Line drawing of metocean buoy
|
|
|
- Jean Kelley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
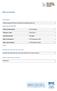
1 AB Safety Flash IMCA Safety Flash 05/13 April 2013 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learnt from them. The information below has been provided in good faith by members and should be reviewed individually by recipients, who will determine its relevance to their own operations. The effectiveness of the IMCA safety flash system depends on receiving reports from members in order to pass on information and avoid repeat incidents. Please consider adding the IMCA secretariat to your internal distribution list for safety alerts and/or manually submitting information on specific incidents you consider may be relevant. All information will be anonymised or sanitised, as appropriate. A number of other organisations issue safety flashes and similar documents which may be of interest to IMCA members. Where these are particularly relevant, these may be summarised or highlighted here. Links to known relevant websites are provided at Additional links should be submitted to webmaster@imca-int.com 1 Explosion Causing Fatal Injury During Maintenance of Metocean Buoy A member has reported an incident in which a crewman was fatally injured during the recovery and maintenance of a metocean buoy, after it had been in use in-sea for a period of around two years. The incident occurred after the buoy was recovered onto a service vessel for cleaning. After retrieval onto the service vessel, the buoy was cleaned, and the task of opening the instrument compartment started. This compartment also held the lead-acid battery packs of the buoy. Access was gained by removing a circular lid secured by 16 bolts. The removal of the bolts had been completed, except for the last bolt which proved to be seized. The decision was made to free this bolt using an angle grinder. Only moments after applying the grinder, an explosion took place which resulted in the lid blowing open and the instrument modules and their mounting plate being projected outwards with great force. These items struck the crewman, causing him to be fatally injured. The buoy had a discus shaped hull that could be split in two to ease transportation. A keel with counterweight was mounted under the hull to stabilise the buoy. A cylinder in the middle of the hull contains all electronic modules, the power package and the wave sensor. The different electronic modules were mounted into special splash proof compartment boxes to secure safe handling of the sensitive electronics. The buoy was equipped with a mast to support the meteorological sensors and the communication antennae. The dimensions in the diagram below are in millimetres. Line drawing of metocean buoy The immediate cause of the explosion was found, on investigation, to be sparks from the grinder igniting an explosive mixture of hydrogen and oxygen which had built up inside the compartment. The hydrogen build-up was assumed to stem from the lead-acid batteries. The lead-acid batteries contained in all metocean buoys of this sort are of the so called valve regulated type, meaning that they are sealed, except for a pressure relief valve. These batteries feature a built-in gas recombination system, and the small amounts of gas released through the valve pass through an additional catalyst before being conveyed to the outside of the buoy. This system is intended to prevent any build-up of hydrogen. The final technical investigation showed no sign of malfunction of the battery venting system. The root cause of the incident was determined to be to a combination of lack of maintenance and a failure to follow existing procedures. The investigation concluded that the following chain of events led to the hydrogen build-up, and eventually the accident.
2 1. Corrosion around lid sealing due to bird droppings and rain or sea spray caused the sealing to fail; 2. Water, sea salt and bird dropping (guano) ingression into the instrument compartment past the leaking lid sealing; 3. Corrosion and subsequent volume increase on details of battery rack due to ingression; 4. Increased pressure on batteries from rack, resulting in cracked battery cases; 5. Hydrogen build up due to one or more of these effects; 6. Corrosion of aluminium, accelerated by guano and sea salts dissolved in water; 7. Corrosion due to spilled battery acid from cracked batteries; 8. Gas leakage from cracked battery cases; 9. Hydrogen escapes due to leaking lid sealing and increasing temperature; 10. Grinder ignites hydrogen. The following further points were noted: The existing user documentation for these metocean buoys states that the buoys have to be purged before opening the lid to the instrument compartment. The buoys incorporate valves to allow for this procedure. In this incident this procedure was not followed; There was a warning in the manual against ignition sources; There were instructions in the manual on purging the instrument compartment; A protective cover over the instrument compartment lid and also bird spikes (to prevent birds landing on the buoy) were available and were to be fitted at that time. The following actions were taken: Improvements to warning signs and clearer instructions were developed, and also improved designs for the instrument compartment and battery rack; Development of clearer instructions, which emphasize that at all times the buoys should be treated with the assumption that they could contain an explosive gas mixture. The following precautions have now been identified: Exercise particular care with buoys that have not operated normally in the period prior to retrieval; Equalise the pressure inside the buoy to the ambient air pressure by opening the gas filling valves; Purge the interior of the buoy with air or nitrogen in order to remove any possibility of hydrogen gas, using the procedure described in the user manual; Do not allow any ignition source - including power tools - near the buoy until it is fully opened; Maintain a safe distance. Only the minimum required number of persons should be in the vicinity of the buoy until it is fully opened. Never stand in direct line of the instrument compartment lid; When flushing has been completed, proceed immediately with the opening of the lid; Leave the lid fully open for a further 10 minutes. 2 Battery Damage Caused by Charger Failure The Marine Safety Forum has published the following report regarding damage to batteries caused by the failure of the charger. The incident occurred when an engineer was carrying out planned maintenance of emergency generator. The report can be downloaded from 3 Near Miss: Exposed Live Electrical Cable A member has reported an incident in which a live electrical cable was found exposed. The incident occurred when a vessel had returned to service after a long dry docking. During this period many parts of the vessel were worked on and modifications to the layout of the vessel were made to accommodate new equipment - in particular the fast rescue craft (FRC) and its associated launching davit were removed in order to make room for a new hyperbaric lifeboat (HLB).
3 A member of the crew working near the new hyperbaric lifeboat noticed an electrical cable which was coiled up and stowed between a handrail and an adjacent bulkhead. The ends of the cable were not terminated but had been separated and wrapped up in electrical insulating tape. It was noted that a small amount of smoke was coming from the end of the cable and some sparking (the cable was in contact with the bulkhead). Realising that the cable was live the crewman immediately contacted the deck electrician and asked him to come and investigate. The electrician subsequently traced the cable and made it safe. The cable was identified as the supply to a halogen flood light originally intended as overboard illumination for the launch station of the vessel s FRC. The company s investigation revealed the following: Figure: showing electrical cable and bare live wires There had been inadequate planning and inadequate supervision of the work; The old flood lamp had been removed with no Permit To Work (PTW) or Electrical Isolation (EI) certificates in place. The underlying causes associated with the incident were: Owing to the high workload of vessel staff and the large number of jobs being undertaken simultaneously, there had been a failure of control, in that it had not been possible for ship s officers to observe all tasks and thus ensure that vessel policies were followed; There was no evidence to suggest that any communication was made to ship yard fitters that live electrical supplies were still present within their work area; There had been inadequate planning ahead of the job being undertaken; not all power supplies in the work area were assessed or isolated; All services that were required to be isolated and removed prior to the area being handed over to the third party contractor for the installation of the HLB had been successfully completed. The requirement to remove the overboard light was not part of this original scope of work; The third-party contractor deviated from their original work scope and removed the flood lamp without the necessary PTW and EI in place; The third-party contractor did not follow the Management of Change procedure. Our member identified the following lessons: The induction to the vessel during dry dock is to be reviewed and will include additional information regarding the Management of Change procedures; The use of a single point of contact for each work area was not in place while the vessel was in dry dock. This would have allowed the third-party contractor to approach their contact and arrange the necessary PTW and EI for the additional works they required; Although this work area still had additional works to be carried out, the area was not fully surveyed once the initial works had been completed prior to handover. Further information on shipyard safety can be found in IMCA SEL 032/M 221 Guidance on safety in shipyards.
4 4 Finger and Hand Injuries A member has reported two incidents in which crew suffered finger or hand injuries. In the first incident, the injured person was preparing a meal in the galley. He placed a chopping board on a worktop and placed a knife on top of the chopping board. As he moved around the galley, carrying out various tasks, the knife slipped from the chopping board and landed with the blade protruding over the edge of the worktop. The injured person was unaware of this and while walking past the worktop his right hand made contact with the blade of the knife, causing a 2 cm laceration to the fleshy part of the hand, between the base of his thumb and index finger. The wound was cleaned and closed with three sutures. The injured person resumed normal duties the following day. In the second incident, the injured person was working in the Bell Hangar. At the time of the incident an external auditor was carrying out an audit of the dive system. As part of the audit the diving bell was required to be moved over the access and inspection pit. Once the bell was transferred over the access pit two axle stands were placed under the bell s bump frame. The first axle stand was required to be adjusted for height; during this adjustment the injured persons right index finger got nipped in the extension mechanism. This resulted in an injury to the tip of the right index finger, which the injured person initially considered trivial and finished his work task. On examination his finger was bleeding and when reported to the medic a protective dressing was applied. Figure: 2 cm laceration caused by knife blade The company s investigation revealed that the root causes of the incident were: The cook was attempting to undertake too many tasks at the same time whilst working alone at a busy time; Assistance from other team members was not sought during a busy period in the galley; Existing safety systems were not followed, i.e. knife handling policy and Task Based Risk Assessment (TBRA). Figure: Illustration of where finger was pinched during adjustment of the axle stand The company s investigation revealed that the root causes of the incident were: Because they deemed the activity to be routine, persons doing the task did not communicate the need to move the dive bell and therefore there was no supervisory support in place at the time; No Task Based Risk Assessment (TBRA) or toolbox talk / pre-task assessment was carried out; The team involved in the task failed to consider conducting risk assessment as a priority before carrying out the task. The company s investigation included a review of both incidents to identify whether there was any commonality between the root causes of both incidents. Some of the lessons learnt include: Ask for help if and when required especially working in potentially hazardous areas (bell garage) and / or busy working areas (galley during meal service times); Appropriate supervision/supervisory support is essential in ensuring policies and safe methods of work/working tools are used; Supervisors should be informed of any hazardous activities being undertaken, before starting, to ensure adequate levels of additional personnel and / or supervision is provided to ensure HSE policies and management system requirement are applied; Safety policies and safe systems of work are put in place to assist in the protection of people, the environment, plant and equipment etc. Failure to comply with these has a detrimental effect on safety and can lead to instances of injury, damage or loss as demonstrated by the two finger injury incidents; Inadequate planning and risk assessing work tasks can result in potential hazards and control measures being overlooked.
5 5 High Potential Near Miss During Equipment Testing A member has reported an incident in which a heavy metal work table was dragged nearly a metre by a forklift truck. The incident occurred during troubleshooting of a heavy duty multi-strand electrical cable. Technicians connected the cable between a metal worktable vice and the rear towing / pull pin of a forklift truck, in order to allow stretching and tensioning of the cable. Once the stretched cable was tested, the tension was released and the forklift truck shut down. The cable was not disconnected from either the worktable vice or the forklift. A short time later, another employee boarded the forklift truck, started the engine and began to drive away. The cable jerked taught and pulled the metal worktable forward approximately 1m before warning shouts were recognized and the forklift was stopped. No personnel were injured and no equipment was damaged. However, the potential for personnel to have been injured and equipment to have been damaged was very high had personnel been at the work table or had the work table been pulled over. At the time of the incident there were a number of costly pieces of electronic equipment on the work bench. Figures: (Left) Work bench (Middle) electrical cable being tested (Right) Fork lift truck The company s investigation revealed the following: There were no test procedures for the set-up and use of the forklift for stretching and tensioning the cable; There was no job safety analysis (JSA) addressing actual or potential hazards of stretching and tensioning the cable with the forklift in order to support troubleshooting of the electrical cable; The electrical cable had not been removed from either the worktable vice or the forklift once the tensioning had been completed; There was inadequate communications between employees no communication took place between the personnel using the forklift for testing and the operator who sought to drive the forklift from the area; The operator who boarded the forklift did not inspect or walk around the vehicle before starting up and driving away; There were inadequate guards or barriers the forklift had not been secured to prevent access (i.e., no warning signs, labels, the key had not been removed from the ignition, etc.); The testing of the cable was rushed to completion without a thorough review of all aspects of equipment, personnel and process. Further investigation revealed the following root causes: Inadequate leadership/supervision Proper management of the overall testing process, equipment, and personnel would have prevented this near miss incident. Contributing factors to this root cause include inadequate work planning, inadequate identification and evaluation of the potential loss/hazards/risks, and inadequate or missing documentation (JSA, procedures, and/or instructions, etc.) which would have provided better control of work; Poor communication between peers No communications took place between the operator and the using department before the operator started the forklift and drove away; Improper motivation The failure of the operator to visually check the status of the forklift prior to use demonstrated complacency with the dangers and hazards of forklift operations. Our member took the following actions: Testing methods, especially when unique or uncommon, should be documented and a Job Safety Analysis performed to ensure all hazards and risks are identified, understood and mitigated against; Controls for equipment, personnel and process should be planned, defined and monitored for compliance by assigned, responsible personnel;
6 Ensured that improved communication processes were established and maintained to prevent recurrence of same or similar incidents; Continued to reinforce safety protocols, practices and behaviours with all personnel to overcome complacency to work place hazards. 6 Pressure Switch Location for Fixed Fire Suppression Systems The United States Coast Guard has published the following report regarding an engine room fire in a vessel. The safety alert addresses the location of fire suppression system pressure switches aboard vessels. These critical components sense the activation of the system and then electrically secure the ventilation systems operating in the protected space. Securing the ventilation is essential in extinguishing a fire onboard a vessel. It assists in isolating the fire within the space, minimizes the introduction of additional oxygen to fuel the fire and prevents the loss of fire suppression agents from the space. Recently, a vessel with an installed fixed CO 2 fire suppression system suffered extensive damage due to a fire that started in the engine room. During the fire-fighting efforts the crew reported that the engine room ventilation could not be secured. A post incident damage survey of the vessel revealed that the pressure switch used to secure the ventilation was located within the engine room. Members may wish to check the location of these switches onboard their vessels, and ensure that they are properly located. The report can be downloaded from
IMCA Safety Flash 10/11 September 2011
 IMCA Safety Flash 10/11 September 2011 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learnt from them. The information below has been provided in good
IMCA Safety Flash 10/11 September 2011 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learnt from them. The information below has been provided in good
Safety Flash. IMCA Safety Flash 07/13 May Near Miss: Failure of Gas Quad Fitting
 AB Safety Flash IMCA Safety Flash 07/13 May 2013 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learnt from them. The information below has been provided
AB Safety Flash IMCA Safety Flash 07/13 May 2013 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learnt from them. The information below has been provided
Safety Flash. IMCA Safety Flash 10/09 July Compact Fluorescent Lights Interfering with Communications Equipment
 AB Safety Flash IMCA Safety Flash 10/09 July 2009 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learnt from them. The information below has been provided
AB Safety Flash IMCA Safety Flash 10/09 July 2009 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learnt from them. The information below has been provided
Safety Flash. IMCA Safety Flash 08/10 December Welding of Shackles. 2 Lacerated Chin Caused by Flying Wedge
 AB Safety Flash IMCA Safety Flash 08/10 December 2010 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learnt from them. The information below has been
AB Safety Flash IMCA Safety Flash 08/10 December 2010 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learnt from them. The information below has been
Safety Flash. IMCA Safety Flash 16/13 October What is a Safety Flash?
 AB Safety Flash IMCA Safety Flash 16/13 October 2013 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learnt from them. The information below has been provided
AB Safety Flash IMCA Safety Flash 16/13 October 2013 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learnt from them. The information below has been provided
An airbag was attached to the WCR tool and inflated to allow the WCR tool to rotate on the pipeline and free the diver.
 AB Safety Flash IMCA Safety Flash 03/09 March 2009 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learnt from them. The information below has been provided
AB Safety Flash IMCA Safety Flash 03/09 March 2009 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learnt from them. The information below has been provided
This is a summary of the safety flash incidents reported during 2017, highlighting some trends worthy of note and one or two matters of interest.
 Safety Flash IMCA Safety Flash 01/18 January 2018 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learnt from them. The information below has been provided
Safety Flash IMCA Safety Flash 01/18 January 2018 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learnt from them. The information below has been provided
IMCA Safety Flash 08/03 July 2003
 A B IMCA Safety Flash 08/03 July 2003 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learned from them. The information below has been provided in good
A B IMCA Safety Flash 08/03 July 2003 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learned from them. The information below has been provided in good
Site of yoke being supported by shore-side crane
 AB Safety Flash IMCA Safety Flash 16/09 November 2009 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learnt from them. The information below has been
AB Safety Flash IMCA Safety Flash 16/09 November 2009 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learnt from them. The information below has been
IMCA Safety Flash 05/10 July 2010
 AB IMCA Safety Flash 05/10 July 2010 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learnt from them. The information below has been provided in good
AB IMCA Safety Flash 05/10 July 2010 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learnt from them. The information below has been provided in good
IMCA Safety Flash 08/05 July 2005
 AB IMCA Safety Flash 08/05 July 2005 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learned from them. The information below has been provided in good
AB IMCA Safety Flash 08/05 July 2005 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learned from them. The information below has been provided in good
SEVERE INJURY WITH HAND AMPUTATION AND SKULL FRACTURE
 HSE Bulletin Page no.1 SEVERE INJURY WITH HAND AMPUTATION AND SKULL FRACTURE Type of accident: Data of accident: Job position: Type of activity: Activity performed: Lost Time Injury March, 14 th 2003 Motorman
HSE Bulletin Page no.1 SEVERE INJURY WITH HAND AMPUTATION AND SKULL FRACTURE Type of accident: Data of accident: Job position: Type of activity: Activity performed: Lost Time Injury March, 14 th 2003 Motorman
THE BAKER REPORT HOW FINDINGS HAVE BEEN USED BY JOHNSON MATTHEY TO REVIEW THEIR MANUFACTURING OPERATIONS
 THE BAKER REPORT HOW FINDINGS HAVE BEEN USED BY JOHNSON MATTHEY TO REVIEW THEIR MANUFACTURING OPERATIONS Colin P. Lynas, Elizabeth Campbell and Hendrik J. Koornhof Johnson Matthey Catalysts This paper
THE BAKER REPORT HOW FINDINGS HAVE BEEN USED BY JOHNSON MATTHEY TO REVIEW THEIR MANUFACTURING OPERATIONS Colin P. Lynas, Elizabeth Campbell and Hendrik J. Koornhof Johnson Matthey Catalysts This paper
IMCA Safety Flash 03/00 July 2000
 AB IMCA Safety Flash 03/00 July 2000 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learned from them. The information below has been provided in good
AB IMCA Safety Flash 03/00 July 2000 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learned from them. The information below has been provided in good
Safety Flash. IMCA Safety Flash 08/09 June Near Miss Dropped Clump Weight
 AB Safety Flash IMCA Safety Flash 08/09 June 2009 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learnt from them. The information below has been provided
AB Safety Flash IMCA Safety Flash 08/09 June 2009 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learnt from them. The information below has been provided
IMCA Safety Flash 04/00 July 2000
 AB IMCA Safety Flash 04/00 July 2000 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learned from them. The information below has been provided in good
AB IMCA Safety Flash 04/00 July 2000 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learned from them. The information below has been provided in good
Risk assessment. Assessment details. Task. Introduction. Please complete the form as fully and accurately as you can. Assessors job title
 Risk assessment Introduction Please complete the form as fully and accurately as you can. Assessment details Name of organisation Assessor's name Assessors job title Any Company John Smith Manager Date
Risk assessment Introduction Please complete the form as fully and accurately as you can. Assessment details Name of organisation Assessor's name Assessors job title Any Company John Smith Manager Date
IMCA Safety Flash 11/03 September 2003
 AB IMCA Safety Flash 11/03 September 2003 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learned from them. The information below has been provided in
AB IMCA Safety Flash 11/03 September 2003 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learned from them. The information below has been provided in
Emergency Response Plans
 PO Box 2114 Woonona East NSW 2517 (WOLLONGONG) PTY LTD Ph: 0417 420 760 Fax: 02 4283 2216 A/H: 02 4283 7727 EPA Licence: 11788 ABN: 57 079 336 799 Unit 11 Lot 1 York Place Woonona NSW 2517 Emergency Response
PO Box 2114 Woonona East NSW 2517 (WOLLONGONG) PTY LTD Ph: 0417 420 760 Fax: 02 4283 2216 A/H: 02 4283 7727 EPA Licence: 11788 ABN: 57 079 336 799 Unit 11 Lot 1 York Place Woonona NSW 2517 Emergency Response
Savard Labor & Marine Staffing, Inc. Compressed Gas Safety Program Rev3/14
 Compressed Gas Safety Program Purpose: The purpose of this safety policy and procedure is to establish guidelines for the protection and safety of this company s employees who handle and use compressed
Compressed Gas Safety Program Purpose: The purpose of this safety policy and procedure is to establish guidelines for the protection and safety of this company s employees who handle and use compressed
Health and Safety Executive. Key aspects of HS(G) 253. Andrew Hall HID CI 1G. HM Specialist Inspector (Mechanical)
 Health and Safety Executive Key aspects of HS(G) 253 Andrew Hall HID CI 1G HM Specialist Inspector (Mechanical) Human Factors Human Failures can be grouped into: Errors And Violations Errors are not intended
Health and Safety Executive Key aspects of HS(G) 253 Andrew Hall HID CI 1G HM Specialist Inspector (Mechanical) Human Factors Human Failures can be grouped into: Errors And Violations Errors are not intended
IMCA Safety Flash 02/
 AB IMCA Safety Flash 02/10 2010 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learnt from them. The information below has been provided in good faith
AB IMCA Safety Flash 02/10 2010 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learnt from them. The information below has been provided in good faith
Isolation Lockout and Tagging
 PURPOSE To define the minimum system requirements for isolation of plant and equipment from hazardous substances, mechanical, electrical or other energy sources to protect all workers from personal injury
PURPOSE To define the minimum system requirements for isolation of plant and equipment from hazardous substances, mechanical, electrical or other energy sources to protect all workers from personal injury
WORK PROGRAMME. Draft amended guidelines for simulated launching of free-fall lifeboats
 E MARITIME SAFETY COMMITTEE 97th session Agenda item 19 MSC 97/INF.3 2 August 2016 ENGLISH ONLY WORK PROGRAMME Draft amended guidelines for simulated launching of free-fall lifeboats Submitted by the Marshall
E MARITIME SAFETY COMMITTEE 97th session Agenda item 19 MSC 97/INF.3 2 August 2016 ENGLISH ONLY WORK PROGRAMME Draft amended guidelines for simulated launching of free-fall lifeboats Submitted by the Marshall
Total s Golden rules
 Total s Golden rules Golden rule No. 12: Simultaneous operations or co-activities This presentation resumes in part the document that won an award at the 2011 World Day for Safety at work, written by:
Total s Golden rules Golden rule No. 12: Simultaneous operations or co-activities This presentation resumes in part the document that won an award at the 2011 World Day for Safety at work, written by:
Health and Safety Guidance Note No 37
 Health and Safety Guidance Note No 37 THE SAFE USE AND STORAGE OF GAS CYLINDERS Accidents involving gas cylinders can cause serious injury or even death. The legal term for gas cylinders is transportable
Health and Safety Guidance Note No 37 THE SAFE USE AND STORAGE OF GAS CYLINDERS Accidents involving gas cylinders can cause serious injury or even death. The legal term for gas cylinders is transportable
THE OSHA LOCK-OUT/TAG-OUT STANDARD
 PRESENTER'S GUIDE "LOCK-OUT/TAG-OUT" Training for THE OSHA LOCK-OUT/TAG-OUT STANDARD Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today...and Tomorrow OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM
PRESENTER'S GUIDE "LOCK-OUT/TAG-OUT" Training for THE OSHA LOCK-OUT/TAG-OUT STANDARD Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today...and Tomorrow OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM
(2) but does not include a shaft, trench or tunnel that is a mine or is part of the workings of a mine.
 Health and Safety Procedure - Confined Spaces Section 1 - Background and Purpose (1) Confined spaces are, for the purposes of this procedure, defined as the following which is the definition under the
Health and Safety Procedure - Confined Spaces Section 1 - Background and Purpose (1) Confined spaces are, for the purposes of this procedure, defined as the following which is the definition under the
A MESSAGE FROM THE MD
 A MESSAGE FROM THE MD The Life Saving Rules set out clear and simple dos and don ts covering activities with the highest potential safety risk and apply to all employees and contractors. The best-performing
A MESSAGE FROM THE MD The Life Saving Rules set out clear and simple dos and don ts covering activities with the highest potential safety risk and apply to all employees and contractors. The best-performing
This written Compressed Gas Plan is kept at the corporate office and in the written Safety & Health Program.
 Safety & Health Program 10627 Midwest Industrial Boulevard, St. Louis, MO Phone: 314-785-6425 Fax: 314-785-6426 Compressed Gas Plan Purpose It is the policy of EMA to permit only trained and authorized
Safety & Health Program 10627 Midwest Industrial Boulevard, St. Louis, MO Phone: 314-785-6425 Fax: 314-785-6426 Compressed Gas Plan Purpose It is the policy of EMA to permit only trained and authorized
There are three fuelling systems which use LNG/CNG and which may be found in vehicles today:
 UKRO Humberside Education Workshop 2017 NATURAL GAS POWERED VEHICLES Some LGV manufacturers (currently IVECO and SCANIA) are able to offer and Alternative Fueled vehicles that use Compresses Natural Gas
UKRO Humberside Education Workshop 2017 NATURAL GAS POWERED VEHICLES Some LGV manufacturers (currently IVECO and SCANIA) are able to offer and Alternative Fueled vehicles that use Compresses Natural Gas
Drum / cylinder handling
 Page 1 of 8 Drum / cylinder handling This Technical Measures Document covers the storage and handling of toxic and flammable substances in drums and cylinders and refers to relevant codes of practice and
Page 1 of 8 Drum / cylinder handling This Technical Measures Document covers the storage and handling of toxic and flammable substances in drums and cylinders and refers to relevant codes of practice and
RISK ASSESSMENT A UNIVERSITY GUIDE TO PRACTICAL RISK ASSESSMENT UNDER THE MANAGEMENT OF HEALTH AND SAFETY AT WORK REGULATIONS 1992
 RISK ASSESSMENT A UNIVERSITY GUIDE TO PRACTICAL RISK ASSESSMENT UNDER THE MANAGEMENT OF HEALTH AND SAFETY AT WORK REGULATIONS 1992 PERSONNEL DIVISION REVIEWED AUTUMN 1999 CONTENTS Page 1 INTRODUCTION 1
RISK ASSESSMENT A UNIVERSITY GUIDE TO PRACTICAL RISK ASSESSMENT UNDER THE MANAGEMENT OF HEALTH AND SAFETY AT WORK REGULATIONS 1992 PERSONNEL DIVISION REVIEWED AUTUMN 1999 CONTENTS Page 1 INTRODUCTION 1
Suitability of Work Equipment
 These regulations came into effect on the 5th December 1998 and replace PUWER 1992. They cover almost all equipment used at work, including tool box tools such as hammers, knives etc. They also cover machinery
These regulations came into effect on the 5th December 1998 and replace PUWER 1992. They cover almost all equipment used at work, including tool box tools such as hammers, knives etc. They also cover machinery
SAFETY POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL All Euramax Subsidiaries. Number K-3.0 Welding Safety Procedures
 Number K-3.0 Issued: 1/2009 Revised: 3/2016 Page 1 of 3 1.0 PURPOSE: To standardize procedures associated with production and maintenance welding and to minimize the potential risk of accident or injury
Number K-3.0 Issued: 1/2009 Revised: 3/2016 Page 1 of 3 1.0 PURPOSE: To standardize procedures associated with production and maintenance welding and to minimize the potential risk of accident or injury
U.S. CONCRETE, INC. SAFETY POLICY and PROCEDURE MANUAL
 SAFE -14 Page 1 of 8 U.S. CONCRETE, INC. SAFETY POLICY and PROCEDURE MANUAL FUNCTION Safety TOPIC Hotwork Permit Program OBJECTIVE(S): GENERAL POLICY: To provide a work atmosphere that is conducive to
SAFE -14 Page 1 of 8 U.S. CONCRETE, INC. SAFETY POLICY and PROCEDURE MANUAL FUNCTION Safety TOPIC Hotwork Permit Program OBJECTIVE(S): GENERAL POLICY: To provide a work atmosphere that is conducive to
Version 1.0 March 2016
 POL Permit to Work Information for Shipping Agents Version 1.0 March 2016 Page 1 of 9 Introduction The objective of the Permit to Work process is to ensure Port Otago Limited and its operational Staff,
POL Permit to Work Information for Shipping Agents Version 1.0 March 2016 Page 1 of 9 Introduction The objective of the Permit to Work process is to ensure Port Otago Limited and its operational Staff,
Section 4. Fundamentals of Accident/Incident Prevention. Accidents/Incidents are Preventable
 Fundamentals of Accident/Incident Prevention Accidents/Incidents are Preventable Many people believe that accidents are the inevitable result of unchangeable circumstances, fate, or a matter of bad luck.
Fundamentals of Accident/Incident Prevention Accidents/Incidents are Preventable Many people believe that accidents are the inevitable result of unchangeable circumstances, fate, or a matter of bad luck.
1. Objective of the initiative To ensure that all employees and subcontractors are aware of the risks associated with working at height.
 Safety Initiative 02 Working at Height May 2011 CONTENTS 1. Objective of the initiative 2. Overview. 3. Implementation 4. Duties 5. Hierarchy of Controls 6. Workplace Inspections 7. Fragile Surfaces 8.
Safety Initiative 02 Working at Height May 2011 CONTENTS 1. Objective of the initiative 2. Overview. 3. Implementation 4. Duties 5. Hierarchy of Controls 6. Workplace Inspections 7. Fragile Surfaces 8.
SERIES & NO. SMI - 115
 1 of 7 1.0 PURPOSE To provide a system of handling and storing compressed gas and fuel gas cylinders. This instruction details the materials and methods used to handle and store cylinders. All contractors
1 of 7 1.0 PURPOSE To provide a system of handling and storing compressed gas and fuel gas cylinders. This instruction details the materials and methods used to handle and store cylinders. All contractors
PLANT HAZARD AND EQUIPMENT RISK ASSESSMENT
 Plant Identification : HAULOTTE LIGHT BOOMS 3522A (HTA 13P); 4527A (HTA 16P); 5533A (HTA 19P) and 3632T (HTT 13) Potential Hazard Entanglement Can anything become entangled in moving parts? Crushing/Striking
Plant Identification : HAULOTTE LIGHT BOOMS 3522A (HTA 13P); 4527A (HTA 16P); 5533A (HTA 19P) and 3632T (HTT 13) Potential Hazard Entanglement Can anything become entangled in moving parts? Crushing/Striking
INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF CLASSIFICATION SOCIETIES. Interpretations of the. IGF Code
 INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF CLASSIFICATION SOCIETIES s of the IGF Code CONTENTS GF1 Test for gas fuel tank s high level alarm Rev.1 July 2017 GF2 Ship Steel Protection against Liquefied Gas Fuel (Part
INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF CLASSIFICATION SOCIETIES s of the IGF Code CONTENTS GF1 Test for gas fuel tank s high level alarm Rev.1 July 2017 GF2 Ship Steel Protection against Liquefied Gas Fuel (Part
Low Voltage Electricity System Safety Rules & Associated Safety Guidance
 Annex J To Loughborough University Facilities Management (FM) Health and Safety Policy Low Voltage Electricity System Safety Rules & Associated Safety Guidance 1. Introduction a. These Safety Rules are
Annex J To Loughborough University Facilities Management (FM) Health and Safety Policy Low Voltage Electricity System Safety Rules & Associated Safety Guidance 1. Introduction a. These Safety Rules are
EXHIBITION Guide. Roles and Responsibilities OS11. A handbook for exhibitors and contractors
 Appendix 1 Health & Safety Declaration, Roles and Responsibilities Each exhibitor and Informa appointed contractor must complete the Health and Safety Declaration form provided below to confirm they have
Appendix 1 Health & Safety Declaration, Roles and Responsibilities Each exhibitor and Informa appointed contractor must complete the Health and Safety Declaration form provided below to confirm they have
Surface Supplied Mixed Gas Diving Operations
 AB The International Marine Contractors Association Surface Supplied Mixed Gas Diving Operations www.imca-int.com IMCA D 030 Rev. 1 August 2005 AB The International Marine Contractors Association (IMCA)
AB The International Marine Contractors Association Surface Supplied Mixed Gas Diving Operations www.imca-int.com IMCA D 030 Rev. 1 August 2005 AB The International Marine Contractors Association (IMCA)
PASSENGER SHIPS Guidelines for preparation of Hull Structural Surveys
 (Feb 2010) PASSENGER SHIPS Guidelines for preparation of Hull Structural Surveys Contents 1 Introduction 2 Preparations for Survey 2.1 General 2.2 Conditions for survey 2.3 Access to structures 2.4 Survey
(Feb 2010) PASSENGER SHIPS Guidelines for preparation of Hull Structural Surveys Contents 1 Introduction 2 Preparations for Survey 2.1 General 2.2 Conditions for survey 2.3 Access to structures 2.4 Survey
SLOP RECEPTION AND PROCESSING FACILITIES
 RULES FOR CLASSIFICATION OF SHIPS NEWBUILDINGS SPECIAL SERVICE AND TYPE ADDITIONAL CLASS PART 5 CHAPTER 8 SLOP RECEPTION AND PROCESSING FACILITIES JANUARY 2011 CONTENTS PAGE Sec. 1 General Requirements...
RULES FOR CLASSIFICATION OF SHIPS NEWBUILDINGS SPECIAL SERVICE AND TYPE ADDITIONAL CLASS PART 5 CHAPTER 8 SLOP RECEPTION AND PROCESSING FACILITIES JANUARY 2011 CONTENTS PAGE Sec. 1 General Requirements...
Section J. How to develop safety elements for project safety management system. How to develop safety elements for project SMS
 Section J How to develop safety elements for project safety management system 1. Once the project management has developed or adopted a safety policy, it needs to develop safety elements to meet the objectives
Section J How to develop safety elements for project safety management system 1. Once the project management has developed or adopted a safety policy, it needs to develop safety elements to meet the objectives
Surface exploration drilling
 Checklist Surface exploration drilling This checklist is intended to assist employers to identify common hazards and manage risks associated with surface exploration drilling. June 2017 Background In surface
Checklist Surface exploration drilling This checklist is intended to assist employers to identify common hazards and manage risks associated with surface exploration drilling. June 2017 Background In surface
Confined Space Entry Safety Program
 Confined Space Entry Safety Program Table of Contents SCOPE...2 DEFINITIONS..2 PROGRAM ELEMENTS...3 SPACE EVALUATION...4 IDENTIFICATION AND CLASSIFICATION...4 POSTING...4 RECLASSIFICATION OF PERMIT SPACE...4
Confined Space Entry Safety Program Table of Contents SCOPE...2 DEFINITIONS..2 PROGRAM ELEMENTS...3 SPACE EVALUATION...4 IDENTIFICATION AND CLASSIFICATION...4 POSTING...4 RECLASSIFICATION OF PERMIT SPACE...4
Process Safety Management Of Highly Hazardous Chemicals OSHA 29 CFR
 Process Safety Management Of Highly Hazardous Chemicals OSHA 29 CFR 1910.119 PSM - Definition Not all refining hazards are caused by the same factors or involve ve the same degree of potential damage.
Process Safety Management Of Highly Hazardous Chemicals OSHA 29 CFR 1910.119 PSM - Definition Not all refining hazards are caused by the same factors or involve ve the same degree of potential damage.
Spirax Compact FREME Flash Recovery Energy Management Equipment
 IM-UK-cFREME UK Issue 1 Spirax Compact FREME Flash Recovery Energy Management Equipment Installation and Maintenance Instructions 1. Safety information 2. General product information 3. Installation 4.
IM-UK-cFREME UK Issue 1 Spirax Compact FREME Flash Recovery Energy Management Equipment Installation and Maintenance Instructions 1. Safety information 2. General product information 3. Installation 4.
Chapter 2 Preparations for Tank Cleaning Work
 Chapter 2 Preparations for Tank Cleaning Work Preparatory Procedures for Tank Cleaning Work Make preparations for tank cleaning work according to the procedures given below. 1. Formulating the tank cleaning
Chapter 2 Preparations for Tank Cleaning Work Preparatory Procedures for Tank Cleaning Work Make preparations for tank cleaning work according to the procedures given below. 1. Formulating the tank cleaning
Confined Space Entry. My Experience so far.
 Confined Space Entry My Experience so far My Experience so far Complacency to Confined Space working Is the area a Confined Space No company procedures Poor risk assessments A lot of confusion Staff &
Confined Space Entry My Experience so far My Experience so far Complacency to Confined Space working Is the area a Confined Space No company procedures Poor risk assessments A lot of confusion Staff &
Control of Hazardous Energy Lockout / Tagout Program
 Control of Hazardous Energy Lockout / Tagout Program August 2016 Table of Contents Purpose... 1 Scope and Application... 1 Responsibilities... 1 Environmental Health and Safety Personnel (EH&S)... 1 Directors
Control of Hazardous Energy Lockout / Tagout Program August 2016 Table of Contents Purpose... 1 Scope and Application... 1 Responsibilities... 1 Environmental Health and Safety Personnel (EH&S)... 1 Directors
Working at Height. Policy and Procedures. Author: Beth Webster Assistant Safety Advisor. On behalf of School Safety Committee.
 Working at Height Policy and Procedures Author: Beth Webster Assistant Safety Advisor Authorised by: Issued by: John Stephenson Safety Office On behalf of School Safety Committee Review Date: NO LATER
Working at Height Policy and Procedures Author: Beth Webster Assistant Safety Advisor Authorised by: Issued by: John Stephenson Safety Office On behalf of School Safety Committee Review Date: NO LATER
Eliminating Dropped Objects at the Worksite
 Eliminating Dropped Objects at the Worksite Allen Smith, DROPS GLOBAL Eliminating Dropped Objects at the Worksite Allen Smith, DROPS GLOBAL ABOUT DROPS: dropsonline.org Oil & Gas Industry Workgroup focused
Eliminating Dropped Objects at the Worksite Allen Smith, DROPS GLOBAL Eliminating Dropped Objects at the Worksite Allen Smith, DROPS GLOBAL ABOUT DROPS: dropsonline.org Oil & Gas Industry Workgroup focused
EKC International FZE. Safety Instructions For Handling & Inspection Manual For Refillable Seamless Steel Gas Cylinders
 Safety Instructions For Handling & Inspection Manual For Refillable Seamless Steel Gas Cylinders MKT/WI/02 Page 1 of 6 1. Sensitivity of cylinder materials to operating conditions and their solution. Material
Safety Instructions For Handling & Inspection Manual For Refillable Seamless Steel Gas Cylinders MKT/WI/02 Page 1 of 6 1. Sensitivity of cylinder materials to operating conditions and their solution. Material
Periodic Survey of Fuel Installations on Ships other than Liquefied Gas Carriers utilizing gas or other low flash point fuels
 (Jan 2017) Periodic Survey of Fuel Installations on Ships other than Liquefied Gas Carriers utilizing gas or other low flash point fuels CONTENTS 1. Application 2. Special Survey 2.1 Schedule 2.2 Scope
(Jan 2017) Periodic Survey of Fuel Installations on Ships other than Liquefied Gas Carriers utilizing gas or other low flash point fuels CONTENTS 1. Application 2. Special Survey 2.1 Schedule 2.2 Scope
Instrument Operating Manual
 Instrument Operating Manual INDEX NO. SUBJECT PAGE 1 INFORMATION 3 2 SAFETY 4 3 INTENDED USE 4 4 COMMISSIONING & OPERATION 5 5 MAINTENANCE 6 2 INFORMATION The pressure gauges described in the operating
Instrument Operating Manual INDEX NO. SUBJECT PAGE 1 INFORMATION 3 2 SAFETY 4 3 INTENDED USE 4 4 COMMISSIONING & OPERATION 5 5 MAINTENANCE 6 2 INFORMATION The pressure gauges described in the operating
Digital Melting Point Apparatus
 Digital Melting Point Apparatus Heating Plateau Ramping Start/Stop Plateau set Ramp stop Hold User Guide Version 1.1 Heating Viewing tube Sample Chamber IEC power inlet socket Power on/off Temperature
Digital Melting Point Apparatus Heating Plateau Ramping Start/Stop Plateau set Ramp stop Hold User Guide Version 1.1 Heating Viewing tube Sample Chamber IEC power inlet socket Power on/off Temperature
SAFETY QUALITY TECHNOLOGY. Guidance on Safe Isolation Procedures
 SAFETY QUALITY TECHNOLOGY Guidance on Safe Isolation Procedures Introduction Every year, people working on construction sites suffer electric shock and burn injuries some of which, tragically, are fatal.
SAFETY QUALITY TECHNOLOGY Guidance on Safe Isolation Procedures Introduction Every year, people working on construction sites suffer electric shock and burn injuries some of which, tragically, are fatal.
The invisible killer - electrical safety in the food and drink industry
 The invisible killer - electrical safety in the food and drink industry Jackie Wooldridge Head of Health & Safety 2 Sisters Food Group A game of chance? - Introduction to electrical hazards 1. Take turns
The invisible killer - electrical safety in the food and drink industry Jackie Wooldridge Head of Health & Safety 2 Sisters Food Group A game of chance? - Introduction to electrical hazards 1. Take turns
To comply with the OHS Act, the responsible manager must carry out and document the following:
 Owner: Manager Health, Wellbeing and Safety Last Update: 10 January 2018 Contents 1. Purpose... 1 2. Minimum Compliance Requirements... 1 3. Definitions... 2 4. Legislative requirements under the OHS Act
Owner: Manager Health, Wellbeing and Safety Last Update: 10 January 2018 Contents 1. Purpose... 1 2. Minimum Compliance Requirements... 1 3. Definitions... 2 4. Legislative requirements under the OHS Act
Scope: This plan applies to all personnel, including contractors, who enter or work in confined spaces, or supervise such activities.
 11/13/1995 4 5/20/2013 1 of 10 Authority and Scope Regulation: 29 CFR 1910.146 Scope: This plan applies to all personnel, including contractors, who enter or work in confined spaces, or supervise such
11/13/1995 4 5/20/2013 1 of 10 Authority and Scope Regulation: 29 CFR 1910.146 Scope: This plan applies to all personnel, including contractors, who enter or work in confined spaces, or supervise such
HIGH-IMPACT. Leader s Guide
 Videos for Safety Meetings 9401 HIGH-IMPACT EYE SAFETY Leader s Guide MCMXCIV, ERI PRODUCTIONS HIGH-IMPACT EYE SAFETY This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation.
Videos for Safety Meetings 9401 HIGH-IMPACT EYE SAFETY Leader s Guide MCMXCIV, ERI PRODUCTIONS HIGH-IMPACT EYE SAFETY This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation.
SOUTHEAST REGIONAL MAINTENANCE CENTER LOCAL STANDARD ITEM CFR Part , Operator Qualification and Certification
 SOUTHEAST REGIONAL MAINTENANCE CENTER LOCAL STANDARD ITEM ITEM NO: 099-74SE DATE: 18 FEB 2014 CATEGORY: I 1. SCOPE: 1.1 Title: General Safety Requirements; accomplish 2. REFERENCES: 2.1 Standard Items
SOUTHEAST REGIONAL MAINTENANCE CENTER LOCAL STANDARD ITEM ITEM NO: 099-74SE DATE: 18 FEB 2014 CATEGORY: I 1. SCOPE: 1.1 Title: General Safety Requirements; accomplish 2. REFERENCES: 2.1 Standard Items
SOP GEN-007X Crane and Winch Operations
 Page 1 of 7 SOP GEN-007X 1.0 Introduction 2.0 Responsibility 3.0 References 4.0 Training and Qualifications 5.0 Operational Inspections 6.0 Maintenance and Load Tests 7.0 Cranes 8.0 Winches 9.0 Mobile
Page 1 of 7 SOP GEN-007X 1.0 Introduction 2.0 Responsibility 3.0 References 4.0 Training and Qualifications 5.0 Operational Inspections 6.0 Maintenance and Load Tests 7.0 Cranes 8.0 Winches 9.0 Mobile
CITY AND COUNTY OF DENVER CR&CF RISK UNIT Compressed Gas Safety Standard
 CITY AND COUNTY OF DENVER CR&CF RISK UNIT 65.5.11 Compressed Gas Safety Standard 1.0 Introduction 2.0 Scope This standard has been developed to protect all City and County of Denver employees and contractors
CITY AND COUNTY OF DENVER CR&CF RISK UNIT 65.5.11 Compressed Gas Safety Standard 1.0 Introduction 2.0 Scope This standard has been developed to protect all City and County of Denver employees and contractors
MANUAL GAS MANIFOLDS
 MANUAL GAS MANIFOLDS Phoenix Pipeline Products Limited. Unit 8, McKenzie Industrial Park, Tel No.: 44 (0) 161 428 7200 Bird Hall Lane, Fax No.: 44 (0) 161 428 7010 Stockport, Email: info@p3-phoenix.com
MANUAL GAS MANIFOLDS Phoenix Pipeline Products Limited. Unit 8, McKenzie Industrial Park, Tel No.: 44 (0) 161 428 7200 Bird Hall Lane, Fax No.: 44 (0) 161 428 7010 Stockport, Email: info@p3-phoenix.com
PSSI 36 General Confined Spaces, Tunnels, Culverts and Similar Spaces
 1. SCOPE This document now includes provision for safe access to cable tunnels and culverts previously covered in PSSI 37 which is now withdrawn. The term Confined Space is defined in the Confined Spaces
1. SCOPE This document now includes provision for safe access to cable tunnels and culverts previously covered in PSSI 37 which is now withdrawn. The term Confined Space is defined in the Confined Spaces
US Pipelines & Logistics Contractor Toolkit
 US Pipelines & Logistics Contractor Toolkit Contents Q2 2017 Golden Rules spotlight Energy isolation WYE? What s Your Exposure? HSSE safety share Trailer safety awareness Lessons learned Root cause analysis:
US Pipelines & Logistics Contractor Toolkit Contents Q2 2017 Golden Rules spotlight Energy isolation WYE? What s Your Exposure? HSSE safety share Trailer safety awareness Lessons learned Root cause analysis:
Fire Safety Hot Work Permit Policy/ Procedures
 Fire Safety Hot Work Permit Policy/ Procedures INTRODUCTION Serious fires frequently occur during maintenance and construction operations, where work is proceeding on either machinery, plant or the fabric
Fire Safety Hot Work Permit Policy/ Procedures INTRODUCTION Serious fires frequently occur during maintenance and construction operations, where work is proceeding on either machinery, plant or the fabric
GAS FUEL VALVE FORM AGV5 OM 8-03
 ALTRONIC AGV5 OPERATING MANUAL GAS FUEL VALVE FORM AGV5 OM 8-03 WARNING: DEVIATION FROM THESE INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS MAY LEAD TO IMPROPER ENGINE OPERATION WHICH COULD CAUSE PERSONAL INJURY TO OPERATORS
ALTRONIC AGV5 OPERATING MANUAL GAS FUEL VALVE FORM AGV5 OM 8-03 WARNING: DEVIATION FROM THESE INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS MAY LEAD TO IMPROPER ENGINE OPERATION WHICH COULD CAUSE PERSONAL INJURY TO OPERATORS
ANNEX AMENDMENTS TO THE INTERNATIONAL CODE FOR FIRE SAFETY SYSTEMS (FSS CODE) CHAPTER 15 INERT GAS SYSTEMS
 Annex 3, page 2 ANNEX AMENDMENTS TO THE INTERNATIONAL CODE FOR FIRE SAFETY SYSTEMS (FSS CODE) CHAPTER 15 INERT GAS SYSTEMS The text of existing chapter 15 is replaced by the following: "1 Application This
Annex 3, page 2 ANNEX AMENDMENTS TO THE INTERNATIONAL CODE FOR FIRE SAFETY SYSTEMS (FSS CODE) CHAPTER 15 INERT GAS SYSTEMS The text of existing chapter 15 is replaced by the following: "1 Application This
AIDGC PRESENTATION MARCH 2006 HAZARDOUS AREAS STANDARDS & CLASSIFICATION
 AIDGC PRESENTATION MARCH 2006 HAZARDOUS AREAS STANDARDS & CLASSIFICATION Jeff Strath Principal Engineer Paterson Flood Engineers Pty Ltd www.pfe.com.au INTRODUCTION This presentation provides an overview
AIDGC PRESENTATION MARCH 2006 HAZARDOUS AREAS STANDARDS & CLASSIFICATION Jeff Strath Principal Engineer Paterson Flood Engineers Pty Ltd www.pfe.com.au INTRODUCTION This presentation provides an overview
IMCA Safety Flash 02/03 February 2003
 AB IMCA Safety Flash 02/03 February 2003 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learned from them. The information below has been provided in
AB IMCA Safety Flash 02/03 February 2003 These flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing wider dissemination of lessons learned from them. The information below has been provided in
Hampstead Hill School Health and Safety Policy: Confined Spaces
 All Hampstead Hill School Policies are always to be read and considered in conjunction with Equal Opportunities, Race Equality and Inclusion Policies. This Policy of Hampstead Hill School applies to all
All Hampstead Hill School Policies are always to be read and considered in conjunction with Equal Opportunities, Race Equality and Inclusion Policies. This Policy of Hampstead Hill School applies to all
Ocean Observatories Initiative. Coastal & Global Scale Nodes. Hydrogen Safety. OOI Surface Mooring Hydrogen Safety Review
 Ocean Observatories Initiative Coastal & Global Scale Nodes Hydrogen Safety CP01 Mooring Timeline: 21 November 2013: CP01CNSM was deployed and transitioned to shore controlled operations. 17 Feb. 2014:
Ocean Observatories Initiative Coastal & Global Scale Nodes Hydrogen Safety CP01 Mooring Timeline: 21 November 2013: CP01CNSM was deployed and transitioned to shore controlled operations. 17 Feb. 2014:
Safe management of industrial steam and hot water boilers A guide for owners, managers and supervisors of boilers, boiler houses and boiler plant
 Health and Safety Executive Safe management of industrial steam and hot water boilers A guide for owners, managers and supervisors of boilers, boiler houses and boiler plant Background Accidents involving
Health and Safety Executive Safe management of industrial steam and hot water boilers A guide for owners, managers and supervisors of boilers, boiler houses and boiler plant Background Accidents involving
Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment Form. Risk Assessment
 Identification and Assessment Form Assessment Tool & Machine Work General Various injuries (including potential fatalities) All staff complete safety induction programme at the start of the module. instructed
Identification and Assessment Form Assessment Tool & Machine Work General Various injuries (including potential fatalities) All staff complete safety induction programme at the start of the module. instructed
IMCA DP Station Keeping Bulletin 04/18 November 2018
 DP STATION KEEPING BULLETIN IMCA DP Station Keeping Bulletin 04/18 November 2018 The following event trees have been compiled from recent reports received by IMCA. The originators granted IMCA permission
DP STATION KEEPING BULLETIN IMCA DP Station Keeping Bulletin 04/18 November 2018 The following event trees have been compiled from recent reports received by IMCA. The originators granted IMCA permission
Entry Level Requirements and Basic Introductory Course Outline for New Remotely Operated Vehicle (ROV) Personnel
 AB Entry Level Requirements and Basic Introductory Course Outline for New Remotely Operated Vehicle (ROV) Personnel International Marine Contractors Association www.imca-int.com IMCA R 002 Rev. 2 May 2009
AB Entry Level Requirements and Basic Introductory Course Outline for New Remotely Operated Vehicle (ROV) Personnel International Marine Contractors Association www.imca-int.com IMCA R 002 Rev. 2 May 2009
Songa Mercur King Post Failure
 Songa Mercur King Post Failure Mike Ferguson Mercur Rig Manager DrillSafe Forum Brisbane 3 Dec 2009 King Post Failure 1. The Songa Mercur 2. The incident 3. Background to the incident 4. Consequence 5.
Songa Mercur King Post Failure Mike Ferguson Mercur Rig Manager DrillSafe Forum Brisbane 3 Dec 2009 King Post Failure 1. The Songa Mercur 2. The incident 3. Background to the incident 4. Consequence 5.
Original Date of Issue: 04/09
 POLICIES AND PROCEDURES DEPARTMENT: Environmental Health and Safety SUBJECT: Electrical Safety Program Original Date of Issue: 04/09 Reviewed 12/2011 Revised 12/2011 BACKGROUND ELECTRIC SHOCK It is well
POLICIES AND PROCEDURES DEPARTMENT: Environmental Health and Safety SUBJECT: Electrical Safety Program Original Date of Issue: 04/09 Reviewed 12/2011 Revised 12/2011 BACKGROUND ELECTRIC SHOCK It is well
This document provides guidance to conducting health and safety inspections at the University, to ensure Hazards are identified and controlled.
 Health and Safety Guideline: HSG 10.1 Health and Safety Inspections and Testing 1. Purpose This document provides guidance to conducting health and safety inspections at the University, to ensure Hazards
Health and Safety Guideline: HSG 10.1 Health and Safety Inspections and Testing 1. Purpose This document provides guidance to conducting health and safety inspections at the University, to ensure Hazards
Safety Services Guidance. Guidance on: The Provision and Use of Work Equipment Regulations 1998 (PUWER)
 Guidance on: The Provision and Use of Work Equipment Regulations 1998 (PUWER) Key word(s) : Work equipment. Using, maintaining and repairing. Information, instruction and supervision. Risk Assessment.
Guidance on: The Provision and Use of Work Equipment Regulations 1998 (PUWER) Key word(s) : Work equipment. Using, maintaining and repairing. Information, instruction and supervision. Risk Assessment.
AUTOMATIC GAS MANIFOLDS
 AUTOMATIC GAS MANIFOLDS Phoenix Pipeline Products Limited. Unit 8, McKenzie Industrial Park, Tel No.: 44 (0) 161 428 7200 Bird Hall Lane, Fax No.: 44 (0) 161 428 7010 Stockport, Email: info@p3-phoenix.com
AUTOMATIC GAS MANIFOLDS Phoenix Pipeline Products Limited. Unit 8, McKenzie Industrial Park, Tel No.: 44 (0) 161 428 7200 Bird Hall Lane, Fax No.: 44 (0) 161 428 7010 Stockport, Email: info@p3-phoenix.com
DSEAR- Storage, Use and handling of gas cylinders guidance.
 OHSS: Storage, Use and handling of gas cylinders guidance 202 DSEAR- Storage, Use and handling of gas cylinders guidance. Contents Introduction... 2 General recommendations for storage, use and handling....
OHSS: Storage, Use and handling of gas cylinders guidance 202 DSEAR- Storage, Use and handling of gas cylinders guidance. Contents Introduction... 2 General recommendations for storage, use and handling....
THE UNIVERSITY OF SHEFFIELD ACCIDENT AND INCIDENT REPORTING AND INVESTIGATION POLICY AND PROCEDURES
 THE UNIVERSITY OF SHEFFIELD ACCIDENT AND INCIDENT REPORTING AND INVESTIGATION POLICY AND PROCEDURES Page 1 of 10 Document Created November 2012 CONTENTS Page No 1 INTRODUCTION 3 2 REPORTING ACCIDENTS,
THE UNIVERSITY OF SHEFFIELD ACCIDENT AND INCIDENT REPORTING AND INVESTIGATION POLICY AND PROCEDURES Page 1 of 10 Document Created November 2012 CONTENTS Page No 1 INTRODUCTION 3 2 REPORTING ACCIDENTS,
GUIDANCE FOR MANAGING THE RISKS ASSOCIATED WITH END OF LIFE LPG VEHICLES
 GUIDANCE FOR MANAGING THE RISKS ASSOCIATED WITH END OF LIFE LPG VEHICLES NSW QUAD BIKE SAFETY IMPROVEMENT PROGRAM SNAPSHOT 2016 17 Disclaimer This publication may contain information about the regulation
GUIDANCE FOR MANAGING THE RISKS ASSOCIATED WITH END OF LIFE LPG VEHICLES NSW QUAD BIKE SAFETY IMPROVEMENT PROGRAM SNAPSHOT 2016 17 Disclaimer This publication may contain information about the regulation
Permit To Work. A permit to work system is designed to ensure that all necessary actions are taken before,during,and after most of task on plant.
 Permit To Work A permit to work system is designed to ensure that all necessary actions are taken before,during,and after most of task on plant. Permit to work are formal documents specifying the work
Permit To Work A permit to work system is designed to ensure that all necessary actions are taken before,during,and after most of task on plant. Permit to work are formal documents specifying the work
SOP. Working in Confined Spaces
 Purpose This procedure outlines the requirements for the management of entry into confined spaces in all work areas with the intention of minimising risks to health and safety from any potential hazards
Purpose This procedure outlines the requirements for the management of entry into confined spaces in all work areas with the intention of minimising risks to health and safety from any potential hazards
PSM TRAINING COURSES. Courses can be conducted in multi-languages
 Courses can be conducted in multi-languages One set of hardcopy course notes will be sent to client for printing and distribution to course participants. The courses will be held at the client s training
Courses can be conducted in multi-languages One set of hardcopy course notes will be sent to client for printing and distribution to course participants. The courses will be held at the client s training
Working Environment Safety Assessment
 For your own safety and/or safety of your workforce, and to improve the efficiency of your business practices, you should be aware of, and be up to date with, the key safety issues and good practices relevant
For your own safety and/or safety of your workforce, and to improve the efficiency of your business practices, you should be aware of, and be up to date with, the key safety issues and good practices relevant
Identify Hazards, Before They Identify You! ~Jayson Stoddard~
 2015 Mine Safety Welcome! Identify Hazards, Before They Identify You! ~Jayson Stoddard~ Working Together to Achieve 0 Incidents Report All Incidents This would be any and all injuries as well as near miss
2015 Mine Safety Welcome! Identify Hazards, Before They Identify You! ~Jayson Stoddard~ Working Together to Achieve 0 Incidents Report All Incidents This would be any and all injuries as well as near miss
Technical Information
 Subject Information for Boat Davit Limit Switches from the UK Government and Marshall Islands Government To whom it may concern Technical Information No. TEC-0865 Date 28 September 2011 The UK Government
Subject Information for Boat Davit Limit Switches from the UK Government and Marshall Islands Government To whom it may concern Technical Information No. TEC-0865 Date 28 September 2011 The UK Government
PART Q CONTROL OF HAZARDOUS ENERGY (LOCKOUT-TAGOUT)
 PART Q CONTROL OF HAZARDOUS ENERGY (LOCKOUT-TAGOUT) WAC Page 296-307-320 Control of hazardous energy (lockout-tagout). 1 296-307-32001 What does this section cover? 1 296-307-32003 When does this section
PART Q CONTROL OF HAZARDOUS ENERGY (LOCKOUT-TAGOUT) WAC Page 296-307-320 Control of hazardous energy (lockout-tagout). 1 296-307-32001 What does this section cover? 1 296-307-32003 When does this section
Accident Report. San Constanzo Flooding approximately 35 miles east of Gisborne on 18 January 2004
 Accident Report San Constanzo Flooding approximately 35 miles east of Gisborne on 18 January 2004 SUMMARY Leaking seams in the vessel s wooden hull, allowed water to enter the vessel and flood the forward
Accident Report San Constanzo Flooding approximately 35 miles east of Gisborne on 18 January 2004 SUMMARY Leaking seams in the vessel s wooden hull, allowed water to enter the vessel and flood the forward
