Pressure Equalization Tube Placement with Adenoidectomy or Pressure Equalization Tube Placement with Nasopharyngoscopy (and Possible Adenoidectomy)
|
|
|
- Blanche Little
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NORTH COUNTY EAR, NOSE AND THROAT HEAD AND NECK SURGERY Pediatric and Adult 2023 West Vista Way, Suite J Vista, California (760) Fax (760) Pressure Equalization Tube Placement with Adenoidectomy or Pressure Equalization Tube Placement with Nasopharyngoscopy (and Possible Adenoidectomy) It has been recommended that your child undergo pressure equalization tube placement with adenoidectomy or pressure equalization tube with nasopharyngoscopy (and possible adenoidectomy). Pressure equalization tube placement is also known as "ear tube," "ventilation tube," "tympanostomy tube" or "PE tube" placement. This information must be read completely before signing the surgical consent form. The information serves as the "informed consent" regarding the risks and benefits of the procedure. Please initial the risks on the last 2 pages, sign the last page, and bring the last 2 pages with you on the day of surgery. How do ear tubes work? Understanding the middle ear and the Eustachian tube. To understand how ear tubes work, you must first know about the middle ear and Eustachian tube. The ear has three parts: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. The eardrum is a very thin membrane that separates the outer ear from the middle ear. The middle ear is an air chamber. It is connected to the back of the nose and throat via a narrow tube called the Eustachian tube. The Eustachian tube is a pressure-equalizing valve and a drainage tube. Normally, the Eustachian tube opens with swallowing and yawning. In infants and young children, the Eustachian tube is narrow and flat. By age 7 or so, the Eustachian tube is larger and more upright which improves its ability to function. Many problems within the middle ear space are related to the Eustachian tube. Blockage of the Eustachian tube creates negative pressure in the middle ear and over time can pull the eardrum inward. If this occurs, clear fluid may be drawn from mucous membranes into the middle ear space causing a fluid buildup. This frequently occurs in children with upper respiratory infections or allergic symptoms. Sometimes the fluid can last a long time. When it does it is called "chronic" fluid, or "chronic otitis media with effusion." If bacteria or a virus enters the middle ear fluid through the Eustachian tube, a pus infection can accumulate behind the ear drum. This is called "acute otitis media" and is often accompanied by symptoms of fever, ear pain, irritability and sometimes drainage (if the infection ruptured the eardrum.) If not treated, both recurrent episodes of acute otitis media as well as chronic otitis media with effusion can have potentially serious complications. These include permanent hearing loss, middle ear and eardrum scarring, middle ear skin cyst formation, or even (at the extreme) meningitis. What are "adenoids" and how are they important?
2 The "adenoid" is tonsil-like tissue that is located in the back of the nose, next to the opening of the Eustachian tube. Even though there is only one adenoid, we often call it "adenoids." Children approximately 3 years of age and older are likely to have enlarged adenoids. Adenoids can be large because of allergies or just the normal germs to which children are exposed. The adenoids can physically block the opening of the Eustachian tube. Also, the adenoids can be chronically inflamed ("chronic adenoiditis") and can seed germs up into the middle ear. In children less than 3 years old, the adenoids are usually less of a concern. However, adenoidectomy may be indicated even in a 2 year old if your child is preparing for their second set of PE tubes in the setting of suspected adenoid enlargement. What are pressure equalization tubes? Since it is not possible to surgically alter the actual Eustachian tube, a PE tube is placed within the eardrum to serve as an artificial Eustachian tube. It is a small, usually round piece of specialized plastic with a tiny hole in the center. PE tubes stay in place about 6 months to two years before they fall out on their own into the ear canal. Some children require a longer tube which can stay in much longer. I would have mentioned this to you if I felt your child would need this. Although PE tubes greatly decrease the frequency of middle ear infections, it is still possible to get one. A tube will allow the infection to drain out into the ear canal so that pain, fever, and the possibility of hearing loss are minimized. What are potential reasons for pressure equalization tube placement? - A substantial hearing loss in patients with any type of otitis media - Poor response to antibiotics - Chronic otitis media with fluid for more than 3 months - Recurrent episodes of acute otitis media - Chronic retraction of the eardrum What is a "nasopharyngoscopy"? In some children, it is possible to determine by history and physical examination that the adenoids are a contributing factor and that adenoidectomy is appropriate during the PE tube surgery. However, in other children it may be atypical or unclear whether the adenoids are an issue. In these children I will look at the back of the nose with a narrow telescope placed through one side of the nose to see if the adenoids are a problem. Children require I.V. (intravenous catheter) placement and a breathing tube in the windpipe for adenoidectomy, but not for PE tube placement or nasopharyngoscopy. Therefore, we would not want to place the I.V. or breathing tube unless we were confident the adenoids were an issue. What happens during the procedure? The ear surgery is performed under a microscope. Wax is removed and a small incision ("myringotomy") is made in the front part of the ear drum. Fluid, pus, and/or debris are suctioned from the middle ear space and a tiny pressure equalization tube is placed in the ear drum. This takes about 5 minutes
3 If nasopharyngoscopy is performed, a few drops of decongestant are placed in the nose and a telescope is placed as above. This takes about 2 minutes. If adenoids are concerning because of size and/or inflammation, an I.V. and breathing tube will be placed. This takes about 5 minutes Adenoidectomy is performed through the mouth. It is slightly more invasive and that is why an I.V. and breathing tube are required. The adenoids are seen with a specialized mirror. Curved instruments are used to reach up behind the nose and remove the adenoids. Gentle cauterization is usually required as well. This takes about 15 to 20 minutes. What happens on the day of surgery? This is a common surgical procedure and is usually performed in an outpatient surgical center. The anesthesiologist, operating room nurse, and I will see you in the pre-operation holding area. Children do not have the I.V. placed before the surgery. Your child is then taken to the operating room. Your child is placed under general anesthesia by breathing a light anesthesia medicine through a mask. The procedures are then performed. This will take 15 to 30 minutes total depending on whether the adenoids are removed. We then go to the recovery room and I come speak with you. Your child may be fussy or calm, fully awake or still asleep. These are all normal variations of recovery from anesthesia. There will be EKG (heart monitor) wires, an oxygen probe on the fingertip or toe, a blood pressure cuff, a tube blowing humidified oxygen near the pillow, possibly an I.V., and a lot of nurses, technicians, beeping, and buzzing. All of this is normal! It is also normal to see blood-tinged fluid on the cotton balls in the ears. The cotton balls may even fall out in the recovery room. Very rarely a child may be nauseous and vomit. You may see fresh blood from the nose, in the saliva, or even blood clot in the vomitous. Does my child stay the night? This is an outpatient procedure. Most children go home within a few hours of surgery. What do I expect the first few days? Your child may be irritable and tired the first 24 to 48 hours after surgery. You can expect a small amount of thin, blood-tinged drainage from the ears (more if there was active infection at the time of surgery) for about 2-3 days. There may be blood in the saliva and nose secretions for the first 24 hours. When should my child return to school/daycare/sports? This is at your discretion. Generally, children may return to school/daycare within one to two days. Some children have more soreness and stay out of school for 3 to 4 days. They may resume normal activity and sports as tolerated and as long as there is no bleeding. However, swimming should be avoided for one week. What should my child eat?
4 Lighter foods and plenty of liquids are encouraged during the first 24 hours. A normal diet may be resumed the following morning. Some children prefer soft food for 3 to 4 days. When will my child follow-up in clinic? The clinic will provide you a follow-up for anywhere from 2 to 6 weeks after surgery. The timing is not critical. Do I need to keep water out of my children's ears? Dirty bath or shower water should not get into the ear. Form-fitting ear plugs or a cotton ball lined with a very thin layer of Vaseline (for occlusion) should be worn during bathing. Ocean and lake water is very dirty and requires double protection, including both form-fitting ear plugs and a neoprene headband. Chlorinated pool water is controversial. I would prefer your child wear ear plugs for swimming, but an acceptable alternative is to use 5 drops of Floxin Otic in each ear after swimming. Please let me know if you need refills of these drops. Children who do not wear ear plugs may have an increased incidence of yellow drainage episodes and tube infection. Attached to this information packet is a form for a very nice brand of ear plugs and neoprene headbands. What are the benefits of surgery? 1) 90% reduction in acute middle ear infections - As the number of middle ear infections declines after surgery, the need for antibiotics is also reduced, and decreases the likelihood of developing antibiotic-resistant bacterial ear infections. 2) Resolution of conductive hearing loss - The most common type of hearing loss related to chronic otitis media with effusion (chronic fluid) and acute otitis media is a "conductive" hearing loss. After removal of fluid from the middle ear space during PE tube placement, the conductive hearing loss is usually resolved. (Of note, most children will have a few decibels of "inconsequential" very low frequency conductive hearing loss just because of the biomechanics of having an ear tube in the ear drum. It might show up if a post-operative audiogram was performed.) 3) Minimize or prevent the longer term complications of chronic ear disease including: - Permanent, irregular holes in the eardrum - Severe scarring within and between the eardrum and tiny middle ear bones - Bone deterioration - Cholesteatoma (middle ear cyst of dead skin cells) - Development of eardrum retraction pockets - Permanent conductive hearing loss 4) Improve speech development - As ear tubes help correct conductive hearing losses that occur with fluid behind the eardrum, they can also help improve speech development. Some aspects of development are especially vulnerable to the intermittent hearing losses caused by even brief episodes of fluid behind the eardrum.
5 5) Removal of the adenoids greatly decreases the possibility of middle ear problems returning once the tubes fall out and the eardrums heal closed. What are the risks of surgery? 1) Bleeding There is a very minimal risk of ear bleeding and, when it does happen, is usually associated with a severe ear infection at the time of surgery. Rarely, adenoid-bed bleeding can last 2 days and present with teaspoon-size clots. This is self-limited, with a <0.5% incidence of repeat surgery to control bleeding sites. 2) Infection* Without antibiotic ear drops after surgery, there may be as much as a 50% chance of a draining infection of the tubes in the first 2 weeks after surgery. The ear drops should be used as directed. If there was an active middle ear infection at the time of tube placement, the ear drops will be prescribed for a longer period and I may also prescribe an oral antibiotic. Antibiotics are given to prevent infection in the adenoid-bed and to reduce post-operative pain. 1% of children require additional antibiotics for an adenoid-bed infection. 3) Pain Pain from the ear tubes themselves is not expected. However, your child may continue to tug at the ears or say the ears feel funny because they are getting used to normal sounds and normal ear pressures after having clogged ears for so long. The pain in the adenoid-bed will feel like a bad sore throat and lasts about 2 to 7 days. About 10% of children may complain of vague neck pain for about a month after surgery. 4) Draining ear episodes* 15-25% of children will have green-yellow drainage from the ear at least once during the duration that the tubes are in. This may, rarely, be a middle ear infection draining through the open ear tubes (the ear tubes are doing their job). More likely, it is infected granulation tissue around the tube which is a temporary body reaction to the tubes. There may be blood if it is granulation tissue. This is easily treated with appropriate antibiotic ear drops. Very rarely a tube may itself become permanently infected and cause recalcitrant drainage requiring tube removal. 5) Hearing loss* There is a <1% incidence of nerve hearing loss following PE tube placement. 6) Tube blockage - 7% of ear tubes become blocked by wax, granulation tissue, or dried mucous. Drops are usually successful in unblocking them and only rarely would a tube need to be removed because it remained non-functional. 7) Eardrum scarring* - Also known as "tympanosclerosis" or "myringosclerosis." There is a 15% incidence of this. It is a "cosmetic" problem in that it only very rarely stiffens the eardrum enough to decrease sound wave transmission. 8) Localized eardrum weakness* - 2% of eardrum holes will heal with a weak ("atrophic") area at the site of the prior tube. It is a "cosmetic" problem in that it only very rarely collapses enough to decrease sound wave transmission. 9) Need for another set of PE tubes - This is not a risk of the procedure, per se, but rather a potential risk of the underlying disease process. In other words, after the ear tubes fall out and the ear drum heals closed, the original middle ear problems and Eustachian tube problems may come back. 5 to 10 % of children require at least one repeat set of tubes.
6 10) Cholesteatoma (middle ear cyst of dead skin cells)* - There is a 1% chance that the margins of the eardrum at the site of the prior PE tube will invaginate into the middle ear space and cause a skin cyst. This is very severe and usually requires surgery. 11) Retained PE tube - Less than 5% of tubes stay in longer than 3 years at which time a brief anesthesia may be required to remove the tube. 12) Early PE tube extrusion - 4% of ear tubes fall out before 6 months. This is usually in younger children and is usually associated with a middle ear infection that generates enough pus to push the tube out. 13) Persistent hole in eardrum* - There is a 2% chance that a hole will remain in the eardrum after the tubes falls out. Some of these holes will require a patch procedure or graft surgery to close the hole. 14) Nasally voice (due to "velopharyngeal insufficiency") - All children will have a nasally voice for several weeks to a few months after surgery. This is due to swelling in the back of the nose and palate/uvula area. Approximately 1 in 1,200 children develop prolonged velopharyngeal insufficiency/nasally voice that requires surgery. *Much more likely to occur if PE tube is not placed and the chronic ear issues allowed to progress. Please let me know if you have any questions. Julie A. Berry, M.D.
7 Pressure Equalization Tube Placement with Adenoidectomy or Pressure Equalization Tube Placement with Nasopharyngoscopy (and Possible Adenoidectomy) Patient Name Date of Birth Please initial that you understand the risks, sign the last page, and bring both pages with you to give to me on the day of surgery. (initial) Bleeding There is a very minimal risk of ear bleeding and, when it does happen, is usually associated with a severe ear infection at the time of surgery. Rarely, adenoidbed bleeding can last 2 days and present with teaspoon-size clots. This is self-limited, with a <0.5% incidence of repeat surgery to control bleeding sites. (initial) Infection Without antibiotic ear drops after surgery, there may be as much as a 50% chance of a draining infection of the tubes in the first 2 weeks after surgery. The ear drops should be used as directed. If there was an active middle ear infection at the time of tube placement, the ear drops will be prescribed for a longer period and I may also prescribe an oral antibiotic. Antibiotics are given to prevent infection in the adenoid-bed and to reduce postoperative pain. 1% of children require additional antibiotics for an adenoid-bed infection. (initial) Pain Pain from the ear tubes themselves is not expected. However, your child may continue to tug at the ears or say the ears feel funny because they are getting used to normal sounds and normal ear pressures after having clogged ears for so long. The pain in the adenoidbed will feel like a bad sore throat and lasts about 2 to 7 days. About 10% of children may complain of vague neck pain for about a month after surgery. (initial) Draining ear episodes 15-25% of children will have green-yellow drainage from the ear at least once during the duration that the tubes are in. This may, rarely, be a middle ear infection draining through the open ear tubes (the ear tubes are doing their job). More likely, it is infected granulation tissue around the tube which is a temporary body reaction to the tubes. There may be blood if it is granulation tissue. This is easily treated with appropriate antibiotic ear drops. Very rarely a tube may itself become permanently infected and cause recalcitrant drainage requiring tube removal. (initial) Hearing loss There is a <1% incidence of nerve hearing loss following PE tube placement. (initial) Tube blockage - 7% of ear tubes become blocked by wax, granulation tissue, or dried mucous. Drops are usually successful in unblocking them and only rarely would a tube need to be removed because it remained non-functional. (initial) Eardrum scarring - Also known as "tympanosclerosis" or "myringosclerosis." There is a 15% incidence of this. It is a "cosmetic" problem in that it only very rarely stiffens the eardrum enough to decrease sound wave transmission.
8 (initial) Localized eardrum weakness - 2% of eardrum holes will heal with a weak ("atrophic") area at the site of the prior tube. It is a "cosmetic" problem in that it only very rarely collapses enough to decrease sound wave transmission. (initial) Need for another set of PE tubes - This is not a risk of the procedure, per se, but rather a potential risk of the underlying disease process. In other words, after the ear tubes fall out and the ear drum heals closed, the original middle ear problems and Eustachian tube problems may come back. 5 to 10 % of children require at least one repeat set of tubes. (initial) Cholesteatoma (middle ear cyst of dead skin cells) - There is a 1% chance that the margins of the eardrum at the site of the prior PE tube will invaginate into the middle ear space and cause a skin cyst. This is very severe and usually requires surgery. (initial) Retained PE tube - Less than 5% of tubes stay in longer than 3 years at which time a brief anesthesia may be required to remove the tube. (initial) Early PE tube extrusion - 4% of ear tubes fall out before 6 months. This is usually in younger children and is usually associated with a middle ear infection that generates enough pus to push the tube out. (initial) Persistent hole in eardrum - There is a 2% chance that a hole will remain in the eardrum after the tubes falls out. Some of these holes will require a patch procedure or graft surgery to close the hole. (initial) Nasally voice (due to "velopharyngeal insufficiency") - All children will have a nasally voice for several weeks to a few months after surgery. This is due to swelling in the back of the nose and palate/uvula area. Approximately 1 in 1,200 children develop prolonged velopharyngeal insufficiency/nasally voice that requires surgery. I understand the above risks and wish for my child to proceed with surgery. Parent/Guardian Signature Date
Care after Tonsil and Adenoid Surgery with Pain Management
 Otolaryngology Care after Tonsil and Adenoid Surgery with Pain Management Contents: Tonsil and Adenoid Surgery Pain Medicine after Outpatient Surgery Pain Medicine Logs Please mail completed pain medicine
Otolaryngology Care after Tonsil and Adenoid Surgery with Pain Management Contents: Tonsil and Adenoid Surgery Pain Medicine after Outpatient Surgery Pain Medicine Logs Please mail completed pain medicine
What is the Eustachian tube and what does it do?
 Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) can cause dulled hearing. It is usually a temporary problem that lasts a week or so and most commonly occurs during and after a cold. There
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) can cause dulled hearing. It is usually a temporary problem that lasts a week or so and most commonly occurs during and after a cold. There
Michigan Ear Institute. Eustachian Tube Problems.
 Michigan Ear Institute Eustachian Tube Problems www.michiganear.com DOCTORS Jack M. Kartush, MD Dennis I. Bojrab, MD Michael J. LaRouere, MD John J. Zappia, MD, FACS Eric W. Sargent, MD, FACS Seilesh C.
Michigan Ear Institute Eustachian Tube Problems www.michiganear.com DOCTORS Jack M. Kartush, MD Dennis I. Bojrab, MD Michael J. LaRouere, MD John J. Zappia, MD, FACS Eric W. Sargent, MD, FACS Seilesh C.
A DISCUSSION OF EUSTACHIAN TUBE PROBLEMS
 35 A DISCUSSION OF EUSTACHIAN TUBE PROBLEMS So all may hear... BY THE HOUSE CLINIC Main Office 2100 West Third Street, First Floor Los Angeles, California 90057 Telephone:(213)483-9930 FAX(213)484-5900
35 A DISCUSSION OF EUSTACHIAN TUBE PROBLEMS So all may hear... BY THE HOUSE CLINIC Main Office 2100 West Third Street, First Floor Los Angeles, California 90057 Telephone:(213)483-9930 FAX(213)484-5900
Patient Information for the: Humanitarian Device for use in the Control of Air Leaks
 Patient Information for the: Humanitarian Device for use in the Control of Air Leaks Glossary Airway: The tubes in the lungs that pass air to and from the lung tissue. Anesthesia: Technique to make the
Patient Information for the: Humanitarian Device for use in the Control of Air Leaks Glossary Airway: The tubes in the lungs that pass air to and from the lung tissue. Anesthesia: Technique to make the
OTITIS MEDIA WITH EFFUSION ----(OME) Dr Uzma Kiani PG-ENT, BBH 24 th Jan.2011
 OTITIS MEDIA WITH EFFUSION ----(OME) Dr Uzma Kiani PG-ENT, BBH 24 th Jan.2011 1 一 overview Otitis media with effusion (OME) is characterized by accumulation of fluid in the middle ear, conductive hearing
OTITIS MEDIA WITH EFFUSION ----(OME) Dr Uzma Kiani PG-ENT, BBH 24 th Jan.2011 1 一 overview Otitis media with effusion (OME) is characterized by accumulation of fluid in the middle ear, conductive hearing
Michigan Ear Institute
 Michigan Ear Institute Eustachian Tube Problems www.michiganear.com 15-56111-111 BOOK Eustachian Tube Problems.indd 1 2/13/18 10:36 A DOCTORS Dennis I. Bojrab, MD Seilesh C. Babu, MD John J. Zappia, MD,
Michigan Ear Institute Eustachian Tube Problems www.michiganear.com 15-56111-111 BOOK Eustachian Tube Problems.indd 1 2/13/18 10:36 A DOCTORS Dennis I. Bojrab, MD Seilesh C. Babu, MD John J. Zappia, MD,
Orbital decompression surgery. See also information leaflets on: ~ Thyroid Eye Disease ~ Upper lid lowering ~ Proptosis
 Orbital decompression surgery See also information leaflets on: ~ Thyroid Eye Disease ~ Upper lid lowering ~ Proptosis Qu: What is the orbit? The eye, its surrounding muscles, nerves and fatty tissue lie
Orbital decompression surgery See also information leaflets on: ~ Thyroid Eye Disease ~ Upper lid lowering ~ Proptosis Qu: What is the orbit? The eye, its surrounding muscles, nerves and fatty tissue lie
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system. Objective sheet 3 Notes
 1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
COMMUNITY RESPONSE TO MEDICAL EMERGENCIES:
 COMMUNITY RESPONSE TO MEDICAL EMERGENCIES: For any on-campus emergency, dial x456 from an on campus phone or From a cell phone dial 508-494-9010. A medical emergency can occur anywhere on campus. The reaction
COMMUNITY RESPONSE TO MEDICAL EMERGENCIES: For any on-campus emergency, dial x456 from an on campus phone or From a cell phone dial 508-494-9010. A medical emergency can occur anywhere on campus. The reaction
Understanding Tracheostomy Care for your Child
 Understanding Tracheostomy Care for your Child 2 Inside this guide: This guide will help you learn how to take care of your child s tracheostomy (trach). It is important to ask questions. You will be given
Understanding Tracheostomy Care for your Child 2 Inside this guide: This guide will help you learn how to take care of your child s tracheostomy (trach). It is important to ask questions. You will be given
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
 What is? Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBO therapy) is a medical treatment that helps treat many different medical conditions. It involves breathing 100% oxygen while in a pressurized chamber. How does it
What is? Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBO therapy) is a medical treatment that helps treat many different medical conditions. It involves breathing 100% oxygen while in a pressurized chamber. How does it
Guarding for Organized Swim Groups
 Day 2 Inspection Guarding for Organized Swim Groups Organized groups may visit your facility. Day care groups Camps Youth organizations Groups can be part of your facility or an outside group They should
Day 2 Inspection Guarding for Organized Swim Groups Organized groups may visit your facility. Day care groups Camps Youth organizations Groups can be part of your facility or an outside group They should
NOTES PATIENT DETAILS
 NOTES PATIENT DETAILS Patient Name: Patient MRN: Department: Date of Insertion: Type of Central Line: Size of Central Line: Booklet given and explained by: Signed: CONTACT NUMBERS Hospital Telephone No:
NOTES PATIENT DETAILS Patient Name: Patient MRN: Department: Date of Insertion: Type of Central Line: Size of Central Line: Booklet given and explained by: Signed: CONTACT NUMBERS Hospital Telephone No:
Breathing Process: Inhalation
 Airway Chapter 6 Breathing Process: Inhalation Active part of breathing Diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract, allowing the lungs to expand. The decrease in pressure allows lungs to fill with air.
Airway Chapter 6 Breathing Process: Inhalation Active part of breathing Diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract, allowing the lungs to expand. The decrease in pressure allows lungs to fill with air.
Adult, Child and Infant Exam
 CPR Pro for the Professional Rescuer Adult, Child and Infant Exam Instructions: Read each of the following questions carefully and then place an X over the correct answer on the separate answer sheet provided.
CPR Pro for the Professional Rescuer Adult, Child and Infant Exam Instructions: Read each of the following questions carefully and then place an X over the correct answer on the separate answer sheet provided.
Understanding Tracheostomy Care
 Understanding Tracheostomy Care Inside this guide: This guide will help you learn how to take care of your tracheostomy (trach). It is important to ask questions. You will be given time to learn. Working
Understanding Tracheostomy Care Inside this guide: This guide will help you learn how to take care of your tracheostomy (trach). It is important to ask questions. You will be given time to learn. Working
County of Santa Clara Emergency Medical Services System
 County of Santa Clara Emergency Medical Services System Policy # 700-S01 Ebola Virus Prevention and Control EBOLA VIRUS PREVENTION AND CONTROL Effective: October 30, 2014 Replaces: October 8, 2014 (Version
County of Santa Clara Emergency Medical Services System Policy # 700-S01 Ebola Virus Prevention and Control EBOLA VIRUS PREVENTION AND CONTROL Effective: October 30, 2014 Replaces: October 8, 2014 (Version
Chapter 9 Airway Respirations Metabolism Oxygen Requirements Respiratory Anatomy Respiratory Anatomy Respiratory Anatomy Diaphragm
 1 Chapter 9 Airway 2 Respirations Every cell of the body requires to survive Oxygen must come in and carbon must go out 3 Metabolism Metabolism--Process where the body s cells convert food to Adequate
1 Chapter 9 Airway 2 Respirations Every cell of the body requires to survive Oxygen must come in and carbon must go out 3 Metabolism Metabolism--Process where the body s cells convert food to Adequate
ALFRED HYPERBARIC SERVICE. Service and Care. Information for Patients
 ALFRED HYPERBARIC SERVICE Service and Care Information for Patients ALFRED HEALTH Alfred Hyperbaric Service The Alfred Commercial Road Melbourne, VIC 3004 Phone (03) 9076 2269 Fax (03) 9076 3052 This booklet
ALFRED HYPERBARIC SERVICE Service and Care Information for Patients ALFRED HEALTH Alfred Hyperbaric Service The Alfred Commercial Road Melbourne, VIC 3004 Phone (03) 9076 2269 Fax (03) 9076 3052 This booklet
Manual: Biphasic Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP) Ventilation
 RCH@Home Manual: Biphasic Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP) Ventilation 1. Commonly used terms... 2 1.1 Inspiration... 2 1.2 Expiration... 2 1.3 Breath rate (bpm)... 2 1.4 Ventilation... 2 1.5 Biphasic
RCH@Home Manual: Biphasic Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP) Ventilation 1. Commonly used terms... 2 1.1 Inspiration... 2 1.2 Expiration... 2 1.3 Breath rate (bpm)... 2 1.4 Ventilation... 2 1.5 Biphasic
First Aid Handbook. Contents
 First Aid Handbook Contents Bleeding Cuts or Wounds... 2 Hands-Only CPR for Adults... 3 Thermal Burns Treatment... 4 For All Burns... 4 For First-Degree Burns (Affecting Top Layer of Skin)... 4 For Second-Degree
First Aid Handbook Contents Bleeding Cuts or Wounds... 2 Hands-Only CPR for Adults... 3 Thermal Burns Treatment... 4 For All Burns... 4 For First-Degree Burns (Affecting Top Layer of Skin)... 4 For Second-Degree
Mechanical Ventilation
 Mechanical Ventilation Chapter 4 Mechanical Ventilation Equipment When providing mechanical ventilation for pediatric casualties, it is important to select the appropriately sized bag-valve mask or endotracheal
Mechanical Ventilation Chapter 4 Mechanical Ventilation Equipment When providing mechanical ventilation for pediatric casualties, it is important to select the appropriately sized bag-valve mask or endotracheal
Standards and guidelines for care and management of patients requiring oxygen therapy.
 PURPOSE Standards and guidelines for care and management of patients requiring oxygen therapy. STANDARDS Ongoing management of oxygen therapy requires a prescriber s order. The order must specify oxygen
PURPOSE Standards and guidelines for care and management of patients requiring oxygen therapy. STANDARDS Ongoing management of oxygen therapy requires a prescriber s order. The order must specify oxygen
You Might Also Like. I look forward helping you focus your instruction while saving tons of time. Kesler Science Station Lab Activities 40%+ Savings!
 Thanks Connect Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over
Thanks Connect Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over
Assuming you thoroughly understand what eustachian tube dysfunction is, the question now becomes how does one use nasal sprays to correctly treat
 Assuming you thoroughly understand what eustachian tube dysfunction is, the question now becomes how does one use nasal sprays to correctly treat this disorder. Of note, fluid in the middle ears is treated
Assuming you thoroughly understand what eustachian tube dysfunction is, the question now becomes how does one use nasal sprays to correctly treat this disorder. Of note, fluid in the middle ears is treated
smart guide Equalising Like a Pro
 smart guide Equalising Like a Pro 1 Outer ear canal Ear Ossicles Vestibule Oval Window Semicircular canals Shutterstock.com/Penpa J Cochlea Middle ear Middle ear Round Window Eustachian tube DAN S SMART
smart guide Equalising Like a Pro 1 Outer ear canal Ear Ossicles Vestibule Oval Window Semicircular canals Shutterstock.com/Penpa J Cochlea Middle ear Middle ear Round Window Eustachian tube DAN S SMART
Procedure 85 Attaching The Humidifier To The Oxygen Flow Meter Or Regulator. Procedure 86 Administering Oxygen Through A Nasal Cannula
 Chapter 12 Respiratory Procedures Procedure 81 Checking Capillary Refill Procedure 82 Using A Pulse Oximeter Procedure 83 Preparing Wall-Outlet Oxygen Procedure 84 Preparing The Oxygen Cylinder Procedure
Chapter 12 Respiratory Procedures Procedure 81 Checking Capillary Refill Procedure 82 Using A Pulse Oximeter Procedure 83 Preparing Wall-Outlet Oxygen Procedure 84 Preparing The Oxygen Cylinder Procedure
Balloon Gastrostomy (BG) Tube
 Balloon Gastrostomy (BG) Tube Post insertion advice Please follow hospital/ Consultant advice for care of the tube and stoma site for the first 28 days (if the BG tube has been placed as a first gastrostomy
Balloon Gastrostomy (BG) Tube Post insertion advice Please follow hospital/ Consultant advice for care of the tube and stoma site for the first 28 days (if the BG tube has been placed as a first gastrostomy
Section 2.9 Decannulation
 Bite- sized training from the GTC Section 2.9 Decannulation This is one of a series of bite- sized chunks of educational material developed by the Global Tracheostomy Collaborative. The GTC has developed
Bite- sized training from the GTC Section 2.9 Decannulation This is one of a series of bite- sized chunks of educational material developed by the Global Tracheostomy Collaborative. The GTC has developed
Oxygen Therapy. What tests can be done to determine the need for oxygen?
 Oxygen Therapy Oxygen is in the air we breathe and is necessary to live. When we breathe in, oxygen enters the lungs and it goes into the blood. When the lungs cannot transfer enough oxygen into the blood,
Oxygen Therapy Oxygen is in the air we breathe and is necessary to live. When we breathe in, oxygen enters the lungs and it goes into the blood. When the lungs cannot transfer enough oxygen into the blood,
BASIC KNOWLEDGE OF LABORATORY FIRST AID
 BASIC KNOWLEDGE OF LABORATORY FIRST AID RV: 02/02/2015 prevencio@uv.es Page 1 of 7 . General issues to be considered by the rescuer in the event of an accident are described below: - Proceed as follows:
BASIC KNOWLEDGE OF LABORATORY FIRST AID RV: 02/02/2015 prevencio@uv.es Page 1 of 7 . General issues to be considered by the rescuer in the event of an accident are described below: - Proceed as follows:
What is a wound? An injury to the skin and some times other deeper soft tissues. Types:
 1 Dr. Samer Sara What is a wound? An injury to the skin and some times other deeper soft tissues. Types: Open wounds: Skin is torn or cut, often leads to bleeding. Closed wounds: Skin is not affected and
1 Dr. Samer Sara What is a wound? An injury to the skin and some times other deeper soft tissues. Types: Open wounds: Skin is torn or cut, often leads to bleeding. Closed wounds: Skin is not affected and
Oxygen prescription. Dr Julian Forton. Consultant in paediatric respiratory medicine Noah s Ark Children s Hospital for Wales
 Oxygen prescription Dr Julian Forton. Consultant in paediatric respiratory medicine Noah s Ark Children s Hospital for Wales Oxygen prescription chart EXCEPTION: Oxygen may be given without a prescription
Oxygen prescription Dr Julian Forton. Consultant in paediatric respiratory medicine Noah s Ark Children s Hospital for Wales Oxygen prescription chart EXCEPTION: Oxygen may be given without a prescription
Patient information for thoracosocopic pleurectomy
 Patient information for thoracosocopic pleurectomy Full name of procedure: Video-assisted thoracoscopic apical bullectomy (blebectomy), apical pleurectomy, basal pleural abrasion Short name: (VATS) Pleurectomy
Patient information for thoracosocopic pleurectomy Full name of procedure: Video-assisted thoracoscopic apical bullectomy (blebectomy), apical pleurectomy, basal pleural abrasion Short name: (VATS) Pleurectomy
Complex Care Hub Manual: Oxygen Therapy
 Complex Care Hub Manual: Oxygen Therapy Table of Contents RCH@Home Manual: Oxygen Therapy... 1 1. What is oxygen therapy?... 2 2. Symptoms of low oxygen... 2 3. Giving oxygen at home and in the community...
Complex Care Hub Manual: Oxygen Therapy Table of Contents RCH@Home Manual: Oxygen Therapy... 1 1. What is oxygen therapy?... 2 2. Symptoms of low oxygen... 2 3. Giving oxygen at home and in the community...
Liquid Medical Oxygen Medicinal gas, cryogenic Package Leaflet: Information for the User
 Liquid Medical Oxygen Medicinal gas, cryogenic Package Leaflet: Information for the User Liquid Medical Oxygen, Oxygen 99.5%, Medicinal gas, cryogenic Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start
Liquid Medical Oxygen Medicinal gas, cryogenic Package Leaflet: Information for the User Liquid Medical Oxygen, Oxygen 99.5%, Medicinal gas, cryogenic Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start
FIRST AID GUIDE Dr. Michael Stachiw, Ph.D.
 FIRST AID GUIDE Revised May 19, 2003 This first aid guide is provided as a set of general instructions in using the materials included in the average first aid kit. It should be noted that this guide is
FIRST AID GUIDE Revised May 19, 2003 This first aid guide is provided as a set of general instructions in using the materials included in the average first aid kit. It should be noted that this guide is
Important Notices. Mouthpiece. Used properly, POWERbreathe can be used safely by almost anyone without any harmful side effects.
 Mouthpiece Valve lower chamber tensioner knob End Cap load calibrated spring Important Notices Used properly, POWERbreathe can be used safely by almost anyone without any harmful side effects. 1. If you
Mouthpiece Valve lower chamber tensioner knob End Cap load calibrated spring Important Notices Used properly, POWERbreathe can be used safely by almost anyone without any harmful side effects. 1. If you
Page: 1 of 6 Responsible faculty: (Signature/Date)
 Author: Tiffanie Brooks Brad Goodwin Paul B Stonum 1 of 6 Responsible faculty: (Signature/Date) I. Purpose: This document was created by the ACS staff as a guideline for anesthesia monitoring during surgery,
Author: Tiffanie Brooks Brad Goodwin Paul B Stonum 1 of 6 Responsible faculty: (Signature/Date) I. Purpose: This document was created by the ACS staff as a guideline for anesthesia monitoring during surgery,
Instructions/Procedure for Use of the Speaking Valve
 Instructions/Procedure for Use of the Speaking Valve Notes on the use of the speaking valve for ventilator-dependent and non-ventilator dependent patients The speaking valve is a one-way valve that allows
Instructions/Procedure for Use of the Speaking Valve Notes on the use of the speaking valve for ventilator-dependent and non-ventilator dependent patients The speaking valve is a one-way valve that allows
Principles of Providing First Aid
 First Aid Principles of Providing First Aid Immediate care that is provided to the victim of injury or illness to minimize the adverse effects until experts take over. Proper first aid can mean the difference
First Aid Principles of Providing First Aid Immediate care that is provided to the victim of injury or illness to minimize the adverse effects until experts take over. Proper first aid can mean the difference
Pressure. There are a number of factors that put you at risk. Limited mobility can place extended pressure on an area of your body.
 Pressure Preventing pressure sores is a daily concern for individuals who have a spinal cord injury (SCI). You want to stay healthy and avoid this serious skin problem in order to be free to do whatever
Pressure Preventing pressure sores is a daily concern for individuals who have a spinal cord injury (SCI). You want to stay healthy and avoid this serious skin problem in order to be free to do whatever
How Your Ears Respond to Pressure. 6 Methods to Equalize Your Ears. 10 Tips that Make Equalizing Easier. How to Deal with Other Ear Problems.
 DAN s Smart Guide to Ear Equalization Beat the Squeeze: Equalize Like a Pro How Your Ears Respond to Pressure. 6 Methods to Equalize Your Ears. 10 Tips that Make Equalizing Easier. How to Deal with Other
DAN s Smart Guide to Ear Equalization Beat the Squeeze: Equalize Like a Pro How Your Ears Respond to Pressure. 6 Methods to Equalize Your Ears. 10 Tips that Make Equalizing Easier. How to Deal with Other
Information about oxygen
 Information about oxygen INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS, CARERS AND FAMILIES 1 Why have I been given oxygen? Oxygen is vital for our bodies and having low oxygen levels can make you feel very unwell. There are
Information about oxygen INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS, CARERS AND FAMILIES 1 Why have I been given oxygen? Oxygen is vital for our bodies and having low oxygen levels can make you feel very unwell. There are
FACTSHEET F36 UNDERSTANDING YOUR HOME OXYGEN THERAPY. Why do I need oxygen therapy at home? How will oxygen therapy help me?
 UNDERSTANDING YOUR HOME OXYGEN THERAPY This factsheet aims to give you information about how home oxygen therapy will help you, how it is provided, the equipment involved and how to use it. Why do I need
UNDERSTANDING YOUR HOME OXYGEN THERAPY This factsheet aims to give you information about how home oxygen therapy will help you, how it is provided, the equipment involved and how to use it. Why do I need
R S A B C CPR. Basic Life Support Flow Chart Check for danger. Check Response. Send for Help. Check Airway. Check for Breathing.
 CPR CPR is the technique of the manual inflation of the lungs with oxygen, and compression of the heart, therefore pumping oxygenated blood around the body, and keeping the vital organs supplied with oxygen.
CPR CPR is the technique of the manual inflation of the lungs with oxygen, and compression of the heart, therefore pumping oxygenated blood around the body, and keeping the vital organs supplied with oxygen.
Tracheostomy and Ventilator Education Program Module 11: Emergency Preparedness
 Tracheostomy and Ventilator Education Program Module 11: Emergency Preparedness Disclaimer This material is intended for use by trained family members and caregivers of children with tracheostomies who
Tracheostomy and Ventilator Education Program Module 11: Emergency Preparedness Disclaimer This material is intended for use by trained family members and caregivers of children with tracheostomies who
Having a one-way valve after laryngectomy. Information for patients Speech and Language Therapy
 Having a one-way valve after laryngectomy Information for patients Speech and Language Therapy Air To lungs Air Larynx To lungs To stomach A. Before laryngectomy B. After laryngectomy Air Muscles vibrating
Having a one-way valve after laryngectomy Information for patients Speech and Language Therapy Air To lungs Air Larynx To lungs To stomach A. Before laryngectomy B. After laryngectomy Air Muscles vibrating
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System
 Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
On the Go with Oxygen
 On the Go with Oxygen People with chronic lung disease may need oxygen therapy. Oxygen therapy is used to normalize the oxygen level in blood during sleep, rest, activity and during acute illnesses in
On the Go with Oxygen People with chronic lung disease may need oxygen therapy. Oxygen therapy is used to normalize the oxygen level in blood during sleep, rest, activity and during acute illnesses in
FISH GET GAS, TOO SCOTT SPERBER SHERMAN OAKS CES DECEMBER 4, Background on Pressure
 FISH GET GAS, TOO SCOTT SPERBER SHERMAN OAKS CES DECEMBER 4, 2004 Background on Pressure If you have ever held your breath and dived to the bottom of a swimming pool, you may have felt pressure on your
FISH GET GAS, TOO SCOTT SPERBER SHERMAN OAKS CES DECEMBER 4, 2004 Background on Pressure If you have ever held your breath and dived to the bottom of a swimming pool, you may have felt pressure on your
Cold Weather Emergencies
 Cold Weather Emergencies Introduction Medical emergencies can result from exposure to heat or cold. Certain populations are at higher risk for heat and cold emergencies. Children Older people People with
Cold Weather Emergencies Introduction Medical emergencies can result from exposure to heat or cold. Certain populations are at higher risk for heat and cold emergencies. Children Older people People with
OXYGEN THERAPY. Teaching plan
 OXYGEN THERAPY Teaching plan To use this lesson for self-study, the learner should read the material, do the activity, and take the test. For group study, the leader may give each learner a copy of the
OXYGEN THERAPY Teaching plan To use this lesson for self-study, the learner should read the material, do the activity, and take the test. For group study, the leader may give each learner a copy of the
First Aid Exercises 1
 First Aid Exercises 1 1 A N S W E R T H E Q U E S T I O N S I N Y O U R O W N W O R D S! What are the emergency numbers you should remember? What kind of information should you give when you call for help?
First Aid Exercises 1 1 A N S W E R T H E Q U E S T I O N S I N Y O U R O W N W O R D S! What are the emergency numbers you should remember? What kind of information should you give when you call for help?
Ventilation Tubes Specification Sheet
 Product Overview The NETWORK ENT Ventilation Tubes are designed for easy placement through the tympanic membrane to ventilate the middle ear space, and, if present, drain accumulations of fluid from the
Product Overview The NETWORK ENT Ventilation Tubes are designed for easy placement through the tympanic membrane to ventilate the middle ear space, and, if present, drain accumulations of fluid from the
live outside the body and can often be treaded by antibiotics. need other organisms to live and prevention of is critical.
 Name: Chapter 7: Before Providing Care and Victim Assessment After you rescue a victim from the water, your next steps are to any - conditions by performing a assessment. What is a bloodborne pathogen?
Name: Chapter 7: Before Providing Care and Victim Assessment After you rescue a victim from the water, your next steps are to any - conditions by performing a assessment. What is a bloodborne pathogen?
Other diseases or age process
 1 BLS For Healthcare Providers 2 Time is Critical! begins to die in 4 to 6 minutes Brain matter cannot regenerate itself In order to sustain life, the human body must have going in and out and must be
1 BLS For Healthcare Providers 2 Time is Critical! begins to die in 4 to 6 minutes Brain matter cannot regenerate itself In order to sustain life, the human body must have going in and out and must be
REEFTRIP.com. Medical Questionnaire Dive Medical Recreational AS Section Abbott Street, Cairns T: E:
 REEFTRIP.com 100 Abbott Street, Cairns T: 07 4037 2700 E: info@reeftrip.com Medical Questionnaire Dive Medical Recreational AS4005.1 Please complete the following Section 1 1 Surname: Given Names 2 Date
REEFTRIP.com 100 Abbott Street, Cairns T: 07 4037 2700 E: info@reeftrip.com Medical Questionnaire Dive Medical Recreational AS4005.1 Please complete the following Section 1 1 Surname: Given Names 2 Date
Compressed Medical Oxygen Medicinal gas, compressed
 Compressed Medical Oxygen Medicinal gas, compressed Package Leaflet: Information for the User Compressed Medical Oxygen Oxygen 99.5% Medicinal gas, compressed Read all of this leaflet carefully before
Compressed Medical Oxygen Medicinal gas, compressed Package Leaflet: Information for the User Compressed Medical Oxygen Oxygen 99.5% Medicinal gas, compressed Read all of this leaflet carefully before
facial protection range
 facial protection RaNGE 2 facial protection The Universal facial protection range includes; UniProtect Standard Face Masks FluidProtect Fluid Resistant Face Masks EyeProtect Eye Wear UniProtect Respirators
facial protection RaNGE 2 facial protection The Universal facial protection range includes; UniProtect Standard Face Masks FluidProtect Fluid Resistant Face Masks EyeProtect Eye Wear UniProtect Respirators
Caring for a balloon retained gastrostomy tube (Pexact or RIG tube) GI Unit Patient Information Leaflet
 Caring for a balloon retained gastrostomy tube (Pexact or RIG tube) GI Unit Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is about caring for a balloon retained gastrostomy tube. It includes information
Caring for a balloon retained gastrostomy tube (Pexact or RIG tube) GI Unit Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is about caring for a balloon retained gastrostomy tube. It includes information
FIRST AID. Toolbox Talk
 FIRST AID Toolbox Talk Cuts 1. Stop the Bleeding Apply direct pressure on the area. 2. Clean and Protect Clean the area with warm water and gentle soap. Apply an antibiotic ointment to reduce chance of
FIRST AID Toolbox Talk Cuts 1. Stop the Bleeding Apply direct pressure on the area. 2. Clean and Protect Clean the area with warm water and gentle soap. Apply an antibiotic ointment to reduce chance of
Effective Date: September, 2011 Revised: August 17, 2016 OXYGEN, ADMINISTRATION OF
 OXYGEN, ADMINISTRATION OF Purpose: Supplemental oxygen may be required to meet metabolic demands of students who have chronic respiratory or cardiac conditions. Oxygen therapy treats or prevents hypoxia
OXYGEN, ADMINISTRATION OF Purpose: Supplemental oxygen may be required to meet metabolic demands of students who have chronic respiratory or cardiac conditions. Oxygen therapy treats or prevents hypoxia
FIRST AID. Study Topics. At a minimum, the following topics are to be studied for the first aid exam.
 FIRST AID Study Topics At a minimum, the following topics are to be studied for the first aid exam. TOPIC Avoid getting air in stomach during rescue breathing Burns Kinds of Burns & Care Calling for Help
FIRST AID Study Topics At a minimum, the following topics are to be studied for the first aid exam. TOPIC Avoid getting air in stomach during rescue breathing Burns Kinds of Burns & Care Calling for Help
Saint Bernard First Aid Coloring Book
 Saint Bernard First Aid Coloring Book Illustrated by Nicole Poppleton Do you know how to dial 911? A CUT OR A SCRAPE NOSE BLEEDS Sit or stand upright to slow the flow of blood. Do not tip your head back.
Saint Bernard First Aid Coloring Book Illustrated by Nicole Poppleton Do you know how to dial 911? A CUT OR A SCRAPE NOSE BLEEDS Sit or stand upright to slow the flow of blood. Do not tip your head back.
Effective First Aid. Keeps a victim calm and helps them recover faster.
 1 First Aid Overview Marcy Thobaben, LPN EMT-B Bluegrass Health & Safety, Inc. Disclaimer: This presentation is for information and background only and is not intended to certify or train anyone in First
1 First Aid Overview Marcy Thobaben, LPN EMT-B Bluegrass Health & Safety, Inc. Disclaimer: This presentation is for information and background only and is not intended to certify or train anyone in First
ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Oxygen Therapy
 For faculty use only Educator s name Score Date ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Oxygen Therapy Student s name Date Verify order Patient record Assess for procedure need Identify, gather, and prepare equipment
For faculty use only Educator s name Score Date ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Oxygen Therapy Student s name Date Verify order Patient record Assess for procedure need Identify, gather, and prepare equipment
extricare NPWT Foam Kit Instruction for Use
 extricare NPWT Foam Kit Instruction for Use www.devonmedicalinc.com 1.866.446.0092 Manufactured For: Devon Medical, Inc. 1100 1st Avenue, Suite 202 King of Prussia PA 19406, USA www.devonmedicalinc.com
extricare NPWT Foam Kit Instruction for Use www.devonmedicalinc.com 1.866.446.0092 Manufactured For: Devon Medical, Inc. 1100 1st Avenue, Suite 202 King of Prussia PA 19406, USA www.devonmedicalinc.com
Guide to Cold Stress at Work
 Guide to Cold Stress at Work WCB Website: www.wcb.pe.ca Toll free in Atlantic Canada: 1-800-237-5049 Revised: Jan/06 Cold Stress at Work Working in the cold is part of the job for many Prince Edward Islanders.
Guide to Cold Stress at Work WCB Website: www.wcb.pe.ca Toll free in Atlantic Canada: 1-800-237-5049 Revised: Jan/06 Cold Stress at Work Working in the cold is part of the job for many Prince Edward Islanders.
2) an acute situation in which hypoxemia is suspected.
 I. Subject: Oxygen Therapy II. Policy: Oxygen therapy shall be initiated upon a physician's order by health care professionals trained in the set-up and principles of safe oxygen administration. Oxygen
I. Subject: Oxygen Therapy II. Policy: Oxygen therapy shall be initiated upon a physician's order by health care professionals trained in the set-up and principles of safe oxygen administration. Oxygen
War Surgery Dr. Abdulwahid INTRODUCTION: AIRWAY, BREATHING
 War Surgery Dr. Abdulwahid INTRODUCTION: AIRWAY, BREATHING The aims of war surgery: Save life Avoid infectious complications Save limbs Minimize residual disability The outcome is influenced by: Type of
War Surgery Dr. Abdulwahid INTRODUCTION: AIRWAY, BREATHING The aims of war surgery: Save life Avoid infectious complications Save limbs Minimize residual disability The outcome is influenced by: Type of
Definition An uninterrupted path between the atmosphere and the alveoli
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Airway Management (Class 9) Airway Definition An uninterrupted path between the atmosphere and the alveoli Methods of opening the airway Positioning Left lateral recumbent
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Airway Management (Class 9) Airway Definition An uninterrupted path between the atmosphere and the alveoli Methods of opening the airway Positioning Left lateral recumbent
THE AMERICAN SAFETY & HEALTH INSTITUTE ADULT CPR EXAM
 THE AMERICAN SAFETY & HEALTH INSTITUTE ADULT CPR EXAM 1. During an adult victim s assessment, responder should check victim for responsiveness. If no response, responder should first: A. Check for signals
THE AMERICAN SAFETY & HEALTH INSTITUTE ADULT CPR EXAM 1. During an adult victim s assessment, responder should check victim for responsiveness. If no response, responder should first: A. Check for signals
TITLE: Pulse Oximetry COMPETENCY #: Resp #1 NEW COMPETENCY REVISION DATE: 10/18/12 EMPLOYEE NAME. DATE INITIAL RE-EVALUATION ANNUAL (if required) PRN
 : Pulse Oximetry COMPETENCY #: Resp #1 NEW COMPETENCY REVISION : 10/18/12 INITIAL RE-EVALUATION ANNUAL (if required) PRN 1. Verifies physician order. 2. Gathers equipment and supplies. 3. Knocks on door
: Pulse Oximetry COMPETENCY #: Resp #1 NEW COMPETENCY REVISION : 10/18/12 INITIAL RE-EVALUATION ANNUAL (if required) PRN 1. Verifies physician order. 2. Gathers equipment and supplies. 3. Knocks on door
STRANGLES. What are the dangers?
 STRANGLES What is it? Strangles is caused by a bacteria. The full name of this bacteria is Streptococcus Equi subsp Equi. The bacteria infects the upper respiratory tract (e.g. around the head). It causes
STRANGLES What is it? Strangles is caused by a bacteria. The full name of this bacteria is Streptococcus Equi subsp Equi. The bacteria infects the upper respiratory tract (e.g. around the head). It causes
NORMAN KNIGHT HYPERBARIC MEDICINE CENTER
 NORMAN KNIGHT HYPERBARIC MEDICINE CENTER The heroic firefighters of Massachusetts, who receive emergency hyperbaric oxygen treatment for smoke inhalation, were among the first people to benefit from the
NORMAN KNIGHT HYPERBARIC MEDICINE CENTER The heroic firefighters of Massachusetts, who receive emergency hyperbaric oxygen treatment for smoke inhalation, were among the first people to benefit from the
IATA Guidance for airline health and safety staff on the medical response to Cabin Air Quality Events
 IATA Guidance for airline health and safety staff on the medical response to Cabin Air Quality Events (Smoke, Fumes/odours) 1. Introduction Much controversy exists in relation to the potential health ramifications
IATA Guidance for airline health and safety staff on the medical response to Cabin Air Quality Events (Smoke, Fumes/odours) 1. Introduction Much controversy exists in relation to the potential health ramifications
Balloon Dilation of the Eustachian Tube
 Protocol Balloon Dilation of the Eustachian Tube (701158) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 01/01/19 Next Review Date: 09/19 Preauthorization No Review Dates: 09/18 This protocol considers this test or procedure
Protocol Balloon Dilation of the Eustachian Tube (701158) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 01/01/19 Next Review Date: 09/19 Preauthorization No Review Dates: 09/18 This protocol considers this test or procedure
KimVent * Closed Suction System Solutions for the Home Care Pediatric Patient. Instructions for Use. Ballard* Trach Care* Technology
 KimVent * Closed Suction System Solutions for the Home Care Pediatric Patient Ballard* Trach Care* Technology Instructions for Use Use this space to keep all important telephone numbers in one place. Important
KimVent * Closed Suction System Solutions for the Home Care Pediatric Patient Ballard* Trach Care* Technology Instructions for Use Use this space to keep all important telephone numbers in one place. Important
THAL EQUINE LLC Regional Equine Hospital Horse Owner Education & Resources Santa Fe, New Mexico
 THAL EQUINE LLC Regional Equine Hospital Horse Owner Education & Resources Santa Fe, New Mexico 505-438-6590 www.thalequine.com Colic Surgery: What Horse Owners Should Know Tonight, at midnight, you are
THAL EQUINE LLC Regional Equine Hospital Horse Owner Education & Resources Santa Fe, New Mexico 505-438-6590 www.thalequine.com Colic Surgery: What Horse Owners Should Know Tonight, at midnight, you are
3.6. The Respiratory System
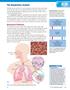 The Respiratory System Whether you are aware of it or not, you breathe in and out 15 times each minute on average. This rate increases automatically if your physical activity increases. With normal breathing,
The Respiratory System Whether you are aware of it or not, you breathe in and out 15 times each minute on average. This rate increases automatically if your physical activity increases. With normal breathing,
Patient Home Care Information
 The simplicity of PICO Patient Home Care Information Date: Your nurse: Your doctor: Other useful numbers: Introduction This patient handbook will provide you with important information while you are receiving
The simplicity of PICO Patient Home Care Information Date: Your nurse: Your doctor: Other useful numbers: Introduction This patient handbook will provide you with important information while you are receiving
Urgent Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
 Urgent Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn: what hyperbaric oxygen therapy is what it helps treat what happens after your therapy who to call if you
Urgent Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn: what hyperbaric oxygen therapy is what it helps treat what happens after your therapy who to call if you
Universal Precautions
 First Aid Safety First Aid is a matter of Personal Choice. The Company does not require employees to provide first aid for fellow employees. We have a medical provider close by to provide these services.
First Aid Safety First Aid is a matter of Personal Choice. The Company does not require employees to provide first aid for fellow employees. We have a medical provider close by to provide these services.
FUNDAMENTAL CRITERIA FOR FIRST AID INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 1 FUNDAMENTAL CRITERIA FOR FIRST AID INTRODUCTION Soldiers may have to depend upon their first aid knowledge and skills to save themselves or other soldiers. They may be able to save a life, prevent
CHAPTER 1 FUNDAMENTAL CRITERIA FOR FIRST AID INTRODUCTION Soldiers may have to depend upon their first aid knowledge and skills to save themselves or other soldiers. They may be able to save a life, prevent
Objectives: Assisting with Medication, Checking vital Signs
 Assisting with Medication, Checking vital Signs Duty: Assist Client with Personal Hygiene Task : A.12 Remind client to take medication A.17 Check client s temperature A.18 Check client s pulse A.19 Check
Assisting with Medication, Checking vital Signs Duty: Assist Client with Personal Hygiene Task : A.12 Remind client to take medication A.17 Check client s temperature A.18 Check client s pulse A.19 Check
UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 9.01 GENERAL FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. Brings oxygenated air to the alveoli B. Removes air containing carbon dioxide C. Filters, warms, and humidifies
UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 9.01 GENERAL FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. Brings oxygenated air to the alveoli B. Removes air containing carbon dioxide C. Filters, warms, and humidifies
VENTILATORS PURPOSE OBJECTIVES
 VENTILATORS PURPOSE To familiarize and acquaint the transfer Paramedic with the skills and knowledge necessary to adequately maintain a ventilator in the interfacility transfer environment. COGNITIVE OBJECTIVES
VENTILATORS PURPOSE To familiarize and acquaint the transfer Paramedic with the skills and knowledge necessary to adequately maintain a ventilator in the interfacility transfer environment. COGNITIVE OBJECTIVES
CHAPTER 3: TAKING ACTION AND CARING FOR BREATHING EMERGENCIES Multiple Choice
 CHAPTER 3: TAKING ACTION AND CARING FOR BREATHING EMERGENCIES Multiple Choice Circle the correct answer. 1. One of the first steps to follow in an emergency is a. Transporting the victim to the hospital.
CHAPTER 3: TAKING ACTION AND CARING FOR BREATHING EMERGENCIES Multiple Choice Circle the correct answer. 1. One of the first steps to follow in an emergency is a. Transporting the victim to the hospital.
Pop Quiz. What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach?
 Pop Quiz What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach? Respiratory System Review Cellular respiration: obtain glucose and oxygen, get
Pop Quiz What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach? Respiratory System Review Cellular respiration: obtain glucose and oxygen, get
HOSPITAL: Date: Date: Date: Date:
 HOSPITAL: Respiratory Care Services Policy and Procedure Manual Policy and Procedure Area: Respiratory Care Services Policy Number: Current Effective Date Review Date Revised Date StabilTube Performed
HOSPITAL: Respiratory Care Services Policy and Procedure Manual Policy and Procedure Area: Respiratory Care Services Policy Number: Current Effective Date Review Date Revised Date StabilTube Performed
Staying Warm in the Winter
 Staying Warm in the Winter When winter arrives it doesn t mean an end to enjoying the outdoors. Staying active during the winter months is essential! Instead, it s important to keep warm while working
Staying Warm in the Winter When winter arrives it doesn t mean an end to enjoying the outdoors. Staying active during the winter months is essential! Instead, it s important to keep warm while working
Assessing the Victim
 CHAPTER 4 Assessing the Victim (Video Assessing the victim and recovery position) Assess the Victim Check scene for safety Initial assessment for life-threatening conditions Unresponsiveness Lack of normal
CHAPTER 4 Assessing the Victim (Video Assessing the victim and recovery position) Assess the Victim Check scene for safety Initial assessment for life-threatening conditions Unresponsiveness Lack of normal
Construction Technology Safety Board WHMIS
 WHMIS Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System (WHMIS) Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System (WHMIS) is a national system for providing employers and workers with information to recognize
WHMIS Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System (WHMIS) Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System (WHMIS) is a national system for providing employers and workers with information to recognize
leaders in enteral delivery
 feeding kit user guide leaders in enteral delivery 10 20 30 ml 1 medicina balloon gastrostomy Reorder No. 82-281 FIVE GRAM LUBRICATING JELLY Water Soluble STERILE unless opened or damaged 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
feeding kit user guide leaders in enteral delivery 10 20 30 ml 1 medicina balloon gastrostomy Reorder No. 82-281 FIVE GRAM LUBRICATING JELLY Water Soluble STERILE unless opened or damaged 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
First Aid - immediate care that is given to the victim of an injury or illness until experts can take over - Oftentimes, it s the difference between
 First Aid First Aid - immediate care that is given to the victim of an injury or illness until experts can take over - Oftentimes, it s the difference between life and death or recovery vs permanent disability
First Aid First Aid - immediate care that is given to the victim of an injury or illness until experts can take over - Oftentimes, it s the difference between life and death or recovery vs permanent disability
PaidaLajin for Acute symptoms
 PaidaLajin for Acute symptoms The following are recommendations on how to use PaidaLajin to relieve acute symptoms. These methods can be used to deal with various healing reactions as well. The only difference
PaidaLajin for Acute symptoms The following are recommendations on how to use PaidaLajin to relieve acute symptoms. These methods can be used to deal with various healing reactions as well. The only difference
Hip Replacement (Posterior) Precautions: What to Expect at Home
 Hip Replacement (Posterior) Precautions: What to Expect at Home Your Recovery You will need to be careful to protect your new joint after hip replacement surgery. Along with doing your physical therapy
Hip Replacement (Posterior) Precautions: What to Expect at Home Your Recovery You will need to be careful to protect your new joint after hip replacement surgery. Along with doing your physical therapy
Colic Surgery Is it the Right Decision for. My Horse?
 Colic Surgery Is it the Right Decision for My Horse? Britany Nehring-Lappin, DVM Colic is the basic term for any abdominal pain a horse experiences. Abdominal pain can have numerous causes but in the horse
Colic Surgery Is it the Right Decision for My Horse? Britany Nehring-Lappin, DVM Colic is the basic term for any abdominal pain a horse experiences. Abdominal pain can have numerous causes but in the horse
