Respiratory Physiology. ED Primary Teaching
|
|
|
- Evangeline McGee
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Respiratory Physiology ED Primary Teaching
2 Functions of the respiratory system Gas exchange with O2 and CO2 Surfactant production Defence - IgA and macrophages Filer - pollutants and thromboembolism Metabolises some compounds - converts AT I to II, inactivates bradykinin, breakdown of prostaglandins and leukotrines Reservoir of blood
3 Respiratory Physiology Oxygen transport chain Ventilation > Pulmonary gas exchange > Oxygen in blood > Local tissue perfusion > Diffusion at tissue level > Tissue utilisation of oxygen
4 Ventilation The physiology of room air: Contains about 21% O2 78% nitrogen 1% other gasses It is the role of ventilation to provide oxygen to the gas exchanging mechanisms of the lungs Ventilation is also inherently related to blood flow Ventilation: Airway anatomy Resp muscle function and chest wall mechanics and lung volumes Neurological control of ventilation
5 Airway and airflow Trachea divides into R and L bronchi which then divide into lobar and segmental bronchi These continue to divide down into segmental bronchi and terminal bronchioles which are the smallest airways without alveoli Bronchi and terminal bronchioles make up the conducting airway the function of which is to lead the air to the gas exchanging reigon and these airways constitutes ANATOMICAL DEAD SPACE - 150mL The anatomical portion of the lung distal to these terminal bronchioles form the acinus and is the functional respiratory unit
6 Respiratory muscular function Inspiratory muscles Diaphragm External intercostals Accessory inspiratory muscles such as the scalene and SCM Muscles of head and neck Expiratory muscles - usually a passive process which relies of the elastic recoil of the lungs When under anesthesia or at extremes of exercise expiration may become active with activation of the abdominal wall muscles or internal intercostals
7 Lung Volumes
8 Total lung capacity - amount of gas in the lungs at a maximal inspiration (normal 6L for adults males, and 4.2L for adult females) Vital capacity - amount of gas that can be exhaled after a maximal inspiration Residual volume - amount of gas remaining in the lungs after a maximal expiration (20% of the total lung capacity) Total lung capacity = Vital capacity + Residual volume
9 Tidal volume = the amount of gas an individual inspires or expires during normal breathing 7-8% of total lung capacity Approximately 500 ml Tidal volume x RR = minute ventilation Inspiratory reserve volume - the amount of gas an individual can inhale above a normal tidal inspiration (normal 60% of TLC) Expiratory reserve volume - the amount of gas an individual can exhale below a normal tidal expiration (normally 20% of TLC) TV + IRV + ERV = Vital capacity Functional residual capacity - The amount of gas in the lungs after tidal expiration - usually 40% of TLC (cannot be measured with spirometry and is measured indirectly using helium dilution or nitrogen washout) The FRC = ERV + RV The FRC is the balance between the tendency of the chest wall to spring out and the tendency of the lung to collapse
10 Lung capacities 4 types of capacities - inspiratory capacity, TLC, VC, FRC The addition of two volumes makes a capacity Inspiratory capacity - the amount of gas an individual can inhale at the end of tidal expiration Includes TV and IRV - 60% of TLC
11
12 Pressure volume curve A graphical representation of the relationship between pressure and volume during inspiration and expiration Bottom of loop is either 0 or PEEP and top of loop is peak inspiratory pressure Compliance is an imaginary line drawn between the start of inspiration and expiration Increased compliance (left shift) - emphysema and asthma (small changes in pressures generate large changes in volume) Decreased compliance (right shift) - ARDS (large changes in pressures are required to generate small changes in volume) Work of breathing is area within the curve and equals pressure x volume
13 Closing capacity The volume at which the small airways close during expiration Under normal circumstances the FRC is greater than the closing capacity, however if the FRC was to decrease then this would no longer be the case and the small airways may close at the end of normal tidal expiration - causing collapse and atelectasis Closing capacity increases with age and equals FRC in a sitting patient by the age of 66
14 Chest wall mechanics Compliance - change in volume/change in pressure Can be a static principle when there is no airflow and is determined by the change in volume for a given pressure Can be a dynamic relationship during breathing, where airflow resistance becomes a factor The lung is generally more distendable at lower volumes and stiffer at higher volumes The compliance of a lung can be altered in pathology such as fibrosis or alveolar oedema (decreased) and COPD and asthma (increased) This means that for a given change in volume there is a greater rise in system pressure and has implications for mechanical ventilation
15 Chest wall mechanics - some pathophysiology Asthma - increased lung compliance Compliance is lowest at FRC (think about the first breath into a balloon) meaning that a large change in pressure is required to facilitate a small change in volume In patients with asthma their FRC is increased because of air trapping due to DAC due to broncho-constriction Therefore during an attack the compliance is increased (like breathing air into an already filled balloon) ARDS - decreased lung compliance
16
17 Deadspace The volume of a breath that does not participate in gas exchange - it is ventilation without perfusion Physiological or total dead space is the sum of anatomical dead space and alveolar dead space Anatomic dead space is the volume of gas within the conducting zone, as opposed to the transitional and respiratory zone and includes trachea, bronchioles, bronchus and terminal bronchioles It is approximately 2ml/kg in the upright patient Alveolar dead space is the volume gas within the under perfused alveoli and thus not participating in gas exchange either - it is usually negligible int he awake and healthy patient The ratio of physiological dead space to tidal volume is 1:3
18 Regional differences in ventilation and blood flow Distribution of blood in lungs Decreases almost linearly from the bottom to the top More blood in dependent areas If that section of the lung is ventilated but not perfused this is alveolar dead space Multiple physiological zones Zone 1 - alveolar pressure > arterial pressure > venous pressure Zone 2 - arterial pressure > alveolar pressure > venous pressure Zone 3 - arteria pressure > venous pressure > alveoli pressure
19
20 Properties of pulmonary vasculature Pulmonary artery pressure is 15mmHg (8-25) LAP is about 5mmHg This means that the entire CO moves across a circuit who's pressure difference is only 10 The pulmonary vascular resistance = 10mmHg/5L/min = 2mmHg/L/min Comparable calculations for the systemic circuit show its resistance to be about 10 times greater What factors effect pulmonary resistance The high distensibility, the small amount of vascular smooth muscle, and the low intravascular pressures lead to a greater importance of passive extravascular effects of pulmonary resistance (lung volumes, alveolar and intra pleural pressures etc.) A paradoxical characteristic of the pulmonary vasculature is the higher flows generally associated with lower resistance Why?
21 Flow and resistance in the pulmonary circulation Why does PVR fall as flow increases? Two reasons Capillaries that were already open, ow distend further Capillaries that were formerly closed now open Alveolar and intrapleural resistance - PVR depends on the transmural pressure gradient. Pressure inside (blood vessel) - pressure outside (blood vessel) As this gradient decreases the diameter of the vessel decreases and therefore VR increases
22 Lung volumes and vascular resistance Lung volumes effect pulmonary circulation - this interaction differs depending on wether the lung is above or below FRC Above FRC - as lung volume increases above FRC the pulmonary vessels outside the alveoli are distended so their resistance falls, on the other hand septal capillaries in the alveolar wall are stretched so that their diameters are reduces - the net effect is an increase in overall pulmonary vascular resistance since the narrowing of the septic capillaries is the dominant effect Below FRC - As lung volume decreases below FRC the pulmonary vessels outside the alveoli tend to collapse as their walls are no longer being stretched by the surrounding lung tissue - this leads to an increase in resistance and this causes and increase in pulmonary vascular resistance
23 Gravity and vascular resistance In general flow is greatest in the dependent potion of the lung and least in the non dependent potions of the lung Zones of the lung Zone 1 - alveolar pressure is greater than both local pulmonary arterial and venous pressures Therefore vessels are compressed and there is no flow Palv > Pa > Pv Zone 2 - Pulmonary arterial pressure is greater than alveolar pressure The alveolar pressure is greater than the venous pressure so the downstream pressure is alveolar pressure This situation is determined vascular waterfall where the flow is independent of the eventual venous pressure and depends only on the difference between pulmonary arterial pressure and alveolar pressure Pa > Palv > Pv Zone 3 - Pulmonary artery pressure is greater than pulmonary venous pressure and alveolar pressure The venous pressure is greater than the alveolar pressure so the flow is dependent on the AV pressure difference Under normal conditions zone 1 does not occur A patient on a PPV with PEEP may have substantial about of zone 1 because alveolar pressure s always positive
24 Chemical factors and their role in pulmonary blood flow Hypoxic vasoconstriction - by far the most important modulator of smooth muscle tone in the pulmonary arterioles is the partial pressure of O2 in the alveolus PAO2. Smooth muscle in pulmonary artieroles responds in the oppositte way to SM In systemic arterioles when exposed to hypoxic conditions Low PO2 produces constriction in pulmonary vessels This degree of hypoxic vasoconstriction becomes more pronounced once PaO2 drops below 100mmHg The receptors (not neurally regulated) that regulate this response respond to PAO2 rather than PO2 in the blood and it is unclear how this happens
25 The utility of hypoxic vasoconstriction Limits blood flow through the lung of the foetus > elevation of PAO2 with the first breath greatly reduces resistance to blood flow in the lung Improves matching of blood flow with ventilation If a region of lung is poorly ventilated, PAO2 int he region decreases, the resulting vasoconstriction decreases blood flow to that region - therefore blood that doesn't go there will go to the alveoli that are more adequately ventilated Changes in altitude Produces vasoconstriction throughout the circuit which leads to better perfusion of the apical regions and improves the VQ ratio in their region of the lung Consequences of hypoxic vasoconstriction Increased work for RV and RVH > irreversible growth in smooth muscle of pulmonary arterial walls leading the pulmonary HTN
26 Other functions of the respiratory system Reservoir - when you sit from standing, blood from legs goes to RA, the RV pumps this into the lungs but not all of this makes it to the LV this prevents CO from increasing excessively as one goes from an upright to a lying down position Filter - Acts as a vascular filter for small clots Surfactant - made by T2alveolar cells Conversion of ATI to ATII by ACE Makes IgA for immune system Secretion of mucus Lung removes serotonin from the blood Prostaglandin E2 is produced by the lungs of the fetus and it serves as a smooth muscle relaxant keeping the DA open
Introduction. Respiration. Chapter 10. Objectives. Objectives. The Respiratory System
 Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation. Chad & Angela
 Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation Chad & Angela Respiratory Structures Basic Structures of Respiration Nasal/Oral Cavities Larynx Trachea Bronchi Secondary Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Mechanics of Ventilation
Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation Chad & Angela Respiratory Structures Basic Structures of Respiration Nasal/Oral Cavities Larynx Trachea Bronchi Secondary Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Mechanics of Ventilation
Respiratory System Physiology. Dr. Vedat Evren
 Respiratory System Physiology Dr. Vedat Evren Respiration Processes involved in oxygen transport from the atmosphere to the body tissues and the release and transportation of carbon dioxide produced in
Respiratory System Physiology Dr. Vedat Evren Respiration Processes involved in oxygen transport from the atmosphere to the body tissues and the release and transportation of carbon dioxide produced in
The physiological functions of respiration and circulation. Mechanics. exercise 7. Respiratory Volumes. Objectives
 exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
Pulmonary Circulation
 Pulmonary Circulation resin cast of pulmonary arteries resin cast of pulmonary veins Blood Flow to the Lungs Pulmonary Circulation Systemic Circulation Blood supply to the conducting zone provided by the
Pulmonary Circulation resin cast of pulmonary arteries resin cast of pulmonary veins Blood Flow to the Lungs Pulmonary Circulation Systemic Circulation Blood supply to the conducting zone provided by the
Respiratory System. Part 2
 Respiratory System Part 2 Respiration Exchange of gases between air and body cells Three steps 1. Ventilation 2. External respiration 3. Internal respiration Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation consists
Respiratory System Part 2 Respiration Exchange of gases between air and body cells Three steps 1. Ventilation 2. External respiration 3. Internal respiration Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation consists
Collin County Community College. Lung Physiology
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 9 Respiratory System 1 Lung Physiology Factors affecting Ventillation 1. Airway resistance Flow = Δ P / R Most resistance is encountered
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 9 Respiratory System 1 Lung Physiology Factors affecting Ventillation 1. Airway resistance Flow = Δ P / R Most resistance is encountered
Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation
 Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing and the first step in the respiratory process. Pulmonary ventilation brings in air with a new supply
Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing and the first step in the respiratory process. Pulmonary ventilation brings in air with a new supply
VENTILATION AND PERFUSION IN HEALTH AND DISEASE. Dr.HARIPRASAD VS
 VENTILATION AND PERFUSION IN HEALTH AND DISEASE Dr.HARIPRASAD VS Ventilation Total ventilation - total rate of air flow in and out of the lung during normal tidal breathing. Alveolar ventilation -represents
VENTILATION AND PERFUSION IN HEALTH AND DISEASE Dr.HARIPRASAD VS Ventilation Total ventilation - total rate of air flow in and out of the lung during normal tidal breathing. Alveolar ventilation -represents
Respiratory System. Prepared by: Dorota Marczuk-Krynicka, MD, PhD
 Respiratory System Prepared by: Dorota Marczuk-Krynicka, MD, PhD Lungs: Ventilation Perfusion Gas Exchange - Diffusion 1. Airways and Airway Resistance (AWR) 2. Mechanics of Breathing and Lung (Elastic)
Respiratory System Prepared by: Dorota Marczuk-Krynicka, MD, PhD Lungs: Ventilation Perfusion Gas Exchange - Diffusion 1. Airways and Airway Resistance (AWR) 2. Mechanics of Breathing and Lung (Elastic)
Respiration (revised 2006) Pulmonary Mechanics
 Respiration (revised 2006) Pulmonary Mechanics PUL 1. Diagram how pleural pressure, alveolar pressure, airflow, and lung volume change during a normal quiet breathing cycle. Identify on the figure the
Respiration (revised 2006) Pulmonary Mechanics PUL 1. Diagram how pleural pressure, alveolar pressure, airflow, and lung volume change during a normal quiet breathing cycle. Identify on the figure the
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Atmosphere Tissue cell External respiration Alveoli of lungs 1 Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Atmosphere Tissue cell External respiration Alveoli of lungs 1 Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere
3/24/2009 LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD. 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm 1 KEY WORDS TO KNOW BOYLE S LAW INTERCOSTAL NERVES PHRENIC NERVE DIAPHRAGM EXTERNAL INTERCOSTAL
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm 1 KEY WORDS TO KNOW BOYLE S LAW INTERCOSTAL NERVES PHRENIC NERVE DIAPHRAGM EXTERNAL INTERCOSTAL
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system
 CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
4/18/12 MECHANISM OF RESPIRATION. Every Breath You Take. Fun Facts
 Objectives MECHANISM OF RESPIRATION Dr Badri Paudel Explain how the intrapulmonary and intrapleural pressures vary during ventilation and relate these pressure changes to Boyle s law. Define the terms
Objectives MECHANISM OF RESPIRATION Dr Badri Paudel Explain how the intrapulmonary and intrapleural pressures vary during ventilation and relate these pressure changes to Boyle s law. Define the terms
Lung Volumes and Ventilation
 Respiratory System ssrisuma@rics.bwh.harvard.edu Lung Volumes and Ventilation Minute ventilation Volume of an inspired or expired air per minute = tidal volume (V T ) x respiratory rate Dead space ventilation
Respiratory System ssrisuma@rics.bwh.harvard.edu Lung Volumes and Ventilation Minute ventilation Volume of an inspired or expired air per minute = tidal volume (V T ) x respiratory rate Dead space ventilation
CHAPTER 3: The cardio-respiratory system
 : The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
: The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
Test Bank for Pilbeams Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition by Cairo
 Test Bank for Pilbeams Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition by Cairo Link full download: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-pilbeams-mechanicalventilation-physiological-and-clinical-applications-6th-edition-by-cairo/
Test Bank for Pilbeams Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition by Cairo Link full download: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-pilbeams-mechanicalventilation-physiological-and-clinical-applications-6th-edition-by-cairo/
Pulmonary Circulation Linda Costanzo Ph.D.
 Pulmonary Circulation Linda Costanzo Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The differences between pressures in the pulmonary and systemic circulations. 2. How
Pulmonary Circulation Linda Costanzo Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The differences between pressures in the pulmonary and systemic circulations. 2. How
April KHALED MOUSA BACHA. Physiology #2. Dr. Nayef AL-Gharaibeh. Pulmonary volumes & capacities
 25 th April Physiology #2 Pulmonary volumes & capacities Dr. Nayef AL-Gharaibeh KHALED MOUSA BACHA We will start this lecture by explaining an important concept from the previous one: Intrapleural pressure
25 th April Physiology #2 Pulmonary volumes & capacities Dr. Nayef AL-Gharaibeh KHALED MOUSA BACHA We will start this lecture by explaining an important concept from the previous one: Intrapleural pressure
Respiratory System Review
 KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
The Respiratory System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Organs of the Respiratory system
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Organs of the Respiratory system
Airway: the tubes through which air flows between atmosphere and alveoli. Upper airway. Lower airway
 Respiration Yu Yanqin ( 虞燕琴 ), PhD Dept. of fph Physiology Zhejiang University, School of Medicine Respiration Definition: the bodily processes involved in exchange of oxygen (O 2 ) and carbon dioxide
Respiration Yu Yanqin ( 虞燕琴 ), PhD Dept. of fph Physiology Zhejiang University, School of Medicine Respiration Definition: the bodily processes involved in exchange of oxygen (O 2 ) and carbon dioxide
Respiration - Human 1
 Respiration - Human 1 At the end of the lectures on respiration you should be able to, 1. Describe events in the respiratory processes 2. Discuss the mechanism of lung ventilation in human 3. Discuss the
Respiration - Human 1 At the end of the lectures on respiration you should be able to, 1. Describe events in the respiratory processes 2. Discuss the mechanism of lung ventilation in human 3. Discuss the
BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
 96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The tissues exchange O 2 directly with the air in
96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The tissues exchange O 2 directly with the air in
BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
 96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The cell exchange O 2 directly with the air in the
96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The cell exchange O 2 directly with the air in the
The Respiratory System Part I. Dr. Adelina Vlad
 The Respiratory System Part I Dr. Adelina Vlad The Respiratory Process Breathing automatic, rhythmic and centrally-regulated mechanical process by which the atmospheric gas moves into and out of the lungs
The Respiratory System Part I Dr. Adelina Vlad The Respiratory Process Breathing automatic, rhythmic and centrally-regulated mechanical process by which the atmospheric gas moves into and out of the lungs
TV = Tidal volume (500ml) IRV = Inspiratory reserve volume (3,000 ml)
 By: Amin alajlouni Lec: 2nd record Date: 29/10/2017 First of all, this is my first sheet so excuse any mistakes I might make and let's start: As we said before in our last lecture about lung capacities
By: Amin alajlouni Lec: 2nd record Date: 29/10/2017 First of all, this is my first sheet so excuse any mistakes I might make and let's start: As we said before in our last lecture about lung capacities
 Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange
 Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
Lung Volumes and Capacities
 Lung Volumes and Capacities Normally the volume of air entering the lungs during a single inspiration is approximately equal to the volume leaving on the subsequent expiration and is called the tidal volume.
Lung Volumes and Capacities Normally the volume of air entering the lungs during a single inspiration is approximately equal to the volume leaving on the subsequent expiration and is called the tidal volume.
Physiology (3) Pulmonary Function Test:
 Pulmonary Function Test: Today we will continue with the pulmonary function test, and the question is: why do we do pulmonary function tests for patients? Can pulmonary function tests tell us what type
Pulmonary Function Test: Today we will continue with the pulmonary function test, and the question is: why do we do pulmonary function tests for patients? Can pulmonary function tests tell us what type
Respiratory system & exercise. Dr. Rehab F Gwada
 Respiratory system & exercise Dr. Rehab F Gwada Objectives of lecture Outline the major anatomical components & important functions of the respiratory system. Describe the mechanics of ventilation. List
Respiratory system & exercise Dr. Rehab F Gwada Objectives of lecture Outline the major anatomical components & important functions of the respiratory system. Describe the mechanics of ventilation. List
RSPT 1060 OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES EQUATION OF MOTION. MODULE C Applied Physics Lesson #1 - Mechanics. Ventilation vs.
 RSPT 1060 MODULE C Applied Physics Lesson #1 - Mechanics OBJECTIVES At the end of this module, the student should be able to define the terms and abbreviations used in the module. draw & explain the equation
RSPT 1060 MODULE C Applied Physics Lesson #1 - Mechanics OBJECTIVES At the end of this module, the student should be able to define the terms and abbreviations used in the module. draw & explain the equation
Section Two Diffusion of gases
 Section Two Diffusion of gases Lecture 5: Partial pressure and the composition of gasses in air. Factors affecting diffusion of gases. Ventilation perfusion ratio effect on alveolar gas concentration.
Section Two Diffusion of gases Lecture 5: Partial pressure and the composition of gasses in air. Factors affecting diffusion of gases. Ventilation perfusion ratio effect on alveolar gas concentration.
Physiology of Respiration
 Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY
 Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Respiration External respiration ventilation gas exchange Internal respiration cellular respiration gas exchange Respiratory Cycle Inspiration
Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Respiration External respiration ventilation gas exchange Internal respiration cellular respiration gas exchange Respiratory Cycle Inspiration
Lab 3. The Respiratory System (designed by Heather E. M. Liwanag with T.M. Williams)
 Name Lab Partners Lab 3. The Respiratory System (designed by Heather E. M. Liwanag with T.M. Williams) Part 1. Lung Volumes and Capacities Objectives 1. Obtain graphical representation of lung capacities
Name Lab Partners Lab 3. The Respiratory System (designed by Heather E. M. Liwanag with T.M. Williams) Part 1. Lung Volumes and Capacities Objectives 1. Obtain graphical representation of lung capacities
Respiration. The ins and outs
 Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 1
 Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The term "respiration" in its most complete meaning is: a. breathing b. oxygen transport c. carbon dioxide transport d. cellular energy production e. all of
Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The term "respiration" in its most complete meaning is: a. breathing b. oxygen transport c. carbon dioxide transport d. cellular energy production e. all of
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 11 Respiratory System 2 Pulmonary Ventilation Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session plan o Pulmonary Ventilation
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 11 Respiratory System 2 Pulmonary Ventilation Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session plan o Pulmonary Ventilation
Boards and Beyond: Pulmonary
 Boards and Beyond: Pulmonary A Companion Book to the Boards and Beyond Website Jason Ryan, MD, MPH i ii Table of Contents Pulmonary Anatomy 1 Treatment of COPD/Asthma 45 Pulmonary Physiology 4 Pneumonia
Boards and Beyond: Pulmonary A Companion Book to the Boards and Beyond Website Jason Ryan, MD, MPH i ii Table of Contents Pulmonary Anatomy 1 Treatment of COPD/Asthma 45 Pulmonary Physiology 4 Pneumonia
The Physiologic Basis of DLCO testing. Brian Graham Division of Respirology, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine University of Saskatchewan
 The Physiologic Basis of DLCO testing Brian Graham Division of Respirology, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine University of Saskatchewan Objectives Review gas transport from inhaled gas to the rest of the
The Physiologic Basis of DLCO testing Brian Graham Division of Respirology, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine University of Saskatchewan Objectives Review gas transport from inhaled gas to the rest of the
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System
 VI edit Pag 451-499 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System V edit. Pag 459-509 Tissue cell Alveoli of lungs Atmosphere 1 External respiration Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere and air sacs
VI edit Pag 451-499 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System V edit. Pag 459-509 Tissue cell Alveoli of lungs Atmosphere 1 External respiration Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere and air sacs
Physiology - lecture 3
 Physiology - lecture 3 Residual Volume (RV):the amount of gas remaining in the lung at the end of a maximal exhalation Tidal Volume (TV):the volume of gas inhaled and exhaled during one respiratory cycle.
Physiology - lecture 3 Residual Volume (RV):the amount of gas remaining in the lung at the end of a maximal exhalation Tidal Volume (TV):the volume of gas inhaled and exhaled during one respiratory cycle.
Outline - Respiratory System. Function of the respiratory system Parts of the respiratory system Mechanics of breathing Regulation of breathing
 Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
Breathing. Physics of Breathing 11/14/2011. Function of Respiratory Tract. Structure of Respiratory Tract. Parts of the Respiratory Tract
 Breathing Function of Respiratory Tract The respiratory tract is a series of spaces and semirigid tubes designed to convey air into and out of the respiratory organs (lungs). Parts of the Respiratory Tract
Breathing Function of Respiratory Tract The respiratory tract is a series of spaces and semirigid tubes designed to convey air into and out of the respiratory organs (lungs). Parts of the Respiratory Tract
Initiation and Management of Airway Pressure Release Ventilation (APRV)
 Initiation and Management of Airway Pressure Release Ventilation (APRV) Eric Kriner RRT Pulmonary Critical Care Clinical Specialist Pulmonary Services Department Medstar Washington Hospital Center Disclosures
Initiation and Management of Airway Pressure Release Ventilation (APRV) Eric Kriner RRT Pulmonary Critical Care Clinical Specialist Pulmonary Services Department Medstar Washington Hospital Center Disclosures
Respiratory Anatomy and Physiology. Respiratory Anatomy. Function of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory Anatomy and Physiology Michaela Dixon Clinical Development Nurse PICU BRHFC Respiratory Anatomy Function of the Respiratory System - In conjunction with the cardiovascular system, to supply
Respiratory Anatomy and Physiology Michaela Dixon Clinical Development Nurse PICU BRHFC Respiratory Anatomy Function of the Respiratory System - In conjunction with the cardiovascular system, to supply
Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation
 Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation - Physical principles of gases: Pressure of a gas is caused by the movement of its molecules against a surface (more concentration
Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation - Physical principles of gases: Pressure of a gas is caused by the movement of its molecules against a surface (more concentration
LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
 66 LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB Assignments: Due before lab: Quiz: Three Respiratory Interactive Physiology Animations pages 69 73. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
66 LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB Assignments: Due before lab: Quiz: Three Respiratory Interactive Physiology Animations pages 69 73. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
PROBLEM SET 9. SOLUTIONS April 23, 2004
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.542J: Quantitative Physiology: Organ Transport Systems Instructors: Roger Mark and Jose Venegas MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Departments
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.542J: Quantitative Physiology: Organ Transport Systems Instructors: Roger Mark and Jose Venegas MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Departments
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY. Anaesthesiology Block 18 (GNK 586) Prof Pierre Fourie
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Anaesthesiology Block 18 (GNK 586) Prof Pierre Fourie Outline Ventilation Diffusion Perfusion Ventilation-Perfusion relationship Work of breathing Control of Ventilation 2 This image
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Anaesthesiology Block 18 (GNK 586) Prof Pierre Fourie Outline Ventilation Diffusion Perfusion Ventilation-Perfusion relationship Work of breathing Control of Ventilation 2 This image
82 Respiratory Tract NOTES
 82 Respiratory Tract NOTES RESPIRATORY TRACT The respiratory tract conducts air to the lungs where gaseous exchange occurs. It is separated into air-conducting and respiratory (where gas exchange occurs)
82 Respiratory Tract NOTES RESPIRATORY TRACT The respiratory tract conducts air to the lungs where gaseous exchange occurs. It is separated into air-conducting and respiratory (where gas exchange occurs)
The Human Respiratory System
 The Human Respiratory System Maryam Maheri Kiana Kayoda, Nazalia, Emerald Bocobo NPB 101 L section 008 TA: Ashneel Krishna 2/26/2015 Introduction: The respiratory system allows gas exchange between cells
The Human Respiratory System Maryam Maheri Kiana Kayoda, Nazalia, Emerald Bocobo NPB 101 L section 008 TA: Ashneel Krishna 2/26/2015 Introduction: The respiratory system allows gas exchange between cells
Capnography in the Veterinary Technician Toolbox. Katie Pinner BS, LVT Bush Advanced Veterinary Imaging Richmond, VA
 Capnography in the Veterinary Technician Toolbox Katie Pinner BS, LVT Bush Advanced Veterinary Imaging Richmond, VA What are Respiration and Ventilation? Respiration includes all those chemical and physical
Capnography in the Veterinary Technician Toolbox Katie Pinner BS, LVT Bush Advanced Veterinary Imaging Richmond, VA What are Respiration and Ventilation? Respiration includes all those chemical and physical
GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY
 GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY Atmospheric Pressure Intra-Alveolar Pressure Inspiration 760 mm HG at Sea Level (= 1 atm) Pressure due to gases (N2, O2, CO2, Misc.) Pressure inside the alveolus (air sac) Phrenic
GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY Atmospheric Pressure Intra-Alveolar Pressure Inspiration 760 mm HG at Sea Level (= 1 atm) Pressure due to gases (N2, O2, CO2, Misc.) Pressure inside the alveolus (air sac) Phrenic
1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives
 1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives To understand the functions of the circulatory system. To be able to identify the differences between veins, arteries
1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives To understand the functions of the circulatory system. To be able to identify the differences between veins, arteries
Respiration. The resspiratory system
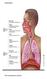 Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
2.1.1 List the principal structures of the
 physiology 2.1.1 List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx -
physiology 2.1.1 List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx -
2. State the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a normal breathing.
 CLASS XI BIOLOGY Breathing And Exchange of Gases 1. Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Answer: Vital Capacity (VC): The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration.
CLASS XI BIOLOGY Breathing And Exchange of Gases 1. Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Answer: Vital Capacity (VC): The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration.
I Physical Principles of Gas Exchange
 Respiratory Gases Exchange Dr Badri Paudel, M.D. 2 I Physical Principles of Gas Exchange 3 Partial pressure The pressure exerted by each type of gas in a mixture Diffusion of gases through liquids Concentration
Respiratory Gases Exchange Dr Badri Paudel, M.D. 2 I Physical Principles of Gas Exchange 3 Partial pressure The pressure exerted by each type of gas in a mixture Diffusion of gases through liquids Concentration
Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University in Brno. Biophysics of breathing.
 Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University in Brno Biophysics of breathing. Spirometry 1 Lecture outline Mechanisms of gas exchange between organism and
Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University in Brno Biophysics of breathing. Spirometry 1 Lecture outline Mechanisms of gas exchange between organism and
Fashionable, don t you think?
 Fashionable, don t you think? 1. Passageway 2. Structure 3. Passageway 4. What is the name of the structure labeled with # 9 in the model at left? 5. What is the name of the structure labeled with # 11
Fashionable, don t you think? 1. Passageway 2. Structure 3. Passageway 4. What is the name of the structure labeled with # 9 in the model at left? 5. What is the name of the structure labeled with # 11
Respiratory system. Role. Ventilation consists of 4 (5) steps : oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide elimination ph balance sound and voice formation
 Respiratory system Role oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide elimination ph balance sound and voice formation Ventilation consists of 4 (5) steps : 1. pulmonary ventilation gas exchange between lungs and
Respiratory system Role oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide elimination ph balance sound and voice formation Ventilation consists of 4 (5) steps : 1. pulmonary ventilation gas exchange between lungs and
25/4/2016. Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten
 25/4/2016 Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten Respiratory System Introduction: - We breath while we are sleeping, talking, working and resting. - Respiratory diseases are abundant
25/4/2016 Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten Respiratory System Introduction: - We breath while we are sleeping, talking, working and resting. - Respiratory diseases are abundant
Respiratory System Lab
 Respiratory System Lab Note: Review the safety materials and wear goggles when working with chemicals. Read the entire exercise before you begin. Take time to organize the materials you will need and set
Respiratory System Lab Note: Review the safety materials and wear goggles when working with chemicals. Read the entire exercise before you begin. Take time to organize the materials you will need and set
Module Two. Objectives: Objectives cont. Objectives cont. Objectives cont.
 Transition to the New National EMS Education Standards: EMT-B B to EMT Module Two Objectives: Upon completion, each participant will do the following to a degree of accuracy that meets the Ntl EMS Education
Transition to the New National EMS Education Standards: EMT-B B to EMT Module Two Objectives: Upon completion, each participant will do the following to a degree of accuracy that meets the Ntl EMS Education
Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired
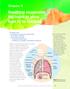 Chapter 6 Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired This chapter covers: the structure of the human gas exchange system the mechanism of breathing gas exchange in the alveoli the concept
Chapter 6 Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired This chapter covers: the structure of the human gas exchange system the mechanism of breathing gas exchange in the alveoli the concept
HMP 210: MEDICAL PHYSIOLOGY III. Dr Lee Ngugi Kigera
 HMP 210: MEDICAL PHYSIOLOGY III Dr Lee Ngugi Kigera HMP 200: RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY AND MECHANICS OF RESPIRATION HMP 201: TRANSPORT OF GASES AND RESPIRATORY CONTROL Reference books Review of Medical Physiology
HMP 210: MEDICAL PHYSIOLOGY III Dr Lee Ngugi Kigera HMP 200: RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY AND MECHANICS OF RESPIRATION HMP 201: TRANSPORT OF GASES AND RESPIRATORY CONTROL Reference books Review of Medical Physiology
Chapter 17 Mechanics of Breathing
 1 Chapter 17 Mechanics of Breathing Running Problem COPD: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (impaired air exchanged) - Chronic Bronchitis: (Blue Bloaters) Bluish tinge of skin and tendency to be overweight
1 Chapter 17 Mechanics of Breathing Running Problem COPD: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (impaired air exchanged) - Chronic Bronchitis: (Blue Bloaters) Bluish tinge of skin and tendency to be overweight
Human gas exchange. Question Paper. Save My Exams! The Home of Revision. Cambridge International Examinations. 56 minutes. Time Allowed: Score: /46
 Human gas exchange Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International Examinations Respiration Human gas exchange Question Paper Time llowed: 56 minutes
Human gas exchange Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International Examinations Respiration Human gas exchange Question Paper Time llowed: 56 minutes
Respiratory Physiology 2
 Respiratory Physiology 2 Session Objectives. What you will cover Gaseous Exchange Control of Breathing Rate Your objectives are State the function of support structures and epithelia of the bronchial tree
Respiratory Physiology 2 Session Objectives. What you will cover Gaseous Exchange Control of Breathing Rate Your objectives are State the function of support structures and epithelia of the bronchial tree
respiratory cycle. point in the volumes: 500 milliliters. for men. expiration, up to 1200 milliliters extra makes breathing Respiratory
 10 II. RESPIRATORY VOLUMES, CAPACITIES & PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS Respiratory volume is the term used for various volumes of air moved by or associated with the lungs at a given point in the respiratory
10 II. RESPIRATORY VOLUMES, CAPACITIES & PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS Respiratory volume is the term used for various volumes of air moved by or associated with the lungs at a given point in the respiratory
PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Parts of the Respiratory System The RS can be divided into two parts: 1. Respiratory Tract, (path that air follows). Nasal passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi,
PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Parts of the Respiratory System The RS can be divided into two parts: 1. Respiratory Tract, (path that air follows). Nasal passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi,
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system. Objective sheet 3 Notes
 1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
(A) The partial pressure in the lungs is higher than in the blood, and oxygen diffuses out of the lungs passively.
 DAT Biology - Problem Drill 12: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement about the partial pressure of oxygen inside the lungs is correct? Question #01 (A) The partial pressure in
DAT Biology - Problem Drill 12: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement about the partial pressure of oxygen inside the lungs is correct? Question #01 (A) The partial pressure in
CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
 268 BIOLOGY CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES 17.1 Respiratory Organs 17.2 Mechanism of Breathing 17.3 Exchange of Gases 17.4 Transport of Gases 17.5 Regulation of Respiration 17.6 Disorders of
268 BIOLOGY CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES 17.1 Respiratory Organs 17.2 Mechanism of Breathing 17.3 Exchange of Gases 17.4 Transport of Gases 17.5 Regulation of Respiration 17.6 Disorders of
VENTILATION STRATEGIES FOR THE CRITICALLY UNWELL
 VENTILATION STRATEGIES FOR THE CRITICALLY UNWELL Dr Nick Taylor Visiting Emergency Specialist Teaching Hospital Karapitiya Senior Specialist and Director ED Training Clinical Lecturer, Australian National
VENTILATION STRATEGIES FOR THE CRITICALLY UNWELL Dr Nick Taylor Visiting Emergency Specialist Teaching Hospital Karapitiya Senior Specialist and Director ED Training Clinical Lecturer, Australian National
Lung Volumes and Capacities
 BIOL242 Lung Volumes and Capacities Measurement of lung volumes provides a tool for understanding normal function of the lungs as well as disease states. The breathing cycle is initiated by expansion of
BIOL242 Lung Volumes and Capacities Measurement of lung volumes provides a tool for understanding normal function of the lungs as well as disease states. The breathing cycle is initiated by expansion of
Anatomy and Physiology Part 11: Of Blood and Breath by: Les Sellnow
 Anatomy and Physiology Part 11: Of Blood and Breath by: Les Sellnow There are few similarities between horses and automobiles, but in a manner of speaking, the horse's circulatory and respiratory systems
Anatomy and Physiology Part 11: Of Blood and Breath by: Les Sellnow There are few similarities between horses and automobiles, but in a manner of speaking, the horse's circulatory and respiratory systems
Chapter 15. Lecture and Animation Outline
 Chapter 15 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
Chapter 15 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
Chapter 17 The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and Regulation of Breathing
 Chapter 17 The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and Regulation of Breathing Overview of Pulmonary Circulation o Diffusion of Gases o Exchange of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide o Transport of Gases in the Blood
Chapter 17 The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and Regulation of Breathing Overview of Pulmonary Circulation o Diffusion of Gases o Exchange of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide o Transport of Gases in the Blood
Recitation question # 05
 Recitation and Lab # 05 The goal of this recitations / labs is to review material related to the CV and respiratory lectures for the second test of this course. Info required to answer this recitation
Recitation and Lab # 05 The goal of this recitations / labs is to review material related to the CV and respiratory lectures for the second test of this course. Info required to answer this recitation
Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy. Haneul Lee, DSc, PT
 Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy Haneul Lee, DSc, PT OBJECTIVE 1. Explain the principle physiological function of the pulmonary system 2. Outline the major anatomical components of the respiratory system.
Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy Haneul Lee, DSc, PT OBJECTIVE 1. Explain the principle physiological function of the pulmonary system 2. Outline the major anatomical components of the respiratory system.
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
PROBLEM SET 8. SOLUTIONS April 15, 2004
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.542J: Quantitative Physiology: Organ Transport Systems Instructors: Roger Mark and Jose Venegas MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Departments
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.542J: Quantitative Physiology: Organ Transport Systems Instructors: Roger Mark and Jose Venegas MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Departments
Chapter 4: Ventilation Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE
 Instant download and all chapters Test Bank Respiratory Care Anatomy and Physiology Foundations for Clinical Practice 3rd Edition Will Beachey https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-respiratory-care-anatomy-physiologyfoundations-clinical-practice-3rd-edition-will-beachey/
Instant download and all chapters Test Bank Respiratory Care Anatomy and Physiology Foundations for Clinical Practice 3rd Edition Will Beachey https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-respiratory-care-anatomy-physiologyfoundations-clinical-practice-3rd-edition-will-beachey/
1 CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES https://biologyaipmt.com/
 1 CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES https://biologyaipmt.com/ CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES Oxygen (O2) is utilised by the organisms to indirectly break down nutrient molecules like
1 CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES https://biologyaipmt.com/ CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES Oxygen (O2) is utilised by the organisms to indirectly break down nutrient molecules like
Alveolus and Respiratory Membrane
 Alveolus and Respiratory Membrane thin membrane where gas exchange occurs in the lungs, simple squamous epithelium (Squamous cells have the appearance of thin, flat plates. They fit closely together in
Alveolus and Respiratory Membrane thin membrane where gas exchange occurs in the lungs, simple squamous epithelium (Squamous cells have the appearance of thin, flat plates. They fit closely together in
Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment
 Name: Date: Mark: / 45 Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
Name: Date: Mark: / 45 Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
Respiratory Physiology
 chapter 4 Respiratory Physiology I. LUNG VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES A. Lung volumes (Figure 4-1) 1. Tidal volume (TV) is the volume inspired or expired with each normal breath. 2. Inspiratory reserve volume
chapter 4 Respiratory Physiology I. LUNG VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES A. Lung volumes (Figure 4-1) 1. Tidal volume (TV) is the volume inspired or expired with each normal breath. 2. Inspiratory reserve volume
THE MECHANICS of RESPIRATION. Introduction
 THE MECHANICS of RESPIRATION Dr. James Duffin Departments of Physiology and Anaesthesia General Learning Objectives: 1. How is air moved into and out of the lungs? 2. What mechanical factors affect the
THE MECHANICS of RESPIRATION Dr. James Duffin Departments of Physiology and Anaesthesia General Learning Objectives: 1. How is air moved into and out of the lungs? 2. What mechanical factors affect the
By: Aseel Jamil Al-twaijer. Lec : physical principles of gas exchange
 By: Aseel Jamil Al-twaijer Lec : physical principles of gas exchange Date:30 /10/2017 this lecture is about the exchange of gases between the blood and the alveoli. I might add some external definitions
By: Aseel Jamil Al-twaijer Lec : physical principles of gas exchange Date:30 /10/2017 this lecture is about the exchange of gases between the blood and the alveoli. I might add some external definitions
UNIQUE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION MUST, AT ALL TIMES, ACCEPT THE ENTIRE CARDIAC OUTPUT
 UNIQUE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION MUST, AT ALL TIMES, ACCEPT THE ENTIRE CARDIAC OUTPUT UNIQUE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION
UNIQUE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION MUST, AT ALL TIMES, ACCEPT THE ENTIRE CARDIAC OUTPUT UNIQUE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION
Structures of the Respiratory System include:
 Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at gaseous exchange in humans in terms of o Ventilation o Inspiration o Expiration o Transport of gases o Homeostatic
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at gaseous exchange in humans in terms of o Ventilation o Inspiration o Expiration o Transport of gases o Homeostatic
Control of Respiration. Central Control of Ventilation
 Central Control of Goal: maintain sufficient ventilation with minimal energy Process steps: mechanics + aerodynamics Points of Regulation Breathing rate and depth, coughing, swallowing, breath holding
Central Control of Goal: maintain sufficient ventilation with minimal energy Process steps: mechanics + aerodynamics Points of Regulation Breathing rate and depth, coughing, swallowing, breath holding
