Pharynx one of the visceral tubes the common chamber of the respiratory and digestive tracts located behind the nasal and oral cavities funnel-shaped
|
|
|
- Fay Theresa Barrett
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pharynx and soft palate Pharynx one of the visceral tubes the common chamber of the respiratory and digestive tracts located behind the nasal and oral cavities funnel-shaped in form 12 cm in length; its greatest width is about 5 cm and narrowest 1.5 cm 1
2 Pharynx Nasopharynx extends from the base of skull to the level of the soft palate; has a respiratory function Oropharynx extends from the soft palate to the hyoid bone Laryngopharynx extends from the level of the hyoid bone to the lower border of the cricoid cartilage, continuous with the esophagus 2
3 Nasopharynx Pharyngeal orifice of auditory tube Pharyngeal recess Torus of auditory tube Salpingopharyngeal fold Pharyngeal tonsil Torus of auditory tube the elevation behind the orifice, which is produced by underlying cartilage of the auditory tube salpingopharyngeal fold produced by the salpingopharyngeus, which extends from the lower part of the torus to palatopharyngeus pharyngeal recess a slit-like recess behind the salpingopharyngeal fold pharyngeal tonsil a collection of lymphatic tissue lying on the roof of the pharynx 3
4 Nasopharynx Levator veli palatini m. Salpingopharyngeus m. Tensor veli palatini m. Ascending palatini a. 4
5 Oropharynx Palatopharyngeal arch Palatoglossal arch Palatine tonsil Oropharynx extends from the soft palate to the hyoid bone palatine tonsil the mass of lymphatic tissue between the two folds 5
6 Oropharynx Lesser palaine a. Ascending pharyngeal a. Ascending palatine a. Dorsal lingual a. Facial a. 6
7 Oropharynx Sup. constrictor m. Palatoglossal m. Palatopharyngeal l m. Styloglossal m. Glossopharyngeal n. Stylopharyngeal m. Hyoglossal m. Mid. constrictor m. Stylohyoid ligament 7
8 Laryngopharynx Piriform recess Laryngopharynx extends from the level of the hyoid bone to the lower border of the cricoid cartilage, continuous with the esophagus piriform recess lies between the hyoid bone, thyrohyoid membrane and thyroid cartilage laterally, and the aryepiglottic fold and the arytenoid and cricoid cartilages medially 8
9 Wall of pharynx Pharyngobasilar fascia Pharyngobasilar fascia a strong fibrous submucosal layer exposing in the interval between the superior constrictor muscle and the base of the skull Circular coat: sup. constrictor, mid. constrictor, and inf. constrictor 9
10 Longitudinal coat: salpingopharyngeus, palatopharygeus, and stylopharyngeus Wall of pharynx salpingopharyngeus from lower part of auditory tube to joins fibers of palatopharyngeus muscle Palatopharyngeus from posterior border of hard palate and palatine aponeurosis to side of pharynx Stylopharyngeus from styloid process to posterior border of thyroid cartilage and wall of pharynx nerve supply glossopharyngeal n 10
11 Structures of the pharyngeal wall superior constrictor from medial pterygoid plate, pterygoid hamulus, pterygomandibular raphe, mylohyoid line, side of tongue to median raphe of pharynx 11
12 Structures of the pharyngeal wall middle constrictor: from lesser and greater horns of hyoid bone; stylohyoid ligament to median raphe of pharynx inferior constrictor : from the oblique line of thyroid cartilage; side of 12 cricoid cartilage to median raphe of pharynx
13 Structures passing through intervals between Auditory tube Skull and superior constrictor levator veli palatini, ascending palatine a., auditory tube 13
14 Structures passing through intervals between Sup. constrictor Skull and superior constrictor levator veli palatini, ascending palatine a., auditory tube Mid. constrictor Inf. constrictor Superior constrictor and middle constrictor styolpharyngeus y m., glossopharyngeal n.; and stylohyoid lig Middle constrictor and inferior constrictor internal laryngeal n., superior laryngeal l a. Inferior constrictor and esophagus recurrent laryngeal n., inferior laryngeal a. 14
15 Structures passing through intervals between Superior constrictor and middle constrictor styolpharyngeus m., glossopharyngeal n.; and stylohyoid lig 15
16 Soft palate 16
17 Soft palate tensor veli palatini from sphenoid bone, lateral surface of the auditory tube,,pass around the hamulus of the medial pterygoid plate to aponeurosis of the soft palate nerve supply: mandibular n. levator veli palatini from petrous portion of temporal bone, medial surface of the auditory tube to aponeurosis of the soft palate 17
18 Soft palate 18
19 Soft palate Musculus uvular from posterior nasal spine of hard palate to connective tissue of uvula 19
20 Soft palate Palatopharyngeal m. Palatoglossal m. palatopharyngeus from posterior border of hard palate and palatine aponeurosis to side of pharynx palatoglossus from the side of the tongue to inferior surface of the soft palate 20
21 Blood supply of pharynx a) ascending pharyngeal branch of external carotid a. b) ascending palatine branch of facial a. c) tonsil branch of facial a. d) descending palatine a. from maxillary a. 21
22 Nerve supply of pharynx 1) motor: glossopharyngeal n (IX) innervate the stylopharyngeus m ; 1) motor: glossopharyngeal n. (IX) innervate the stylopharyngeus m.; mandibular n. (V3) innervate the tensor veli palatini m; the remaining muscles by the pharyngeal branch of the vagus (or accessory n.) 22
23 Nerve supply of pharynx 2) h b ill h b 2) sensory: nasopharynx by maxillary n.; oropharynx by glossopharyngeal n; larygopharynx by vagus n. 23
24 Borders of the infratemporal fossa Lat. pterygoid m. Med. pterygoid m. 24
25 Borders of the infratemporal fossa 25
26 Borders of the infratemporal fossa 26
27 Removal of head Identify the sympathetic trunk and the large superior cervical sympathetic ti ganglion, cut one side of it just superior to SCG, and leave it to the prevertebral region 27
28 28
29 Removal of head Hold the cervical viscera forward 29
30 Removal of head Cut rectus capitis lateralis, rectus capitis anterior, and longus capitis 30
31 Orientation of the cranial nerves Safeguard cranial nerves IX, X, XI and XII 31
32 Orientation of the cranial nerves A CN IX L E.A CN XII down CN X I.A Int.V SCG CN XI 32
33 Orientation of the cranial nerves 33
34 Orientation of the cranial nerves 34
35 Subdivisons of pharynx: nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx Nasopharynx: salpingopharyngeus, pharyngeal tonsil, tensor veli palatini, levator veli palatini. Oropharynx: palatoglossal m., palatopharyngeal m.; palatine tonsil Larygopharynx: piriform recess Blood supply of pharynx: ascending pharyngeal a., facial a., maxillary a., lingual a. Nerve innervation of pharynx Motor: pharyngeal plexus, glossopharyngeal n., mandibular n. Sensory: nasopharynx (maxillary n.), oropharynx (glossopharyngeal g n.), laryngopharynx y (vagus n.) 35
36 Structure of the pharynx wall Mucous membrane Muscular layer Circular coat: superior, middle, inferior constrictor m. Longitudinal coat: stylopharyngeus, tl salpingopharyngeus, palatopharyngeus m. Pharyngobasilar fascia Structure passing through intervals between Skull and superior constrictor: levator veli palatine, ascending palatine a., auditory tube Superior and middle constrictor: stylopharyngeus m., glossopharyngeal n., stylohyoid lig. Middle and inferior constrictor: internal laryngeal n., superior laryngeal a. Inferior constrictor and esophagus: recurrent laryngeal n., inferior laryngeal a Muscules of the soft palate: tensor veli palatini, levator veli palatini, palatoglossus, palatopharyngeus, musculus uvular 36
37 Pharynx and Soft Palate Dr. Lue, Grossanatomy Pharynx one of the visceral tubes the common chamber of the respiratory and digestive tracts located behind the nasal and oral cavities funnel-shaped in form 12 cm in length; its greatest breath is about 5 cm and narrowest 1.5 cm Subdivisions without anterior wall, the pharynx communicates directly with the nasal, oral, and laryngeal cavities; posterior wall lies against the prevertebral layer of deep cervical fascia; it is subdivided accordingly A. Nasopharynx: extends from the base of skull to the level of the soft palate; has a respiratory function Anteriorly, choanae (two posterior nasal apertures), nasal septum Wall of the pharynx Pharyngeal orifice of the auditory tube: Torus of auditory tube: the elevation behind the orifice, which is produced by underlying cartilage of the auditory tube salpingopharyngeal fold: produced by the salpingopharyngeus, which extends from the lower part of the torus to palatopharyngeus pharyngeal recess: a slit-like recess behind the salpingopharyngeal fold pharyngeal tonsil: a collection of lymphatic tissue lying on the roof of the pharynx; enlarged adenoids tensor veli palatini m. levator veli palatini m. B. Oropharynx extends from the soft palate to the hyoid bone palatoglossal arch: produced by the palatoglossal m. palatopharyngeal arch: produced by palatopharyngeal m. palatine tonsil: the mass of lymphatic tissue between the two folds. Five tonsillar arteries to the palatine tonsil: a) descending palatine a. from maxillary a. 1
38 b) ascending pharyngeal branch of external carotid a. c) ascending palatine branch of facial a. d) tonsil branch of facial a. e) dorsal lingual branches of the lingual a. C. Laryngopharynx extends from the level of the hyoid bone to the lower border of the cricoid cartilage, continuous with the esophagus. piriform recess: lies between the hyoid bone, thyrohyoid membrane and thyroid cartilage laterally, and the aryepiglottic fold and the arytenoid and cricoid cartilages medially; Foreign bodies such as fish bones may lodge in this recess. Blood supply of pharynx: arteries a) ascending pharyngeal branch of external carotid a. b) ascending palatine branch of facial a. c) tonsil branch of facial a. d) descending palatine a. from maxillary a. veins: pharyngeal venous plexus via pterygoid plexus internal jugular v. Nerve supply of pharynx: 1) motor: glossopharyngeal n. (IX) innervate the stylopharyngeus m.; mandibular n. (V3) innervate the tensor veli palatini m; the remaining muscles by the pharyngeal branch of the vagus (or accessory n.) 2) sensory: nasopharynx aid by maxillary n.; oropharynx supply from glossopharyngeal n; laryngpharynx supply from vagus n Structure of the pharyngeal wall: Mucous membrane is continuous with the lining of the adjacent chambers Pharyngobasilar fascia a strong fibrous submucosal layer exposing in the interval between the superior constrictor muscle and the base of the skull Muscular layer divided into two groups: Circular coat consists of the three constrictor muscles superior constrictor: from medial pterygoid plate, pterygoid hamulus, pterygomandibular raphe, mylohyoid line, side of tongue to median raphe of pharynx 2
39 middle constrictor: from lesser and greater horns of hyoid bone; stylohyoid ligament to median raphe of pharynx inferior constrictor : from the oblique line of thyroid cartilage; side of cricoid cartilage to median raphe of pharynx each muscle meets its fellow in the posterior median plane at the fibrous pharyngeal raphe which extends up to attach to the pharyngeal tubercle of the occipital bone action participate in act of swallowing nerve supply from pharyngeal plexus the inferior constrictor muscle is also supplied by the external branch of superior laryngeal nerve Longitudinal coat also consists of three muscles which originate separately and blend at their insertions Stylopharyngeus: from styloid process to posterior border of thyroid cartilage and wall of pharynx action elevates larynx and pharynx nerve supply glossopharyngeal n. Palatopharyngeus: from posterior border of hard palate and palatine aponeurosis to side of pharynx action approximates palatopharyngeal folds nerve supply pharyngeal plexus salpingopharyngeus: from lower part of auditory tube to joins fibers of palatopharyngeus muscle action same as that of the palatopharyngeus m. nerve supply - pharyngeal plexus Buccopharyngeal fascia - the areolar coat covers the muscles, is continuous with the buccinator fascia, and contains pharyngeal venous and nerve plexuses Structures passing through intervals between: A. Skull and superior constrictor levator veli palatini, ascending palatine artery, auditory tube B. Superior constrictor and middle constrictor stylopharyngeus m., glossopharyngeal n.; and stylohyoid lig. C. Middle constrictor and inferior constrictor internal laryngeal n., superior laryngeal a. 3
40 D. Inferior constrictor and esophagus recurrent laryngeal n., inferior laryngeal a. Soft Palate Muscles of the soft palate tensor veli palatini: from sphenoid bone, lateral surface of the auditory tube, pass around the hamulus of the medial pterygoid plate to aponeurosis of the soft palate action: tenses the plate, opens the auditory tube nerve supply: mandibular n. levator veli palatini: from petrous portion of temporal bone, medial surface of the ausitory tube to aponeurosis of the soft palate action: lifts the soft plate nerve supply: pharyngeal plexus. palatoglossus: from the side of the tongue to inferior surface of the soft palate action: pulls the tongue superiorly, tenses the plate nerve supply: pharyngeal plexus palatopharyngeus: from posterior border of hard palate and palatine aponeurosis to posterior border of thyroid cartilage and side of pharynx action: lifts the larynx, tense the plate nerve supply: pharyngeal plexus musculus uvular: from posterior nasal spine of hard palate to connective tissue of uvula action: elevate and retract uvula; thickens central region of soft plate nerve supply: pharyngeal plexus 4
Tikrit University College of Dentistry nd
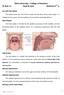 Lec [10] The Palate The palate forms the roof of the mouth a the floor of the nasal cavit It is divided into two parts: the hard palate in front a the soft palate behi. Hard Palate The hard palate is formed
Lec [10] The Palate The palate forms the roof of the mouth a the floor of the nasal cavit It is divided into two parts: the hard palate in front a the soft palate behi. Hard Palate The hard palate is formed
Otitis media. An anatomical perspective
 Otitis media An anatomical perspective 1 Presentation prepared by: Brian Palmer, D.D.S. Kansas City, Missouri, USA December, 2001. 2 Knowledge is most meaningful when shared with others. WARNING Some of
Otitis media An anatomical perspective 1 Presentation prepared by: Brian Palmer, D.D.S. Kansas City, Missouri, USA December, 2001. 2 Knowledge is most meaningful when shared with others. WARNING Some of
UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 9.01 GENERAL FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. Brings oxygenated air to the alveoli B. Removes air containing carbon dioxide C. Filters, warms, and humidifies
UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 9.01 GENERAL FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. Brings oxygenated air to the alveoli B. Removes air containing carbon dioxide C. Filters, warms, and humidifies
2/28/18. Respiratory System. 1 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Introduction. Anatomy. Physiology. Respiratory System
 Introduction Respiratory System Chapter 28 Respiration: We inhale air, extract oxygen from it, exhale air Cardiovascular and respiratory systems work together Failure of either system: - Disruption of
Introduction Respiratory System Chapter 28 Respiration: We inhale air, extract oxygen from it, exhale air Cardiovascular and respiratory systems work together Failure of either system: - Disruption of
DEEP DISSECTIONS OF THE VEINS OF THE BOVINE HEAD: UNPUBLISHED WORK BY PROF. J. M. W. LEROUX ( )
 Onderstepoort J. vet. Res., 59, 211-218 (1992) DEEP DISSECTIONS OF THE VEINS OF THE BOVINE HEAD: UNPUBLISHED WORK BY PROF. J. M. W. LEROUX (1926-1991) MALlE M. S. SMUTS and A. J. BEZUIDENHOUT, Department
Onderstepoort J. vet. Res., 59, 211-218 (1992) DEEP DISSECTIONS OF THE VEINS OF THE BOVINE HEAD: UNPUBLISHED WORK BY PROF. J. M. W. LEROUX (1926-1991) MALlE M. S. SMUTS and A. J. BEZUIDENHOUT, Department
Be sure you understand these four functions of the respiratory system before you begin this lab.
 Biology 212: Human Anatomy and Physiology II ************************************************************************************************************* RESPIRATORY ANATOMY & VENTILATION *************************************************************************************************************
Biology 212: Human Anatomy and Physiology II ************************************************************************************************************* RESPIRATORY ANATOMY & VENTILATION *************************************************************************************************************
People need lots of things to survive, but the most urgent need from moment to moment
 Chapter 8 Oxygenating the Machine: The Respiratory System In This Chapter Tracking respiration: In with oxygen, out with carbon dioxide Identifying the organs and muscles of the respiratory tract Taking
Chapter 8 Oxygenating the Machine: The Respiratory System In This Chapter Tracking respiration: In with oxygen, out with carbon dioxide Identifying the organs and muscles of the respiratory tract Taking
B. Lining - epithelium
 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Function supply body with oxygen and remove carbon dioxide. This process is called respiration, can be broken down into 4 components. I. Pulmonary Ventilation or breathing movement of
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Function supply body with oxygen and remove carbon dioxide. This process is called respiration, can be broken down into 4 components. I. Pulmonary Ventilation or breathing movement of
Batter s box. Game 1. Respiratory system essentials. Options. The respiratory system consists of the respiratory tract, the 1
 Game 1 Batter s box Fill in the blanks with the appropriate words. Hint: Some answers are used more than once. Respiratory system essentials The respiratory system consists of the respiratory tract, the
Game 1 Batter s box Fill in the blanks with the appropriate words. Hint: Some answers are used more than once. Respiratory system essentials The respiratory system consists of the respiratory tract, the
Chapter 15. Lecture and Animation Outline
 Chapter 15 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
Chapter 15 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
The Respiratory System. Medical Terminology
 The Respiratory System Medical Terminology The respiratory system is where gas exchange occurs via respiration; inhalation/exhalation. pick up oxygen from inhaled air expels carbon dioxide and water sinus
The Respiratory System Medical Terminology The respiratory system is where gas exchange occurs via respiration; inhalation/exhalation. pick up oxygen from inhaled air expels carbon dioxide and water sinus
Clinical Respiratory System Quiz
 Quiz Description Clinical Respiratory System Quiz Q.1) Q.2) Q.3) Q.4) Q.5) Q.6) What is NOT true about Asthma? It can be triggered by air temperature and allergens. It is the inflammation of the throat.
Quiz Description Clinical Respiratory System Quiz Q.1) Q.2) Q.3) Q.4) Q.5) Q.6) What is NOT true about Asthma? It can be triggered by air temperature and allergens. It is the inflammation of the throat.
Internal Anatomy of Fish
 Internal Anatomy of Fish The Systems of a Fish Skeletal System Muscular System Respiratory System Digestive System Circulatory System Nervous System Reproductive System Special Organs Skeletal System
Internal Anatomy of Fish The Systems of a Fish Skeletal System Muscular System Respiratory System Digestive System Circulatory System Nervous System Reproductive System Special Organs Skeletal System
Chapter 23: Respiratory System
 Chapter 23: Respiratory System I. Functions of the Respiratory System A. List and describe the five major functions of the respiratory system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. II. Anatomy and Histology of the Respiratory
Chapter 23: Respiratory System I. Functions of the Respiratory System A. List and describe the five major functions of the respiratory system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. II. Anatomy and Histology of the Respiratory
Initial stage of fetal development of the pharyngotympanic tube cartilage with special reference to muscle attachments to the tube
 Original Article pissn 2093-3665 eissn 2093-3673 Initial stage of fetal development of the pharyngotympanic tube cartilage with special reference to muscle attachments to the tube Yukio Katori 1, Jose
Original Article pissn 2093-3665 eissn 2093-3673 Initial stage of fetal development of the pharyngotympanic tube cartilage with special reference to muscle attachments to the tube Yukio Katori 1, Jose
Chapter 23 Respiratory System
 Chapter 23 Respiratory System I. Functions of the Respiratory System: 1. Gas Exchange 2. Regulatory (blood ph) 3. Voice Production 4. Olfaction 5. Protection II. Anatomy & Histology of the Respiratory
Chapter 23 Respiratory System I. Functions of the Respiratory System: 1. Gas Exchange 2. Regulatory (blood ph) 3. Voice Production 4. Olfaction 5. Protection II. Anatomy & Histology of the Respiratory
The Respiratory System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 15 The Respiratory System Chapter 15 Learning Outcomes 15-1 15-2 Describe the primary functions of the respiratory
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 15 The Respiratory System Chapter 15 Learning Outcomes 15-1 15-2 Describe the primary functions of the respiratory
1 Henry Strong Denison Scholar for
 THE PALATE ANALOGUE: AN APPROACH TO UNDERSTANDING VELOPHARYNGEAL FUNCTION By A. LEE DELLON 1 and JOHN E. HooPES, M.D. Division of Plastic Surgery, The ffohns Hopkins University School of Medicine and Theffohns
THE PALATE ANALOGUE: AN APPROACH TO UNDERSTANDING VELOPHARYNGEAL FUNCTION By A. LEE DELLON 1 and JOHN E. HooPES, M.D. Division of Plastic Surgery, The ffohns Hopkins University School of Medicine and Theffohns
82 Respiratory Tract NOTES
 82 Respiratory Tract NOTES RESPIRATORY TRACT The respiratory tract conducts air to the lungs where gaseous exchange occurs. It is separated into air-conducting and respiratory (where gas exchange occurs)
82 Respiratory Tract NOTES RESPIRATORY TRACT The respiratory tract conducts air to the lungs where gaseous exchange occurs. It is separated into air-conducting and respiratory (where gas exchange occurs)
The Respiratory System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Organs of the Respiratory system
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Organs of the Respiratory system
Exercise 18B Class Chondrichthyes Cartilaginous Fishes
 AP Biology Chapter 24 Exercise #18: Chordates: Fish Cartilaginous Fishes Lab Guide Exercise 18B Class Chondrichthyes Cartilaginous Fishes This group contains about 970 species that are characterized by
AP Biology Chapter 24 Exercise #18: Chordates: Fish Cartilaginous Fishes Lab Guide Exercise 18B Class Chondrichthyes Cartilaginous Fishes This group contains about 970 species that are characterized by
Review. 1. Which of the following statements regarding the Adam s apple is FALSE?
 Chapter 25 Review 1. Which of the following statements regarding the Adam s apple is FALSE? A. It is inferior to the cricoid cartilage. B. It is formed by the thyroid cartilage. C. It is the uppermost
Chapter 25 Review 1. Which of the following statements regarding the Adam s apple is FALSE? A. It is inferior to the cricoid cartilage. B. It is formed by the thyroid cartilage. C. It is the uppermost
Frog Dissection. External Observation
 Frog Dissection External Observation Use the diagram below to locate and identify the external features of the head. Find the mouth, external nares, tympani (ear drum), eyes, and nictitating membranes
Frog Dissection External Observation Use the diagram below to locate and identify the external features of the head. Find the mouth, external nares, tympani (ear drum), eyes, and nictitating membranes
(Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System
 (Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System I. (Slide 2) The Respiratory Tract A) Major structures and regions of the respiratory Tract/Route INTO body 1) nose 2) nasal cavity 3) pharynx 4) glottis 5)
(Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System I. (Slide 2) The Respiratory Tract A) Major structures and regions of the respiratory Tract/Route INTO body 1) nose 2) nasal cavity 3) pharynx 4) glottis 5)
PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Parts of the Respiratory System The RS can be divided into two parts: 1. Respiratory Tract, (path that air follows). Nasal passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi,
PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Parts of the Respiratory System The RS can be divided into two parts: 1. Respiratory Tract, (path that air follows). Nasal passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi,
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Human Anatomy & Physiology 19 Karen Webb Smith Unit Five Respiratory System URLs http://yucky.kids.discovery.com/flash/body/pg000138.html http://www.stemnet.nf.ca/~dpower/resp/exchange.htm #Breathing http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/
Human Anatomy & Physiology 19 Karen Webb Smith Unit Five Respiratory System URLs http://yucky.kids.discovery.com/flash/body/pg000138.html http://www.stemnet.nf.ca/~dpower/resp/exchange.htm #Breathing http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/
Frog Dissection. PreLab: 1. Where do frogs get their energy? Draw a simple food chain to illustrate.
 Name Date Frog Dissection Class # PreLab: Amphibian Reading As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but they must return to water to reproduce. Eggs are laid
Name Date Frog Dissection Class # PreLab: Amphibian Reading As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but they must return to water to reproduce. Eggs are laid
Dogfish Shark Dissection
 Dogfish Shark Dissection Name Date Period Fun Facts: Materials: The teeth of sharks are modified scales embedded in the skin of its mouth Sharks have pits on their face used to detect electric fields Sharks
Dogfish Shark Dissection Name Date Period Fun Facts: Materials: The teeth of sharks are modified scales embedded in the skin of its mouth Sharks have pits on their face used to detect electric fields Sharks
B-immobility from structural or organic damage
 DRAGON'S TOUCH weaknesses of the human anatomy by: Hei Long This volume (and the ones to follow) concentrates on the 43 major pressure points of the body. Of course, there are quite a few more, but these
DRAGON'S TOUCH weaknesses of the human anatomy by: Hei Long This volume (and the ones to follow) concentrates on the 43 major pressure points of the body. Of course, there are quite a few more, but these
Chapter 23: The Respiratory System
 Chapter 23: The Respiratory System I. The Respiratory System: An Introduction, p. 814 Objectives: 1. Describe the primary functions of the respiratory system. 2. Explain how the delicate respiratory exchange
Chapter 23: The Respiratory System I. The Respiratory System: An Introduction, p. 814 Objectives: 1. Describe the primary functions of the respiratory system. 2. Explain how the delicate respiratory exchange
Chapter 16 Respiratory System
 Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Ventilation 12/1/2012. Clarification of Terminology. Osteology of Ventilation
 Clarification of Terminology : the mechanical process by which air is inhaled and exhaled through the lungs. It describes only the movement of air. Respiration: a term used to describe the gas exchange
Clarification of Terminology : the mechanical process by which air is inhaled and exhaled through the lungs. It describes only the movement of air. Respiration: a term used to describe the gas exchange
UROMASTIX DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 UROMASTIX DIGESTIVE SYSTEM by Dr. Rashmi Tripathi Department of Zoology Brahmanand College, Kanpur DIGESTIVE SYSTEM : The digestive system consists of (A) Alimentary canal and (B) Associated digestive
UROMASTIX DIGESTIVE SYSTEM by Dr. Rashmi Tripathi Department of Zoology Brahmanand College, Kanpur DIGESTIVE SYSTEM : The digestive system consists of (A) Alimentary canal and (B) Associated digestive
-8- spinous. nape caudal fin. body depth. pectoral fin. anus. total length Fig. 4
 click for previous page -8-1.3 Illustrated Glossary of Technical Terms and Measurements External Morphology and Measurements spinous dorsal fin soft nape caudal fin interorbital body depth snout lateral
click for previous page -8-1.3 Illustrated Glossary of Technical Terms and Measurements External Morphology and Measurements spinous dorsal fin soft nape caudal fin interorbital body depth snout lateral
Outline - Respiratory System. Function of the respiratory system Parts of the respiratory system Mechanics of breathing Regulation of breathing
 Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
ALBERTA CANCER REGISTRY
 Cancer Care ALBERTA CANCER REGISTRY 2009 Annual Report of Cancer Statistics December 2012 ISSN: 1705-0251 Contents About The Alberta Cancer Registry... 2 Introduction... 3 Highlights... 3 Data... 3...
Cancer Care ALBERTA CANCER REGISTRY 2009 Annual Report of Cancer Statistics December 2012 ISSN: 1705-0251 Contents About The Alberta Cancer Registry... 2 Introduction... 3 Highlights... 3 Data... 3...
Respiratory System Anatomy. Chapter 23
 Chapter 23 The Respiratory System Structurally, the respiratory system is divided into upper and lower divisions or tracts. The upper respiratory tract consists of the nose, pharynx and associated structures.
Chapter 23 The Respiratory System Structurally, the respiratory system is divided into upper and lower divisions or tracts. The upper respiratory tract consists of the nose, pharynx and associated structures.
(Guttural Pouch) in the Thoroughbred Equine -A Silicon Mold Approach-
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 76(6): 335-346, March, 2000 Macroscopic Anatomy of the Auditory Tube Diverticulum (Guttural Pouch) in the Thoroughbred Equine -A Silicon Mold Approach- By Dugarjaviin MANGLAI.
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 76(6): 335-346, March, 2000 Macroscopic Anatomy of the Auditory Tube Diverticulum (Guttural Pouch) in the Thoroughbred Equine -A Silicon Mold Approach- By Dugarjaviin MANGLAI.
Respiratory system. Premedical - Biology
 Respiratory system Premedical - Biology Composition of atmosphere Nitrogen (N 2 ) 840 ppmv (78.084%) Oxygen (O 2 ) 209,460 ppmv (20.946%) Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) 387 ppmv (0.0387%) Argon (Ar), Neon (Ne),
Respiratory system Premedical - Biology Composition of atmosphere Nitrogen (N 2 ) 840 ppmv (78.084%) Oxygen (O 2 ) 209,460 ppmv (20.946%) Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) 387 ppmv (0.0387%) Argon (Ar), Neon (Ne),
Respiratory System. 1. muscular tube lined by mucous membrane 2. throat 3. nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx
 I. Functions of the Respiratory System A. gas exchange B. prevent dehydration C. sound D. olfaction E. ph regulation II. Anatomy of the Respiratory System A. Nose 1. external nares vestibule nasal cavity
I. Functions of the Respiratory System A. gas exchange B. prevent dehydration C. sound D. olfaction E. ph regulation II. Anatomy of the Respiratory System A. Nose 1. external nares vestibule nasal cavity
Alberta Cancer Registry
 C A N C E R C A R E Alberta Cancer Registry 2007 Annual Report of Cancer Statistics ISSN: 1705-0251 June 2010 1 Alberta Cancer Registry 2007 Annual Report of Cancer Statistics Contents About The Alberta
C A N C E R C A R E Alberta Cancer Registry 2007 Annual Report of Cancer Statistics ISSN: 1705-0251 June 2010 1 Alberta Cancer Registry 2007 Annual Report of Cancer Statistics Contents About The Alberta
Lab 17. The Respiratory System. Laboratory Objectives
 Lab 17 The Respiratory System Laboratory Objectives Identify and describe the anatomical structures of the respiratory system. Describe the relationship between volume and pressure. Describe changes in
Lab 17 The Respiratory System Laboratory Objectives Identify and describe the anatomical structures of the respiratory system. Describe the relationship between volume and pressure. Describe changes in
L9 Frog Dissection- External Page 1 of 7 STUDENT LABORATORY PACKET. Student s Name Modified from Prentice Hall Lab. Manual Lab Instructor Date Points
 L9 Frog Dissection- External Page 1 of 7 STUDENT LABORATORY PACKET Lab 9: Bull Frog: External Examination Student s Name Modified from Prentice Hall Lab. Manual Lab Instructor Date Points Objective: 1.
L9 Frog Dissection- External Page 1 of 7 STUDENT LABORATORY PACKET Lab 9: Bull Frog: External Examination Student s Name Modified from Prentice Hall Lab. Manual Lab Instructor Date Points Objective: 1.
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM OF RABBIT:
 RESPIRATION The term respiration means exchange of gases (particularly oxygen and carbon dioxide) between an organism and its medium. Physiologically, the term respiration may be defined as a biochemical
RESPIRATION The term respiration means exchange of gases (particularly oxygen and carbon dioxide) between an organism and its medium. Physiologically, the term respiration may be defined as a biochemical
Fish. Water Dwelling Animals
 Fish Water Dwelling Animals Class Agnatha (Jawless fish) They are believed to be the most primitive and oldest vertebrates. Lamprey and hagfish are the only 2 living members of this class and are placed
Fish Water Dwelling Animals Class Agnatha (Jawless fish) They are believed to be the most primitive and oldest vertebrates. Lamprey and hagfish are the only 2 living members of this class and are placed
Gen Bio 2 Lab #10: Chondrichthyes and Osteichthyes
 Name: Date Gen Bio 2 Lab #10: Chondrichthyes and Osteichthyes Pre-Lab Reading: pages 687-690 Pre-Lab Vocabulary: 1) Ampullae of Lorenzini 2) Claspers 3) Lateral line 4) Ovoviviparous 5) Squalene 6) Viviparous
Name: Date Gen Bio 2 Lab #10: Chondrichthyes and Osteichthyes Pre-Lab Reading: pages 687-690 Pre-Lab Vocabulary: 1) Ampullae of Lorenzini 2) Claspers 3) Lateral line 4) Ovoviviparous 5) Squalene 6) Viviparous
Station 3. Appendicular and Axial skeleton
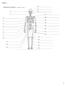 Station 1 1 Station 2 2 Station 3 Appendicular and Axial skeleton AXIAL SKELETON APPENDICULAR SKELETON 3 Station 4 4 Station 5 5 Station 5 6 Station 6 1. How many vertebrae make up the spine? 2. How many
Station 1 1 Station 2 2 Station 3 Appendicular and Axial skeleton AXIAL SKELETON APPENDICULAR SKELETON 3 Station 4 4 Station 5 5 Station 5 6 Station 6 1. How many vertebrae make up the spine? 2. How many
Developing a 3D model of the tongue and mouth to assess pressure generation and predict bolus flow when swallowing
 Developing a 3D model of the tongue and mouth to assess pressure generation and predict bolus flow when swallowing Marie Greuel (Team Leader), Tyler Lieberthal (Communicator), Kelly Hanneken (BWIG), Denise
Developing a 3D model of the tongue and mouth to assess pressure generation and predict bolus flow when swallowing Marie Greuel (Team Leader), Tyler Lieberthal (Communicator), Kelly Hanneken (BWIG), Denise
Chapter 30 Nonvertebrate Chordates, Fishes, and Amphibians Name
 Chapter 30 Nonvertebrate Chordates, Fishes, and Amphibians Name Lab Dissecting a Perch Background Information Fish are the largest group of vertebrates found in fresh and salt water. In fact, over 25,000
Chapter 30 Nonvertebrate Chordates, Fishes, and Amphibians Name Lab Dissecting a Perch Background Information Fish are the largest group of vertebrates found in fresh and salt water. In fact, over 25,000
Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System
 Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System Animals require a continuous supply of oxygen (O 2 ) for cellular respiration, and they must expel carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), the waste product of this
Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System Animals require a continuous supply of oxygen (O 2 ) for cellular respiration, and they must expel carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), the waste product of this
Structures of the Respiratory System include:
 Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
DISSECTION 101 THE FROG
 DISSECTION 101 THE FROG Dissection helps us understand how living things function. Dissection is analytical. Dissection is an adventure. Discussion Frog anatomy is unique in that it does resemble human
DISSECTION 101 THE FROG Dissection helps us understand how living things function. Dissection is analytical. Dissection is an adventure. Discussion Frog anatomy is unique in that it does resemble human
Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment
 Name: Date: Mark: / 45 Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
Name: Date: Mark: / 45 Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
Perch Dissection Lab
 Name: Block: Due Date: Perch Dissection Lab Background The fish in the class Osteichthyes have bony skeletons. There are three groups of the bony fish: ray-finned, lobe-finned, and the lungfish. The perch
Name: Block: Due Date: Perch Dissection Lab Background The fish in the class Osteichthyes have bony skeletons. There are three groups of the bony fish: ray-finned, lobe-finned, and the lungfish. The perch
AN INVESTIGATION OF VELOPHARYNGEAL CLOSURE WITH LINEAR REGRESSION. Anish Sana. December, 2015
 AN INVESTIGATION OF VELOPHARYNGEAL CLOSURE WITH LINEAR REGRESSION by Anish Sana December, 2015 Director of Thesis: Dr. Nasseh Tabrizi Major Department: Computer Science Cleft lip and palate is a common
AN INVESTIGATION OF VELOPHARYNGEAL CLOSURE WITH LINEAR REGRESSION by Anish Sana December, 2015 Director of Thesis: Dr. Nasseh Tabrizi Major Department: Computer Science Cleft lip and palate is a common
25/4/2016. Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten
 25/4/2016 Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten Respiratory System Introduction: - We breath while we are sleeping, talking, working and resting. - Respiratory diseases are abundant
25/4/2016 Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten Respiratory System Introduction: - We breath while we are sleeping, talking, working and resting. - Respiratory diseases are abundant
Module 17 Respiratory System
 Module 17 Respiratory System Objective 1. List the functions of the respiratory system. Name the four respiratory processes. Assignment: Tortora, p. 874 or Wiley Plus 23 Chapter Opener Functions: 1. Provides
Module 17 Respiratory System Objective 1. List the functions of the respiratory system. Name the four respiratory processes. Assignment: Tortora, p. 874 or Wiley Plus 23 Chapter Opener Functions: 1. Provides
Chapter 12 Part 2. The Worms Platyhelminthes, Nematoda & Annelida
 Chapter 12 Part 2 The Worms Platyhelminthes, Nematoda & Annelida Phylum: Platyhelminthes Examples: Flatworms, Planaria sp., tapeworms and blood flukes Acoelomate, Invertebrate, Simplest critter w/ bilateral
Chapter 12 Part 2 The Worms Platyhelminthes, Nematoda & Annelida Phylum: Platyhelminthes Examples: Flatworms, Planaria sp., tapeworms and blood flukes Acoelomate, Invertebrate, Simplest critter w/ bilateral
Shark Lab Key. dorsal surface. click on picture for ventral surface
 Shark Lab Key Study this basic information about the spiny dogfish shark. Print this Shark Lab Report Guide. Pre-Lab Research Study this website. It provides several useful videos of large shark dissections.
Shark Lab Key Study this basic information about the spiny dogfish shark. Print this Shark Lab Report Guide. Pre-Lab Research Study this website. It provides several useful videos of large shark dissections.
Shark Dissection Dogfish Squalus acanthias
 Name Shark Dissection Dogfish Squalus acanthias Fun Facts: The teeth of sharks are modified scales embedded in the skin of its mouth Sharks have pits on their face used to detect electric fields Sharks
Name Shark Dissection Dogfish Squalus acanthias Fun Facts: The teeth of sharks are modified scales embedded in the skin of its mouth Sharks have pits on their face used to detect electric fields Sharks
sclerosis: a video clip demonstrati
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation The patulous eustachian tube compli sclerosis: a video clip demonstrati Takasaki, Kenji; Kumagami, Hidetaka Takahashi, Haruo The Laryngoscope,
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation The patulous eustachian tube compli sclerosis: a video clip demonstrati Takasaki, Kenji; Kumagami, Hidetaka Takahashi, Haruo The Laryngoscope,
Respiration. Chapter 33
 Respiration Chapter 33 Learning Objectives: Understand the basis of gas exchange and factors that influence diffusion of gases in and out of tissues Compare and contrast different respiratory systems among
Respiration Chapter 33 Learning Objectives: Understand the basis of gas exchange and factors that influence diffusion of gases in and out of tissues Compare and contrast different respiratory systems among
Triticeal cartilage: the forgotten cartilage
 DOI 10.1007/s00276-017-1841-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Triticeal cartilage: the forgotten cartilage Iain Wilson 1 J. Stevens 1 J. Gnananandan 1 A. Nabeebaccus 2 A. Sandison 3 A. Hunter 1 Received: 21 October 2016
DOI 10.1007/s00276-017-1841-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Triticeal cartilage: the forgotten cartilage Iain Wilson 1 J. Stevens 1 J. Gnananandan 1 A. Nabeebaccus 2 A. Sandison 3 A. Hunter 1 Received: 21 October 2016
Lesson 27. Objectives: At the end of this lesson you should be able to:
 Lesson 27 Lesson Outline: Evolution of Respiratory Mechanisms Cutaneous Exchange Evolution of Respiratory Mechanisms - Water Breathers o Origin of pharyngeal slits from corner of mouth o Origin of skeletal
Lesson 27 Lesson Outline: Evolution of Respiratory Mechanisms Cutaneous Exchange Evolution of Respiratory Mechanisms - Water Breathers o Origin of pharyngeal slits from corner of mouth o Origin of skeletal
Bio 182- Ecology Unit Outline 1
 Bio 182- Ecology Unit Outline 1 Respiration Introduction 1. Multicellular organisms require oxygen to generate E using cellular respiration 2. Wastes released as CO2 3. Summary equation for cellular respiration:
Bio 182- Ecology Unit Outline 1 Respiration Introduction 1. Multicellular organisms require oxygen to generate E using cellular respiration 2. Wastes released as CO2 3. Summary equation for cellular respiration:
Chapter 9 Airway Respirations Metabolism Oxygen Requirements Respiratory Anatomy Respiratory Anatomy Respiratory Anatomy Diaphragm
 1 Chapter 9 Airway 2 Respirations Every cell of the body requires to survive Oxygen must come in and carbon must go out 3 Metabolism Metabolism--Process where the body s cells convert food to Adequate
1 Chapter 9 Airway 2 Respirations Every cell of the body requires to survive Oxygen must come in and carbon must go out 3 Metabolism Metabolism--Process where the body s cells convert food to Adequate
Breathing: The normal rate is about 14 to 20 times a minute. Taking in of air is called Inspiration and the forcing out of air is called Expiration.
 Biology 12 Respiration Divisions of Respiration Breathing: entrance and exit of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration: exchange of gases(o2 and CO2) between air (in alveoli) and blood Internal
Biology 12 Respiration Divisions of Respiration Breathing: entrance and exit of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration: exchange of gases(o2 and CO2) between air (in alveoli) and blood Internal
Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42. Gas Exchange pp Gas Exchange. Gas Exchange in Fish pp Gas Exchange in Fish
 Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42 Fig. 42.24 Gas Exchange pp.979-989 Gas exchange involves the uptake of oxygen and the discharge of carbon dioxide (i.e. respiration or breathing). It is necessary for cellular
Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42 Fig. 42.24 Gas Exchange pp.979-989 Gas exchange involves the uptake of oxygen and the discharge of carbon dioxide (i.e. respiration or breathing). It is necessary for cellular
a. Kingdom: b. Phylum: c. Class: d. Order: e. Family: f. Genus: g. Species:
 Pre-lab Discussion: The earthworm belongs to a group of animals called annelids (segmented worms). The body of an annelid is usually divided internally and externally into well-defined segments, which
Pre-lab Discussion: The earthworm belongs to a group of animals called annelids (segmented worms). The body of an annelid is usually divided internally and externally into well-defined segments, which
Classification. Phylum Chordata
 AP Biology Chapter 23 Exercise #17: Chordates: Urochordata & Cephalochordata Lab Guide Chordates show remarkable diversity. Most are vertebrates. All animals that belong to this phylum MUST, at some point
AP Biology Chapter 23 Exercise #17: Chordates: Urochordata & Cephalochordata Lab Guide Chordates show remarkable diversity. Most are vertebrates. All animals that belong to this phylum MUST, at some point
Emergency Medical Technician 60 Questions
 Emergency Medical Technician 60 Questions 1. Which of the following is your primary goal during airway management? a. Ensure clear, unobstructed breathing. b. Ensure that CPR is effective. c. Provide a
Emergency Medical Technician 60 Questions 1. Which of the following is your primary goal during airway management? a. Ensure clear, unobstructed breathing. b. Ensure that CPR is effective. c. Provide a
Wilderness First Responder Course Peak 7 Adventures
 Wilderness First Responder Course Peak 7 Adventures The practice of the healing arts (including Wilderness First Responder) does not lend itself well to a cook book approach. There are endless variations
Wilderness First Responder Course Peak 7 Adventures The practice of the healing arts (including Wilderness First Responder) does not lend itself well to a cook book approach. There are endless variations
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 1
 Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The term "respiration" in its most complete meaning is: a. breathing b. oxygen transport c. carbon dioxide transport d. cellular energy production e. all of
Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The term "respiration" in its most complete meaning is: a. breathing b. oxygen transport c. carbon dioxide transport d. cellular energy production e. all of
Fish Dissection. 1. Place the preserved perch on the dissecting tray. Locate the head region. Examine the eyes. 6. What is the name of these flaps?
 Name: Date: Per: Introduction: Fish Dissection In this lab students will work within a group to learn from the dissection of a Perch. Dissection gives the student the opportunity to observe the location
Name: Date: Per: Introduction: Fish Dissection In this lab students will work within a group to learn from the dissection of a Perch. Dissection gives the student the opportunity to observe the location
Respiration. The ins and outs
 Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
Dogfish Shark Dissection Introduction 1. What are two reasons why spiny dogfish are used for study in laboratories?
 Dogfish Shark Dissection Introduction 1. What are two reasons why spiny dogfish are used for study in laboratories? 2. Someone who studies fish is called an. 3. Sharks and fish belong to the Phylum a.
Dogfish Shark Dissection Introduction 1. What are two reasons why spiny dogfish are used for study in laboratories? 2. Someone who studies fish is called an. 3. Sharks and fish belong to the Phylum a.
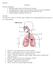
3/24/2009 LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD. 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm 1 KEY WORDS TO KNOW BOYLE S LAW INTERCOSTAL NERVES PHRENIC NERVE DIAPHRAGM EXTERNAL INTERCOSTAL
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm 1 KEY WORDS TO KNOW BOYLE S LAW INTERCOSTAL NERVES PHRENIC NERVE DIAPHRAGM EXTERNAL INTERCOSTAL
Chapter 22. Respiratory System
 Chapter 22 Respiratory System Breathing all our body processes directly or indirectly require ATP ATP synthesis requires oxygen and produces carbon dioxide drives the need to breathe to take in oxygen,
Chapter 22 Respiratory System Breathing all our body processes directly or indirectly require ATP ATP synthesis requires oxygen and produces carbon dioxide drives the need to breathe to take in oxygen,
On the So-called Accessory Respiratory Organ "Gill-helix" Found in Some Clupeiform Fishes, with Special Reference to Its Function and Its Genealogy
 On the So-called Accessory Respiratory Organ "Gill-helix" Found in Some Clupeiform Fishes, with Special Reference to Its Function and Its Genealogy by Nisuke TAKAHASI (Faculty of Education, Kumamoto University,
On the So-called Accessory Respiratory Organ "Gill-helix" Found in Some Clupeiform Fishes, with Special Reference to Its Function and Its Genealogy by Nisuke TAKAHASI (Faculty of Education, Kumamoto University,
Fishes are vertebrates that have characteristics allowing them to live and reproduce in water.
 Section 1: are vertebrates that have characteristics allowing them to live and reproduce in water. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the features of
Section 1: are vertebrates that have characteristics allowing them to live and reproduce in water. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the features of
Using the figure above, match the following: 4. Tidal volume. 5. Inspiratory reserve volume. 6. Residual volume. 7. Expiratory reserve volume.
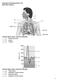 Respiratory Physiology Practice Test BIOL 4350: Hamilton Using the figure above, match the following: 1. Primary bronchus 2. Larynx 3. Trachea Using the figure above, match the following: 4. Tidal volume.
Respiratory Physiology Practice Test BIOL 4350: Hamilton Using the figure above, match the following: 1. Primary bronchus 2. Larynx 3. Trachea Using the figure above, match the following: 4. Tidal volume.
Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration)
 Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration) 1 Question 1 Why do organisms need food? Organisms need food for obtaining energy to perform the vital functions. Question 2 What is a respiratory substrate?
Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration) 1 Question 1 Why do organisms need food? Organisms need food for obtaining energy to perform the vital functions. Question 2 What is a respiratory substrate?
SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION
 SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION WHEN WE BREATHE, WHAT DO WE BREATHE IN? O2, N2, CO2, O3, NO2 (gas fumes), CO, pollutant, fragrants, toxins, etc. WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF BREATHING IN? WHAT DOES OUR BODY WANT? O2 WHY?
SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION WHEN WE BREATHE, WHAT DO WE BREATHE IN? O2, N2, CO2, O3, NO2 (gas fumes), CO, pollutant, fragrants, toxins, etc. WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF BREATHING IN? WHAT DOES OUR BODY WANT? O2 WHY?
Respiratory System 1
 Respiratory System 1 Outline Respiratory structures Gills Air-Breathing Animals Amphibians and Reptiles Mammals Birds Structures and Mechanisms of Breathing 2 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Respiratory System 1 Outline Respiratory structures Gills Air-Breathing Animals Amphibians and Reptiles Mammals Birds Structures and Mechanisms of Breathing 2 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system. Objective sheet 3 Notes
 1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System
 Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
1/10/2013. Topic 16: Sensory Organs. How do receptors work?
 Topic 6: Sensory Organs How do sensory receptors work? Cutaneous receptors Prorioceptors Chemoreceptors Electroreceptors Lateral line system Auditory receptors Photoreceptors How do receptors work? nerve
Topic 6: Sensory Organs How do sensory receptors work? Cutaneous receptors Prorioceptors Chemoreceptors Electroreceptors Lateral line system Auditory receptors Photoreceptors How do receptors work? nerve
Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class
 I. Name the following : Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class 1. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. 2. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous
I. Name the following : Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class 1. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. 2. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous
Orbital decompression surgery. See also information leaflets on: ~ Thyroid Eye Disease ~ Upper lid lowering ~ Proptosis
 Orbital decompression surgery See also information leaflets on: ~ Thyroid Eye Disease ~ Upper lid lowering ~ Proptosis Qu: What is the orbit? The eye, its surrounding muscles, nerves and fatty tissue lie
Orbital decompression surgery See also information leaflets on: ~ Thyroid Eye Disease ~ Upper lid lowering ~ Proptosis Qu: What is the orbit? The eye, its surrounding muscles, nerves and fatty tissue lie
Perch Dissection Lab
 Perch Dissection Lab Introduction: The fish in the class Osteichthyes have bony skeletons. There are three groups of the bony fish - -- ray-finned fish, lobe-finned fish, and the lung fish. The perch is
Perch Dissection Lab Introduction: The fish in the class Osteichthyes have bony skeletons. There are three groups of the bony fish - -- ray-finned fish, lobe-finned fish, and the lung fish. The perch is
SOME NOTES ON THE ANTERIOR DORSAL FIN AND VENOUS DRAINAGE IN CALLORHINCHUS (HOLOCEPHALI)
 Papers and Proceedings of the Royal Society of Tasmania, Vol.109, 1975. SOME NOTES ON THE ANTERIOR DORSAL FIN AND VENOUS DRAINAGE IN CALLORHINCHUS (HOLOCEPHALI) N.J.B. Piomley and Noel Dilly (ms. received
Papers and Proceedings of the Royal Society of Tasmania, Vol.109, 1975. SOME NOTES ON THE ANTERIOR DORSAL FIN AND VENOUS DRAINAGE IN CALLORHINCHUS (HOLOCEPHALI) N.J.B. Piomley and Noel Dilly (ms. received
Laryngeal Mask Airway (LMA) Indications and Use for the NH EMT-Intermediate and Paramedic
 Laryngeal Mask Airway (LMA) Indications and Use for the NH EMT-Intermediate and Paramedic New Hampshire Division of Fire Standards & Training and Emergency Medical Services Introduction The LMA was invented
Laryngeal Mask Airway (LMA) Indications and Use for the NH EMT-Intermediate and Paramedic New Hampshire Division of Fire Standards & Training and Emergency Medical Services Introduction The LMA was invented
MEROCEL HEMOX SPONGES
 MEROCEL HEMOX SPONGES Now with oxidized cellulose, a clinically proven hemostatic agent G. H. I. A. B. C. D. E. F. Post-op sinus dressings Merocel hemox is constructed of high-density, micropore Merocel
MEROCEL HEMOX SPONGES Now with oxidized cellulose, a clinically proven hemostatic agent G. H. I. A. B. C. D. E. F. Post-op sinus dressings Merocel hemox is constructed of high-density, micropore Merocel
Anatomy and Physiology Part 11: Of Blood and Breath by: Les Sellnow
 Anatomy and Physiology Part 11: Of Blood and Breath by: Les Sellnow There are few similarities between horses and automobiles, but in a manner of speaking, the horse's circulatory and respiratory systems
Anatomy and Physiology Part 11: Of Blood and Breath by: Les Sellnow There are few similarities between horses and automobiles, but in a manner of speaking, the horse's circulatory and respiratory systems
Lesson 28. Function - Respiratory Pumps in Air Breathers Buccal Force Pump Aspiration Pump - Patterns of Gas Transfer in Chordates
 Lesson 28 Lesson Outline: Evolution of Respiratory Mechanisms - Air Breathers Form - Accessory Air Breathing Organs Facultative vs Obligate - Lungs Function - Respiratory Pumps in Air Breathers Buccal
Lesson 28 Lesson Outline: Evolution of Respiratory Mechanisms - Air Breathers Form - Accessory Air Breathing Organs Facultative vs Obligate - Lungs Function - Respiratory Pumps in Air Breathers Buccal
External Anatomy Dissection Guide
 External Anatomy Dissection Guide Dissection is the cutting of a dead animal or a plant into separate parts for the purpose of careful and detailed examination and study. The external anatomy is as important
External Anatomy Dissection Guide Dissection is the cutting of a dead animal or a plant into separate parts for the purpose of careful and detailed examination and study. The external anatomy is as important
Respiratory System Unit
 Respiratory System Unit An integrative unit including lessons in Science, Art, Math, Health, and Literature 3rd Grade Anatomy Wegner 1 Introduction: The respiratory system allows the human body to take
Respiratory System Unit An integrative unit including lessons in Science, Art, Math, Health, and Literature 3rd Grade Anatomy Wegner 1 Introduction: The respiratory system allows the human body to take
Branchial Circulation in Macropodus Opercularis L.
 The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 55, Issue 3 (May, 1955) 1955-05 Branchial Circulation in Macropodus
The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 55, Issue 3 (May, 1955) 1955-05 Branchial Circulation in Macropodus
Chapter 35. Table of Contents. Section 1 Mollusca. Section 2 Annelida. Mollusks and Annelids
 Mollusks and Annelids Table of Contents Section 1 Mollusca Section 2 Annelida Section 1 Mollusca Objectives Describe the key characteristics of mollusks. Describe the body plan of mollusks. Name the characteristics
Mollusks and Annelids Table of Contents Section 1 Mollusca Section 2 Annelida Section 1 Mollusca Objectives Describe the key characteristics of mollusks. Describe the body plan of mollusks. Name the characteristics
