Lung Capacity. Science and Engineering Practices: S.1A.1; S.1A.2; S.1A.4; S.1A.5; S.1A.7
|
|
|
- Jean Baldwin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SC Academic Standards: NGSS DCI: Science and Engineering Practices: S.1A.1; S.1A.2; S.1A.4; S.1A.5; S.1A.7 Crosscutting Concepts: Patterns; Cause and Effect: Mechanism and Explanation; Systems and Systems Models; Energy and Matter: Flows, Cycles, and Conservation; and Stability and Change. Focus Question(s): What is my lung capacity? What factors affect lung capacity? Conceptual Understanding: Plants and animals have physical characteristics that allow them to receive information from the environment. Structural adaptations within groups of plants and animals allow them to better survive and reproduce. Life is the quality that differentiates living things (organisms) from nonliving objects or those that were once living. All organisms are made up of cells, need food and water, a way to dispose of waste, and an environment in which they can live. Because of the diversity of life on Earth, scientists have developed a way to organize groups of organisms according to their characteristic traits, making it easier to identify and study them. The Animal Kingdom includes a diversity of organisms that have many characteristics in common. Classification of animals is based on structures that function in growth, reproduction, and survival. Animals have both structural and behavioral adaptations that increase the chances of reproduction and survival in changing environments. Multicellular organisms (including humans) are complex systems with specialized cells that perform specific functions. Organs and organ systems are composed of cells that function to serve the needs of cells which in turn serve the needs of the organism. Background: Lungs are balloon- like structures in the chest that are used to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide between your blood and the atmosphere. As you inhale (breathe in), air is drawn into your lungs. As you exhale (breathe out),
2 you expel gases from your lungs. In the lungs, oxygen from inhaled air moves into your blood (the liquid in animals that carries nutrients and oxygen to cells and takes away wastes) and is carried to the cells throughout the body to produce energy. Also in the lungs, carbon dioxide (a gaseous waste) leaves the blood and enters tubes, then is expelled when you exhale. The breathing rate of a healthy adult at rest is about 12 times a minute. A baby breathes faster, about 30 times a minute. Normally, you breathe through your nose. Air enters the nose and moves down the back of the pharynx (the throat), where it enters the trachea (the breathing tube). At the end of the trachea, the passage splits to form two tubes called bronchi that lead to the lungs. In the lungs, each bronchus divides many times, forming small tubes called bronchioles. At the end of each bronchiole is a balloon- shaped structure called an alviolus (air sac). The lungs contain millions of alvioli, and around each are many capillaries. A capillary is the body's smallest blood vessel. Through the capillaries, oxygen from inhaled air is transferred, by diffusion, to the blood, and waste from the blood is diffused into the lungs before being exhaled. The average total lung capacity of an adult human male is about 6 liters of air but only a small amount of this capacity is used during normal breathing. The lung capacity of freediver and world record holder Herbert Nitsch is measured to be 10 Liters. The amount of air that you move in and out of your lungs while breathing normally is called TIDAL VOLUME. This amount of air provides enough oxygen for a person who is resting. Tidal volume is only a fraction of the total lung capacity, about 500 ml; it is possible to inhale and exhale more forcefully and blow out more than 500 ml. In this activity, you will be measuring the vital capacity (the greatest volume you can force out in one deep breath) and the tidal volume (the normal amount of air expelled in one breath) of your own lungs, this actual number can then be compared with a number derived from an equation that measures vital capacity. In effect, you are measuring an actual number, based on laboratory measurements, to a theoretical number, based on an equation. If you have any breathing difficulties (asthma or other condition), you should not participate in this activity, instead only take the data on your lab partner or group. Breathing in very deeply (your inspiratory reserve), then exhaling as much as you can (contracting your thoracic and abdominal muscles), can increase tidal volume to about 1.4 liters this is your expiratory reserve volume. The maximum amount of air moved in and out of the lungs is called your Vital Capacity. Some air that we breathe never even reaches our lungs - instead it fills our nasal cavities, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles. These passages aren't used in gas exchange so they are considered to be dead air space. To make sure that the inhaled air gets to the lungs, we need to breathe slowly and deeply. Even when we exhale deeply some air is still in the lungs (about 1,000 ml, or 1 Liter this is called the residual volume). This air isn't useful for gas exchange. There are certain types of diseases of the lung where residual volume builds up because the person cannot
3 fully empty the lungs. This means that the vital capacity is also reduced because their lungs are filled with useless air. Many things may affect your vital capacity including smoking, obesity, pregnancy, and how often you exercise. Fast- moving exercise causes your heart and breathing rates to increase, delivering fresh oxygen to your bloodstream and energy to your muscles. Your lung capacity can be increased through regular aerobic workouts, but only by a modest amount (5-15%). Specific changes in lung volumes also occur during pregnancy. Functional residual capacity drops 18 20% typically falling from 1.7 to 1.35 liters, due to the compression of the diaphragm by the uterus. Total lung capacity: the volume in the lungs at maximal inflation, the sum of VC TLC and RV. Tidal volume: that volume of air moved into or out of the lungs during quiet TV breathing (VT indicates a subdivision of the lung; when tidal volume is precisely measured, as in gas exchange calculation, the symbol VT or VT is used.) Residual volume: the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a maximal RV exhalation Expiratory reserve volume: the maximal volume of air that can be exhaled from ERV the end- expiratory position Inspiratory reserve volume: the maximal volume that can be inhaled from the IRV end- inspiratory level IC Inspiratory capacity: the sum of IRV and TV Inspiratory vital capacity: the maximum volume of air inhaled from the point of IVC maximum expiration VC Vital capacity: the volume of air breathed out after the deepest inhalation. VT Tidal volume: that volume of air moved into or out of the lungs during quiet breathing (VT indicates a subdivision of the lung; when tidal volume is precisely measured, as in gas exchange calculation, the symbol VT or VT is used.) Functional residual capacity: the volume in the lungs at the end- expiratory position
4 Average lung volumes in healthy adults Value (litres) Volume In men In women Inspiratory reserve volume Tidal volume Expiratory reserve volume Residual volume Vital Capacity Total In this lab we will investigate how lung volume (expiratory reserve volume) might differ as a result of heavy exercise. Materials: for each group: a two liter plastic soda bottle (clear, labels ripped off), 2 feet of aquarium tubing, plastic dishpan or shoebox, masking tape, pen.
5 Procedure: 1. Place a strip of masking tape down the side of the soda bottle. 2. Fill the soda bottle with water and screw the top on to bottle. 3. Fill dishpan ½ way full with water 4. Place soda bottle upside down in dishpan, so neck and opening are under water then remove the cap (one student needs to keep ahold of the bottle so that it remains upright. DO NOT allow air bubbles to enter the bottle). 5. Place one end of the aquarium tubing inside the bottle opening (under water) 6. Take a normal breath and exhale through the tubing. Your breath should displace the water in the bottle. 7. Mark the water level on the tape after you are done breathing out. 8. Refill bottle and return it to dishpan. 9. Take a very deep breath and try to exhale all that you possibly can through the tubing then mark the new water level on the tape. 10. Refill bottle and return it to dishpan. 11. Run up and down the stairs (or other physical cardio exercise) and then again take a deep breath and try to exhale all that you possibly can through the tubing then mark the third water level on the tape. 12. Now, calculate your normal vital capacity (expiratory reserve before exercise) using a formula you can then compare what you measured with the answer you get using just a formula. Male Vital Capacity Calculation = Body Surface Area * 2500 Female Vital Capacity = Body Surface Area * 2000 Where Body Surface Area = (SQRT ((height in cm * mass in kg)/3600)
6 Student Name AVERAGE (normal: tidal volume) (expiratory reserve volume: before exercise) (expiratory reserve volume: after exercise) Lung Capacity as calculated using formula Table 1. Data on lung capacity (liters) before and after strenuous exercise. Data Analysis: Make a bar graph of the average lung capacity (expiratory reserve) before and after heavy exercise. Are they different? Estimated Vital Capacity: Research has shown that the capacity of a person's lungs is proportional to the surface area of his or her body. To find the surface area, you will need to know your height and weight. There are a couple of different ways to calculate your body surface area mathematically. Either use the equation Body Surface Area = (SQRT ((height in cm * mass in kg)/3600) or go to a website that has an automatic calculator. Once you have calculated your surface area, a second equation will calculate your estimated vital capacity: Vital Capacity - Males: SA x 2500 Vital Capacity - Females SA x 2000 Extensions: Have students research different lung diseases. Try to Measure Tidal Volume by stretching a round balloon several times. Then, Inhale normally and then exhale normally into the balloon. Do not force your breathing. Pinch the end of the balloon and measure its diameter at the widest point (place balloon on a table, and hold a ruler up to it). Repeat this so that you have 3 total measurements and can take the average and record in the data table. Then, to measure Vital Capacity, repeat, only this time inhale as much air as you can and exhale our forcefully into the balloon.
7 Reflection Questions: How does lung capacity differ for people who live at high altitudes? (A person who is born and lives at sea level will develop a slightly smaller lung capacity than a person who spends their life at a high altitude. This is because the partial pressure of oxygen is lower at higher altitude, which as a result means that oxygen less readily diffuses into the bloodstream. In response to higher altitude, the body's diffusing capacity increases in order to process more air. When someone living at or near sea level travels to locations at high altitudes (like Denver, Colorado!) that person can develop a condition called altitude sickness because their lungs remove adequate amounts of carbon dioxide but they do not take in enough oxygen. (In normal individuals, buildup of carbon dioxide (not lack of oxygen) is the primary determinant of respiratory drive.) How does regular exercise change lung capacity? (In general regular exercise does not substantially change measures of pulmonary function such as total lung capacity, the volume of air in the lungs after taking the largest breath possible (TLC), and forced vital capacity, the amount of air able to be blown out after taking the largest breath possible (FVC). Studies comparing TLC and FVC show little difference between regular exercisers and non- exercisers, in fact. So even though people often report feeling out of breath or winded during exercise, it is unlikely that pulmonary function limits their ability to exercise, unless they have a disease that specifically impairs lung function such as asthma, bronchitis or emphysema. What we might see in this lab is that immediately after exercising, the student is so out of breath that their expiratory reserve is smaller but the amount of expiratory reserve you have should stay stable whether you are in shape or not). How does exercise help you get oxygen to your cells? (One of the largest differences between an exerciser and a nonexerciser concerns the heart's ability to pump blood and consequently deliver oxygen to working muscles. Cardiac output is a major limiting factor for prolonged exercise. In addition, an exerciser typically has a larger blood volume, is better able to extract oxygen from the air in the lungs and is better able to extract oxygen from the blood at the working muscles than a sedentary individual is. Gas exchange involves not only oxygen delivery but also the removal of carbon dioxide, which is a byproduct of energy metabolism, and this process is also more efficient in an exerciser. Fast- moving exercise causes your heart and breathing rates to increase, delivering fresh oxygen to your bloodstream and energy to your muscles.
8 Your lung capacity can be increased through regular aerobic workouts, but only by a modest amount. Regular aerobic exercise strengthens and tones the heart and lungs, enabling the pulmonary system to increase the maximum amount of oxygen that the lungs can handle. The average person s lung capacity can be improved only 5 percent to 15 percent even with frequent intense aerobic workouts). What might make your lung volume change? (Specific changes in lung volumes occur during pregnancy. Functional residual capacity drops 18 20% typically falling from 1.7 to 1.35 liters, due to the compression of the diaphragm by the uterus. During pregnancy, the mother s total lung capacity decreases and so does the expiratory reserve volume, though tidal volume increases about 30% - so enough oxygen reaches the fetus. Also,? (A person who is born and lives at sea level will develop a slightly smaller lung capacity than a person who spends their life at a high altitude. This is because the partial pressure of oxygen is lower at higher altitude, which as a result means that oxygen less readily diffuses into the bloodstream. In response to higher altitude, the body's diffusing capacity increases in order to process more air. When someone living at or near sea level travels to locations at high altitudes (like Denver, Colorado!) that person can develop a condition called altitude sickness because their lungs remove adequate amounts of carbon dioxide but they do not take in enough oxygen. (In normal individuals, buildup of carbon dioxide (not lack of oxygen) is the primary determinant of respiratory drive.) Why is it important to measure tidal volume and vital capacity three times and then get an average? (replication! - to be more confident in your data). Compare your data to other members of the class. How can you account for differences? (different sex, weight, height, some may exercise regularly, some may smoke, lung disease, genetics..) How does your measured vital capacity compare to the vital capacity you estimated using the formula? Which do you think is more accurate and why? (probably what you measured is more accurate. You could calculate percent error too!).
9 How might an athlete's vital capacity compare to a non- athlete? Explain your reasoning. (Your lung capacity can be increased through regular aerobic workouts, but only by a modest amount. Regular aerobic exercise strengthens and tones the heart and lungs, enabling the pulmonary system to increase the maximum amount of oxygen that the lungs can handle. The average person s lung capacity can be improved only 5 percent to 15 percent even with frequent intense aerobic workouts). Models and Explanations: In this lab we explored how heavy exercise might affect lung volumes, specifically expiratory reserve volumes. A student who demonstrates understanding of this concept can explain the difference between tidal volume, vital capacity, total lung volume, and inspiratory and expiratory reserve volumes and can explain several factors that might influence lung capacity (like sex, exercise, lung disease, height and weight, pregnancy, smoking.). This student will be able to discuss the results of his/her controlled experiment and reference the independent, dependent, and controlled variables. Bibliography: Barbeau, T., Camper, J., King, P., Knowles, T., Pike, L., Pryor, G., D., Eaton, E., and Turner, L. (2010). Biology 104 Laboratory: Human Biology. Francis Marion University custom publishing, Florence SC, USA. Boundless. (2014 ). and Volume. Boundless Anatomy and Physiology. Retrieved November 25, 2014 from anatomy- and- physiology- textbook/the- respiratory- system- 22/lung- volumes- and- capacities- 209/lung- capacity- and- volume / Campbell Biology (9 th edition). (2010). Benjamin Cummings Publishing. Mercks manual online. (2014) Airflow, lung volumes and the Flow- Volume Loop. Retrieved December 3, 2014 from onary_function_pft/airflow_lung_volumes_and_flow- volume_loop.html Measuring. (n.d.). Retrieved November 25, 2014 from
10 Student Worksheet: Lungs are balloon- like structures in the chest that are used to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide between your blood and the atmosphere. As you inhale (breathe in), air is drawn into your lungs. As you exhale (breathe out), you expel gases from your lungs. In the lungs, oxygen from inhaled air moves into your blood (the liquid in animals that carries nutrients and oxygen to cells and takes away wastes) and is carried to the cells throughout the body to produce energy. Also in the lungs, carbon dioxide (a gaseous waste) leaves the blood and enters tubes, then is expelled when you exhale. The breathing rate of a healthy adult at rest is about 12 times a minute. A baby breathes faster, about 30 times a minute. Student Name AVERAGE (normal: tidal volume) (expiratory reserve volume: before exercise) (expiratory reserve volume: after exercise) Lung Capacity as calculated using formula Table 1. Data on lung capacity (Liters) before and after strenuous exercise. Estimated Vital Capacity: Research has shown that the capacity of a person's lungs is proportional to the surface area of his or her body. To find the surface area, you will need to know your height and weight. There are a couple of different ways to calculate your body surface area mathematically. Either use the equation Body Surface Area = (SQRT ((height in cm * mass in kg)/3600) or go to a website that has an automatic calculator. Once you have calculated your surface area, a second equation will calculate your estimated vital capacity: Vital Capacity - Males: SA x 2500 Vital Capacity - Females SA x 2000 Height (cm) Mass (kg) Surface Area Vital Capacity
11 Reflection Questions: How does heavy exercise affect my lung volume (expiratory reserve)? How does lung capacity differ for people who live at high altitudes? What other factors might make your lung volume change? Why is it important to measure tidal volume and vital capacity three times and then get an average? Compare your data to other members of the class. How can you account for differences? How does your measured vital capacity compare to the vital capacity you estimated using the formula? Which do you think is more accurate and why? How might an athlete's vital capacity compare to a non- athlete? Explain your reasoning.
Respiratory System Lab
 Respiratory System Lab Note: Review the safety materials and wear goggles when working with chemicals. Read the entire exercise before you begin. Take time to organize the materials you will need and set
Respiratory System Lab Note: Review the safety materials and wear goggles when working with chemicals. Read the entire exercise before you begin. Take time to organize the materials you will need and set
The physiological functions of respiration and circulation. Mechanics. exercise 7. Respiratory Volumes. Objectives
 exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
Honors Physiology The Respiratory System
 Honors Physiology Name: The Respiratory System Objective: To create a model of our respiratory system, understanding the relationship between structure and function. Warm Up Questions: 1. What is the function
Honors Physiology Name: The Respiratory System Objective: To create a model of our respiratory system, understanding the relationship between structure and function. Warm Up Questions: 1. What is the function
Measuring Lung Capacity
 Measuring Lung Capacity 1 Name Measuring Lung Capacity Background Information: We need a constant supply of oxygen in order to stay alive. We use oxygen to break down food to release energy and produce
Measuring Lung Capacity 1 Name Measuring Lung Capacity Background Information: We need a constant supply of oxygen in order to stay alive. We use oxygen to break down food to release energy and produce
A Liter a Lung Measuring Lung Capacity
 A Liter a Lung Measuring Lung Capacity OBJECTIVE In this investigation, students will compare the actual and expected vital capacities of their classmates. LEVEL Middle Grades Life Science CONNECTIONS
A Liter a Lung Measuring Lung Capacity OBJECTIVE In this investigation, students will compare the actual and expected vital capacities of their classmates. LEVEL Middle Grades Life Science CONNECTIONS
Lab 3. The Respiratory System (designed by Heather E. M. Liwanag with T.M. Williams)
 Name Lab Partners Lab 3. The Respiratory System (designed by Heather E. M. Liwanag with T.M. Williams) Part 1. Lung Volumes and Capacities Objectives 1. Obtain graphical representation of lung capacities
Name Lab Partners Lab 3. The Respiratory System (designed by Heather E. M. Liwanag with T.M. Williams) Part 1. Lung Volumes and Capacities Objectives 1. Obtain graphical representation of lung capacities
Cornell Institute for. Biology Teachers. Respirometry Part I: Lung Volumes and Capacities. Lab issue/rev. date: 12/12/96. Title:
 Cornell Institute for Biology Teachers Copyright Cornell Institute for Biology Teachers, 1999. This work may be copied by the original recipient from CIBT to provide copies for users working under the
Cornell Institute for Biology Teachers Copyright Cornell Institute for Biology Teachers, 1999. This work may be copied by the original recipient from CIBT to provide copies for users working under the
Measuring Lung Capacity
 Name Class Date Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Measuring Lung Capacity Introduction The amount of air that you move in and out of your lungs depends on how quickly you are breathing. The
Name Class Date Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Measuring Lung Capacity Introduction The amount of air that you move in and out of your lungs depends on how quickly you are breathing. The
CHAPTER 3: The cardio-respiratory system
 : The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
: The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
April KHALED MOUSA BACHA. Physiology #2. Dr. Nayef AL-Gharaibeh. Pulmonary volumes & capacities
 25 th April Physiology #2 Pulmonary volumes & capacities Dr. Nayef AL-Gharaibeh KHALED MOUSA BACHA We will start this lecture by explaining an important concept from the previous one: Intrapleural pressure
25 th April Physiology #2 Pulmonary volumes & capacities Dr. Nayef AL-Gharaibeh KHALED MOUSA BACHA We will start this lecture by explaining an important concept from the previous one: Intrapleural pressure
Collin County Community College. Lung Physiology
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 9 Respiratory System 1 Lung Physiology Factors affecting Ventillation 1. Airway resistance Flow = Δ P / R Most resistance is encountered
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 9 Respiratory System 1 Lung Physiology Factors affecting Ventillation 1. Airway resistance Flow = Δ P / R Most resistance is encountered
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system
 CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
Respiration Lab Instructions
 Respiration Lab Instructions This laboratory investigation can be performed in any order. Be sure to read all instructions for each section before performing the experiment. PART 1 STUDENT WET SPIROMETER
Respiration Lab Instructions This laboratory investigation can be performed in any order. Be sure to read all instructions for each section before performing the experiment. PART 1 STUDENT WET SPIROMETER
Respiratory System Review
 KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
Physiology of the Respiratory System
 Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Physiology of the Respiratory System References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Physiology of the Respiratory System References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning
LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
 66 LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB Assignments: Due before lab: Quiz: Three Respiratory Interactive Physiology Animations pages 69 73. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
66 LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB Assignments: Due before lab: Quiz: Three Respiratory Interactive Physiology Animations pages 69 73. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
Gas Exchange ACTIVITY OVERVIEW SUMMARY KEY CONCEPTS AND PROCESS SKILLS KEY VOCABULARY. Teacher s Guide B-75 L A B O R ATO R Y
 Gas Exchange 17 40- to 2 50-minute sessions ACTIVITY OVERVIEW L A B O R ATO R Y SUMMARY This activity explores the role of the respiratory system in the regulation of gases in the blood. Students investigate
Gas Exchange 17 40- to 2 50-minute sessions ACTIVITY OVERVIEW L A B O R ATO R Y SUMMARY This activity explores the role of the respiratory system in the regulation of gases in the blood. Students investigate
3/24/2009 LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD. 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm 1 KEY WORDS TO KNOW BOYLE S LAW INTERCOSTAL NERVES PHRENIC NERVE DIAPHRAGM EXTERNAL INTERCOSTAL
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm 1 KEY WORDS TO KNOW BOYLE S LAW INTERCOSTAL NERVES PHRENIC NERVE DIAPHRAGM EXTERNAL INTERCOSTAL
PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Parts of the Respiratory System The RS can be divided into two parts: 1. Respiratory Tract, (path that air follows). Nasal passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi,
PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Parts of the Respiratory System The RS can be divided into two parts: 1. Respiratory Tract, (path that air follows). Nasal passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi,
Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class
 I. Name the following : Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class 1. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. 2. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous
I. Name the following : Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class 1. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. 2. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous
Lung Volumes and Capacities
 Lung Volumes and Capacities Normally the volume of air entering the lungs during a single inspiration is approximately equal to the volume leaving on the subsequent expiration and is called the tidal volume.
Lung Volumes and Capacities Normally the volume of air entering the lungs during a single inspiration is approximately equal to the volume leaving on the subsequent expiration and is called the tidal volume.
Mechanisms of Breathing. Vital Capacity
 Mechanisms of Breathing Mechanics of Breathing Two muscles are involved in the mechanics of breathing: Diaphragm = large sheet of muscle located beneath the lungs that is the primary muscle in breathing
Mechanisms of Breathing Mechanics of Breathing Two muscles are involved in the mechanics of breathing: Diaphragm = large sheet of muscle located beneath the lungs that is the primary muscle in breathing
Name Date of Data Collection. Class Period Lab Days/Period Teacher. Measuring Lung Capacity
 Measuring Lung Capacity Background: The amount of air that you move in and out of your lungs while breathing normally is referred to as TIDAL VOLUME. While it is possible to inhale and exhale more forcefully
Measuring Lung Capacity Background: The amount of air that you move in and out of your lungs while breathing normally is referred to as TIDAL VOLUME. While it is possible to inhale and exhale more forcefully
Human gas exchange. Question Paper. Save My Exams! The Home of Revision. Cambridge International Examinations. 56 minutes. Time Allowed: Score: /46
 Human gas exchange Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International Examinations Respiration Human gas exchange Question Paper Time llowed: 56 minutes
Human gas exchange Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International Examinations Respiration Human gas exchange Question Paper Time llowed: 56 minutes
25/4/2016. Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten
 25/4/2016 Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten Respiratory System Introduction: - We breath while we are sleeping, talking, working and resting. - Respiratory diseases are abundant
25/4/2016 Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten Respiratory System Introduction: - We breath while we are sleeping, talking, working and resting. - Respiratory diseases are abundant
OB11 Carry out qualitative tests to compare the carbon dioxide levels of inhaled and exhaled air
 Biology: 5. Respiration and Breathing Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier OB9 Syllabus Describe the process of aerobic respiration
Biology: 5. Respiration and Breathing Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier OB9 Syllabus Describe the process of aerobic respiration
Respiratory system & exercise. Dr. Rehab F Gwada
 Respiratory system & exercise Dr. Rehab F Gwada Objectives of lecture Outline the major anatomical components & important functions of the respiratory system. Describe the mechanics of ventilation. List
Respiratory system & exercise Dr. Rehab F Gwada Objectives of lecture Outline the major anatomical components & important functions of the respiratory system. Describe the mechanics of ventilation. List
Introduction. Respiration. Chapter 10. Objectives. Objectives. The Respiratory System
 Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
Capnography in the Veterinary Technician Toolbox. Katie Pinner BS, LVT Bush Advanced Veterinary Imaging Richmond, VA
 Capnography in the Veterinary Technician Toolbox Katie Pinner BS, LVT Bush Advanced Veterinary Imaging Richmond, VA What are Respiration and Ventilation? Respiration includes all those chemical and physical
Capnography in the Veterinary Technician Toolbox Katie Pinner BS, LVT Bush Advanced Veterinary Imaging Richmond, VA What are Respiration and Ventilation? Respiration includes all those chemical and physical
practices makes perfect
 Human Respiratory system Chapter 1: Respiration PMR 03, 08 1. The human respiratory system consists of: a... b... c.. d... e. Our body has.. lungs (right & left). f. Each lung consists of the, and alveoli.
Human Respiratory system Chapter 1: Respiration PMR 03, 08 1. The human respiratory system consists of: a... b... c.. d... e. Our body has.. lungs (right & left). f. Each lung consists of the, and alveoli.
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system. Objective sheet 3 Notes
 1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
Sc ienc e 9-Biology Work sheet 8-2 A Single Breat h & Tak ing Care
 Unit 2 Your Living Body Sc ienc e 9-Biology Work sheet 8-2 A Single Breat h & Tak ing Care Name No pen or pencil No Textbook 20 Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Read pages 159-167
Unit 2 Your Living Body Sc ienc e 9-Biology Work sheet 8-2 A Single Breat h & Tak ing Care Name No pen or pencil No Textbook 20 Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Read pages 159-167
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System
 Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
RESPIRATION AND EXCRETION
 CHAPTER 13 RESPIRATION AND EXCRETION SECTION 13 1 The Respiratory System (pages 430-438) This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Introduction
CHAPTER 13 RESPIRATION AND EXCRETION SECTION 13 1 The Respiratory System (pages 430-438) This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Introduction
Structures of the Respiratory System include:
 Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
Respiratory Physiology
 Respiratory Physiology Background Information: When inspiring, the pleura attached to the internal chest wall is pulled outward as the thoracic cavity expands. The pleural cavity [space between the outer
Respiratory Physiology Background Information: When inspiring, the pleura attached to the internal chest wall is pulled outward as the thoracic cavity expands. The pleural cavity [space between the outer
Video. Respiration System. You will use 3 pages of your journal for this lesson. 1. One page for hand written notes onto a journal page
 Respiratory System Video Respiration System You will use 3 pages of your journal for this lesson. 1. One page for hand written notes onto a journal page 2. 2 nd page for diagram 3. 3 rd page for chart
Respiratory System Video Respiration System You will use 3 pages of your journal for this lesson. 1. One page for hand written notes onto a journal page 2. 2 nd page for diagram 3. 3 rd page for chart
Pulmonary Function I (modified by C. S. Tritt, April 10, 2006) Volumes and Capacities
 I. Introduction Pulmonary Function I (modified by C. S. Tritt, April 10, 2006) Volumes and Capacities The volume of air a person inhales (inspires) and exhales (expires) can be measured with a spirometer
I. Introduction Pulmonary Function I (modified by C. S. Tritt, April 10, 2006) Volumes and Capacities The volume of air a person inhales (inspires) and exhales (expires) can be measured with a spirometer
 Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
Respiratory System Physiology. Dr. Vedat Evren
 Respiratory System Physiology Dr. Vedat Evren Respiration Processes involved in oxygen transport from the atmosphere to the body tissues and the release and transportation of carbon dioxide produced in
Respiratory System Physiology Dr. Vedat Evren Respiration Processes involved in oxygen transport from the atmosphere to the body tissues and the release and transportation of carbon dioxide produced in
Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired
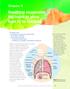 Chapter 6 Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired This chapter covers: the structure of the human gas exchange system the mechanism of breathing gas exchange in the alveoli the concept
Chapter 6 Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired This chapter covers: the structure of the human gas exchange system the mechanism of breathing gas exchange in the alveoli the concept
1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives
 1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives To understand the functions of the circulatory system. To be able to identify the differences between veins, arteries
1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives To understand the functions of the circulatory system. To be able to identify the differences between veins, arteries
The Respiratory System
 Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, complete the flowchart
Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, complete the flowchart
Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation. Chad & Angela
 Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation Chad & Angela Respiratory Structures Basic Structures of Respiration Nasal/Oral Cavities Larynx Trachea Bronchi Secondary Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Mechanics of Ventilation
Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation Chad & Angela Respiratory Structures Basic Structures of Respiration Nasal/Oral Cavities Larynx Trachea Bronchi Secondary Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Mechanics of Ventilation
TV = Tidal volume (500ml) IRV = Inspiratory reserve volume (3,000 ml)
 By: Amin alajlouni Lec: 2nd record Date: 29/10/2017 First of all, this is my first sheet so excuse any mistakes I might make and let's start: As we said before in our last lecture about lung capacities
By: Amin alajlouni Lec: 2nd record Date: 29/10/2017 First of all, this is my first sheet so excuse any mistakes I might make and let's start: As we said before in our last lecture about lung capacities
The Respiratory System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Organs of the Respiratory system
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Organs of the Respiratory system
Chapter 1: Respiration
 Chapter 1: Respiration Respiration Human Breathing Mechanism Transport of oxygen Importance of a healthy respiratory system Respiratory system lungs inhalation exhalation Diffusion of oxygen by blood Transport
Chapter 1: Respiration Respiration Human Breathing Mechanism Transport of oxygen Importance of a healthy respiratory system Respiratory system lungs inhalation exhalation Diffusion of oxygen by blood Transport
Fashionable, don t you think?
 Fashionable, don t you think? 1. Passageway 2. Structure 3. Passageway 4. What is the name of the structure labeled with # 9 in the model at left? 5. What is the name of the structure labeled with # 11
Fashionable, don t you think? 1. Passageway 2. Structure 3. Passageway 4. What is the name of the structure labeled with # 9 in the model at left? 5. What is the name of the structure labeled with # 11
BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
 96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The tissues exchange O 2 directly with the air in
96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The tissues exchange O 2 directly with the air in
Name period date assigned date due date returned
 Name period date assigned date due date returned procedure 1. Take one balloon and stretch it out 2. Take one deep breath and blow into the balloon until you cannot breath out anymore. Do Not Take A Second
Name period date assigned date due date returned procedure 1. Take one balloon and stretch it out 2. Take one deep breath and blow into the balloon until you cannot breath out anymore. Do Not Take A Second
The Breathing System
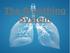 The Breathing System Learning Intentions 1. Students should Know how Breathing happens 2. Name and know the functions of the Breathing System 3. Know how the organs work and how they work with other systems
The Breathing System Learning Intentions 1. Students should Know how Breathing happens 2. Name and know the functions of the Breathing System 3. Know how the organs work and how they work with other systems
inquiry question How does the respiratory system contribute to energy production for movement? UNCORRECTED PAGE PROOFS
 inquiry question How does the respiratory system contribute to energy production for movement? chapter 7 Structure and functions of the respiratory system The respiratory system is the starting point for
inquiry question How does the respiratory system contribute to energy production for movement? chapter 7 Structure and functions of the respiratory system The respiratory system is the starting point for
2.1.1 List the principal structures of the
 physiology 2.1.1 List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx -
physiology 2.1.1 List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx -
BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
 96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The cell exchange O 2 directly with the air in the
96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The cell exchange O 2 directly with the air in the
A breath of fresh air
 A breath of fresh air BIG IDEAS You are learning to: Describe the structure of the lungs Explain how the lungs clean themselves Interpret patterns in data Where are the lungs and what do they do? The lungs
A breath of fresh air BIG IDEAS You are learning to: Describe the structure of the lungs Explain how the lungs clean themselves Interpret patterns in data Where are the lungs and what do they do? The lungs
Respiration. The resspiratory system
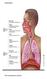 Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
Respiratory System Homework
 Respiratory System Homework The R S is the body s breathing equipment. Similar to the D system, it takes S from outside the body (G, particularly O ), circulates them through the body to C and T, then
Respiratory System Homework The R S is the body s breathing equipment. Similar to the D system, it takes S from outside the body (G, particularly O ), circulates them through the body to C and T, then
Human Respiration Laboratory Experiment By
 Human Respiration Laboratory Experiment By Alison L., Thurow, Brittany Baierlein, Rachel C. Holsinger and Robin L. Cooper Department of Biology, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY 40506 0225, USA. Purpose:
Human Respiration Laboratory Experiment By Alison L., Thurow, Brittany Baierlein, Rachel C. Holsinger and Robin L. Cooper Department of Biology, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY 40506 0225, USA. Purpose:
You Are Really Full of Hot Air!
 You Are Really Full of Hot Air! Student Information Page 5B Activity Introduction: You re just full of hot air! How many times has someone said this to you when they didn t quite believe what you were
You Are Really Full of Hot Air! Student Information Page 5B Activity Introduction: You re just full of hot air! How many times has someone said this to you when they didn t quite believe what you were
SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION
 SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION WHEN WE BREATHE, WHAT DO WE BREATHE IN? O2, N2, CO2, O3, NO2 (gas fumes), CO, pollutant, fragrants, toxins, etc. WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF BREATHING IN? WHAT DOES OUR BODY WANT? O2 WHY?
SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION WHEN WE BREATHE, WHAT DO WE BREATHE IN? O2, N2, CO2, O3, NO2 (gas fumes), CO, pollutant, fragrants, toxins, etc. WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF BREATHING IN? WHAT DOES OUR BODY WANT? O2 WHY?
Outline - Respiratory System. Function of the respiratory system Parts of the respiratory system Mechanics of breathing Regulation of breathing
 Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
Chapter 9 Airway Respirations Metabolism Oxygen Requirements Respiratory Anatomy Respiratory Anatomy Respiratory Anatomy Diaphragm
 1 Chapter 9 Airway 2 Respirations Every cell of the body requires to survive Oxygen must come in and carbon must go out 3 Metabolism Metabolism--Process where the body s cells convert food to Adequate
1 Chapter 9 Airway 2 Respirations Every cell of the body requires to survive Oxygen must come in and carbon must go out 3 Metabolism Metabolism--Process where the body s cells convert food to Adequate
Lung Volumes and Capacities
 BIOL242 Lung Volumes and Capacities Measurement of lung volumes provides a tool for understanding normal function of the lungs as well as disease states. The breathing cycle is initiated by expansion of
BIOL242 Lung Volumes and Capacities Measurement of lung volumes provides a tool for understanding normal function of the lungs as well as disease states. The breathing cycle is initiated by expansion of
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at gaseous exchange in humans in terms of o Ventilation o Inspiration o Expiration o Transport of gases o Homeostatic
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at gaseous exchange in humans in terms of o Ventilation o Inspiration o Expiration o Transport of gases o Homeostatic
Glucose + Oxygen Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy C6H12O CO2 + 6H20 + energy
 Cell Respiration - A food oxidization process in body cells to produce energy - Occurs (happens) in animal cells and plant cells Notes : Metabolic Reactions in Gaseous Exchange CELL RESPIRATION Photosynthesis
Cell Respiration - A food oxidization process in body cells to produce energy - Occurs (happens) in animal cells and plant cells Notes : Metabolic Reactions in Gaseous Exchange CELL RESPIRATION Photosynthesis
Respiratory/Pulmonary Laboratory Experimentation
 Respiratory/Pulmonary Laboratory Experimentation Introduction Anatomy Review The respiratory system has the dubious honor of being the system that permits the transport of gases from the environment inside
Respiratory/Pulmonary Laboratory Experimentation Introduction Anatomy Review The respiratory system has the dubious honor of being the system that permits the transport of gases from the environment inside
Respiration - Human 1
 Respiration - Human 1 At the end of the lectures on respiration you should be able to, 1. Describe events in the respiratory processes 2. Discuss the mechanism of lung ventilation in human 3. Discuss the
Respiration - Human 1 At the end of the lectures on respiration you should be able to, 1. Describe events in the respiratory processes 2. Discuss the mechanism of lung ventilation in human 3. Discuss the
Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation
 Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing and the first step in the respiratory process. Pulmonary ventilation brings in air with a new supply
Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing and the first step in the respiratory process. Pulmonary ventilation brings in air with a new supply
The Respiratory System
 Science Unit: Lesson 4: Human Anatomy How Do We Move? The Respiratory System School year: 2007/2008 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Henderson Annex Elementary School, Vancouver
Science Unit: Lesson 4: Human Anatomy How Do We Move? The Respiratory System School year: 2007/2008 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Henderson Annex Elementary School, Vancouver
Restrictive and Obstructive Airway Diseases
 iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HS-8-1 Restrictive and Obstructive Airway Diseases Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should refer to the User
iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HS-8-1 Restrictive and Obstructive Airway Diseases Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should refer to the User
Monday, ! Today: Respiratory system! 5/20/14! Transport of Blood! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing!
 Monday, 5.19.14! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing! Transport of Blood! What is transported! Nutrients! Oxygen! Carbon Dioxide! Hormones! Antibodies! What it is/does!
Monday, 5.19.14! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing! Transport of Blood! What is transported! Nutrients! Oxygen! Carbon Dioxide! Hormones! Antibodies! What it is/does!
Respiration. The ins and outs
 Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
respiratory cycle. point in the volumes: 500 milliliters. for men. expiration, up to 1200 milliliters extra makes breathing Respiratory
 10 II. RESPIRATORY VOLUMES, CAPACITIES & PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS Respiratory volume is the term used for various volumes of air moved by or associated with the lungs at a given point in the respiratory
10 II. RESPIRATORY VOLUMES, CAPACITIES & PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS Respiratory volume is the term used for various volumes of air moved by or associated with the lungs at a given point in the respiratory
Then the partial pressure of oxygen is x 760 = 160 mm Hg
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: the uptake of molecular oxygen (O2) from the environment and the discharge of
1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: the uptake of molecular oxygen (O2) from the environment and the discharge of
The Respiration System in Humans. Madeline Pitman. Group Members: Kathryn Hillegass Michelle Liu Noelle Owen. Section 62 Danielle Cooper
 1 The Respiration System in Humans Madeline Pitman Group Members: Kathryn Hillegass Michelle Liu Noelle Owen Section 62 Danielle Cooper August 11, 2014 2 A. Introduction Experiment Goals The experiment
1 The Respiration System in Humans Madeline Pitman Group Members: Kathryn Hillegass Michelle Liu Noelle Owen Section 62 Danielle Cooper August 11, 2014 2 A. Introduction Experiment Goals The experiment
Living with. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPD. Breathing and Relaxation
 Living with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPD Breathing and Relaxation Anatomy and Physiology of COPD Breathing Techniques Positions to Reduce Shortness of Breath Relaxation Exercise Breathing
Living with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPD Breathing and Relaxation Anatomy and Physiology of COPD Breathing Techniques Positions to Reduce Shortness of Breath Relaxation Exercise Breathing
RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE
 RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE Respiration Respiration delivery of oxygen to and removal of carbon dioxide from the tissue External respiration ventilation and exchange of gases in the lung Internal
RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE Respiration Respiration delivery of oxygen to and removal of carbon dioxide from the tissue External respiration ventilation and exchange of gases in the lung Internal
Breathing. Physics of Breathing 11/14/2011. Function of Respiratory Tract. Structure of Respiratory Tract. Parts of the Respiratory Tract
 Breathing Function of Respiratory Tract The respiratory tract is a series of spaces and semirigid tubes designed to convey air into and out of the respiratory organs (lungs). Parts of the Respiratory Tract
Breathing Function of Respiratory Tract The respiratory tract is a series of spaces and semirigid tubes designed to convey air into and out of the respiratory organs (lungs). Parts of the Respiratory Tract
Exercise and Respiration Rate
 Activity 17 PS-2820 Physiology: Breathing, respiration rate Exercise and Respiration Rate DataStudio GLX setup file: respiration.glx Qty Equipment and Materials Part Number 1 PASPORT Xplorer GLX PS-2002
Activity 17 PS-2820 Physiology: Breathing, respiration rate Exercise and Respiration Rate DataStudio GLX setup file: respiration.glx Qty Equipment and Materials Part Number 1 PASPORT Xplorer GLX PS-2002
Part 1: Inspiratory and expiratory pressures
 BIOEN 327 Autumn 2013 Experimental procedures Throughout these experiments, record in your notebook the purpose of the experiments, the methods you used, and the results. Where possible, make predictions
BIOEN 327 Autumn 2013 Experimental procedures Throughout these experiments, record in your notebook the purpose of the experiments, the methods you used, and the results. Where possible, make predictions
Chapter 16 Respiratory System
 Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
The Respiratory System
 Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
LAB 3: RESPIRATORY MECHANICS
 BIOEN 327 Autumn 2012 LAB 3: RESPIRATORY MECHANICS Pressures throughout the cardiovascular system are important for the health of the body and of the system itself. Today we explore pulmonary pressures
BIOEN 327 Autumn 2012 LAB 3: RESPIRATORY MECHANICS Pressures throughout the cardiovascular system are important for the health of the body and of the system itself. Today we explore pulmonary pressures
Gas Exchange in Animals. Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2. Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial
 Gas Exchange in Animals Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2 Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial Respiratory surface! skin, gills, lungs Circulatory System O2/CO2
Gas Exchange in Animals Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2 Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial Respiratory surface! skin, gills, lungs Circulatory System O2/CO2
Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy. Haneul Lee, DSc, PT
 Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy Haneul Lee, DSc, PT OBJECTIVE 1. Explain the principle physiological function of the pulmonary system 2. Outline the major anatomical components of the respiratory system.
Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy Haneul Lee, DSc, PT OBJECTIVE 1. Explain the principle physiological function of the pulmonary system 2. Outline the major anatomical components of the respiratory system.
Respiratory Physiology. ED Primary Teaching
 Respiratory Physiology ED Primary Teaching Functions of the respiratory system Gas exchange with O2 and CO2 Surfactant production Defence - IgA and macrophages Filer - pollutants and thromboembolism Metabolises
Respiratory Physiology ED Primary Teaching Functions of the respiratory system Gas exchange with O2 and CO2 Surfactant production Defence - IgA and macrophages Filer - pollutants and thromboembolism Metabolises
Chapter 22 Gas Exchange
 Chapter 22 Gas Exchange PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction: Surviving in Thin Air
Chapter 22 Gas Exchange PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction: Surviving in Thin Air
Then the partial pressure of oxygen is. b) Gases will diffuse down a pressure gradient across a respiratory surface if it is: i) permeable ii) moist
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: Relies on the diffusion of gases down pressure gradients. At sea level, atmosphere
1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: Relies on the diffusion of gases down pressure gradients. At sea level, atmosphere
The Respiratory System. Medical Terminology
 The Respiratory System Medical Terminology The respiratory system is where gas exchange occurs via respiration; inhalation/exhalation. pick up oxygen from inhaled air expels carbon dioxide and water sinus
The Respiratory System Medical Terminology The respiratory system is where gas exchange occurs via respiration; inhalation/exhalation. pick up oxygen from inhaled air expels carbon dioxide and water sinus
REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE 24 SEPTEMBER 2014 Lesson Description
 REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE 24 SEPTEMBER 2014 Lesson Description In this lesson, we revise: Gaseous Exchange in Plants & Animals Gaseous Exchange in Humans Excretion in Humans Focus on the Kidney Gaseous
REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE 24 SEPTEMBER 2014 Lesson Description In this lesson, we revise: Gaseous Exchange in Plants & Animals Gaseous Exchange in Humans Excretion in Humans Focus on the Kidney Gaseous
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 11 Respiratory System 2 Pulmonary Ventilation Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session plan o Pulmonary Ventilation
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 11 Respiratory System 2 Pulmonary Ventilation Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session plan o Pulmonary Ventilation
4/18/12 MECHANISM OF RESPIRATION. Every Breath You Take. Fun Facts
 Objectives MECHANISM OF RESPIRATION Dr Badri Paudel Explain how the intrapulmonary and intrapleural pressures vary during ventilation and relate these pressure changes to Boyle s law. Define the terms
Objectives MECHANISM OF RESPIRATION Dr Badri Paudel Explain how the intrapulmonary and intrapleural pressures vary during ventilation and relate these pressure changes to Boyle s law. Define the terms
SCIENCE- NOTES. Q1. Draw the diagram of human respiratory system and explain the function of the following parts:
 SCIENCE- NOTES NAME: RESPIRATION IN ORGANISMS STD.VII DIV: Q1. Draw the diagram of human respiratory system and explain the function of the following parts: i. Nasal cavity ii. Trachea iii. Lungs iv. Bronchioles
SCIENCE- NOTES NAME: RESPIRATION IN ORGANISMS STD.VII DIV: Q1. Draw the diagram of human respiratory system and explain the function of the following parts: i. Nasal cavity ii. Trachea iii. Lungs iv. Bronchioles
Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system
 Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system 1. Name the following : i. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. ii. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous rings.
Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system 1. Name the following : i. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. ii. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous rings.
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange
 Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System
 Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System Animals require a continuous supply of oxygen (O 2 ) for cellular respiration, and they must expel carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), the waste product of this
Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System Animals require a continuous supply of oxygen (O 2 ) for cellular respiration, and they must expel carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), the waste product of this
You Might Also Like. I look forward helping you focus your instruction while saving tons of time. Kesler Science Station Lab Activities 40%+ Savings!
 Thanks Connect Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over
Thanks Connect Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over
UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 9.01 GENERAL FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. Brings oxygenated air to the alveoli B. Removes air containing carbon dioxide C. Filters, warms, and humidifies
UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 9.01 GENERAL FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. Brings oxygenated air to the alveoli B. Removes air containing carbon dioxide C. Filters, warms, and humidifies
