Respiratory System. 1. muscular tube lined by mucous membrane 2. throat 3. nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx
|
|
|
- Imogen Chandler
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 I. Functions of the Respiratory System A. gas exchange B. prevent dehydration C. sound D. olfaction E. ph regulation II. Anatomy of the Respiratory System A. Nose 1. external nares vestibule nasal cavity internal nares (choanae) 2. paranasal sinuses frontal, sphenoidal, maxillary, ethmoidal 3. nasal conchae turbinates and meatuses warn, moisten and trap 4. nasal mucosa cilia smoker s cough 5. cystic fibrosis thick mucous secretions that block airways genetic B. Pharynx 1. muscular tube lined by mucous membrane 2. throat 3. nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx C. Larynx 1. voice box 2. connects pharynx to trachea 3. thyroid cartilage Adam s apple hyaline thyrohyoid membrane 4. cricoid cartilage landmark for tracheostomy 5. epiglottis 6. arytenoids, cuneiform, and cornicuate cartilages important in supporting and moving the vocal chords 7. voice production elastic ligaments deep to membrane of vocal folds a. contraction causes vocal folds to stretch into airways b. air pushes against them and vibrates strings of a guitar c. pitch controlled by tension on vocal chords males thicker and longer, lower pitch d. volume controlled by air pressure e. whispers almost close rima glottides vocal folds do not vibrate, no pitch 8. laryngitis inflammation of the larynx interferes with contraction of vocal cords or can t vibrate freely D. Trachea 1. windpipe 2. connects larynx to primary bronchi 3. tracheal cartilage rings, keeps airway open 4. tracheostomy hole 5. intubation tube
2 E. Bronchi 1. right and left pulmonary bronchi 2. bronchial tree a. trachea, primary bronchi, secondary bronchi, tertiary bronchi, bronchioles, terminal bronchioles b. walls of bronchi contain rings of cartilage c. walls of bronchioles contain smooth muscle tissue 3. compare tissues as look at tree 4. bronchoscopy illuminated tube, culture, biopsy, meds, clear F. Lungs 1. pleural membrane a. parietal attached to wall of thoracic cavity b. visceral covers lungs c. pleural cavity 2. right lung has three lobes, left has two 3. within lobules of lobes, terminal bronchioles subdivide into respiratory bronchioles which subdivide into alveolar ducts which divide into alveoli arranged in alveolar sacs 4. surfactant in alveolar fluid surface tension at all water air interferes; polar molecules more strongly attracted to each other than to air molecules like keeping a soap bubble from collapsing, keeps alveoli from collapsing a. phospholipids and lipoproteins that keeps alveoli from collapsing after each exhalation 5. pneumonia inflammation of lobules of lung 6. pulmonary embolism clot that blocks that obstructs circulation to the lung tissue 7. pleurisy inflammation of pleural membrane III. Respiratory Physiology A. Pulmonary Ventilation breathing 1. compliance measure of the ease with which the lungs and thoracic wall can be expanded balloon (thin or thick) 2. inspiration inhalation a. Boyle s law pressure is inversely related to volume of gas assuming the temperature is constant jar demo 3. muscles used in respiration a. diaphragm contraction lowers b. external intercostals contraction pulls ribs and sternum up and out c. internal intercostals contraction pulls ribs and sternum down and in 4. pressure a. atmospheric pressure = 760 mm Hg b. intrapleural pressure i. subatmospheric 4.6 mm Hg less than atmospheric causes parietal and visceral pleurae to adhere strongly to each other surfaces moist helps also
3 c. alveolar pressure (intrapulmonic) i. lung volume increases causing alveolar pressure to drop about 2 mm Hg allows alveoli to fill with air 5. expiration exhalation a. inspiratory muscles relax decrease volume b. alveolar pressure increases to 762 mm Hg c. air moves out of lungs 6. breathing patterns a. normal quiet breathing eupnea i. passive no muscle contractractions used ii. elastic recoil of chest wall and lungs b. apnea i. temporary cessation of breathing c. dyspnea labored heavy breathing d. tachypnea rapid breathing e. costal breathing shallow, chest breathing external intercostals f. diaphragmatic breathing diaphragm + accessory inspiratory muscles 7. atelactasis collapsed lung or incomplete expansion of a lung B. Lung Volumes and Capacities 1. respiration one inspiration + one exhalation 2. spirometer used to measure volume of air in a breath and rate of ventilation 3. tidal volume 500 ml volume of one breath 4. minute ventilation amount of air inhaled and exhaled in 1 minute 5. anatomic dead space 150 ml of the 500 ml tidal volume remain in air spaces of the respiratory system about the same as ideal weight in pounds 6. inspiratory reserve volume inspired air above and beyond tidal volume 3100 ml 7. expiratory reserve volume exhaled air above and beyond tidal volume 1200 ml 8. residual volume 1200 ml that cannot be expired due to incollapsible structures in the respiratory system 9. vital capacity 4800 ml inspiratory reserve + tidal volume + expiratory reserve 10. total lung capacity sum of all volumes 6000 ml including residual volume C. Exchange of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide 1. Gas Laws a. Dalton s Law i. each gas in a mixture exerts pressure as if all other gases not present partial pressure ii. gas diffuses from an area where partial pressure is higher to where its partial pressure is lower
4 b. Henry s Law i. the quantity of a gas that will dissolve in a liquid is proportional to the partial pressure of the gas and its solubility coefficient (physical or chemical attraction for water) ii. decompression sickness nitrogen comes out of solution in tissues 2. Respiration a. external respiration i. exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide at the alveoli ii. high altitude sickness total air pressure drops, percentage of oxygen is same, but less abundant due to drop in pressure b. rate depends on i. partial pressure difference of gases ii. surface area for gas exchange iii. diffusion distance iv. solubility and molecular weight of the gases c. internal respiration i. systemic circulation D. Transport of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide 1. Oxygen a. 98.5% of oxygen transported by hemoglobin b. only dissolved oxygen gets sent to tissue cells, bond with hemoglobin must break c. hemoglobin and oxygen partial pressure i. PO 2 determines how much oxygen binds to hemoglobin greater PO 2 = higher saturation of hemoglobin d. other factors that affect the saturation of hemoglobin i. ph Bohr effect as ph decreases, affinity for O 2 decreases, O 2 dissociates due to hydrogen ions binding to amino acids and altering structure ii. partial pressure of CO 2 high CO 2 causes low ph due to formation of carbonic acid (skeletal muscle has lactic acid production that lowers ph and decreases affinity for oxygen) iii. temperature T increases, O 2 released from hemoglobin iv. 2, 3 bisphosphoglycerate BPG formed during glycolysis decreases affinity for oxygen binds to hemoglobin e. fetal hemoglobin i. greater affinity for oxygen ii. binds BPG less strongly iii. important because maternal blood oxygen levels are very low in placenta f. carbon monoxide poisoning i. binds more strongly than oxygen ii. even small concentrations of CO will reduce oxygen carrying ability
5 2. Carbon Dioxide Transport a. 3 forms of carbon dioxide i. dissolved CO 2 in plasma 7% ii. bound to hemoglobin 23% iii. bicarbonate ions in plasma 70% - H 2 CO 3 H + + HCO 3 -, H + combines with hemoglobin, oxygen dissociates, HCO 3 - accumulates in RBC and diffuses down concentration gradient to plasma Cl - ions replace as they diffuse into RBC maintains electrical balance between plasma and RBC chloride shift 3. Haldane Effect a. the more oxygen bound, the less carbon dioxide b. deoxyhemoglobin buffers more hydrogen ions, thereby removing hydrogen ions from solution and promoting the conversion of carbon dioxide to bicarbonateions E. Control of Respiration 1. Neural Control a. Respiratory center medulla oblongata and pons i. Medullary rhythmicity center autorhythmic neurons begin inspirations and inspiratory area becomes active after 3 sec due to impulses from autorhythmic neurons expiratory area normally not active unless forceful ventilation occurs ii. Pneumotaxic area inhibits inspiratory area limits iii. duration of inspiration Apneustic area stimulates inspiratory area prolong inspiration pneumotaxic overrides 2. Chemical Regulation a. chemoreceptors respond to pco 2 and H + changes if these chemicals increase, inspiratory area is stimulated i. hypercapnia increase in blood pco 2 level ii. hypocapnia decrease in blood pco 2 level 3. Inflation Reflex Hering Breuer reflex a. baroreceptors in bronchi and bronchioles b. when stretched, inhibit inspiratory and apneustic areas prevents excessive inflation F. Disease Conditions 1. Emphysema COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) a. alveolar walls degenerate 2. Asthma COPD a. chronic inflammatory disorder b. airways hyperreactive to stimuli 3. Tuberculosis a. bacteria destroy lung tissue replace by fibrous connective tissue
Chapter 15. Lecture and Animation Outline
 Chapter 15 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
Chapter 15 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
(Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System
 (Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System I. (Slide 2) The Respiratory Tract A) Major structures and regions of the respiratory Tract/Route INTO body 1) nose 2) nasal cavity 3) pharynx 4) glottis 5)
(Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System I. (Slide 2) The Respiratory Tract A) Major structures and regions of the respiratory Tract/Route INTO body 1) nose 2) nasal cavity 3) pharynx 4) glottis 5)
Chapter 16 Respiratory System
 Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Respiratory System Physiology. Dr. Vedat Evren
 Respiratory System Physiology Dr. Vedat Evren Respiration Processes involved in oxygen transport from the atmosphere to the body tissues and the release and transportation of carbon dioxide produced in
Respiratory System Physiology Dr. Vedat Evren Respiration Processes involved in oxygen transport from the atmosphere to the body tissues and the release and transportation of carbon dioxide produced in
Chapter 23: Respiratory System
 Chapter 23: Respiratory System I. Functions of the Respiratory System A. List and describe the five major functions of the respiratory system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. II. Anatomy and Histology of the Respiratory
Chapter 23: Respiratory System I. Functions of the Respiratory System A. List and describe the five major functions of the respiratory system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. II. Anatomy and Histology of the Respiratory
Physiology of Respiration
 Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Atmosphere Tissue cell External respiration Alveoli of lungs 1 Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Atmosphere Tissue cell External respiration Alveoli of lungs 1 Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere
2/28/18. Respiratory System. 1 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Introduction. Anatomy. Physiology. Respiratory System
 Introduction Respiratory System Chapter 28 Respiration: We inhale air, extract oxygen from it, exhale air Cardiovascular and respiratory systems work together Failure of either system: - Disruption of
Introduction Respiratory System Chapter 28 Respiration: We inhale air, extract oxygen from it, exhale air Cardiovascular and respiratory systems work together Failure of either system: - Disruption of
The Respiratory System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Organs of the Respiratory system
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Organs of the Respiratory system
Human Biology Respiratory System
 Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY
 Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Respiration External respiration ventilation gas exchange Internal respiration cellular respiration gas exchange Respiratory Cycle Inspiration
Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Respiration External respiration ventilation gas exchange Internal respiration cellular respiration gas exchange Respiratory Cycle Inspiration
UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 9.01 GENERAL FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. Brings oxygenated air to the alveoli B. Removes air containing carbon dioxide C. Filters, warms, and humidifies
UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 9.01 GENERAL FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. Brings oxygenated air to the alveoli B. Removes air containing carbon dioxide C. Filters, warms, and humidifies
82 Respiratory Tract NOTES
 82 Respiratory Tract NOTES RESPIRATORY TRACT The respiratory tract conducts air to the lungs where gaseous exchange occurs. It is separated into air-conducting and respiratory (where gas exchange occurs)
82 Respiratory Tract NOTES RESPIRATORY TRACT The respiratory tract conducts air to the lungs where gaseous exchange occurs. It is separated into air-conducting and respiratory (where gas exchange occurs)
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System
 Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System Animals require a continuous supply of oxygen (O 2 ) for cellular respiration, and they must expel carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), the waste product of this
Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System Animals require a continuous supply of oxygen (O 2 ) for cellular respiration, and they must expel carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), the waste product of this
Outline - Respiratory System. Function of the respiratory system Parts of the respiratory system Mechanics of breathing Regulation of breathing
 Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
Respiratory System. Part 2
 Respiratory System Part 2 Respiration Exchange of gases between air and body cells Three steps 1. Ventilation 2. External respiration 3. Internal respiration Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation consists
Respiratory System Part 2 Respiration Exchange of gases between air and body cells Three steps 1. Ventilation 2. External respiration 3. Internal respiration Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation consists
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Human Anatomy & Physiology 19 Karen Webb Smith Unit Five Respiratory System URLs http://yucky.kids.discovery.com/flash/body/pg000138.html http://www.stemnet.nf.ca/~dpower/resp/exchange.htm #Breathing http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/
Human Anatomy & Physiology 19 Karen Webb Smith Unit Five Respiratory System URLs http://yucky.kids.discovery.com/flash/body/pg000138.html http://www.stemnet.nf.ca/~dpower/resp/exchange.htm #Breathing http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/
Breathing: The normal rate is about 14 to 20 times a minute. Taking in of air is called Inspiration and the forcing out of air is called Expiration.
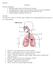 Biology 12 Respiration Divisions of Respiration Breathing: entrance and exit of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration: exchange of gases(o2 and CO2) between air (in alveoli) and blood Internal
Biology 12 Respiration Divisions of Respiration Breathing: entrance and exit of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration: exchange of gases(o2 and CO2) between air (in alveoli) and blood Internal
Respiration. The ins and outs
 Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
Respiratory System Review
 KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System
 VI edit Pag 451-499 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System V edit. Pag 459-509 Tissue cell Alveoli of lungs Atmosphere 1 External respiration Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere and air sacs
VI edit Pag 451-499 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System V edit. Pag 459-509 Tissue cell Alveoli of lungs Atmosphere 1 External respiration Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere and air sacs
Lab 17. The Respiratory System. Laboratory Objectives
 Lab 17 The Respiratory System Laboratory Objectives Identify and describe the anatomical structures of the respiratory system. Describe the relationship between volume and pressure. Describe changes in
Lab 17 The Respiratory System Laboratory Objectives Identify and describe the anatomical structures of the respiratory system. Describe the relationship between volume and pressure. Describe changes in
Respiratory System -Training Handout
 Respiratory System -Training Handout Karen L. Lancour National Rules Committee Chairman Life Science FUNCTIONS: Provides oxygen to the blood stream and removes carbon dioxide Enables sound production or
Respiratory System -Training Handout Karen L. Lancour National Rules Committee Chairman Life Science FUNCTIONS: Provides oxygen to the blood stream and removes carbon dioxide Enables sound production or
Respiration - Human 1
 Respiration - Human 1 At the end of the lectures on respiration you should be able to, 1. Describe events in the respiratory processes 2. Discuss the mechanism of lung ventilation in human 3. Discuss the
Respiration - Human 1 At the end of the lectures on respiration you should be able to, 1. Describe events in the respiratory processes 2. Discuss the mechanism of lung ventilation in human 3. Discuss the
BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
 96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The tissues exchange O 2 directly with the air in
96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The tissues exchange O 2 directly with the air in
Chapter 17 The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and Regulation of Breathing
 Chapter 17 The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and Regulation of Breathing Overview of Pulmonary Circulation o Diffusion of Gases o Exchange of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide o Transport of Gases in the Blood
Chapter 17 The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and Regulation of Breathing Overview of Pulmonary Circulation o Diffusion of Gases o Exchange of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide o Transport of Gases in the Blood
Structures of the Respiratory System include:
 Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface:
 I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface: Common characteristics of respiratory surfaces: a) Moist: allows for the RAPID diffusion of dissolved gasses across its surface. Whereas the respiratory
I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface: Common characteristics of respiratory surfaces: a) Moist: allows for the RAPID diffusion of dissolved gasses across its surface. Whereas the respiratory
GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY
 GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY Atmospheric Pressure Intra-Alveolar Pressure Inspiration 760 mm HG at Sea Level (= 1 atm) Pressure due to gases (N2, O2, CO2, Misc.) Pressure inside the alveolus (air sac) Phrenic
GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY Atmospheric Pressure Intra-Alveolar Pressure Inspiration 760 mm HG at Sea Level (= 1 atm) Pressure due to gases (N2, O2, CO2, Misc.) Pressure inside the alveolus (air sac) Phrenic
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange
 Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
B. Lining - epithelium
 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Function supply body with oxygen and remove carbon dioxide. This process is called respiration, can be broken down into 4 components. I. Pulmonary Ventilation or breathing movement of
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Function supply body with oxygen and remove carbon dioxide. This process is called respiration, can be broken down into 4 components. I. Pulmonary Ventilation or breathing movement of
system. and then into the tissues. Diffusion of wastes such as Carbon Dioxide from tissues into blood and out of blood into the lungs.
 Respiratory System 1.Exchange Why do of we gases breathe? into the Think blood of all and the tissues. reasons Diffusion why we of Oxygen need a respiratory into blood from the lungs system. and then into
Respiratory System 1.Exchange Why do of we gases breathe? into the Think blood of all and the tissues. reasons Diffusion why we of Oxygen need a respiratory into blood from the lungs system. and then into
BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
 96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The cell exchange O 2 directly with the air in the
96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The cell exchange O 2 directly with the air in the
The Respiratory System. Medical Terminology
 The Respiratory System Medical Terminology The respiratory system is where gas exchange occurs via respiration; inhalation/exhalation. pick up oxygen from inhaled air expels carbon dioxide and water sinus
The Respiratory System Medical Terminology The respiratory system is where gas exchange occurs via respiration; inhalation/exhalation. pick up oxygen from inhaled air expels carbon dioxide and water sinus
Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment
 Name: Date: Mark: / 45 Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
Name: Date: Mark: / 45 Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
Chapter 23 Respiratory System
 Chapter 23 Respiratory System I. Functions of the Respiratory System: 1. Gas Exchange 2. Regulatory (blood ph) 3. Voice Production 4. Olfaction 5. Protection II. Anatomy & Histology of the Respiratory
Chapter 23 Respiratory System I. Functions of the Respiratory System: 1. Gas Exchange 2. Regulatory (blood ph) 3. Voice Production 4. Olfaction 5. Protection II. Anatomy & Histology of the Respiratory
Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 3
 Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 3 1. The pressure of a gas: a. is inversely proportional to its volume b. is unaffected by temperature changes c. is directly proportional to its volume d. does not
Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 3 1. The pressure of a gas: a. is inversely proportional to its volume b. is unaffected by temperature changes c. is directly proportional to its volume d. does not
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 11 Respiratory System 2 Pulmonary Ventilation Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session plan o Pulmonary Ventilation
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 11 Respiratory System 2 Pulmonary Ventilation Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session plan o Pulmonary Ventilation
 Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Introduction. Respiration. Chapter 10. Objectives. Objectives. The Respiratory System
 Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
1 CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES https://biologyaipmt.com/
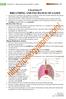 1 CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES https://biologyaipmt.com/ CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES Oxygen (O2) is utilised by the organisms to indirectly break down nutrient molecules like
1 CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES https://biologyaipmt.com/ CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES Oxygen (O2) is utilised by the organisms to indirectly break down nutrient molecules like
CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
 268 BIOLOGY CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES 17.1 Respiratory Organs 17.2 Mechanism of Breathing 17.3 Exchange of Gases 17.4 Transport of Gases 17.5 Regulation of Respiration 17.6 Disorders of
268 BIOLOGY CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES 17.1 Respiratory Organs 17.2 Mechanism of Breathing 17.3 Exchange of Gases 17.4 Transport of Gases 17.5 Regulation of Respiration 17.6 Disorders of
Pop Quiz. What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach?
 Pop Quiz What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach? Respiratory System Review Cellular respiration: obtain glucose and oxygen, get
Pop Quiz What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach? Respiratory System Review Cellular respiration: obtain glucose and oxygen, get
Collin County Community College. Lung Physiology
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 9 Respiratory System 1 Lung Physiology Factors affecting Ventillation 1. Airway resistance Flow = Δ P / R Most resistance is encountered
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 9 Respiratory System 1 Lung Physiology Factors affecting Ventillation 1. Airway resistance Flow = Δ P / R Most resistance is encountered
Respiratory system. Premedical - Biology
 Respiratory system Premedical - Biology Composition of atmosphere Nitrogen (N 2 ) 840 ppmv (78.084%) Oxygen (O 2 ) 209,460 ppmv (20.946%) Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) 387 ppmv (0.0387%) Argon (Ar), Neon (Ne),
Respiratory system Premedical - Biology Composition of atmosphere Nitrogen (N 2 ) 840 ppmv (78.084%) Oxygen (O 2 ) 209,460 ppmv (20.946%) Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) 387 ppmv (0.0387%) Argon (Ar), Neon (Ne),
Respiration. The resspiratory system
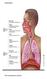 Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system. Objective sheet 3 Notes
 1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
Chapter 22 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 22 The Respiratory System 1 Respiration Pulmonary ventilation (breathing): movement of air into and out of the lungs External respiration: O 2 and CO 2 exchange between the lungs and the blood
Chapter 22 The Respiratory System 1 Respiration Pulmonary ventilation (breathing): movement of air into and out of the lungs External respiration: O 2 and CO 2 exchange between the lungs and the blood
2. State the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a normal breathing.
 CLASS XI BIOLOGY Breathing And Exchange of Gases 1. Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Answer: Vital Capacity (VC): The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration.
CLASS XI BIOLOGY Breathing And Exchange of Gases 1. Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Answer: Vital Capacity (VC): The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration.
BIOLOGY 12 - RESPIRATION - CHAPTER NOTES
 BIOLOGY 12 - RESPIRATION - CHAPTER NOTES We often think of respiration as just breathing. In fact, breathing is just one part of this physiological process. As biologists, we divide respiration up into
BIOLOGY 12 - RESPIRATION - CHAPTER NOTES We often think of respiration as just breathing. In fact, breathing is just one part of this physiological process. As biologists, we divide respiration up into
Using the figure above, match the following: 4. Tidal volume. 5. Inspiratory reserve volume. 6. Residual volume. 7. Expiratory reserve volume.
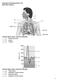 Respiratory Physiology Practice Test BIOL 4350: Hamilton Using the figure above, match the following: 1. Primary bronchus 2. Larynx 3. Trachea Using the figure above, match the following: 4. Tidal volume.
Respiratory Physiology Practice Test BIOL 4350: Hamilton Using the figure above, match the following: 1. Primary bronchus 2. Larynx 3. Trachea Using the figure above, match the following: 4. Tidal volume.
Respiration. Chapter 39
 Respiration Chapter 39 Impacts, Issues Up in Smoke Smoking immobilizes ciliated cells and kills white blood cells that defend the respiratory system; highly addictive nicotine discourages quitting 39.1
Respiration Chapter 39 Impacts, Issues Up in Smoke Smoking immobilizes ciliated cells and kills white blood cells that defend the respiratory system; highly addictive nicotine discourages quitting 39.1
Respiratory system & exercise. Dr. Rehab F Gwada
 Respiratory system & exercise Dr. Rehab F Gwada Objectives of lecture Outline the major anatomical components & important functions of the respiratory system. Describe the mechanics of ventilation. List
Respiratory system & exercise Dr. Rehab F Gwada Objectives of lecture Outline the major anatomical components & important functions of the respiratory system. Describe the mechanics of ventilation. List
Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation. Chad & Angela
 Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation Chad & Angela Respiratory Structures Basic Structures of Respiration Nasal/Oral Cavities Larynx Trachea Bronchi Secondary Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Mechanics of Ventilation
Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation Chad & Angela Respiratory Structures Basic Structures of Respiration Nasal/Oral Cavities Larynx Trachea Bronchi Secondary Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Mechanics of Ventilation
Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation
 Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing and the first step in the respiratory process. Pulmonary ventilation brings in air with a new supply
Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing and the first step in the respiratory process. Pulmonary ventilation brings in air with a new supply
PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Parts of the Respiratory System The RS can be divided into two parts: 1. Respiratory Tract, (path that air follows). Nasal passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi,
PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Parts of the Respiratory System The RS can be divided into two parts: 1. Respiratory Tract, (path that air follows). Nasal passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi,
Respiratory Physiology. Adeyomoye O.I
 Respiratory Physiology By Adeyomoye O.I Outline Introduction Hypoxia Dyspnea Control of breathing Ventilation/perfusion ratios Respiratory/barometric changes in exercise Intra-pulmonary & intra-pleural
Respiratory Physiology By Adeyomoye O.I Outline Introduction Hypoxia Dyspnea Control of breathing Ventilation/perfusion ratios Respiratory/barometric changes in exercise Intra-pulmonary & intra-pleural
IV. FROM AQUATIC TO ATMOSPHERIC BREATHING: THE TRACHEA & THE LUNG
 GAS EXCHANGE AND TRANSPORT I. INTRODUCTION: Heterotrophs oxidize carbon cmpds using O 2 to generate CO 2 & H 2 O. This is cellular respiration II. HOW GAS ENTERS A CELL A. The composition of air: 79% N
GAS EXCHANGE AND TRANSPORT I. INTRODUCTION: Heterotrophs oxidize carbon cmpds using O 2 to generate CO 2 & H 2 O. This is cellular respiration II. HOW GAS ENTERS A CELL A. The composition of air: 79% N
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system
 CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at gaseous exchange in humans in terms of o Ventilation o Inspiration o Expiration o Transport of gases o Homeostatic
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at gaseous exchange in humans in terms of o Ventilation o Inspiration o Expiration o Transport of gases o Homeostatic
Respiratory Physiology 2
 Respiratory Physiology 2 Session Objectives. What you will cover Gaseous Exchange Control of Breathing Rate Your objectives are State the function of support structures and epithelia of the bronchial tree
Respiratory Physiology 2 Session Objectives. What you will cover Gaseous Exchange Control of Breathing Rate Your objectives are State the function of support structures and epithelia of the bronchial tree
Respiratory Anatomy and Physiology. Respiratory Anatomy. Function of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory Anatomy and Physiology Michaela Dixon Clinical Development Nurse PICU BRHFC Respiratory Anatomy Function of the Respiratory System - In conjunction with the cardiovascular system, to supply
Respiratory Anatomy and Physiology Michaela Dixon Clinical Development Nurse PICU BRHFC Respiratory Anatomy Function of the Respiratory System - In conjunction with the cardiovascular system, to supply
Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 1
 Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The term "respiration" in its most complete meaning is: a. breathing b. oxygen transport c. carbon dioxide transport d. cellular energy production e. all of
Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The term "respiration" in its most complete meaning is: a. breathing b. oxygen transport c. carbon dioxide transport d. cellular energy production e. all of
Then the partial pressure of oxygen is x 760 = 160 mm Hg
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: the uptake of molecular oxygen (O2) from the environment and the discharge of
1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: the uptake of molecular oxygen (O2) from the environment and the discharge of
Clinical Respiratory System Quiz
 Quiz Description Clinical Respiratory System Quiz Q.1) Q.2) Q.3) Q.4) Q.5) Q.6) What is NOT true about Asthma? It can be triggered by air temperature and allergens. It is the inflammation of the throat.
Quiz Description Clinical Respiratory System Quiz Q.1) Q.2) Q.3) Q.4) Q.5) Q.6) What is NOT true about Asthma? It can be triggered by air temperature and allergens. It is the inflammation of the throat.
4/18/12 MECHANISM OF RESPIRATION. Every Breath You Take. Fun Facts
 Objectives MECHANISM OF RESPIRATION Dr Badri Paudel Explain how the intrapulmonary and intrapleural pressures vary during ventilation and relate these pressure changes to Boyle s law. Define the terms
Objectives MECHANISM OF RESPIRATION Dr Badri Paudel Explain how the intrapulmonary and intrapleural pressures vary during ventilation and relate these pressure changes to Boyle s law. Define the terms
2.1.1 List the principal structures of the
 physiology 2.1.1 List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx -
physiology 2.1.1 List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx -
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
Respiratory system. Role. Ventilation consists of 4 (5) steps : oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide elimination ph balance sound and voice formation
 Respiratory system Role oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide elimination ph balance sound and voice formation Ventilation consists of 4 (5) steps : 1. pulmonary ventilation gas exchange between lungs and
Respiratory system Role oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide elimination ph balance sound and voice formation Ventilation consists of 4 (5) steps : 1. pulmonary ventilation gas exchange between lungs and
Respiratory System Anatomy. Chapter 23
 Chapter 23 The Respiratory System Structurally, the respiratory system is divided into upper and lower divisions or tracts. The upper respiratory tract consists of the nose, pharynx and associated structures.
Chapter 23 The Respiratory System Structurally, the respiratory system is divided into upper and lower divisions or tracts. The upper respiratory tract consists of the nose, pharynx and associated structures.
Chapter 16 Respiration. Respiration. Steps in Respiration. Functions of the respiratory system
 Chapter 16 Respiration Functions of the respiratory system Respiration The term respiration includes 3 separate functions: Ventilation: Breathing. Gas exchange: Occurs between air and blood in the lungs.
Chapter 16 Respiration Functions of the respiratory system Respiration The term respiration includes 3 separate functions: Ventilation: Breathing. Gas exchange: Occurs between air and blood in the lungs.
Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration)
 Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration) 1 Question 1 Why do organisms need food? Organisms need food for obtaining energy to perform the vital functions. Question 2 What is a respiratory substrate?
Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration) 1 Question 1 Why do organisms need food? Organisms need food for obtaining energy to perform the vital functions. Question 2 What is a respiratory substrate?
25/4/2016. Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten
 25/4/2016 Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten Respiratory System Introduction: - We breath while we are sleeping, talking, working and resting. - Respiratory diseases are abundant
25/4/2016 Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten Respiratory System Introduction: - We breath while we are sleeping, talking, working and resting. - Respiratory diseases are abundant
Bio 182- Ecology Unit Outline 1
 Bio 182- Ecology Unit Outline 1 Respiration Introduction 1. Multicellular organisms require oxygen to generate E using cellular respiration 2. Wastes released as CO2 3. Summary equation for cellular respiration:
Bio 182- Ecology Unit Outline 1 Respiration Introduction 1. Multicellular organisms require oxygen to generate E using cellular respiration 2. Wastes released as CO2 3. Summary equation for cellular respiration:
Section Three Gas transport
 Section Three Gas transport Lecture 6: Oxygen transport in blood. Carbon dioxide in blood. Objectives: i. To describe the carriage of O2 in blood. ii. iii. iv. To explain the oxyhemoglobin dissociation
Section Three Gas transport Lecture 6: Oxygen transport in blood. Carbon dioxide in blood. Objectives: i. To describe the carriage of O2 in blood. ii. iii. iv. To explain the oxyhemoglobin dissociation
Page 1. Chapter 33: Respiration O 2 CO 2
 Chapter 33: Respiration O 2 CO 2 Features of Respiratory Systems: 1) Moist surface (to dissolve gas) 2) Thin cells lining surface 3) Large surface area contacting environment Facilitate Diffusion Methods
Chapter 33: Respiration O 2 CO 2 Features of Respiratory Systems: 1) Moist surface (to dissolve gas) 2) Thin cells lining surface 3) Large surface area contacting environment Facilitate Diffusion Methods
RESPIRATION III SEMESTER BOTANY MODULE II
 III SEMESTER BOTANY MODULE II RESPIRATION Lung Capacities and Volumes Tidal volume (TV) air that moves into and out of the lungs with each breath (approximately 500 ml) Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
III SEMESTER BOTANY MODULE II RESPIRATION Lung Capacities and Volumes Tidal volume (TV) air that moves into and out of the lungs with each breath (approximately 500 ml) Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
Airway: the tubes through which air flows between atmosphere and alveoli. Upper airway. Lower airway
 Respiration Yu Yanqin ( 虞燕琴 ), PhD Dept. of fph Physiology Zhejiang University, School of Medicine Respiration Definition: the bodily processes involved in exchange of oxygen (O 2 ) and carbon dioxide
Respiration Yu Yanqin ( 虞燕琴 ), PhD Dept. of fph Physiology Zhejiang University, School of Medicine Respiration Definition: the bodily processes involved in exchange of oxygen (O 2 ) and carbon dioxide
Chapter 4: Ventilation Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE
 Instant download and all chapters Test Bank Respiratory Care Anatomy and Physiology Foundations for Clinical Practice 3rd Edition Will Beachey https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-respiratory-care-anatomy-physiologyfoundations-clinical-practice-3rd-edition-will-beachey/
Instant download and all chapters Test Bank Respiratory Care Anatomy and Physiology Foundations for Clinical Practice 3rd Edition Will Beachey https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-respiratory-care-anatomy-physiologyfoundations-clinical-practice-3rd-edition-will-beachey/
Emergency Medical Technician 60 Questions
 Emergency Medical Technician 60 Questions 1. Which of the following is your primary goal during airway management? a. Ensure clear, unobstructed breathing. b. Ensure that CPR is effective. c. Provide a
Emergency Medical Technician 60 Questions 1. Which of the following is your primary goal during airway management? a. Ensure clear, unobstructed breathing. b. Ensure that CPR is effective. c. Provide a
Chapter 17 Mechanics of Breathing
 1 Chapter 17 Mechanics of Breathing Running Problem COPD: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (impaired air exchanged) - Chronic Bronchitis: (Blue Bloaters) Bluish tinge of skin and tendency to be overweight
1 Chapter 17 Mechanics of Breathing Running Problem COPD: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (impaired air exchanged) - Chronic Bronchitis: (Blue Bloaters) Bluish tinge of skin and tendency to be overweight
Gas exchange. Tissue cells CO2 CO 2 O 2. Pulmonary capillary. Tissue capillaries
 Gas exchange Pulmonary gas exchange Tissue gas exchange CO 2 O 2 O 2 Tissue cells CO2 CO 2 Pulmonary capillary O 2 O 2 CO 2 Tissue capillaries Physical principles of gas exchange Diffusion: continuous
Gas exchange Pulmonary gas exchange Tissue gas exchange CO 2 O 2 O 2 Tissue cells CO2 CO 2 Pulmonary capillary O 2 O 2 CO 2 Tissue capillaries Physical principles of gas exchange Diffusion: continuous
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange elephant seals gills AP Biology
 alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange O 2 & CO 2 exchange exchange between environment & cells provides O 2 for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange O 2 & CO 2 exchange exchange between environment & cells provides O 2 for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high
Chapter 23: The Respiratory System
 Chapter 23: The Respiratory System I. The Respiratory System: An Introduction, p. 814 Objectives: 1. Describe the primary functions of the respiratory system. 2. Explain how the delicate respiratory exchange
Chapter 23: The Respiratory System I. The Respiratory System: An Introduction, p. 814 Objectives: 1. Describe the primary functions of the respiratory system. 2. Explain how the delicate respiratory exchange
Respiration (revised 2006) Pulmonary Mechanics
 Respiration (revised 2006) Pulmonary Mechanics PUL 1. Diagram how pleural pressure, alveolar pressure, airflow, and lung volume change during a normal quiet breathing cycle. Identify on the figure the
Respiration (revised 2006) Pulmonary Mechanics PUL 1. Diagram how pleural pressure, alveolar pressure, airflow, and lung volume change during a normal quiet breathing cycle. Identify on the figure the
Respiratory System Study Guide, Chapter 16
 Part I. Clinical Applications Name: Respiratory System Study Guide, Chapter 16 Lab Day/Time: 1. A person with ketoacidosis may hyperventilate. Explain why this occurs, and explain why this hyperventilation
Part I. Clinical Applications Name: Respiratory System Study Guide, Chapter 16 Lab Day/Time: 1. A person with ketoacidosis may hyperventilate. Explain why this occurs, and explain why this hyperventilation
LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
 66 LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB Assignments: Due before lab: Quiz: Three Respiratory Interactive Physiology Animations pages 69 73. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
66 LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB Assignments: Due before lab: Quiz: Three Respiratory Interactive Physiology Animations pages 69 73. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
Section Two Diffusion of gases
 Section Two Diffusion of gases Lecture 5: Partial pressure and the composition of gasses in air. Factors affecting diffusion of gases. Ventilation perfusion ratio effect on alveolar gas concentration.
Section Two Diffusion of gases Lecture 5: Partial pressure and the composition of gasses in air. Factors affecting diffusion of gases. Ventilation perfusion ratio effect on alveolar gas concentration.
Ch. 12: Respiratory Physiology
 Ch. 12: Respiratory Physiology Objectives: 1. Review respiratory anatomy. 2. Understand mechanics of breathing. 3. Learn lung volumes & respiratory vocabulary 4. Learn gas exchange at lungs & at body tissues
Ch. 12: Respiratory Physiology Objectives: 1. Review respiratory anatomy. 2. Understand mechanics of breathing. 3. Learn lung volumes & respiratory vocabulary 4. Learn gas exchange at lungs & at body tissues
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM OF RABBIT:
 RESPIRATION The term respiration means exchange of gases (particularly oxygen and carbon dioxide) between an organism and its medium. Physiologically, the term respiration may be defined as a biochemical
RESPIRATION The term respiration means exchange of gases (particularly oxygen and carbon dioxide) between an organism and its medium. Physiologically, the term respiration may be defined as a biochemical
Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class
 I. Name the following : Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class 1. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. 2. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous
I. Name the following : Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class 1. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. 2. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous
Alveolus and Respiratory Membrane
 Alveolus and Respiratory Membrane thin membrane where gas exchange occurs in the lungs, simple squamous epithelium (Squamous cells have the appearance of thin, flat plates. They fit closely together in
Alveolus and Respiratory Membrane thin membrane where gas exchange occurs in the lungs, simple squamous epithelium (Squamous cells have the appearance of thin, flat plates. They fit closely together in
respiratory cycle. point in the volumes: 500 milliliters. for men. expiration, up to 1200 milliliters extra makes breathing Respiratory
 10 II. RESPIRATORY VOLUMES, CAPACITIES & PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS Respiratory volume is the term used for various volumes of air moved by or associated with the lungs at a given point in the respiratory
10 II. RESPIRATORY VOLUMES, CAPACITIES & PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS Respiratory volume is the term used for various volumes of air moved by or associated with the lungs at a given point in the respiratory
CHAPTER 3: The cardio-respiratory system
 : The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
: The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
Gas Exchange in Animals. Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2. Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial
 Gas Exchange in Animals Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2 Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial Respiratory surface! skin, gills, lungs Circulatory System O2/CO2
Gas Exchange in Animals Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2 Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial Respiratory surface! skin, gills, lungs Circulatory System O2/CO2
AP Biology. Chapter 42. Gas Exchange. Optimizing gas exchange. Gas exchange. Gas exchange in many forms. Evolution of gas exchange structures
 alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange & C exchange exchange between environment & cells provides for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high surface area
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange & C exchange exchange between environment & cells provides for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high surface area
2) During exhalation Air is cooled due to condensation and loses its moisture, depositing it on lining in trachea and nose
 Section 10: The Respiratory System A. Functions of the respiratory system: The organs of the respiratory system make sure oxygen enters the body and carbon dioxide leaves the body. 2 stages: Inhalation
Section 10: The Respiratory System A. Functions of the respiratory system: The organs of the respiratory system make sure oxygen enters the body and carbon dioxide leaves the body. 2 stages: Inhalation
Respiratory System. Prepared by: Dorota Marczuk-Krynicka, MD, PhD
 Respiratory System Prepared by: Dorota Marczuk-Krynicka, MD, PhD Lungs: Ventilation Perfusion Gas Exchange - Diffusion 1. Airways and Airway Resistance (AWR) 2. Mechanics of Breathing and Lung (Elastic)
Respiratory System Prepared by: Dorota Marczuk-Krynicka, MD, PhD Lungs: Ventilation Perfusion Gas Exchange - Diffusion 1. Airways and Airway Resistance (AWR) 2. Mechanics of Breathing and Lung (Elastic)
Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems
 alveoli gills Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? respiration for respiration Need O 2 in for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need CO 2
alveoli gills Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? respiration for respiration Need O 2 in for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need CO 2
