Lab 3. The Respiratory System (designed by Heather E. M. Liwanag with T.M. Williams)
|
|
|
- Henry Douglas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name Lab Partners Lab 3. The Respiratory System (designed by Heather E. M. Liwanag with T.M. Williams) Part 1. Lung Volumes and Capacities Objectives 1. Obtain graphical representation of lung capacities and volumes. 2. Compare lung volumes between males and females. 3. Correlate lung volumes with clinical conditions. 4. Determine the effect of exercise on tidal volume and respiratory frequency. Background Measurement of lung volumes provides a tool for understanding normal function of the lungs as well as disease states. The breathing cycle is initiated by expansion of the chest. Contraction of the diaphragm causes it to flatten downward. If chest muscles are used, the ribs expand outward. The resulting increase in chest volume creates a negative pressure that draws air in through the nose and mouth. Normal exhalation is passive, resulting from recoil of the chest wall, diaphragm, and lung tissue. In normal breathing at rest, approximately one-tenth of the total lung capacity is used. Greater amounts are used as needed (i.e., with exercise). The following terms are used to describe lung volumes (see Figure 1): Tidal Volume (TV): The volume of air breathed in and out without conscious effort Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV): The additional volume of air that can be inhaled with maximum effort after a normal inspiration Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV): The additional volume of air that can be forcibly exhaled after normal exhalation Vital Capacity (VC): Residual Volume (RV): The total volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inhalation: VC = TV + IRV + ERV The volume of air remaining in the lungs after maximum exhalation (the lungs can never be completely emptied)
2 Total Lung Capacity (TLC): Minute Ventilation: = VC + RV The volume of air breathed in 1 minute: (TV)(breaths/minute) In this experiment, you will measure lung volumes during normal breathing and with maximum effort. You will correlate lung volumes with a variety of clinical scenarios. You will also determine how exercise impacts both tidal volume and breathing frequency to ensure sufficient delivery of air during periods of increased activity. Figure 1 Procedure Important: Do not attempt this experiment if you are currently suffering from a respiratory ailment such as the cold or flu. 1. Connect the Spirometer to the Vernier computer interface. Open the Bio131 folder on the desktop, then open the Vernier Physiology folder. Double-click the file 19 Lung Volumes. 2. Attach the larger diameter side of a bacterial filter to the Inlet side of the Spirometer. Attach a gray disposable mouthpiece to the other end of the bacterial filter (see Figure 2). Figure 2
3 3. Hold the Spirometer in one or both hands. Brace your arm(s) against a solid surface, such as a table, and click to zero the sensor. Note: The Spirometer must be held straight up and down, as in Figure 2, and not moved during data collection. 4. Collect inhalation and exhalation data. a. Put on the nose plug. b. Click to begin data collection. c. Taking normal breaths, begin data collection with an inhalation and continue to breathe in and out. After 4 cycles of normal inspirations and expirations, fill your lungs as deeply as possible (maximum inspiration) and exhale as fully as possible (maximum expiration). It is essential that maximum effort be expended when performing tests of lung volumes. d. Follow this with at least one additional recovery breath. 5. Click to end data collection. 6. Click the Next Page button,, to see the lung volume data. If the baseline on your graph has drifted, use the Baseline Adjustment feature to bring the baseline volumes closer to zero, as in Figure Select a representative peak and valley in the Tidal Volume portion of your graph. Place the cursor on the peak and click and drag down to the valley that follows it. Enter the y value displayed in the lower left corner of the graph to the nearest 0.1 L as Tidal Volume in Table Move the cursor to the peak that represents your maximum inspiration. Click and drag down the side of the peak until you reach the level of the peaks graphed during normal breathing. Enter the y value displayed in the lower left corner of the graph to the nearest 0.1 L as Inspiratory Reserve Volume in Table Move the cursor to the valley that represents your maximum expiration. Click and drag up the side of the peak until you reach the level of the valleys graphed during normal breathing. Enter the y value displayed in the lower left corner of the graph to the nearest 0.1 L as Expiratory Reserve Volume in Table Calculate the Vital Capacity and enter the total to the nearest 0.1 L in Table 1. VC = TV + IRV + ERV 11. Calculate the Total Lung Capacity and enter the total to the nearest 0.1 L in Table 1. (Use the value of 1.5 L for the RV.) TLC = VC + RV Figure Share your data with your classmates and complete the Class Average columns in Table 1.
4 Effect of Exercise on respiration 13. As you have just discovered the inflow of air into the lungs is affected by both tidal volume and by your breathing frequency. Which of these will change with exercise? In this part of the lab you will assess whether tidal volume or breathing frequency varies in response to different levels of exercise. First, select one or two subjects from your group to serve as the athletes. 14. Repeat the measurements for Tidal Volume as above for your subjects, 1) resting, 2) following a 3 minute walk outside on the road, and 3) following a 3 minute jog/run down the road and back to the lab. It is important to obtain the exercise measurements as soon as the exercise is completed. So the team should be ready with the instruments once the athletes return. As you determine tidal volume, count the number of breaths the subject takes per minute (breathing frequency). Record the data in Table 2.
5 DATA Table 1 Volume measurement (L) Individual (L) Class average (Male) (L) Class average (Female) (L) Tidal Volume (TV) Inspiratory Reserve (IRV) Expiratory Reserve (ERV) Vital Capacity (VC) Residual Volume (RV) Total Lung Capacity (TLC) Table 2 Exercise Level Rest Walking Running Tidal Volume (TV) (Liters) Breathing Frequency (Breaths per minute)
6 Part 2. Effect of Dead Space on Oxygen Availability Objectives 1. Simulate different volumes of dead space. 2. Measure the oxygen concentration within the dead space. 3. Correlate dead space volume with a variety of physiologic challenges. Background In the average adult human, approximately 150 ml of the air that is inhaled with each breath never reaches the alveoli. It fills the nose, mouth, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles, a volume known as the anatomical dead space. This air is not available for gas mixing and exchange. It mixes with newly inhaled air and is recycled back to the alveoli. The relative size of the dead space as compared to functioning lung tissue impacts the efficiency of the respiratory system. Dead space is important in a variety of medical conditions such as asthma, pneumonia, and emphysema, and must be considered in treatments such as artificial ventilation in an intensive care unit. It is also important in physiologic challenges such as diving and high altitude activities. In this experiment, you will use an O 2 Gas Sensor to analyze inhaled and exhaled air while artificially changing the size of the dead space. You will calculate the effect that dead space has on oxygen delivery to the lungs and correlate this with various physiologic challenges. The majority of oxygen is carried in the blood by hemoglobin molecules. This is dependent upon the partial pressure of oxygen, but the binding of oxygen is efficient over a wide range of oxygen pressures. This relationship is demonstrated in the Oxygen-Hemoglobin Dissociation Curve (see Figure 1). In conditions where hemoglobin concentration is low (anemias), oxygen delivery to the tissues is proportionately decreased. Blood transfusions, rather than supplemental oxygen, will increase oxygen delivery to the tissues. Figure 1
7 Procedure Part A. The Effect of Increasing Dead Space on Oxygen Concentration 1. Connect the O 2 Gas Sensor to Channel 1 of the Vernier computer interface. Open the file 24 Effect of Dead Space from the Vernier Physiology folder. 2. Insert the Vernier O 2 Gas Sensor into the CO 2 -O 2 Tee as shown in Figure Click to begin data collection. Place your mouth on the smaller end of the CO 2 -O 2 Tee and begin normal breathing. Data will be collected for 60 s. Figure 2 Figure 3 4. Store this run by choosing Store Latest Run from the Experiment menu. 5. Remove the O 2 Gas Sensor from the CO 2 -O 2 Tee and allow readings to return to ambient levels. Monitor oxygen levels by observing the readings on the screen. Once ambient levels have been reached, re-attach the sensor to the CO 2 -O 2 Tee. 6. Attach the 15 cm PVC pipe to the larger end of the CO 2 -O 2 Tee as shown in Figure Click to begin data collection. Place your mouth on the smaller end of the CO 2 -O 2 Tee and begin normal breathing. Data will be collected for 60 s. 8. Store this run by choosing Store Latest Run from the Experiment menu. 9. Remove the O 2 Gas Sensor from the CO 2 -O 2 Tee and allow readings to return to ambient levels. Monitor oxygen levels by observing the readings on the screen. Once ambient levels have been reached, re-attach the sensor to the CO 2 -O 2 Tee. 10. Attach the 30 cm PVC pipe to the larger end of the CO 2 -O 2 Tee as shown in Figure Click to begin data collection. Place your mouth on the smaller end of the CO 2 -O 2 Tee and begin normal breathing. Data will be collected for 60 s. 12. Click and drag to highlight all data runs from s. Click the Statistics button,. Click the boxes in front of Run 1, Run 2, and Latest and click. Record the mean values to the nearest 0.1% for all three runs in Table 1.
8 Part B. The Effect of Increased Effort on Oxygen Consumption 13. Choose Clear All Data from the Data menu. 14. Remove the 30 cm PVC pipe from the CO 2 -O 2 Tee and ensure that the Tee is well attached to the O 2 Gas Sensor. 15. Click to begin data collection. Place your mouth on the smaller end of the CO 2 -O 2 Tee and begin deeply inhaling and exhaling. Allow 3 s for inhalation and 3 s for exhalation to prevent dizziness. Data will be collected for 60 s. 16. Store this run by choosing Store Latest Run from the Experiment Menu. 17. Remove the O 2 Gas Sensor from the CO 2 -O 2 Tee and allow readings to return to ambient levels. Monitor oxygen levels by observing the readings in the Logger Pro tool bar. Once ambient levels have been reached, re-attach the sensor to the CO 2 -O 2 Tee. 18. Attach the 15 cm PVC pipe to the larger end of the CO 2 -O 2 Tee as shown in Figure Click to begin data collection. Place your mouth on the smaller end of the CO 2 -O 2 Tee and begin deep breathing, as instructed in Step 15. Data will be collected for 60 s. 20. Store this run by choosing Store Latest Run from the Experiment Menu. 21. Remove the O 2 Gas Sensor from the CO 2 -O 2 Tee and allow readings to return to ambient levels. Monitor oxygen levels by observing the readings in the Logger Pro tool bar. Once ambient levels have been reached, re-attach the sensor to the CO 2 -O 2 Tee. 22. Attach the 30 cm PVC pipe to the larger end of the CO 2 -O 2 Tee as shown in Figure Click to begin data collection. Place your mouth on the smaller end of the CO 2 -O 2 Tee and begin deep breathing, as instructed in Step 15. Data will be collected for 60 s. 24. Click and drag to highlight all data runs from s. Click the Statistics button,. Click the boxes in front of Run 1, Run 2, and Latest and click. Record the mean values for all three runs in Table 2.
9 Data Table 1 Normal Breathing Run Description Mean O 2 concentration (%) 1 CO 2 -O 2 Tee alone 2 CO 2 -O 2 Tee + 15 cm PVC pipe 3 CO 2 -O 2 Tee + 30 cm PVC pipe Table 2 Deep Breathing Run Description Mean O 2 concentration (%) 1 CO 2 -O 2 Tee alone 2 CO 2 -O 2 Tee + 15 cm PVC pipe 3 CO 2 -O 2 Tee + 30 cm PVC pipe
10 Name DATA ANALYSIS PART 1. VOLUMES 1. Describe the difference between lung volumes for males and females. What might account for this? 2. Calculate your Minute Volume at rest. (TV breaths/minute) = Minute Volume at rest If you had to take shallow breaths (TV = 0.20 L) to avoid severe pain from rib fractures, what respiratory rate would be required to achieve the same minute volume? 3. On a separate piece of paper create a bar chart showing a) Tidal volume in relation to exercise intensity, b) Breathing Frequency in relation to exercise intensity, and c) minute volume in relation to exercise intensity. Based on your data, which appears to be more important for increasing the delivery of air as the intensity of exercise increases increasing tidal volume or increasing breathing frequency?
11 PART 2. ANATOMICAL DEAD SPACE 1. The varying lengths of PVC pipe act to increase the volume of inhaled air that is not available for gas mixing and exchange the so-called dead space. Calculate the volume of air in the 15 and 30 cm lengths of PVC pipes (πr 2 h), respectively. To each value, add 30 ml to account for the volume of air present in the CO 2 -O 2 Tee. Record your answers in the table below in the column labeled Volume (remember that cm 3 = ml). Add these volumes to your anatomical dead space (150 ml), and enter the total values into the table. Calculation of Dead Space Pipe length Volume of PVC + tee (ml) Anatomical + additional dead space (ml) 15 cm 30 cm 2. Using the table you completed in Question 1, estimate the proportion by which your anatomical dead space was artificially increased by (a) the 15 cm tube. (b) the 30 cm tube. 3. Describe the trend in mean oxygen concentration seen in the data entered in Table 1 as it relates to the anatomical dead space. 4. The average amount of air breathed in and out during normal respirations is approximately 500 ml (this is called tidal volume). The volume of air inhaled and exhaled during deep breaths is approximately 4000 ml (this is called vital capacity). Use these values to explain the difference in trends seen in Table 1 and Table 2.
Lung Volumes and Capacities
 Lung Volumes and Capacities Experiment 19 Measurement of lung volumes provides a tool for understanding normal function of the lungs as well as disease states. The breathing cycle is initiated by expansion
Lung Volumes and Capacities Experiment 19 Measurement of lung volumes provides a tool for understanding normal function of the lungs as well as disease states. The breathing cycle is initiated by expansion
Lung Volumes and Capacities
 BIOL242 Lung Volumes and Capacities Measurement of lung volumes provides a tool for understanding normal function of the lungs as well as disease states. The breathing cycle is initiated by expansion of
BIOL242 Lung Volumes and Capacities Measurement of lung volumes provides a tool for understanding normal function of the lungs as well as disease states. The breathing cycle is initiated by expansion of
Respiratory Response to Physiologic Challenges. Evaluation copy
 Respiratory Response to Physiologic Challenges Computer 20 The respiratory cycle of inspiration and expiration is controlled by complex mechanisms involving neurons in the cerebral cortex, brain stem,
Respiratory Response to Physiologic Challenges Computer 20 The respiratory cycle of inspiration and expiration is controlled by complex mechanisms involving neurons in the cerebral cortex, brain stem,
The physiological functions of respiration and circulation. Mechanics. exercise 7. Respiratory Volumes. Objectives
 exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
Respiration Lab Instructions
 Respiration Lab Instructions This laboratory investigation can be performed in any order. Be sure to read all instructions for each section before performing the experiment. PART 1 STUDENT WET SPIROMETER
Respiration Lab Instructions This laboratory investigation can be performed in any order. Be sure to read all instructions for each section before performing the experiment. PART 1 STUDENT WET SPIROMETER
Respiratory Physiology
 Respiratory Physiology Background Information: When inspiring, the pleura attached to the internal chest wall is pulled outward as the thoracic cavity expands. The pleural cavity [space between the outer
Respiratory Physiology Background Information: When inspiring, the pleura attached to the internal chest wall is pulled outward as the thoracic cavity expands. The pleural cavity [space between the outer
Using Vernier Equipment to Convert Didactically Taught Human Respiration Lab to Inquiry Based Human Respiration Lab
 Using Vernier Equipment to Convert Didactically Taught Human Respiration Lab to Inquiry Based Human Respiration Lab Timothy J. Bradshaw 1, Samuel P. Carmichael II 2, Jason A. Collett 3, Alma F. Ferrier
Using Vernier Equipment to Convert Didactically Taught Human Respiration Lab to Inquiry Based Human Respiration Lab Timothy J. Bradshaw 1, Samuel P. Carmichael II 2, Jason A. Collett 3, Alma F. Ferrier
Restrictive and Obstructive Airway Diseases
 iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HS-8-1 Restrictive and Obstructive Airway Diseases Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should refer to the User
iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HS-8-1 Restrictive and Obstructive Airway Diseases Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should refer to the User
You Are Really Full of Hot Air!
 You Are Really Full of Hot Air! Student Information Page 5B Activity Introduction: You re just full of hot air! How many times has someone said this to you when they didn t quite believe what you were
You Are Really Full of Hot Air! Student Information Page 5B Activity Introduction: You re just full of hot air! How many times has someone said this to you when they didn t quite believe what you were
Pulmonary Function I (modified by C. S. Tritt, April 10, 2006) Volumes and Capacities
 I. Introduction Pulmonary Function I (modified by C. S. Tritt, April 10, 2006) Volumes and Capacities The volume of air a person inhales (inspires) and exhales (expires) can be measured with a spirometer
I. Introduction Pulmonary Function I (modified by C. S. Tritt, April 10, 2006) Volumes and Capacities The volume of air a person inhales (inspires) and exhales (expires) can be measured with a spirometer
Physiology of the Respiratory System
 Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Physiology of the Respiratory System References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Physiology of the Respiratory System References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning
LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
 66 LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB Assignments: Due before lab: Quiz: Three Respiratory Interactive Physiology Animations pages 69 73. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
66 LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB Assignments: Due before lab: Quiz: Three Respiratory Interactive Physiology Animations pages 69 73. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
Introduction. Respiration. Chapter 10. Objectives. Objectives. The Respiratory System
 Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
CHAPTER 3: The cardio-respiratory system
 : The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
: The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
Part 1: Inspiratory and expiratory pressures
 BIOEN 327 Autumn 2013 Experimental procedures Throughout these experiments, record in your notebook the purpose of the experiments, the methods you used, and the results. Where possible, make predictions
BIOEN 327 Autumn 2013 Experimental procedures Throughout these experiments, record in your notebook the purpose of the experiments, the methods you used, and the results. Where possible, make predictions
Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation. Chad & Angela
 Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation Chad & Angela Respiratory Structures Basic Structures of Respiration Nasal/Oral Cavities Larynx Trachea Bronchi Secondary Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Mechanics of Ventilation
Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation Chad & Angela Respiratory Structures Basic Structures of Respiration Nasal/Oral Cavities Larynx Trachea Bronchi Secondary Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Mechanics of Ventilation
Human Respiration Laboratory Experiment By
 Human Respiration Laboratory Experiment By Alison L., Thurow, Brittany Baierlein, Rachel C. Holsinger and Robin L. Cooper Department of Biology, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY 40506 0225, USA. Purpose:
Human Respiration Laboratory Experiment By Alison L., Thurow, Brittany Baierlein, Rachel C. Holsinger and Robin L. Cooper Department of Biology, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY 40506 0225, USA. Purpose:
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system
 CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
 96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The tissues exchange O 2 directly with the air in
96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The tissues exchange O 2 directly with the air in
BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
 96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The cell exchange O 2 directly with the air in the
96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The cell exchange O 2 directly with the air in the
April KHALED MOUSA BACHA. Physiology #2. Dr. Nayef AL-Gharaibeh. Pulmonary volumes & capacities
 25 th April Physiology #2 Pulmonary volumes & capacities Dr. Nayef AL-Gharaibeh KHALED MOUSA BACHA We will start this lecture by explaining an important concept from the previous one: Intrapleural pressure
25 th April Physiology #2 Pulmonary volumes & capacities Dr. Nayef AL-Gharaibeh KHALED MOUSA BACHA We will start this lecture by explaining an important concept from the previous one: Intrapleural pressure
Collin County Community College. Lung Physiology
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 9 Respiratory System 1 Lung Physiology Factors affecting Ventillation 1. Airway resistance Flow = Δ P / R Most resistance is encountered
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 9 Respiratory System 1 Lung Physiology Factors affecting Ventillation 1. Airway resistance Flow = Δ P / R Most resistance is encountered
Lesson 12 New Procedure PULMONARY FUNCTION I
 Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab Lesson 12 New Procedure PULMONARY FUNCTION I Volumes and Capacities For Windows 98SE, Me, 2000 Pro, XP or Mac OS X 10.3-10.4 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D.
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab Lesson 12 New Procedure PULMONARY FUNCTION I Volumes and Capacities For Windows 98SE, Me, 2000 Pro, XP or Mac OS X 10.3-10.4 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D.
Experiment HS-2: Breathing and Gravity
 Experiment HS-2: Breathing and Gravity Background Over a long time, the amount of oxygen (O 2 ) taken up and carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) given off at the tissues is matched with the amount of O 2 taken up and
Experiment HS-2: Breathing and Gravity Background Over a long time, the amount of oxygen (O 2 ) taken up and carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) given off at the tissues is matched with the amount of O 2 taken up and
Respiratory system & exercise. Dr. Rehab F Gwada
 Respiratory system & exercise Dr. Rehab F Gwada Objectives of lecture Outline the major anatomical components & important functions of the respiratory system. Describe the mechanics of ventilation. List
Respiratory system & exercise Dr. Rehab F Gwada Objectives of lecture Outline the major anatomical components & important functions of the respiratory system. Describe the mechanics of ventilation. List
Respiration. Exercise 1A: Breathing in Resting Volunteers Aim: To measure breathing parameters in a resting individual.
 Respiration Background The amount of air that moves in or out of the lungs during any one breathing cycle is called the tidal volume. Above and beyond normal inspiration, it is possible to breathe in additional
Respiration Background The amount of air that moves in or out of the lungs during any one breathing cycle is called the tidal volume. Above and beyond normal inspiration, it is possible to breathe in additional
Fashionable, don t you think?
 Fashionable, don t you think? 1. Passageway 2. Structure 3. Passageway 4. What is the name of the structure labeled with # 9 in the model at left? 5. What is the name of the structure labeled with # 11
Fashionable, don t you think? 1. Passageway 2. Structure 3. Passageway 4. What is the name of the structure labeled with # 9 in the model at left? 5. What is the name of the structure labeled with # 11
Respiratory System Lab
 Respiratory System Lab Note: Review the safety materials and wear goggles when working with chemicals. Read the entire exercise before you begin. Take time to organize the materials you will need and set
Respiratory System Lab Note: Review the safety materials and wear goggles when working with chemicals. Read the entire exercise before you begin. Take time to organize the materials you will need and set
TV = Tidal volume (500ml) IRV = Inspiratory reserve volume (3,000 ml)
 By: Amin alajlouni Lec: 2nd record Date: 29/10/2017 First of all, this is my first sheet so excuse any mistakes I might make and let's start: As we said before in our last lecture about lung capacities
By: Amin alajlouni Lec: 2nd record Date: 29/10/2017 First of all, this is my first sheet so excuse any mistakes I might make and let's start: As we said before in our last lecture about lung capacities
Figure 1. A schematic diagram of the human respiratory system.
 Introduction to Respiration In this experiment, you will investigate various aspects of normal breathing, hyperventilation, rebreathing the effect of changing airway resistance and ways in which to measure
Introduction to Respiration In this experiment, you will investigate various aspects of normal breathing, hyperventilation, rebreathing the effect of changing airway resistance and ways in which to measure
Cornell Institute for. Biology Teachers. Respirometry Part I: Lung Volumes and Capacities. Lab issue/rev. date: 12/12/96. Title:
 Cornell Institute for Biology Teachers Copyright Cornell Institute for Biology Teachers, 1999. This work may be copied by the original recipient from CIBT to provide copies for users working under the
Cornell Institute for Biology Teachers Copyright Cornell Institute for Biology Teachers, 1999. This work may be copied by the original recipient from CIBT to provide copies for users working under the
Respiratory System Review
 KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
Respiration - Human 1
 Respiration - Human 1 At the end of the lectures on respiration you should be able to, 1. Describe events in the respiratory processes 2. Discuss the mechanism of lung ventilation in human 3. Discuss the
Respiration - Human 1 At the end of the lectures on respiration you should be able to, 1. Describe events in the respiratory processes 2. Discuss the mechanism of lung ventilation in human 3. Discuss the
Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy. Haneul Lee, DSc, PT
 Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy Haneul Lee, DSc, PT OBJECTIVE 1. Explain the principle physiological function of the pulmonary system 2. Outline the major anatomical components of the respiratory system.
Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy Haneul Lee, DSc, PT OBJECTIVE 1. Explain the principle physiological function of the pulmonary system 2. Outline the major anatomical components of the respiratory system.
Experiment B-43 Respiration Rates
 1 Experiment B-43 Rates Objectives To learn about the lungs and respiration s. To measure respiration s of the students. To compare female and male respiration s. To compare respiration s before and after
1 Experiment B-43 Rates Objectives To learn about the lungs and respiration s. To measure respiration s of the students. To compare female and male respiration s. To compare respiration s before and after
Measuring Lung Capacity
 Name Class Date Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Measuring Lung Capacity Introduction The amount of air that you move in and out of your lungs depends on how quickly you are breathing. The
Name Class Date Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Measuring Lung Capacity Introduction The amount of air that you move in and out of your lungs depends on how quickly you are breathing. The
Human gas exchange. Question Paper. Save My Exams! The Home of Revision. Cambridge International Examinations. 56 minutes. Time Allowed: Score: /46
 Human gas exchange Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International Examinations Respiration Human gas exchange Question Paper Time llowed: 56 minutes
Human gas exchange Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International Examinations Respiration Human gas exchange Question Paper Time llowed: 56 minutes
A Liter a Lung Measuring Lung Capacity
 A Liter a Lung Measuring Lung Capacity OBJECTIVE In this investigation, students will compare the actual and expected vital capacities of their classmates. LEVEL Middle Grades Life Science CONNECTIONS
A Liter a Lung Measuring Lung Capacity OBJECTIVE In this investigation, students will compare the actual and expected vital capacities of their classmates. LEVEL Middle Grades Life Science CONNECTIONS
The Respiratory System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Organs of the Respiratory system
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Organs of the Respiratory system
1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives
 1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives To understand the functions of the circulatory system. To be able to identify the differences between veins, arteries
1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives To understand the functions of the circulatory system. To be able to identify the differences between veins, arteries
LAB 3: RESPIRATORY MECHANICS
 BIOEN 327 Autumn 2012 LAB 3: RESPIRATORY MECHANICS Pressures throughout the cardiovascular system are important for the health of the body and of the system itself. Today we explore pulmonary pressures
BIOEN 327 Autumn 2012 LAB 3: RESPIRATORY MECHANICS Pressures throughout the cardiovascular system are important for the health of the body and of the system itself. Today we explore pulmonary pressures
Biology 347 General Physiology Lab Basic Pulmonary Functions: Respirometry and Factors that Effect Respiration
 Biology 347 General Physiology Lab Basic Pulmonary Functions: Respirometry and Factors that Effect Respiration Objectives Students will measure breathing parameters in a resting subject. Students will
Biology 347 General Physiology Lab Basic Pulmonary Functions: Respirometry and Factors that Effect Respiration Objectives Students will measure breathing parameters in a resting subject. Students will
 Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Respiratory System Physiology. Dr. Vedat Evren
 Respiratory System Physiology Dr. Vedat Evren Respiration Processes involved in oxygen transport from the atmosphere to the body tissues and the release and transportation of carbon dioxide produced in
Respiratory System Physiology Dr. Vedat Evren Respiration Processes involved in oxygen transport from the atmosphere to the body tissues and the release and transportation of carbon dioxide produced in
Measuring Lung Capacity
 Measuring Lung Capacity 1 Name Measuring Lung Capacity Background Information: We need a constant supply of oxygen in order to stay alive. We use oxygen to break down food to release energy and produce
Measuring Lung Capacity 1 Name Measuring Lung Capacity Background Information: We need a constant supply of oxygen in order to stay alive. We use oxygen to break down food to release energy and produce
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange
 Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
3/24/2009 LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD. 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm 1 KEY WORDS TO KNOW BOYLE S LAW INTERCOSTAL NERVES PHRENIC NERVE DIAPHRAGM EXTERNAL INTERCOSTAL
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm 1 KEY WORDS TO KNOW BOYLE S LAW INTERCOSTAL NERVES PHRENIC NERVE DIAPHRAGM EXTERNAL INTERCOSTAL
Respiratory Physiology 2
 Respiratory Physiology 2 Session Objectives. What you will cover Gaseous Exchange Control of Breathing Rate Your objectives are State the function of support structures and epithelia of the bronchial tree
Respiratory Physiology 2 Session Objectives. What you will cover Gaseous Exchange Control of Breathing Rate Your objectives are State the function of support structures and epithelia of the bronchial tree
respiratory cycle. point in the volumes: 500 milliliters. for men. expiration, up to 1200 milliliters extra makes breathing Respiratory
 10 II. RESPIRATORY VOLUMES, CAPACITIES & PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS Respiratory volume is the term used for various volumes of air moved by or associated with the lungs at a given point in the respiratory
10 II. RESPIRATORY VOLUMES, CAPACITIES & PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS Respiratory volume is the term used for various volumes of air moved by or associated with the lungs at a given point in the respiratory
Exercise and Respiration Rate
 Activity 17 PS-2820 Physiology: Breathing, respiration rate Exercise and Respiration Rate DataStudio GLX setup file: respiration.glx Qty Equipment and Materials Part Number 1 PASPORT Xplorer GLX PS-2002
Activity 17 PS-2820 Physiology: Breathing, respiration rate Exercise and Respiration Rate DataStudio GLX setup file: respiration.glx Qty Equipment and Materials Part Number 1 PASPORT Xplorer GLX PS-2002
Airway: the tubes through which air flows between atmosphere and alveoli. Upper airway. Lower airway
 Respiration Yu Yanqin ( 虞燕琴 ), PhD Dept. of fph Physiology Zhejiang University, School of Medicine Respiration Definition: the bodily processes involved in exchange of oxygen (O 2 ) and carbon dioxide
Respiration Yu Yanqin ( 虞燕琴 ), PhD Dept. of fph Physiology Zhejiang University, School of Medicine Respiration Definition: the bodily processes involved in exchange of oxygen (O 2 ) and carbon dioxide
Then the partial pressure of oxygen is x 760 = 160 mm Hg
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: the uptake of molecular oxygen (O2) from the environment and the discharge of
1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: the uptake of molecular oxygen (O2) from the environment and the discharge of
2.1.1 List the principal structures of the
 physiology 2.1.1 List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx -
physiology 2.1.1 List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx -
Physiology of Respiration
 Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
Then the partial pressure of oxygen is. b) Gases will diffuse down a pressure gradient across a respiratory surface if it is: i) permeable ii) moist
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: Relies on the diffusion of gases down pressure gradients. At sea level, atmosphere
1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: Relies on the diffusion of gases down pressure gradients. At sea level, atmosphere
inquiry question How does the respiratory system contribute to energy production for movement? UNCORRECTED PAGE PROOFS
 inquiry question How does the respiratory system contribute to energy production for movement? chapter 7 Structure and functions of the respiratory system The respiratory system is the starting point for
inquiry question How does the respiratory system contribute to energy production for movement? chapter 7 Structure and functions of the respiratory system The respiratory system is the starting point for
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system. Objective sheet 3 Notes
 1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
Lung Capacity. Science and Engineering Practices: S.1A.1; S.1A.2; S.1A.4; S.1A.5; S.1A.7
 SC Academic Standards: NGSS DCI: Science and Engineering Practices: S.1A.1; S.1A.2; S.1A.4; S.1A.5; S.1A.7 Crosscutting Concepts: Patterns; Cause and Effect: Mechanism and Explanation; Systems and Systems
SC Academic Standards: NGSS DCI: Science and Engineering Practices: S.1A.1; S.1A.2; S.1A.4; S.1A.5; S.1A.7 Crosscutting Concepts: Patterns; Cause and Effect: Mechanism and Explanation; Systems and Systems
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
Respiratory system. Role. Ventilation consists of 4 (5) steps : oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide elimination ph balance sound and voice formation
 Respiratory system Role oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide elimination ph balance sound and voice formation Ventilation consists of 4 (5) steps : 1. pulmonary ventilation gas exchange between lungs and
Respiratory system Role oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide elimination ph balance sound and voice formation Ventilation consists of 4 (5) steps : 1. pulmonary ventilation gas exchange between lungs and
The Respiration System in Humans. Madeline Pitman. Group Members: Kathryn Hillegass Michelle Liu Noelle Owen. Section 62 Danielle Cooper
 1 The Respiration System in Humans Madeline Pitman Group Members: Kathryn Hillegass Michelle Liu Noelle Owen Section 62 Danielle Cooper August 11, 2014 2 A. Introduction Experiment Goals The experiment
1 The Respiration System in Humans Madeline Pitman Group Members: Kathryn Hillegass Michelle Liu Noelle Owen Section 62 Danielle Cooper August 11, 2014 2 A. Introduction Experiment Goals The experiment
Mechanisms of Breathing. Vital Capacity
 Mechanisms of Breathing Mechanics of Breathing Two muscles are involved in the mechanics of breathing: Diaphragm = large sheet of muscle located beneath the lungs that is the primary muscle in breathing
Mechanisms of Breathing Mechanics of Breathing Two muscles are involved in the mechanics of breathing: Diaphragm = large sheet of muscle located beneath the lungs that is the primary muscle in breathing
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at gaseous exchange in humans in terms of o Ventilation o Inspiration o Expiration o Transport of gases o Homeostatic
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at gaseous exchange in humans in terms of o Ventilation o Inspiration o Expiration o Transport of gases o Homeostatic
Physiology - lecture 3
 Physiology - lecture 3 Residual Volume (RV):the amount of gas remaining in the lung at the end of a maximal exhalation Tidal Volume (TV):the volume of gas inhaled and exhaled during one respiratory cycle.
Physiology - lecture 3 Residual Volume (RV):the amount of gas remaining in the lung at the end of a maximal exhalation Tidal Volume (TV):the volume of gas inhaled and exhaled during one respiratory cycle.
2. State the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a normal breathing.
 CLASS XI BIOLOGY Breathing And Exchange of Gases 1. Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Answer: Vital Capacity (VC): The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration.
CLASS XI BIOLOGY Breathing And Exchange of Gases 1. Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Answer: Vital Capacity (VC): The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration.
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 11 Respiratory System 2 Pulmonary Ventilation Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session plan o Pulmonary Ventilation
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 11 Respiratory System 2 Pulmonary Ventilation Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session plan o Pulmonary Ventilation
Outline - Respiratory System. Function of the respiratory system Parts of the respiratory system Mechanics of breathing Regulation of breathing
 Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
Living with. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPD. Breathing and Relaxation
 Living with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPD Breathing and Relaxation Anatomy and Physiology of COPD Breathing Techniques Positions to Reduce Shortness of Breath Relaxation Exercise Breathing
Living with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPD Breathing and Relaxation Anatomy and Physiology of COPD Breathing Techniques Positions to Reduce Shortness of Breath Relaxation Exercise Breathing
IV. FROM AQUATIC TO ATMOSPHERIC BREATHING: THE TRACHEA & THE LUNG
 GAS EXCHANGE AND TRANSPORT I. INTRODUCTION: Heterotrophs oxidize carbon cmpds using O 2 to generate CO 2 & H 2 O. This is cellular respiration II. HOW GAS ENTERS A CELL A. The composition of air: 79% N
GAS EXCHANGE AND TRANSPORT I. INTRODUCTION: Heterotrophs oxidize carbon cmpds using O 2 to generate CO 2 & H 2 O. This is cellular respiration II. HOW GAS ENTERS A CELL A. The composition of air: 79% N
Structures of the Respiratory System include:
 Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HE-4: Respiratory Exchange Ratio (RER)
 Experiment HE-4: Respiratory Exchange Ratio (RER) Before Starting 1. Read the procedures for the experiment completely before beginning the experiment. Have a good understanding of how to perform the experiment
Experiment HE-4: Respiratory Exchange Ratio (RER) Before Starting 1. Read the procedures for the experiment completely before beginning the experiment. Have a good understanding of how to perform the experiment
Cardiovascular and respiratory adjustments to exercise
 Cardiovascular and respiratory adjustments to exercise Additional notes on breathing and use of respiratory belt and pulse transducers Notes on breathing The metabolic activities of tissues use up oxygen
Cardiovascular and respiratory adjustments to exercise Additional notes on breathing and use of respiratory belt and pulse transducers Notes on breathing The metabolic activities of tissues use up oxygen
Gas Exchange in Animals. Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2. Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial
 Gas Exchange in Animals Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2 Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial Respiratory surface! skin, gills, lungs Circulatory System O2/CO2
Gas Exchange in Animals Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2 Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial Respiratory surface! skin, gills, lungs Circulatory System O2/CO2
Respiratory Physiology. ED Primary Teaching
 Respiratory Physiology ED Primary Teaching Functions of the respiratory system Gas exchange with O2 and CO2 Surfactant production Defence - IgA and macrophages Filer - pollutants and thromboembolism Metabolises
Respiratory Physiology ED Primary Teaching Functions of the respiratory system Gas exchange with O2 and CO2 Surfactant production Defence - IgA and macrophages Filer - pollutants and thromboembolism Metabolises
Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired
 Chapter 6 Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired This chapter covers: the structure of the human gas exchange system the mechanism of breathing gas exchange in the alveoli the concept
Chapter 6 Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired This chapter covers: the structure of the human gas exchange system the mechanism of breathing gas exchange in the alveoli the concept
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Atmosphere Tissue cell External respiration Alveoli of lungs 1 Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Atmosphere Tissue cell External respiration Alveoli of lungs 1 Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere
Capnography in the Veterinary Technician Toolbox. Katie Pinner BS, LVT Bush Advanced Veterinary Imaging Richmond, VA
 Capnography in the Veterinary Technician Toolbox Katie Pinner BS, LVT Bush Advanced Veterinary Imaging Richmond, VA What are Respiration and Ventilation? Respiration includes all those chemical and physical
Capnography in the Veterinary Technician Toolbox Katie Pinner BS, LVT Bush Advanced Veterinary Imaging Richmond, VA What are Respiration and Ventilation? Respiration includes all those chemical and physical
PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Parts of the Respiratory System The RS can be divided into two parts: 1. Respiratory Tract, (path that air follows). Nasal passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi,
PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Parts of the Respiratory System The RS can be divided into two parts: 1. Respiratory Tract, (path that air follows). Nasal passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi,
The Respiratory System. Medical Terminology
 The Respiratory System Medical Terminology The respiratory system is where gas exchange occurs via respiration; inhalation/exhalation. pick up oxygen from inhaled air expels carbon dioxide and water sinus
The Respiratory System Medical Terminology The respiratory system is where gas exchange occurs via respiration; inhalation/exhalation. pick up oxygen from inhaled air expels carbon dioxide and water sinus
Human Biology Respiratory System
 Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
4/18/12 MECHANISM OF RESPIRATION. Every Breath You Take. Fun Facts
 Objectives MECHANISM OF RESPIRATION Dr Badri Paudel Explain how the intrapulmonary and intrapleural pressures vary during ventilation and relate these pressure changes to Boyle s law. Define the terms
Objectives MECHANISM OF RESPIRATION Dr Badri Paudel Explain how the intrapulmonary and intrapleural pressures vary during ventilation and relate these pressure changes to Boyle s law. Define the terms
Respiratory/Pulmonary Laboratory Experimentation
 Respiratory/Pulmonary Laboratory Experimentation Introduction Anatomy Review The respiratory system has the dubious honor of being the system that permits the transport of gases from the environment inside
Respiratory/Pulmonary Laboratory Experimentation Introduction Anatomy Review The respiratory system has the dubious honor of being the system that permits the transport of gases from the environment inside
Experiment AMe-1: Small Animal Respiratory Exchange Ratio (RER)
 Experiment AMe-1: Small Animal Respiratory Exchange Ratio (RER) Background There are two main sources of energy available for animal metabolism: carbohydrates (CHO) and fats. These molecules are broken
Experiment AMe-1: Small Animal Respiratory Exchange Ratio (RER) Background There are two main sources of energy available for animal metabolism: carbohydrates (CHO) and fats. These molecules are broken
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
Activity 2: Examining the Effect of Changing Airway Resistance on Respiratory Volumes
 1 BGYC34 PhysioEx Lab 7 Respiratory Systems Mechanics Marking Scheme Part 1 Complete PhysioEx lab #7. Hand-in all of the pages associated with the lab. Note that there are 5 activities to be completed.
1 BGYC34 PhysioEx Lab 7 Respiratory Systems Mechanics Marking Scheme Part 1 Complete PhysioEx lab #7. Hand-in all of the pages associated with the lab. Note that there are 5 activities to be completed.
Regulation of Breathing
 Regulation of Breathing Introduction Breathing involves a complex interaction between many important respiratory organs and the blood. Air is brought into the lungs through the active process of inhalation,
Regulation of Breathing Introduction Breathing involves a complex interaction between many important respiratory organs and the blood. Air is brought into the lungs through the active process of inhalation,
PROBLEM SET 9. SOLUTIONS April 23, 2004
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.542J: Quantitative Physiology: Organ Transport Systems Instructors: Roger Mark and Jose Venegas MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Departments
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.542J: Quantitative Physiology: Organ Transport Systems Instructors: Roger Mark and Jose Venegas MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Departments
REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE 24 SEPTEMBER 2014 Lesson Description
 REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE 24 SEPTEMBER 2014 Lesson Description In this lesson, we revise: Gaseous Exchange in Plants & Animals Gaseous Exchange in Humans Excretion in Humans Focus on the Kidney Gaseous
REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE 24 SEPTEMBER 2014 Lesson Description In this lesson, we revise: Gaseous Exchange in Plants & Animals Gaseous Exchange in Humans Excretion in Humans Focus on the Kidney Gaseous
Boyle s Law: Pressure-Volume Relationship in Gases
 Boyle s Law: Pressure-Volume Relationship in Gases Computer 6 The primary objective of this experiment is to determine the relationship between the pressure and volume of a confined gas. The gas we use
Boyle s Law: Pressure-Volume Relationship in Gases Computer 6 The primary objective of this experiment is to determine the relationship between the pressure and volume of a confined gas. The gas we use
Circulatory And Respiration
 Circulatory And Respiration Composition Of Blood Blood Heart 200mmHg 120mmHg Aorta Artery Arteriole 50mmHg Capillary Bed Venule Vein Vena Cava Heart Differences Between Arteries and Veins Veins transport
Circulatory And Respiration Composition Of Blood Blood Heart 200mmHg 120mmHg Aorta Artery Arteriole 50mmHg Capillary Bed Venule Vein Vena Cava Heart Differences Between Arteries and Veins Veins transport
RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE
 RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE Respiration Respiration delivery of oxygen to and removal of carbon dioxide from the tissue External respiration ventilation and exchange of gases in the lung Internal
RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE Respiration Respiration delivery of oxygen to and removal of carbon dioxide from the tissue External respiration ventilation and exchange of gases in the lung Internal
ALVEOLAR - BLOOD GAS EXCHANGE 1
 ALVEOLAR - BLOOD GAS EXCHANGE 1 Summary: These notes examine the general means by which ventilation is regulated in terrestrial mammals. It then moves on to a discussion of what happens when someone over
ALVEOLAR - BLOOD GAS EXCHANGE 1 Summary: These notes examine the general means by which ventilation is regulated in terrestrial mammals. It then moves on to a discussion of what happens when someone over
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HE-5: Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR)
 Experiment HE-5: Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR) Before Starting 1. Read the procedures for the experiment completely before beginning the experiment. Have a good understanding of how to perform the experiment
Experiment HE-5: Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR) Before Starting 1. Read the procedures for the experiment completely before beginning the experiment. Have a good understanding of how to perform the experiment
Respiration. The resspiratory system
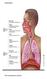 Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY
 GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY Atmospheric Pressure Intra-Alveolar Pressure Inspiration 760 mm HG at Sea Level (= 1 atm) Pressure due to gases (N2, O2, CO2, Misc.) Pressure inside the alveolus (air sac) Phrenic
GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY Atmospheric Pressure Intra-Alveolar Pressure Inspiration 760 mm HG at Sea Level (= 1 atm) Pressure due to gases (N2, O2, CO2, Misc.) Pressure inside the alveolus (air sac) Phrenic
1 CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES https://biologyaipmt.com/
 1 CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES https://biologyaipmt.com/ CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES Oxygen (O2) is utilised by the organisms to indirectly break down nutrient molecules like
1 CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES https://biologyaipmt.com/ CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES Oxygen (O2) is utilised by the organisms to indirectly break down nutrient molecules like
Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class
 I. Name the following : Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class 1. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. 2. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous
I. Name the following : Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class 1. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. 2. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous
Medical Ventilators. Presented by: Edwin Lim
 Medical Ventilators Presented by: Edwin Lim 1 Presentation Outline Respiration and You Medical Ventilators: Why? How? Current Medical Ventilators The Future 2 The Importance of Oxygen People can survive
Medical Ventilators Presented by: Edwin Lim 1 Presentation Outline Respiration and You Medical Ventilators: Why? How? Current Medical Ventilators The Future 2 The Importance of Oxygen People can survive
Respiratory System Homework
 Respiratory System Homework The R S is the body s breathing equipment. Similar to the D system, it takes S from outside the body (G, particularly O ), circulates them through the body to C and T, then
Respiratory System Homework The R S is the body s breathing equipment. Similar to the D system, it takes S from outside the body (G, particularly O ), circulates them through the body to C and T, then
Respiration. The ins and outs
 Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
