Original Article. Contribution of anthropometric characteristics to critical swimming velocity and estimated propulsive force
|
|
|
- Anabel Palmer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Physical Education and Sport (JPES), 17(1), Art 32, pp , 2017 online ISSN: X; p-issn: ; ISSN - L = JPES Original Article Contribution of anthropometric characteristics to critical swimming velocity and estimated propulsive force TOLGA AKŞĐT 1, M. ZEKĐ ÖZKOL 2, FAĐK VURAL 3, EKĐM PEKÜNLÜ 4, RAMAZAN AYDINOĞLU 5, RANA 6 1,2,3,4,5,6 Department of Coaching Education, Faculty of Sport Sciences, Ege University, Đzmir, TURKEY Published online: March 31, 2017 (Accepted for publication January 30, 2017) DOI: /jpes Abstract: The aim of this study was to determine the anthropometric profiles of young male and female swimmers and to investigate the contribution of anthropometric characteristics to two determinants of swimming performance: critical velocity and estimated propulsive force. The study sample consisted of 25 female (age: 12.0 ± 0.9 years, height: ± 8.3 cm, body mass: 42.0 ± 7.8 kg) and 25 male (age: 12.4 ± 1.2 years, height: ± 11.3 cm, body mass: 49.1 ± 12.0 kg) swimmers. The swimmers were grouped in gender categories. For this study, the anthropometry was divided into 3 categories: length (cm), breadth (cm), and girth (cm) measurements. The critical velocity was estimated from 200-m and 400-m freestyle swimming performance. The estimated propulsive force was calculated using arm muscle area. Statistically significant correlation coefficients (ranging from 0.34 to 0.66) were found between the anthropometric characteristics (19 characteristics) and critical velocity for the female swimmers. Regarding swimming performance determinants, the highest correlations were between the hip girth and critical velocity (r = 0.66; p < 0.05) and between the flexed arm and estimated propulsive force (r = 0.87; p < 0.05). For the male swimmers, the highest correlations were between the transverse chest and critical velocity (r = 0.81; p < 0.05) and between the thoracic girth and estimated propulsive force (r = 0.90; p < 0.05). The somatotype analysis showed that the female swimmers were of the ectomesomorph type, and the male swimmers were of the endo-mesomorph type. The skinfold, length, girth and breadth could be used as predictors of critical velocity and estimated propulsive force in young swimmers. This study could help swimming coaches attain objective knowledge about the swimming performance of their athletes after basic anthropometric measurements and help them to benefit from this knowledge while monitoring the athletes developmental process. Keywords: body composition, force, somatotype, performance, swimming Introduction Swimming is a popular sport, and early starting specialization. Although performance and success in elite swimmers depend on various factors, physical parameters (i.e., body height, body mass and somatotype characteristics) are also determinants of swimming performance. In previous studies, physical properties, anthropometric characteristics and some of the strength parameters of swimmers were identified (Cochrane et al., 2015; Richardson, Beerman, Heiss, 2000), and the correlations between these parameters and swimming performance were investigated (Barbosa, Morais, Marques, Costa, & Marinho, 2015; Girold, Calmels, Maurin, Milhau, & Chatard, 2006; Kukolj, Ropret, Ugarkovic, & Jaric, 1999). Critical swimming speed (V crit ) is typically used as a determinant of swimming performance in the literature (Wakayoshi et al., 1992). Various factors, such as physical fitness, motor skills, mental abilities, tactical training and anthropometric profiles affect the performance and success of athletes. Besides other factors, some physical parameters, such as somatotype components, body mass and body height are factors that influence competition success (Martín-Matillas et al., 2013). Somatotype properties yield descriptive and substantive information about the anthropometric profiles of athletes. Some prior studies only included descriptive information on general body properties (body height, body mass and body fat ratio [BFR] of young swimmers) in relation to the age group and gender (Bagnall & Kellett, 1977; Richardson, Beerman, Heiss, Shultz, 2000; Zuniga et al., 2011), whereas in other studies, the relation between various anthropometric characteristics (arm and leg lengths) of swimmers and their performance were identified (Avlonitou, 1994; Zuniga et al., 2011). In another study, upper extremity length, leg strength and grip strength were found to be determinants for 100-m freestyle swimming performance in male swimmers who were 12 to 14 years of age (Geladas, Nassis, & Pavlicevic, 2005). In general, these studies revealed that swimming performance is influenced by physical and anthropometric characteristics. In addition, some studies that investigated the arm muscle area (AMA), strength and swimming performance demonstrated that swimmers with a higher arm strength swim faster, which is an important performance-related Corresponding Author TOLGA AKŞĐT, tolgaaksit74@gmail.com
2 research finding (De Ste Croix, Armstrong, Welsman, & Sharpe, 2009; Hawley & Williams, 1991; Klika & Thorland, 1994; Santos, Barbosa, Melo, Veronese da Costa, & Costa, 2012). Propulsive force is another factor that influences the swimming performance. Propulsive force is highly correlated with swimming speed and performance, according to prior studies (Geladas et al., 2005; Santos et al., 2012; Vitor & Böhme, 2010). Additionally, some anthropometric characteristics are crucial determinants of the estimated propulsive force (EPF) (Cochrane et al., 2015). Despite the existence of a relationship between the EPF and swimming performance, few studies have focused on the effect of the EPF on swimming performance, and there is a lack of sufficient studies on the somatotypes of young swimmers and the relationship between these somatotypes and the two most important swimming performance determinants (EPF and V crit ). Identification of these swimming performance-related variables in young swimmers could significantly contribute to the talent selection process. Therefore, the current study aimed to describe the anthropometric profiles of female and male young swimmers and determine the contribution of some of the anthropometric characteristics to EPF and V crit. Material and Methods Participants We tested male (n = 25) and female (n = 25) junior swimmers between the ages of 11 and 14 who volunteered to participate in this study. All subjects were from the same swimming club who were trained for two hours per day and six days a week. The participants had no injuries or health problems during the tests. This study was conducted in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration and was approved by the Medical Research Ethics Committee of Medical University Hospital (protocol no: 14-4/3), and all participants and their parents gave written informed consent. Procedure The swimmers were grouped according to gender. The measurements were performed in the Olympic indoor swimming pool and university laboratory. Swimmers attended all-out 200-m and 400-m freestyle swimming tests, and the results were used to estimate their V crit using Equation 1, where D1 = swimming distance 1 (200 m), D2 = swimming distance 2 (400 m), T1 = the time for the 200-m swim in seconds and T2 = the time for the 400-m swim in seconds (Wakayoshi et al., 1992). The AMA was calculated using Equation 2, where AC is the arm circumference, SKF is the triceps skinfold and Π = The calculation of the EPF is dependent on the AMA (Equation 3) (Cochrane et al., 2015; Santos et al., 2012). V crit (m sec 1 ) = (D2 D1) / (T2 T1) Eq. 1 AMA (cm 2 ) = (AC [cm] SKF [cm]) 2 / 4 Eq. 2 EPF (kgf) = AMA (cm 2 ) Eq. 3 Anthropometry Measurements The anthropometric measurements were divided into three categories; length (cm), breadth (cm) and girth (cm). Body mass and height were obtained when the swimmers wore light clothing and without shoes via a portable scale to the nearest 0.1 kg and a stadiometer to the nearest 0.1 cm, respectively (Seca, Germany). The measurements were taken according to Lohman et al. (1988). The circumference values were obtained using a single evaluator and a flexible tape measure with a precision of 0.1 cm. Skinfold measurements were taken using a skinfold calliper (Holtain Ltd, Crymych, UK) from 9 body locations (triceps, subscapular, axilla, chest, biceps, suprailiac, abdomen, thigh and calf). These data were used to estimate the body density using two different equations depending on the gender of the participant (Durnin & Rahaman, 1967). The BFR was calculated depending on this estimated body density using the Siri Equation (Siri, 1956). Two measurements were taken from each location on the body, and the mean value was used in the statistical analyses. The somatotype components were calculated according to the equation by Carter (Carter L, 1990). The Body Mass Index (BMI) was calculated as the body mass divided by the stature squared. Statistical Analysis The conformity of the data that had a normal distribution was tested using the Shapiro-Wilk Test and also checked using skewness, kurtosis and coefficient of variation (CV) values. As central tendency measures, the means and standard deviations were used for data that had a normal distribution, and the medians were used for those that had a non-normal distribution. To determine the significant difference between the female and male swimmers, an independent-samples t-test was used for the data that complied with the normal distribution, and the Mann Whitney U test was used for the data that did not comply with the normal distribution. Moreover, absolute differences in dependent variables between genders were also included. For the regression analysis, a stepwise multiple regression model was used in which the anthropometric characteristics and somatotype components were the predictive variables and the V crit and EPF were the outcome variables. An analysis program, SPSS for Windows release 20.0 (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL), was used for the statistical evaluation, and the level of statistical significance was accepted as p
3 Results The descriptive characteristics of the subjects (age, body mass, height, BMI and BFR) and their anthropometric characteristics/body type (endomorphic, mesomorphic and ectomorphic) are provided in Table 1. Table 1. Descriptive characteristics and differences, anthropometric/somatotype characteristics and freestyle swimming performance for the female and male young swimmers [mean ± SD (median)]. Variables Female (n = 25) Male (n = 25) Difference Age (years) 12.0 ± 0.9 (12.0) 12.4 ± 1.2 (12.0) 0.36 Body mass (kg) 42.0 ± ± * Height (cm) ± ± Training Volume (h wk 1 ) BMI [kg m 2 ] 18.1 ± ± * Body fat ratio (%) 13.5 ± ± * (mm) Triceps 11.4 ± 3.3 (11.3) 12.5 ± Subscapular 8.4 ± 3.3 (7.2) 8 ± 2.9 (7.5) 0.34 Midaxillary 7.5 ± 2.9 (7.0) 8.9 ± Chest 7.8 ± 2.2 (7.5) 8.5 ± 3.3 (8.0) 0.68 Biceps 7.6 ± 3.3 (6.2) 7.5 ± Suprailiac 8.8 ± 4.0 (7.0) 14 ± * Abdominal 12.6 ± ± Thigh 16.8 ± ± Calf 14.6 ± ± Sum of 9 skinfolds 97.1 ± 26.7 (93.7) ± (cm) Sitting Height 77.9 ± ± Arm Span ± 9.3 (156.3) ± 15.2 (151.5) 3.5 Arm 69.6 ± ± 11.6 (69.6) 0.18 Forearm 21.1 ± 2.4 (21.4) 23.6 ± 6.5 (22.3) 2.51 Thigh 46.9 ± ± Lower leg 35.2 ± ± Total leg 89.5 ± ± Foot 23.3 ± ± * (cm) Biacromial 28.4 ± ± Transverse chest 22.8 ± ± Bideltoid 35.8 ± ± * Bitrochanteric 26.1 ± ± Biepicondylar humerus 5.9 ± ± * Styloid 5.0 ± ± * Hand 7.2 ± ± * Biepicondylar femur 8.4 ± ± * Foot 8.0 ± ± * (cm) Shoulder 91.9 ± ± * Thoracic 77.6 ± ± Relaxed arm 22.8 ± ± * Flexed arm 24.3 ± ± * Forearm 20.8 ± ± * Wrist 13.9 ± ± * Hip 79.8 ± ± * Upper thigh 45.3 ± ± Calf 30.1 ± ± * Ankle 19.8 ± ± * Somatotype Endomorphy 3.2 ± ± Mesomorphy 3.7 ± 1.2 (3.4) 5.0 ± * Ectomorphy 3.6 ± ± * Swimming performance 200 m (sec) ± ± * 400 m (sec) ± ± 44.8 (326.0) 0.51* V crit (m sec -1 ) 1.05 ± ± * Propulsive performance AMA (cm 2 ) 34.8 ± ± 12.2 (39.3) 6.14 EPF (kgf) 22.4 ± ± 7.8 (25.2) 3.95 Note: *p 0.05; BMI: Body mass index; V crit : Critical swimming velocity; AMA: Arm muscle area; EPF: Estimated propulsive force. 214
4 Correlations between the anthropometric characteristics, somatotype components, V crit and EPF are summarized in Table 2. Table 2. Zero-order correlations between the anthropometric/somatotype characteristics and the critical swimming velocity/epf. Variable V crit EPF Female Male Female Male Triceps Subcapular Midaxillary Chest Biceps 0.34* Suprailiac * * Abdominal Thight Calf 0.42* Sitting Height 0.54* 0.68* 0.75* 0.81* Arm Span 0.40* 0.75* 0.67* 0.77* Forearm * Thigh * 0.62* 0.52* Lower leg 0.47* 0.75* * Total leg * 0.63* 0.59* Foot 0.44* 0.78* 0.64* 0.68* Biacromial * 0.52* 0.81* Transverse Chest 0.55* 0.81* 0.68* 0.83* Bideltoid 0.57* 0.80* 0.71* 0.84* Bitrochanteric 0.57* 0.71* 0.71* 0.77* Biepicondylar humerus 0.37* 0.73* 0.60* 0.75* Styloid * 0.42* 0.62* Hand * 0.57* 0.74* Biepicondylar femur * 0.38* 0.70* Foot * 0.50* 0.82* Shoulder 0.64* 0.77* 0.77* 0.82* Thoracic 0.60* 0.64* 0.82* 0.90* Relaxed Arm 0.52* 0.63* 0.83* 0.73* Flexed Arm 0.61* 0.65* 0.87* 0.80* Forearm 0.49* 0.70* 0.82* 0.84* Wrist * 0.69* 0.78* Hip 0.66* 0.72* 0.81* 0.74* Upper Thigh 0.61* 0.61* 0.79* 0.66* Calf 0.50* 0.69* 0.60* 0.68* Ankle 0.45* 0.70* 0.76* 0.64* Somatotype Endomorphy Mesomorphy Ectomorphy -0.55* Note: *r significant at p V crit : Critical swimming velocity; EPF: Estimated propulsive force. Statistically significant correlation coefficients (ranging from 0.34 to 0.66) were found between the anthropometric characteristics (19 characteristics) and V crit for the female swimmers. The highest correlation was between hip girth and V crit (r = 0.66; p < 0.05). The correlations between the anthropometric characteristics (24 characteristics) and EPF were also statistically significant (from 0.38 to 0.87). The highest correlation was between the flexed arm and EPF (r = 0.87; p < 0.05). While all girth ( ) and breadth ( ) measurements were significantly correlated with the EPF, none of the skinfold measurements showed significant correlations. Additionally, for the male swimmers, statistically significant correlation coefficients (between 0.37 and 0.81) were found between anthropometric characteristics (27 characteristics) and V crit. The highest correlation was between the transverse chest and V crit (r = 0.81; p < 0.05). Correlations between the anthropometric characteristics (26 characteristics) and the EPF were also statistically significant (between 0.39 and 0.90). The highest correlation was between the thoracic girth and the EPF (r = 0.90; p < 0.05). Regarding the somatotype component, a significant negative correlation was found between ectomorphy and V crit only for the female swimmers (r = 0.55; p < 0.05). 215
5 The results of the stepwise regression analyses are shown in Tables 3-4. The V crit ranged between 17.8% (calf skinfold) and 63.4% (bitrochanteric, styloid, biepicondlhumerus) for the female swimmers. Additionally, the EPF ranged between 51.3% (sitting height) and 76.2% (flexed arm). For the male swimmers, the V crit ranged between 40.5% (suprailiac, triceps) and 66.4% (transverse chest), and the EPF ranged between 51.3% (suprailiac, triceps, subscapular skinfold) and 91.2% (thoracic, flexed arm, upper thigh). Table 3. Multiple regression equations used to predict the V crit in the young swimmers Female (n= 25) Male (n= 25) Outcome Constant Predictor R Constant Predictor Variable (SE) Variables cumulative (SE) Variables V crit (0.07) Calf (0.04) Suprailiac (0.10) (0.07) 0.01 (0.01) Triceps V crit 0.37 (0.33) V crit 0.74 (0.32) 0.02 (0.05) 0.02 (0.09) 0.03 (0.07) 0.27 (0.06) 0.14 (0.05) Sitting Heigh Thight Bitrochanteric Styloid Biepic.humerus (0.24) 0.87 (0.16) 0.06 (0.01) 0.44 (0.01) R cumulative Foot 61.6 T. Chest 66.4 V crit 0.14 (0.21) 0.11 (0.03) Hip (0.18) 0.01 (0.02) Shoulder 60.1 V crit 1.54 (0.09) 0.07 (0.01) 0.06 (0.01) Somatotype Ectomorphy Mesomorphy Somatotype Note: V crit : Critical swimming velocity; SE: Standard error; B: Unstandardized coefficients Table 4. Multiple regression equations used to predict the EPF in the young swimmers Female (n = 25) Male (n = 25) Outcome Variable Constant (SE) EPF EPF 35.9 (10.63) EPF (11.03) EPF (4.81) 0.74 (0.13) 1.51 (0.30) 1.68 (0.19) Predictor Variables R cumulative Constant (SE) 22.9 (3.81) Sitting Height (13.14) Bideltoid (8.12) Flexed Arm (5.29) 0.60 (0.21) 1.46 (0.37) 1.65 (0.59) 1.13 (0.16) 1.63 (0.21) 0.58 (0.07) 1.79 (0.38) 0.87 (0.25) Predictor Variables Suprailiac Triceps Subscapular Sitting Height R cumulative Bideltoid 71.8 Thoracic Flexed Arm Upp. Thigh EPF Somatotype Somatotype Note: EPF: Estimated propulsive force; SE: Standard error; B: Unstandardized coefficients Discussion In this study, the mean ages of the female and male swimmers were 12.0 ± 0.9 and 12.4 ± 1.2, respectively. Although the body mass and height measurements for the 12-year-old swimmers in the studies by Cochrane et al. (2015) and Ricardo (2011) were higher than those found in our study, the mass and height results in two other studies are consistent with our findings (Barbosa et al., 2015; Geladas et al., 2005; Marinho et al., 2009). However, the BFR measurements for the male swimmers in the current study was lower than that of a similar age group in the study by Cochrane et al. (2015). Here, statistically significant positive correlations were found between the V crit and various anthropometric characteristics (biceps, calf, sitting height, arm span, lower leg, foot, transverse chest, bideltoid, bitrochanteric, biepicondylar humerus, shoulder, thoracic, relaxed arm, flexed arm, fore arm, hip, upper thigh, calf and ankle) in the female swimmers. In contrast, a statistically significant negative correlation was found between the V crit and ectomorphy. These findings are consistent with the literature (Geladas et al., 2005; Grimston & Hay, 1986). In males, all lengths, breadths, girths and suprailiac skinfold measurements were significantly correlated with swimming performance (Table 2). In particular, positive correlations between the swimming performance and sitting height, arm span, lower leg and foot lengths for both genders clarify the contribution of these lengths to swimming performance. In
6 agreement with these findings, the positive effects of extremity length on propulsive force, which is an important factor in swimming performance, were demonstrated in prior literature. (Geladas et al., 2005) Significant correlations were found between the EPF and all anthropometric measurements (except for the skinfold, forearm and lower leg measurements) for the female swimmers. For the male swimmers, while all girths, breadths, and lengths (except for the forearm) were significantly correlated with the EPF, for the skinfold measurements, only the suprailiac showed a significant correlation. Positive effects of the long extremities and body segments on propulsive force generation have been previously reported in the literature (Grimston & Hay, 1986). Our results revealed that for male swimmers (V crit : , EPF: ) there was a higher correlation between swimming performance determinants and length measures than for female swimmers (V crit : , EPF: ). This trend was also valid for correlations related to girth and breadth measures (Table 2). These significant correlations between swimming performance determinants and length measures are also supported by similar results in another prior study (Grimston & Hay, 1986). Swimmers with long extremities have better pull, slide and performance characteristics (Grimston & Hay, 1986; Sharp, Troup, & Costill, 1982; Toussaint & Hollander, 1994), which could explain these significant correlations. In this study, the higher correlations in males may have two possible reasons. 1) The mean age of male swimmers was 0.36 years greater than for the females, and the males had significantly shorter swimming times compared to the females (23 s and 51 s shorter for 200 m and 400 m, respectively). 2) For the anthropometric characteristics (foot length; bideltoid, styloid, hand, biepicondylar femur, and foot breadths and all girths except for the thoracic and upper thigh) that may have positive effects on the 200-m and 400-m swimming performances, V crit and EPF were significantly greater for the males (p < 0.05). The stepwise regression technique indicated that changes in the V crit and EPF could be explained via anthropometric characteristics. A change in the V crit was explained via the skinfolds, lengths, breadths and girths for both genders. For males, the same variables explained the change in the EPF. However, for the females, only the lengths, breadths and girths explained the significant amount of variance in the EPF. For the females, the change in V crit for the calf (skinfold) was 17.8%, for the sitting height and thigh combination (length), it was 49.9%, for the bitrochanteric, styloid, and biepicondylar humerus combination (breadth), it was 63.4% and for the hip (girth), it was 43.7%. For the males, the change in V crit for the suprailiac and triceps combination (skinfold) was 40.5%, for the foot (length), it was 61.2%, for the transverse chest (breadth), it was 66.4%, and for the shoulder (girth), it was 60.1%. For both the females and males, significant variances in the EPF for the sitting height (length) were 54.9% and 66.1%, respectively, and for the bideltoid (breadth), they were 51.3% and 71.8%, respectively. For the females, only the flexed arm (girth) explained the 76.2% of variance in the EPF; however, in males, this percentage increased up to 91.2% when the thoracic, the flexed arm and upper thigh combination was used. For the males, additionally, the suprailiac, triceps and subscapular combination (skinfold) explained the significant amount of variance (51.3%) in the EPF. The somatotype values in the females and males were and , respectively. The males were significantly more mesomorphic and less ectomorphic than the females (Table 1). Ecto-mesomorphy was the dominant somatotype in the females, whereas endo-mesomorphy was dominant in the males. Ectomorphy (31.3%) and mesomorphy (26.5) were the best predictors that explained the variance in V crit, which is consistent with the findings of Siders et al. (1993). However, no somatotype component explained the change in the EPF for both genders. Between the somatotype components, only ectomorphy had a moderate significant correlation (r = 0.55) with V crit for the females. Other components had low level insignificant correlations with V crit and EPF (ranging from 0.31 to 0.30). Lyttle et al. (1998) reported that slenderness makes a significant contribution to the hydrodynamic efficiency during swimming. In our study, the significant change in V crit due to the ectomorphy and the relationship between these variables in females supports this opinion. Conclusion In brief, skinfold, length, girth and breadth measures could be used as predictors of the V crit and EPF in young swimmers. The combination of ectomorphy and mesomorphy could only significantly explain the change in V crit for females in terms of somatotype components. The girth measures were highly correlated with swimming performance for both genders. The practical advantage of this study is that basic and affordable anthropometric tests could be used to identify talented young swimmers by assessing the anthropometric characteristics that influence swimming performance. In addition, swimming coaches should focus on monitoring anthropometric characteristics that are important for swimming performance. Acknowledgement The authors would like to thank all of the swimmers and coaches for their support during this study. This study was supported by Ege University Research Foundation (Project Number: 2014/BĐL/032). We declare no conflicts of interest. References Avlonitou, E. (1994). Somatometric variables for preadolescent swimmers. Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness, 34(2),
7 Bagnall, K. M., & Kellett, D. W. (1977). A study of potential Olympic swimmers: I, the starting point. British journal of sports medicine, 11(3), Barbosa, T. M., Morais, J. E., Marques, M. C., Costa, M. J., & Marinho, D. A. (2015). The power output and sprinting performance of young swimmers. Journal of strength and conditioning research, 29(2), Carter L, H. B. (1990). Somatotyping-Development and Application. Cambridge: Cambridge University. Cochrane, K. C., Housh, T. J., Smith, C. M., Hill, E. C., Jenkins, N. D. M., Johnson, G. O., & Cramer, J. T. (2015). Relative contributions of strength, anthropometric, and body composition characteristics to estimated propulsive force in young male swimmers. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 29(6), De Ste Croix, M. B. A., Armstrong, N., Welsman, J. R., & Sharpe, P. (2009). Longitudinal changes in isokinetic leg strength in year-olds. Annals of Human Biology, 29(1), Durnin, J. V, & Rahaman, M. M. (1967). The assessment of the amount of fat in the human body from measurements of skinfold thickness. The British Journal of Nutrition, 21(3), Geladas, N. D., Nassis, G. P., & Pavlicevic, S. (2005). Somatic and physical traits affecting sprint swimming performance in young swimmers. International Journal of Sports Medicine, 26(2), Girold, S., Calmels, P., Maurin, D., Milhau, N., & Chatard, J. C. (2006). Assisted and resisted sprint training in swimming. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 20(3), Grimston, S. K., & Hay, J. G. (1986). Relationships among anthropometric and stroking characteristics of college swimmers. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 18(1), Hawley, J. A, & Williams, M. M. (1991). Relationship between upper body anaerobic power and freestyle swimming performance. International Journal of Sports Medicine, 12(1), 1 5. Klika, R. J., & Thorland, W. G. (1994). Physiological determinants of sprint swimming performance in children and young adults. Pediatric Exercise Science, 6, Kukolj, M., Ropret, R., Ugarkovic, D., & Jaric, S. (1999). Anthropometric, strength, and power predictors of sprinting performance. Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness, 39(2), Lohman, T. G., Roche, A. F., & Martorell, R. (1988). Anthropometric standardization reference manual. Human Kinetics Books, 177. Lyttle, A., Blanksby, B., Elliott, B., & Lloyd, D. (1998). The effect of depth and velocity on drag during the streamlined guide. Journal of Swimming Research, 13, Marinho, D. A., Garrido, N., Barbosa, T. M., Canelas, R., Silva, A. J., Costa, A. M., Reis, V. M., & Marques, M. C. (2009). Monitoring swimming sprint performance during a training cycle. Journal of Physical Education and Sport, 25(4),1-6. Martín-Matillas, M., Valadés, D., Hernández-Hernández, E., Olea-Serrano, F., Sjöström, M., Delgado- Fernández, M., & Delgado-Fernández, M. (2013). Anthropometric, body composition and somatotype characteristics of elite female volleyball players from the highest Spanish league. Journal of Sport Science, 32, Richardson, J., Beerman, K.,Heiss, C.,& Shultz, J.(2000). Comparison of body weight and body fat classifications of competitive school-age club swimmers. Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, 100(2), Ricardo, F. (2011). Aerobic evaluation of young swimmers using the critical velocity test a brief report. Journal of Physical Education and Sport, 11(2), Sharp, R. L., Troup, J. P., & Costill, D. L. (1982). Relationship between power and sprint freestyle swimming. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 14(1), Siders, W. A., Lukaski, H. C., & Bolonchuk, W. W. (1993). Relationships among swimming performance, body composition and somatotype in competitive collegiate swimmers. Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness, 33(2), Siri, W. E. (1956). Gross Composition of the Body," in Advances in Biological and Medical Physics. (J. H. L. and C. A. Tobias, Ed.). New York: Academic Press. Toussaint, H. M., & Hollander, A. P. (1994). Energetics of competitive swimming: implications for training programmes. Sports Medicine, 18(6), Santos, M. A., Barbosa, M. L., Melo, W.V., Veronese da Costa, A., & Costa, M.C. (2012). Estimate of propulsive force in front crawl swimming in young athletes. Open Access Journal of Sports Medicine, 3, Vitor, F. D. M., & Böhme, M. T. S. (2010). Performance of young male swimmers in the 100-meters front crawl. Pediatric Exercise Science, 22(2), Wakayoshi, K., Ikuta, K., Yoshida, T., Udo, M., Moritani, T., Mutoh, Y., & Miyashita, M. (1992). Determination and validity of critical velocity as an index of swimming performance in the competitive swimmer. European Journal of Applied Physiology and Occupational Physiology, 64(2), Zuniga, J., Housh, T. J., Mielke, M., Hendrix, C. R., Camic, C. L., Johnson, G. O., & Schmidt, R. J. (2011). Gender comparisons of anthropometric characteristics of young sprint swimmers. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 25(1),
INFORMATION SHEET FOR PROSPECTIVE VOLUNTEERS IN THE STUDY
 APPENDICES 126 APPENDIX A INFORMATION SHEET FOR PROSPECTIVE VOLUNTEERS IN THE STUDY PHYSIOLOGICAL AND ANTHROPOMETRICAL COMPARISONS BETWEEN THE TRIATHLETE, RUNNER, CYCLIST AND SWIMMER A study by Jonathan
APPENDICES 126 APPENDIX A INFORMATION SHEET FOR PROSPECTIVE VOLUNTEERS IN THE STUDY PHYSIOLOGICAL AND ANTHROPOMETRICAL COMPARISONS BETWEEN THE TRIATHLETE, RUNNER, CYCLIST AND SWIMMER A study by Jonathan
BODY FORM INFLUENCES ON THE DRAG EXPERIENCED BY JUNIOR SWIMMERS. Australia, Perth, Australia
 1 BODY FORM INFLUENCES ON THE DRAG EXPERIENCED BY JUNIOR SWIMMERS Andrew Lyttle 1, Nat Benjanuvatra 2, Brian A Blanksby 2, Bruce C Elliott 2 1 Western Australian Institute of Sport, Perth, Australia 2
1 BODY FORM INFLUENCES ON THE DRAG EXPERIENCED BY JUNIOR SWIMMERS Andrew Lyttle 1, Nat Benjanuvatra 2, Brian A Blanksby 2, Bruce C Elliott 2 1 Western Australian Institute of Sport, Perth, Australia 2
At What Extent Physical Training Can Minimize Gender Differences in Male and Female Trained Swimmers? - A Comparative Analysis
 International Journal of Sports and Physical Education (IJSPE) Volume 3, Issue 1, 2017, PP 24-28 ISSN 2454-6380 http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2454-6380.0301005 www.arcjournals.org At What Extent Physical
International Journal of Sports and Physical Education (IJSPE) Volume 3, Issue 1, 2017, PP 24-28 ISSN 2454-6380 http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2454-6380.0301005 www.arcjournals.org At What Extent Physical
DETERMINANT FACTORS RELATED TO PERFORMANCE IN YOUNG SWIMMERS
 DETERMINANT FACTORS RELATED TO PERFORMANCE IN YOUNG SWIMMERS Luís Rama1 João Santos2, Paulo Gomes2, Francisco Alves3 1Faculdade de Ciências do Desporto e Educação Física, Universidade de Coimbra, Portugal
DETERMINANT FACTORS RELATED TO PERFORMANCE IN YOUNG SWIMMERS Luís Rama1 João Santos2, Paulo Gomes2, Francisco Alves3 1Faculdade de Ciências do Desporto e Educação Física, Universidade de Coimbra, Portugal
POSITION-SPECIFIC ANTHROPOMETRIC PROFILES: 2011 WOMEN'S 19 EUROPEAN HANDBALL CHAMPIONSHIP
 POSITION-SPECIFIC ANTHROPOMETRIC PROFILES: 2011 WOMEN'S 19 EUROPEAN HANDBALL CHAMPIONSHIP František URBAN 1, Róbert KANDRÁČ 2, František TÁBORSKÝ 3 1 Member of Union of University Handball Teachers / EHF
POSITION-SPECIFIC ANTHROPOMETRIC PROFILES: 2011 WOMEN'S 19 EUROPEAN HANDBALL CHAMPIONSHIP František URBAN 1, Róbert KANDRÁČ 2, František TÁBORSKÝ 3 1 Member of Union of University Handball Teachers / EHF
Study of anthropometric characteristics among the university level archers
 2017; 2(2): 515-519 ISSN: 2456-0057 IJPNPE 2017; 2(2): 515-519 2017 IJPNPE www.journalofsports.com Received: 27-05-2017 Accepted: 28-06-2017 Ritika Physical Education Teacher, Sri Guru Harkrishan Public
2017; 2(2): 515-519 ISSN: 2456-0057 IJPNPE 2017; 2(2): 515-519 2017 IJPNPE www.journalofsports.com Received: 27-05-2017 Accepted: 28-06-2017 Ritika Physical Education Teacher, Sri Guru Harkrishan Public
Predictors of race time in male ironman triathletes: physical characteristics, training, or prerace experience?
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2010 Predictors of race time in male ironman triathletes: physical characteristics,
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2010 Predictors of race time in male ironman triathletes: physical characteristics,
POSITION-SPECIFIC ANTHROPOMETRIC PROFILES: 2011 WOMEN'S 17 EUROPEAN HANDBALL CHAMPIONSHIP
 POSITION-SPECIFIC ANTHROPOMETRIC PROFILES: 2011 WOMEN'S 17 EUROPEAN HANDBALL CHAMPIONSHIP František URBAN 1, Róbert KANDRÁČ 2, František TÁBORSKÝ 3 1 Member of the Union of University Handball Teachers
POSITION-SPECIFIC ANTHROPOMETRIC PROFILES: 2011 WOMEN'S 17 EUROPEAN HANDBALL CHAMPIONSHIP František URBAN 1, Róbert KANDRÁČ 2, František TÁBORSKÝ 3 1 Member of the Union of University Handball Teachers
This article has been downloaded from JPES Journal of Physical Education an Sport Vol 25, no 4, December, 2009 e ISSN: p ISSN:
 C I T I U S A L T I U S F O R T I U S - J O U R N A L O F P H Y S I C A L E D U C A T I O N A N D S P O R T This article has been downloaded from SHORT REPORT Online Publication Date: 10 December 2009
C I T I U S A L T I U S F O R T I U S - J O U R N A L O F P H Y S I C A L E D U C A T I O N A N D S P O R T This article has been downloaded from SHORT REPORT Online Publication Date: 10 December 2009
Validation of a Step Test in Children Ages 7-11
 Validation of a Step Test in Children Ages 7-11 Emilene Clark Aurora Fry Colleen Smith Tonya Thomas Primary Advisor: Jim Farris, PT, PhD April 20, 2011 Background Exercise Testing Maximal Testing Sub-maximal
Validation of a Step Test in Children Ages 7-11 Emilene Clark Aurora Fry Colleen Smith Tonya Thomas Primary Advisor: Jim Farris, PT, PhD April 20, 2011 Background Exercise Testing Maximal Testing Sub-maximal
Generating Power in the Pool: An Analysis of Strength Conditioning and its Effect on Athlete Performance
 Generating Power in the Pool: An Analysis of Strength Conditioning and its Effect on Athlete Performance 1 Introduction S.D. Hoffmann Carthage College shoffmann@carthage.edu November 12 th, 2014 Abstract
Generating Power in the Pool: An Analysis of Strength Conditioning and its Effect on Athlete Performance 1 Introduction S.D. Hoffmann Carthage College shoffmann@carthage.edu November 12 th, 2014 Abstract
CRNOGORSKA SPORTSKA AKADEMIJA, Sport Mont časopis br. 43,44,45.
 UDC 797.21 Bergun Meric Bingul, Ozlem Tore, Kocaeli University, School of Physical Education and Sport (Kocaeli, Turkey) Cigdem Bulgan, Halic University, School of Physical Education and Sport (İstanbul,
UDC 797.21 Bergun Meric Bingul, Ozlem Tore, Kocaeli University, School of Physical Education and Sport (Kocaeli, Turkey) Cigdem Bulgan, Halic University, School of Physical Education and Sport (İstanbul,
Performance of Young Male Swimmers in the 100-Meters Front Crawl
 Pediatric Exercise Science, 2010, 22, 278-287 2010 Human Kinetics, Inc. Performance of Young Male Swimmers in the 100-Meters Front Crawl Fabrício de Mello Vitor and Maria Tereza Silveira Böhme University
Pediatric Exercise Science, 2010, 22, 278-287 2010 Human Kinetics, Inc. Performance of Young Male Swimmers in the 100-Meters Front Crawl Fabrício de Mello Vitor and Maria Tereza Silveira Böhme University
WHAT CAN WE LEARN FROM COMPETITION ANALYSIS AT THE 1999 PAN PACIFIC SWIMMING CHAMPIONSHIPS?
 WHAT CAN WE LEARN FROM COMPETITION ANALYSIS AT THE 1999 PAN PACIFIC SWIMMING CHAMPIONSHIPS? Bruce Mason and Jodi Cossor Biomechanics Department, Australian Institute of Sport, Canberra, Australia An analysis
WHAT CAN WE LEARN FROM COMPETITION ANALYSIS AT THE 1999 PAN PACIFIC SWIMMING CHAMPIONSHIPS? Bruce Mason and Jodi Cossor Biomechanics Department, Australian Institute of Sport, Canberra, Australia An analysis
Leg Power in Elite Male Fencers: A Comparative Study among the Three Competitive Disciplines
 Leg Power in Elite Male Fencers: A Comparative Study among the Three Competitive Disciplines Gustavo D. Aquilino, Aldo F. Longo, Néstor A. Lentini. Exercise Physiology Laboratory, National Sport High Performance
Leg Power in Elite Male Fencers: A Comparative Study among the Three Competitive Disciplines Gustavo D. Aquilino, Aldo F. Longo, Néstor A. Lentini. Exercise Physiology Laboratory, National Sport High Performance
2012 CALIFORNIA PHYSICAL FITNESS TEST. e-template REFERENCE GUIDE
 2012 CALIFORNIA PHYSICAL FITNESS TEST e-template REFERENCE GUIDE Evalumetrics Inc. January 2012 2012 New e-template Features Starting this year, the e-template contains several new worksheets, with color-coded
2012 CALIFORNIA PHYSICAL FITNESS TEST e-template REFERENCE GUIDE Evalumetrics Inc. January 2012 2012 New e-template Features Starting this year, the e-template contains several new worksheets, with color-coded
A Comparative Study of Running Agility, Jumping Ability and Throwing Ability among Cricket Players
 Research Journal of Physical Education Sciences ISSN 2320 9011 A Comparative Study of Running Agility, Jumping Ability and Throwing Ability among Cricket Players Abstract Karunesh Kumar 1, Manjit Singh
Research Journal of Physical Education Sciences ISSN 2320 9011 A Comparative Study of Running Agility, Jumping Ability and Throwing Ability among Cricket Players Abstract Karunesh Kumar 1, Manjit Singh
Relationship of physical characteristics, power and swimming time in sprint swimmers
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Annals of Biological Research, 2014, 5 (8):24-29 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0976-1233 CODEN (USA): ABRNBW Relationship of
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Annals of Biological Research, 2014, 5 (8):24-29 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0976-1233 CODEN (USA): ABRNBW Relationship of
DO HEIGHT AND WEIGHT PLAY AN IMPORTANT ROLE IN BLOCK AND ATTACK EFFICIENCY IN HIGH-LEVEL MEN S VOLLEYBALL?
 Papers on Anthropology XXVI/1, 2017, pp. 64 71 DO HEIGHT AND WEIGHT PLAY AN IMPORTANT ROLE IN BLOCK R. Stamm, M. Stamm, A. Jairu, R. Toop, R. Tuula, P. V. João DO HEIGHT AND WEIGHT PLAY AN IMPORTANT ROLE
Papers on Anthropology XXVI/1, 2017, pp. 64 71 DO HEIGHT AND WEIGHT PLAY AN IMPORTANT ROLE IN BLOCK R. Stamm, M. Stamm, A. Jairu, R. Toop, R. Tuula, P. V. João DO HEIGHT AND WEIGHT PLAY AN IMPORTANT ROLE
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 112 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 112 (2015 ) 540 545 7th Asia-Pacific Congress on Sports Technology, APCST 2015 Movement variability of professional pool billiards
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 112 (2015 ) 540 545 7th Asia-Pacific Congress on Sports Technology, APCST 2015 Movement variability of professional pool billiards
COMPARISON STUDY BETWEEN THE EFFICIENY OF THE START TECHNIQUES IN THE ROMANIAN COMPETITIVE SWIMMING
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series IX: Sciences of Human Kinetics Vol. 6 (55) No. 1 2013 COMPARISON STUDY BETWEEN THE EFFICIENY OF THE START TECHNIQUES IN THE ROMANIAN COMPETITIVE
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series IX: Sciences of Human Kinetics Vol. 6 (55) No. 1 2013 COMPARISON STUDY BETWEEN THE EFFICIENY OF THE START TECHNIQUES IN THE ROMANIAN COMPETITIVE
to understand the characteristics which are the result The present study is based on a cross-section sample of
 Brit J. Sports Med. - Vol. 14, Nos 2 & 3, August 1980, pp. 139-144 KINANTHROPOMETRY AND PERFORMANCE OF TOP RANKING INDIAN BASKETBALL PLAYERS H. S. SODHI, PhD Sports Medicine Research Laboratory, Netaii
Brit J. Sports Med. - Vol. 14, Nos 2 & 3, August 1980, pp. 139-144 KINANTHROPOMETRY AND PERFORMANCE OF TOP RANKING INDIAN BASKETBALL PLAYERS H. S. SODHI, PhD Sports Medicine Research Laboratory, Netaii
A CROSS-SECTIONAL ANALYSIS OF SKILL RELATED PHYSICAL FITNESS COMPONENTS OF KAYAKING AND ROWING PLAYERS
 European Journal of Physical Education and Sport Science ISSN: 2501-1235 ISSN-L: 2501-1235 Available on-line at: www.oapub.org/edu doi: 10.5281/zenodo.1050701 Volume 3 Issue 10 2017 A CROSS-SECTIONAL ANALYSIS
European Journal of Physical Education and Sport Science ISSN: 2501-1235 ISSN-L: 2501-1235 Available on-line at: www.oapub.org/edu doi: 10.5281/zenodo.1050701 Volume 3 Issue 10 2017 A CROSS-SECTIONAL ANALYSIS
International Journal for Life Sciences and Educational Research. School of Physical Education, Karpagam University, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu, India
 International Journal for Life Sciences and Educational Research Vol. 2 (1), pp. 20-24 January - 2014 Available online at http://www.ijlser.com E-ISSN : 2321-1229; P ISSN : 2321-1180 Research Article Effect
International Journal for Life Sciences and Educational Research Vol. 2 (1), pp. 20-24 January - 2014 Available online at http://www.ijlser.com E-ISSN : 2321-1229; P ISSN : 2321-1180 Research Article Effect
Journal of Human Sport and Exercise E-ISSN: Universidad de Alicante España
 Journal of Human Sport and Exercise E-ISSN: 1988-5202 jhse@ua.es Universidad de Alicante España MARINHO, DANIEL A.; AMORIM, RUI A.; COSTA, ALDO M.; MARQUES, MÁRIO C.; PÉREZ- TURPIN, JOSÉ A.; NEIVA, HENRIQUE
Journal of Human Sport and Exercise E-ISSN: 1988-5202 jhse@ua.es Universidad de Alicante España MARINHO, DANIEL A.; AMORIM, RUI A.; COSTA, ALDO M.; MARQUES, MÁRIO C.; PÉREZ- TURPIN, JOSÉ A.; NEIVA, HENRIQUE
Changes in a Top-Level Soccer Referee s Training, Match Activities, and Physiology Over an 8-Year Period: A Case Study
 Case Study International Journal of Sports Physiology and Performance, 2011, 6, 281-286 2011 Human Kinetics, Inc. Changes in a Top-Level Soccer Referee s Training, Match Activities, and Physiology Over
Case Study International Journal of Sports Physiology and Performance, 2011, 6, 281-286 2011 Human Kinetics, Inc. Changes in a Top-Level Soccer Referee s Training, Match Activities, and Physiology Over
REVIEW OF LITERATURE
 Chapter -2 exä xã Éy _ àxütàâüx REVIEW OF LITERATURE The research scholar has made sincere effort to locate and collect the literature relevant to this study. The related literatures collected from different
Chapter -2 exä xã Éy _ àxütàâüx REVIEW OF LITERATURE The research scholar has made sincere effort to locate and collect the literature relevant to this study. The related literatures collected from different
Comparison of Active Drag Using the MRT-Method and the MAD-System in Front Crawl Swimming
 Proceedings Comparison of Active Drag Using the MRT-Method and the MAD-System in Front Crawl Swimming Kenzo Narita 1, *, Futoshi Ogita 2, Motomu Nakashima 3 and Hideki Takagi 4 1 Doctoral Program in Physical
Proceedings Comparison of Active Drag Using the MRT-Method and the MAD-System in Front Crawl Swimming Kenzo Narita 1, *, Futoshi Ogita 2, Motomu Nakashima 3 and Hideki Takagi 4 1 Doctoral Program in Physical
University of Canberra. This thesis is available in print format from the University of Canberra Library.
 University of Canberra This thesis is available in print format from the University of Canberra Library. If you are the author of this thesis and wish to have the whole thesis loaded here, please contact
University of Canberra This thesis is available in print format from the University of Canberra Library. If you are the author of this thesis and wish to have the whole thesis loaded here, please contact
Stride Frequency, Body Fat Percentage, and the Amount of Knee Flexion Affect the Race Time of Male Cross Country Runners
 Stride Frequency, Body Fat Percentage, and the Amount of Knee Flexion Affect the Race Time of Male Cross Country Runners Vineel Mallavarapu 1 and Kevin Finn 2 1 Cedar Falls High School, Cedar Falls, IA
Stride Frequency, Body Fat Percentage, and the Amount of Knee Flexion Affect the Race Time of Male Cross Country Runners Vineel Mallavarapu 1 and Kevin Finn 2 1 Cedar Falls High School, Cedar Falls, IA
Incidence of anthropometric variables on the performance of top Optimist sailors
 Original Article Incidence of anthropometric variables on the performance of top Optimist sailors ANTONIO PALOMINO-MARTÍN 1, DIEGO QUINTANA-SANTANA 2, MIRIAM ESTHER QUIROGA- ESCUDERO 1, ADELINA GONZÁLEZ-MUÑOZ
Original Article Incidence of anthropometric variables on the performance of top Optimist sailors ANTONIO PALOMINO-MARTÍN 1, DIEGO QUINTANA-SANTANA 2, MIRIAM ESTHER QUIROGA- ESCUDERO 1, ADELINA GONZÁLEZ-MUÑOZ
Analysis of energy systems in Greco-Roman and freestyle wrestlers participated in 2015 and 2016 world championships
 Analysis of energy systems in Greco-Roman and freestyle wrestlers participated in 2015 and 2016 world championships Abstract. Aim: The aim of this study was analysis of energy systems in Greco- Roman (GR)
Analysis of energy systems in Greco-Roman and freestyle wrestlers participated in 2015 and 2016 world championships Abstract. Aim: The aim of this study was analysis of energy systems in Greco- Roman (GR)
subjects included in group A were members of other
 Brit. J. Sports Med. - Vol. 11, No. 3, September 1977, pp. 133-137 A STUDY OF TH PHYSICAL WORKING CAPACITY OF GALIC FOOTBALLRS AND HURLRS A.W. S. WATSON, B.Sc., M.Sc., Ph.D., F.R.A.M.I. Department of Physiology,
Brit. J. Sports Med. - Vol. 11, No. 3, September 1977, pp. 133-137 A STUDY OF TH PHYSICAL WORKING CAPACITY OF GALIC FOOTBALLRS AND HURLRS A.W. S. WATSON, B.Sc., M.Sc., Ph.D., F.R.A.M.I. Department of Physiology,
An Exploratory Study of Psychomotor Abilities among Cricket Players of Different Level of Achievement
 Research Journal of Physical Education Sciences ISSN 2320 9011 An Exploratory Study of Psychomotor Abilities among Cricket Players of Different Level of Achievement Abstract Baljinder Singh Bal and Ranjeet
Research Journal of Physical Education Sciences ISSN 2320 9011 An Exploratory Study of Psychomotor Abilities among Cricket Players of Different Level of Achievement Abstract Baljinder Singh Bal and Ranjeet
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF FEMALE BASKETBALL PLAYERS ACCORDING TO PLAYING POSITION
 Acta Facultatis Educationis Physicae Universitatis Comenianae Vol. 55 No 1 2015 PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF FEMALE BASKETBALL PLAYERS ACCORDING TO PLAYING POSITION Richard Kucsa, Peter Mačura Department
Acta Facultatis Educationis Physicae Universitatis Comenianae Vol. 55 No 1 2015 PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF FEMALE BASKETBALL PLAYERS ACCORDING TO PLAYING POSITION Richard Kucsa, Peter Mačura Department
A COMPARATIVE STUDY ON RESPIRATORY PARAMETERS BETWEEN SHORT DISTANCE AND LONG DISTANCE SWIMMERS
 A COMPARATIVE STUDY ON RESPIRATORY PARAMETERS BETWEEN SHORT DISTANCE AND LONG DISTANCE SWIMMERS Baghel Priya PhD scholar, LNIPE, Gwalior, M.P., India ABSTRACT The purpose of the study was to find out the
A COMPARATIVE STUDY ON RESPIRATORY PARAMETERS BETWEEN SHORT DISTANCE AND LONG DISTANCE SWIMMERS Baghel Priya PhD scholar, LNIPE, Gwalior, M.P., India ABSTRACT The purpose of the study was to find out the
Chapter I examines the anthropometric and physiological factors that. determine success in sport. More specifically it discusses the somatotype
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Chapter I examines the anthropometric and physiological factors that determine success in sport. More specifically it discusses the somatotype ratings, VO 2 max and running economy
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Chapter I examines the anthropometric and physiological factors that determine success in sport. More specifically it discusses the somatotype ratings, VO 2 max and running economy
The Effect of a Seven Week Exercise Program on Golf Swing Performance and Musculoskeletal Screening Scores
 The Effect of a Seven Week Exercise Program on Golf Swing Performance and Musculoskeletal Screening Scores 2017 Mico Hannes Olivier Bachelor of Sport Science Faculty of Health Sciences and Medicine Bond
The Effect of a Seven Week Exercise Program on Golf Swing Performance and Musculoskeletal Screening Scores 2017 Mico Hannes Olivier Bachelor of Sport Science Faculty of Health Sciences and Medicine Bond
ALTITUDE TRAINING FOR IMPROVING SWIMMING PERFORMANCE AT SEA LEVEL. MITSUMASA MIYASHITA, YOSHITERU MUTOH and YOSHIHARU YAMAMOTO.
 ALTITUDE TRAINING FOR IMPROVING SWIMMING PERFORMANCE AT SEA LEVEL MITSUMASA MIYASHITA, YOSHITERU MUTOH and YOSHIHARU YAMAMOTO Abstract The present study was designed to investigate the effects of low altitude
ALTITUDE TRAINING FOR IMPROVING SWIMMING PERFORMANCE AT SEA LEVEL MITSUMASA MIYASHITA, YOSHITERU MUTOH and YOSHIHARU YAMAMOTO Abstract The present study was designed to investigate the effects of low altitude
Analysis of Body Mass Components in Young Basketball Players
 Analysis of Body Mass Components in Young Basketball Players Lj. Efremovska 1, S. Nikolic 1, V. Maleska-Ivanovska 1, J. Pluncevic-Gligorovska 1, L. Todorovska 1, I. Karagjozova 1, E. Ivanovska 2 1 Department
Analysis of Body Mass Components in Young Basketball Players Lj. Efremovska 1, S. Nikolic 1, V. Maleska-Ivanovska 1, J. Pluncevic-Gligorovska 1, L. Todorovska 1, I. Karagjozova 1, E. Ivanovska 2 1 Department
A Comparative Analysis of Motor Fitness Components among Sprinters, Throwers and Jumpers
 Research Journal of Physical Education Sciences ISSN 2320 9011 A Comparative Analysis of Motor Fitness Components among, and Abstract Manjit Singh 1*, Sukhbir Singh 2 and Baljinder Singh Bal 3 1 Department
Research Journal of Physical Education Sciences ISSN 2320 9011 A Comparative Analysis of Motor Fitness Components among, and Abstract Manjit Singh 1*, Sukhbir Singh 2 and Baljinder Singh Bal 3 1 Department
Is Body Fat a Predictor of Race Time in Female Long-Distance Inline Skaters?
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is Body Fat a Predictor of Race Time in Female Long-Distance Inline Skaters? Beat Knechtle* 1,2, MD; Patrizia Knechtle 1 ; Thomas Rosemann 2, MD, PhD; Romuald Lepers 3, PhD Authors Affiliation:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is Body Fat a Predictor of Race Time in Female Long-Distance Inline Skaters? Beat Knechtle* 1,2, MD; Patrizia Knechtle 1 ; Thomas Rosemann 2, MD, PhD; Romuald Lepers 3, PhD Authors Affiliation:
Key words: biomechanics, injury, technique, measurement, strength, evaluation
 Becker, T., & Havriluk, R. (2006). Bilateral and anterior-posterior muscular imbalances in swimmers. In J. P. Vilas-Boas, F. Alves, A. Marques (Eds.), Biomechanics and Medicine in Swimming X. Portuguese
Becker, T., & Havriluk, R. (2006). Bilateral and anterior-posterior muscular imbalances in swimmers. In J. P. Vilas-Boas, F. Alves, A. Marques (Eds.), Biomechanics and Medicine in Swimming X. Portuguese
An Investigation on the Anthropometric Profile and Its Relationship with Physical Performance of Adolescent Indian Swimmers A Comparative Study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 3 Ver. I (March. 2017), PP 118-126 www.iosrjournals.org An Investigation on the Anthropometric
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 3 Ver. I (March. 2017), PP 118-126 www.iosrjournals.org An Investigation on the Anthropometric
The Influence of Load Carrying Modes on Gait variables of Healthy Indian Women
 The Influence of Load Carrying Modes on Gait variables of Healthy Indian Women *Guha Thakurta A, Iqbal R and De A National Institute of Industrial Engineering, Powai, Vihar Lake, Mumbai-400087, India,
The Influence of Load Carrying Modes on Gait variables of Healthy Indian Women *Guha Thakurta A, Iqbal R and De A National Institute of Industrial Engineering, Powai, Vihar Lake, Mumbai-400087, India,
Effects of interval sprint trainings on lactate level and heart rate in elite swimmers
 Volume: 14 Issue: 2 Year: 2017 Effects of interval sprint trainings on lactate level and heart rate in elite swimmers Bülent Turna 1 Selma Civar Yavuz 2 Mahmut Alp 3 Kenan Işıldak 4 Abstract The aim of
Volume: 14 Issue: 2 Year: 2017 Effects of interval sprint trainings on lactate level and heart rate in elite swimmers Bülent Turna 1 Selma Civar Yavuz 2 Mahmut Alp 3 Kenan Işıldak 4 Abstract The aim of
Journal of Quantitative Analysis in Sports
 Journal of Quantitative Analysis in Sports Volume 6, Issue 1 21 Article 5 Age and Winning Professional Golf Tournaments Gizachew Tiruneh University of Central Arkansas, gtiruneh@uca.edu Copyright c 21
Journal of Quantitative Analysis in Sports Volume 6, Issue 1 21 Article 5 Age and Winning Professional Golf Tournaments Gizachew Tiruneh University of Central Arkansas, gtiruneh@uca.edu Copyright c 21
RELATIONSHIP OF ANTHROPOMETRIC MEASUREMENT ON THE PERFORMANCE OF SWIMMERS AUTHOR
 RELATIONSHIP OF ANTHROPOMETRIC MEASUREMENT ON THE PERFORMANCE OF SWIMMERS AUTHOR Mr. MUKESH KUMAR TAKER Research Scholar Poornima University, Jaipur Mr. MOHAN LAL Research Scholar singhania university
RELATIONSHIP OF ANTHROPOMETRIC MEASUREMENT ON THE PERFORMANCE OF SWIMMERS AUTHOR Mr. MUKESH KUMAR TAKER Research Scholar Poornima University, Jaipur Mr. MOHAN LAL Research Scholar singhania university
Simulation analysis of the influence of breathing on the performance in breaststroke
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 34 (2012 ) 736 741 9 th Conference of the International Sports Engineering Association (ISEA) Simulation analysis of the influence of breathing
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 34 (2012 ) 736 741 9 th Conference of the International Sports Engineering Association (ISEA) Simulation analysis of the influence of breathing
The Effect of Tether Speed on Muscle Activation and Recruitment Patterns
 The Effect of Tether Speed on Muscle Activation and Recruitment Patterns Dr.Casey Lee Dr. Adrian Burden and Dr. Carl Payton Manchester Metropolitan University, UK May 1-4, 2013 INTRODUCTION Power can be
The Effect of Tether Speed on Muscle Activation and Recruitment Patterns Dr.Casey Lee Dr. Adrian Burden and Dr. Carl Payton Manchester Metropolitan University, UK May 1-4, 2013 INTRODUCTION Power can be
NO ASSOCIATION BETWEEN SKINFOLD THICKNESSES AND RACE PERFORMANCE IN MALE ULTRA-ENDURANCE CYCLISTS IN A 600 KM ULTRA-CYCLING MARATHON
 2009, vol. 10 (2), 91 95 NO ASSOCIATION BETWEEN SKINFOLD THICKNESSES AND RACE PERFORMANCE IN MALE ULTRA-ENDURANCE CYCLISTS IN A 600 KM ULTRA-CYCLING MARATHON DOI: 10.2478/v10038-009-0018-y Beat Knechtle
2009, vol. 10 (2), 91 95 NO ASSOCIATION BETWEEN SKINFOLD THICKNESSES AND RACE PERFORMANCE IN MALE ULTRA-ENDURANCE CYCLISTS IN A 600 KM ULTRA-CYCLING MARATHON DOI: 10.2478/v10038-009-0018-y Beat Knechtle
INTERACTION OF STEP LENGTH AND STEP RATE DURING SPRINT RUNNING
 INTERACTION OF STEP LENGTH AND STEP RATE DURING SPRINT RUNNING Joseph P. Hunter 1, Robert N. Marshall 1,, and Peter J. McNair 3 1 Department of Sport and Exercise Science, The University of Auckland, Auckland,
INTERACTION OF STEP LENGTH AND STEP RATE DURING SPRINT RUNNING Joseph P. Hunter 1, Robert N. Marshall 1,, and Peter J. McNair 3 1 Department of Sport and Exercise Science, The University of Auckland, Auckland,
Anthropometrical Measurement, Physiological and Biomotorical Testing in Identifying Young Talented Volleyball Athletes
 692 Anthropometrical Measurement, Physiological and Biomotorical Testing in Identifying Young Talented Volleyball Athletes * Dr. Kusnanik, NW Abstract The purpose of this research was to get equation model
692 Anthropometrical Measurement, Physiological and Biomotorical Testing in Identifying Young Talented Volleyball Athletes * Dr. Kusnanik, NW Abstract The purpose of this research was to get equation model
The relationship between different age swimmers flip turn temporal and kinematic characteristics
 604 ISSN 1392 1207. MECHANIKA. 2017 Volume 23(4): 604 609 The relationship between different age swimmers flip turn temporal and kinematic characteristics Valentina SKYRIENE*, Milda DUBOSIENE**, Mindaugas
604 ISSN 1392 1207. MECHANIKA. 2017 Volume 23(4): 604 609 The relationship between different age swimmers flip turn temporal and kinematic characteristics Valentina SKYRIENE*, Milda DUBOSIENE**, Mindaugas
Marathon performance in relation to body fat percentage and training indices in recreational male runners
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2013 Marathon performance in relation to body fat percentage and training indices
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2013 Marathon performance in relation to body fat percentage and training indices
University of Kassel Swim Start Research
 University of Kassel Swim Start Research Sebastian Fischer & Armin Kibele Institute for Sports and Sport Science, University of Kassel, Germany Research Fields: Swim Start research I. Materials and Equipment
University of Kassel Swim Start Research Sebastian Fischer & Armin Kibele Institute for Sports and Sport Science, University of Kassel, Germany Research Fields: Swim Start research I. Materials and Equipment
Gizachew Tiruneh, Ph. D., Department of Political Science, University of Central Arkansas, Conway, Arkansas
 Gizachew Tiruneh, Ph. D., Department of Political Science, University of Central Arkansas, Conway, Arkansas [A revised version of the paper is published by the Journal of Quantitative Analysis in Sports,
Gizachew Tiruneh, Ph. D., Department of Political Science, University of Central Arkansas, Conway, Arkansas [A revised version of the paper is published by the Journal of Quantitative Analysis in Sports,
Comparison of Selected Psychological and Anthropometric Characteristics between Successful and Unsuccessful Volleyball Players
 IOSR Journal of Sports and Physical Education (IOSR-JSPE) e-issn: 2347-6737, p-issn: 2347-6745, Volume 3, Issue 6 (Nov. Dec. 2016), PP 38-42 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison of Selected Psychological and
IOSR Journal of Sports and Physical Education (IOSR-JSPE) e-issn: 2347-6737, p-issn: 2347-6745, Volume 3, Issue 6 (Nov. Dec. 2016), PP 38-42 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison of Selected Psychological and
Analysis of Foot Pressure Variation with Change in Stride Length
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-853, p-issn: 2279-861.Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. IV (Oct. 214), PP 46-51 Dr. Charudatta V. Shinde, M.S. MCh ( Orthopaedics ), Dr. Weijie
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-853, p-issn: 2279-861.Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. IV (Oct. 214), PP 46-51 Dr. Charudatta V. Shinde, M.S. MCh ( Orthopaedics ), Dr. Weijie
RELATIONS BETWEEN KINEMATIC PARAMETERS OF SPRINTER S RUNNING AND SPECIFIC MOTOR ABILITIES
 22 Resaarch in Kinesiology 204, Vol. 4, No., pp. 22-28 RELATIONS BETWEEN KINEMATIC PARAMETERS OF SPRINTER S RUNNING AND SPECIFIC MOTOR ABILITIES Iva Blažević, Dario Novak 2 and Vilko Petrić 2 Juraj Dobrila
22 Resaarch in Kinesiology 204, Vol. 4, No., pp. 22-28 RELATIONS BETWEEN KINEMATIC PARAMETERS OF SPRINTER S RUNNING AND SPECIFIC MOTOR ABILITIES Iva Blažević, Dario Novak 2 and Vilko Petrić 2 Juraj Dobrila
Sex Differences in Growth and Performance of Track and Field Athletes Years
 Journal of Human Kinetics volume 24 2010, 79 85 Section III Sport, Physical Education & Recreation 79 Sex Differences in Growth and Performance of Track and Field Athletes 11 15 Years by Robert M. Malina
Journal of Human Kinetics volume 24 2010, 79 85 Section III Sport, Physical Education & Recreation 79 Sex Differences in Growth and Performance of Track and Field Athletes 11 15 Years by Robert M. Malina
Morphology and Hydrodynamic Resistance in Young Swimmers
 Pediatric Exercise Science, 2001, 13, 246-255 O 2001 Human Kinetics Publishers. Inc. Morphology and Hydrodynamic Resistance in Young Swimmers Nataphoom Benjanuvatra, Brian A. Blanksby, and Bruce C. Elliott
Pediatric Exercise Science, 2001, 13, 246-255 O 2001 Human Kinetics Publishers. Inc. Morphology and Hydrodynamic Resistance in Young Swimmers Nataphoom Benjanuvatra, Brian A. Blanksby, and Bruce C. Elliott
Steeplechase Hurdle Economy, Mechanics, and Performance
 Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Theses and Dissertations 2013-06-27 Steeplechase Hurdle Economy, Mechanics, and Performance Sarah Ingebretsen Brigham Young University - Provo Follow this
Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Theses and Dissertations 2013-06-27 Steeplechase Hurdle Economy, Mechanics, and Performance Sarah Ingebretsen Brigham Young University - Provo Follow this
Comparative study on morphological differences of Indian male jumpers, runners and throwers
 2015; 2(2): 92-96 P-ISSN: 2394-1685 E-ISSN: 2394-1693 Impact Factor (ISRA): 4.69 IJPESH 2015; 2(2): 92-96 2015 IJPESH www.kheljournal.com Received: 22-09-2015 Accepted: 24-10-2015 Assistant Professor Physical
2015; 2(2): 92-96 P-ISSN: 2394-1685 E-ISSN: 2394-1693 Impact Factor (ISRA): 4.69 IJPESH 2015; 2(2): 92-96 2015 IJPESH www.kheljournal.com Received: 22-09-2015 Accepted: 24-10-2015 Assistant Professor Physical
Anthropometric Profile and Special Judo Fitness levels of Indian Judo Players
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Anthropometric Profile and Special Judo Fitness levels of Indian Judo Players Jayasudha Katralli *, MD; Shivaprasad S. Goudar, MD, MHPE Authors Affiliation: Department of Physiology, J.N.M.C.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Anthropometric Profile and Special Judo Fitness levels of Indian Judo Players Jayasudha Katralli *, MD; Shivaprasad S. Goudar, MD, MHPE Authors Affiliation: Department of Physiology, J.N.M.C.
The Physical and Physiological Characteristics of 3x3. Results of Medical Study & Scientific Test
 The Physical and Physiological Characteristics of 3x3 Results of Medical Study & Scientific Test Prepared by Dr. Paul Montgomery & Brendan Maloney (Aspetar Orthopaedic Hospital) In cooperation with FIBA
The Physical and Physiological Characteristics of 3x3 Results of Medical Study & Scientific Test Prepared by Dr. Paul Montgomery & Brendan Maloney (Aspetar Orthopaedic Hospital) In cooperation with FIBA
RELATIONSHIP OF SELECTED KINEMATIC VARIABLES WITH THE PERFORMANCE OF DOUBLE HANDEDBACKHAND IN TENNIS. Rajesh Kumar, M.P.Ed,
 RELATIONSHIP OF SELECTED KINEMATIC VARIABLES WITH THE PERFORMANCE OF DOUBLE HANDEDBACKHAND IN TENNIS Rajesh Kumar, M.P.Ed, Department of Sports Biomechanics, LNIPE, Gwalior (M.P.), India Dr.Y.S.Rajpoot,
RELATIONSHIP OF SELECTED KINEMATIC VARIABLES WITH THE PERFORMANCE OF DOUBLE HANDEDBACKHAND IN TENNIS Rajesh Kumar, M.P.Ed, Department of Sports Biomechanics, LNIPE, Gwalior (M.P.), India Dr.Y.S.Rajpoot,
Competitive Performance of Elite Olympic-Distance Triathletes: Reliability and Smallest Worthwhile Enhancement
 SPORTSCIENCE sportsci.org Original Research / Performance Competitive Performance of Elite Olympic-Distance Triathletes: Reliability and Smallest Worthwhile Enhancement Carl D Paton, Will G Hopkins Sportscience
SPORTSCIENCE sportsci.org Original Research / Performance Competitive Performance of Elite Olympic-Distance Triathletes: Reliability and Smallest Worthwhile Enhancement Carl D Paton, Will G Hopkins Sportscience
ABSTRACT AUTHOR. Kinematic Analysis of the Women's 400m Hurdles. by Kenny Guex. he women's 400m hurdles is a relatively
 Study Kinematic Analysis of the Women's 400m Hurdles by IAAF 27:1/2; 41-51, 2012 by Kenny Guex ABSTRACT The women's 400m hurdles is a relatively new discipline and a complex event that cannot be approached
Study Kinematic Analysis of the Women's 400m Hurdles by IAAF 27:1/2; 41-51, 2012 by Kenny Guex ABSTRACT The women's 400m hurdles is a relatively new discipline and a complex event that cannot be approached
The relationship between front crawl swimming performance and hydrodynamic variables during leg kicking in age group swimmers
 Original paper The relationship between front crawl swimming performance and hydrodynamic variables during leg kicking in age group swimmers Daniel A. Marinho, Roberto C. Oliveira, Aldo M. Costa University
Original paper The relationship between front crawl swimming performance and hydrodynamic variables during leg kicking in age group swimmers Daniel A. Marinho, Roberto C. Oliveira, Aldo M. Costa University
Journal of Human Sport and Exercise E-ISSN: Universidad de Alicante España
 Journal of Human Sport and Exercise E-ISSN: 1988-5202 jhse@ua.es Universidad de Alicante España Vaso, Martin; Knechtle, Beat; Rüst, Christoph Alexander; Rosemann, Thomas; Lepers, Romuald Age of peak swim
Journal of Human Sport and Exercise E-ISSN: 1988-5202 jhse@ua.es Universidad de Alicante España Vaso, Martin; Knechtle, Beat; Rüst, Christoph Alexander; Rosemann, Thomas; Lepers, Romuald Age of peak swim
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 191 ( 2015 ) WCES 2014
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 191 ( 2015 ) 495 499 WCES 2014 Comparison of Anthropometric Characteristics Between Athletes and Non-athletes
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 191 ( 2015 ) 495 499 WCES 2014 Comparison of Anthropometric Characteristics Between Athletes and Non-athletes
APPROACH RUN VELOCITIES OF FEMALE POLE VAULTERS
 APPROACH RUN VELOCITIES OF FEMALE POLE VAULTERS Peter M. McGinnis, Physical Education Department, SUNY College at Cortland, Cortland, New York INTRODUCTION Running speed is an important determinant of
APPROACH RUN VELOCITIES OF FEMALE POLE VAULTERS Peter M. McGinnis, Physical Education Department, SUNY College at Cortland, Cortland, New York INTRODUCTION Running speed is an important determinant of
Journal of Human Sport and Exercise E-ISSN: Universidad de Alicante España
 Journal of Human Sport and Exercise E-ISSN: 1988-5202 jhse@ua.es Universidad de Alicante España KALINA, TOMAS; CACEK, JAN; KMETOVA, LINDA The running economy difference between running barefoot and running
Journal of Human Sport and Exercise E-ISSN: 1988-5202 jhse@ua.es Universidad de Alicante España KALINA, TOMAS; CACEK, JAN; KMETOVA, LINDA The running economy difference between running barefoot and running
FITNESSGRAM Scorecard (for Males , and Adults 18+) Females see last pages
 FITNESSGRAM Scorecard (for Males 14-17+, and Adults 18+) Females see last pages Name: Date: Age: Weight Health Weight: Height: lbs inches Inches 2 : BMI: = (lbs x 703) / inches 2 Skinfold Measures See:
FITNESSGRAM Scorecard (for Males 14-17+, and Adults 18+) Females see last pages Name: Date: Age: Weight Health Weight: Height: lbs inches Inches 2 : BMI: = (lbs x 703) / inches 2 Skinfold Measures See:
RELATION BETWEEN MAXIMAL ANAEROBIC POWER OUTPUT AND TESTS ON ROWING ERGOMETER
 Acta Facultatis Educationis Physicae Universitatis Comenianae Vol. 57 No 1 2017 RELATION BETWEEN MAXIMAL ANAEROBIC POWER OUTPUT AND TESTS ON ROWING ERGOMETER Matej Šmída, Michal Clementis, Dušan Hamar,
Acta Facultatis Educationis Physicae Universitatis Comenianae Vol. 57 No 1 2017 RELATION BETWEEN MAXIMAL ANAEROBIC POWER OUTPUT AND TESTS ON ROWING ERGOMETER Matej Šmída, Michal Clementis, Dušan Hamar,
Anthropometric characteristics and body composition of Italian national wrestlers
 This article was downloaded by: [Luciana Zaccagni] On: 20 July 2011, At: 22:42 Publisher: Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954 Registered office: Mortimer
This article was downloaded by: [Luciana Zaccagni] On: 20 July 2011, At: 22:42 Publisher: Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954 Registered office: Mortimer
Research nurses trained in the method are responsible for recording all anthropometric measurements from all subjects.
 Anthropometric measures No: 007D 1. Introduction Anthropometric measurements are widely used to predict body density or fat content. A variety of different procedures can be done. For this project waist/hip
Anthropometric measures No: 007D 1. Introduction Anthropometric measurements are widely used to predict body density or fat content. A variety of different procedures can be done. For this project waist/hip
Relationship between Judo Skills Acquisition Ability and Body Composition of Individuals at Different Growth and Development Stages
 Kamla-Raj 2012 Anthropologist, 14(3): 261-267 (2012) Relationship between Judo Skills Acquisition Ability and Body Composition of Individuals at Different Growth and Development Stages O. E. Nabofa Exercise
Kamla-Raj 2012 Anthropologist, 14(3): 261-267 (2012) Relationship between Judo Skills Acquisition Ability and Body Composition of Individuals at Different Growth and Development Stages O. E. Nabofa Exercise
Anaerobic and aerobic contributions to 800 m and 8 km season bests
 Short Communication Anaerobic and aerobic contributions to 8 m and 8 km season bests Julia C. Blumkaitis, Christopher L. Sandefur, Christopher A. Fahs, Lindy M. Rossow Objective: Both anaerobic and aerobic
Short Communication Anaerobic and aerobic contributions to 8 m and 8 km season bests Julia C. Blumkaitis, Christopher L. Sandefur, Christopher A. Fahs, Lindy M. Rossow Objective: Both anaerobic and aerobic
A Case Study of Leadership in Women s Intercollegiate Softball. By: DIANE L. GILL and JEAN L. PERRY
 A Case Study of Leadership in Women s Intercollegiate Softball By: DIANE L. GILL and JEAN L. PERRY Gill, D.L. & Perry, J.L. (1979). A case study of leadership in women's intercollegiate softball. International
A Case Study of Leadership in Women s Intercollegiate Softball By: DIANE L. GILL and JEAN L. PERRY Gill, D.L. & Perry, J.L. (1979). A case study of leadership in women's intercollegiate softball. International
REVIEW OF LITERATURE
 REVIEW OF LITERATURE The researcher of this study has done extensive review to find out the related literature in various libraries as well as he has gone through various websites. The relevant studies
REVIEW OF LITERATURE The researcher of this study has done extensive review to find out the related literature in various libraries as well as he has gone through various websites. The relevant studies
PLEASE SCROLL DOWN FOR ARTICLE
 This article was downloaded by: [Canadian Research Knowledge Network] On: 9 February 2009 Access details: Access Details: [subscription number 789349985] Publisher Routledge Informa Ltd Registered in England
This article was downloaded by: [Canadian Research Knowledge Network] On: 9 February 2009 Access details: Access Details: [subscription number 789349985] Publisher Routledge Informa Ltd Registered in England
Comparative characteristics of elite New Zealand and South African u/16 rugby players with reference to gamespecific
 original research ARTICLE Comparative characteristics of elite New Zealand and South African u/16 rugby players with reference to gamespecific skills, physical abilities and anthropometric data Emanuel
original research ARTICLE Comparative characteristics of elite New Zealand and South African u/16 rugby players with reference to gamespecific skills, physical abilities and anthropometric data Emanuel
Montana Hayes. Height: 72 inches (6 0 ) or 1.83 meters Weight: lbs or 70.4 kg BMI: Sum of Three Site Skinfold Calculations
 Montana Hayes Montana is a women s track and field athlete at Concordia University, Nebraska. She competes in the multievents (indoor pentathlon and outdoor heptathlon). In training for these events, Montana
Montana Hayes Montana is a women s track and field athlete at Concordia University, Nebraska. She competes in the multievents (indoor pentathlon and outdoor heptathlon). In training for these events, Montana
The Mechanics of Modern BREASTSTROKE Swimming Dr Ralph Richards
 The Mechanics of Modern BREASTSTROKE Swimming Dr Ralph Richards Breaststroke is the least efficient of the four competition strokes because a large amount of water resistance is created due to body position
The Mechanics of Modern BREASTSTROKE Swimming Dr Ralph Richards Breaststroke is the least efficient of the four competition strokes because a large amount of water resistance is created due to body position
Resistance to Fatigue and Success in Competitive Swimming. Steven C. Myers, Los Alamos High School Jake A. Bailey, University of Northern Colorado
 Resistance to Fatigue and Success in Competitive Swimming Steven C. Myers, Los Alamos High School Jake A. Bailey, University of Northern Colorado Introduction Developing and training successful competitive
Resistance to Fatigue and Success in Competitive Swimming Steven C. Myers, Los Alamos High School Jake A. Bailey, University of Northern Colorado Introduction Developing and training successful competitive
Review Supplement Info Waist-to hip Ratio, Gurth Measurements & Skin Fold
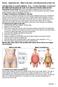 THIS MATERIAL IS A SUPPLEMENTAL TOOL. IT IS NOT INTENDED TO REPLACE INFORMATION PROVIDED IN YOUR TEXT AND/OR STUDENT HAND-BOOKS. Assessing Percent Body Fat: While hydrostatic weighing and the Bod Pod are
THIS MATERIAL IS A SUPPLEMENTAL TOOL. IT IS NOT INTENDED TO REPLACE INFORMATION PROVIDED IN YOUR TEXT AND/OR STUDENT HAND-BOOKS. Assessing Percent Body Fat: While hydrostatic weighing and the Bod Pod are
The Examination of Upper Limb Ambidexterity in Wrestling Snap Down Technique
 Bridgewater State University Virtual Commons - Bridgewater State University Movement Arts, Health Promotion and Leisure Studies Faculty Publications Movement Arts, Health Promotion and Leisure Studies
Bridgewater State University Virtual Commons - Bridgewater State University Movement Arts, Health Promotion and Leisure Studies Faculty Publications Movement Arts, Health Promotion and Leisure Studies
CRUCIAL SWIMMING VELOCITY PARAMETERS IN 2000 M FRONT CRAWL PERFORMANCE
 2007, vol. 8 (1), 15 20 CRUCIAL SWIMMING VELOCITY PARAMETERS IN 2000 M FRONT CRAWL PERFORMANCE Marek Strzała 1 *, Aleksander Tyka 2, Piotr Krężałek 3 1 Department of Theory and Methodology of Water Sports,
2007, vol. 8 (1), 15 20 CRUCIAL SWIMMING VELOCITY PARAMETERS IN 2000 M FRONT CRAWL PERFORMANCE Marek Strzała 1 *, Aleksander Tyka 2, Piotr Krężałek 3 1 Department of Theory and Methodology of Water Sports,
Changes in Anthropometric and Physiological Characteristics of Male Collegiate Rugby Union Players Throughout a Season
 Illinois State University ISU ReD: Research and edata Theses and Dissertations 3-5-2017 Changes in Anthropometric and Physiological Characteristics of Male Collegiate Rugby Union Players Throughout a Season
Illinois State University ISU ReD: Research and edata Theses and Dissertations 3-5-2017 Changes in Anthropometric and Physiological Characteristics of Male Collegiate Rugby Union Players Throughout a Season
A Group of Factors Influencing the Development of the Greeks Volleyball Athletes at School Age
 Journal of Sports Science 5 (27) 2-37 doi:.725/2332-783/27..3 D DAVID PUBLISHING A Group of Factors Influencing the Development of the Greeks Volleyball Athletes at School Age Achilleopoulos John, Lamprousi
Journal of Sports Science 5 (27) 2-37 doi:.725/2332-783/27..3 D DAVID PUBLISHING A Group of Factors Influencing the Development of the Greeks Volleyball Athletes at School Age Achilleopoulos John, Lamprousi
SIMULTANEOUS RECORDINGS OF VELOCITY AND VIDEO DURING SWIMMING
 Portuguese Journal of Sport Sciences. 6:supl. 2, 32-35, 2006 SIMULTANEOUS RECORDINGS OF VELOCITY AND VIDEO DURING SWIMMING Albert B. Craig 1, Budd Termin2, and David R. Pendergast 2 1University of Rochester,
Portuguese Journal of Sport Sciences. 6:supl. 2, 32-35, 2006 SIMULTANEOUS RECORDINGS OF VELOCITY AND VIDEO DURING SWIMMING Albert B. Craig 1, Budd Termin2, and David R. Pendergast 2 1University of Rochester,
Changes in speed and efficiency in the front crawl swimming technique at 100m track
 Proceeding 10th INSHS International Christmas Sport Scientific Conference, 4-5 December 2015. International Network of Sport and Health Science. Szombathely, Hungary Changes in speed and efficiency in
Proceeding 10th INSHS International Christmas Sport Scientific Conference, 4-5 December 2015. International Network of Sport and Health Science. Szombathely, Hungary Changes in speed and efficiency in
PHYSICAL FITNESS FOR LAWN BOWLING. by Rob Judson September 2002
 PHYSICAL FITNESS FOR LAWN BOWLING by Rob Judson September 2002 Page 2 General Fitness and Health Lawn bowls imposes lower physical demands than many other sports impose on players. The general physiological
PHYSICAL FITNESS FOR LAWN BOWLING by Rob Judson September 2002 Page 2 General Fitness and Health Lawn bowls imposes lower physical demands than many other sports impose on players. The general physiological
Journal of Human Sport and Exercise E-ISSN: Universidad de Alicante España
 Journal of Human Sport and Exercise E-ISSN: 1988-5202 jhse@ua.es Universidad de Alicante España KUNITSON, VLADIMIR; PORT, KRISTJAN; PEDAK, KIRSTI Relationship between isokinetic muscle strength and 100
Journal of Human Sport and Exercise E-ISSN: 1988-5202 jhse@ua.es Universidad de Alicante España KUNITSON, VLADIMIR; PORT, KRISTJAN; PEDAK, KIRSTI Relationship between isokinetic muscle strength and 100
Gender Differences in Competition: Evidence from Swimming Data Shoko Yamane 1 Ryohei Hayashi 2
 Gender Differences in Competition: Evidence from Swimming Data Shoko Yamane 1 Ryohei Hayashi 2 Abstract We examine that the gender differences in the sensitivity of the influence from others using swimming
Gender Differences in Competition: Evidence from Swimming Data Shoko Yamane 1 Ryohei Hayashi 2 Abstract We examine that the gender differences in the sensitivity of the influence from others using swimming
TECHNOLOGY FOR DECREASING ACTIVE DRAG AT THE MAXIMAL SWIMMING VELOCITY
 TECHNOLOGY FOR DECREASING ACTIVE DRAG AT THE MAXIMAL SWIMMING VELOCITY Sergei Kolmogorov, Sergei Lyapin, Olga Rumyantseva and J. Paulo Vilas-Boas 1 Centroconcept, Pomor University, Arkhangelsk, Russia
TECHNOLOGY FOR DECREASING ACTIVE DRAG AT THE MAXIMAL SWIMMING VELOCITY Sergei Kolmogorov, Sergei Lyapin, Olga Rumyantseva and J. Paulo Vilas-Boas 1 Centroconcept, Pomor University, Arkhangelsk, Russia
Running Head: ANTHROPOMETRY, JUMP POWER, AND POSITION
 Anthropometry, jump power, and position 1 Running Head: ANTHROPOMETRY, JUMP POWER, AND POSITION CORRELATIONS AMONG ANTHROPOMETRIC PARAMETERS, JUMP POWER, AND POSITION IN PROFESSIONAL BASKETBALL PLAYERS
Anthropometry, jump power, and position 1 Running Head: ANTHROPOMETRY, JUMP POWER, AND POSITION CORRELATIONS AMONG ANTHROPOMETRIC PARAMETERS, JUMP POWER, AND POSITION IN PROFESSIONAL BASKETBALL PLAYERS
Leg skinfold thicknesses and race performance in male 24-hour ultra-marathoners
 Leg skinfold thicknesses and race performance in male 24-hour ultra-marathoners Beat Knechtle, MD, Patrizia Knechtle, Christoph Alexander Rüst, and Thomas Rosemann, MD, PhD The association of skinfold
Leg skinfold thicknesses and race performance in male 24-hour ultra-marathoners Beat Knechtle, MD, Patrizia Knechtle, Christoph Alexander Rüst, and Thomas Rosemann, MD, PhD The association of skinfold
