Subjective Evaluation for the Driving Conditions at Signalized Intersection and Roundabout by Before-After Analysis
|
|
|
- Harry Baldwin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Subjective Evaluation for the Driving Conditions at Signalized Intersection and Roundabout by Before-After Analysis Koji SUZUKI Associate professor Graduate School of Engineering, Nagoya Institute of Technology, Gokiso-cho, Showa-ku, Nagoya, Aichi, , Japan, Phone and Fax: Kiyoaki MORIMOTO Master course student Graduate School of Engineering, Nagoya Institute of Technology, Gokiso-cho, Showa-ku, Nagoya, Aichi, , Japan, Phone and Fax: Zheng JIAN Doctor course student Graduate School of Engineering, Nagoya Institute of Technology, Gokiso-cho, Showa-ku, Nagoya, Aichi, , Japan, Phone and Fax:
2 2 ABSTRACT This study investigated safety confirmation behaviors such as looking both ways near a crosswalk and the evaluation of driving satisfaction before and after the conversion of a signalized intersection (SI) to a roundabout (RAB) in Iida city, Japan. Drivers behaviors when entering or exiting the SI and RAB were captured by two in-vehicle video cameras, a drive recorder, and a GPS logger. In addition, after navigating a route, the participants were asked to evaluate driving satisfaction using a 4-point rating scale. The instantaneous speeds and distances of safety confirmation, the necessary deceleration rate for safe stopping, the number of safety confirmation behaviors, and the subjective evaluation of driving satisfaction, were completely analyzed at the SI and RAB. The effectiveness of converting SIs to RABs was quantitatively investigated. Some interesting findings were presented, which can provide some helpful guidance on discussions concerning the feasibility of introducing RAB in Japan.
3 3 INTRODUCTION According to the traffic accident statistics compiled by the National Police Agency in Japan (2013), the total number of traffic accidents has been gradually decreasing year by year, and only 4,411 fatal traffic accidents occurred in However, it is also noted that among all traffic facilities more than half of the traffic accidents happened at or near intersections. Therefore, it is necessary to take effective measures to improve traffic safety at intersections. Over the last 20 years, more and more intersections have been converted to roundabouts (RABs) in Europe and USA as an effective control facility for less traffic (Elvik 2003, Flannery and Datta 1996, Robinson et al. 2000, Persaud et al. 2001). The RAB is a roadway intersection designed to facilitate traffic flow and reduce the incidence of serious accidents. RABs have oneway traffic in a circulatory roadway around a central island, together with entries and exits separated by splitter islands. Unlike a traffic signal, wherein the vehicle entrance to a junction is controlled by allocation of green times (Abu-Lebdeh et al. 2007, Heydecker 2004), vehicles entering RABs must give way to vehicles already in it. Compared with unsignalized and signalized intersections, RABs have two advantages: capacity and safety. The RAB has a larger capacity than intersections as left turns are omitted (Sisiopiku and Oh 2001). Moreover, because all traffic flows are required to circulate around the central island in the same direction, conflict points are largely reduced. Hence, the RAB can reduce the number and severity of traffic accidents (Persaud et al. 2001, Stuwe 1991). It is also believed to have an effect on reducing pollutant emissions (Coelho et al. 2006, Höglund 1994). In recent years, comprehensive research on the feasibility of introducing RABs have also been conducted in Japan (IATSS Report 2011, 2012). In particular, compared with signalized intersections (SIs), the RAB is more effective during a power outage caused by earthquakes or tsunamis, which occur often in Japan (Nakamura et al. 2009, Munehiro et al. 2009, Takigawa et al. 2010). As a result, on February 5th 2013, SIs in Iida city was converted to RABs for the first time in Japan. Although there were a few studies concerning the effects of RAB conversions in the U.S.A. (Persaud et al. 2001, Gross et al. 2013), a before-after study associated with driving behaviors has not been conducted in Japan, which has left-hand traffic and drivers may not have been accustomed
4 4 to the new facility. The current study therefore investigated the safety confirmation behaviors and the evaluation of driving satisfaction before and after the conversion of SIs to RABs in Iida city using driving experiments. STUDY SITES AND DRIVING EXPERIMENTS On February 5, 2013, the Towa-cho SI was converted to a RAB for the first time in Japan. FIGURE 1 displays the geometries of the SI and RAB. The setback distance of crosswalk from the circulatory road for all legs are set 5.5 m for the RAB, which is longer than that for the SI. All the entries of the RAB is controlled with a stop sign because yield traffic control is not permitted in Japan. In addition, the roads follow the left-hand traffic convention. Driving experiments were conducted: before the conversion on May 8th and 9th, 2012, with four participants, immediately after the conversion on February 5th and 6th, 2013, with two participants, and after the conversion on May 8th and 11m 1.3m a. Towa-cho SI (before conversion) 6m 12m 3.6m 3.0m 5.5m 3.0m 6m Setback distance of crosswalk b. Towa-cho RAB (after conversion) FIGURE 1 Geometries Geometry of the SI and RAB 9th 2013 with four participants. The experimental vehicle was equipped with two in-vehicle video cameras, a drive recorder with GPS locator-equipped, and a stand-alone GPS logger. The equipment specifications are summarized in TABLE 1. Data on vehicle movements and surrounding traffic conditions were obtained, along with data on the in-vehicle driving behaviors of participants every 0.1 s. The
5 5 equipped experimental vehicle and the setting of in-vehicle video cameras are shown in FIGURE 2. Considering driving fatigue, we divided all the driving routes into two types. The participants were required to run 10 routes of only one type at a time. The routes in each type are identified in FIGURE 3. After navigating a route, the participants were asked to evaluate driving satisfaction about the route using a 4-point rating scale: 1 - very easy, 2 - easy, 3 - slightly difficult, and 4 - difficult. In addition, when the participant confirms the existence of pedestrians at the entrances or exits of intersections as shown in FIGURE 4, they notify the surveyor sitting in the passenger seat of their confirmation behavior by speaking out I confirmed it. The surveyor then recorded the time into the drive recorder manually. Therefore, we obtained information about participants' safety confirmation behaviors and the vehicle movements such as the vehicle speed, and the location at that time. The required time for each test type was approximately 40 minutes. Equipment Product name (Maker) TABLE1 Equipment specifications Video-camera Recorder HDR-CX590V (SONY) Drive Recorder SRcomm (Datatech) GPS Logger G-Rays2 (Wintec) Size: W*H*D [mm] 54*64* *140*55 64*40*17 Weight[g] Sampling frequency 5Mbps 10Hz 1Hz FIGURE 2 The equipped experimental vehicle and the setting of in-vehicle video cameras
6 6 FIGURE 3 Driving routes into types A and B FIGURE 4 Definition of starting and terminal points for safety confirmation DRIVING BEHAVIORS AT THE EXITS OF SI AND RAB In this section, both the driving behaviors and vehicle movements at the exits of the SI and RAB were investigated. The T-test is used to explain the difference between the two groups. In this study,*, **, and *** denote that the differences are statistically significant at the 1%, 5%, and 10%
7 7 level, respectively. In addition, based on left turns and right turns, driving behaviors are divided in two groups. Analysis of instantaneous speeds of safety confirmation at the exits of the intersection The instantaneous speeds when the participants start confirming traffic conditions at the crosswalks or on the opposite sides of roads can be obtained by the driving recorder. The statistical summary of the instantaneous speeds collected before the conversion (SI), immediately after the conversion (RAB 1) and after the conversion (RAB 2) are presented in FIGURE 5. [km/h] SI RAB 1 RAB 2 SI RAB 1 RAB 2 Left turns Right turns (N=24) (N=24) (N=28) (N=25) (N=22) (N=23) FIGURE 5 The statistical summary of instantaneous speeds when confirming safety at the exits of SI and RAB It is noted that for left turns, the mean speed when confirming safety at RAB 1 are clearly lower than the mean speed at the SI. The T-test (T-value = 5.10*) also reflects this difference. Due to fact that the vehicle is required to stop in front of crosswalks, before entering the RAB in accordance with the stop sign, and has to give way to vehicles already in the RAB, it is very hard for the vehicle to accelerate to a high speed over the short driving distance. Owing to this configuration of RAB, the vehicle speeds are constrained. On the contrary, for right turns, the mean speeds at RAB 1 and RAB 2 are greater than that at the SI. From the T-test, the differences are also statistically significant (T-value = -1.71***, 4.90*, respectively). When turning right, drivers have to stop temporarily within the SI and check traffic conditions at crosswalks or on opposite sides of the roads. Such driving behaviors limit vehicle speeds at SIs. It is also found that
8 8 the standard deviation of speeds at RAB 1 and RAB 2 is less than that at the SI. Hence, the driving behavior of right-turning traffic at RAB is more stable and smooth than traffic at the SI. Analysis of distances of safety confirmation at the exits of the intersection The starting and terminal points of safety confirmation are defined in FIGURE 4. In driving experiments, participants were asked to notify the surveyor sitting in the passenger seat of their confirmation behaviors by speaking out I confirmed it. The surveyor recorded the time by using the drive recorder. Therefore, the starting points of safety confirmation can be obtained. The terminal points of safety confirmation are represented by the red lines in FIGURE 4. The statistical summary of the distances between starting and terminal points at the exits of intersection is displayed in FIGURE 6. [m] SI RAB 1 RAB 2 SI RAB 1 RAB 2 Left turns Right turns (N=24) (N=24) (N = 28) (N = 25) (N = 22) (N = 23) FIGURE 6 The statistical summary of distances between starting and terminal points at the exits of SI and RAB From FIGURE 6, for left turns, the differences between the SI and RAB in distances are not significant (T-value = 1.38, -1.35, respectively). However, for right turns, the distances between starting and terminal points are significantly different based on the T-test (T-value = *, -8.30*, respectively) at the SI and RAB. The mean distances at RAB 1 and RAB 2 are greater than 15 m, but at the SI, the value is less than 8 m. This indicates that when turning right at the RAB, the driver can confirm safety earlier than when turning right at the SI.
9 9 Necessary deceleration rate for safe stopping at the exits of intersection In this research, in order to evaluate potential traffic risks for pedestrians when turning left or right at the exits of the SI and RAB, we define the necessary deceleration rate for safe stopping before the crosswalk by using the instantaneous speeds and distances of safety confirmation. The necessary deceleration rate for safe stopping is represented by the following equation 2 vt NDR 2 (1) where vt is the instantaneous speed when the driver is checking traffic conditions and xt is the distance between the starting point and internal point of safety confirmation. In addition, we assume that the deceleration is linear. [m/s 2 ] 3 x t SI RAB 1 RAB 2 SI RAB 1 RAB 2 Left turns Right turns (N = 24) (N=24) (N =28) (N = 25) (N = 22) (N = 23) FIGURE 7 The statistical summary of the necessary deceleration rate before the crosswalk at the exit of intersection FIGURE 7 displays the statistical summary of NDR. It is noted that for both left and right turns, the mean NDR at the RAB is obviously less than the mean NDR at the SI. With the T values = 3.30*, 1.84*** respectively, such differences are also statistically significant. For left turns, there is a small difference in distances between starting and terminal points of safety confirmation at the SI and RAB. However, the instantaneous speeds of safety confirmation at the RAB are clearly lower than those at the SI. On the another hand, for right turns, although vehicles are faster at the RAB than vehicles at the SI when checking traffic conditions, the starting time of safety confirmation at the RAB is earlier than that at the SI. The NDR analysis indicates that the RAB can constrain severe deceleration and has an effect on comfortable driving compared with the SI.
10 10 Number of safety confirmation behaviors Subsequently, we investigated the frequency of drivers' safety confirmation behaviors through the video cameras. In this research, safety confirmation behaviors characterized as with rotating his/her head, with eye movement and with both rotating his/her head and eye movement are focused on and treated as the same. For each participant, the number of safety confirmation behaviors between the starting and terminal points are counted using image analysis. The frequency of the safety confirmation behaviors at the SI and RAB is statistically analyzed, as shown in FIGURE 7. Number SI RAB 1 RAB 2 SI RAB 1 RAB 2 Left turns Right turns (N = 20) (N = 24) (N = 28) (N = 21) (N = 22) (N = 23) FIGURE 8 Number of safety confirmation behaviors at the SI and RAB From FIGURE 8, for both left and right turns, the mean number of safety confirmation behaviors at RAB 1 is higher than the mean number at the SI. The difference in the mean number is also statistically significant, with a T-value of -2.66* and -5.51* for left and right turns, respectively. However, the differences between the SI and RAB 2 for left turns are not statistically significant, though the differences at right turns are still statistically significant. It can be considered that the test drivers at RAB 2 became familiar with the left turning drive at the roundabout. This suggests that drivers are more cautious when going through the RAB than when driving at the SI.
11 11 SUBJECTIVE EVALUATION FOR DRIVING SATISFACTION In Persaud et al. (2001) and Gross et al. (2013), the observed crash data were used to check the safety effectiveness of converting SIs to RABs. The subjective evaluation was seldom carried out in previous studies. Numerical scores of driving satisfaction In this study, after running through a route, the participant was asked to evaluate driving satisfaction about the route, by using a 4-point rating scale: 1 - very easy, 2 - easy, 3 - slightly difficult, and 4 - difficult. To facilitate statistical analysis, the Likert Scale (Allen et al. 2007) is applied to convert the qualitative responses to the quantitative scores. The Likert Scale equation is shown below and the numerical values based on driving survey data are listed in TABLE 2. σ = y i 1 y i R i Here, σ is the sigma value, yi is the y-value of normal distribution and Ri is the relative frequency of each item i (2) TABLE 2 The converted numerical scores using the Likert Scale Study sites SI, RAB 1, and RAB 2 Variables y i R i σ Score 1: Very easy : Easy : Slightly difficult : Difficult
12 12 Score SI RAB 1 RAB 2 SI RAB 1 RAB 2 SI RAB 1 RAB 2 Left turns Right turns No turns (N = 27) (N = 22) (N = 28) (N = 29) (N = 22) (N = 24) (N = 14) (N = 14) (N =19) FIGURE 9 Evaluation scores of driving satisfaction at the SI and RAB The evaluation scores of driving satisfaction at the SI and RAB are illustrated in FIGURE 9. For left turns, there is no significant difference in evaluation scores at the SI and RAB 1; however, the differences between SI and RAB 2 are statistically significant (T-value = -2.99*). Therefore, when turning left, drivers feel at ease driving in RAB 2 in accordance with habituation. On the other hand, for right turns and no turns at the SI and RAB 1, apparent differences in driving satisfaction are observed. The T-values for right turns and no turns are 3.58* and 3.11*, respectively. The mean score at the SI is clearly higher than the mean score at RAB 1. It means that drivers felt less satisfied when running immediately after introducing the RAB. This may be due to the fact that most drivers have not become accustomed to the RAB. In addition, the roads near the intersection were under construction and traffic was locally constrained when conducting driving experiments at RAB 1. To some extent, such factors may impact driving satisfaction at RABs. Though there are no differences between the SI and RAB 2, it is also found that the drivers evaluation is improved from this same figure. Discriminant analysis of driving satisfaction To find out the factors that influence driving satisfaction, discriminant analysis was conducted at the RAB. The analysis results are listed in TABLE 3. Here, if the sign of unstandardized or
13 13 standardized parameter of a variable is negative/positive, the value of the corresponding variable driving satisfaction will also be increased/decreased. From TABLE 3, if there is a leading vehicle within the RAB, driving satisfaction will be decreased. If the instantaneous speed when confirming safety is less than 15 km/h, drivers will evaluate the driving at a low level. When the instantaneous speed of safety confirmation is greater than 15 km/h, drivers will be satisfied with traffic conditions. When the gradient of the RAB is less than 180º, drivers can achieve high satisfaction. TABLE 3 Discriminant analysis for evaluation of traffic conditions at the RAB Variable Unstandardized parameter Constant Dummy of existence of leading vehicle within RAB Standardized parameter f-value Significance Dummy of gradient of RAB less than 180º Dummy of instantaneous speed of safety confirming between 10 km/h and 15 km/h Dummy of instantaneous speed of safety confirming between 15 km/h and 20 km/h Dummy of instantaneous speed of safety confirming between 0 km/h and 5 km/h Canonical correlation 0.62 Wilks Lambda 0.62 Significance 0.00 Percentage of correct predictions 87.30% CONCLUSIONS As an effective control facility for lower traffic, RABs have become popular in Europe and the U.S.A. In recent years, the feasibility of installing RABs in Japan has also been comprehensively discussed. On February 5th, 2013, a SI in Iida city was converted to a RAB for the first time in Japan. In this research, driving experiments were conducted at the SI before the conversion and the RAB immediately after and a longer time after the conversion). A before-after study associated
14 14 with driving behaviors was conducted. The instantaneous speeds and distances of safety confirmation, the necessary deceleration rate for safe stopping, the number of safety confirmation behaviors, and subjective evaluations for driving satisfaction, were completely analyzed for left and right turns at the SI and RAB. The study's findings are as follows: 1. For left turns, the mean speed when confirming safety at the RAB are clearly lower than the mean speed at the SI. Owing to the configuration of the RAB, the speed is constrained. For right turns the mean speeds at RAB 1 and RAB 2 are greater than that at the SI. The standard deviation of the instantaneous speeds at the RAB is less than that at the SI. Hence, traffic at the RAB is more stable and smooth than traffic at the SI. 2. From the analysis of distances of safety confirmation, for right turns, the distances between starting and terminal points are significantly different at the SI and RAB. It indicates that when turning right at the RAB, the driver can confirm safety earlier than when turning right at the SI. 3. For both left and right turns, the mean necessary deceleration rate at the RAB is less than that at the SI. This means that the RAB can constrain severe deceleration and has an effect on comfortable driving compared with the SI. 4. The mean number of safety confirmation behaviors at the RAB is more than the mean number at the SI for both left and right turns. This indicates that drivers are more cautious when going through the RAB than the SI. 5. It is also noted that for left turns, there are no significant differences in evaluation scores of driving satisfaction at the SI and RAB. For right turns and no turns immediately after introducing the RAB, although the mean score at the SI is higher than the mean score at the RAB, the evaluation for traffic at the RAB were improved with time. This indicates that unaccustomed drivers do not feel burdened by going through the RAB. 6. Discriminant analysis shows that the existence of a leading vehicle within the RAB, the instantaneous speed of safety confirmation, and the gradient of the RAB can significantly influence driving satisfaction. Although careful consideration was given to the study, there remain some issues needing further discussion. Owing to the small number of participants, limited survey site, the drivers' characteristics such as age, gender, and driving experience, were not thoroughly reflected in the
15 15 study and the findings are not widely representative. Crash data that can directly show safety benefits of the SI and RAB were not included in the study. These factors will be considered in our future work. REFERENCES Abu-Lebdeh, G., Chen, H. and Benekohal, R. F. (2007). Modeling traffic output for design of dynamic multi-cycle control in congested conditions. Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems 11(1), Allen, I., Elaine, Seaman, Christopher A. (2007). Likert Scales and Data Analyses. Quality Progress, Vol. 40, Coelho, M. C., Farias, T. L. and Rouphail, N. M. (2006). Effect of roundabout operations on pollutant emissions, Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment 11(5), Elvik, R. (2003). Effects on road safety of converting intersections to roundabouts: review of evidence from non-us studies. Transportation Research Record: journal of the Transportation research Board 1847(1), Flannery, A. and Datta, T. K. (1996). Modern roundabouts and traffic crash experience in united states. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board 1553(1), Gross, F., Lyon C., Persaud B., and Srinivasan R. (2013). Safety effectiveness of converting signalized intersections to roundabouts. Accident Analysis & Prevention Heydecker, B. (2004). Objectives, stimulus and feedback in signal control of road traffic. Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems 8(2), Höglund, P. G. (1994). Alternative intersection design-possible way of reducing air pollutant emissions from road and street traffic? Science of the total environment 146, IATSS Report Ⅱ (2011), Towards the application of safe and economical roundabouts. IATSS Report Ⅲ (2012), Towards the application of safe and economical roundabouts. Munehiro K., Takahashi N., Kasai S., (2009). An experimental study on roundabout in Tomakomai Test Truck of Hokkaido, Japan society of traffic engineers, Vol. 44, No. 3. (In Japanese)
16 16 Nakamura H., Oguchi T. Mabuchi H., Yoshioka, K (2009). Planning and design guide of roundabouts in Japan, Japan society of traffic engineers, Vol.44, No. 3. (In Japanese) National Police Agency (2013), Traffic accidents situation in Japan, Persaud, B. N., Retting, R. A., Garder, P. E. and Lord, D. (2001). Safety effect of roundabout conversions in the united states: Empirical bayes observational before-after study. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board 1751(1), 1 8. Robinson, B. W., Rodegerdts, L., et al. (2000). Roundabouts: An informational guide, Technical report, Federal Highway Administration. Sisiopiku, V. P. and Oh, H.-U. (2001). Evaluation of roundabout performance using SIDRA. Journal of transportation engineering 127(2), Stuwe, B. (1991). Capacity and safety of roundabouts - German results, Intersections without Traffic Signals II, Springer, pp Takigawa R., Oguchi T., Oneyama H. and Shikata S. (2010). Safety confirmatory behavior at roundabouts and conventional non-signalized intersections. Proc. of Infrastructure Planning (JSCE), No. 41. (In Japanese)
Analysis of the Interrelationship Among Traffic Flow Conditions, Driving Behavior, and Degree of Driver s Satisfaction on Rural Motorways
 Analysis of the Interrelationship Among Traffic Flow Conditions, Driving Behavior, and Degree of Driver s Satisfaction on Rural Motorways HIDEKI NAKAMURA Associate Professor, Nagoya University, Department
Analysis of the Interrelationship Among Traffic Flow Conditions, Driving Behavior, and Degree of Driver s Satisfaction on Rural Motorways HIDEKI NAKAMURA Associate Professor, Nagoya University, Department
Updated Roundabout Analysis Methodology
 Updated Roundabout Analysis Methodology In 1998, the Transportation Planning Analysis Unit (TPAU) working as part of the Roundabout Task Group selected the interim roundabout methodologies of the SIDRA
Updated Roundabout Analysis Methodology In 1998, the Transportation Planning Analysis Unit (TPAU) working as part of the Roundabout Task Group selected the interim roundabout methodologies of the SIDRA
Every time a driver is distracted,
 Walking on the Wild Side: Distracted Pedestrians and Traffic Safety Brendan J. Russo, Emmanuel James, Christopher Y. Aguilar, Edward J. Smaglik Every time a driver is distracted, including by their cellphone,
Walking on the Wild Side: Distracted Pedestrians and Traffic Safety Brendan J. Russo, Emmanuel James, Christopher Y. Aguilar, Edward J. Smaglik Every time a driver is distracted, including by their cellphone,
ANALYSIS OF SATURATION FLOW RATE FLUCTUATION FOR SHARED LEFT-TURN LANE AT SIGNALIZD INTERSECTIONS *
 ANALYSIS OF SATURATION FLOW RATE FLUCTUATION FOR SHARED LEFT-TURN LANE AT SIGNALIZD INTERSECTIONS * By Peng CHEN**, Hideki NAKAMURA*** and Miho ASANO**** 1. Introduction In urban corridor performance evaluation,
ANALYSIS OF SATURATION FLOW RATE FLUCTUATION FOR SHARED LEFT-TURN LANE AT SIGNALIZD INTERSECTIONS * By Peng CHEN**, Hideki NAKAMURA*** and Miho ASANO**** 1. Introduction In urban corridor performance evaluation,
TECHNICAL MEMORANDUM VDOT Central Region On Call Task Order
 Kittelson & Associates, Inc. T R A N S P O R T A T I O N E N G I N E E R I N G / P L A N N I N G 1850 Centennial Park Drive, Suite 130, 20191 P 703-885-8970 F 703-885-8971 TECHNICAL MEMORANDUM VDOT Central
Kittelson & Associates, Inc. T R A N S P O R T A T I O N E N G I N E E R I N G / P L A N N I N G 1850 Centennial Park Drive, Suite 130, 20191 P 703-885-8970 F 703-885-8971 TECHNICAL MEMORANDUM VDOT Central
Roundabout Design: Safety and Capacity Background Paper July 25, 2004
 Roundabout Design: Safety and Capacity Background Paper July 25, 2004 Introduction According to the May 13, 2000 Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) Status Report, roundabouts have been shown
Roundabout Design: Safety and Capacity Background Paper July 25, 2004 Introduction According to the May 13, 2000 Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) Status Report, roundabouts have been shown
Project Report. South Kirkwood Road Traffic Study. Meadows Place, TX October 9, 2015
 Meadows Place, TX October 9, 2015 Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Data Collection... 1 3 Existing Roadway Network... 2 4 Traffic Volume Development... 2 5 Warrant Analysis... 3 6 Traffic Control Alternative
Meadows Place, TX October 9, 2015 Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Data Collection... 1 3 Existing Roadway Network... 2 4 Traffic Volume Development... 2 5 Warrant Analysis... 3 6 Traffic Control Alternative
Saturation Flow Rate, Start-Up Lost Time, and Capacity for Bicycles at Signalized Intersections
 Transportation Research Record 1852 105 Paper No. 03-4180 Saturation Flow Rate, Start-Up Lost Time, and Capacity for Bicycles at Signalized Intersections Winai Raksuntorn and Sarosh I. Khan A review of
Transportation Research Record 1852 105 Paper No. 03-4180 Saturation Flow Rate, Start-Up Lost Time, and Capacity for Bicycles at Signalized Intersections Winai Raksuntorn and Sarosh I. Khan A review of
Evaluating Roundabout Capacity, Level of Service and Performance
 Roundabouts with Metering Signals ITE 2009 Annual Meeting, San Antonio, Texas, USA, August 9-12, 2009 Evaluating Roundabout Capacity, Level of Service and Performance Presenter: Rahmi Akçelik rahmi.akcelik@sidrasolutions.com
Roundabouts with Metering Signals ITE 2009 Annual Meeting, San Antonio, Texas, USA, August 9-12, 2009 Evaluating Roundabout Capacity, Level of Service and Performance Presenter: Rahmi Akçelik rahmi.akcelik@sidrasolutions.com
Available online at ScienceDirect. Analysis of Pedestrian Clearance Time at Signalized Crosswalks in Japan
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 32 ( 2014 ) 301 308 5th International Conference on Ambient Systems, Networks and Technologies (ANT-2014) Analysis of Pedestrian
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 32 ( 2014 ) 301 308 5th International Conference on Ambient Systems, Networks and Technologies (ANT-2014) Analysis of Pedestrian
The Case for Roundabouts:
 The Case for Roundabouts: What the Research Shows Annual Meeting AASHTO Subcommittee on Design Orlando, FL, June 14, 2006 Susan Ferguson, PH.D. Delays at red lights getting longer Wall Street Journal,
The Case for Roundabouts: What the Research Shows Annual Meeting AASHTO Subcommittee on Design Orlando, FL, June 14, 2006 Susan Ferguson, PH.D. Delays at red lights getting longer Wall Street Journal,
Evaluation and Improvement of the Roundabouts
 The 2nd Conference on Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2016, *, ** Published Online **** 2016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/wjet http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/wjet.2014.***** Evaluation and
The 2nd Conference on Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2016, *, ** Published Online **** 2016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/wjet http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/wjet.2014.***** Evaluation and
TOWARDS A BETTER UNDERSTANDING OF MODERN ROUNDABOUTS
 TOWARDS A BETTER UNDERSTANDING OF MODERN ROUNDABOUTS C KROGSCHEEPERS, M WATTERS*, C TICHAUER**, F VAN RENSSEN** and G MATTHEE*** ITS Engineers (Pty) Ltd, 5 th Floor, Imperial Bank Terraces, Carl Cronje
TOWARDS A BETTER UNDERSTANDING OF MODERN ROUNDABOUTS C KROGSCHEEPERS, M WATTERS*, C TICHAUER**, F VAN RENSSEN** and G MATTHEE*** ITS Engineers (Pty) Ltd, 5 th Floor, Imperial Bank Terraces, Carl Cronje
Study on fatal accidents in Toyota city aimed at zero traffic fatality
 Study on fatal accidents in Toyota city aimed at zero traffic fatality Toru Kiuchi, Yoshihisa Kanno, Makoto Shiota Toyota Motor Corporation, 1 Toyota-cho, Toyota-shi, Aichi 471-8571, Japan Abstract - Since
Study on fatal accidents in Toyota city aimed at zero traffic fatality Toru Kiuchi, Yoshihisa Kanno, Makoto Shiota Toyota Motor Corporation, 1 Toyota-cho, Toyota-shi, Aichi 471-8571, Japan Abstract - Since
EVALUATION OF GROUP-BASED SIGNAL CONTROL THROUGH FIELD OPERATIONAL TESTS *
 EVALUATION OF GROUP-BASED SIGNAL CONTROL THROUGH FIELD OPERATIONAL TESTS * By Nan KANG **, Wael ALHAJYASEEN ***, Hideki NAKAMURA ****, Miho ASANO ***** and Keshuang TANG ****** 1. Introduction At signalized
EVALUATION OF GROUP-BASED SIGNAL CONTROL THROUGH FIELD OPERATIONAL TESTS * By Nan KANG **, Wael ALHAJYASEEN ***, Hideki NAKAMURA ****, Miho ASANO ***** and Keshuang TANG ****** 1. Introduction At signalized
Roundabout Design 101: Roundabout Capacity Issues
 Design 101: Capacity Issues Part 2 March 7, 2012 Presentation Outline Part 2 Geometry and Capacity Choosing a Capacity Analysis Method Modeling differences Capacity Delay Limitations Variation / Uncertainty
Design 101: Capacity Issues Part 2 March 7, 2012 Presentation Outline Part 2 Geometry and Capacity Choosing a Capacity Analysis Method Modeling differences Capacity Delay Limitations Variation / Uncertainty
Local road mountable roundabouts are there safety benefits?
 Local road mountable roundabouts are there safety benefits? Nimmi Monash University Accident Research Centre Abstract Roundabouts are internationally accepted as being highly effective in improving safety
Local road mountable roundabouts are there safety benefits? Nimmi Monash University Accident Research Centre Abstract Roundabouts are internationally accepted as being highly effective in improving safety
Roundabout Design Aid PREPARED BY TRAFFIC AND SAFETY
 Roundabout Design Aid PREPARED BY TRAFFIC AND SAFETY May 2018 Engineering Manual Preamble This manual provides guidance to administrative, engineering, and technical staff. Engineering practice requires
Roundabout Design Aid PREPARED BY TRAFFIC AND SAFETY May 2018 Engineering Manual Preamble This manual provides guidance to administrative, engineering, and technical staff. Engineering practice requires
Pedestrian Safety at Roundabouts
 Countermeasure Strategies for Pedestrian Safety Pedestrian Safety at Roundabouts Hillary Isebrands Federal Highway Administration January 6, 2016 Today s Presentation Introduction and housekeeping Audio
Countermeasure Strategies for Pedestrian Safety Pedestrian Safety at Roundabouts Hillary Isebrands Federal Highway Administration January 6, 2016 Today s Presentation Introduction and housekeeping Audio
Designing a Traffic Circle By David Bosworth For MATH 714
 Designing a Traffic Circle By David Bosworth For MATH 714 Abstract We all have had the experience of sitting in a traffic jam, or we ve seen cars bunched up on a road for some no apparent reason. The use
Designing a Traffic Circle By David Bosworth For MATH 714 Abstract We all have had the experience of sitting in a traffic jam, or we ve seen cars bunched up on a road for some no apparent reason. The use
Relative safety of alternative intersection designs
 Urban Transport XII: Urban Transport and the Environment in the 21st Century 379 Relative safety of alternative intersection designs L. C. Wadhwa 1 & M. Thomson 2 1 James Cook University Townsville Queensland
Urban Transport XII: Urban Transport and the Environment in the 21st Century 379 Relative safety of alternative intersection designs L. C. Wadhwa 1 & M. Thomson 2 1 James Cook University Townsville Queensland
ITARDA INFORMATION. No.128. Special feature
 ITARDA INFORMATION No.128 Special feature Special feature Accidents when four-wheel vehicles are reversing ~ Drivers must thoroughly check behind them, especially in parking lots! ~ Introduction You may
ITARDA INFORMATION No.128 Special feature Special feature Accidents when four-wheel vehicles are reversing ~ Drivers must thoroughly check behind them, especially in parking lots! ~ Introduction You may
Available online at ScienceDirect International Symposium of Transport Simulation (ISTS 16 Conference), July 7~8, 2016
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Transportation Research Procedia 21 (2017) 87 97 www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia 2016 International Symposium of Transport Simulation (ISTS 16 Conference),
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Transportation Research Procedia 21 (2017) 87 97 www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia 2016 International Symposium of Transport Simulation (ISTS 16 Conference),
Analysis of Unsignalized Intersection
 International Journal of Constructive Research in Civil Engineering (IJCRCE) Volume 2, Issue 1, 2016, PP 30-36 ISSN 2454-8693 (Online) www.arcjournals.org Analysis of Unsignalized Intersection B.Ramkumar
International Journal of Constructive Research in Civil Engineering (IJCRCE) Volume 2, Issue 1, 2016, PP 30-36 ISSN 2454-8693 (Online) www.arcjournals.org Analysis of Unsignalized Intersection B.Ramkumar
The Effect of Pavement Marking on Speed. Reduction in Exclusive Motorcycle Lane. in Malaysia
 Contemporary Engineering Sciences, Vol. 3, 2010, no. 3, 149-155 The Effect of Pavement Marking on Speed Reduction in Exclusive Motorcycle Lane in Malaysia Seyed Farzin Faezi PhD student in highway and
Contemporary Engineering Sciences, Vol. 3, 2010, no. 3, 149-155 The Effect of Pavement Marking on Speed Reduction in Exclusive Motorcycle Lane in Malaysia Seyed Farzin Faezi PhD student in highway and
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW
 CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW 2.1 Introduction This chapter presents some background information of the available literature related to the development of accident rates, accident models and accident statistic
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW 2.1 Introduction This chapter presents some background information of the available literature related to the development of accident rates, accident models and accident statistic
Safety and Active Transport. Dr. Maureen Carew, Medical Officer of Health Renfrew County and District Health Unit May 30, 2014
 Safety and Active Transport Dr. Maureen Carew, Medical Officer of Health Renfrew County and District Health Unit May 30, 2014 Active Transport Vision Increase levels of walking and cycling Reduce vehicle
Safety and Active Transport Dr. Maureen Carew, Medical Officer of Health Renfrew County and District Health Unit May 30, 2014 Active Transport Vision Increase levels of walking and cycling Reduce vehicle
A Review of Roundabout Safety Performance in the United States
 A Review of Roundabout Safety Performance in the United States 1.0 Introduction Aimee Flannery, Ph.D. Lily Elefteriadou, Ph.D. Roundabouts are a new form of at-grade intersection design that have been
A Review of Roundabout Safety Performance in the United States 1.0 Introduction Aimee Flannery, Ph.D. Lily Elefteriadou, Ph.D. Roundabouts are a new form of at-grade intersection design that have been
Intersection Improvement: Sturgeon Road, Silver Avenue and Murray Park Road Roundabout. Welcome. Public Information Session
 Intersection Improvement: 1 Welcome WHY IS AN INTERSECTION IMPROVEMENT NEEDED? 2 Traffic volumes for Sturgeon Road, Silver Avenue and Murray Park Road exceed the capacity of the existing 4-way stop controlled
Intersection Improvement: 1 Welcome WHY IS AN INTERSECTION IMPROVEMENT NEEDED? 2 Traffic volumes for Sturgeon Road, Silver Avenue and Murray Park Road exceed the capacity of the existing 4-way stop controlled
DOI /HORIZONS.B P23 UDC : (497.11) PEDESTRIAN CROSSING BEHAVIOUR AT UNSIGNALIZED CROSSINGS 1
 DOI 10.20544/HORIZONS.B.03.1.16.P23 UDC 656.142.054:159.922(497.11) PEDESTRIAN CROSSING BEHAVIOUR AT UNSIGNALIZED CROSSINGS 1 JelenaMitrovićSimić 1, Valentina Basarić, VukBogdanović Department of Traffic
DOI 10.20544/HORIZONS.B.03.1.16.P23 UDC 656.142.054:159.922(497.11) PEDESTRIAN CROSSING BEHAVIOUR AT UNSIGNALIZED CROSSINGS 1 JelenaMitrovićSimić 1, Valentina Basarić, VukBogdanović Department of Traffic
Title: Modeling Crossing Behavior of Drivers and Pedestrians at Uncontrolled Intersections and Mid-block Crossings
 Title: Modeling Crossing Behavior of Drivers and Pedestrians at Uncontrolled Intersections and Mid-block Crossings Objectives The goal of this study is to advance the state of the art in understanding
Title: Modeling Crossing Behavior of Drivers and Pedestrians at Uncontrolled Intersections and Mid-block Crossings Objectives The goal of this study is to advance the state of the art in understanding
Effects of Traffic Signal Retiming on Safety. Peter J. Yauch, P.E., PTOE Program Manager, TSM&O Albeck Gerken, Inc.
 Effects of Traffic Signal Retiming on Safety Peter J. Yauch, P.E., PTOE Program Manager, TSM&O Albeck Gerken, Inc. Introduction It has long been recognized that traffic signal timing can have an impact
Effects of Traffic Signal Retiming on Safety Peter J. Yauch, P.E., PTOE Program Manager, TSM&O Albeck Gerken, Inc. Introduction It has long been recognized that traffic signal timing can have an impact
An Operational Analysis of Modern Roundabouts in the United States
 An Operational Analysis of Modern Roundabouts in the United States Brian Zirkel from Lynbrook, New York is a 2012 graduate of Villanova University s College of Engineering. He finished with a B.S. in Civil
An Operational Analysis of Modern Roundabouts in the United States Brian Zirkel from Lynbrook, New York is a 2012 graduate of Villanova University s College of Engineering. He finished with a B.S. in Civil
Advance Yield Markings Reduce Motor Vehicle/Pedestrian. Conflicts at Multilane Crosswalks with an Uncontrolled Approach.
 Advance Yield Markings Reduce Motor Vehicle/Pedestrian Conflicts at Multilane Crosswalks with an Uncontrolled Approach by Ron Van Houten Mount Saint Vincent University J.E. Louis Malenfant Center for Education
Advance Yield Markings Reduce Motor Vehicle/Pedestrian Conflicts at Multilane Crosswalks with an Uncontrolled Approach by Ron Van Houten Mount Saint Vincent University J.E. Louis Malenfant Center for Education
ESTIMATION OF THE EFFECT OF AUTONOMOUS EMERGENCY BRAKING SYSTEMS FOR PEDESTRIANS ON REDUCTION IN THE NUMBER OF PEDESTRIAN VICTIMS
 ESTIMATION OF THE EFFECT OF AUTONOMOUS EMERGENCY BRAKING SYSTEMS FOR PEDESTRIANS ON REDUCTION IN THE NUMBER OF PEDESTRIAN VICTIMS Toshiyuki, Yanaoka Yukou, Takahashi Honda R&D Co.,Ltd. Automobile R&D Center
ESTIMATION OF THE EFFECT OF AUTONOMOUS EMERGENCY BRAKING SYSTEMS FOR PEDESTRIANS ON REDUCTION IN THE NUMBER OF PEDESTRIAN VICTIMS Toshiyuki, Yanaoka Yukou, Takahashi Honda R&D Co.,Ltd. Automobile R&D Center
Roundabouts. By: Nezamuddin, Valparaiso University. February 19, 2015
 Roundabouts By: Nezamuddin, Valparaiso University February 19, 2015 Outline 1. Background on Roundabouts 2. Silhavy Rd. Corridor Improvement Project in Valparaiso, IN 3. 5-points Roundabout in Valparaiso,
Roundabouts By: Nezamuddin, Valparaiso University February 19, 2015 Outline 1. Background on Roundabouts 2. Silhavy Rd. Corridor Improvement Project in Valparaiso, IN 3. 5-points Roundabout in Valparaiso,
Chapter 5 DATA COLLECTION FOR TRANSPORTATION SAFETY STUDIES
 Chapter 5 DATA COLLECTION FOR TRANSPORTATION SAFETY STUDIES 5.1 PURPOSE (1) The purpose of the Traffic Safety Studies chapter is to provide guidance on the data collection requirements for conducting a
Chapter 5 DATA COLLECTION FOR TRANSPORTATION SAFETY STUDIES 5.1 PURPOSE (1) The purpose of the Traffic Safety Studies chapter is to provide guidance on the data collection requirements for conducting a
CALIBRATION OF THE PLATOON DISPERSION MODEL BY CONSIDERING THE IMPACT OF THE PERCENTAGE OF BUSES AT SIGNALIZED INTERSECTIONS
 CALIBRATION OF THE PLATOON DISPERSION MODEL BY CONSIDERING THE IMPACT OF THE PERCENTAGE OF BUSES AT SIGNALIZED INTERSECTIONS By Youan Wang, Graduate Research Assistant MOE Key Laboratory for Urban Transportation
CALIBRATION OF THE PLATOON DISPERSION MODEL BY CONSIDERING THE IMPACT OF THE PERCENTAGE OF BUSES AT SIGNALIZED INTERSECTIONS By Youan Wang, Graduate Research Assistant MOE Key Laboratory for Urban Transportation
Traffic circles. February 9, 2009
 Traffic circles February 9, 2009 Abstract The use of a traffic circle is a relatively common means of controlling traffic in an intersection. Smaller Traffic circles can be especially effective in routing
Traffic circles February 9, 2009 Abstract The use of a traffic circle is a relatively common means of controlling traffic in an intersection. Smaller Traffic circles can be especially effective in routing
A Review of Roundabout Speeds in north Texas February 28, 2014
 Denholm 1 A Review of Roundabout Speeds in north Texas February 28, 2014 Word Count: 6,118 words (2,618 + 11 figures x 250 + 3 tables x 250) John P. Denholm III Lee Engineering, LLC 3030 LBJ FRWY, Ste.
Denholm 1 A Review of Roundabout Speeds in north Texas February 28, 2014 Word Count: 6,118 words (2,618 + 11 figures x 250 + 3 tables x 250) John P. Denholm III Lee Engineering, LLC 3030 LBJ FRWY, Ste.
At each type of conflict location, the risk is affected by certain parameters:
 TN001 April 2016 The separated cycleway options tool (SCOT) was developed to partially address some of the gaps identified in Stage 1 of the Cycling Network Guidance project relating to separated cycleways.
TN001 April 2016 The separated cycleway options tool (SCOT) was developed to partially address some of the gaps identified in Stage 1 of the Cycling Network Guidance project relating to separated cycleways.
RAMP CROSSWALK TREATMENT FOR SAN DIEGO AIRPORT, TERMINAL ONE
 RAMP CROSSWALK TREATMENT FOR SAN DIEGO AIRPORT, TERMINAL ONE AUTHORS Faisal Hamood, P.Eng, M.Eng. Scott O. Kuznicki, P.E. Leonard Perry, Ph.D. SUBMITTAL DATE Friday, May 12 th, 2017 SUBMITTED FOR THE Annual
RAMP CROSSWALK TREATMENT FOR SAN DIEGO AIRPORT, TERMINAL ONE AUTHORS Faisal Hamood, P.Eng, M.Eng. Scott O. Kuznicki, P.E. Leonard Perry, Ph.D. SUBMITTAL DATE Friday, May 12 th, 2017 SUBMITTED FOR THE Annual
Effect of Signs and Striping on Roundabout Safety: An Observational Before/After Study
 Effect of Signs and Striping on Roundabout Safety: An Observational Before/After Study Veronica Richfield Research Engineer University of Minnesota, Department of Civil Engineering 500 Pillsbury Dr., Minneapolis,
Effect of Signs and Striping on Roundabout Safety: An Observational Before/After Study Veronica Richfield Research Engineer University of Minnesota, Department of Civil Engineering 500 Pillsbury Dr., Minneapolis,
Keywords: multiple linear regression; pedestrian crossing delay; right-turn car flow; the number of pedestrians;
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Scien ce s 96 ( 2013 ) 1997 2003 13th COTA International Conference of Transportation Professionals (CICTP 2013)
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Scien ce s 96 ( 2013 ) 1997 2003 13th COTA International Conference of Transportation Professionals (CICTP 2013)
1. Introduction. 2. Survey Method. Volume 6 Issue 5, May Licensed Under Creative Commons Attribution CC BY
 A Study on Performance of an Urban Arterial Corridor Guggilla Raju 1, Rontala Ashwini 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, GCET 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering,
A Study on Performance of an Urban Arterial Corridor Guggilla Raju 1, Rontala Ashwini 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, GCET 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering,
Relationship of Road Lane Width to Safety for Urban and Suburban Arterials
 Relationship of Road Lane Width to Safety for Urban and Suburban Arterials Phd. Alma AFEZOLLI Polytechnic University of Tirana Construction and Infrastructure Department of Civil Engineering Faculty Tirana,
Relationship of Road Lane Width to Safety for Urban and Suburban Arterials Phd. Alma AFEZOLLI Polytechnic University of Tirana Construction and Infrastructure Department of Civil Engineering Faculty Tirana,
Analysis of Car-Pedestrian Impact Scenarios for the Evaluation of a Pedestrian Sensor System Based on the Accident Data from Sweden
 136 S.N. Huang, J.K. Yang Division of Vehicle Safety, Chalmers University of Technology, Göteborg, Sweden F. Eklund Automotive Safety Electronics, Autoliv Electronics AB, Linköping, Sweden Analysis of
136 S.N. Huang, J.K. Yang Division of Vehicle Safety, Chalmers University of Technology, Göteborg, Sweden F. Eklund Automotive Safety Electronics, Autoliv Electronics AB, Linköping, Sweden Analysis of
Public Opinion, Traffic Performance, the Environment, and Safety After Construction of Double-Lane Roundabouts
 Public Opinion, Traffic Performance, the Environment, and Safety After Construction of Double-Lane Roundabouts TRB 93 rd Annual Meeting Washington, D.C. January 15, 2014 Wen Hu, Ph.D. Intersection crashes
Public Opinion, Traffic Performance, the Environment, and Safety After Construction of Double-Lane Roundabouts TRB 93 rd Annual Meeting Washington, D.C. January 15, 2014 Wen Hu, Ph.D. Intersection crashes
PERCEPTUAL PAVEMENT MARKINGS AND THEIR APPLICATION
 PERCEPTUAL PAVEMENT MARKINGS AND THEIR APPLICATION Li Chang-cheng 1,2, Tang Jun-jun 2, Han Hui 2 (1 Beijing University of Technology, Beijing 100124, China; 2 Key Laboratory of Road Safety Ministry of
PERCEPTUAL PAVEMENT MARKINGS AND THEIR APPLICATION Li Chang-cheng 1,2, Tang Jun-jun 2, Han Hui 2 (1 Beijing University of Technology, Beijing 100124, China; 2 Key Laboratory of Road Safety Ministry of
Safety Impacts of Roundabouts on Bicycles and Pedestrians
 Safety Impacts of Roundabouts on Bicycles and Pedestrians USFHWA Max Henkle CVEN 5602 December 6, 2012 Contents Abstract... 2 Introduction... 3 Modern Roundabout Design Guidelines... 3 Dangerous Intersections...
Safety Impacts of Roundabouts on Bicycles and Pedestrians USFHWA Max Henkle CVEN 5602 December 6, 2012 Contents Abstract... 2 Introduction... 3 Modern Roundabout Design Guidelines... 3 Dangerous Intersections...
Grade Separated Intersection
 Grade Separated Intersection Lecture Notes in Transportation Systems Engineering Prof. Tom V. Mathew Contents 1 Overview 1 2 Classification of Intersection 2 2.1 Grade Separated Intersection...........................
Grade Separated Intersection Lecture Notes in Transportation Systems Engineering Prof. Tom V. Mathew Contents 1 Overview 1 2 Classification of Intersection 2 2.1 Grade Separated Intersection...........................
Transportation Research Forum
 Transportation Research Forum Modeling through Traffic Speed at Roundabouts along Urban and Suburban Street Arterials Author(s): Bashar H. Al-Omari, Khalid A. Ghuzlan, and Lina B. Al-Helo Source: Journal
Transportation Research Forum Modeling through Traffic Speed at Roundabouts along Urban and Suburban Street Arterials Author(s): Bashar H. Al-Omari, Khalid A. Ghuzlan, and Lina B. Al-Helo Source: Journal
ROUNDABOUTS/TRAFFIC CIRCLES
 GENERAL 1. Description This standard identifies minimum requirements that shall be met for Roundabouts and Neighborhood Traffic Circles in the design and construction of elements for Arlington County Horizontal
GENERAL 1. Description This standard identifies minimum requirements that shall be met for Roundabouts and Neighborhood Traffic Circles in the design and construction of elements for Arlington County Horizontal
Relative Vulnerability Matrix for Evaluating Multimodal Traffic Safety. O. Grembek 1
 337 Relative Vulnerability Matrix for Evaluating Multimodal Traffic Safety O. Grembek 1 1 Safe Transportation Research and Education Center, Institute of Transportation Studies, University of California,
337 Relative Vulnerability Matrix for Evaluating Multimodal Traffic Safety O. Grembek 1 1 Safe Transportation Research and Education Center, Institute of Transportation Studies, University of California,
Introduction Roundabouts are an increasingly popular alternative to traffic signals for intersection control in the United States. Roundabouts have a
 HIGH-CAPACITY ROUNDABOUT INTERSECTION ANALYSIS: GOING AROUND IN CIRCLES David Stanek, PE and Ronald T. Milam, AICP Abstract. Roundabouts have become increasingly popular in recent years as an innovative
HIGH-CAPACITY ROUNDABOUT INTERSECTION ANALYSIS: GOING AROUND IN CIRCLES David Stanek, PE and Ronald T. Milam, AICP Abstract. Roundabouts have become increasingly popular in recent years as an innovative
MRI-2: Integrated Simulation and Safety
 MRI-2: Integrated Simulation and Safety Year 3 2 nd Quarterly Report Submitted by: Dr. Essam Radwan, P.E. (PI), Ahmed.Radwan@ucf.edu Dr. Hatem Abou-Senna, P.E., habousenna@ucf.edu Dr. Mohamed Abdel-Aty,
MRI-2: Integrated Simulation and Safety Year 3 2 nd Quarterly Report Submitted by: Dr. Essam Radwan, P.E. (PI), Ahmed.Radwan@ucf.edu Dr. Hatem Abou-Senna, P.E., habousenna@ucf.edu Dr. Mohamed Abdel-Aty,
Reducing Speed: The C-Roundabout
 Reducing Speed: The C-Roundabout Ivan Jurisich (PRESENTER) NZCE (Civil) BSc(Maths) MPhil (Civil Eng) Member of ITE Traffic Engineering Solutions Ltd Phone: +649 366 7532 Email: ivan.jurisich@tes.net.nz
Reducing Speed: The C-Roundabout Ivan Jurisich (PRESENTER) NZCE (Civil) BSc(Maths) MPhil (Civil Eng) Member of ITE Traffic Engineering Solutions Ltd Phone: +649 366 7532 Email: ivan.jurisich@tes.net.nz
NCHRP Project Crossing Solutions at Roundabouts and Channelized Turn Lanes for Pedestrians with Vision Disabilities UNC-CH CH Highway Safety Res
 An Overview: NCHRP Project 3-783 Crossing Solutions at Roundabouts and Channelized Turn Lanes for Pedestrians with Vision Disabilities: R. G. Hughes, Ph.D. and R. Srinivasan,, Ph.D. UNC Highway Safety
An Overview: NCHRP Project 3-783 Crossing Solutions at Roundabouts and Channelized Turn Lanes for Pedestrians with Vision Disabilities: R. G. Hughes, Ph.D. and R. Srinivasan,, Ph.D. UNC Highway Safety
Reduction of Speed Limit at Approaches to Railway Level Crossings in WA. Main Roads WA. Presenter - Brian Kidd
 Australasian College of Road Safety Conference A Safe System: Making it Happen! Melbourne 1-2 September 2011 Reduction of Speed Limit at Approaches to Railway Level Crossings in WA Radalj T 1, Kidd B 1
Australasian College of Road Safety Conference A Safe System: Making it Happen! Melbourne 1-2 September 2011 Reduction of Speed Limit at Approaches to Railway Level Crossings in WA Radalj T 1, Kidd B 1
Crash Patterns in Western Australia. Kidd B., Main Roads Western Australia Willett P., Traffic Research Services
 Crash Patterns in Western Australia Kidd B., Main Roads Western Australia Willett P., Traffic Research Services Abstract Examination of crash patterns is one way of identifying key factors on which focus
Crash Patterns in Western Australia Kidd B., Main Roads Western Australia Willett P., Traffic Research Services Abstract Examination of crash patterns is one way of identifying key factors on which focus
An Analysis of the Travel Conditions on the U. S. 52 Bypass. Bypass in Lafayette, Indiana.
 An Analysis of the Travel Conditions on the U. S. 52 Bypass in Lafayette, Indiana T. B. T readway Research Assistant J. C. O ppenlander Research Engineer Joint Highway Research Project Purdue University
An Analysis of the Travel Conditions on the U. S. 52 Bypass in Lafayette, Indiana T. B. T readway Research Assistant J. C. O ppenlander Research Engineer Joint Highway Research Project Purdue University
A Strategy to Reduce Older Driver Injuries at Intersections Using More Accommodating Roundabout Design Practices
 A Strategy to Reduce Older Driver Injuries at Intersections Using More Accommodating Roundabout Design Practices by Dr. Dominique Lord* Department of Civil Engineering Texas A&M University, TAMU 3136 College
A Strategy to Reduce Older Driver Injuries at Intersections Using More Accommodating Roundabout Design Practices by Dr. Dominique Lord* Department of Civil Engineering Texas A&M University, TAMU 3136 College
Exploring Pedestrian Scramble Options in a Single-Lane Roundabout: Experimental Delay Analysis
 Al-Ghandour 0 0 0 0 Exploring Pedestrian Scramble Options in a Single-Lane Roundabout: Experimental Delay Analysis Majed Al-Ghandour, Ph.D., P.E. Engineering Manager, Assistant Branch Manager Program Development
Al-Ghandour 0 0 0 0 Exploring Pedestrian Scramble Options in a Single-Lane Roundabout: Experimental Delay Analysis Majed Al-Ghandour, Ph.D., P.E. Engineering Manager, Assistant Branch Manager Program Development
Relationship Between Child Pedestrian Accidents and City Planning in Zarqa, Jordan
 112 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1281 Relationship Between Child Pedestrian Accidents and City Planning in Zarqa, Jordan ADU H. AL-BALBISSI, MOHAMED T. ABOUL-ELA, AND SABAH SAMMOUR The relationship between
112 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1281 Relationship Between Child Pedestrian Accidents and City Planning in Zarqa, Jordan ADU H. AL-BALBISSI, MOHAMED T. ABOUL-ELA, AND SABAH SAMMOUR The relationship between
City of Prince Albert Statement of POLICY and PROCEDURE. Department: Public Works Policy No. 66. Section: Transportation Issued: July 14, 2014
 Page: 1 of 8 1 POLICY 1.01 The City shall follow all of the specifications in the Manual of Uniform Traffic Control Devices for Canada, prepared by the National Committee of Uniform Traffic Control, and
Page: 1 of 8 1 POLICY 1.01 The City shall follow all of the specifications in the Manual of Uniform Traffic Control Devices for Canada, prepared by the National Committee of Uniform Traffic Control, and
Roundabouts in Edmonton - A Comparison to the State-of-the-Art
 Roundabouts in Edmonton - A Comparison to the State-of-the-Art Authors: Carl Clayton, P.Eng. P.E. PTOE Stantec Consulting Ltd. Chuan Kua, P.Eng. City of Edmonton, Transportation and Streets Brice Stephenson,
Roundabouts in Edmonton - A Comparison to the State-of-the-Art Authors: Carl Clayton, P.Eng. P.E. PTOE Stantec Consulting Ltd. Chuan Kua, P.Eng. City of Edmonton, Transportation and Streets Brice Stephenson,
TRAFFIC CALMING TOOLBOX. For the residents of the City of Decatur, Georgia
 TRAFFIC CALMING TOOLBOX For the residents of the City of Decatur, Georgia 2 City of Decatur Traffic Calming Toolbox Public Works Department 2635 Talley Street Decatur, GA 30030 404.377.5571 3 Welcome to
TRAFFIC CALMING TOOLBOX For the residents of the City of Decatur, Georgia 2 City of Decatur Traffic Calming Toolbox Public Works Department 2635 Talley Street Decatur, GA 30030 404.377.5571 3 Welcome to
1.3.4 CHARACTERISTICS OF CLASSIFICATIONS
 Geometric Design Guide for Canadian Roads 1.3.4 CHARACTERISTICS OF CLASSIFICATIONS The principal characteristics of each of the six groups of road classifications are described by the following figure
Geometric Design Guide for Canadian Roads 1.3.4 CHARACTERISTICS OF CLASSIFICATIONS The principal characteristics of each of the six groups of road classifications are described by the following figure
Memorandum 1. INTRODUCTION. To: Cc: From: Denise Marshall Northumberland County
 255 Adelaide Street West Toronto, ON M5H 1X9 www.hdrinc.com File: 4.0 Memorandum To: Cc: From: Denise Marshall Northumberland County Tony Reitmeier HDR Guinevere Ngau HDR Andrew O Connor HDR Date: August
255 Adelaide Street West Toronto, ON M5H 1X9 www.hdrinc.com File: 4.0 Memorandum To: Cc: From: Denise Marshall Northumberland County Tony Reitmeier HDR Guinevere Ngau HDR Andrew O Connor HDR Date: August
Analysis of Signalized Intersection Crashes Nasima Bhuiyan, EmelindaM. Parentela and Venkata S. Inapuri
 Analysis of Signalized Intersection Crashes Nasima Bhuiyan, EmelindaM. arentela and Venkata S. Inapuri Abstract The goals of providing high levels of mobility and intersection efficiency while simultaneously
Analysis of Signalized Intersection Crashes Nasima Bhuiyan, EmelindaM. arentela and Venkata S. Inapuri Abstract The goals of providing high levels of mobility and intersection efficiency while simultaneously
Roundabout Design 101: Principles, Process, and Documentation
 Design 101: Principles, Process, and Documentation Part 1 March 7, 2012 Well designed roundabouts should minimize accidents, delay and costs for everyone using the intersection. This session covers the
Design 101: Principles, Process, and Documentation Part 1 March 7, 2012 Well designed roundabouts should minimize accidents, delay and costs for everyone using the intersection. This session covers the
4/27/2016. Introduction
 EVALUATING THE SAFETY EFFECTS OF INTERSECTION SAFETY DEVICES AND MOBILE PHOTO ENFORCEMENT AT THE CITY OF EDMONTON Karim El Basyouny PhD., Laura Contini M.Sc. & Ran Li, M.Sc. City of Edmonton Office of
EVALUATING THE SAFETY EFFECTS OF INTERSECTION SAFETY DEVICES AND MOBILE PHOTO ENFORCEMENT AT THE CITY OF EDMONTON Karim El Basyouny PhD., Laura Contini M.Sc. & Ran Li, M.Sc. City of Edmonton Office of
USA Parkway Traffic Operations Analysis, Roundabout Option. Pedro Rodriguez, NDOT; Bryan Gant, Jacobs; Randy Travis, NDOT
 Technical Memorandum TO: Hoang Hong, NDOT DATE: September 21, 2012 FROM: SUBJECT: COPIES: John Karachepone, Jacobs USA Parkway Traffic Operations Analysis, Pedro Rodriguez, NDOT; Bryan Gant, Jacobs; Randy
Technical Memorandum TO: Hoang Hong, NDOT DATE: September 21, 2012 FROM: SUBJECT: COPIES: John Karachepone, Jacobs USA Parkway Traffic Operations Analysis, Pedro Rodriguez, NDOT; Bryan Gant, Jacobs; Randy
Bhagwant N. Persaud* Richard A. Retting Craig Lyon* Anne T. McCartt. May *Consultant to the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety
 Review of The Impact of Red Light Cameras (Photo-Red Enforcement) on Crashes in Virginia by Nicholas J. Garber, John S. Miller, R. Elizabeth Abel, Saeed Eslambolchi, and Santhosh K. Korukonda Bhagwant
Review of The Impact of Red Light Cameras (Photo-Red Enforcement) on Crashes in Virginia by Nicholas J. Garber, John S. Miller, R. Elizabeth Abel, Saeed Eslambolchi, and Santhosh K. Korukonda Bhagwant
BLACK SPOTS MANAGEMENT - SLOVENIAN EXPERIENCE
 BLACK SPOTS MANAGEMENT - SLOVENIAN EXPERIENCE PhD Marko Renčelj, Assoc. Prof. Matjaž Šraml, University of Maribor, Faculty for Civil Engineering X International Symposium "ROAD ACCIDENTS PREVENTION 2010"
BLACK SPOTS MANAGEMENT - SLOVENIAN EXPERIENCE PhD Marko Renčelj, Assoc. Prof. Matjaž Šraml, University of Maribor, Faculty for Civil Engineering X International Symposium "ROAD ACCIDENTS PREVENTION 2010"
Appendix A Literature Review
 Appendix A Literature Review Appendix A Literature Review... 1 List of Tables and Figures... 3 Chapter 1: Executive Summary... 4 1.1 Scope and Organization of the Literature Review... 4 1.2 Findings from
Appendix A Literature Review Appendix A Literature Review... 1 List of Tables and Figures... 3 Chapter 1: Executive Summary... 4 1.1 Scope and Organization of the Literature Review... 4 1.2 Findings from
Deaths/injuries in motor vehicle crashes per million hours spent travelling, July 2007 June 2011 (All ages) Mode of travel
 Cyclists CRASH STATISTICS FOR THE YEAR ENDED 31 DECEMBER 211 Prepared by the Ministry of Transport CRASH FACTSHEET 212 Cyclists have a number of risk factors that do not affect car drivers. The main risk
Cyclists CRASH STATISTICS FOR THE YEAR ENDED 31 DECEMBER 211 Prepared by the Ministry of Transport CRASH FACTSHEET 212 Cyclists have a number of risk factors that do not affect car drivers. The main risk
A Traffic Operations Method for Assessing Automobile and Bicycle Shared Roadways
 A Traffic Operations Method for Assessing Automobile and Bicycle Shared Roadways A Thesis Proposal By James A. Robertson Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
A Traffic Operations Method for Assessing Automobile and Bicycle Shared Roadways A Thesis Proposal By James A. Robertson Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
In the spring of 2006, national newspaper headlines screamed
 Toll vs. Nontoll: Toll Facilities Are Safer By Jeff Campbell In the spring of 2006, national newspaper headlines screamed that toll plazas were the most dangerous place on the highway. The articles were
Toll vs. Nontoll: Toll Facilities Are Safer By Jeff Campbell In the spring of 2006, national newspaper headlines screamed that toll plazas were the most dangerous place on the highway. The articles were
20 meters beyond the circulating part of the roundabout. Includes pedestrian and
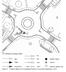 Table A1 Roundabout segments Roundabout segment Entry lane Segment 1 Segment 2 Circulatory road Segment 3 Description 20 100 meters off the roundabout. Oncoming traffic, queues associated with congestion.
Table A1 Roundabout segments Roundabout segment Entry lane Segment 1 Segment 2 Circulatory road Segment 3 Description 20 100 meters off the roundabout. Oncoming traffic, queues associated with congestion.
An Examination and Recommendation for Current Practices in Roundabout Lighting
 An Examination and Recommendation for Current Practices in Roundabout Lighting July 31, 2004 Paul Lutkevich, Parsons Brinckerhoff Quade & Douglas, Inc Professional Associate 75 Arlington St. Boston, MA
An Examination and Recommendation for Current Practices in Roundabout Lighting July 31, 2004 Paul Lutkevich, Parsons Brinckerhoff Quade & Douglas, Inc Professional Associate 75 Arlington St. Boston, MA
133 rd Street and 132 nd /Hemlock Street 132 nd Street and Foster Street MINI ROUNDABOUTS. Overland Park, Kansas
 133 rd Street and 132 nd /Hemlock Street 132 nd Street and Foster Street MINI ROUNDABOUTS Overland Park, Kansas September 1, 2017 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION... 1 2. LITERATURE REVIEW... 1 3. CONCEPT
133 rd Street and 132 nd /Hemlock Street 132 nd Street and Foster Street MINI ROUNDABOUTS Overland Park, Kansas September 1, 2017 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION... 1 2. LITERATURE REVIEW... 1 3. CONCEPT
Overhead Pedestrian Crossings Economic Evaluation through Vehicle Operating Cost and Travel Time Savings
 OUSL Journal (2014) Vol 7, (pp77-94) Overhead Pedestrian Crossings Economic Evaluation through Vehicle Operating Cost and Travel Time Savings K. M. G. N. S. Kumara, V. K. M. Pinnagoda and K. S. Weerasekera
OUSL Journal (2014) Vol 7, (pp77-94) Overhead Pedestrian Crossings Economic Evaluation through Vehicle Operating Cost and Travel Time Savings K. M. G. N. S. Kumara, V. K. M. Pinnagoda and K. S. Weerasekera
Combined impacts of configurational and compositional properties of street network on vehicular flow
 Combined impacts of configurational and compositional properties of street network on vehicular flow Yu Zhuang Tongji University, Shanghai, China arch-urban@163.com Xiaoyu Song Tongji University, Shanghai,
Combined impacts of configurational and compositional properties of street network on vehicular flow Yu Zhuang Tongji University, Shanghai, China arch-urban@163.com Xiaoyu Song Tongji University, Shanghai,
Manual 2010 roundabout capacity model
 An assessment of the Highway Capacity Manual 2010 roundabout capacity model TRB International Roundabout Conference Carmel, Indiana, USA, 18 20 May 2011 Presenter: Rahmi Akçelik Copyright 2000 2011 Akcelik
An assessment of the Highway Capacity Manual 2010 roundabout capacity model TRB International Roundabout Conference Carmel, Indiana, USA, 18 20 May 2011 Presenter: Rahmi Akçelik Copyright 2000 2011 Akcelik
Evaluation of service quality for pedestrian crossing flow at signalized intersection
 Evaluation of service quality for pedestrian crossing flow at signalized intersection Assist. Prof. Dr. Mehdi Al-Kubaisi Republic of Iraq University of Anbar-College of Engineering- Civil Department Email:
Evaluation of service quality for pedestrian crossing flow at signalized intersection Assist. Prof. Dr. Mehdi Al-Kubaisi Republic of Iraq University of Anbar-College of Engineering- Civil Department Email:
COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF TRAFFIC PERFORMANCE OF SMALL AND LARGE CENTRAL ISLAND ROTARIES IN MINNA, NIGERIA
 Part-I: Natural and Applied Sciences ISSN-L: 2223-9553, ISSN: 2223-9944 OMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF TRAFFI PERFORMANE OF SMALL AND LARGE ENTRAL ISLAND ROTARIES IN MINNA, NIGERIA M. Abubakar 1, P. N. Ndoke 2
Part-I: Natural and Applied Sciences ISSN-L: 2223-9553, ISSN: 2223-9944 OMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF TRAFFI PERFORMANE OF SMALL AND LARGE ENTRAL ISLAND ROTARIES IN MINNA, NIGERIA M. Abubakar 1, P. N. Ndoke 2
Roundabouts in Australia: the state of the art on models and applications
 Roundabouts in Australia: the state of the art on models and applications Seminar Presentation One-day International Meeting on Roundabouts Università di Pisa - Corso di TECNICA del TRAFFICO, Livorno,
Roundabouts in Australia: the state of the art on models and applications Seminar Presentation One-day International Meeting on Roundabouts Università di Pisa - Corso di TECNICA del TRAFFICO, Livorno,
MEASURING CONTROL DELAY AT SIGNALIZED INTERSECTIONS: CASE STUDY FROM SOHAG, EGYPT
 MEASURING CONTROL DELAY AT SIGNALIZED INTERSECTIONS: CASE STUDY FROM SOHAG, EGYPT Ibrahim H. Hashim 1, Talaat A. Abdel-Wahed 2 and Ahmed M. Mandor 3 1 Associate Prof., Civil Eng. Dept., Faculty of Engineering,
MEASURING CONTROL DELAY AT SIGNALIZED INTERSECTIONS: CASE STUDY FROM SOHAG, EGYPT Ibrahim H. Hashim 1, Talaat A. Abdel-Wahed 2 and Ahmed M. Mandor 3 1 Associate Prof., Civil Eng. Dept., Faculty of Engineering,
Roundabout Performance Analysis When Introducing Slip Lanes
 Al-Ghandour, illiams, Rasdorf, chroeder ubmitted for Presentation and Paper 1 st International Conference on Access Management Athens, Greece June 14-17, 2011 ponsored by Transportation Research Board
Al-Ghandour, illiams, Rasdorf, chroeder ubmitted for Presentation and Paper 1 st International Conference on Access Management Athens, Greece June 14-17, 2011 ponsored by Transportation Research Board
aasidra for Roundabouts INTRODUCTION
 aasidra for Roundabouts INTRODUCTION Rahmi Akçelik Director, Akcelik & Associates Pty Ltd Adjunct Professor, Monash University Mark Besley Director, Akcelik & Associates Pty Ltd TRB Roundabout Conference
aasidra for Roundabouts INTRODUCTION Rahmi Akçelik Director, Akcelik & Associates Pty Ltd Adjunct Professor, Monash University Mark Besley Director, Akcelik & Associates Pty Ltd TRB Roundabout Conference
J Street and Folsom Boulevard Lane Conversion Project (T ) Before and After Traffic Evaluation
 J Street and Folsom Boulevard Lane Conversion Project (T15125400) Before and After Traffic Evaluation Prepared by Transportation Division June 2014 Executive Summary On February 12, 2013, the City of Sacramento
J Street and Folsom Boulevard Lane Conversion Project (T15125400) Before and After Traffic Evaluation Prepared by Transportation Division June 2014 Executive Summary On February 12, 2013, the City of Sacramento
William Castro Associated Professor, Faculty of Engineering, Universidad Nacional de Colombia Bogotá, Colombia,
 ANALYSIS AND COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO-LANE ROUNDABOUTS AND TURBO ROUNDABOUTS BASED ON A ROAD SAFETY AUDIT METHODOLOGY AND MICROSIMULATION: A CASE STUDY IN URBAN AREA Lenin A. Bulla Associated Professor,
ANALYSIS AND COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO-LANE ROUNDABOUTS AND TURBO ROUNDABOUTS BASED ON A ROAD SAFETY AUDIT METHODOLOGY AND MICROSIMULATION: A CASE STUDY IN URBAN AREA Lenin A. Bulla Associated Professor,
Anatomy of Injury Severity and Fatality in Indonesian Traffic Accidents
 412 J. Eng. Technol. Sci., Vol. 49, No. 3, 2017, 412-422 Anatomy of Injury Severity and Fatality in Indonesian Traffic Accidents Sigit Puji Santosa 1*, Andi Isra Mahyuddin 1 & Febrianto Guntur Sunoto 2
412 J. Eng. Technol. Sci., Vol. 49, No. 3, 2017, 412-422 Anatomy of Injury Severity and Fatality in Indonesian Traffic Accidents Sigit Puji Santosa 1*, Andi Isra Mahyuddin 1 & Febrianto Guntur Sunoto 2
Introduction 4/28/ th International Conference on Urban Traffic Safety April 25-28, 2016 EDMONTON, ALBERTA, CANADA
 4/28/2016 EVALUATING THE SAFETY EFFECTS OF INTERSECTION SAFETY DEVICES AND MOBILE PHOTO ENFORCEMENT AT THE CITY OF EDMONTON Karim El Basyouny PhD., Laura Contini M.Sc. & Ran Li, M.Sc. City of Edmonton
4/28/2016 EVALUATING THE SAFETY EFFECTS OF INTERSECTION SAFETY DEVICES AND MOBILE PHOTO ENFORCEMENT AT THE CITY OF EDMONTON Karim El Basyouny PhD., Laura Contini M.Sc. & Ran Li, M.Sc. City of Edmonton
Scientific Analysis of Road Traffic Accidents. Requirements and Training Needs. Saving Lives through Accident Research
 Saving Lives through Accident Research Scientific Analysis of Road Traffic Accidents Requirements and Training Needs SAFE Annual Convention Shimla Overview Importance of In-Depth Accident Data (the feedback
Saving Lives through Accident Research Scientific Analysis of Road Traffic Accidents Requirements and Training Needs SAFE Annual Convention Shimla Overview Importance of In-Depth Accident Data (the feedback
Use of Throw Distances of Pedestrians and Bicyclists as Part of a Scientific Accident Reconstruction Method 1
 contents Introduction xi CHAPTER 1 Use of Throw Distances of Pedestrians and Bicyclists as Part of a Scientific Accident Reconstruction Method 1 Introduction 2 Basis of Speed Calculation 2 New Results
contents Introduction xi CHAPTER 1 Use of Throw Distances of Pedestrians and Bicyclists as Part of a Scientific Accident Reconstruction Method 1 Introduction 2 Basis of Speed Calculation 2 New Results
PEDESTRIAN ACCOMMODATIONS DPS 201 AT ROUNDABOUTS
 PEDESTRIAN ACCOMMODATIONS DPS 201 AT ROUNDABOUTS WHY THEY WORK FOR PEDESTRIANS IF DESIGNED CORRECTLY Separated sidewalks direct peds to crosswalks Splitter island Slow speed exit Truck apron Crosswalk
PEDESTRIAN ACCOMMODATIONS DPS 201 AT ROUNDABOUTS WHY THEY WORK FOR PEDESTRIANS IF DESIGNED CORRECTLY Separated sidewalks direct peds to crosswalks Splitter island Slow speed exit Truck apron Crosswalk
Design Traffic Technical Memorandum
 State Road 7 Extension PD&E Study Design Traffic Technical Memorandum Palm Beach County, FL October 2010 State Road 7 Extension PD&E Study Design Traffic Technical Memorandum Palm Beach County, FL Prepared
State Road 7 Extension PD&E Study Design Traffic Technical Memorandum Palm Beach County, FL October 2010 State Road 7 Extension PD&E Study Design Traffic Technical Memorandum Palm Beach County, FL Prepared
Traffic Impact Study WestBranch Residential Development Davidson, NC March 2016
 Traffic Impact Study WestBranch Residential Development Davidson, NC March 216 TRAFFIC IMPACT STUDY FOR THE WestBranch Residential Development LOCATED IN DAVIDSON, NC Prepared For: Lennar Carolinas, LLC
Traffic Impact Study WestBranch Residential Development Davidson, NC March 216 TRAFFIC IMPACT STUDY FOR THE WestBranch Residential Development LOCATED IN DAVIDSON, NC Prepared For: Lennar Carolinas, LLC
