Getting the Most Out of Your Underwater Experience:
|
|
|
- Darlene Craig
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Getting the Most Out of Your Underwater Experience: An introduction to identifying the fish, creatures, and coral of the Virgin Islands Part II: Creatures and Coral Brian Naess, Research Associate Institute for the Environment, UNC-Chapel Hill
2 Credits All photos taken by ENST 259 instructors: Brian Naess, Liz Naess, Andrew George, Kolya Lachinsky All identifications for class photos based on the 3 book series by Paul Humann and Ned Deloach: Reef Fish Identification, Reef Creature Identification, and Reef Coral Identification of Florida, Caribbean, and Bahamas published by New World Publications, Inc. Disclaimer: Visual identification of many creatures like sponges and tunicates is at best an educated guess!
3 3 Main Divisions Fish sharks, eels, rays Creatures crabs, shrimp, clams, starfish, anemones, lobsters, squid, octopus, worms, cucumbers, tunicates, sponges, urchins, turtles Coral hard and soft varieties, marine plants and algae
4 * Images scanned from Reef Creature Identification: Florida, Caribbean, Bahamas by Paul Humann and Ned DeLoach Creatures
5 We ll Focus On Cnidarians: Hydroids, Anemones, Zoanthids, and Corallimorphs Segmented Worms: Fireworms, Feather duster worms, Calcareous tube worms Crustaceans: Shrimp, Lobsters, and Crabs Mollusks: Snails, Bivalves, Squid, and Octopuses Echinoderms: Sea stars, Urchins, and Cucumbers Tunicates and Sponges Sea Turtles: Green and Hawksbill turtles
6 What to Look For 0) What Kind of Creature Is It? 1a) Shape 1b) Distinctive Traits 2) Color 3) Behavior 4) Location 5) Size
7 Cnidarians: Hydroids, Anemones, Zoanthids, and Corallimorphs Hydroids Usually colonial; branched skeleton resembling feathers or ferns Arrangement of stalk, branches, and polyps key to identification Anemones Solitary polyps attached to bottom Tentacles vary in length, shape, color, and number Zoanthids Usually smaller than anemones Oral disc has no tentacles except two rings of tentacles around outer edge Corallimorphs Tentacles radiate out from center and form concentric circles Protruding mouth Where to Look Hydroids All areas of reef Anemones All areas of reef. Bodies often hidden in recesses. Zoanthids - Many live on sponges. Others found on all areas of reef. Corallimorphs Most attach to solid structure, often in protected areas. * Descriptions taken from Reef Creature Identification: Florida, Caribbean, Bahamas by Paul Humann and Ned DeLoach. Page 62-66
8 Cnidarians: Hydroids, Anemones, Zoanthids, and Corallimorphs Christmas tree hydroid Giant Anemone Giant Anemone Feather plume hydroid Warty Corallimorph Mat Zoanthid
9 Segmented Worms Fireworms Bundles of sharp, white bristles that will penetrate the skin and break off Feather Duster Worms Bodies hidden inside parchment-like tubes attached to reef Feather-like radioles that extend from tube act as gills and capture plankton Calcareous Tube Worms Tubes often hidden in rock or coral Colorful radioles form spirals and whorls Where to Look Fireworms Can be found crawling all over, especially on gorgonians and fire coral Feather duster worms All reef and nearreef areas. Often shy and retract in tube Calcareous tube worms All areas of reef. Tubes often encased in live coral. * Descriptions taken from Reef Creature Identification: Florida, Caribbean, Bahamas by Paul Humann and Ned DeLoach. Page 140-1
10 Segmented Worms Christmas tree worm Bearded fireworm Star horseshoe worm
11 Crustaceans: Shrimp, Lobsters, and Crabs Shrimp Long, hair-like antennae Lobsters Bottom-dwellers, clawless Spiny lobsters have long, conical antennae Slipper lobsters have plate-like antennae Crabs Claws, three to four pairs of legs Usually secretive, hiding in recesses and in association with anemones and urchins Where to Look Shrimp Under overhangs, recesses and in association with anemones. Usually more than one. Lobsters Caves, recesses. Look for antennae. Often more than one. Crabs Caves, recesses, behind urchins. If you see long-spined urchin next to wall, look behind urchin for nimble spray crab. * Descriptions taken from Reef Creature Identification: Florida, Caribbean, Bahamas by Paul Humann and Ned DeLoach. Page 164-6
12 Crustaceans: Shrimp, Lobsters, and Crabs Banded coral shrimp Peppermint shrimp Pederson cleaner shrimp Spotted cleaner shrimp
13 Crustaceans: Shrimp, Lobsters, and Crabs Spanish lobster Caribbean spiny lobster Spotted spiny lobster
14 Crustaceans: Shrimp, Lobsters, and Crabs Yellowline arrow crab Nimble spray crab Blotched swimming crab
15 Mollusks: Snails, Bivalves, Squid, and Octopuses Snails/Gastropods Identified by shell shape, sculpturing, color pattern, etc. Snail s body normally hidden, but you may see tube-like mouth and/or two tentacles with eyes Bivalves Two shells hinged together by a ligament Squid Eight arms with two longer tentacles. Stabilizing swim fins along the sides. Usually in groups of 3 or more. Octopuses Eight arms of equal length, globular/bag-like body Incredible ability to camouflage Where to Look Snails Sea grass, sand, shallow reef areas. Some attach/feed on gorgonians Bivalves Cracks, recesses, attached to structure like pilings, sometimes attached to gorgonians Squid Usually shallow, reef/near-reef areas. Octopuses Hard to spot unless moving. Can be in recesses. Look for piles of shells. * Descriptions taken from Reef Creature Identification: Florida, Caribbean, Bahamas by Paul Humann and Ned DeLoach. Page 256-8
16 Mollusks: Snails, Bivalves, Squid, and Octopuses Atlantic wing-oyster Crown conch Rough fileclam
17 Mollusks: Snails, Bivalves, Squid, and Octopuses Caribbean reef squid Common octopus
18 Echinoderms: Sea stars, Urchins, and Cucumbers Sea stars Central disc with typically five triangular arms Incredible regenerative abilities Brittle stars Long, thin arms with flattened central disc Sea urchins Spherical bodies with long, protective spines Sea cucumbers Sausage shaped bodies crawling across reef or sand Where to Look Sea stars Sea grass, sandy areas Brittle stars Sponges, fire coral, under rocks Sea urchins Everywhere, particularly in shallow reef/near reef areas. Sea cucumbers Sandy areas, sea grass beds, and reef rubble areas. * Descriptions taken from Reef Creature Identification: Florida, Caribbean, Bahamas by Paul Humann and Ned DeLoach. Page 350-3
19 Echinoderms: Sea stars, Urchins, and Cucumbers Cushion sea star Banded arm brittle star Common comet star Sponge brittle star
20 Echinoderms: Sea stars, Urchins, and Cucumbers Rock-boring urchin West Indian sea egg Long-spined urchin Donkey dung sea cucumber
21 Tunicates and Sponges Tunicates Attached to substrate on one end, two siphons at the other end for food and oxygen Can close their siphons quickly when disturbed Highly evolved with nervous system and complex muscles Sponges Water passes through numerous small pores where food and oxygen are filtered out, then exits out one or more large excurrent openings Many different sizes, colors, and shapes (barrel, ball, tube, rope, encrusting, etc.) Simplest multicellular animal Where to Look Tunicates Reef areas, sometimes attached to gorgonians. Often bodies are hidden in crevices. Sponges Usually near/on reefs, reef walls, overhangs, sometimes attached to substrate like gorgonians, mangrove roots, etc. * Descriptions taken from Reef Creature Identification: Florida, Caribbean, Bahamas by Paul Humann and Ned DeLoach. Pgs 14,400
22 Tunicates Blue bell tunicates Painted tunicates Overgrowing mat tunicates Strawberry tunicates
23 Sponges Black ball sponge Scattered pore rope sponge Branching tube sponge Orange icing sponge Brown bowl sponge Red-orange encrusting sponge
24 Sea Turtles Marine reptiles that only come ashore to lay eggs All species of turtles are endangered We ll see hawksbill and green turtles Where to Look Sea turtles will most often be found in sea grass areas, feeding on turtle grass. You may find them swimming over deeper water, and you may spot them surfacing for air from the beach. Hawksbill turtles have generally brown shells with mottled markings, overlapping plates on their shells, and an overhanging upper beak Hawksbill turtles have two pairs of plates between the eyes Green turtles have brown to dark brown shells that are generally unmarked, though they can have mottled markings like the hawksbill or wave-like/brush-stroke patterns Green turtles have only two plates between the eyes. * Descriptions taken from Reef Fish Identification: Florida, Caribbean, Bahamas by Paul Humann and Ned DeLoach. Pg 481
25 Sea Turtles Green turtle Hawksbill turtle
26 Quiz Banded tube-dwelling anemone* Visual ID: Translucent brown-and-white banded outer tentacles, whitish oral disc and central tentacles. Habitat and Behavior: Inhabit areas of sand and coral rubble. Nocturnal, solitary polyps extend from parchment-like tube buried in sand. * Description taken from Reef Creature Identification: Florida, Caribbean, Bahamas by Paul Humann and Ned DeLoach. Pg 118
27 Quiz Reticulated brittle star* Visual ID: Reticulated network of fine dark lines on bone white to bluish disc. Arms whitish to pale yellow with brownish bands and short spines. Habitat and Behavior: Inhabit sandy areas around reefs. Hide under slabs of coral and rubble. * Description taken from Reef Creature Identification: Florida, Caribbean, Bahamas by Paul Humann and Ned DeLoach. Pg 370
28 Quiz Flamingo tongue* Visual ID: Cream-white mantle covered with orangish, often somewhat rectangular spots with black outlines. Shell is lustrous cream to white. Habitat and Behavior: Attach to and feed on gorgonians in all types of habitats. * Description taken from Reef Creature Identification: Florida, Caribbean, Bahamas by Paul Humann and Ned DeLoach. Pg 282
29 3 Main Divisions Fish sharks, eels, rays Creatures crabs, shrimp, clams, starfish, anemones, lobsters, squid, octopus, worms, cucumbers, tunicates, sponges, urchins, turtles Coral hard and soft varieties, marine plants and algae
30 Coral * Images scanned from Reef Coral Identification: Florida, Caribbean, Bahamas by Paul Humann and Ned DeLoach
31 We ll Focus On Hydrocorals: Fire coral Gorgonians: Sea rods, Sea plumes, and Sea fans Stony corals: Branching & pillar corals, Finger corals, Star corals, Brain corals, and Cup corals Marine plants and Algae
32 Fire Coral Hydrocorals Actually member of hydroid family Two types of polyps: sensory/stinging encircling stout feeding polyps Sting caused by nematocysts on tentacles 3 different flavors: blade, branching, and box Look for mustard color with white ends; white hairs
33 Gorgonians Polyps have 8 tentacles Stems and branches all have central trunk Entire coral colony attached at a single point Pay special attention to arrangement of polyps, as it can be helpful in identification
34 Gorgonians Sea Rods Knobby sea rod Porous sea rod
35 Gorgonians Sea Plumes Sea plume forest Rough sea plume
36 Gorgonians Sea Fans Wide mesh sea fan Common sea fan
37 Stony Corals Hermatypic reef-building Colonies increase size by asexual budding Tentacles in multiples of six
38 Stony Corals Branching and pillar corals Pillar coral Elkhorn coral Staghorn coral
39 Stony Corals Finger corals Branched finger coral Clubtip finger coral
40 Stony Corals Star corals Boulder star coral Blushing star coral Elliptical star coral Lobed star coral
41 Stony Corals Brain corals Boulder brain coral Symmetrical brain coral Grooved brain coral
42 Stony Corals Cup corals Orange cup coral
43 Marine Plants and Algae Photosynthetic Marine plants have roots, stems, leaves, and flowers Example: Sea grasses Algae attach to substrate using rhizoids, have stalks rather than stems, and blades instead of leaves Examples: Brown, green, and red algae * Descriptions taken from Reef Coral Identification: Florida, Caribbean, Bahamas by Paul Humann and Ned DeLoach. Pgs188-9
44 Marine Plants and Algae Sea grass Turtle grass
45 Marine Plants and Algae Brown algae White scroll alga and Y Branched alga
46 Marine Plants and Algae Green algae Green feather alga Green grape alga Bristle ball brush
47 Marine Plants and Algae Red algae Fuzz ball alga Y-Twig alga
48 Quiz Black-ball sponge, elliptical star coral, etc.
49 Quiz Bluestriped grunt (juv.), erect rope sponge, smooth star coral, etc.
50 Quiz Clubtip finger coral, elkhorn coral, turtle grass, watercress alga
51 Quiz Common octopus, orange ball sponge, some type of vase sponge, long-spined urchin, etc.
52 Tips for Productive Snorkeling Good fitting mask Take your time Reefs are 3D swim down and explore Don t use fins in shallow water Stay horizontal in water less than 20 deep Look for overhangs, openings, caves Focus on one thing at a time Spend some time in the shallows Little fish are just as cool as big fish!
53
ABCs & Name the parts!
 ABCs & Name the parts! Objective: These two activities are used to introduce the students to the variety of marine life living in European waters while learning their ABCs and practicing their letter writing.
ABCs & Name the parts! Objective: These two activities are used to introduce the students to the variety of marine life living in European waters while learning their ABCs and practicing their letter writing.
Animal Diversity. Kingdom Animalia
 7ch11 Animal Diversity Kingdom Animalia Animal Characteristics 1. animals are eukaryotes and are multicellular 2. cells are specialized for different functions (vision,digestion,reproduction) 3. protein,
7ch11 Animal Diversity Kingdom Animalia Animal Characteristics 1. animals are eukaryotes and are multicellular 2. cells are specialized for different functions (vision,digestion,reproduction) 3. protein,
Reef Watch Guidelines
 Reef Watch Guidelines What is Reef Watch? Reef watch is a simple one-dive-one-survey method to record the health of coral reefs. The method is easily learnt and it is even easier to participate in the
Reef Watch Guidelines What is Reef Watch? Reef watch is a simple one-dive-one-survey method to record the health of coral reefs. The method is easily learnt and it is even easier to participate in the
A DAY AT THE WHITNEY LAB The Whitney Laboratory for Marine Bioscience An Institute for Marine Research and Biotechnology
 A DAY AT THE WHITNEY LAB The Whitney Laboratory for Marine Bioscience An Institute for Marine Research and Biotechnology STUDENT NAME: What s For Lunch? The Mission In this activity, you will make an educated
A DAY AT THE WHITNEY LAB The Whitney Laboratory for Marine Bioscience An Institute for Marine Research and Biotechnology STUDENT NAME: What s For Lunch? The Mission In this activity, you will make an educated
 OCTOPUS Found throughout the world in tropical, warm and cold temperate waters - the octopus is a bottom dweller, spending much of its life in hiding, usually in a hole among rocks. All octopus species
OCTOPUS Found throughout the world in tropical, warm and cold temperate waters - the octopus is a bottom dweller, spending much of its life in hiding, usually in a hole among rocks. All octopus species
ADVANCED INVERTEBRATES HAVE COMPLEX BODIES AND INTERNAL SYSTEMS
 ADVANCED INVERTEBRATES HAVE COMPLEX BODIES AND INTERNAL SYSTEMS Arthropoda Most successful phylum on Earth Exoskeleton chitin Striated muscle Articulation Crayfish, lobsters, shrimp, crabs Echinodermata
ADVANCED INVERTEBRATES HAVE COMPLEX BODIES AND INTERNAL SYSTEMS Arthropoda Most successful phylum on Earth Exoskeleton chitin Striated muscle Articulation Crayfish, lobsters, shrimp, crabs Echinodermata
Chapter 6 SPONGES. Invertebrates. Sponges. Pore-Bearers. Movement of Water
 Invertebrates Chapter 6 Animals Without Backbones Animals that lack a backbone are called invertebrates. It is estimated that 97% of all species of animals are invertebrates. With the exception of insects,
Invertebrates Chapter 6 Animals Without Backbones Animals that lack a backbone are called invertebrates. It is estimated that 97% of all species of animals are invertebrates. With the exception of insects,
Lecture Benthic Ecology
 Lecture Benthic Ecology Benthos Unlike the drifting plankton and swimming nekton, benthic organisms commonly referred to as benthos live on or near the ocean bottom A benthic habitat may be shallow or
Lecture Benthic Ecology Benthos Unlike the drifting plankton and swimming nekton, benthic organisms commonly referred to as benthos live on or near the ocean bottom A benthic habitat may be shallow or
Classification Station [Grades 6-8]
![Classification Station [Grades 6-8] Classification Station [Grades 6-8]](/thumbs/93/112617681.jpg) Classification Station [Grades 6-8] Georgia Standards of Excellence Addressed: S7L1. Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information to investigate the diversity of living organisms and how they can be compared
Classification Station [Grades 6-8] Georgia Standards of Excellence Addressed: S7L1. Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information to investigate the diversity of living organisms and how they can be compared
Edible, and. Coral Reefs! Photo: CEDixon
 Spreadable, Edible, and Incredible Coral Reefs! Carrie Dixon Discovery Hall Programs Dauphin Island Sea Lab, AL Photo: CEDixon National Science Content Standards Life Science Content Standard, Grades K-4:
Spreadable, Edible, and Incredible Coral Reefs! Carrie Dixon Discovery Hall Programs Dauphin Island Sea Lab, AL Photo: CEDixon National Science Content Standards Life Science Content Standard, Grades K-4:
Exploring Tide Pools. Exploring Tide Pools. Visit for thousands of books and materials.
 Exploring Tide Pools A Reading A Z Level R Leveled Reader Word Count: 1,617 LEVELED READER R Exploring Tide Pools Written by Trica Oshant Hawkins Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials.
Exploring Tide Pools A Reading A Z Level R Leveled Reader Word Count: 1,617 LEVELED READER R Exploring Tide Pools Written by Trica Oshant Hawkins Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials.
Monterey Bay Aquarium Fieldtrip Worksheet
 Attach ticket stub here. Name: Class: B11 or B3A Lab day & time: Monterey Bay Aquarium Fieldtrip Worksheet General Information Address: 886 Cannery Row Monterey, California 93940 Hours: 10am 6pm (May vary
Attach ticket stub here. Name: Class: B11 or B3A Lab day & time: Monterey Bay Aquarium Fieldtrip Worksheet General Information Address: 886 Cannery Row Monterey, California 93940 Hours: 10am 6pm (May vary
Over the next few weeks, we will be learning all about the Coral Reef Ecosystems that surround much of the Australian coastline.
 Over the next few weeks, we will be learning all about the Coral Reef Ecosystems that surround much of the Australian coastline. You will need to complete the tasks set out below and hand them in at the
Over the next few weeks, we will be learning all about the Coral Reef Ecosystems that surround much of the Australian coastline. You will need to complete the tasks set out below and hand them in at the
Key Stage 1 ACTIVITY BOOK Ages 5-7
 Key Stage 1 ACTIVITY BOOK Ages 5-7 Teacher Answer Booklet Hi! My name is Seamor. Answer my questions as we go around the aquarium. Front Room 1. What colour are the Crawfish in the front room? Orange/Brown
Key Stage 1 ACTIVITY BOOK Ages 5-7 Teacher Answer Booklet Hi! My name is Seamor. Answer my questions as we go around the aquarium. Front Room 1. What colour are the Crawfish in the front room? Orange/Brown
Oyster Reef in the Classroom A Hands-On Laboratory Approach
 Grade Level: 7 Oyster Reef in the Classroom A Hands-On Laboratory Approach Subject Area: Life Science Virginia Standards of Learning: LS.4, LS.7, LS.8, LS. 11 Objectives: Students will: Understand the
Grade Level: 7 Oyster Reef in the Classroom A Hands-On Laboratory Approach Subject Area: Life Science Virginia Standards of Learning: LS.4, LS.7, LS.8, LS. 11 Objectives: Students will: Understand the
4 Reef Watch Guidelines
 11 4 Reef Watch Guidelines Reef watch is a simple one-dive-one-survey method to record the health of a coral reef. You can easily learn the method and take part in the programme. On your dive or snorkel
11 4 Reef Watch Guidelines Reef watch is a simple one-dive-one-survey method to record the health of a coral reef. You can easily learn the method and take part in the programme. On your dive or snorkel
V live on FARM B! F A R M B
 6-3.1 Vertebrates and Invertebrates 6-3.2 Obtaining Resources 6-3.3 Endothermic and Ectothermic 6-1.3 Dichotomous Keys List as many animals as you can in the space provided. Leave 2 small columns blank.
6-3.1 Vertebrates and Invertebrates 6-3.2 Obtaining Resources 6-3.3 Endothermic and Ectothermic 6-1.3 Dichotomous Keys List as many animals as you can in the space provided. Leave 2 small columns blank.
 Echinoderms Name Means: Echino- Spiny Derm- Skin About 7,000 species No Head! No Brain! No ventral, dorsal, posterior, or anterior sides! Do have oral (mouth) and aboral sides. Symmetry: Larvae are
Echinoderms Name Means: Echino- Spiny Derm- Skin About 7,000 species No Head! No Brain! No ventral, dorsal, posterior, or anterior sides! Do have oral (mouth) and aboral sides. Symmetry: Larvae are
Key Stage 1 ACTIVITY BOOK Ages 5-7
 Key Stage 1 ACTIVITY BOOK Ages 5-7 Name: Class: Date: Hi! My name is Seamor. Answer my questions as we go around the aquarium. Front Room 1. What colour are the Crawfish in the front room? 2. Draw a line
Key Stage 1 ACTIVITY BOOK Ages 5-7 Name: Class: Date: Hi! My name is Seamor. Answer my questions as we go around the aquarium. Front Room 1. What colour are the Crawfish in the front room? 2. Draw a line
V live on FARM B! F A R M B. I make A MESS! A M E S S. ONLY 3-5% of all animals! 95-97% of all animals!
 Weeks 2, 3 & 4 6.L.4B.1 Vertebrates and Invertebrates 6.L.4B.5 Endothermic and Ectothermic List as many animals as you can in the space provided. Leave 2 small columns blank. A B C D E F G H I J K L M
Weeks 2, 3 & 4 6.L.4B.1 Vertebrates and Invertebrates 6.L.4B.5 Endothermic and Ectothermic List as many animals as you can in the space provided. Leave 2 small columns blank. A B C D E F G H I J K L M
Oceans Alive Resource Book
 E-BOOK CODE: REAU5023 Special School Photocopy Master Edition Oceans Alive Resource Book Image courtesy Microsoft Design Gallery by Sandy Tasker Contents OCEANS ALIVE Contents... 3 The Wonderful World
E-BOOK CODE: REAU5023 Special School Photocopy Master Edition Oceans Alive Resource Book Image courtesy Microsoft Design Gallery by Sandy Tasker Contents OCEANS ALIVE Contents... 3 The Wonderful World
MARINE SCIENCE. Monday 16 Apr 2018
 MARINE SCIENCE Monday 16 Apr 2018 Guest Teacher Grab a copy of the How Scientists Classify Marine Life article & question worksheet from the front counter. Using the article Read the information. Answer
MARINE SCIENCE Monday 16 Apr 2018 Guest Teacher Grab a copy of the How Scientists Classify Marine Life article & question worksheet from the front counter. Using the article Read the information. Answer
Chapter 7. Marine Animals Without a Backbone
 Chapter 7 Marine Animals Without a Backbone Molluscs Characteristics of Phylum: More than 200,000 species Name means "soft body" Basic body plan head, muscular foot and visceral mass in most species Mantle-
Chapter 7 Marine Animals Without a Backbone Molluscs Characteristics of Phylum: More than 200,000 species Name means "soft body" Basic body plan head, muscular foot and visceral mass in most species Mantle-
All about Jenkinson s Aquarium. By The Tiger Class February
 All about Jenkinson s Aquarium By The Tiger Class February 2 2017 Table of Contents 1. Introduction 3 2. Harbor Seals 4,5 3. Penguins 6,7 4. Pythons 8 5. Fish 9 6. Sea Urchins 10 7. Eels 11 8. Stingrays
All about Jenkinson s Aquarium By The Tiger Class February 2 2017 Table of Contents 1. Introduction 3 2. Harbor Seals 4,5 3. Penguins 6,7 4. Pythons 8 5. Fish 9 6. Sea Urchins 10 7. Eels 11 8. Stingrays
Symmetry. Asymmetrical- no shape. Radial- same in half when cut any angle. Bilateral- having a distinct right and left side
 Symmetry Asymmetrical- no shape Radial- same in half when cut any angle Bilateral- having a distinct right and left side Invertebrates 95% of Animals No Backbone The simplest animals and they do not have
Symmetry Asymmetrical- no shape Radial- same in half when cut any angle Bilateral- having a distinct right and left side Invertebrates 95% of Animals No Backbone The simplest animals and they do not have
Chapter 28 Arthropods and Echinoderms. Body Terms. Evolution has led to:
 Chapter 28 Arthropods and Echinoderms Introduction to Arthropods jointed feet Most diverse and successful animals Over 750,000 species identified Segmented bodies Tough exoskeleton Jointed appendages Body
Chapter 28 Arthropods and Echinoderms Introduction to Arthropods jointed feet Most diverse and successful animals Over 750,000 species identified Segmented bodies Tough exoskeleton Jointed appendages Body
Any Age. Ocean Animals. Express Lapbook SAMPLE PAGE. A Journey Through Learning
 A J T L Any Age Ocean Animals Express Lapbook Mini Lapbook, Study Guide, Activities, and Crafts A Journey Through Learning www.ajourneythroughlearning.com Copyright 2013 A Journey Through Learning 1 Authors-Paula
A J T L Any Age Ocean Animals Express Lapbook Mini Lapbook, Study Guide, Activities, and Crafts A Journey Through Learning www.ajourneythroughlearning.com Copyright 2013 A Journey Through Learning 1 Authors-Paula
WARM UP Week 1 MONDAY WEDNESDAY. Using the animals booklet 1 page 23 list the 7 structures animals use to help them escape from predators.
 Animal Warm-Ups 7 Weeks THURSDAY WARM UP Week 1 Using your Animals Booklet Week 1 page 23, list the 10 structures animals use to obtain resources for energy. Using the animals booklet 1 page 23 list the
Animal Warm-Ups 7 Weeks THURSDAY WARM UP Week 1 Using your Animals Booklet Week 1 page 23, list the 10 structures animals use to obtain resources for energy. Using the animals booklet 1 page 23 list the
Kingdom Animalia. Eukaryotic Multicellular Heterotrophs Lack Cell Walls
 Kingdom Animalia Eukaryotic Multicellular Heterotrophs Lack Cell Walls Must do: Feed, Respiration, Circulation, Excretion, Response, Movement, and Reproduction Symmetry Asymmetrical- no shape Radial- same
Kingdom Animalia Eukaryotic Multicellular Heterotrophs Lack Cell Walls Must do: Feed, Respiration, Circulation, Excretion, Response, Movement, and Reproduction Symmetry Asymmetrical- no shape Radial- same
PHYLUM: PLATHYHELMINTHES
 PHYLUM: PLATHYHELMINTHES FLATWORMS Free living (living independently i.e. not attached) Bilaterally symmetrical with a definite front and back, and with left and right sides. Mobile creeping animals. Concentration
PHYLUM: PLATHYHELMINTHES FLATWORMS Free living (living independently i.e. not attached) Bilaterally symmetrical with a definite front and back, and with left and right sides. Mobile creeping animals. Concentration
Spiny skinned animals with radial symmetrical body plan. Rays emanating from a common center. Internal skeleton of hardened plates of calcium
 Echinodermata Spiny skinned animals with radial symmetrical body plan. Rays emanating from a common center. Internal skeleton of hardened plates of calcium carbonate. Water vascular system and tube feet
Echinodermata Spiny skinned animals with radial symmetrical body plan. Rays emanating from a common center. Internal skeleton of hardened plates of calcium carbonate. Water vascular system and tube feet
Coral Reef Activity Book
 Coral Reef Activity Book Coral Reefs for health, for wealth, for life Did you know... Coral reefs can be found in all tropical areas of the world. Corals can also be found in deep cold oceans. Most corals
Coral Reef Activity Book Coral Reefs for health, for wealth, for life Did you know... Coral reefs can be found in all tropical areas of the world. Corals can also be found in deep cold oceans. Most corals
A-Z San Diego Animal Guide
 A-Z San Diego Animal Guide Anemone- Anémona Aa I have stinging tentacles to catch my prey. I am a cousin of jellyfish and corals. I get protection from the sun and predators by covering my body with seashells,
A-Z San Diego Animal Guide Anemone- Anémona Aa I have stinging tentacles to catch my prey. I am a cousin of jellyfish and corals. I get protection from the sun and predators by covering my body with seashells,
Specimen Collection and Classification Activity
 Specimen Collection and Classification Activity Understanding the classification of animals is an important building block of science education, yet most adults cannot tell you how to group the most common
Specimen Collection and Classification Activity Understanding the classification of animals is an important building block of science education, yet most adults cannot tell you how to group the most common
Kingdom Animalia: Sponges. Types of Body Symmetry Radial body parts are symmetrical around a central point (like a pie)
 Kingdom Animalia: Phylum Characteristics Types of Body Symmetry Radial body parts are symmetrical around a central point (like a pie) Bilateral right and left sides are alike and roughly equally proportional
Kingdom Animalia: Phylum Characteristics Types of Body Symmetry Radial body parts are symmetrical around a central point (like a pie) Bilateral right and left sides are alike and roughly equally proportional
Phylum Mollusca (soft bodied)
 Phylum Mollusca (soft bodied) Most described species in the animal kingdom next to Phylum Arthropoda ~100,000 species... Marine, freshwater and terrestrial. 35,000 fossil species. Most diverse group of
Phylum Mollusca (soft bodied) Most described species in the animal kingdom next to Phylum Arthropoda ~100,000 species... Marine, freshwater and terrestrial. 35,000 fossil species. Most diverse group of
Echinoderms. Phylum Echinodermata
 Echinoderms Phylum Echinodermata spiny skinned or hedgehog skin sea stars (starfish), sea urchins, sea cucumbers 6000 species radial symmetry in 2 o development bilateral symmetry in larva http://www.biologyreference.com/dn-ep/echinoderm.html
Echinoderms Phylum Echinodermata spiny skinned or hedgehog skin sea stars (starfish), sea urchins, sea cucumbers 6000 species radial symmetry in 2 o development bilateral symmetry in larva http://www.biologyreference.com/dn-ep/echinoderm.html
Introductory List to Local Marine Animals
 Introductory List to Local Marine Animals During your visit to the Huntsman you will have the opportunity to see and investigate many different types of marine animals, especially invertebrates. Below
Introductory List to Local Marine Animals During your visit to the Huntsman you will have the opportunity to see and investigate many different types of marine animals, especially invertebrates. Below
30. I thought coral growth and reef growth were the same. Is there a difference?
 About reefs 29. Corals are minute invertebrates, yet they can build vast reefs such as the Great Barrier Reef in Australia, which is the largest natural structure in the ocean. How is a coral reef formed?
About reefs 29. Corals are minute invertebrates, yet they can build vast reefs such as the Great Barrier Reef in Australia, which is the largest natural structure in the ocean. How is a coral reef formed?
`Mollusks. may or may not form a hard, calcium carbonate shell. Trochophore Larva
 `Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Soft-bodied invertebrate covered with protective mantle that may or may not form a hard, calcium carbonate shell Includes chitons, snails, slugs, clams, oysters, squid, octopus,
`Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Soft-bodied invertebrate covered with protective mantle that may or may not form a hard, calcium carbonate shell Includes chitons, snails, slugs, clams, oysters, squid, octopus,
Mollusks Soft-bodied Invertebrates
 Mollusks Soft-bodied Invertebrates Phylum Mollusca Very diverse - more species of molluscs than any other group in the ocean. Phylum includes: Bivalves (2 shells); ex. Clam Gastropods (1 shell, coiled);
Mollusks Soft-bodied Invertebrates Phylum Mollusca Very diverse - more species of molluscs than any other group in the ocean. Phylum includes: Bivalves (2 shells); ex. Clam Gastropods (1 shell, coiled);
Phylum Mollusca. Soft-bodied animals. Internal or external shell. Include snails, slugs, clams, squids and octopi
 Phylum Mollusca Soft-bodied animals Internal or external shell Include snails, slugs, clams, squids and octopi Trochophore: free-swimming larval stage of an aquatic mollusk True coeloms Have complex organ
Phylum Mollusca Soft-bodied animals Internal or external shell Include snails, slugs, clams, squids and octopi Trochophore: free-swimming larval stage of an aquatic mollusk True coeloms Have complex organ
Ocean Environmental Science Art Workshop
 Ocean Environmental Science Art Workshop An integrated learning module for primary schools designed and facilitated by the artist Angela Rossen The images here show the workshop with the students in Year
Ocean Environmental Science Art Workshop An integrated learning module for primary schools designed and facilitated by the artist Angela Rossen The images here show the workshop with the students in Year
ZOOXANTHELLAE SEA STAR CALCAREOUS GREEN ALGAE PHYTOPLANKTON FRONT. Genus: Zooxanthella
 FRONT SEA STAR Genus: Asterias Species: forbesi Size: 13 cm (5 in.) radius Range: Gulf of Mexico to Texas ZOOXANTHELLAE Genus: Zooxanthella Species: Size: Microscopic Range: Tropical and temperate oceans
FRONT SEA STAR Genus: Asterias Species: forbesi Size: 13 cm (5 in.) radius Range: Gulf of Mexico to Texas ZOOXANTHELLAE Genus: Zooxanthella Species: Size: Microscopic Range: Tropical and temperate oceans
A. Porifera (sponges): B. Cnidaria (jellies, hydra, sea anemones, and corals):
 Invertebrates Notes A. Porifera (sponges): Porifera literally means. Most sponges are. They are that collect food particles from the water as they pass through flagellated cells called. These cells then
Invertebrates Notes A. Porifera (sponges): Porifera literally means. Most sponges are. They are that collect food particles from the water as they pass through flagellated cells called. These cells then
 Kingdom: Animalia Phylum:Mollusca Classes: Bivalva, Gastropoda, Cephalopoda http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0a7j5prl8hc&feature=related http://www2.beavercreek.k12.oh.us/videos/45/pgr45_700k.asf What is
Kingdom: Animalia Phylum:Mollusca Classes: Bivalva, Gastropoda, Cephalopoda http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0a7j5prl8hc&feature=related http://www2.beavercreek.k12.oh.us/videos/45/pgr45_700k.asf What is
2 Mollusks and Annelid Worms
 CHAPTER 15 2 Mollusks and Annelid Worms SECTION Invertebrates BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the four features of mollusks? What are
CHAPTER 15 2 Mollusks and Annelid Worms SECTION Invertebrates BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the four features of mollusks? What are
EXTRACREDIT PROJECT ANIMALS OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA S OCEAN
 BIO 10 FUNDAMENTALS OF BIOLOGY Instructor: K. Villatoro Student s Name: EXTRACREDIT PROJECT ANIMALS OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA S OCEAN WELCOME TO THE CABRILLO MARINE AQUARIUM! This site was chosen because
BIO 10 FUNDAMENTALS OF BIOLOGY Instructor: K. Villatoro Student s Name: EXTRACREDIT PROJECT ANIMALS OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA S OCEAN WELCOME TO THE CABRILLO MARINE AQUARIUM! This site was chosen because
Phylum Mollusca. More than 500,000 known species. Class Polyplacophora. Class Bivalvia. Class Gastropoda. Class Cephalopoda
 Phylum Mollusca Class Polyplacophora Class Gastropoda Class Bivalvia Class Cephalopoda chitons Snails Sea slugs nudibranchs clams Squid Octopus Cuttlefish Nautilus More than 500,000 known species A bag,
Phylum Mollusca Class Polyplacophora Class Gastropoda Class Bivalvia Class Cephalopoda chitons Snails Sea slugs nudibranchs clams Squid Octopus Cuttlefish Nautilus More than 500,000 known species A bag,
Front Room. 1. There are several different types of flatfish in the pier tank. Name two species of flatfish you can see. and
 Key Stage 2 Lower ACTIVITY BOOK Ages 7-9 Name: Class: Date: Front Room Welcome to Anglesey Sea Zoo! Hi! My name is Seamor, and in this activity book my friends and I will give you lots of fun facts about
Key Stage 2 Lower ACTIVITY BOOK Ages 7-9 Name: Class: Date: Front Room Welcome to Anglesey Sea Zoo! Hi! My name is Seamor, and in this activity book my friends and I will give you lots of fun facts about
Barnacles attach to hard surfaces and use their legs to catch tiny particles of food, including plankton from the water around them.
 Food Web Resources - Food Chain Cards Barnacles attach to hard surfaces and use their legs to catch tiny particles of food, including plankton from the water around them Barnacle Edible crabs use their
Food Web Resources - Food Chain Cards Barnacles attach to hard surfaces and use their legs to catch tiny particles of food, including plankton from the water around them Barnacle Edible crabs use their
Phylum Mollusca. Includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids.
 Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids. Bivalves Nautilus Characteristics Soft-bodied invertebrate Covered with protective mantle that may or may
Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids. Bivalves Nautilus Characteristics Soft-bodied invertebrate Covered with protective mantle that may or may
TEACHER BACKGROUND - Creatures of the Deep Sea FOR SEA Institute of Marine Science 2001 J. A. Kolb
 Pacific Viperfish The Pacific viperfish feeds on lanternfish and squid. It has a very large mouth and fang-like teeth. Once the viperfish catches something, it won't get away. Its size ranges from 22-30
Pacific Viperfish The Pacific viperfish feeds on lanternfish and squid. It has a very large mouth and fang-like teeth. Once the viperfish catches something, it won't get away. Its size ranges from 22-30
Following Information Compliments of Avadon Divers, Placencia Belize
 Following Information Compliments of Avadon Divers, Placencia Belize The Blue Hole & Lighthouse Reef Trips to this atoll are done only when there are good surface conditions as it is a 3-hour boat ride
Following Information Compliments of Avadon Divers, Placencia Belize The Blue Hole & Lighthouse Reef Trips to this atoll are done only when there are good surface conditions as it is a 3-hour boat ride
Phylum Molluska.
 Phylum Molluska www.onacd.ca 3 Main Classes of Mollusks GASTROPODA : includes limpets, snails, slugs and whelks BIVALVIA: includes clams, oysters, muscles, scallops and shipworms CEPHALOPODA: includes
Phylum Molluska www.onacd.ca 3 Main Classes of Mollusks GASTROPODA : includes limpets, snails, slugs and whelks BIVALVIA: includes clams, oysters, muscles, scallops and shipworms CEPHALOPODA: includes
Saltwater detective guide
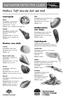 Saltwater detective guide Molluscs: Soft muscular foot and shell Gastropods Snail Description: rounded shell, grey/brown/cream colours. Various sizes: 5 30 mm Habitat: sand or mudflats and Whelk Description:
Saltwater detective guide Molluscs: Soft muscular foot and shell Gastropods Snail Description: rounded shell, grey/brown/cream colours. Various sizes: 5 30 mm Habitat: sand or mudflats and Whelk Description:
Tide Pools Starfish eating a mussel
 Tide Pools Lesson 6 T ide pools form in rocks where water collects in depressions in the rocks during low tide. A variety of plants and animals live their entire life in a tide pool. Many animals that
Tide Pools Lesson 6 T ide pools form in rocks where water collects in depressions in the rocks during low tide. A variety of plants and animals live their entire life in a tide pool. Many animals that
INDICATOR BENTHIC MACROINVERTEBRATE SPECIES AND THEIR CHARACTERISTICS
 Coelenterata (Hydras) Turbellaria (Flatworms) A tube with tentacles Reproduces asexually by budding Movement: sessile, attached or fixed, not free moving Colour: clear to whitish Flattened shape Distinct
Coelenterata (Hydras) Turbellaria (Flatworms) A tube with tentacles Reproduces asexually by budding Movement: sessile, attached or fixed, not free moving Colour: clear to whitish Flattened shape Distinct
Kelp Forest Conservation Food web activity
 Kelp Forest Conservation Food web activity Activity Steps Cut out the kelp forest food web organisms cards. Have students form small groups. Pass out one food web organism and to each group. Using a blank
Kelp Forest Conservation Food web activity Activity Steps Cut out the kelp forest food web organisms cards. Have students form small groups. Pass out one food web organism and to each group. Using a blank
Title: May 31 2:42 PM (1 of 23) Phylum Mollusca
 Title: May 31 2:42 PM (1 of 23) Phylum Mollusca Title: May 31 3:25 PM (2 of 23) often referred to as mollusks second largest phylum has 7 classes only looking at 4 bilateral symmetry, true body cavity
Title: May 31 2:42 PM (1 of 23) Phylum Mollusca Title: May 31 3:25 PM (2 of 23) often referred to as mollusks second largest phylum has 7 classes only looking at 4 bilateral symmetry, true body cavity
TIDE POOLS and CORAL REEFS
 THEMATIC UNIT TIDE POOLS and CORAL REEFS Written by Jeanne King Edited by Patricia Miriani Sima Illustrated by Cheryl Buhler Teacher Created Resources, Inc. 6421 Industry Way Westminster, CA 92683 www.teachercreated.com
THEMATIC UNIT TIDE POOLS and CORAL REEFS Written by Jeanne King Edited by Patricia Miriani Sima Illustrated by Cheryl Buhler Teacher Created Resources, Inc. 6421 Industry Way Westminster, CA 92683 www.teachercreated.com
What is an insect? An insect is an invertebrate (an animal with no spine) that has three pairs of legs and three
 What is an insect? An insect is an invertebrate (an animal with no spine) that has three pairs of legs and three Small minnow mayfly body divisions. The mouth, antennae, and eyes are located on the head;
What is an insect? An insect is an invertebrate (an animal with no spine) that has three pairs of legs and three Small minnow mayfly body divisions. The mouth, antennae, and eyes are located on the head;
Phylum: Porifera (sponges)
 Phylum: Porifera (sponges) (8,761 known species) General Description: Simplest animals, multicellular No organs or body systems Skeleton composed of spongin (soft) and spicules (hard) Symmetry: Asymmetrical
Phylum: Porifera (sponges) (8,761 known species) General Description: Simplest animals, multicellular No organs or body systems Skeleton composed of spongin (soft) and spicules (hard) Symmetry: Asymmetrical
Class Polychaeta: Marine Worms
 Class Polychaeta: Marine Worms Animal Phyla Phylum Mollusca (Snails, Clams, Octopods and Allies): Radula: rasping tongue Shell: 3 layers, mostly calcium carbonate Inner-most = nacre = mother of pearl Mantle:
Class Polychaeta: Marine Worms Animal Phyla Phylum Mollusca (Snails, Clams, Octopods and Allies): Radula: rasping tongue Shell: 3 layers, mostly calcium carbonate Inner-most = nacre = mother of pearl Mantle:
Underwater Secrets of a Marine Protected Area. A Lesson Plan for Grades 4 to 8. Power Point Prepared by Susan Miller
 Underwater Secrets of a Marine Protected Area A Lesson Plan for Grades 4 to 8 Power Point Prepared by Susan Miller Photographs by Jerry Loomis, California State Parks Ranger Josh Pederson, MPA SIMoN Steve
Underwater Secrets of a Marine Protected Area A Lesson Plan for Grades 4 to 8 Power Point Prepared by Susan Miller Photographs by Jerry Loomis, California State Parks Ranger Josh Pederson, MPA SIMoN Steve
Animal Evolution: Chordate and Vertebrate Evolution and Diversity (Learning Outline)
 Animal Evolution: Chordate and Vertebrate Evolution and Diversity (Learning Outline) 1. Distinguishing features of the phylum Chordata and representative organisms. 2. Highlights of evolutionary steps
Animal Evolution: Chordate and Vertebrate Evolution and Diversity (Learning Outline) 1. Distinguishing features of the phylum Chordata and representative organisms. 2. Highlights of evolutionary steps
Coral Reefs N Q U. Visit for thousands of books and materials.
 Coral Reefs A Reading A Z Level N Leveled Book Word Count: 615 N Q U Written by Paula Schricker Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials. www.readinga-z.com Photo Credits: Front cover:
Coral Reefs A Reading A Z Level N Leveled Book Word Count: 615 N Q U Written by Paula Schricker Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials. www.readinga-z.com Photo Credits: Front cover:
Terms of Use. Copyright Natural Beach Living
 Terms of Use All rights reserved. No part of this packet may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form by any means - electronic, mechanical, photo-copies, recording, or otherwise
Terms of Use All rights reserved. No part of this packet may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form by any means - electronic, mechanical, photo-copies, recording, or otherwise
Aquarium entrance stamp here
 Aquarium entrance stamp here Bio 11 - ZOOLOGY Instructor: K. Villatoro Student s Name: CLASSIFICATION OF KINGDOM ANIMALIA WELCOME TO THE CABRILLO MARINE AQUARIUM! This site was chosen because it exhibits
Aquarium entrance stamp here Bio 11 - ZOOLOGY Instructor: K. Villatoro Student s Name: CLASSIFICATION OF KINGDOM ANIMALIA WELCOME TO THE CABRILLO MARINE AQUARIUM! This site was chosen because it exhibits
BeCome a BSAC Beachcomber!
 BeCome a BSAC Beachcomber! Welcome to the BSAC Beachcomber! Let s learn together and discover some fascinating facts about the amazing creatures living in the rock pools along our seashore... Who we are
BeCome a BSAC Beachcomber! Welcome to the BSAC Beachcomber! Let s learn together and discover some fascinating facts about the amazing creatures living in the rock pools along our seashore... Who we are
Phylum Mollusca. By: Christa Jewett, Instructor
 Phylum Mollusca By: Christa Jewett, Instructor For since the creation of the world God s invisible qualities His eternal power and divine nature have been clearly seen, being understood from what has been
Phylum Mollusca By: Christa Jewett, Instructor For since the creation of the world God s invisible qualities His eternal power and divine nature have been clearly seen, being understood from what has been
What are the four main characteristics of arthropods? What are two types of metamorphosis in insects?
 CHAPTER 15 3 Arthropods SECTION Invertebrates BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the four main characteristics of arthropods? What are two
CHAPTER 15 3 Arthropods SECTION Invertebrates BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the four main characteristics of arthropods? What are two
Protostomes vs Deuterostomes. Phylum Mollusca
 Protostomes vs Deuterostomes Animals that have a true coelom and complete digestive system can be divided into two main groups. This division is based on the way their embryos develop and the way in which
Protostomes vs Deuterostomes Animals that have a true coelom and complete digestive system can be divided into two main groups. This division is based on the way their embryos develop and the way in which
Ocean Series Coral Reefs
 Ocean Series Coral Reefs Coral is part of the animal kingdom, a member of the scientific phylum Cnidaria along with other marine creatures including sea jellies. Sea jellies have a soft gelatinous body
Ocean Series Coral Reefs Coral is part of the animal kingdom, a member of the scientific phylum Cnidaria along with other marine creatures including sea jellies. Sea jellies have a soft gelatinous body
Environmental Learning Outside the Classroom (ELOC)
 Environmental Learning Outside the Classroom (ELOC) This guidebook provides lesson ideas and activities to get students engaged with outdoor learning. Created by the Virgin Islands Marine Advisory Service
Environmental Learning Outside the Classroom (ELOC) This guidebook provides lesson ideas and activities to get students engaged with outdoor learning. Created by the Virgin Islands Marine Advisory Service
Seventh Grade. Maui Ocean Center Learning Worksheet. Name: Our mission is to foster understanding, wonder and respect for Hawai i s Marine Life.
 Name: Maui Ocean Center Learning Worksheet Seventh Grade Our mission is to foster understanding, wonder and respect for Hawai i s Marine Life. Based on benchmarks SC.6.3.1, SC. 7.3.1, SC. 7.3.2, SC. 7.5.4
Name: Maui Ocean Center Learning Worksheet Seventh Grade Our mission is to foster understanding, wonder and respect for Hawai i s Marine Life. Based on benchmarks SC.6.3.1, SC. 7.3.1, SC. 7.3.2, SC. 7.5.4
Chapter 29 Echinoderms and Invertebrate Chordates. Section Echinoderms. I. What Is An Echinoderm? 11/1/2010. Biology II Mrs.
 Chapter 29 Echinoderms and Invertebrate Chordates Section 29.1 - Echinoderms Biology II Mrs. Michaelsen I. What Is An Echinoderm? A. Move by means of hydraulic, suction cuptipped appendages. B. Skin covered
Chapter 29 Echinoderms and Invertebrate Chordates Section 29.1 - Echinoderms Biology II Mrs. Michaelsen I. What Is An Echinoderm? A. Move by means of hydraulic, suction cuptipped appendages. B. Skin covered
ARTHROPODS JOINTED-LEGS ARTHROPODS ARE THE LARGEST GROUP OF ANIMALS!
 ARTHROPODS JOINTED-LEGS ARTHROPODS ARE THE LARGEST GROUP OF ANIMALS! WHO S WHO? SHRIMP ISOPOD SPIDER CRAB BARNACLE LOBSTER BASIC CHARACTERISTICS BILATERAL SYMMETRY SEGMENTED ANIMALS JOINTED BODY & PARTS
ARTHROPODS JOINTED-LEGS ARTHROPODS ARE THE LARGEST GROUP OF ANIMALS! WHO S WHO? SHRIMP ISOPOD SPIDER CRAB BARNACLE LOBSTER BASIC CHARACTERISTICS BILATERAL SYMMETRY SEGMENTED ANIMALS JOINTED BODY & PARTS
PART 2 CORAL REEF ECOLOGY
 PART 2 CORAL REEF ECOLOGY Coral reefs are rocky mounds and/or ridges formed in the sea by marine organisms through the accumulation and deposition of limestone (calcium carbonate). The reef framework provides
PART 2 CORAL REEF ECOLOGY Coral reefs are rocky mounds and/or ridges formed in the sea by marine organisms through the accumulation and deposition of limestone (calcium carbonate). The reef framework provides
I n t r o d u c t i o n. A n i m a l s
 I n t r o d u c t i o n t o A n i m a l s What is an Animal? Taxonomy: Kingdom Animalia Type of Cells: Eukaryotic Cellular Organization: Multicellular Reproduction: Sexual / Asexual Feeding: Heterotrophic
I n t r o d u c t i o n t o A n i m a l s What is an Animal? Taxonomy: Kingdom Animalia Type of Cells: Eukaryotic Cellular Organization: Multicellular Reproduction: Sexual / Asexual Feeding: Heterotrophic
Part 4: Ocean Life Zones
 Part 4: Ocean Life Zones 1 Factors that Affect Life in the Ocean 1. Amount of sunlight 2. Temperature of the water 3. Water pressure How does depth affect each of these? Where would you expect to find
Part 4: Ocean Life Zones 1 Factors that Affect Life in the Ocean 1. Amount of sunlight 2. Temperature of the water 3. Water pressure How does depth affect each of these? Where would you expect to find
Phylum Mollusca Classes
 Lecture Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Classes Aculifera with spicules Aplacophora - mollusks without shells Polyplacophora ( Amphineura) chiton, eight plates, intertidal Conchifera with shells Monoplacophora
Lecture Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Classes Aculifera with spicules Aplacophora - mollusks without shells Polyplacophora ( Amphineura) chiton, eight plates, intertidal Conchifera with shells Monoplacophora
Have You Wondered? College of Marine Sciences, Shanghai Ocean University
 Have You Wondered? 1. What role sponges play in marine ecosystems? 2. Why some animals are radially symmetrical? 3. If all gelatinous animals are jellyfishes? 4. What flatworms are? 5. What a lophophorate
Have You Wondered? 1. What role sponges play in marine ecosystems? 2. Why some animals are radially symmetrical? 3. If all gelatinous animals are jellyfishes? 4. What flatworms are? 5. What a lophophorate
Making the Most of Your Monitoring Using Macroinvertebrates
 Making the Most of Your Monitoring Using Macroinvertebrates Benthic Macroinvertebrates What are they? Why are they important? Provide food for fish and other organisms Feed on algae, organic matter, and
Making the Most of Your Monitoring Using Macroinvertebrates Benthic Macroinvertebrates What are they? Why are they important? Provide food for fish and other organisms Feed on algae, organic matter, and
Marine Math. A 4 th Grade Field Trip Guide to The Texas State Aquarium STUDENT BOOKLET
 Marine Math A 4 th Grade Field Trip Guide to The Texas State Aquarium STUDENT BOOKLET Copyright Erin Saenz, 2010. Permission granted for educational purposes only. This permission does not extend to copying
Marine Math A 4 th Grade Field Trip Guide to The Texas State Aquarium STUDENT BOOKLET Copyright Erin Saenz, 2010. Permission granted for educational purposes only. This permission does not extend to copying
Origin and Importance! ! Fish were the first vertebrates to appear on Earth about 500 million years ago.
 2/9/14 Origin and Importance Evolution Marine Fish Fish were the first vertebrates to appear on Earth about 500 million years ago. Fish are the most economically important organism and are a vital source
2/9/14 Origin and Importance Evolution Marine Fish Fish were the first vertebrates to appear on Earth about 500 million years ago. Fish are the most economically important organism and are a vital source
Coral Reef Basics and Its Impact on Ocean Life
 2012 Coral Reef Basics and Its Impact on Ocean Life Biology 1010 Professor LynneGilbert-Norton 4/25/2012 Contents Introduction... 2 Coral Explained... 2 Evolution... 3 Eating Habits... 4 Location... 4
2012 Coral Reef Basics and Its Impact on Ocean Life Biology 1010 Professor LynneGilbert-Norton 4/25/2012 Contents Introduction... 2 Coral Explained... 2 Evolution... 3 Eating Habits... 4 Location... 4
1 P a g e. Crabs of the Maroochy Wetlands Sanctuary. Compiled by Robyn Howard August 2011
 Identifying Crabs at Maroochy Wetlands Sanctuary The old saying Rules were meant to be broken seems to apply when it comes to crab identification. In general, the Ocypodid family have long eye-stalks and
Identifying Crabs at Maroochy Wetlands Sanctuary The old saying Rules were meant to be broken seems to apply when it comes to crab identification. In general, the Ocypodid family have long eye-stalks and
Chapter 5 Marine Protozoans and Invertebrates
 Chapter 5 Marine Protozoans and Invertebrates I. The Protozoans A. Kindgom Protista a catch-all category B. Characteristics 1. Mode of nutrition 2. Single-celled or multicellular? 3. Cell structure 4.
Chapter 5 Marine Protozoans and Invertebrates I. The Protozoans A. Kindgom Protista a catch-all category B. Characteristics 1. Mode of nutrition 2. Single-celled or multicellular? 3. Cell structure 4.
Lightning Whelk. Atlan)c Moon Snail
 Giant Atlan)c Cockle Can live in shallow water up to 30 meters (100 feet) deep. Have a muscular foot to burrow into sand. Both halves are the same size and shape ( equivalves ). Can be eaten in chowder.
Giant Atlan)c Cockle Can live in shallow water up to 30 meters (100 feet) deep. Have a muscular foot to burrow into sand. Both halves are the same size and shape ( equivalves ). Can be eaten in chowder.
THE TALE OF COASTAL CRITTERS Save Our Shores In partnership with Wilderness Leadership School Sponsored by
 www.tidaltao.com THE TALE OF COASTAL CRITTERS Save Our Shores In partnership with Wilderness Leadership School Sponsored by MEET CODY ABOUT THE SEA Under the depths of the KwaZulu-Natal sea Lives a blue-eyed
www.tidaltao.com THE TALE OF COASTAL CRITTERS Save Our Shores In partnership with Wilderness Leadership School Sponsored by MEET CODY ABOUT THE SEA Under the depths of the KwaZulu-Natal sea Lives a blue-eyed
Ch17_Animals. Animals Multicellular eukaryotes. What is an animal? Animal development. Main differences with plants Main differences with fungi
 Animals Multicellular eukaryotes Domain Domain Kingdoms Main differences with plants Main differences with fungi What is an animal? Domain Nutritional mode: Heterotrophic (Ingestive) Level of organization:
Animals Multicellular eukaryotes Domain Domain Kingdoms Main differences with plants Main differences with fungi What is an animal? Domain Nutritional mode: Heterotrophic (Ingestive) Level of organization:
F I E L D T R I P CHAPERONE GUIDE
 kindergarten F I E L D T R I P CHAPERONE GUIDE Chaperones: Use this guide to move your group through the Aquarium s galleries. The background information, guided questions, and activities will keep your
kindergarten F I E L D T R I P CHAPERONE GUIDE Chaperones: Use this guide to move your group through the Aquarium s galleries. The background information, guided questions, and activities will keep your
Mollusks- soft bodied
 Mollusks- soft bodied Objectives Understand the taxonomic relationships and major features of mollusks Learn the external and internal anatomy of the clam and squid Understand the major advantages and
Mollusks- soft bodied Objectives Understand the taxonomic relationships and major features of mollusks Learn the external and internal anatomy of the clam and squid Understand the major advantages and
Fantastic Fish. Lesson 10. Leafy Sea Dragon
 Fantastic Fish Lesson 10 Fish are cold-blooded vertebrates that live in streams, lakes and oceans. They are abundant in both fresh and salt water. There are over 28,000 known species of fish on the planet.
Fantastic Fish Lesson 10 Fish are cold-blooded vertebrates that live in streams, lakes and oceans. They are abundant in both fresh and salt water. There are over 28,000 known species of fish on the planet.
CHAPTER 22. Echinoderms 22-1
 CHAPTER 22 Echinoderms 22-1 Phylum Echinodermata: Diversity and Characteristics Characteristics All members have a calcareous skeleton Spiny endoskeleton consists of plates Unique water-vascular system
CHAPTER 22 Echinoderms 22-1 Phylum Echinodermata: Diversity and Characteristics Characteristics All members have a calcareous skeleton Spiny endoskeleton consists of plates Unique water-vascular system
What and Where are the Coral Reefs?
 Coral reefs first formed more than 500 million years ago in warm tropical climates, and since that time they have successfully developed and supported a tremendous array of plant and animal life. Covering
Coral reefs first formed more than 500 million years ago in warm tropical climates, and since that time they have successfully developed and supported a tremendous array of plant and animal life. Covering
Frequency of Percnon gibbesi in relation to. Diadema antillarum at Rodney s Rock
 Frequency of Percnon gibbesi in relation to Diadema antillarum at Rodney s Rock By: Rickey Wallace Study Abroad Dominica Summer 2007 Texas A&M University Dr. Bob Wharton Dr. Jim Woolley Abstract The nimble
Frequency of Percnon gibbesi in relation to Diadema antillarum at Rodney s Rock By: Rickey Wallace Study Abroad Dominica Summer 2007 Texas A&M University Dr. Bob Wharton Dr. Jim Woolley Abstract The nimble
shapes, textures, and patterns. What s more, the change can occur in an instant!
 By Kira Freed If someone asked you to think of a few animals that use camouflage, which ones would come to mind? Chameleons and leopards, and perhaps polar bears? Would you believe that octopuses and their
By Kira Freed If someone asked you to think of a few animals that use camouflage, which ones would come to mind? Chameleons and leopards, and perhaps polar bears? Would you believe that octopuses and their
Name Date Period. Mollusk Review TORSION HEMOLYMPH SESSILE TROCHOPHORE ADDUCTOR KIDNEY HEMOCOEL MANTLE CHROMATOPHORES VISCERAL MASS
 Name Date Period Mollusk Review MOLLUSK VOCABULARY: Match the word with its definition. TORSION HEMOLYMPH SESSILE TROCHOPHORE ADDUCTOR KIDNEY HEMOCOEL MANTLE CHROMATOPHORES VISCERAL MASS Free-swimming
Name Date Period Mollusk Review MOLLUSK VOCABULARY: Match the word with its definition. TORSION HEMOLYMPH SESSILE TROCHOPHORE ADDUCTOR KIDNEY HEMOCOEL MANTLE CHROMATOPHORES VISCERAL MASS Free-swimming
