Effect of Riser-Seabed Interaction on the Dynamic Behavior of Risers
|
|
|
- Nelson Baldwin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Oil, Gas and Petrochemical Technology Vol. 4, No. 1, pp Effect of Riser-Seabed Interaction on the Dynamic Behavior of Risers Abdolrahim Taheri 1,*, Reza Siahtiri 2 1 Assistant Professor, Offshore Structural Engineering Department, Petroleum University of Technology, Iran 2 M.Sc. in Offshore Structural Engineering, Petroleum University of Technology, Iran ARTICLE INFO Article history: Received: November 17, 2016 Accepted: November 04, 2017 Keywords: Steel catenary riser Touchdown point Seabed soil type Riser-seabed interaction Linear seabed model * Corresponding author; rahim.taheri@put.ac.ir Tel.: Fax: ABSTRACT In recent years, the production of oil and gas has been developed in deep water depths which exceed 500m. Deep water developments are being followed strongly in different parts of the world (Caspian Sea, Gulf of Mexico, etc.). The movement of floater causes severe stress at the touchdown point (TDP) in steel catenary risers (SCR). The main objective of this study was to simulate the exact behavior of the riser in the vicinity of the touchdown zone (TDZ) by implementing linear SCR-seabed interaction model. Hence, present study attempted to investigate the riser-seabed interaction during lateral cyclic pipe movements and also the influence of seabed evolution around the TDZ based on the vertical cyclic movements. Moreover, The significance of the soil types in the response of riser pipeline at TDP was analyzed based on the vertical and lateral interaction. The fully non-linear time domain finite element model was utilized to simulate the riser behavior.
2 41 A. Taheri & R. Siahtiri 1. Introduction In recent years, the production of oil and gas has been taking place in water depths which exceed 500m. Deep water developments are being followed strongly in different parts of the world (e.g. Caspian Sea, Gulf of Mexico, etc.). The Sardar-e Jangal gas field is an Iranian natural gas field which is located in the Geographical coordinates longitudinal and 37.7 latitudinal. The total proven reserves at this field are noticeable. Therefore, doing a study in this area, according to the environmental conditions of the Caspian Sea is increasingly essential [1]. Riser system is a key element in providing safety in all phases from drilling, completion/workover, production/injection to export. The main function of riser is to transport fluids or gas from seabed to a host platform. Steel Catenary Riser (SCR) is one of the direct alternatives to flexible riser. It may be used at larger diameters, higher pressures and temperatures and may be produced more easily. SCR can be suspended in longer lengths, removing the need for mid-depth buoys. Steel lines are cheaper than flexible and may be used in greater water depths without a disproportionate increase in cost. At the seabed, the need of riser base, stress joint or flex joint have been eliminated. This reduces the complexity of riser system and cost savings are made as a result of simplified riser system [2]. A SCR attached to a floating at its upper, encounters fluctuations in and near its Touchdown Zone (TDZ) under different environmental conditions. In other words, the riser is continuously subject to oscillatory environmental loads. ROV observations of installed SCRs have shown deep trenches cutting into the seabed in the TDZ [3]. Therefore, it is important to develop better understanding and modeling of the SCR soil interaction mechanism to provide a realistic technique for determining dynamic response and strength performance in the TDZ. Oil and gas fields fluctuate in geology and environments, and the result of these differences are the different designs of the riser systems. SCRs are subjected to various types of loads and deformations that range from the routine to the extreme or accidental. The purpose of SCRs design is to design a riser system that can tolerate load effects throughout its expected lifetime. The design is safe if the resistance is more than response and the ratio of response over resistance shall be less than the acceptance criteria or allowable factor. Safety factor shall be incorporated in the design check in order to account for various uncertainties due to natural variability, inaccuracy in analysis procedures and the control of load effects and uncertainties in structural resistance. Siahtiri and Taheri [1] analyzed all of the possible loads which can affect the SCR, for instance hydrostatic and propagation collapse, and obtained the structural parameters of SCR such as wall thickness and riser pipe diameter according to the standard design guidelines [2, 4] based on the Caspian sea severe environmental condition with 100 return period for wave and 10 return period for current and wind. Recent studies have focused on elaborating the SCR seabed interaction. Aubeny and Biscontin [5] considers the riser-seafloor interaction problem in terms of a pipe resting on a bed of springs, the stiffness characteristics of which are described by nonlinear load-deflection P-y curves.
3 Journal of Oil, Gas and Petrochemical Technology Vol. 4, No. 1, pp Also, Wang et al. [6] conducted the laboratory tests to investigate the SCRseabed interaction during lateral cyclic riser movements and the influence of seabed evolution around the TDZ on the following vertical cyclic pipe movements. Hejazi and Kimiaei [7] proposed an equivalent linear soil stiffness instead of nonlinearly modelled seabed soil. They showed the design procedures for SCRs based on the linear soil models for the seabed are not only simple but also it usually leads to conservative results. The riser-soil interaction consists of seabed stiffness and equivalent friction to represent the soil resistance to movement of the pipe. The equivalent friction resistance is based on the coulomb friction for non-cohesive soil, cohesive soil or a combination of the two (silt, sand). Therefore, it is important to predict the soil contact pressure, equivalent friction and soil stiffness [8]. The numerical results for the assessment of the SCR's global response at the critical point in the TDZ are presented, so that the seabed is modeled using a linear seabed model in the vertical direction [9], and Coulomb friction soil models in the lateral seabed direction [10-11]. The main objective of this study was to simulate the exact behavior of the riser in the vicinity of the touchdown zone by implementing linear SCR-seabed interaction model. Most previous studies have focused on riser-seabed interaction in the vertical direction at the TDZ. Therefore, present study attempted to investigate the riser-seabed interaction during lateral cyclic pipe movements and the influence of seabed evolution around the TDZ based on the vertical cyclic movements. Moreover, the significance of the soil types in the response of riser pipeline at TDP was analyzed based on the vertical and lateral interactions. The fully non-linear time domain finite element model was used to simulate the riser behavior. 2. Numerical modeling of riser-seabed interaction The dynamic analysis is a time simulation of the motions of the model over a specified period of time, starting from the position derived by the static analysis. Based on dynamic force equilibrium equation, one specifies a constant time step for the numeric integration scheme. Force equilibrium is achieved in each time step by iteration. Typical numerical integration methods include Newmark-β, Wilson method, etc. OrcaFlex also employs Generalized-α implicit integration scheme and Forward Euler Explicit integration scheme [12]. Even though the riser is submerged, it is still affected by surface forces, as these create motions on the floater which translates directly to the riser itself. Because SCR does not have tensioner systems, it relies on self-weight to keep the tension. Increased vertical motion gives reduced tension, which can cause buckling and instability. Since the system is all connected, both the motion and offset of the floater constitute a source of static and dynamic loading on the riser. The main data needed for riser designs are: Static offset (mean offset due to wave, wind and current) and Wave frequency motions (First-order wave induced motions) [4]. Floating Production Unit (FPU) can be subjected to the large static displacements. The static vessel offset regarding the operating extreme response analysis is 10% of water depth for intact mooring and 12% for one mooring line failure condition. These displacements are in the plane and
4 43 A. Taheri & R. Siahtiri out of plane of a SCR. A generic configuration of an SCR attached to a floating platform system has been considered as shown in Figure 1. It is believed that the riser dynamics has important contributions to fatigue life, so the dynamic effects of the riser including the drag, inertia and added mass were included for a more realistic investigation. The system has been studied through displacement-controlled, quasi-static and dynamic analyses with the floating excitation based on the generic approximated RAOs from Caspian Sea. No hydrodynamic software is needed to extract vessel RAO under environmental loads, which is usually a common practice in loadcontrolled analyses [13]. In this study, a semi-submersible vessel was used as shown in Figure 2. Hence, Response Amplitude Operators (RAOs) for semi-submersibles were applied as shown in Figure 3. This RAO was integrated into the model used in OrcaFlex. Figure 1. Static configuration of SCR under floating offset Figure 2. Semi-FPU and SCR modeling in OrcaFlex software
5 Journal of Oil, Gas and Petrochemical Technology Vol. 4, No. 1, pp Figure 3. Approximation FPU RAO in head seas, wave heading = 0 The main factors to control the magnitude of bending stress in the riser pipe are riser characteristics, environmental criteria and touchdown zone (TDZ) characteristics. The movement and oscillation of the SCR in the TDZ will cause severe stress and dynamic embedment of the SCR into the seabed. A typical schematic illustration of the SCR seabed interaction in the TDZ is given in Figure 4. Figure 4. Schematic illustration of the pipe interaction issue 3. Case study 3.1. Environmental conditions Wave condition can be described by either a deterministic design, or by applying wave spectra. Most spectra are described in terms of significant wave height ( ), spectral peak period ), spectral shape and direction. For Caspian Sea, a 100-year return period is given as [1]: According to the dominant spectra wave in Caspian Sea, finally, the
6 45 A. Taheri & R. Siahtiri JONSWAP was used in the analyses of this paper. The resulting spectrum was: s( f ) a e f 2 p 4 g 1.25( ) f a e (1) 4 5 (2 ) f Where [( f f p 2 2 p ] ) / 2 f When When f f f p f p In Eq. (1), γ, typically the value of 3.3 is recommended for general usage, is the peak frequency and the values of α as the coefficient are 0.08 and respectively. The corresponding 10-year current profile has been shown in Table 1 [1, 14]. Table 1. Current speed vs. water depth Water depth (m) Current speed (m/s) 0 at water surface Steel catenary riser model description The SCR descends from a semisubmersible in a simple hanging catenary configuration, transitioning to a flow-line after 700m, and the SCR is connected to the floating at a mean top angle of 20 O to the vertical, as shown in Figure 1. The outside diameter is 461mm (18in) with a wall thickness of 21mm (0.825in) and a total riser pipe length is 2500m. The inertia coefficient CM used in this analysis is 2.0, and the added mass coefficient is one [1] Seabed soil condition The riser-soil interaction model consists of seabed stiffness and equivalent friction definition to represent the soil resistance to movement of the pipe. The equivalent friction resistance is mainly based on the coulomb friction for non-cohesive soil (sand), cohesive soil (clay) or a combination of the two (i.e. silt and sand), related to the soil density and the contact pressure between the soil and the pipe. Therefore, it is important to predict the soil contact pressure, equivalent friction and the soil stiffness accurately [8]. In the linear seabed models, the seabed is normally modelled as a spring and damped surface with a spring reaction force that is proportional to the depth of the penetration and the contact area, plus a damping force that is proportional to the rate of penetration. The seabed stiffness is constant of proportionality of the spring force and equals the spring reaction force per unit area of contact per unit depth of penetration. The seabed damping is the constant of proportionality of the damping force, and is the percentage of critical damping. The seabed characteristics are illustrated in Ta, which is extracted from tests conducted by Wagner [11]. Soil spring stiffness (k0) is constant and its unit is force per square length. Up-load displacement is equal to down-load displacement. Due to the influence of linear spring, the foundation support force increases without limit by increasing the relative displacement in proportion to
7 Journal of Oil, Gas and Petrochemical Technology Vol. 4, No. 1, pp the spring constant [15] Lateral displacement model Existing industry procedure to estimate the soil resistance is coulomb friction model which expresses the lateral resistance as the product of the effective submerged pipeline vertical force (submerged pipe weight minus hydrodynamic lift force) and a soil friction coefficient which depends on the soil type. The conventional riser-soil design procedure is modeling the interaction with spring links at intervals along the SCR flow-line. These links provide a bilinear soil resistance in the lateral direction as shown in Figure 5. Regarding the Coulomb friction model, the seabed friction force has a magnitude of up to, where is the friction coefficient and V is the seabed reaction force, and acts tangential to the seabed plane. The SCR, which is in contact with the seabed, maintains a friction target position, and a friction force is applied that acts on this target position. The breakout force is the maximum force needed to move the pipe from its stable position on the seabed. A linear model of the friction force is employed and is given by F K Ay to a magnitude of not more V than, where is the displacement from the un-sheared position, is the seabed shear stiffness, and A is the contact diameter multiplied by the length of the line represented by the node. The Coulomb friction models the friction force of V to V which occurs as a linear variation over the deflection range y breakout to ybreakout. Here y breakout is given by ybreakout V / Ks A [10]. V y s K s Figure 5. Coulomb friction model 4. Results and discussion 4.1. Global SCR response Due to the unavailability of the exact specifications of soil types in
8 47 A. Taheri & R. Siahtiri Caspian Sea for this study, the simulations were implemented for each soil type, which are listed in Table 2. It can be seen that the soft clay puts a greater effect on the riser stresses (such as Radial, Circumferential and Wall tension) at touchdown area, which can eventually lead to more damage to the riser (Figures 6, 7 and 8). Therefore, in this study the soft clay was selected as the soil type. The model analyses exhibited the maximum variation in the bending stress near the TDZ, which depended on the excursion and cyclic motions of the production units. As shown in Figures 6 and 7, for the soft clay both the seabed normal resistance was minimized and the pipe displacement in the seabed was maximized. Moreover, Figure 8 shows that the Von Mises combination stresses for the soft clay is bigger than the other soils. Table 2. Approximate soil properties of the model [11] Soil types Sliding Friction Coefficient ( Stiffness (kn/m/m 2 ) Soft clay Stiff clay Loose sand Dense sand Figure 6. Seabed resistance in each soil type Figure 7. Seabed penetration in each soil type
9 Journal of Oil, Gas and Petrochemical Technology Vol. 4, No. 1, pp Figure 8. Effect of different soil types on stresses at TDP The allowable Von Mises stresses of the riser are shown in Table 3. For the 0, 180 (in-plane load cases) and 90 (out-of-plane load case) wave and current directions, where the floater is in the mean, near and far position. The floating production unit offsets and dynamic motions in a severe environment influence the stresses in the TDZ, where the riser starts to contact the seabed. The riser was analyzed for the extreme operating intact mooring conditions. The extreme analyses were conducted for the load cases defined by API RP 2RD, and the strength analysis was performed for near (when the vessel offset was closest to the TDP, see Figure 9), far (when the vessel drifted away from the TDP) and transverse vessel position offsets and a 100-year wave combined with a 10-year current. The most critical section for the Von Mises stress occurred at the TDZ [2, 4]. The seabed interaction model has an influence on the calculated Von Mises stresses. For example, in the case study of 0 wave and current direction, Von Mises utilisation factor is 0.78 for the linear soil model as compared with 0.8 for the rigid seabed model. Therefore, the evaluation of the dynamic response depends on the employed soil model. The soil parameters have an invisible influence on the global risers dynamic response. Although the results show that the riser has a sufficient margin for the strength performance, it is important to note that the strength analyses are carried out with the same floating production unit offsets, wave and current data for both the near and far positions and intact extreme operating conditions. Wave and current direction Table 3. Strength analyses results (3-hour simulation time length) Mooring Riser offset Max Von Mises condition position stress/ at TDP Allowable stress/ 0 Intact Near Mean 0.71 Far Intact Transverse +Y Mean 0.71 Transverse -Y Intact Near Mean 0.72 Far 0.7
10 49 A. Taheri & R. Siahtiri Figure 9. Static configuration of SCR under vessel offset After modeling the riser at each position of the floating platform separately, the dynamic cyclic motions of the riser within the TDZ increased the riser's embedment beyond that produced by the static load. The bending moment and shear force were obtained and demonstrated together as a function of the riser arc length measured from the floating production unit. The floating offset governed the maximum bending moment and shear force at the TDP as shown in Figure 10. Figure 10. Riser static response for the 180 wave and current direction 4.2. Riser seabed vertical interaction response The dynamic riser-seabed penetration is explained as seabed penetration/d, and dynamic seabed contact resistance, explained as seabed resistance/d, which can be seen in Figures 11 and 12, for the 180 wave and current direction, respectively. The riser's vertical cyclic fluctuation had a significant effect on the riser at the TDZ. The linear soil model in the vertical direction was implemented to model. As can be seen in Figure 11, the soil resistance in linear seabed model reduced,correspondingly, the riser's penetration into the seabed increased when the soil was modeled as linear (Figure 12). Finally, as can be seen from Figure 13, the linear seabed model
11 Journal of Oil, Gas and Petrochemical Technology Vol. 4, No. 1, pp exerted the greatest influence on the riser at the TDP compared with the rigid seabed. As an important consequence, the linear soil model can provide consevative results compared with the rigid soil model. It also enable us to obtain the global riser dynamic performance at the TDZ more accurately. Figure 11. Dynamic SCR-seabed contact resistance in the near case (3-hour simulation) Figure 12. Displacement of SCR at the TDP Figure 13. Maximum Von Mises stress at the TDP
12 51 A. Taheri & R. Siahtiri 4.3. Riser seabed lateral interaction response A linear seabed model was used to investigate the riser-soil interaction on soft clay seabed and then it was compared with the riser-soil interaction on rigid seabed models. In addition, it was integrated with the lateral riser-soil interaction models, the Coulomb friction soil model. In this model, the riser-soil response for the 100-year wave and 10-year current is investigated in the lateral direction (90 ). The model was used to simulate the risers response by obtaining its lateral displacement. This lateral displacement on the seabed, using the severe environmental condition, has been presented in Figure 14. The analysis was done using the Coulomb friction model. Figure 14 displays the influence of the linear and rigid soil models on the specified arc length (1120 m) of the riser in the TDZ during a 3-hour simulation time. The lateral riser's movement in the TDZ obtained with the linear soil model was smaller than the rigid soil model for the same sliding friction factor ( ) due to the effect of the passive soil resistance. 0.2 Figure 14. SCR seabed lateral interaction at arc length 1120m (3-hour simulation) 5. Conclusion The main objective of this study was to simulate the dynamic behavior of the riser in the vicinity of the touchdown zone by implementing linear SCRseabed interaction model. In this paper, the effect of irregular wave angle of the incidence on riser and the contribution of floater transfer functions were considered. It was found that the maximum variation in the bending moment near the TDZ, depended on the offset and cyclic motion of the floater. This paper described a detailed analysis of the SCR connected to a semisubmersible in Caspian Sea environment. The dynamic analysis was performed for wave and current directions of 0, 180 and 90 (out-of-plane load case). The conclusion was that the maximum Von Mises stress of the SCR in TDP is at 180 wave and current direction when the FPU was in the near position. The significance of the soil types in the response of riser pipeline at TDP
13 Journal of Oil, Gas and Petrochemical Technology Vol. 4, No. 1, pp was analyzed based on the vertical and lateral interaction. The fully non-linear time domain finite element model was used to simulate the riser behavior. This paper discussed the significance of SCR-seabed interaction in the design of SCR for deep-water applications and reported the results of analysis of an SCR on soft clay in 700m depth of water for Sardar-e Jangal gas field. Past studies mostly focused on riser-soil interaction in the vertical direction. Therefore, present paper aimed to investigate the riser-soil interaction during the lateral cyclic pipe movements and the influence of seabed evolution around the TDZ based on the vertical cyclic pipe movements. Moreover, the significance of the soil types in the response of riser pipeline at the TDP was analyzed based on the vertical and lateral interaction. It was shown that the lateral displacement obtained with a linear soil model was smaller than the rigid soil model. Also, it was found that the differences between the sliding friction coefficients in the linear soil model with, were negligible in the vertical interaction. However, it was so significant in the lateral SCR-seabed interaction due to the passive soil resistance. Finally, it is concluded that the proper riser-soil vertical and lateral interaction model enables designers to obtain the global riser dynamic performance in the TDZ more accurately. Nomenclature D F FPSO FPU RAO H s K SCR t TDZ TLP T p TDP V y z ' Pipe outer diameter (mm) Sliding resistance of the pipeline along soil surface (kn/m) Floating production storage and offloading Floating production unit Response amplitude operation Significant wave height (m) Soil stiffness (kn/m/m 2 ) Steel catenary riser Pipe wall thickness (mm) Touchdown zone Tension leg platform Wave peak period (s) Touchdown point Vertical seabed reaction force (kn/m) Displacement from the unsheared position in lateral direction (m) Embedment depth of pipe below the seabed (m) Submerged unit weight of soil (kn/m 3 ) Sliding friction factor References [1] A. Taheri, R. Siahtiri, Steel Catenary Riser-Seabed Interaction Due to Caspian Sea Environmental Conditions, Jounal of Rehabilitation in Civil Engineering, vol. 2, pp , [2] API-RP-2RD. Recommended Practice For Design of Risers for Floating Production Systems, USA, 2009.
14 53 A. Taheri & R. Siahtiri [3] C. Bridge, H. Howells, Observations and modeling of steel catenary riser trenches,, International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference, ISOPE, July 1-6, Lisbon, Portugal, pp , [4] DNV-OS-F201, Offshore Standard For Dynamic Risers, Norway, [5] C.P. Aubeny, G. Biscontin, Seafloor-Riser Interaction Model, International Jounal of Geomechanics, vol. 9, pp , [6] L. Wang, K. Li, F. Yuan, Lateral Cyclic Interaction Between Catenary Riser and Soft Seabed Hinged Joint, Phys. Procedia, vol. 63, pp , [7] R. Hejazi, M. Kimiaei, Equivalent Linear Soil Stiffness in Fatigue Design of Steel Catenary Risers, Ocean Eng., vol. 111, pp , [8] Y. Bai, Pipelines and Risers, Elsevier Ocean Engineering Book Series, [9] X. Bai, W. Huang, M. Augusto, Riser-Soil Interaction Model Effects on the Dynamic Behavior of a Steel Catenary Riser, Mar. Struct., vol. 41, pp , [10] H. Elosta, S. Huang, A. Incecik, Dynamic Response of Steel Catenary Riser Using a Seabed Interaction under Random Loads, Ocean Eng., vol. 69, pp , [11] D.A. Wagner, J.D. Murff, Pipe-soil interaction model, Offshore Technology Conference, OTC, April 27-30, Houston, Texas, USA, [12] M. Randolph and P. Quiggin, Non-linear hysteretic seabed model for catenary pipeline contact, International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering, OMAE, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, [13] H. Shiri, Response of Steel Catenary Risers on Hysteretic Non-Linear Seabed, Appl. Ocean Res., vol. 44, pp , [14] M.E. McCormick, Ocean Engineering Mechanics, First edit. Cambridge University Press, [15] J.H. You, Numerical Model for Steel Catenary Riser on Seafloor Support, Master s Thesis, Offshore Technology Research Center, Texas A&M University, Texas, 2005.
15 Journal of Oil, Gas and Petrochemical Technology Vol. 4, No. 1, pp تأثیر اندرکنش رایزر و خاک بستر دریا بر روی رفتار دینامیکی 2 عبدالرحیم طاهری 1 * رضا سیاه تیری 1. استادیار گروه مهندسی سازه های فراساحل دانشگاه صنعت نفت ایران 2. کارشناس ارشد گروه مهندسی سازه های فراساحل دانشگاه صنعت نفت ایران چكيده در سال های اخیر تولید نفت و گاز به سمت آب های عمیق با عمق بیش از 155 متر توسعه یافته است. در حال حاضر این توسعه در نقاط مختلف آب های عمیق دنیا محقق شده است )بطور مثال دریای خزر خلیج مکزیک و غیره(. حرکت نوسانی شناور سبب ایجاد تنش های شدید در نقطه تماس رایز با بستر دریا میشود. هدف اصلی از این مطالعه شبیه سازی رفتار دقیق رایزر در محل تماس با بستر دریا با در نظر گرفتن مدل خطی اندرکنش خاک و بستر دریا میباشد. این مقاله به بررسی اندرکنش رایزر و خاک بستر در حین نوسان جانبی خط لوله رایزر و در نتیجه اثر تغییر شکل های خاک بستر در ناحیه تماس براساس حرکت نوسانی در جهت قائم میپردازد. بعالوه تاثیر انواع خاک بر پاسخ خط لوله رایزر در نقطه تماس با بستر دریا بر اساس اندرکنش قائم و اندرکنش جانبی آنالیز شده است. جهت شبیه سازی دقیق رفتار رایزر از یک مدل اجزای محدودی غیر خطی در حوزه زمان استفاده شده است. مشخصات مقاله تاریخچة مقاله: دریافت: 22 آبان 1931 پذیرش نهایی: 19 آبان 1931 کلمات کلیدی: رایزر کتنری فوالدی ناحیه تماس با بستر نوع خاک بستر دریا اندرکنش رایزر و خاک بستر دریا مدل خطی خاک بستر * عهدهدار مکاتبات رایانامه: rahim.taheri@put.ac.ir تلفن: دورنگار:
Learn more at
 Full scale model tests of a steel catenary riser C. Bridge 1, H. Howells 1, N. Toy 2, G. Parke 2, R. Woods 2 1 2H Offshore Engineering Ltd, Woking, Surrey, UK 2 School of Engineering, University of Surrey,
Full scale model tests of a steel catenary riser C. Bridge 1, H. Howells 1, N. Toy 2, G. Parke 2, R. Woods 2 1 2H Offshore Engineering Ltd, Woking, Surrey, UK 2 School of Engineering, University of Surrey,
Offshore engineering science
 Offshore engineering science In this research stream theoretical models advanced geotechnical models and new numerical techniques were used in applied offshore engineering topics such as loading, design
Offshore engineering science In this research stream theoretical models advanced geotechnical models and new numerical techniques were used in applied offshore engineering topics such as loading, design
RIGID RISERS FOR TANKER FPSOs
 RIGID RISERS FOR TANKER FPSOs Stephen A. Hatton 2H Offshore Engineering Ltd. SUMMARY Recent development work on the subject of dynamic rigid (steel pipe) risers demonstrates that their scope of application
RIGID RISERS FOR TANKER FPSOs Stephen A. Hatton 2H Offshore Engineering Ltd. SUMMARY Recent development work on the subject of dynamic rigid (steel pipe) risers demonstrates that their scope of application
Steel Lazy Wave Risers A Step Change in Riser Technology for the NWS
 Steel Lazy Wave Risers A Step Change in Riser Technology for the NWS Tze King Lim, Dhyan Deka, Elizabeth Tellier, Hugh Howells AOG 2018, Perth 15 th March 2018 Agenda Lazy wave risers an enabling technology
Steel Lazy Wave Risers A Step Change in Riser Technology for the NWS Tze King Lim, Dhyan Deka, Elizabeth Tellier, Hugh Howells AOG 2018, Perth 15 th March 2018 Agenda Lazy wave risers an enabling technology
Offshore Oil and Gas Platforms for Deep Waters
 Offshore Oil and Gas Platforms for Deep Waters Atilla Incecik Department of Naval Architecture, Ocean and Marine Engineering University of Strathclyde, Glasgow, UK (atilla.incecik@strath.ac.uk) Summary
Offshore Oil and Gas Platforms for Deep Waters Atilla Incecik Department of Naval Architecture, Ocean and Marine Engineering University of Strathclyde, Glasgow, UK (atilla.incecik@strath.ac.uk) Summary
Time-domain Nonlinear Coupled Analyses Covering Typical Mooring and Riser Configurations for FPSOs
 PAU, FRANCE 5-7 APRIL 2016 Time-domain Nonlinear Coupled Analyses Covering Typical Mooring and Riser Configurations for FPSOs Author: Fan Joe Zhang Presenter: Styrk Finne DNV GL - Software Contents Typical
PAU, FRANCE 5-7 APRIL 2016 Time-domain Nonlinear Coupled Analyses Covering Typical Mooring and Riser Configurations for FPSOs Author: Fan Joe Zhang Presenter: Styrk Finne DNV GL - Software Contents Typical
Proceedings of the ASME th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE2011
 Proceedings of the ASME 2011 30th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE2011 June 19-24, 2011, Rotterdam, The Netherlands Proceedings of the ASME 2011 30th International
Proceedings of the ASME 2011 30th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE2011 June 19-24, 2011, Rotterdam, The Netherlands Proceedings of the ASME 2011 30th International
STRIDE PROJECT Steel Risers in Deepwater Environments Achievements
 STRIDE PROJECT Steel Risers in Deepwater Environments Achievements 1999-21 Neil Willis Principal Engineer 2H Offshore Engineering 6 th Annual Deepwater Technologies and Developments Conference 21 The presentation
STRIDE PROJECT Steel Risers in Deepwater Environments Achievements 1999-21 Neil Willis Principal Engineer 2H Offshore Engineering 6 th Annual Deepwater Technologies and Developments Conference 21 The presentation
REVISITING GLOBAL RESPONSE OF FPSOS IN SHALLOW WATER AND THE RISER ANALYSIS REQUIREMENTS
 REVISITING GLOBAL RESPONSE OF FPSOS IN SHALLOW WATER AND THE RISER ANALYSIS REQUIREMENTS AMIR H. IZADPARAST SENIOR RESEARCH ENGINEER, HYDRODYNAMICS AND MOORING TECHNOLOGY, SOFEC JIAXING CHEN RESEARCH ENGINEER,
REVISITING GLOBAL RESPONSE OF FPSOS IN SHALLOW WATER AND THE RISER ANALYSIS REQUIREMENTS AMIR H. IZADPARAST SENIOR RESEARCH ENGINEER, HYDRODYNAMICS AND MOORING TECHNOLOGY, SOFEC JIAXING CHEN RESEARCH ENGINEER,
Catenary Offset Buoyant Riser Assembly for Malaysian Deepwater
 Catenary Offset Buoyant Riser Assembly for Malaysian Deepwater F.E. Jamaludin, a and J. Koto, a,b,* a) Faculty of Mechanical Engineering,Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81200 Skudai, Johor Bahru, Malaysia
Catenary Offset Buoyant Riser Assembly for Malaysian Deepwater F.E. Jamaludin, a and J. Koto, a,b,* a) Faculty of Mechanical Engineering,Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81200 Skudai, Johor Bahru, Malaysia
Flexible Spools Solution at Hybrid Risers Base A. Karnikian, Total and S. Tarbadar, M. Bonnissel, S. Legeay, Technip France
 DOT-2014 Flexible Spools Solution at Hybrid Risers Base A. Karnikian, Total and S. Tarbadar, M. Bonnissel, S. Legeay, Technip France Copyright 2014, Deep Offshore Technology International This paper was
DOT-2014 Flexible Spools Solution at Hybrid Risers Base A. Karnikian, Total and S. Tarbadar, M. Bonnissel, S. Legeay, Technip France Copyright 2014, Deep Offshore Technology International This paper was
Coupling and Analysis of 981 Deep Water Semi-submersible. Drilling Platform and the Mooring System
 4th International Conference on Renewable Energy and Environmental Technology (ICREET 2016) Coupling and Analysis of 981 Deep Water Semi-submersible Drilling Platform and the Mooring System XuDong Wang1,
4th International Conference on Renewable Energy and Environmental Technology (ICREET 2016) Coupling and Analysis of 981 Deep Water Semi-submersible Drilling Platform and the Mooring System XuDong Wang1,
The Benefits Of Composite Materials In Deepwater Riser Applications. 26 th March 2015 Hassan Saleh Senior Engineer 2H Offshore Engineering Ltd
 The Benefits Of Composite Materials In Deepwater Riser Applications 26 th March 2015 Hassan Saleh Senior Engineer 2H Offshore Engineering Ltd Composite Benefits and Challenges Composite Materials offer
The Benefits Of Composite Materials In Deepwater Riser Applications 26 th March 2015 Hassan Saleh Senior Engineer 2H Offshore Engineering Ltd Composite Benefits and Challenges Composite Materials offer
INDEX OF REVISIONS DESCRIPTION AND/OR AFFECTED SHEETS
 I-ET-300.00-59-27-PPC-00 CLIENT OR JOB OR PROJECT PRODUCTION DEVELOPMENT CC Fro m UNITS AND PRODUCTION SYSTEMS CENPES INDEX OF REVISIONS REV. DESCRIPTION AND/OR AFFECTED S 0 ORIGINAL ORIGINAL REV. A REV.
I-ET-300.00-59-27-PPC-00 CLIENT OR JOB OR PROJECT PRODUCTION DEVELOPMENT CC Fro m UNITS AND PRODUCTION SYSTEMS CENPES INDEX OF REVISIONS REV. DESCRIPTION AND/OR AFFECTED S 0 ORIGINAL ORIGINAL REV. A REV.
Learn more at
 STRIDE JIP Phase III SUT Talk 15th November 2 Offshore VIV monitoring (vortex induced vibration) Catenary riser interaction with deepwater seabeds 3 Full Scale Riser Monitoring To get real measurements
STRIDE JIP Phase III SUT Talk 15th November 2 Offshore VIV monitoring (vortex induced vibration) Catenary riser interaction with deepwater seabeds 3 Full Scale Riser Monitoring To get real measurements
E02 Rigid hinged stinger with piggyback line
 E02 Rigid hinged stinger with piggyback line This model represents a rigid stinger hinged off the back of a lay vessel using the pipelay supports feature. In addition to the lay pipe, another line is included
E02 Rigid hinged stinger with piggyback line This model represents a rigid stinger hinged off the back of a lay vessel using the pipelay supports feature. In addition to the lay pipe, another line is included
TLP Minimum tendon tension design and tendon down-stroke investigation
 Published by International Association of Ocean Engineers Journal of Offshore Engineering and Technology Available online at www.iaoejoet.org TLP Minimum tendon tension design and tendon down-stroke investigation
Published by International Association of Ocean Engineers Journal of Offshore Engineering and Technology Available online at www.iaoejoet.org TLP Minimum tendon tension design and tendon down-stroke investigation
OMAE INVESTIGATION ON THE USE OF DIFFERENT APPROACHES TO MOORING ANALYSIS AND APPROPRIATE SAFETY FACTORS
 Proceedings of the ASME 212 31 st International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE212 June 1-15, 212, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil OMAE212-84121 INVESTIGATION ON THE USE OF DIFFERENT APPROACHES
Proceedings of the ASME 212 31 st International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE212 June 1-15, 212, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil OMAE212-84121 INVESTIGATION ON THE USE OF DIFFERENT APPROACHES
Learn more at
 vs. for Deepwater Applications Technical Appraisal John McGrail and Frank Lim 2H Offshore Engineering Limited Woking, UK ABSTRACT This paper provides a technical appraisal of the use of Single Line Offset
vs. for Deepwater Applications Technical Appraisal John McGrail and Frank Lim 2H Offshore Engineering Limited Woking, UK ABSTRACT This paper provides a technical appraisal of the use of Single Line Offset
Deepwater Floating Production Systems An Overview
 Deepwater Floating Production Systems An Overview Introduction In addition to the mono hull, three floating structure designs Tension leg Platform (TLP), Semisubmersible (Semi), and Truss Spar have been
Deepwater Floating Production Systems An Overview Introduction In addition to the mono hull, three floating structure designs Tension leg Platform (TLP), Semisubmersible (Semi), and Truss Spar have been
Design Challenges & Solutions for Large Diameter Export Risers
 Design Challenges & Solutions for Large Diameter Export Risers Elizabeth Tellier, Hugh Howells & Mark Cerkovnik 2H Offshore Engineering AOG 2011 Agenda WA export riser design challenges Development options
Design Challenges & Solutions for Large Diameter Export Risers Elizabeth Tellier, Hugh Howells & Mark Cerkovnik 2H Offshore Engineering AOG 2011 Agenda WA export riser design challenges Development options
The Adequacy of Pushover Analysis to Evaluate Vulnerability of Masonry Infilled Steel Frames Subjected to Bi-Directional Earthquake Loading
 The Adequacy of Pushover Analysis to Evaluate Vulnerability of Masonry Infilled Steel Frames Subjected to Bi-Directional Earthquake Loading B.Beheshti Aval & M. Mohammadzadeh K.N.Toosi University of Technology,
The Adequacy of Pushover Analysis to Evaluate Vulnerability of Masonry Infilled Steel Frames Subjected to Bi-Directional Earthquake Loading B.Beheshti Aval & M. Mohammadzadeh K.N.Toosi University of Technology,
Learn more at
 IBP1833_06 COST EFFICIENT ARTIFICIAL BUOYANT SEABED DRILLING SOLUTION Dan Moutrey 1, Frank Lim 2 Copyright 2006, Instituto Brasileiro de Petróleo e Gás - IBP This Technical Paper was prepared for presentation
IBP1833_06 COST EFFICIENT ARTIFICIAL BUOYANT SEABED DRILLING SOLUTION Dan Moutrey 1, Frank Lim 2 Copyright 2006, Instituto Brasileiro de Petróleo e Gás - IBP This Technical Paper was prepared for presentation
Feasibility of Steel Lazy Wave Risers in the North Sea
 NH GRAND HOTEL KRASNAPOLSKY AMSTERDAM 3-5 APRIL 2017 Feasibility of Steel Lazy Wave Risers in the North Sea Rohit Shankaran 2H Offshore Engineering Ltd. Agenda Risers in deepwater North Sea Are steel catenary
NH GRAND HOTEL KRASNAPOLSKY AMSTERDAM 3-5 APRIL 2017 Feasibility of Steel Lazy Wave Risers in the North Sea Rohit Shankaran 2H Offshore Engineering Ltd. Agenda Risers in deepwater North Sea Are steel catenary
Abstract. 1. Introduction. 2. Design Requirements. Naval Engineer - INTERMOOR DO BRASIL 2. Petroleum Engineer INTERMOOR DO BRASIL 3
 IBP1687_14 MOORING SYSTEM FOR A SEMI-SUBMERSIBLE RIG IN ULTRA-DEEPWATER AND UNDER SEVERE CURRENTS Debora C. B. Ralha 1, Manuela C. Corrêa 2, Jeremy Abercrombie 3 and Karina G. Pinheiro 1 Copyright 2014,
IBP1687_14 MOORING SYSTEM FOR A SEMI-SUBMERSIBLE RIG IN ULTRA-DEEPWATER AND UNDER SEVERE CURRENTS Debora C. B. Ralha 1, Manuela C. Corrêa 2, Jeremy Abercrombie 3 and Karina G. Pinheiro 1 Copyright 2014,
Catenary Mooring Chain Eigen Modes and the Effects on Fatigue Life
 Catenary Mooring Chain Eigen Modes and the Effects on Fatigue Life Tor Anders Nygaard and Jacobus de Vaal, IFE Morten Hviid Madsen and Håkon Andersen, Dr.techn Olav Olsen AS Jorge Altuzarra, Vicinay Marine
Catenary Mooring Chain Eigen Modes and the Effects on Fatigue Life Tor Anders Nygaard and Jacobus de Vaal, IFE Morten Hviid Madsen and Håkon Andersen, Dr.techn Olav Olsen AS Jorge Altuzarra, Vicinay Marine
RELIABILITY ASSESSMENT, STATIC AND DYNAMIC RESPONSE OF TRANSMISSION LINE TOWER: A COMPARATIVE STUDY
 RELIABILITY ASSESSMENT, STATIC AND DYNAMIC RESPONSE OF TRANSMISSION LINE TOWER: A COMPARATIVE STUDY Yusuf Mansur Hashim M. Tech (Structural Engineering) Student, Sharda University, Greater Noida, (India)
RELIABILITY ASSESSMENT, STATIC AND DYNAMIC RESPONSE OF TRANSMISSION LINE TOWER: A COMPARATIVE STUDY Yusuf Mansur Hashim M. Tech (Structural Engineering) Student, Sharda University, Greater Noida, (India)
Preliminary study of moored power cables
 Preliminary study of moored power cables Joana Prat (1), Joaquín del Río (2), Alejandro Arbos (3) (1) Dept. Matemàtica Aplicada 4. Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, EPSEVG-UPC. Víctor Balaguer s/n,
Preliminary study of moored power cables Joana Prat (1), Joaquín del Río (2), Alejandro Arbos (3) (1) Dept. Matemàtica Aplicada 4. Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, EPSEVG-UPC. Víctor Balaguer s/n,
COUPLED DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF MOORING LINES FOR DEEP WATER FLOATING SYSTEMS
 Proceedings of International Conference in Ocean Engineering, ICOE Proceedings 2009 of ICOE 2009 Coupled Dynamic Analysis IIT Madras, of Chennai, Mooring India. Lines for Deep Water Floating Systems 1-5
Proceedings of International Conference in Ocean Engineering, ICOE Proceedings 2009 of ICOE 2009 Coupled Dynamic Analysis IIT Madras, of Chennai, Mooring India. Lines for Deep Water Floating Systems 1-5
The Impact of Composites on Future Deepwater Riser Configurations
 The Impact of Composites on Future Deepwater Riser Configurations Thomas Brown 2H Offshore Engineering Ltd NH GRAND HOTEL KRASNAPOLSKY AMSTERDAM 3-5 APRIL 2017 Deepwater Riser Technology Today s deepwater
The Impact of Composites on Future Deepwater Riser Configurations Thomas Brown 2H Offshore Engineering Ltd NH GRAND HOTEL KRASNAPOLSKY AMSTERDAM 3-5 APRIL 2017 Deepwater Riser Technology Today s deepwater
EFFECT OF VORTEX INDUCED VIBRATION ON FATIGUE DAMAGE OF TOP-TENSIONED RISER SUBJECTED TO CURRENT LOAD
 EFFECT OF VORTEX INDUCED VIBRATION ON FATIGUE DAMAGE OF TOP-TENSIONED RISER SUBJECTED TO CURRENT LOAD Ke Xin Lai 1,2, Do Kyun Kim 1,2,3 and Eileen Wee Chin Wong 1,4 1 Ocean and Ship Technology Research
EFFECT OF VORTEX INDUCED VIBRATION ON FATIGUE DAMAGE OF TOP-TENSIONED RISER SUBJECTED TO CURRENT LOAD Ke Xin Lai 1,2, Do Kyun Kim 1,2,3 and Eileen Wee Chin Wong 1,4 1 Ocean and Ship Technology Research
Adaptive Pushover Analysis of Irregular RC Moment Resisting Frames
 Kalpa Publications in Civil Engineering Volume 1, 2017, Pages 132 136 ICRISET2017. International Conference on Research and Innovations in Science, Engineering &Technology. Selected papers in Civil Engineering
Kalpa Publications in Civil Engineering Volume 1, 2017, Pages 132 136 ICRISET2017. International Conference on Research and Innovations in Science, Engineering &Technology. Selected papers in Civil Engineering
MODELLING MOORING LINE BEHAVIOUR TO DETERMINE THE IMPACT FORCE ON SQUID EGG BEDS
 10 th South African Conference on Computational and Applied Mechanics Potchefstroom 3 5 October 2016 MODELLING MOORING LINE BEHAVIOUR TO DETERMINE THE IMPACT FORCE ON SQUID EGG BEDS Vutlhari A Maluleke*
10 th South African Conference on Computational and Applied Mechanics Potchefstroom 3 5 October 2016 MODELLING MOORING LINE BEHAVIOUR TO DETERMINE THE IMPACT FORCE ON SQUID EGG BEDS Vutlhari A Maluleke*
Stress and deformation of offshore piles under structural and wave loading
 Stress and deformation of offshore piles under structural and wave loading Author Eicher, Jackie, Guan, Hong, Jeng, Dong-Sheng Published 2003 Journal Title Ocean Engineering DOI https://doi.org/10.1016/s0029-8018(02)00031-8
Stress and deformation of offshore piles under structural and wave loading Author Eicher, Jackie, Guan, Hong, Jeng, Dong-Sheng Published 2003 Journal Title Ocean Engineering DOI https://doi.org/10.1016/s0029-8018(02)00031-8
Wellhead, Conductor and Casing Fatigue Causes and Mitigation Tze King Lim, Elizabeth Tellier, Hugh Howells 2H Offshore Engineering
 Wellhead, Conductor and Casing Fatigue Causes and Mitigation Tze King Lim, Elizabeth Tellier, Hugh Howells 2H Offshore Engineering ABSTRACT Drilling operations for subsea wells are typically carried out
Wellhead, Conductor and Casing Fatigue Causes and Mitigation Tze King Lim, Elizabeth Tellier, Hugh Howells 2H Offshore Engineering ABSTRACT Drilling operations for subsea wells are typically carried out
Analysis of dilatometer test in calibration chamber
 Analysis of dilatometer test in calibration chamber Lech Bałachowski Gdańsk University of Technology, Poland Keywords: calibration chamber, DMT, quartz sand, FEM ABSTRACT: Because DMT in calibration test
Analysis of dilatometer test in calibration chamber Lech Bałachowski Gdańsk University of Technology, Poland Keywords: calibration chamber, DMT, quartz sand, FEM ABSTRACT: Because DMT in calibration test
Hydrodynamic Analysis of a Heavy Lift Vessel during Offshore Installation Operations
 Presentation for Defense of Master Thesis Hydrodynamic Analysis of a Heavy Lift Vessel during Offshore Installation Operations Speaker: Bin Wang Supervisor: Prof. Robert Bronsart 23 rd Feb, 2015 Nantes
Presentation for Defense of Master Thesis Hydrodynamic Analysis of a Heavy Lift Vessel during Offshore Installation Operations Speaker: Bin Wang Supervisor: Prof. Robert Bronsart 23 rd Feb, 2015 Nantes
Edit this text for your title
 Edit this text for your title MEK 4450 Marine Operations Edit this text for your sub-title Presenter name, location, date etc. Kværner ASA / DNV, Fall 2013 Lesson 2/3 Lift phases Load out Transportation
Edit this text for your title MEK 4450 Marine Operations Edit this text for your sub-title Presenter name, location, date etc. Kværner ASA / DNV, Fall 2013 Lesson 2/3 Lift phases Load out Transportation
2 FUSION FITTINGS FOR USE WITH POLYETHYLENE PRESSURE PIPES DESIGN FOR DYNAMIC STRESSES
 Industry Guidelines Part 2 FUSION FITTINGS FOR USE WITH POLYETHYLENE PRESSURE PIPES DESIGN FOR DYNAMIC STRESSES ISSUE 5.1 Ref: POP10B 15 MAR 2010 Disclaimer In formulating this guideline PIPA has relied
Industry Guidelines Part 2 FUSION FITTINGS FOR USE WITH POLYETHYLENE PRESSURE PIPES DESIGN FOR DYNAMIC STRESSES ISSUE 5.1 Ref: POP10B 15 MAR 2010 Disclaimer In formulating this guideline PIPA has relied
DEEP WATER DRILLING RISER TECHNOLOGY, VIV & FATIGUE MANAGEMENT
 DEEP WATER DRILLING RISER TECHNOLOGY, VIV & FATIGUE MANAGEMENT by Dr Hugh Howells 2H Offshore Engineering Limited Drilling Engineering Association (Europe), 4th Quarter Meeting, Paris 1998 SCOPE OF PRESENTATION
DEEP WATER DRILLING RISER TECHNOLOGY, VIV & FATIGUE MANAGEMENT by Dr Hugh Howells 2H Offshore Engineering Limited Drilling Engineering Association (Europe), 4th Quarter Meeting, Paris 1998 SCOPE OF PRESENTATION
Application of pushover analysis in estimating seismic demands for large-span spatial structure
 28 September 2 October 2009, Universidad Politecnica de Valencia, Spain Alberto DOMINGO and Carlos LAZARO (eds.) Application of pushover analysis in estimating seismic demands for large-span spatial structure
28 September 2 October 2009, Universidad Politecnica de Valencia, Spain Alberto DOMINGO and Carlos LAZARO (eds.) Application of pushover analysis in estimating seismic demands for large-span spatial structure
A NOVEL FLOATING OFFSHORE WIND TURBINE CONCEPT: NEW DEVELOPMENTS
 A NOVEL FLOATING OFFSHORE WIND TURBINE CONCEPT: NEW DEVELOPMENTS L. Vita, U.S.Paulsen, T.F.Pedersen Risø-DTU Technical University of Denmark, Roskilde, Denmark luca.vita@risoe.dk Abstract: A novel concept
A NOVEL FLOATING OFFSHORE WIND TURBINE CONCEPT: NEW DEVELOPMENTS L. Vita, U.S.Paulsen, T.F.Pedersen Risø-DTU Technical University of Denmark, Roskilde, Denmark luca.vita@risoe.dk Abstract: A novel concept
Proceedings of the ASME nd International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE2013 June 9-14, 2013, Nantes, France
 Proceedings of the ASME 2013 32nd International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE2013 June 9-14, 2013, Nantes, France OMAE2013-10675 THE EFFECT OF WAVE ENERGY SPREADING ON THE MOORING
Proceedings of the ASME 2013 32nd International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE2013 June 9-14, 2013, Nantes, France OMAE2013-10675 THE EFFECT OF WAVE ENERGY SPREADING ON THE MOORING
Comparison and Sensitivity Investigations of a CALM and SALM Type Mooring System for Wave Energy Converters
 J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 214, 2, 93-122; doi:1.339/jmse2193 Article OPEN ACCESS Journal of Marine Science and Engineering ISSN 277-1312 www.mdpi.com/journal/jmse Comparison and Sensitivity Investigations of a
J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 214, 2, 93-122; doi:1.339/jmse2193 Article OPEN ACCESS Journal of Marine Science and Engineering ISSN 277-1312 www.mdpi.com/journal/jmse Comparison and Sensitivity Investigations of a
Aidin Kazemi Daliri, Sepanta Naimi*
 JER Manuscript Template 1 The fixed marine risers dynamic analysis with 1 st and 5 th order rogue wave Aidin Kazemi Daliri, Sepanta Naimi* Department of Civil Engineering, Specialty of Coastal Engineering,
JER Manuscript Template 1 The fixed marine risers dynamic analysis with 1 st and 5 th order rogue wave Aidin Kazemi Daliri, Sepanta Naimi* Department of Civil Engineering, Specialty of Coastal Engineering,
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF PIPELINE GLOBAL WALKING WITH SPANNING AND LATERAL BUCKLING
 Proceedings of the ASME 2014 33rd International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE2014 June 8-13, 2014, San Francisco, California, USA OMAE2014-24159 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF PIPELINE
Proceedings of the ASME 2014 33rd International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE2014 June 8-13, 2014, San Francisco, California, USA OMAE2014-24159 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF PIPELINE
Numerical modelling of disconnectable turret mooring systems
 Numerical modelling of disconnectable turret mooring systems A. Duggal, S. Ryu & O. De Andrade Research & Development Department, SOFEC Inc., USA. Abstract Floating, Production, Storage, and Offloading
Numerical modelling of disconnectable turret mooring systems A. Duggal, S. Ryu & O. De Andrade Research & Development Department, SOFEC Inc., USA. Abstract Floating, Production, Storage, and Offloading
Theory of a vertically loaded Suction Pile in CLAY
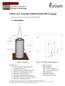 11 Theory of a vertically loaded Suction Pile in CLAY Mainly based on the et Norske Veritas NV-RP-E303 1. Convention Water COG h L Soil COG t Figure 1 Suction Pile Figure 2 Suction pile with main parameters
11 Theory of a vertically loaded Suction Pile in CLAY Mainly based on the et Norske Veritas NV-RP-E303 1. Convention Water COG h L Soil COG t Figure 1 Suction Pile Figure 2 Suction pile with main parameters
Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics
 Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics Volume 9, 2010 http://acousticalsociety.org/ 159th Meeting Acoustical Society of America/NOISE-CON 2010 Baltimore, Maryland 19-23 April 2010 Session 1pBB: Biomedical
Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics Volume 9, 2010 http://acousticalsociety.org/ 159th Meeting Acoustical Society of America/NOISE-CON 2010 Baltimore, Maryland 19-23 April 2010 Session 1pBB: Biomedical
Learn more at
 Bottom Weighted Riser A Novel Design for Re-location and Disconnection Frank Lim and John McGrail 2H Offshore Engineering Ltd. Woking, Surrey, United Kingdom ABSTRACT Flexible pipe risers have limitations
Bottom Weighted Riser A Novel Design for Re-location and Disconnection Frank Lim and John McGrail 2H Offshore Engineering Ltd. Woking, Surrey, United Kingdom ABSTRACT Flexible pipe risers have limitations
Analysis and Research of Mooring System. Jiahui Fan*
 nd International Conference on Computer Engineering, Information Science & Application Technology (ICCIA 07) Analysis and Research of Mooring System Jiahui Fan* School of environment, North China Electric
nd International Conference on Computer Engineering, Information Science & Application Technology (ICCIA 07) Analysis and Research of Mooring System Jiahui Fan* School of environment, North China Electric
Low Cost Flexible Production System for Remote Ultra-Deepwater Gulf of Mexico Field Development
 Low Cost Flexible Production System for Remote Ultra-Deepwater Gulf of Mexico Field Development 10121-4404-03 Jelena Vidic-Perunovic, Doris, Inc. Lars Ødeskaug, Sevan Marine ASA RPSEA Ultra-Deepwater Technology
Low Cost Flexible Production System for Remote Ultra-Deepwater Gulf of Mexico Field Development 10121-4404-03 Jelena Vidic-Perunovic, Doris, Inc. Lars Ødeskaug, Sevan Marine ASA RPSEA Ultra-Deepwater Technology
EFFECT OF DIFFERENT MOORING SYSTEMS ON HYDRODYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF AN OFFSHORE WIND TURBINE
 EFFECT OF DIFFERENT MOORING SYSTEMS ON HYDRODYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF AN OFFSHORE WIND TURBINE Sabri ALKAN 1, Ayhan Mentes 2, Ismail H. Helvacioglu 2, Nagihan Turkoglu 2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering,
EFFECT OF DIFFERENT MOORING SYSTEMS ON HYDRODYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF AN OFFSHORE WIND TURBINE Sabri ALKAN 1, Ayhan Mentes 2, Ismail H. Helvacioglu 2, Nagihan Turkoglu 2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Feasibility study of a semi floating spar buoy wind turbine anchored with a spherical joint to the sea floor
 Feasibility study of a semi floating spar buoy wind turbine anchored with a spherical joint to the sea floor María Sanz Martínez DTU Wind Energy DK-4000 Roskilde, Denmark msma@dtu.dk Anand Natarajan DTU
Feasibility study of a semi floating spar buoy wind turbine anchored with a spherical joint to the sea floor María Sanz Martínez DTU Wind Energy DK-4000 Roskilde, Denmark msma@dtu.dk Anand Natarajan DTU
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS OF BARGE FLOATER WITH MOONPOOL FOR 5 MW WIND TURBINE
 EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS OF BARGE FLOATER WITH MOONPOOL FOR 5 MW WIND TURBINE 1 MR. G.VIJAYA KUMAR, 2 DR. R. PANNEER SELVAM 1 M.S. Research Scholar, Department of Ocean Engineering, IIT Madras, Chennai,
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS OF BARGE FLOATER WITH MOONPOOL FOR 5 MW WIND TURBINE 1 MR. G.VIJAYA KUMAR, 2 DR. R. PANNEER SELVAM 1 M.S. Research Scholar, Department of Ocean Engineering, IIT Madras, Chennai,
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON THE HYDRODYNAMIC BEHAVIORS OF TWO CONCENTRIC CYLINDERS
 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON THE HYDRODYNAMIC BEHAVIORS OF TWO CONCENTRIC CYLINDERS *Jeong-Rok Kim 1), Hyeok-Jun Koh ), Won-Sun Ruy 3) and Il-Hyoung Cho ) 1), 3), ) Department of Ocean System Engineering, Jeju
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON THE HYDRODYNAMIC BEHAVIORS OF TWO CONCENTRIC CYLINDERS *Jeong-Rok Kim 1), Hyeok-Jun Koh ), Won-Sun Ruy 3) and Il-Hyoung Cho ) 1), 3), ) Department of Ocean System Engineering, Jeju
Computationally Efficient Determination of Long Term Extreme Out-of-Plane Loads for Offshore Turbines
 Computationally Efficient Determination of Long Term Extreme Out-of-Plane Loads for Offshore Turbines Anand Natarajan Senior Scientist Wind Energy Department, Risø DTU Denmark Introduction IEC 61400-1
Computationally Efficient Determination of Long Term Extreme Out-of-Plane Loads for Offshore Turbines Anand Natarajan Senior Scientist Wind Energy Department, Risø DTU Denmark Introduction IEC 61400-1
Analysis of Shear Lag in Steel Angle Connectors
 University of New Hampshire University of New Hampshire Scholars' Repository Honors Theses and Capstones Student Scholarship Spring 2013 Analysis of Shear Lag in Steel Angle Connectors Benjamin Sawyer
University of New Hampshire University of New Hampshire Scholars' Repository Honors Theses and Capstones Student Scholarship Spring 2013 Analysis of Shear Lag in Steel Angle Connectors Benjamin Sawyer
Top Tensioned Riser Challenges and Solutions for Dry Tree Facilities in Asia Pacific
 June 2011 Top Tensioned Riser Challenges and Solutions for Dry Tree Facilities in Asia Pacific Daniel Brooker, MCS Kenny Presentation Agenda 1. Objectives 2. Top Tensioned Riser (TTR) Selection Drivers
June 2011 Top Tensioned Riser Challenges and Solutions for Dry Tree Facilities in Asia Pacific Daniel Brooker, MCS Kenny Presentation Agenda 1. Objectives 2. Top Tensioned Riser (TTR) Selection Drivers
ASSESSMENT AND ANALYSIS OF PIPELINE BUCKLES
 ASSESSMENT AND ANALYSIS OF PIPELINE BUCKLES GE Oil & Gas PII Pipeline Solutions Inessa Yablonskikh Principal Consultant Aberdeen, November, 14 th 2007 Assessment And Analysis Of Pipeline Buckles Introduction
ASSESSMENT AND ANALYSIS OF PIPELINE BUCKLES GE Oil & Gas PII Pipeline Solutions Inessa Yablonskikh Principal Consultant Aberdeen, November, 14 th 2007 Assessment And Analysis Of Pipeline Buckles Introduction
A Novel Platform for Drilling in Harsh High-Latitude Environments.
 AADE-7-NTCE-73 A Novel Platform for Drilling in Harsh High-Latitude Environments. Brian Roberts, Technip; Chunqun Ji, Technip; Jim O Sullivan, Technip and Terje Eilertsen, Technip. Copyright 27, AADE This
AADE-7-NTCE-73 A Novel Platform for Drilling in Harsh High-Latitude Environments. Brian Roberts, Technip; Chunqun Ji, Technip; Jim O Sullivan, Technip and Terje Eilertsen, Technip. Copyright 27, AADE This
ON-BOTTOM STABILITY CALCULATIONS FOR FIBRE OPTIC SUBMARINE CABLES
 ON-BOTTOM STABILITY CALCULATIONS FOR FIBRE OPTIC SUBMARINE CABLES Inge Vintermyr (Nexans ray AS) Email: Nexans ray AS, PO.Box 6450 Etterstad, N-0605 Oslo, ray. Abstract: This
ON-BOTTOM STABILITY CALCULATIONS FOR FIBRE OPTIC SUBMARINE CABLES Inge Vintermyr (Nexans ray AS) Email: Nexans ray AS, PO.Box 6450 Etterstad, N-0605 Oslo, ray. Abstract: This
DETRMINATION OF A PLUNGER TYPE WAVE MAKER CHARACTERISTICE IN A TOWING TANK
 The 9 th International Conference on Coasts, Ports and Marine Structures (ICOPMAS 2010) 29 Nov.-1 Dec. 2010 (Tehran) DETRMINATION OF A PLUNGER TYPE WAVE MAKER CHARACTERISTICE IN A TOWING TANK sayed mohammad
The 9 th International Conference on Coasts, Ports and Marine Structures (ICOPMAS 2010) 29 Nov.-1 Dec. 2010 (Tehran) DETRMINATION OF A PLUNGER TYPE WAVE MAKER CHARACTERISTICE IN A TOWING TANK sayed mohammad
Study to Establish Relations for the Relative Strength of API 650 Cone Roof Roof-to-Shell and Shell-to- Bottom Joints
 Thunderhead Engineering Consultants I N C O R P O R A T E D 1006 Poyntz Ave. Manhattan, KS 66502-5459 785-770-8511 www. thunderheadeng.com Study to Establish Relations for the Relative Strength of API
Thunderhead Engineering Consultants I N C O R P O R A T E D 1006 Poyntz Ave. Manhattan, KS 66502-5459 785-770-8511 www. thunderheadeng.com Study to Establish Relations for the Relative Strength of API
OMAE WET TREE SEMI-SUBMERSIBLE WITH SCRS FOR 4,000 FT WATER DEPTH IN THE GULF OF MEXICO
 Proceedings of the ASME 2011 30th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE2011 June 19-24, 2011, Rotterdam, The Netherlands OMAE2011-50002 WET TREE SEMI-SUBMERSIBLE WITH
Proceedings of the ASME 2011 30th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE2011 June 19-24, 2011, Rotterdam, The Netherlands OMAE2011-50002 WET TREE SEMI-SUBMERSIBLE WITH
Tension-Leg-Buoy (TLB) Platforms for Offshore Wind Turbines
 Tension-Leg-Buoy (TLB) Platforms for Offshore Wind Turbines EERA DeepWind'2014 Deep Sea Offshore Wind R&D Conference, Trondheim, 22-24 January 2014 Tor Anders Nygaard, Institute for Energy Technology (IFE),
Tension-Leg-Buoy (TLB) Platforms for Offshore Wind Turbines EERA DeepWind'2014 Deep Sea Offshore Wind R&D Conference, Trondheim, 22-24 January 2014 Tor Anders Nygaard, Institute for Energy Technology (IFE),
Modelling of Extreme Waves Related to Stability Research
 Modelling of Extreme Waves Related to Stability Research Janou Hennig 1 and Frans van Walree 1 1. Maritime Research Institute Netherlands,(MARIN), Wageningen, the Netherlands Abstract: The paper deals
Modelling of Extreme Waves Related to Stability Research Janou Hennig 1 and Frans van Walree 1 1. Maritime Research Institute Netherlands,(MARIN), Wageningen, the Netherlands Abstract: The paper deals
Determination of the Design Load for Structural Safety Assessment against Gas Explosion in Offshore Topside
 Determination of the Design Load for Structural Safety Assessment against Gas Explosion in Offshore Topside Migyeong Kim a, Gyusung Kim a, *, Jongjin Jung a and Wooseung Sim a a Advanced Technology Institute,
Determination of the Design Load for Structural Safety Assessment against Gas Explosion in Offshore Topside Migyeong Kim a, Gyusung Kim a, *, Jongjin Jung a and Wooseung Sim a a Advanced Technology Institute,
UNIT-I SOIL EXPLORATION
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : Geotechnical Engineering - II (16CE127) Year & Sem: III-B.Tech & II-Sem
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : Geotechnical Engineering - II (16CE127) Year & Sem: III-B.Tech & II-Sem
Offshore platforms survivability to underwater explosions: part I
 Computational Ballistics III 123 Offshore platforms survivability to underwater explosions: part I A. A. Motta 1, E. A. P. Silva 2, N. F. F. Ebecken 2 & T. A. Netto 2 1 Brazilian Navy Research Institute,
Computational Ballistics III 123 Offshore platforms survivability to underwater explosions: part I A. A. Motta 1, E. A. P. Silva 2, N. F. F. Ebecken 2 & T. A. Netto 2 1 Brazilian Navy Research Institute,
Low Cost Flexible Production System for Remote Ultra-Deepwater Gulf of Mexico (GOM) Field Development, Phase 2
 Low Cost Flexible Production System for Remote Ultra-Deepwater Gulf of Mexico (GOM) Field Development, Phase 2 10121-4404-03 Jelena Vidic-Perunovic Doris, Inc. 1 Best of RPSEA 10 Years of Research - Ultra-Deepwater
Low Cost Flexible Production System for Remote Ultra-Deepwater Gulf of Mexico (GOM) Field Development, Phase 2 10121-4404-03 Jelena Vidic-Perunovic Doris, Inc. 1 Best of RPSEA 10 Years of Research - Ultra-Deepwater
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING Volume 1, No 4, 2010
 Effect of geometric dimensions on the transmission coefficient of floating breakwaters Mohammad Hosein Tadayon, Khosro Bargi 2, Hesam Sharifian, S. Reza Hoseini - Ph.D student, Department of Civil Engineering,
Effect of geometric dimensions on the transmission coefficient of floating breakwaters Mohammad Hosein Tadayon, Khosro Bargi 2, Hesam Sharifian, S. Reza Hoseini - Ph.D student, Department of Civil Engineering,
Lateral Load Analysis Considering Soil-Structure Interaction. ANDREW DAUMUELLER, PE, Ph.D.
 Lateral Load Analysis Considering Soil-Structure Interaction ANDREW DAUMUELLER, PE, Ph.D. Overview Introduction Methods commonly used to account for soil-structure interaction for static loads Depth to
Lateral Load Analysis Considering Soil-Structure Interaction ANDREW DAUMUELLER, PE, Ph.D. Overview Introduction Methods commonly used to account for soil-structure interaction for static loads Depth to
Development of Self-Installing Deepwater Spar. Ashit Jadav February 2017
 Development of Self-Installing Deepwater Spar Ashit Jadav February 2017 Contents Introduction & Background ACE Spar breakdown Installation Sequence Main particulars, Hull design and Weight control Stability
Development of Self-Installing Deepwater Spar Ashit Jadav February 2017 Contents Introduction & Background ACE Spar breakdown Installation Sequence Main particulars, Hull design and Weight control Stability
MINIMUM DECK HEIGHT OF A SEMI-SUBMERSIBLE PLATFORM ACCORDING TO BLACK SEA ENVIRONMENT
 MINIMUM DECK HEIGHT OF A SEMI-SUBMERSIBLE PLATFORM ACCORDING TO BLACK SEA ENVIRONMENT Ionuț-Cristian SCURTU Principal instructor, Navy Academy Mircea cel Batran Constanta, Romania Abstract-The fast evolution
MINIMUM DECK HEIGHT OF A SEMI-SUBMERSIBLE PLATFORM ACCORDING TO BLACK SEA ENVIRONMENT Ionuț-Cristian SCURTU Principal instructor, Navy Academy Mircea cel Batran Constanta, Romania Abstract-The fast evolution
Friction properties of the face of a hand-held tennis racket
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 34 (2012 ) 544 549 9 th Conference of the International Sports Engineering Association (ISEA) Friction properties of the face of a hand-held
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 34 (2012 ) 544 549 9 th Conference of the International Sports Engineering Association (ISEA) Friction properties of the face of a hand-held
Non-Linear Seismic Analysis of Multi-Storey Building
 Non-Linear Seismic Analysis of Multi-Storey Building Uzair Khan 1 1 M.Tech (Structural & Construction Engineering) Department of Civil Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Jalandhar. Hina Gupta
Non-Linear Seismic Analysis of Multi-Storey Building Uzair Khan 1 1 M.Tech (Structural & Construction Engineering) Department of Civil Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Jalandhar. Hina Gupta
Tutorial. BOSfluids. Relief valve
 Tutorial Relief valve The Relief valve tutorial describes the theory and modeling process of a pressure relief valve or safety valve. It covers the algorithm BOSfluids uses to model the valve and a worked
Tutorial Relief valve The Relief valve tutorial describes the theory and modeling process of a pressure relief valve or safety valve. It covers the algorithm BOSfluids uses to model the valve and a worked
A New Thermoplastic Composite Riser for Deepwater Application
 A New Thermoplastic Composite Riser for Deepwater Application Martin van Onna, Managing Director Airborne Composite Tubulars Patrick O Brien, Group Director Strategic Business & Marketing, Wood Group Kenny
A New Thermoplastic Composite Riser for Deepwater Application Martin van Onna, Managing Director Airborne Composite Tubulars Patrick O Brien, Group Director Strategic Business & Marketing, Wood Group Kenny
V-H-M Yield Surface describing Soil Structure Interaction of Sub-sea Structures and Wind Turbines on Caisson Foundations in Soft Clays
 NGM 2016 Reykjavik Proceedings of the 17 th Nordic Geotechnical Meeting Challenges in Nordic Geotechnic 25 th 28 th of May V-H-M Yield Surface describing Soil Structure Interaction of Sub-sea Structures
NGM 2016 Reykjavik Proceedings of the 17 th Nordic Geotechnical Meeting Challenges in Nordic Geotechnic 25 th 28 th of May V-H-M Yield Surface describing Soil Structure Interaction of Sub-sea Structures
17J Third Edition, January 2008 Specification for Unbonded Flexible Pipe
 API Specification 17J Third Edition, January 2008 National Adoption of ISO 13628:2006(Identical) Petroleum and natural gas industries Design and operation of subsea production systems Part 2: Unbonded
API Specification 17J Third Edition, January 2008 National Adoption of ISO 13628:2006(Identical) Petroleum and natural gas industries Design and operation of subsea production systems Part 2: Unbonded
GEA FOR ADVANCED STRUCTURAL DYNAMIC ANALYSIS
 SMART SOLUTIONS FOR VIBRATION MONITORING GEA FOR ADVANCED STRUCTURAL DYNAMIC ANALYSIS ANALYSIS OF CIVIL STRUCTURES - EXPO MERLATA PEDESTRIAN BRIDGE ABSTRACT Civil structures and in particular bridges and
SMART SOLUTIONS FOR VIBRATION MONITORING GEA FOR ADVANCED STRUCTURAL DYNAMIC ANALYSIS ANALYSIS OF CIVIL STRUCTURES - EXPO MERLATA PEDESTRIAN BRIDGE ABSTRACT Civil structures and in particular bridges and
ISOLATION OF NON-HYDROSTATIC REGIONS WITHIN A BASIN
 ISOLATION OF NON-HYDROSTATIC REGIONS WITHIN A BASIN Bridget M. Wadzuk 1 (Member, ASCE) and Ben R. Hodges 2 (Member, ASCE) ABSTRACT Modeling of dynamic pressure appears necessary to achieve a more robust
ISOLATION OF NON-HYDROSTATIC REGIONS WITHIN A BASIN Bridget M. Wadzuk 1 (Member, ASCE) and Ben R. Hodges 2 (Member, ASCE) ABSTRACT Modeling of dynamic pressure appears necessary to achieve a more robust
A PHASE-AMPLITUDE ITERATION SCHEME FOR THE OPTIMIZATION OF DETERMINISTIC WAVE SEQUENCES
 Proceedings of the ASME 29 28th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE29 May 31 - June, 29, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA Proceedings of the ASME 28th International Conference
Proceedings of the ASME 29 28th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE29 May 31 - June, 29, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA Proceedings of the ASME 28th International Conference
The wind tunnel tests of wind pressure acting on the derrick of deepwater semi-submersible drilling platform
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Energy Procedia 14 (2012) 1267 1272 2011 2nd International Conference on Advances in Energy Engineering (ICAEE2011) The wind tunnel tests of wind pressure acting
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Energy Procedia 14 (2012) 1267 1272 2011 2nd International Conference on Advances in Energy Engineering (ICAEE2011) The wind tunnel tests of wind pressure acting
computed using Equation 3-18 by setting the 2nd term equal to 0 and K A equal to K o and using the pressure distribution as shown in Figure 3-23.
 computed using Equation 3-18 by setting the 2nd term equal to 0 and K A equal to K o and using the pressure distribution as shown in Figure 3-23. (2) For the resisting side, passive pressure theory indicates
computed using Equation 3-18 by setting the 2nd term equal to 0 and K A equal to K o and using the pressure distribution as shown in Figure 3-23. (2) For the resisting side, passive pressure theory indicates
Dynamic analysis of offshore floating wind turbines
 Dynamic analysis of offshore floating wind turbines Hasan Bagbanci Centre for Marine Technology and Engineering (CENTEC), Instituto Superior Técnico Technical University of Lisbon, Lisboa, Portugal ABSTRACT:
Dynamic analysis of offshore floating wind turbines Hasan Bagbanci Centre for Marine Technology and Engineering (CENTEC), Instituto Superior Técnico Technical University of Lisbon, Lisboa, Portugal ABSTRACT:
Reinforced Soil Retaining Walls-Design and Construction
 Lecture 32 Reinforced Soil Retaining Walls-Design and Construction Prof. G L Sivakumar Babu Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560012 Example calculation An 8 m high
Lecture 32 Reinforced Soil Retaining Walls-Design and Construction Prof. G L Sivakumar Babu Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560012 Example calculation An 8 m high
Quantification of the Effects of Turbulence in Wind on the Flutter Stability of Suspension Bridges
 Quantification of the Effects of Turbulence in Wind on the Flutter Stability of Suspension Bridges T. Abbas 1 and G. Morgenthal 2 1 PhD candidate, Graduate College 1462, Department of Civil Engineering,
Quantification of the Effects of Turbulence in Wind on the Flutter Stability of Suspension Bridges T. Abbas 1 and G. Morgenthal 2 1 PhD candidate, Graduate College 1462, Department of Civil Engineering,
Wind effects on tall building frames-influence of dynamic parameters
 Indian Journal of Science and Technology Vol. 3 No. 5 (May 21) ISSN: 974-6846 583 Wind effects on tall building frames-influence of dynamic parameters B. Dean Kumar 1 and B.L.P. Swami 2 1 Department of
Indian Journal of Science and Technology Vol. 3 No. 5 (May 21) ISSN: 974-6846 583 Wind effects on tall building frames-influence of dynamic parameters B. Dean Kumar 1 and B.L.P. Swami 2 1 Department of
Wave Forces on a Moored Vessel from Numerical Wave Model Results
 Wave Forces on a Moored Vessel from Numerical Wave Model Results ABSTRACT P W O BRIEN OMC International Pty Ltd, Melbourne, Australia O WEILER WL Delft Hydraulics, Delft, The Netherlands M BORSBOOM WL
Wave Forces on a Moored Vessel from Numerical Wave Model Results ABSTRACT P W O BRIEN OMC International Pty Ltd, Melbourne, Australia O WEILER WL Delft Hydraulics, Delft, The Netherlands M BORSBOOM WL
Available online at ScienceDirect. Energy Procedia 80 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia ( ) 6 th Deep Sea Offshore Wind R&D Conference, EERA DeepWind' Coupled mooring systems for floating wind farms Marek Goldschmidt*,
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia ( ) 6 th Deep Sea Offshore Wind R&D Conference, EERA DeepWind' Coupled mooring systems for floating wind farms Marek Goldschmidt*,
OTC MS. Free Span Rectification by Pipeline Lowering (PL) Method N. I. Thusyanthan, K. Sivanesan & G. Murphy
 OTC-24699-MS Free Span Rectification by Pipeline Lowering (PL) Method N. I. Thusyanthan, K. Sivanesan & G. Murphy Copyright 2014, Offshore Technology Conference This paper was prepared for presentation
OTC-24699-MS Free Span Rectification by Pipeline Lowering (PL) Method N. I. Thusyanthan, K. Sivanesan & G. Murphy Copyright 2014, Offshore Technology Conference This paper was prepared for presentation
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 10, October ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 10, October-2016 172 DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF MINI TENSION LEG PLATFORMS UNDER RANDOM WAVES Shibin P Shaji, Dr. Jayalekshmi R. Abstract
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 10, October-2016 172 DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF MINI TENSION LEG PLATFORMS UNDER RANDOM WAVES Shibin P Shaji, Dr. Jayalekshmi R. Abstract
Elastic-Plastic Finite Element Analysis for Zhongwei--guiyang Natural Gas Pipeline Endangered by Collapse
 Abstract Elastic-Plastic Finite Element Analysis for Zhongwei--guiyang Natural Gas Pipeline Endangered by Collapse Gengxin Wu,Peng Zhang,Zhixiang Li,Zunhai Ke,Guizhi Li,Anmin Jiang 2 School of Civil Engineering
Abstract Elastic-Plastic Finite Element Analysis for Zhongwei--guiyang Natural Gas Pipeline Endangered by Collapse Gengxin Wu,Peng Zhang,Zhixiang Li,Zunhai Ke,Guizhi Li,Anmin Jiang 2 School of Civil Engineering
Operations. On The Use of Safety Moorings in DP Operations
 Return to Session Directory DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE October 7-8, 28 Operations On The Use of Safety Moorings in DP Operations Nils Albert Jenssen Kongsberg Maritime, (Kongsberg Norway) Abstract
Return to Session Directory DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE October 7-8, 28 Operations On The Use of Safety Moorings in DP Operations Nils Albert Jenssen Kongsberg Maritime, (Kongsberg Norway) Abstract
Study of Passing Ship Effects along a Bank by Delft3D-FLOW and XBeach1
 Study of Passing Ship Effects along a Bank by Delft3D-FLOW and XBeach1 Minggui Zhou 1, Dano Roelvink 2,4, Henk Verheij 3,4 and Han Ligteringen 2,3 1 School of Naval Architecture, Ocean and Civil Engineering,
Study of Passing Ship Effects along a Bank by Delft3D-FLOW and XBeach1 Minggui Zhou 1, Dano Roelvink 2,4, Henk Verheij 3,4 and Han Ligteringen 2,3 1 School of Naval Architecture, Ocean and Civil Engineering,
Risers for Deepwater FPSO s
 Risers for Deepwater FPSO s John Bob-Manuel Senior Engineer 2H Offshore Engineering Ltd. March 2013 Agenda 2H overview Challenges of Deepwater Operations Freestanding Riser Overview Riser Configurations
Risers for Deepwater FPSO s John Bob-Manuel Senior Engineer 2H Offshore Engineering Ltd. March 2013 Agenda 2H overview Challenges of Deepwater Operations Freestanding Riser Overview Riser Configurations
COUPLED AND UNCOUPLED ANALYSIS OF Y-WIND SEMI WIND TURBINE FOUNDATION
 COUPLED AND UNCOUPLED ANALYSIS OF Y-WIND SEMI WIND TURBINE FOUNDATION HYOUNGCHUL KIM VL OFFSHORE (GRADUATE INTERN) SUNG YOUN BOO VL OFFSHORE (VICE PRESIDENT) Proceedings of the 23 rd Offshore Symposium,
COUPLED AND UNCOUPLED ANALYSIS OF Y-WIND SEMI WIND TURBINE FOUNDATION HYOUNGCHUL KIM VL OFFSHORE (GRADUATE INTERN) SUNG YOUN BOO VL OFFSHORE (VICE PRESIDENT) Proceedings of the 23 rd Offshore Symposium,
Innovative and Robust Design. With Full Extension of Offshore Engineering and Design Experiences.
 Innovative and Robust Design by VL Offshore With Full Extension of Offshore Engineering and Design Experiences www.vloffshore.com Y Wind Semi Designed by VL Offshore The Y Wind Semi platform (foundation)
Innovative and Robust Design by VL Offshore With Full Extension of Offshore Engineering and Design Experiences www.vloffshore.com Y Wind Semi Designed by VL Offshore The Y Wind Semi platform (foundation)
