Title Tsunami during 2011 East Japan Eart. The final publication is available より本文ファイルは に公開.
|
|
|
- Shannon Allison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Title Combined Failure Mechanism of a Bre Tsunami during 2011 East Japan Eart Author(s) Iai, Susumu Citation Geotechnical, Geological and Earthq 37: Issue Date URL The final publication is available Righthttp://dx.doi.org/ / より本文ファイルは に公開. Type Journal Article Textversion author Kyoto University
2 Combined Failure Mechanism of a Breakwater Subject to Tsunami during 2011 East Japan Earthquake Susumu Iai Professor, Disaster Prevention Research Institute, Kyoto University, Japan ABSTRACT In this study, a centrifuge model tests and effective stress analyses are performed on a breakwater subject to Tsunami such as those serious damaged during 2011 East Japan Earthquake (Magnitude 9.0). The centrifuge model tests at a scale of 1/200 are performed to simulate the failure of a breakwater subject to Tsunami. With the effective stress analyses, this study demonstrates the importance of the mechanism of failure in the rubble mound due to seepage flow of pore water in addition to the force of Tsunami action. Keywords: breakwater, failure mechanism, Tsunami, seepage flow INTRODUCTION An earthquake with a Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) magnitude 9.0 hit north east Japan at 14:46, March 11, JMA named this earthquake 2011 Tohoku-Pacific Ocean earthquake. This earthquake is the greatest in its magnitude since the modern earthquake monitoring system was established in Japan. Recorded heights of the tsunamis were higher than 7.3m at Soma, higher than 4.2m at Oarai, and higher than 4.1m at Kamaishi. The impact of the tsunamis is also the greatest since the existing design methodology was adopted for designing breakwaters. The existing design methodology of a breakwater is based on limit equilibrium by considering wave force acting from the lateral side and additional pressure acting underneath the caisson as shown in Figure 1. The most typical example of the damage to breakwater was the one at the Kamaishi Harbor. In this example, the breakwater was specifically designed for protection against the impact of tsunami and constructed at the mouth of the Kamaishi harbor at a depth of 63m or less over the length of 990m in the northern part and 670m in the southern part 1
3 with an opening of 300m in between. However, the breakwater was devastated by the tsunami. This may be partly due to the failure of design procedure then adopted but also a symbolic event for indicating the serious impact by the tsunami. Figure 2 shows a typical cross section of the break water. The breakwater is a composite of caisson and rubble mound. Based on the visual data (video) monitored from the coastal line, the first arrival of the tsunami was at about 15:24 (about 40 minutes after the earthquake). The break water was not damaged by this first arrival of the tsunami. Figure 1 Existing design procedure of a breakwater Figure 2 Cross section of a composite breakwater at Kamaishi Harbour (unit in m) 2
4 However, there was a continual overtopping of water at the top of the breakwater. At about 15:32, when the height of the tsunami was reduced, serious devastation of the breakwater was visually confirmed by the monitored visual data. At 15:59, the devastation was progressed further and many of the caissons fell into the harbor side from the rubble mound. The rubble mound was also seriously devastated even to the extent that about half of its original body of the rubble mound was lost. In order to investigate the primary mechanism of failure of this type of a breakwater due to Tsunami, a series of centrifuge model tests and effective analyses are performed in this study. As a straight forward extension of the existing design procedure shown in Figure 1, the primary mechanism of failure was considered by a hydrodynamics expert group due to erosion of rubble mound by the water flow through opening between caissons as shown in Figure 3. As parallel efforts to that group, this study was performed with the objective of evaluating the effect of seepage flow through the rubble mound due to water head difference due to Tsunami in combination with the wave force action. Figure 3 Primary mechanism of failure hypothesized by a hydrodynamics expert group CENTRIFUGE MODEL TESTS Tsunami Generator in Centrifuge and Model Test Conditions 3
5 The centrifuge at Disaster Prevention Research Institute, Kyoto University, (effective radius 2.5m) was used for the centrifuge model tests in this study. The equipment for simulating Tsunami in the centrifuge is shown in Figure 4. In this equipment, the remote-control valve at the bottom of the water tank is opened for generating Tsunami-like water flow toward caisson and overflowing water at the other end of the model (left in this figure) is absorbed in a tentative storage pit for reducing the effect of reflecting wave from the (left side) wall of the container. The centrifuge model tests were performed for a caisson 21m high in prototype with a scaling factor of 1/200 by adopting the generalized scaling relation (Iai et al. 2005) in a 25g centrifugal acceleration field. Four cases were performed by varying initial sea water level and water level difference due to Tsunami as shown in Table 1. The material of rubble mound was also varied by using Silica No.1 sand that consists of particles scaled in 1/200 of the prototype rubble and Silica No.4 sand that artificially reduces the effect of seepage flow in the rubble mound. Pure water was used for centrifuge tests. The rubble mound model was made by water pluviation. 4
6 Figure 4 Equipment for simulating Tsunami in centrifuge model tests (unit in mm in model scale) Table 1 Model test cases Centrifuge Test Results Figure 5 shows the results of the centrifuge test for Cases-2 and 4 with respect to the deformation. As described earlier, Case-2 was performed for simulating the prototype condition. As shown in (a-1) in this figure, when the Tsunami at the water level difference of 10.3m acts on the caisson, the caisson remains standing without deformation. At the same time, bubbles appear on the bay side (left side), indicating that a seepage flow of water through the rubble mound begins at this instance. After a certain period of time ((a-2) in the same figure), rubble mound gradually deforms in a bearing capacity failure mode with inclined load together with the caisson toward the direction of Tsunami wave force. The caisson eventually falls down from the rubble mound and the rubble mound exhibits a residual failure mode that resembles the classic circular failure mode. These failure modes of the caisson and the rubble mound are consistent with those investigated and identified at Kamaishi Harbour after 2011 East Japan earthquake. This fact is indicative of the fact that the mechanism of failure due to tsunami is considered due to the combined effect of seepage flow and wave action. However, the mechanism of erosion progressing from the harbor side also produces the similar failure mode. Thus, the mechanism of failure has to be studies further by performing effective stress analysis as described later. Case-4 was performed as comparison to Case-2 by artificially reducing the effect of seepage flow in the rubble mound. Even if artificially reduced, the effect of seepage flow still exists so that a combined failure mode is also observed as shown in (b-1) 5
7 through (b-3) in Figure 5. However, the failure mode in Case-4 is more or less dominated by sliding of caisson rather than deep failure mode of rabble mound. This fact indicate that if there is no seepage flow, then sliding failure mode will be dominant as often considered in the existing design procedure described earlier. (a-1) (b-1) (a-2) (b-2) (a-3) (b-3) (a) Case-2 (b) Case-4 Figure 5 Deformation of caisson and rubble mound model EFFECTIVE STRESS ANALYSIS Effective Stress Model For the effective stress analysis of a breakwater subject to seepage flow and wave action, the strain space multiple mechanism model with a cocktail glass model is used (Iai et al. 2011). In the strain space multiple mechanism model, the effective stress, defined as 6
8 extension positive, is given based on a dyad defined by the unit vector n along the direction of the branch between the particles in contact with each other and the unit vector t normal to n as follows: 1 σ ' = pi+ q dωdω 4π t n (1) t n = t n+ n t (2) where p denotes effective confining pressure (compression positive), I denotes second order identity tensor, q denotes micromechanical stress contributions to macroscopic deviator stress due to virtual simple shear mechanism (called virtual simple shear stress), and t n denotes second order tensor representing the virtual simple shear mechanism. Out of the double integration, the integration with respect to ( 0 through π) ω = is taken over a virtual plane spanned by the direction vectors n and t with ω /2 being the angle of n relative to the reference local coordinate defined in the virtual plane, while the integration with respect to the solid angle Ω is taken over a surface of a unit sphere to give a three dimensional average of two dimensional mechanisms. The integrated form of the constitutive equation, i.e. direct stress strain relationship, is derived by relating the macroscopic strain tensor ε to the macroscopic effective stress σ ' through the structure defined by Equation (1). The first step to derive this relationship is to define the volumetric strain ε (extension positive) and the virtual simple shear strains γ as the projections of the macroscopic strain field to the second order tensors representing volumetric and virtual simple shear mechanisms as follows: ε = I : ε (3) γ = t n : ε (4) where the double dot symbol denotes double contraction. In order to take into account the effect of volumetric strain due to dilatancy ε d, effective volumetric strain ε ' is introduced by ε' = ε εd (5) where the rate of volumetric strain due to dilatancy is given by the projection of strain rate field to a second order tensor I d as ε = I ε (6) d d : 7
9 The scalar variables defined in Equations (4) and (5) as the projection of macroscopic strain field are used to define the isotropic stress p and virtual simple shear stress q in Equation (1) through path dependent functions as p = p( ε ') (7) q = q( γ ) (8) In the strain space multiple mechanism model, the virtual simple shear mechanism is formulated as a non-linear hysteretic function, where a back-bone curve is given by the following hyperbolic function; γ / γv q( γ ) = qv 1 + γ / γ (9) v The parameters qv and γ v defining the hyperbolic function are the shear strength and the reference strain of the virtual simple shear mechanism, respectively. The isotropic component in Equation (7) is defined by a hysteretic tangential bulk modulus depending on the loading/unloading (L/U) condition as where p 0 : initial confining pressure, K pressure. K dp rk L/U = = K U0 d ε ' p0 U0 p l K : tangential bulk modulus at initial confining (10) Dilatancy in Equation (5) in the Cocktail glass model is decomposed into contractive component c d ε d and dilative component ε d as ε = ε + ε (11) c d d d d However, in this study, effect of dilatancy of the rubble mound was assumed negligibly small and dilatancy was ignored. Load Conditions for Simulating Tsunami The effective stress analysis of a breakwater was performed for prototype scaled from the centrifuge model, including a caisson 21m high. As shown in Figure 6, joint element is specified at the bottom of the caisson to allow sliding and separation between the 8
10 caisson and the rubble mound. After static gravity analysis to set the initial conditions for dynamic Tsunami analysis, Tsunami wave force was applied on the caisson as equivalent static distributed force as shown in Figure 7. In order to analyze the effect of seepage flow due to sea level difference, excess pore water pressure was applied at the rubble mound. External force due to sea level difference is also simulated by equivalent lateral static force on the caisson. Figure 6 Finite element mesh of a breakwater for analysis (prototype scale) Figure 7 Load conditions for simulating wave force due to Tsunami 9
11 Distribution and magnitude of the wave force due to Tsunami adopted for the analysis (Figure 7) was determined based on the proposal by Tanimoto et al (1984). This proposal has been also adopted in the existing design procedure of a breakwater (Figure 1). The effective stress analyses were performed for Cases-1 through 4 with the material parameters used for the rubble mound shown in Table 2. These parameters were determined by undrained cyclic shear tests using hollow cylinder specimen and by permeability test with constant water level difference. The initial sea levels for Cases-1 through 4 were simplified for the analysis as shown in Figure 6. The sea level differences were also simplified as 15m for Cases-1 and 3, and 11m for Cases-2 and 4. Table 2 Material parameters of rubble mound Results of the Effective Stress Analyses The results of analysis of Case-2 are presented below. Figure 8 (a) shows residual deformation of a breakwater with both Tsunami wave force on the caisson and seepage flow in the rubble mound. The tilting of the caisson is associated with a significant deformation of rubble mound. This mode of failure is consistent with that observed at the centrifuge model test. In comparison to this result, deformation of a breakwater due to Tsunami wave force only is negligibly small as shown in Figure 8 (b). These results of the analyses indicate that primary mechanism of failure of a breakwater due to Tsunami is combined failure mechanism due to Tsunami wave force and seepage flow in the rubble mound due to water level difference associated with Tsunami. In addition, distribution of an inverse of safety factor with respect to Mohr-Coulomb failure criterion in the rubble mound is shown in Figure 9. As shown in Figure 9(a), the rubble mound beneath the caisson undergoes a compression shear due to the overburden from the caisson before Tsunami. When the Tsunami wave force and seepage flow act on the rubble mound, significant area of cross section of rubble mound are brought close to a shear failure condition as shown in Figure 9(b). However, if only the Tsunami 10
12 wave for acts, there is not a significant change in the rubble mound with respect to its stress status. These results also supports the previous notion that the primary mechanism of failure of a breakwater due to Tsunami is combined failure mechanism involving seepage flow in the rubble mound. (a) Analysis with wave force and seepage flow (b) Analysis with wave force only Figure 8 Residual deformation of a breakwater 11
13 (a) Initial condition for dynamic analysis (b) Residual status due to Tsunami wave force and seepage flow Index: 1/Safety Factor (c) Residual status due to Tsunami wave force only Figure 9 Distribution of 1/Safety Factor in the rubble mound CONCLUSIONS In this study, a centrifuge model tests and effective stress analyses are performed on a breakwater subject to Tsunami such as those serious damaged during 2011 East Japan Earthquake (Magnitude 9.0). Both the centrifuge model tests at a scale of 1/200 and the effective stress analyses demonstrate the importance of the mechanism of failure in the rubble mound due to seepage flow of pore water in addition to the wave force of Tsunami action. REREFERENCES: Iai, S., Tobita, T. and Nakahara, T. (2005): Generalized scaling relations for dynamic centrifuge tests, Geotechnique, 55(5):
14 Iai, S., Tobita, T., Ozutsumi, O. and Ueda, K. (2011): Dilatancy of granular materials in a strain space multiple mechanism model, International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 35(3): Tanimoto, K., Tsuruya, K., and Nakano, S. (1984): Tsunami wave force and failure mechanism of bulkhead due to Tsunami during 1983 Nihonkai-chubu earthquake, Proc. 31th Research Conference on Coastal Engineering, (in Japanese) 13
New Reinforcing Technique for Mitigation of Earthquake-induced Failure of Breakwater
 6 th International Conference on Earthquake Geotechnical Engineering 1-4 November 2015 Christchurch, New Zealand New Reinforcing Technique for Mitigation of Earthquake-induced Failure of Breakwater B.
6 th International Conference on Earthquake Geotechnical Engineering 1-4 November 2015 Christchurch, New Zealand New Reinforcing Technique for Mitigation of Earthquake-induced Failure of Breakwater B.
Analysis of dilatometer test in calibration chamber
 Analysis of dilatometer test in calibration chamber Lech Bałachowski Gdańsk University of Technology, Poland Keywords: calibration chamber, DMT, quartz sand, FEM ABSTRACT: Because DMT in calibration test
Analysis of dilatometer test in calibration chamber Lech Bałachowski Gdańsk University of Technology, Poland Keywords: calibration chamber, DMT, quartz sand, FEM ABSTRACT: Because DMT in calibration test
Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
 43 Module 3: Lecture - 5 on Compressibility and Consolidation Contents Stresses in soil from surface loads; Terzaghi s 1-D consolidation theory; Application in different boundary conditions; Ramp loading;
43 Module 3: Lecture - 5 on Compressibility and Consolidation Contents Stresses in soil from surface loads; Terzaghi s 1-D consolidation theory; Application in different boundary conditions; Ramp loading;
STUDY ON TSUNAMI PROPAGATION INTO RIVERS
 ABSTRACT STUDY ON TSUNAMI PROPAGATION INTO RIVERS Min Roh 1, Xuan Tinh Nguyen 2, Hitoshi Tanaka 3 When tsunami wave propagation from the narrow river mouth, water surface is raised and fluctuated by long
ABSTRACT STUDY ON TSUNAMI PROPAGATION INTO RIVERS Min Roh 1, Xuan Tinh Nguyen 2, Hitoshi Tanaka 3 When tsunami wave propagation from the narrow river mouth, water surface is raised and fluctuated by long
SHAKING TABLE TESTS AND EFFECTIVE STRESS ANALYSES ON THE DYNAMIC BEHAVIOR OF WEDGED CAISSONS
 SHAKING TABLE TESTS AND EFFECTIVE STRESS ANALYSES ON THE DYNAMIC BEHAVIOR OF WEDGED CAISSONS Takahiro SUGANO 1, Katsumi KISHITANI 2, Masaaki MITO 3, Kou NISHINAKAGAWA 4, Shin'ichi IDO 5, Masanori SHIMA
SHAKING TABLE TESTS AND EFFECTIVE STRESS ANALYSES ON THE DYNAMIC BEHAVIOR OF WEDGED CAISSONS Takahiro SUGANO 1, Katsumi KISHITANI 2, Masaaki MITO 3, Kou NISHINAKAGAWA 4, Shin'ichi IDO 5, Masanori SHIMA
FRAGILITY CURVES FOR GRAVITY-TYPE QUAY WALLS BASED ON EFFECTIVE STRESS ANALYSES
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 24 Paper No. 34 FRAGILITY CURVES FOR GRAVITY-TYPE QUAY WALLS BASED ON EFFECTIVE STRESS ANALYSES Koji ICHII 1 SUMMARY
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 24 Paper No. 34 FRAGILITY CURVES FOR GRAVITY-TYPE QUAY WALLS BASED ON EFFECTIVE STRESS ANALYSES Koji ICHII 1 SUMMARY
Critical Pool Level and Stability of Slopes in Granular Soils
 TECHNICAL NOTES Critical Pool Level and Stability of Slopes in Granular Soils Radoslaw L. Michalowski, F.ASCE 1 Abstract: The influence of pore-water pressure and the pool water pressure on stability of
TECHNICAL NOTES Critical Pool Level and Stability of Slopes in Granular Soils Radoslaw L. Michalowski, F.ASCE 1 Abstract: The influence of pore-water pressure and the pool water pressure on stability of
The Failure of the Kamaishi Tsunami Protection Breakwater
 PT-13: Coastal and Ocean Engineering ENGI.8751 Undergraduate Student Forum Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science, Memorial University, St. John s, NL, Canada March, 2013 Paper Code. (PT-13 - Tucker)
PT-13: Coastal and Ocean Engineering ENGI.8751 Undergraduate Student Forum Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science, Memorial University, St. John s, NL, Canada March, 2013 Paper Code. (PT-13 - Tucker)
COURSE NUMBER: ME 321 Fluid Mechanics I Fluid statics. Course teacher Dr. M. Mahbubur Razzaque Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BUET
 COURSE NUMBER: ME 321 Fluid Mechanics I Fluid statics Course teacher Dr. M. Mahbubur Razzaque Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BUET 1 Fluid statics Fluid statics is the study of fluids in
COURSE NUMBER: ME 321 Fluid Mechanics I Fluid statics Course teacher Dr. M. Mahbubur Razzaque Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BUET 1 Fluid statics Fluid statics is the study of fluids in
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 112 (2015 ) 40 45
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering ( ) 7th Asia-Pacific Congress on Sports Technology, APCST 3-Dimensional joint torque calculation of compression sportswear using
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering ( ) 7th Asia-Pacific Congress on Sports Technology, APCST 3-Dimensional joint torque calculation of compression sportswear using
THE EFFECT OF EMBEDMENT DEPTH ON BEARING CAPACITY OF STRIP FOOTING IN COHESIVE FRICTIONAL MEDIUM
 Proceedings of the 4 th International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2018), 9~11 February 2018, KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh (ISBN-978-984-34-3502-6) THE EFFECT OF EMBEDMENT
Proceedings of the 4 th International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2018), 9~11 February 2018, KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh (ISBN-978-984-34-3502-6) THE EFFECT OF EMBEDMENT
UNIT-I SOIL EXPLORATION
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : Geotechnical Engineering - II (16CE127) Year & Sem: III-B.Tech & II-Sem
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : Geotechnical Engineering - II (16CE127) Year & Sem: III-B.Tech & II-Sem
Learn more at
 Full scale model tests of a steel catenary riser C. Bridge 1, H. Howells 1, N. Toy 2, G. Parke 2, R. Woods 2 1 2H Offshore Engineering Ltd, Woking, Surrey, UK 2 School of Engineering, University of Surrey,
Full scale model tests of a steel catenary riser C. Bridge 1, H. Howells 1, N. Toy 2, G. Parke 2, R. Woods 2 1 2H Offshore Engineering Ltd, Woking, Surrey, UK 2 School of Engineering, University of Surrey,
Theory of a vertically loaded Suction Pile in CLAY
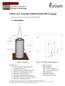 11 Theory of a vertically loaded Suction Pile in CLAY Mainly based on the et Norske Veritas NV-RP-E303 1. Convention Water COG h L Soil COG t Figure 1 Suction Pile Figure 2 Suction pile with main parameters
11 Theory of a vertically loaded Suction Pile in CLAY Mainly based on the et Norske Veritas NV-RP-E303 1. Convention Water COG h L Soil COG t Figure 1 Suction Pile Figure 2 Suction pile with main parameters
Cubzac-les-Ponts Experimental Embankments on Soft Clay
 Cubzac-les-Ponts Experimental Embankments on Soft Clay GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1, 7 - th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada TP T Main: +1 3 9 Fax: +1 3 39 Introduction In the 197 s, a series
Cubzac-les-Ponts Experimental Embankments on Soft Clay GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1, 7 - th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada TP T Main: +1 3 9 Fax: +1 3 39 Introduction In the 197 s, a series
Probabilistic Design Tools for Vertical Breakwaters
 Probabilistic Design Tools for Vertical Breakwaters HOCINE OUMERACI, ANDREAS KORTENHAUS Technical University of Braunschweig, Leichtweifi-Institut fur Wasserbau, Braunschweig, Germany WILLIAM ALLSOP HR
Probabilistic Design Tools for Vertical Breakwaters HOCINE OUMERACI, ANDREAS KORTENHAUS Technical University of Braunschweig, Leichtweifi-Institut fur Wasserbau, Braunschweig, Germany WILLIAM ALLSOP HR
An integrated three-dimensional model of wave-induced pore pressure and effective stresses in a porous seabed: II. Breaking waves
 An integrated three-dimensional model of wave-induced pore pressure and effective stresses in a porous seabed: II. Breaking waves Author Jeng, D., Zhang, Hong Published 2005 Journal Title Ocean Engineering
An integrated three-dimensional model of wave-induced pore pressure and effective stresses in a porous seabed: II. Breaking waves Author Jeng, D., Zhang, Hong Published 2005 Journal Title Ocean Engineering
Investigation of Stresses in Ring Stiffened Circular Cylinder
 International Journal of Engineering and Technical Research (IJETR) ISSN: 2321-869, Volume-2, Issue-9, September 214 Investigation of Stresses in Ring Stiffened Circular Cylinder Neetesh N. Thakre, Dr.
International Journal of Engineering and Technical Research (IJETR) ISSN: 2321-869, Volume-2, Issue-9, September 214 Investigation of Stresses in Ring Stiffened Circular Cylinder Neetesh N. Thakre, Dr.
Objectives deals with forces applied by fluids at rest or in rigid-body motion.
 Objectives deals with forces applied by fluids at rest or in rigid-body motion. The fluid property responsible for those forces is pressure, which is a normal force exerted by a fluid per unit area. discussion
Objectives deals with forces applied by fluids at rest or in rigid-body motion. The fluid property responsible for those forces is pressure, which is a normal force exerted by a fluid per unit area. discussion
Chapter 3 PRESSURE AND FLUID STATICS
 Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd Edition Yunus A. Cengel, John M. Cimbala McGraw-Hill, 2010 Chapter 3 PRESSURE AND FLUID STATICS Lecture slides by Hasan Hacışevki Copyright The McGraw-Hill
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd Edition Yunus A. Cengel, John M. Cimbala McGraw-Hill, 2010 Chapter 3 PRESSURE AND FLUID STATICS Lecture slides by Hasan Hacışevki Copyright The McGraw-Hill
WAVE LOAD ACTING ON HORIZONTAL PLATE DUE TO BORE
 Proceedings of the 6 th International Conference on the Application of Physical Modelling in Coastal and Port Engineering and Science (Coastlab16) Ottawa, Canada, May 10-13, 2016 Copyright : Creative Commons
Proceedings of the 6 th International Conference on the Application of Physical Modelling in Coastal and Port Engineering and Science (Coastlab16) Ottawa, Canada, May 10-13, 2016 Copyright : Creative Commons
REBUILDING COMPOSITE BREAKWATERS FOLLOWING THE 2011 TOHOKU TSUNAMI: LESSONS LEARNT AND DOES IT MAKE SENSE TO REINFORCE?
 Proceedings of Coastal Engineering, JCE, Vol.3, 212, November REBUILDING COMPOITE BREAKWATER FOLLOWING THE 211 TOHOKU TUNAMI: LEON LEARNT AND DOE IT MAKE ENE TO REINFORCE? Miguel Esteban1, Rafael Aranguiz
Proceedings of Coastal Engineering, JCE, Vol.3, 212, November REBUILDING COMPOITE BREAKWATER FOLLOWING THE 211 TOHOKU TUNAMI: LEON LEARNT AND DOE IT MAKE ENE TO REINFORCE? Miguel Esteban1, Rafael Aranguiz
Tresca s or Mises Yield Condition in Pressure Vessel Design
 Tresca s or Mises Yield Condition in Pressure Vessel Design Franz Rauscher Institute for Pressure Vessels and Plant Technology Vienna University of Technology Austria Why using Tresca s yield condition
Tresca s or Mises Yield Condition in Pressure Vessel Design Franz Rauscher Institute for Pressure Vessels and Plant Technology Vienna University of Technology Austria Why using Tresca s yield condition
Vertical Uplift Capacity of a Group of Equally Spaced Helical Screw Anchors in Sand
 SECM/15/080 Vertical Uplift Capacity of a Group of Equally Spaced Helical Screw Anchors in Sand S. Mukherjee 1* and Dr. S. Mittal 2 1 Amity University, Noida, India 2 Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee,
SECM/15/080 Vertical Uplift Capacity of a Group of Equally Spaced Helical Screw Anchors in Sand S. Mukherjee 1* and Dr. S. Mittal 2 1 Amity University, Noida, India 2 Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee,
Development of New Type of Breakwater Reinforced with Steel Piles against a Huge Tsunami
 Technical Report UDC 627. 235 : 550. 344. 4 Development of New Type of Breakwater Reinforced with Steel Piles against a Huge Tsunami Shunsuke MORIYASU* Shin OIKAWA Shinji TAENAKA Noriyoshi HARATA Ryuta
Technical Report UDC 627. 235 : 550. 344. 4 Development of New Type of Breakwater Reinforced with Steel Piles against a Huge Tsunami Shunsuke MORIYASU* Shin OIKAWA Shinji TAENAKA Noriyoshi HARATA Ryuta
APPENDIX G SCA BASIN CALCULATIONS
 ONONDAGA LAKE SEDIMENT MANAGEMENT FINAL DESIGN APPENDIX G SCA BASIN CALCULATIONS p:\honeywell -syr\444853 - lake detail design\09 reports\9.22 sediment management final design\110930 submittal\110906 onon
ONONDAGA LAKE SEDIMENT MANAGEMENT FINAL DESIGN APPENDIX G SCA BASIN CALCULATIONS p:\honeywell -syr\444853 - lake detail design\09 reports\9.22 sediment management final design\110930 submittal\110906 onon
2.1 Introduction to pressure vessels
 2.1 Introduction to pressure vessels Pressure vessels in the form of cylinders and tanks are used for storing variety of liquids and gasses at different temperatures and pressures. Some of the substances
2.1 Introduction to pressure vessels Pressure vessels in the form of cylinders and tanks are used for storing variety of liquids and gasses at different temperatures and pressures. Some of the substances
JSEE. Slope Stability and Bearing Capacity of Footings on Top of Slopes Under Repeated Dynamic Loads. 1. Introduction
 JSEE Vol. 18, No. 3, 2016 This is an extended version of the paper presented in SEE7 conference, peer-reviewed again and approved by the JSEE editorial board. Slope Stability and Bearing Capacity of Footings
JSEE Vol. 18, No. 3, 2016 This is an extended version of the paper presented in SEE7 conference, peer-reviewed again and approved by the JSEE editorial board. Slope Stability and Bearing Capacity of Footings
CHAPTER 5: VACUUM TEST WITH VERTICAL DRAINS
 CHAPTER 5: VACUUM TEST WITH VERTICAL DRAINS 5.1 Introduction Using surcharging as the sole soil consolidation mean can take a long time to reach the desired soil settlement. Soil consolidation using prefabricated
CHAPTER 5: VACUUM TEST WITH VERTICAL DRAINS 5.1 Introduction Using surcharging as the sole soil consolidation mean can take a long time to reach the desired soil settlement. Soil consolidation using prefabricated
DAMAGE TO STORAGE TANKS CAUSED BY THE 2011 TOHOKU EARTHQUAKE AND TSUNAMI AND PROPOSAL FOR STRUCTURAL ASSESSMENT METHOD FOR CYLINDRICAL STORAGE TANKS
 DAMAGE TO STORAGE TANKS CAUSED BY THE 2011 TOHOKU EARTHQUAKE AND TSUNAMI AND PROPOSAL FOR STRUCTURAL ASSESSMENT METHOD FOR CYLINDRICAL STORAGE TANKS Takashi Ibata Isho Nakachi Dr. Kazuo Ishida Junichi
DAMAGE TO STORAGE TANKS CAUSED BY THE 2011 TOHOKU EARTHQUAKE AND TSUNAMI AND PROPOSAL FOR STRUCTURAL ASSESSMENT METHOD FOR CYLINDRICAL STORAGE TANKS Takashi Ibata Isho Nakachi Dr. Kazuo Ishida Junichi
Numerical Simulations of a Train of Air Bubbles Rising Through Stagnant Water
 Numerical Simulations of a Train of Air Bubbles Rising Through Stagnant Water Hong Xu, Chokri Guetari ANSYS INC. Abstract Transient numerical simulations of the rise of a train of gas bubbles in a liquid
Numerical Simulations of a Train of Air Bubbles Rising Through Stagnant Water Hong Xu, Chokri Guetari ANSYS INC. Abstract Transient numerical simulations of the rise of a train of gas bubbles in a liquid
Stress and deformation of offshore piles under structural and wave loading
 Stress and deformation of offshore piles under structural and wave loading Author Eicher, Jackie, Guan, Hong, Jeng, Dong-Sheng Published 2003 Journal Title Ocean Engineering DOI https://doi.org/10.1016/s0029-8018(02)00031-8
Stress and deformation of offshore piles under structural and wave loading Author Eicher, Jackie, Guan, Hong, Jeng, Dong-Sheng Published 2003 Journal Title Ocean Engineering DOI https://doi.org/10.1016/s0029-8018(02)00031-8
The tensile capacity of suction caissons in sand under rapid loading
 Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics: ISFOG 25 Gourvenec & Cassidy (eds) 25 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 415 3963 X The tensile capacity of suction caissons in sand under rapid loading Guy T. Houlsby,
Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics: ISFOG 25 Gourvenec & Cassidy (eds) 25 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 415 3963 X The tensile capacity of suction caissons in sand under rapid loading Guy T. Houlsby,
computed using Equation 3-18 by setting the 2nd term equal to 0 and K A equal to K o and using the pressure distribution as shown in Figure 3-23.
 computed using Equation 3-18 by setting the 2nd term equal to 0 and K A equal to K o and using the pressure distribution as shown in Figure 3-23. (2) For the resisting side, passive pressure theory indicates
computed using Equation 3-18 by setting the 2nd term equal to 0 and K A equal to K o and using the pressure distribution as shown in Figure 3-23. (2) For the resisting side, passive pressure theory indicates
V-H-M Yield Surface describing Soil Structure Interaction of Sub-sea Structures and Wind Turbines on Caisson Foundations in Soft Clays
 NGM 2016 Reykjavik Proceedings of the 17 th Nordic Geotechnical Meeting Challenges in Nordic Geotechnic 25 th 28 th of May V-H-M Yield Surface describing Soil Structure Interaction of Sub-sea Structures
NGM 2016 Reykjavik Proceedings of the 17 th Nordic Geotechnical Meeting Challenges in Nordic Geotechnic 25 th 28 th of May V-H-M Yield Surface describing Soil Structure Interaction of Sub-sea Structures
The behaviour of tsunamis
 195 The behaviour of tsunamis Maurice N. Brearley 1 Introduction The behaviour of tsunamis is not easily understood. Readers comments on a recently published paper [3] show that a mathematical analysis
195 The behaviour of tsunamis Maurice N. Brearley 1 Introduction The behaviour of tsunamis is not easily understood. Readers comments on a recently published paper [3] show that a mathematical analysis
STUDY ON UPWARD MOVEMENT OF FINES FROM SANDY SEABED UNDER CYCLIC WATER PRESSURE CHANGE DUE TO WAVES
 C- Fourth International Conference on Scour and Erosion STUDY ON UPWARD MOVEMENT OF FINES FROM SANDY SEABED UNDER CYCLIC WATER PRESSURE CHANGE DUE TO WAVES Takashi TSUCHIDA, Akihiro MATSUI and Ryoichi
C- Fourth International Conference on Scour and Erosion STUDY ON UPWARD MOVEMENT OF FINES FROM SANDY SEABED UNDER CYCLIC WATER PRESSURE CHANGE DUE TO WAVES Takashi TSUCHIDA, Akihiro MATSUI and Ryoichi
SCIENCE OF TSUNAMI HAZARDS
 SCIENCE OF TSUNAMI HAZARDS ISSN 8755-6839 Journal of Tsunami Society International Volume 31 Number 2 2012 SEA LEVEL SIGNALS CORRECTION FOR THE 2011 TOHOKU TSUNAMI A. Annunziato 1 1 Joint Research Centre,
SCIENCE OF TSUNAMI HAZARDS ISSN 8755-6839 Journal of Tsunami Society International Volume 31 Number 2 2012 SEA LEVEL SIGNALS CORRECTION FOR THE 2011 TOHOKU TSUNAMI A. Annunziato 1 1 Joint Research Centre,
A NEW GOLF-SWING ROBOT MODEL UTILIZING SHAFT ELASTICITY
 Journal of Sound and Vibration (1998) 17(1), 17 31 Article No. sv981733 A NEW GOLF-SWING ROBOT MODEL UTILIZING SHAFT ELASTICITY S. SUZUKI Department of Mechanical System Engineering, Kitami Institute of
Journal of Sound and Vibration (1998) 17(1), 17 31 Article No. sv981733 A NEW GOLF-SWING ROBOT MODEL UTILIZING SHAFT ELASTICITY S. SUZUKI Department of Mechanical System Engineering, Kitami Institute of
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad CIVIL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 00 04 CIVIL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name Course Code Regulation Course Structure Course Coordinator Course Faculty
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 00 04 CIVIL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name Course Code Regulation Course Structure Course Coordinator Course Faculty
Application of pushover analysis in estimating seismic demands for large-span spatial structure
 28 September 2 October 2009, Universidad Politecnica de Valencia, Spain Alberto DOMINGO and Carlos LAZARO (eds.) Application of pushover analysis in estimating seismic demands for large-span spatial structure
28 September 2 October 2009, Universidad Politecnica de Valencia, Spain Alberto DOMINGO and Carlos LAZARO (eds.) Application of pushover analysis in estimating seismic demands for large-span spatial structure
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING Volume 1, No 4, 2010
 Effect of geometric dimensions on the transmission coefficient of floating breakwaters Mohammad Hosein Tadayon, Khosro Bargi 2, Hesam Sharifian, S. Reza Hoseini - Ph.D student, Department of Civil Engineering,
Effect of geometric dimensions on the transmission coefficient of floating breakwaters Mohammad Hosein Tadayon, Khosro Bargi 2, Hesam Sharifian, S. Reza Hoseini - Ph.D student, Department of Civil Engineering,
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON THE HYDRODYNAMIC BEHAVIORS OF TWO CONCENTRIC CYLINDERS
 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON THE HYDRODYNAMIC BEHAVIORS OF TWO CONCENTRIC CYLINDERS *Jeong-Rok Kim 1), Hyeok-Jun Koh ), Won-Sun Ruy 3) and Il-Hyoung Cho ) 1), 3), ) Department of Ocean System Engineering, Jeju
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON THE HYDRODYNAMIC BEHAVIORS OF TWO CONCENTRIC CYLINDERS *Jeong-Rok Kim 1), Hyeok-Jun Koh ), Won-Sun Ruy 3) and Il-Hyoung Cho ) 1), 3), ) Department of Ocean System Engineering, Jeju
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 CIVIL ENGINEERING Tutorial Question Bank Name : FOUNDATION ENGINEERING Code : A60126 Class : III B. Tech II Semester Branch
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 CIVIL ENGINEERING Tutorial Question Bank Name : FOUNDATION ENGINEERING Code : A60126 Class : III B. Tech II Semester Branch
Study to Establish Relations for the Relative Strength of API 650 Cone Roof Roof-to-Shell and Shell-to- Bottom Joints
 Thunderhead Engineering Consultants I N C O R P O R A T E D 1006 Poyntz Ave. Manhattan, KS 66502-5459 785-770-8511 www. thunderheadeng.com Study to Establish Relations for the Relative Strength of API
Thunderhead Engineering Consultants I N C O R P O R A T E D 1006 Poyntz Ave. Manhattan, KS 66502-5459 785-770-8511 www. thunderheadeng.com Study to Establish Relations for the Relative Strength of API
RESEARCH ON STABILITY OF OPENING SECTION AT BAYMOUTH BREAKWATER Junichiro SAKUNAKA 1 and Taro ARIKAWA 2
 RESEARCH ON STABILITY OF OPENING SECTION AT BAYMOUTH BREAKWATER Junichiro SAKUNAKA 1 and Taro ARIKAWA 2 The baymouth breakwater is to protect the port area from tsunami. It narrows the bay mouth and prevents
RESEARCH ON STABILITY OF OPENING SECTION AT BAYMOUTH BREAKWATER Junichiro SAKUNAKA 1 and Taro ARIKAWA 2 The baymouth breakwater is to protect the port area from tsunami. It narrows the bay mouth and prevents
THE STABILITY OF THE PIPELINE LAID ON A PORO-ELASTIC SEABED
 www.arpapress.com/volumes/vol17issue1/ijrras_17_1_04.pdf THE STABILITY OF THE PIPELINE LAID ON A PORO-ELASTIC SEABED Ren Yanrong Science School, Beijing Institute of Civil Engineering and Architecture,
www.arpapress.com/volumes/vol17issue1/ijrras_17_1_04.pdf THE STABILITY OF THE PIPELINE LAID ON A PORO-ELASTIC SEABED Ren Yanrong Science School, Beijing Institute of Civil Engineering and Architecture,
MODEL SHAKE TABLE TEST ON THE SEISMIC PERFORMANCE OF GRAVITY TYPE QUAY WALL WITH DIFFERENT FOUNDATION GROUND PROPERTIES
 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August -6, Paper No. 5 MODEL SHAKE TABLE TEST ON THE SEISMIC PERFORMANCE OF GRAVITY TYPE QUAY WALL WITH DIFFERENT FOUNDATION GROUND
th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August -6, Paper No. 5 MODEL SHAKE TABLE TEST ON THE SEISMIC PERFORMANCE OF GRAVITY TYPE QUAY WALL WITH DIFFERENT FOUNDATION GROUND
LABORATORY EXPERIMENTS FOR WAVE RUN-UP ON THE TETRAPOD ARMOURED RUBBLE MOUND STRUCTURE WITH A STEEP FRONT SLOPE
 Proceedings of the 6 th International Conference on the Application of Physical Modelling in Coastal and Port Engineering and Science (Coastlab16) Ottawa, Canada, May 10-13, 2016 Copyright : Creative Commons
Proceedings of the 6 th International Conference on the Application of Physical Modelling in Coastal and Port Engineering and Science (Coastlab16) Ottawa, Canada, May 10-13, 2016 Copyright : Creative Commons
A STUDY ON LIQUEFIED GROUND DISRUPTION EFFECTS ON LIQUID STORAGE TANK BEHAVIOR
 143 A STUDY ON LIQUEFIED GROUND DISRUPTION EFFECTS ON LIQUID STORAGE EHAVIOR Mutsuhiro YOSHIZAWA 1, Sadatomo ONIMARU 2, Akihiko UCHIDA 3 And Munenori HATANAKA 4 SUMMARY Three liquid storage tanks located
143 A STUDY ON LIQUEFIED GROUND DISRUPTION EFFECTS ON LIQUID STORAGE EHAVIOR Mutsuhiro YOSHIZAWA 1, Sadatomo ONIMARU 2, Akihiko UCHIDA 3 And Munenori HATANAKA 4 SUMMARY Three liquid storage tanks located
The Adequacy of Pushover Analysis to Evaluate Vulnerability of Masonry Infilled Steel Frames Subjected to Bi-Directional Earthquake Loading
 The Adequacy of Pushover Analysis to Evaluate Vulnerability of Masonry Infilled Steel Frames Subjected to Bi-Directional Earthquake Loading B.Beheshti Aval & M. Mohammadzadeh K.N.Toosi University of Technology,
The Adequacy of Pushover Analysis to Evaluate Vulnerability of Masonry Infilled Steel Frames Subjected to Bi-Directional Earthquake Loading B.Beheshti Aval & M. Mohammadzadeh K.N.Toosi University of Technology,
Chapter 9 Solids and Fluids
 2/17/16 Chapter 9 Solids and Fluids Units of Chapter 9 Solids and Elastic Moduli Fluids: Pressure and Pascal s Buoyancy and Archimedes Fluid Dynamics and Bernoulli s Surface Tension, Viscosity, and Poiseuille
2/17/16 Chapter 9 Solids and Fluids Units of Chapter 9 Solids and Elastic Moduli Fluids: Pressure and Pascal s Buoyancy and Archimedes Fluid Dynamics and Bernoulli s Surface Tension, Viscosity, and Poiseuille
A CASE STUDY CONSIDERING A 3-D PUSHOVER ANALYSIS PROCEDURE
 ABSTRACT : A CASE STUDY CONSIDERING A 3-D PUSHOVER ANALYSIS PROCEDURE W. Huang 1 and P. L. Gould 2 1 KPFF Consulting Engineers, Los Angeles, CA, USA 2 Professor, Washington University, Saint Louis, MO,
ABSTRACT : A CASE STUDY CONSIDERING A 3-D PUSHOVER ANALYSIS PROCEDURE W. Huang 1 and P. L. Gould 2 1 KPFF Consulting Engineers, Los Angeles, CA, USA 2 Professor, Washington University, Saint Louis, MO,
Analysis of Shear Lag in Steel Angle Connectors
 University of New Hampshire University of New Hampshire Scholars' Repository Honors Theses and Capstones Student Scholarship Spring 2013 Analysis of Shear Lag in Steel Angle Connectors Benjamin Sawyer
University of New Hampshire University of New Hampshire Scholars' Repository Honors Theses and Capstones Student Scholarship Spring 2013 Analysis of Shear Lag in Steel Angle Connectors Benjamin Sawyer
Irrigation &Hydraulics Department lb / ft to kg/lit.
 CAIRO UNIVERSITY FLUID MECHANICS Faculty of Engineering nd Year CIVIL ENG. Irrigation &Hydraulics Department 010-011 1. FLUID PROPERTIES 1. Identify the dimensions and units for the following engineering
CAIRO UNIVERSITY FLUID MECHANICS Faculty of Engineering nd Year CIVIL ENG. Irrigation &Hydraulics Department 010-011 1. FLUID PROPERTIES 1. Identify the dimensions and units for the following engineering
BIOREACTOR LANDFILLS: GEOTECHNICAL ASPECTS OF STABILITY EVALUATION
 BIOREACTOR LANDFILLS: GEOTECHNICAL ASPECTS OF STABILITY EVALUATION Presented by James Law SCS Engineers Master Class ISWA Congress 2009 Lisbon 10 October 2009 PRESENTATION OVERVIEW Landfill Slope Stability
BIOREACTOR LANDFILLS: GEOTECHNICAL ASPECTS OF STABILITY EVALUATION Presented by James Law SCS Engineers Master Class ISWA Congress 2009 Lisbon 10 October 2009 PRESENTATION OVERVIEW Landfill Slope Stability
ESTIMATION OF LATERAL SPREAD OF A CAISSON TYPE QUAY CAUSED BY BACK FILL LIQUEFACTION
 ESTIMATION OF LATERAL SPREAD OF A CAISSON TYPE QUAY CAUSED BY BACK FILL LIQUEFACTION Kunio MIZUMOTO 1, Tetsuya TSURUMI 2, Hidekatsu NAKAJIMA 3 And Susumu OKADA 4 SUMMARY It is said on the lateral spread
ESTIMATION OF LATERAL SPREAD OF A CAISSON TYPE QUAY CAUSED BY BACK FILL LIQUEFACTION Kunio MIZUMOTO 1, Tetsuya TSURUMI 2, Hidekatsu NAKAJIMA 3 And Susumu OKADA 4 SUMMARY It is said on the lateral spread
HRPP 464. Wave pressures in and under rubble mound breakwaters. Clemente Cantelmo, William Allsop and Scott Dunn
 HRPP 464 Wave pressures in and under rubble mound breakwaters Clemente Cantelmo, William Allsop and Scott Dunn Reproduced from a paper published in: Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on
HRPP 464 Wave pressures in and under rubble mound breakwaters Clemente Cantelmo, William Allsop and Scott Dunn Reproduced from a paper published in: Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on
Strength Reduction Stability
 1 Introduction Reduction Stability Stability by strength reduction is a procedure where the factor of safety is obtained by weakening the soil in steps in an elastic-plastic finite element analysis until
1 Introduction Reduction Stability Stability by strength reduction is a procedure where the factor of safety is obtained by weakening the soil in steps in an elastic-plastic finite element analysis until
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON OPTIMUM INSTALLATION DEPTH OF PVD UNDER VACUUM CONSOLIDATION ABSTRACT
 EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON OPTIMUM INSTALLATION DEPTH OF PVD UNDER VACUUM CONSOLIDATION EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON OPTIMUM INSTALLATION DEPTH OF PVD UNDER VACUUM CONSOLIDATION J.-C CHAI i), N. MIURA
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON OPTIMUM INSTALLATION DEPTH OF PVD UNDER VACUUM CONSOLIDATION EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON OPTIMUM INSTALLATION DEPTH OF PVD UNDER VACUUM CONSOLIDATION J.-C CHAI i), N. MIURA
ESTIMATION OF TSUNAMI FORCE ACTING ON THE BLOCK ARMORED BREAKWATER DUE TO SOLITON FISSION
 ESTMATON OF TSUNAM FORCE ACTNG ON THE BLOCK ARMORED BREAKWATER DUE TO SOLTON FSSON Sohei Maruyama 1, Tomotsuka Takayama 2, Kenichiro Shimosako 3, Akihiko Yahiro 2, Kojiro Suzuki 3, Toru Aota 1, Masashi
ESTMATON OF TSUNAM FORCE ACTNG ON THE BLOCK ARMORED BREAKWATER DUE TO SOLTON FSSON Sohei Maruyama 1, Tomotsuka Takayama 2, Kenichiro Shimosako 3, Akihiko Yahiro 2, Kojiro Suzuki 3, Toru Aota 1, Masashi
Yasuyuki Hirose 1. Abstract
 Study on Tsunami force for PC box girder Yasuyuki Hirose 1 Abstract In this study, a waterway experiment was performed in order to understand the influence of tsunami forms on tsunami forces acting on
Study on Tsunami force for PC box girder Yasuyuki Hirose 1 Abstract In this study, a waterway experiment was performed in order to understand the influence of tsunami forms on tsunami forces acting on
Tsunami Force Reduction due to Obstacle in Front of Coastal Dike and Evaluation of Collision Force by Driftage
 Journal of Energy and Power Engineering 11 (2017) 300-310 doi: 10.17265/1934-8975/2017.05.003 D DAVID PUBLISHING Tsunami Force Reduction due to Obstacle in Front of Coastal Dike and Evaluation of Collision
Journal of Energy and Power Engineering 11 (2017) 300-310 doi: 10.17265/1934-8975/2017.05.003 D DAVID PUBLISHING Tsunami Force Reduction due to Obstacle in Front of Coastal Dike and Evaluation of Collision
Tension Cracks. Topics Covered. Tension crack boundaries Tension crack depth Query slice data Thrust line Sensitivity analysis.
 Tension Cracks 16-1 Tension Cracks In slope stability analyses with cohesive soils, tension forces may be observed in the upper part of the slope. In general, soils cannot support tension so the results
Tension Cracks 16-1 Tension Cracks In slope stability analyses with cohesive soils, tension forces may be observed in the upper part of the slope. In general, soils cannot support tension so the results
 Kochi University of Technology Aca Study on Dynamic Analysis and Wea Title stem for Golf Swing Author(s) LI, Zhiwei Citation 高知工科大学, 博士論文. Date of 2015-03 issue URL http://hdl.handle.net/10173/1281 Rights
Kochi University of Technology Aca Study on Dynamic Analysis and Wea Title stem for Golf Swing Author(s) LI, Zhiwei Citation 高知工科大学, 博士論文. Date of 2015-03 issue URL http://hdl.handle.net/10173/1281 Rights
Predicting and Controlling Bubble Clogging in Bioreactor for Bone Tissue Engineering
 Predicting and Controlling Bubble Clogging in Bioreactor for Bone Tissue Engineering Marina Campolo, Dafne Molin, Alfredo Soldati Centro Interdipartimentale di Fluidodinamica e Idraulica and Department
Predicting and Controlling Bubble Clogging in Bioreactor for Bone Tissue Engineering Marina Campolo, Dafne Molin, Alfredo Soldati Centro Interdipartimentale di Fluidodinamica e Idraulica and Department
A New Generator for Tsunami Wave Generation
 Journal of Energy and Power Engineering 10 (2016) 166-172 doi: 10.17265/1934-8975/2016.03.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Tetsuya Hiraishi 1, Ryokei Azuma 1, Nobuhito Mori 2, Toshihiro Yasuda 2 and Hajime Mase
Journal of Energy and Power Engineering 10 (2016) 166-172 doi: 10.17265/1934-8975/2016.03.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Tetsuya Hiraishi 1, Ryokei Azuma 1, Nobuhito Mori 2, Toshihiro Yasuda 2 and Hajime Mase
DAMAGE TO OIL STORAGE TANKS DUE TO TSUNAMI OF THE MW OFF THE PACIFIC COAST OF TOHOKU, JAPAN
 1NCEE Tenth U.S. National Conference on Earthquake Engineering Frontiers of Earthquake Engineering July 21-25, 214 Anchorage, Alaska DAMAGE TO OIL STORAGE TANKS DUE TO TSUNAMI OF THE MW9. 211 OFF THE PACIFIC
1NCEE Tenth U.S. National Conference on Earthquake Engineering Frontiers of Earthquake Engineering July 21-25, 214 Anchorage, Alaska DAMAGE TO OIL STORAGE TANKS DUE TO TSUNAMI OF THE MW9. 211 OFF THE PACIFIC
Typical factors of safety for bearing capacity calculation in different situations
 Typical factors of safety for bearing capacity calculation in different situations Density of soil: In geotechnical engineering, one deals with several densities such as dry density, bulk density, saturated
Typical factors of safety for bearing capacity calculation in different situations Density of soil: In geotechnical engineering, one deals with several densities such as dry density, bulk density, saturated
INCLINOMETER DEVICE FOR SHIP STABILITY EVALUATION
 Proceedings of COBEM 2009 Copyright 2009 by ABCM 20th International Congress of Mechanical Engineering November 15-20, 2009, Gramado, RS, Brazil INCLINOMETER DEVICE FOR SHIP STABILITY EVALUATION Helena
Proceedings of COBEM 2009 Copyright 2009 by ABCM 20th International Congress of Mechanical Engineering November 15-20, 2009, Gramado, RS, Brazil INCLINOMETER DEVICE FOR SHIP STABILITY EVALUATION Helena
THEORETICAL FORMULAE FOR WAVE SLAMMING LOADS ON SLENDER CIRCULAR CYLINDERS AND APPLICATION FOR SUPPORT STRUCTURES OF WIND TURBINES
 THEORETICAL FORMULAE FOR WAVE SLAMMING LOADS ON SLENDER CIRCULAR CYLINDERS AND APPLICATION FOR SUPPORT STRUCTURES OF WIND TURBINES JAN WIENKE jwie@gl-group.com, Germanischer Lloyd, Vorsetzen 35 20459 Hamburg,
THEORETICAL FORMULAE FOR WAVE SLAMMING LOADS ON SLENDER CIRCULAR CYLINDERS AND APPLICATION FOR SUPPORT STRUCTURES OF WIND TURBINES JAN WIENKE jwie@gl-group.com, Germanischer Lloyd, Vorsetzen 35 20459 Hamburg,
DESIGN OPTIMIZATION OF WORK ROLL CHOCK AND BACKUP ROLL CHOCK IN COLD ROLLING MILL
 DESIGN OPTIMIZATION OF WORK ROLL CHOCK AND BACKUP ROLL CHOCK IN COLD ROLLING MILL Tukesh Sahu 1, Prof. G.R.Kesheory 2 1M.Tech Scholar, Department of Mechanical Engineering, VITS Indore, MP, India 2Assistant
DESIGN OPTIMIZATION OF WORK ROLL CHOCK AND BACKUP ROLL CHOCK IN COLD ROLLING MILL Tukesh Sahu 1, Prof. G.R.Kesheory 2 1M.Tech Scholar, Department of Mechanical Engineering, VITS Indore, MP, India 2Assistant
Finite Element Modal Analysis of Twin Ball Screw Driving Linear Guide Feed Unit Table
 2016 3 rd International Conference on Mechanical, Industrial, and Manufacturing Engineering (MIME 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-313-7 Finite Element Modal Analysis of Twin Ball Screw Driving Linear Guide Feed
2016 3 rd International Conference on Mechanical, Industrial, and Manufacturing Engineering (MIME 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-313-7 Finite Element Modal Analysis of Twin Ball Screw Driving Linear Guide Feed
EVALUATION OF TSUNAMI FLUID FORCE ACTING ON THE BRIDGE DECK
 JOINT CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS 9th International Conference on Urban Earthquake Engineering/ th Asia Conference on Earthquake Engineering March -8,, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Tokyo, Japan EVALUATION
JOINT CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS 9th International Conference on Urban Earthquake Engineering/ th Asia Conference on Earthquake Engineering March -8,, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Tokyo, Japan EVALUATION
Reinforced Soil Retaining Walls-Design and Construction
 Lecture 32 Reinforced Soil Retaining Walls-Design and Construction Prof. G L Sivakumar Babu Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560012 Example calculation An 8 m high
Lecture 32 Reinforced Soil Retaining Walls-Design and Construction Prof. G L Sivakumar Babu Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560012 Example calculation An 8 m high
3D CDF MODELING OF SHIP S HEELING MOMENT DUE TO LIQUID SLOSHING IN TANKS A CASE STUDY
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 17, No. 4 21 3D CDF ODELING OF SHIP S HEELING OENT DUE TO LIQUID SLOSHING IN TANKS A CASE STUDY Przemysaw Krata, Jacek Jachowski Gdynia aritime University,
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 17, No. 4 21 3D CDF ODELING OF SHIP S HEELING OENT DUE TO LIQUID SLOSHING IN TANKS A CASE STUDY Przemysaw Krata, Jacek Jachowski Gdynia aritime University,
PROPOSAL OF NEW PROCEDURES FOR IMPROVED TSUNAMI FORECAST BY APPLYING COASTAL AND OFFSHORE TSUNAMI HEIGHT RATIO
 PROPOSAL OF NEW PROCEDURES FOR IMPROVED TSUNAMI FORECAST BY APPLYING COASTAL AND OFFSORE TSUNAMI EIGT RATIO Weniza MEE0997 Supervisor: Yutaka AYASI Yushiro FUJII ABSTRACT Regression analysis was performed
PROPOSAL OF NEW PROCEDURES FOR IMPROVED TSUNAMI FORECAST BY APPLYING COASTAL AND OFFSORE TSUNAMI EIGT RATIO Weniza MEE0997 Supervisor: Yutaka AYASI Yushiro FUJII ABSTRACT Regression analysis was performed
E.2 CAP SETTLEMENT RA D AND OUTBOARD
 DRAFT ONONDAGA LAKE CAPPING, DREDGING AND HABITAT INTERMEDIATE DESIGN E.2 CAP SETTLEMENT RA D AND OUTBOARD Parsons P;\Honeywell-SYR\444576 2008 Capping\09 Reports\9.1 Capping and Dredge Area & Depth IDS\Appendices\Appendix
DRAFT ONONDAGA LAKE CAPPING, DREDGING AND HABITAT INTERMEDIATE DESIGN E.2 CAP SETTLEMENT RA D AND OUTBOARD Parsons P;\Honeywell-SYR\444576 2008 Capping\09 Reports\9.1 Capping and Dredge Area & Depth IDS\Appendices\Appendix
Calibration and Validation of the Shell Fatigue Model Using AC10 and AC14 Dense Graded Hot Mix Asphalt Fatigue Laboratory Data
 Article Calibration and Validation of the Shell Fatigue Model Using AC10 and AC14 Dense Graded Hot Mix Asphalt Fatigue Laboratory Data Mofreh Saleh University of Canterbury, Private Bag 4800, Christchurch,
Article Calibration and Validation of the Shell Fatigue Model Using AC10 and AC14 Dense Graded Hot Mix Asphalt Fatigue Laboratory Data Mofreh Saleh University of Canterbury, Private Bag 4800, Christchurch,
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 14 Fluids Fluids at rest pressure vs. depth Pascal s principle Archimedes s principle Buoynat forces Fluids in motion: Continuity & Bernoulli equations 1. How deep
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 14 Fluids Fluids at rest pressure vs. depth Pascal s principle Archimedes s principle Buoynat forces Fluids in motion: Continuity & Bernoulli equations 1. How deep
Title. Author(s)HOSSEINI, M.; FARSHADMANESH, P. Issue Date Doc URL. Type. Note. File Information
 Title EVALUATING THE EFFECT OF MULTIPLE VERTICAL ORTHOGONA PHENOMENON IN RECTANGULAR TANKS SUBJECTED TO 3-DIMEN EXCITATIONS Author(s)HOSSEINI, M.; FARSHADMANESH, P. Issue Date 2013-09-11 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/54196
Title EVALUATING THE EFFECT OF MULTIPLE VERTICAL ORTHOGONA PHENOMENON IN RECTANGULAR TANKS SUBJECTED TO 3-DIMEN EXCITATIONS Author(s)HOSSEINI, M.; FARSHADMANESH, P. Issue Date 2013-09-11 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/54196
Simulation and mathematical modeling for racket position and attitude of table tennis
 Acta Technica 62 No. 3A/2017, 135 142 c 2017 Institute of Thermomechanics CAS, v.v.i. Simulation and mathematical modeling for racket position and attitude of table tennis Jiansi Song 1 Abstract. Racket
Acta Technica 62 No. 3A/2017, 135 142 c 2017 Institute of Thermomechanics CAS, v.v.i. Simulation and mathematical modeling for racket position and attitude of table tennis Jiansi Song 1 Abstract. Racket
A MICRO-BUBBLE INJECTION METHOD FOR A COUNTERMEASURE AGAINST LIQUEFACTION
 4 th International Conference on Earthquake Geotechnical Engineering June 25-28, 27 Paper No. 1764 A MICRO-BUBBLE INJECTION METHOD FOR A COUNTERMEASURE AGAINST LIQUEFACTION Koichi NAGAO 1, Yoichi AZEGAMI
4 th International Conference on Earthquake Geotechnical Engineering June 25-28, 27 Paper No. 1764 A MICRO-BUBBLE INJECTION METHOD FOR A COUNTERMEASURE AGAINST LIQUEFACTION Koichi NAGAO 1, Yoichi AZEGAMI
Mechanical Stabilisation for Permanent Roads
 Mechanical Stabilisation for Permanent Roads Tim Oliver VP Global Applications Technology Tensar International toliver@tensar.co.uk Effect of geogrid on particle movement SmartRock Effect of geogrid on
Mechanical Stabilisation for Permanent Roads Tim Oliver VP Global Applications Technology Tensar International toliver@tensar.co.uk Effect of geogrid on particle movement SmartRock Effect of geogrid on
LOCALLY CONCENTRATED SEVERE BEACH EROSION ON SEISHO COAST CAUSED BY TYPHOON T0709
 F-4 Fourth International Conference on Scour and Erosion 2008 LOCALLY CONCENTRATED SEVERE BEACH EROSION ON SEISHO COAST CAUSED BY TYPHOON T0709 Yoshimitsu TAJIMA 1 and Shinji SATO 2 1 Member of JSCE, Associate
F-4 Fourth International Conference on Scour and Erosion 2008 LOCALLY CONCENTRATED SEVERE BEACH EROSION ON SEISHO COAST CAUSED BY TYPHOON T0709 Yoshimitsu TAJIMA 1 and Shinji SATO 2 1 Member of JSCE, Associate
FLUID MECHANICS Time: 1 hour (ECE-301) Max. Marks :30
 B.Tech. [SEM III(ME&CE)] QUIZ TEST-1 (Session : 2013-14) Time: 1 hour (ECE-301) Max. Marks :30 Note: Attempt all questions. PART A Q1. The velocity of the fluid filling a hollow cylinder of radius 0.1
B.Tech. [SEM III(ME&CE)] QUIZ TEST-1 (Session : 2013-14) Time: 1 hour (ECE-301) Max. Marks :30 Note: Attempt all questions. PART A Q1. The velocity of the fluid filling a hollow cylinder of radius 0.1
Bearing Capacity and Settlement Response of PMS Tanks on Cohesionless Soil Lithology in Lekki, Lagos of Nigeria
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Applied Engineering and Scientific Research,, ():- (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN: 8 Bearing Capacity and
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Applied Engineering and Scientific Research,, ():- (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN: 8 Bearing Capacity and
σ = force / surface area force act upon In the image above, the surface area would be (Face height) * (Face width).
 Aortic Root Inflation Introduction You have already learned about the mechanical properties of materials in the cantilever beam experiment. In that experiment you used bending forces to determine the Young
Aortic Root Inflation Introduction You have already learned about the mechanical properties of materials in the cantilever beam experiment. In that experiment you used bending forces to determine the Young
P-04 Stainless Steel Corrugated Hoses and Metal Bellows Expansion Joints
 Guideline No.P-04 (201510) P-04 Stainless Steel Corrugated Hoses and Metal Bellows Expansion Joints Issued date: 20 th October 2015 China Classification Society Foreword This Guideline is a part of CCS
Guideline No.P-04 (201510) P-04 Stainless Steel Corrugated Hoses and Metal Bellows Expansion Joints Issued date: 20 th October 2015 China Classification Society Foreword This Guideline is a part of CCS
DUE TO EXTERNAL FORCES
 17B.6 DNS ON GROWTH OF A VERTICAL VORTEX IN CONVECTION DUE TO EXTERNAL FORCES Ryota Iijima* and Tetsuro Tamura Tokyo Institute of Technology, Yokohama, Japan 1. INTRODUCTION Various types of vertical vortices,
17B.6 DNS ON GROWTH OF A VERTICAL VORTEX IN CONVECTION DUE TO EXTERNAL FORCES Ryota Iijima* and Tetsuro Tamura Tokyo Institute of Technology, Yokohama, Japan 1. INTRODUCTION Various types of vertical vortices,
Critical face pressure and backfill pressure in shield TBM tunneling on soft ground
 Critical face pressure and backfill pressure in shield TBM tunneling on soft ground Kiseok Kim 1), Juyoung Oh 2), Hyobum Lee 3) and Hangseok Choi 4) 1), 3), 4) Department of civil engineering, Korea University,
Critical face pressure and backfill pressure in shield TBM tunneling on soft ground Kiseok Kim 1), Juyoung Oh 2), Hyobum Lee 3) and Hangseok Choi 4) 1), 3), 4) Department of civil engineering, Korea University,
Elastic-Plastic Finite Element Analysis for Zhongwei--guiyang Natural Gas Pipeline Endangered by Collapse
 Abstract Elastic-Plastic Finite Element Analysis for Zhongwei--guiyang Natural Gas Pipeline Endangered by Collapse Gengxin Wu,Peng Zhang,Zhixiang Li,Zunhai Ke,Guizhi Li,Anmin Jiang 2 School of Civil Engineering
Abstract Elastic-Plastic Finite Element Analysis for Zhongwei--guiyang Natural Gas Pipeline Endangered by Collapse Gengxin Wu,Peng Zhang,Zhixiang Li,Zunhai Ke,Guizhi Li,Anmin Jiang 2 School of Civil Engineering
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 112 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ciencedirect Procedia ngineering 112 (2015 ) 443 448 7th Asia-Pacific Congress on ports Technology, APCT 2015 Kinematics of arm joint motions in basketball shooting
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ciencedirect Procedia ngineering 112 (2015 ) 443 448 7th Asia-Pacific Congress on ports Technology, APCT 2015 Kinematics of arm joint motions in basketball shooting
Time rate of swelling of compacted highly plastic clay soil from Sudan
 Time rate of swelling of compacted highly plastic clay soil from Sudan 1 A M Elsharief, 2 Mai Sufian 1 University of Khartoum, Khartoum, Sudan 2 Sudan University of Science and Technology, Khartoum, Sudan
Time rate of swelling of compacted highly plastic clay soil from Sudan 1 A M Elsharief, 2 Mai Sufian 1 University of Khartoum, Khartoum, Sudan 2 Sudan University of Science and Technology, Khartoum, Sudan
Analysis and Research of Mooring System. Jiahui Fan*
 nd International Conference on Computer Engineering, Information Science & Application Technology (ICCIA 07) Analysis and Research of Mooring System Jiahui Fan* School of environment, North China Electric
nd International Conference on Computer Engineering, Information Science & Application Technology (ICCIA 07) Analysis and Research of Mooring System Jiahui Fan* School of environment, North China Electric
LOW PRESSURE EFFUSION OF GASES revised by Igor Bolotin 03/05/12
 LOW PRESSURE EFFUSION OF GASES revised by Igor Bolotin 03/05/ This experiment will introduce you to the kinetic properties of low-pressure gases. You will make observations on the rates with which selected
LOW PRESSURE EFFUSION OF GASES revised by Igor Bolotin 03/05/ This experiment will introduce you to the kinetic properties of low-pressure gases. You will make observations on the rates with which selected
Artificial headlands for coastal restoration
 Artificial headlands for coastal restoration J. S. Mani Professor, Department of Ocean Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Madras, Chennai 636, India Abstract Construction of a satellite harbour
Artificial headlands for coastal restoration J. S. Mani Professor, Department of Ocean Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Madras, Chennai 636, India Abstract Construction of a satellite harbour
CENGRS GEOTECHNICA PVT. LTD. Job No Sheet No. 1
 CENGRS GEOTECHNICA PVT. LTD. Job No. 214030 Sheet No. 1 INTERIM REPORT ON GEOTECHNICAL INVESTIGATION FOR PROPOSED 66 KV GRID PLOT AT G-7, DWARKA, NEW DELHI. 1.0 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Project Description M/s.
CENGRS GEOTECHNICA PVT. LTD. Job No. 214030 Sheet No. 1 INTERIM REPORT ON GEOTECHNICAL INVESTIGATION FOR PROPOSED 66 KV GRID PLOT AT G-7, DWARKA, NEW DELHI. 1.0 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Project Description M/s.
An experimental study of internal wave generation through evanescent regions
 An experimental study of internal wave generation through evanescent regions Allison Lee, Julie Crockett Department of Mechanical Engineering Brigham Young University Abstract Internal waves are a complex
An experimental study of internal wave generation through evanescent regions Allison Lee, Julie Crockett Department of Mechanical Engineering Brigham Young University Abstract Internal waves are a complex
PHYSICAL MODELING FOR MEASURING THE EFFECTIVENESS OF SINGLE CURTAIN PILE FOUNDATION BREAKWATER IN INTERMEDIATE WATER DEPTH
 International Journal of GEOMAE, March., 2018 Vol.14, Issue 43, pp.160-166 Geotec., Const. Mat. & Env., DOI: https://doi.org/10.21660/2018.43.43946 ISSN: 2186-2982 (Print), 2186-2990 (Online), Japan PHYSICAL
International Journal of GEOMAE, March., 2018 Vol.14, Issue 43, pp.160-166 Geotec., Const. Mat. & Env., DOI: https://doi.org/10.21660/2018.43.43946 ISSN: 2186-2982 (Print), 2186-2990 (Online), Japan PHYSICAL
