THE EFFECT OF EMBEDMENT DEPTH ON BEARING CAPACITY OF STRIP FOOTING IN COHESIVE FRICTIONAL MEDIUM
|
|
|
- Prosper McGee
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Proceedings of the 4 th International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2018), 9~11 February 2018, KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh (ISBN ) THE EFFECT OF EMBEDMENT DEPTH ON BEARING CAPACITY OF STRIP FOOTING IN COHESIVE FRICTIONAL MEDIUM Hasinur Rahman Nur 1, Md. Shafiqul Islam 2 and Md. Rokonuzzaman 3 1 Undergraduate Student, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Khulna University of Engineering and Technology, Bangladesh, h.r.nur2k12@gmail.com 2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Khulna University of Engineering and Technology, Bangladesh, sumon2k8@yahoo.com 3 Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Khulna University of Engineering and Technology, Bangladesh, rokoncekuet@yahoo.com ABSTRACT In this study, two-dimensional finite-element models incorporating a Mohr-Coulomb elasto-plastic material model were validated for the evaluation of the bearing capacity factors for rough strip footings under vertical loading in c- soil. Earlier proposals are based on empirical data for surface condition in non-frictional medium, whereas a new suggestion for these factors presented in this paper is based on the elasto-plastic model of the soil in cohesive frictional medium considering variable friction angle and embedment depth. All the finite element analyses of this study were carried out using the finite element system ABAQUS. Finally, an attempt is made to propose a more accurate solution to estimate the bearing capacity factors of rough strip footing with equations fitted by simple functions of the soil friction angle and footing embedment depth. Keywords: Foundation, Bearing capacity, Strip footing, Finite element analyses (FEM). 1. INTRODUCTION The bearing capacity of foundations has become a fundamental problem in geotechnical engineering. For all structures placed on a soil foundation, geotechnical engineers must ensure that the soil has sufficient load carrying capacity so that the foundation does not collapse or become unstable under any conceivable loading (Zhu & Michalowski, 2005). A lot of research have been done which proposed approximate techniques for the estimation of bearing capacity of foundation and generally the conventional bearing capacity theory used which is suitable for strip footing but no exact solution has been established. (Terzaghi, 1943) proposed the following formula to calculate the ultimate bearing pressure of soil beneath a strip footing, where the influence of soil cohesion (c), surcharge (q) and the weight of soil (g) are considered independently: Q ult = cn c + qn q + BN γ (1) Where, Q ult= ultimate pressure; B= footing width; D= depth of embedment; γ= unit weight of the soil; c= soil cohesion; N c, N q and N γ= bearing capacity factors dependent only on the angle of the internal friction of soil. Terzaghi calculated all three components in Eq. (1) based on limit equilibrium. Also, (Terzaghi, 1943), (Reissner, 1924), and (Chen, 1975) among others, calculated the bearing capacity factors as follows: N q = K p * exp(п tan ) N c = ( N q 1 ) cot (2) and, Kp ; Where, =internal friction angle. There are several suggestions in different literature for factor N γ (Meyerhof, 1963);(Hansen, 1970);(Vesic, 1973). A newer proposal was derived based on the strict upper bound approach of limit analysis (Michalowski, 1997). N γ = tan (3) ICCESD
2 4 th International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2018) The factor in Eq.(3) is a closed-form approximation from the numerical results for the analysis of Coefficient N γ for Rough and Smooth Strip Footings (Michalowski, 1997). In recent years, both theoretical and experimental investigation of the ultimate bearing capacity of square and circular footings received the attention of many researchers. For example, (Cerato & Lutenegger, 2007) experimentally investigated the bearing capacity factor N γ on sand for both square and circular footings. He found that the square footing provides higher bearing capacity than the circular footing. Similar results were found for the footing resting on sand by (Lavasan, A. A., & Ghazavi, 2012) and (Kiran, M., & Bacha, 2015). These investigations are significant for footings placed on sand, but they do not provide any information in the case of footings resting on frictional-cohesive (c- ) soil. Only few numerical studies (Zhu & Michalowski, 2005); (Kumar & & Khatri, 2011) were performed on (c- ) soil. This study involved numerical investigation of the ultimate bearing capacity with finite element analysis of (c- ) soil for rough strip footings subjected to vertical loading and compared with previous studies through graphical presentation. 2. METHODOLOGY ABAQUS is a software application used for both the modelling and analysis of mechanical components and assemblies (pre-processing). It is most suitable for analyzing the nonlinear behavior of material, failure phenomena and visualizing the finite element analysis result. All the finite element analyses of this study were carried out using the software ABAQUS. Two dimensional model was developed for strip footing analysis for different frictional angles and embedment depth. Simple soil conditions were modelled representing an isotropic linear elastic-perfectly plastic material considering embedment depth H/B= 0, 0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 0.75, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0 and frictional angle from zero degree to 40 degree. Meshing and displacement were applied to the model and ABAQUS was used to arrive at the limit loads (bearing capacity) of rough strip footings. 2.1 Element Size Study On surface footing element size analysis was carried out to fix the element size and meshing as well as displacement. The fixation of mesh element size is an important part of modelling because it determines the amount of element number and time required for the analysis of the model. After fixation of the element size, the type of element was also selected whether it is linear, quadratic or triangular. The quadratic element shows more accurate result and load-displacement curve become constant very quickly. Although triangular element shows more accurate result compared to quadratic but to avoid huge time for the analysis quadratic element were used. 2.2 Modelling Finite element system ABAQUS was used to arrive at the limit loads (bearing capacity) of rough strip footings and different meshing and displacement applied for two dimensional modelling. The model is created in four steps. In the first step which is the initial condition, all boundary conditions are defined as described previously. In the second step, surcharge load is applied on top of the model and gravity load is applied to the whole model. In the third step, a downward movement is applied on top of the soil under footing area where δ is vertical displacement and B is the width of footing. It should be noted that the duration for this l step is 100 seconds to avoid sudden collapse of soil body. Moreover, it is assumed that relative movement between soil and footing is impossible. The boundary conditions ensures no lateral movement will occur. For rough footing lateral displacement are restrained to zero and only vertical displacement occurred. ICCESD
3 4 th International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2018) Materials Simple soil conditions were modelled representing an isotropic linear elastic-perfectly plastic material with uniform undrained shear strength and depth,. A fine grained material subjected to a period of loading sufficiently short such that no drainage will take place. Poisson s ratio ν=0.3, modulus of elasticity was 10 MPa, cohesion was 10Kpa for the calculation of N c. The cohesion varies in between 4E 3 to 6E 3 for N γ & N q. The angle of friction and dilation angle was varying from zero degree to 40 degree. The analysis was done at different embedment depth including surface considering a rough condition for strip footing Meshing The two-dimensional finite element mesh used for analysis of a strip footing of width B and Length zero considered. The mesh extended 15B from the edges of the footing and 10B beneath the footing (shown in figure-1). A number of mesh densities were investigated to achieve a time efficient model and mesh element type was a 8-node linear plane strain quadrilateral, reduced integration and hourglass control. Meshing was done for linear, quadratic element to fix the element for the model and to determine which provide more accurate results. Different type of meshing was tested and finally quadratic meshing was chosen to get more accurate result from the analysis. Meshing is shown in the figure-1 where the footing area contains finer meshing than the outer edge. This was done to reduce the number of elements so that the time of every analysis could be reduced. 15 B 15 B 10 B Figure 1: Meshing with quadratic element for two-dimensional strip footing 3. RESULT AND DISCUSSION 3.1 Validation of Study Earlier proposals of evaluating bearing capacity factors were investigated thoroughly and numerical values were obtained from the previous empirical solutions for estimating bearing capacity factors for bearing capacity factors. Again, values from numerical analysis were obtained from finite element analysis. Both empirical and numerical values were compared through graphical presentations. ICCESD
4 Bearing Capacity Factor 4 th International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2018) Table 1: Calculation of bearing capacity factors of previous study and FEM study Angle Kp Previous study FEM study Nq Nc N Nq Nc N Nc (FEM) Nq (FEM) Nc Prandtl Nq Reissner Friction Angle, (φ) Figure 2: Comparative study of Surcharge and cohesion bearing capacity coefficients The results for the two bearing capacity coefficients, as a function of the friction angle,ϕ, can be found in Figure-2 The analytical solutions of Prandtl and Reissner (short dashed lines) are also shown. The FEM study and analytical solutions for the two bearing capacity factors, N q and N c are found to be identical. ICCESD
5 Bearing Capacity Factor, Nγ 4 th International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2018) Nγ (Michalowski) Nγ (FEM) Friction angle, (φ) Figure 3: Comparative study of bearing capacity coefficient, N The result for the bearing capacity coefficient N, as a function of the friction angle,ϕ, can be found in Figure-3 The analytical solutions of Michalowski is also shown as short dashed lines. The FEM study shows slightly upper values than the previous study. The variation of obtained values from FEM study with previous theoretical study is negotiable. 3.2 Variation of N c in Cohesive Frictional Medium ICCESD
6 Bearing Capacity Factor, Nc 4 th International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2018) H/B=0.1 H/B=0.3 H/B=0.75 H/B=1.5 H/B=0.2 H/B=0.5 H/B=1.0 H/B= Friction Angle (φ) Figure Error! No text of specified style in document.: Variation of N c in cohesive frictional medium Figure-4 shows the graphical representation of bearing capacity factor, N c at different embedment depth in cohesive frictional medium. Here, value of N c increases with the embedment depth. The higher the value of embedment depth, the value of bearing capacity factor, N c also increases accordingly. The nature of increase in different depth is quite similar. Again, value of N c increases with friction angle and dilation angle but rate of change is not similar here. The rate of increasing the value of bearing capacity factor, N c is slow at first. When it crosses 30 degree, the value of rate of change is much higher than before. Rapid change is observed in between 30 degree and 40 degree Variation of Depth Factor for N c in Cohesive Frictional Medium The depth factor of N c is calculated by, = ICCESD
7 4 th International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2018) DEGREE 20 DEGREE DEGREE 30 DEGREE 35 DEGREE 40 DEGREE Depth facor for Nc H/B ratio Figure 5: Variation of depth factor for N c in cohesive frictional medium Figure-5 shows the graphical representation of depth factor for N c at different embedment depth in cohesive frictional medium. Value of H/B ratio is plotted along X-axis and depth factor for N c is plotted along Y-axis. Here, value of depth factor increases with the embedment depth. The nature of increase in different depth is quite different. Rate of change for the first two curvature were quite faster than the others. Value of depth factor increases with friction angle but rate of change is not similar here. 3.3 Variation of N q in Cohesive Frictional Medium Figure-6 shows the graphical representation of bearing capacity factor, N q at different embedment depth in cohesive frictional medium. Value of friction angel is plotted along X- axis and bearing capacity factor, N q is plotted along Y-axis. ICCESD
8 Depth facor for Nq Bearing Capacity Factor, Nq 4 th International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2018) H/B=0.1 H/B=0.3 H/B=0.75 H/B=1.5 H/B=0.2 H/B=0.5 H/B=1.0 H/B= Friction Angle (φ) Figure 6: Variation of N q in cohesive frictional medium Here, value of N q increases with the embedment depth. The higher the value of embedment depth, the value of bearing capacity factor, N q also increases accordingly. The nature of increase in different depth is quite similar. Again, value of N q increases with friction angle and dilation angle but rate of change is not similar here. The value of rate of increasing of bearing capacity factor, N q was slow at first. When it crosses 30 degree, the value of rate of change is much higher than before. Rapid change is observed in between 30 degree and 40 degree Variation of Depth Factor for N q in Cohesive Frictional Medium The depth factor of N q is calculated by, N q= DEGREE 20 DEGREE 25 DEGREE 30 DEGREE 35 DEGREE 40 DEGREE H/B ratio Figure 7: Variation of depth factor for N q in cohesive frictional medium ICCESD
9 Bearing Capacity Factor, Nγ 4 th International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2018) Figure-7 shows the graphical representation of depth factor for N q at different embedment depth in cohesive frictional medium. Value of H/B ratio is plotted along X-axis and depth factor for N q is plotted along Y-axis. Here, value of depth factor increases very slowly with the embedment depth. The nature of increase in different depth is quite slow. Curvature slope is not steep at all and they are about to be horizontal. Huge gap is observed between first and second curvature and similar phenomena found for last curvature too. Value of depth factor increases with friction angle and but rate of change is quite similar here. 3.4 Variation of N in Cohesive Frictional Medium H/B=0.1 H/B=0.3 H/B=0.75 H/B=1.5 H/B=0.2 H/B=0.5 H/B=1.0 H/B= Friction Angle (φ) Figure 8 : Variation of N in cohesive frictional medium Figure-8 shows the graphical representation of bearing capacity factor, N at different embedment depth in cohesive frictional medium. Value of friction angel is plotted along X- axis and bearing capacity factor, N is plotted along Y-axis. Here, value of N increases with the embedment depth. The nature of increase in different depth is quite similar. Again, value of N increases with friction angle and dilation angle but rate of change is not similar here. The rate of increasing the value of bearing capacity factor, N is slow at first. When it crosses 30 degree, the value of rate of change is much higher than before. Rapid change is observed in between 30 degree and 40 degree Variation of Depth Factor for N in Cohesive Frictional Medium The depth factor of N is calculated by, N = ICCESD
10 Depth facor for Nγ 4 th International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2018) DEGREE 20 DEGREE 25 DEGREE 30 DEGREE 35 DEGREE 40 DEGREE H/B ratio Figure 9 : Variation of depth factor for N in cohesive frictional medium Figure-9 shows the graphical representation of depth factor for N at different embedment depth in cohesive frictional medium. Value of H/B ratio is plotted along X-axis and depth factor for N is plotted along Y-axis. Here, value of depth factor increases with the embedment depth. The nature of increase in different depth is quite similar. The speciality for the depth factor of N, straight lines are obtained instead of curvature. Thus, depth factor of N shows some different graphs. Value of depth factor increases with friction angle But rate of change is quite similar here. 3.5 Soil Failure Mechanism Here, Figure-10 shows the line contours of resultant soil displacement at failure for each of the footings modeled at surface (H/B=0) and at different embedment ratios (fig.(b) through fig.(i)). Under plane strain conditions a distinct Prandtl type (1921) mechanism is observed in the finite element analyses Fig.(a). The contours (fig.(b) through fig.(f)) show the failure mechanism of footing in clay soil (ϕ=0). These illustrate the variation in nature of the soil displacement de-pending on embedment ratios. The footings are subjected to a uniform vertical displacement; the contours of resultant displace-ment beneath the rough footing show that the soil moves uni-formly vertically downwards with no relative soil movement on the underside of the footing. The line contours of soil displacement extend in surface upto shallow embedment ratios (i.e., H/B=2). For deep footing (H/B>2), contours start at the corner of footing and do not extend into the surface. Fig.6g through fig. 6j represents the variation of failure mechanism for sandy soil (c=0 and ϕ=30 ) at surface (fig.6g) and different embedment ratios (Ffig.6.h through fig.6j). In all embedment ratios contour line extend to the surface and a triangular wedge zone is observed beneath the footing. A triangular zone is started at the corner of footing and extended to the surface. This zone is also observed at all embedment ratios for frictional soil but, it does not exist in clay soil. ICCESD
11 4 th International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2018) (a) Surface footing (H/B=0) (b) H/B=1 (c) H/B=2 (d) H/B=3 (e) H/B=4 (f) H/B=5 (g) Surface footing (H/B=0) (h) H/B=1 (i) H/B=2 (j) H/B=4 3.6 Parametric Study Figure-10: Soil displacement at failure In this section, the validated solution of numerical models are used to calculate the ultimate bearing capacity factors of rough strip footings. Here, an attempt is made to propose a more accurate solution to estimate the bearing capacity factors of rough strip footing with equations fitted by simple functions of the soil friction angle and footing embedment depth. These best fitted equations are obtained using the data from numerical analysis of finite ICCESD
12 4 th International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2018) element system Abacus. Hence, estimating the ultimate bearing capacity will be much more accurate and easier than previous empirical equations. Proposed equations for bearing capacity factors are: N c = 3.15 * exp( 4.56*φ *H/B ) (1) N q = 0.88 * exp( 6.00*φ *H/B ) (2) N = 0.4 * exp( 7.75*φ ) (3) 4. CONCLUSIONS Frictional angle and embedment depth has huge impact over bearing capacity factors. All the bearing capacity factors are proportional to embedment depth. When embedment depth increases, value of bearing capacity factors also increase. All the bearing capacity factors are also proportional to the friction angle of the medium. When friction angle increases, bearing capacity also increases. Footing at higher embedment depth and higher frictional medium will ensure higher bearing capacity. REFERENCES Cerato, A. B., & Lutenegger, A. J. (2007). Scale effects of shallow foundation bearing capacity on granular material. Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 133(10), Chen, W. F. (1975). Limit analysis and soil plasticity. Elsevier. Hansen, J. B. (1970). A revised and extended formula for bearing capacity. Geoteknisk Inst., Bulletin 28, Kiran, M., & Bacha, N. (2015). An Experimental Study on Behaviour of Bearing Capacity and Settlement of Circular and Square Footing Resting on Reinforced Sand Bed Stratified with Lateritic Soil. In International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology, (Vol. 4, N(ESRSA Publications.). Kumar, J., & & Khatri, V. N. (2011). Bearing capacity factors of circular foundations for a general c ϕ soil using lower bound finite elements limit analysis. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 35(3), Lavasan, A. A., & Ghazavi, M. (2012). Behavior of closely spaced square and circular footings on reinforced sand. Soils and Foundations, 52(1), Meyerhof, G. G. (1963). Some recent research on the bearing capacity of foundations. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 1(1), Michalowski, R. L. (1997). An estimate of the influence of soil weight on bearing capacity using limit analysis. Soils Found., 37(4), Reissner, H. (1924). Zum erddruckproblem. In Proc. 1st Int. Congress for Applied Mechanics (pp ). Delft,The Netherlands. Terzaghi, K. (1943). Theoretical soil mechanics. New York: Wiley. Vesic, A. S. (1973). Analysis of ultimate loads of shallow foundations. J. Soil Mech. Found. Div., 99(1), Zhu, M., & Michalowski, R. L. (2005). Shape factors for limit loads on square and rectangular footings. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 131(2), ICCESD
Typical factors of safety for bearing capacity calculation in different situations
 Typical factors of safety for bearing capacity calculation in different situations Density of soil: In geotechnical engineering, one deals with several densities such as dry density, bulk density, saturated
Typical factors of safety for bearing capacity calculation in different situations Density of soil: In geotechnical engineering, one deals with several densities such as dry density, bulk density, saturated
Vertical Uplift Capacity of a Group of Equally Spaced Helical Screw Anchors in Sand
 SECM/15/080 Vertical Uplift Capacity of a Group of Equally Spaced Helical Screw Anchors in Sand S. Mukherjee 1* and Dr. S. Mittal 2 1 Amity University, Noida, India 2 Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee,
SECM/15/080 Vertical Uplift Capacity of a Group of Equally Spaced Helical Screw Anchors in Sand S. Mukherjee 1* and Dr. S. Mittal 2 1 Amity University, Noida, India 2 Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee,
UNIT-I SOIL EXPLORATION
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : Geotechnical Engineering - II (16CE127) Year & Sem: III-B.Tech & II-Sem
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : Geotechnical Engineering - II (16CE127) Year & Sem: III-B.Tech & II-Sem
Analysis of dilatometer test in calibration chamber
 Analysis of dilatometer test in calibration chamber Lech Bałachowski Gdańsk University of Technology, Poland Keywords: calibration chamber, DMT, quartz sand, FEM ABSTRACT: Because DMT in calibration test
Analysis of dilatometer test in calibration chamber Lech Bałachowski Gdańsk University of Technology, Poland Keywords: calibration chamber, DMT, quartz sand, FEM ABSTRACT: Because DMT in calibration test
Influence of Settlement on Bearing Capacity Analysis of Shallow Foundations on Sandy Clays in the Niger Delta, Nigeria
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Applied Engineering and Scientific Research, 201, 2 (4):20-27 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN: 22 0041 Influence
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Applied Engineering and Scientific Research, 201, 2 (4):20-27 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN: 22 0041 Influence
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad CIVIL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 00 04 CIVIL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name Course Code Regulation Course Structure Course Coordinator Course Faculty
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 00 04 CIVIL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name Course Code Regulation Course Structure Course Coordinator Course Faculty
Critical Pool Level and Stability of Slopes in Granular Soils
 TECHNICAL NOTES Critical Pool Level and Stability of Slopes in Granular Soils Radoslaw L. Michalowski, F.ASCE 1 Abstract: The influence of pore-water pressure and the pool water pressure on stability of
TECHNICAL NOTES Critical Pool Level and Stability of Slopes in Granular Soils Radoslaw L. Michalowski, F.ASCE 1 Abstract: The influence of pore-water pressure and the pool water pressure on stability of
Ground Failure Mechanism of Micoropiled-raft
 Ground Failure Mechanism of Micoropiled-raft T. H. Hwang 1), H. J. Kim 2), and * J.H. Shin 3) 1), 2), 3) Department of Civil Engineering, Konkuk University, Seoul 143-701, Korea 3) jhshin@konkuk.ac.kr
Ground Failure Mechanism of Micoropiled-raft T. H. Hwang 1), H. J. Kim 2), and * J.H. Shin 3) 1), 2), 3) Department of Civil Engineering, Konkuk University, Seoul 143-701, Korea 3) jhshin@konkuk.ac.kr
Critical face pressure and backfill pressure in shield TBM tunneling on soft ground
 Critical face pressure and backfill pressure in shield TBM tunneling on soft ground Kiseok Kim 1), Juyoung Oh 2), Hyobum Lee 3) and Hangseok Choi 4) 1), 3), 4) Department of civil engineering, Korea University,
Critical face pressure and backfill pressure in shield TBM tunneling on soft ground Kiseok Kim 1), Juyoung Oh 2), Hyobum Lee 3) and Hangseok Choi 4) 1), 3), 4) Department of civil engineering, Korea University,
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 CIVIL ENGINEERING Tutorial Question Bank Name : FOUNDATION ENGINEERING Code : A60126 Class : III B. Tech II Semester Branch
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 CIVIL ENGINEERING Tutorial Question Bank Name : FOUNDATION ENGINEERING Code : A60126 Class : III B. Tech II Semester Branch
The tensile capacity of suction caissons in sand under rapid loading
 Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics: ISFOG 25 Gourvenec & Cassidy (eds) 25 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 415 3963 X The tensile capacity of suction caissons in sand under rapid loading Guy T. Houlsby,
Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics: ISFOG 25 Gourvenec & Cassidy (eds) 25 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 415 3963 X The tensile capacity of suction caissons in sand under rapid loading Guy T. Houlsby,
Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
 43 Module 3: Lecture - 5 on Compressibility and Consolidation Contents Stresses in soil from surface loads; Terzaghi s 1-D consolidation theory; Application in different boundary conditions; Ramp loading;
43 Module 3: Lecture - 5 on Compressibility and Consolidation Contents Stresses in soil from surface loads; Terzaghi s 1-D consolidation theory; Application in different boundary conditions; Ramp loading;
Critical Gust Pressures on Tall Building Frames-Review of Codal Provisions
 Dr. B.Dean Kumar Dept. of Civil Engineering JNTUH College of Engineering Hyderabad, INDIA bdeankumar@gmail.com Dr. B.L.P Swami Dept. of Civil Engineering Vasavi College of Engineering Hyderabad, INDIA
Dr. B.Dean Kumar Dept. of Civil Engineering JNTUH College of Engineering Hyderabad, INDIA bdeankumar@gmail.com Dr. B.L.P Swami Dept. of Civil Engineering Vasavi College of Engineering Hyderabad, INDIA
Behavior of Square Footing Resting on Reinforced Sand Subjected to Static Load
 IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 3 Issue 02 July 2016 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 Behavior of Square Footing Resting on Reinforced Sand Subjected to Static
IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 3 Issue 02 July 2016 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 Behavior of Square Footing Resting on Reinforced Sand Subjected to Static
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING Volume 1, No 4, 2010
 Effect of geometric dimensions on the transmission coefficient of floating breakwaters Mohammad Hosein Tadayon, Khosro Bargi 2, Hesam Sharifian, S. Reza Hoseini - Ph.D student, Department of Civil Engineering,
Effect of geometric dimensions on the transmission coefficient of floating breakwaters Mohammad Hosein Tadayon, Khosro Bargi 2, Hesam Sharifian, S. Reza Hoseini - Ph.D student, Department of Civil Engineering,
computed using Equation 3-18 by setting the 2nd term equal to 0 and K A equal to K o and using the pressure distribution as shown in Figure 3-23.
 computed using Equation 3-18 by setting the 2nd term equal to 0 and K A equal to K o and using the pressure distribution as shown in Figure 3-23. (2) For the resisting side, passive pressure theory indicates
computed using Equation 3-18 by setting the 2nd term equal to 0 and K A equal to K o and using the pressure distribution as shown in Figure 3-23. (2) For the resisting side, passive pressure theory indicates
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON OPTIMUM INSTALLATION DEPTH OF PVD UNDER VACUUM CONSOLIDATION ABSTRACT
 EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON OPTIMUM INSTALLATION DEPTH OF PVD UNDER VACUUM CONSOLIDATION EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON OPTIMUM INSTALLATION DEPTH OF PVD UNDER VACUUM CONSOLIDATION J.-C CHAI i), N. MIURA
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON OPTIMUM INSTALLATION DEPTH OF PVD UNDER VACUUM CONSOLIDATION EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON OPTIMUM INSTALLATION DEPTH OF PVD UNDER VACUUM CONSOLIDATION J.-C CHAI i), N. MIURA
Investigation of Stresses in Ring Stiffened Circular Cylinder
 International Journal of Engineering and Technical Research (IJETR) ISSN: 2321-869, Volume-2, Issue-9, September 214 Investigation of Stresses in Ring Stiffened Circular Cylinder Neetesh N. Thakre, Dr.
International Journal of Engineering and Technical Research (IJETR) ISSN: 2321-869, Volume-2, Issue-9, September 214 Investigation of Stresses in Ring Stiffened Circular Cylinder Neetesh N. Thakre, Dr.
Tension Cracks. Topics Covered. Tension crack boundaries Tension crack depth Query slice data Thrust line Sensitivity analysis.
 Tension Cracks 16-1 Tension Cracks In slope stability analyses with cohesive soils, tension forces may be observed in the upper part of the slope. In general, soils cannot support tension so the results
Tension Cracks 16-1 Tension Cracks In slope stability analyses with cohesive soils, tension forces may be observed in the upper part of the slope. In general, soils cannot support tension so the results
Plane Turbulent Wall Jets in Limited Tailwater Depth
 International Journal of Engineering & Technology IJET-IJENS Vol: 11 No: 159 Plane Turbulent Wall Jets in Limited Tailwater Depth Shazy A. Shabayek 1 Abstract This paper presents laboratory study of plane
International Journal of Engineering & Technology IJET-IJENS Vol: 11 No: 159 Plane Turbulent Wall Jets in Limited Tailwater Depth Shazy A. Shabayek 1 Abstract This paper presents laboratory study of plane
CHAPTER 5: VACUUM TEST WITH VERTICAL DRAINS
 CHAPTER 5: VACUUM TEST WITH VERTICAL DRAINS 5.1 Introduction Using surcharging as the sole soil consolidation mean can take a long time to reach the desired soil settlement. Soil consolidation using prefabricated
CHAPTER 5: VACUUM TEST WITH VERTICAL DRAINS 5.1 Introduction Using surcharging as the sole soil consolidation mean can take a long time to reach the desired soil settlement. Soil consolidation using prefabricated
FEA ANALYSIS OF PRESSURE VESSEL WITHDIFFERENT TYPE OF END CONNECTIONS
 FEA ANALYSIS OF PRESSURE VESSEL WITHDIFFERENT TYPE OF END CONNECTIONS Deval Nitin Bhinde 1 and Rajanarsimha S. 2 1 MTech CAD-CAM & Robotics, 2 Facculty, Department of Mechanical Engineering K.J. Somaiya
FEA ANALYSIS OF PRESSURE VESSEL WITHDIFFERENT TYPE OF END CONNECTIONS Deval Nitin Bhinde 1 and Rajanarsimha S. 2 1 MTech CAD-CAM & Robotics, 2 Facculty, Department of Mechanical Engineering K.J. Somaiya
V-H-M Yield Surface describing Soil Structure Interaction of Sub-sea Structures and Wind Turbines on Caisson Foundations in Soft Clays
 NGM 2016 Reykjavik Proceedings of the 17 th Nordic Geotechnical Meeting Challenges in Nordic Geotechnic 25 th 28 th of May V-H-M Yield Surface describing Soil Structure Interaction of Sub-sea Structures
NGM 2016 Reykjavik Proceedings of the 17 th Nordic Geotechnical Meeting Challenges in Nordic Geotechnic 25 th 28 th of May V-H-M Yield Surface describing Soil Structure Interaction of Sub-sea Structures
An Innovative Solution for Water Bottling Using PET
 An Innovative Solution for Water Bottling Using PET A. Castellano, P. Foti, A. Fraddosio, S. Marzano, M.D. Piccioni, D. Scardigno* DICAR Politecnico di Bari, Italy *Via Orabona 4, 70125 Bari, Italy, scardigno@imedado.poliba.it
An Innovative Solution for Water Bottling Using PET A. Castellano, P. Foti, A. Fraddosio, S. Marzano, M.D. Piccioni, D. Scardigno* DICAR Politecnico di Bari, Italy *Via Orabona 4, 70125 Bari, Italy, scardigno@imedado.poliba.it
Displacement-based calculation method on soil-pile interaction of PHC pipe-piles
 Seattle, WA Displacement-based calculation method on soil-pile interaction of PHC pipe-piles Dr. Huang Fuyun Fuzhou University 31 st May, 217 Outline Background ing introduction ing results Simple calculation
Seattle, WA Displacement-based calculation method on soil-pile interaction of PHC pipe-piles Dr. Huang Fuyun Fuzhou University 31 st May, 217 Outline Background ing introduction ing results Simple calculation
m v = 1.04 x 10-4 m 2 /kn, C v = 1.29 x 10-2 cm 2 /min
 2.10 Problems Example 2.1: Design of Shallow Foundation in Saturated Clay Design a square footing to support a column load of 667 kn. The base of the footing will be located 1 m below the ground level
2.10 Problems Example 2.1: Design of Shallow Foundation in Saturated Clay Design a square footing to support a column load of 667 kn. The base of the footing will be located 1 m below the ground level
Stress and deformation of offshore piles under structural and wave loading
 Stress and deformation of offshore piles under structural and wave loading Author Eicher, Jackie, Guan, Hong, Jeng, Dong-Sheng Published 2003 Journal Title Ocean Engineering DOI https://doi.org/10.1016/s0029-8018(02)00031-8
Stress and deformation of offshore piles under structural and wave loading Author Eicher, Jackie, Guan, Hong, Jeng, Dong-Sheng Published 2003 Journal Title Ocean Engineering DOI https://doi.org/10.1016/s0029-8018(02)00031-8
International Journal of Technical Research and Applications e-issn: , Volume 4, Issue 3 (May-June, 2016), PP.
 DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF FEED CHECK VALVE AS CONTROL VALVE USING CFD SOFTWARE R.Nikhil M.Tech Student Industrial & Production Engineering National Institute of Engineering Mysuru, Karnataka, India -570008
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF FEED CHECK VALVE AS CONTROL VALVE USING CFD SOFTWARE R.Nikhil M.Tech Student Industrial & Production Engineering National Institute of Engineering Mysuru, Karnataka, India -570008
Plane Turbulent Wall Jets in Limited Tailwater Depth
 International Journal of Engineering & Technology IJET-IJENS Vol: 11 No: 6 192 Plane Turbulent Wall Jets in Limited Tailwater Depth Shazy A. Shabayek 1 Abstract This paper presents laboratory study of
International Journal of Engineering & Technology IJET-IJENS Vol: 11 No: 6 192 Plane Turbulent Wall Jets in Limited Tailwater Depth Shazy A. Shabayek 1 Abstract This paper presents laboratory study of
Advanced Hydraulics Prof. Dr. Suresh A. Kartha Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati
 Advanced Hydraulics Prof. Dr. Suresh A. Kartha Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module - 4 Hydraulics Jumps Lecture - 4 Features of Hydraulic Jumps (Refer Slide
Advanced Hydraulics Prof. Dr. Suresh A. Kartha Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module - 4 Hydraulics Jumps Lecture - 4 Features of Hydraulic Jumps (Refer Slide
JSEE. Slope Stability and Bearing Capacity of Footings on Top of Slopes Under Repeated Dynamic Loads. 1. Introduction
 JSEE Vol. 18, No. 3, 2016 This is an extended version of the paper presented in SEE7 conference, peer-reviewed again and approved by the JSEE editorial board. Slope Stability and Bearing Capacity of Footings
JSEE Vol. 18, No. 3, 2016 This is an extended version of the paper presented in SEE7 conference, peer-reviewed again and approved by the JSEE editorial board. Slope Stability and Bearing Capacity of Footings
Design and Structural Analysis of Cylindrical Shell
 Design and Structural Analysis of Cylindrical Shell Lokesha 1, Chandan R 2, Byregowda K C 3 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Dr. Ambedkar Institute of Technology Bangalore, India 2,3 Assistant Prof.
Design and Structural Analysis of Cylindrical Shell Lokesha 1, Chandan R 2, Byregowda K C 3 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Dr. Ambedkar Institute of Technology Bangalore, India 2,3 Assistant Prof.
Chapter 4: Single Vertical Arch
 Chapter 4: Single Vertical Arch 4.1 Introduction This chapter considers a single pressurized arch in a vertical plane. This arch is similar to the arches that will be studied in the following chapter.
Chapter 4: Single Vertical Arch 4.1 Introduction This chapter considers a single pressurized arch in a vertical plane. This arch is similar to the arches that will be studied in the following chapter.
Bearing capacity of strip footings on unsaturated soils by the slip line theory
 Bearing capacity of strip footings on unsaturated soils by the slip line theory Thanh Vo 1,a and Adrian Russell 1 1 Centre for Infrastructure Engineering and Safety, School of Civil and Environmental Engineering,
Bearing capacity of strip footings on unsaturated soils by the slip line theory Thanh Vo 1,a and Adrian Russell 1 1 Centre for Infrastructure Engineering and Safety, School of Civil and Environmental Engineering,
Bearing Capacity and Settlement Response of PMS Tanks on Cohesionless Soil Lithology in Lekki, Lagos of Nigeria
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Applied Engineering and Scientific Research,, ():- (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN: 8 Bearing Capacity and
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Applied Engineering and Scientific Research,, ():- (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN: 8 Bearing Capacity and
Lateral Load Analysis Considering Soil-Structure Interaction. ANDREW DAUMUELLER, PE, Ph.D.
 Lateral Load Analysis Considering Soil-Structure Interaction ANDREW DAUMUELLER, PE, Ph.D. Overview Introduction Methods commonly used to account for soil-structure interaction for static loads Depth to
Lateral Load Analysis Considering Soil-Structure Interaction ANDREW DAUMUELLER, PE, Ph.D. Overview Introduction Methods commonly used to account for soil-structure interaction for static loads Depth to
The Adequacy of Pushover Analysis to Evaluate Vulnerability of Masonry Infilled Steel Frames Subjected to Bi-Directional Earthquake Loading
 The Adequacy of Pushover Analysis to Evaluate Vulnerability of Masonry Infilled Steel Frames Subjected to Bi-Directional Earthquake Loading B.Beheshti Aval & M. Mohammadzadeh K.N.Toosi University of Technology,
The Adequacy of Pushover Analysis to Evaluate Vulnerability of Masonry Infilled Steel Frames Subjected to Bi-Directional Earthquake Loading B.Beheshti Aval & M. Mohammadzadeh K.N.Toosi University of Technology,
Title Tsunami during 2011 East Japan Eart. The final publication is available より本文ファイルは に公開.
 Title Combined Failure Mechanism of a Bre Tsunami during 2011 East Japan Eart Author(s) Iai, Susumu Citation Geotechnical, Geological and Earthq 37: 177-186 Issue Date 2015-04-16 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/198459
Title Combined Failure Mechanism of a Bre Tsunami during 2011 East Japan Eart Author(s) Iai, Susumu Citation Geotechnical, Geological and Earthq 37: 177-186 Issue Date 2015-04-16 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/198459
Wave Motion. interference destructive interferecne constructive interference in phase. out of phase standing wave antinodes resonant frequencies
 Wave Motion Vocabulary mechanical waves pulse continuous periodic wave amplitude period wavelength period wave velocity phase transverse wave longitudinal wave intensity displacement amplitude phase velocity
Wave Motion Vocabulary mechanical waves pulse continuous periodic wave amplitude period wavelength period wave velocity phase transverse wave longitudinal wave intensity displacement amplitude phase velocity
BURIED PIPE RESPONSE SUBJECTED TO TRAFFIC LOAD EXPERIMENTAL AND NUMERICAL INVESTIGATIONS
 Geotec., Const. Mat. & Env., ISSN:2186-2990, Japan, DOI: https://doi.org/10.21660/2017.39.91957 BURIED PIPE RESPONSE SUBJECTED TO TRAFFIC LOAD EXPERIMENTAL AND NUMERICAL INVESTIGATIONS *Ahdyeh Mosadegh
Geotec., Const. Mat. & Env., ISSN:2186-2990, Japan, DOI: https://doi.org/10.21660/2017.39.91957 BURIED PIPE RESPONSE SUBJECTED TO TRAFFIC LOAD EXPERIMENTAL AND NUMERICAL INVESTIGATIONS *Ahdyeh Mosadegh
Advanced Hydraulics Prof. Dr. Suresh A. Kartha Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati
 Advanced Hydraulics Prof. Dr. Suresh A. Kartha Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module - 4 Hydraulic Jumps Lecture - 1 Rapidly Varied Flow- Introduction Welcome
Advanced Hydraulics Prof. Dr. Suresh A. Kartha Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module - 4 Hydraulic Jumps Lecture - 1 Rapidly Varied Flow- Introduction Welcome
Analyses of the fuel cell stack assembly pressure
 Journal of Power Sources 145 (2005) 353 361 Analyses of the fuel cell stack assembly pressure Shuo-Jen Lee, Chen-De Hsu, Ching-Han Huang Department of Mechanical Engineering, Yuan Ze University, 135 FarEast
Journal of Power Sources 145 (2005) 353 361 Analyses of the fuel cell stack assembly pressure Shuo-Jen Lee, Chen-De Hsu, Ching-Han Huang Department of Mechanical Engineering, Yuan Ze University, 135 FarEast
Experimental Investigation of Clear-Water Local Scour at Pile Groups
 Experimental Investigation of Clear-Water Local Scour at Pile Groups B. Ataie-Ashtiani 1 and A. A. Beheshti 2 Abstract: Experiments of local scour around pile groups are carried out under steady clear-water
Experimental Investigation of Clear-Water Local Scour at Pile Groups B. Ataie-Ashtiani 1 and A. A. Beheshti 2 Abstract: Experiments of local scour around pile groups are carried out under steady clear-water
FREE OVERFALL IN A HORIZONTAL SMOOTH RECTANGULAR CHANNEL
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 8, Issue 4, April 017, pp. 004 01, Article ID: IJCIET_08_04_8 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=8&itype=4
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 8, Issue 4, April 017, pp. 004 01, Article ID: IJCIET_08_04_8 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=8&itype=4
Influence of Fly Ash Content on Compaction Characteristics of Fly Ash Clay Mixture
 Jordan Journal of Civil Engineering, Volume, No. 1, 16 Influence of Fly Ash Content on Compaction Characteristics of Fly Ash Clay Mixture Ashis Kumar Bera 1)* and Sayan Kundu 2) 1) Associate Professor
Jordan Journal of Civil Engineering, Volume, No. 1, 16 Influence of Fly Ash Content on Compaction Characteristics of Fly Ash Clay Mixture Ashis Kumar Bera 1)* and Sayan Kundu 2) 1) Associate Professor
Analysis of Shear Lag in Steel Angle Connectors
 University of New Hampshire University of New Hampshire Scholars' Repository Honors Theses and Capstones Student Scholarship Spring 2013 Analysis of Shear Lag in Steel Angle Connectors Benjamin Sawyer
University of New Hampshire University of New Hampshire Scholars' Repository Honors Theses and Capstones Student Scholarship Spring 2013 Analysis of Shear Lag in Steel Angle Connectors Benjamin Sawyer
Modeling of thin strip profile during cold rolling on roll crossing and shifting mill
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences - Papers: Part A Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2013 Modeling of thin strip profile during cold
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences - Papers: Part A Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2013 Modeling of thin strip profile during cold
Module 7 Lecture 1. Swelling and Collapse Behavior
 Swelling and Collapse Behavior Module 7 Lecture 1 Collapse and swelling phenomena occur in unsaturated soils during the saturation process. The compacted unsaturated soils, on the dry of optimum, have
Swelling and Collapse Behavior Module 7 Lecture 1 Collapse and swelling phenomena occur in unsaturated soils during the saturation process. The compacted unsaturated soils, on the dry of optimum, have
machine design, Vol.6(2014) No.3, ISSN pp
 machine design, Vol.6(04) No.3, ISSN 8-59 pp. 79-84 ANALYSIS OF CLEARANCES AND DEFORMATIONS AT CYCLOID DISC Mirko BLAGOJEVIĆ * University of Kragujevac, Faculty of Engineering, Kragujevac, Serbia Preliminary
machine design, Vol.6(04) No.3, ISSN 8-59 pp. 79-84 ANALYSIS OF CLEARANCES AND DEFORMATIONS AT CYCLOID DISC Mirko BLAGOJEVIĆ * University of Kragujevac, Faculty of Engineering, Kragujevac, Serbia Preliminary
[Barve, 4(7): July, 2015] ISSN: (I2OR), Publication Impact Factor: 3.785
![[Barve, 4(7): July, 2015] ISSN: (I2OR), Publication Impact Factor: 3.785 [Barve, 4(7): July, 2015] ISSN: (I2OR), Publication Impact Factor: 3.785](/thumbs/96/128298826.jpg) IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY PARAMETRIC STUDY TO UNDERSTAND THE SEISMIC BEHAVIOUR OF INTZE TANK SUPPORTED ON SHAFT Prasad S. Barve *, Ruchi P. Barve * Civil
IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY PARAMETRIC STUDY TO UNDERSTAND THE SEISMIC BEHAVIOUR OF INTZE TANK SUPPORTED ON SHAFT Prasad S. Barve *, Ruchi P. Barve * Civil
Elastic-Plastic Finite Element Analysis for Zhongwei--guiyang Natural Gas Pipeline Endangered by Collapse
 Abstract Elastic-Plastic Finite Element Analysis for Zhongwei--guiyang Natural Gas Pipeline Endangered by Collapse Gengxin Wu,Peng Zhang,Zhixiang Li,Zunhai Ke,Guizhi Li,Anmin Jiang 2 School of Civil Engineering
Abstract Elastic-Plastic Finite Element Analysis for Zhongwei--guiyang Natural Gas Pipeline Endangered by Collapse Gengxin Wu,Peng Zhang,Zhixiang Li,Zunhai Ke,Guizhi Li,Anmin Jiang 2 School of Civil Engineering
APPENDIX G SCA BASIN CALCULATIONS
 ONONDAGA LAKE SEDIMENT MANAGEMENT FINAL DESIGN APPENDIX G SCA BASIN CALCULATIONS p:\honeywell -syr\444853 - lake detail design\09 reports\9.22 sediment management final design\110930 submittal\110906 onon
ONONDAGA LAKE SEDIMENT MANAGEMENT FINAL DESIGN APPENDIX G SCA BASIN CALCULATIONS p:\honeywell -syr\444853 - lake detail design\09 reports\9.22 sediment management final design\110930 submittal\110906 onon
Effect of channel slope on flow characteristics of undular hydraulic jumps
 River Basin Management III 33 Effect of channel slope on flow characteristics of undular hydraulic jumps H. Gotoh, Y. Yasuda & I. Ohtsu Department of Civil Engineering, College of Science and Technology,
River Basin Management III 33 Effect of channel slope on flow characteristics of undular hydraulic jumps H. Gotoh, Y. Yasuda & I. Ohtsu Department of Civil Engineering, College of Science and Technology,
Experiment (13): Flow channel
 Experiment (13): Flow channel Introduction: An open channel is a duct in which the liquid flows with a free surface exposed to atmospheric pressure. Along the length of the duct, the pressure at the surface
Experiment (13): Flow channel Introduction: An open channel is a duct in which the liquid flows with a free surface exposed to atmospheric pressure. Along the length of the duct, the pressure at the surface
Pore-Air Entrapment during Infiltration
 Pore-Air Entrapment during Infiltration GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1200, 700-6th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada T2P 0T8 Main: +1 403 269 2002 Fax: +1 888 463 2239 Introduction Infiltration
Pore-Air Entrapment during Infiltration GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1200, 700-6th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada T2P 0T8 Main: +1 403 269 2002 Fax: +1 888 463 2239 Introduction Infiltration
AERODYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS OF NACA 0012 AIRFOIL SECTION AT DIFFERENT ANGLES OF ATTACK
 AERODYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS OF NACA 0012 AIRFOIL SECTION AT DIFFERENT ANGLES OF ATTACK SUPREETH NARASIMHAMURTHY GRADUATE STUDENT 1327291 Table of Contents 1) Introduction...1 2) Methodology.3 3) Results...5
AERODYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS OF NACA 0012 AIRFOIL SECTION AT DIFFERENT ANGLES OF ATTACK SUPREETH NARASIMHAMURTHY GRADUATE STUDENT 1327291 Table of Contents 1) Introduction...1 2) Methodology.3 3) Results...5
A Review of the Bed Roughness Variable in MIKE 21 FLOW MODEL FM, Hydrodynamic (HD) and Sediment Transport (ST) modules
 A Review of the Bed Roughness Variable in MIKE 1 FLOW MODEL FM, Hydrodynamic (HD) and Sediment Transport (ST) modules by David Lambkin, University of Southampton, UK 1 Bed roughness is considered a primary
A Review of the Bed Roughness Variable in MIKE 1 FLOW MODEL FM, Hydrodynamic (HD) and Sediment Transport (ST) modules by David Lambkin, University of Southampton, UK 1 Bed roughness is considered a primary
ENTUCKY RANSPORTATION C ENTER. College of Engineering
 Research Report KTC-05-34/SPR-297-05-1I T K ENTUCKY RANSPORTATION C ENTER College of Engineering USE OF ULTRA-LIGHTWEIGHT GEOFOAM TO REDUCE STRESSES IN HIGHWAY CULVERT EXTENSIONS Our Mission We provide
Research Report KTC-05-34/SPR-297-05-1I T K ENTUCKY RANSPORTATION C ENTER College of Engineering USE OF ULTRA-LIGHTWEIGHT GEOFOAM TO REDUCE STRESSES IN HIGHWAY CULVERT EXTENSIONS Our Mission We provide
Experimental Method to Analyse Limit Load in Pressure Vessel
 International OPEN ACCESS Journal Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Dilip M. Patel 1, Dr. Bimlesh Kumar 2 1 Mechanical Department D.N.Patel COE, Shahada 2 Mechanical Department COE, Faizpur Abstract:
International OPEN ACCESS Journal Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Dilip M. Patel 1, Dr. Bimlesh Kumar 2 1 Mechanical Department D.N.Patel COE, Shahada 2 Mechanical Department COE, Faizpur Abstract:
The application of shakedown approach to granular pavement layers
 The application of shakedown approach to granular pavement layers Greg Arnold Nottingham Centre for Pavement Engineering (NCPE), University of Nottingham, UK Andrew Dawson Nottingham Centre for Pavement
The application of shakedown approach to granular pavement layers Greg Arnold Nottingham Centre for Pavement Engineering (NCPE), University of Nottingham, UK Andrew Dawson Nottingham Centre for Pavement
Cubzac-les-Ponts Experimental Embankments on Soft Clay
 Cubzac-les-Ponts Experimental Embankments on Soft Clay GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1, 7 - th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada TP T Main: +1 3 9 Fax: +1 3 39 Introduction In the 197 s, a series
Cubzac-les-Ponts Experimental Embankments on Soft Clay GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1, 7 - th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada TP T Main: +1 3 9 Fax: +1 3 39 Introduction In the 197 s, a series
Application of pushover analysis in estimating seismic demands for large-span spatial structure
 28 September 2 October 2009, Universidad Politecnica de Valencia, Spain Alberto DOMINGO and Carlos LAZARO (eds.) Application of pushover analysis in estimating seismic demands for large-span spatial structure
28 September 2 October 2009, Universidad Politecnica de Valencia, Spain Alberto DOMINGO and Carlos LAZARO (eds.) Application of pushover analysis in estimating seismic demands for large-span spatial structure
Strength Reduction Stability
 1 Introduction Reduction Stability Stability by strength reduction is a procedure where the factor of safety is obtained by weakening the soil in steps in an elastic-plastic finite element analysis until
1 Introduction Reduction Stability Stability by strength reduction is a procedure where the factor of safety is obtained by weakening the soil in steps in an elastic-plastic finite element analysis until
Fatigue Analysis of English-Willow Cricket Bat
 Fatigue Analysis of English-Willow Cricket Bat Mr. Rajshekhar Chimmat 1, Mr. Shreenidhi Kulkarni 2 1M.Tech. Scholar, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, KLS Gogte Institute of Technology, Belagavi, Karnataka,
Fatigue Analysis of English-Willow Cricket Bat Mr. Rajshekhar Chimmat 1, Mr. Shreenidhi Kulkarni 2 1M.Tech. Scholar, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, KLS Gogte Institute of Technology, Belagavi, Karnataka,
Engineering Practice on Ice Propeller Strength Assessment Based on IACS Polar Ice Rule URI3
 10th International Symposium on Practical Design of Ships and Other Floating Structures Houston, Texas, United States of America 2007 American Bureau of Shipping Engineering Practice on Ice Propeller Strength
10th International Symposium on Practical Design of Ships and Other Floating Structures Houston, Texas, United States of America 2007 American Bureau of Shipping Engineering Practice on Ice Propeller Strength
STRESS ANALYSIS OF BELL CRANK LEVER
 STRESS ANALYSIS OF BELL CRANK LEVER Mr. M. M. Dange 1, Prof. S. R. Zaveri 2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, R.C.E.R.T., R.T.M.N.U, Chandrapur, (India) 2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, R.C.E.R.T.,
STRESS ANALYSIS OF BELL CRANK LEVER Mr. M. M. Dange 1, Prof. S. R. Zaveri 2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, R.C.E.R.T., R.T.M.N.U, Chandrapur, (India) 2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, R.C.E.R.T.,
Pressuremeters in Geotechnical Design
 Pressuremeters in Geotechnical Design B.G. CLARKE Department of Civil Engineering University of Newcastle upon Tyne BLACK1E ACADEMIC & PROFESSIONAL An Imprint of Chapman & Hall London Glasgow Weinheim
Pressuremeters in Geotechnical Design B.G. CLARKE Department of Civil Engineering University of Newcastle upon Tyne BLACK1E ACADEMIC & PROFESSIONAL An Imprint of Chapman & Hall London Glasgow Weinheim
Irrigation &Hydraulics Department lb / ft to kg/lit.
 CAIRO UNIVERSITY FLUID MECHANICS Faculty of Engineering nd Year CIVIL ENG. Irrigation &Hydraulics Department 010-011 1. FLUID PROPERTIES 1. Identify the dimensions and units for the following engineering
CAIRO UNIVERSITY FLUID MECHANICS Faculty of Engineering nd Year CIVIL ENG. Irrigation &Hydraulics Department 010-011 1. FLUID PROPERTIES 1. Identify the dimensions and units for the following engineering
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON THE HYDRODYNAMIC BEHAVIORS OF TWO CONCENTRIC CYLINDERS
 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON THE HYDRODYNAMIC BEHAVIORS OF TWO CONCENTRIC CYLINDERS *Jeong-Rok Kim 1), Hyeok-Jun Koh ), Won-Sun Ruy 3) and Il-Hyoung Cho ) 1), 3), ) Department of Ocean System Engineering, Jeju
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON THE HYDRODYNAMIC BEHAVIORS OF TWO CONCENTRIC CYLINDERS *Jeong-Rok Kim 1), Hyeok-Jun Koh ), Won-Sun Ruy 3) and Il-Hyoung Cho ) 1), 3), ) Department of Ocean System Engineering, Jeju
A Hare-Lynx Simulation Model
 1 A Hare- Simulation Model What happens to the numbers of hares and lynx when the core of the system is like this? Hares O Balance? S H_Births Hares H_Fertility Area KillsPerHead Fertility Births Figure
1 A Hare- Simulation Model What happens to the numbers of hares and lynx when the core of the system is like this? Hares O Balance? S H_Births Hares H_Fertility Area KillsPerHead Fertility Births Figure
Variable Face Milling to Normalize Putter Ball Speed and Maximize Forgiveness
 Proceedings Variable Face Milling to Normalize Putter Ball Speed and Maximize Forgiveness Jacob Lambeth *, Dustin Brekke and Jeff Brunski Cleveland Golf, 5601 Skylab Rd. Huntington Beach, CA 92647, USA;
Proceedings Variable Face Milling to Normalize Putter Ball Speed and Maximize Forgiveness Jacob Lambeth *, Dustin Brekke and Jeff Brunski Cleveland Golf, 5601 Skylab Rd. Huntington Beach, CA 92647, USA;
Aerodynamic Analyses of Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine By Different Blade Airfoil Using Computer Program
 ISSN : 2250-3021 Aerodynamic Analyses of Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine By Different Blade Airfoil Using Computer Program ARVIND SINGH RATHORE 1, SIRAJ AHMED 2 1 (Department of Mechanical Engineering Maulana
ISSN : 2250-3021 Aerodynamic Analyses of Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine By Different Blade Airfoil Using Computer Program ARVIND SINGH RATHORE 1, SIRAJ AHMED 2 1 (Department of Mechanical Engineering Maulana
This file is part of the following reference: Access to this file is available from:
 ResearchOnline@JCU This file is part of the following reference: Shahriar, Mohammad Abu Naser (2014) Settlement of shallow foundations due to rise of water table in granular soils. PhD thesis, James Cook
ResearchOnline@JCU This file is part of the following reference: Shahriar, Mohammad Abu Naser (2014) Settlement of shallow foundations due to rise of water table in granular soils. PhD thesis, James Cook
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 112 (2015 ) 40 45
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering ( ) 7th Asia-Pacific Congress on Sports Technology, APCST 3-Dimensional joint torque calculation of compression sportswear using
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering ( ) 7th Asia-Pacific Congress on Sports Technology, APCST 3-Dimensional joint torque calculation of compression sportswear using
Study on Fire Plume in Large Spaces Using Ground Heating
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 11 (2011) 226 232 The 5 th Conference on Performance-based Fire and Fire Protection Engineering Study on Fire Plume in Large Spaces Using
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 11 (2011) 226 232 The 5 th Conference on Performance-based Fire and Fire Protection Engineering Study on Fire Plume in Large Spaces Using
This document downloaded from vulcanhammer.net vulcanhammer.info Chet Aero Marine
 This document downloaded from vulcanhammer.net vulcanhammer.info Chet Aero Marine Don t forget to visit our companion site http://www.vulcanhammer.org Use subject to the terms and conditions of the respective
This document downloaded from vulcanhammer.net vulcanhammer.info Chet Aero Marine Don t forget to visit our companion site http://www.vulcanhammer.org Use subject to the terms and conditions of the respective
Non-Linear Seismic Analysis of Multi-Storey Building
 Non-Linear Seismic Analysis of Multi-Storey Building Uzair Khan 1 1 M.Tech (Structural & Construction Engineering) Department of Civil Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Jalandhar. Hina Gupta
Non-Linear Seismic Analysis of Multi-Storey Building Uzair Khan 1 1 M.Tech (Structural & Construction Engineering) Department of Civil Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Jalandhar. Hina Gupta
Theory of a vertically loaded Suction Pile in CLAY
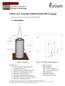 11 Theory of a vertically loaded Suction Pile in CLAY Mainly based on the et Norske Veritas NV-RP-E303 1. Convention Water COG h L Soil COG t Figure 1 Suction Pile Figure 2 Suction pile with main parameters
11 Theory of a vertically loaded Suction Pile in CLAY Mainly based on the et Norske Veritas NV-RP-E303 1. Convention Water COG h L Soil COG t Figure 1 Suction Pile Figure 2 Suction pile with main parameters
AIRFLOW GENERATION IN A TUNNEL USING A SACCARDO VENTILATION SYSTEM AGAINST THE BUOYANCY EFFECT PRODUCED BY A FIRE
 - 247 - AIRFLOW GENERATION IN A TUNNEL USING A SACCARDO VENTILATION SYSTEM AGAINST THE BUOYANCY EFFECT PRODUCED BY A FIRE J D Castro a, C W Pope a and R D Matthews b a Mott MacDonald Ltd, St Anne House,
- 247 - AIRFLOW GENERATION IN A TUNNEL USING A SACCARDO VENTILATION SYSTEM AGAINST THE BUOYANCY EFFECT PRODUCED BY A FIRE J D Castro a, C W Pope a and R D Matthews b a Mott MacDonald Ltd, St Anne House,
19.1 Problem: Maximum Discharge
 19.1 Problem: Maximum Discharge In partially full channel having an equilateral triangular cross section, the rate of discharge is Q = KAR/3 in which K is a constant, A flow area, R is the hydraulic mean
19.1 Problem: Maximum Discharge In partially full channel having an equilateral triangular cross section, the rate of discharge is Q = KAR/3 in which K is a constant, A flow area, R is the hydraulic mean
CFD Analysis of Supersonic Nozzle with Varying Divergent Profile
 CFD Analysis of Supersonic Nozzle with Varying Divergent Profile Kaviya sundar #1, Thanikaivel Murugan. D *2 # UG Degree holder, B.E. Aeronautical Engineering, Jeppiaar Engineering college, Chennai, India,
CFD Analysis of Supersonic Nozzle with Varying Divergent Profile Kaviya sundar #1, Thanikaivel Murugan. D *2 # UG Degree holder, B.E. Aeronautical Engineering, Jeppiaar Engineering college, Chennai, India,
Structural Design and Analysis of the New Mobile Refuge Chamber
 Key Engineering Materials Online: 2013-09-10 ISSN: 1662-9795, Vol. 584, pp 175-178 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/kem.584.175 2014 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Structural Design and Analysis of
Key Engineering Materials Online: 2013-09-10 ISSN: 1662-9795, Vol. 584, pp 175-178 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/kem.584.175 2014 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Structural Design and Analysis of
Study to Establish Relations for the Relative Strength of API 650 Cone Roof Roof-to-Shell and Shell-to- Bottom Joints
 Thunderhead Engineering Consultants I N C O R P O R A T E D 1006 Poyntz Ave. Manhattan, KS 66502-5459 785-770-8511 www. thunderheadeng.com Study to Establish Relations for the Relative Strength of API
Thunderhead Engineering Consultants I N C O R P O R A T E D 1006 Poyntz Ave. Manhattan, KS 66502-5459 785-770-8511 www. thunderheadeng.com Study to Establish Relations for the Relative Strength of API
Saturated-Unsaturated Consolidation
 Introduction Saturated-Unsaturated Consolidation This example looks at the volume change behavior of a saturated-unsaturated column under loading, wetting and drying conditions. Feature Highlights GeoStudio
Introduction Saturated-Unsaturated Consolidation This example looks at the volume change behavior of a saturated-unsaturated column under loading, wetting and drying conditions. Feature Highlights GeoStudio
Chapter 2 Hydrostatics and Control
 Chapter 2 Hydrostatics and Control Abstract A submarine must conform to Archimedes Principle, which states that a body immersed in a fluid has an upward force on it (buoyancy) equal to the weight of the
Chapter 2 Hydrostatics and Control Abstract A submarine must conform to Archimedes Principle, which states that a body immersed in a fluid has an upward force on it (buoyancy) equal to the weight of the
Determination of Burst Pressure of Spherical Shell
 International Journal for Ignited Minds (IJIMIINDS) Determination of Burst Pressure of Spherical Shell Balaji J a & Shivappa H A b a PG Student, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering,Dr. Ambedkar Institute of
International Journal for Ignited Minds (IJIMIINDS) Determination of Burst Pressure of Spherical Shell Balaji J a & Shivappa H A b a PG Student, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering,Dr. Ambedkar Institute of
Vibrations of table tennis racket composite wood blades: modeling and experiments
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 34 (2012 ) 694 699 9 th Conference of the International Sports Engineering Association (ISEA) Vibrations of table tennis racket composite
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 34 (2012 ) 694 699 9 th Conference of the International Sports Engineering Association (ISEA) Vibrations of table tennis racket composite
Blast Damage Consideratons for Horizontal Pressure Vessel and Potential for Domino Effects
 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 26, 2012 Guest Editors: Valerio Cozzani, Eddy De Rademaeker Copyright 2012, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-17-4; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 26, 2012 Guest Editors: Valerio Cozzani, Eddy De Rademaeker Copyright 2012, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-17-4; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
REPORT GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION FOR THE PROPOSED BLOCK-1 SUB-STATION SY NO-44, NEAR KYATAGANACHERLU VILLAGE
 REPORT ON GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION FOR THE PROPOSED BLOCK-1 SUB-STATION SY NO-44, NEAR KYATAGANACHERLU VILLAGE CLIENT: KARNATAKA SOLAR POWER DEVELOPMENT CORPORATION BANGALORE 0 GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION
REPORT ON GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION FOR THE PROPOSED BLOCK-1 SUB-STATION SY NO-44, NEAR KYATAGANACHERLU VILLAGE CLIENT: KARNATAKA SOLAR POWER DEVELOPMENT CORPORATION BANGALORE 0 GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION
Vibration Analysis and Test of Backup Roll in Temper Mill
 Sensors & Transducers 2013 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.com Vibration Analysis and Test of Backup Roll in Temper Mill Yuanmin Xie College of Machinery and Automation, Wuhan University of Science and
Sensors & Transducers 2013 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.com Vibration Analysis and Test of Backup Roll in Temper Mill Yuanmin Xie College of Machinery and Automation, Wuhan University of Science and
SHEAR PERFORMANCE OF RC FOOTING BEAMS BY CAP-TIE SYSTEM USING WELDED STIRRUPS
 The 7th International Conference of Asian Concrete Federation SUSTAINABLE CONCRETE FOR NOW AND THE FUTURE 3 Oct 2 Nov, 216, Hanoi, Vietnam www.acf216.vn SHEAR PERFORMANCE OF RC FOOTING BEAMS BY CAP-TIE
The 7th International Conference of Asian Concrete Federation SUSTAINABLE CONCRETE FOR NOW AND THE FUTURE 3 Oct 2 Nov, 216, Hanoi, Vietnam www.acf216.vn SHEAR PERFORMANCE OF RC FOOTING BEAMS BY CAP-TIE
Using sea bed roughness as a wave energy dissipater
 Island Sustainability II 203 Using sea bed roughness as a wave energy dissipater T. Elgohary 1, R. Elgohary 1 & M. Hagrass 2 1 Department of Civil Engineering (Irrigation and Hydraulic), The Tenth of Ramadan
Island Sustainability II 203 Using sea bed roughness as a wave energy dissipater T. Elgohary 1, R. Elgohary 1 & M. Hagrass 2 1 Department of Civil Engineering (Irrigation and Hydraulic), The Tenth of Ramadan
Waves. harmonic wave wave equation one dimensional wave equation principle of wave fronts plane waves law of reflection
 Waves Vocabulary mechanical wave pulse continuous periodic wave amplitude wavelength period frequency wave velocity phase transverse wave longitudinal wave intensity displacement wave number phase velocity
Waves Vocabulary mechanical wave pulse continuous periodic wave amplitude wavelength period frequency wave velocity phase transverse wave longitudinal wave intensity displacement wave number phase velocity
3. GRADUALLY-VARIED FLOW (GVF) AUTUMN 2018
 3. GRADUALLY-VARIED FLOW (GVF) AUTUMN 2018 3.1 Normal Flow vs Gradually-Varied Flow V 2 /2g EGL (energy grade line) Friction slope S f h Geometric slope S 0 In flow the downslope component of weight balances
3. GRADUALLY-VARIED FLOW (GVF) AUTUMN 2018 3.1 Normal Flow vs Gradually-Varied Flow V 2 /2g EGL (energy grade line) Friction slope S f h Geometric slope S 0 In flow the downslope component of weight balances
EFFECT OF CORNER CUTOFFS ON FLOW CHARACTERISTICS AROUND A SQUARE CYLINDER
 EFFECT OF CORNER CUTOFFS ON FLOW CHARACTERISTICS AROUND A SQUARE CYLINDER Yoichi Yamagishi 1, Shigeo Kimura 1, Makoto Oki 2 and Chisa Hatayama 3 ABSTRACT It is known that for a square cylinder subjected
EFFECT OF CORNER CUTOFFS ON FLOW CHARACTERISTICS AROUND A SQUARE CYLINDER Yoichi Yamagishi 1, Shigeo Kimura 1, Makoto Oki 2 and Chisa Hatayama 3 ABSTRACT It is known that for a square cylinder subjected
Transactions on Ecology and the Environment vol 12, 1996 WIT Press, ISSN
 Open boundary condition for unsteady open-channel flow K. Mizumura Civil Engineering Department, Kanazawa Institute of Technology, 7-1 Ogigaoka, Nonoichimachi, Ishikawa Pref. 921, Japan Abstract Initial
Open boundary condition for unsteady open-channel flow K. Mizumura Civil Engineering Department, Kanazawa Institute of Technology, 7-1 Ogigaoka, Nonoichimachi, Ishikawa Pref. 921, Japan Abstract Initial
APPLICATION OF PUSHOVER ANALYSIS ON EARTHQUAKE RESPONSE PREDICATION OF COMPLEX LARGE-SPAN STEEL STRUCTURES
 APPLICATION OF PUSHOVER ANALYSIS ON EARTHQUAKE RESPONSE PREDICATION OF COMPLEX LARGE-SPAN STEEL STRUCTURES J.R. Qian 1 W.J. Zhang 2 and X.D. Ji 3 1 Professor, 3 Postgraduate Student, Key Laboratory for
APPLICATION OF PUSHOVER ANALYSIS ON EARTHQUAKE RESPONSE PREDICATION OF COMPLEX LARGE-SPAN STEEL STRUCTURES J.R. Qian 1 W.J. Zhang 2 and X.D. Ji 3 1 Professor, 3 Postgraduate Student, Key Laboratory for
Bottom End-Closure Design Optimization of DOT-39 Non-Refillable Refrigerant Cylinders
 Y. Kisioglu a) Department of Mechanical Education, Kocaeli University, Izmit, Kocaeli, 41100, Turkey J. R. Brevick Industrial and Systems Engineering, The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio G. L. Kinzel
Y. Kisioglu a) Department of Mechanical Education, Kocaeli University, Izmit, Kocaeli, 41100, Turkey J. R. Brevick Industrial and Systems Engineering, The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio G. L. Kinzel
Reinforced Soil Retaining Walls-Design and Construction
 Lecture 32 Reinforced Soil Retaining Walls-Design and Construction Prof. G L Sivakumar Babu Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560012 Example calculation An 8 m high
Lecture 32 Reinforced Soil Retaining Walls-Design and Construction Prof. G L Sivakumar Babu Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560012 Example calculation An 8 m high
Influence of rounding corners on unsteady flow and heat transfer around a square cylinder
 Influence of rounding corners on unsteady flow and heat transfer around a square cylinder S. K. Singh Deptt. of Mech. Engg., M. B. M. Engg. College / J. N. V. University, Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India Abstract
Influence of rounding corners on unsteady flow and heat transfer around a square cylinder S. K. Singh Deptt. of Mech. Engg., M. B. M. Engg. College / J. N. V. University, Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India Abstract
