respiratory cycle. point in the volumes: 500 milliliters. for men. expiration, up to 1200 milliliters extra makes breathing Respiratory
|
|
|
- Emil Baldwin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 10 II. RESPIRATORY VOLUMES, CAPACITIES & PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS Respiratory volume is the term used for various volumes of air moved by or associated with the lungs at a given point in the respiratory cycle. There are four major types of respiratory volumes: Tidal volume (TV) is the amount of air that normally enterss the lungs during quiet breathing, which is about 500 milliliters. Expiratory reserve volume (ERV) is the amount of air youu can forcefully exhale past a normal tidal expiration, up to 1200 milliliters for men. Inspiratory reserve volume ( IRV) is produced by a deep inhalation, pastt a tidal inspiration. This is the extra volume that can be brought into the lungs during a forced inspiration. Residual volume (RV) is the air left in the lungs if you exhale as much airr as possible. The residual volume makes breathing easier by preventing the alveoli from collapsing. Respiratory volume is dependent on a variety of factors, and measuring the different types of respiratory volumes can provide important clues about a person s respiratory health. Respiratory capacities are the combination of two or more selectedd volumes, which further describes the amount of air in the lungs during a given time. In other words, capacities are mostly measurements of elasticity and compliance. Total lung capacity (TLC) is the sum of all of the lung volumes (TV, ERV, IRV, and RV) ), which represents the total amount of air a person can hold in the lungs after a forceful inhalation. TLC is about 6000 ml air for men, and about 4200 ml for women. Vital capacity (VC) is the amount of air a person can movee into or out of his or her lungs, and is the sum of all of the volumes except residual volume (TV, ERV, and IRV), which is between 4000 and 5000 milliliters. These two graphs show (a) respiratory volumes and (b) the combination of volumes that resultss in respiratory capacity. Spirometry (meaning the measuring of breath) is the most common of the pulmonary function tests (PFTs), measuring lung function, specifically the amount (volume) and/or speed (flow) of air that can be inhaled and exhaled. The spirometry test is performed using a device called a spirometer, which comes in several different varieties.
2 III. GAS EXCHANGE IN THE BODY A) SOME GENERALITIES ABOUT GASES 11 1) DALTONS LAW OF PARTIAL PRESSURES - most gases are mixtures of gases. The pressure of the gas is therefore a summation of all thee individual pressures of the individual component gases, each of which has a PARTIAL PRESSURE: NOTE: Notice the partial pressures add up! 2) HENRY S LAW - gases dissolve in a liquid (in other words, move into the liquid) in proportion to their individual partial pressures. * In other words, gases willl diffuse down their partial pressure gradients at different rate or speed, depending on their pressure gradients. Air is a mixture of over 100 gases. EXAMPLE: AIR It is 79% Nitrogen gas (N2), 20% oxygen gas (O2), 2 and less than 1% is the rest (carbon dioxide = CO 2, water vapor, neon, helium, etc.). - Eventually, gases will reach equilibrium, and movement will stop. An equivalent way of stating the law is that, all things being about equal, the solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure of the gas above the liquid. * What has to be about equal? Recall hydrophobic versus hydrophilic substances. In this example, both gases (N 2 and O 2 ) have comparable solubility in water. NOTE: YOU CAN THINK OF PARTIAL PRESSURE GRADIENTS LIKE CONCENTRATIONN GRADIENTS! Particles move down own individual gradients! But do not think they are the same!
3 12 B) PARTIAL PRESSURES (PP) OF GASES IN ALVEOLI, BLOODSTREAM & TISSUESS - IN GENERAL: we maintain PP gradients for O 2 and CO 2 in order to keep things flowing the way we want them to flow! *at the lungs, we want O 2 to move into the blood stream so we can transport it to the tissues, and CO 2 to move out of blood into alveoli so it can be expired. * at the tissues, we want O 2 to move out of the blood stream (into the tissues) and CO 2 to move out of tissues and into the blood, so it can be transported to lungs and expired. - NOTE: all movement of RESPIRATORY GASES = passive movement! NEVER pump! - QUESTION: how are these gradients maintained? Why doesn t thee system go to equilibrium, thereby stopping the flow of respiratory gases? 1. Blood circulation: Blood is ALWAYS CIRCULATING - remember, I told you in the Blood Vessel chapter that it was important for blood flow to never stop--now you know why. If it does, diffusion stops, CO 2 builds up in the cells, and they die. First to die are brain cells, because CO 2 is an acid (lowers ph; seee later). 2. Ventilation: New, oxygenated air is always being brought into the alveoli through inspiration, maintaining a PP gradient. If you want to see how long it takes for diffusion to stop if new air isn t brought in, see how long you can hold your breath! 3. Hemoglobin: Both CO 2 and O 2 are attached to a carrierr molecule (red blood cell) as soon as they enter the blood plasma (not shown on image). Therefore, they are no longer CO 2 and O 2, which maintains the gradient. 4. Chemical Reactions: Cellular metabolism keeps the ppp O 2 low inside the cell. Another reaction keeps CO 2 low in the blood near the cell: Once in water (serum), CO 2 is immediately converted to bicarbonate (not shown on image see later). Therefore, it is no longer COO 2, and the gradient is maintained. - ANOTHER QUESTION: remember, I told you that air has a LOT more O 2 than CO 2. If that s the case, then the CO 2 gradient must be SMALLER than the O 2 gradient; so O 2 must diffuse must faster than CO 2. How does the system keep CO 2 from building up if it diffuses so slow? *ANSWER: the above statement is true; however, CO 2 is much more SOLUBLE IN WATER than O 2, (20 times more soluble!). This makes up for the lower PP gradient. This solubility of carbon dioxide will become very important later!
4 13 - NOTE ONE OTHER THING: the system depends on passive movement, which is why the RESPIRATORY MEMBRANE must be so thin. Anything that lowers the membrane s diffusion capability damages the system, and lets CO2 build up. * PNEUMONIA - tissue becomes edematous & takes in more fluid; lowers movement of gases, patient poisons himself. * EMPHYSEMA - walls between adjacent alveoli break down, causing alveoli to fuse together. Larger alveoli = less surface area; eventually, not enough to maintain diffusion rates of CO2. Patient poisons himself. C) TRANSPORT OF RESPIRATOR RY GASES IN BLOOD - We have seen how we get the gases in & out of the alveoli and cells passive transport by maintaining pp gradients. But, how do we transport these gases to the cells (O 2 ) and to the lungs (CO 2 ) in the first place? NOTE: I will discuss the transport of these 2 gases separately, even though we will see their transport is link to each other, and you can t really separate them! 1) TRANSPORT OF OXYGEN - Oxygen gas is carried to the cells for their use. Therefore, blood plasma must be able to carry it DESPITE THE FACT THAT IT IS NOT VERY SOLUBLE IN WATER! To combat this, we attach it to a carrierr molecule in the RBC - HEMOGLOBIN (Hb) * Also, we must not only be able to carry it, by the system has to have a way of letting it go once it has arrive at the tissues that need oxygen for cellular respiration:
5 14 ASSOCIATION & DISSOCIATION or LOADING & UNLOADING of O2 - SO, in order to deal with these 2 requirements, oxygen is transported in the plasma in 2 ways: 1. Directly dissolve in plasma - only about 1.5% 2. Attached to hemoglobin about 98.5% - RECALL FROM BLOOD CELL CHAPTER: Hemoglobin = 4 polypeptide chains, each with an iron-containing bonding group (= the HEME group). * iron in the heme group of hemoglobin - easily OXIDIZEDD (picks up an O 2 ) in the following reaction: - As 1 Hb picks up an O 2, Hb changes shape, and it becomes progressively easier for subsequent O 2 to attach. Therefore, Hb tends to FULLY SATURATE with oxygen. * Also, the UNLOADING of 1 molecule of O 2 makes it easier for subsequent O 2 s to unload. * IN OTHER WORDS, the AFFINITY for Hb to O 2 changes.
6 15 *** IMPORTANT POINT: since the affinity for Hb to O 2 changes, when blood is near tissues that are METABOLICAL LY ACTIVE (that is, have a very low P (O 2 ) there is a veryy high PP gradient, and the molecules let go of oxygen quicker, which then FACILITATES UNLOADING! In this way, the system assures that oxygen is only unloaded at tissues that really need it!!!!! Below is what is called the Oxygen-hemoglobin Dissociation Curve (under normal conditions), with an explanation to make it easier: - We are watching Hb s AFFINITY to oxygen change! - Variables that affect Hb s AFFINITY for O 2 : O 2 1. PP O 2 - more O 2 = more formation of HbO
7 2. ph = THE BOHR EFFECT: Acidity affects Hb saturation More acidic blood (low ph) releases O 2, while less acidic blood releases less O 2. Also see dissociation curve below! PP CO 2 - because it s an acid (= hydrogen donor!) Because it is an acid (Bohr Effect), and changes shape of Hb. 4. Temperaturee See dissociation curve below! The Effects of ph and Temperature to the Oxygen Dissociation Curve 5. A chemical called BPG, which is a natural by-product of metabolism. Some hormones (NE, epinephrine, GH, testosterone) increase production of BPG by the cells! ALL OF THESE ALLOW THE RBC TO GIVE UP OXYGEN WHERE IT IS MOST NEEDED. - HYPOXIA - any impairment to O 2 delivery at the cells. * CYANOTIC ( blue skin ) - first sign of hypoxia. Look at mucosae & nail beds. * ANEMIC HYPOXIA - low # RBC, or abnormal Hb. * ISCHEMIC HYPOXIA - blocked circulation. * HISTOXIC HYPOXIA - cells are unable to use O2, despitee the fact that delivery is normal. Usually caused by METABOLIC TOXINS (CYANIDE stops the Electron Transport Chain, etc.). * HYPOXEMIC HYPOXIA - reduced arterial pp O2; caused by a pulmonary disease or breathing air with low concentration of O2; e.g. DROWNING. CARBON MONOXIDE (CO) POISONING - Hb hass a 200 X greater affinity for CO than O2; soon, all heme groups are occupied by CO.
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system
 CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
 Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
CHAPTER 3: The cardio-respiratory system
 : The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
: The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
Collin County Community College. Lung Physiology
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 9 Respiratory System 1 Lung Physiology Factors affecting Ventillation 1. Airway resistance Flow = Δ P / R Most resistance is encountered
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 9 Respiratory System 1 Lung Physiology Factors affecting Ventillation 1. Airway resistance Flow = Δ P / R Most resistance is encountered
Respiration - Human 1
 Respiration - Human 1 At the end of the lectures on respiration you should be able to, 1. Describe events in the respiratory processes 2. Discuss the mechanism of lung ventilation in human 3. Discuss the
Respiration - Human 1 At the end of the lectures on respiration you should be able to, 1. Describe events in the respiratory processes 2. Discuss the mechanism of lung ventilation in human 3. Discuss the
Respiratory System Physiology. Dr. Vedat Evren
 Respiratory System Physiology Dr. Vedat Evren Respiration Processes involved in oxygen transport from the atmosphere to the body tissues and the release and transportation of carbon dioxide produced in
Respiratory System Physiology Dr. Vedat Evren Respiration Processes involved in oxygen transport from the atmosphere to the body tissues and the release and transportation of carbon dioxide produced in
RESPIRATION III SEMESTER BOTANY MODULE II
 III SEMESTER BOTANY MODULE II RESPIRATION Lung Capacities and Volumes Tidal volume (TV) air that moves into and out of the lungs with each breath (approximately 500 ml) Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
III SEMESTER BOTANY MODULE II RESPIRATION Lung Capacities and Volumes Tidal volume (TV) air that moves into and out of the lungs with each breath (approximately 500 ml) Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
Chapter 17 The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and Regulation of Breathing
 Chapter 17 The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and Regulation of Breathing Overview of Pulmonary Circulation o Diffusion of Gases o Exchange of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide o Transport of Gases in the Blood
Chapter 17 The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and Regulation of Breathing Overview of Pulmonary Circulation o Diffusion of Gases o Exchange of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide o Transport of Gases in the Blood
Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY
 Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Respiration External respiration ventilation gas exchange Internal respiration cellular respiration gas exchange Respiratory Cycle Inspiration
Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Respiration External respiration ventilation gas exchange Internal respiration cellular respiration gas exchange Respiratory Cycle Inspiration
2. State the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a normal breathing.
 CLASS XI BIOLOGY Breathing And Exchange of Gases 1. Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Answer: Vital Capacity (VC): The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration.
CLASS XI BIOLOGY Breathing And Exchange of Gases 1. Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Answer: Vital Capacity (VC): The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration.
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Atmosphere Tissue cell External respiration Alveoli of lungs 1 Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Atmosphere Tissue cell External respiration Alveoli of lungs 1 Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere
Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 3
 Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 3 1. The pressure of a gas: a. is inversely proportional to its volume b. is unaffected by temperature changes c. is directly proportional to its volume d. does not
Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 3 1. The pressure of a gas: a. is inversely proportional to its volume b. is unaffected by temperature changes c. is directly proportional to its volume d. does not
P215 Respiratory System, Part 2
 P15 Respiratory System, Part Gas Exchange Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide constant need for oxygen constant production of carbon dioxide exchange (and movement) lung alveoli pulmonary arteries pulmonary capillaries
P15 Respiratory System, Part Gas Exchange Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide constant need for oxygen constant production of carbon dioxide exchange (and movement) lung alveoli pulmonary arteries pulmonary capillaries
BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
 96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The tissues exchange O 2 directly with the air in
96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The tissues exchange O 2 directly with the air in
Alveolus and Respiratory Membrane
 Alveolus and Respiratory Membrane thin membrane where gas exchange occurs in the lungs, simple squamous epithelium (Squamous cells have the appearance of thin, flat plates. They fit closely together in
Alveolus and Respiratory Membrane thin membrane where gas exchange occurs in the lungs, simple squamous epithelium (Squamous cells have the appearance of thin, flat plates. They fit closely together in
BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
 96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The cell exchange O 2 directly with the air in the
96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The cell exchange O 2 directly with the air in the
Chapter 23. Gas Exchange and Transportation
 Chapter 23 Gas Exchange and Transportation What is air? Mixture of gasses 78.6 % nitrogen 20.9% oxygen 0.04% carbon dioxide 0 4% water vapor depending on temperature and humidity and minor gases argon,
Chapter 23 Gas Exchange and Transportation What is air? Mixture of gasses 78.6 % nitrogen 20.9% oxygen 0.04% carbon dioxide 0 4% water vapor depending on temperature and humidity and minor gases argon,
Physiology of Respiration
 Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
Section Three Gas transport
 Section Three Gas transport Lecture 6: Oxygen transport in blood. Carbon dioxide in blood. Objectives: i. To describe the carriage of O2 in blood. ii. iii. iv. To explain the oxyhemoglobin dissociation
Section Three Gas transport Lecture 6: Oxygen transport in blood. Carbon dioxide in blood. Objectives: i. To describe the carriage of O2 in blood. ii. iii. iv. To explain the oxyhemoglobin dissociation
The physiological functions of respiration and circulation. Mechanics. exercise 7. Respiratory Volumes. Objectives
 exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE
 RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE Respiration Respiration delivery of oxygen to and removal of carbon dioxide from the tissue External respiration ventilation and exchange of gases in the lung Internal
RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE Respiration Respiration delivery of oxygen to and removal of carbon dioxide from the tissue External respiration ventilation and exchange of gases in the lung Internal
Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation
 Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation - Physical principles of gases: Pressure of a gas is caused by the movement of its molecules against a surface (more concentration
Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation - Physical principles of gases: Pressure of a gas is caused by the movement of its molecules against a surface (more concentration
Gas exchange. Tissue cells CO2 CO 2 O 2. Pulmonary capillary. Tissue capillaries
 Gas exchange Pulmonary gas exchange Tissue gas exchange CO 2 O 2 O 2 Tissue cells CO2 CO 2 Pulmonary capillary O 2 O 2 CO 2 Tissue capillaries Physical principles of gas exchange Diffusion: continuous
Gas exchange Pulmonary gas exchange Tissue gas exchange CO 2 O 2 O 2 Tissue cells CO2 CO 2 Pulmonary capillary O 2 O 2 CO 2 Tissue capillaries Physical principles of gas exchange Diffusion: continuous
Section Two Diffusion of gases
 Section Two Diffusion of gases Lecture 5: Partial pressure and the composition of gasses in air. Factors affecting diffusion of gases. Ventilation perfusion ratio effect on alveolar gas concentration.
Section Two Diffusion of gases Lecture 5: Partial pressure and the composition of gasses in air. Factors affecting diffusion of gases. Ventilation perfusion ratio effect on alveolar gas concentration.
GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY
 GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY Atmospheric Pressure Intra-Alveolar Pressure Inspiration 760 mm HG at Sea Level (= 1 atm) Pressure due to gases (N2, O2, CO2, Misc.) Pressure inside the alveolus (air sac) Phrenic
GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY Atmospheric Pressure Intra-Alveolar Pressure Inspiration 760 mm HG at Sea Level (= 1 atm) Pressure due to gases (N2, O2, CO2, Misc.) Pressure inside the alveolus (air sac) Phrenic
Respiratory system & exercise. Dr. Rehab F Gwada
 Respiratory system & exercise Dr. Rehab F Gwada Objectives of lecture Outline the major anatomical components & important functions of the respiratory system. Describe the mechanics of ventilation. List
Respiratory system & exercise Dr. Rehab F Gwada Objectives of lecture Outline the major anatomical components & important functions of the respiratory system. Describe the mechanics of ventilation. List
Respiratory System Study Guide, Chapter 16
 Part I. Clinical Applications Name: Respiratory System Study Guide, Chapter 16 Lab Day/Time: 1. A person with ketoacidosis may hyperventilate. Explain why this occurs, and explain why this hyperventilation
Part I. Clinical Applications Name: Respiratory System Study Guide, Chapter 16 Lab Day/Time: 1. A person with ketoacidosis may hyperventilate. Explain why this occurs, and explain why this hyperventilation
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System
 VI edit Pag 451-499 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System V edit. Pag 459-509 Tissue cell Alveoli of lungs Atmosphere 1 External respiration Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere and air sacs
VI edit Pag 451-499 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System V edit. Pag 459-509 Tissue cell Alveoli of lungs Atmosphere 1 External respiration Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere and air sacs
I Physical Principles of Gas Exchange
 Respiratory Gases Exchange Dr Badri Paudel, M.D. 2 I Physical Principles of Gas Exchange 3 Partial pressure The pressure exerted by each type of gas in a mixture Diffusion of gases through liquids Concentration
Respiratory Gases Exchange Dr Badri Paudel, M.D. 2 I Physical Principles of Gas Exchange 3 Partial pressure The pressure exerted by each type of gas in a mixture Diffusion of gases through liquids Concentration
Chapter 23. Gas Exchange and Transportation
 Chapter 23 Gas Exchange and Transportation What is air? Mixture of gasses 78.6 % nitrogen 20.9% oxygen 0.04% carbon dioxide 0 4% water vapor depending on temperature and humidity other minor gases argon,
Chapter 23 Gas Exchange and Transportation What is air? Mixture of gasses 78.6 % nitrogen 20.9% oxygen 0.04% carbon dioxide 0 4% water vapor depending on temperature and humidity other minor gases argon,
Respiratory physiology II.
 Respiratory physiology II. Learning objectives: 29. Pulmonary gas exchange. 30. Oxygen transport in the blood. 31. Carbon-dioxide transport in the blood. 1 Pulmonary gas exchange The transport mechanism
Respiratory physiology II. Learning objectives: 29. Pulmonary gas exchange. 30. Oxygen transport in the blood. 31. Carbon-dioxide transport in the blood. 1 Pulmonary gas exchange The transport mechanism
Respiratory System Review
 KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
Lung Volumes and Capacities
 Lung Volumes and Capacities Normally the volume of air entering the lungs during a single inspiration is approximately equal to the volume leaving on the subsequent expiration and is called the tidal volume.
Lung Volumes and Capacities Normally the volume of air entering the lungs during a single inspiration is approximately equal to the volume leaving on the subsequent expiration and is called the tidal volume.
Introduction. Respiration. Chapter 10. Objectives. Objectives. The Respiratory System
 Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
Respiratory System Lab
 Respiratory System Lab Note: Review the safety materials and wear goggles when working with chemicals. Read the entire exercise before you begin. Take time to organize the materials you will need and set
Respiratory System Lab Note: Review the safety materials and wear goggles when working with chemicals. Read the entire exercise before you begin. Take time to organize the materials you will need and set
AIIMS, New Delhi. Dr. K. K. Deepak, Prof. & HOD, Physiology AIIMS, New Delhi Dr. Geetanjali Bade, Asst. Professor AIIMS, New Delhi
 Course : PG Pathshala-Biophysics Paper 13 : Physiological Biophysics Module 17 : Gas transport and pulmonary circulation Principal Investigator: Co-Principal Investigator: Paper Coordinator: Content Writer:
Course : PG Pathshala-Biophysics Paper 13 : Physiological Biophysics Module 17 : Gas transport and pulmonary circulation Principal Investigator: Co-Principal Investigator: Paper Coordinator: Content Writer:
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange
 Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
2.1.1 List the principal structures of the
 physiology 2.1.1 List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx -
physiology 2.1.1 List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx -
Oxygen and Carbon dioxide Transport. Dr. Laila Al-Dokhi
 Oxygen and Carbon dioxide Transport Dr. Laila Al-Dokhi Objectives 1. Understand the forms of oxygen transport in the blood, the importance of each. 2. Differentiate between O2 capacity, O2 content and
Oxygen and Carbon dioxide Transport Dr. Laila Al-Dokhi Objectives 1. Understand the forms of oxygen transport in the blood, the importance of each. 2. Differentiate between O2 capacity, O2 content and
Chapter 16 Respiratory System
 Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Gases and Respiration. Respiration Overview I
 Respiration Overview I Respiration Overview II Gas Laws Equation of State: PV = nrt Same volumes of different gases have same # of molecules BTPS: body temp, atmospheric pressure, saturated ATPS: ambient
Respiration Overview I Respiration Overview II Gas Laws Equation of State: PV = nrt Same volumes of different gases have same # of molecules BTPS: body temp, atmospheric pressure, saturated ATPS: ambient
IV. FROM AQUATIC TO ATMOSPHERIC BREATHING: THE TRACHEA & THE LUNG
 GAS EXCHANGE AND TRANSPORT I. INTRODUCTION: Heterotrophs oxidize carbon cmpds using O 2 to generate CO 2 & H 2 O. This is cellular respiration II. HOW GAS ENTERS A CELL A. The composition of air: 79% N
GAS EXCHANGE AND TRANSPORT I. INTRODUCTION: Heterotrophs oxidize carbon cmpds using O 2 to generate CO 2 & H 2 O. This is cellular respiration II. HOW GAS ENTERS A CELL A. The composition of air: 79% N
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange elephant seals gills AP Biology
 alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange O 2 & CO 2 exchange exchange between environment & cells provides O 2 for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange O 2 & CO 2 exchange exchange between environment & cells provides O 2 for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high
LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
 66 LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB Assignments: Due before lab: Quiz: Three Respiratory Interactive Physiology Animations pages 69 73. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
66 LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB Assignments: Due before lab: Quiz: Three Respiratory Interactive Physiology Animations pages 69 73. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems
 alveoli gills Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? respiration for respiration Need O 2 in for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need CO 2
alveoli gills Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? respiration for respiration Need O 2 in for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need CO 2
AP Biology. Chapter 42. Gas Exchange. Optimizing gas exchange. Gas exchange. Gas exchange in many forms. Evolution of gas exchange structures
 alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange & C exchange exchange between environment & cells provides for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high surface area
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange & C exchange exchange between environment & cells provides for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high surface area
Respiratory Physiology 2
 Respiratory Physiology 2 Session Objectives. What you will cover Gaseous Exchange Control of Breathing Rate Your objectives are State the function of support structures and epithelia of the bronchial tree
Respiratory Physiology 2 Session Objectives. What you will cover Gaseous Exchange Control of Breathing Rate Your objectives are State the function of support structures and epithelia of the bronchial tree
HCO - 3 H 2 CO 3 CO 2 + H H H + Breathing rate is regulated by blood ph and C02. CO2 and Bicarbonate act as a ph Buffer in the blood
 Breathing rate is regulated by blood ph and C02 breathing reduces plasma [CO2]; plasma [CO2] increases breathing. When C02 levels are high, breating rate increases to blow off C02 In low C02 conditions,
Breathing rate is regulated by blood ph and C02 breathing reduces plasma [CO2]; plasma [CO2] increases breathing. When C02 levels are high, breating rate increases to blow off C02 In low C02 conditions,
AP Biology. Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems. Gas exchange. Why do we need a respiratory system? Optimizing gas exchange. Gas exchange in many forms
 alveoli Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems gills elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? Need O 2 in food respiration for respiration for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need
alveoli Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems gills elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? Need O 2 in food respiration for respiration for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need
RESPIRATORY GAS EXCHANGE
 RESPIRATORY GAS EXCHANGE Alveolar PO 2 = 105 mmhg; Pulmonary artery PO 2 = 40 mmhg PO 2 gradient across respiratory membrane 65 mmhg (105 mmhg 40 mmhg) Results in pulmonary vein PO 2 ~100 mmhg Partial
RESPIRATORY GAS EXCHANGE Alveolar PO 2 = 105 mmhg; Pulmonary artery PO 2 = 40 mmhg PO 2 gradient across respiratory membrane 65 mmhg (105 mmhg 40 mmhg) Results in pulmonary vein PO 2 ~100 mmhg Partial
CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
 268 BIOLOGY CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES 17.1 Respiratory Organs 17.2 Mechanism of Breathing 17.3 Exchange of Gases 17.4 Transport of Gases 17.5 Regulation of Respiration 17.6 Disorders of
268 BIOLOGY CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES 17.1 Respiratory Organs 17.2 Mechanism of Breathing 17.3 Exchange of Gases 17.4 Transport of Gases 17.5 Regulation of Respiration 17.6 Disorders of
April KHALED MOUSA BACHA. Physiology #2. Dr. Nayef AL-Gharaibeh. Pulmonary volumes & capacities
 25 th April Physiology #2 Pulmonary volumes & capacities Dr. Nayef AL-Gharaibeh KHALED MOUSA BACHA We will start this lecture by explaining an important concept from the previous one: Intrapleural pressure
25 th April Physiology #2 Pulmonary volumes & capacities Dr. Nayef AL-Gharaibeh KHALED MOUSA BACHA We will start this lecture by explaining an important concept from the previous one: Intrapleural pressure
Respiratory system. Premedical - Biology
 Respiratory system Premedical - Biology Composition of atmosphere Nitrogen (N 2 ) 840 ppmv (78.084%) Oxygen (O 2 ) 209,460 ppmv (20.946%) Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) 387 ppmv (0.0387%) Argon (Ar), Neon (Ne),
Respiratory system Premedical - Biology Composition of atmosphere Nitrogen (N 2 ) 840 ppmv (78.084%) Oxygen (O 2 ) 209,460 ppmv (20.946%) Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) 387 ppmv (0.0387%) Argon (Ar), Neon (Ne),
Yanal. Jumana Jihad. Jamil Nazzal. 0 P a g e
 2 Yanal Jumana Jihad Jamil Nazzal 0 P a g e note: this sheet was written and corrected according to the records from section 2 so you may find differences in the arrangement of topics from the records
2 Yanal Jumana Jihad Jamil Nazzal 0 P a g e note: this sheet was written and corrected according to the records from section 2 so you may find differences in the arrangement of topics from the records
The Respiratory System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Organs of the Respiratory system
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Organs of the Respiratory system
Lab 3. The Respiratory System (designed by Heather E. M. Liwanag with T.M. Williams)
 Name Lab Partners Lab 3. The Respiratory System (designed by Heather E. M. Liwanag with T.M. Williams) Part 1. Lung Volumes and Capacities Objectives 1. Obtain graphical representation of lung capacities
Name Lab Partners Lab 3. The Respiratory System (designed by Heather E. M. Liwanag with T.M. Williams) Part 1. Lung Volumes and Capacities Objectives 1. Obtain graphical representation of lung capacities
Respiration (revised 2006) Pulmonary Mechanics
 Respiration (revised 2006) Pulmonary Mechanics PUL 1. Diagram how pleural pressure, alveolar pressure, airflow, and lung volume change during a normal quiet breathing cycle. Identify on the figure the
Respiration (revised 2006) Pulmonary Mechanics PUL 1. Diagram how pleural pressure, alveolar pressure, airflow, and lung volume change during a normal quiet breathing cycle. Identify on the figure the
Circulatory And Respiration
 Circulatory And Respiration Composition Of Blood Blood Heart 200mmHg 120mmHg Aorta Artery Arteriole 50mmHg Capillary Bed Venule Vein Vena Cava Heart Differences Between Arteries and Veins Veins transport
Circulatory And Respiration Composition Of Blood Blood Heart 200mmHg 120mmHg Aorta Artery Arteriole 50mmHg Capillary Bed Venule Vein Vena Cava Heart Differences Between Arteries and Veins Veins transport
Respiratory system. Role. Ventilation consists of 4 (5) steps : oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide elimination ph balance sound and voice formation
 Respiratory system Role oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide elimination ph balance sound and voice formation Ventilation consists of 4 (5) steps : 1. pulmonary ventilation gas exchange between lungs and
Respiratory system Role oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide elimination ph balance sound and voice formation Ventilation consists of 4 (5) steps : 1. pulmonary ventilation gas exchange between lungs and
CHAPTER 6. Oxygen Transport. Copyright 2008 Thomson Delmar Learning
 CHAPTER 6 Oxygen Transport Normal Blood Gas Value Ranges Table 6-1 OXYGEN TRANSPORT Oxygen Dissolved in the Blood Plasma Dissolve means that the gas maintains its precise molecular structure About.003
CHAPTER 6 Oxygen Transport Normal Blood Gas Value Ranges Table 6-1 OXYGEN TRANSPORT Oxygen Dissolved in the Blood Plasma Dissolve means that the gas maintains its precise molecular structure About.003
Pco2 *20times = 0.6, 2.4, so the co2 carried in the arterial blood in dissolved form is more than the o2 because of its solubility.
 Physiology, sheet #9 Oxygen, is first dissolved in the plasma and the cytosol of the rbc, we have around blood constitutes 7% of our body weight, oxygen, in the capillaries is present in the rbc s and
Physiology, sheet #9 Oxygen, is first dissolved in the plasma and the cytosol of the rbc, we have around blood constitutes 7% of our body weight, oxygen, in the capillaries is present in the rbc s and
Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation. Chad & Angela
 Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation Chad & Angela Respiratory Structures Basic Structures of Respiration Nasal/Oral Cavities Larynx Trachea Bronchi Secondary Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Mechanics of Ventilation
Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation Chad & Angela Respiratory Structures Basic Structures of Respiration Nasal/Oral Cavities Larynx Trachea Bronchi Secondary Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Mechanics of Ventilation
1 CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES https://biologyaipmt.com/
 1 CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES https://biologyaipmt.com/ CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES Oxygen (O2) is utilised by the organisms to indirectly break down nutrient molecules like
1 CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES https://biologyaipmt.com/ CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES Oxygen (O2) is utilised by the organisms to indirectly break down nutrient molecules like
Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System
 Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System Animals require a continuous supply of oxygen (O 2 ) for cellular respiration, and they must expel carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), the waste product of this
Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System Animals require a continuous supply of oxygen (O 2 ) for cellular respiration, and they must expel carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), the waste product of this
Human Biology Respiratory System
 Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
Recitation question # 05
 Recitation and Lab # 05 The goal of this recitations / labs is to review material related to the CV and respiratory lectures for the second test of this course. Info required to answer this recitation
Recitation and Lab # 05 The goal of this recitations / labs is to review material related to the CV and respiratory lectures for the second test of this course. Info required to answer this recitation
Respiration. The ins and outs
 Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
Chapter 16 Respiration. Respiration. Steps in Respiration. Functions of the respiratory system
 Chapter 16 Respiration Functions of the respiratory system Respiration The term respiration includes 3 separate functions: Ventilation: Breathing. Gas exchange: Occurs between air and blood in the lungs.
Chapter 16 Respiration Functions of the respiratory system Respiration The term respiration includes 3 separate functions: Ventilation: Breathing. Gas exchange: Occurs between air and blood in the lungs.
TV = Tidal volume (500ml) IRV = Inspiratory reserve volume (3,000 ml)
 By: Amin alajlouni Lec: 2nd record Date: 29/10/2017 First of all, this is my first sheet so excuse any mistakes I might make and let's start: As we said before in our last lecture about lung capacities
By: Amin alajlouni Lec: 2nd record Date: 29/10/2017 First of all, this is my first sheet so excuse any mistakes I might make and let's start: As we said before in our last lecture about lung capacities
Breathing: The normal rate is about 14 to 20 times a minute. Taking in of air is called Inspiration and the forcing out of air is called Expiration.
 Biology 12 Respiration Divisions of Respiration Breathing: entrance and exit of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration: exchange of gases(o2 and CO2) between air (in alveoli) and blood Internal
Biology 12 Respiration Divisions of Respiration Breathing: entrance and exit of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration: exchange of gases(o2 and CO2) between air (in alveoli) and blood Internal
Essential Skills Course Acute Care Module. Respiratory Day 2 (Arterial Blood Gases) Pre course Workbook
 Essential Skills Course Acute Care Module Respiratory Day 2 (Arterial Blood Gases) Pre course Workbook Acknowledgements This pre course workbook has been complied and updated with reference to the original
Essential Skills Course Acute Care Module Respiratory Day 2 (Arterial Blood Gases) Pre course Workbook Acknowledgements This pre course workbook has been complied and updated with reference to the original
Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University in Brno. Biophysics of breathing.
 Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University in Brno Biophysics of breathing. Spirometry 1 Lecture outline Mechanisms of gas exchange between organism and
Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University in Brno Biophysics of breathing. Spirometry 1 Lecture outline Mechanisms of gas exchange between organism and
Respiration. The resspiratory system
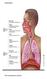 Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
system. and then into the tissues. Diffusion of wastes such as Carbon Dioxide from tissues into blood and out of blood into the lungs.
 Respiratory System 1.Exchange Why do of we gases breathe? into the Think blood of all and the tissues. reasons Diffusion why we of Oxygen need a respiratory into blood from the lungs system. and then into
Respiratory System 1.Exchange Why do of we gases breathe? into the Think blood of all and the tissues. reasons Diffusion why we of Oxygen need a respiratory into blood from the lungs system. and then into
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 11 Respiratory System 2 Pulmonary Ventilation Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session plan o Pulmonary Ventilation
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 11 Respiratory System 2 Pulmonary Ventilation Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session plan o Pulmonary Ventilation
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired
 Chapter 6 Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired This chapter covers: the structure of the human gas exchange system the mechanism of breathing gas exchange in the alveoli the concept
Chapter 6 Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired This chapter covers: the structure of the human gas exchange system the mechanism of breathing gas exchange in the alveoli the concept
660 mm Hg (normal, 100 mm Hg, room air) Paco, (arterial Pc02) 36 mm Hg (normal, 40 mm Hg) % saturation 50% (normal, 95%-100%)
 148 PHYSIOLOGY CASES AND PROBLEMS Case 26 Carbon Monoxide Poisoning Herman Neiswander is a 65-year-old retired landscape architect in northern Wisconsin. One cold January morning, he decided to warm his
148 PHYSIOLOGY CASES AND PROBLEMS Case 26 Carbon Monoxide Poisoning Herman Neiswander is a 65-year-old retired landscape architect in northern Wisconsin. One cold January morning, he decided to warm his
Respiratory Medicine. A-A Gradient & Alveolar Gas Equation Laboratory Diagnostics. Alveolar Gas Equation. See online here
 Respiratory Medicine A-A Gradient & Alveolar Gas Equation Laboratory Diagnostics See online here Alveolar gas equation helps to calculate the partial pressure of oxygen in alveoli and A-a gradient is the
Respiratory Medicine A-A Gradient & Alveolar Gas Equation Laboratory Diagnostics See online here Alveolar gas equation helps to calculate the partial pressure of oxygen in alveoli and A-a gradient is the
Then the partial pressure of oxygen is. b) Gases will diffuse down a pressure gradient across a respiratory surface if it is: i) permeable ii) moist
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: Relies on the diffusion of gases down pressure gradients. At sea level, atmosphere
1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: Relies on the diffusion of gases down pressure gradients. At sea level, atmosphere
Table of Contents. By Adam Hollingworth
 By Adam Hollingworth Table of Contents Oxygen Cascade... 2 Diffusion... 2 Laws of Diffusion... 2 Diffusion & Perfusion Limitations... 3 Oxygen Uptake Along Pulmon Capillary... 4 Measurement of Diffusing
By Adam Hollingworth Table of Contents Oxygen Cascade... 2 Diffusion... 2 Laws of Diffusion... 2 Diffusion & Perfusion Limitations... 3 Oxygen Uptake Along Pulmon Capillary... 4 Measurement of Diffusing
(Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System
 (Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System I. (Slide 2) The Respiratory Tract A) Major structures and regions of the respiratory Tract/Route INTO body 1) nose 2) nasal cavity 3) pharynx 4) glottis 5)
(Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System I. (Slide 2) The Respiratory Tract A) Major structures and regions of the respiratory Tract/Route INTO body 1) nose 2) nasal cavity 3) pharynx 4) glottis 5)
Physiology - lecture 3
 Physiology - lecture 3 Residual Volume (RV):the amount of gas remaining in the lung at the end of a maximal exhalation Tidal Volume (TV):the volume of gas inhaled and exhaled during one respiratory cycle.
Physiology - lecture 3 Residual Volume (RV):the amount of gas remaining in the lung at the end of a maximal exhalation Tidal Volume (TV):the volume of gas inhaled and exhaled during one respiratory cycle.
Monday, ! Today: Respiratory system! 5/20/14! Transport of Blood! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing!
 Monday, 5.19.14! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing! Transport of Blood! What is transported! Nutrients! Oxygen! Carbon Dioxide! Hormones! Antibodies! What it is/does!
Monday, 5.19.14! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing! Transport of Blood! What is transported! Nutrients! Oxygen! Carbon Dioxide! Hormones! Antibodies! What it is/does!
The Physiologic Basis of DLCO testing. Brian Graham Division of Respirology, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine University of Saskatchewan
 The Physiologic Basis of DLCO testing Brian Graham Division of Respirology, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine University of Saskatchewan Objectives Review gas transport from inhaled gas to the rest of the
The Physiologic Basis of DLCO testing Brian Graham Division of Respirology, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine University of Saskatchewan Objectives Review gas transport from inhaled gas to the rest of the
Respiratory Anatomy and Physiology. Respiratory Anatomy. Function of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory Anatomy and Physiology Michaela Dixon Clinical Development Nurse PICU BRHFC Respiratory Anatomy Function of the Respiratory System - In conjunction with the cardiovascular system, to supply
Respiratory Anatomy and Physiology Michaela Dixon Clinical Development Nurse PICU BRHFC Respiratory Anatomy Function of the Respiratory System - In conjunction with the cardiovascular system, to supply
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Pop Quiz. What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach?
 Pop Quiz What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach? Respiratory System Review Cellular respiration: obtain glucose and oxygen, get
Pop Quiz What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach? Respiratory System Review Cellular respiration: obtain glucose and oxygen, get
αo 2 : solubility coefficient of O 2
 Version 2006 Dr. Puntarica Suwanprathes 1) Fick s law of diffusion 2) facts which limit gas transfer 3) diffusion capacity gas volume gaseous phase dissolved gas exert pressure*** Solubility of Gas C =P.
Version 2006 Dr. Puntarica Suwanprathes 1) Fick s law of diffusion 2) facts which limit gas transfer 3) diffusion capacity gas volume gaseous phase dissolved gas exert pressure*** Solubility of Gas C =P.
PICU Resident Self-Study Tutorial The Basic Physics of Oxygen Transport. I was told that there would be no math!
 Physiology of Oxygen Transport PICU Resident Self-Study Tutorial I was told that there would be no math! INTRODUCTION Christopher Carroll, MD Although cells rely on oxygen for aerobic metabolism and viability,
Physiology of Oxygen Transport PICU Resident Self-Study Tutorial I was told that there would be no math! INTRODUCTION Christopher Carroll, MD Although cells rely on oxygen for aerobic metabolism and viability,
Paul V. Jennemann Maryland Radon Laboratory, Inc Corporate Court, Suite E Ellicott City, MD 21042
 RADON VS PROGENY Paul V. Jennemann Maryland Radon Laboratory, Inc. 3220 Corporate Court, Suite E Ellicott City, MD 21042 1. INTRODUCTION Any one who has taken a radon training course should be familiar
RADON VS PROGENY Paul V. Jennemann Maryland Radon Laboratory, Inc. 3220 Corporate Court, Suite E Ellicott City, MD 21042 1. INTRODUCTION Any one who has taken a radon training course should be familiar
By: Aseel Jamil Al-twaijer. Lec : physical principles of gas exchange
 By: Aseel Jamil Al-twaijer Lec : physical principles of gas exchange Date:30 /10/2017 this lecture is about the exchange of gases between the blood and the alveoli. I might add some external definitions
By: Aseel Jamil Al-twaijer Lec : physical principles of gas exchange Date:30 /10/2017 this lecture is about the exchange of gases between the blood and the alveoli. I might add some external definitions
ALVEOLAR - BLOOD GAS EXCHANGE 1
 ALVEOLAR - BLOOD GAS EXCHANGE 1 Summary: These notes examine the general means by which ventilation is regulated in terrestrial mammals. It then moves on to a discussion of what happens when someone over
ALVEOLAR - BLOOD GAS EXCHANGE 1 Summary: These notes examine the general means by which ventilation is regulated in terrestrial mammals. It then moves on to a discussion of what happens when someone over
Gas Exchange in Animals. Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2. Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial
 Gas Exchange in Animals Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2 Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial Respiratory surface! skin, gills, lungs Circulatory System O2/CO2
Gas Exchange in Animals Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2 Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial Respiratory surface! skin, gills, lungs Circulatory System O2/CO2
08 Respiration. #79 Respiration realeases energy from food
 08 Respiration #79 Respiration realeases energy from food Respiration is the chemical reactions that break down nutrient molecules in living cells to release energy. In humans, our cells need energy (ATP)
08 Respiration #79 Respiration realeases energy from food Respiration is the chemical reactions that break down nutrient molecules in living cells to release energy. In humans, our cells need energy (ATP)
Gas Exchange & Circulation
 Why is gas exchange important? Gas Exchange & Circulation Read Ch. 42 start with 42.5: Gas Exchange in Animals Respiration: C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2! Energy + CO 2 + H 2 O Photosynthesis: Energy + CO 2 + H 2
Why is gas exchange important? Gas Exchange & Circulation Read Ch. 42 start with 42.5: Gas Exchange in Animals Respiration: C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2! Energy + CO 2 + H 2 O Photosynthesis: Energy + CO 2 + H 2
I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface:
 I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface: Common characteristics of respiratory surfaces: a) Moist: allows for the RAPID diffusion of dissolved gasses across its surface. Whereas the respiratory
I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface: Common characteristics of respiratory surfaces: a) Moist: allows for the RAPID diffusion of dissolved gasses across its surface. Whereas the respiratory
Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration)
 Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration) 1 Question 1 Why do organisms need food? Organisms need food for obtaining energy to perform the vital functions. Question 2 What is a respiratory substrate?
Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration) 1 Question 1 Why do organisms need food? Organisms need food for obtaining energy to perform the vital functions. Question 2 What is a respiratory substrate?
Airway: the tubes through which air flows between atmosphere and alveoli. Upper airway. Lower airway
 Respiration Yu Yanqin ( 虞燕琴 ), PhD Dept. of fph Physiology Zhejiang University, School of Medicine Respiration Definition: the bodily processes involved in exchange of oxygen (O 2 ) and carbon dioxide
Respiration Yu Yanqin ( 虞燕琴 ), PhD Dept. of fph Physiology Zhejiang University, School of Medicine Respiration Definition: the bodily processes involved in exchange of oxygen (O 2 ) and carbon dioxide
