Objectives: Assisting with Medication, Checking vital Signs
|
|
|
- Kristian Gaines
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Assisting with Medication, Checking vital Signs Duty: Assist Client with Personal Hygiene Task : A.12 Remind client to take medication A.17 Check client s temperature A.18 Check client s pulse A.19 Check client s respirations A.20 Check client s blood pressure Objectives: List four guidelines for assisting with medications. Identify the five rights of medications. Describe steps for assisting a client with medications. Identify observations about medications that should be reported. Identify proper medication storage. Explain importance of monitoring vital signs.
2 Guidelines for assisting a client with taking their medication: Aides never handle or administer medications unless specifically trained to do so. Aides can assist a client in taking their medication by bringing the medication container to the clients and reminding them to take their meds. Document that client took medication, the time and any other medications or food taken at same time. Record and report any reactions to the medication. Report if client refused to take medication, took wrong medication, dose or at the wrong time, of if medication container is missing or empty.
3 The five rights of medication assistance are: The right client (check the client s name on the label) The right medication (check the name of medication and expiration date) The right time (check label on what time or how often and compare with instructions in care plan) The right route (check label for instructions on how it is to be taken) The right amount (check label for dosage)
4 Steps for assisting with medications include: Check the five rights of assisting with medications. Bring container to client. Position client for taking medication Provide food or water.. Open and close containers. Observe client taking medication. Document time that client took medication Report reactions. Return medication to storage.
5 Actions aides are generally not permitted to do: Touch the inside of the medicine bottle or pills. Put any medication in the client s mouth. Break apart or crush capsules or tablets. Mix medication with food or drink. Assist with medication if the client s name is different from that on the label. Assist with medication when label has been removed. Assist client with medicine at a time when it is not ordered Insert suppositories into the rectum or vagina. Put drops into the eye, ear, or nose Apply prescription medications to the skin
6 Report side effects such as: Nausea and vomiting Diarrhea Confusion or drowsiness Headache Rash or itching Dizziness Immediately report signs of a serious allergic reaction: Hives or extensive rash Fever Difficulty breathing Swelling of throat or eyes Call 911 if reaction is severe or for an overdose
7 Guidelines for proper storage of medications: Keep medication in one place. Assure all mediations are properly labeled. Refrigerate if required; place away from food. Keep out of the reach of children or disoriented client. Have client properly discard expired medication not in trash.
8 Temperature, pulse, respirations and blood pressure are called vital signs. Accurate measurements provide important information about the client s health. Check the care plan for which vital signs should be checked and the frequency. Perform this task only if fully trained to do so. Record accrurately and report abnormal readings. Observations of a client s condition might lead the aide to check vital signs. For example, if the client complains of dizziness, check their pulse; if the client feels feverish, check the temperature. Always report abnormal readings.
9 Temperature refers to body heat and is measured with a digital or glass thermometer. Areas commonly used for measuring temperature are the mouth (oral), anus (rectal), armpit (axillary) and ear (tympanic). Temperature is measured in Fahrenheit (F) in the United States. Body temperature varies from person to person. Normal ranges are Oral: F Rectal: F (most accurate) Axillary: F (least accurate) Tympanic: F
10 Elevate temperature may be caused by: Infection Emotions Exercise Warm surroundings Pain Drinking hot fluids Dehydration Sub-normal temperatures maybe caused by: Shock Burns Drinking cold fluids Cold surroundings
11 There are different types of thermometers: Glass mercury-filled thermometers: these pose a risk of exposure to the mercury, which is poisonous, if the thermometer breaks. Glass mercury-free thermometer filled with alcohol and not hazardous. These are identified by a red colored temperature measuring column. Digital thermometers display the temperature in a digital display. These are safer and more commonly used for taking temperature for a home client. All thermometers must be cleaned between clients, or protective covers must be used.
12 Guidelines for using a glass thermometer: Shake down to 96 F or lower. Place the bulb under the client s tongue (slender bulb), or under armpit (slender bulb), or into the rectum (round bulb and colored red). Never leave a client unattended with a thermometer in place. Hold at eye level to read the temperature at the line where the mercury ends. Do not clean a glass thermometer in hot water, as this may cause it to break.
13 Guidelines for using a digital thermometer: Use a disposable sheath over the stem. Be sure the reading is zero before taking temperature. Read temperature when thermometer beeps. Replace the battery when indicator reads low. Sanitize the stem after removing and discarding the sheath.
14 Guidelines for taking an oral temperature: Wait at least 15 minutes to take a temperature after client eats or drinks or smokes. Never take an oral temperature if client is confused or, cannot breath with mouth closed, is unconscious, is under six years of age, has seizures or is on oxygen. Place under tongue for 5 minutes when using a glass thermometer.
15 Guidelines for taking a rectal temperature: Always wear gloves and provide privacy. Place client in side-lying position and prevent any movements that could cause injury. Lubricate thermometer tip before inserting. Leave glass thermometer in place for 3 minutes. Hold on to thermometer at all times. Guidelines for taking an axillary temperature: Place the thermometer in the center of the armpit. Place the clients arm across his or her chest. Leave a glass thermometer in place for 10 minutes.
16 Pulse - the number of heartbeats per minute. Measuring the rate, rhythm and force can provide important about the client s health. Normal rate is beats per minute for adults. Count for a full minute. A slow/weak pulse may indicate dehydration, infection, shock or be caused by certain medications. An increased pulse may be caused by exercise, pain, fever, emotions, heart conditions, illness. Report and record all abnormalities.
17 The pulse can be felt easily at the points of the body where the arteries are closest to the skin. Three most common points for checking the pulse are: Radial felt at the wrist. Brachial felt a t the bend in the elbow; pulse tends to be stronger than at the wrists. Apical using a stethoscope, the heart beat can be heard at the apex of the heart. The pulse can be felt at the carotid artery in the neck. The carotid site is used only when the pulse is too weak to feel radial or brachial pulse, as pressure on the carotid artery can interfere with heart s rate.
18 Respirations - breathing air into and out of the lungs. Each respiration as two parts: inspiration (breathing in) and expiration (breathing out). One inspiration and one expiration equals one respiration. Normal rate is breaths per minute. Count for a full minute. To count respirations, watch or feel the client s chest rise and fall. Count when the client is resting and do not let the client know you are counting breaths.
19 Increased respirations may be caused by fever, emotions, exercise, or infections. Decreased respirations may be due to medications or illness. Breathing problems may indicate a medical emergency. Report immediately if respirations are: Very slow or fast Noisy Shallow Shortness of breath Labored Wheezing
20 Blood pressure (BP) measures the pressure in the arterial system. BP varies form person to person and can change from minute to minute. Age, hereditary and physical condition, health problems and medications can affect BP. Systolic The top number, which is also the higher of the two numbers, measures the pressure in the arteries when the heart beats (when the heart muscle contracts) Diastolic The bottom number, which is also the lower of the two numbers, measures the pressure in the arteries between heartbeats (when the heart muscle is resting between beats and refilling with blood).
21 Equipment used to measure BP are a stethoscope and sphygmomanometer. It is important to use the correct cuff size to get an accurate BP reading. The cuff must be completely deflated before positioning it on the client s upper arm. BP is heard a the brachial artery. It is not always easy to perfect the skill of hearing the first and last sounds of the BP. Students may have to do the procedure over and over again and have the instructor or another student check technique and results for correctness.
22 Hypertension is high blood pressure. Hypotension is low blood pressure Normal BP = <120/80 Pre-hypertension = /80-89 Hypertension = >140/90 Hypertension crisis = >180/110 Hypotension = <90/60
23 Weight changes may indicate problems. Accurately measuring the client s weight can provide important information about the client s health such as poor nutrition or water retention. Guidelines for measuring weight of an ambulatory client: Report any weight loss no matter how small. Weigh at the same time of the day. Have the client wear same or similar clothing and empty their bladder. Client should not lean on or touch the scale or nearby fixtures or furniture, as this could alter the reading.
TEMPERATURE, PULSE, RESPIRATIONS. Abbreviated: TPR
 TEMPERATURE, PULSE, RESPIRATIONS Abbreviated: TPR TEMPERATURE The measurement of core body heat ROUTES TO MEASURE Oral: By mouth TEMPERATURE Rectally: By rectum Axillary: Under the arm in the armpit Tympanic:
TEMPERATURE, PULSE, RESPIRATIONS Abbreviated: TPR TEMPERATURE The measurement of core body heat ROUTES TO MEASURE Oral: By mouth TEMPERATURE Rectally: By rectum Axillary: Under the arm in the armpit Tympanic:
Method of measuring bodytemperature. Temperature: Body temperature is the degree of heat maintained by the body. Heat is lost
 VITAL SIGNS What do you mean by VITAL SIGNS? Ms. Esther Jennifer STAFF NURSE - ICU World largest thermometer Vital signs include 1. body temperature, 2. pulse, 3. respiration and 4. blood pressure. IMPORTANCE:
VITAL SIGNS What do you mean by VITAL SIGNS? Ms. Esther Jennifer STAFF NURSE - ICU World largest thermometer Vital signs include 1. body temperature, 2. pulse, 3. respiration and 4. blood pressure. IMPORTANCE:
Anthropometric Measurements and Vital Signs
 CHAPTER 19 Anthropometric Measurements and Vital Signs Learning Outcomes Cognitive Domain 1. Spell and define key terms 2. Explain the procedures for measuring a patient s height and weight 3. Identify
CHAPTER 19 Anthropometric Measurements and Vital Signs Learning Outcomes Cognitive Domain 1. Spell and define key terms 2. Explain the procedures for measuring a patient s height and weight 3. Identify
Anthropometric Measurements and Vital Signs
 CHAPTER 19 Anthropometric Measurements and Vital Signs Learning Outcomes Cognitive Domain 1. Spell and define key terms 2. Explain the procedures for measuring a patient s height and weight 3. Identify
CHAPTER 19 Anthropometric Measurements and Vital Signs Learning Outcomes Cognitive Domain 1. Spell and define key terms 2. Explain the procedures for measuring a patient s height and weight 3. Identify
Circulation and Respiration: Vital Signs Student Version
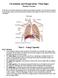 Circulation and Respiration: Vital Signs Student Version In this lab, you will learn about the circulatory and respiratory systems. You will test the capacity of your lungs, measure your blood pressure
Circulation and Respiration: Vital Signs Student Version In this lab, you will learn about the circulatory and respiratory systems. You will test the capacity of your lungs, measure your blood pressure
FIRST AID. Study Topics. At a minimum, the following topics are to be studied for the first aid exam.
 FIRST AID Study Topics At a minimum, the following topics are to be studied for the first aid exam. TOPIC Avoid getting air in stomach during rescue breathing Burns Kinds of Burns & Care Calling for Help
FIRST AID Study Topics At a minimum, the following topics are to be studied for the first aid exam. TOPIC Avoid getting air in stomach during rescue breathing Burns Kinds of Burns & Care Calling for Help
Module IV Administration of Medications and Treatments Handouts
 Module IV Administration of Medications and Treatments Handouts Preparing for Medication Administration A. Use a designated area to prepare and administer medications. The area must be: Clean and clutter
Module IV Administration of Medications and Treatments Handouts Preparing for Medication Administration A. Use a designated area to prepare and administer medications. The area must be: Clean and clutter
Vital Signs Monitoring
 Vital Signs Monitoring Practical Skills Teaching Year 2 Medical Students MB BCh 2013-2014 Contents Introduction to workshop... 4 Overall Session Aim... 5 Intended Learning Outcomes... 5 Workshop Structure
Vital Signs Monitoring Practical Skills Teaching Year 2 Medical Students MB BCh 2013-2014 Contents Introduction to workshop... 4 Overall Session Aim... 5 Intended Learning Outcomes... 5 Workshop Structure
FUNDAMENTAL CRITERIA FOR FIRST AID INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 1 FUNDAMENTAL CRITERIA FOR FIRST AID INTRODUCTION Soldiers may have to depend upon their first aid knowledge and skills to save themselves or other soldiers. They may be able to save a life, prevent
CHAPTER 1 FUNDAMENTAL CRITERIA FOR FIRST AID INTRODUCTION Soldiers may have to depend upon their first aid knowledge and skills to save themselves or other soldiers. They may be able to save a life, prevent
Chapter 10 First Aid and Field Sanitation
 Review Questions Chapter 10 First Aid and Field Sanitation 1. True or False. The three reasons for performing first aid are to save lives, prevent further injuries, and prevent infection? 1. True 2. False
Review Questions Chapter 10 First Aid and Field Sanitation 1. True or False. The three reasons for performing first aid are to save lives, prevent further injuries, and prevent infection? 1. True 2. False
TITLE: Pulse Oximetry COMPETENCY #: Resp #1 NEW COMPETENCY REVISION DATE: 10/18/12 EMPLOYEE NAME. DATE INITIAL RE-EVALUATION ANNUAL (if required) PRN
 : Pulse Oximetry COMPETENCY #: Resp #1 NEW COMPETENCY REVISION : 10/18/12 INITIAL RE-EVALUATION ANNUAL (if required) PRN 1. Verifies physician order. 2. Gathers equipment and supplies. 3. Knocks on door
: Pulse Oximetry COMPETENCY #: Resp #1 NEW COMPETENCY REVISION : 10/18/12 INITIAL RE-EVALUATION ANNUAL (if required) PRN 1. Verifies physician order. 2. Gathers equipment and supplies. 3. Knocks on door
First Aid - immediate care that is given to the victim of an injury or illness until experts can take over - Oftentimes, it s the difference between
 First Aid First Aid - immediate care that is given to the victim of an injury or illness until experts can take over - Oftentimes, it s the difference between life and death or recovery vs permanent disability
First Aid First Aid - immediate care that is given to the victim of an injury or illness until experts can take over - Oftentimes, it s the difference between life and death or recovery vs permanent disability
Oxygen Therapy. Respiratory Rehabilitation Program. What is oxygen?
 Respiratory Rehabilitation Program What is oxygen? Oxygen Therapy Oxygen is a colourless, tasteless, odorless gas that you need to live. Oxygen is found in the air you breathe at a concentration of 21%.
Respiratory Rehabilitation Program What is oxygen? Oxygen Therapy Oxygen is a colourless, tasteless, odorless gas that you need to live. Oxygen is found in the air you breathe at a concentration of 21%.
DENTAL TREATMENT ROOM EMERGENCIES
 CHAPTER 9 DENTAL TREATMENT ROOM EMERGENCIES INTRODUCTION Medical emergencies can and do occur in dental clinics. They can be life threatening as a result of a medical condition or an accident (e.g., chemicals
CHAPTER 9 DENTAL TREATMENT ROOM EMERGENCIES INTRODUCTION Medical emergencies can and do occur in dental clinics. They can be life threatening as a result of a medical condition or an accident (e.g., chemicals
HOME BLOOD PRESSURE KIT INSTRUCTIONS TRILINGUAL INSTRUCTION GUIDE MODEL UA-100
 HOME BLOOD PRESSURE KIT INSTRUCTIONS TRILINGUAL INSTRUCTION GUIDE MODEL UA-100 IMPORTANT INFORMATION Please read this important information before using your monitor. Please remember that only a medical
HOME BLOOD PRESSURE KIT INSTRUCTIONS TRILINGUAL INSTRUCTION GUIDE MODEL UA-100 IMPORTANT INFORMATION Please read this important information before using your monitor. Please remember that only a medical
English Español Português Italiano Deutch Français INSTRUCTION MANUAL FOR DIGITAL BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR MODEL CH-656C. - Eng 1 -
 English Español Português Italiano Deutch Français INSTRUCTION MANUAL FOR DIGITAL BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR MODEL CH-656C M - Eng 1 - CLEANING METHOD OF CUFF After cleaning the cuff with a neutral detergent,
English Español Português Italiano Deutch Français INSTRUCTION MANUAL FOR DIGITAL BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR MODEL CH-656C M - Eng 1 - CLEANING METHOD OF CUFF After cleaning the cuff with a neutral detergent,
HEAT ILLNESS PREVENTION PLAN
 www.westhillscollege.com HEAT ILLNESS PREVENTION PLAN October, 2008 Status: Last Revised July, 2008 Approved WHCCD Risk Management Committee 10/10/08 WHCCD Board of Trustees approval 12/16/08 HEAT ILLNESS
www.westhillscollege.com HEAT ILLNESS PREVENTION PLAN October, 2008 Status: Last Revised July, 2008 Approved WHCCD Risk Management Committee 10/10/08 WHCCD Board of Trustees approval 12/16/08 HEAT ILLNESS
Contest Description: Under Equipment and Materials
 First Aid/CPR Please note the following changes in the Standards:It is important to remember that the contestant needs a partner for the 2 man CPR segment. The partner will not take the written test and
First Aid/CPR Please note the following changes in the Standards:It is important to remember that the contestant needs a partner for the 2 man CPR segment. The partner will not take the written test and
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE ARTSANA MERCURY SPHYGMOMANOMETER
 Page 1 of 8 1. Scope This Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) applies to the staff and students using the Artsana Mercury Sphygmomanometer in the Pharmacy Practice Resource Unit (PPRU) at the Pharmacy Department,
Page 1 of 8 1. Scope This Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) applies to the staff and students using the Artsana Mercury Sphygmomanometer in the Pharmacy Practice Resource Unit (PPRU) at the Pharmacy Department,
The National Aquatic Safety Company, LLC WATER SENTRY EXAM B
 WATER SENTRY EXAM B 1. Most parks conduct safety checks to insure that the attractions are safe for operation at the beginning of the day, prior to the arrival of the general public. 2. Safety checks are
WATER SENTRY EXAM B 1. Most parks conduct safety checks to insure that the attractions are safe for operation at the beginning of the day, prior to the arrival of the general public. 2. Safety checks are
1 out of every 5,555 of drivers dies in car accidents 1 out of every 7692 pregnant women die from complications 1 out of every 116,666 skydives ended
 1 out of every 5,555 of drivers dies in car accidents 1 out of every 7692 pregnant women die from complications 1 out of every 116,666 skydives ended in a fatality in 2000 1 out of every 126,626 marathon
1 out of every 5,555 of drivers dies in car accidents 1 out of every 7692 pregnant women die from complications 1 out of every 116,666 skydives ended in a fatality in 2000 1 out of every 126,626 marathon
CONTENTS SPECIFICATIONS GENERAL INFORMATION RECOMMENDED USE OPERATING PRINCIPLE TIPS ON TAKING YOUR BLOOD PRESSURE 3-4 BATTERY INSTALLATION
 IFU SBPMON107 CONTENTS SPECIFICATIONS GENERAL INFORMATION RECOMMENDED USE OPERATING PRINCIPLE TIPS ON TAKING YOUR BLOOD PRESSURE BATTERY INSTALLATION CORRECT POSITION FOR MEASUREMENT POSITIONING THE CUFF
IFU SBPMON107 CONTENTS SPECIFICATIONS GENERAL INFORMATION RECOMMENDED USE OPERATING PRINCIPLE TIPS ON TAKING YOUR BLOOD PRESSURE BATTERY INSTALLATION CORRECT POSITION FOR MEASUREMENT POSITIONING THE CUFF
HEAT STRESS Prevention Program
 HEAT STRESS Prevention Program FACTS Although heat-related illness and death are readily preventable, the CDC reports an annual average of 600 Heat related deaths and over 7,000 Heat related illnesses
HEAT STRESS Prevention Program FACTS Although heat-related illness and death are readily preventable, the CDC reports an annual average of 600 Heat related deaths and over 7,000 Heat related illnesses
REF CH-302B IDENTIFICATION OF PARTS
 English TM INSTRUCTION MANUAL FOR DIGITAL BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR REF CH-302B IDENTIFICATION OF PARTS Exhaust button Air-release system Bulb Systolic blood pressure display section Diastolic blood pressure/pulse
English TM INSTRUCTION MANUAL FOR DIGITAL BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR REF CH-302B IDENTIFICATION OF PARTS Exhaust button Air-release system Bulb Systolic blood pressure display section Diastolic blood pressure/pulse
The National Aquatic Safety Company, LLC WATER SENTRY EXAM A
 WATER SENTRY EXAM A 1. One of the most important variables in determining the survivability of a non-breathing victim is. A. Time to intervention in restoring breathing. B. Time to local EMS response.
WATER SENTRY EXAM A 1. One of the most important variables in determining the survivability of a non-breathing victim is. A. Time to intervention in restoring breathing. B. Time to local EMS response.
R S A B C CPR. Basic Life Support Flow Chart Check for danger. Check Response. Send for Help. Check Airway. Check for Breathing.
 CPR CPR is the technique of the manual inflation of the lungs with oxygen, and compression of the heart, therefore pumping oxygenated blood around the body, and keeping the vital organs supplied with oxygen.
CPR CPR is the technique of the manual inflation of the lungs with oxygen, and compression of the heart, therefore pumping oxygenated blood around the body, and keeping the vital organs supplied with oxygen.
Heat Stress Prevention Written Program Laredo ISD Safety/Risk/Emergency Management Department
 Heat Stress Prevention Written Program Laredo ISD Safety/Risk/Emergency Management Department HEAT STRESSS PROGRAM 2016 LJP/ 1 1.0 Purpose This Heat Stress Prevention Program has been developed to provide
Heat Stress Prevention Written Program Laredo ISD Safety/Risk/Emergency Management Department HEAT STRESSS PROGRAM 2016 LJP/ 1 1.0 Purpose This Heat Stress Prevention Program has been developed to provide
First Aid Exercises 1
 First Aid Exercises 1 1 A N S W E R T H E Q U E S T I O N S I N Y O U R O W N W O R D S! What are the emergency numbers you should remember? What kind of information should you give when you call for help?
First Aid Exercises 1 1 A N S W E R T H E Q U E S T I O N S I N Y O U R O W N W O R D S! What are the emergency numbers you should remember? What kind of information should you give when you call for help?
PHY100 s Lab: The Relationship Between Liquid Pressure and Depth as it applies to Blood Pressure. Course & Sec:
 PHY100 s Lab: The Relationship Between Liquid Pressure and Depth as it applies to Blood Pressure Name: Lab Partner: Course & Sec: Date: Disclaimer: The procedures in this lab are not according to proper
PHY100 s Lab: The Relationship Between Liquid Pressure and Depth as it applies to Blood Pressure Name: Lab Partner: Course & Sec: Date: Disclaimer: The procedures in this lab are not according to proper
Guide to Cold Stress at Work
 Guide to Cold Stress at Work WCB Website: www.wcb.pe.ca Toll free in Atlantic Canada: 1-800-237-5049 Revised: Jan/06 Cold Stress at Work Working in the cold is part of the job for many Prince Edward Islanders.
Guide to Cold Stress at Work WCB Website: www.wcb.pe.ca Toll free in Atlantic Canada: 1-800-237-5049 Revised: Jan/06 Cold Stress at Work Working in the cold is part of the job for many Prince Edward Islanders.
Preventing Further Injury
 Poolside First Aid Preventing Further Injury Provide appropriate first aid treatment after removing the patron from immediate danger Remain calm and in control of the situation Call for assistance and
Poolside First Aid Preventing Further Injury Provide appropriate first aid treatment after removing the patron from immediate danger Remain calm and in control of the situation Call for assistance and
REEFTRIP.com. Medical Questionnaire Dive Medical Recreational AS Section Abbott Street, Cairns T: E:
 REEFTRIP.com 100 Abbott Street, Cairns T: 07 4037 2700 E: info@reeftrip.com Medical Questionnaire Dive Medical Recreational AS4005.1 Please complete the following Section 1 1 Surname: Given Names 2 Date
REEFTRIP.com 100 Abbott Street, Cairns T: 07 4037 2700 E: info@reeftrip.com Medical Questionnaire Dive Medical Recreational AS4005.1 Please complete the following Section 1 1 Surname: Given Names 2 Date
PREPARATION AND SELF-ADMINISTRATION INSTRUCTIONS FOR PATIENTS
 PREPARATION AND SELF-ADMINISTRATION INSTRUCTIONS FOR PATIENTS Hereditary Angioedema Jenny, a real HAE patient TAKE CONTROL OF YOUR HEREDITARY ANGIOEDEMA (HAE) TREATMENT WITH SELF-ADMINISTRATION Choosing
PREPARATION AND SELF-ADMINISTRATION INSTRUCTIONS FOR PATIENTS Hereditary Angioedema Jenny, a real HAE patient TAKE CONTROL OF YOUR HEREDITARY ANGIOEDEMA (HAE) TREATMENT WITH SELF-ADMINISTRATION Choosing
3.1.3 Weight. Frequency. Weight is obtained at the baseline examination and annually. Equipment
 The excerpt from the SPRINT Manual of Procedures (MOP) below, dated November 1, 2010, includes instructions about blood pressure measurement. Recruitment for the SPRINT trial began on November 8, 2010;
The excerpt from the SPRINT Manual of Procedures (MOP) below, dated November 1, 2010, includes instructions about blood pressure measurement. Recruitment for the SPRINT trial began on November 8, 2010;
CONTROL OF EXTERNAL BLEEDING
 CONTROL OF EXTERNAL BLEEDING Responsibility Never hesitate to call 911 Life Safety is most important! It is the responsibility of every individual to learn to recognize the warning signs of a medical emergency.
CONTROL OF EXTERNAL BLEEDING Responsibility Never hesitate to call 911 Life Safety is most important! It is the responsibility of every individual to learn to recognize the warning signs of a medical emergency.
EMERGENCY ACTION PLAN
 EMERGENCY ACTION PLAN This Emergency Action Plan (EAP) is designed to assist Sun Prairie Youth Football (SPYF) coaches in responding to emergency situations during practice or games. The development and
EMERGENCY ACTION PLAN This Emergency Action Plan (EAP) is designed to assist Sun Prairie Youth Football (SPYF) coaches in responding to emergency situations during practice or games. The development and
Breathing Process: Inhalation
 Airway Chapter 6 Breathing Process: Inhalation Active part of breathing Diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract, allowing the lungs to expand. The decrease in pressure allows lungs to fill with air.
Airway Chapter 6 Breathing Process: Inhalation Active part of breathing Diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract, allowing the lungs to expand. The decrease in pressure allows lungs to fill with air.
First Aid Awareness 2011
 First Aid Awareness 2011 What is First Aid? First Aid is the initial, or immediate assistance, given to someone who has been injured or taken ill, before the arrival of the qualified medical assistance
First Aid Awareness 2011 What is First Aid? First Aid is the initial, or immediate assistance, given to someone who has been injured or taken ill, before the arrival of the qualified medical assistance
Does this topic relate to the work the crew is doing? If not, choose another topic.
 TRAINING GUIDE COLD 1994 Before you begin the meeting... Does this topic relate to the work the crew is doing? If not, choose another topic. Did you read this Training Guide and fill in the blanks where
TRAINING GUIDE COLD 1994 Before you begin the meeting... Does this topic relate to the work the crew is doing? If not, choose another topic. Did you read this Training Guide and fill in the blanks where
Oregon Scientific Wrist Blood Pressure Monitor (BPW211)
 Oregon Scientific Wrist Blood Pressure Monitor (BPW211) User Manual TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 2 Key features... 2 Main unit... 2 Plastic storage container... 2 LCD display symbols... 3 Safety and
Oregon Scientific Wrist Blood Pressure Monitor (BPW211) User Manual TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 2 Key features... 2 Main unit... 2 Plastic storage container... 2 LCD display symbols... 3 Safety and
Bleeding: Chapter 22 page 650
 Bleeding: Chapter 22 page 650 The Significance of Bleeding When patient have serious external blood loss it is often difficult to determine the amount of blood that is present because it may be absorbed
Bleeding: Chapter 22 page 650 The Significance of Bleeding When patient have serious external blood loss it is often difficult to determine the amount of blood that is present because it may be absorbed
Model UB-328. Wrist Digital Blood Pressure Monitor. Instruction Manual. Manuel d instructions. Manual de Instrucciones. Manuale di Istruzioni
 Wrist Digital Blood Pressure Monitor Model UB-328 Instruction Manual Manuel d instructions Manual de Instrucciones Manuale di Istruzioni WM+PD4000913 ENGLISH Dear Customers Congratulations. You have purchased
Wrist Digital Blood Pressure Monitor Model UB-328 Instruction Manual Manuel d instructions Manual de Instrucciones Manuale di Istruzioni WM+PD4000913 ENGLISH Dear Customers Congratulations. You have purchased
AMERICAN HEART ASSOCIATION UPDATES:
 INTRODUCTION TO CPR AMERICAN HEART ASSOCIATION UPDATES: October 18, 2010 If a bystander is not trained in CPR, the bystander should provide compression-only CPR (see below) for the adult victim who suddenly
INTRODUCTION TO CPR AMERICAN HEART ASSOCIATION UPDATES: October 18, 2010 If a bystander is not trained in CPR, the bystander should provide compression-only CPR (see below) for the adult victim who suddenly
EXTREME HEAT. Extreme Heat Related Terms. Heat Wave - Prolonged period of excessive heat, often combined with excessive humidity.
 Residents of southeast Louisiana are typically accustomed to dealing with warm, humid weather. But extreme and prolonged heat and humidity conditions can result in serious medical emergencies, even for
Residents of southeast Louisiana are typically accustomed to dealing with warm, humid weather. But extreme and prolonged heat and humidity conditions can result in serious medical emergencies, even for
Environmental Considerations
 Environmental Considerations I. Hyperthermia a. Heat stress i. Take extreme caution in hot, humid weather ii. Every year athletes die from heat related causes iii. Body temperature must be obtained by
Environmental Considerations I. Hyperthermia a. Heat stress i. Take extreme caution in hot, humid weather ii. Every year athletes die from heat related causes iii. Body temperature must be obtained by
PREPARATION AND SELF-ADMINISTRATION INSTRUCTIONS FOR PATIENTS
 PREPARATION AND SELF-ADMINISTRATION INSTRUCTIONS FOR PATIENTS Hereditary Angioedema TAKE CONTROL OF HEREDITARY ANGIOEDEMA (HAE) TREATMENT WITH FLEXIBLE ADMINISTRATION Choosing to treat with CINRYZE (C1
PREPARATION AND SELF-ADMINISTRATION INSTRUCTIONS FOR PATIENTS Hereditary Angioedema TAKE CONTROL OF HEREDITARY ANGIOEDEMA (HAE) TREATMENT WITH FLEXIBLE ADMINISTRATION Choosing to treat with CINRYZE (C1
API Canada. Table of Contents
 API Canada Doc. Type: Language: Total Pages: Function responsible: Security Level: Derived from: Replaces: WIA EN 1 of 10 Environment Health & Safety 2 Prepared by: Checked by: Approved by: Sunday Sobkiw
API Canada Doc. Type: Language: Total Pages: Function responsible: Security Level: Derived from: Replaces: WIA EN 1 of 10 Environment Health & Safety 2 Prepared by: Checked by: Approved by: Sunday Sobkiw
E C C. American Heart Association. Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers. Written Examinations. March 2011
 E C C American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Written Examinations Contents: Examination Memo Student Answer Sheet Version A Exam Version A Answer Key Version A Reference
E C C American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Written Examinations Contents: Examination Memo Student Answer Sheet Version A Exam Version A Answer Key Version A Reference
Breathing Emergencies
 Breathing Emergencies Unit Three, Lesson Two - Breathing Emergencies Slide 1 Signs of a Breathing Emergency Restless, excitement, sleepy, dizzy Blue lips, mouth, and/or fingertips Silent, but look of surprise,
Breathing Emergencies Unit Three, Lesson Two - Breathing Emergencies Slide 1 Signs of a Breathing Emergency Restless, excitement, sleepy, dizzy Blue lips, mouth, and/or fingertips Silent, but look of surprise,
Scarborough Fire Department Scarborough, Maine Standard Operating Procedures
 Scarborough Fire Department Scarborough, Maine Standard Operating Procedures Book: Emergency Operations Chapter: Firefighting Operations Subject: 3320 - Rehabilitation Sector Revision Date: 3/11/2009 revised
Scarborough Fire Department Scarborough, Maine Standard Operating Procedures Book: Emergency Operations Chapter: Firefighting Operations Subject: 3320 - Rehabilitation Sector Revision Date: 3/11/2009 revised
Heat Stress Prevention Program
 Heat Stress Prevention Program Training for Supervisors and Employees Environmental Health and Safety Training Program Objectives Protect employees from outdoor heat hazards by: Identifying, evaluating
Heat Stress Prevention Program Training for Supervisors and Employees Environmental Health and Safety Training Program Objectives Protect employees from outdoor heat hazards by: Identifying, evaluating
Adult, Child and Infant Exam
 CPR Pro for the Professional Rescuer Adult, Child and Infant Exam Instructions: Read each of the following questions carefully and then place an X over the correct answer on the separate answer sheet provided.
CPR Pro for the Professional Rescuer Adult, Child and Infant Exam Instructions: Read each of the following questions carefully and then place an X over the correct answer on the separate answer sheet provided.
Safety Training pi polandt xs pi ow hark.c ha noffice om rk.c.or om g
 Safety Training 2016 Safety Training 2016 NOTICE!!! This training module provides an overview of the RNLL Safety Program. At least once annually, the manager and/or at least one coach from each team must
Safety Training 2016 Safety Training 2016 NOTICE!!! This training module provides an overview of the RNLL Safety Program. At least once annually, the manager and/or at least one coach from each team must
Sports Wrist Digital Blood Pressure Monitor Item #
 Instruction Manual Sports Wrist Digital Blood Pressure Monitor Item # 04-885-001 Please read this guidebook completely before operating this unit. Limited Five-Year Warranty The warrantor guarantees that
Instruction Manual Sports Wrist Digital Blood Pressure Monitor Item # 04-885-001 Please read this guidebook completely before operating this unit. Limited Five-Year Warranty The warrantor guarantees that
Client s Guide to Prenoxad Injection
 Client s Guide to Prenoxad Injection When you or someone you represent has been prescribed Prenoxad Injection (naloxone hydrochloride 1mg/1ml solution for injection) Introduction The purpose of this booklet
Client s Guide to Prenoxad Injection When you or someone you represent has been prescribed Prenoxad Injection (naloxone hydrochloride 1mg/1ml solution for injection) Introduction The purpose of this booklet
Chapter 9: Safety and First Aid
 Chapter 9: Personal Safety 9.1 Personal Safety Every one has the right to be protected. Violent crime has become a major health problem. Among these crimes are homicide and robbery. Homicide is the killing
Chapter 9: Personal Safety 9.1 Personal Safety Every one has the right to be protected. Violent crime has become a major health problem. Among these crimes are homicide and robbery. Homicide is the killing
PERSONAL INJURY PATIENT HISTORY
 PERSONAL INJURY PATIENT HISTORY Name Date Address Phone Cell Phone E-Mail For text reminders, your cell phone provider: Date of Birth: Social Security Number: Date of the accident: Time: AM PM What city
PERSONAL INJURY PATIENT HISTORY Name Date Address Phone Cell Phone E-Mail For text reminders, your cell phone provider: Date of Birth: Social Security Number: Date of the accident: Time: AM PM What city
LESSON 8: COLD WEATHER INJURIES
 LESSON 8: COLD WEATHER INJURIES dehydration frostbite hypothermia insulate precipitation subcutaneous superficial CLOTHING When in cold weather, you should wear several layers of loose clothing and dress
LESSON 8: COLD WEATHER INJURIES dehydration frostbite hypothermia insulate precipitation subcutaneous superficial CLOTHING When in cold weather, you should wear several layers of loose clothing and dress
Saint Bernard First Aid Coloring Book
 Saint Bernard First Aid Coloring Book Illustrated by Nicole Poppleton Do you know how to dial 911? A CUT OR A SCRAPE NOSE BLEEDS Sit or stand upright to slow the flow of blood. Do not tip your head back.
Saint Bernard First Aid Coloring Book Illustrated by Nicole Poppleton Do you know how to dial 911? A CUT OR A SCRAPE NOSE BLEEDS Sit or stand upright to slow the flow of blood. Do not tip your head back.
Event 203 First Aid Webelos Training Material
 The First Aid competitive event for Camperall will consist of 2 different First Aid components, a scenario challenge and a stretcher course challenge. The stretcher challenge will include constructing
The First Aid competitive event for Camperall will consist of 2 different First Aid components, a scenario challenge and a stretcher course challenge. The stretcher challenge will include constructing
Wildland Fire School. Heat Illness Prevention Program
 Monterey County Fire Training Officers Association www.mcftoa.org Heat Illness Prevention Program I. Purpose: The purpose of this program is to provide a safe training environment for attendees and participants
Monterey County Fire Training Officers Association www.mcftoa.org Heat Illness Prevention Program I. Purpose: The purpose of this program is to provide a safe training environment for attendees and participants
Crew Training. Section A: Crew Efficiency Factors, Risk Factors and Team Coordination Training. BCM AUX through BCM AUX
 Crew Training We Will Cover: Section A: Crew Efficiency Factors, Risk Factors and Team Coordination Training BCM-01-01-AUX through BCM-01-04-AUX Section B: Physical Fitness, First Aid and Survival BCM-02-01-AUX
Crew Training We Will Cover: Section A: Crew Efficiency Factors, Risk Factors and Team Coordination Training BCM-01-01-AUX through BCM-01-04-AUX Section B: Physical Fitness, First Aid and Survival BCM-02-01-AUX
Chapter 2. Lesson 8. Cold Weather Injuries. What You Will Learn to Do. Linked Core Abilities. Skills and Knowledge You Will Gain along the Way
 Lesson 8 Cold Weather Injuries Key Terms dehydration frostbite hypothermia insulate precipitation subcutaneous superficial What You Will Learn to Do Determine first aid treatment for cold weather injuries
Lesson 8 Cold Weather Injuries Key Terms dehydration frostbite hypothermia insulate precipitation subcutaneous superficial What You Will Learn to Do Determine first aid treatment for cold weather injuries
Heat and Cold Emergencies. Shelley Westwood, RN, BSN
 Heat and Cold Emergencies Shelley Westwood, RN, BSN Exposure to Heat Overexposure to heat can cause a chemical imbalance that prevents the body s cooling system from working properly. Causes of overexposure
Heat and Cold Emergencies Shelley Westwood, RN, BSN Exposure to Heat Overexposure to heat can cause a chemical imbalance that prevents the body s cooling system from working properly. Causes of overexposure
Hole Watch Attendant. 1 Copyright 2014 by PEC Safety Management, Inc. PPT-SM-HOLEWATCH 2014
 Hole Watch Attendant 1 Copyright by PEC Safety Management, Inc. Confined Spaces Two types of confined spaces Non-permit required confined spaces Permit-required confined spaces 2 Confined Spaces Non-permit
Hole Watch Attendant 1 Copyright by PEC Safety Management, Inc. Confined Spaces Two types of confined spaces Non-permit required confined spaces Permit-required confined spaces 2 Confined Spaces Non-permit
Rescue Swimmer Refresher Course. Practical First Aid Training/Mock Trauma LT 2.2
 Rescue Swimmer Refresher Course Practical First Aid Training/Mock Trauma LT 2.2 Enabling Objectives Respond to an emergency per current American Red Cross standards. Administer CPR per current American
Rescue Swimmer Refresher Course Practical First Aid Training/Mock Trauma LT 2.2 Enabling Objectives Respond to an emergency per current American Red Cross standards. Administer CPR per current American
Universal Precautions
 First Aid Safety First Aid is a matter of Personal Choice. The Company does not require employees to provide first aid for fellow employees. We have a medical provider close by to provide these services.
First Aid Safety First Aid is a matter of Personal Choice. The Company does not require employees to provide first aid for fellow employees. We have a medical provider close by to provide these services.
WHY IS PREVENTION IMPORTANT?
 A GUIDE TO TRUST THE POWER OF PREVENTION < 2 > WHY IS PREVENTION IMPORTANT? Hereditary angioedema (HAE) symptoms can range in severity. Some attacks may be mild or temporarily disabling, but others can
A GUIDE TO TRUST THE POWER OF PREVENTION < 2 > WHY IS PREVENTION IMPORTANT? Hereditary angioedema (HAE) symptoms can range in severity. Some attacks may be mild or temporarily disabling, but others can
Semi-Automatic Blood Pressure Monitor with Memory
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Semi-Automatic Blood Pressure Monitor with Memory 61-268-001 (Adult size cuff) Please read this instruction manual completely before operating this unit. English Spanish Limited Five
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Semi-Automatic Blood Pressure Monitor with Memory 61-268-001 (Adult size cuff) Please read this instruction manual completely before operating this unit. English Spanish Limited Five
Health, Safety, Security and Environment
 Document owner and change code Document Owner Aaron Perronne Title HSSE Manager Mark X Change Code Description X N/A First Issue A Typographical/Grammatical correction; formatting change; text clarification-no
Document owner and change code Document Owner Aaron Perronne Title HSSE Manager Mark X Change Code Description X N/A First Issue A Typographical/Grammatical correction; formatting change; text clarification-no
A comprehensive effort to prevent heat stress will improve worker safety and boost productivity.
 June 1st, 2006 Vol. 57 No. 11 Recognizing and preventing heat stress A comprehensive effort to prevent heat stress will improve worker safety and boost productivity. By Karen Lewis & Helen Murphy Hot summer
June 1st, 2006 Vol. 57 No. 11 Recognizing and preventing heat stress A comprehensive effort to prevent heat stress will improve worker safety and boost productivity. By Karen Lewis & Helen Murphy Hot summer
OXYGEN THERAPY. Teaching plan
 OXYGEN THERAPY Teaching plan To use this lesson for self-study, the learner should read the material, do the activity, and take the test. For group study, the leader may give each learner a copy of the
OXYGEN THERAPY Teaching plan To use this lesson for self-study, the learner should read the material, do the activity, and take the test. For group study, the leader may give each learner a copy of the
PIMA MEDICAL INSTITUTE RADIOGRAPHY PROGRAM ARRT GENERAL PATIENT CARE COMPETENCIES CPR
 CPR STUDENT CLINICAL SITE Perform CPR Demonstrate the proper techniques utilized for CPR Provided preceptor with a copy of current CPR certification card *Not * If a competency is initialed as Not, it
CPR STUDENT CLINICAL SITE Perform CPR Demonstrate the proper techniques utilized for CPR Provided preceptor with a copy of current CPR certification card *Not * If a competency is initialed as Not, it
HEAT ILLNESS PREVENTION TRAINING. Presented by: Du-All 2018
 HEAT ILLNESS PREVENTION TRAINING Presented by: Du-All 2018 TRAINING GOALS Increase awareness and commitment to safety and health at the work site Review the regulatory language and heat illness preventive
HEAT ILLNESS PREVENTION TRAINING Presented by: Du-All 2018 TRAINING GOALS Increase awareness and commitment to safety and health at the work site Review the regulatory language and heat illness preventive
Cold Weather Safety Program
 Title: Cold Weather Safety program Effective Date: 12/6/2014 Control Number: THG_0052 Revision Number: 1 Date: 10/23/2015 Annual Review Completed: 5/13/2015 Cold Weather Safety Program CONTENTS I. INTRODUCTION
Title: Cold Weather Safety program Effective Date: 12/6/2014 Control Number: THG_0052 Revision Number: 1 Date: 10/23/2015 Annual Review Completed: 5/13/2015 Cold Weather Safety Program CONTENTS I. INTRODUCTION
U.S. ARMY MEDICAL DEPARTMENT CENTER AND SCHOOL FORT SAM HOUSTON, TEXAS TAKING VITAL SIGNS SUBCOURSE MD0531 EDITION 100
 U.S. ARMY MEDICAL DEPARTMENT CENTER AND SCHOOL FORT SAM HOUSTON, TEXAS 78234-6100 TAKING VITAL SIGNS SUBCOURSE MD0531 EDITION 100 DEVELOPMENT This subcourse is approved for resident and correspondence
U.S. ARMY MEDICAL DEPARTMENT CENTER AND SCHOOL FORT SAM HOUSTON, TEXAS 78234-6100 TAKING VITAL SIGNS SUBCOURSE MD0531 EDITION 100 DEVELOPMENT This subcourse is approved for resident and correspondence
2.This section will move into the Airway Management, Rescue Breaths & Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR).
 Wilderness First Aid Fundamentals The period between the World Wars saw an increased awareness in personal first aid training. To cover all eventualities, from accidents at work to travel in foreign lands.
Wilderness First Aid Fundamentals The period between the World Wars saw an increased awareness in personal first aid training. To cover all eventualities, from accidents at work to travel in foreign lands.
COMMUNITY RESPONSE TO MEDICAL EMERGENCIES:
 COMMUNITY RESPONSE TO MEDICAL EMERGENCIES: For any on-campus emergency, dial x456 from an on campus phone or From a cell phone dial 508-494-9010. A medical emergency can occur anywhere on campus. The reaction
COMMUNITY RESPONSE TO MEDICAL EMERGENCIES: For any on-campus emergency, dial x456 from an on campus phone or From a cell phone dial 508-494-9010. A medical emergency can occur anywhere on campus. The reaction
California State University Bakersfield Heat Illness Prevention Policy. Revised November 2017
 California State University Bakersfield Heat Illness Prevention Policy Revised November 2017 THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK 1 Contents 1.0 Policy... 3 2.0 Authority... 3 3.0 Scope... 3 4.0 Definitions...
California State University Bakersfield Heat Illness Prevention Policy Revised November 2017 THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK 1 Contents 1.0 Policy... 3 2.0 Authority... 3 3.0 Scope... 3 4.0 Definitions...
Clinical- Vital Signs and Indirect Calorimetry. Kendra Manwill
 Clinical- Vital Signs and Indirect Calorimetry Kendra Manwill Vital Signs- Pulse Normal: 60-100 Radial: Use first and middle fingers Count 15 sec, multiply by 4 Brachial Just medial to biceps tendon Vital
Clinical- Vital Signs and Indirect Calorimetry Kendra Manwill Vital Signs- Pulse Normal: 60-100 Radial: Use first and middle fingers Count 15 sec, multiply by 4 Brachial Just medial to biceps tendon Vital
HOW TO PERFORM A PHYSICAL EXAM IN YOUR HORSE. Carolina Lopez, DVM Equine Medicine Resident College of Veterinary Medicine Washington State University
 HOW TO PERFORM A PHYSICAL EXAM IN YOUR HORSE Carolina Lopez, DVM Equine Medicine Resident College of Veterinary Medicine Washington State University Case Scenario You know your horse Eating behavior Habits
HOW TO PERFORM A PHYSICAL EXAM IN YOUR HORSE Carolina Lopez, DVM Equine Medicine Resident College of Veterinary Medicine Washington State University Case Scenario You know your horse Eating behavior Habits
BASIC KNOWLEDGE OF LABORATORY FIRST AID
 BASIC KNOWLEDGE OF LABORATORY FIRST AID RV: 02/02/2015 prevencio@uv.es Page 1 of 7 . General issues to be considered by the rescuer in the event of an accident are described below: - Proceed as follows:
BASIC KNOWLEDGE OF LABORATORY FIRST AID RV: 02/02/2015 prevencio@uv.es Page 1 of 7 . General issues to be considered by the rescuer in the event of an accident are described below: - Proceed as follows:
Procedure 85 Attaching The Humidifier To The Oxygen Flow Meter Or Regulator. Procedure 86 Administering Oxygen Through A Nasal Cannula
 Chapter 12 Respiratory Procedures Procedure 81 Checking Capillary Refill Procedure 82 Using A Pulse Oximeter Procedure 83 Preparing Wall-Outlet Oxygen Procedure 84 Preparing The Oxygen Cylinder Procedure
Chapter 12 Respiratory Procedures Procedure 81 Checking Capillary Refill Procedure 82 Using A Pulse Oximeter Procedure 83 Preparing Wall-Outlet Oxygen Procedure 84 Preparing The Oxygen Cylinder Procedure
1 st Response Information Sheets. For use with the full 1 st Response course.
 1 st Response Information Sheets For use with the full 1 st Response course. Aims and objectives The aim of 1 st Response is to ensure Girlguiding/Scouting members are kept as safe as possible while they
1 st Response Information Sheets For use with the full 1 st Response course. Aims and objectives The aim of 1 st Response is to ensure Girlguiding/Scouting members are kept as safe as possible while they
premium wrist blood pressure monitor
 LIFESTYLE premium wrist blood pressure monitor instruction manual Model: MD 1010 WBPM10 Series / MD 13400 Contents Introduction... 5 Safety Information... 6 General...6 Safe handling of batteries...7 Service
LIFESTYLE premium wrist blood pressure monitor instruction manual Model: MD 1010 WBPM10 Series / MD 13400 Contents Introduction... 5 Safety Information... 6 General...6 Safe handling of batteries...7 Service
https://youtu.be/5r7havfzxek
 CPR https://youtu.be/5r7havfzxek CPR Saves Lives Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation or CPR and defibrillation within 3-5 minutes can save over 50% of cardiac arrest victims CPR followed by AED saves thousands
CPR https://youtu.be/5r7havfzxek CPR Saves Lives Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation or CPR and defibrillation within 3-5 minutes can save over 50% of cardiac arrest victims CPR followed by AED saves thousands
2.9 Burns. Burns damage the soft tissue of the body and may be caused by:
 2.9 Burns Burns damage the soft tissue of the body and may be caused by: 2.9.1 Heat Burns Heat burns from different sources, e.g. flame, friction, scalding or solar radiation, are generally treated in
2.9 Burns Burns damage the soft tissue of the body and may be caused by: 2.9.1 Heat Burns Heat burns from different sources, e.g. flame, friction, scalding or solar radiation, are generally treated in
ISAF OFFSHORE SPECIAL REGULATIONS Appendix E
 Formatted Page - 72 - APPENDIX E Hypothermia WHAT IS IT? A condition in which exposure to cold air and/or water lowers body core temperature. Death can result from too low a brain and heart temperature.
Formatted Page - 72 - APPENDIX E Hypothermia WHAT IS IT? A condition in which exposure to cold air and/or water lowers body core temperature. Death can result from too low a brain and heart temperature.
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Initiate Rescue Breathing on an Adult. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 Initiate Rescue Breathing on an Adult. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-12. TASK TAUGHT 081-831-0018, Open the Airway. 081-831-0048, Perform Rescue Breathing. LESSON
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 Initiate Rescue Breathing on an Adult. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-12. TASK TAUGHT 081-831-0018, Open the Airway. 081-831-0048, Perform Rescue Breathing. LESSON
PROGRAMMES IN A BOX /01/2009: /2009: EMERGENCY AID (2( OF 3)
 PROGRAMMES IN A BOX w/c 12/0 /01/2009: /2009: EMERGENCY AID (2( OF 3) Time Activity Notes Who 5 Welcome & Opening Ceremony Start the evening and explain to them what they will be doing that evening. 10
PROGRAMMES IN A BOX w/c 12/0 /01/2009: /2009: EMERGENCY AID (2( OF 3) Time Activity Notes Who 5 Welcome & Opening Ceremony Start the evening and explain to them what they will be doing that evening. 10
Heat Stress Prevention
 Heat Stress Prevention University Facilities Internal Procedure: July 1, 2013 Effective date: July 1, 2013 Last Modified: April 2013 Approved by: Bob Wells 1.0 Program Objective UF has implemented this
Heat Stress Prevention University Facilities Internal Procedure: July 1, 2013 Effective date: July 1, 2013 Last Modified: April 2013 Approved by: Bob Wells 1.0 Program Objective UF has implemented this
STAYING ON TRACK WITH CINRYZE THERAPY
 YOUR GUIDE TO STAYING ON TRACK WITH CINRYZE THERAPY Indication CINRYZE (C1 esterase inhibitor [human]) is an injectable prescription medicine that is used to help prevent swelling and/or painful attacks
YOUR GUIDE TO STAYING ON TRACK WITH CINRYZE THERAPY Indication CINRYZE (C1 esterase inhibitor [human]) is an injectable prescription medicine that is used to help prevent swelling and/or painful attacks
LESSON 2: THE FIRST LIFE- SAVING STEPS
 LESSON 2: THE FIRST LIFE- SAVING STEPS automatic external defibrillators (AEDs) cardiac arrest heart attack heimlich maneuver rescue breathing stroke INTRODUCTION In emergency situations, the people involved
LESSON 2: THE FIRST LIFE- SAVING STEPS automatic external defibrillators (AEDs) cardiac arrest heart attack heimlich maneuver rescue breathing stroke INTRODUCTION In emergency situations, the people involved
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. When you have completed this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 LESSON OBJECTIVES Heat Injuries. When you have completed this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Identify the causes of heat cramps, heat exhaustion, and heat stroke. 4-2. Identify
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 LESSON OBJECTIVES Heat Injuries. When you have completed this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Identify the causes of heat cramps, heat exhaustion, and heat stroke. 4-2. Identify
SOUTHEASTERN MASSACHUSETTS EMS COUNCIL
 SOUTHEASTERN MASSACHUSETTS EMS COUNCIL REGION V EMERGENCY INCIDENT REHABILITATION GUIDELINES SOUTHEASTERN MASSACHUSETTS EMS COUNCIL P.O. BOX 1197 HYANNIS, MA 02601 508/771-4510 & 1-800-932-REG5 (1-800-932-7345)
SOUTHEASTERN MASSACHUSETTS EMS COUNCIL REGION V EMERGENCY INCIDENT REHABILITATION GUIDELINES SOUTHEASTERN MASSACHUSETTS EMS COUNCIL P.O. BOX 1197 HYANNIS, MA 02601 508/771-4510 & 1-800-932-REG5 (1-800-932-7345)
Magdalen Court School
 Introduction Working in a cold environment whether it be cold weather, cold water, or an indoor freezer is part of the job for many British Columbia workers. One of the major hazards you face when working
Introduction Working in a cold environment whether it be cold weather, cold water, or an indoor freezer is part of the job for many British Columbia workers. One of the major hazards you face when working
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Perform Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation on a Child or Infant. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 6 Perform Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation on a Child or Infant. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 6-1 through 6-7. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 6 Perform Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation on a Child or Infant. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 6-1 through 6-7. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
The First Ten Minutes
 The First Ten Minutes A guide for school personnel responding to health related emergencies in the school setting Reprinted with the permission of: Office of Community Health Conemaugh Health System Table
The First Ten Minutes A guide for school personnel responding to health related emergencies in the school setting Reprinted with the permission of: Office of Community Health Conemaugh Health System Table
Medical Aspects of Diving in the Offshore Oil Industry
 Medical Aspects of Diving in the Offshore Oil Industry Dr Stephen Watt Retired Consultant in Respiratory and Hyperbaric Medicine Chairman, Diving Medical Advisory Committee What is diving? Diving = Commuting
Medical Aspects of Diving in the Offshore Oil Industry Dr Stephen Watt Retired Consultant in Respiratory and Hyperbaric Medicine Chairman, Diving Medical Advisory Committee What is diving? Diving = Commuting
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER. Exembol Multidose 100 mg/ml concentrate for solution for infusion. Argatroban Monohydrate
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Exembol Multidose 100 mg/ml concentrate for solution for infusion Argatroban Monohydrate Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine.
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Exembol Multidose 100 mg/ml concentrate for solution for infusion Argatroban Monohydrate Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine.
