Infrared thermography of the damage of natural gut string
|
|
|
- Flora Chambers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Infrared thermography of the damage of natural gut string by M.P. Luong CNRS UMR 7649, Laboratoire de Mécanique des Solides, Ecole Polytechnique, Palaiseau Cedex, Abstract: The paper aims to illustrate three advantages of infrared thermography as a non-destructive, noncontact and in real time technique (a) to detect the occurrence of intrinsic dissipation localisation, (b) to observe the progressive damage processes and mechanisms of gut string failure, and to determine the optimal tensions for each type of tennis strings. Experimental results evidence a limit of acceptable damage beyond which string will fail due to coalescence of defects and/or weakness zones. In addition this useful technique has been used for a quantitative evaluation of fretting fatigue of tennis strings. 1. Introduction Damage and failure behaviour of natural gut strings and others types of tennis racket strings in synthetic products are an important consideration for skilled tennis players who should be extremely aware of their equipment s performance relative to their personal needs and game style. What mechanical performance in string tensions that will best fit the player s requirements? Borg strung his rackets at 80 pounds (367 N) and strings often broke from the high tension. On the contrary, McEnroe chose 48 pounds (220 N) for stringing his rackets. Commonly the recommendations are in a range of about 55 to 65 pounds (250 N to 295 N). The tension is very important as it has a direct effect on power and control. As a general rule, the looser the tension, says in the 50-pound range, the less control the player has. The racket acts more like a trampoline and the ball may fly off the strings and appear to have more speed. Tighter strings, say in the 60-pound range, will give more control over the shot. The pros often string their rackets in the 70-pound range. This gives them a lot of control but the strings break faster. Much engineering research has been conducted to determine optimal string tension for different size rackets made from various types of materials [7]. The limit of acceptable damage in tension for most of these tennis strings could likely be ranged between these two values. This work proposes to determine objectively this tension threshold from the material point of view, using an infrared thermographic technique and may suggest to manufacturers material optimisation of string products. In addition this technique can be used as a non-destructive, non-contact and in real time method for inspection and ready evaluation of stress concentration in strung rackets. 2. Proposed method This work considers the intrinsic dissipation, generated by plasticity, as a highly sensitive and accurate indicator of damage manifestation. Thanks to the thermomechanical coupling [9], infrared thermography is used to observe the physical processes of damage and to detect the onset and the evolution of damage and failure processes of tennis string when the string specimen is subjected to increasing tensile loading. It readily gives a measure of the material damage and permits to evaluate the limit of a progressive damaging process under tension beyond which the material is led to failure. Infrared thermography is a convenient technique for producing heat images from the invisible radiant energy emitted from stationary or moving objects at any distance and without surface contact or in any way influencing the actual surface temperature of the
2 objects viewed. The temperature rise ahead of a fatigue crack has been measured using a thermographic camera [1] in order to demonstrate the local heating at the tip predicted by Barenblatt et al. [3]. Attempts have been made to measure and characterise the heat generated during the cyclic straining of composite materials [12]. The scanning infrared camera has been used to visualise the surface-temperature field on steel and Fiberglasepoxy composite samples during fatigue tests [5]. Recently this infrared thermographic technique has been applied in sport engineering [10], [11]. For this work, the scanning camera utilises a unique infrared detector in a sophisticated electronics system in order to detect radiated energy and to convert it into a detailed real time thermal image in a colour and monochrome video system. Response times are shorter than one microsecond. Temperature differences in the heat patterns are discernible instantly and represented by several distinct hues. The quantity of energy W (W.m -2. m -1 ), emitted as infrared radiation, is a function of the temperature and emissivity of the specimen. The higher the temperature, the more important the emitted energy. Differences of radiated energy correspond to differences of temperature. Since the received radiation has non-linear relationship to the object s temperature, and can be affected by atmosphere damping and includes reflected radiation from object s surroundings, calibration and correction procedures have to be applied. Knowing the temperature of the reference, the object s temperature can then be calculated with a sensitivity of 0.1 C at 20 C. The infrared scanner unit converts electromagnetic thermal energy radiated from the tested specimen into electronic video signals. These signals are amplified and transmitted via an interconnecting cable to display monitor where the signals are further amplified and the resultant image is displayed on the screen. 3. Experimental result Mechanical properties of tennis racket strings are mainly dependent on its type (natural gut, artificial gut, nylon, graphite string, synthetic products, etc.), nature and structure. Manufacturers give players a choice of string styles. The higher the number, the thinner the gauge (or thickness) of the string. Consumers can choose 15-gauge, 16-gauge, 17-gauge, 18-gauge and even 19-gauge strings: the lower the gauge number, the lighter the string. Lower gauge strings, like 16, last longer and are good for players who hit with a lot of spin. Thinner gauges of string are livelier and can impart more ball spin but likely break sooner. This fact suggests that there is an instantaneous non-linear phenomenon creating large displacements and large deformations due to Coulomb friction at string nodes: wear by fretting. This aspect will be examined thereafter in the case of natural gut. Better players like to use 17-gauge or 18-gauge as this gives them more touch and feel. The effect of varying string tensions is important to skilled players wanting to improve their shot velocity and control. The looser the strings (within the recommended range), the higher the ball velocity after impact [6]. When string is loaded, it deforms as a whole in spite of its heterogeneous characteristics and its localised defects. Stress concentrations occur and result in localised forces that are sufficient to promote plasticity and inelasticity. At the structural level, breakdown appears as micro cracking and possibly slippage at component interfaces. Failure mechanisms of string specimens subject to tensile loading are readily evidenced by infrared thermography in this work. Uniaxial tensile tests were carried out for 2 types of tennis strings: natural gut and synthetic fibres. 4. Natural gut string Gut is an animal s natural fibre, manufactured from the smooth muscle portion of sheep or beef intestines (Figure 1a) through sophisticated chemical process of washing, bleaching, twisting, drying, and refining to ensure strength and uniformity [2]. When loaded in tension
3 (2a), natural gut string undergoes plasticity (2b-2c) that is detected by infrared thermography. Subtractions of raw thermal images evidence dissipative phenomenon (2d- 2e) that locates the failure of gut string. When tensile loading is applied up to failure (Figure 1b), the evolution of dissipation suggests the definition of a limit of acceptable damage (LAD) that separates low and high regimes of dissipation or damage manifestation (Figure 3). 5. Synthetic string Material composites have increased the diversity of design and manufacturing for sports products. There are a large variety of synthetic products (Figure 4a) including nylon, artificial gut, graphite string, oil-filled string, etc. Very specific designs are targeted to match the physical and levels of each player. How to characterise their mechanical performance in term of damage and durability? In the interaction of the ball and the strings, the kinetic energy of the ball is converted into potential energy stored in both ball and string deformation. By storing a larger fraction of the incoming energy in the strings, less is dissipated, and more is returned to the ball s rebounding kinetic energy [4]. The shock vibrations of the wrist joint are transmitted from the racket with an impulse at the impact location and several vibration mode components of the racket frame and strings [8]. The higher the string tensions the higher the vibration frequency. This fact influences the feel or comfort of the arm or hand in an impact. As tension increases, the elasticity of these materials degrades. Dissipation occurs and infrared thermography readily detects the manifestation and localisation of damage. When tensile loading is applied up to failure, the evolution of dissipation suggests the definition of a limit of acceptable damage (LAD) that separates low and high regimes of dissipation or damage (Figure 4b), similarly as for natural gut (Figure 5). 6. Dry sliding of natural gut string at nodes In order to produce ball spin in tennis, the player must accelerate the racket head through impact to brush the backside of the ball : upward for topspin, downward for underspin and sideways for sidespin. The more vertical (or horizontal) the racket swings (in either direction), the more ball spin will be produced. The amount of spin a player imparts on the ball, combined with a high stroke velocity, generates dry sliding between longitudinal and transverse strings at nodes located in the racket s effective hitting zone. Relative movements between longitudinal and transverse strings occur depending on the type of ball-racket impact. They lead to tribological phenomena, such as friction, wear, pitting and fretting fatigue. Fretting is a major problem in optimising tennis strings. It is defined as the surface damage induced by small-amplitude oscillatory displacements between strings in contact. This damage can either be wear or crack nucleation, depending on the prescribed forces or the displacements amplitude. Infrared thermography has been used to estimate tribological parameters, such as a frictional temperature rise, the shape and the size contact of the contact area. We consider a contact problem, in which a moving longitudinal string (9cm long) is in contact with a fixed transverse string (5cm long). The two strings were initially stretched at 200N. An electromagnetic vibrator at a frequency of 1Hz controls the cyclic motion of the longitudinal string. Force sensors respectively measure the normal and tangential contact forces during testing (Figure 6). Infrared thermography readily detects heat dissipation by Coulomb friction at contact location where sliding occurs between longitudinal and transverse gut strings in the following
4 cases: initial normal contact force NCF = 50N (Figure 6). The experimental data demonstrates that wear phenomena occurring in tennis rackets could be of interest in case of long matches such as the men s final of 1988 US open Tennis Tournament Lendl versus Wilander (4 hours, 54 minutes with several thousands of strokes). The main parameters identified are string tension, racket stiffness, effects of spin, hitting power, etc. 6. Conclusion This work has demonstrated that the dissipativity of tennis string material under tension or frictional loading is highly sensitive and accurate manifestation of damage. Owing to the thermomechanical coupling, infrared thermography offers the possibility of a non-destructive, non-contact testing of string degradation and damage. It provides a ready evaluation of a limit of acceptable damage under load, beyond which the string will fail. The opportunities offered by thermal techniques with remote operation and fast surface-scanning rates are particularly attractive for sport equipment. References [1] ATTERMO, R. and ÖSTBERG, G., Measurements of the temperature rise of a fatigue crack, International Fracture Mechanics, 7, 1971, p [2] BABOLAT, D. L., Squash, Tennis, Badminton, CH/F/B, 1996, p 2-14 [3] BARENBLATT, G. I., ENTOV, V. M. and SALGANIK, R. L., On the influence of vibrational heating on the fracture propagation in polymeric materials, IUTAM Symp. Thermoinelasticity, East Kilbride, 1968 [4] BRODY, H., The modern tennis racket, The Engineering of Sport, ed. by Haake, Balkema, ISBN , 1996, p [5] CHARLES, J. A., APPL,. J. & FRANCIS, J. E., Using the scanning infrared camera in experimental fatigue studies, Experimental Mechanics, 14(4), 1975, p [6] GROPPEL, J. L., High Tech Tennis, Leisure Press, Champaign, Illinois, 2 nd Edition, ISBN , 1992 [7] GROPPEL, J. L., SHIN, I. S., THOMAS, J. A. and WELK, G. J., The effects of string type and tension on impact in midsized and oversized tennis racquets, International Journal of Sport Biomechanics, 3, 1987, p [8] KAWAZOE, Y., TOMOSUE, R. and YOSHINARI, K., Performance prediction of tennis rackets with different racket head size: impact shock vibrations of a racket grip and a player s wrist joint, The Engineering of Sport, ed. by Haake, 1998 Blackwell Science, ISBN , p [9] LUONG, M. P., Infrared thermography of macrostructural aspects of thermoplasticity, Micro- and Macrostructural Aspects of Thermoplasticity, ed. by Bruhns & Stein, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Solid Mechanics and its Applications, 62, 1999, p [10] LUONG, M. P., PARGANIN, D. and LOIZEAU, J., Non destructive detection of damage in soccer balls using infrared thermography, The Engineering of Sport, ed. by Haake, Blackwell Science, ISBN , 1998, p [11] PARGANIN, D., LUONG, M. P. and LOIZEAU J. (1998) Infrared scanning of damage in sail materials, The Engineering of Sport, ed. by Haake, 1998 Blackwell Science, ISBN , 1998, p [12] REIFSNIDER, K. L. and WILLIAMS, R. S., Determination of fatigue-related heat emission in composite materials, Experimental Mechanics, 14(12), 1974, p
5 Tension (N) Tension (N) Elonga tion (m m ) 1a. Electronic microscope view 1b. Tension-elongation curve Figure 1 : Natural gut string (2b) (2c) (2a) (2bd) (2cd) Figure 2 : Tension on natural gut string (2a), raw thermal images (2b and 2c) at different tensile levels preceding failure and their corresponding dissipation localisation (2bd and 2cd) LAD D is s ipation ( C) Figure 3 : Limit of acceptable damage of natural gut string in tension
6 Tension (N) 0,8 0,6 0,4 LAD 0, Dissipation ( C) 4a. Electronic microscope view 4b. Limit of acceptable damage Figure 4 : Synthetic fibres string (5a) (5b) (5c) (5ad) (5bd) (5cd) Figure 5 : Successive thermal images at different tensile levels (5a-5b-5c) preceding failure and their corresponding dissipation locations (5ad-5bd-5cd) 6a. Experimental set-up for fretting fatigue testing 6b. Heat dissipation after 10 load cycles 6c. Heat dissipation after 20 load cycles Figure 6 : Investigating dry sliding of natural gut string at nodes
*2, *4 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Saitama Institute of Technology, 1690, Okabe, Saitama, , Japan
 1900 C No.. 05-0903 72718(2006-6) *1 *2, * Mechanism of Racket Spin Performance in Tennis (Spin Performance Improvement by Lubrication of String Intersections with Super High Speed Video Analysis) Yoshihiko
1900 C No.. 05-0903 72718(2006-6) *1 *2, * Mechanism of Racket Spin Performance in Tennis (Spin Performance Improvement by Lubrication of String Intersections with Super High Speed Video Analysis) Yoshihiko
*4 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Saitama Institute of Technology, 1690, Okabe, Saitama, , Japan
 19 CNo.. 5-93 72718(26-6) *1 *2, * Mechanism of Racket Spin Performance in Tennis (Spin Performance Improvement by Lubrication of String Intersections with Super High Speed Video Analysis) Yoshihiko KAWAZOE
19 CNo.. 5-93 72718(26-6) *1 *2, * Mechanism of Racket Spin Performance in Tennis (Spin Performance Improvement by Lubrication of String Intersections with Super High Speed Video Analysis) Yoshihiko KAWAZOE
A MODEL FOR ANALYSIS OF THE IMPACT BETWEEN A TENNIS RACKET AND A BALL
 A MODEL FOR ANALYSIS OF THE IMPACT BETWEEN A TENNIS RACKET AND A BALL Hiroshi Maeda, Masaaki Okauchi and Yoshio Shimada Faculty of Engineering, Oita University, Oita City, Oita, Japan The purpose of this
A MODEL FOR ANALYSIS OF THE IMPACT BETWEEN A TENNIS RACKET AND A BALL Hiroshi Maeda, Masaaki Okauchi and Yoshio Shimada Faculty of Engineering, Oita University, Oita City, Oita, Japan The purpose of this
Friction properties of the face of a hand-held tennis racket
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 34 (2012 ) 544 549 9 th Conference of the International Sports Engineering Association (ISEA) Friction properties of the face of a hand-held
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 34 (2012 ) 544 549 9 th Conference of the International Sports Engineering Association (ISEA) Friction properties of the face of a hand-held
Procedia Engineering 00 2 (2010) (2009) Properties of friction during the impact between tennis racket surface and ball
 Procedia Engineering 00 2 (2010) (2009) 000 000 2973 2978 Procedia Engineering www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia 8 th Conference of the International Sports Engineering Association (ISEA) Properties of
Procedia Engineering 00 2 (2010) (2009) 000 000 2973 2978 Procedia Engineering www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia 8 th Conference of the International Sports Engineering Association (ISEA) Properties of
Journal of System Design and Dynamics
 Mechanism of Tennis Racket Spin Performance* (Ultra-High-Speed Video Analysis of Spin Performance Improvement by Lubrication of String Intersections) Yoshihiko KAWAZOE**, Kenji OKIMOTO*** and Keiko OKIMOTO***
Mechanism of Tennis Racket Spin Performance* (Ultra-High-Speed Video Analysis of Spin Performance Improvement by Lubrication of String Intersections) Yoshihiko KAWAZOE**, Kenji OKIMOTO*** and Keiko OKIMOTO***
Finite Element Simulation of Ball-On-Tennis Racket Impacts Using ABAQUS/CAE
 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-03, Issue-05, pp-151-155 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Finite Element Simulation of Ball-On-Tennis
American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-03, Issue-05, pp-151-155 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Finite Element Simulation of Ball-On-Tennis
Wave and particle models of physical phenomena
 Ch15Lectures Page 1 Chapter 15: Travelling Waves and Sound Wave and particle models of physical phenomena In mechanics, we made frequent use of particle models of physical phenomena; in this course we'll
Ch15Lectures Page 1 Chapter 15: Travelling Waves and Sound Wave and particle models of physical phenomena In mechanics, we made frequent use of particle models of physical phenomena; in this course we'll
Slide 1 / The distance traveled by a wave in one period is called? Frequency Period Speed of wave Wavelength Amplitude
 Slide 1 / 20 1 The distance traveled by a wave in one period is called? Frequency Period Speed of wave Wavelength mplitude Slide 2 / 20 2 Which of the following is the speed of a wave traveling with a
Slide 1 / 20 1 The distance traveled by a wave in one period is called? Frequency Period Speed of wave Wavelength mplitude Slide 2 / 20 2 Which of the following is the speed of a wave traveling with a
ITF Coaches Education Programme Biomechanics of the forehand stroke
 ITF Coaches Education Programme Biomechanics of the forehand stroke Original article: Bahamonde, R. (2001). ITF CSSR, 24, 6-8 Introduction The tennis forehand stroke has changed drastically over the last
ITF Coaches Education Programme Biomechanics of the forehand stroke Original article: Bahamonde, R. (2001). ITF CSSR, 24, 6-8 Introduction The tennis forehand stroke has changed drastically over the last
15815 Super Spring - Student
 Accessories Needed, Not Included: PURPOSE 15815 Super Spring - Student Required Accessories: string (2 to 4 meters needed) C-clamp (or any other fixed clamp on a bench) Stopwatch masking tape or labels
Accessories Needed, Not Included: PURPOSE 15815 Super Spring - Student Required Accessories: string (2 to 4 meters needed) C-clamp (or any other fixed clamp on a bench) Stopwatch masking tape or labels
An underwater explosion is an explosion where the point of detonation is below the surface of the water.
 Underwater Explosion 1 Introduction An underwater explosion is an explosion where the point of detonation is below the surface of the water. Underwater explosion are categorized in accordance with their
Underwater Explosion 1 Introduction An underwater explosion is an explosion where the point of detonation is below the surface of the water. Underwater explosion are categorized in accordance with their
Chapter 11 Waves. Waves transport energy without transporting matter. The intensity is the average power per unit area. It is measured in W/m 2.
 Chapter 11 Waves Energy can be transported by particles or waves A wave is characterized as some sort of disturbance that travels away from a source. The key difference between particles and waves is a
Chapter 11 Waves Energy can be transported by particles or waves A wave is characterized as some sort of disturbance that travels away from a source. The key difference between particles and waves is a
Chapter 11 Waves. Waves transport energy without transporting matter. The intensity is the average power per unit area. It is measured in W/m 2.
 Energy can be transported by particles or waves: Chapter 11 Waves A wave is characterized as some sort of disturbance that travels away from a source. The key difference between particles and waves is
Energy can be transported by particles or waves: Chapter 11 Waves A wave is characterized as some sort of disturbance that travels away from a source. The key difference between particles and waves is
PHYSICS - GIANCOLI CALC 4E CH 15: WAVE MOTION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: WHAT IS A WAVE? A WAVE is a moving disturbance (oscillation) that carries energy. - A common example is a wave on a string, where the moving string carries energy We re only
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: WHAT IS A WAVE? A WAVE is a moving disturbance (oscillation) that carries energy. - A common example is a wave on a string, where the moving string carries energy We re only
Multi-directional Vibration Analysis of Cricket bats
 Multi-directional Vibration Analysis of Cricket bats Sabu John & Zhu Bang Li RMIT University, Department of Mechanical & Manufacturing Engineering, Bundoora East Campus, Bundoora, Vic. 3083, Australia.
Multi-directional Vibration Analysis of Cricket bats Sabu John & Zhu Bang Li RMIT University, Department of Mechanical & Manufacturing Engineering, Bundoora East Campus, Bundoora, Vic. 3083, Australia.
Resonance in Transverse Waves. Regents Physics
 Title: Resonance in Transverse Waves Original: Revision: Authors: Appropriate Level: Abstract: Time Required: NY Standards Met: Special Notes: 1 July 2004 4 April 2008 Charlene Rydgren, Jeff Harbold, George
Title: Resonance in Transverse Waves Original: Revision: Authors: Appropriate Level: Abstract: Time Required: NY Standards Met: Special Notes: 1 July 2004 4 April 2008 Charlene Rydgren, Jeff Harbold, George
The ERSA and the industry will support MRTs competence and expertise by actively encouraging players to seek out MRTs for racquet sales and service.
 Supplimentary Study Guide Introduction The ERSA / USRSA initiated the original stringer Certification program in 1986 to recognize individuals with a basic level of stringing competence. Today s Master
Supplimentary Study Guide Introduction The ERSA / USRSA initiated the original stringer Certification program in 1986 to recognize individuals with a basic level of stringing competence. Today s Master
Waves Multiple Choice
 Waves Multiple Choice PSI Physics Name: 1. The distance traveled by a wave in one period is called? A. Frequency B. Period C. Speed of wave D. Wavelength E. Amplitude 2. Which of the following is the speed
Waves Multiple Choice PSI Physics Name: 1. The distance traveled by a wave in one period is called? A. Frequency B. Period C. Speed of wave D. Wavelength E. Amplitude 2. Which of the following is the speed
SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ANALYSIS OF ELASTOMERIC O-RINGS AND SPRING SEALS FRACTURED DURING RAPID GAS DECOMPRESSION.
 SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ANALYSIS OF ELASTOMERIC O-RINGS AND SPRING SEALS FRACTURED DURING RAPID GAS DECOMPRESSION. T. Mbwadzawo* and A. Hodzic Composite Systems Innovation Centre, Department of Mechanical
SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ANALYSIS OF ELASTOMERIC O-RINGS AND SPRING SEALS FRACTURED DURING RAPID GAS DECOMPRESSION. T. Mbwadzawo* and A. Hodzic Composite Systems Innovation Centre, Department of Mechanical
Core Concept. PowerPoint Lectures Physical Science, 8e. Chapter 5 Wave Motions and Sound. New Symbols for this Chapter 2/20/2011
 PowerPoint Lectures Physical Science, 8e Chapter 5 Wave Motions and Sound New Symbols for this Chapter T-Period f-frequency v-wave speed λ-wavelength A-Amplitude Sound is transmitted as increased and decreased
PowerPoint Lectures Physical Science, 8e Chapter 5 Wave Motions and Sound New Symbols for this Chapter T-Period f-frequency v-wave speed λ-wavelength A-Amplitude Sound is transmitted as increased and decreased
Define transverse waves and longitudinal waves. Draw a simple diagram of each
 AP Physics Study Guide Chapters 11, 12, 24 Waves, Sound, Light & Interference Name Write the equation that defines each quantity, include units for all quantities. wave speed-wavelength equation natural
AP Physics Study Guide Chapters 11, 12, 24 Waves, Sound, Light & Interference Name Write the equation that defines each quantity, include units for all quantities. wave speed-wavelength equation natural
Wave Motion. interference destructive interferecne constructive interference in phase. out of phase standing wave antinodes resonant frequencies
 Wave Motion Vocabulary mechanical waves pulse continuous periodic wave amplitude period wavelength period wave velocity phase transverse wave longitudinal wave intensity displacement amplitude phase velocity
Wave Motion Vocabulary mechanical waves pulse continuous periodic wave amplitude period wavelength period wave velocity phase transverse wave longitudinal wave intensity displacement amplitude phase velocity
Transverse waves cause particles to vibrate perpendicularly to the direction of the wave's motion (e.g. waves on a string, ripples on a pond).
 Waves Introduction A vibration must be the source of a wave. Waves in turn also cause vibrations. They are intrinsically connected. Waves transmit energy. There are different ways in which waves can be
Waves Introduction A vibration must be the source of a wave. Waves in turn also cause vibrations. They are intrinsically connected. Waves transmit energy. There are different ways in which waves can be
Chapter # 08 Waves. [WAVES] Chapter # 08
![Chapter # 08 Waves. [WAVES] Chapter # 08 Chapter # 08 Waves. [WAVES] Chapter # 08](/thumbs/94/121079132.jpg) Chapter # 08 Waves Q2) Write short answers of the following questions. i) What is the difference between progressive and stationary waves? Answer: Progressive Waves 1 Progressive waves are the result of
Chapter # 08 Waves Q2) Write short answers of the following questions. i) What is the difference between progressive and stationary waves? Answer: Progressive Waves 1 Progressive waves are the result of
Oblique impact of a tennis ball on the strings of a tennis racket
 Oblique impact of a tennis ball on the strings of a tennis racket Rod Cross Physics Department, University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia. Abstract Measurements are presented of the friction force acting
Oblique impact of a tennis ball on the strings of a tennis racket Rod Cross Physics Department, University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia. Abstract Measurements are presented of the friction force acting
GEA FOR ADVANCED STRUCTURAL DYNAMIC ANALYSIS
 SMART SOLUTIONS FOR VIBRATION MONITORING GEA FOR ADVANCED STRUCTURAL DYNAMIC ANALYSIS ANALYSIS OF CIVIL STRUCTURES - EXPO MERLATA PEDESTRIAN BRIDGE ABSTRACT Civil structures and in particular bridges and
SMART SOLUTIONS FOR VIBRATION MONITORING GEA FOR ADVANCED STRUCTURAL DYNAMIC ANALYSIS ANALYSIS OF CIVIL STRUCTURES - EXPO MERLATA PEDESTRIAN BRIDGE ABSTRACT Civil structures and in particular bridges and
Mechanical waves Electromagnetic waves
 Waves Energy can be transported by transfer of matter. For example by a thrown object. Energy can also be transported by wave motion without the transfer of matter. For example by sound waves and electromagnetic
Waves Energy can be transported by transfer of matter. For example by a thrown object. Energy can also be transported by wave motion without the transfer of matter. For example by sound waves and electromagnetic
Today: waves. Exam Results. Wave Motion. What is moving? Motion of a piece of the rope. Energy transport
 Exam: Exam scores posted on Learn@UW No homework due next week Exam Results D C BC B AB A Today: waves Have studied Newton s laws, motion of particles, momentum, energy, etc. Laws for describing things
Exam: Exam scores posted on Learn@UW No homework due next week Exam Results D C BC B AB A Today: waves Have studied Newton s laws, motion of particles, momentum, energy, etc. Laws for describing things
Original Article. The effectiveness of serve in tennis depending on the placement of palm across the racket grip inwards or outwards
 Journal of Physical Education and Sport (JPES), 14(4), Art 89, pp. 576-580, 2014 online ISSN: 2247-806X; p-issn: 2247 8051; ISSN - L = 2247-8051 JPES Original Article The effectiveness of serve in tennis
Journal of Physical Education and Sport (JPES), 14(4), Art 89, pp. 576-580, 2014 online ISSN: 2247-806X; p-issn: 2247 8051; ISSN - L = 2247-8051 JPES Original Article The effectiveness of serve in tennis
Sound waves... light waves... water waves...
 Sound waves... light waves... water waves... 1S-13 Slinky on Stand Creating longitudinal compression waves in a slinky What happens when you pull back and release one end of the slinky? 4/11/2011 Physics
Sound waves... light waves... water waves... 1S-13 Slinky on Stand Creating longitudinal compression waves in a slinky What happens when you pull back and release one end of the slinky? 4/11/2011 Physics
Waves. Kevin Small or
 Waves Opening note: X-rays can penetrate your body. Sound waves can make thinks vibrate; water waves can knock you over in the sea. Infrared waves can warm you up and slinky waves are fun to play with.
Waves Opening note: X-rays can penetrate your body. Sound waves can make thinks vibrate; water waves can knock you over in the sea. Infrared waves can warm you up and slinky waves are fun to play with.
Properties of waves. Definition:
 Properties of waves A wave motion is the ability of transferring energy from one point (the source) to another point without there being any transfer of matter between the two points. Waves are either
Properties of waves A wave motion is the ability of transferring energy from one point (the source) to another point without there being any transfer of matter between the two points. Waves are either
g L Agenda Chapter 13 Problem 28 Equations of Motion for SHM: What if we have friction or drag? Driven Oscillations; Resonance 4/30/14 k m f = 1 2π
 Agenda Today: HW quiz, More simple harmonic motion and waves Thursday: More waves Midterm scores will be posted by Thursday. Chapter 13 Problem 28 Calculate the buoyant force due to the surrounding air
Agenda Today: HW quiz, More simple harmonic motion and waves Thursday: More waves Midterm scores will be posted by Thursday. Chapter 13 Problem 28 Calculate the buoyant force due to the surrounding air
Physics Mechanics
 1 Physics 170 - Mechanics Lecture 33 Waves Wave notion 2 A wave pulse is a disturbance that propagates through a medium. It transfers energy without transferring matter; the energy is a combination of
1 Physics 170 - Mechanics Lecture 33 Waves Wave notion 2 A wave pulse is a disturbance that propagates through a medium. It transfers energy without transferring matter; the energy is a combination of
Analysis of fatigue failure in D-shaped karabiners
 Analysis of fatigue failure in D-shaped karabiners K.B. Blair, D.R. Custer, J.M. Graham, and M.H. Okal Center for Sports Innovation, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, USA Abstract In order to determine
Analysis of fatigue failure in D-shaped karabiners K.B. Blair, D.R. Custer, J.M. Graham, and M.H. Okal Center for Sports Innovation, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, USA Abstract In order to determine
Redesign of a Tennis Racket for Reduced Vibrations and Improved Control and Power. MENG 370 Design Project Report Fall 2012 Semester
 MENG 370: Element Machine Design, Fall 2012, Professor: Jong B. Lee, Ph.D. 1 Redesign of a Tennis Racket for Reduced Vibrations and Improved Control and Power MENG 370 Design Project Report Fall 2012 Semester
MENG 370: Element Machine Design, Fall 2012, Professor: Jong B. Lee, Ph.D. 1 Redesign of a Tennis Racket for Reduced Vibrations and Improved Control and Power MENG 370 Design Project Report Fall 2012 Semester
Waves-Wave Basics. 1. Which type of wave requires a material medium through which to travel? 1. sound 2. television 3. radio 4.
 Waves-Wave Basics 1. Which type of wave requires a material medium through which to travel? 1. sound 2. television 3. radio 4. x ray 2. A single vibratory disturbance moving through a medium is called
Waves-Wave Basics 1. Which type of wave requires a material medium through which to travel? 1. sound 2. television 3. radio 4. x ray 2. A single vibratory disturbance moving through a medium is called
Impact of a ball on a surface with tangential compliance
 Impact of a ball on a surface with tangential compliance Rod Cross a Department of Physics, University of Sydney, Sydney, New South Wales 26, Australia Received 8 September 29; accepted 2 January 2 A simple
Impact of a ball on a surface with tangential compliance Rod Cross a Department of Physics, University of Sydney, Sydney, New South Wales 26, Australia Received 8 September 29; accepted 2 January 2 A simple
Chs. 16 and 17 Mechanical Waves
 Chs. 16 and 17 Mechanical Waves The nature of waves A wave is a traveling disturbance that carries energy from one place to another, and even though matter may be disturbed as a wave travels through a
Chs. 16 and 17 Mechanical Waves The nature of waves A wave is a traveling disturbance that carries energy from one place to another, and even though matter may be disturbed as a wave travels through a
Mechanical Waves. Chapter 15. PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman
 Chapter 15 Mechanical Waves PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Wayne Anderson Goals for Chapter 15 To study the properties and
Chapter 15 Mechanical Waves PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Wayne Anderson Goals for Chapter 15 To study the properties and
EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SELECTED TAKRAW BALLS IN MALAYSIA
 Experimental Analysis Of Mechanical Properties Movement, Of Selected Health & Takraw Exercise, Balls 3, 57-63, In Malaysia 2014 EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SELECTED TAKRAW BALLS IN
Experimental Analysis Of Mechanical Properties Movement, Of Selected Health & Takraw Exercise, Balls 3, 57-63, In Malaysia 2014 EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SELECTED TAKRAW BALLS IN
The Kinematics Analysis of Wu Yibing's Tennis Forehand Technique Xin WEN, Ji-he ZHOU and Chuan-jia DU
 218 International Conference on Mechanical, Electronic and Information Technology (ICMEIT 218) ISBN: 978-1-6595-548-3 The Kinematics Analysis of Wu Yibing's Tennis Forehand Technique Xin WEN, Ji-he ZHOU
218 International Conference on Mechanical, Electronic and Information Technology (ICMEIT 218) ISBN: 978-1-6595-548-3 The Kinematics Analysis of Wu Yibing's Tennis Forehand Technique Xin WEN, Ji-he ZHOU
Preview. Vibrations and Waves Section 1. Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion. Section 2 Measuring Simple Harmonic Motion. Section 3 Properties of Waves
 Vibrations and Waves Section 1 Preview Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Section 2 Measuring Simple Harmonic Motion Section 3 Properties of Waves Section 4 Wave Interactions Vibrations and Waves Section
Vibrations and Waves Section 1 Preview Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Section 2 Measuring Simple Harmonic Motion Section 3 Properties of Waves Section 4 Wave Interactions Vibrations and Waves Section
Learn more at
 Full scale model tests of a steel catenary riser C. Bridge 1, H. Howells 1, N. Toy 2, G. Parke 2, R. Woods 2 1 2H Offshore Engineering Ltd, Woking, Surrey, UK 2 School of Engineering, University of Surrey,
Full scale model tests of a steel catenary riser C. Bridge 1, H. Howells 1, N. Toy 2, G. Parke 2, R. Woods 2 1 2H Offshore Engineering Ltd, Woking, Surrey, UK 2 School of Engineering, University of Surrey,
Impact Fatigue on Suction Valve Reed: New Experimental Approach
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2004 Impact Fatigue on Suction Valve Reed: New Experimental Approach Michele Libralato ACC
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2004 Impact Fatigue on Suction Valve Reed: New Experimental Approach Michele Libralato ACC
Measurement of court speed and bounce. Rod Cross, Physics Department, Sydney University 2nd July 2006
 1 Measurement of court speed and bounce Rod Cross, Physics Department, Sydney University 2nd July 2006 The speed of a surface refers to the change in ball speed in a direction parallel to the surface.
1 Measurement of court speed and bounce Rod Cross, Physics Department, Sydney University 2nd July 2006 The speed of a surface refers to the change in ball speed in a direction parallel to the surface.
THE BACKSPIN BACKHAND DRIVE IN TENNIS TO BALLS OF VARYING HEIGHT. B. Elliott and M. Christmass
 THE BACKSPIN BACKHAND DRIVE IN TENNIS TO BALLS OF VARYING HEIGHT B. Elliott and M. Christmass The Department of Human Movement The University of Western Australia Nedlands, Australia INTRODUCfION Modem
THE BACKSPIN BACKHAND DRIVE IN TENNIS TO BALLS OF VARYING HEIGHT B. Elliott and M. Christmass The Department of Human Movement The University of Western Australia Nedlands, Australia INTRODUCfION Modem
STRUCTURAL INTEGRITY EVALUATION OF CNG COMPOSITE CYLINDERS BY ACOUSTIC EMISSION MONITORING
 STRUCTURAL INTEGRITY EVALUATION OF CNG COMPOSITE CYLINDERS BY ACOUSTIC EMISSION MONITORING OLIVIER SKAWINSKI 1, PATRICE HULOT 1, CHRISTOPHE BINÉTRUY 1 and CHRISTIAN RASCHE 2 1 Department of Polymers and
STRUCTURAL INTEGRITY EVALUATION OF CNG COMPOSITE CYLINDERS BY ACOUSTIC EMISSION MONITORING OLIVIER SKAWINSKI 1, PATRICE HULOT 1, CHRISTOPHE BINÉTRUY 1 and CHRISTIAN RASCHE 2 1 Department of Polymers and
PHYSICS - CLUTCH CH 16: WAVES & SOUND.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: WHAT IS A WAVE? A WAVE is a moving disturbance (oscillation) that carries energy. - A common example is a wave on a string, where the moving string carries energy We re only
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: WHAT IS A WAVE? A WAVE is a moving disturbance (oscillation) that carries energy. - A common example is a wave on a string, where the moving string carries energy We re only
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 112 (2015 ) 40 45
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering ( ) 7th Asia-Pacific Congress on Sports Technology, APCST 3-Dimensional joint torque calculation of compression sportswear using
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering ( ) 7th Asia-Pacific Congress on Sports Technology, APCST 3-Dimensional joint torque calculation of compression sportswear using
Section 4.2. Travelling Waves
 Section 4.2 Travelling Waves Wave Motion A wave is the motion of a disturbance Mechanical waves require Some source of disturbance A medium that can be disturbed Some physical connection between or mechanism
Section 4.2 Travelling Waves Wave Motion A wave is the motion of a disturbance Mechanical waves require Some source of disturbance A medium that can be disturbed Some physical connection between or mechanism
SNAKY SPRING WAVE DEMONSTRATION ITEM # ENERGY - MOTION
 T E A C H E G U I R D S E SNAKY SPRING WAVE DEMONSTRATION ITEM # 3640-00 ENERGY - MOTION Waves are all around us. From sound waves, to electromagnetic waves, to seismic waves, we experience wave motion
T E A C H E G U I R D S E SNAKY SPRING WAVE DEMONSTRATION ITEM # 3640-00 ENERGY - MOTION Waves are all around us. From sound waves, to electromagnetic waves, to seismic waves, we experience wave motion
Exploring the relationship between the pressure of the ball and coefficient of restitution.
 Exploring the relationship between the pressure of the ball and coefficient of restitution. When I started thinking about possible investigations I knew I wanted to create a lab that was related to sports.
Exploring the relationship between the pressure of the ball and coefficient of restitution. When I started thinking about possible investigations I knew I wanted to create a lab that was related to sports.
Analysis of Backward Falls Caused by Accelerated Floor Movements Using a Dummy
 Original Article Analysis of Backward Falls Caused by Accelerated Floor Movements Using a Dummy Hisao NAGATA 1 * and Hisato OHNO 2 1 National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health, 1 4 6 Umezono,
Original Article Analysis of Backward Falls Caused by Accelerated Floor Movements Using a Dummy Hisao NAGATA 1 * and Hisato OHNO 2 1 National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health, 1 4 6 Umezono,
STRUCTURAL INTEGRITY EVALUATION OF CNG COMPOSITE CYLINDERS BY ACOUSTIC EMISSION MONITORING
 STRUCTURAL INTEGRITY EVALUATION OF CNG COMPOSITE CYLINDERS BY ACOUSTIC EMISSION MONITORING Olivier Skawinski, Patrice Hulot, Christophe Binétruy and Christian Rasche Department of Polymers and Composites
STRUCTURAL INTEGRITY EVALUATION OF CNG COMPOSITE CYLINDERS BY ACOUSTIC EMISSION MONITORING Olivier Skawinski, Patrice Hulot, Christophe Binétruy and Christian Rasche Department of Polymers and Composites
Exam Results, HW4 reminder. Wave Motion. Today: waves. What is moving? Motion of a piece of the rope. Exam Results. Average
 Exam Results, HW4 reminder Exam: Class average = 14.1/20 ( at B/BC boundary) Exam scores posted this afternoon on Learn@UW Exam solutions will be posted on course web page HW3 (short) assigned at WileyPLUS
Exam Results, HW4 reminder Exam: Class average = 14.1/20 ( at B/BC boundary) Exam scores posted this afternoon on Learn@UW Exam solutions will be posted on course web page HW3 (short) assigned at WileyPLUS
Introduction. Strand E Unit 2: The Nature of Waves. Learning Objectives. Introduction.
 Learning Objectives At the end of this unit you should be able to Describe the main features of diffraction, refraction and reflection, and use the law of reflection. Describe how two progressive waves
Learning Objectives At the end of this unit you should be able to Describe the main features of diffraction, refraction and reflection, and use the law of reflection. Describe how two progressive waves
Introduction to Waves. If you do not have access to equipment, the following experiments can be observed here:
 Introduction to Waves If you do not have access to equipment, the following experiments can be observed here: http://tinyurl.com/lupz3dh 1.1 There is a tray with water in it. This can model throwing a
Introduction to Waves If you do not have access to equipment, the following experiments can be observed here: http://tinyurl.com/lupz3dh 1.1 There is a tray with water in it. This can model throwing a
Chapter 15 Wave Motion. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 15 Wave Motion 15-1 Characteristics of Wave Motion All types of traveling waves transport energy. Study of a single wave pulse shows that it is begun with a vibration and is transmitted through
Chapter 15 Wave Motion 15-1 Characteristics of Wave Motion All types of traveling waves transport energy. Study of a single wave pulse shows that it is begun with a vibration and is transmitted through
A Scientific Approach for Diagnosing a Junior Tennis Player s Swing and Determining Optimum Racquet Parameters
 ISSN 1750-9823 (print) International Journal of Sports Science and Engineering Vol. 07 (2013) No. 01, pp. 060-064 A Scientific Approach for Diagnosing a Junior Tennis Player s Swing and Determining Optimum
ISSN 1750-9823 (print) International Journal of Sports Science and Engineering Vol. 07 (2013) No. 01, pp. 060-064 A Scientific Approach for Diagnosing a Junior Tennis Player s Swing and Determining Optimum
Physics 1-2 Mr. Chumbley Physics: Chapter 11 p
 Physics 1-2 Mr. Chumbley Physics: Chapter 11 p. 362-401 Section 1 p. 364 371 Section 2 p. 372-377 Simple Harmonic Motion There exist many different situations in which objects oscillate in regular, repeating
Physics 1-2 Mr. Chumbley Physics: Chapter 11 p. 362-401 Section 1 p. 364 371 Section 2 p. 372-377 Simple Harmonic Motion There exist many different situations in which objects oscillate in regular, repeating
Tennis Elbow is currently one of the most diagnosed conditions in the western world. It is extremely common, and can be excruciatingly painful.
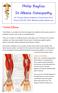 43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Tennis Elbow Tennis Elbow is currently one of the most diagnosed conditions in the western world. It is
43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Tennis Elbow Tennis Elbow is currently one of the most diagnosed conditions in the western world. It is
Exploring the relationship between the pressure of the ball and coefficient of restitution.
 Exploring the relationship between the pressure of the ball and coefficient of restitution. When I started thinking about possible investigations I knew I wanted to create a lab that was related to sports.
Exploring the relationship between the pressure of the ball and coefficient of restitution. When I started thinking about possible investigations I knew I wanted to create a lab that was related to sports.
Today: waves. Exam Results, HW4 reminder. Chapter 8: Wave Motion. What is moving? Energy transport. Motion of a piece of the rope
 Exam Results, HW4 reminder Exam: Class average = 13.6/20 ( at B/BC boundary) Exam scores posted this afternoon on Learn@UW Exam solutions are on course web page March Chap 7: Question A, Exercises 2 Griffith
Exam Results, HW4 reminder Exam: Class average = 13.6/20 ( at B/BC boundary) Exam scores posted this afternoon on Learn@UW Exam solutions are on course web page March Chap 7: Question A, Exercises 2 Griffith
CHAPTER 8: MECHANICAL WAVES TRANSMIT ENERGY IN A VARIETY OF WAYS
 CHAPTER 8: MECHANICAL WAVES TRANSMIT ENERGY IN A VARIETY OF WAYS DISCLAIMER FOR MOST QUESTIONS IN THIS CHAPTER Waves are always in motion, as they transmit energy and information from one point to another.
CHAPTER 8: MECHANICAL WAVES TRANSMIT ENERGY IN A VARIETY OF WAYS DISCLAIMER FOR MOST QUESTIONS IN THIS CHAPTER Waves are always in motion, as they transmit energy and information from one point to another.
J. J. Daly Metal Improvement Company Paramus New Jersey USA
 Shot Peening-Current Trends, Future Prospects J. J. Daly Metal Improvement Company Paramus New Jersey USA The shot peening process is sparingly used compared to other processes such as heat treating, plating,
Shot Peening-Current Trends, Future Prospects J. J. Daly Metal Improvement Company Paramus New Jersey USA The shot peening process is sparingly used compared to other processes such as heat treating, plating,
Pre AP Physics: Unit 7 Vibrations, Waves, and Sound. Clear Creek High School
 Pre AP Physics: Unit 7 Vibrations, Waves, and Sound Clear Creek High School Simple Harmonic Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Constant periodic motion of an object. An object oscillates back and forth along
Pre AP Physics: Unit 7 Vibrations, Waves, and Sound Clear Creek High School Simple Harmonic Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Constant periodic motion of an object. An object oscillates back and forth along
Standing Waves in a String
 Standing Waves in a String OBJECTIVE To understand the circumstances necessary to produce a standing wave. To observe and define the quantities associated with a standing wave. To determine the wavelength
Standing Waves in a String OBJECTIVE To understand the circumstances necessary to produce a standing wave. To observe and define the quantities associated with a standing wave. To determine the wavelength
Using Experimental Procedure to Improve the Efficiency of the Two Stand Reversing Cold Mill
 Using Experimental Procedure to Improve the Efficiency of the Two Stand Reversing Cold Mill Mohammad Heydari Vini 1* 1 Instructor, Department of Engineering, Islamic Azad University, Mobarakeh Branch,
Using Experimental Procedure to Improve the Efficiency of the Two Stand Reversing Cold Mill Mohammad Heydari Vini 1* 1 Instructor, Department of Engineering, Islamic Azad University, Mobarakeh Branch,
Lesson 14: Simple harmonic motion, Waves (Sections )
 Circular Motion and Simple Harmonic Motion The projection of uniform circular motion along any ais (the -ais here) is the same as simple harmonic motion. We use our understanding of uniform circular motion
Circular Motion and Simple Harmonic Motion The projection of uniform circular motion along any ais (the -ais here) is the same as simple harmonic motion. We use our understanding of uniform circular motion
Ch13. Vibrations and Waves HW# 1, 5, 9, 13, 19, 29, 35, 37, 39, 41, 43, 47, 51, 53, 61
 Ch13. Vibrations and Waves HW# 1, 5, 9, 13, 19, 29, 35, 37, 39, 41, 43, 47, 51, 53, 61 If you displace a system that obeys Hooke s Law, It will follow simple harmonic motion. The system will oscillate.
Ch13. Vibrations and Waves HW# 1, 5, 9, 13, 19, 29, 35, 37, 39, 41, 43, 47, 51, 53, 61 If you displace a system that obeys Hooke s Law, It will follow simple harmonic motion. The system will oscillate.
Phys1111K: Superposition of waves on a string Name:
 Phys1111K: Superposition of waves on a string Name: Group Members: Date: TA s Name: Apparatus: PASCO mechanical vibrator, PASCO interface, string, mass hanger (50 g) and set of masses, meter stick, electronic
Phys1111K: Superposition of waves on a string Name: Group Members: Date: TA s Name: Apparatus: PASCO mechanical vibrator, PASCO interface, string, mass hanger (50 g) and set of masses, meter stick, electronic
Finite element analysis of tennis racquet in order to avoid tennis injuries
 Finite element analysis of tennis racquet in order to avoid tennis injuries Gurpeer Singh 1, Dr Perminderjit Singh 2 1 M.E. Scholar, Department of Mechanical Engineering, PEC University Of Technology,
Finite element analysis of tennis racquet in order to avoid tennis injuries Gurpeer Singh 1, Dr Perminderjit Singh 2 1 M.E. Scholar, Department of Mechanical Engineering, PEC University Of Technology,
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP PHYSICS LSN 11-7: WAVE MOTION LSN 11-8: TYPES OF WAVES; LONGITUDINAL AND TRANSVERSE LSN 11-9: ENERGY TRANSPORTED BY WAVES Physics of Waves Questions From Reading
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP PHYSICS LSN 11-7: WAVE MOTION LSN 11-8: TYPES OF WAVES; LONGITUDINAL AND TRANSVERSE LSN 11-9: ENERGY TRANSPORTED BY WAVES Physics of Waves Questions From Reading
NATURE AND PROPERTIES OF WAVES P.1
 NATURE AND ROERTIES OF WAVES.1 DSE AER IA 218 14. Which of the following statements about waves is/are correct? (1) Longitudinal waves can transmit energy from one place to another but transverse waves
NATURE AND ROERTIES OF WAVES.1 DSE AER IA 218 14. Which of the following statements about waves is/are correct? (1) Longitudinal waves can transmit energy from one place to another but transverse waves
Waves. harmonic wave wave equation one dimensional wave equation principle of wave fronts plane waves law of reflection
 Waves Vocabulary mechanical wave pulse continuous periodic wave amplitude wavelength period frequency wave velocity phase transverse wave longitudinal wave intensity displacement wave number phase velocity
Waves Vocabulary mechanical wave pulse continuous periodic wave amplitude wavelength period frequency wave velocity phase transverse wave longitudinal wave intensity displacement wave number phase velocity
Effects of string tension and impact location on tennis playing
 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 23 (2009) 2990~2997 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology www.springerlink.com/content/1738-494x DOI 10.1007/s12206-009-0903-5 Effects of string tension
Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 23 (2009) 2990~2997 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology www.springerlink.com/content/1738-494x DOI 10.1007/s12206-009-0903-5 Effects of string tension
Similarly to elastic waves, sound and other propagated waves are graphically shown by the graph:
 Phys 300/301 Physics: Algebra/Trig Eugene Hecht, 3e. Prepared 01/24/06 11.0 Waves & Sounds There are two fundamental waves of transporting energy and momentum: particles and waves. While they seem opposites,
Phys 300/301 Physics: Algebra/Trig Eugene Hecht, 3e. Prepared 01/24/06 11.0 Waves & Sounds There are two fundamental waves of transporting energy and momentum: particles and waves. While they seem opposites,
Thermal properties of Fiber ropes
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Oct 16, 2018 Thermal properties of Fiber ropes Bossolini, Elena; Nielsen, Ole Wennerberg; Oland, Espen; Sørensen, Mads Peter; Veje, Christian Publication date: 2016 Document
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Oct 16, 2018 Thermal properties of Fiber ropes Bossolini, Elena; Nielsen, Ole Wennerberg; Oland, Espen; Sørensen, Mads Peter; Veje, Christian Publication date: 2016 Document
Section 1 Types of Waves. Distinguish between mechanical waves and electromagnetic waves.
 Section 1 Types of Waves Objectives Recognize that waves transfer energy. Distinguish between mechanical waves and electromagnetic waves. Explain the relationship between particle vibration and wave motion.
Section 1 Types of Waves Objectives Recognize that waves transfer energy. Distinguish between mechanical waves and electromagnetic waves. Explain the relationship between particle vibration and wave motion.
RELIABILITY ASSESSMENT, STATIC AND DYNAMIC RESPONSE OF TRANSMISSION LINE TOWER: A COMPARATIVE STUDY
 RELIABILITY ASSESSMENT, STATIC AND DYNAMIC RESPONSE OF TRANSMISSION LINE TOWER: A COMPARATIVE STUDY Yusuf Mansur Hashim M. Tech (Structural Engineering) Student, Sharda University, Greater Noida, (India)
RELIABILITY ASSESSMENT, STATIC AND DYNAMIC RESPONSE OF TRANSMISSION LINE TOWER: A COMPARATIVE STUDY Yusuf Mansur Hashim M. Tech (Structural Engineering) Student, Sharda University, Greater Noida, (India)
Vibrations of table tennis racket composite wood blades: modeling and experiments
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 34 (2012 ) 694 699 9 th Conference of the International Sports Engineering Association (ISEA) Vibrations of table tennis racket composite
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 34 (2012 ) 694 699 9 th Conference of the International Sports Engineering Association (ISEA) Vibrations of table tennis racket composite
The validity of a rigid body model of a cricket ball-bat impact
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 34 (2012 ) 682 687 9 th Conference of the International Sports Engineering Association (ISEA) The validity of a rigid body model of a cricket
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 34 (2012 ) 682 687 9 th Conference of the International Sports Engineering Association (ISEA) The validity of a rigid body model of a cricket
LONG METAL SPRING ITEM # ENERGY - MOTION
 T E A C H E G U I R D S E LONG METAL SPRING ITEM # 3638-01 ENERGY - MOTION Waves are all around us. From sound waves, to electromagnetic waves, to seismic waves, we experience wave motion on a daily basis.
T E A C H E G U I R D S E LONG METAL SPRING ITEM # 3638-01 ENERGY - MOTION Waves are all around us. From sound waves, to electromagnetic waves, to seismic waves, we experience wave motion on a daily basis.
Study on Intensity of Blast Wave Generated from Vessel Bursting by Gas Explosion
 5 th ICDERS August 7, 15 Leeds, UK Study on Intensity of Blast Wave Generated from Vessel Bursting by Gas Explosion Matsunaga, T., Mogi, T., Dobashi, R. Graduated School of Engineering, The University
5 th ICDERS August 7, 15 Leeds, UK Study on Intensity of Blast Wave Generated from Vessel Bursting by Gas Explosion Matsunaga, T., Mogi, T., Dobashi, R. Graduated School of Engineering, The University
Vibration Analysis and Test of Backup Roll in Temper Mill
 Sensors & Transducers 2013 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.com Vibration Analysis and Test of Backup Roll in Temper Mill Yuanmin Xie College of Machinery and Automation, Wuhan University of Science and
Sensors & Transducers 2013 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.com Vibration Analysis and Test of Backup Roll in Temper Mill Yuanmin Xie College of Machinery and Automation, Wuhan University of Science and
Traveling Waves vs. Standing Waves
 The Physics Classroom» Physics Tutorial» Waves» Traveling Waves vs. Standing Waves Waves - Lesson 4 - Standing Waves Traveling Waves vs. Standing Waves Traveling Waves vs. Standing Waves Formation of Standing
The Physics Classroom» Physics Tutorial» Waves» Traveling Waves vs. Standing Waves Waves - Lesson 4 - Standing Waves Traveling Waves vs. Standing Waves Traveling Waves vs. Standing Waves Formation of Standing
Lab 2: Superposition of waves on a string
 Lab 2: Superposition of waves on a string Name: Group Members: Date: TA s Name: Apparatus: PASCO mechanical vibrator, PASCO interface, string, mass hanger (50 g) and set of masses, meter stick, electronic
Lab 2: Superposition of waves on a string Name: Group Members: Date: TA s Name: Apparatus: PASCO mechanical vibrator, PASCO interface, string, mass hanger (50 g) and set of masses, meter stick, electronic
Air entrainment in Dip coating under vacuum
 Air entrainment in Dip coating under vacuum M.I. Khan, R. Patel, H. Benkreira, IRC, School of Engineering, Design and Technology, University of Bradford, BD7 1DP, Abstract Air entrainment studies in dip
Air entrainment in Dip coating under vacuum M.I. Khan, R. Patel, H. Benkreira, IRC, School of Engineering, Design and Technology, University of Bradford, BD7 1DP, Abstract Air entrainment studies in dip
Harmonics and Sound Exam Review
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ Harmonics and Sound Exam Review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is not an example
Name: Class: _ Date: _ Harmonics and Sound Exam Review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is not an example
Waves and Sound. Honors Physics
 Waves and Sound Honors Physics Simple Harmonic Motion Refers to repetitive, cyclical motion (like a pendulum or waves) Can be described with sine curve For a pendulum only T 2 L g Example problem The world
Waves and Sound Honors Physics Simple Harmonic Motion Refers to repetitive, cyclical motion (like a pendulum or waves) Can be described with sine curve For a pendulum only T 2 L g Example problem The world
A QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS OF THE HIGH RACQUET POSITION BACKHAND DRIVE OF AN ELITE RACQUETBALL PLAYER
 A QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS OF THE HIGH RACQUET POSITION BACKHAND DRIVE OF AN ELITE RACQUETBALL PLAYER John R. Stevenson Wayne P. Hollander Since 1950, when Joe Sobek put strings on his paddleball paddle, the
A QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS OF THE HIGH RACQUET POSITION BACKHAND DRIVE OF AN ELITE RACQUETBALL PLAYER John R. Stevenson Wayne P. Hollander Since 1950, when Joe Sobek put strings on his paddleball paddle, the
Slide 2 / 28 Wave Motion. A wave travels along its medium, but the individual particles just move up and down.
 Slide 1 / 28 Waves Slide 2 / 28 Wave Motion A wave travels along its medium, but the individual particles just move up and down. Slide 3 / 28 Wave Motion All types of traveling waves transport energy.
Slide 1 / 28 Waves Slide 2 / 28 Wave Motion A wave travels along its medium, but the individual particles just move up and down. Slide 3 / 28 Wave Motion All types of traveling waves transport energy.
DYNAMIC CRUSH TEST ON HYDROGEN PRESSURIZED CYLINDER
 DYNAMIC CRUSH TEST ON HYDROGEN PRESSURIZED CYLINDER Hiroyuki Mitsuishi 1, Koichi Oshino 2, Shogo Watanabe 2 1 Japan Automobile Research Institute, Takaheta1328-23, Shirosato, Ibaraki, 311-4316, Japan 2
DYNAMIC CRUSH TEST ON HYDROGEN PRESSURIZED CYLINDER Hiroyuki Mitsuishi 1, Koichi Oshino 2, Shogo Watanabe 2 1 Japan Automobile Research Institute, Takaheta1328-23, Shirosato, Ibaraki, 311-4316, Japan 2
A It is halved. B It is doubled. C It is quadrupled. D It remains the same.
 WAVES UNIT REVIEW EN: CALIFORNIA STATE QUESTIONS: 1. A sound wave is produced in a metal cylinder by striking one end. Which of the following occurs as the wave travels along the cylinder? A Its amplitude
WAVES UNIT REVIEW EN: CALIFORNIA STATE QUESTIONS: 1. A sound wave is produced in a metal cylinder by striking one end. Which of the following occurs as the wave travels along the cylinder? A Its amplitude
Conditions for occurrence of vortex shedding on a large cable stayed bridge. Full scale data from monitoring system
 Conditions for occurrence of vortex shedding on a large cable stayed bridge. Full scale data from monitoring system O. Flamand 1, F. De Oliveira 1 and A. Stathopoulos-Vlamis, P. Papanikolas 2 1 Centre
Conditions for occurrence of vortex shedding on a large cable stayed bridge. Full scale data from monitoring system O. Flamand 1, F. De Oliveira 1 and A. Stathopoulos-Vlamis, P. Papanikolas 2 1 Centre
-Elastic strain energy (duty factor decreases at higher speeds). Higher forces act on feet. More tendon stretch. More energy stored in tendon.
 As velocity increases ( ) (i.e. increasing Froude number v 2 / gl) the component of the energy cost of transport associated with: -Internal kinetic energy (limbs accelerated to higher angular velocity).
As velocity increases ( ) (i.e. increasing Froude number v 2 / gl) the component of the energy cost of transport associated with: -Internal kinetic energy (limbs accelerated to higher angular velocity).
LOW-CYCLE FATIGUE LIFE OF AW 1050 ALUMINIUM ALLOY FSW AND TIG WELDED JOINTS
 Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design Albufeira/Portugal 11-15 June 217. Editors J.F. Silva Gomes and S.A. Meguid. Publ. INEGI/FEUP (217) PAPER REF: 6499
Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design Albufeira/Portugal 11-15 June 217. Editors J.F. Silva Gomes and S.A. Meguid. Publ. INEGI/FEUP (217) PAPER REF: 6499
Numerical Simulations of a Train of Air Bubbles Rising Through Stagnant Water
 Numerical Simulations of a Train of Air Bubbles Rising Through Stagnant Water Hong Xu, Chokri Guetari ANSYS INC. Abstract Transient numerical simulations of the rise of a train of gas bubbles in a liquid
Numerical Simulations of a Train of Air Bubbles Rising Through Stagnant Water Hong Xu, Chokri Guetari ANSYS INC. Abstract Transient numerical simulations of the rise of a train of gas bubbles in a liquid
