Prediction of Simulated Blood Pooling in the Leg Segment of an Aircraft Pilot Under G Stress. Dr Munna Khan*, Dr SK Guha +
|
|
|
- Anis Taylor
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Technical Communication Prediction of Simulated Blood Pooling in the Leg Segment of an Aircraft Pilot Under G Stress Dr Munna Khan*, Dr SK Guha + ABSTRACT It has been found that G induced loss of consciousness (G-LOC) can abruptly result in pilot incapacitation, mission compromise, loss of aircraft and loss of life. The G-LOC is due to reduced blood flow to the nervous system and reduced flow of blood occurs because of blood pooling in the lower extremity of the aircraft pilot. Therefore, blood pooling has been investigated properly and predicted in the leg segment of aircraft pilot quantitatively, which may be used to avoid the G-LOC. Applied pressure used for occluding the veins is assumed equal to its hydrostatic pressure acting on the leg segment of aircraft pilot during high G stress. The different amount of blood pooling simulated in the leg segment of human volunteers using venous occlusion plethysmography (VOP). Electrical Impedance plethysmography (EIP) has been used to measure simulated blood pooling of leg segment in the laboratory. A characteristic curve is drawn between occluding cuff pressure and its corresponding simulated blood pooling. The drawn curve has been assumed equivalent to the curve drawn between hydrostatic pressure (P H ) and its corresponding blood pooling (V) in leg segment under high G-stress. A new formula has been presented using technical geometry that predicts blood pooling in the leg segment of an aircraft pilot against the inertial forces between 1 to 10 G. The predicted range of blood pooling in leg segment of aircraft pilot is 0 to 399 ml. The various graphs have been plotted for blood pooling and hydrostatic pressure of the calf versus inertial forces of aircraft pilot under G stress. Prediction of blood pooling has been made for leg segment of an aircraft pilot using VOP, EIP and technical geometry. A desired profile for inflation of anti-g suit has been proposed to counter the blood pooling occurring during high G maneuvers. IJASM 2004; 48(1): Keywords: Simulated blood pooling, VOP, EIP, Technical geometry, G-LOC, Anti G-suit. Acceleration is an unique environment, which acts directly and continuously upon the body of aircraft pilots during all gravity (G) exposures. The 1 G acceleration is experienced while we stand still on the ground and 2G by making a 60 degree banked turn [1]. Further higher G values are experienced in the human centrifuge. The human centrifuge may be described into four generations such as First Generation ( ): Single generation of freedom, slow G onset, passive cab; Second Generation ( ): Multi axis (2 degree of freedom), some visuals, some gimbaled; Third Generation ( ): 6 G/sec, some flight simulation, gimbaled (active) cab; Fourth Generation (1998-present): G/ sec, full flight simulation, gimbaled (active) cab [2]. The G tolerance of the aircraft pilots is increased by so called G protective methods such that anti-g suits (AGS), anti- G straining maneuvers (AGSM), positive pressure breathing during G (PBG) and body reclining systems. All countermeasures achieve their results restricting the flow of blood from and/or forcing blood to flow into particular body segments of the pilot in G cycle [3]. The G is taken as +Gz when the body is accelerated in the headward direction. Blood is constantly pumped into the head against gravity and continued, no matter how hard the heart may work [4,5]. If the +Gz is of high value, little or no blood flow reaches to the head; the eyes and brain exhaust their limited sugar and oxygen supplies and cease to function [6]. Maintenance of * Senior Lecturer, Dept of Electrical Engineering, Jamia Millia Islamia, New Delhi + Professor, Centre for Biomedical Engineering, IIT Delhi
2 adequate retinal blood flow is necessary for a full field of vision. The decrement of retinal blood flow causes loss of peripheral vision, central vision, and finally leading to a complete blackout. It leads a threat that can abruptly result in pilot incapacitation, mission compromise, loss of aircraft and loss of life [7]. The G-LOC is the transition from normal consciousness to a state of unconsciousness that results when blood flow to the nervous system is reduced below the critical level necessary to support conscious function. The blood pooling in the different lower body segments is responsible for blood flow decrement that occurs in the head and nervous system [2,6]. Earlier, scientists measured the fluid and blood volume change of abdomen, thigh, and calf of aircraft pilot using electrical impedance plethysmography [8,9,10]. The approximate values were defined and failed to give accurate measurements of blood volume change. None of them predicted blood volume or blood volume change in any body segment of the pilot. However, authors analyzed and attempted to predict simulated blood pooling in the leg segment of an aircraft pilot in their earlier study [11]. In the present research paper, a detailed study has been given to predict blood pooling in the leg segment of an aircraft pilot under G stress. Materials and methods Sphygmomanometer The sphygmomanometer is mainly used to measure blood pressure of a person in day-to-day life. The sphygmomanometer consists of an inflatable pressure cuff and a mercury or aneroid manometer to measure the pressure in the cuff. The cuff consists of a rubber bladder inside an inelastic fabric covering it, that can be wrapped around the upper arm and fastened with either hooks or a Velcro fastener. The cuff is normally inflated manually with a rubber bulb and deflated slowly through a needle valve. In present study, sphygmomanometer has been used to simulate leg segment blood pooling of an aircraft in leg of human volunteers in the laboratory. The blood pooling was simulated by placing a blood pressure cuff around the thigh of human volunteers. When the cuff was inflated to pressures beyond venous pressure but below arterial pressure, blood pooling in the leg below the cuff was recorded. The simulated blood pooling has been measured using electrical impedance plethysmography, a non-invasive technique. 48 Electrical Impedance Plethysmograph A number of instruments are available commercially with different characteristics and rating for electrical impedance plethysmography. But Electrical Impedance Plethysmograph (EIP) used to measure simulated blood pooling has been designed and developed in the laboratory keeping good sensitivity and reliability. It comprises a circuit consisting of integrated chip (IC) of 20 KHz oscillator coupled through a transformer to a modified Kelvin s bridge. The current is kept constant at 3 milli ampere. Electrical impedance has been measured by balancing the bridge and observing the result on digital display through an amplifier. Let all blood vessels of the leg segment be represented by a single cylinder of height equal to length of the leg segment. Cylinder consists of skin, fat, muscles, bones and blood vessels. It is also assumed that the entry of blood changes the diameter only, while the height (Length) remains constant during venous occluding plethysmography. The influence of acceleration and gravitational forces on the cylinder filled with blood is such that subsequent Eqn. 1 gives hydrostatic pressure (P H ) at any point. P H = ρ Gh...(1) ρ = Specific density of blood, G = Inertial force in G units, and h = blood column height The hydrostatic pressure developed by inertial response of the blood within the vascular system opposes the systemic arterial pressure of the heart (100 to 120 mm Hg). At higher G, hydrostatic pressure developed significantly reduces blood flow to the brain and consequently blood pooling occurs in the lower body of aircraft pilot. Blood pooling of leg segment of pilot has been simulated in laboratory using sphygmomanometer on the principle of venous occlusion plethysmography. In the present study, 10 healthy volunteers between the age group of 20 to 45 years were allowed to relax for 5 minutes in the laboratory before the study. The procedure of experiment was explained thoroughly and
3 Z 0 their consents were taken. Subjects were then made to sit on a chair comfortably. The blood pooling was simulated in leg segment of volunteers using sphygmomanometer and measured noninvasively using electrical impedance plethysmography with tetrapolar configuration. In practice, both bipolar and tetrapolar electrode systems have been employed with EIP [10]. Of these tetrapolar system has a definite advantage, that it provides a uniform current density distribution in the body segment and measures impedance with less electrode interface artifact and impedance errors. In tetrapolar system a pair of surface electrodes (I 1, I 2 ) are used as current electrodes to introduce low intensity constant current at high frequency into the leg segment. A separate pair of electrodes (E 1, E 2 ) measures changes accompanying physiological events. Voltage has been measured across E 1 - E 2 that is directly proportional to leg segment electrical impedance (LEI) of human subject. Use of surface circular flat electrodes as well as band type electrodes has been advocated by a number of scientists. But, types of electrodes insignificantly affect the EIP output. Therefore in the present case, 4 band electrodes have been used for convenience. The current electrodes (I 1, I 2 ) were placed around the bottom of leg and below the knee joint to drive 3 milli ampere at 20 KHz of constant current onto leg segment. Potential electrodes E 1 -E 2 were placed towards inner side of current electrodes maintaining a distance of 2 cm. Constant spacing was kept between each current and voltage electrode for repeatable results. All the four electrodes were connected to a Kelvin s Double Bridge to quantitate impedance value. Bridge was balanced by varying the resistive and capacitive component alternatively. Thereafter, LEI of human leg was observed on the digital output display of electrical impedance plethysmograph. The LEI lowered during simulated blood pooling in the leg segment of human volunteers. A cuff placed around the thigh just above the knee joint and inflated quickly to a pressure of 20, 40, 60, 80, 100, 120, and 140 mm Hg. Applied cuff pressures induced different amount of blood pooling in leg below the cuff. The inflation of pressure cuff was maintained for 5 seconds to record electrical impedance of leg segment of human volunteers. The magnitude of blood pooling is assumed to be constant for observation time of 5 seconds at every specific applied cuff pressure. The average values were taken for LEI of human volunteers against the applied cuff pressures and shown in Table 1. The values of electrical impedance change has been used to calculate simulated blood pooling in the leg segment using following Eqn. 2. Blood pooling in the leg segment = 3( Z / Z 0 )V...(2) Where Z = Change in electrical impedance of leg segment, = Normal impedance of leg segment. V = Volume of leg segment without blood pooling and calculated measuring length and perimeter at mid of the leg segment of human volunteers. TABLE I : Measurement Of Blood Accumulation In The Leg Segment Using Impedance Technique. Applied on the thigh (mmhg) Average Electrical Impedance (Ohms) L E G S E G M E N T Electrical Impedance Change (Ohms) Simulated Blood pooling (ml) The 0-10 G equivalent pressures were applied in one sitting and same day on one human volunteer. Thereafter, electrical impedance measurements were made for leg segment of volunteers. The experiments repeated for other subjects on different days and completed within 15 days. Average value of leg segment electrical impedance (LEI) calculated at different cuff pressures and used for further prediction of simulated blood pooling. A characteristic curve has been drawn between computed blood pooling and occluding cuff pressure around thigh. The drawn curve shows linear relationship between the simulated blood pooling values and occluding pressures in the cuff. In sitting posture, occluding cuff pressure inducing simulated blood pooling in the leg segment is assumed equal to its hydrostatic pressure acting during high G 49
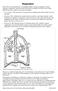
4 maneuvers. It implied that characteristic curve drawn between occluding cuff pressures and its corresponding blood pooling has been considered equivalent to the curve drawn between hydrostatic pressure ( ) and blood pooling (V) of leg segment under G stress. A line approximately passing through all points has been drawn and shown in Fig. 1. The technical geometry of mathematics further used to derive the new expression for predicted blood pooling in the leg segment. The derived equation is given below: Blood Pooling = [{(52 PH -340)/15}-21.7] ml...(3) Table II. Prediction Of Blood Pooling In The Leg Segment During High G Maneuvers. Inertial Force in G units Hydrostatic Pressure (mm Hg) Predicted blood Pooling in leg seqment (ml) ml respectively. Anti G-suit is to be deflated to corresponding pressure level if selected blood pooling level falls below the previous level. Results and discussions Fig 1: Detail Of Technical Geometry Used To Derive New Expression For Prediction Of Simulated Blood Pooling In The Leg Segment. Hydrostatic pressure acting on the leg segment has been found for the given values of G from Eqn. 1. The main effect of high G maneuvers is the blood pooling in the lower extremities of an aircraft pilot such as the abdomen, thighs and legs. Finally the values of blood pooling have been predicted using Eqn. 3. Table II shows prediction of various values of blood pooling in the leg segment of pilot against the G variation from 1 to 10. Further a correlation curve is plotted between inertial forces versus predicted blood pooling of leg segment. Leg segment Electrical Impedance (LEI) of human volunteers measured using EIP with tetrapolar electrodes configuration and found as 46.0 ohms at normal physiological conditions. Prediction of LEI was also made separately through computer model and found as 46.7 ohms; the value corresponds well with experimental value of 46.0 ohms. The lowered values of LEI have been recorded for different amount of simulated blood pooling. A new expression has been presented for the prediction of simulated blood pooling in the segment of human volunteers. The graphical representation of predicted blood pooling in the leg segment versus inertial forces is shown in Fig. 2. Pressurization levels of an anti G-suit have been proposed against the predicted range of blood pooling in the leg segment under G stress. First pressure level of anti-g suit is in the range of mm Hg, if predicted blood pooling is from 0 to 90 ml in leg segment. A corresponding amount of air/o 2 producing first level is passed into anti G-suit from sources. Other pressure ranges such as mm Hg, mm Hg, mm Hg and mm Hg have been defined for blood pooling range of ml, ml, ml and Fig 2: Predicted Simulated Blood Pooling In The Leg Segment Of An Aircraft Pilot. 50
5 The blood pooling increases approximately in the linear fashion with increasing the inertial forces in G units. Further pressurization levels have been proposed for an anti G-suit against simulated blood pooling in the leg segment of volunteers and shown in Fig. 3. Simulation and modeling processes with slight modification may be used to predict thigh, abdomen and arm blood pooling. Findings of various blood pooling may be used to correlate to the vision of pilots that would start a new era of research in aerospace medicine [10]. Fig 3: Proposed Pressurization Levels For An Anti G - Suit Of An Aircraft Pilot Under G Stress. The high inertial and gravitational forces are responsible for producing blood pooling in the lower extremities especially legs of aircraft pilot. Blood pooling plays an important role during complete blackout and G- induced loss of consciousness (G-LOC). These visual symptoms begin to occur when arterial pressure (P a ) at eye level falls below 50 mm Hg. Blackout occurs, if P a equals the intraocular pressure of approximately 20 mm Hg (3, 12). Every pilot has a G-tolerance limit that even with existing protective technology can be exceeded and results in G-LOC. The values of predicted blood pooling may be useful to design a perfect anti-g protection system. The leg coverage of the anti-g suit is being considered the basic component of anti-g protection systems. The leg coverage of the anti-g suit has been recently increased with the development of the advance technology anti-g suit (ATAGS). Flight test results yielded an increased G - level and duration tolerance, by improving blood flow through the skeletal leg muscles (13). It increases the total vascular resistance below the heart, maintaining blood volume distribution within the body, which is found at 1G environment. The results of present study may be used or useful to modify anti-g suit that would remove or reduce the blood pooling in the leg segment of aircraft pilot under G-stress. Thus modifications in the form of advanced anti G-suit will increase the G-tolerance of aircraft pilot. Importance of the predictions will also become more significant when it has to be applied on normal pilots operating in adverse G conditions. The blood pooling of leg segment has been predicted using a totally new approach. An approach can be applied to the pilots before attending actual high G flights and corrective measure would be decided. The predictions of blood pooling in the leg segments may also be exploited in the medical therapy options such as for treating deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and angina pectoris of heart patients. DVT continues to be one of the most common causes of death in the course of medical and surgical illness. It may be diagnosed using a pressure cuff placed on the thigh and inflated to 200 mm Hg to cause the increase of blood volume in the limb. An impedance ratio calculated for leg segment at normal and with increased blood volume helps in detection of DVT [14]. A concept of applied external pressure to lower body segment may be used in Enhanced External Counter Pulsation (EECP). The EECP is a non-invasive technique for treatment of chronic angina due to coronary artery disease [15]. The EECP uses unique equipment to inflate and deflate a series of pneumatic compressive cuffs enclosing the lower extremities. A padded table in which three sets of electronically controlled inflation and deflation valves are located may be administering treatment. These valves are connected to specially designed adjustable cuffs wrapped around patient s calves, lower thighs and upper thighs, including the buttocks. Electrical impedance plethysmography (EIP) is a reliable, promising and non-invasive technique for measurement of blood volume changes [10, 16,17]. The prediction of the blood pooling is based on the measurements of blood pooling using EIP. The experimental verification will be made by measuring the blood pooling in the leg segment of an aircraft pilot in the centrifuge test runs. Based on the results obtained, a system may be designed and developed easily that would measure blood pooling in the lower extremities of an aircraft pilot [17]. A microcomputer controlled biofeedback controller may also be designed and 51
6 developed for an anti G-suit. The inflation / deflation of an anti G-suit would be according to the actual blood pooling of aircraft pilot [18]. Conclusion The sphygmomanometer has been used to simulate leg segment blood pooling of an aircraft pilot in the laboratory. Placing and inflation of a blood pressure cuff around the thigh of human volunteers has simulated the blood pooling. When the cuff was inflated to pressures beyond venous pressure but below arterial pressure, blood pooling in the leg below the cuff was recorded. The difference of simulated blood pooling has been measured noninvasively using electrical impedance plethysmography (EIP). The measured values of simulated blood pooling are used to derive a new expression. This new expression predicts a particular amount of blood pooling for each value of G. The range of blood pooling predicted is from 0 to 399 ml in the leg segment of an aircraft pilot under different G stress. The minimum and maximum pressures of air, which are already applied in the anti-g suit according to gravitational forces, have been proposed to different levels of blood pooling. If these proposed levels of air are to be pumped into the anti G-suit, then corresponding blood pooling would vanish or reduce significantly. References 1. Watson D. G-LOC, Could it happen to you? AOPA (Australia) Magazine 1990; 43(8): 1-10 (Web pages). 2. Modak S, Singh AK, Gomez G. Human centrifuge: A tool for research and training. Ind J Aerosp Med 2001; 45(2): Burton RR, Whinnery JE. Biodynamics. Sustained Acceleration. In: DeHart RL, editor. Fundamentals of aerospace medicine. 2nd ed. Maryland, USA: William & Wilkins, 1996; 9: Chevalier PA, Reed Jr JH, Vandenberg RA, Wood EH. Effect of gravitational and inertial force on vertical distribution of pulmonary blood flow. Aviat Space Environ Med 1978; 49(6): Chornuk MA, Myron A, Bernard SL, Burns JW, Glenny RW, Sheriff DD et. al. Effects of inertial load and countermeasures on the distribution of pulmonary blood flow. J Appl Physiol 2000; 89; Whinnery JE. Observations on the neurophysiologic theory of acceleration (+G Z ) induced loss of consciousness. Aviat Space Environ Med 1989; 60: Whinnery JE, Burton RR, Boll PA, Eddy DR. Characterization of resulting incapacitation following unexpected +G Z induced loss of consiousness. Aviat Space Environ Med 1987; 58: Burton RR. G-induced loss of consciousness-definition, history, current status. Avia Space Environ Med 1988; 59: Ebert TJ, Smith JJ, Barney JA, Merrill DC, Smith GK. The use of thoracic impedance for determining thoracic blood volume changes in man. Aviat Space Environ Med 1986; 57: Gotshall RW and Devrath LR. Bioelectric impedance as an index of thoracic fluid. Aviat Space Environ Med 1999; 70: Khan M, Guha SK. Prediction of electrical impedance parameters for the simulated leg segment of an aircraft pilot under G-stress. Aviat Space Environ Med 2002; 73(6): Khan M, Guha SK. Prediction of blood pooling in the leg segment of aircraft pilot during high G maneuvers. Presented at the Golden Jubilee Conference of Indian Society of Aerospace Medicine. IAM Bangalore, India 2002 Feb. 5-8: Wood EH and Sturm RE. Human centrifuge non-invasive measurements of arterial pressure at eye level during Gz acceleration. Aviat Space Environ Med 1989; 60 (10 Pt 1): Balldin UL, Bahlback GO, Larsson LE. Full coverage anti-g suit (abstract). Aviat Space Environ Med 1988; 59: Johnston KW, Kakkar VV, Spindler JJ, et al. A simple method for detecting deep vein thrombosis: an improved electrical impedance technique. Am J Surg 1974; 127: Stys TP, Lawson WE, Hui JC, et al. Effects of enhanced external counter pulsation on stress radionuclide coronary perfusion and exercise capacity in chronic stable angina pectoris. Am J Cardiol 2002; 89 (7): Krutz RW, Burton RR, Forster EM. Physiologic correlates of protection afforded by anti-g suits. Aviat Space Environ Med 1990; 61: Montgomery LD, Hanish HM, Burns JW. A system to measure lower body volume changes during rapid onset high-g acceleration. Avia Space Environ Med 1988; 59: Moore TW, Foley J, Shankara Reddy BR, Kepics F, Jaron D. An experimental microcomputer controlled system for synchronized pulsating anti-gravity suit. Aviat Space Environ Med 1987; 58:
PHY100 s Lab: The Relationship Between Liquid Pressure and Depth as it applies to Blood Pressure. Course & Sec:
 PHY100 s Lab: The Relationship Between Liquid Pressure and Depth as it applies to Blood Pressure Name: Lab Partner: Course & Sec: Date: Disclaimer: The procedures in this lab are not according to proper
PHY100 s Lab: The Relationship Between Liquid Pressure and Depth as it applies to Blood Pressure Name: Lab Partner: Course & Sec: Date: Disclaimer: The procedures in this lab are not according to proper
BLOOD PRESSURE SENSOR BT17i USER S GUIDE
 BLOOD PRESSURE SENSOR BT17i USER S GUIDE CENTRE FOR MICROCOMPUTER APPLICATIONS http://www.cma-science.nl Short description The Blood Pressure sensor BT17i allows measuring arterial blood pressure. The
BLOOD PRESSURE SENSOR BT17i USER S GUIDE CENTRE FOR MICROCOMPUTER APPLICATIONS http://www.cma-science.nl Short description The Blood Pressure sensor BT17i allows measuring arterial blood pressure. The
transients' of large amplitude can be imposed on the arterial, cardiac and Since both coughing and the Valsalva manoeuvre raise intrathoracic pressure
 351 J. Physiol. (I953) I22, 35I-357 EFFECTS OF COUGHING ON INTRATHORACIC PRESSURE, ARTERIAL PRESSURE AND PERIPHERAL BLOOD FLOW BY E. P. SHARPEY-SCHAFER From the Department of Medicine, St Thomas's Hospital
351 J. Physiol. (I953) I22, 35I-357 EFFECTS OF COUGHING ON INTRATHORACIC PRESSURE, ARTERIAL PRESSURE AND PERIPHERAL BLOOD FLOW BY E. P. SHARPEY-SCHAFER From the Department of Medicine, St Thomas's Hospital
Anti-g-Garment Development and Testing
 Anti-g-Garment Development and Testing 1) Anti-g-Garment. Introduction and Use in space flights. A g-suit, or anti-g suit, is a flight suit worn by pilots and astronauts who are subject to high levels
Anti-g-Garment Development and Testing 1) Anti-g-Garment. Introduction and Use in space flights. A g-suit, or anti-g suit, is a flight suit worn by pilots and astronauts who are subject to high levels
Lab #2: Blood pressure and peripheral circulation
 Lab #2: Blood pressure and peripheral circulation Vertebrates have a closed circulatory system where the blood is always enclosed within blood vessels or the heart. Blood is pumped from the heart (the
Lab #2: Blood pressure and peripheral circulation Vertebrates have a closed circulatory system where the blood is always enclosed within blood vessels or the heart. Blood is pumped from the heart (the
Respiration. Figure 22: Schematic representation of the respiratory system
 Respiration One of the seven characteristics of something which is living is respiration. Strictly speaking, respiration is the process that takes place at cellular level and is one of three different
Respiration One of the seven characteristics of something which is living is respiration. Strictly speaking, respiration is the process that takes place at cellular level and is one of three different
Pulmonary Circulation
 Pulmonary Circulation resin cast of pulmonary arteries resin cast of pulmonary veins Blood Flow to the Lungs Pulmonary Circulation Systemic Circulation Blood supply to the conducting zone provided by the
Pulmonary Circulation resin cast of pulmonary arteries resin cast of pulmonary veins Blood Flow to the Lungs Pulmonary Circulation Systemic Circulation Blood supply to the conducting zone provided by the
BLOOD PRESSURE SENSOR 0377i
 BLOOD PRESSURE SENSOR 0377i USER S GUIDE CENTRE FOR MICROCOMPUTER APPLICATIONS http://www.cma-science.nl Short description The Blood Pressure sensor 0377i is used to measure arterial blood pressure in
BLOOD PRESSURE SENSOR 0377i USER S GUIDE CENTRE FOR MICROCOMPUTER APPLICATIONS http://www.cma-science.nl Short description The Blood Pressure sensor 0377i is used to measure arterial blood pressure in
Noninvasive Blood Pressure Measurement. D. J. McMahon rev cewood
 Noninvasive Blood Pressure Measurement D. J. McMahon 141018 rev cewood 2017-10-23 Key Points Noninvasive Blood Pressure Measurement: - ways to measure pressure, direct mechanical measurement: Bourdon Tube
Noninvasive Blood Pressure Measurement D. J. McMahon 141018 rev cewood 2017-10-23 Key Points Noninvasive Blood Pressure Measurement: - ways to measure pressure, direct mechanical measurement: Bourdon Tube
The +Gz-induced loss of consciousness curve
 The +Gz-induced loss of consciousness curve Whinnery and Forster Whinnery and Forster Extreme Physiology & Medicine 2013, 2:19 (6 June 2013) Whinnery and Forster Extreme Physiology & Medicine 2013, 2:19
The +Gz-induced loss of consciousness curve Whinnery and Forster Whinnery and Forster Extreme Physiology & Medicine 2013, 2:19 (6 June 2013) Whinnery and Forster Extreme Physiology & Medicine 2013, 2:19
3.1.3 Weight. Frequency. Weight is obtained at the baseline examination and annually. Equipment
 The excerpt from the SPRINT Manual of Procedures (MOP) below, dated November 1, 2010, includes instructions about blood pressure measurement. Recruitment for the SPRINT trial began on November 8, 2010;
The excerpt from the SPRINT Manual of Procedures (MOP) below, dated November 1, 2010, includes instructions about blood pressure measurement. Recruitment for the SPRINT trial began on November 8, 2010;
The physiological functions of respiration and circulation. Mechanics. exercise 7. Respiratory Volumes. Objectives
 exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
Experiment. THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN VOLUME AND TEMPERATURE, i.e.,charles Law. By Dale A. Hammond, PhD, Brigham Young University Hawaii
 Experiment THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN VOLUME AND TEMPERATURE, i.e.,charles Law By Dale A. Hammond, PhD, Brigham Young University Hawaii The objectives of this experiment are to... LEARNING OBJECTIVES introduce
Experiment THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN VOLUME AND TEMPERATURE, i.e.,charles Law By Dale A. Hammond, PhD, Brigham Young University Hawaii The objectives of this experiment are to... LEARNING OBJECTIVES introduce
MIL-STD-883G METHOD
 STEADY-STATE LIFE 1. PURPOSE. The steady-state life test is performed for the purpose of demonstrating the quality or reliability of devices subjected to the specified conditions over an extended time
STEADY-STATE LIFE 1. PURPOSE. The steady-state life test is performed for the purpose of demonstrating the quality or reliability of devices subjected to the specified conditions over an extended time
plethysmographic methods that when the subject was pinched on the upper
 24 J. Physiol. (I95I) II2, 24-2I 6I2.I5.6II.976 THE DECREASE IN HAND BLOOD FLOW FOLLOWING INFLATION OF AN ARTERIAL OCCLUSION CUFF ON THE OPPOSITE ARM BY IAN C. RODDIE From the Department of Physiology,
24 J. Physiol. (I95I) II2, 24-2I 6I2.I5.6II.976 THE DECREASE IN HAND BLOOD FLOW FOLLOWING INFLATION OF AN ARTERIAL OCCLUSION CUFF ON THE OPPOSITE ARM BY IAN C. RODDIE From the Department of Physiology,
Pressure profiling of compression bandages by a computerized instrument
 Indian Journal of.fibre & Textile Research Vol. 37, June 2012, pp. 114-119 Pressure profiling of compression bandages by a computerized instrument A Das a, B Kumar, T Mittal, M Singh & S Prajapati Department
Indian Journal of.fibre & Textile Research Vol. 37, June 2012, pp. 114-119 Pressure profiling of compression bandages by a computerized instrument A Das a, B Kumar, T Mittal, M Singh & S Prajapati Department
Circulation and Respiration: Vital Signs Student Version
 Circulation and Respiration: Vital Signs Student Version In this lab, you will learn about the circulatory and respiratory systems. You will test the capacity of your lungs, measure your blood pressure
Circulation and Respiration: Vital Signs Student Version In this lab, you will learn about the circulatory and respiratory systems. You will test the capacity of your lungs, measure your blood pressure
Experiment 13: Make-Up Lab for 1408/1420
 Experiment 13: Make-Up Lab for 1408/1420 This is only for those that have approval. Students without approval will not be allowed to perform the lab. The pre-lab must be turned in at the beginning of lab.
Experiment 13: Make-Up Lab for 1408/1420 This is only for those that have approval. Students without approval will not be allowed to perform the lab. The pre-lab must be turned in at the beginning of lab.
INSTRUCTION MANUAL. Automatic Blood Pressure Monitor with Fit Cuff. =Fit Cuff=!"#$% IA1B. Model
 IA1B INSTRUCTION MANUAL Automatic Blood Pressure Monitor with Fit Cuff =Fit Cuff=!"#$% Model IA1B Contents Introduction... 2 Notes on Safety... 3 Know Your Unit... 5 Quick Reference Guide... 7 Initial
IA1B INSTRUCTION MANUAL Automatic Blood Pressure Monitor with Fit Cuff =Fit Cuff=!"#$% Model IA1B Contents Introduction... 2 Notes on Safety... 3 Know Your Unit... 5 Quick Reference Guide... 7 Initial
Recitation question # 05
 Recitation and Lab # 05 The goal of this recitations / labs is to review material related to the CV and respiratory lectures for the second test of this course. Info required to answer this recitation
Recitation and Lab # 05 The goal of this recitations / labs is to review material related to the CV and respiratory lectures for the second test of this course. Info required to answer this recitation
Mitos Fluika Pressure and Vacuum Pumps Datasheet
 Unit 1, Anglian Business Park, Orchard Road, Royston, Hertfordshire, SG8 5TW, UK T: +44 (0)1763 242491 F: +44 (0)1763 246125 E: sales@dolomite-microfluidics.com W: www.dolomite-microfluidics.com Dolomite
Unit 1, Anglian Business Park, Orchard Road, Royston, Hertfordshire, SG8 5TW, UK T: +44 (0)1763 242491 F: +44 (0)1763 246125 E: sales@dolomite-microfluidics.com W: www.dolomite-microfluidics.com Dolomite
Mechanical and physiological effect of partial pressure suit: Experiment and numerical study
 Technology and Health Care 25 (2017) S35 S44 DOI 10.3233/THC-171304 IOS Press S35 Mechanical and physiological effect of partial pressure suit: Experiment and numerical study Tao Yang a,b, Li Ding a, Haibo
Technology and Health Care 25 (2017) S35 S44 DOI 10.3233/THC-171304 IOS Press S35 Mechanical and physiological effect of partial pressure suit: Experiment and numerical study Tao Yang a,b, Li Ding a, Haibo
Pressure Measurement
 Pressure Measurement Manometers Sensors, Transducers Ashish J. Modi Lecturer, Dept. of Mech.Engg., Shri S.V.M. inst. Of Technology, Bharuch Pressure Pressure is a force per unit area exerted by a fluid
Pressure Measurement Manometers Sensors, Transducers Ashish J. Modi Lecturer, Dept. of Mech.Engg., Shri S.V.M. inst. Of Technology, Bharuch Pressure Pressure is a force per unit area exerted by a fluid
Experimental Study of Water Hammer Pressure in a Commercial Pipe
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) Experimental Study of Water Hammer Pressure in a Commercial Pipe Ashish Kumar Patel 1 1 (School of Mechanical Engineering, Lovely Professional
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) Experimental Study of Water Hammer Pressure in a Commercial Pipe Ashish Kumar Patel 1 1 (School of Mechanical Engineering, Lovely Professional
Ch.6. Dr.Rajaa Pressure
 Ch.6. Dr.Rajaa Pressure أ.م.د. رجاء سهيل جنم Pressure: It is the force per unit area in a gas or liquid. (For solid the term pressure is replaced by "stress"). Units: In metric system pressure is measured
Ch.6. Dr.Rajaa Pressure أ.م.د. رجاء سهيل جنم Pressure: It is the force per unit area in a gas or liquid. (For solid the term pressure is replaced by "stress"). Units: In metric system pressure is measured
DETRMINATION OF A PLUNGER TYPE WAVE MAKER CHARACTERISTICE IN A TOWING TANK
 The 9 th International Conference on Coasts, Ports and Marine Structures (ICOPMAS 2010) 29 Nov.-1 Dec. 2010 (Tehran) DETRMINATION OF A PLUNGER TYPE WAVE MAKER CHARACTERISTICE IN A TOWING TANK sayed mohammad
The 9 th International Conference on Coasts, Ports and Marine Structures (ICOPMAS 2010) 29 Nov.-1 Dec. 2010 (Tehran) DETRMINATION OF A PLUNGER TYPE WAVE MAKER CHARACTERISTICE IN A TOWING TANK sayed mohammad
Technical Note. Determining the surface tension of liquids by measurements on pendant drops
 Technical Note Pendant Drop Measurements Technical note: TN316e Industry section: all Author: FT, TW Date: 12/2010 Method: Drop Shape Analyzer DSA100 Keywords: Methods, surface tension, interfacial tension,
Technical Note Pendant Drop Measurements Technical note: TN316e Industry section: all Author: FT, TW Date: 12/2010 Method: Drop Shape Analyzer DSA100 Keywords: Methods, surface tension, interfacial tension,
SPH 4C Unit 4 Hydraulics and Pneumatic Systems
 SPH 4C Unit 4 Hydraulics and Pneumatic Systems Properties of Fluids and Pressure Learning Goal: I can explain the properties of fluids and identify associated units. Definitions: Fluid: A substance that
SPH 4C Unit 4 Hydraulics and Pneumatic Systems Properties of Fluids and Pressure Learning Goal: I can explain the properties of fluids and identify associated units. Definitions: Fluid: A substance that
Noise Characteristics Of A Check Valve Installed In R22 And R410A Scroll Compressors
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 22 Noise Characteristics Of A Check Valve Installed In R22 And R41A Scroll Compressors M.
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 22 Noise Characteristics Of A Check Valve Installed In R22 And R41A Scroll Compressors M.
BIOPAC Blood Flow Monitor
 BIOPAC Blood Flow Monitor Technique - Laser Doppler Flowmetry (LDF) The LDF100C is a laser Doppler blood perfusion monitor used to measure real-time micro-vascular red blood cell perfusion in tissue. LDF100C
BIOPAC Blood Flow Monitor Technique - Laser Doppler Flowmetry (LDF) The LDF100C is a laser Doppler blood perfusion monitor used to measure real-time micro-vascular red blood cell perfusion in tissue. LDF100C
bespoke In general health and rehabilitation Breath-by-breath multi-functional respiratory gas analyser In human performance
 Introduction Expired Gas Analysis or indirect calorimetry, can be used to measure ventilation and the fractions of oxygen and carbon dioxide in expired air. From these measurements, the body's oxygen consumption
Introduction Expired Gas Analysis or indirect calorimetry, can be used to measure ventilation and the fractions of oxygen and carbon dioxide in expired air. From these measurements, the body's oxygen consumption
I.CHEM.E. SYMPOSIUM SERIES NO. 97 BUOYANCY-DRIVEN NATURAL VENTILATION OP ENCLOSED SPACES
 BUOYANCY-DRIVEN NATURAL VENTILATION OP ENCLOSED SPACES M. R. Marshall* and P. L. Stewart-Darling* A simple mathematical model for the buoyancy driven ventilation of an enclosed space, using a two-pipe
BUOYANCY-DRIVEN NATURAL VENTILATION OP ENCLOSED SPACES M. R. Marshall* and P. L. Stewart-Darling* A simple mathematical model for the buoyancy driven ventilation of an enclosed space, using a two-pipe
3. REQUIRED EQUIPMENT
 TEC? 700-700 Materiel Test Procedure 5-2-540 White Sands Missile Range I. OBJECTIVE U. S. ARMY TEST AND EVALUATION COMMAND COMMON ENGINEERING TEST PROCEDURE MISSILEBORNE GAS OPERATED POWER SUPPLY TESTS
TEC? 700-700 Materiel Test Procedure 5-2-540 White Sands Missile Range I. OBJECTIVE U. S. ARMY TEST AND EVALUATION COMMAND COMMON ENGINEERING TEST PROCEDURE MISSILEBORNE GAS OPERATED POWER SUPPLY TESTS
DTo DTI DEFENCI ASTOUIO. flxt[ct ANTTL. Canadaliit
 DTo DTI DEFENCI ASTOUIO flxt[ct ANTTL Canadaliit November 1989 DCIEM No. 89-RR-47 +Gz PROTECTION IN THE FUTURE - REVIEW OF SCIENTIFIC LITERATURE F. Buick, Ph.D. * DTIC ELECTE F80919901 Defence and Civil
DTo DTI DEFENCI ASTOUIO flxt[ct ANTTL Canadaliit November 1989 DCIEM No. 89-RR-47 +Gz PROTECTION IN THE FUTURE - REVIEW OF SCIENTIFIC LITERATURE F. Buick, Ph.D. * DTIC ELECTE F80919901 Defence and Civil
6, AUTýHC]RC, TA - 01 WU NTIS CRA&i Same as block 7 DTIC TAB rsamett ablckj7t( TV WNSPEcMD F Unannounced
![6, AUTýHC]RC, TA - 01 WU NTIS CRA&i Same as block 7 DTIC TAB rsamett ablckj7t( TV WNSPEcMD F Unannounced 6, AUTýHC]RC, TA - 01 WU NTIS CRA&i Same as block 7 DTIC TAB rsamett ablckj7t( TV WNSPEcMD F Unannounced](/thumbs/95/126002163.jpg) * -- - _ AD-A275 348 PAGE ýj, TITIE [AND I.' 'L 30 December 93 _ Final Sept 92 - Dec 93-7 -, Comparative Centrifuge Evaluation of the Air Force Advanced Technology Anti-G Suit (ATAGS) and the Navy PE -
* -- - _ AD-A275 348 PAGE ýj, TITIE [AND I.' 'L 30 December 93 _ Final Sept 92 - Dec 93-7 -, Comparative Centrifuge Evaluation of the Air Force Advanced Technology Anti-G Suit (ATAGS) and the Navy PE -
Measuring Lung Capacity
 Name Class Date Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Measuring Lung Capacity Introduction The amount of air that you move in and out of your lungs depends on how quickly you are breathing. The
Name Class Date Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Measuring Lung Capacity Introduction The amount of air that you move in and out of your lungs depends on how quickly you are breathing. The
OIML R 16-1 RECOMMENDATION. Edition 2002 (E) ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION. Non-invasive mechanical sphygmomanometers
 INTERNATIONAL RECOMMENDATION OIML R 16-1 Edition 2002 (E) Non-invasive mechanical sphygmomanometers Sphygmomanomètres non invasifs mécaniques OIML R 16-1 Edition 2002 (E) ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE
INTERNATIONAL RECOMMENDATION OIML R 16-1 Edition 2002 (E) Non-invasive mechanical sphygmomanometers Sphygmomanomètres non invasifs mécaniques OIML R 16-1 Edition 2002 (E) ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE
CONTENTS SPECIFICATIONS GENERAL INFORMATION RECOMMENDED USE OPERATING PRINCIPLE TIPS ON TAKING YOUR BLOOD PRESSURE 3-4 BATTERY INSTALLATION
 IFU SBPMON107 CONTENTS SPECIFICATIONS GENERAL INFORMATION RECOMMENDED USE OPERATING PRINCIPLE TIPS ON TAKING YOUR BLOOD PRESSURE BATTERY INSTALLATION CORRECT POSITION FOR MEASUREMENT POSITIONING THE CUFF
IFU SBPMON107 CONTENTS SPECIFICATIONS GENERAL INFORMATION RECOMMENDED USE OPERATING PRINCIPLE TIPS ON TAKING YOUR BLOOD PRESSURE BATTERY INSTALLATION CORRECT POSITION FOR MEASUREMENT POSITIONING THE CUFF
User Applied Force to Assistive Jogger s Interface During Gait
 User Applied Force to Assistive Jogger s Interface During Gait Senior Capstone: Assistive Jogger MEE 443 Mechanical Engineering Laboratories University of Maine April 13, 2010 By: Joey Passarelli Alexander
User Applied Force to Assistive Jogger s Interface During Gait Senior Capstone: Assistive Jogger MEE 443 Mechanical Engineering Laboratories University of Maine April 13, 2010 By: Joey Passarelli Alexander
PROBLEM SET 7. Assigned: April 1, 2004 Due: April 9, 2004
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.542J: Quantitative Physiology: Organ Transport Systems Instructors: Roger Mark and Jose Venegas MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Departments
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.542J: Quantitative Physiology: Organ Transport Systems Instructors: Roger Mark and Jose Venegas MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Departments
Physiological Considerations for Compression Bandaging
 Physiological Considerations for Compression Bandaging Harvey N. Mayrovitz, Ph.D. Professor of Physiology College of Medical Sciences Nova Southeastern University mayrovit@nsu.nova.edu At the completion
Physiological Considerations for Compression Bandaging Harvey N. Mayrovitz, Ph.D. Professor of Physiology College of Medical Sciences Nova Southeastern University mayrovit@nsu.nova.edu At the completion
Pulmonary Circulation Linda Costanzo Ph.D.
 Pulmonary Circulation Linda Costanzo Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The differences between pressures in the pulmonary and systemic circulations. 2. How
Pulmonary Circulation Linda Costanzo Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The differences between pressures in the pulmonary and systemic circulations. 2. How
Aerodynamic Analysis of a Symmetric Aerofoil
 214 IJEDR Volume 2, Issue 4 ISSN: 2321-9939 Aerodynamic Analysis of a Symmetric Aerofoil Narayan U Rathod Department of Mechanical Engineering, BMS college of Engineering, Bangalore, India Abstract - The
214 IJEDR Volume 2, Issue 4 ISSN: 2321-9939 Aerodynamic Analysis of a Symmetric Aerofoil Narayan U Rathod Department of Mechanical Engineering, BMS college of Engineering, Bangalore, India Abstract - The
Aneroid Sphygmomanometer. Use, Care, & Maintenance
 Aneroid Sphygmomanometer Use, Care, & Maintenance 1 Device Description and Intended Use An aneroid sphygmomanometer is used by professional healthcare providers and individuals trained in the auscultatory
Aneroid Sphygmomanometer Use, Care, & Maintenance 1 Device Description and Intended Use An aneroid sphygmomanometer is used by professional healthcare providers and individuals trained in the auscultatory
MANUAL BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR BPM 168B Contents Blood Pressure Monitor Intended Use What is blood pressure?
 MANUAL BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR BPM 168B Contents 01... Blood Pressure Monitor Intended Use 02... 1. What is blood pressure? 02... 2. Why is it useful measure blood pressure at home?... A. WHO blood pressure
MANUAL BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR BPM 168B Contents 01... Blood Pressure Monitor Intended Use 02... 1. What is blood pressure? 02... 2. Why is it useful measure blood pressure at home?... A. WHO blood pressure
The University of Hong Kong Department of Physics Experimental Physics Laboratory
 The University of Hong Kong Department of Physics Experimental Physics Laboratory PHYS2260 Heat and Waves 2260-1 LABORATORY MANUAL Experiment 1: Adiabatic Gas Law Part A. Ideal Gas Law Equipment Required:
The University of Hong Kong Department of Physics Experimental Physics Laboratory PHYS2260 Heat and Waves 2260-1 LABORATORY MANUAL Experiment 1: Adiabatic Gas Law Part A. Ideal Gas Law Equipment Required:
Hydrotherapy. Aquatics and Whirlpools
 Hydrotherapy Aquatics and Whirlpools History of Hydrotherapy Usage One of the oldest forms of heat application Initially used for relaxation History of Hydrotherapy ordinary containers are not as therapeutic
Hydrotherapy Aquatics and Whirlpools History of Hydrotherapy Usage One of the oldest forms of heat application Initially used for relaxation History of Hydrotherapy ordinary containers are not as therapeutic
Engineering: Measurement Technology Pressure/Level (SCQF level 6)
 National Unit Specification: general information CODE F5KT 12 SUMMARY This Unit can be delivered as part of a National Qualification Group Award but can also be taken as a free-standing Unit. This Unit
National Unit Specification: general information CODE F5KT 12 SUMMARY This Unit can be delivered as part of a National Qualification Group Award but can also be taken as a free-standing Unit. This Unit
WATER HYDRAULIC HIGH SPEED SOLENOID VALVE AND ITS APPLICATION
 WATER HYDRAULIC HIGH SPEED SOLENOID VALVE AND ITS APPLICATION Akihito MITSUHATA *, Canghai LIU *, Ato KITAGAWA * and Masato KAWASHIMA ** * Department of Mechanical and Control Engineering, Graduate school
WATER HYDRAULIC HIGH SPEED SOLENOID VALVE AND ITS APPLICATION Akihito MITSUHATA *, Canghai LIU *, Ato KITAGAWA * and Masato KAWASHIMA ** * Department of Mechanical and Control Engineering, Graduate school
A (not so) brief conversation concerning HemaClear pressure
 A (not so) brief conversation concerning HemaClear pressure Orthopedic Surgeon: OK, I am convinced that the HemaClear works well, but please tell me about the pressure in the limb beneath the ring - I
A (not so) brief conversation concerning HemaClear pressure Orthopedic Surgeon: OK, I am convinced that the HemaClear works well, but please tell me about the pressure in the limb beneath the ring - I
Pressure and Depth. In a static, non-moving fluid
 Pressure and Depth In a static, non-moving fluid Static Fluids Being on the surface of the earth, you can say that we dwell on the bottom of an ocean of air. The pressure we experience is primarily caused
Pressure and Depth In a static, non-moving fluid Static Fluids Being on the surface of the earth, you can say that we dwell on the bottom of an ocean of air. The pressure we experience is primarily caused
The Gas Laws: Boyle's Law and Charles Law
 Exercise 6 Page 1 Illinois Central College CHEMISTRY 130 Name The Gas Laws: Boyle's Law and Charles Law Objective The simple laws governing the properties of gases can be readily demonstrated experimentally.
Exercise 6 Page 1 Illinois Central College CHEMISTRY 130 Name The Gas Laws: Boyle's Law and Charles Law Objective The simple laws governing the properties of gases can be readily demonstrated experimentally.
Medical Center, San Francisco, Cal.,
 628 J. Phy8iol. (1966), 183, 628-636 With 4 text-figure8 Printed in Great Britain THE INTERRELATION OF THERMOREGULATORY AND BARORECEPTOR REFLEXES IN THE CONTROL OF THE BLOOD VESSELS IN THE HUMAN FOREARM
628 J. Phy8iol. (1966), 183, 628-636 With 4 text-figure8 Printed in Great Britain THE INTERRELATION OF THERMOREGULATORY AND BARORECEPTOR REFLEXES IN THE CONTROL OF THE BLOOD VESSELS IN THE HUMAN FOREARM
DYNAMIC COMPRESSION THERAPY
 PULSE PRESS DYNAMIC COMPRESSION THERAPY MULTITEC 12 User Manual May 2011 0120 CONTENTS:- SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS ELECTROMAGNETIC INTERFERENCE DESCRIPTION OF CONTROLS MODE SELECTION OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS CARE
PULSE PRESS DYNAMIC COMPRESSION THERAPY MULTITEC 12 User Manual May 2011 0120 CONTENTS:- SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS ELECTROMAGNETIC INTERFERENCE DESCRIPTION OF CONTROLS MODE SELECTION OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS CARE
Simulation analysis of the influence of breathing on the performance in breaststroke
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 34 (2012 ) 736 741 9 th Conference of the International Sports Engineering Association (ISEA) Simulation analysis of the influence of breathing
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 34 (2012 ) 736 741 9 th Conference of the International Sports Engineering Association (ISEA) Simulation analysis of the influence of breathing
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON THE HYDRODYNAMIC BEHAVIORS OF TWO CONCENTRIC CYLINDERS
 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON THE HYDRODYNAMIC BEHAVIORS OF TWO CONCENTRIC CYLINDERS *Jeong-Rok Kim 1), Hyeok-Jun Koh ), Won-Sun Ruy 3) and Il-Hyoung Cho ) 1), 3), ) Department of Ocean System Engineering, Jeju
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON THE HYDRODYNAMIC BEHAVIORS OF TWO CONCENTRIC CYLINDERS *Jeong-Rok Kim 1), Hyeok-Jun Koh ), Won-Sun Ruy 3) and Il-Hyoung Cho ) 1), 3), ) Department of Ocean System Engineering, Jeju
Test Method of Trap Performance for Induced Siphonage
 VII.4 Test Method of Trap Performance for Induced Siphonage K. Sakaue (1), H. Kuriyama (2), H. Iizuka (3), M. Kamata (4) (1) sakaue@ isc.meiji.ac.jp School of Science and Technology, Meiji University,
VII.4 Test Method of Trap Performance for Induced Siphonage K. Sakaue (1), H. Kuriyama (2), H. Iizuka (3), M. Kamata (4) (1) sakaue@ isc.meiji.ac.jp School of Science and Technology, Meiji University,
Analysis of Pressure Rise During Internal Arc Faults in Switchgear
 Analysis of Pressure Rise During Internal Arc Faults in Switchgear ASANUMA, Gaku ONCHI, Toshiyuki TOYAMA, Kentaro ABSTRACT Switchgear include devices that play an important role in operations such as electric
Analysis of Pressure Rise During Internal Arc Faults in Switchgear ASANUMA, Gaku ONCHI, Toshiyuki TOYAMA, Kentaro ABSTRACT Switchgear include devices that play an important role in operations such as electric
LYMPHA PRESS MANUFACTURED BY MEGO AFEK IMPORTED BY LYMPHA PRESS USA, Ltd. USERS MANUAL LYMPHA PRESS MODEL 201-M
 LYMPHA PRESS MANUFACTURED BY MEGO AFEK IMPORTED BY LYMPHA PRESS USA, Ltd. USERS MANUAL LYMPHA PRESS MODEL 201-M THE LYMPHA PRESS MODEL 201-M IS A THERAPEUTIC DEVICE FOR THE CONTROL OF LYMPHEDEMA OF THE
LYMPHA PRESS MANUFACTURED BY MEGO AFEK IMPORTED BY LYMPHA PRESS USA, Ltd. USERS MANUAL LYMPHA PRESS MODEL 201-M THE LYMPHA PRESS MODEL 201-M IS A THERAPEUTIC DEVICE FOR THE CONTROL OF LYMPHEDEMA OF THE
International Journal of Technical Research and Applications e-issn: , Volume 4, Issue 3 (May-June, 2016), PP.
 DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF FEED CHECK VALVE AS CONTROL VALVE USING CFD SOFTWARE R.Nikhil M.Tech Student Industrial & Production Engineering National Institute of Engineering Mysuru, Karnataka, India -570008
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF FEED CHECK VALVE AS CONTROL VALVE USING CFD SOFTWARE R.Nikhil M.Tech Student Industrial & Production Engineering National Institute of Engineering Mysuru, Karnataka, India -570008
W. D. A. SMITH Research Department of Anaesthetics, Royal College of Surgeons of England, London
 Brit. 1. Anaesth. (1962), 34, 136 A METHOD OF RECORDING SYSTOLIC BLOOD PRESSURE BY W. D. A. SMITH Research Department of Anaesthetics, Royal College of Surgeons of England, London The method of recording
Brit. 1. Anaesth. (1962), 34, 136 A METHOD OF RECORDING SYSTOLIC BLOOD PRESSURE BY W. D. A. SMITH Research Department of Anaesthetics, Royal College of Surgeons of England, London The method of recording
AQAI SIS MODULES AND MODELS PAGE 1. AQAI Simulator Interface Software AQAI SIS
 AQAI SIS MODULES AND MODELS PAGE 1 AQAI Simulator Interface Software AQAI SIS AQAI SIS MODULES AND MODELS PAGE 2 AQAI SIS CONTENTS: AQAI SIS General information AQAI SIS Models and Modules Combining SIS
AQAI SIS MODULES AND MODELS PAGE 1 AQAI Simulator Interface Software AQAI SIS AQAI SIS MODULES AND MODELS PAGE 2 AQAI SIS CONTENTS: AQAI SIS General information AQAI SIS Models and Modules Combining SIS
Pressure Measurements
 ME 22.302 Mechanical Lab I Pressure Measurements Dr. Peter Avitabile University of Massachusetts Lowell Pressure - 122601-1 Copyright 2001 A transducer is a device that converts some mechanical quantity
ME 22.302 Mechanical Lab I Pressure Measurements Dr. Peter Avitabile University of Massachusetts Lowell Pressure - 122601-1 Copyright 2001 A transducer is a device that converts some mechanical quantity
An Impeller Blade Analysis of Centrifugal Gas Compressor Using CFD
 An Impeller Blade Analysis of Centrifugal Gas Compressor Using CFD Vivek V. Kulkarni Department of Mechanical Engineering KLS Gogte Institute of Technology, Belagavi, Karnataka Dr. Anil T.R. Department
An Impeller Blade Analysis of Centrifugal Gas Compressor Using CFD Vivek V. Kulkarni Department of Mechanical Engineering KLS Gogte Institute of Technology, Belagavi, Karnataka Dr. Anil T.R. Department
LOW PRESSURE EFFUSION OF GASES adapted by Luke Hanley and Mike Trenary
 ADH 1/7/014 LOW PRESSURE EFFUSION OF GASES adapted by Luke Hanley and Mike Trenary This experiment will introduce you to the kinetic properties of low-pressure gases. You will make observations on the
ADH 1/7/014 LOW PRESSURE EFFUSION OF GASES adapted by Luke Hanley and Mike Trenary This experiment will introduce you to the kinetic properties of low-pressure gases. You will make observations on the
Design and Development of Pressure Sensing Bandage
 GRD Journals- Global Research and Development Journal for Engineering Volume 2 Issue 5 April 2017 ISSN: 2455-5703 Design and Development of Pressure Sensing Bandage Pudhumozhi Subramanian Department of
GRD Journals- Global Research and Development Journal for Engineering Volume 2 Issue 5 April 2017 ISSN: 2455-5703 Design and Development of Pressure Sensing Bandage Pudhumozhi Subramanian Department of
σ = force / surface area force act upon In the image above, the surface area would be (Face height) * (Face width).
 Aortic Root Inflation Introduction You have already learned about the mechanical properties of materials in the cantilever beam experiment. In that experiment you used bending forces to determine the Young
Aortic Root Inflation Introduction You have already learned about the mechanical properties of materials in the cantilever beam experiment. In that experiment you used bending forces to determine the Young
Pressure in Human Body
 3. Direct Pressure Fundamental concepts Diaphragm-type pressure transducers Dynamics of catheter-transducer system Catheter-tip pressure transducers Implantable pressure transducers Pressure measurements
3. Direct Pressure Fundamental concepts Diaphragm-type pressure transducers Dynamics of catheter-transducer system Catheter-tip pressure transducers Implantable pressure transducers Pressure measurements
The Discussion of this exercise covers the following points:
 Exercise 3-2 Orifice Plates EXERCISE OBJECTIVE In this exercise, you will study how differential pressure flowmeters operate. You will describe the relationship between the flow rate and the pressure drop
Exercise 3-2 Orifice Plates EXERCISE OBJECTIVE In this exercise, you will study how differential pressure flowmeters operate. You will describe the relationship between the flow rate and the pressure drop
Study on Fire Plume in Large Spaces Using Ground Heating
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 11 (2011) 226 232 The 5 th Conference on Performance-based Fire and Fire Protection Engineering Study on Fire Plume in Large Spaces Using
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 11 (2011) 226 232 The 5 th Conference on Performance-based Fire and Fire Protection Engineering Study on Fire Plume in Large Spaces Using
The Discussion of this exercise covers the following points:
 Exercise 5-3 Wet Reference Leg EXERCISE OBJECTIVE Learn to measure the level in a vessel using a wet reference leg. DISCUSSION OUTLINE The Discussion of this exercise covers the following points: Measuring
Exercise 5-3 Wet Reference Leg EXERCISE OBJECTIVE Learn to measure the level in a vessel using a wet reference leg. DISCUSSION OUTLINE The Discussion of this exercise covers the following points: Measuring
THE DANGERS OF USING A THREE-WAY VALVE AS A STOPCOCK IN A TRANSDUCER SYSTEM FOR MEASURING VENOUS BLOOD PRESSURE
 THE DANGERS OF USING A THREE-WAY VALVE AS A STOPCOCK IN A TRANSDUCER SYSTEM FOR MEASURING VENOUS BLOOD PRESSURE J. W. SIVIITH~ PH.D., P.ENr ~ THE SYSTEM shown in Figure 1 has been widely used for the measuring
THE DANGERS OF USING A THREE-WAY VALVE AS A STOPCOCK IN A TRANSDUCER SYSTEM FOR MEASURING VENOUS BLOOD PRESSURE J. W. SIVIITH~ PH.D., P.ENr ~ THE SYSTEM shown in Figure 1 has been widely used for the measuring
Vortex Meters for Liquids, Gas, and Steam
 A Measuring Principle Comes of Age: Vortex Meters for Liquids, Gas, and Steam Dipl.-Hyd. Oliver Seifert, Product Management Vortex Meters at Flowtec AG, and Ellen-Christine Reiff, M.A., Editor s Office,
A Measuring Principle Comes of Age: Vortex Meters for Liquids, Gas, and Steam Dipl.-Hyd. Oliver Seifert, Product Management Vortex Meters at Flowtec AG, and Ellen-Christine Reiff, M.A., Editor s Office,
Pressure Measurement. Introduction. Engr325 Instrumentation. Dr Curtis Nelson 3/12/18
 3/12/18 Pressure Measurement Engr325 Instrumentation Dr Curtis Nelson Introduction A cluster of 72 helium-filled balloons over Temecula, California in April of 2003. The helium balloons displace approximately
3/12/18 Pressure Measurement Engr325 Instrumentation Dr Curtis Nelson Introduction A cluster of 72 helium-filled balloons over Temecula, California in April of 2003. The helium balloons displace approximately
Characterizers for control loops
 Characterizers for control loops By: F. G. Shinskey (May 1999) Introduction Commercial controllers such as the PID series (proportional, integral, derivative, and their combinations) are linear devices
Characterizers for control loops By: F. G. Shinskey (May 1999) Introduction Commercial controllers such as the PID series (proportional, integral, derivative, and their combinations) are linear devices
Effect of Coiled Capillary Tube Pitch on Vapour Compression Refrigeration System Performance
 Effect of Coiled Capillary Tube Pitch on Vapour Compression Refrigeration System Performance Mutalubi Aremu Akintunde Federal University of Technology, Department of Mechanical Engineering Akure, Ondo
Effect of Coiled Capillary Tube Pitch on Vapour Compression Refrigeration System Performance Mutalubi Aremu Akintunde Federal University of Technology, Department of Mechanical Engineering Akure, Ondo
Bloodpressure measurement, improvement of oscillometric method.
 Bloodpressure measurement, improvement of oscillometric method. Øystein Stene, Lars Jørgen Kristoffersen, Waldemar Sulkowski Høgskolen i Narvik, Sivilingeniørutdanningen, postboks 385, N-8501 Narvik Norway,
Bloodpressure measurement, improvement of oscillometric method. Øystein Stene, Lars Jørgen Kristoffersen, Waldemar Sulkowski Høgskolen i Narvik, Sivilingeniørutdanningen, postboks 385, N-8501 Narvik Norway,
Navy Fighter Pilots Tolerate Higher-G Maneuvers Thanks to Oxygen Regulator Bellows
 Navy Fighter Pilots Tolerate Higher-G Maneuvers Thanks to Oxygen Regulator Bellows Low Spring-Rate Sensor Applies Positive Pressure Breathing for G with Quick, Consistent Response Produced by: Mission
Navy Fighter Pilots Tolerate Higher-G Maneuvers Thanks to Oxygen Regulator Bellows Low Spring-Rate Sensor Applies Positive Pressure Breathing for G with Quick, Consistent Response Produced by: Mission
REF CH-302B IDENTIFICATION OF PARTS
 English TM INSTRUCTION MANUAL FOR DIGITAL BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR REF CH-302B IDENTIFICATION OF PARTS Exhaust button Air-release system Bulb Systolic blood pressure display section Diastolic blood pressure/pulse
English TM INSTRUCTION MANUAL FOR DIGITAL BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR REF CH-302B IDENTIFICATION OF PARTS Exhaust button Air-release system Bulb Systolic blood pressure display section Diastolic blood pressure/pulse
Physiological Considerations for Compression Bandaging. Harvey N. Mayrovitz, Ph.D.
 Physiological Considerations for Compression Bandaging Harvey N. Mayrovitz, Ph.D. Objectives Therapeutic Compression Principles and Definitions Physiological Effects Mechanisms of Action Differential Features
Physiological Considerations for Compression Bandaging Harvey N. Mayrovitz, Ph.D. Objectives Therapeutic Compression Principles and Definitions Physiological Effects Mechanisms of Action Differential Features
LUGB Vortex Flowmeter
 LUGB Vortex Flowmeter Overview LUGB swirl flowmeter is also called as vortex flowmeter, it is a new of flowmeter which is developed according to fluid vibration theory, widely used for fluid measurement
LUGB Vortex Flowmeter Overview LUGB swirl flowmeter is also called as vortex flowmeter, it is a new of flowmeter which is developed according to fluid vibration theory, widely used for fluid measurement
LOW PRESSURE EFFUSION OF GASES revised by Igor Bolotin 03/05/12
 LOW PRESSURE EFFUSION OF GASES revised by Igor Bolotin 03/05/ This experiment will introduce you to the kinetic properties of low-pressure gases. You will make observations on the rates with which selected
LOW PRESSURE EFFUSION OF GASES revised by Igor Bolotin 03/05/ This experiment will introduce you to the kinetic properties of low-pressure gases. You will make observations on the rates with which selected
Semi-Automatic Blood Pressure Monitor with Memory
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Semi-Automatic Blood Pressure Monitor with Memory 61-268-001 (Adult size cuff) Please read this instruction manual completely before operating this unit. English Spanish Limited Five
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Semi-Automatic Blood Pressure Monitor with Memory 61-268-001 (Adult size cuff) Please read this instruction manual completely before operating this unit. English Spanish Limited Five
Experiment Instructions. Circulating Pumps Training Panel
 Experiment Instructions Circulating Pumps Training Panel Experiment Instructions This manual must be kept by the unit. Before operating the unit: - Read this manual. - All participants must be instructed
Experiment Instructions Circulating Pumps Training Panel Experiment Instructions This manual must be kept by the unit. Before operating the unit: - Read this manual. - All participants must be instructed
AQUATIC THERAPY PRESENTED BY MICKEY BARON, PHYSICAL THERAPIST
 AQUATIC THERAPY PRESENTED BY MICKEY BARON, PHYSICAL THERAPIST WATER COVERS 72% OF THE EARTH S SURFACE 2/3 OF THE HUMAN BODY IS COMPOSED OF WATER IN WATER YOU WORK BOTH HALVES OF EACH MUSCLE WATER PROVIDES
AQUATIC THERAPY PRESENTED BY MICKEY BARON, PHYSICAL THERAPIST WATER COVERS 72% OF THE EARTH S SURFACE 2/3 OF THE HUMAN BODY IS COMPOSED OF WATER IN WATER YOU WORK BOTH HALVES OF EACH MUSCLE WATER PROVIDES
What is Boyle s law and how can it be demonstrated?
 Name: Relationship Between Gas Variables Gas Laws Simulation Introduction: Scientists in the late 1800 s noted relationships between various variables related to gases (pressure, volume, temperature),
Name: Relationship Between Gas Variables Gas Laws Simulation Introduction: Scientists in the late 1800 s noted relationships between various variables related to gases (pressure, volume, temperature),
Presented to the Israel Annual Conference on Aerospace Sciences, 2009 RISK-ANALYSIS A SUPPLEMENT TO DAMAGE-TOLERANCE ANALYSIS
 RISK-ANALYSIS A SUPPLEMENT TO DAMAGE-TOLERANCE ANALYSIS Abraham Brot Engineering Division Israel Aerospace Industries Ben-Gurion Airport, Israel abrot@iai.co.il ABSTRACT Risk-analysis, based on probabilistic
RISK-ANALYSIS A SUPPLEMENT TO DAMAGE-TOLERANCE ANALYSIS Abraham Brot Engineering Division Israel Aerospace Industries Ben-Gurion Airport, Israel abrot@iai.co.il ABSTRACT Risk-analysis, based on probabilistic
SOLUTIONS Homework #1
 SOLUTIONS Homework #1 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING IN MEDICINE AND BIOLOGY ECEN 1001- Fall 2003 R. Mihran Due Tuesday, 9/9/03 Question 1: a) Chapter 1 of the text discusses the fact that a significant fraction
SOLUTIONS Homework #1 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING IN MEDICINE AND BIOLOGY ECEN 1001- Fall 2003 R. Mihran Due Tuesday, 9/9/03 Question 1: a) Chapter 1 of the text discusses the fact that a significant fraction
INSTRUCTION MANUAL MANUAL INFLATION BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL MANUAL INFLATION BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR Model HEM-412C TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 3 Know Your Unit 4 Quick Reference Guide 5 Battery Installation/Replacement 6 How To Apply The Arm
INSTRUCTION MANUAL MANUAL INFLATION BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR Model HEM-412C TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 3 Know Your Unit 4 Quick Reference Guide 5 Battery Installation/Replacement 6 How To Apply The Arm
Linear Infl ation Technology Non-invasive Blood Pressure Measurement. inibp Case Report Experiences in OR
 Linear Infl ation Technology Non-invasive Blood Pressure inibp Case Report Experiences in OR C ONTENTS Introduction 2 Technological Description of inibp inibp advantages 2 inibp technology adapts to each
Linear Infl ation Technology Non-invasive Blood Pressure inibp Case Report Experiences in OR C ONTENTS Introduction 2 Technological Description of inibp inibp advantages 2 inibp technology adapts to each
LAB 13: FLUIDS OBJECTIVES
 217 Name Date Partners LAB 13: FLUIDS Fluids are an important part of our body OBJECTIVES OVERVIEW Fluid Properties To learn how some fundamental physical principles apply to fluids. To understand the
217 Name Date Partners LAB 13: FLUIDS Fluids are an important part of our body OBJECTIVES OVERVIEW Fluid Properties To learn how some fundamental physical principles apply to fluids. To understand the
HOME BLOOD PRESSURE KIT INSTRUCTIONS TRILINGUAL INSTRUCTION GUIDE MODEL UA-100
 HOME BLOOD PRESSURE KIT INSTRUCTIONS TRILINGUAL INSTRUCTION GUIDE MODEL UA-100 IMPORTANT INFORMATION Please read this important information before using your monitor. Please remember that only a medical
HOME BLOOD PRESSURE KIT INSTRUCTIONS TRILINGUAL INSTRUCTION GUIDE MODEL UA-100 IMPORTANT INFORMATION Please read this important information before using your monitor. Please remember that only a medical
Independent Health Facilities
 Independent Health Facilities Assessment Protocol for Pulmonary Function Studies - Technologist Assessor INSTRUCTIONS: Please complete ( ) the attached protocol during the assessment. Ensure that all the
Independent Health Facilities Assessment Protocol for Pulmonary Function Studies - Technologist Assessor INSTRUCTIONS: Please complete ( ) the attached protocol during the assessment. Ensure that all the
ELEVATION CORRECTION FACTORS FOR RADON MONITORS*
 ELEVATION CORRECTION FACTORS FOR E-PERM@ RADON MONITORS* P. Kotrappa and L. R. Stiefl Abstract-E-PERMm radon monitors are based on the principle of electret ion chambers and are usually calibrated in a
ELEVATION CORRECTION FACTORS FOR E-PERM@ RADON MONITORS* P. Kotrappa and L. R. Stiefl Abstract-E-PERMm radon monitors are based on the principle of electret ion chambers and are usually calibrated in a
Study of Passing Ship Effects along a Bank by Delft3D-FLOW and XBeach1
 Study of Passing Ship Effects along a Bank by Delft3D-FLOW and XBeach1 Minggui Zhou 1, Dano Roelvink 2,4, Henk Verheij 3,4 and Han Ligteringen 2,3 1 School of Naval Architecture, Ocean and Civil Engineering,
Study of Passing Ship Effects along a Bank by Delft3D-FLOW and XBeach1 Minggui Zhou 1, Dano Roelvink 2,4, Henk Verheij 3,4 and Han Ligteringen 2,3 1 School of Naval Architecture, Ocean and Civil Engineering,
The Discussion of this exercise covers the following points: Pumps Basic operation of a liquid pump Types of liquid pumps The centrifugal pump.
 Exercise 2-3 Centrifugal Pumps EXERCISE OBJECTIVE In this exercise, you will become familiar with the operation of a centrifugal pump and read its performance chart. You will also observe the effect that
Exercise 2-3 Centrifugal Pumps EXERCISE OBJECTIVE In this exercise, you will become familiar with the operation of a centrifugal pump and read its performance chart. You will also observe the effect that
Analysis of Shear Lag in Steel Angle Connectors
 University of New Hampshire University of New Hampshire Scholars' Repository Honors Theses and Capstones Student Scholarship Spring 2013 Analysis of Shear Lag in Steel Angle Connectors Benjamin Sawyer
University of New Hampshire University of New Hampshire Scholars' Repository Honors Theses and Capstones Student Scholarship Spring 2013 Analysis of Shear Lag in Steel Angle Connectors Benjamin Sawyer
Module 2, Add on Lesson Depth Sensor. Teacher. 90 minutes
 Module 2, Add on Lesson Depth Sensor 90 minutes Teacher Purpose of this lesson Investigate the relationship between pressure and depth Construct a sensor to measure the depth of water Graph data and reason
Module 2, Add on Lesson Depth Sensor 90 minutes Teacher Purpose of this lesson Investigate the relationship between pressure and depth Construct a sensor to measure the depth of water Graph data and reason
Homeostasis and Negative Feedback Concepts and Breathing Experiments 1
 Homeostasis and Negative Feedback Concepts and Breathing Experiments 1 I. Homeostasis and Negative Feedback Homeostasis refers to the maintenance of relatively constant internal conditions. For example,
Homeostasis and Negative Feedback Concepts and Breathing Experiments 1 I. Homeostasis and Negative Feedback Homeostasis refers to the maintenance of relatively constant internal conditions. For example,
Vital Signs Monitoring
 Vital Signs Monitoring Practical Skills Teaching Year 2 Medical Students MB BCh 2013-2014 Contents Introduction to workshop... 4 Overall Session Aim... 5 Intended Learning Outcomes... 5 Workshop Structure
Vital Signs Monitoring Practical Skills Teaching Year 2 Medical Students MB BCh 2013-2014 Contents Introduction to workshop... 4 Overall Session Aim... 5 Intended Learning Outcomes... 5 Workshop Structure
