The Respiratory System Part I. Dr. Adelina Vlad
|
|
|
- Marilyn Arnold
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Respiratory System Part I Dr. Adelina Vlad
2 The Respiratory Process Breathing automatic, rhythmic and centrally-regulated mechanical process by which the atmospheric gas moves into and out of the lungs Respiration the overall process of metabolites oxidation for the production of energy by living organisms; it includes breathing Respiratory process: External respiration + Internal (mitochondrial) respiration
3 The Respiratory Process External respiration - the exchange of O2 and CO2 between the atmosphere and the mitochondria A dual process of transporting - O2 from the atmosphere to the mitochondria - CO2 from the mitochondria to the atmosphere Internal respiration (oxidative phosphorylation) - the oxidation of carbon-containing compounds to form CO2 The lectures on respiratory physiology focus on external respiration
4 External Respiration Can be divided into four major functions: 1) Pulmonary ventilation 2) Diffusion of O2 and CO2 between the alveoli and the blood 3) Transport of O2 and CO2 in the blood and body fluids, to and from the body s tissue cells 4) Regulation of ventilation
5 Air pump Components of the Respiratory System delivers air to and removes air from the alveolar air spaces = alveolar ventilation consist of the lungs and the airways, the rib cage and the thoracic cavity with the muscles of respiration Surface for gas exchange represented by the alveoli Circulatory system internal convective system that delivers O2 to and removes CO2 from the tissues Mechanisms for carrying O2 and CO2 in the blood red blood cells are the main players Mechanisms for locally regulating the distribution of ventilation and perfusion complex feedback loops to regulate air flow and blood flow in the lungs Mechanisms for centrally regulating ventilation
6 The respiratory apparatus in humans
7 Nonrespiratory Roles of the Lungs Olfaction Ventilation is essential for delivering odorants to the olfactory epithelium Sniffing allows one to sample the chemicals in the air without the risk of bringing potential noxious agents deep into the lungs Left-ventricular reservoir The blood contained in the highly compliant pulmonary vessels is an important buffer for filling the left ventricle The left heart can sustain cardiac output for about two beats only with blood from pulmonary circulation
8 Filtering small emboli from the blood The pulmonary vasculature can trap microscopic emboli present in the venous blood (e.g., blood clots, fat, air bubbles) before they reach the left heart If the emboli are few and small, the affected alveoli can recover their function; if pulmonary emboli are large or frequent, they can cause serious symptoms or death Emboli made up of cancer cells may find a breeding ground for supporting metastatic disease Biochemical reactions The pulmonary capillary endothelium plays an important role in converting angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a reaction that is catalyzed by angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE), and selectively removes agents from the circulation (PGE1, PGE2, PGF2a, leukotrienes, serotonin, bradykinin)
9 Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary mechanics - is the physics of the lungs, airways and chest wall - explains how the body moves air in (inspiration) and out (expiration) of the lungs
10 The functional chest wall includes the rib cage, diaphragm, and abdomen
11 Inspiration Is an active process that implies contaction of: primary muscles of inspiration during a quiet breathing: diaphragm external intercostals secondary muscles of inspiration during a forced breathing: sternocleidomastoids anterior serrati scalenes
12 Expiration Is passive durig a quiet breathing Is active during a forced breathing and occurs by contracting the accessory muscle of expiration: internal intercostals rectus abdominis external obliques
13 Pressures That Cause the Movement of Air In and Out of the Lungs During inspiration and expiration the air moves in and out of the lungs due to variations of the: 1. Intrapleural pressure 2. Alveolar pressure 3. Transpulmonary pressure
14 Chest Wall Lung Interaction The lungs are elastic structures, kept distended inside the thoracic cavity due to their interaction with the chest wall This interaction occurs via the intrapleural space, which is a potential cavity between the visceral and parietal pleural membranes
15 Chest Wall Lung Interaction Elastic recoil of the lungs their tendency to collapse Elastic recoil of the chest wall its tendency to pull the thoracic cage outward The chest wall and the lungs pull away from each other relative vacuum between them that makes the pressure inside the intrapleural space lower than the barometric pressure (the intrapleural pressure is negative)
16 Intrapleural Pressure, PIP Is the pressure of the fluid inside the intrapleural space and has negative values Gravity and the respiratory movements influence PIP values: By pulling the lungs downward gravity makes PIP more negative to the apex compared to the base of the thoracic cavity of an upright subject At the beginning of inspiration, PIP is about 5 cm H2O; at the end of a quiet inspiration, PIP decreases to an average of about 7.5 cm H2O Upright subject
17 PIP and the Pleural Fluid Pleural fluid - transudat with mucoid characteristic, favoring slippage of the lungs during ventilation The pumping of the fluid from the intrapleural space by the lymphatics into the mediastinum, the superior surface of the diaphragm, and the lateral surfaces of the parietal pleura maintains a negative PIP
18 Alveolar Pressure, PA Is the pressure of the air inside the alveoli When the glottis is open and no air flows into or out of the lungs, the pressures in all parts of the respiratory tree, including the alveoli (PA), are equal to atmospheric pressure (PB) PA PB governs the gas exchange between the lungs and the atmosphere; the alveolar pressure, PA, is a dynamic element, directly involved in producing air flow
19 Transpulmonary Pressure (PTP) Is the force responsible for keeping the alveoli open, expressed as the pressure gradient across the alveolar wall: PTP = PA PIP PA should be always > PIP (PTP > 0) in order to maintain the lungs expanded in the thoracic cavity PTP is a static parameter which does not cause airflow, but determines lung volume (VL) PIP has a static component (-PTP) that determines lung volume and a dynamic component (PA) that determines air flow
20 PIP, PA and PTP During Quiet Breathing PIP is the pressure directly controlled by the activity of the respiratory muscles; PA and PTP flow from PIP The negative shift in PIP occurring during inspiration has two effects: PA becomes more negative and PTP is made more positive
21 Static Compliance of the Lungs Is the extent to which the lungs will expand for each unit increase in transpulmonary pressure (a measure of how easy it is to inflate the lungs): C=DVL/DPTP Static compliance - determined at a steady state, when the glottis was open and the breathing movements were stopped, allowing no airflow Elastance the compliance reciprocal, a measure of the elastic recoil of the lungs: E=1/C The characteristics of static compliance are determined by the elastic forces of the lungs, represented by: (1) elastic forces of the lung tissue itself (2) elastic forces caused by surface tension of the fluid that lines the inside walls of the alveoli and other lung air spaces
22 Static Pressure-Volume Curves for Lungs in Health and Disease The compliance decreases at high lung volumes due to anatomic and viscous limitations Fibrosis: stiff lungs due to fibrous tissue deposition, with decreased compliance (elastic recoil is much greater) Emphysema: floppy lungs as a result of elastin destruction, with increased compliance (much less elastic recoil)
23 Compliance Diagram in a Healthy Person This diagram shows compliance of the lungs alone 1. Stable VL at low lung volumes it is difficult to pop open an almost completely collapsed airway; rising PTP has little effect on VL 2. Opening of airways the first increases in VL reflect the popping open of the proximal airways, followed by their expansion and recruitment of others 3. Linear expansion of open airways when all the airways are open, making PIP more negative by chest wall expansion inflates the lungs and increases VL in a linear fashion 4. Limit of airway inflation at high VL lungs compliance decreases
24 Hysteresis Defines the difference between the inflation and deflation compliance paths It exists because a greater pressure difference is required to open a previously closed (or narrowed) airway than to keep an open airway from closing
25 Surface Tension When water forms a surface with air, the water molecules on the surface of the water have a strong attraction for one another the water surface is always attempting to contract On the inner surfaces of the alveoli the water surface is also attempting to contract (surface water molecules tend to dive into the bulk, decreasing the area of the airwater interface), causing an elastic contractile force of the entire lungs, called the surface tension elastic force the surface tension contributes to the elastic recoil
26 Effect of Surface Tension on Compliance Lungs inflated with saline solution (= no air-water interface and null surface tension) have an up to three times higher compliance, proving that the surface tension at the air-water interface accounts for about two thirds of the elastic recoil of the lungs (von Neergaard, 1929) surface tension decreases lung compliance In lungs inflated with saline solution hysteresis is much smaller as well Laplace s equation:
27 Effect of Surface Tension on Total Alveolar Surface Area The pressure generated as a result of surface tension in occluded alveoli is inversely affected by the radius of the alveolus (Laplace s equation): the smaller the alveolus radius, the higher the pressure needed to keep it open as alveoli have different sizes and are interconnected, smaller alveoli would tend to collapse in bigger ones, decreasing the total alveolar surface area (gas exchange area)
28 Pulmonary Surfactant Surfactant is a surface active agent in water = reduces the surface tension of water (e.g. pressure generated in occluded alveoli of identical size is 18 cm H2O without and 4 cm H2O with surfactant) Due to its components with both hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties, the surfactant gets into the surface of the air-water interface and decreases here the density of water molecules
29 The most important components of the pulmonary surfactant are the phospholipid dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine, surfactant apoproteins, and calcium ions It is secreted by type II alveolar epithelial cells starting the 6 th and 7 th month of gestation respiratory distress syndrome of the newborn in underdeveloped infants due to insufficient secretion of surfactant By reducing alveolar surface tension, the surfactant reduces the elastic forces of the lung and increases compliance
30 Chest Wall Compliance The thoracic cage has its own elastic and viscous characteristics The compliance of the entire pulmonary system (the lungs and thoracic cage together) is measured while expanding the lungs of a totally relaxed person The compliance of the combined lung-thorax system is almost one half that of the lungs alone When the lungs are expanded to high volumes or compressed to low volumes the limitations of the chest wall become extreme and the compliance of the combined lung-thorax system can be less than one fifth that of the lungs alone
31 Work of Breathing Under resting conditions, the respiratory muscles perform work to cause inspiration, and not expiration The work of inspiration can be divided into three fractions: (1) Work required to expand the lungs against the lung and chest elastic forces, called compliance work or elastic work (2) Work required to overcome the viscosity of the lung and chest wall structures, called tissue resistance work (3) Work required to overcome airway resistance to movement of air into the lungs, called airway resistance work
32 Lung Volumes and Capacities VC = IRV + TV + ERV VC = IC + ERV TLC = VC + RV TLC = IC + FRC FRC = ERV + RV IRV = Inspiratory reserve volume TV = Tidal volume ERV = Expiratory reserve volume RV = Residual volume TLC = Total lung capacity IC = Inspiratory capacity FRC = Functional residual capacity VC = Vital Capacity L L L L L L L L
33 The magnitude of IRV depends on Lung compliance any disorder causing a decrease in compliance is decreasing IRV Muscle strength IRV decreases if the respiratory muscles are weak or if their innervation is compromised Comfort pain limits the ability to perform a maximal inspiration Flexibility of skeleton IRV is decreased by joint stiffness (arthritis, kyphoscoliosis) Posture IRV is lower in a recumbent position because the movement of the diaphragm downward is more difficult without the help of the gravity The magnitude of ERV depends on the same factors, plus the strength of the accessory expiratory muscles
34 Functional Residual Capacity FRC the volume of air that remains in the lungs at the end of each normal expiration To measure FRC the spirometer is used in an indirect manner, e.g. by determining the degree of dilution of the helium after the subject has breathed, starting from the end of a normal expiration, air mixed with He at a known initial concentration: Knowing FRC, one can calculate RV and TLC as well:
35 Alveolar Ventilation The scope of pulmonary ventilation is the renewal of the air in the gas exchange areas: the alveoli, alveolar sacs, alveolar ducts, and respiratory bronchioles Alveolar ventilation is the rate at which new air reaches gas exchange areas Alveolar ventilation is one of the major factors determining the concentrations of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the alveoli Anatomic dead space respiratory passages where gas exchange does not occur; the air from the dead space just fills the proximal (conducting) airways, and never reaches exchange areas it is not used for refreshing the alveolar air
36 Physiologic dead space - on occasion, some of the alveoli themselves are nonfunctional or only partially functional because of absent or poor blood flow through the adjacent pulmonary capillaries = alveolar dead space - When the alveolar dead space is included in the total measurement of dead space, this is called the physiologic dead space The rate of alveolar ventilation: where VT is the tidal volume, and VD is the physiologic dead space volume., Normally, alveolar ventilation would equal 12 x ( ) = 4200 ml/min
4/18/12 MECHANISM OF RESPIRATION. Every Breath You Take. Fun Facts
 Objectives MECHANISM OF RESPIRATION Dr Badri Paudel Explain how the intrapulmonary and intrapleural pressures vary during ventilation and relate these pressure changes to Boyle s law. Define the terms
Objectives MECHANISM OF RESPIRATION Dr Badri Paudel Explain how the intrapulmonary and intrapleural pressures vary during ventilation and relate these pressure changes to Boyle s law. Define the terms
Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation. Chad & Angela
 Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation Chad & Angela Respiratory Structures Basic Structures of Respiration Nasal/Oral Cavities Larynx Trachea Bronchi Secondary Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Mechanics of Ventilation
Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation Chad & Angela Respiratory Structures Basic Structures of Respiration Nasal/Oral Cavities Larynx Trachea Bronchi Secondary Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Mechanics of Ventilation
Introduction. Respiration. Chapter 10. Objectives. Objectives. The Respiratory System
 Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
Airway: the tubes through which air flows between atmosphere and alveoli. Upper airway. Lower airway
 Respiration Yu Yanqin ( 虞燕琴 ), PhD Dept. of fph Physiology Zhejiang University, School of Medicine Respiration Definition: the bodily processes involved in exchange of oxygen (O 2 ) and carbon dioxide
Respiration Yu Yanqin ( 虞燕琴 ), PhD Dept. of fph Physiology Zhejiang University, School of Medicine Respiration Definition: the bodily processes involved in exchange of oxygen (O 2 ) and carbon dioxide
Respiratory System. Part 2
 Respiratory System Part 2 Respiration Exchange of gases between air and body cells Three steps 1. Ventilation 2. External respiration 3. Internal respiration Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation consists
Respiratory System Part 2 Respiration Exchange of gases between air and body cells Three steps 1. Ventilation 2. External respiration 3. Internal respiration Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation consists
Respiratory System Physiology. Dr. Vedat Evren
 Respiratory System Physiology Dr. Vedat Evren Respiration Processes involved in oxygen transport from the atmosphere to the body tissues and the release and transportation of carbon dioxide produced in
Respiratory System Physiology Dr. Vedat Evren Respiration Processes involved in oxygen transport from the atmosphere to the body tissues and the release and transportation of carbon dioxide produced in
Collin County Community College. Lung Physiology
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 9 Respiratory System 1 Lung Physiology Factors affecting Ventillation 1. Airway resistance Flow = Δ P / R Most resistance is encountered
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 9 Respiratory System 1 Lung Physiology Factors affecting Ventillation 1. Airway resistance Flow = Δ P / R Most resistance is encountered
Respiration - Human 1
 Respiration - Human 1 At the end of the lectures on respiration you should be able to, 1. Describe events in the respiratory processes 2. Discuss the mechanism of lung ventilation in human 3. Discuss the
Respiration - Human 1 At the end of the lectures on respiration you should be able to, 1. Describe events in the respiratory processes 2. Discuss the mechanism of lung ventilation in human 3. Discuss the
Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 1
 Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The term "respiration" in its most complete meaning is: a. breathing b. oxygen transport c. carbon dioxide transport d. cellular energy production e. all of
Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The term "respiration" in its most complete meaning is: a. breathing b. oxygen transport c. carbon dioxide transport d. cellular energy production e. all of
Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation
 Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing and the first step in the respiratory process. Pulmonary ventilation brings in air with a new supply
Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing and the first step in the respiratory process. Pulmonary ventilation brings in air with a new supply
Respiratory system. Role. Ventilation consists of 4 (5) steps : oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide elimination ph balance sound and voice formation
 Respiratory system Role oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide elimination ph balance sound and voice formation Ventilation consists of 4 (5) steps : 1. pulmonary ventilation gas exchange between lungs and
Respiratory system Role oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide elimination ph balance sound and voice formation Ventilation consists of 4 (5) steps : 1. pulmonary ventilation gas exchange between lungs and
The physiological functions of respiration and circulation. Mechanics. exercise 7. Respiratory Volumes. Objectives
 exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
The Respiratory System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Organs of the Respiratory system
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Organs of the Respiratory system
Physiology - lecture 3
 Physiology - lecture 3 Residual Volume (RV):the amount of gas remaining in the lung at the end of a maximal exhalation Tidal Volume (TV):the volume of gas inhaled and exhaled during one respiratory cycle.
Physiology - lecture 3 Residual Volume (RV):the amount of gas remaining in the lung at the end of a maximal exhalation Tidal Volume (TV):the volume of gas inhaled and exhaled during one respiratory cycle.
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange
 Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
RSPT 1060 OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES EQUATION OF MOTION. MODULE C Applied Physics Lesson #1 - Mechanics. Ventilation vs.
 RSPT 1060 MODULE C Applied Physics Lesson #1 - Mechanics OBJECTIVES At the end of this module, the student should be able to define the terms and abbreviations used in the module. draw & explain the equation
RSPT 1060 MODULE C Applied Physics Lesson #1 - Mechanics OBJECTIVES At the end of this module, the student should be able to define the terms and abbreviations used in the module. draw & explain the equation
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system
 CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Test Bank for Pilbeams Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition by Cairo
 Test Bank for Pilbeams Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition by Cairo Link full download: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-pilbeams-mechanicalventilation-physiological-and-clinical-applications-6th-edition-by-cairo/
Test Bank for Pilbeams Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition by Cairo Link full download: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-pilbeams-mechanicalventilation-physiological-and-clinical-applications-6th-edition-by-cairo/
Respiration. The resspiratory system
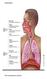 Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
25/4/2016. Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten
 25/4/2016 Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten Respiratory System Introduction: - We breath while we are sleeping, talking, working and resting. - Respiratory diseases are abundant
25/4/2016 Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten Respiratory System Introduction: - We breath while we are sleeping, talking, working and resting. - Respiratory diseases are abundant
CHAPTER 3: The cardio-respiratory system
 : The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
: The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
Physiology of Respiration
 Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
Respiratory Physiology. ED Primary Teaching
 Respiratory Physiology ED Primary Teaching Functions of the respiratory system Gas exchange with O2 and CO2 Surfactant production Defence - IgA and macrophages Filer - pollutants and thromboembolism Metabolises
Respiratory Physiology ED Primary Teaching Functions of the respiratory system Gas exchange with O2 and CO2 Surfactant production Defence - IgA and macrophages Filer - pollutants and thromboembolism Metabolises
Respiratory System Review
 KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
If we want more acid we keep the carbon dioxide inside our body 4-enables speech
 By: Laith Sorour Lec 1 Date: 26/10/2017 *-*Yo, don t listen to record while reading the sheet, I left the minutes where doctor started new subjective so if you don t understand a point you can listen to
By: Laith Sorour Lec 1 Date: 26/10/2017 *-*Yo, don t listen to record while reading the sheet, I left the minutes where doctor started new subjective so if you don t understand a point you can listen to
April KHALED MOUSA BACHA. Physiology #2. Dr. Nayef AL-Gharaibeh. Pulmonary volumes & capacities
 25 th April Physiology #2 Pulmonary volumes & capacities Dr. Nayef AL-Gharaibeh KHALED MOUSA BACHA We will start this lecture by explaining an important concept from the previous one: Intrapleural pressure
25 th April Physiology #2 Pulmonary volumes & capacities Dr. Nayef AL-Gharaibeh KHALED MOUSA BACHA We will start this lecture by explaining an important concept from the previous one: Intrapleural pressure
HMP 210: MEDICAL PHYSIOLOGY III. Dr Lee Ngugi Kigera
 HMP 210: MEDICAL PHYSIOLOGY III Dr Lee Ngugi Kigera HMP 200: RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY AND MECHANICS OF RESPIRATION HMP 201: TRANSPORT OF GASES AND RESPIRATORY CONTROL Reference books Review of Medical Physiology
HMP 210: MEDICAL PHYSIOLOGY III Dr Lee Ngugi Kigera HMP 200: RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY AND MECHANICS OF RESPIRATION HMP 201: TRANSPORT OF GASES AND RESPIRATORY CONTROL Reference books Review of Medical Physiology
Boards and Beyond: Pulmonary
 Boards and Beyond: Pulmonary A Companion Book to the Boards and Beyond Website Jason Ryan, MD, MPH i ii Table of Contents Pulmonary Anatomy 1 Treatment of COPD/Asthma 45 Pulmonary Physiology 4 Pneumonia
Boards and Beyond: Pulmonary A Companion Book to the Boards and Beyond Website Jason Ryan, MD, MPH i ii Table of Contents Pulmonary Anatomy 1 Treatment of COPD/Asthma 45 Pulmonary Physiology 4 Pneumonia
Physiology (3) Pulmonary Function Test:
 Pulmonary Function Test: Today we will continue with the pulmonary function test, and the question is: why do we do pulmonary function tests for patients? Can pulmonary function tests tell us what type
Pulmonary Function Test: Today we will continue with the pulmonary function test, and the question is: why do we do pulmonary function tests for patients? Can pulmonary function tests tell us what type
Outline - Respiratory System. Function of the respiratory system Parts of the respiratory system Mechanics of breathing Regulation of breathing
 Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
Respiration (revised 2006) Pulmonary Mechanics
 Respiration (revised 2006) Pulmonary Mechanics PUL 1. Diagram how pleural pressure, alveolar pressure, airflow, and lung volume change during a normal quiet breathing cycle. Identify on the figure the
Respiration (revised 2006) Pulmonary Mechanics PUL 1. Diagram how pleural pressure, alveolar pressure, airflow, and lung volume change during a normal quiet breathing cycle. Identify on the figure the
82 Respiratory Tract NOTES
 82 Respiratory Tract NOTES RESPIRATORY TRACT The respiratory tract conducts air to the lungs where gaseous exchange occurs. It is separated into air-conducting and respiratory (where gas exchange occurs)
82 Respiratory Tract NOTES RESPIRATORY TRACT The respiratory tract conducts air to the lungs where gaseous exchange occurs. It is separated into air-conducting and respiratory (where gas exchange occurs)
Respiration. The ins and outs
 Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
Respiratory Physiology 2
 Respiratory Physiology 2 Session Objectives. What you will cover Gaseous Exchange Control of Breathing Rate Your objectives are State the function of support structures and epithelia of the bronchial tree
Respiratory Physiology 2 Session Objectives. What you will cover Gaseous Exchange Control of Breathing Rate Your objectives are State the function of support structures and epithelia of the bronchial tree
Lung Volumes and Ventilation
 Respiratory System ssrisuma@rics.bwh.harvard.edu Lung Volumes and Ventilation Minute ventilation Volume of an inspired or expired air per minute = tidal volume (V T ) x respiratory rate Dead space ventilation
Respiratory System ssrisuma@rics.bwh.harvard.edu Lung Volumes and Ventilation Minute ventilation Volume of an inspired or expired air per minute = tidal volume (V T ) x respiratory rate Dead space ventilation
Chapter 15. Lecture and Animation Outline
 Chapter 15 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
Chapter 15 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
Chapter 16 Respiratory System
 Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Respiratory System. Prepared by: Dorota Marczuk-Krynicka, MD, PhD
 Respiratory System Prepared by: Dorota Marczuk-Krynicka, MD, PhD Lungs: Ventilation Perfusion Gas Exchange - Diffusion 1. Airways and Airway Resistance (AWR) 2. Mechanics of Breathing and Lung (Elastic)
Respiratory System Prepared by: Dorota Marczuk-Krynicka, MD, PhD Lungs: Ventilation Perfusion Gas Exchange - Diffusion 1. Airways and Airway Resistance (AWR) 2. Mechanics of Breathing and Lung (Elastic)
Lung Volumes and Capacities
 Lung Volumes and Capacities Normally the volume of air entering the lungs during a single inspiration is approximately equal to the volume leaving on the subsequent expiration and is called the tidal volume.
Lung Volumes and Capacities Normally the volume of air entering the lungs during a single inspiration is approximately equal to the volume leaving on the subsequent expiration and is called the tidal volume.
UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 9.01 GENERAL FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. Brings oxygenated air to the alveoli B. Removes air containing carbon dioxide C. Filters, warms, and humidifies
UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 9.01 GENERAL FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. Brings oxygenated air to the alveoli B. Removes air containing carbon dioxide C. Filters, warms, and humidifies
THE MECHANICS of RESPIRATION. Introduction
 THE MECHANICS of RESPIRATION Dr. James Duffin Departments of Physiology and Anaesthesia General Learning Objectives: 1. How is air moved into and out of the lungs? 2. What mechanical factors affect the
THE MECHANICS of RESPIRATION Dr. James Duffin Departments of Physiology and Anaesthesia General Learning Objectives: 1. How is air moved into and out of the lungs? 2. What mechanical factors affect the
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 11 Respiratory System 2 Pulmonary Ventilation Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session plan o Pulmonary Ventilation
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 11 Respiratory System 2 Pulmonary Ventilation Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session plan o Pulmonary Ventilation
LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
 66 LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB Assignments: Due before lab: Quiz: Three Respiratory Interactive Physiology Animations pages 69 73. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
66 LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB Assignments: Due before lab: Quiz: Three Respiratory Interactive Physiology Animations pages 69 73. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
(A) The partial pressure in the lungs is higher than in the blood, and oxygen diffuses out of the lungs passively.
 DAT Biology - Problem Drill 12: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement about the partial pressure of oxygen inside the lungs is correct? Question #01 (A) The partial pressure in
DAT Biology - Problem Drill 12: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement about the partial pressure of oxygen inside the lungs is correct? Question #01 (A) The partial pressure in
Physiology of the Respiratory System
 Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Physiology of the Respiratory System References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Physiology of the Respiratory System References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Atmosphere Tissue cell External respiration Alveoli of lungs 1 Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Atmosphere Tissue cell External respiration Alveoli of lungs 1 Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere
Respiratory system & exercise. Dr. Rehab F Gwada
 Respiratory system & exercise Dr. Rehab F Gwada Objectives of lecture Outline the major anatomical components & important functions of the respiratory system. Describe the mechanics of ventilation. List
Respiratory system & exercise Dr. Rehab F Gwada Objectives of lecture Outline the major anatomical components & important functions of the respiratory system. Describe the mechanics of ventilation. List
(Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System
 (Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System I. (Slide 2) The Respiratory Tract A) Major structures and regions of the respiratory Tract/Route INTO body 1) nose 2) nasal cavity 3) pharynx 4) glottis 5)
(Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System I. (Slide 2) The Respiratory Tract A) Major structures and regions of the respiratory Tract/Route INTO body 1) nose 2) nasal cavity 3) pharynx 4) glottis 5)
Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University in Brno. Biophysics of breathing.
 Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University in Brno Biophysics of breathing. Spirometry 1 Lecture outline Mechanisms of gas exchange between organism and
Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University in Brno Biophysics of breathing. Spirometry 1 Lecture outline Mechanisms of gas exchange between organism and
IV. FROM AQUATIC TO ATMOSPHERIC BREATHING: THE TRACHEA & THE LUNG
 GAS EXCHANGE AND TRANSPORT I. INTRODUCTION: Heterotrophs oxidize carbon cmpds using O 2 to generate CO 2 & H 2 O. This is cellular respiration II. HOW GAS ENTERS A CELL A. The composition of air: 79% N
GAS EXCHANGE AND TRANSPORT I. INTRODUCTION: Heterotrophs oxidize carbon cmpds using O 2 to generate CO 2 & H 2 O. This is cellular respiration II. HOW GAS ENTERS A CELL A. The composition of air: 79% N
Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired
 Chapter 6 Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired This chapter covers: the structure of the human gas exchange system the mechanism of breathing gas exchange in the alveoli the concept
Chapter 6 Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired This chapter covers: the structure of the human gas exchange system the mechanism of breathing gas exchange in the alveoli the concept
BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
 96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The tissues exchange O 2 directly with the air in
96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The tissues exchange O 2 directly with the air in
 Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
2. State the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a normal breathing.
 CLASS XI BIOLOGY Breathing And Exchange of Gases 1. Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Answer: Vital Capacity (VC): The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration.
CLASS XI BIOLOGY Breathing And Exchange of Gases 1. Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Answer: Vital Capacity (VC): The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration.
Breathing. Physics of Breathing 11/14/2011. Function of Respiratory Tract. Structure of Respiratory Tract. Parts of the Respiratory Tract
 Breathing Function of Respiratory Tract The respiratory tract is a series of spaces and semirigid tubes designed to convey air into and out of the respiratory organs (lungs). Parts of the Respiratory Tract
Breathing Function of Respiratory Tract The respiratory tract is a series of spaces and semirigid tubes designed to convey air into and out of the respiratory organs (lungs). Parts of the Respiratory Tract
Alveolus and Respiratory Membrane
 Alveolus and Respiratory Membrane thin membrane where gas exchange occurs in the lungs, simple squamous epithelium (Squamous cells have the appearance of thin, flat plates. They fit closely together in
Alveolus and Respiratory Membrane thin membrane where gas exchange occurs in the lungs, simple squamous epithelium (Squamous cells have the appearance of thin, flat plates. They fit closely together in
BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
 96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The cell exchange O 2 directly with the air in the
96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The cell exchange O 2 directly with the air in the
1 CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES https://biologyaipmt.com/
 1 CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES https://biologyaipmt.com/ CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES Oxygen (O2) is utilised by the organisms to indirectly break down nutrient molecules like
1 CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES https://biologyaipmt.com/ CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES Oxygen (O2) is utilised by the organisms to indirectly break down nutrient molecules like
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY. Anaesthesiology Block 18 (GNK 586) Prof Pierre Fourie
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Anaesthesiology Block 18 (GNK 586) Prof Pierre Fourie Outline Ventilation Diffusion Perfusion Ventilation-Perfusion relationship Work of breathing Control of Ventilation 2 This image
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Anaesthesiology Block 18 (GNK 586) Prof Pierre Fourie Outline Ventilation Diffusion Perfusion Ventilation-Perfusion relationship Work of breathing Control of Ventilation 2 This image
Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy. Haneul Lee, DSc, PT
 Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy Haneul Lee, DSc, PT OBJECTIVE 1. Explain the principle physiological function of the pulmonary system 2. Outline the major anatomical components of the respiratory system.
Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy Haneul Lee, DSc, PT OBJECTIVE 1. Explain the principle physiological function of the pulmonary system 2. Outline the major anatomical components of the respiratory system.
Chapter 17 Mechanics of Breathing
 1 Chapter 17 Mechanics of Breathing Running Problem COPD: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (impaired air exchanged) - Chronic Bronchitis: (Blue Bloaters) Bluish tinge of skin and tendency to be overweight
1 Chapter 17 Mechanics of Breathing Running Problem COPD: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (impaired air exchanged) - Chronic Bronchitis: (Blue Bloaters) Bluish tinge of skin and tendency to be overweight
Respiratory System Homework
 Respiratory System Homework The R S is the body s breathing equipment. Similar to the D system, it takes S from outside the body (G, particularly O ), circulates them through the body to C and T, then
Respiratory System Homework The R S is the body s breathing equipment. Similar to the D system, it takes S from outside the body (G, particularly O ), circulates them through the body to C and T, then
CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
 268 BIOLOGY CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES 17.1 Respiratory Organs 17.2 Mechanism of Breathing 17.3 Exchange of Gases 17.4 Transport of Gases 17.5 Regulation of Respiration 17.6 Disorders of
268 BIOLOGY CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES 17.1 Respiratory Organs 17.2 Mechanism of Breathing 17.3 Exchange of Gases 17.4 Transport of Gases 17.5 Regulation of Respiration 17.6 Disorders of
Section Two Diffusion of gases
 Section Two Diffusion of gases Lecture 5: Partial pressure and the composition of gasses in air. Factors affecting diffusion of gases. Ventilation perfusion ratio effect on alveolar gas concentration.
Section Two Diffusion of gases Lecture 5: Partial pressure and the composition of gasses in air. Factors affecting diffusion of gases. Ventilation perfusion ratio effect on alveolar gas concentration.
Respiratory Physiology
 Respiratory Physiology Background Information: When inspiring, the pleura attached to the internal chest wall is pulled outward as the thoracic cavity expands. The pleural cavity [space between the outer
Respiratory Physiology Background Information: When inspiring, the pleura attached to the internal chest wall is pulled outward as the thoracic cavity expands. The pleural cavity [space between the outer
Lab 3. The Respiratory System (designed by Heather E. M. Liwanag with T.M. Williams)
 Name Lab Partners Lab 3. The Respiratory System (designed by Heather E. M. Liwanag with T.M. Williams) Part 1. Lung Volumes and Capacities Objectives 1. Obtain graphical representation of lung capacities
Name Lab Partners Lab 3. The Respiratory System (designed by Heather E. M. Liwanag with T.M. Williams) Part 1. Lung Volumes and Capacities Objectives 1. Obtain graphical representation of lung capacities
3/24/2009 LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD. 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm 1 KEY WORDS TO KNOW BOYLE S LAW INTERCOSTAL NERVES PHRENIC NERVE DIAPHRAGM EXTERNAL INTERCOSTAL
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm 1 KEY WORDS TO KNOW BOYLE S LAW INTERCOSTAL NERVES PHRENIC NERVE DIAPHRAGM EXTERNAL INTERCOSTAL
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Human Biology Respiratory System
 Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
TV = Tidal volume (500ml) IRV = Inspiratory reserve volume (3,000 ml)
 By: Amin alajlouni Lec: 2nd record Date: 29/10/2017 First of all, this is my first sheet so excuse any mistakes I might make and let's start: As we said before in our last lecture about lung capacities
By: Amin alajlouni Lec: 2nd record Date: 29/10/2017 First of all, this is my first sheet so excuse any mistakes I might make and let's start: As we said before in our last lecture about lung capacities
2.1.1 List the principal structures of the
 physiology 2.1.1 List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx -
physiology 2.1.1 List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx -
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system. Objective sheet 3 Notes
 1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at gaseous exchange in humans in terms of o Ventilation o Inspiration o Expiration o Transport of gases o Homeostatic
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at gaseous exchange in humans in terms of o Ventilation o Inspiration o Expiration o Transport of gases o Homeostatic
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System
 VI edit Pag 451-499 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System V edit. Pag 459-509 Tissue cell Alveoli of lungs Atmosphere 1 External respiration Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere and air sacs
VI edit Pag 451-499 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System V edit. Pag 459-509 Tissue cell Alveoli of lungs Atmosphere 1 External respiration Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere and air sacs
2/28/18. Respiratory System. 1 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Introduction. Anatomy. Physiology. Respiratory System
 Introduction Respiratory System Chapter 28 Respiration: We inhale air, extract oxygen from it, exhale air Cardiovascular and respiratory systems work together Failure of either system: - Disruption of
Introduction Respiratory System Chapter 28 Respiration: We inhale air, extract oxygen from it, exhale air Cardiovascular and respiratory systems work together Failure of either system: - Disruption of
The Respiratory System. Medical Terminology
 The Respiratory System Medical Terminology The respiratory system is where gas exchange occurs via respiration; inhalation/exhalation. pick up oxygen from inhaled air expels carbon dioxide and water sinus
The Respiratory System Medical Terminology The respiratory system is where gas exchange occurs via respiration; inhalation/exhalation. pick up oxygen from inhaled air expels carbon dioxide and water sinus
GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY
 GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY Atmospheric Pressure Intra-Alveolar Pressure Inspiration 760 mm HG at Sea Level (= 1 atm) Pressure due to gases (N2, O2, CO2, Misc.) Pressure inside the alveolus (air sac) Phrenic
GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY Atmospheric Pressure Intra-Alveolar Pressure Inspiration 760 mm HG at Sea Level (= 1 atm) Pressure due to gases (N2, O2, CO2, Misc.) Pressure inside the alveolus (air sac) Phrenic
Then the partial pressure of oxygen is x 760 = 160 mm Hg
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: the uptake of molecular oxygen (O2) from the environment and the discharge of
1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: the uptake of molecular oxygen (O2) from the environment and the discharge of
Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY
 Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Respiration External respiration ventilation gas exchange Internal respiration cellular respiration gas exchange Respiratory Cycle Inspiration
Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Respiration External respiration ventilation gas exchange Internal respiration cellular respiration gas exchange Respiratory Cycle Inspiration
Pulmonary Circulation
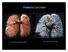 Pulmonary Circulation resin cast of pulmonary arteries resin cast of pulmonary veins Blood Flow to the Lungs Pulmonary Circulation Systemic Circulation Blood supply to the conducting zone provided by the
Pulmonary Circulation resin cast of pulmonary arteries resin cast of pulmonary veins Blood Flow to the Lungs Pulmonary Circulation Systemic Circulation Blood supply to the conducting zone provided by the
REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE 24 SEPTEMBER 2014 Lesson Description
 REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE 24 SEPTEMBER 2014 Lesson Description In this lesson, we revise: Gaseous Exchange in Plants & Animals Gaseous Exchange in Humans Excretion in Humans Focus on the Kidney Gaseous
REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE 24 SEPTEMBER 2014 Lesson Description In this lesson, we revise: Gaseous Exchange in Plants & Animals Gaseous Exchange in Humans Excretion in Humans Focus on the Kidney Gaseous
PROBLEM SET 9. SOLUTIONS April 23, 2004
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.542J: Quantitative Physiology: Organ Transport Systems Instructors: Roger Mark and Jose Venegas MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Departments
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.542J: Quantitative Physiology: Organ Transport Systems Instructors: Roger Mark and Jose Venegas MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Departments
Chapter 23: Respiratory System
 Chapter 23: Respiratory System I. Functions of the Respiratory System A. List and describe the five major functions of the respiratory system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. II. Anatomy and Histology of the Respiratory
Chapter 23: Respiratory System I. Functions of the Respiratory System A. List and describe the five major functions of the respiratory system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. II. Anatomy and Histology of the Respiratory
Mechanics of ventilation: static lung mechanics
 Mechanics of ventilation: static lung mechanics Specific learning objectives: Elastic properties of lung and chest wall Compliance: measure of elastic properties of lung An isolated lung tends to contract
Mechanics of ventilation: static lung mechanics Specific learning objectives: Elastic properties of lung and chest wall Compliance: measure of elastic properties of lung An isolated lung tends to contract
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
Human gas exchange. Question Paper. Save My Exams! The Home of Revision. Cambridge International Examinations. 56 minutes. Time Allowed: Score: /46
 Human gas exchange Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International Examinations Respiration Human gas exchange Question Paper Time llowed: 56 minutes
Human gas exchange Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International Examinations Respiration Human gas exchange Question Paper Time llowed: 56 minutes
Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42. Gas Exchange pp Gas Exchange. Gas Exchange in Fish pp Gas Exchange in Fish
 Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42 Fig. 42.24 Gas Exchange pp.979-989 Gas exchange involves the uptake of oxygen and the discharge of carbon dioxide (i.e. respiration or breathing). It is necessary for cellular
Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42 Fig. 42.24 Gas Exchange pp.979-989 Gas exchange involves the uptake of oxygen and the discharge of carbon dioxide (i.e. respiration or breathing). It is necessary for cellular
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY RELEVANT TO HFOV
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY RELEVANT TO Physiology of CMV 1 What is? Ventilation using a relatively high continuous distending pressure at the airway opening, around which an oscillatory wave is generated to
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY RELEVANT TO Physiology of CMV 1 What is? Ventilation using a relatively high continuous distending pressure at the airway opening, around which an oscillatory wave is generated to
Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation
 Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation - Physical principles of gases: Pressure of a gas is caused by the movement of its molecules against a surface (more concentration
Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation - Physical principles of gases: Pressure of a gas is caused by the movement of its molecules against a surface (more concentration
Activity 2: Examining the Effect of Changing Airway Resistance on Respiratory Volumes
 1 BGYC34 PhysioEx Lab 7 Respiratory Systems Mechanics Marking Scheme Part 1 Complete PhysioEx lab #7. Hand-in all of the pages associated with the lab. Note that there are 5 activities to be completed.
1 BGYC34 PhysioEx Lab 7 Respiratory Systems Mechanics Marking Scheme Part 1 Complete PhysioEx lab #7. Hand-in all of the pages associated with the lab. Note that there are 5 activities to be completed.
STATIC BIOMECHANICS OF THE MAMMALIAN RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 1
 STATIC BIOMECHANICS OF THE MAMMALIAN RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 1 Summary: We begin a consideration of breathing in mammals. We will start with the definitions of a series of sub- volumes of the total volume of
STATIC BIOMECHANICS OF THE MAMMALIAN RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 1 Summary: We begin a consideration of breathing in mammals. We will start with the definitions of a series of sub- volumes of the total volume of
1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives
 1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives To understand the functions of the circulatory system. To be able to identify the differences between veins, arteries
1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives To understand the functions of the circulatory system. To be able to identify the differences between veins, arteries
Monday, ! Today: Respiratory system! 5/20/14! Transport of Blood! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing!
 Monday, 5.19.14! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing! Transport of Blood! What is transported! Nutrients! Oxygen! Carbon Dioxide! Hormones! Antibodies! What it is/does!
Monday, 5.19.14! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing! Transport of Blood! What is transported! Nutrients! Oxygen! Carbon Dioxide! Hormones! Antibodies! What it is/does!
Module Two. Objectives: Objectives cont. Objectives cont. Objectives cont.
 Transition to the New National EMS Education Standards: EMT-B B to EMT Module Two Objectives: Upon completion, each participant will do the following to a degree of accuracy that meets the Ntl EMS Education
Transition to the New National EMS Education Standards: EMT-B B to EMT Module Two Objectives: Upon completion, each participant will do the following to a degree of accuracy that meets the Ntl EMS Education
Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration)
 Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration) 1 Question 1 Why do organisms need food? Organisms need food for obtaining energy to perform the vital functions. Question 2 What is a respiratory substrate?
Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration) 1 Question 1 Why do organisms need food? Organisms need food for obtaining energy to perform the vital functions. Question 2 What is a respiratory substrate?
RESPIRATORY GAS EXCHANGE
 RESPIRATORY GAS EXCHANGE Alveolar PO 2 = 105 mmhg; Pulmonary artery PO 2 = 40 mmhg PO 2 gradient across respiratory membrane 65 mmhg (105 mmhg 40 mmhg) Results in pulmonary vein PO 2 ~100 mmhg Partial
RESPIRATORY GAS EXCHANGE Alveolar PO 2 = 105 mmhg; Pulmonary artery PO 2 = 40 mmhg PO 2 gradient across respiratory membrane 65 mmhg (105 mmhg 40 mmhg) Results in pulmonary vein PO 2 ~100 mmhg Partial
Pulmonary Circulation Linda Costanzo Ph.D.
 Pulmonary Circulation Linda Costanzo Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The differences between pressures in the pulmonary and systemic circulations. 2. How
Pulmonary Circulation Linda Costanzo Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The differences between pressures in the pulmonary and systemic circulations. 2. How
respiratory cycle. point in the volumes: 500 milliliters. for men. expiration, up to 1200 milliliters extra makes breathing Respiratory
 10 II. RESPIRATORY VOLUMES, CAPACITIES & PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS Respiratory volume is the term used for various volumes of air moved by or associated with the lungs at a given point in the respiratory
10 II. RESPIRATORY VOLUMES, CAPACITIES & PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS Respiratory volume is the term used for various volumes of air moved by or associated with the lungs at a given point in the respiratory
