Research Article Pedometers and Aerobic Capacity: Evaluating an Elementary After-School Running Program
|
|
|
- Rosanna Houston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 e Scientific World Journal, Article ID , 6 pages Research Article Pedometers and Aerobic Capacity: Evaluating an Elementary After-School Running Program Elizabeth Wanless, 1 Lawrence W. Judge, 1 Shannon T. Dieringer, 1 David Bellar, 2 James Johnson, 1 and Sheli Plummer 1 1 School of Physical Education, Sport, and Exercise Science, HP 360P, Ball State University, Muncie, IN 47304, USA 2 School of Kinesiology, University of Louisiana at Lafayette, Lafayette, LA 70504, USA Correspondence should be addressed to Lawrence W. Judge; lwjudge@bsu.edu Received 30 August 2013; Accepted 8 December 2013; Published 2 March 2014 Academic Editors: D. Caselli and L. H. Kuller Copyright 2014 Elizabeth Wanless et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Childhood obesity affects 1 of every 6 youth in the United States. One contributing factor to this statistic is a lack of physical activity (PA). Demands related to accountability which are placed on educators to demonstrate academic achievement often result in resistance to allocating time during the school day for PA. One possible solution is to consider utilizing time after school to integrate PA programs. The purpose of this study was to assess the impact of a 12-week after-school pedometer-focused PA program on aerobic capacity and to examine the relationship between step count and aerobic capacity in elementary school aged children. A group of elementary students (n =24; 9.5 ± 0.9 years) participated in a 12-week pedometer-focused PA program that included pretraining and posttraining fitness testing via the 20-meter version of the PACER test. Paired sample t-tests revealed significant differences between the pretest (M = 21.0 laps, SD = 9.9) and posttest (M = 25.2 laps, SD = 12.2) scores (t = 4.04, P 0.001). A Pearson correlation revealed no significant relationship between individual step count and the difference between PACER preand posttest (r = 0.318, P = 0.130). The program improved aerobic capacity, but an increase in pedometer-calculated step count was not a predictor. 1. Introduction Obesity-related risk factors and diseases are becoming increasingly prevalent in pediatric populations. Over the past thirty years, the obesity rate in the United States has escalated, creating an epidemic (15% to 30% in adults, 5% to 18% in adolescents years, and 6% to 19% in children 6 11 years) [1]. Obesity has been linked to numerous medical complications (e.g., hypertension, stroke, certain types of cancer, and coronary heart disease), as well as lower cognitive performance and reductions in brain structural integrity [2]. Furthermore, the impact of obesity on the development of type2diabetesissoprofoundthattheonsetofthisdiseaseis now befalling American youth. The approach to address these health concerns may include alternative strategies which focusmoreonpreventionratherthanontreatment.given that the effects of obesity and inactivity begin during childhood and multiply as children reach adulthood, prevention may be the most effective strategy to address these growing concerns. Having identified a concern regarding inactivity and obesity, the next step may be to identify and implement effective intervention strategies. One such strategy is the development of programs through partnerships with schools. As such, this strategy may provide the framework needed to implement prevention strategies through increased physical activity (PA) and education. Research suggests that regular participation in PA plays an important role in sustaining good health and has been a topic of investigation for several decades [3]. The Center for Disease Control (CDC) via the US Department of Health and Human Services recently outlined PA guidelines for American youth. These guidelines recommend that pediatric populations (ages 6 17) should engage in 60 minutes or more of moderate to vigorous PA daily with vigorous activity occurring a minimum of 3 days per week [3 5]. The CDC also suggests that the PA be aerobic and focus on muscle
2 2 The Scientific World Journal and bone-strengthening activities [3 5]. The American College of Sports Medicine [5] developed the guidelines further by suggesting four areas of focus: cardiorespiratory exercise, resistance exercise, flexibility exercise, and neuromotor exercise. The need for enhancing appropriate PA levels in order to reverse increasing trends of obesity and the prevalence of other health-related diseases associated with physical inactivity is at an all-time high [6 8]. Previous research has indicated that most American youth do not meet the recommended CDC guidelines [9, 10]. Additionally, researchers have reported that pediatric populations who engage in the recommended dose of PA are at lower risk of cardiovascular diseases and diabetes and have increased muscle and bone strength, cognitive and brain functioning, and psychosocial and mental health [2, 4, 11 14]. Finally, pediatric populations whoparticipateinpaaremorelikelytoengageinhabitualpa and sport [15]. Additionally, research studies have linked the amount of PA engaged during pediatric years with PA levels during adolescence and adulthood [16]. In addition to the health benefits, academic achievement hasalsobeenlinkedtopalevels.researchindicatesthatdaily PA improves concentration and academic achievement and can enhance test scores in math, reading, and writing [17, 18]. For these reasons, researchers have urged school administrators to implement long-term school-based interventions in order to prevent and manage childhood obesity [19]. The implementation of PA programming will ideally benefit learning and achievement for students. Several studies have stated that providing increased time for PA (e.g., physical education and after-school PA programs) can lead to better concentration, reduced disruptive behaviors, and higher test scores in reading, math, and writing [20]. It has also been proven that when students are involved in a PA program there is an improved rate of academic learning per unit of class time [21] and that increased time spent in physical education does not negatively affect student scores. Although the research suggests that the recommended dose of PA increases health and academic performance, only 8% of elementary schools, 6.4% of middle schools, and 5.8% of high schools provide daily physical education to all of their students [22]. Additionally, 20% of all elementary schools in the USA have eliminated recess in favor of increased classroom time under pressure to improve student achievement [20], makingviable solutionsduringtheschool day seemingly limited. In an effort to identify effective strategies to optimize student achievement, many school administrators are seeking to provide alternative programs, which engage students, provide social/emotional outlets, and increase PA as a means to improve the overall student performance. One alternative strategy that school administrators are beginning to utilize is after-school programming. Limitedresearchhasbeenconductedontheeffectsof after-school programs on increasing PA levels of the pediatric participants involved [23]. With a dearth of data from schoolbased interventions, the overall results may initially seem less promising than anticipated; and the efficacy is yet still undefined [24]. In a review of the literature conducted by Pate and O Neill [23], twelve after-school programs were evaluated. The authors concluded that the findings were mixed in regard to increasing PA levels of each of the programs studied. However, each intervention method, conversely, resulted in the formation of some type of healthful lifestyle habit. Additionally, Carrel et al. [25] investigated the effects of a 9-month after-school PA program on body composition and cardiovascular fitness of elementary school children. Both body composition and cardiovascular fitness improved significantly for obese and nonobese pediatric participants. An analysis by Gonzales-Suarez et al. [19] showedthatlongrunning programs were more effective in preventing childhood obesity if they combined PA and classroom learning; in fact, the longer the program, the more effective it proved to be. Although there is a need for further investigation and understanding of after-school programs, the preliminary evidence supports promoting after-school programming to increase PA levels and increase aerobic capacity of pediatric populations. In order to further investigate the benefits of after-school PA programs, it is important to use a validated measurement system. The use of pedometers to chart PA also continues to grow in popularity. Pedometers have gained widespread acceptance among PA researchers over the past decade [26]. A literature review conducted by Bravata et al. [27] evaluated 26 studies with a total of 2767 adult pedometerusing participants. Participants increased steps by an average of 2,491 steps in comparison with a control that did not utilize pedometers. As a result, participants increased PA by an average of 26.9%, significantly decreased their body mass index by 0.38, and decreased blood pressure. Given these results, which demonstrate the effectiveness of pedometers coupled with the notion that pedometers can be inexpensive, there is an indication that pedometers may also be an effective and accurate tool for measuring PA in pediatric populations [28 30]. The purpose of this study was to assess the impact of a pedometer-focused 12-week after-school PA program on aerobiccapacityaswellastherelationshipbetweenstepcount and aerobic capacity in elementary school aged children. 2. Materials and Methods 2.1. Participants. A group of elementary students (n =24), 9.5 ± 0.9 years (range 8 to 12) the ratio between males and females was equally distributed participated in and completed a pedometer-focused 12-week after-school PA program called Step up for Health (SUH). The SUH staff conducted outreach and registration activities with the aim of maximizing students and parents /guardians knowledge of the program and increasing the convenience of the registration process. Prior to the beginning of testing, all procedures were approved by a local university s International Review Board (IRB). Once approved, parental consent forms were sent home with all potential participants (students grades 3 6). Written and oral explanations (e.g., child assent) regarding procedures and potential risks to the participants were provided to parents from whom parental consent had beenobtained.afteratwo-weekperiod,theprocedurewas
3 The Scientific World Journal 3 repeated to recruit more participants for the program. After obtaining parental permission and written or oral assent from each participant, baseline measurements were taken. A total of 34 students enrolled in the program but 10 dropped out for variousreasonsanddidnotcompletethefinalassessment Procedures for the Step Up for Health After-School Running Program. This 12-week after-school running program was designed for elementary students in grades 3 through 6. The overall two-day-a-week program design was based upon a series of progressive walking/jogging workouts as well as PA centered games and activities. The program made use of the localschoolfacilitiestoholdthebiweekly,one-hoursessions. The types of activities and the format of each session were held consistent across the entire program. A typical session began with a meeting with all of the participants to explain whattheschedulewasfortheday.then,pedometerswere passed out and the participants engaged in a warm-up activity (e.g., Kangaroo Tag), followed by group stretching. After the warm-up the participants engaged in a group discussion involving a running tip (e.g., controlled breathing) and thenbrokeintopreestablishedteamsandcompletedthe prescribed running workout (e.g., 10-minute interval run). After the workout the participants completed a group activity (e.g., scavenger hunt) and a cool-down and recorded their pedometer steps. In addition, home workouts were provided to encourage participants to engage in PA at home and to promote exercise as a family activity. Each participant was assigned a pedometer to wear in order to track his or her steps taken during each session of the program. A daily step goal was provided, and each participant was instructed to make daily pedometer step goals. The pedometer step counts were then calculated and converted to miles, allowing the participants to have a better understanding of the accomplishments. The supervisor of the program provided the participants with rules and guidelines on using their pedometer to ensure that the pedometer was being used appropriately. Additionally, personal journals were assigned to each participant in order to record step totals and document his/her thoughts and reflect on the activity session. A licensed physical education teacher underwent a oneweek training, conducted by an experienced university faculty in physical education, prior to the start of the program. The licensed physical education teacher with the support of university faculty supervised all sessions Procedures for Fitness Testing. The Cooper Institute created Fitnessgram in 1982 in order to provide physical education teachers with a convenient way to evaluate fitness and report fitness levels to students and parents. In 2012, the President s Council on Fitness, Sports and Nutrition (PCFSN) adopted the Fitnessgram as the new school-based PA and health promotion program. The assessments were createdtoevaluatethefiveareasofhealth-relatedfitness: cardiovascular fitness (aerobic capacity), muscular strength, muscular endurance, flexibility, and body composition [31]. One of the assessments, the progressive aerobic cardiovascular endurance run (PACER), also known as the multistage fitness test, was used to assess cardiovascular fitness. ThePACERtesthasbeenshowntobeavalidandreliable assessment related to a participant s VO2 max or aerobic capacity. The participants must jog/run 20 meters each time a signal sounds using the Fitnessgram Testing Administration CD. With the passing of each minute, the running time is reduced by one half second, encouraging the participants to increase their running speed and pace themselves with the length of time allowed [31]. Each participant can fail to reach the designated line, before the beep tempo sounds, once before being eliminated. The highest lap attained before failing to keep pace with the beep tempo is recorded as the score. This assessment was chosen as a measure for pre- and posttesting. Participants were familiarized with the test prior to the pretest trial. During this test, each participant s score was recorded as the total number of laps. This assessment was conducted during week one and week twelve of the program to track improvements across the program. Prior to the beginning of the program, the licensed physical education teacher, who acted as the supervisor to the program, underwent a one-hour training to ensure that she was familiar with administering the test. The participants were briefed on best practices on calculating and recording PACER results. Each participant was paired with a peer during the test, and the participants were divided into smaller groups of 6 8 participants to ensure appropriate counting. Scoring of the test was performed with the assistance of undergraduate students enrolled in a physical education course of study. The student received training on the PACER test prior to being recruited to assist with the project Data Analysis. Data was first analyzed for normality via Shapiro-Wilk procedures and was not found to be significantly deviant from being normally distributed (P > 0.05).Subsequently,paired samples t-test was employed in order to assess differences in pre- and postworkout data. A Pearson bivariate correlation was utilized to determine the relationship between individual step count and the difference between PACER pre- and posttest data. Significance was set aprioritoalpha<0.05 for all analyses, and all statistical analyses were performed using SPSS version Results As a group, the elementary student participants totalled 1,388,155 steps for the project; individual steps ranged from 27,419 to 62,158 steps for the duration of the program (M = 47, 867, SD = 9332). A paired sample t-test revealed significant differences between the PACER pretest (M = 21.0 laps, SD = 9.9)(Figure 1) and posttest (M = 25.2 laps, SD = 12.2) scores (t = 4.04, P 0.001)(Figure 2). These results indicate that there was improvement in aerobic capacity as a result of participating in the 12-week program. However, Pearson correlation revealed no significant relationship between
4 4 The Scientific World Journal 10 Mean = 2.54 Std. dev. = N=24 10 Mean = 3.00 Std. dev. = 1.18 N= Frequency 6 Frequency Initial PACER assessment results Final PACER assessment results Figure 1: Histogram of initial 20-meter PACER assessment. Frequencies are groups by 1 (1 10 laps), 2 (11 20 laps), 3 (21 30 laps), 4(31 40laps),and5(greaterthan40laps). Figure 2: Histogram of final 20-meter PACER assessment. Frequenciesaregroupsby1(1 10laps),2(11 20laps),3(21 30laps),4(31 40 laps), and 5 (greater than 40 laps). the difference in individual step count and the difference between PACER pre- and posttest (r = 0.318, P = 0.130). 4. Discussion This study evaluated the impact of a pedometer-focused 12- week after-school PA program on aerobic capacity as well as the relationship between step count and aerobic capacity in elementary school aged children. The following discussion addresses three topics: program effectiveness in terms of aerobic capacity, incorporating pedometers, and after-school programming as a solution to physical education decline while the obesity epidemic is on the rise Program Effectiveness in terms of Aerobic Capacity. Limited research has been conducted on the effects of afterschool PA programs.pate and O Neill [23] reviewed twelve after-school programs and found mixed results with respect to the relationship between increased PA and improved aerobic capacity. The current study evaluated the effects of an after-school running program on pretest and posttest PACER scores, a widely accepted measure of aerobic capacity. The study results indicated that PACER scores significantly increased from program start to finish. Although this finding could not be compared with a control group of students, it does support previous conclusions from Pate and O Neil [23], which found varied effects of after-school PA programs. Additionally, a study by Carrel et al. [25] indicated that afterschool initiatives can improve cardiovascular fitness. In a related study by Judge et al. [32], fitness assessments were conducted via the PACER test of 76 elementary students who participated in an eight-week after-school training program. Paired sample t-tests revealed significant differences between the pretest (M = 11.9 laps, SD = 7.3) and posttest (M = 21.3 laps, SD = 11.5)onthePACERtest Incorporating Pedometers. The results of this study demonstrate the positive impact of the after-school PA program on the aerobic capacity of the participants; however, step count did not predict improvement in aerobic capacity. This may be largely due to the variation in starting levels of fitness of the participants and the data collection of the pedometer being limited to only a volume of training assessment. Pedometers lack the ability to track intensity of movement which is critical to determining zones (light, moderate,andvigorous)oftraining.theresultsrevealingthat pedometer step count and aerobic capacity were not linked may seem contradictory to the overwhelming support for the use of pedometers as a tool to increase PA in adults [27]. However, Bravata et al. [27] showed several health benefits foradultsasaresultofpedometerusebywayofincreasing PA not directly related to increase in aerobic capacity. Further studies are needed to assess the value of pedometers as a tool toencourageincreasedpaandimprovedaerobiccapacityin both adults and children. Bravata et al. [27] acknowledged goal setting as one of the key determinants in participant PA increase and health benefit acquisition. Participant goals for steps per day, according to existing pediatric guidelines, are 15,000 steps/day for boys and 12,000 steps/day for girls [33]. These are reasonable targets for children with respect to improving health outcomes [33]. Perhaps one of the reasons why aerobic capacity did not increase as a result of pedometer-use was the neglect of program leaders to include goals for participants.
5 The Scientific World Journal 5 A benchmark is needed for future running programs that include pedometers. In order to obtain that data, additional research is needed to more fully understand the impact of goal setting on increased PA levels for pediatric participants. Research concerning different levels of steps taken in order to comprehend how this type of goal setting may affect PA levels and aerobic capacity for pediatric participants would aid in setting a benchmark for future running programs incorporating pedometers. Because pedometers have gained widespread acceptance, their accuracy in step count has also been a source of research study. Schneider et al. [34] tested accuracy among three brands in different conditions of walking among adult users. The authors reported a large variation in accuracy by brand. This may have limited the predictive value of the step count scores in the present investigation After-School Programming as a Solution. Schools have access to nearly all of a nation s youngsters. Developing strong partnerships with our schools may provide the framework needed to focus on the prevention through increased activity and education. Physical inactivity in American youth is an ongoing concern. It has been suggested that school-based programs be promoted to increase the opportunities for pediatric populations to engage in the recommended daily dose of PA. Although initiatives have been implemented and preestablished structures (e.g., physical education) provide an opportunity for pediatric populations to be active duringtheschoolday,studentsarestillnotmeetingthe recommendations. It seems that, with academic rigor being emphasizedinschools,thereislittletimeforpa.anattractive and fairly unexplored method to promote increased daily PA is structured after-school programming. Although this study helped to confirm results of previous studies which indicate that after-school running programs have the potential to increase aerobic capacity and PA, afterschool programs geared for twice a week in this study and three times a week for others fall very short of the CDC guidelines which recommend 60 minutes of exercise a day for all students attending the school [3]. However, in order for an afterschool running program to meet recommended CDC guidelines and produce the desired benefits, the program must be offered daily and students must be strongly encouraged to participate. This suggestion may be a further drain on school resources and, for that reason, may not be plausible. The after-school programming to meet CDC requirements may not provide a total solution to address obesity and meet the needs of students, but certainly it would play an important role in meeting those needs. However, the culture of inactivity is more complicated than a simple solution of increased PA after-school can solve. Addressing the underlying behavioral and psychological mechanisms leading to the rising obesity trajectories is also an important step to solving the problem [32]. Further research is warranted in order to understand the effectiveness of an after-school PA/running program on the overall fitness of the participants. 5. Conclusions The initial success of the SUH after-school running program as a service-learning project provides a working model for implementation of similar projects in the future. Although thisprojectwasfocuseduponimplementationinanelementary school setting, application of these concepts by other academic units with similar goals of positively impacting their community through PA is recommended. According to the findings in this project, students fitness levels can be improved through a program such as SUH that utilized pedometers as motivation to succeed. In this current study, the aerobic capacity of the students was improved even though pedometer step count was not a predictor. Future studies may wish to consider expanding to include all K-12 students and examine all aspects of fitness to better understand and promote healthy lifestyles in pediatric populations. Conflict of Interests The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper. References [1] Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Childhood obesity facts. Adolescent and School Health, 2013, [2] P.L.Yau,M.G.Castro,A.Tagani,W.H.TsuiA,andConvit, Obesity and metabolic syndrome and functional and structural brain impairments in adolescence, Pediatrics, vol. 130, no. 4, pp , [3] Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, How much physical activity do children need, 2011, cdc.gov/physicalactivity/everyone/guidelines/children.html. [4] U. S. Department of Health and Human Services, Activity Guidelines for Americans, Department of Health and Human Services, Washington, DC, USA, [5] American College of Sports Medicine, ACSM new recommendations on quantity and quality of exercise, 2011, /08/01/acsm-issues-new-recommendations-on-quantityand-quality-of-exercise. [6] Center for Disease Control, State indicator report on physical activity, 2010 national action guide, 2010, State Indicator Report 2010 Action Guide.pdf. [7] E.B.Kahn,L.T.Ramsey,R.C.Brownsonetal., Theeffectiveness of interventions to increase physical activity: a systematic review, The American Preventive Medicine, vol. 22, no.4,pp ,2002. [8] D. E. R. Warburton, C. W. Nicol, and S. S. D. Bredin, Health benefits of physical activity: the evidence, Canadian Medical Association Journal,vol.174,no.6,2006. [9]D.K.Eaton,L.Kann,S.Kinchenetal., Youthriskbehavior surveillance, United States, 2005, The School Health, vol. 76, no. 7, pp , [10] R. R. Pate, P. S. Freedson, J. F. Sallis et al., Compliance with physical activity guidelines: prevalence in a population of children and youth, Annals of Epidemiology, vol. 12, no. 5, pp , 2002.
6 6 The Scientific World Journal [11] L. B. Andersen, M. Harro, L. B. Sardinha et al., Physical activity and clustered cardiovascular risk in children: a cross-sectional study (The European Youth Heart Study), The Lancet,vol.368, no.9532,pp ,2006. [12] C. H. Hillman, K. I. Erickson, and A. F. Kramer, Be smart, exercise your heart: exercise effects on brain and cognition, Nature Reviews Neuroscience,vol.9,no.1,pp.58 65,2008. [13]W.B.Strong,R.M.Malina,C.J.R.Blimkieetal., Evidence based physical activity for school-age youth, Pediatrics,vol.146,no.6,pp ,2005. [14] M. C. Riddell and K. E. Iscoe, Physical activity, sport, and pediatric diabetes, Pediatric Diabetes, vol.7,no.1,pp.60 70, [15] R. M. Malina, Movement proficiency in childhood: implications for physical activity and youth sport, Kinesiologia Slovenica,vol.18,pp.19 34,2012. [16] J. F. Sallis, T. L. McKenzie, J. E. Alcaraz, B. Kolody, N. Faucette, and M. F. Hovell, The effects of a 2-year physical education program (SPARK) on physical activity and fitness in elementary school students, The American Public Health,vol.87, no. 8, pp , [17] J. R. Best, Effects of physical activity on children s executive function: contributions of experimental research on aerobic exercise, Developmental Review, vol. 30, no. 4, pp , [18] J.F.Sallis,T.L.McKenzie,B.Kolody,M.Lewis,S.Marshall,and P. Rosengard, Effects of health-related physical education on academic achievement: project SPARK, Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport,vol.70,no.2,pp ,1999. [19] C. Gonzalez-Suarez, A. Worley, K. Grimmer-Somers, and V. Dones, School-based interventions on childhood obesity: a meta-analysis, The American Preventive Medicine, vol.37,no.5,pp ,2009. [20] D. Satcher, Healthy and ready to learn, Educational Leadership, vol.63,no.1,pp.26 30,2005. [21] H. Taras, Physical activity and student performance at school, School Health, vol. 75, no. 6, pp , [22] School Health Policies and Programs Study (CDC), Fact sheet physical education and activity: from CDC s School Health Policies and Programs Study (SHPPS) 2000, School Health,vol.71,no.7,2001. [23] R. R. Pate and J. R. O Neill, After-school interventions to increase physical activity among youth, British Sports Medicine,vol.43,no.1,pp.14 18,2009. [24] P. J. Veugelers and A. L. Fitzgerald, Effectiveness of school programs in preventing childhood obesity: a multilevel comparison, The American Public Health, vol.95,no.3, pp , [25] A. L. Carrel, J. Logue, H. Deininger, R. R. Clark, V. Curtis, and P. Montague, An afterschool exercise program improves fitness, and body composition in elementary school children, Journal Education and Sports Management,vol.3,pp.32 36,2011. [26] D. R. Bassett Jr., B. E. Ainsworth, S. R. Leggett et al., Accuracy of five electronic pedometers for measuring distance walked, Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, vol.28,no.8,pp , [27] D. M. Bravata, C. Smith-Spangler, V. Sundaram et al., Using pedometers to increase physical activity and improve health: a systematic review, the American Medical Association, vol. 298, no. 19, pp , [28] S. A. Clemes and S. J. Biddle, The use of pedometers for monitoring physical activity in children and adolescents: measurement consideration, JournalofPhysicalActivityandHealth, vol. 10, no. 2, pp , [29] R. Jago, K. Watson, T. Baranowski et al., Pedometer reliability, validity and daily activity targets among 10- to 15-year-old boys, Sports Sciences,vol.24,no.3,pp ,2006. [30] E. McNamara, Z. Hudson, and S. J. C. Taylor, Measuring activity levels of young people: the validity of pedometers, British Medical Bulletin,vol.95,no.1,pp ,2010. [31] G. J. Welk and M. D. Meredith, Eds., Fitnessgram/Activitygram Reference Guide,TheCooperInstitute,Dallas,Tex,USA,2008. [32] L. W. Judge, D. Pierce, J. Peterson et al., Engaging experiential service learning through a co-curricular club: the chase Charlie races, ICHPERD-SD Research,vol. 1,pp.30 38, [33] J. Scott Duncan, G. Schofield, and E. K. Duncan, Step count recommendations for children based on body fat, Preventive Medicine,vol.44,no.1,pp.42 44,2007. [34] P. L. Schneider, S. E. Crouter, O. Lukajic, and D. R. Bassett Jr., Accuracy and reliability of 10 pedometers for measuring steps over a 400-m walk, Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, vol. 35, no. 10, pp , 2003.
7 MEDIATORS of INFLAMMATION The Scientific World Journal Gastroenterology Research and Practice Diabetes Research International Endocrinology Immunology Research Disease Markers Submit your manuscripts at BioMed Research International PPAR Research Obesity Ophthalmology Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Stem Cells International Oncology Parkinson s Disease Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine AIDS Behavioural Neurology Research and Treatment Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity
An Examination of the Effects of a Curriculum Based Pedometer Program in Two Age Groups: Adults and Pre-Adolescent Children
 1 of 5 5/5/2010 1:38 PM Home Current Issue Editorial Board Instructions for Authors Contact Lethbridge Undergraduate Research Journal ISSN 1718-8482 An Examination of the Effects of a Curriculum Based
1 of 5 5/5/2010 1:38 PM Home Current Issue Editorial Board Instructions for Authors Contact Lethbridge Undergraduate Research Journal ISSN 1718-8482 An Examination of the Effects of a Curriculum Based
Aerobic Capacity. Need Additional Resources?
 Aerobic Capacity Aerobic capacity is perhaps the most important component of any fitness program. Research indicates that acceptable levels of aerobic capacity are associated with a reduced risk of high
Aerobic Capacity Aerobic capacity is perhaps the most important component of any fitness program. Research indicates that acceptable levels of aerobic capacity are associated with a reduced risk of high
SQUASH CANADA TECHNICAL AND FITNESS TESTING PROTOCOL MANUAL
 SQUASH CANADA TECHNICAL AND FITNESS TESTING PROTOCOL MANUAL Revised April 2010 Table of Contents Introduction to Squash Canada... 3 Need for Technical & Fitness Testing Protocols... 3 Long Term Player
SQUASH CANADA TECHNICAL AND FITNESS TESTING PROTOCOL MANUAL Revised April 2010 Table of Contents Introduction to Squash Canada... 3 Need for Technical & Fitness Testing Protocols... 3 Long Term Player
Health and Community Design: The Local Government Role in Promoting Active Living
 Health and Community Design: The Local Government Role in Promoting Active Living Rich Killingsworth, Director Active Living by Design National Program Office University of North Carolina School of Public
Health and Community Design: The Local Government Role in Promoting Active Living Rich Killingsworth, Director Active Living by Design National Program Office University of North Carolina School of Public
EvaluationoftheAARPRed HatSocietyStep&Stride WithRuby:AYear-Long WalkingProgram. ExecutiveSummary
 EvaluationoftheAARPRed HatSocietyStep&Stride WithRuby:AYear-Long WalkingProgram ExecutiveSummary July2008 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Introduction In 2007, AARP developed a year-long walking program, Step & Stride
EvaluationoftheAARPRed HatSocietyStep&Stride WithRuby:AYear-Long WalkingProgram ExecutiveSummary July2008 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Introduction In 2007, AARP developed a year-long walking program, Step & Stride
Walking Meetings: The Research on Why We should Walk and Talk
 Walking Meetings: The Research on Why We should Walk and Talk Dr. Brandy Parker Dr. Lodge McCammon June 2015 Walking Meetings Most organizations would agree that employees are their biggest asset. Having
Walking Meetings: The Research on Why We should Walk and Talk Dr. Brandy Parker Dr. Lodge McCammon June 2015 Walking Meetings Most organizations would agree that employees are their biggest asset. Having
P. A. C. E. R. Progressive Aerobic Cardiovascular Endurance Run. Manual
 P. A. C. E. R. Progressive Aerobic Cardiovascular Endurance Run Manual About the PACER The Progressive Aerobic Cardiovascular Endurance Run (PACER) is a multistage shuttle run created by Leger and Lambert
P. A. C. E. R. Progressive Aerobic Cardiovascular Endurance Run Manual About the PACER The Progressive Aerobic Cardiovascular Endurance Run (PACER) is a multistage shuttle run created by Leger and Lambert
Health Beyond Healthcare The Chronic Disease Impacts of Neighborhood Design. Erik J. Aulestia, AICP Principal, Torti Gallas + Partners
 Health Beyond Healthcare The Chronic Disease Impacts of Neighborhood Design Erik J. Aulestia, AICP Principal, Torti Gallas + Partners Prior to 20th Century How should a city look and function? Architects
Health Beyond Healthcare The Chronic Disease Impacts of Neighborhood Design Erik J. Aulestia, AICP Principal, Torti Gallas + Partners Prior to 20th Century How should a city look and function? Architects
Walking for Heart Health in Rural Women
 Walking for Heart Health in Rural Women ELISABETH MARIGLIANO, BSN, RN 1, 2 PAMELA STEWART FAHS, PHD, RN 1 CRISTINA LUDDEN, MS 2 BINGHAMTON UNIVERSITY, STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK, DECKER SCHOOL OF NURSING
Walking for Heart Health in Rural Women ELISABETH MARIGLIANO, BSN, RN 1, 2 PAMELA STEWART FAHS, PHD, RN 1 CRISTINA LUDDEN, MS 2 BINGHAMTON UNIVERSITY, STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK, DECKER SCHOOL OF NURSING
JEPonline Journal of Exercise Physiologyonline
 Walking Technique and Estimated VO 2 max Values 21 JEPonline Journal of Exercise Physiologyonline Official Journal of The American Society of Exercise Physiologists (ASEP) ISSN 1097-9751 An International
Walking Technique and Estimated VO 2 max Values 21 JEPonline Journal of Exercise Physiologyonline Official Journal of The American Society of Exercise Physiologists (ASEP) ISSN 1097-9751 An International
Vector Rope Trainer Cardiovascular Program Fitness Level: GENERAL
 Cardiovascular Program Fitness Level: GENERAL These are exercise options. Mix and match as preferred during each workout session. Frequency: Two to three days per week Start with 3 minutes of light pace
Cardiovascular Program Fitness Level: GENERAL These are exercise options. Mix and match as preferred during each workout session. Frequency: Two to three days per week Start with 3 minutes of light pace
The Effect of a Seven Week Exercise Program on Golf Swing Performance and Musculoskeletal Screening Scores
 The Effect of a Seven Week Exercise Program on Golf Swing Performance and Musculoskeletal Screening Scores 2017 Mico Hannes Olivier Bachelor of Sport Science Faculty of Health Sciences and Medicine Bond
The Effect of a Seven Week Exercise Program on Golf Swing Performance and Musculoskeletal Screening Scores 2017 Mico Hannes Olivier Bachelor of Sport Science Faculty of Health Sciences and Medicine Bond
A COMPARATIVE STUDY ON RESPIRATORY PARAMETERS BETWEEN SHORT DISTANCE AND LONG DISTANCE SWIMMERS
 A COMPARATIVE STUDY ON RESPIRATORY PARAMETERS BETWEEN SHORT DISTANCE AND LONG DISTANCE SWIMMERS Baghel Priya PhD scholar, LNIPE, Gwalior, M.P., India ABSTRACT The purpose of the study was to find out the
A COMPARATIVE STUDY ON RESPIRATORY PARAMETERS BETWEEN SHORT DISTANCE AND LONG DISTANCE SWIMMERS Baghel Priya PhD scholar, LNIPE, Gwalior, M.P., India ABSTRACT The purpose of the study was to find out the
Train to Train Ages female Ages male
 Train to Train Ages 11-15 female Ages 12-16 male The objective of the Train to Train stage is to further develop sports specific skills, begin to introduce competition, and start to emphasize support training
Train to Train Ages 11-15 female Ages 12-16 male The objective of the Train to Train stage is to further develop sports specific skills, begin to introduce competition, and start to emphasize support training
A CROSS-SECTIONAL ANALYSIS OF SKILL RELATED PHYSICAL FITNESS COMPONENTS OF KAYAKING AND ROWING PLAYERS
 European Journal of Physical Education and Sport Science ISSN: 2501-1235 ISSN-L: 2501-1235 Available on-line at: www.oapub.org/edu doi: 10.5281/zenodo.1050701 Volume 3 Issue 10 2017 A CROSS-SECTIONAL ANALYSIS
European Journal of Physical Education and Sport Science ISSN: 2501-1235 ISSN-L: 2501-1235 Available on-line at: www.oapub.org/edu doi: 10.5281/zenodo.1050701 Volume 3 Issue 10 2017 A CROSS-SECTIONAL ANALYSIS
Syllabus for HPE 098 Triathlon Training 1 Credit Hour Spring 2016
 Syllabus for HPE 098 Triathlon Training 1 Credit Hour Spring 2016 I. COURSE DESCRIPTION Designed for students who have demonstrated a high level of health fitness and desire to improve or maintain their
Syllabus for HPE 098 Triathlon Training 1 Credit Hour Spring 2016 I. COURSE DESCRIPTION Designed for students who have demonstrated a high level of health fitness and desire to improve or maintain their
Syllabus for HPE 098 Triathlon Training 1 Credit Hour Fall 2016
 Syllabus for HPE 098 Triathlon Training 1 Credit Hour Fall 2016 I. COURSE DESCRIPTION Designed for students who have demonstrated a high level of health fitness and desire to improve or maintain their
Syllabus for HPE 098 Triathlon Training 1 Credit Hour Fall 2016 I. COURSE DESCRIPTION Designed for students who have demonstrated a high level of health fitness and desire to improve or maintain their
Acknowledgements. Sport Canada. Canadian Sport for Life (CS4L) Contributors. Richard Way Istvan Balyi Steve Norris Colin Higgs Charles Cardinal
 Acknowledgements Sport Canada Coaching Association of Canada National Coaching Certification Program Canadian Sport for Life (CS4L) Contributors Richard Way Istvan Balyi Steve Norris Colin Higgs Charles
Acknowledgements Sport Canada Coaching Association of Canada National Coaching Certification Program Canadian Sport for Life (CS4L) Contributors Richard Way Istvan Balyi Steve Norris Colin Higgs Charles
Childhood Obesity: A Policy Perspective
 Leadership for Healthy Communities Advancing Policies to Support Healthy Eating and Active Living Childhood Obesity: A Policy Perspective Elizabeth Hinman elizabeth@leadershipforhealthycommunities.org
Leadership for Healthy Communities Advancing Policies to Support Healthy Eating and Active Living Childhood Obesity: A Policy Perspective Elizabeth Hinman elizabeth@leadershipforhealthycommunities.org
2nd International Conference on Management Science and Industrial Engineering (MSIE 2013)
 2nd International Conference on Management Science and Industrial Engineering (MSIE 2013) The Experimental Research of the Impact of Volleyball on the Physical and Mental Health for Female University Students
2nd International Conference on Management Science and Industrial Engineering (MSIE 2013) The Experimental Research of the Impact of Volleyball on the Physical and Mental Health for Female University Students
Clinical Study Synopsis
 Clinical Study Synopsis This Clinical Study Synopsis is provided for patients and healthcare professionals to increase the transparency of Bayer's clinical research. This document is not intended to replace
Clinical Study Synopsis This Clinical Study Synopsis is provided for patients and healthcare professionals to increase the transparency of Bayer's clinical research. This document is not intended to replace
Research Article Effects of Walking Direction and Cognitive Challenges on Gait in Persons with Multiple Sclerosis
 Multiple Sclerosis International Volume 2013, Article ID 859323, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/859323 Research Article Effects of Walking Direction and Cognitive Challenges on Gait in Persons
Multiple Sclerosis International Volume 2013, Article ID 859323, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/859323 Research Article Effects of Walking Direction and Cognitive Challenges on Gait in Persons
FITNESSGRAM Scorecard (for Males , and Adults 18+) Females see last pages
 FITNESSGRAM Scorecard (for Males 14-17+, and Adults 18+) Females see last pages Name: Date: Age: Weight Health Weight: Height: lbs inches Inches 2 : BMI: = (lbs x 703) / inches 2 Skinfold Measures See:
FITNESSGRAM Scorecard (for Males 14-17+, and Adults 18+) Females see last pages Name: Date: Age: Weight Health Weight: Height: lbs inches Inches 2 : BMI: = (lbs x 703) / inches 2 Skinfold Measures See:
Are We Driving Our Kids to Unhealthy Habits? 2013 Active Healthy Kids Canada Report Card on Physical Activity for Children and Youth
 Are We Driving Our Kids to Unhealthy Habits? 2013 Active Healthy Kids Canada Report Card on Physical Activity for Children and Youth Active Healthy Kids Canada is a national charitable organization established
Are We Driving Our Kids to Unhealthy Habits? 2013 Active Healthy Kids Canada Report Card on Physical Activity for Children and Youth Active Healthy Kids Canada is a national charitable organization established
Pedometers: Answers to FAQs from Teachers
 Pedometers: Answers to FAQs from Teachers Cuddihy, Thomas F; Pangrazi, Robert P; Tomson, L Michaud. Journal of Physical Education, Recreation & Dance 76. 2 (Feb 2005): 36-40,55. Abstract In Japan, pedometers
Pedometers: Answers to FAQs from Teachers Cuddihy, Thomas F; Pangrazi, Robert P; Tomson, L Michaud. Journal of Physical Education, Recreation & Dance 76. 2 (Feb 2005): 36-40,55. Abstract In Japan, pedometers
VALIDATION OF THE PHYSICAL ACTIVITY INDEX (PAI) AS A MEASURE OF TOTAL ACTIVITY LOAD AND TOTAL KILOCALORIE EXPENDITURE
 VALIDATION OF THE PHYSICAL ACTIVITY INDEX (PAI) AS A MEASURE OF TOTAL ACTIVITY LOAD AND TOTAL KILOCALORIE EXPENDITURE DURING SUBMAXIMAL TREADMILL WALKING by Kimberly Anne Weary-Smith B.S. Slippery Rock
VALIDATION OF THE PHYSICAL ACTIVITY INDEX (PAI) AS A MEASURE OF TOTAL ACTIVITY LOAD AND TOTAL KILOCALORIE EXPENDITURE DURING SUBMAXIMAL TREADMILL WALKING by Kimberly Anne Weary-Smith B.S. Slippery Rock
Board /Authority Approved Course Hockey Academy 10
 Board /Authority Approved Course Hockey Academy 10 North Okanagan Shuswap School District 83 Developed By: Terry Shykora Date Developed: May 2018 School Name: A L Fortune Secondary School Superintendent
Board /Authority Approved Course Hockey Academy 10 North Okanagan Shuswap School District 83 Developed By: Terry Shykora Date Developed: May 2018 School Name: A L Fortune Secondary School Superintendent
Investigation of Winning Factors of Miami Heat in NBA Playoff Season
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae The Open Cybernetics & Systemics Journal, 2015, 9, 2793-2798 2793 Open Access Investigation of Winning Factors of Miami Heat in NBA Playoff Season
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae The Open Cybernetics & Systemics Journal, 2015, 9, 2793-2798 2793 Open Access Investigation of Winning Factors of Miami Heat in NBA Playoff Season
Interventions to increase physical activity amongst older people
 Interventions to increase physical activity amongst older people Prof David French School of Psychological Sciences University of Manchester Percent Physical activity by age (England, 2008) Proportion
Interventions to increase physical activity amongst older people Prof David French School of Psychological Sciences University of Manchester Percent Physical activity by age (England, 2008) Proportion
The role of fitness testing in the evaluation of primary school running programmes
 The role of fitness testing in the evaluation of primary school running programmes Making Strides in School Symposium National Centre for Sport and Exercise Medicine 7 th September 2016 Prof. Stuart Fairclough
The role of fitness testing in the evaluation of primary school running programmes Making Strides in School Symposium National Centre for Sport and Exercise Medicine 7 th September 2016 Prof. Stuart Fairclough
VALIDITY OF SELECTED CARDIOVASCULAR FIELD-BASED TEST AMONG MALAYSIAN HEALTHY FEMALE ADULT. S. H. Azmi 1,*, and N. Sulaiman 2
 Journal of Fundamental and Applied Sciences ISSN 1112-9867 Research Article Special Issue Available online at http://www.jfas.info VALIDITY OF SELECTED CARDIOVASCULAR FIELD-BASED TEST AMONG MALAYSIAN HEALTHY
Journal of Fundamental and Applied Sciences ISSN 1112-9867 Research Article Special Issue Available online at http://www.jfas.info VALIDITY OF SELECTED CARDIOVASCULAR FIELD-BASED TEST AMONG MALAYSIAN HEALTHY
Homeostasis and Negative Feedback Concepts and Breathing Experiments 1
 Homeostasis and Negative Feedback Concepts and Breathing Experiments 1 I. Homeostasis and Negative Feedback Homeostasis refers to the maintenance of relatively constant internal conditions. For example,
Homeostasis and Negative Feedback Concepts and Breathing Experiments 1 I. Homeostasis and Negative Feedback Homeostasis refers to the maintenance of relatively constant internal conditions. For example,
Coaching Applications The Effect of Intermittent Hypoxic Exposure plus Sea Level Swimming Training on Anaerobic Swimming Performance
 J. Swimming Research, Vol. 19:2 (2012) Coaching Applications plus Sea Level Swimming Training on Anaerobic Swimming Performance Miller A.N. 1 and George K. 2 Department of Biomolecular and Sports Science,
J. Swimming Research, Vol. 19:2 (2012) Coaching Applications plus Sea Level Swimming Training on Anaerobic Swimming Performance Miller A.N. 1 and George K. 2 Department of Biomolecular and Sports Science,
WALK this WAY. Leader s Guide
 Leader s Guide The Physical Activity Resource Centre (PARC) is the Centre of Excellence for physical activity promotion in Ontario and supports professionals working in public health, community health,
Leader s Guide The Physical Activity Resource Centre (PARC) is the Centre of Excellence for physical activity promotion in Ontario and supports professionals working in public health, community health,
INVESTIGATION OF SAQ TRAINING VERSES SPRINT INTERVAL TRAINING IMPACT ON BASKETBALL THROW FOR ACCURACY OF MEN BASKETBALL PLAYERS
 INVESTIGATION OF SAQ TRAINING VERSES SPRINT INTERVAL TRAINING IMPACT ON BASKETBALL THROW FOR ACCURACY OF MEN BASKETBALL PLAYERS I. Devi Vara Prasad, Ph. D. Assistant Professor, Co-ordinator, B.P.Ed., Course,
INVESTIGATION OF SAQ TRAINING VERSES SPRINT INTERVAL TRAINING IMPACT ON BASKETBALL THROW FOR ACCURACY OF MEN BASKETBALL PLAYERS I. Devi Vara Prasad, Ph. D. Assistant Professor, Co-ordinator, B.P.Ed., Course,
Table 3. PFT Data Collection Requirements for the 20m PACER
 20m PACER or Progressive Aerobic Cardiovascular Endurance Run. The 20m from the number of laps (20m in distance) that are completed. Unlike the other two Aerobic Capacity to run as long as possible across
20m PACER or Progressive Aerobic Cardiovascular Endurance Run. The 20m from the number of laps (20m in distance) that are completed. Unlike the other two Aerobic Capacity to run as long as possible across
Walkable Communities and Adolescent Weight
 Walkable Communities and Adolescent Weight Sandy Slater, PhD Assistant Professor, University of Illinois at Chicago, School of Public Health Research Scientist, UIC Institute for Health Research and Policy
Walkable Communities and Adolescent Weight Sandy Slater, PhD Assistant Professor, University of Illinois at Chicago, School of Public Health Research Scientist, UIC Institute for Health Research and Policy
Physical Fitness For Futsal Referee Of Football Association In Thailand
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Physical Fitness For Futsal Referee Of Football Association In Thailand To cite this article: Thaweesub Koeipakvaen Acting Sub L.t. 2018 J. Phys.:
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Physical Fitness For Futsal Referee Of Football Association In Thailand To cite this article: Thaweesub Koeipakvaen Acting Sub L.t. 2018 J. Phys.:
The Effects of an ActiPed Pedometer Intervention Program on Body Composition and. Aerobic Capacity of Youth in a School System in East Tennessee
 The Effects of an ActiPed Pedometer Intervention Program on Body Composition and Aerobic Capacity of Youth in a School System in East Tennessee A dissertation presented to the faculty of the Department
The Effects of an ActiPed Pedometer Intervention Program on Body Composition and Aerobic Capacity of Youth in a School System in East Tennessee A dissertation presented to the faculty of the Department
USING WIRELESS PEDOMETERS TO MEASURE CHILDREN S PHYSICAL ACTIVITY: HOW RELIABLE IS THE FITBIT ZIP TM?
 USING WIRELESS PEDOMETERS TO MEASURE CHILDREN S PHYSICAL ACTIVITY: HOW RELIABLE IS THE FITBIT ZIP TM? Tingting Xu 1, Erik Jon Byker 2*, and Monica Rae Gonzales 3 1 Stephen F. Austin State University, Nacogdoches,
USING WIRELESS PEDOMETERS TO MEASURE CHILDREN S PHYSICAL ACTIVITY: HOW RELIABLE IS THE FITBIT ZIP TM? Tingting Xu 1, Erik Jon Byker 2*, and Monica Rae Gonzales 3 1 Stephen F. Austin State University, Nacogdoches,
LEVEL OF VO2 MAX CAPACITY VOLLEYBALL PLAYERS
 LEVEL OF VO2 MAX CAPACITY VOLLEYBALL PLAYERS Wojciech BAJOREK ABCDEF, Joanna PIECH BCD Faculty of Physical Education, University of Rzeszow, Rzeszow, Poland Keywords: volleyball oxygen uptake beep test
LEVEL OF VO2 MAX CAPACITY VOLLEYBALL PLAYERS Wojciech BAJOREK ABCDEF, Joanna PIECH BCD Faculty of Physical Education, University of Rzeszow, Rzeszow, Poland Keywords: volleyball oxygen uptake beep test
Energy Systems and Growth
 Energy Systems and Growth Understanding Energy Systems and Growth Understanding how your body produces energy is vital to understanding why you train in certain ways to enhance your energy systems and
Energy Systems and Growth Understanding Energy Systems and Growth Understanding how your body produces energy is vital to understanding why you train in certain ways to enhance your energy systems and
Physical activity has a number of benefits
 Health Policy Brief September 2018 Walking Among California Adults Susan H. Babey, Joelle Wolstein, and Allison L. Diamant SUMMARY: This policy brief describes two types of walking among California adults:
Health Policy Brief September 2018 Walking Among California Adults Susan H. Babey, Joelle Wolstein, and Allison L. Diamant SUMMARY: This policy brief describes two types of walking among California adults:
Kids Can BIKE! A Parks and Recreation Program to Promote Youth Cycling
 University of Tennessee, Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange Masters Theses Graduate School 8-2012 Kids Can BIKE! A Parks and Recreation Program to Promote Youth Cycling Jessica Lynn
University of Tennessee, Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange Masters Theses Graduate School 8-2012 Kids Can BIKE! A Parks and Recreation Program to Promote Youth Cycling Jessica Lynn
Using Pedometers. to Promote Physical Activity at School
 Using Pedometers to Promote Physical Activity at School Worldwide, at least 155 million school-age children are overweight or obese, according to estimates by the International Obesity Task Force (IOTF)
Using Pedometers to Promote Physical Activity at School Worldwide, at least 155 million school-age children are overweight or obese, according to estimates by the International Obesity Task Force (IOTF)
Peel Health Initiatives Health and Urban Form
 Region of Peel Public Health Peel Health Initiatives Health and Urban Form alpha Conference June 9, 2008 Gayle Bursey Director, Chronic Disease and Injury Prevention Declaration No part of the information
Region of Peel Public Health Peel Health Initiatives Health and Urban Form alpha Conference June 9, 2008 Gayle Bursey Director, Chronic Disease and Injury Prevention Declaration No part of the information
NBA TEAM SYNERGY RESEARCH REPORT 1
 NBA TEAM SYNERGY RESEARCH REPORT 1 NBA Team Synergy and Style of Play Analysis Karrie Lopshire, Michael Avendano, Amy Lee Wang University of California Los Angeles June 3, 2016 NBA TEAM SYNERGY RESEARCH
NBA TEAM SYNERGY RESEARCH REPORT 1 NBA Team Synergy and Style of Play Analysis Karrie Lopshire, Michael Avendano, Amy Lee Wang University of California Los Angeles June 3, 2016 NBA TEAM SYNERGY RESEARCH
A Comparative Study of Running Agility, Jumping Ability and Throwing Ability among Cricket Players
 Research Journal of Physical Education Sciences ISSN 2320 9011 A Comparative Study of Running Agility, Jumping Ability and Throwing Ability among Cricket Players Abstract Karunesh Kumar 1, Manjit Singh
Research Journal of Physical Education Sciences ISSN 2320 9011 A Comparative Study of Running Agility, Jumping Ability and Throwing Ability among Cricket Players Abstract Karunesh Kumar 1, Manjit Singh
Making Middle Distance Superstars: The Science
 Making Middle Distance Superstars: The Science Wisconsin Track and Field Clinic 2018 1/29/2018 1 Scott Christensen Stillwater, Minnesota, head coach for 33 years. 1997 National High School Champions (The
Making Middle Distance Superstars: The Science Wisconsin Track and Field Clinic 2018 1/29/2018 1 Scott Christensen Stillwater, Minnesota, head coach for 33 years. 1997 National High School Champions (The
Get Oregon kids. Walking, biking and rolling to school planning guide
 Get Oregon kids Walking, biking and rolling to school planning guide The Oregon Health Authority produced this guide with assistance from the Oregon Department of Education, Oregon Department of Transportation
Get Oregon kids Walking, biking and rolling to school planning guide The Oregon Health Authority produced this guide with assistance from the Oregon Department of Education, Oregon Department of Transportation
Why walk? Introducing Heart Foundation Walking! What is Heart Foundation Walking? Your role. Host Organisation
 An Introduction Why walk? It s an inexpensive form of physical activity It s easy doesn t require special skills or equipment It has psychological and community benefits improves mental health and social
An Introduction Why walk? It s an inexpensive form of physical activity It s easy doesn t require special skills or equipment It has psychological and community benefits improves mental health and social
THE APPLICATION OF BASKETBALL COACH S ASSISTANT DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEM
 THE APPLICATION OF BASKETBALL COACH S ASSISTANT DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEM LIANG WU Henan Institute of Science and Technology, Xinxiang 453003, Henan, China E-mail: wuliang2006kjxy@126.com ABSTRACT In the
THE APPLICATION OF BASKETBALL COACH S ASSISTANT DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEM LIANG WU Henan Institute of Science and Technology, Xinxiang 453003, Henan, China E-mail: wuliang2006kjxy@126.com ABSTRACT In the
Monitoring of performance an training in rowers
 Monitoring of performance an training in rowers Jaak Jürimäe Demands of the Sport High maximal oxygen consumption (VO 2max ); Ability to perform at a high percentage of VO 2max for the duration of event;
Monitoring of performance an training in rowers Jaak Jürimäe Demands of the Sport High maximal oxygen consumption (VO 2max ); Ability to perform at a high percentage of VO 2max for the duration of event;
An Analysis of the Components of Sport Imagery in Basketball Players
 An Analysis of the Components of Sport Imagery in Basketball Players Nishan Singh Deol Department of Physical Education, Punjabi University, Patiala, India Davinder Singh Department of Physical Education,
An Analysis of the Components of Sport Imagery in Basketball Players Nishan Singh Deol Department of Physical Education, Punjabi University, Patiala, India Davinder Singh Department of Physical Education,
Methods. Mark A. Tully and Margaret E. Cupples. Study Design
 Journal of Physical Activity and Health, 2011, 8, 663-667 2011 Human Kinetics, Inc. UNISTEP (University Students Exercise and Physical Activity) Study: A Pilot Study of the Effects of Accumulating 10,000
Journal of Physical Activity and Health, 2011, 8, 663-667 2011 Human Kinetics, Inc. UNISTEP (University Students Exercise and Physical Activity) Study: A Pilot Study of the Effects of Accumulating 10,000
Grade 1 Game Title: Capture the Cone Teaching Games for Understanding Category: Target Games
 Grade 1 Game Title: Capture the Cone Teaching Games for Understanding Category: Target Games Outcomes: 1.1 Health- related Fitness Variation: Add pedometers to show students how much physical activity
Grade 1 Game Title: Capture the Cone Teaching Games for Understanding Category: Target Games Outcomes: 1.1 Health- related Fitness Variation: Add pedometers to show students how much physical activity
The Effects of Chronic Creatine Supplementation on Performance and Body Composition of Female Athletes. by Megan Brenner
 The Effects of Chronic Creatine Supplementation on Performance and Body Composition of Female Athletes by Megan Brenner Thesis submitted to the Faculty of Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University
The Effects of Chronic Creatine Supplementation on Performance and Body Composition of Female Athletes by Megan Brenner Thesis submitted to the Faculty of Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University
[10] KEYWORDS: travel behaviour, congestion, health.
![[10] KEYWORDS: travel behaviour, congestion, health. [10] KEYWORDS: travel behaviour, congestion, health.](/thumbs/86/93172570.jpg) GLOBAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCED ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGIES AND SCIENCES THE CONTRIBUTION OF URBAN PLANNING AND ITS IMPLEMENTATION TO THE BEHAVIOR OF MEDAN CITY RESIDENTS TO THE LEVEL OF HEALTH Kaspan Eka Putra
GLOBAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCED ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGIES AND SCIENCES THE CONTRIBUTION OF URBAN PLANNING AND ITS IMPLEMENTATION TO THE BEHAVIOR OF MEDAN CITY RESIDENTS TO THE LEVEL OF HEALTH Kaspan Eka Putra
The best indicator of an individual s and expanding access to parks and open space.
 Health & Wellness Create a Safe and Healthy Built Environment Artist s rendering, 2014 Health is important to Loveland residents, and stakeholders see the many strong connections between quality of life,
Health & Wellness Create a Safe and Healthy Built Environment Artist s rendering, 2014 Health is important to Loveland residents, and stakeholders see the many strong connections between quality of life,
Smart Growth: Residents Social and Psychological Benefits, Costs and Design Barbara Brown
 Smart Growth: Residents Social and Psychological Benefits, Costs and Design Barbara Brown By Scott Siedor 11 At the invitation of the Goodwin-Niering Center for the Environment, Barbara Brown came to Connecticut
Smart Growth: Residents Social and Psychological Benefits, Costs and Design Barbara Brown By Scott Siedor 11 At the invitation of the Goodwin-Niering Center for the Environment, Barbara Brown came to Connecticut
Parent Guide to BC Hockey s Long Term Player Development Model
 Parent Guide to BC Hockey s Long Term Player Development Model INTRODUCTION The Parent Guide to BC Hockey s Long Term Player Development is designed for parents as being THE key stakeholders in their child
Parent Guide to BC Hockey s Long Term Player Development Model INTRODUCTION The Parent Guide to BC Hockey s Long Term Player Development is designed for parents as being THE key stakeholders in their child
LIFETIME FITNESS HEALTHY NUTRITION. UNIT 2 Lesson 14 FLEXIBILITY LEAN BODY COMPOSITION
 LIFETIME FITNESS HEALTHY NUTRITION MUSCULAR STRENGTH AEROBIC ENDURANCE UNIT 2 Lesson 14 FLEXIBILITY LEAN BODY COMPOSITION MUSCULAR ENDURANCE Created by Derek G. Becher B.P.E., B. Ed., AFLCA Resistance
LIFETIME FITNESS HEALTHY NUTRITION MUSCULAR STRENGTH AEROBIC ENDURANCE UNIT 2 Lesson 14 FLEXIBILITY LEAN BODY COMPOSITION MUSCULAR ENDURANCE Created by Derek G. Becher B.P.E., B. Ed., AFLCA Resistance
Training with Hockey IntelliGym
 Training with Hockey IntelliGym Presented by: Kevin McLaughlin, Senior Director of Hockey Development, USA Hockey Danny Dankner, CEO, Applied Cognitive Engineering (ACE) Training Hockey Sense The Big Picture
Training with Hockey IntelliGym Presented by: Kevin McLaughlin, Senior Director of Hockey Development, USA Hockey Danny Dankner, CEO, Applied Cognitive Engineering (ACE) Training Hockey Sense The Big Picture
Impact of a Pilot Walking School Bus Intervention on Children s Pedestrian Safety Behaviors
 Impact of a Pilot Walking School Bus Intervention on Children s Pedestrian Safety Behaviors Jason A. Mendoza, MD, MPH Assistant Professor of Pediatrics USDA/ARS Children s Nutrition Research Center, Academic
Impact of a Pilot Walking School Bus Intervention on Children s Pedestrian Safety Behaviors Jason A. Mendoza, MD, MPH Assistant Professor of Pediatrics USDA/ARS Children s Nutrition Research Center, Academic
Femke De Meester 1*, Delfien Van Dyck 1,2, Ilse De Bourdeaudhuij 1 and Greet Cardon 1
 De Meester et al. BMC Public Health 2014, 14:631 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Parental perceived neighborhood attributes: associations with active transport and physical activity among 10 12 year old children
De Meester et al. BMC Public Health 2014, 14:631 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Parental perceived neighborhood attributes: associations with active transport and physical activity among 10 12 year old children
Summary Report: Built Environment, Health and Obesity
 Research and education Built Environment Edmonton Project Summary Report: Built Environment, Health and Obesity Introduction In 2007 the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the Heart and Stroke
Research and education Built Environment Edmonton Project Summary Report: Built Environment, Health and Obesity Introduction In 2007 the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the Heart and Stroke
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 116 ( 2014 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 116 ( 2014 ) 5025 5029 5 th World Conference on Educational Sciences - WCES 2013 A Comparison study of
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 116 ( 2014 ) 5025 5029 5 th World Conference on Educational Sciences - WCES 2013 A Comparison study of
Why tennis? 34 reasons to play tennis
 Why tennis? 34 reasons to play tennis Health, fitness, fun make sport excellent choice by Jack Groppel, Ph.D., USPTA Master Professional We ve all heard tennis referred to as the "sport for a lifetime."
Why tennis? 34 reasons to play tennis Health, fitness, fun make sport excellent choice by Jack Groppel, Ph.D., USPTA Master Professional We ve all heard tennis referred to as the "sport for a lifetime."
Miles To Go Before I Sleep How Much Mileage Is Enough? By Jason R. Karp, M.S.
 Miles To Go Before I Sleep How Much Mileage Is Enough? By Jason R. Karp, M.S. As featured in the May 2007 issue of Running Times Magazine I recently finished reading the book, How to Think Like Einstein.
Miles To Go Before I Sleep How Much Mileage Is Enough? By Jason R. Karp, M.S. As featured in the May 2007 issue of Running Times Magazine I recently finished reading the book, How to Think Like Einstein.
Presence and duration of reactivity to pedometers in adults
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository Presence and duration of reactivity to pedometers in adults This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an author.
Loughborough University Institutional Repository Presence and duration of reactivity to pedometers in adults This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an author.
Physical Activity. Assessment Why Physical Activity Is Important? Background Information Tips: Walking Steps Tips: Walking Minutes Goals
 Physical Activity Assessment Why Physical Activity Is Important? Background Information Tips: Steps Tips: Minutes Goals 34 Assessment Next, we will talk about physical activity. Before getting started,
Physical Activity Assessment Why Physical Activity Is Important? Background Information Tips: Steps Tips: Minutes Goals 34 Assessment Next, we will talk about physical activity. Before getting started,
Optimizing Muscular Strength-to-Weight Ratios in Rock Climbing
 BEAST FINGERS CL IMBIN G RESEARCH MARCH 2018 Optimizing Muscular Strength-to-Weight Ratios in Rock Climbing BY AMAN A N DERSO N A C K N O W L EDG E MENT S We want to thank Dr. Christoph Lutter, and Steven
BEAST FINGERS CL IMBIN G RESEARCH MARCH 2018 Optimizing Muscular Strength-to-Weight Ratios in Rock Climbing BY AMAN A N DERSO N A C K N O W L EDG E MENT S We want to thank Dr. Christoph Lutter, and Steven
The Impact of Policy and Environmental Outcomes on Youth Physical Activity
 The Impact of Policy and Environmental Outcomes on Youth Physical Activity Childhood Obesity Conference, San Diego, CA June 30, 2011 Sandy Slater, PhD Assistant Professor, University of Illinois at Chicago,
The Impact of Policy and Environmental Outcomes on Youth Physical Activity Childhood Obesity Conference, San Diego, CA June 30, 2011 Sandy Slater, PhD Assistant Professor, University of Illinois at Chicago,
Chapter I examines the anthropometric and physiological factors that. determine success in sport. More specifically it discusses the somatotype
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Chapter I examines the anthropometric and physiological factors that determine success in sport. More specifically it discusses the somatotype ratings, VO 2 max and running economy
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Chapter I examines the anthropometric and physiological factors that determine success in sport. More specifically it discusses the somatotype ratings, VO 2 max and running economy
An Exploratory Study of Psychomotor Abilities among Cricket Players of Different Level of Achievement
 Research Journal of Physical Education Sciences ISSN 2320 9011 An Exploratory Study of Psychomotor Abilities among Cricket Players of Different Level of Achievement Abstract Baljinder Singh Bal and Ranjeet
Research Journal of Physical Education Sciences ISSN 2320 9011 An Exploratory Study of Psychomotor Abilities among Cricket Players of Different Level of Achievement Abstract Baljinder Singh Bal and Ranjeet
COMMUNITY SUPPORT PROGRAM
 COMMUNITY SUPPORT PROGRAM Providers contracted for this level of care or service will be expected to comply with all requirements of these service-specific performance specifications. Additionally, providers
COMMUNITY SUPPORT PROGRAM Providers contracted for this level of care or service will be expected to comply with all requirements of these service-specific performance specifications. Additionally, providers
The effect of deliberate practice on the technique of national calibre swimmers
 Lupo Corrado, Giancarlo Condello, and Antonio Tessitore. (2014). Women s Water Polo World Championships: Technical and Tactical Aspects of Winning and Losing Teams in Close and Unbalanced Games. Journal
Lupo Corrado, Giancarlo Condello, and Antonio Tessitore. (2014). Women s Water Polo World Championships: Technical and Tactical Aspects of Winning and Losing Teams in Close and Unbalanced Games. Journal
San José State University Kinesiology KIN 38-02, Beginning Jogging, 28296, Spring Semester, 2017
 San José State University Kinesiology KIN 38-02, Beginning Jogging, 28296, Spring Semester, 2017 Course and Contact Information Instructor: James Fonda Office Location: SPX 170 Telephone: o. (408) 924-2073
San José State University Kinesiology KIN 38-02, Beginning Jogging, 28296, Spring Semester, 2017 Course and Contact Information Instructor: James Fonda Office Location: SPX 170 Telephone: o. (408) 924-2073
Sledge Hockey NatioNal team FitNeSS testing guidelines
 Sledge Hockey National Team Fitness Testing Guidelines ABOUT THIS RESOURCE This manual is designed to serve as a guideline for sledge hockey players and coaches who are striving to take their game to the
Sledge Hockey National Team Fitness Testing Guidelines ABOUT THIS RESOURCE This manual is designed to serve as a guideline for sledge hockey players and coaches who are striving to take their game to the
ALTITUDE TRAINING FOR IMPROVING SWIMMING PERFORMANCE AT SEA LEVEL. MITSUMASA MIYASHITA, YOSHITERU MUTOH and YOSHIHARU YAMAMOTO.
 ALTITUDE TRAINING FOR IMPROVING SWIMMING PERFORMANCE AT SEA LEVEL MITSUMASA MIYASHITA, YOSHITERU MUTOH and YOSHIHARU YAMAMOTO Abstract The present study was designed to investigate the effects of low altitude
ALTITUDE TRAINING FOR IMPROVING SWIMMING PERFORMANCE AT SEA LEVEL MITSUMASA MIYASHITA, YOSHITERU MUTOH and YOSHIHARU YAMAMOTO Abstract The present study was designed to investigate the effects of low altitude
Pedestrian Safety Initiatives National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA)
 Pedestrian Safety Initiatives National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) Report to the Transportation Research Board Pedestrian Safety Committee January 2010 Leah Walton Safety Countermeasures
Pedestrian Safety Initiatives National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) Report to the Transportation Research Board Pedestrian Safety Committee January 2010 Leah Walton Safety Countermeasures
HGH for Sale Natural Anti-Aging Human Growth Hormone
 HGH for Sale Natural Anti-Aging Human Growth Hormone Human growth hormone is one of the hottest supplement trends on the market, and now you can purchase top-quality HGH to be delivered right to your home!
HGH for Sale Natural Anti-Aging Human Growth Hormone Human growth hormone is one of the hottest supplement trends on the market, and now you can purchase top-quality HGH to be delivered right to your home!
Is lung capacity affected by smoking, sport, height or gender. Table of contents
 Sample project This Maths Studies project has been graded by a moderator. As you read through it, you will see comments from the moderator in boxes like this: At the end of the sample project is a summary
Sample project This Maths Studies project has been graded by a moderator. As you read through it, you will see comments from the moderator in boxes like this: At the end of the sample project is a summary
NCCP Swimming 301 Course Summary
 1 INTRODUCTION 3:30 This module provides coaches with an overview of the 301 course, what is expected of the coaches and most importantly what coaches can expect to get out of attending the 301 course.
1 INTRODUCTION 3:30 This module provides coaches with an overview of the 301 course, what is expected of the coaches and most importantly what coaches can expect to get out of attending the 301 course.
Comparison of Three Tests for Assesing the Aerobic Aptitude to the Elite Swimmers
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Scienc es 117 ( 2014 ) 307 311 ICSPEK 2013 Comparison of Three Tests for Assesing the Aerobic Aptitude to the Elite
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Scienc es 117 ( 2014 ) 307 311 ICSPEK 2013 Comparison of Three Tests for Assesing the Aerobic Aptitude to the Elite
Learn to Train Ages 8-11 females Ages 9-12 males
 Learn to Train Ages 8-11 females Ages 9-12 males The objective of the Learn to Train stage is to refine overall sport skills and develop sports specific skills. General Description of the Learn to Train
Learn to Train Ages 8-11 females Ages 9-12 males The objective of the Learn to Train stage is to refine overall sport skills and develop sports specific skills. General Description of the Learn to Train
A Comparison of American Red Cross- and YMCA-Preferred Approach Methods Used to Rescue Near-Drowning Victims
 International Journal of Aquatic Research and Education Volume 1 Number 1 Article 4 2-1-2007 A Comparison of American Red Cross- and YMCA-Preferred Approach Methods Used to Rescue Near-Drowning Victims
International Journal of Aquatic Research and Education Volume 1 Number 1 Article 4 2-1-2007 A Comparison of American Red Cross- and YMCA-Preferred Approach Methods Used to Rescue Near-Drowning Victims
The student will be able to bob ten times without holding their nose. float on their stomach and back for a minimum of ten seconds.
 Unit: Basic Skills Grade Level: 6-8 Estimated Time: 5 classes Level/Track: All Date Approved: August 27, 2018 F. Analyze the effects of positive and negative interactions of adolescent group members in
Unit: Basic Skills Grade Level: 6-8 Estimated Time: 5 classes Level/Track: All Date Approved: August 27, 2018 F. Analyze the effects of positive and negative interactions of adolescent group members in
Active Travel Strategy Dumfries and Galloway
 Active Travel Strategy Dumfries and Galloway Our Active Travel Strategy The agreed Interventions for Dumfries and Galloway Council s Local Transport Strategy includes an action to Develop an Active Travel
Active Travel Strategy Dumfries and Galloway Our Active Travel Strategy The agreed Interventions for Dumfries and Galloway Council s Local Transport Strategy includes an action to Develop an Active Travel
Age gradient in the cost-effectiveness of bicycle helmets Kopjar B, Wickizer T M
 Age gradient in the cost-effectiveness of bicycle helmets Kopjar B, Wickizer T M Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that meets the criteria for inclusion on NHS EED. Each
Age gradient in the cost-effectiveness of bicycle helmets Kopjar B, Wickizer T M Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that meets the criteria for inclusion on NHS EED. Each
A Group of Factors Influencing the Development of the Greeks Volleyball Athletes at School Age
 Journal of Sports Science 5 (27) 2-37 doi:.725/2332-783/27..3 D DAVID PUBLISHING A Group of Factors Influencing the Development of the Greeks Volleyball Athletes at School Age Achilleopoulos John, Lamprousi
Journal of Sports Science 5 (27) 2-37 doi:.725/2332-783/27..3 D DAVID PUBLISHING A Group of Factors Influencing the Development of the Greeks Volleyball Athletes at School Age Achilleopoulos John, Lamprousi
2017 International Conference on Advanced Education, Psychology and Sports Science (AEPSS 2017)
 2017 International Conference on Advanced Education, Psychology and Sports Science (AEPSS 2017) Investigation and Research on the Current Situation of Football Extracurricular Activities and Soccer Clubs
2017 International Conference on Advanced Education, Psychology and Sports Science (AEPSS 2017) Investigation and Research on the Current Situation of Football Extracurricular Activities and Soccer Clubs
Validation of a Step Test in Children Ages 7-11
 Validation of a Step Test in Children Ages 7-11 Emilene Clark Aurora Fry Colleen Smith Tonya Thomas Primary Advisor: Jim Farris, PT, PhD April 20, 2011 Background Exercise Testing Maximal Testing Sub-maximal
Validation of a Step Test in Children Ages 7-11 Emilene Clark Aurora Fry Colleen Smith Tonya Thomas Primary Advisor: Jim Farris, PT, PhD April 20, 2011 Background Exercise Testing Maximal Testing Sub-maximal
TAMPA BAY UNITED ACADEMY PHILOSOPHY & CURRICULUM
 TAMPA BAY UNITED ACADEMY PHILOSOPHY & CURRICULUM MISSION The mission of the Tampa Bay United Academy is to provide the best possible coaching and instruction for our young players to ensure proper development
TAMPA BAY UNITED ACADEMY PHILOSOPHY & CURRICULUM MISSION The mission of the Tampa Bay United Academy is to provide the best possible coaching and instruction for our young players to ensure proper development
EUROPASS SUPPLEMENT TO THE DIPLOMA OF
 EUROPASS SUPPLEMENT TO THE DIPLOMA OF NAME OF THE DIPLOMA Técnico Deportivo en Fútbol (Sports Instructor in Football) ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
EUROPASS SUPPLEMENT TO THE DIPLOMA OF NAME OF THE DIPLOMA Técnico Deportivo en Fútbol (Sports Instructor in Football) ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Effects of Age and Body Mass Index on Accuracy of Simple Moderate Vigorous Physical Activity Monitor Under Controlled Condition
 Received: May., 011 Accepted: Jul. 8, 011 Published online: Jul. 5, 011 Original Article Effects of Age and Body Mass Index on Accuracy of Simple Moderate Vigorous Physical Activity Monitor Under Controlled
Received: May., 011 Accepted: Jul. 8, 011 Published online: Jul. 5, 011 Original Article Effects of Age and Body Mass Index on Accuracy of Simple Moderate Vigorous Physical Activity Monitor Under Controlled
The Optimal Downhill Slope for Acute Overspeed Running
 International Journal of Sports Physiology and Performance, 2008, 3, 88-93 2008 Human Kinetics, Inc. The Optimal Downhill Slope for Acute Overspeed Running William P. Ebben Purpose: This study evaluated
International Journal of Sports Physiology and Performance, 2008, 3, 88-93 2008 Human Kinetics, Inc. The Optimal Downhill Slope for Acute Overspeed Running William P. Ebben Purpose: This study evaluated
The Physical and Physiological Characteristics of 3x3. Results of Medical Study & Scientific Test
 The Physical and Physiological Characteristics of 3x3 Results of Medical Study & Scientific Test Prepared by Dr. Paul Montgomery & Brendan Maloney (Aspetar Orthopaedic Hospital) In cooperation with FIBA
The Physical and Physiological Characteristics of 3x3 Results of Medical Study & Scientific Test Prepared by Dr. Paul Montgomery & Brendan Maloney (Aspetar Orthopaedic Hospital) In cooperation with FIBA
Risk Factors Involved in Cheerleading Injuries
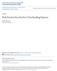 University of Arkansas, Fayetteville ScholarWorks@UARK Health, Human Performance and Recreation Undergraduate Honors Theses Health, Human Performance and Recreation 5-2016 Risk Factors Involved in Cheerleading
University of Arkansas, Fayetteville ScholarWorks@UARK Health, Human Performance and Recreation Undergraduate Honors Theses Health, Human Performance and Recreation 5-2016 Risk Factors Involved in Cheerleading
The Ten Toe Express Program
 The Ten Toe Express Program A campaign to promote walking and transit use in St. Louis Rail~Volution Conference November 3, 2007 Jessi Erickson, MPH Purpose of Presentation Background on physical activity
The Ten Toe Express Program A campaign to promote walking and transit use in St. Louis Rail~Volution Conference November 3, 2007 Jessi Erickson, MPH Purpose of Presentation Background on physical activity
