Available online at ScienceDirect. Transportation Research Procedia 10 (2015 )
|
|
|
- Katrina Atkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Available online at ScienceDirect Transportation Research Procedia 10 (2015 ) th Euro Working Group on Transportation, EWGT 2015, July 2015, Delft, The Netherlands Anticipatory service network design of bike sharing systems Bruno A. Neumann-Saavedra a,, Patrick Vogel a, Dirk C. Mattfeld a a Decision Support Group, Technische Universität Braunschweig, Mühlenpfordtstraße 23, Braunschweig, Germany Abstract Today s conurbations suffer from inefficiency in transportation systems. Bike sharing systems (BSS) combine the advantages of public and private transportation to better exploit the given transportation infrastructure. They provide bikes for short-term trips at automated rental stations. However, spatio-temporal variation of bike rentals leads to imbalances in the distribution of bikes, causing full or empty stations in the course of the day. Ensuring the reliable provision of bike and free bike racks is crucial for the viability of these systems. On the tactical planning level, target fill levels of bikes at stations are determined to provide reliability in service. On the operational planning level, the BSS operator relocates bikes in vehicles among stations based on target fill levels. A recent approach in tactical service network design (SND) anticipates relocation operations of BSS by means of a dynamic transportation model yielding the required demand of relocation services (RS). A RS is described by pickup and return station, time period, and the number of relocated bikes. RS represent the design decision for implementing a service between two stations in each period for each day of the system operation. The output of the SND model are the time-dependent target fill levels at stations and the set of cost-efficient RS to facilitate these target fill levels. However, the existing approach neglects the sequence of RS into tours, thus leading to a weak anticipation of operational decisions. We extend an existing SND approach by including the concept of service tours (ST). RS are sequenced in ST which start and end at the depot. Experiments shows that the ST obtained by the extended SND yield a stronger anticipation of operational decisions. c 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier by Elsevier B.V. B. This V. is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license ( Selection and peer-review under responsibility of Delft University of Technology. Peer-review under responsibility of Delft University of Technology Keywords: bike sharing systems; service network design; operational anticipation 1. Introduction In recent years, shared mobility systems (SMS) have been proposed to tackle the critical problems of metropolises, e.g., traffic congestion and high air pollution. In this context, bike sharing systems (BSS) have emerged as a flexible and sustainable means of shared mobility. BSS combine the advantages of public and private transportation to better exploit the given transportation infrastructure. BSS offer bike rentals through automated rental stations. Each rental station provides a limited number of bikes and free bike racks for users. Free-of-charge short-term trips are usually offered to motivate the usage of the bike fleet (Büttner and Petersen, 2011). However, the acceptance of BSS depends on the service level of the system, i.e., the Corresponding author. Tel.: ; fax: address: b.neumann-saavedra@tu-braunschweig.de The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license ( Peer-review under responsibility of Delft University of Technology doi: /j.trpro
2 356 Bruno A. Neumann-Saavedra et al. / Transportation Research Procedia 10 ( 2015 ) successful provision of bikes and free bike racks when demanded (Shaheen et al., 2010). Rentals at empty stations, as well as return of bikes at full stations are not possible. Due to spatio-temporal demand variation in combination with one-way-trips, providing suitable bike fill levels at each station during the day is challenging. On the tactical planning level, target fill levels need to be determined for each station through the course of the day, to allow rentals and returns when demanded. Due to the limited capacity of stations, high fill levels increase rental probability but decrease return probability and vice versa. On the operational planning level, the BSS operator relocates bikes among stations based on target fill levels. Hence, a vehicle fleet starts tours from the depot, carries out a sequence of relocation operations, and returns to the depot. Relocation operations and fill levels are interdependent since bike relocations are required to compensate inadequate fill levels. However, relocation operations result in significant costs, affecting the viability of BSS (Büttner and Petersen, 2011). Neglecting information on the relocation operations in the tactical planning level leads to suboptimal decisions on fill levels. Therefore, anticipation of operational decisions is required. Vogel et al. (2015) proposed a service network design (SND) approach to cover tactical planning issues of BSS. Relocation operations are anticipated by a computationally tractable dynamic transportation model yielding relocation services (RS). RS represent the design decision for implementing a service between two stations in a period of the day of the system operation, e.g., a workday. In addition, demand scenarios are obtained as input for the SND by a data analysis approach. Thus, typical demand flows between stations are obtained in terms of time-dependent origindestination (OD) matrices. In the remind of this paper, we refer to the SND approach proposed by Vogel et al. (2015) as SND-RS. However, SND-RS does not sequence the RS into tours. Information about empty trips of vehicles are neglected, leading to a weak anticipation of operational decisions. Therefore, we extend the SND-RS, adding the concept of service tours (ST), which leads to a stronger anticipation of operational decisions. In this work, the new SND approach is called SND-ST. The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Recent tactical planning approaches for SMS, including the SND-RS and their drawbacks, are discussed Section 2. The SND-ST and its MIP formulation are subject of Section 3. In Section 4, SND-RS and SND-ST are compared with regard to the fill levels and their operational anticipation. Computational experiments show that both SND approaches obtain similar fill levels as tactical decisions whereas the SND-ST yields extended information in terms of the requirements to manage the vehicle fleet though the ST. Finally, conclusions and future work are presented in Section Service network design of bike sharing systems The literature has mainly focused on the strategic and operational planning for SMS. However, literature on tactical planning is scarce. We present approaches which consider anticipation of operational decisions in the tactical planning level. Correia and Antunes (2012) present three MIP formulations to maximize the total daily profit of one-way car sharing systems. In particular, revenue of trips paid by clients, costs of the depot, maintenance and depreciation of vehicles, and costs of dynamic vehicle relocations are taken into account. Cars are repositioned during the night to reset initial fill levels. This approach is validated by simulation techniques (Jorge et al., 2012). Sayarshad et al. (2012) maximize profit in BSS though a LP formulation yielding the minimum number of bikes that minimizes unmet demand, unutilized bikes, and relocation operations. Boyacı et al. (2015) introduce an optimization framework for car sharing systems which aims at maximizing their revenue. A MIP formulation considers an imaginary hub station to reduce the complexity that relocation operation involves in the MIP. Regarding tactical planning without anticipation of operational decisions, different approaches are presented by George and Xia (2011); Raviv and Kolka (2013); Cepolina and Farina (2012); Schuijbroek et al. (2013); Shu et al. (2013). Recent researches do not sufficiently cover the integration of the tactical and operational planning level. Furthermore, most optimization approaches are intractable for medium and large scale problems. Therefore, Vogel et al. (2015) propose the SND-SR yielding main tactical issues in addition with a suitable anticipation of operational decisions. The SND-RS follows the work of Crainic (2000) and Wieberneit (2008) in freight transportation since this field covers most of BSS characteristics. The optimization model takes the form of a MIP which determines target fill levels at each bike station and time point minimizing the expected cost of RS while ensuring a predefined service
3 Bruno A. Neumann-Saavedra et al. / Transportation Research Procedia 10 ( 2015 ) level. Different demand scenarios are generated by a data analysis approach. Hourly aggregation is considered prudent after preliminary analysis of trip data. Demand scenarios are used as input for the optimization model. The SND-RS considers a given BSS infrastructure consisting in n bike stations, without loss of generality we assume N = {1,..., n}, i N is called bike station. Each bike station has a limited capacity s i, representing the number of bike racks. In the BSS, a total number of b bikes are available for rentals. Following the aggregation criteria suggested by Vogel et al. (2015), a workday is discretized in (hourly) time periods and represented by the set T = {0, 1,..., t, t max } including the first time period of the next workday t max. Trip demand, represented by timedepending origin-destination (OD) matrices, is denoted by f ij,t. To find target fill levels B i,t at each station and time period in the the BSS, R ij,t bikes are relocated from station i to station j in time period t. In order to avoid many bike relocation decisions with low a volume of relocated bikes, a consolidation of R ij,t to RS RS ij,t is required. RS are obtained by a computationally tractable dynamic transportation model yielding an anticipation of the relocation operations. A RS is defined as the transportation of bikes between two stations in a time period by the use of a vehicle. On each RS, a maximal lot size l of bikes can be relocated. Regarding the anticipation of operational costs, the fixed costs ct ij comprise the travel of a vehicle between to points whereas the variable costs ch t represent the handling costs to relocate a bike in a time period. Thus, cost-efficient RS alleviate bike imbalances providing system reliability from a user point of view. Fig. 1. Modeling relocation operations as a dynamic transportation model (SND-RS) Figure 1 shows how relocation operations are anticipated by SND-RS, represented as a time-space network diagram with n = 3 bike stations and a scheduling period where t max = 5 is the last time point. A number of B i,t bikes are allocated at each station i N in a time point t T. The arrows represent the RS that can be set up when required. SND-RS modeling supposes that a RS always takes only one time period. For example, a RS departing from station 2att = 1 takes one time period and arrives at station 3 at t = 2. At each bike station and time period, a self-defined service level regarding the minimal number of bikes sb i,t and free bike racks sbr i,t is expected. Despite a large set up of RS, user demand cannot be completely satisfied in some situations, i.e., there are not enough bikes or free bike racks at some stations due to high bike demand or insufficient infrastructure. Service violation is denoted as the sum of the total missing bikes MB i,t and missing bikes racks MBR i,t in the system. In addition, the final and initial fill level at a station should match due to cyclic demand patterns since RS are only set up for one given demand scenario. Therefore, allocation violation is defined as the sum of the absolute values of the difference between the initial and final fill level at each station. Although the SND-RS formulation is computationally tractable for medium instances in terms of finding suitable solutions in a prudent time (Vogel et al., 2014), it neglects both the sequence of the RS into routes and the empty trips, which a vehicle should make to visit a station with need of a RS. For this reason, the SND-RS leads to a weak anticipation of operational decisions since a vehicle fleet can not be managed efficiently when information about the empty trips is not provided. Therefore, we propose an extension of the SND-RS by including the concept of ST in the optimization model.
4 358 Bruno A. Neumann-Saavedra et al. / Transportation Research Procedia 10 ( 2015 ) Extending current service network design approach of bike sharing systems to define service tours We present the SND-ST which includes the ST in the SND-RS formulation as a stronger anticipation of operational decisions. Now, RS are sequenced into services tours. ST are somehow an abstraction of the vehicle fleet meaning that a capacitated vehicle is assigned to each ST when implemented in the operational planning level. ST start and end at the initial point, e.g., a depot. A station needs to be visited during the ST to be served by a RS. However, bike relocations among all visited stations may not be necessary. Therefore, we introduce the concept of empty service (ES), i.e., a relocations service in which no bikes are relocated. Thus, SND-ST yields cost-efficient ST satisfying the service level expectations. Figure 2 shows an exemplary ST of the SND-ST. This is the same time-space network diagram as presented in Figure 1, but now a depot is included. The solid arrows represent RS whereas the dashed arrows illustrate ES between two stations. Thus, RS with bike relocations are now connected by ES. Fig. 2. An exemplary ST in the SND-ST Regarding the optimization model, we denote now N = {0, 1,..., n} as the set of bike stations, considering a depot without capacity as i = 0. A maximal number of K ST can be implemented due to a limited number of vehicles. Sets N = {0, 1,..., n} : set of stations, considering the first element of the set as an uncapacitated depot T = {0,..., t, t max } : set of periods, e.g., hours of the day. For resetting the number of allocated bikes at the end of the day, t max includes the first period of the next day Decision variables B i,t R + 0 : number of bikes at station i in time period t R ij,t R + 0 : relocated bikes between stations i and j in time period t RS ij,t {0, 1} : RS (or ES) between stations i and j in time period t MB i,t R + 0 : number of missing bikes at station i in time period t MR i,t R + 0 : number of missing bike racks at station i in time period t Parameters s i : size of stations in terms of bike racks at station i b : total number of bikes in the system f ij,t : bike flow between stations i and j in time period t ch t : average handling costs of one relocated bike in time period t ct ij : average transportation costs of a relocation operation between stations i and j cm : penalization costs per service violation cb : penalization costs per allocation violation
5 Bruno A. Neumann-Saavedra et al. / Transportation Research Procedia 10 ( 2015 ) l : lot size (capacity) for RS sb i,t : bike safety buffer at station i in time period t sbr i,t : bike rack safety buffer at station i in time period t K : maximal number of ST that can be set up With the notation, the optimization model reads as follows: min z = t ( ctij RS ij,t + ch t R ij,t ) + cm i=0 t=0 i=1 t=0 i=1 t ( ) MBi,t + MR i,t + cb B i,0 B i,tmax (1) subject to B i,t+1 = B i,t + ( ) f ji,t f ij,t + R ji,t R ij,t, i N \{0}, t T \ tmax (2) B i,t f ij,t + f ji,t R ij,t + MB i,t sb i,t, i N \{0}, t T \ t max (3) s i B i,t f ji,t + f ij,t R ji,t + MR i,t sbr i,t, i N \{0}, T \ t max (4) R ij,t l RS ij,t, i, j N, t T \ t max (5) B i,t = b, i=1 RS 0 j,0 K RS j0, t K t T (6) (7) (8) RS ij,0 = 0, RS ji, t = 0 i N \{0}, j N (9) RS ji,t 1 = RS ij,t, i N, t T \ t max (10) B i,t, MB i,t, MR i,t, R ij,t 0, RS ij,t {0, 1} i, j N, t T (11) The objective function (1) minimizes the total cost of relocation tours including recourse costs for penalizing both service and allocation violation. A RS includes fixed costs and variable costs, defined by the one-time cost for the particular transport, and the handling costs for each individual bike transported (when required), respectively. The flow conservation equation (2) shows the number of bikes in each station according to the previous bike flows. Thus, the number of bikes in a station in a time period depends on the number of bikes, demand flows, and relocated bikes in the previous period. The availability of bikes and free bike racks is ensured by constraints (3) and (4) when no service violation exists. On the one side, constraint (3) guarantees a minimal safety buffer of bikes. This buffer of bikes should be bigger than the number of allocated bikes minus customer rentals plus returns minus relocation pickups. On the other side, a minimal safety buffer of free bike racks on each station, i.e., the total number of bike
6 360 Bruno A. Neumann-Saavedra et al. / Transportation Research Procedia 10 ( 2015 ) racks at station minus the number of allocated bikes minus customer returns plus a certain proportion of rentals minus relocation returns, is guaranteed in constraint (4). If the safety buffer of bikes and/or free bike racks cannot be satisfied, potentially missing bikes and/or missing free bike racks are considered to guarantee feasibility. Constraints (3) and (4) ensure that rented bikes and used bike racks are not available for relocation activities in the particular time period. If a RS is set up, a maximal lot size of bikes can be relocated (5). All bikes in the system need to be allocated at stations (6). It is important to highlight that equations (1-6) built the SND-RS. Additional constraints are added to include the concept of ST in the MIP. In particular, ST start and end in the depot (7-9). A ST has to visit a node before leaving it (10). Finally, for both SND-RS and SND-ST, decisions to set up RS (or ES) are modeled by binary variables whereas all other variable sets are non-negative (11). 4. Experimental results In this section, the aim of the experiment is to evaluate the defined ST, obtained fill levels, and compare them with the anticipation of SND-RS. Following the experiment set up by Vogel et al. (2015), input data are: A BSS which comprises n = 59 bike stations with a total number of 1253 bike racks and a total of b = 627 available bikes means of an 50% of the average fill level. Cluster analysis based on rental activities classifies bike stations into working, residential, leisure, mixed or tourist. A demand scenario with 1569 trips during the workday is considered. Time is discretized in terms of t max = 24 (hourly) time periods. We assume that RS and ES take one hour on average. Handling costs depend on the time of the day. Between time periods 8 to 17 day-time handling costs are set to ch day = 4AC, while night-time handling costs are ch night = 7AC. Transportation costs are assumed to be independent of the time of day and amount to c it = 0.5AC per kilometer. The lot size of RS is l = 20. Bike and free bike rack safety buffers are set to zero for each station and time period. Regarding the penalization costs, we consider the allocation violation more critical than the service violation due to the cycling demand scenario. Unlimited capacity to set up RS and ST is considered (K = ). Both SND-RS and SND-RT were implemented in Java using the ILOG Concert Technology to access CPLEX An Intel Xeon X7550 CPU at 2GHz processor with 128 RAM was used to run the experiments. All experiments were run for a maximal running-time of 30 minutes. Table 1. Comparison of SND-RS and SND-ST SND-RS SND-ST Optimality gap 1.98% 68.50% Relocated bikes Relocation services Service violation 0 0 Allocation violation 0 1 Empty services Undefined 57 Service tours Undefined 10 Operational costs Table 1 presents the results of comparing the SND-RS and SND-ST instances solved with CPLEX. Based on the optimality gap, initial tests show that a near-optimal solution can be obtained for the SND-RS instance. The solution obtained for the SND-ST instance may be far away from the optimal solution. Note that the additional constraints induced by the representation of ST make the SND-ST computationally more challenging. (Meta-)heuristic approaches may allow to obtain solutions of better quality in a reasonable computation time. Regarding the anticipation of operational decisions, both SND approaches present similarities in terms of the relocation decisions. In particular, SND-RS
7 Bruno A. Neumann-Saavedra et al. / Transportation Research Procedia 10 ( 2015 ) presents a better consolidation of bike relocations to RS. 4 more RS are set up in SND-ST but only one additional bike is relocated. In addition, SND-RS yields a solution without penalization costs whereas 1 allocation violation is obtained by the SND-ST. However, additional information about the number of ST and ES is provided by SND-ST due to it suggest 10 relocation tours and a total of 57 ES. Therefore, anticipation of operational costs is higher in SND- ST since SND-RS neglects ES and their associated costs. SND-ST yields thus a stronger anticipation of operational decisions. Fig. 3. Time-space network with RS and empty trips set up of SND approaches As shown in Table 1, there are similarities between both SND approaches with regard to the generated RS. To observe the RS and ST obtained by the instances, two time-space networks are presented in Figure 3 as a graphical output illustration of the SND-RS and SND-ST. Full lines illustrate RS and ES are represented by dashed lines. The thickness of lines indicates the amount of relocated bikes by a RS. The representation is limited to periods 8-17, as RS only occur in this timespan. A black node represents the depot in the SND-RT. RS with a high volume of relocated bikes are set up in the peak hours of the morning and afternoon whereas RS with a low volume of relocated bikes are set up during the rest of the day. However, SND-ST presents less flexibility to set up RS since they should be preceded by either a RS or an ES. Sometimes, a ST stays in a station in a time period. This situation does not consider operational costs in the MIP formulation. RS always take one time period. RS definition results therefore in the tendency that a ST does not set up two RS successively since the handling cost would be excessive. For instance,
8 362 Bruno A. Neumann-Saavedra et al. / Transportation Research Procedia 10 ( 2015 ) bikes returned at a station would be intermediately picked up by another RS meaning that bikes are not available two time periods. Because the setting up of a ST does not implicate costs, a solution with many ES is generated. Limiting the number of ST and a reformulation of the time-space network, e.g., a RS can take more than one time period, would generate more effective RS and ST. Regarding the night-time in the SND-ST, all relocation tours stay in a station between time periods 1 and 7 after having an ES in the first time period and before starting the set up of RS at time period 8. After time period 17, almost all ST return to the depot. Due to symmetries in the time-space network, the solution quality does not depend on the time period in the night in which the empty trips are set up. Fig. 4. Boxplots of fill levels per cluster for peak hours Now, we present and compare the obtained fill levels for both SND approaches. Fill levels are represented in Figure 4 by means of box plots per cluster and time period. A box plot illustrates the distribution of bikes at stations, which are classified as a same cluster type. In particular, morning and afternoon peak hours are our focus of attention since higher user rental activity is presented in these time periods. The obtained fill levels in both SND approaches present similar patterns. Stations classified as belonging to the working cluster run with a low fill level in the morning peak hour and high fill level in the afternoon peak hour. Although fill levels are dispersed in a similar range, i.e., between 0% and 65% in the morning peak hour and between 40% and 85% in the afternoon pick hour, the medians are very different when SND approaches are compared. For instance, more stations run almost empty in the morning peak hour of the SND-ST resulting in a lower median value than the SND-RS in the same hour. However, average fill levels are similar, especially in the afternoon peak hour with around 10% difference. Precisely the opposite patterns are observed in stations belonging to the residential cluster since they present high fill levels in the morning peak hour (between 80% and 100%) and low fill levels in the afternoon peak hour (between 0% and 65%). In addition, average and median fill levels are almost the same. Regarding leisure and mixed stations, an extremely high variance occurs due different trip purposes. Demand at stations of tourist clusters is rather low and therefore these stations are used as buffer stations, i.e., they run full or empty to compensate fill levels in near stations. However, tourist cluster stations
9 Bruno A. Neumann-Saavedra et al. / Transportation Research Procedia 10 ( 2015 ) are few, and therefore the boxplot is not representative with this cluster type. We assume that due to our low solution quality obtained for the SND-ST, big improvements can be achieved with regard to the fill levels. In addition, different scenarios, e.g., a limited number of ST, can affect the fill levels. 5. Conclusions and future work In this paper, we have extended the SND-RS including the concept of ST as a stronger anticipation of operational decisions. ST consider indirectly the vehicle fleet since a capacitated vehicle is assigned to each ST when they are implemented. SND-ST suggests a vehicle fleet size which fulfills user expectations and almost matches initial and final fill levels at stations. Additional constraints in the MIP formulation make the SND-ST more challenging from a computational point of view. Experiments show similarities in the set up of RS. RS are concentrated during the day, especially in the morning and afternoon peak hours. We prove that SND-RS yields applicable fill levels since fill levels obtained thought the SND-ST present similar patterns. It is up to future research to design of sophisticated search techniques in order to find better-quality solutions for the SND-ST. For instance, if outputs of the SND-RS, e.g., RS, fill levels, can speed up the searching process in the SND-RT. An adapted version of the hybrid metaheuristic, which obtains good-quality solutions for the SND-RS in Vogel et al. (2014), can be adapted to the SND-ST. In addition, limited number of ST should be considered since the real-world BSS have a determined number of vehicles. Acknowledgements We thank Gewista Werbegesellschaft m.b.h for providing data from their project Citybike Wien. References Boyacı, B., Zografos, K.G., Geroliminis, N., An optimization framework for the development of efficient one-way car-sharing systems. European Journal of Operational Research 240, Büttner, J., Petersen, T., Optimising Bike Sharing in European Cities-A Handbook. Cepolina, E.M., Farina, A., A new shared vehicle system for urban areas. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies 21, Correia, G.H., Antunes, A.P., Optimization approach to depot location and trip selection in one-way carsharing systems. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review 48, Crainic, T.G., Service network design in freight transportation. European Journal of Operational Research 122, George, D.K., Xia, C.H., Fleet-sizing and service availability for a vehicle rental system via closed queueing networks. European Journal of Operational Research 211, Jorge, D., Correia, G., Barnhart, C., Testing the validity of the mip approach for locating carsharing stations in one-way systems. Procedia- Social and Behavioral Sciences 54, Raviv, T., Kolka, O., Optimal inventory management of a bike-sharing station. IIE Transactions 45, Sayarshad, H., Tavassoli, S., Zhao, F., A multi-periodic optimization formulation for bike planning and bike utilization. Applied Mathematical Modelling 36, Schuijbroek, J., Hampshire, R., van Hoeve, W.J., Inventory rebalancing and vehicle routing in bike sharing systems. Shaheen, S.A., Guzman, S., Zhang, H., Bikesharing in europe, the americas, and asia. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board 2143, Shu, J., Chou, M.C., Liu, Q., Teo, C.P., Wang, I.L., Models for effective deployment and redistribution of bicycles within public bicyclesharing systems. Operations Research 61, Vogel, P., Ehmke, J.F., Mattfeld, D.C., Service network design of bike sharing systems, working paper. Vogel, P., Neumann-Saavedra, B.A., Mattfeld, D.C., A hybrid metaheuristic to solve the resource allocation problem in bike sharing systems, in: Hybrid Metaheuristics. Springer, pp Wieberneit, N., Service network design for freight transportation: a review. OR spectrum 30,
SIDT 2017 XXII SEMINARIO SCIENTIFICO DELLA SOCIETÀ ITALIANA DOCENTI DI TRASPORTI
 SIDT 2017 XXII SEMINARIO SCIENTIFICO DELLA SOCIETÀ ITALIANA DOCENTI DI TRASPORTI POLITECNICO DI BARI TOWARDS SUSTAINABLE CITIES: INNOVATIVE SOLUTIONS FOR MOBILITY AND LOGISTICS SEPTEMBER 14-15, 2017 SESSION
SIDT 2017 XXII SEMINARIO SCIENTIFICO DELLA SOCIETÀ ITALIANA DOCENTI DI TRASPORTI POLITECNICO DI BARI TOWARDS SUSTAINABLE CITIES: INNOVATIVE SOLUTIONS FOR MOBILITY AND LOGISTICS SEPTEMBER 14-15, 2017 SESSION
A IMPROVED VOGEL S APPROXIMATIO METHOD FOR THE TRA SPORTATIO PROBLEM. Serdar Korukoğlu 1 and Serkan Ballı 2.
 Mathematical and Computational Applications, Vol. 16, No. 2, pp. 370-381, 2011. Association for Scientific Research A IMPROVED VOGEL S APPROXIMATIO METHOD FOR THE TRA SPORTATIO PROBLEM Serdar Korukoğlu
Mathematical and Computational Applications, Vol. 16, No. 2, pp. 370-381, 2011. Association for Scientific Research A IMPROVED VOGEL S APPROXIMATIO METHOD FOR THE TRA SPORTATIO PROBLEM Serdar Korukoğlu
An optimisation algorithm to establish the location of stations of a mixed fleet biking system: an application to the city of Lisbon
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 54 ( 2012 ) 513 524 EWGT 2012 15th meeting of the EURO Working Group on Transportation An optimisation algorithm to establish
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 54 ( 2012 ) 513 524 EWGT 2012 15th meeting of the EURO Working Group on Transportation An optimisation algorithm to establish
ScienceDirect. Microscopic Simulation on the Design and Operational Performance of Diverging Diamond Interchange
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Transportation Research Procedia 6 (2015 ) 198 212 4th International Symposium of Transport Simulation-ISTS 14, 1-4 June 2014, Corsica, France Microscopic
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Transportation Research Procedia 6 (2015 ) 198 212 4th International Symposium of Transport Simulation-ISTS 14, 1-4 June 2014, Corsica, France Microscopic
Product Decomposition in Supply Chain Planning
 Mario R. Eden, Marianthi Ierapetritou and Gavin P. Towler (Editors) Proceedings of the 13 th International Symposium on Process Systems Engineering PSE 2018 July 1-5, 2018, San Diego, California, USA 2018
Mario R. Eden, Marianthi Ierapetritou and Gavin P. Towler (Editors) Proceedings of the 13 th International Symposium on Process Systems Engineering PSE 2018 July 1-5, 2018, San Diego, California, USA 2018
Available online at ScienceDirect. Transportation Research Procedia 20 (2017 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Transportation Research Procedia 20 (2017 ) 709 716 12th International Conference "Organization and Traffic Safety Management in Large Cities", SPbOTSIC-2016,
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Transportation Research Procedia 20 (2017 ) 709 716 12th International Conference "Organization and Traffic Safety Management in Large Cities", SPbOTSIC-2016,
Tokyo: Simulating Hyperpath-Based Vehicle Navigations and its Impact on Travel Time Reliability
 CHAPTER 92 Tokyo: Simulating Hyperpath-Based Vehicle Navigations and its Impact on Travel Time Reliability Daisuke Fukuda, Jiangshan Ma, Kaoru Yamada and Norihito Shinkai 92.1 Introduction Most standard
CHAPTER 92 Tokyo: Simulating Hyperpath-Based Vehicle Navigations and its Impact on Travel Time Reliability Daisuke Fukuda, Jiangshan Ma, Kaoru Yamada and Norihito Shinkai 92.1 Introduction Most standard
BICYCLE SHARING SYSTEM: A PROPOSAL FOR SURAT CITY
 BICYCLE SHARING SYSTEM: A PROPOSAL FOR SURAT CITY Vishal D. Patel 1, Himanshu J. Padhya 2 M.E Student, Civil Engineering Department, Sarvajanik College of Engineering and Technology, Surat, Gujarat, India
BICYCLE SHARING SYSTEM: A PROPOSAL FOR SURAT CITY Vishal D. Patel 1, Himanshu J. Padhya 2 M.E Student, Civil Engineering Department, Sarvajanik College of Engineering and Technology, Surat, Gujarat, India
Available online at ScienceDirect. Transportation Research Procedia 2 (2014 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Transportation Research Procedia 2 (2014 ) 264 272 The Conference on in Pedestrian and Evacuation Dynamics 2014 (PED2014) Exhaustive analysis with
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Transportation Research Procedia 2 (2014 ) 264 272 The Conference on in Pedestrian and Evacuation Dynamics 2014 (PED2014) Exhaustive analysis with
Optimizing Cyclist Parking in a Closed System
 Optimizing Cyclist Parking in a Closed System Letu Qingge, Killian Smith Gianforte School of Computing, Montana State University, Bozeman, MT 59717, USA Abstract. In this paper, we consider the two different
Optimizing Cyclist Parking in a Closed System Letu Qingge, Killian Smith Gianforte School of Computing, Montana State University, Bozeman, MT 59717, USA Abstract. In this paper, we consider the two different
Estimating benefits of travel demand management measures
 Estimating benefits of travel demand management measures E. ~ani~uchi' and H. Hirao Department of Civil Engineering Systems, Kyoto University, Japan Abstract This paper presents models for estimating benefits
Estimating benefits of travel demand management measures E. ~ani~uchi' and H. Hirao Department of Civil Engineering Systems, Kyoto University, Japan Abstract This paper presents models for estimating benefits
Keywords: Highway Intersection, Intersection Accidents, Crash Type, Crash Contributing, Statistical Analysis, Design Factors
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Scienc es 96 ( 2013 ) 205 209 13th COTA International Conference of Transportation Professionals (CICTP 2013) ANALYSIS
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Scienc es 96 ( 2013 ) 205 209 13th COTA International Conference of Transportation Professionals (CICTP 2013) ANALYSIS
The Evolution of Transport Planning
 The Evolution of Transport Planning On Proportionality and Uniqueness in Equilibrium Assignment Michael Florian Calin D. Morosan Background Several bush-based algorithms for computing equilibrium assignments
The Evolution of Transport Planning On Proportionality and Uniqueness in Equilibrium Assignment Michael Florian Calin D. Morosan Background Several bush-based algorithms for computing equilibrium assignments
Advanced Materials Research Vol
 Advanced Materials Research Online: 2013-09-04 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vol. 790, pp 510-514 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.790.510 2013 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Public bicycle System Station Deployment
Advanced Materials Research Online: 2013-09-04 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vol. 790, pp 510-514 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.790.510 2013 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Public bicycle System Station Deployment
A Game Theoretic Study of Attack and Defense in Cyber-Physical Systems
 The First International Workshop on Cyber-Physical Networking Systems A Game Theoretic Study of Attack and Defense in Cyber-Physical Systems ChrisY.T.Ma Advanced Digital Sciences Center Illinois at Singapore
The First International Workshop on Cyber-Physical Networking Systems A Game Theoretic Study of Attack and Defense in Cyber-Physical Systems ChrisY.T.Ma Advanced Digital Sciences Center Illinois at Singapore
Available online at ScienceDirect. Analysis of Pedestrian Clearance Time at Signalized Crosswalks in Japan
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 32 ( 2014 ) 301 308 5th International Conference on Ambient Systems, Networks and Technologies (ANT-2014) Analysis of Pedestrian
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 32 ( 2014 ) 301 308 5th International Conference on Ambient Systems, Networks and Technologies (ANT-2014) Analysis of Pedestrian
Evacuation Time Minimization Model using Traffic Simulation and GIS Technology
 Evacuation Time Minimization Model using Traffic Simulation and GIS Technology Daisik Danny Nam, Presenter Ph.D. Student Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of California, Irvine
Evacuation Time Minimization Model using Traffic Simulation and GIS Technology Daisik Danny Nam, Presenter Ph.D. Student Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of California, Irvine
Using Farecard Data to Suggest Cycling Policies in Singapore. Ashwani Kumar Viet Anh Nguyen Kwong Meng Teo Amedeo Odoni
 Using Farecard Data to Suggest Cycling Policies in Singapore Ashwani Kumar Viet Anh Nguyen Kwong Meng Teo Amedeo Odoni Based on our paper published in the journal Annals of Operations Research in April
Using Farecard Data to Suggest Cycling Policies in Singapore Ashwani Kumar Viet Anh Nguyen Kwong Meng Teo Amedeo Odoni Based on our paper published in the journal Annals of Operations Research in April
VGI for mapping change in bike ridership
 VGI for mapping change in bike ridership D. Boss 1, T.A. Nelson* 2 and M. Winters 3 1 Unviersity of Victoria, Victoria, Canada 2 Arizona State University, Arizona, USA 3 Simon Frasier University, Vancouver,
VGI for mapping change in bike ridership D. Boss 1, T.A. Nelson* 2 and M. Winters 3 1 Unviersity of Victoria, Victoria, Canada 2 Arizona State University, Arizona, USA 3 Simon Frasier University, Vancouver,
A computational study of on-demand accuracy level decomposition for twostage stochastic programs
 A computational study of on-demand accuracy level decomposition for twostage stochastic programs Christian Wolf, Universität Paderborn, Germany Csaba I. Fábián, Kecskemét College, Hungary Achim Koberstein,
A computational study of on-demand accuracy level decomposition for twostage stochastic programs Christian Wolf, Universität Paderborn, Germany Csaba I. Fábián, Kecskemét College, Hungary Achim Koberstein,
A Novel Gear-shifting Strategy Used on Smart Bicycles
 2012 International Conference on Industrial and Intelligent Information (ICIII 2012) IPCSIT vol.31 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore A Novel Gear-shifting Strategy Used on Smart Bicycles Tsung-Yin
2012 International Conference on Industrial and Intelligent Information (ICIII 2012) IPCSIT vol.31 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore A Novel Gear-shifting Strategy Used on Smart Bicycles Tsung-Yin
Utilization of the spare capacity of exclusive bus lanes based on a dynamic allocation strategy
 Urban Transport XX 173 Utilization of the spare capacity of exclusive bus lanes based on a dynamic allocation strategy X. Wang 1 & Q. Li 2 1 Department of Transportation Management Engineering, Zhejiang
Urban Transport XX 173 Utilization of the spare capacity of exclusive bus lanes based on a dynamic allocation strategy X. Wang 1 & Q. Li 2 1 Department of Transportation Management Engineering, Zhejiang
A Model for Tuna-Fishery Policy Analysis: Combining System Dynamics and Game Theory Approach
 A Model for Tuna-Fishery Policy Analysis: Combining System Dynamics and Game Theory Approach E. Widodo, Budianto Department of Industrial Engineering, Institut Teknologi Sepuluh Nopember, ITS, Surabaya,
A Model for Tuna-Fishery Policy Analysis: Combining System Dynamics and Game Theory Approach E. Widodo, Budianto Department of Industrial Engineering, Institut Teknologi Sepuluh Nopember, ITS, Surabaya,
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 112 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 112 (2015 ) 540 545 7th Asia-Pacific Congress on Sports Technology, APCST 2015 Movement variability of professional pool billiards
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 112 (2015 ) 540 545 7th Asia-Pacific Congress on Sports Technology, APCST 2015 Movement variability of professional pool billiards
consist of friends, is open to all ages, and considers fair play of paramount importance. The matches are played without referees, since, according to
 Indoor football scheduling Dries Goossens Frits Spieksma Abstract This paper deals with a real-life scheduling problem from an amateur indoor football league. The league consists of a number of divisions,
Indoor football scheduling Dries Goossens Frits Spieksma Abstract This paper deals with a real-life scheduling problem from an amateur indoor football league. The league consists of a number of divisions,
Roundabouts along Rural Arterials in South Africa
 Krogscheepers & Watters 0 0 Word count: 00 text + figures = 0 equivalent words including Title and Abstract. Roundabouts along Rural Arterials in South Africa Prepared for: rd Annual Meeting of Transportation
Krogscheepers & Watters 0 0 Word count: 00 text + figures = 0 equivalent words including Title and Abstract. Roundabouts along Rural Arterials in South Africa Prepared for: rd Annual Meeting of Transportation
The Incremental Evolution of Gaits for Hexapod Robots
 The Incremental Evolution of Gaits for Hexapod Robots Abstract Gait control programs for hexapod robots are learned by incremental evolution. The first increment is used to learn the activations required
The Incremental Evolution of Gaits for Hexapod Robots Abstract Gait control programs for hexapod robots are learned by incremental evolution. The first increment is used to learn the activations required
Three New Methods to Find Initial Basic Feasible. Solution of Transportation Problems
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 11, 2017, no. 37, 1803-1814 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/ams.2017.75178 Three New Methods to Find Initial Basic Feasible Solution of Transportation
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 11, 2017, no. 37, 1803-1814 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/ams.2017.75178 Three New Methods to Find Initial Basic Feasible Solution of Transportation
i) Linear programming
 Problem statement Sailco Corporation must determine how many sailboats should be produced during each of the next four quarters (one quarter = three months). The demand during each of the next four quarters
Problem statement Sailco Corporation must determine how many sailboats should be produced during each of the next four quarters (one quarter = three months). The demand during each of the next four quarters
Comparative Study of VISSIM and SIDRA on Signalized Intersection
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Scien ce s 96 ( 2013 ) 2004 2010 13th COTA International Conference of Transportation Professionals (CICTP 2013)
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Scien ce s 96 ( 2013 ) 2004 2010 13th COTA International Conference of Transportation Professionals (CICTP 2013)
An analysis on feasibility of park & cycle ride system in a Japanese local city
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 54 ( 2012 ) 37 46 EWGT 2012 15th meeting of the EURO Working Group on Transportation An analysis on feasibility of park
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 54 ( 2012 ) 37 46 EWGT 2012 15th meeting of the EURO Working Group on Transportation An analysis on feasibility of park
COST ESTIMATION. Fully Allocated Causal Factor Models Temporal Variation Models Incremental Fixed Variable Cost Models
 COST ESTIMATION Outline 1. Roles for Cost Models 2. Conventional Model Types Fully Allocated Causal Factor Models Temporal Variation Models Incremental Fixed Variable Cost Models 3. New Approaches HASTUS
COST ESTIMATION Outline 1. Roles for Cost Models 2. Conventional Model Types Fully Allocated Causal Factor Models Temporal Variation Models Incremental Fixed Variable Cost Models 3. New Approaches HASTUS
Cod (Gadus morhua) in subdivisions 24 32, eastern Baltic stock (eastern Baltic Sea) *
 ICES Advice on fishing opportunities, catch, and effort Baltic Sea Ecoregion Published 31 May 2017 Version 2: 1 June 2017 Version 3: 8 June 2017 Version 4: 8 March 2018 DOI: 10.17895/ices.pub.3096 Cod
ICES Advice on fishing opportunities, catch, and effort Baltic Sea Ecoregion Published 31 May 2017 Version 2: 1 June 2017 Version 3: 8 June 2017 Version 4: 8 March 2018 DOI: 10.17895/ices.pub.3096 Cod
Congestion Management in Singapore. Assoc Prof Anthony TH CHIN Department of Economics National University of Singapore
 Congestion Management in Singapore Assoc Prof Anthony TH CHIN Department of Economics National University of Singapore anthonychin@nus.edu.sg Introduction 2 Introduction and What is Traffic Congestion?
Congestion Management in Singapore Assoc Prof Anthony TH CHIN Department of Economics National University of Singapore anthonychin@nus.edu.sg Introduction 2 Introduction and What is Traffic Congestion?
Online Companion to Using Simulation to Help Manage the Pace of Play in Golf
 Online Companion to Using Simulation to Help Manage the Pace of Play in Golf MoonSoo Choi Industrial Engineering and Operations Research, Columbia University, New York, NY, USA {moonsoo.choi@columbia.edu}
Online Companion to Using Simulation to Help Manage the Pace of Play in Golf MoonSoo Choi Industrial Engineering and Operations Research, Columbia University, New York, NY, USA {moonsoo.choi@columbia.edu}
The Application of Pedestrian Microscopic Simulation Technology in Researching the Influenced Realm around Urban Rail Transit Station
 Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering 4 (2016) 242-246 doi: 10.17265/2328-2142/2016.05.002 D DAVID PUBLISHING The Application of Pedestrian Microscopic Simulation Technology in Researching
Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering 4 (2016) 242-246 doi: 10.17265/2328-2142/2016.05.002 D DAVID PUBLISHING The Application of Pedestrian Microscopic Simulation Technology in Researching
Nathan L. Teigland 1
 Nathan L. Teigland 1 Source: The Bike-sharing World Map, www.bikesharingmap.com. Used for educational purposes. 2 Source: New York Citi Bike (http://www.citibikenyc.com/), used for educational purposes.
Nathan L. Teigland 1 Source: The Bike-sharing World Map, www.bikesharingmap.com. Used for educational purposes. 2 Source: New York Citi Bike (http://www.citibikenyc.com/), used for educational purposes.
Keywords: multiple linear regression; pedestrian crossing delay; right-turn car flow; the number of pedestrians;
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Scien ce s 96 ( 2013 ) 1997 2003 13th COTA International Conference of Transportation Professionals (CICTP 2013)
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Scien ce s 96 ( 2013 ) 1997 2003 13th COTA International Conference of Transportation Professionals (CICTP 2013)
Available online at ScienceDirect. Transportation Research Procedia 14 (2016 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Transportation Research Procedia 14 (2016 ) 2334 2343 6th Transport Research Arena April 18-21, 2016 Study of the establishment of the regional cycling
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Transportation Research Procedia 14 (2016 ) 2334 2343 6th Transport Research Arena April 18-21, 2016 Study of the establishment of the regional cycling
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO RELIABILITY
 i CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO RELIABILITY ii CHAPTER-1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Introduction: In the present scenario of global competition and liberalization, it is imperative that Indian industries become fully
i CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO RELIABILITY ii CHAPTER-1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Introduction: In the present scenario of global competition and liberalization, it is imperative that Indian industries become fully
A Point-Based Algorithm to Generate Final Table States of Football Tournaments
 International Journal of Computing Academic Research (IJCAR) ISSN 2305-9184, Volume 7, Number 3 (June 2018), pp.38-42 MEACSE Publications http://www.meacse.org/ijcar A Point-Based Algorithm to Generate
International Journal of Computing Academic Research (IJCAR) ISSN 2305-9184, Volume 7, Number 3 (June 2018), pp.38-42 MEACSE Publications http://www.meacse.org/ijcar A Point-Based Algorithm to Generate
Quantifying the Bullwhip Effect of Multi-echelon System with Stochastic Dependent Lead Time
 Quantifying the Bullwhip Effect of Multi-echelon System with Stochastic Dependent Lead Time Ngoc Anh Dung Do 1, Peter Nielsen 1, Zbigniew Michna 2, and Izabela Ewa Nielsen 1 1 Aalborg University, Department
Quantifying the Bullwhip Effect of Multi-echelon System with Stochastic Dependent Lead Time Ngoc Anh Dung Do 1, Peter Nielsen 1, Zbigniew Michna 2, and Izabela Ewa Nielsen 1 1 Aalborg University, Department
EFFICIENCY OF TRIPLE LEFT-TURN LANES AT SIGNALIZED INTERSECTIONS
 EFFICIENCY OF TRIPLE LEFT-TURN LANES AT SIGNALIZED INTERSECTIONS Khaled Shaaban, Ph.D., P.E., PTOE (a) (a) Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Qatar University (a) kshaaban@qu.edu.qa
EFFICIENCY OF TRIPLE LEFT-TURN LANES AT SIGNALIZED INTERSECTIONS Khaled Shaaban, Ph.D., P.E., PTOE (a) (a) Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Qatar University (a) kshaaban@qu.edu.qa
Queue analysis for the toll station of the Öresund fixed link. Pontus Matstoms *
 Queue analysis for the toll station of the Öresund fixed link Pontus Matstoms * Abstract A new simulation model for queue and capacity analysis of a toll station is presented. The model and its software
Queue analysis for the toll station of the Öresund fixed link Pontus Matstoms * Abstract A new simulation model for queue and capacity analysis of a toll station is presented. The model and its software
Author s Name Name of the Paper Session. Positioning Committee. Marine Technology Society. DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE September 18-19, 2001
 Author s Name Name of the Paper Session PDynamic Positioning Committee Marine Technology Society DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE September 18-19, 2001 POWER PLANT SESSION A New Concept for Fuel Tight DP
Author s Name Name of the Paper Session PDynamic Positioning Committee Marine Technology Society DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE September 18-19, 2001 POWER PLANT SESSION A New Concept for Fuel Tight DP
Volume-to-Capacity Estimation of Signalized Road Networks for Metropolitan Transportation Planning
 Volume-to-Capacity Estimation of Signalized Road Networks for Metropolitan Transportation Planning Hao Xu (Corresponding Author) Research Associate Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering Texas
Volume-to-Capacity Estimation of Signalized Road Networks for Metropolitan Transportation Planning Hao Xu (Corresponding Author) Research Associate Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering Texas
Application of Bayesian Networks to Shopping Assistance
 Application of Bayesian Networks to Shopping Assistance Yang Xiang, Chenwen Ye, and Deborah Ann Stacey University of Guelph, CANADA Abstract. We develop an on-line shopping assistant that can help a e-shopper
Application of Bayesian Networks to Shopping Assistance Yang Xiang, Chenwen Ye, and Deborah Ann Stacey University of Guelph, CANADA Abstract. We develop an on-line shopping assistant that can help a e-shopper
Miscalculations on the estimation of annual energy output (AEO) of wind farm projects
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 57 (2014 ) 698 705 2013 ISES Solar World Congress Miscalculations on the estimation of annual energy output (AEO) of wind farm projects
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 57 (2014 ) 698 705 2013 ISES Solar World Congress Miscalculations on the estimation of annual energy output (AEO) of wind farm projects
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 112 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 112 (2015 ) 418 423 7th Asia-Pacific Congress on Sports Technology, APCST 2015 Comparison of the aerodynamic performance of
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 112 (2015 ) 418 423 7th Asia-Pacific Congress on Sports Technology, APCST 2015 Comparison of the aerodynamic performance of
Lane changing and merging under congested conditions in traffic simulation models
 Urban Transport 779 Lane changing and merging under congested conditions in traffic simulation models P. Hidas School of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of New South Wales, Australia Abstract
Urban Transport 779 Lane changing and merging under congested conditions in traffic simulation models P. Hidas School of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of New South Wales, Australia Abstract
CONDUITS DST-Tel Aviv-Yafo Case Study
 CONDUITS DST-Tel Aviv-Yafo Case Study Introduction The city of Tel Aviv-Yafo is the nucleus of the Tel Aviv metropolitan area and serves as the financial and cultural centre of Israel. With a population
CONDUITS DST-Tel Aviv-Yafo Case Study Introduction The city of Tel Aviv-Yafo is the nucleus of the Tel Aviv metropolitan area and serves as the financial and cultural centre of Israel. With a population
Replay using Recomposition: Alignment-Based Conformance Checking in the Large
 Replay using Recomposition: Alignment-Based Conformance Checking in the Large Wai Lam Jonathan Lee 2, H.M.W. Verbeek 1, Jorge Munoz-Gama 2, Wil M.P. van der Aalst 1, and Marcos Sepúlveda 2 1 Architecture
Replay using Recomposition: Alignment-Based Conformance Checking in the Large Wai Lam Jonathan Lee 2, H.M.W. Verbeek 1, Jorge Munoz-Gama 2, Wil M.P. van der Aalst 1, and Marcos Sepúlveda 2 1 Architecture
Bike Renting Data Analysis: The Case of Dublin City
 Bike Renting Data Analysis: The Case of Dublin City Thanh Thoa Pham Thi *, Joe Timoney, Shyram Ravichandran, Peter Mooney, Adam Winstanley Department of Computer Science, Maynooth University Summary Public
Bike Renting Data Analysis: The Case of Dublin City Thanh Thoa Pham Thi *, Joe Timoney, Shyram Ravichandran, Peter Mooney, Adam Winstanley Department of Computer Science, Maynooth University Summary Public
WELCOME TO OPEN HOUSE # 1 June 14, 2017
 Langstaff Road Weston Road to Highway 7 Class Environmental Assessment Study WELCOME TO OPEN HOUSE # 1 June 14, 2017 Please sign in and join our mailing list Purpose of Open House #1 & Study Area York
Langstaff Road Weston Road to Highway 7 Class Environmental Assessment Study WELCOME TO OPEN HOUSE # 1 June 14, 2017 Please sign in and join our mailing list Purpose of Open House #1 & Study Area York
 Siła-Nowicka, K. (2018) Analysis of Actual Versus Permitted Driving Speed: a Case Study from Glasgow, Scotland. In: 26th Annual GIScience Research UK Conference (GISRUK 2018), Leicester, UK, 17-20 Apr
Siła-Nowicka, K. (2018) Analysis of Actual Versus Permitted Driving Speed: a Case Study from Glasgow, Scotland. In: 26th Annual GIScience Research UK Conference (GISRUK 2018), Leicester, UK, 17-20 Apr
Introduction Roundabouts are an increasingly popular alternative to traffic signals for intersection control in the United States. Roundabouts have a
 HIGH-CAPACITY ROUNDABOUT INTERSECTION ANALYSIS: GOING AROUND IN CIRCLES David Stanek, PE and Ronald T. Milam, AICP Abstract. Roundabouts have become increasingly popular in recent years as an innovative
HIGH-CAPACITY ROUNDABOUT INTERSECTION ANALYSIS: GOING AROUND IN CIRCLES David Stanek, PE and Ronald T. Milam, AICP Abstract. Roundabouts have become increasingly popular in recent years as an innovative
Scaling up of ADAS Traffic Impacts to German Cities
 10th ITS European Congress, Helsinki, Finland 16 19 June 2014 TP 0220 Scaling up of ADAS Traffic Impacts to German Cities Judith Geßenhardt 1*, Oliver Fakler 2, Tobias Schendzielorz 3, Fritz Busch 1 1.
10th ITS European Congress, Helsinki, Finland 16 19 June 2014 TP 0220 Scaling up of ADAS Traffic Impacts to German Cities Judith Geßenhardt 1*, Oliver Fakler 2, Tobias Schendzielorz 3, Fritz Busch 1 1.
1. Introduction. 2. Survey Method. Volume 6 Issue 5, May Licensed Under Creative Commons Attribution CC BY
 A Study on Performance of an Urban Arterial Corridor Guggilla Raju 1, Rontala Ashwini 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, GCET 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering,
A Study on Performance of an Urban Arterial Corridor Guggilla Raju 1, Rontala Ashwini 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, GCET 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering,
Applying Bi-objective Shortest Path Methods to Model Cycle Route-choice
 Applying Bi-objective Shortest Path Methods to Model Cycle Route-choice Chris Van Houtte, Judith Y. T. Wang, and Matthias Ehrgott September 30, 2009 Outline Commuter Cyclists Motivation Choice Set Route
Applying Bi-objective Shortest Path Methods to Model Cycle Route-choice Chris Van Houtte, Judith Y. T. Wang, and Matthias Ehrgott September 30, 2009 Outline Commuter Cyclists Motivation Choice Set Route
Honest Mirror: Quantitative Assessment of Player Performances in an ODI Cricket Match
 Honest Mirror: Quantitative Assessment of Player Performances in an ODI Cricket Match Madan Gopal Jhawar 1 and Vikram Pudi 2 1 Microsoft, India majhawar@microsoft.com 2 IIIT Hyderabad, India vikram@iiit.ac.in
Honest Mirror: Quantitative Assessment of Player Performances in an ODI Cricket Match Madan Gopal Jhawar 1 and Vikram Pudi 2 1 Microsoft, India majhawar@microsoft.com 2 IIIT Hyderabad, India vikram@iiit.ac.in
TIMETABLING IN SPORTS AND ENTERTAINMENT
 TIMETABLING IN SPORTS AND ENTERTAINMENT Introduction More complicated applications of interval scheduling and timetabling: scheduling of games in tournaments scheduling of commercials on network television
TIMETABLING IN SPORTS AND ENTERTAINMENT Introduction More complicated applications of interval scheduling and timetabling: scheduling of games in tournaments scheduling of commercials on network television
DYNAMIC LANES FOR AUCKLAND
 Dynamic Lanes for Auckland MENEZES M. and INMAN R. Page 1 DYNAMIC LANES FOR AUCKLAND Authors: INMAN, Robert BA (Hons) Previously Auckland Transport Senior Traffic Engineer Now Aurecon Robert.Inman@aurecongroup.com
Dynamic Lanes for Auckland MENEZES M. and INMAN R. Page 1 DYNAMIC LANES FOR AUCKLAND Authors: INMAN, Robert BA (Hons) Previously Auckland Transport Senior Traffic Engineer Now Aurecon Robert.Inman@aurecongroup.com
TOWARDS A BIKE-FRIENDLY CANADA A National Cycling Strategy Overview
 TOWARDS A BIKE-FRIENDLY CANADA A National Cycling Strategy Overview NationalCyclingStrategFrameworkv3.indd 1 Potential for this modal shift can be found in municipalities of all sizes, in every population
TOWARDS A BIKE-FRIENDLY CANADA A National Cycling Strategy Overview NationalCyclingStrategFrameworkv3.indd 1 Potential for this modal shift can be found in municipalities of all sizes, in every population
Determining bicycle infrastructure preferences A case study of Dublin
 *Manuscript Click here to view linked References 1 Determining bicycle infrastructure preferences A case study of Dublin Brian Caulfield 1, Elaine Brick 2, Orla Thérèse McCarthy 1 1 Department of Civil,
*Manuscript Click here to view linked References 1 Determining bicycle infrastructure preferences A case study of Dublin Brian Caulfield 1, Elaine Brick 2, Orla Thérèse McCarthy 1 1 Department of Civil,
Bikesharing in. Barcelona
 Bikesharing in Barcelona 01 THE EVOLUTION OF TRANSPORT MODEL FOR INDIVIDUALS USING BICYCLES 2 THE EVOLUTION OF TRANSPORT MODEL FOR INDIVIDUALS USING BICYCLES 80 s-90 s Private motorized vehicle as a the
Bikesharing in Barcelona 01 THE EVOLUTION OF TRANSPORT MODEL FOR INDIVIDUALS USING BICYCLES 2 THE EVOLUTION OF TRANSPORT MODEL FOR INDIVIDUALS USING BICYCLES 80 s-90 s Private motorized vehicle as a the
EFFECTS OF TRANSIT SIGNAL PRIORITY ON BUS RAPID TRANSIT SYSTEM. Sahil Chawla, Shalini Sinha and Khelan Modi
 EFFECTS OF TRANSIT SIGNAL PRIORITY ON BUS RAPID TRANSIT SYSTEM Sahil Chawla, Shalini Sinha and Khelan Modi PRESENTATION STRUCTURE INTRODUCTION AIM / OBJECTIVES STUDY APPROACH LITERATURE REVIEW MODEL DEVELOPMENT
EFFECTS OF TRANSIT SIGNAL PRIORITY ON BUS RAPID TRANSIT SYSTEM Sahil Chawla, Shalini Sinha and Khelan Modi PRESENTATION STRUCTURE INTRODUCTION AIM / OBJECTIVES STUDY APPROACH LITERATURE REVIEW MODEL DEVELOPMENT
Predicting Bike Usage for New York City s Bike Sharing System
 Computational Sustainability: Papers from the 2015 AAAI Workshop Predicting Bike Usage for New York City s Bike Sharing System Divya Singhvi, 1 Somya Singhvi, 1 Peter I. Frazier, 1 Shane G. Henderson,
Computational Sustainability: Papers from the 2015 AAAI Workshop Predicting Bike Usage for New York City s Bike Sharing System Divya Singhvi, 1 Somya Singhvi, 1 Peter I. Frazier, 1 Shane G. Henderson,
Demonstration of Possibilities to Introduce Semi-actuated Traffic Control System at Dhanmondi Satmasjid Road by Using CORSIM Simulation Software
 Paper ID: TE-043 746 International Conference on Recent Innovation in Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development () Department of Civil Engineering DUET - Gazipur, Bangladesh Demonstration of Possibilities
Paper ID: TE-043 746 International Conference on Recent Innovation in Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development () Department of Civil Engineering DUET - Gazipur, Bangladesh Demonstration of Possibilities
Traffic circles. February 9, 2009
 Traffic circles February 9, 2009 Abstract The use of a traffic circle is a relatively common means of controlling traffic in an intersection. Smaller Traffic circles can be especially effective in routing
Traffic circles February 9, 2009 Abstract The use of a traffic circle is a relatively common means of controlling traffic in an intersection. Smaller Traffic circles can be especially effective in routing
ENHANCED PARKWAY STUDY: PHASE 2 CONTINUOUS FLOW INTERSECTIONS. Final Report
 Preparedby: ENHANCED PARKWAY STUDY: PHASE 2 CONTINUOUS FLOW INTERSECTIONS Final Report Prepared for Maricopa County Department of Transportation Prepared by TABLE OF CONTENTS Page EXECUTIVE SUMMARY ES-1
Preparedby: ENHANCED PARKWAY STUDY: PHASE 2 CONTINUOUS FLOW INTERSECTIONS Final Report Prepared for Maricopa County Department of Transportation Prepared by TABLE OF CONTENTS Page EXECUTIVE SUMMARY ES-1
A STUDY ON GAP-ACCEPTANCE OF UNSIGNALIZED INTERSECTION UNDER MIXED TRAFFIC CONDITIONS
 A STUDY ON GAP-ACCEPTANCE OF UNSIGNALIZED INTERSECTION UNDER MIXED TRAFFIC CONDITIONS S.Siva Gowri Prasad 1, Ramesh Surisetty 2, Suresh Kumar ch 3 1 Assistant professor, Department, of Civil Engineering,
A STUDY ON GAP-ACCEPTANCE OF UNSIGNALIZED INTERSECTION UNDER MIXED TRAFFIC CONDITIONS S.Siva Gowri Prasad 1, Ramesh Surisetty 2, Suresh Kumar ch 3 1 Assistant professor, Department, of Civil Engineering,
Traffic safety analysis of intersections between the residential entrance and urban road
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 96 ( 2013 ) 1001 1007 13th COTA International Conference of Transportation Professionals (CICTP 2013) Traffic
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 96 ( 2013 ) 1001 1007 13th COTA International Conference of Transportation Professionals (CICTP 2013) Traffic
ScienceDirect. Investigation of the aerodynamic characteristics of an aerofoil shaped fuselage UAV model
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 90 (2014 ) 225 231 10th International Conference on Mechanical Engineering, ICME 2013 Investigation of the aerodynamic characteristics
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 90 (2014 ) 225 231 10th International Conference on Mechanical Engineering, ICME 2013 Investigation of the aerodynamic characteristics
Chapter Capacity and LOS Analysis of a Signalized I/S Overview Methodology Scope Limitation
 Chapter 37 Capacity and LOS Analysis of a Signalized I/S 37.1 Overview The Highway Capacity Manual defines the capacity as the maximum howdy rate at which persons or vehicle can be reasonably expected
Chapter 37 Capacity and LOS Analysis of a Signalized I/S 37.1 Overview The Highway Capacity Manual defines the capacity as the maximum howdy rate at which persons or vehicle can be reasonably expected
WELCOME. City of Greater Sudbury. Transportation Demand Management Plan
 WELCOME City of Greater Sudbury Transportation Demand Management Plan Public Consultation Session St. Andrew s Place, Activity Hall 111 Larch Street Wednesday September 13, 2017 6:00 to 8:00 pm Welcome
WELCOME City of Greater Sudbury Transportation Demand Management Plan Public Consultation Session St. Andrew s Place, Activity Hall 111 Larch Street Wednesday September 13, 2017 6:00 to 8:00 pm Welcome
AGENDA. Stakeholder Workshop
 AGENDA Stakeholder Workshop 19 th February DLF City Club, Gurgaon IBI GROUP Defining the cities of tomorrow 1 WORKSHOP AGENDA IBI GROUP Defining the cities of tomorrow 2 INTRODUCTION TO THE PBS GUIDANCE
AGENDA Stakeholder Workshop 19 th February DLF City Club, Gurgaon IBI GROUP Defining the cities of tomorrow 1 WORKSHOP AGENDA IBI GROUP Defining the cities of tomorrow 2 INTRODUCTION TO THE PBS GUIDANCE
Aerodynamic Analysis of a Symmetric Aerofoil
 214 IJEDR Volume 2, Issue 4 ISSN: 2321-9939 Aerodynamic Analysis of a Symmetric Aerofoil Narayan U Rathod Department of Mechanical Engineering, BMS college of Engineering, Bangalore, India Abstract - The
214 IJEDR Volume 2, Issue 4 ISSN: 2321-9939 Aerodynamic Analysis of a Symmetric Aerofoil Narayan U Rathod Department of Mechanical Engineering, BMS college of Engineering, Bangalore, India Abstract - The
A SEMI-PRESSURE-DRIVEN APPROACH TO RELIABILITY ASSESSMENT OF WATER DISTRIBUTION NETWORKS
 A SEMI-PRESSURE-DRIVEN APPROACH TO RELIABILITY ASSESSMENT OF WATER DISTRIBUTION NETWORKS S. S. OZGER PhD Student, Dept. of Civil and Envir. Engrg., Arizona State Univ., 85287, Tempe, AZ, US Phone: +1-480-965-3589
A SEMI-PRESSURE-DRIVEN APPROACH TO RELIABILITY ASSESSMENT OF WATER DISTRIBUTION NETWORKS S. S. OZGER PhD Student, Dept. of Civil and Envir. Engrg., Arizona State Univ., 85287, Tempe, AZ, US Phone: +1-480-965-3589
Gdynia s bicycle model
 Gdynia s bicycle model Problems related to cycling network and demand modelling Michał Miszewski, city of Gdynia Development of tool for transport analysis - MST Statistical data (baseline and forecasts)
Gdynia s bicycle model Problems related to cycling network and demand modelling Michał Miszewski, city of Gdynia Development of tool for transport analysis - MST Statistical data (baseline and forecasts)
EE 364B: Wind Farm Layout Optimization via Sequential Convex Programming
 EE 364B: Wind Farm Layout Optimization via Sequential Convex Programming Jinkyoo Park 1 Introduction In a wind farm, the wakes formed by upstream wind turbines decrease the power outputs of downstream
EE 364B: Wind Farm Layout Optimization via Sequential Convex Programming Jinkyoo Park 1 Introduction In a wind farm, the wakes formed by upstream wind turbines decrease the power outputs of downstream
International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology. (A High Impact Factor, Monthly, Peer Reviewed Journal)
 A Preliminary Study on Possible Alternate Roadways to Reduce Traffic Hazards at Velachery Township in Chennai Traffic Flow Minimization- a Prelimary Study Deepak R, Gangha G Department of Civil Engineering,
A Preliminary Study on Possible Alternate Roadways to Reduce Traffic Hazards at Velachery Township in Chennai Traffic Flow Minimization- a Prelimary Study Deepak R, Gangha G Department of Civil Engineering,
El Centro Mobility Hub
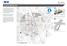 The El Centro drive shed comprises a major portion of the El Centro downtown area, which is well served by bus routes. The proposals intend to promote use of public transit through improvements and enhancements
The El Centro drive shed comprises a major portion of the El Centro downtown area, which is well served by bus routes. The proposals intend to promote use of public transit through improvements and enhancements
21.07 TRANSPORT CONNECTIVITY AND INFRASTRUCTURE
 21.07 TRANSPORT CONNECTIVITY AND INFRASTRUCTURE 21.07-1 Connectivity and Choice Transport connectivity and mode choice are critical to achieving productive, sustainable and socially just cities. Travel
21.07 TRANSPORT CONNECTIVITY AND INFRASTRUCTURE 21.07-1 Connectivity and Choice Transport connectivity and mode choice are critical to achieving productive, sustainable and socially just cities. Travel
MICROSIMULATION USING FOR CAPACITY ANALYSIS OF ROUNDABOUTS IN REAL CONDITIONS
 Session 5. Transport and Logistics System Modelling Proceedings of the 11 th International Conference Reliability and Statistics in Transportation and Communication (RelStat 11), 19 22 October 2011, Riga,
Session 5. Transport and Logistics System Modelling Proceedings of the 11 th International Conference Reliability and Statistics in Transportation and Communication (RelStat 11), 19 22 October 2011, Riga,
The Orienteering Problem
 The Orienteering Problem Bruce L. Golden, Larry Levy, and Rakesh Vohra* College of Business and Management, University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland 20742 Onenteenng is a sport in which start and
The Orienteering Problem Bruce L. Golden, Larry Levy, and Rakesh Vohra* College of Business and Management, University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland 20742 Onenteenng is a sport in which start and
Optimal Weather Routing Using Ensemble Weather Forecasts
 Optimal Weather Routing Using Ensemble Weather Forecasts Asher Treby Department of Engineering Science University of Auckland New Zealand Abstract In the United States and the United Kingdom it is commonplace
Optimal Weather Routing Using Ensemble Weather Forecasts Asher Treby Department of Engineering Science University of Auckland New Zealand Abstract In the United States and the United Kingdom it is commonplace
Bike sharing in 10 European countries report. Module 7: Poland
 Working Document Number: D 2.4 Work package: Bike sharing in 10 European countries report. Module 7: Poland WP2 Date of Preparation: 29.11.2010 Author(s): Magdalena Kowalewska, Rafał Ejsmont Editor(s):
Working Document Number: D 2.4 Work package: Bike sharing in 10 European countries report. Module 7: Poland WP2 Date of Preparation: 29.11.2010 Author(s): Magdalena Kowalewska, Rafał Ejsmont Editor(s):
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 147 (2016 ) 74 80
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 147 (2016 ) 74 80 11th conference of the International Sports Engineering Association, ISEA 2016 Comparison of the aerodynamic
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 147 (2016 ) 74 80 11th conference of the International Sports Engineering Association, ISEA 2016 Comparison of the aerodynamic
Methodology for analysing capacity and level of service for signalized intersections (HCM 2000)
 Methodology for analysing capacity and level of service for signalized intersections (HCM 2000) Ivana Nedevska 1, Slobodan Ognjenović 2,* and Elena Gusakova 3 1 GEING Krebs und Kiefer-Skopje, Macedonia
Methodology for analysing capacity and level of service for signalized intersections (HCM 2000) Ivana Nedevska 1, Slobodan Ognjenović 2,* and Elena Gusakova 3 1 GEING Krebs und Kiefer-Skopje, Macedonia
Pedestrian traffic flow operations on a platform: observations and comparison with simulation tool SimPed
 Pedestrian traffic flow operations on a platform: observations and comparison with simulation tool SimPed W. Daamen & S. P. Hoogendoorn Department Transport & Planning, Delft University of Technology,
Pedestrian traffic flow operations on a platform: observations and comparison with simulation tool SimPed W. Daamen & S. P. Hoogendoorn Department Transport & Planning, Delft University of Technology,
Model of Quantitative Evaluation of Traffic Circulation Plan Based on Traffic Conflicts
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 43 ( 2012 ) 245 254 8 th International Conference on Traffic and Transportation Studies Changsha, China, August 1 3,
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 43 ( 2012 ) 245 254 8 th International Conference on Traffic and Transportation Studies Changsha, China, August 1 3,
BICYCLE PARKING IN RESIDENTIAL AREAS
 Infrastructure Give Cycling a Push INFRASTRUCTURE/ PARKING BICYCLE PARKING IN RESIDENTIAL AREAS Overview In residential areas, all residents should have safe overnight storage for a bicycle. This is crucial
Infrastructure Give Cycling a Push INFRASTRUCTURE/ PARKING BICYCLE PARKING IN RESIDENTIAL AREAS Overview In residential areas, all residents should have safe overnight storage for a bicycle. This is crucial
Evaluation and Improvement of the Roundabouts
 The 2nd Conference on Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2016, *, ** Published Online **** 2016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/wjet http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/wjet.2014.***** Evaluation and
The 2nd Conference on Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2016, *, ** Published Online **** 2016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/wjet http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/wjet.2014.***** Evaluation and
FACTSHEET on Bike sharing and public bicycle system
 FACTSHEET on Bike sharing and public bicycle system This paper was prepared by: SOLUTIONS project This project was funded by the Seventh Framework Programme (FP7) of the European Commission www.uemi.net
FACTSHEET on Bike sharing and public bicycle system This paper was prepared by: SOLUTIONS project This project was funded by the Seventh Framework Programme (FP7) of the European Commission www.uemi.net
Aspects Regarding Priority Settings in Unsignalized Intersections and the Influence on the Level of Service
 Aspects Regarding Priority Settings in Unsignalized Intersections and the Influence on the Level of Service Dumitru Ilie, Matei Lucian, Vînatoru Matei, Racilă Laurențiu and Oprica Theodor Abstract The
Aspects Regarding Priority Settings in Unsignalized Intersections and the Influence on the Level of Service Dumitru Ilie, Matei Lucian, Vînatoru Matei, Racilă Laurențiu and Oprica Theodor Abstract The
Delay Analysis of Stop Sign Intersection and Yield Sign Intersection Based on VISSIM
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Scien ce s 96 ( 2013 ) 2024 2031 13th COTA International Conference of Transportation Professionals (CICTP 2013)
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Scien ce s 96 ( 2013 ) 2024 2031 13th COTA International Conference of Transportation Professionals (CICTP 2013)
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 84 (2014 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 84 (014 ) 97 93 014 ISSST, 014 International Symposium on Safety Science and Technology Research of emergency venting time in
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 84 (014 ) 97 93 014 ISSST, 014 International Symposium on Safety Science and Technology Research of emergency venting time in
Numerical Simulations of a Three-Lane Traffic Model Using Cellular Automata. A. Karim Daoudia and Najem Moussa
 CHINESE JOURNAL OF PHYSICS VOL. 41, NO. 6 DECEMBER 2003 Numerical Simulations of a Three-Lane Traffic Model Using Cellular Automata A. Karim Daoudia and Najem Moussa LMSPCPV, Dépt. de Physique, FST, B.P.
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PHYSICS VOL. 41, NO. 6 DECEMBER 2003 Numerical Simulations of a Three-Lane Traffic Model Using Cellular Automata A. Karim Daoudia and Najem Moussa LMSPCPV, Dépt. de Physique, FST, B.P.
Proposed. City of Grand Junction Complete Streets Policy. Exhibit 10
 Proposed City of Grand Junction Complete Streets Policy Exhibit 10 1 City of Grand Junction Complete Streets Policy Vision: The Complete Streets Vision is to develop a safe, efficient, and reliable travel
Proposed City of Grand Junction Complete Streets Policy Exhibit 10 1 City of Grand Junction Complete Streets Policy Vision: The Complete Streets Vision is to develop a safe, efficient, and reliable travel
TRANSPORTATION ANALYSIS REPORT US Route 6 Huron, Erie County, Ohio
 TRANSPORTATION ANALYSIS REPORT US Route 6 Huron, Erie County, Ohio December 12, 2012 Prepared for: The City of Huron 417 Main Huron, OH 44839 Providing Practical Experience Technical Excellence and Client
TRANSPORTATION ANALYSIS REPORT US Route 6 Huron, Erie County, Ohio December 12, 2012 Prepared for: The City of Huron 417 Main Huron, OH 44839 Providing Practical Experience Technical Excellence and Client
