MCHS-Mankato Cytology. Cytology Specimens
|
|
|
- Lester Stokes
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MCHS-Mankato Cytology Cytology Specimens PURPOSE / PRINCIPLE The acceptance of cytopathology as a current and valid discipline in medicine is largely due to the work of George N. Papanicolaou, MD. Papanicolaou began to publish material on the cytologic method and in 1928 suggested that this method was of value in the screening and diagnosis of cervical cancer. The use of cytology as a diagnostic tool may be applied to any organ or fluid from the body. The specimen may be exfoliated cells in a fluid such as urine, sputum, pleural, etc. or cells that have been more forcibly removed by a scraper, brush, or needle. These specimens would include both liquid based and conventional pap smears, specimens from endoscopic brushings, and fine needle aspirations. QUALITY ASSURANCE Pap smear screening is performed by cytotechnologists (registered or registry eligible by the American Society of Clinical Pathologists). Pathologists (physicians who are certified by the American Board of Pathology) perform interpretation of reactive/reparative changes and all cellular abnormalities on pap smears and all interpretations on non-gynecological cytology. Supervisory eligible personnel rescreen approximately 10% of all negative cases to confirm the original diagnosis and reduce the percentage of false negative findings. Quality assurance monitors evaluate on an on- going basis the performance of all testing personnel as well as the performance of the overall laboratory. Continuing education and quality assurance conferences are held regularly between pathologists and cytotechnologists to discuss educational, difficult, interesting or unusual cases. SPECIMENS Cytology Collection Supplies Cytology requisitions ThinPrep containers and collection devices Glass slides for conventional pap smears Spray fixative 50% alcohol containers for non-gyn cytology specimens Sputum cytology containers-saccomanno (green) fluid. Plastic/cardboard slide carriers Specimen transport bags Requisition Cytology specimens must be submitted with a properly filled-out cytology requisition in order to process the specimen. A separate cytology requisition should be submitted for each source/specimen site. If concurrent biopsy material is also submitted, it should be submitted with a corresponding histology requisition. The requisition contains an area for patient demographics (name, address, DOB/ age), social security number (optional), and specimen collection date, submitting physician name, patient medical record or chart number, and billing instructions. Insurance information can be provided on an insurance sheet from your institution. The requisition also contains an area for the source and site of specimens as well as an area to request additional testing. Requisitions come preprinted with a facility name and their corresponding requestor number on them, make sure your facility name is on the requisition. Do not use requisitions from another institution as it may delay the results. Pertinent history and clinical information as it relates to the specimen should be provided using the reference below. Gynecologic Specimens Date of last menstrual period (LMP) Pregnant or Post-Partum Non-Gynecologic Specimens Clinical diagnosis and history History of cancer type and location Page 1 of 11
2 History of IUD Abnormal bleeding Recent intrauterine instrumentation Radiation therapy Endometriosis Polyps Visible lesion(s) DES exposure in utero Recent colposcopy or biopsy (provide diagnosis) Herpes HPV (condyloma) Hormone therapy/ birth control pills Previous abnormal cytology cases should provide: Date of previous abnormal Treatment Normal subsequent cytology cases TB, liver cirrhosis, congestive heart failure, etc. Radiologic findings to date, suspected lesion Any systemic disease Dyspnea Hemoptysis Radiation therapy (date, reason and location) Drug therapy or other medications Hormone therapy Exposure to carcinogens Tobacco use (specify) Recent viral infections Unexplained, continued weight loss Occupation (if relevant) Past abnormal cytology Specimen Labeling All primary specimen containers MUST be labeled with two (2) identifiers at the time of collection. Submitted slides may be labeled with a single identifier, but 2 identifiers are preferred. Examples of acceptable identifiers include but are not limited to: patient name, date of birth (DOB), hospital number, requisition number, accession number, or a unique random number. A location (e.g., hospital room number or surgical suite number) is NOT an acceptable identifier. Specimen Transport of Cytology Specimens For all specimens submitted on glass slides the patient s name should be legibly printed (pencil or indelible ink) on the frosted end of each glass slide. For non-gynecologic specimens, each specimen container must be labeled with the patient s name and the specimen type / site and second identifier. Pap smears should be placed into plastic or cardboard slide containers and then into the plastic biohazard transport bag (1 specimen/bag). Non-gynecologic specimens that are submitted as fluids should be transported in a sealable container, and placed in a plastic transport bag whenever possible. For all specimens the transport bag should be securely zipped shut and the requisition placed into the pocket on the outside of the bag. Specimen Rejection of Cytology Specimens Cytology specimens submitted without a patient name on the specimen will be returned to the client for patient identification. We are required to verify patient identification for all specimens submitted. Specimens which cannot be processed or tested due to inadequate fixation, leaking specimen containers, slides received shattered beyond repair etc. will not be processed. A report indicating the reason for specimen rejection will be issued to the client and no charges will be made for those specimens. Every attempt will be made to prevent delay in testing or compromised results for the safety of you and your patient. Fixation Methods Immediate fixation of cytology specimens is critical to the preservation of the cellular components. It is important that no air-drying occurs prior to fixation. If a smear is already air-dried it should not be put in alcohol fixative. Please note on the requisition and on the slides when submitting both fixed and air-dried slides. Formalin fixation is not appropriate for cytology specimens. Specimens should not be exposed to formalin or formalin fumes. This alters the cells and interferes with the staining reactions. There are several fixation techniques available, depending on the type and volume of the specimen. See specimen collection techniques and fixation procedures for specific details. Page 2 of 11
3 1. Spray Fixative suitable for specimens that are submitted on a slide(s). This would include specimens such as Pap smears, FNA specimens, and endoscopic brushing specimens % alcohol (usually used within a Coplin jar) - suitable for specimens that are submitted on a slide(s). This would include specimens such as Pap smears, FNA specimens, and endoscopic brushing specimens. The slides should be immersed in the alcohol for a minimum of 15 minutes. Alternatively, the fixative may be pipetted onto a slide until the smear is totally saturated and then allowed to dry. 3. Saccomanno Collection Fluid a green colored fixative for the collection of sputum % Alcohol - a clear fixative for the collection of fluid specimens. A 50/50 ratio of specimen to fixative is appropriate. Quick Reference Guide to Fixation Techniques Specimen Type Recommended Fixation Technique Comments Large Volume Specimens: Mix with equal amounts of 50% Alcohol Refrigerate the unfixed Abdominal and Pelvic washings Fix no more than 50 ml of specimen; portion of the specimen if Body Cavity Fluids (pleural, peritoneal) submit the remainder of body cavity fluid possible. unfixed. Urines Gastric/Esophageal washings Small Volume Specimens: Mix with equal amounts of 50% Alcohol With very small amounts of FNA (fluid not slides) Use 10 ml of fixative if specimen fluid it may be easier to Breast fluid volume is under 10 ml. transfer the fixative into the CSF collection device (syringe, Cyst fluid suction collection tubes) first. Synovial fluid Then into a suitable container Bronchial washing to submit the specimen. Direct Smears: 95% alcohol: The slides should be All slides should be Pap Smears immersed in the alcohol for a minimum completely dry before placing FNA specimens Brushings of 15 minutes. Alternatively, the fixative them into cardboard Nipple Secretions may be pipetted onto a slide until the smear is totally saturated and then allowed to dry. or Spray fix: Hold the bottle of spray fix 3-4 inches from the slide and disperse an even layer of fixative over the slide. containers. The endoscopic brush may be submitted in 50% alcohol after the slides have been prepared. PROCEDURE Gyn Specimen Collection Techniques and Fixation Non-Gyn Specimen Collection Techniques and Fixation Page 3 of 11
4 Gyn Specimen Collection Techniques and Fixation Procedures: Conventional Gynecological Sources Vaginal, Cervical, Endocervical Smears For optimal gynecologic cytology, it is recommended that the cellular samples be obtained from the ectocervix and the endocervix for each case and spread on one slide. For atrophic women it is recommended that the spatula be moistened prior to taking the smear. If a specimen is submitted for hormone effect analysis (maturation index), the specimen should be taken from the upper vaginal wall, and placed on a separate slide. If an endometrial abnormality is suspected, a vaginal pool specimen may be submitted. The use of the endocervical brush (in non-pregnant patients) in addition to the spatula is highly recommended. Optimally, the patient should abstain from intercourse, douching, or the use vaginal contraceptives during the 24 hours prior to collection. Pap smear collection should be avoided during the menstrual phase. The following procedure should be used to help ensure an acceptable specimen: 1. Label frosted end of slide or VCE slide with the patient s name and DOB. The name should be legibly printed using a pencil or indelible ink. Do not use a grease pencil or ball point pen. If a two part case is being submitted (R + L cervix, MI etc.) make sure each slide is labeled with the appropriate site information. NOTE: If using unfrosted slides use a diamond point pen. 2. Ectocervical/Endocervical Specimen a. Cervical Scraper Method: Insert the elongated tip of the scraper into the external os and gently rotate completely around using the tip as a pivot point. The cellular material obtained by this method will usually contain cells from the squamo-columnar junction. If this method does not prove satisfactory, we recommend the use of the cytobrush to obtain the endocervical specimen. b. Cytobrush Method: After sampling the ectocervix with a spatula, gently insert the cytobrush into the endocervical canal until only the bristles closest to the handle are exposed. Slowly rotate one half to one full turn. Remove pulling straight out. 3. Material obtained should be evenly and thinly spread on the section of the slide farthest from the frosted end. When using the cytobrush the cells should be unrolled or untwisted onto the slide, not painted on which can cause air-drying and distortion of the cells. 4. Immediately fix the specimen. This is accomplished by holding the bottle of spray fix 3-4 inches from the slide and dispersing an even layer of fixative over the slide. Alcohol fixation may be substituted for the spray fix. Place the slide in a Coplin jar with 95% ethyl or reagent alcohol, the slide can be removed after 15 minutes. 5. Allow the specimen to dry completely and place in cardboard or plastic slide holders. 6. Place the plastic/cardboard specimen container in the sealable compartment of the transport bag and securely zip shut. Place the requisition in the pocket on the outside of the bag. Liquid Based Gynecological Sources MCHS - Cytology uses the Hologic (ThinPrep) collection vials. Specimens may be collected with the brush/ spatula combination or the broom method. Immediate dispersal of the specimen into the fixative is imperative with either collection method. Vial holders (eggs) are available upon request. Endocervical Brush/Spatula Procedure: 1.. Obtain an adequate sampling from the ectocervix using a plastic spatula, use of wood spatulas is not recommended. 2. Rinse the spatula as quickly as possible in the PreservCyt Solution vial by swirling the spatula vigorously in the vial 10 times. Discard the spatula. 3. Obtain an adequate sampling from the endocervix using an endocervical brush device. 4. Insert the brush into the cervix until only the bottom-most fibers are exposed. 5. Slowly rotate 1/2 turn in one direction. DO NOT OVER ROTATE. 6. Rinse the brush as quickly as possible in the PreservCyt Solution by rotating the device in the solution 10 times while pushing against the PreservCyt vial wall. Page 4 of 11
5 Endocervical Brush/Spatula Procedure: 7. Swirl the brush vigorously to further release material. 8. Discard the brush. 9. Tighten the cap so that the black torque line on the cap passes the black torque line on the vial. 10. Record the patient s name and ID number on the vial. 11. Record the patient information and medical history on the cytology requisition form. 12. Place the vial and requisition in a specimen bag form transport to the laboratory. Broom Like Device Procedure 1. Obtain an adequate sampling from the cervix using a broom-like device. Insert the central bristles of the broom into the endocervical canal deep enough to allow the shorter bristles to fully contact the ectocervix. Push gently, and rotate the broom in a clockwise direction five times. 2. Rinse the broom as quickly as possible into the PreservCyt Solution vial by pushing the broom into the bottom of the vial 10 times, forcing the bristles apart. 3. As a final step, swirl the broom vigorously to further release material. 4. Discard the collection device. 5. Tighten the cap so the black torque line on the cap passes the black torque line on the vial. 6. Record the patient s name and ID number on the vial. 7. Record the patient information and medical history on the cytology requisition. 8. Check that the information on the container and the requisition are complete and identical. 9. Check that the cover on the specimen container has been tightened and is not leaking. 10 Place specimen container in the sealable compartment of the transport bag and securely zip shut. 11. Place the requisition in the pocket on the outside of the bag. Non-Gyn Specimen Collection Techniques and Fixation Procedures Sputum Cytology 1. Have patient brush teeth and rinse mouth with water. 2. Cough vigorously to bring up material from deep in the lungs. DO NOT JUST CLEAR THE THROAT OR SPIT SALIVA, WHAT IS NEEDED IS A DEEP COUGH PRODUCING MATERIAL FROM THE LUNGS. 3. Expectorate (spit) the material into a container of Saccomanno fixative. 4. A teaspoon of material per day is adequate 5. Repeat this procedure for 3 consecutive days (same bottle of fixative may be used). 6. Label specimen bottle with patient s name, physician, and specimen type. 7. Check that the information on the container and the requisition are complete and identical. 8. Check that the cover on the specimen container has been tightened and is not leaking. 9. Place specimen container in the sealable compartment of the transport bag and securely zip shut. 10. Place the requisition in the pocket on the outside of the bag. Page 5 of 11
6 Breast Cyst and Nipple Secretion Cytology (for solid masses of the breast see FNA of Solid Masses) Breast Cyst Fluid 1. Cyst fluid (more than 0.5 ml) can be expelled directly into a labeled bottle of 50% alcohol without making any smeared slide preparations. 2. Alternatively, slides can be prepared as follows: a. Label two slides with the patient s name and second identifier. b. The material is transferred to one slide and smeared by placing the second labeled slide on top and pulling the two slides apart, or as in a blood smear preparation. c. Immediately after preparation (1-3 seconds), spray the slides with spray fixative to prevent the cells from undergoing drying or degenerative changes. d. Allow the slides to adequately dry and place in a cardboard or plastic slide holder. Nipple Secretions 1. A labeled slide can be touched directly to the drop of secretion on the nipple and then immediately spray fixed. 2. If the secretion is abundant or thick, smear the specimen by placing another labeled slide on top and pulling the two smears apart, or smearing as in a blood smear preparation. The slides should be spray fixed immediately (within 1-3 seconds). 3. Allow the slides to adequately dry and place in a cardboard or plastic slide holder. 4. In addition to the required information on the requisition, it should also include: If the mass is cystic or solid, whether the specimen is an aspirate or secretion, any pertinent history, radiologic findings, and whether the mass appears clinically suspicious for malignancy. Check that the information on the container and the requisition are complete and identical. Place plastic/cardboard specimen container in the sealable compartment of the transport bag and securely zip shut. Place the requisition in the pocket on the outside of the bag. Fine Needle Aspiration of Solid Masses (recommended technique) The FNA utilizes the cutting action of the needle tip to obtain material, so be vigorous not timid, in aspirating solid masses. In addition to the required information on the requisition, it should also include: if the mass is cystic or solid, any pertinent history, radiologic findings, and whether the mass appears clinically suspicious for malignancy Material Needed: gauge needles 5, 10, or 20 cc syringes Alcohol or Betadine swabs Sterile gloves Glass microscope slides Spray fixative or Coplin jar filled with 95% alcohol Specimen container with 50% alcohol Syringe holder (gun) optional Anesthesia optional Assistant 1. Explain the procedure to the patient and get consent form signed. 2. Set up materials a. Place needle on the syringe (and in the gun, if used). b. Label multiple slides with patient s name and second identifier. c. On a nearby flat surface arrange the slides to facilitate smearing and fixing. d. Spray fixative or open Coplin jar of 95% alcohol in close proximity to the slides. e. Open specimen container 50% alcohol. f. Assistant ready to help by smearing and fixing slides. (1) Put on gloves. Page 6 of 11
7 (2) Sterilize skin over area to be punctured using alcohol or Betadine swabs. (3) Inject local anesthesia (into skin only) if desired. (4) Fix lesion between fingers. (5) Insert needle into lesion. (6) Apply full vacuum to the needle by pulling back on the plunger. (7) Immediately make 5-10 quick, 2-5 mm in and out excursions into the lesion (do not allow the needle to exit the skin). Aspirate the lesion for 5 10 seconds, if however, blood gets to the needle hub it is time to stop and prepare the smears before the specimen clots in the needle. (8) RELEASE THE VACUUM by letting the plunger return to its equilibrium point. (9) Remove the needle from the lesion and the patient. (10) Quickly and carefully remove the needle, aspirate 5-10 cc of air into the syringe reaffix the needle. (11) Expel semi-liquid aspirate onto slide (one small drop per slide). (12) The assistant should immediately smear material on the slide by placing another labeled slide onto the first slide and pulling the slides apart. To minimize crushing of the specimen, allow only capillary action to hold the slides together while pulling them apart. (13) Fix immediately (1-2 seconds) by spraying or dropping into the Coplin jar of 95% alcohol (see NOTE below). (14) It is often helpful to have some air-dried smears as well. If adequate fixed material is obtained, 2 or 3 air-dried smears should be prepared and labeled as such. (15) Rinse any remaining material from the needle and syringe in 50% alcohol and submit along with the slides. (16) Repeat the entire process, performing 2-5 separate passes per lesion (depending on site and material obtained) for a total of 6-10 smears. Separate needles and syringes should be used. (17) Obtain hemostasis and bandage patient. (18) Submit the specimen in a transport bag with a completely filled out Cytology requisition. NOTE: Slides can be removed after 15 minutes and sent in a plastic or cardboard slide holder instead of submitting the Coplin jar. Make sure slides are labeled as fixed. Body Fluids Large volume (Pleural, Peritoneal) 1. Submit specimens fixed in 50% alcohol. Use equal amounts of fixative and specimen for proper fixation. 2. For volumes over 100 ml, submit 50 ml in fixative and the rest unfixed. NOTE: A cell block is routinely attempted on all body fluids, but does not always survive processing. 3. Label specimen container(s) with patients name, specimen type, and second identifier. 4. Check that the information on the container and the requisition are complete and identical. 5. Check that the cover on the specimen container has been tightened and is not leaking. 6. Place specimen container in the sealable compartment of the transport bag and securely zip shut. 7. Place the requisition in the pocket on the outside of the bag. Body Fluids Small volume (Breast, CSF, Synovial, etc.) 1. Fix the specimen in 50% alcohol. Use equal amount of fixative and specimen to obtain proper fixation. Excess fixative is acceptable for very small specimen amounts. Use 10 ml of fixative if specimen volume is under 10 ml. 2. Label specimen with patient s name, specimen type, and second identifier. 3. Check that the information on the container and the requisition are complete and identical. 4. Check that the cover on the specimen container has been tightened and is not leaking. Page 7 of 11
8 Body Fluids Small volume (Breast, CSF, Synovial, etc.) 5. Place specimen container in the sealable compartment of the transport bag and securely zip shut. 6. Place the requisition in the pocket on the outside of the bag. Body Fluids - Urine 1. Agitate specimen to mix contents and fix specimen in 50% alcohol. Use equal amount of fixative and specimen to obtain proper fixation. 2. Label specimen with patient s name, specimen type, and second identifier. 3. Indicate if specimen is post instrumentation/catheterized or voided on the requisition. 4. Check that the information on the container and the requisition are complete and identical. 5. Check that the cover on the specimen container has been tightened and is not leaking. 6. Place specimen container in the sealable compartment of the transport bag and securely zip shut. 7. Place the requisition in the pocket on the outside of the bag. Washings (Bronchial, Bladder, Gastric, Pelvic, Esophageal, etc.) 1. Fix the specimen in 50% alcohol. Use equal amount of fixative and specimen to obtain proper fixation. Excess fixative is acceptable for very small specimen amounts. Use 10 ml of fixative if specimen volume is under 10 ml. 2. Label specimen container with patient s name, specimen type and second identifier. 3. Check that the information on the container and the requisition are complete and identical. 4. Check that the cover on the specimen container has been tightened and is not leaking. 5. Place specimen container in the sealable compartment of the transport bag and securely zip shut. 6. Place the requisition in the pocket on the outside of the bag. Brushings (Bronchial, Gastric, Esophageal, etc.) 1. Label slides with patient name and site of area brushed. 2. Smear specimen from the brush onto the slide. 3. Fix slides immediately in a Coplin jar filled with 95% alcohol for 15 minutes or if this is unavailable spray with cytology fixative. 4. Submit the brush by placing it into a container of 50% alcohol. 5. Label specimen container with patient s name, specimen type, and second identifier. 6. Check that the information on the container and the requisition are complete and identical. 7. Check that the cover on the specimen container has been tightened and is not leaking. 8. Place specimen container or plastic/cardboard slide holder in the sealable compartment of the transport bag and securely zip shut. 9. Place the requisition in the pocket on the outside of the bag. Direct Smears of the Skin (Tzanck-Herpes) 1. Label slides with patient s name and lesion site. 2. If the lesion is extremely dry, soak under a moist towel for 10 minutes. 3. The sample may be obtained by the use of a scraper (tongue depressor) or by scraping or pressing the slide on/across the lesion. If a scraper is used, transfer the material to a slide. 4. Fix the slides immediately in 95% alcohol for 15 minutes or spray fix. 5. Air dried slides may be submitted in addition to the fixed slides (please note AIR on slides and requisition). Page 8 of 11
9 Direct Smears of the Skin (Tzanck-Herpes) 6. Check that the information on the container and the requisition are complete and identical. 7. Place plastic/cardboard specimen container in the sealable compartment of the transport bag and securely zip shut. 8. Place the requisition in the pocket on the outside of the bag. Anal-rectal sample An anal-rectal sample can be collected with the patient in either the lateral recumbent or dorsal lithotomy position. If the patient is already having a gynecologic exam, lithotomy is often more convenient. The specimen can be collected before or after the gynecologic exam. For male patients, lateral recumbency is more commonly used with the patient lying on his side with knees drawn up toward the chest. 1. A tap water moistened Dacron swab or cytobrush is used (cytobrush may be more uncomfortable for the patient). 2. The swab or brush is inserted about 5-6 cm into the anal canal past the anal verge, into the rectal vault. 3. Firm lateral pressure is applied to the swab/brush handle as it is rotated and slowly withdrawn from the anal canal, inscribing a cone-shaped arc. Care should be taken to ensure that the transition zone is sampled. A swab or smear of the peri-anal skin is an unsatisfactory sample. 4. The swab or brush is then placed in a vial of PreservCyt (Pap smear container) and agitated vigorously several times to release the cellular material. 5. Discard the collection device. 6. The specimen may be smeared onto a glass slide as other brushings are but HPV testing cannot be performed on a glass slide sample. 7. Label the vial with the patients name and second identifier. 8. Check that the cover on the specimen container has been tightened and is not leaking. 9. Place specimen container in the sealable compartment of the transport bag and securely zip shut. 10. Place the requisition in the pocket on the outside of the bag. REPORTING/INTERPRETING RESULTS The 2001 Bethesda Reporting System: Gynecologic Cytopathology Reports o The 2001 Bethesda System is used for reporting results of gynecological specimens. The primary interpretation is shown between asterisks on the final report and has three general categories: Unsatisfactory for Evaluation: The specimen does not yield diagnostic information. Additional statement(s) will state the reason that the specimen is unsatisfactory. Negative for Intraepithelial Lesion or Malignancy: This indicates that the findings are normal. Epithelial Cell Abnormality: This category is used to indicate there are abnormal cells present. o Additional statements in the body of the text will describe the severity and type of the abnormality, and may include a recommendation for further action. o Additional statements that may appear in the body of the text include: presence of organisms, presence or absence of endocervical cells (non-hysterectomy patients), obscuring elements, hormone pattern if applicable, and location of testing (if not the lab where specimen is submitted). A statement of adequacy should conclude the body of report. The area below the body of the report should contain the patient clinical information that was provided on the requisition. Page 9 of 11
10 Non-Gynecologic Cytopathology Reports o The primary interpretations used for reporting are: Unsatisfactory Specimen for Evaluation Non-Diagnostic Negative for Malignancy Suspicious for Malignancy Highly Suspicious for Malignancy Positive for Malignancy Diagnosis - for cases that require an explanatory text, similar to a histology report. o Additional statements regarding specimen content, cellular abnormality or other pertinent findings will follow the primary diagnosis when applicable. An adequacy statement should conclude the body of the report. The area below the report should contain the patient clinical information that was provided on the requisition. Page 10 of 11
11 Attachment 1 Cytology Test Listing Effective Date: 06/09/2014 Test Code Test Specimen Requirements 104 or Pap Smear A properly collected, fixed and labeled specimen - See Specimen Collection Techniques for conventional pap smears for details A cytology requisition that is completely and properly filled out See Cytology Place specimen and requisition in transport bag and place in area designated for courier pickup. See Specimen Transport of Cytology Specimens for details. 108 Thin Layer A properly collected, fixed and labeled specimen - See Specimen Collection Techniques or Pap Smear for thin layer pap smears for details A cytology requisition that is completely and properly filled out See Cytology Place specimen and requisition in transport bag and place in area designated for courier pickup. See Specimen Transport of Cytology Specimens for details. 137 Sputum A properly collected, fixed and labeled specimen. - See Specimen Collection Techniques for sputum for details. A cytology requisition that is completely and properly filled out See Cytology Place specimen and requisition in transport bag and place in area designated for courier pickup. See Specimen Transport of Cytology Specimens for details 172 Bronchial Washings A properly collected, fixed and labeled specimen - See Specimen Collection Techniques for washings for details. A cytology requisition that is completely and properly filled out See Cytology Place specimen and requisition in transport bag and place in area designated for courier pickup. See Specimen Transport of Cytology Specimens for details 175 Bronchial Brushing A properly collected, fixed and labeled specimen - See Specimen Collection Techniques for brushing specimens for details. A cytology requisition that is completely and properly filled out See Cytology Place specimen and requisition in transport bag and place in area designated for courier pickup. See Specimen Transport of Cytology Specimens for details 290 Fine Needle Aspirations A properly collected, fixed and labeled specimen - See Specimen Collection Techniques for FNA (solid and cystic) specimens for details. A cytology requisition that is completely and properly filled out, indicate exact specimen site. Example: FNA of thyroid not FNA of neck. See Cytology. Place specimen and requisition in transport bag and place in area designated for courier pickup. See Specimen Transport of Cytology Specimens for details 110 Body Fluids Includes large/small volume fluids, non-bronchial brushings/washings, urines, herpes smears. A properly collected, fixed and labeled specimen - See Specimen Collection Techniques for body fluids for details. A cytology requisition that is completely and properly filled out See Cytology Place specimen and requisition in transport bag and place in area designated for courier pickup. See Specimen Transport of Cytology Specimens for details 125 HPV Typing Additional test that may be ordered in conjunction with a thin layer pap smears. Indicate in the available area on the requisition. 127 Chlamydia Additional test that may be ordered in conjunction with a thin layer pap smears. Indicate in the available area of the requisition. 129 Neisseria Gonorrhoea Additional test that may be ordered in conjunction with a thin layer pap smears. Indicate in the available area of the requisition. Page 11 of 11
Title of Manual: Specimen Collection Document Number: GPA To provide the proper collection protocol for Candida Vaginitis testing.
 Page 1 of 5 I._PURPOSE To provide the proper collection protocol for Candida Vaginitis testing. II. MATERIALS Reagents Supplies Equipment Cervical sampling: CytoBrush & Spatula or Broom in ThinPrep or
Page 1 of 5 I._PURPOSE To provide the proper collection protocol for Candida Vaginitis testing. II. MATERIALS Reagents Supplies Equipment Cervical sampling: CytoBrush & Spatula or Broom in ThinPrep or
Title of Manual: Specimen Collection Document Number: GPA.SPC To provide the proper collection protocol for Trichomonas Vaginalis testing.
 Page 1 of 5 I._PURPOSE To provide the proper collection protocol for testing. II. MATERIALS Reagents Supplies Equipment Cervical sampling: CytoBrush & Spatula or Broom in ThinPrep or SurePath Liquid Based
Page 1 of 5 I._PURPOSE To provide the proper collection protocol for testing. II. MATERIALS Reagents Supplies Equipment Cervical sampling: CytoBrush & Spatula or Broom in ThinPrep or SurePath Liquid Based
TEV-TROPIN [somatropin (rdna origin) for injection] 5 mg & 10 mg
![TEV-TROPIN [somatropin (rdna origin) for injection] 5 mg & 10 mg TEV-TROPIN [somatropin (rdna origin) for injection] 5 mg & 10 mg](/thumbs/74/70163471.jpg) TEV-TROPIN [somatropin (rdna origin) for injection] 5 mg & 10 mg TEV-TROPIN (somatropin for injection) Information for the Patient or Parent Read all instructions before proceeding. Do not mix (reconstitute)
TEV-TROPIN [somatropin (rdna origin) for injection] 5 mg & 10 mg TEV-TROPIN (somatropin for injection) Information for the Patient or Parent Read all instructions before proceeding. Do not mix (reconstitute)
ThinPrep 2000 System Operator s Manual
 ThinPrep 2000 System Operator s Manual Hologic, Inc. 250 Campus Drive Marlborough, MA 01752 USA Tel: 1-800-442-9892 1-508-263-2900 Fax: 1-508-229-2795 Web: www.hologic.com MAN-02585-001 Caution: Federal
ThinPrep 2000 System Operator s Manual Hologic, Inc. 250 Campus Drive Marlborough, MA 01752 USA Tel: 1-800-442-9892 1-508-263-2900 Fax: 1-508-229-2795 Web: www.hologic.com MAN-02585-001 Caution: Federal
1.0 PURPOSE The purpose of this procedure is to describe the use of basic aseptic technique.
 1.0 PURPOSE The purpose of this procedure is to describe the use of basic aseptic technique. 2.0 RESPONSIBILITY 2.1 It is the responsibility of each employee working in a laboratory setting to follow this
1.0 PURPOSE The purpose of this procedure is to describe the use of basic aseptic technique. 2.0 RESPONSIBILITY 2.1 It is the responsibility of each employee working in a laboratory setting to follow this
AT Kelly Torso. Directions for Use
 AT Kelly Torso Directions for Use 260-00001 2 Table of Contents Recommends 4 Items Included 5 Skills Taught 5 Preparing the Manikin for Use 6 Head 6 Lungs 6 Abdominal Thrust 6 Instructions for Use 6 Airway
AT Kelly Torso Directions for Use 260-00001 2 Table of Contents Recommends 4 Items Included 5 Skills Taught 5 Preparing the Manikin for Use 6 Head 6 Lungs 6 Abdominal Thrust 6 Instructions for Use 6 Airway
AT Kelly Torso. Directions for Use
 AT Kelly Torso Directions for Use Table of Contents Recommends 4 Items Included 5 Skills Taught 5 Preparing the Manikin for Use 6 Head 6 Lungs 6 Abdominal Thrust 6 Instructions for Use 6 Airway Management
AT Kelly Torso Directions for Use Table of Contents Recommends 4 Items Included 5 Skills Taught 5 Preparing the Manikin for Use 6 Head 6 Lungs 6 Abdominal Thrust 6 Instructions for Use 6 Airway Management
PREPARATION AND SELF-ADMINISTRATION INSTRUCTIONS FOR PATIENTS
 PREPARATION AND SELF-ADMINISTRATION INSTRUCTIONS FOR PATIENTS Hereditary Angioedema Jenny, a real HAE patient TAKE CONTROL OF YOUR HEREDITARY ANGIOEDEMA (HAE) TREATMENT WITH SELF-ADMINISTRATION Choosing
PREPARATION AND SELF-ADMINISTRATION INSTRUCTIONS FOR PATIENTS Hereditary Angioedema Jenny, a real HAE patient TAKE CONTROL OF YOUR HEREDITARY ANGIOEDEMA (HAE) TREATMENT WITH SELF-ADMINISTRATION Choosing
Specimen Collection. Lead Screen Filter Paper Testing Dried Blood Spots (DBS) Laboratory Services February 2017
 1 Specimen Collection Lead Screen Filter Paper Testing Dried Blood Spots (DBS) Laboratory Services February 2017 2 Agenda Why Use Lead Screen Filter Paper Testing? Before You Begin Collection Drying &
1 Specimen Collection Lead Screen Filter Paper Testing Dried Blood Spots (DBS) Laboratory Services February 2017 2 Agenda Why Use Lead Screen Filter Paper Testing? Before You Begin Collection Drying &
Patients Guide for Self Administering Intravenous Antibiotics General points
 Patients Guide for Self Administering Intravenous Antibiotics General points An intravenous line is an open route for infection therefore you need to prevent this by washing your hands before any procedure
Patients Guide for Self Administering Intravenous Antibiotics General points An intravenous line is an open route for infection therefore you need to prevent this by washing your hands before any procedure
PERFORMANCE OF A FINGERSTICK
 PERFORMANCE OF A FINGERSTICK Follow the procedure as outlined above for greeting and identifying the patient. As always, properly fill out appropriate requisition forms, indicating the test(s) ordered.
PERFORMANCE OF A FINGERSTICK Follow the procedure as outlined above for greeting and identifying the patient. As always, properly fill out appropriate requisition forms, indicating the test(s) ordered.
RECOMBINATE. [Antihemophilic Factor (Recombinant)] (For intravenous use only)
![RECOMBINATE. [Antihemophilic Factor (Recombinant)] (For intravenous use only) RECOMBINATE. [Antihemophilic Factor (Recombinant)] (For intravenous use only)](/thumbs/79/80305643.jpg) Website for more information: http://www.recombinate.com/ INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE RECOMBINATE [Antihemophilic Factor (Recombinant)] (For intravenous use only) Do not attempt to do an infusion to yourself
Website for more information: http://www.recombinate.com/ INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE RECOMBINATE [Antihemophilic Factor (Recombinant)] (For intravenous use only) Do not attempt to do an infusion to yourself
TITLE: Pulse Oximetry COMPETENCY #: Resp #1 NEW COMPETENCY REVISION DATE: 10/18/12 EMPLOYEE NAME. DATE INITIAL RE-EVALUATION ANNUAL (if required) PRN
 : Pulse Oximetry COMPETENCY #: Resp #1 NEW COMPETENCY REVISION : 10/18/12 INITIAL RE-EVALUATION ANNUAL (if required) PRN 1. Verifies physician order. 2. Gathers equipment and supplies. 3. Knocks on door
: Pulse Oximetry COMPETENCY #: Resp #1 NEW COMPETENCY REVISION : 10/18/12 INITIAL RE-EVALUATION ANNUAL (if required) PRN 1. Verifies physician order. 2. Gathers equipment and supplies. 3. Knocks on door
Procedure 85 Attaching The Humidifier To The Oxygen Flow Meter Or Regulator. Procedure 86 Administering Oxygen Through A Nasal Cannula
 Chapter 12 Respiratory Procedures Procedure 81 Checking Capillary Refill Procedure 82 Using A Pulse Oximeter Procedure 83 Preparing Wall-Outlet Oxygen Procedure 84 Preparing The Oxygen Cylinder Procedure
Chapter 12 Respiratory Procedures Procedure 81 Checking Capillary Refill Procedure 82 Using A Pulse Oximeter Procedure 83 Preparing Wall-Outlet Oxygen Procedure 84 Preparing The Oxygen Cylinder Procedure
TJF-Q180V Cleaning and Disinfection Checklist
 TJF-Q180V Cleaning and Disinfection Checklist TJF-Q180V Cleaning and Disinfection Checklist This checklist is used to evaluate and confirm if cleaning and disinfection of the TJF-Q180V has been performed
TJF-Q180V Cleaning and Disinfection Checklist TJF-Q180V Cleaning and Disinfection Checklist This checklist is used to evaluate and confirm if cleaning and disinfection of the TJF-Q180V has been performed
Title of Manual: Specimen Collection Document Number: GPA.SPC.45.0
 Capillary Blood Page 1 of 5 I. PURPOSE This procedure provides guidelines on the proper technique for collecting diagnostic capillary blood specimens via skin puncture or heel puncture (infant only). Blood
Capillary Blood Page 1 of 5 I. PURPOSE This procedure provides guidelines on the proper technique for collecting diagnostic capillary blood specimens via skin puncture or heel puncture (infant only). Blood
Blood Smear. Year Group: BVSc3 + Document number: CSL_L02
 Year Group: BVSc3 + Document number: CSL_L02 Equipment for this station: Equipment list: Whole blood in heparin or EDTA tube N.B: Use substitute blood (instead of real blood) if practising this skill in
Year Group: BVSc3 + Document number: CSL_L02 Equipment for this station: Equipment list: Whole blood in heparin or EDTA tube N.B: Use substitute blood (instead of real blood) if practising this skill in
Venepuncture. Clinical Skills. Venepuncture. Dr Brian Jenkins (Clinical Skills Lead) Sian Williams (Clinical Skills Manager)
 Clinical Skills Venepuncture Dr Brian Jenkins (Clinical Skills Lead) Sian Williams (Clinical Skills Manager) Aims and Objectives Aims and Objectives The aim of this module is to facilitate learning regarding
Clinical Skills Venepuncture Dr Brian Jenkins (Clinical Skills Lead) Sian Williams (Clinical Skills Manager) Aims and Objectives Aims and Objectives The aim of this module is to facilitate learning regarding
Aseptic Techniques. Techniques for Sterile Compounding. Pharmacy Technician Training Systems Passassured, LLC
 Aseptic Techniques Techniques for Sterile Compounding Pharmacy Technician Training Systems Passassured, LLC Aseptic Techniques, Tech for Sterile Compounding PassAssured's Pharmacy Technician Training Program
Aseptic Techniques Techniques for Sterile Compounding Pharmacy Technician Training Systems Passassured, LLC Aseptic Techniques, Tech for Sterile Compounding PassAssured's Pharmacy Technician Training Program
PREPARATION AND SELF-ADMINISTRATION INSTRUCTIONS FOR PATIENTS
 PREPARATION AND SELF-ADMINISTRATION INSTRUCTIONS FOR PATIENTS Hereditary Angioedema TAKE CONTROL OF HEREDITARY ANGIOEDEMA (HAE) TREATMENT WITH FLEXIBLE ADMINISTRATION Choosing to treat with CINRYZE (C1
PREPARATION AND SELF-ADMINISTRATION INSTRUCTIONS FOR PATIENTS Hereditary Angioedema TAKE CONTROL OF HEREDITARY ANGIOEDEMA (HAE) TREATMENT WITH FLEXIBLE ADMINISTRATION Choosing to treat with CINRYZE (C1
TJF-Q180V Cleaning and Disinfection Checklist
 TJF-Q180V Cleaning and Disinfection Checklist TJF-Q180V Cleaning and Disinfection Checklist This checklist is used to evaluate and confirm if cleaning and disinfection of the TJF-Q180V has been performed
TJF-Q180V Cleaning and Disinfection Checklist TJF-Q180V Cleaning and Disinfection Checklist This checklist is used to evaluate and confirm if cleaning and disinfection of the TJF-Q180V has been performed
Module 14: Blood Collection and Handling DBS
 Module 14: Blood Collection and Handling DBS Purpose To provide the participants with skills to collect and handle dried blood spots (DBS) for EQA purposes Pre-requisite Modules Module 6: Safety at HIV
Module 14: Blood Collection and Handling DBS Purpose To provide the participants with skills to collect and handle dried blood spots (DBS) for EQA purposes Pre-requisite Modules Module 6: Safety at HIV
Satisfaction. For you and your patients.
 WOMEN S HEALTH SOLUTIONS Satisfaction. For you and your patients. Tissue Removal System & Aquilex Tissue of One solution for hysteroscopic tissue removal. Operative O.D. of 6 mm minimizes the risk of perforation
WOMEN S HEALTH SOLUTIONS Satisfaction. For you and your patients. Tissue Removal System & Aquilex Tissue of One solution for hysteroscopic tissue removal. Operative O.D. of 6 mm minimizes the risk of perforation
RECONSTITUTION AND ADMINISTRATION INSTRUCTIONS FOR HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS
 RECONSTITUTION AND ADMINISTRATION INSTRUCTIONS FOR HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS TRUST THE POWER OF PREVENTION WITH CINRYZE Whether your patients are new to treatment or are continuing their journey, remind
RECONSTITUTION AND ADMINISTRATION INSTRUCTIONS FOR HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS TRUST THE POWER OF PREVENTION WITH CINRYZE Whether your patients are new to treatment or are continuing their journey, remind
Specimen Collection Procedures
 Specimen Collection Procedures I. Overview The following are the procedures for collecting urine and blood samples from participants in the VADA program. If the precise method of sample collection varies
Specimen Collection Procedures I. Overview The following are the procedures for collecting urine and blood samples from participants in the VADA program. If the precise method of sample collection varies
imágenes en el Hospital Clinic
 Experiencias en telepatología y digitalización masiva de Centre de Diagnòstic Biomèdic imágenes en el Hospital Clinic Jaume Ordi M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pathology Hospital Clínic Barcelona jordi@clinic.ub.es
Experiencias en telepatología y digitalización masiva de Centre de Diagnòstic Biomèdic imágenes en el Hospital Clinic Jaume Ordi M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pathology Hospital Clínic Barcelona jordi@clinic.ub.es
Standard Operating Procedures (v9 5/1/17)
 Standard Operating Procedures (v9 5/1/17) Safe Working Practices for Cell Sorting on the Influx Table of Contents I. General Facility Information II. Facility Orientation and Training III. Approval to
Standard Operating Procedures (v9 5/1/17) Safe Working Practices for Cell Sorting on the Influx Table of Contents I. General Facility Information II. Facility Orientation and Training III. Approval to
COLLECTION OF BLOOD. Types of patients
 COLLECTION OF BLOOD Capillary Sampling The specimen of choice for laboratory analysis is generally a venous specimen. For blood gas analysis, the specimen of choice originates from an arterial draw. When
COLLECTION OF BLOOD Capillary Sampling The specimen of choice for laboratory analysis is generally a venous specimen. For blood gas analysis, the specimen of choice originates from an arterial draw. When
Infutrace is a formaldehyde & phenol vapor reducing agent
 Infutrace is a formaldehyde & phenol vapor reducing agent Is not a fixative. Is non hazardous for shipping, handling, storage and disposal. Produces a significant reduction of formaldehyde and phenol vapors
Infutrace is a formaldehyde & phenol vapor reducing agent Is not a fixative. Is non hazardous for shipping, handling, storage and disposal. Produces a significant reduction of formaldehyde and phenol vapors
Tissue-Plus. User Manual. O.C.T. Compound. Optimal Cutting Temperature Embedding Medium for Frozen Tissue Specimens
 Tissue-Plus O.C.T. Compound Optimal Cutting Temperature Embedding Medium for Frozen Tissue Specimens User Manual Embedding Embedding Media Tissue-Plus O.C.T. Compound Tissue-Plus O.C.T. Compound is a water-soluble
Tissue-Plus O.C.T. Compound Optimal Cutting Temperature Embedding Medium for Frozen Tissue Specimens User Manual Embedding Embedding Media Tissue-Plus O.C.T. Compound Tissue-Plus O.C.T. Compound is a water-soluble
SPEMS SKILLS PROFICIENCY CRITERIA Paramedic
 SPEMS SKILLS PROFICIENCY CRITERIA Paramedic The following skills are required at the Paramedic Level: 1. King Airway 2. IV 3. Endotracheal Intubation 4. Adult EZ IO 5. Pedi EZ IO 6. Pleural Decompression
SPEMS SKILLS PROFICIENCY CRITERIA Paramedic The following skills are required at the Paramedic Level: 1. King Airway 2. IV 3. Endotracheal Intubation 4. Adult EZ IO 5. Pedi EZ IO 6. Pleural Decompression
Standard. Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA) Repair Trainer. Part No: 60610
 User Guide Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA) Repair Trainer Part No: 6060 Standard Part No: 065-088 Issue, June 005 04 Limbs & Things For more Vascular training products visit limbsandthings.com Limbs &
User Guide Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA) Repair Trainer Part No: 6060 Standard Part No: 065-088 Issue, June 005 04 Limbs & Things For more Vascular training products visit limbsandthings.com Limbs &
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA) Repair Trainer User Guide
 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA) Repair Trainer User Guide Designed and manufactured by Limbs & Things Limited, Sussex Street, St. Philips, Bristol, BS 0RA, UK. Telephone: +44 (0)7 3 0500 Fax: +44 (0)7
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA) Repair Trainer User Guide Designed and manufactured by Limbs & Things Limited, Sussex Street, St. Philips, Bristol, BS 0RA, UK. Telephone: +44 (0)7 3 0500 Fax: +44 (0)7
TECHNICAL BULLETIN. TriControls. Control Materials for Liquid QC and Calibration Verification
 i-stat TECHNICAL BULLETIN Tris Materials for Liquid QC and OVERVIEW As part of the READi initiative (Responds, Enhances, And Delivers innovations), Abbott Point of Care (APOC) has released a new set of
i-stat TECHNICAL BULLETIN Tris Materials for Liquid QC and OVERVIEW As part of the READi initiative (Responds, Enhances, And Delivers innovations), Abbott Point of Care (APOC) has released a new set of
PREPARING GAS SAMPLES IN LARGE PLASTIC SYRINGES
 PREPARING GAS SAMPLES IN LARGE PLASTIC SYRINGES A wide variety of gases can be prepared safely inside a 60 ml plastic syringe. Here you will practice making carbon dioxide, so that you know the technique
PREPARING GAS SAMPLES IN LARGE PLASTIC SYRINGES A wide variety of gases can be prepared safely inside a 60 ml plastic syringe. Here you will practice making carbon dioxide, so that you know the technique
HEALTH SERVICES CODE A.6 CATEGORY: RN - SNP
 NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE ARTERIAL BLOOD SAMPLING (NEONATAL) A. Umbilical Catheter Blood Collection B. Radial Arterial Line CATEGORY: RN - SNP PURPOSE To obtain blood samples for laboratory analysis NURSING
NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE ARTERIAL BLOOD SAMPLING (NEONATAL) A. Umbilical Catheter Blood Collection B. Radial Arterial Line CATEGORY: RN - SNP PURPOSE To obtain blood samples for laboratory analysis NURSING
RECONSTITUTION AND ADMINISTRATION INSTRUCTIONS FOR HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS. Hereditary Angioedema
 RECONSTITUTION AND ADMINISTRATION INSTRUCTIONS FOR HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS Hereditary Angioedema TRUST PROVEN PREVENTION WITH CINRYZE Whether your patients are new to treatment or are continuing their
RECONSTITUTION AND ADMINISTRATION INSTRUCTIONS FOR HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS Hereditary Angioedema TRUST PROVEN PREVENTION WITH CINRYZE Whether your patients are new to treatment or are continuing their
BIOSAFETY SELF AUDIT PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR/PERMIT HOLDER: CONTAINMENT LEVEL: 1 2 (Shaded) RISK GROUP: 1 2 AUDIT TO BE COMPLETED BY (DATE):
 Page 1 of 5 BIOSAFETY PROGRAM BIOSAFETY SELF AUDIT PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR/PERMIT HOLDER: SELF AUDIT COMPLETED BY: LABORATORY ROOM NUMBER: CONTAINMENT LEVEL: 1 2 (Shaded) RISK GROUP: 1 2 DATE OF AUDIT:
Page 1 of 5 BIOSAFETY PROGRAM BIOSAFETY SELF AUDIT PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR/PERMIT HOLDER: SELF AUDIT COMPLETED BY: LABORATORY ROOM NUMBER: CONTAINMENT LEVEL: 1 2 (Shaded) RISK GROUP: 1 2 DATE OF AUDIT:
Varithena Delivery System Instructions for Use INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE Please read the Product Monograph before using the product.
 Varithena Delivery System Instructions for Use INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE Please read the Product Monograph before using the product. The Instructions for Use are for the entire Varithena TM system. There are
Varithena Delivery System Instructions for Use INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE Please read the Product Monograph before using the product. The Instructions for Use are for the entire Varithena TM system. There are
HemoCue Hb Procedure Template
 HemoCue Hb 201 + Procedure Template PURPOSE The HemoCue Hb 201 + System is used for the quantitative determination of hemoglobin in blood using a specially designed analyzer, HemoCue Hb 201 +, and specially
HemoCue Hb 201 + Procedure Template PURPOSE The HemoCue Hb 201 + System is used for the quantitative determination of hemoglobin in blood using a specially designed analyzer, HemoCue Hb 201 +, and specially
Caring for a balloon retained gastrostomy tube (Pexact or RIG tube) GI Unit Patient Information Leaflet
 Caring for a balloon retained gastrostomy tube (Pexact or RIG tube) GI Unit Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is about caring for a balloon retained gastrostomy tube. It includes information
Caring for a balloon retained gastrostomy tube (Pexact or RIG tube) GI Unit Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is about caring for a balloon retained gastrostomy tube. It includes information
EXERCISE 4: MICROCOLLECTION AND HEMATOCRITS. Hematocrit Skills: 5 points Capillary Puncture Skills: 26 points
 EXERCISE 4: MICROCOLLECTION AND HEMATOCRITS Hematocrit Skills: 5 points Capillary Puncture Skills: 26 points Objectives: 1. List three types of patients who may be candidates for capillary puncture and
EXERCISE 4: MICROCOLLECTION AND HEMATOCRITS Hematocrit Skills: 5 points Capillary Puncture Skills: 26 points Objectives: 1. List three types of patients who may be candidates for capillary puncture and
Arterial Punctures Blood Gas Collections (ABG)
 Arterial Punctures Blood Gas Collections (ABG) Danny Grabau, CPT, (NHA) Clinical Core Laboratory Services Phlebotomy Education Assistant Randy Gruhlke, MS, PBT(ASCP) Associate Program Director, Phlebotomy
Arterial Punctures Blood Gas Collections (ABG) Danny Grabau, CPT, (NHA) Clinical Core Laboratory Services Phlebotomy Education Assistant Randy Gruhlke, MS, PBT(ASCP) Associate Program Director, Phlebotomy
County of Santa Clara Emergency Medical Services System
 County of Santa Clara Emergency Medical Services System Policy # 700-S01 Ebola Virus Prevention and Control EBOLA VIRUS PREVENTION AND CONTROL Effective: October 30, 2014 Replaces: October 8, 2014 (Version
County of Santa Clara Emergency Medical Services System Policy # 700-S01 Ebola Virus Prevention and Control EBOLA VIRUS PREVENTION AND CONTROL Effective: October 30, 2014 Replaces: October 8, 2014 (Version
Patient Information for the: Humanitarian Device for use in the Control of Air Leaks
 Patient Information for the: Humanitarian Device for use in the Control of Air Leaks Glossary Airway: The tubes in the lungs that pass air to and from the lung tissue. Anesthesia: Technique to make the
Patient Information for the: Humanitarian Device for use in the Control of Air Leaks Glossary Airway: The tubes in the lungs that pass air to and from the lung tissue. Anesthesia: Technique to make the
MyoSure Tissue Removal System. For you and your patients.
 Tissue Removal System All-in-one Solution. For you and your patients. One solution for hysteroscopic tissue removal. Now there s a fast, convenient way to remove intrauterine pathology with two powerful
Tissue Removal System All-in-one Solution. For you and your patients. One solution for hysteroscopic tissue removal. Now there s a fast, convenient way to remove intrauterine pathology with two powerful
Tools to Enhance Laboratory Biosafety and Biosecurity Performing Risk Assessments
 Tools to Enhance Laboratory Biosafety and Biosecurity Performing Risk Assessments Selection of Safety Practices Biosecurity in the Laboratory Safety Orientation and Training Biosafety Competencies Audits,
Tools to Enhance Laboratory Biosafety and Biosecurity Performing Risk Assessments Selection of Safety Practices Biosecurity in the Laboratory Safety Orientation and Training Biosafety Competencies Audits,
Department of Laboratories St. Louis, MO ISSUE DATE: June 2007 REVISION DATE: July 2010 REVIEWED DATE: May 2017 PRINCIPILE:
 Page 1 of 6 PROCEDURE: HEMOCUE HEMOGLOBIN 201+ ANALYZER ISSUE DATE: June 2007 REVISION DATE: July 2010 REVIEWED DATE: May 2017 PRINCIPILE: The HemoCue B-Hemoglobin 201+ system consists of disposable microcuvettes
Page 1 of 6 PROCEDURE: HEMOCUE HEMOGLOBIN 201+ ANALYZER ISSUE DATE: June 2007 REVISION DATE: July 2010 REVIEWED DATE: May 2017 PRINCIPILE: The HemoCue B-Hemoglobin 201+ system consists of disposable microcuvettes
Newborn Nursing Skills and ALS Simulator LF01400U Instruction Manual
 Newborn Nursing Skills and ALS Simulator LF01400U Instruction Manual Products by Nasco About the Simulator Meeting your neonatal resuscitation program course curriculum, the Life/form Newborn Nursing Skills
Newborn Nursing Skills and ALS Simulator LF01400U Instruction Manual Products by Nasco About the Simulator Meeting your neonatal resuscitation program course curriculum, the Life/form Newborn Nursing Skills
Varithena Delivery System Instructions for Use
 Varithena Delivery System Instructions for Use Please read all prescribing information before using the product. The Instructions for Use are for the entire Varithena system. There are 2 packaging configurations:
Varithena Delivery System Instructions for Use Please read all prescribing information before using the product. The Instructions for Use are for the entire Varithena system. There are 2 packaging configurations:
limbsandthings.com Advanced Venepuncture Arm User Guide For more skills training products visit Limbs & Things Ltd.
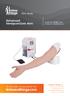 User Guide Advanced Venepuncture Arm Product No: 00290 (Light) Product No: 00298 (Brown) For more skills training products visit limbsandthings.com Limbs & Things Ltd. Sussex Street, St Philips Bristol,
User Guide Advanced Venepuncture Arm Product No: 00290 (Light) Product No: 00298 (Brown) For more skills training products visit limbsandthings.com Limbs & Things Ltd. Sussex Street, St Philips Bristol,
Articulating Legs with Intraosseous Infusion Simulator LF03840U Instruction Manual
 Articulating Legs with Intraosseous Infusion Simulator LF03840U Instruction Manual Products by Nasco C. O. A. D. B. E. M. I. J. G. K. H. F. N. L. About the Simulator Designed to attach easily to any Life/form
Articulating Legs with Intraosseous Infusion Simulator LF03840U Instruction Manual Products by Nasco C. O. A. D. B. E. M. I. J. G. K. H. F. N. L. About the Simulator Designed to attach easily to any Life/form
Laboratory Safety Training. Environmental Health and Safety
 Laboratory Safety Training Environmental Health and Safety Why You Need Lab Safety Training Hazardous materials and/or equipment. You need to understand the risks and how to mitigate them. OSU requires
Laboratory Safety Training Environmental Health and Safety Why You Need Lab Safety Training Hazardous materials and/or equipment. You need to understand the risks and how to mitigate them. OSU requires
Before you start sampling, be sure to read
 6. DISSOLVED OXYGEN MONITORING: MONITORING: Using the Titration Method Before you start sampling, be sure to read the following pages to familiarize yourself with the equipment and the procedures that
6. DISSOLVED OXYGEN MONITORING: MONITORING: Using the Titration Method Before you start sampling, be sure to read the following pages to familiarize yourself with the equipment and the procedures that
Understanding Tracheostomy Care
 Understanding Tracheostomy Care Inside this guide: This guide will help you learn how to take care of your tracheostomy (trach). It is important to ask questions. You will be given time to learn. Working
Understanding Tracheostomy Care Inside this guide: This guide will help you learn how to take care of your tracheostomy (trach). It is important to ask questions. You will be given time to learn. Working
MSD 96-Well MULTI-ARRAY and MULTI-SPOT Human Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (hg-csf) Ultrasensitive Assay
 MSD 96-Well MULTI-ARRAY and MULTI-SPOT Human Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (hg-csf) Ultrasensitive Assay Summary This assay measures Human Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) in a 96-well
MSD 96-Well MULTI-ARRAY and MULTI-SPOT Human Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (hg-csf) Ultrasensitive Assay Summary This assay measures Human Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) in a 96-well
Module IV Administration of Medications and Treatments Handouts
 Module IV Administration of Medications and Treatments Handouts Preparing for Medication Administration A. Use a designated area to prepare and administer medications. The area must be: Clean and clutter
Module IV Administration of Medications and Treatments Handouts Preparing for Medication Administration A. Use a designated area to prepare and administer medications. The area must be: Clean and clutter
WHAT TO DO WITH ILL OR DEAD FROGS
 WHAT TO DO WITH ILL OR DEAD FROGS Lee Berger and Rick Speare School of Public Health, Tropical Medicine & Rehabilitation Sciences, James Cook University, Townsville, Qld, 4811 CONTENTS 1. Introduction...
WHAT TO DO WITH ILL OR DEAD FROGS Lee Berger and Rick Speare School of Public Health, Tropical Medicine & Rehabilitation Sciences, James Cook University, Townsville, Qld, 4811 CONTENTS 1. Introduction...
VOLUMETRIC TECHNIQUES
 REVISED 10/14 CHEMISTRY 1101L VOLUMETRIC TECHNIQUES Volume measurements are important in many experimental procedures. Sometimes volume measurements must be exact; other times they can be approximate.
REVISED 10/14 CHEMISTRY 1101L VOLUMETRIC TECHNIQUES Volume measurements are important in many experimental procedures. Sometimes volume measurements must be exact; other times they can be approximate.
Veterinary Science Handling and Restraining Practicum. Restraint of the Cat for Cephalic IV Catheter Placement
 Career Development Event Last updated: //3 Handling and Restraining Practicum Restraint of the Cat for Cephalic IV Catheter Placement. The student places the cat in sternal recumbency on an 6 examination
Career Development Event Last updated: //3 Handling and Restraining Practicum Restraint of the Cat for Cephalic IV Catheter Placement. The student places the cat in sternal recumbency on an 6 examination
University of New Haven DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY and CHEMICAL ENGINEERING
 University of New Haven DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY and CHEMICAL ENGINEERING A. Instructions: Student: Read carefully the following laboratory rules, safety precaution, and regulations. Your laboratory conduct
University of New Haven DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY and CHEMICAL ENGINEERING A. Instructions: Student: Read carefully the following laboratory rules, safety precaution, and regulations. Your laboratory conduct
K-STATE GRAIN QUALITY RESEARCH PROGRAM STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES
 K-STATE GRAIN QUALITY RESEARCH PROGRAM STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES Date: March 3, 2005 Principal Investigator: Jane Lingenfelser Building and Rooms: Waters Rm. 001, Shellenberger Rm 316 Evaluation 1:
K-STATE GRAIN QUALITY RESEARCH PROGRAM STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES Date: March 3, 2005 Principal Investigator: Jane Lingenfelser Building and Rooms: Waters Rm. 001, Shellenberger Rm 316 Evaluation 1:
Soft Tissue Trauma. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Recognize and manage various types of soft tissue injuries. State function of skin
 Soft Tissue Trauma Lesson Goal Recognize and manage various types of soft tissue injuries Lesson Objectives State function of skin List and describe 3 layers of skin Explain why BSI is a critical safety
Soft Tissue Trauma Lesson Goal Recognize and manage various types of soft tissue injuries Lesson Objectives State function of skin List and describe 3 layers of skin Explain why BSI is a critical safety
Oral Dosing (Gavage) in Adult Mice and Rats SOP
 UBC Animal Care Guidelines SOP: ACC-2012-Tech09 Submitted by: Kari Jones Last date revised: Feb 2015 Revised by: Kris Andrews, Shelly McErlane Date approved: October 2012 Oral Dosing (Gavage) in Adult
UBC Animal Care Guidelines SOP: ACC-2012-Tech09 Submitted by: Kari Jones Last date revised: Feb 2015 Revised by: Kris Andrews, Shelly McErlane Date approved: October 2012 Oral Dosing (Gavage) in Adult
CCM Approval: IACUC Approval:
 CCM Approval: IACUC Approval: 1.0 Purpose: The purpose of this SOP is to describe the necessary procedures for the safe administration of potentially hazardous agents 1 to rodents via injection, drinking
CCM Approval: IACUC Approval: 1.0 Purpose: The purpose of this SOP is to describe the necessary procedures for the safe administration of potentially hazardous agents 1 to rodents via injection, drinking
Basic Flows in a Microfluidic Device
 Basic Flows in a Microfluidic Device Vishal Tandon 1 Introduction Microfluidic devices are used to transport, mix, and separate analytes in small sample volumes for chemical or biological analysis. Understanding
Basic Flows in a Microfluidic Device Vishal Tandon 1 Introduction Microfluidic devices are used to transport, mix, and separate analytes in small sample volumes for chemical or biological analysis. Understanding
Aseptic processing. the starting material to the finished product, should be controlled by Validation Control of the aseptic process
 10 Aseptic processing When products are prepared aseptically in unlicensed units there is usually no possibility of quality control of the product before release and use. Consequently quality assurance
10 Aseptic processing When products are prepared aseptically in unlicensed units there is usually no possibility of quality control of the product before release and use. Consequently quality assurance
Balloon Gastrostomy (BG) Tube
 Balloon Gastrostomy (BG) Tube Post insertion advice Please follow hospital/ Consultant advice for care of the tube and stoma site for the first 28 days (if the BG tube has been placed as a first gastrostomy
Balloon Gastrostomy (BG) Tube Post insertion advice Please follow hospital/ Consultant advice for care of the tube and stoma site for the first 28 days (if the BG tube has been placed as a first gastrostomy
Part II. Under Construction Station Instructions. Lab Station A - Blue Print: There is O 2 Here!
 Lab Station A - Blue Print: There is O 2 Here! Description: In this lab, you will consider the problem: What happened to the oxygen in the air we breathed in? Air that enters the body upon inhalation contains
Lab Station A - Blue Print: There is O 2 Here! Description: In this lab, you will consider the problem: What happened to the oxygen in the air we breathed in? Air that enters the body upon inhalation contains
User manual STARLOCK. Careways International - Innovation Quality Performance
 EN User manual LOCK Careways International - Innovation Quality Performance Content About this manual... 3 The Starlock cushion... 4 1 Warnings... 5 2 Important parts... 6 3 Use... 8 3.1 The right amount
EN User manual LOCK Careways International - Innovation Quality Performance Content About this manual... 3 The Starlock cushion... 4 1 Warnings... 5 2 Important parts... 6 3 Use... 8 3.1 The right amount
PEDIATRIC INJECTABLE TRAINING ARM SIMULATOR LF00958U INSTRUCTION MANUAL
 PEDIATRIC INJECTABLE TRAINING ARM SIMULATOR LF00958U INSTRUCTION MANUAL DO NOT REMOVE FILM FROM TUBING! THIS PRODUCT CONTAINS DRY NATURAL RUBBER! Products by NASCO About the Simulator The Life/form Pediatric
PEDIATRIC INJECTABLE TRAINING ARM SIMULATOR LF00958U INSTRUCTION MANUAL DO NOT REMOVE FILM FROM TUBING! THIS PRODUCT CONTAINS DRY NATURAL RUBBER! Products by NASCO About the Simulator The Life/form Pediatric
Port - Body in a Box User s Manual
 Port - Body in a Box - 5010 User s Manual 308 South Sequoia Parkway Canby, Oregon 97013 USA ph. 503.651.5050 fax 503.651.5052 email info@vatainc.com Thank you for purchasing VATA s Port - Body in a Box
Port - Body in a Box - 5010 User s Manual 308 South Sequoia Parkway Canby, Oregon 97013 USA ph. 503.651.5050 fax 503.651.5052 email info@vatainc.com Thank you for purchasing VATA s Port - Body in a Box
Soft Tissue Injuries
 KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES Soft Tissue Injuries 1. List two signs of closed wounds. 2. List four purposes of bandaging. 3. Describe the best initial defence against infection of an open wound. 4. Describe how
KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES Soft Tissue Injuries 1. List two signs of closed wounds. 2. List four purposes of bandaging. 3. Describe the best initial defence against infection of an open wound. 4. Describe how
Biology Lab Safety Procedures and Information
 Biology Lab Safety Procedures and Information Health and safety are paramount values in science classrooms, laboratories and field activities. You are expected to learn, understand and comply with ACC
Biology Lab Safety Procedures and Information Health and safety are paramount values in science classrooms, laboratories and field activities. You are expected to learn, understand and comply with ACC
Assisting with Insertion. Care of Intraspinal Catheters
 Guidelines included: Assisting with an Insertion Care of Various types of Intraspinal s Care of the Intraspinal Infusion Monitoring Removal of the Short Term Non Assisting with Insertion INR should be
Guidelines included: Assisting with an Insertion Care of Various types of Intraspinal s Care of the Intraspinal Infusion Monitoring Removal of the Short Term Non Assisting with Insertion INR should be
Unblocking the MicroSprayer Aerosolizer Model IA-1B With the High Pressure Reverse Cleaning Adapter. Instructions for Use
 Penn-Century, Inc. 7670 Queen Street Suite 200 Wyndmoor, PA 19038-8031 USA 215-753-6540 Tel 215-220-3040 Fax www.penncentury.com Unblocking the MicroSprayer Aerosolizer Model IA-1B With the High Pressure
Penn-Century, Inc. 7670 Queen Street Suite 200 Wyndmoor, PA 19038-8031 USA 215-753-6540 Tel 215-220-3040 Fax www.penncentury.com Unblocking the MicroSprayer Aerosolizer Model IA-1B With the High Pressure
ASPHALT PLANT LEVEL 1
 ASPHALT PLANT LEVEL 1 Module 6: Maximum Specific Gravity FM 1 T 209 FDOT Course Release: 10, Module 6 1 Specification Year: January 2015 The terms Gmm or Maximum Specific Gravity or Rice gravity are often
ASPHALT PLANT LEVEL 1 Module 6: Maximum Specific Gravity FM 1 T 209 FDOT Course Release: 10, Module 6 1 Specification Year: January 2015 The terms Gmm or Maximum Specific Gravity or Rice gravity are often
Objectives: Assisting with Medication, Checking vital Signs
 Assisting with Medication, Checking vital Signs Duty: Assist Client with Personal Hygiene Task : A.12 Remind client to take medication A.17 Check client s temperature A.18 Check client s pulse A.19 Check
Assisting with Medication, Checking vital Signs Duty: Assist Client with Personal Hygiene Task : A.12 Remind client to take medication A.17 Check client s temperature A.18 Check client s pulse A.19 Check
Standard. Standard. Venepuncture Arm. Light. Part No: Brown. Part No: Black. Part No: 00332
 Setup Guide Standard Standard Light. Part No: 000 Brown. Part No: 00 Black. Part No: 00 Part No: 065-964 Issue, June 0 0 Limbs & Things For more skills training products visit limbsandthings.com Limbs
Setup Guide Standard Standard Light. Part No: 000 Brown. Part No: 00 Black. Part No: 00 Part No: 065-964 Issue, June 0 0 Limbs & Things For more skills training products visit limbsandthings.com Limbs
User's Manual. MixRite TF 10. Edition 05.08
 User's Manual MixRite TF 10 Edition 05.08 1 Tefen MixRite TF 10 fertilizer and chemicals Injector Congratulations on your purchase of one of Tefen s high quality products. To get the best results from
User's Manual MixRite TF 10 Edition 05.08 1 Tefen MixRite TF 10 fertilizer and chemicals Injector Congratulations on your purchase of one of Tefen s high quality products. To get the best results from
Physiology of the Respiratory System
 Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Physiology of the Respiratory System References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Physiology of the Respiratory System References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning
Laryngeal Mask Airway (LMA) Indications and Use for the NH EMT-Intermediate and Paramedic
 Laryngeal Mask Airway (LMA) Indications and Use for the NH EMT-Intermediate and Paramedic New Hampshire Division of Fire Standards & Training and Emergency Medical Services Introduction The LMA was invented
Laryngeal Mask Airway (LMA) Indications and Use for the NH EMT-Intermediate and Paramedic New Hampshire Division of Fire Standards & Training and Emergency Medical Services Introduction The LMA was invented
FIRST AID. Toolbox Talk
 FIRST AID Toolbox Talk Cuts 1. Stop the Bleeding Apply direct pressure on the area. 2. Clean and Protect Clean the area with warm water and gentle soap. Apply an antibiotic ointment to reduce chance of
FIRST AID Toolbox Talk Cuts 1. Stop the Bleeding Apply direct pressure on the area. 2. Clean and Protect Clean the area with warm water and gentle soap. Apply an antibiotic ointment to reduce chance of
Nursing Guide Portsystems
 Quality and Experience Portsystems This nursing-guide is intended to answer general questions concerning port catheter systems. All other questions should be addressed to your attending physician or nursing
Quality and Experience Portsystems This nursing-guide is intended to answer general questions concerning port catheter systems. All other questions should be addressed to your attending physician or nursing
FOR SAFE AND CORRECT USE
 FOREWARD Thank you for purchasing the Model AP-20 sampling pump. The Model AP-20 pump is designed specifically for use with Kitagawa detector tubes. This system with the available Kitagawa detector tubes
FOREWARD Thank you for purchasing the Model AP-20 sampling pump. The Model AP-20 pump is designed specifically for use with Kitagawa detector tubes. This system with the available Kitagawa detector tubes
Anatomy Lab Safety Plan
 Anatomy Lab Safety Plan Fall 2007 I. Anatomy Program The Anatomy program is run by the Biology Department at SFSU to provide an in depth understanding of the human body through study and practical experience.
Anatomy Lab Safety Plan Fall 2007 I. Anatomy Program The Anatomy program is run by the Biology Department at SFSU to provide an in depth understanding of the human body through study and practical experience.
VIKING DIVING SERVICES, Inc Application for employment
 VIKING DIVING SERVICES, Inc Application for employment IRS W-4 Personal Information Nickname Present address City State Zip code Phone Cell Refereed by Place of Birth Date of Birth Email address Emergency
VIKING DIVING SERVICES, Inc Application for employment IRS W-4 Personal Information Nickname Present address City State Zip code Phone Cell Refereed by Place of Birth Date of Birth Email address Emergency
Safety and operating instructions
 BV 20H Safety and operating instructions Beams and screeds BV 20H Contents Contents Introduction........................................................................ 5 About the Safety and operating
BV 20H Safety and operating instructions Beams and screeds BV 20H Contents Contents Introduction........................................................................ 5 About the Safety and operating
BPS-2, Rev TABLE OF CONTENTS
 BPS-2, Rev. 050404 Bilayer Perfusion System Model BPS-2 125 Dixwell Avenue, Hamden, CT 06514 (800) 599-4203 / (203) 776-0664 (203) 776-1278 fax www.warneronline.com BPS-2, Rev. 050404 TABLE OF CONTENTS
BPS-2, Rev. 050404 Bilayer Perfusion System Model BPS-2 125 Dixwell Avenue, Hamden, CT 06514 (800) 599-4203 / (203) 776-0664 (203) 776-1278 fax www.warneronline.com BPS-2, Rev. 050404 TABLE OF CONTENTS
Advanced IV Hand LF01139U & LF01146U Instruction Manual
 Advanced IV Hand LF01139U & LF01146U Instruction Manual WARNING: This product contains dry natural rubber. Do not remove film from tubing! Products by Nasco List of Components 3 cc syringe with needle
Advanced IV Hand LF01139U & LF01146U Instruction Manual WARNING: This product contains dry natural rubber. Do not remove film from tubing! Products by Nasco List of Components 3 cc syringe with needle
Instruction Sheet. Important Note: Information that requires special emphasis. Note: Information that supplements points in the main text.
 Hach LDO Sensor Instruction Sheet 00745589 Safety Precautions Please read this entire instruction sheet before operating this sensor. Pay particular attention to all danger and caution statements. Failure
Hach LDO Sensor Instruction Sheet 00745589 Safety Precautions Please read this entire instruction sheet before operating this sensor. Pay particular attention to all danger and caution statements. Failure
Emily Winslow, MD April 1, 2014 SSAT Career Development Grant Update. Summary
 Summary Emily Winslow, MD April 1, 2014 SSAT Career Development Grant Update The primary aim of this grant was to develop and pilot the use of an MRI compatible box that would allow precise radiographic-pathologic
Summary Emily Winslow, MD April 1, 2014 SSAT Career Development Grant Update The primary aim of this grant was to develop and pilot the use of an MRI compatible box that would allow precise radiographic-pathologic
Competency Record for Sonic Cleaning
 Competency Record for Sonic Cleaning Name: Competency Achieved: (Date) Evaluator: Learner: Comments: Background information on sonic testing ST 79; 2009A section 7.5.3.3 states this on weekly testing Mechanical
Competency Record for Sonic Cleaning Name: Competency Achieved: (Date) Evaluator: Learner: Comments: Background information on sonic testing ST 79; 2009A section 7.5.3.3 states this on weekly testing Mechanical
ASAHI Neurovascular Guide Wire
 ASAHI Neurovascular Guide Wire AMK-DT244 Ver.1.00 / 11TS073 Legal manufacturer Consult instructions for use Do not use if package is damaged RX ONLY Caution: Federal (USA) Law restricts this device to
ASAHI Neurovascular Guide Wire AMK-DT244 Ver.1.00 / 11TS073 Legal manufacturer Consult instructions for use Do not use if package is damaged RX ONLY Caution: Federal (USA) Law restricts this device to
Chest Drains. All Covenant Health Intermediate Care Nursery staff. Needle Aspiration
 Approved by: Chest Drains Gail Cameron Director, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Neonatal Nursery Policy & Procedures Manual : April 2013 Next Review April 2016 Dr. Ensenat Medical Director,
Approved by: Chest Drains Gail Cameron Director, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Neonatal Nursery Policy & Procedures Manual : April 2013 Next Review April 2016 Dr. Ensenat Medical Director,
INSTRUCTIONS: CHEMICAL ANALYSIS OF ACTIVE SULFIDES IN OIL-BASED DRILLING FLUID
 OFI Testing Equipment Chemical Analysis of Active Sulfides Instructions Page 1 of 4 INSTRUCTIONS: CHEMICAL ANALYSIS OF ACTIVE SULFIDES IN OIL-BASED DRILLING FLUID DESCRIPTION: 1. The Garrett Gas Train
OFI Testing Equipment Chemical Analysis of Active Sulfides Instructions Page 1 of 4 INSTRUCTIONS: CHEMICAL ANALYSIS OF ACTIVE SULFIDES IN OIL-BASED DRILLING FLUID DESCRIPTION: 1. The Garrett Gas Train
[USING THE VITROBOT April 9, Using the Vitrobot
 Using the Vitrobot The Vitrobot Mk 3 (aka Mark III, Mark 3, etc.) can control both the local temperature and the local humidity during the process of plunge-freezing a grid for cryoem. It does require
Using the Vitrobot The Vitrobot Mk 3 (aka Mark III, Mark 3, etc.) can control both the local temperature and the local humidity during the process of plunge-freezing a grid for cryoem. It does require
FIELD TIP SHEET. Mark the bag with black permanent marker before filling it with water.
 Maine Healthy Beaches Program Field Methods Esperanza Stancioff March 2007 FIELD TIP SHEET When taking a sample, be sure to: Mark the bag with black permanent marker before filling it with water. Mark
Maine Healthy Beaches Program Field Methods Esperanza Stancioff March 2007 FIELD TIP SHEET When taking a sample, be sure to: Mark the bag with black permanent marker before filling it with water. Mark
MyoSure Hysteroscopic Tissue Removal System MyoSure LITE Tissue Removal Device Instructions for Use
 MyoSure Hysteroscopic Tissue Removal System MyoSure LITE Tissue Removal Device Instructions for Use PLEASE READ ALL INFORMATION CAREFULLY. ONLY Description The MyoSure Tissue Removal System consists of
MyoSure Hysteroscopic Tissue Removal System MyoSure LITE Tissue Removal Device Instructions for Use PLEASE READ ALL INFORMATION CAREFULLY. ONLY Description The MyoSure Tissue Removal System consists of
THE UNIVERSITY OF NEWCASTLE - DISCIPLINE OF MEDICAL BIOCHEMISTRY
 THE UNIVERSITY OF NEWCASTLE - DISCIPLINE OF MEDICAL BIOCHEMISTRY Page: 1 of 9 1. Risk Assessment: This risk assessment has been prepared using the National Safety Council of Australia Risk Score Calculator
THE UNIVERSITY OF NEWCASTLE - DISCIPLINE OF MEDICAL BIOCHEMISTRY Page: 1 of 9 1. Risk Assessment: This risk assessment has been prepared using the National Safety Council of Australia Risk Score Calculator
