY J. M Y. AMEGASHIE FCILT TECHNICAL DIRECTOR GRSP GHANA TABLE 1: ANNUAL DISTRIBUTION OF FATALITIES BY ROAD USER CLASS ROAD USER CLASS Year PED CAR HGV BUS/MI NI BUS M/CYCLE PICK-
STUDY AND ANALYSIS OF ACCIDENTS ON NH 71-A
 STUDY AND ANALYSIS OF ACCIDENTS ON NH 71-A SARANSH Department of Civil Engineering Institute of technology and science Bhiwani S.S KAZAL Department of Civil Engineering. Institute of technology and science
STUDY AND ANALYSIS OF ACCIDENTS ON NH 71-A SARANSH Department of Civil Engineering Institute of technology and science Bhiwani S.S KAZAL Department of Civil Engineering. Institute of technology and science
road safety issues 2002 road trauma for TNZ Region Two July 2003 Road deaths Estimated social cost of crashes* Major road safety issues
 road safety issues July 23 22 road trauma for TNZ Region Two The Land Transport Safety Authority (LTSA) has prepared this road safety issues report. It is based on reported crash data and trends for the
road safety issues July 23 22 road trauma for TNZ Region Two The Land Transport Safety Authority (LTSA) has prepared this road safety issues report. It is based on reported crash data and trends for the
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET), ISSN (Print), AND TECHNOLOGY (IJCIET)
 INTERNATIONAL ISSN 0976 6316(Online), Volume JOURNAL 5, Issue 6, June (2014), OF pp. 16-24 CIVIL IAEME ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (IJCIET) ISSN 0976 6308 (Print) ISSN 0976 6316(Online) Volume 5, Issue
INTERNATIONAL ISSN 0976 6316(Online), Volume JOURNAL 5, Issue 6, June (2014), OF pp. 16-24 CIVIL IAEME ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (IJCIET) ISSN 0976 6308 (Print) ISSN 0976 6316(Online) Volume 5, Issue
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW
 CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW 2.1 Introduction This chapter presents some background information of the available literature related to the development of accident rates, accident models and accident statistic
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW 2.1 Introduction This chapter presents some background information of the available literature related to the development of accident rates, accident models and accident statistic
Draft Report: Traffic Crashes in the Denver Region
 Click to edit Master title style Click to edit Master title style Draft Report: Traffic Crashes in the Denver Region Presented by: Steve Cook Board Nov. 16, 2016 Click Report Click to to edit on edit Master
Click to edit Master title style Click to edit Master title style Draft Report: Traffic Crashes in the Denver Region Presented by: Steve Cook Board Nov. 16, 2016 Click Report Click to to edit on edit Master
SITUATIONS AND CHALLENGES OF ROAD SAFETY IN CHINA
 SITUATIONS AND CHALLENGES OF ROAD SAFETY IN CHINA Li Yaning Road Administration of Beijing Municipal Commission of Transport No.317, Guangnei Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R. China E-mail: liyaning@bjlzj.gov.cn
SITUATIONS AND CHALLENGES OF ROAD SAFETY IN CHINA Li Yaning Road Administration of Beijing Municipal Commission of Transport No.317, Guangnei Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R. China E-mail: liyaning@bjlzj.gov.cn
A review of traffic safety in Finnish municipalities
 Urban Transport XII: Urban Transport and the Environment in the 21st Century 439 A review of traffic safety in Finnish municipalities N. Karasmaa, E. Räty, T. Kari & T. Ernvall Laboratory of Transportation
Urban Transport XII: Urban Transport and the Environment in the 21st Century 439 A review of traffic safety in Finnish municipalities N. Karasmaa, E. Räty, T. Kari & T. Ernvall Laboratory of Transportation
ANALYSIS OF THE TRENDS IN ACCIDENT RATES IN SRI LANKA
 ANALYSIS OF THE TRENDS IN ACCIDENT RATES IN SRI LANKA Amal S. Kumarage 1, Cammilus R. Abeygoonawardena 2 and Ravindra Wijesundera 3 ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION In Sri Lanka, both the vehicle population as well
ANALYSIS OF THE TRENDS IN ACCIDENT RATES IN SRI LANKA Amal S. Kumarage 1, Cammilus R. Abeygoonawardena 2 and Ravindra Wijesundera 3 ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION In Sri Lanka, both the vehicle population as well
BICYCLE INFRASTRUCTURE PREFERENCES A CASE STUDY OF DUBLIN
 Proceedings 31st August 1st ITRN2011 University College Cork Brick, McCarty and Caulfield: Bicycle infrastructure preferences A case study of Dublin BICYCLE INFRASTRUCTURE PREFERENCES A CASE STUDY OF DUBLIN
Proceedings 31st August 1st ITRN2011 University College Cork Brick, McCarty and Caulfield: Bicycle infrastructure preferences A case study of Dublin BICYCLE INFRASTRUCTURE PREFERENCES A CASE STUDY OF DUBLIN
Institute of Transportation Engineers Safety Action Plan
 I Institute of Transportation Engineers Safety Action Plan 1. Introduction 2. Intersection Crashes 3. Keep Vehicles on the Road 4. Minimize Consequences When Vehicles Leave the Road 5. School Crossing
I Institute of Transportation Engineers Safety Action Plan 1. Introduction 2. Intersection Crashes 3. Keep Vehicles on the Road 4. Minimize Consequences When Vehicles Leave the Road 5. School Crossing
G AT E WAY PLAN. Community BRIEFING KIT GATEWAY BIKE
 G AT E WAY PLAN GATEWAY BIKE Community BRIEFING KIT PLAN August 2016 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 1 THE BENEFITS OF A BIKEABLE COMMUNITY... 2 ECONOMY...2 SAFETY...3 HEALTH...3 HOUSEHOLD SPENDING...3
G AT E WAY PLAN GATEWAY BIKE Community BRIEFING KIT PLAN August 2016 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 1 THE BENEFITS OF A BIKEABLE COMMUNITY... 2 ECONOMY...2 SAFETY...3 HEALTH...3 HOUSEHOLD SPENDING...3
FACTS AND FIGURES: MAKING THE CASE FOR COMPLETE STREETS IN LEE COUNTY
 FACTS AND FIGURES: MAKING THE CASE FOR COMPLETE STREETS IN LEE COUNTY Safety: Close to 5,000 pedestrians and bicyclists die each year on U.S. roads, and more than 70,000 are injured. [Mean Streets, Surface
FACTS AND FIGURES: MAKING THE CASE FOR COMPLETE STREETS IN LEE COUNTY Safety: Close to 5,000 pedestrians and bicyclists die each year on U.S. roads, and more than 70,000 are injured. [Mean Streets, Surface
CHAPTER 9: SAFETY 9.1 TRAFFIC SAFETY INTERSECTION COLLISIONS
 CHAPTER 9: SAFETY 9.1 TRAFFIC SAFETY Creating a transportation network that is not only efficient but also safe is a key objective of the General Plan and the WBCMP. To assess the current safety conditions
CHAPTER 9: SAFETY 9.1 TRAFFIC SAFETY Creating a transportation network that is not only efficient but also safe is a key objective of the General Plan and the WBCMP. To assess the current safety conditions
LECTUR 10 CHARACTERISTICS OF THE DRIVER, THE PEDESTRIAN, THE VEHICLE AND THE ROAD. One problem that faces traffic and transportation engineers is:
 LECTUR 10 CHARACTERISTICS OF THE DRIVER, THE PEDESTRIAN, THE VEHICLE AND THE ROAD 3.1 DRIVER CHARACTERISTICS Physiological Measurable and Usually Quantifiable Psychological Much more difficult to measure
LECTUR 10 CHARACTERISTICS OF THE DRIVER, THE PEDESTRIAN, THE VEHICLE AND THE ROAD 3.1 DRIVER CHARACTERISTICS Physiological Measurable and Usually Quantifiable Psychological Much more difficult to measure
A location model for pedestrian crossings in arterial streets
 A location model for pedestrian crossings in arterial streets B. Amini¹ & H. Ghahramani² ¹Department of Civil Engineering, International University of Imam Khomeini, Iran ²Iran University of Science and
A location model for pedestrian crossings in arterial streets B. Amini¹ & H. Ghahramani² ¹Department of Civil Engineering, International University of Imam Khomeini, Iran ²Iran University of Science and
DOT HS September Crash Factors in Intersection-Related Crashes: An On-Scene Perspective
 DOT HS 811 366 September 2010 Crash Factors in Intersection-Related Crashes: An On-Scene Perspective DISCLAIMER This publication is distributed by the U.S. Department of Transportation, National Highway
DOT HS 811 366 September 2010 Crash Factors in Intersection-Related Crashes: An On-Scene Perspective DISCLAIMER This publication is distributed by the U.S. Department of Transportation, National Highway
Comparing the Crash Injury Severity Risk Factors at High-Volume and Low-Volume Intersections with Different Traffic Control in Alabama
 International Journal of Statistics and Applications 2018, 8(4): 173-188 DOI: 10.5923/j.statistics.20180804.03 Comparing the Crash Injury Severity Risk Factors at High-Volume and Low-Volume Intersections
International Journal of Statistics and Applications 2018, 8(4): 173-188 DOI: 10.5923/j.statistics.20180804.03 Comparing the Crash Injury Severity Risk Factors at High-Volume and Low-Volume Intersections
ANALYSIS OF ACCIDENT SURVEY ON PEDESTRIANS ON NATIONAL HIGHWAY 16 USING STATISTICAL METHODS
 ANALYSIS OF ACCIDENT SURVEY ON PEDESTRIANS ON NATIONAL HIGHWAY 16 USING STATISTICAL METHODS K.SWETHA Assistant Professor Civil Department, Sai Ganapati Engineering College, JNTUK, Visakhapatnam, India,
ANALYSIS OF ACCIDENT SURVEY ON PEDESTRIANS ON NATIONAL HIGHWAY 16 USING STATISTICAL METHODS K.SWETHA Assistant Professor Civil Department, Sai Ganapati Engineering College, JNTUK, Visakhapatnam, India,
A Framework For Integrating Pedestrians into Travel Demand Models
 A Framework For Integrating Pedestrians into Travel Demand Models Kelly J. Clifton Intersections Seminar University of Toronto September 22, 2017 Portland, Oregon, USA Region Population~ 2.4 M Urban Growth
A Framework For Integrating Pedestrians into Travel Demand Models Kelly J. Clifton Intersections Seminar University of Toronto September 22, 2017 Portland, Oregon, USA Region Population~ 2.4 M Urban Growth
Anatomy Of The Traffic Accidents On The Road
 ISSN (e): 2250 3005 Volume, 07 Issue, 04 April 2017 International Journal of Computational Engineering Research (IJCER) Anatomy Of The Traffic Accidents On The Road Rahmatullah S. 1, M. Yamin Jinca 2,
ISSN (e): 2250 3005 Volume, 07 Issue, 04 April 2017 International Journal of Computational Engineering Research (IJCER) Anatomy Of The Traffic Accidents On The Road Rahmatullah S. 1, M. Yamin Jinca 2,
Road safety training for professional drivers: worldwide practices
 International Conference on Traffic Safety: The impact of Education and Training on Traffic Behaviour Abu Dhabi, UAE 1-2 November, 2017 Road safety training for professional drivers: worldwide practices
International Conference on Traffic Safety: The impact of Education and Training on Traffic Behaviour Abu Dhabi, UAE 1-2 November, 2017 Road safety training for professional drivers: worldwide practices
Road Safety: African Action Plan for the Global Decade of Action for Road Safety
 The First Ordinary Session of the African Union Specialized Technical Committee on Transport, Intercontinental and Interregional Infrastructures, Energy and Tourism THEME: Financing Infrastructure in Africa
The First Ordinary Session of the African Union Specialized Technical Committee on Transport, Intercontinental and Interregional Infrastructures, Energy and Tourism THEME: Financing Infrastructure in Africa
ANALYSIS OF PEDESTRIAN ACCIDENTS IN IRBID CITY, JORDAN
 ANALYSIS OF PEDESTRIAN ACCIDENTS IN IRBID CITY, JORDAN Bashar Al-Omari 1 & Eman Obaidat Civil Engineering Department Jordan University of Science & Technology E-Mail: bahomari@just.edu.jo Summary: The
ANALYSIS OF PEDESTRIAN ACCIDENTS IN IRBID CITY, JORDAN Bashar Al-Omari 1 & Eman Obaidat Civil Engineering Department Jordan University of Science & Technology E-Mail: bahomari@just.edu.jo Summary: The
Cabrillo College Transportation Study
 Cabrillo College Transportation Study Planning and Research Office Terrence Willett, Research Analyst, Principle Author Jing Luan, Director of Planning and Research Judy Cassada, Research Specialist Shirley
Cabrillo College Transportation Study Planning and Research Office Terrence Willett, Research Analyst, Principle Author Jing Luan, Director of Planning and Research Judy Cassada, Research Specialist Shirley
The Effect of Pavement Marking on Speed. Reduction in Exclusive Motorcycle Lane. in Malaysia
 Contemporary Engineering Sciences, Vol. 3, 2010, no. 3, 149-155 The Effect of Pavement Marking on Speed Reduction in Exclusive Motorcycle Lane in Malaysia Seyed Farzin Faezi PhD student in highway and
Contemporary Engineering Sciences, Vol. 3, 2010, no. 3, 149-155 The Effect of Pavement Marking on Speed Reduction in Exclusive Motorcycle Lane in Malaysia Seyed Farzin Faezi PhD student in highway and
ABSTRACT PEDESTRIAN - VEHICULAR CRASHES: THE INFLUENCE OF PERSONAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS. Carolina V. Burnier, M.Sc., 2005
 ABSTRACT Title: PEDESTRIAN - VEHICULAR CRASHES: THE INFLUENCE OF PERSONAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS Carolina V. Burnier, M.Sc., 2005 Directed By: Dr. Kelly J. Clifton, Department of Civil and Environmental
ABSTRACT Title: PEDESTRIAN - VEHICULAR CRASHES: THE INFLUENCE OF PERSONAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS Carolina V. Burnier, M.Sc., 2005 Directed By: Dr. Kelly J. Clifton, Department of Civil and Environmental
Findings on the Effectiveness of Intersection Treatments included in the Victorian Statewide Accident Black Spot Program
 Findings on the Effectiveness of Intersection Treatments included in the Victorian Statewide Accident Black Spot Program Nimmi Candappa, Jim Scully, Stuart Newstead and Bruce Corben, Monash University
Findings on the Effectiveness of Intersection Treatments included in the Victorian Statewide Accident Black Spot Program Nimmi Candappa, Jim Scully, Stuart Newstead and Bruce Corben, Monash University
Pedestrian Safety in Cities
 Pedestrian Safety in Cities Priorities for India Geetam Tiwari MoUD Chair Professor, Coordinator, TRIPP Indian Institute of Technology Delhi, India URBAN MOBILITY INDIA 2013 IIT Delhi 2013 RTI in Urban
Pedestrian Safety in Cities Priorities for India Geetam Tiwari MoUD Chair Professor, Coordinator, TRIPP Indian Institute of Technology Delhi, India URBAN MOBILITY INDIA 2013 IIT Delhi 2013 RTI in Urban
What s Health Got to Do With It? Health and Land Use Planning
 What s Health Got to Do With It? Health and Land Use Planning CANDACE RUTT, PH.D. EXECUTIVE DIRECTOR APRIL 13 TH, 2016 Planning and Public Health Planning + Public Health Healthy Communities Healthier
What s Health Got to Do With It? Health and Land Use Planning CANDACE RUTT, PH.D. EXECUTIVE DIRECTOR APRIL 13 TH, 2016 Planning and Public Health Planning + Public Health Healthy Communities Healthier
20 meters beyond the circulating part of the roundabout. Includes pedestrian and
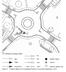 Table A1 Roundabout segments Roundabout segment Entry lane Segment 1 Segment 2 Circulatory road Segment 3 Description 20 100 meters off the roundabout. Oncoming traffic, queues associated with congestion.
Table A1 Roundabout segments Roundabout segment Entry lane Segment 1 Segment 2 Circulatory road Segment 3 Description 20 100 meters off the roundabout. Oncoming traffic, queues associated with congestion.
A review of game-theoretic models of road user behaviour
 A review of game-theoretic models of road user behaviour 25th ICTCT Workshop, Hasselt University November 8-9, 2012 Rune Elvik, Institute of Transport Economics Theory is needed in the study of road user
A review of game-theoretic models of road user behaviour 25th ICTCT Workshop, Hasselt University November 8-9, 2012 Rune Elvik, Institute of Transport Economics Theory is needed in the study of road user
SLOW DOWN A STUDY OF SPEEDING ON MCGUINNESS BLVD
 SLOW DOWN A STUDY OF SPEEDING ON MCGUINNESS BLVD ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This report was prepared by Shawn Macias, in consultation with the McGuinness Boulevard Working Group. This report would not have been
SLOW DOWN A STUDY OF SPEEDING ON MCGUINNESS BLVD ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This report was prepared by Shawn Macias, in consultation with the McGuinness Boulevard Working Group. This report would not have been
SCHOOL CROSSING PROTECTION CRITERIA
 CITY OF MADISON TRAFFIC ENGINEERING SCHOOL CROSSING PROTECTION CRITERIA January 2016 Adopted as Policy on August 31, 1976, by Common Council by Amended Resolution #29,540 Amended on September 14, 1976,
CITY OF MADISON TRAFFIC ENGINEERING SCHOOL CROSSING PROTECTION CRITERIA January 2016 Adopted as Policy on August 31, 1976, by Common Council by Amended Resolution #29,540 Amended on September 14, 1976,
Effects of Automated Speed Enforcement in Montgomery County, Maryland, on Vehicle Speeds, Public Opinion, and Crashes
 Effects of Automated Speed Enforcement in Montgomery County, Maryland, on Vehicle Speeds, Public Opinion, and Crashes August 2015 Wen Hu Insurance Institute for Highway Safety Anne T. McCartt Insurance
Effects of Automated Speed Enforcement in Montgomery County, Maryland, on Vehicle Speeds, Public Opinion, and Crashes August 2015 Wen Hu Insurance Institute for Highway Safety Anne T. McCartt Insurance
Every time a driver is distracted,
 Walking on the Wild Side: Distracted Pedestrians and Traffic Safety Brendan J. Russo, Emmanuel James, Christopher Y. Aguilar, Edward J. Smaglik Every time a driver is distracted, including by their cellphone,
Walking on the Wild Side: Distracted Pedestrians and Traffic Safety Brendan J. Russo, Emmanuel James, Christopher Y. Aguilar, Edward J. Smaglik Every time a driver is distracted, including by their cellphone,
APPENDIX C. Systems Performance Report C-1
 APPENDIX C Systems Performance Report C-1 System Performance Report & Requirements According to the FAST Act, a long range transportation plan needs to include a system performance report and subsequent
APPENDIX C Systems Performance Report C-1 System Performance Report & Requirements According to the FAST Act, a long range transportation plan needs to include a system performance report and subsequent
Field and Analytical Investigation of Accidents Data on the Egyptian Road Network
 J. Civil Eng. Architect. Res. Vol. 4, No. 2, 2017, pp. 1923-1930 Received: January 23, 2016; Published: February 25, 2017 Journal of Civil Engineering and Architecture Research Field and Analytical Investigation
J. Civil Eng. Architect. Res. Vol. 4, No. 2, 2017, pp. 1923-1930 Received: January 23, 2016; Published: February 25, 2017 Journal of Civil Engineering and Architecture Research Field and Analytical Investigation
