Relationship of physical characteristics, power and swimming time in sprint swimmers
|
|
|
- Jocelin Sharp
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Available online at Annals of Biological Research, 2014, 5 (8):24-29 ( ISSN CODEN (USA): ABRNBW Relationship of physical characteristics, power and swimming time in sprint swimmers Michelle Sheena Peters *, Sadhan Berry ** and Shyamal Koley *** *Indian Spinal Injuries Centre, Institute of Rehabilitation Sciences, Vasant Kunj, New Delhi, **Indian Spinal Injuries Centre, Institute of Rehabilitation Sciences, Vasant Kunj, New Delhi, ***Department of Sports Medicine and Physiotherapy, Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar, Punjab, India ABSTRACT Short distance sprint swimming is a sport which requires production of high intensity force in a relatively short period of time. Thus it depends on the power developed by both the upper and lower limbs, especially in short distance events. On the other hand, swimming performance is a multifactorial phenomenon involving energetics, biomechanics, hydrodynamics, strength parameters and anthropometrics. There are four different style of swimming which have different requirements as per the technique in terms of power and the anthropometric characteristics. The present study evaluated the relationship of physical characteristics, power and swimming time in sprint swimmers. A total of 118 competitive sprint swimmers boys (n=64), girls (n=54) aged 9-17 years, with at least 1 year of swimming experience were chosen. They underwent anthropometric testing followed by power testing of the upper and lower extremities and finally the recording of the 50m sprint swimming time in their respective strokes. In results, statistically significant positive correlations (p<0.001) were found between the physical characteristic variables with the upper and lower extremity power and significant negative correlations (p<0.001) with swimming time. Also statistically significant negative correlations (p<0.001) were found between the swimming time with the upper and lower extremity power. It may be concluded that the physical characteristics were positively correlated with the muscular power and negatively correlated with the swimming time. Also the swimming time was negatively correlated with the muscular power. Keywords: Physical characteristics. Anthropometric variables. Power. Swimmers. INTRODUCTION Power and strength sports require the ability to generate high amount of force in relatively short period of time [12]. The ability of high rate of force development is the central to success in activities that rely on jumping, change of direction, and/or sprinting performance [12]. And swimming is a sport which involves all of these activities. Swimming depends on the power developed by both the upper and the lower limbs, especially in short distance events [6]. Swimming races include elements of a start, turn and clean swimming distance [4]. A study reported that the starting time helped explain 23% of the performance in the male competitors and as much as 40% in female competitors [28]. The time during the start covers almost 25% of the total time needed to swim 25 m and 10% of that needed at the 50 m matches and about 5% in 100m matches [7,19]. Secondly, the performance can also be determined by the turn time resulting in change of direction in the shortest time possible [25]. Turns provide increased propulsion [30]. Thirdly, as the propulsive force generated by the swimmer is, in dynamic equilibrium 24
2 conditions, the resistance of the water increases geometrically in proportion to the square of velocity. Therefore, a greater ability to generate propulsive force seems to contribute effectively to a better displacement in water [22]. The role of upper limb muscle power is even more essential as 85-90% of the propulsive power comes from the arms and swimming athletes primarily use their arms to generate forward thrust [2,26]. Indeed, one of the studies found only a small contribution of the legs to propulsion (approximately 10%) while another reported only about 15% at Front Crawl [2]. Swimming performance is a multifactorial phenomenon [20]. Swimmers physical characteristics have been examined to determine the characteristics of successful sprint swimmers [27]. Chronological age of top class athletes indicates the time at which peak performance might be expected and it is lower in case of swimming [17]. It seems that anthropometric characteristics are highly related with young swimmers performance. For instance, positive correlations between hand and foot size with swimming performance exists [16]. Studies have been conducted to establish the relationship between the muscular power and the swimming time. But, as far our knowledge, there is no literature available which gives a relationship between the physical characteristics and muscle power also taking into consideration the swimming performance, especially in Indian population. For this purpose, this present study aims to find out the relationship between the physical characteristics, power and swimming time in sprint swimmers. MATERIALS AND METHODS Subjects A total of 118 competitive sprint swimmers (64 boys and 54 girls) of 50m and 100m from all four style of swimming i.e. freestyle (n=39), breastroke (n=28), butterfly (n=23) and backstroke (n=28); aged 9-17 years (mean age ±S.D ± 2.55 years) with at least 1 year of competitive swimming experience participated in the study. Out of these, 67 were state level swimmers, 40 were national level swimmers, 3 were international level swimmers and 8 were school level swimmers. Long distance swimmers or swimmers with any knee, back or shoulder injury of past 6 months were excluded. All the participants and their parents or coaches gave their consent for participation in the study. The study was approved by the institutional ethical committee. Procedure Anthropometric Testing The subjects were randomly selected and tested for the anthropometric variables. The age was recorded as the chronological age in years. Standing height was recorded by the anthropometric rod to the nearest 0.2m. Weight was recorded by the standard weighing scale to the nearest 0.5kg. Skinfold measurement was done by the Harpenden skinfold calliper to the nearest 0.2mm. The girths and the diameters were recorded by the flexible measuring tape on the dominant side of the body in centimetres. Chest girth was recorded at the end of normal tidal expiration at the nipple level in males and just below the breasts for females. The lengths were recorded by the anthropometric rod or the small sliding calliper in centimetres. Biacromial and biiliac breadth were recorded by the anthropometric rod in centimetres [27]. Lower Extremity Power Testing The power of the lower extremity was tested with the countermovement jump test. After the sub maximal trials, the standing reach height was measured to the nearest centimetre. To perform the countermovement jump, the subjects performed the countermovement then extended and jumped as high as possible touching the wall with the hand nearest to the wall. The vertical jump height was recorded in meters and entered into Lewis formula to calculate the power [24]. Upper Extremity Power Testing The power of the upper extremity was tested with the closed kinetic chain upper extremity stability test. Two pieces of athletic tape (1.5 in width) were placed on the ground parallel to each other 36 in apart for subjects 12 years or older and 24 inches for younger than 12 years. The subject in the push-up position touched the lines by crossing and touching the opposite line. Three trials of 15 seconds were recorded by a standard stopwatch followed by 45 seconds of rest. A power score was then developed [11]. Swimming Time The subjects performed their usual swimming warm-up routine in the pool before giving the trial. The subjects were then asked to perform a 50m sprint in the pool and the sprint time was recorded by stop-watches manually by two recorders [10]. 25
3 Statistical Analysis IBM SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences) software version 19 was used for statistical analysis. Pearson product-moment correlations were used to examine the correlations between physical characteristics variables, power values and swimming time of all the subjects. A criterion alpha level of p 0.05 was used to determine the statistical significance. RESULTS Table 1. Correlation coefficients of physical characteristics with upper extremity power, lower extremity power and swimming time ST Variables r p r p r p Age (yr) HT (cm) WT (kg) BSK (mm) TSK (mm) SSSK (mm) SUSK (mm) ABSK (mm) AARG (cm) AAFG (cm) FAG (cm) CG (cm) GLG (cm) THG (cm) CFG (cm) HED (cm) FED (cm) FAL (cm) HNDL (cm) TUEL (cm) SHNL (cm) FTL (cm) TLEL (cm) BACB (cm) BILB (cm) HT= Height, WT= Weight, BSK= Biceps skinfold, TSK= Triceps Skinfold, SSSK= Subscapular skinfold, SUSK= Suprailiac Skinfold, ABSK= Abdominal Skinfold, AARG= Arm relaxed girth, AAFG= Arm flexed girth, FAG= Forearm girth, CG= Chest girth, GLG= Gluteal girth, THG= Thigh girth, CFG= Calf girth, HED=Humerus biepicondylar diameter, FED= Femur biepicondylar diameter, FAL= Forearm length, HNDL= Hand length, TUEL= Total upper extremity length, SHNL= Shank length, FTL= Foot length, TLEL= Total lower extremity length, BACB= Biacromial breadth, BILB= Biiliac breadth. Figure 1. Relationship of total upper extremity length with upper extremity power TUEL 80 Linear (TUEL) Linear () TUEL Correlation coefficients of physical characteristics with upper extremity power, lower extremity power and swimming time were shown in Table 1. Highly significant positive correlations (p<0.01) were found between all the physical characteristics with the upper extremity power (except, triceps skinfold) and with the lower extremity power (p< ) (except, triceps skinfold). Statistically significant negative correlations (p< ) were also observed between all the physical characteristics with swimming time (except biceps, triceps and 26
4 abdominal skinfolds). The relationship of total upper extremity length with upper extremity power was shown in Fig.1. Table 2 showed the correlation coefficients of swimming time with upper and lower extremity power. Statistically significant negative correlations (p<0.001) were noted between the swimming time and upper as well as lower extremity power. The relationship of lower extremity power with swimming time was given in Fig.2. Table 2. Correlation coefficients of swimming time with upper extremity power and lower extremity power = r p r p ST Upper extremity power, = Lower extremity power, ST= Swimming time Figure 2. Relationship of lower extremity power with swimming time ST ST Linear () Linear (ST) DISCUSSION Mechanical power is often referred to as the rate of doing work and is calculated by multiplying force by velocity or the amount of work a muscle can produce per unit of time [12]. The present study correlated the physical characteristics variables with the muscular power and the swimming time thus showing positive correlation of physical characteristics with the upper and lower extremity power (p<0.001) except the triceps skinfold. Therefore, the age also correlated positively with the muscular power (p<0.001). The swimmers in our study were young (9-17 years) and it was seen that swimmers of age group years had higher power values on the power testing as compared to the swimmers of age group 9-12 years. Young age and training load led to higher muscular power production in swimmers of the present study. Similar results were seen in the previous studies which found that swimmers had been achieving peak performances in a very younger age [29]. In another study, anaerobic power production was found to be greater in trained pubescent athletes as compared to non-athletes of the same age [15]. These factors supported the positive correlations of age with the muscle power in our study. The results of the present study showed that girths, diameters, breadths, height, weight and lengths were positively correlated with muscle power (p<0.01). Swimmers of the present study performed high intensity short distance swimming sprints; therefore an increase in the value of girths, diameters or breadths resulted in increased power values. Also both male and female swimmers were tall and heavy with long limbs. Taller swimmers performed better on the power testing as compared to shorter swimmers in the present study. Studies had proven that a large cross sectional area of the muscle was presented with increased muscle strength generating characteristics. And, due to skeletal and hormonal maturity during childhood and adolescence, increase in the muscle performance resulted due to muscle related changes in the muscle enzyme activity, an increased proportion of type II fibres etc [18]. According to the same study, pubertal development led to greater muscle mass and force production due to increased height and bone length [18]. On the other hand, short sprint swimming required short bursts of high intensity activity which was further dependent on muscle cross sectional area and fibre distribution according to yet another study [3]. Thus, these results supported the relationship of physical characteristics with muscular power in our study. The present study showed significant positive correlations (p<0.001) of muscle power with biceps, subscapular, suprailiac and abdominal skinfolds but not with triceps skinfold. It was found that a swimmer who had greater body 27
5 fat did not always perform better on power tests as compared to a lean swimmer and vice versa. However, according to a previous study, it could be reasoned that the performance in swimming was influenced by the propelling power and in minimizing the resistance to advance in the liquid environment. Thus, physical conditioning of the swimmer, including body fat contributed as well to an extent [23]. Other studies showed that the larger proportion of fat mass in the female swimmers might have allowed the females to kick at a higher rate and thus resulted in greater propulsive efficiency and accounted for a better buoyancy profile of female swimmers than the male swimmers [27]. However, very few literatures are available which reflect the relationship between the body fat content and the muscle power especially in swimmers. The present study showed a statistically significant negative correlation of the physical characteristics with the swimming time (p<0.01). Therefore, age, height, weight and lengths also correlated negatively with the swimming time (p<0.01). It was seen that junior age group swimmers (13-17 years) acquired lesser swimming time than subjunior swimmers (9-12 years); it was mainly due to the effect of physical growth, for example, increased height, and weight and limb lengths. Earlier researches showed both male and female swimmers tended to be taller than the nonathletes of the respective gender. This difference in the stature of swimmers reflected the growth and development of early maturation [23]. Another study showed that the sprint swimmers were taller and heavier than the middle and long-distance swimmers [8]. Increased height resulted in increased longer limbs and thus increased stroke lengths according to a previous study, which decreased the swimming time [1, 9, 21]. The present study showed that the suprailiac skinfold (p<0.01) and the subscapular skinfold (p<0.05) correlated negatively with the swimming time except the biceps, triceps and abdominal skinfolds. As seen earlier in the present study, more body fat did not affect the swimming performance; in fact it led to a decrease in the swimming time. The age group of the swimmers and the training hours of the swimmers (3-4 hours/day) in the present study might have also led to such a result. According to an earlier research, more than required body fat is an inhibitor of the sporting performance and negatively correlated with the swimming time [23,27]. According to another study, higher buoyancy improved the swimming performance but more in the longer distance events [8]. Also, it was seen in previous studies that the pre-pubertal boys presented higher fat percentile than the pubertal boys and higher skinfold values were observed due to less training load [23]. In the present study, girths, diameters and breadths (p<0.01) were negatively correlated with the swimming time. Since swimmers of our study demonstrated muscularity and increased cross-sectional area, it led to greater muscular power and thus decreased swimming time as it would improve the propulsive efficiency. On the other hand, swimmers who had larger bodies demonstrated poor swimming performance in the present study. According to an earlier study, the energy cost was an important determinant in swimming. Energy cost was defined as the energy expenditure per unit of distance [8]. The larger body dimensions were associated with a decrease in buoyancy, increase in drag (active and passive), limited acquisition of water driving abilities, increased energy cost and deterioration in swimming performance [8]. The swimming time in the present study correlated negatively with the upper and lower extremity (p<0.01). In our study, the short sprint swimmers translated the increased muscular power in decreased swimming time due to better propulsive efficiency. It was similar to the previous studies which had proven that the upper body power was correlated highly with the swimming time [14]. A number of other studies had emphasised the important role of muscular power as a determinant of athletic performance. They also showed high correlations between measures of short-term (<45sec) maximal upper body power and freestyle swimming speed [13]. Swimming performances which required anaerobic power of the legs was influenced by strong dive and turn according to earlier studies [5,27,28]. Thus, these studies supported the relationship of swimming time and muscular power in the present study. CONCLUSION The present study concluded that the physical characteristics had a positive association with the upper extremity power, the lower extremity power and a negative association with the swimming time except biceps, triceps and abdominal skinfolds. Thus the present study was useful in determining the strength and conditioning aspects of the swimmers based on their anthropometric and physiological profile. Also swimming time had statistically significant negative correlations with the upper and the lower extremities power. Thus the study helped to understand the young Indian swimming population and also to devise training programs for training their strengths and weaknesses. Hence, the present study concludes that there exists a relationship between physical characteristics, power and swimming time in sprint swimmers. 28
6 REFERENCES [1] Alexander, MJL. Comparison of Biomechanical Aspects of Performance in Male and Female Athletes In: Proceedings of 15 th International Symposium on Biomechanics in Sports; 1997, Denton, Texas, USA. [2] Barbosa, TM., Marinho, DA., Costa, M.J. and Silva, AJ. (2011). Biomechanics of Competitive Swimming Strokes, Biomechanics in Applications, Dr Vaclav Klika (Ed.),, 2011, doi: / [3] Bencke, J., Daamsgaard, R., Saekmose, A., Jorgensen, P., Jorgensen, K. and Klausen, K. Scandinavian Journal of Medicine and Science in Sports, 2002, 12: [4] Beretic, I., Đurovic, M., Okicic, T. and Dopsaj, M. Journal of Sports Science and Medicine, 2013, 12: [5] Bishop, C., Cree, J., Read, P., Chavda, S., Edwards, M. and Turner, A. Strength and Conditioning for Sprint Swimming, 2013, 35(6): 1-6. [6] Chelly, MS., Hermassi, S. and Shephard, RJ. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 2010, 24(6): [7] Davies, B., Murphy, A., Whitty, A. and Watsford, M. Australian Conference of Science and Medicine in Sport. Accessible from [8] Dellal, A., Wong, DP. Ambassa, S. and Smith, AW. International Journal of Motor Learning and Sport Performance, 2011, 1: [9] Durovic, M., Beretic, I., Dopsaj, M., Pesic, M. and Okicic, T. Physical Education And Sport, 2012, 10(4): [10] Geladas, ND., Nassis, GP. and Pavlicevic, S. International Journal Of Sports Medicine, 2005, 26: [11] Goldbeck, TG. and Davies, GJ. Journal of Sports Rehabilitation, 2009, 9(1): [12] Gregory, HG. and Sophia, N. Strength and Conditioning Journal, 2012, 34(6):2-12. [13] Hawley, JA., Williams, MM., Vickovic, MM. and Handcock, PJ. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 1992, 26(3): [14] Malegaonkar, S., Khandekar, SV. and Jaweed, S. Indian Medical Gazette, 2011, 5: [15] Mero, A., Kauhanen, H., Peltola, E., Vuorimma, T. and Komi, PV. The Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness, 1990, 30(1): [16] Morais, JE., Garrido, ND., Marques, MC., Silva, AJ., Marinho, DA. and Barbosa, TM. Journal of Human Kinetics, 2013, 39: [17] Nande, PJ., Mudafale, V. and Vali, SA. The Internet Journal of Nutrition and Wellness, 2009, 8(1): 1-6. [18] Neu, CM., Rauch, F., Rittweger, J., Manz, F. and Schoenau, E. American Journal of Physiology- Endocrinology and Metabolism, 2002, 283: [19] Papadopoulos, C., Sambanis, M., Gissis, I., Noussios, G., Gandiraga, E., Manolopoulos, E. and Papadimitriou, ID. Biology of Sport, 2009, 26 (4): [20] Sadowsky, J., Mastalerz, A., Gromeisz, W. and Tomasz, N. Journal of Human Kinetics, 2012, 32: [21] Sanchez, JA. and Arellauno, R. Stroke Index Values according to Level, Gender, Swimming Style and Event Race Distance. International Symposium on Biomechanics and Sports, 2002, pp [22] Santos, MAM., Barbosa, ML., Melo, WVC., Costa, AV. and Costa, MC. Open Access Journal of Sports Medicine, 2012, 3: [23] Schneider, P. and Meyer, F. Revista Brasileira de Medicina do Esporte, 2005, 11(4): [24] Stockbrugger, BA. and Haennel, RG. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 2001, 15(4): [25] Veiga, S., Cala, A., Frutos, PB. and Navarro, E. Journal of Sports Science and Medicine, 2013, 12: [26] Wanivenhaus, F., Fox, AJS., Chaudhury, S. and Rodeo, SA. Sports Health, 2012, 4(3): [27] Wells, GD., Schneiderman-Walker. J. and Plyley, M. Pediatric Exercise Science, 2006, 17: [28] West, DJ., Owen, NJ., Cunningham, DJ., Cook, CJ. and Kilduff, LP. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 2011, 25(4): [29] Wolfrum, M., Knechtle, B., Rust, CA., Rosemann, T. and Lepers, R. Sports Science, Medicine and Rehabilitation, 2013, 5(29):1-10. [30] Wolfrum, M., Knechtle, B., Rust, CA., Rosemann, T. and Lepers, R. Springer Plus, 2013, 2:
BODY FORM INFLUENCES ON THE DRAG EXPERIENCED BY JUNIOR SWIMMERS. Australia, Perth, Australia
 1 BODY FORM INFLUENCES ON THE DRAG EXPERIENCED BY JUNIOR SWIMMERS Andrew Lyttle 1, Nat Benjanuvatra 2, Brian A Blanksby 2, Bruce C Elliott 2 1 Western Australian Institute of Sport, Perth, Australia 2
1 BODY FORM INFLUENCES ON THE DRAG EXPERIENCED BY JUNIOR SWIMMERS Andrew Lyttle 1, Nat Benjanuvatra 2, Brian A Blanksby 2, Bruce C Elliott 2 1 Western Australian Institute of Sport, Perth, Australia 2
Original Article. Contribution of anthropometric characteristics to critical swimming velocity and estimated propulsive force
 Journal of Physical Education and Sport (JPES), 17(1), Art 32, pp. 212 218, 2017 online ISSN: 2247-806X; p-issn: 2247 8051; ISSN - L = 2247-8051 JPES Original Article Contribution of anthropometric characteristics
Journal of Physical Education and Sport (JPES), 17(1), Art 32, pp. 212 218, 2017 online ISSN: 2247-806X; p-issn: 2247 8051; ISSN - L = 2247-8051 JPES Original Article Contribution of anthropometric characteristics
INFORMATION SHEET FOR PROSPECTIVE VOLUNTEERS IN THE STUDY
 APPENDICES 126 APPENDIX A INFORMATION SHEET FOR PROSPECTIVE VOLUNTEERS IN THE STUDY PHYSIOLOGICAL AND ANTHROPOMETRICAL COMPARISONS BETWEEN THE TRIATHLETE, RUNNER, CYCLIST AND SWIMMER A study by Jonathan
APPENDICES 126 APPENDIX A INFORMATION SHEET FOR PROSPECTIVE VOLUNTEERS IN THE STUDY PHYSIOLOGICAL AND ANTHROPOMETRICAL COMPARISONS BETWEEN THE TRIATHLETE, RUNNER, CYCLIST AND SWIMMER A study by Jonathan
A COMPARATIVE STUDY ON RESPIRATORY PARAMETERS BETWEEN SHORT DISTANCE AND LONG DISTANCE SWIMMERS
 A COMPARATIVE STUDY ON RESPIRATORY PARAMETERS BETWEEN SHORT DISTANCE AND LONG DISTANCE SWIMMERS Baghel Priya PhD scholar, LNIPE, Gwalior, M.P., India ABSTRACT The purpose of the study was to find out the
A COMPARATIVE STUDY ON RESPIRATORY PARAMETERS BETWEEN SHORT DISTANCE AND LONG DISTANCE SWIMMERS Baghel Priya PhD scholar, LNIPE, Gwalior, M.P., India ABSTRACT The purpose of the study was to find out the
An Exploratory Study of Psychomotor Abilities among Cricket Players of Different Level of Achievement
 Research Journal of Physical Education Sciences ISSN 2320 9011 An Exploratory Study of Psychomotor Abilities among Cricket Players of Different Level of Achievement Abstract Baljinder Singh Bal and Ranjeet
Research Journal of Physical Education Sciences ISSN 2320 9011 An Exploratory Study of Psychomotor Abilities among Cricket Players of Different Level of Achievement Abstract Baljinder Singh Bal and Ranjeet
WHAT CAN WE LEARN FROM COMPETITION ANALYSIS AT THE 1999 PAN PACIFIC SWIMMING CHAMPIONSHIPS?
 WHAT CAN WE LEARN FROM COMPETITION ANALYSIS AT THE 1999 PAN PACIFIC SWIMMING CHAMPIONSHIPS? Bruce Mason and Jodi Cossor Biomechanics Department, Australian Institute of Sport, Canberra, Australia An analysis
WHAT CAN WE LEARN FROM COMPETITION ANALYSIS AT THE 1999 PAN PACIFIC SWIMMING CHAMPIONSHIPS? Bruce Mason and Jodi Cossor Biomechanics Department, Australian Institute of Sport, Canberra, Australia An analysis
DETERMINANT FACTORS RELATED TO PERFORMANCE IN YOUNG SWIMMERS
 DETERMINANT FACTORS RELATED TO PERFORMANCE IN YOUNG SWIMMERS Luís Rama1 João Santos2, Paulo Gomes2, Francisco Alves3 1Faculdade de Ciências do Desporto e Educação Física, Universidade de Coimbra, Portugal
DETERMINANT FACTORS RELATED TO PERFORMANCE IN YOUNG SWIMMERS Luís Rama1 João Santos2, Paulo Gomes2, Francisco Alves3 1Faculdade de Ciências do Desporto e Educação Física, Universidade de Coimbra, Portugal
A Comparative Study of Running Agility, Jumping Ability and Throwing Ability among Cricket Players
 Research Journal of Physical Education Sciences ISSN 2320 9011 A Comparative Study of Running Agility, Jumping Ability and Throwing Ability among Cricket Players Abstract Karunesh Kumar 1, Manjit Singh
Research Journal of Physical Education Sciences ISSN 2320 9011 A Comparative Study of Running Agility, Jumping Ability and Throwing Ability among Cricket Players Abstract Karunesh Kumar 1, Manjit Singh
A Comparative Analysis of Motor Fitness Components among Sprinters, Throwers and Jumpers
 Research Journal of Physical Education Sciences ISSN 2320 9011 A Comparative Analysis of Motor Fitness Components among, and Abstract Manjit Singh 1*, Sukhbir Singh 2 and Baljinder Singh Bal 3 1 Department
Research Journal of Physical Education Sciences ISSN 2320 9011 A Comparative Analysis of Motor Fitness Components among, and Abstract Manjit Singh 1*, Sukhbir Singh 2 and Baljinder Singh Bal 3 1 Department
Key words: biomechanics, injury, technique, measurement, strength, evaluation
 Becker, T., & Havriluk, R. (2006). Bilateral and anterior-posterior muscular imbalances in swimmers. In J. P. Vilas-Boas, F. Alves, A. Marques (Eds.), Biomechanics and Medicine in Swimming X. Portuguese
Becker, T., & Havriluk, R. (2006). Bilateral and anterior-posterior muscular imbalances in swimmers. In J. P. Vilas-Boas, F. Alves, A. Marques (Eds.), Biomechanics and Medicine in Swimming X. Portuguese
The Physical and Physiological Characteristics of 3x3. Results of Medical Study & Scientific Test
 The Physical and Physiological Characteristics of 3x3 Results of Medical Study & Scientific Test Prepared by Dr. Paul Montgomery & Brendan Maloney (Aspetar Orthopaedic Hospital) In cooperation with FIBA
The Physical and Physiological Characteristics of 3x3 Results of Medical Study & Scientific Test Prepared by Dr. Paul Montgomery & Brendan Maloney (Aspetar Orthopaedic Hospital) In cooperation with FIBA
The effect of deliberate practice on the technique of national calibre swimmers
 Lupo Corrado, Giancarlo Condello, and Antonio Tessitore. (2014). Women s Water Polo World Championships: Technical and Tactical Aspects of Winning and Losing Teams in Close and Unbalanced Games. Journal
Lupo Corrado, Giancarlo Condello, and Antonio Tessitore. (2014). Women s Water Polo World Championships: Technical and Tactical Aspects of Winning and Losing Teams in Close and Unbalanced Games. Journal
COMPARISON STUDY BETWEEN THE EFFICIENY OF THE START TECHNIQUES IN THE ROMANIAN COMPETITIVE SWIMMING
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series IX: Sciences of Human Kinetics Vol. 6 (55) No. 1 2013 COMPARISON STUDY BETWEEN THE EFFICIENY OF THE START TECHNIQUES IN THE ROMANIAN COMPETITIVE
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series IX: Sciences of Human Kinetics Vol. 6 (55) No. 1 2013 COMPARISON STUDY BETWEEN THE EFFICIENY OF THE START TECHNIQUES IN THE ROMANIAN COMPETITIVE
Predictors of race time in male ironman triathletes: physical characteristics, training, or prerace experience?
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2010 Predictors of race time in male ironman triathletes: physical characteristics,
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2010 Predictors of race time in male ironman triathletes: physical characteristics,
At What Extent Physical Training Can Minimize Gender Differences in Male and Female Trained Swimmers? - A Comparative Analysis
 International Journal of Sports and Physical Education (IJSPE) Volume 3, Issue 1, 2017, PP 24-28 ISSN 2454-6380 http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2454-6380.0301005 www.arcjournals.org At What Extent Physical
International Journal of Sports and Physical Education (IJSPE) Volume 3, Issue 1, 2017, PP 24-28 ISSN 2454-6380 http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2454-6380.0301005 www.arcjournals.org At What Extent Physical
International Journal for Life Sciences and Educational Research. School of Physical Education, Karpagam University, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu, India
 International Journal for Life Sciences and Educational Research Vol. 2 (1), pp. 20-24 January - 2014 Available online at http://www.ijlser.com E-ISSN : 2321-1229; P ISSN : 2321-1180 Research Article Effect
International Journal for Life Sciences and Educational Research Vol. 2 (1), pp. 20-24 January - 2014 Available online at http://www.ijlser.com E-ISSN : 2321-1229; P ISSN : 2321-1180 Research Article Effect
A CROSS-SECTIONAL ANALYSIS OF SKILL RELATED PHYSICAL FITNESS COMPONENTS OF KAYAKING AND ROWING PLAYERS
 European Journal of Physical Education and Sport Science ISSN: 2501-1235 ISSN-L: 2501-1235 Available on-line at: www.oapub.org/edu doi: 10.5281/zenodo.1050701 Volume 3 Issue 10 2017 A CROSS-SECTIONAL ANALYSIS
European Journal of Physical Education and Sport Science ISSN: 2501-1235 ISSN-L: 2501-1235 Available on-line at: www.oapub.org/edu doi: 10.5281/zenodo.1050701 Volume 3 Issue 10 2017 A CROSS-SECTIONAL ANALYSIS
Sex Differences in Growth and Performance of Track and Field Athletes Years
 Journal of Human Kinetics volume 24 2010, 79 85 Section III Sport, Physical Education & Recreation 79 Sex Differences in Growth and Performance of Track and Field Athletes 11 15 Years by Robert M. Malina
Journal of Human Kinetics volume 24 2010, 79 85 Section III Sport, Physical Education & Recreation 79 Sex Differences in Growth and Performance of Track and Field Athletes 11 15 Years by Robert M. Malina
SIMULTANEOUS RECORDINGS OF VELOCITY AND VIDEO DURING SWIMMING
 Portuguese Journal of Sport Sciences. 6:supl. 2, 32-35, 2006 SIMULTANEOUS RECORDINGS OF VELOCITY AND VIDEO DURING SWIMMING Albert B. Craig 1, Budd Termin2, and David R. Pendergast 2 1University of Rochester,
Portuguese Journal of Sport Sciences. 6:supl. 2, 32-35, 2006 SIMULTANEOUS RECORDINGS OF VELOCITY AND VIDEO DURING SWIMMING Albert B. Craig 1, Budd Termin2, and David R. Pendergast 2 1University of Rochester,
A study on the effect of limb length and arm strength on the ball release velocity in cricket
 2016; 3(6): 389-393 P-ISSN: 2394-1685 E-ISSN: 2394-1693 Impact Factor (ISRA): 5.38 IJPESH 2016; 3(6): 389-393 2016 IJPESH www.kheljournal.com Received: 07-09-2016 Accepted: 08-10-2016 Neptune Ghosh M.P.Ed,
2016; 3(6): 389-393 P-ISSN: 2394-1685 E-ISSN: 2394-1693 Impact Factor (ISRA): 5.38 IJPESH 2016; 3(6): 389-393 2016 IJPESH www.kheljournal.com Received: 07-09-2016 Accepted: 08-10-2016 Neptune Ghosh M.P.Ed,
The Influence of Load Carrying Modes on Gait variables of Healthy Indian Women
 The Influence of Load Carrying Modes on Gait variables of Healthy Indian Women *Guha Thakurta A, Iqbal R and De A National Institute of Industrial Engineering, Powai, Vihar Lake, Mumbai-400087, India,
The Influence of Load Carrying Modes on Gait variables of Healthy Indian Women *Guha Thakurta A, Iqbal R and De A National Institute of Industrial Engineering, Powai, Vihar Lake, Mumbai-400087, India,
Study of anthropometric characteristics among the university level archers
 2017; 2(2): 515-519 ISSN: 2456-0057 IJPNPE 2017; 2(2): 515-519 2017 IJPNPE www.journalofsports.com Received: 27-05-2017 Accepted: 28-06-2017 Ritika Physical Education Teacher, Sri Guru Harkrishan Public
2017; 2(2): 515-519 ISSN: 2456-0057 IJPNPE 2017; 2(2): 515-519 2017 IJPNPE www.journalofsports.com Received: 27-05-2017 Accepted: 28-06-2017 Ritika Physical Education Teacher, Sri Guru Harkrishan Public
Generating Power in the Pool: An Analysis of Strength Conditioning and its Effect on Athlete Performance
 Generating Power in the Pool: An Analysis of Strength Conditioning and its Effect on Athlete Performance 1 Introduction S.D. Hoffmann Carthage College shoffmann@carthage.edu November 12 th, 2014 Abstract
Generating Power in the Pool: An Analysis of Strength Conditioning and its Effect on Athlete Performance 1 Introduction S.D. Hoffmann Carthage College shoffmann@carthage.edu November 12 th, 2014 Abstract
GROUND REACTION FORCE DOMINANT VERSUS NON-DOMINANT SINGLE LEG STEP OFF
 GROUND REACTION FORCE DOMINANT VERSUS NON-DOMINANT SINGLE LEG STEP OFF Sara Gharabaghli, Rebecca Krogstad, Sara Lynch, Sofia Saavedra, and Tamara Wright California State University, San Marcos, San Marcos,
GROUND REACTION FORCE DOMINANT VERSUS NON-DOMINANT SINGLE LEG STEP OFF Sara Gharabaghli, Rebecca Krogstad, Sara Lynch, Sofia Saavedra, and Tamara Wright California State University, San Marcos, San Marcos,
Leg Power in Elite Male Fencers: A Comparative Study among the Three Competitive Disciplines
 Leg Power in Elite Male Fencers: A Comparative Study among the Three Competitive Disciplines Gustavo D. Aquilino, Aldo F. Longo, Néstor A. Lentini. Exercise Physiology Laboratory, National Sport High Performance
Leg Power in Elite Male Fencers: A Comparative Study among the Three Competitive Disciplines Gustavo D. Aquilino, Aldo F. Longo, Néstor A. Lentini. Exercise Physiology Laboratory, National Sport High Performance
The Effect of Altitude on Growth of Anthropometric and Motor Performance of 14 Year Old Adolescence
 The Effect of Altitude on Growth of Anthropometric and Motor Performance of 14 Year Old Adolescence Jyan Chandra Gurung* Kadamtala High School, Kadamtala, West Bengal, India. *Corresponding author. Tel:
The Effect of Altitude on Growth of Anthropometric and Motor Performance of 14 Year Old Adolescence Jyan Chandra Gurung* Kadamtala High School, Kadamtala, West Bengal, India. *Corresponding author. Tel:
Journal of Human Sport and Exercise E-ISSN: Universidad de Alicante España
 Journal of Human Sport and Exercise E-ISSN: 1988-5202 jhse@ua.es Universidad de Alicante España Vaso, Martin; Knechtle, Beat; Rüst, Christoph Alexander; Rosemann, Thomas; Lepers, Romuald Age of peak swim
Journal of Human Sport and Exercise E-ISSN: 1988-5202 jhse@ua.es Universidad de Alicante España Vaso, Martin; Knechtle, Beat; Rüst, Christoph Alexander; Rosemann, Thomas; Lepers, Romuald Age of peak swim
The Mechanics of Modern BREASTSTROKE Swimming Dr Ralph Richards
 The Mechanics of Modern BREASTSTROKE Swimming Dr Ralph Richards Breaststroke is the least efficient of the four competition strokes because a large amount of water resistance is created due to body position
The Mechanics of Modern BREASTSTROKE Swimming Dr Ralph Richards Breaststroke is the least efficient of the four competition strokes because a large amount of water resistance is created due to body position
Swimming Breaststroke Checklist Marion Alexander, Yumeng Li, Adam Toffan, Biomechanics Lab, U of Manitoba
 Swimming Breaststroke Checklist Marion Alexander, Yumeng Li, Adam Toffan, Biomechanics Lab, U of Manitoba Glide: -The feet come together, with the hips and knees fully extended. The legs may not be closed
Swimming Breaststroke Checklist Marion Alexander, Yumeng Li, Adam Toffan, Biomechanics Lab, U of Manitoba Glide: -The feet come together, with the hips and knees fully extended. The legs may not be closed
This article has been downloaded from JPES Journal of Physical Education an Sport Vol 25, no 4, December, 2009 e ISSN: p ISSN:
 C I T I U S A L T I U S F O R T I U S - J O U R N A L O F P H Y S I C A L E D U C A T I O N A N D S P O R T This article has been downloaded from SHORT REPORT Online Publication Date: 10 December 2009
C I T I U S A L T I U S F O R T I U S - J O U R N A L O F P H Y S I C A L E D U C A T I O N A N D S P O R T This article has been downloaded from SHORT REPORT Online Publication Date: 10 December 2009
Effectively Improving Technique of Developing Swimmers. Ryan Atkison, MSc, CSCS Sport Biomechanist Canadian Sport Institute Ontario
 Effectively Improving Technique of Developing Swimmers Ryan Atkison, MSc, CSCS Sport Biomechanist Canadian Sport Institute Ontario Effectively Improving Technique of Developing Swimmers *Traditional swimming
Effectively Improving Technique of Developing Swimmers Ryan Atkison, MSc, CSCS Sport Biomechanist Canadian Sport Institute Ontario Effectively Improving Technique of Developing Swimmers *Traditional swimming
RELATIONSHIP OF SELECTED KINEMATIC VARIABLES WITH THE PERFORMANCE OF DOUBLE HANDEDBACKHAND IN TENNIS. Rajesh Kumar, M.P.Ed,
 RELATIONSHIP OF SELECTED KINEMATIC VARIABLES WITH THE PERFORMANCE OF DOUBLE HANDEDBACKHAND IN TENNIS Rajesh Kumar, M.P.Ed, Department of Sports Biomechanics, LNIPE, Gwalior (M.P.), India Dr.Y.S.Rajpoot,
RELATIONSHIP OF SELECTED KINEMATIC VARIABLES WITH THE PERFORMANCE OF DOUBLE HANDEDBACKHAND IN TENNIS Rajesh Kumar, M.P.Ed, Department of Sports Biomechanics, LNIPE, Gwalior (M.P.), India Dr.Y.S.Rajpoot,
CRNOGORSKA SPORTSKA AKADEMIJA, Sport Mont časopis br. 43,44,45.
 UDC 797.21 Bergun Meric Bingul, Ozlem Tore, Kocaeli University, School of Physical Education and Sport (Kocaeli, Turkey) Cigdem Bulgan, Halic University, School of Physical Education and Sport (İstanbul,
UDC 797.21 Bergun Meric Bingul, Ozlem Tore, Kocaeli University, School of Physical Education and Sport (Kocaeli, Turkey) Cigdem Bulgan, Halic University, School of Physical Education and Sport (İstanbul,
Timing 1. The hips and shoulders rotate at the end of the catch to assist in the acceleration of the stroke.
 Freestyle Body Position 1. Head position should be comfortable at a 45º angle with the water line slightly above the goggles. 2. Hips and shoulders should remain high in the water with a straight line
Freestyle Body Position 1. Head position should be comfortable at a 45º angle with the water line slightly above the goggles. 2. Hips and shoulders should remain high in the water with a straight line
POSITION-SPECIFIC ANTHROPOMETRIC PROFILES: 2011 WOMEN'S 17 EUROPEAN HANDBALL CHAMPIONSHIP
 POSITION-SPECIFIC ANTHROPOMETRIC PROFILES: 2011 WOMEN'S 17 EUROPEAN HANDBALL CHAMPIONSHIP František URBAN 1, Róbert KANDRÁČ 2, František TÁBORSKÝ 3 1 Member of the Union of University Handball Teachers
POSITION-SPECIFIC ANTHROPOMETRIC PROFILES: 2011 WOMEN'S 17 EUROPEAN HANDBALL CHAMPIONSHIP František URBAN 1, Róbert KANDRÁČ 2, František TÁBORSKÝ 3 1 Member of the Union of University Handball Teachers
Chapter III. Methodology
 Chapter III Methodology 31 Chapter III METHODOLOGY In this chapter, the procedure adopted for the selection of subjects and variables, criterion measures, reliability of the data, administration of the
Chapter III Methodology 31 Chapter III METHODOLOGY In this chapter, the procedure adopted for the selection of subjects and variables, criterion measures, reliability of the data, administration of the
Steeplechase Hurdle Economy, Mechanics, and Performance
 Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Theses and Dissertations 2013-06-27 Steeplechase Hurdle Economy, Mechanics, and Performance Sarah Ingebretsen Brigham Young University - Provo Follow this
Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Theses and Dissertations 2013-06-27 Steeplechase Hurdle Economy, Mechanics, and Performance Sarah Ingebretsen Brigham Young University - Provo Follow this
The purpose of the study was to compare the physical fitness components of elite swimmers and nonswimmers Karnataka university dharwad
 2018; 4(8): 124-128 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2018; 4(8): 124-128 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 01-06-2018 Accepted: 03-07-2018 Dr. Suresh B Patil Asst.
2018; 4(8): 124-128 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2018; 4(8): 124-128 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 01-06-2018 Accepted: 03-07-2018 Dr. Suresh B Patil Asst.
DO HEIGHT AND WEIGHT PLAY AN IMPORTANT ROLE IN BLOCK AND ATTACK EFFICIENCY IN HIGH-LEVEL MEN S VOLLEYBALL?
 Papers on Anthropology XXVI/1, 2017, pp. 64 71 DO HEIGHT AND WEIGHT PLAY AN IMPORTANT ROLE IN BLOCK R. Stamm, M. Stamm, A. Jairu, R. Toop, R. Tuula, P. V. João DO HEIGHT AND WEIGHT PLAY AN IMPORTANT ROLE
Papers on Anthropology XXVI/1, 2017, pp. 64 71 DO HEIGHT AND WEIGHT PLAY AN IMPORTANT ROLE IN BLOCK R. Stamm, M. Stamm, A. Jairu, R. Toop, R. Tuula, P. V. João DO HEIGHT AND WEIGHT PLAY AN IMPORTANT ROLE
2015, Vol. 27, No. 1, ISSN (Print) Eirik Haukali & Leif Inge Tjelta* University of Stavanger, Norway. Abstract
 International Journal of Applied Sports Sciences ISSN 2233-7946 (Online) 2015, Vol. 27, No. 1, 26-32. ISSN 1598-2939 (Print) c Korea Institute of Sport Science http://www.sports.re.kr/eng/05publication/callforpaper.jsp
International Journal of Applied Sports Sciences ISSN 2233-7946 (Online) 2015, Vol. 27, No. 1, 26-32. ISSN 1598-2939 (Print) c Korea Institute of Sport Science http://www.sports.re.kr/eng/05publication/callforpaper.jsp
Comparison of Active Drag Using the MRT-Method and the MAD-System in Front Crawl Swimming
 Proceedings Comparison of Active Drag Using the MRT-Method and the MAD-System in Front Crawl Swimming Kenzo Narita 1, *, Futoshi Ogita 2, Motomu Nakashima 3 and Hideki Takagi 4 1 Doctoral Program in Physical
Proceedings Comparison of Active Drag Using the MRT-Method and the MAD-System in Front Crawl Swimming Kenzo Narita 1, *, Futoshi Ogita 2, Motomu Nakashima 3 and Hideki Takagi 4 1 Doctoral Program in Physical
POSITION-SPECIFIC ANTHROPOMETRIC PROFILES: 2011 WOMEN'S 19 EUROPEAN HANDBALL CHAMPIONSHIP
 POSITION-SPECIFIC ANTHROPOMETRIC PROFILES: 2011 WOMEN'S 19 EUROPEAN HANDBALL CHAMPIONSHIP František URBAN 1, Róbert KANDRÁČ 2, František TÁBORSKÝ 3 1 Member of Union of University Handball Teachers / EHF
POSITION-SPECIFIC ANTHROPOMETRIC PROFILES: 2011 WOMEN'S 19 EUROPEAN HANDBALL CHAMPIONSHIP František URBAN 1, Róbert KANDRÁČ 2, František TÁBORSKÝ 3 1 Member of Union of University Handball Teachers / EHF
If you have a swimming background and you want to add distance or repetitions to the workouts, you are more than welcome to do that.
 12 Week Sprint Distance Plan, Int-Adv. This program should be used by an athlete in their second year or triathlon or beyond. The program consists of 3 workouts per week in each sport, 1-2 days of strength
12 Week Sprint Distance Plan, Int-Adv. This program should be used by an athlete in their second year or triathlon or beyond. The program consists of 3 workouts per week in each sport, 1-2 days of strength
Rugby Fitness Testing Protocols. Order of Testing:
 6 P a g e Rugby Fitness Testing Protocols Order of Testing: Testing can be completed in any order, with the exception of the ENDURANCE Test (1200m) which HAS TO BE completed at the end of the session.
6 P a g e Rugby Fitness Testing Protocols Order of Testing: Testing can be completed in any order, with the exception of the ENDURANCE Test (1200m) which HAS TO BE completed at the end of the session.
12 Week Winter Maintenance Olympic Bridge to Half Ironman
 12 Week Winter Maintenance Olympic Bridge to Half Ironman This program should be used for an athlete who is coming off an Olympic Distance Race and: 1. They have a very strong base of 4-6 months of consistent
12 Week Winter Maintenance Olympic Bridge to Half Ironman This program should be used for an athlete who is coming off an Olympic Distance Race and: 1. They have a very strong base of 4-6 months of consistent
TECHNOLOGY FOR DECREASING ACTIVE DRAG AT THE MAXIMAL SWIMMING VELOCITY
 TECHNOLOGY FOR DECREASING ACTIVE DRAG AT THE MAXIMAL SWIMMING VELOCITY Sergei Kolmogorov, Sergei Lyapin, Olga Rumyantseva and J. Paulo Vilas-Boas 1 Centroconcept, Pomor University, Arkhangelsk, Russia
TECHNOLOGY FOR DECREASING ACTIVE DRAG AT THE MAXIMAL SWIMMING VELOCITY Sergei Kolmogorov, Sergei Lyapin, Olga Rumyantseva and J. Paulo Vilas-Boas 1 Centroconcept, Pomor University, Arkhangelsk, Russia
Jodi M. Cossor and Bruce R. Mason Australian lnstitute of Sport Biomechanics Department, Canberra, Australia
 B~omechanics Symposia 2001 / Unlversily of San Francisco SWIM START PERFORMANCES AT THE SYDNEY 2000 OLYMPIC GAMES Jodi M. Cossor and Bruce R. Mason Australian lnstitute of Sport Biomechanics Department,
B~omechanics Symposia 2001 / Unlversily of San Francisco SWIM START PERFORMANCES AT THE SYDNEY 2000 OLYMPIC GAMES Jodi M. Cossor and Bruce R. Mason Australian lnstitute of Sport Biomechanics Department,
PREVIEW ONLY SWIMMING FAST SWIMMING IN AUSTRALIA PHYSIOTHERAPY ASSESSMENT OF SWIMMERS. Cameron Elliott. These notes are a preview. Slides are limited.
 Be sure to convert to your own time zone at Cameron Elliott B.App.Sc (Physio) PHYSIOTHERAPY ASSESSMENT OF SWIMMERS Cameron Elliott SWIMMING IN AUSTRALIA Over 160,000 adults participate in organised swimming
Be sure to convert to your own time zone at Cameron Elliott B.App.Sc (Physio) PHYSIOTHERAPY ASSESSMENT OF SWIMMERS Cameron Elliott SWIMMING IN AUSTRALIA Over 160,000 adults participate in organised swimming
Relationship among Speed, Power & Fatigue Index of Cricket Players
 Relationship among Speed, Power & Fatigue Index of Cricket Players Kumar 1, Ashok; Kathayat 2, Lokendra Bahadur; and Kadam 3, Govind Article Authorship & Affiliation Details Communication Date: Dec 24,
Relationship among Speed, Power & Fatigue Index of Cricket Players Kumar 1, Ashok; Kathayat 2, Lokendra Bahadur; and Kadam 3, Govind Article Authorship & Affiliation Details Communication Date: Dec 24,
INTERACTION OF STEP LENGTH AND STEP RATE DURING SPRINT RUNNING
 INTERACTION OF STEP LENGTH AND STEP RATE DURING SPRINT RUNNING Joseph P. Hunter 1, Robert N. Marshall 1,, and Peter J. McNair 3 1 Department of Sport and Exercise Science, The University of Auckland, Auckland,
INTERACTION OF STEP LENGTH AND STEP RATE DURING SPRINT RUNNING Joseph P. Hunter 1, Robert N. Marshall 1,, and Peter J. McNair 3 1 Department of Sport and Exercise Science, The University of Auckland, Auckland,
subjects included in group A were members of other
 Brit. J. Sports Med. - Vol. 11, No. 3, September 1977, pp. 133-137 A STUDY OF TH PHYSICAL WORKING CAPACITY OF GALIC FOOTBALLRS AND HURLRS A.W. S. WATSON, B.Sc., M.Sc., Ph.D., F.R.A.M.I. Department of Physiology,
Brit. J. Sports Med. - Vol. 11, No. 3, September 1977, pp. 133-137 A STUDY OF TH PHYSICAL WORKING CAPACITY OF GALIC FOOTBALLRS AND HURLRS A.W. S. WATSON, B.Sc., M.Sc., Ph.D., F.R.A.M.I. Department of Physiology,
Resistance to Fatigue and Success in Competitive Swimming. Steven C. Myers, Los Alamos High School Jake A. Bailey, University of Northern Colorado
 Resistance to Fatigue and Success in Competitive Swimming Steven C. Myers, Los Alamos High School Jake A. Bailey, University of Northern Colorado Introduction Developing and training successful competitive
Resistance to Fatigue and Success in Competitive Swimming Steven C. Myers, Los Alamos High School Jake A. Bailey, University of Northern Colorado Introduction Developing and training successful competitive
Ranell Hobson Traditional Phases of the 100m
 Traditional Phases of the 100m The 100m sprint has four distinct phases that should be addressed by the coach - the start, the acceleration phase, the transition phase and the maximum velocity phase (Winkleman,
Traditional Phases of the 100m The 100m sprint has four distinct phases that should be addressed by the coach - the start, the acceleration phase, the transition phase and the maximum velocity phase (Winkleman,
Anthropometrical Measurement, Physiological and Biomotorical Testing in Identifying Young Talented Volleyball Athletes
 692 Anthropometrical Measurement, Physiological and Biomotorical Testing in Identifying Young Talented Volleyball Athletes * Dr. Kusnanik, NW Abstract The purpose of this research was to get equation model
692 Anthropometrical Measurement, Physiological and Biomotorical Testing in Identifying Young Talented Volleyball Athletes * Dr. Kusnanik, NW Abstract The purpose of this research was to get equation model
The relationship between different age swimmers flip turn temporal and kinematic characteristics
 604 ISSN 1392 1207. MECHANIKA. 2017 Volume 23(4): 604 609 The relationship between different age swimmers flip turn temporal and kinematic characteristics Valentina SKYRIENE*, Milda DUBOSIENE**, Mindaugas
604 ISSN 1392 1207. MECHANIKA. 2017 Volume 23(4): 604 609 The relationship between different age swimmers flip turn temporal and kinematic characteristics Valentina SKYRIENE*, Milda DUBOSIENE**, Mindaugas
A COMPARISON OF SELECTED BIOMECHANICAL PARAMETERS OF FRONT ROW SPIKE BETWEEN SHORT SET AND HIGH SET BALL
 A COMPARISON OF SELECTED BIOMECHANICAL PARAMETERS OF FRONT ROW SPIKE BETWEEN SHORT SET AND HIGH SET BALL PAPAN MONDAL a AND SUDARSAN BHOWMICK b,* a Assistant Professor, Department of Physical Education,
A COMPARISON OF SELECTED BIOMECHANICAL PARAMETERS OF FRONT ROW SPIKE BETWEEN SHORT SET AND HIGH SET BALL PAPAN MONDAL a AND SUDARSAN BHOWMICK b,* a Assistant Professor, Department of Physical Education,
RELATION BETWEEN MAXIMAL ANAEROBIC POWER OUTPUT AND TESTS ON ROWING ERGOMETER
 Acta Facultatis Educationis Physicae Universitatis Comenianae Vol. 57 No 1 2017 RELATION BETWEEN MAXIMAL ANAEROBIC POWER OUTPUT AND TESTS ON ROWING ERGOMETER Matej Šmída, Michal Clementis, Dušan Hamar,
Acta Facultatis Educationis Physicae Universitatis Comenianae Vol. 57 No 1 2017 RELATION BETWEEN MAXIMAL ANAEROBIC POWER OUTPUT AND TESTS ON ROWING ERGOMETER Matej Šmída, Michal Clementis, Dušan Hamar,
RELATIONSHIP OF ANTHROPOMETRIC MEASUREMENT ON THE PERFORMANCE OF SWIMMERS AUTHOR
 RELATIONSHIP OF ANTHROPOMETRIC MEASUREMENT ON THE PERFORMANCE OF SWIMMERS AUTHOR Mr. MUKESH KUMAR TAKER Research Scholar Poornima University, Jaipur Mr. MOHAN LAL Research Scholar singhania university
RELATIONSHIP OF ANTHROPOMETRIC MEASUREMENT ON THE PERFORMANCE OF SWIMMERS AUTHOR Mr. MUKESH KUMAR TAKER Research Scholar Poornima University, Jaipur Mr. MOHAN LAL Research Scholar singhania university
FITNESSGRAM Scorecard (for Males , and Adults 18+) Females see last pages
 FITNESSGRAM Scorecard (for Males 14-17+, and Adults 18+) Females see last pages Name: Date: Age: Weight Health Weight: Height: lbs inches Inches 2 : BMI: = (lbs x 703) / inches 2 Skinfold Measures See:
FITNESSGRAM Scorecard (for Males 14-17+, and Adults 18+) Females see last pages Name: Date: Age: Weight Health Weight: Height: lbs inches Inches 2 : BMI: = (lbs x 703) / inches 2 Skinfold Measures See:
to understand the characteristics which are the result The present study is based on a cross-section sample of
 Brit J. Sports Med. - Vol. 14, Nos 2 & 3, August 1980, pp. 139-144 KINANTHROPOMETRY AND PERFORMANCE OF TOP RANKING INDIAN BASKETBALL PLAYERS H. S. SODHI, PhD Sports Medicine Research Laboratory, Netaii
Brit J. Sports Med. - Vol. 14, Nos 2 & 3, August 1980, pp. 139-144 KINANTHROPOMETRY AND PERFORMANCE OF TOP RANKING INDIAN BASKETBALL PLAYERS H. S. SODHI, PhD Sports Medicine Research Laboratory, Netaii
The Most Common Athletic Injuries among Swimmers: The Case for University Students in Jordan
 Advances in Physical Education, 2016, 6, 52-58 Published Online May 2016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ape http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ape.2016.62006 The Most Common Athletic Injuries among Swimmers:
Advances in Physical Education, 2016, 6, 52-58 Published Online May 2016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ape http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ape.2016.62006 The Most Common Athletic Injuries among Swimmers:
Swimming Glossary & Useful Information The Strokes
 Swimming Glossary & Useful Information The Strokes Freestyle (abv. Free or F/C) (UK: front-crawl) Freestyle is the fastest swimming stroke of all. It is used in open water and triathlon swimming. Strictly
Swimming Glossary & Useful Information The Strokes Freestyle (abv. Free or F/C) (UK: front-crawl) Freestyle is the fastest swimming stroke of all. It is used in open water and triathlon swimming. Strictly
Construction of Physical Fitness Test Items Norms of National Level Taekwondo Players
 American International Journal of Research in Humanities, Arts and Social Sciences Available online at http://www.iasir.net ISSN (Print): 2328-3734, ISSN (Online): 2328-3696, ISSN (CD-ROM): 2328-3688 AIJRHASS
American International Journal of Research in Humanities, Arts and Social Sciences Available online at http://www.iasir.net ISSN (Print): 2328-3734, ISSN (Online): 2328-3696, ISSN (CD-ROM): 2328-3688 AIJRHASS
The Swimmer s Shoulder
 The Swimmer s Shoulder Corey Kunzer PT, DPT, SCS ATC, CSCS Becca Gsumer, PT, DPT Mayo Clinic 26 th Annual Symposium on Sports Medicine November 12 th, 2016 2016 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures No relevant financial
The Swimmer s Shoulder Corey Kunzer PT, DPT, SCS ATC, CSCS Becca Gsumer, PT, DPT Mayo Clinic 26 th Annual Symposium on Sports Medicine November 12 th, 2016 2016 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures No relevant financial
Performance of Young Male Swimmers in the 100-Meters Front Crawl
 Pediatric Exercise Science, 2010, 22, 278-287 2010 Human Kinetics, Inc. Performance of Young Male Swimmers in the 100-Meters Front Crawl Fabrício de Mello Vitor and Maria Tereza Silveira Böhme University
Pediatric Exercise Science, 2010, 22, 278-287 2010 Human Kinetics, Inc. Performance of Young Male Swimmers in the 100-Meters Front Crawl Fabrício de Mello Vitor and Maria Tereza Silveira Böhme University
SWIMMING IN AUSTRALIA September-October 2004
 SWIMMING IN AUSTRALIA September-October 2004 TALENT IDENTIFICATION & DEVELOPMENT By Dr R. Richards Presented at 1999 ASCTA Convention INTRODUCTION Many great coaches are discovered once they have uncovered
SWIMMING IN AUSTRALIA September-October 2004 TALENT IDENTIFICATION & DEVELOPMENT By Dr R. Richards Presented at 1999 ASCTA Convention INTRODUCTION Many great coaches are discovered once they have uncovered
UNDERSTANDING AND INTERPRETING YOUR S.T.A.R.S. RESULTS
 UNDERSTANDING AND INTERPRETING YOUR S.T.A.R.S. RESULTS As you read through your S.T.A.R.S. athlete report, consider each of your test results and make a list of which areas fell below the normal range.
UNDERSTANDING AND INTERPRETING YOUR S.T.A.R.S. RESULTS As you read through your S.T.A.R.S. athlete report, consider each of your test results and make a list of which areas fell below the normal range.
Western Australian Coaches Conference
 Season Planning Western Australian Coaches Conference Drew McGregor Swimming Queensland Coach Development Season Planning Western Australian Coaches Conference Drew McGregor Swimming Queensland Coach Development
Season Planning Western Australian Coaches Conference Drew McGregor Swimming Queensland Coach Development Season Planning Western Australian Coaches Conference Drew McGregor Swimming Queensland Coach Development
TEMPORAL ANALYSIS OF THE JAVELIN THROW
 TEMPORAL ANALYSIS OF THE JAVELIN THROW Derek M. Helenbergerl, Michael T. Sanders 2, and Lawrence D. Abraha~n',~ Biomedical Engineering, Intercollegiate Athletics for Men, Kinesiology & Health Education
TEMPORAL ANALYSIS OF THE JAVELIN THROW Derek M. Helenbergerl, Michael T. Sanders 2, and Lawrence D. Abraha~n',~ Biomedical Engineering, Intercollegiate Athletics for Men, Kinesiology & Health Education
SAL & AIS Talent Identification Findings. Drew McGregor - Coach, AIS Swimming Lachlan Mitchell - PhD Scholar, AIS Physiology
 SAL & AIS Talent Identification Findings Drew McGregor - Coach, AIS Swimming Lachlan Mitchell - PhD Scholar, AIS Physiology Talent vs. Potential What should we be trying to identify? Talent Natural aptitude
SAL & AIS Talent Identification Findings Drew McGregor - Coach, AIS Swimming Lachlan Mitchell - PhD Scholar, AIS Physiology Talent vs. Potential What should we be trying to identify? Talent Natural aptitude
This article has been downloaded from JPES Journal of Physical Education an Sport Vol 24, no 3, September, 2009 e ISSN: p ISSN:
 C I T I U S A L T I U S F O R T I U S - J O U R N A L O F P H Y S I C A L E D U C A T I O N A N D S P O R T This article has been downloaded from JPES ORIGINAL RESEARCH INTRODUCTION Shooting is the principal
C I T I U S A L T I U S F O R T I U S - J O U R N A L O F P H Y S I C A L E D U C A T I O N A N D S P O R T This article has been downloaded from JPES ORIGINAL RESEARCH INTRODUCTION Shooting is the principal
The effect of cognitive intervention on stroke distance in age-group swimmers
 The effect of cognitive intervention on stroke distance in age-group swimmers Anna C Schmidt 1, Bodo E Ungerechts 2 1 University of Göttingen, Department of Society and Training, Germany ² University of
The effect of cognitive intervention on stroke distance in age-group swimmers Anna C Schmidt 1, Bodo E Ungerechts 2 1 University of Göttingen, Department of Society and Training, Germany ² University of
Energy Systems and Growth
 Energy Systems and Growth Understanding Energy Systems and Growth Understanding how your body produces energy is vital to understanding why you train in certain ways to enhance your energy systems and
Energy Systems and Growth Understanding Energy Systems and Growth Understanding how your body produces energy is vital to understanding why you train in certain ways to enhance your energy systems and
An Investigation on the Anthropometric Profile and Its Relationship with Physical Performance of Adolescent Indian Swimmers A Comparative Study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 3 Ver. I (March. 2017), PP 118-126 www.iosrjournals.org An Investigation on the Anthropometric
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 3 Ver. I (March. 2017), PP 118-126 www.iosrjournals.org An Investigation on the Anthropometric
Qualitative Analysis of Jumping Standing Long Jump Goals Note: Standing Long Jump
 Qualitative Analysis of Jumping Standing Long Jump *Any time a person or object is launched into the air Ex- jumping, diving, gymnastics, throwing, or striking Goals: 1. Distance Ex: standing long jump,
Qualitative Analysis of Jumping Standing Long Jump *Any time a person or object is launched into the air Ex- jumping, diving, gymnastics, throwing, or striking Goals: 1. Distance Ex: standing long jump,
LONG TERM ATHLETE DEVELOPMENT TESTING
 LONG TERM ATHLETE DEVELOPMENT TESTING GENERAL ATHLETIC, SWIMMING and SYNCHRO SKILLS LEARN TO TRAIN 9-10 & 11-12 TRAIN TO TRAIN 11-12 & 13-15 2018-2019 Season 2017-2018 Skills Land Video If this link does
LONG TERM ATHLETE DEVELOPMENT TESTING GENERAL ATHLETIC, SWIMMING and SYNCHRO SKILLS LEARN TO TRAIN 9-10 & 11-12 TRAIN TO TRAIN 11-12 & 13-15 2018-2019 Season 2017-2018 Skills Land Video If this link does
ASSISTED AND RESISTED METHODS FOR SPEED DEVELOPMENT (PART 1)
 ASSISTED AND RESISTED METHODS FOR SPEED DEVELOPMENT (PART 1) By Adrian Faccioni Adrian Faccioni, a lecturer at the Centre of Sports Studies, University of Canberra, Australia, presents a detailed evaluation
ASSISTED AND RESISTED METHODS FOR SPEED DEVELOPMENT (PART 1) By Adrian Faccioni Adrian Faccioni, a lecturer at the Centre of Sports Studies, University of Canberra, Australia, presents a detailed evaluation
SWIMMING EXERCISES FOR STIMULATING ARM PULL SUPPORT REACTION. Jeļena Solovjova, Egita Sproģe, Evita Volkova
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH PAPER LASE JOURNAL OF SPORT SCIENCE 2011/2/1 57 SWIMMING EXERCISES FOR STIMULATING ARM PULL SUPPORT REACTION Jeļena Solovjova, Egita Sproģe, Evita Volkova Latvian Academy of Sport Education,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH PAPER LASE JOURNAL OF SPORT SCIENCE 2011/2/1 57 SWIMMING EXERCISES FOR STIMULATING ARM PULL SUPPORT REACTION Jeļena Solovjova, Egita Sproģe, Evita Volkova Latvian Academy of Sport Education,
#408 Stir Fried Noodles Presented by Marietta Mehanni
 #408 Presented by Marietta Mehanni www.mariettamehanni.com The Noodle Noodles have been a long-time popular item in the aqua class. Initially introduced as a rehabilitation tool, it now used for a variety
#408 Presented by Marietta Mehanni www.mariettamehanni.com The Noodle Noodles have been a long-time popular item in the aqua class. Initially introduced as a rehabilitation tool, it now used for a variety
Colin Jackson's Hurdle Clearance Technique
 Colin Jackson's Hurdle Clearance Technique By Milan Čoh, Biomechanical Laboratory, Faculty of Sport, University of Ljubljana, Slovenia INTRODUCTION Colin Jackson is, uncontestedly, one of the greatest
Colin Jackson's Hurdle Clearance Technique By Milan Čoh, Biomechanical Laboratory, Faculty of Sport, University of Ljubljana, Slovenia INTRODUCTION Colin Jackson is, uncontestedly, one of the greatest
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN TAEKWONDO ROUNDHOUSE KICK EXECUTED BY THE FRONT AND BACK LEG - A BIOMECHANICAL STUDY
 268 Isas 2000! Hong Kong DIFFERENCE BETWEEN TAEKWONDO ROUNDHOUSE KICK EXECUTED BY THE FRONT AND BACK LEG - A BIOMECHANICAL STUDY Pui-Wah Kong, Tze-Chung Luk and Youlian Hong The Chinese University of Hong
268 Isas 2000! Hong Kong DIFFERENCE BETWEEN TAEKWONDO ROUNDHOUSE KICK EXECUTED BY THE FRONT AND BACK LEG - A BIOMECHANICAL STUDY Pui-Wah Kong, Tze-Chung Luk and Youlian Hong The Chinese University of Hong
Comparative characteristics of elite New Zealand and South African u/16 rugby players with reference to gamespecific
 original research ARTICLE Comparative characteristics of elite New Zealand and South African u/16 rugby players with reference to gamespecific skills, physical abilities and anthropometric data Emanuel
original research ARTICLE Comparative characteristics of elite New Zealand and South African u/16 rugby players with reference to gamespecific skills, physical abilities and anthropometric data Emanuel
Chapter I examines the anthropometric and physiological factors that. determine success in sport. More specifically it discusses the somatotype
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Chapter I examines the anthropometric and physiological factors that determine success in sport. More specifically it discusses the somatotype ratings, VO 2 max and running economy
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Chapter I examines the anthropometric and physiological factors that determine success in sport. More specifically it discusses the somatotype ratings, VO 2 max and running economy
Chapter III PROCEDURE SELECTION OF SUBJECTS
 69 Chapter III PROCEDURE In this chapter, the selection of subjects, selection of variables, criterion measures, collection of data, reliability of data, administration of tests/procedure of recording
69 Chapter III PROCEDURE In this chapter, the selection of subjects, selection of variables, criterion measures, collection of data, reliability of data, administration of tests/procedure of recording
Coaching the Hurdles
 Coaching the Hurdles Monica Gary, Sprints & Hurdles Coach Purdue University Important components to consider in hurdle training: a. Rhythm for the hurdler is the primary concern for the coach -short rhythm
Coaching the Hurdles Monica Gary, Sprints & Hurdles Coach Purdue University Important components to consider in hurdle training: a. Rhythm for the hurdler is the primary concern for the coach -short rhythm
APPROACH RUN VELOCITIES OF FEMALE POLE VAULTERS
 APPROACH RUN VELOCITIES OF FEMALE POLE VAULTERS Peter M. McGinnis, Physical Education Department, SUNY College at Cortland, Cortland, New York INTRODUCTION Running speed is an important determinant of
APPROACH RUN VELOCITIES OF FEMALE POLE VAULTERS Peter M. McGinnis, Physical Education Department, SUNY College at Cortland, Cortland, New York INTRODUCTION Running speed is an important determinant of
The Optimal Downhill Slope for Acute Overspeed Running
 International Journal of Sports Physiology and Performance, 2008, 3, 88-93 2008 Human Kinetics, Inc. The Optimal Downhill Slope for Acute Overspeed Running William P. Ebben Purpose: This study evaluated
International Journal of Sports Physiology and Performance, 2008, 3, 88-93 2008 Human Kinetics, Inc. The Optimal Downhill Slope for Acute Overspeed Running William P. Ebben Purpose: This study evaluated
ARE YOU A SLOW- OR A FAST-TWITCH RUNNER?
 ARE YOU A SLOW- OR A FAST-TWITCH RUNNER? How can we individualize our training towards our different goals based on our muscular makeup? In this article you will learn how to decide if you are a Fast-twitch,
ARE YOU A SLOW- OR A FAST-TWITCH RUNNER? How can we individualize our training towards our different goals based on our muscular makeup? In this article you will learn how to decide if you are a Fast-twitch,
FITNESS TESTING PKG. REPORT AND SPARQ PROTOCOL
 FITNESS TESTING PKG. REPORT AND PROTOCOL BC SOCCER FITNESS TEST PACKAGE INTRODUCTION Over the past 6 years, BC Soccer Provincial Team Programs and the CSA National Training Centre Program West have been
FITNESS TESTING PKG. REPORT AND PROTOCOL BC SOCCER FITNESS TEST PACKAGE INTRODUCTION Over the past 6 years, BC Soccer Provincial Team Programs and the CSA National Training Centre Program West have been
Monitoring of performance an training in rowers
 Monitoring of performance an training in rowers Jaak Jürimäe Demands of the Sport High maximal oxygen consumption (VO 2max ); Ability to perform at a high percentage of VO 2max for the duration of event;
Monitoring of performance an training in rowers Jaak Jürimäe Demands of the Sport High maximal oxygen consumption (VO 2max ); Ability to perform at a high percentage of VO 2max for the duration of event;
ADVANCED SWIMMING PROGRAM
 Ready, Set - GOAL! ADVANCED SWIMMING PROGRAM Welcome to Ready, Set, Goal- Swim. Ready Set Goal is a four month physical activity training tool for beginner, intermediate and advanced level participants.
Ready, Set - GOAL! ADVANCED SWIMMING PROGRAM Welcome to Ready, Set, Goal- Swim. Ready Set Goal is a four month physical activity training tool for beginner, intermediate and advanced level participants.
RIGGING INTRODUCTION ADJUSTMENTS
 RIGGING In rowing rigging is a generic term used to cover both gearing and the rig. Strictly speaking rigging applies to the type of boat and oars while gearing is the arrangement to match the load to
RIGGING In rowing rigging is a generic term used to cover both gearing and the rig. Strictly speaking rigging applies to the type of boat and oars while gearing is the arrangement to match the load to
VALIDITY OF SELECTED CARDIOVASCULAR FIELD-BASED TEST AMONG MALAYSIAN HEALTHY FEMALE ADULT. S. H. Azmi 1,*, and N. Sulaiman 2
 Journal of Fundamental and Applied Sciences ISSN 1112-9867 Research Article Special Issue Available online at http://www.jfas.info VALIDITY OF SELECTED CARDIOVASCULAR FIELD-BASED TEST AMONG MALAYSIAN HEALTHY
Journal of Fundamental and Applied Sciences ISSN 1112-9867 Research Article Special Issue Available online at http://www.jfas.info VALIDITY OF SELECTED CARDIOVASCULAR FIELD-BASED TEST AMONG MALAYSIAN HEALTHY
Changes in speed and efficiency in the front crawl swimming technique at 100m track
 Proceeding 10th INSHS International Christmas Sport Scientific Conference, 4-5 December 2015. International Network of Sport and Health Science. Szombathely, Hungary Changes in speed and efficiency in
Proceeding 10th INSHS International Christmas Sport Scientific Conference, 4-5 December 2015. International Network of Sport and Health Science. Szombathely, Hungary Changes in speed and efficiency in
Strength and Conditioning
 Strength and Conditioning The Importance of Strength and Conditioning for Swimmers All the top swimmers in the world today engage in some form of strength and conditioning training to complement their
Strength and Conditioning The Importance of Strength and Conditioning for Swimmers All the top swimmers in the world today engage in some form of strength and conditioning training to complement their
Review Supplement Info Waist-to hip Ratio, Gurth Measurements & Skin Fold
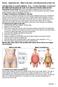 THIS MATERIAL IS A SUPPLEMENTAL TOOL. IT IS NOT INTENDED TO REPLACE INFORMATION PROVIDED IN YOUR TEXT AND/OR STUDENT HAND-BOOKS. Assessing Percent Body Fat: While hydrostatic weighing and the Bod Pod are
THIS MATERIAL IS A SUPPLEMENTAL TOOL. IT IS NOT INTENDED TO REPLACE INFORMATION PROVIDED IN YOUR TEXT AND/OR STUDENT HAND-BOOKS. Assessing Percent Body Fat: While hydrostatic weighing and the Bod Pod are
Weightlifting for Improved Swimming Performance University of Michigan Strength and Conditioning - Olympic Sports
 Weightlifting for Improved Swimming Performance University of Michigan Strength and Conditioning - Olympic Sports Katlyn Haycock MS, CSCS, SCCC, USAW-1 Strength and Conditioning Coach, Olympic Sports Outline
Weightlifting for Improved Swimming Performance University of Michigan Strength and Conditioning - Olympic Sports Katlyn Haycock MS, CSCS, SCCC, USAW-1 Strength and Conditioning Coach, Olympic Sports Outline
Towards determining absolute velocity of freestyle swimming using 3-axis accelerometers
 Towards determining absolute velocity of freestyle swimming using 3-axis accelerometers Author Stamm, Andy, Thiel, David, Burkett, Brendan, James, Daniel Published 2011 Journal Title Procedia Engineering
Towards determining absolute velocity of freestyle swimming using 3-axis accelerometers Author Stamm, Andy, Thiel, David, Burkett, Brendan, James, Daniel Published 2011 Journal Title Procedia Engineering
THE TECHNICAL ECONOMY INDEX: A tool for cyclic sports
 THE TECHNICAL ECONOMY INDEX: A tool for cyclic sports Enid M Ginn PhD The Performance Edge: Fitness & Health Services In aquatic sports such as swimming, kayaking and rowing, a high degree of technical
THE TECHNICAL ECONOMY INDEX: A tool for cyclic sports Enid M Ginn PhD The Performance Edge: Fitness & Health Services In aquatic sports such as swimming, kayaking and rowing, a high degree of technical
A Pilot Study on Electromyographic Analysis of Single and Double Revolution Jumps in Figure Skating
 Journal of Exercise Science and Physiotherapy, Vol. 5, No. 1: 14-19, 2009 A Pilot Study on Electromyographic Analysis of Single and Double Revolution Jumps in Figure Skating Taylor¹, C. L. and Psycharakis²,
Journal of Exercise Science and Physiotherapy, Vol. 5, No. 1: 14-19, 2009 A Pilot Study on Electromyographic Analysis of Single and Double Revolution Jumps in Figure Skating Taylor¹, C. L. and Psycharakis²,
