Ceramic Processing Research
|
|
|
- Rafe Burke
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Ceramic Processing Research. Vol. 13, No. 3, pp. 267~271 (2012) J O U R N A L O F Ceramic Processing Research The effect of the pore structure of a high surface area hydrated lime in a humid environment Taimin Noh a, Hyun-Gyoo Shin b, Ho Hwan Chun c, Herbert Giesche d and Heesoo Lee a, * a School of Materials Science and Engineering, Pusan National University, Busan , Korea b Material Testing Center, Korea Testing Laboratory, Seoul , Korea c Department of Naval Architecture & Ocean Engineering, Pusan National University, Busan , Korea d NYSCC at Alfred University, Alfred, NY 14802, USA The degradation behavior of hydrated lime sorbent exposed to a humid environment was investigated in terms of a change of the pore structure, phase transition, and particle aggregation. Di-ethylene glycol (DEG)-coated quicklime was hydrated to prepare a sorbent with a high surface area. The hydrated lime sorbent was maintained in a consistent chamber at 50 ο C and 60% relative humidity for 168 h. As the degradation time of the sorbents exposed to the humid environment was increased, the calcite phase fraction was increased due to the carbonation process, whereas the reactivity for SO 2 gas was reduced. A decrease in the specific surface area of the sorbents, from 45.8 m 2 /g to 7.6 m 2 /g, was also observed with elapsed degradation time. Also the clogging of small size pores having a size range of 30~40Å was observed due to the particle aggregation and the carbonation process by the humidity. Consequently, the degradation of hydrated lime sorbent in a humid environment was attributed to a collapse of the pore structure originating from the carbonation process and the particle aggregation. Key words: Hydrated lime sorbent, Humid environment, Pore structure, Particle aggregation, Carbonation process. Introduction The in-duct sorbent injection method to remove SO 2 emissions from combustion systems is one of the dry flue gas desulfurization (FGD) processes. During this process, alkaline sorbent particles are introduced into a flue gas in the duct between the air pre-heater and the particulate control device in which the temperature and the humidity are controlled. As for an alkaline sorbent for SO 2 removal, hydrated lime or slaked lime (calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH) 2 ) is widely used [1]. In order to improve the desulfurization efficiency of the system, hydrated lime sorbent must have a small particle size, a high specific surface area, a high pore volume, and a large pore diameter [2]. The properties of the sorbent such as its specific surface area and porosity take an important role in removing the SO 2. Previous studies have shown that the reaction towards SO 2 gas depends strongly on the specific surface area of the sorbent [3, 4]. Numerous studies have shown how preparation of the sorbent affects the efficiency in removing SO 2, and modeled the reaction mechanisms [3, 5-9]. However, it is not enough to study the performance decay and the degradation behavior of hydrated lime sorbent. In *Corresponding author: Tel : Fax: heesoo@pusan.ac.kr general, the as-produced hydrated lime sorbent, in industry, can be preserved in a silo or storage facilities before it is sprayed into dry FGD systems. During this period of storage, the sorbent is exposed to a humid environment and the reactivity for SO 2 gas is decreased. The degraded sorbent cannot be used for SO 2 gas removal or a larger amount of degraded sorbent must be sprayed into the dry FGD system than that of as-produced sorbent. Therefore, a study of the degradation behavior of hydrated lime sorbent in a humid environment is needed to find possible solutions to prolong the efficiency for SO 2 removal and improve the durability. Previously, we have studied the degradation behavior of hydrated lime sorbent in a humid environment. As for the degraded sorbent in a humid environment, a decrease in the specific surface area with elapsed degradation time was observed and it resulted from the carbonation reaction and the aggregation of the sorbent [10]. In this study, we have investigated the change the of pore structure with respect to a decrease in the specific surface area in the degraded sorbent. The pore structure of the hydrated lime sorbent was examined by nitrogen adsorption-desorption isotherms and pore size distributions. The effects of the carbonation reaction and the aggregation with regard to change of the pore structure have also been discussed. Experimental Hydrated lime sorbent for SO 2 removal was prepared 267
2 268 Taimin Noh, Hyun-Gyoo Shin, Ho Hwan Chun, Herbert Giesche and Heesoo Lee using the hydration method. To obtain quicklime, limestone was calcined at 1100 ο C for 3 h. Di-ethylene glycol (DEG) as a dispersion agent was added to the quicklime powder and the DEG-coated quicklime was hydrated using distilled water. Then the hydrated lime sorbent was obtained through the reaction between the DEG-coated quicklime and distilled water of 1.8 times the stoichiometric amount. This preparation method for the hydrated lime sorbent with a high specific surface area was described previously [11, 12]. A degradation test of the as-prepared sorbent was progressed under atmospheric pressure using a chamber maintained at a constant temperature of 50 ο C and a humidity of 60% relative humidity (RH) for up to 168 h. Such conditions of the degradation tests have been described in our previous publication [10]. The crystal phases of the hydrated lime sorbents were analyzed using an X-ray diffractometer (Bruker, D8 Advance). XRD patterns were recorded in the 2θ range of using Cu Kα ( Å) radiation. The SO 2 reactivity of hydrated lime sorbents was measured using a thermo-gravimetric (TG) analyzer (SHIMADZU, TMA- 60H). N 2 gas containing 2,000 ppm SO 2 gas was used as a standard reaction gas to analyze the sulfation reactivity. The flow rate of the gas was 100 ml/minute and the sulfation reaction was held at 350 ο C for 4 h. Specific surface areas and pore structure studies were determined by nitrogen adsorption isotherms measured at 77 K using a N 2 adsorption analyzer (Micromeritics ASAP 2010). The Brunauer, Emmett and Teller (BET) and Barrett, Joyner and Halenda (BJH) models were used to estimate the specific surface area and the pore structure of the sorbents according to the nitrogen adsorption isotherms. Morphological analysis was performed in a field emission-scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM, Hitachi S-4800) and selected area electron diffraction (SAED) patterns were also observed by a transmission electron microscope (TEM,JEN 2100F). Results and Discussion In figure 1, XRD patterns show the phase transition from potlandite to calcite of the hydrated lime sorbents as a function of degradation time. The as-prepared sorbent indicates a complete hydration of quicklime (CaO) into portlandite (Ca(OH) 2 ). However, the degraded sorbents exposed to the humid environment for 24~168 h showed that the portlandite phase fraction was reduced, whereas the calcite phase fraction was increased because of the carbonation process. In particular, the decrease of the (101) main peak of portlandite and the growth of the (104) main peak of calcite were remarkable. The longer time the hydrated limes were exposed to the humid environment, the less the amount of the portlandite phase and the more the amount of the calcite phase became. Fig. 1. XRD patterns of hydrated lime sorbents as-prepared (0 h) and degraded which were exposed to a humid environment for up to 168 h. Fig. 2. Reactivity test toward SO 2 gas of as-prepared sorbent and degraded sorbents. Figure 2 describes the reactivity test toward SO 2 gas of hydrated lime sorbents from thermo-gravimetric analysis. As seen from Fig. 2, the as-prepared sorbent showed a weight increase to 120 wt% and the degraded sorbents for 48 h and for 168 h showed 113 wt% and 104 wt% increase, respectively. The as-prepared sorbent towards SO 2 gas showed a greater reactivity than the degraded sorbents. The slope obtained from the weight changetime curves can be interpreted as the reactivity of the sorbents. At an initial time of 60 minutes, the slopes were taken and the as-prepared sorbent also exhibited the highest value compared to the other slopes. These results indicate that the hydrated lime sorbents show a degraded SO 2 removal performance when exposed to a humid environment. In order to verify the relations between the specific
3 The effect of the pore structure of a high surface area hydrated lime in a humid environment 269 Table 1. The variation in the specific surface area of hydrated lime sorbents as a function of degradation time. Degradation time 0 h 24 h 48 h 96 h 168 h Specific surface area (m 2 /g) Fig. 4. Pore size distributions of hydrated lime sorbents asprepared and degraded for 48 h and 168 h. Fig. 3. Nitrogen adsorption and desorption isotherms of hydrated lime sorbents as-prepared and degraded for 48 h and 168 h. The open symbols are adsorption points, the filled symbols are desorption points. surface area, the pore structure, and its performance decay, the specific surface areas and the pore structure of the hydrated limes were measured as a function of degradation time and recorded in table 1. It was observed that the specific surface area of the asprepared sorbent was larger than that of the sorbent degraded in the humid environment. The as-prepared sorbent shows a specific surface area of 45.7 m 2 /g and the degraded sorbents for 48 h and 168 h show specific surface areas of 14.6 m 2 /g and 7.6 m 2 /g, respectively. The BJH (Barret-Joyner-Halenda) method was employed to obtain additional information on the pore shape, the pore volume, and the pore size distribution of the sorbents. The corresponding adsorption/desorption isotherms of gaseous nitrogen at 77 K are reported in Fig. 3. Isotherms were of type II and reflect the nonporous nature of solids. The largest adsorption volume of nitrogen was observed for the as-prepared sorbent and the adsorption capacity of the sorbents decreased with elapsed degradation time. All of the curves indicate the presence of macropores (size > 50 nm), shown by the sharp rise near P/P 0 values of 1. All isotherms showed a large type H3 hysteresis loop, which did not exhibit any limiting adsorption at high P/P 0. The presence of very large pores, still containing vapor at the end of the adsorption stage of the experiment, results in an adsorption isotherm that is still rising at (P/P 0 ) max, i.e., an isotherm of type II with an H3 hysteresis loop. This isotherm is incomplete, in the sense that is does not contain the capillarycondensation signature of the largest pores present [13]. The shapes of the pores also determine the type of the hysteresis loops. H3 hysteresis is usually found in solids consisting of aggregates or agglomerates of plate-like particles forming slit shaped pores with a nonuniform size and shape [14]. Overall, the isotherm hysteresis loops became small and the sorption capacity decreased with the process of degradation time. The asprepared sorbent and the sorbent degraded in the humid environment had aggregates of plate-like particles with slit shaped pores through the type of hysteresis loops. Figure 4 indicates the pore size distribution plots obtained using the BJH method. The as-prepared sorbent and the sorbents degraded for 48h and 168h were measured. It can be seen that most of pores are mesoscale in the range of Å in diameter. It was assumed that the pores having a size range of 30~40 Å came from the presence of slit pores in interparticle or intraparticle regions and the pores over 100 Å were affected by large voids in the aggregates. The positions of the maximum in the pore diameter do not vary, but that of the pore volume significantly changed with elapsed degradation time. For the asprepared sorbent, the pore volume over the range from 30 Å to almost 40 Å was the highest value. After being exposed to the humid environment for 48 h, the total pore volume was decreased, in particular, the volume of pores having a diameter of about 35 Å was decreased abruptly. For the sorbent degraded for 168h, there is almost no porosity in this size range existing and pores in the range from 100 Å to 1000 Å were decreased slightly. In the degradation process, the pore volume of about Å was reduced significantly, however, the volume of pores having sizes 100 Å Å was little changed. The change of the pore structure is likely the result of the clogging of small size pores due to the particle
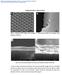
4 270 Taimin Noh, Hyun-Gyoo Shin, Ho Hwan Chun, Herbert Giesche and Heesoo Lee Fig. 5. SEM morphologies and SAED patterns of (a,c) as-prepared and (b,d) degraded for 168 h sample. aggregation and the carbonation process. Carbon dioxide (CO2) diffuses from the environment into the pores of the calcium hydroxide sorbent, partly filled with water from the humidity. Then, the formation and the growth of calcium carbonate in the pores will contribute to a clogging of the pore structure [15] and the silt pores may also disappear due to the aggregation. Based on this pore collapse process, it is suggested that the exposure of hydrated lime sorbent to a humid environment decreases the pore volume and so its performance for SO2 removal is reduced. Figure 5 shows SEM morphologies of the asprepared sorbent and the sorbent degraded for 168 h. In our previous study [10], we have observed the morphologies of the sorbent produced by hydration of quicklime at a low magnification. At a higher magnification, the particles of the as-prepared sorbent (Fig. 5(a)) were aggregates of irregularly stacked small calcium hydroxide crystals with a nm size. The sorbent degraded for 168 h in Fig. 5(b) shows a larger primary crystal size of nm and significant aggregation of the crystals. The shape and size of the crystals became more regular and the aggregation had occurred severely compared to that of the as-prepared sorbent. The observed specific surface area reduction can be explained by taking into account the increased particle sizes and disappearance of voids or pores due to the aggregation as mentioned above. In Fig. 5(c), the selected area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern of the as-prepared sorbent shows continuous ring like patterns. The patterns indicate particles with a finer size and weak crystallinity. The SAED patterns of Fig. 5(d) show more evident and speckled patterns. It seems that the crystals have growth because of the aggregation process and calcite crystallization and so the ring patterns were made up of discrete spots. Conclusions The degradation behavior of hydrated lime sorbent exposed to a humid environment was studied in terms of pore clogging and pore collapse. The weight gains, which indicate a reactivity toward SO2, were decreased from 120 wt% to 104 wt% with elapsed degradation time and the specific surface area was also decreased from 45.8 m2/g to 7.6 m2/g. The hydrated lime sorbents (portlandite) absorbed CO2 gas from the environment which then resulted in turning into the calcium carbonate (calcite). This can be expected that CO2 diffused into the pores of the hydrated lime sorbent, partly filled with water from the humidity, and then the formation and the growth of the calcium carbonate in the pores occur. Also the silt pores having a size range of 30~40 Å may also disappear owing to aggregation by humidity. Consequently, the decrease in the specific surface area concerning SO2 removal efficiency was contributed to by pore clogging and pore collapse due to the carbonation process and the particle aggregation.
5 The effect of the pore structure of a high surface area hydrated lime in a humid environment 271 Acknowledgement This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MEST) (NO ). References 1. Z.O. Siagi, M. Mbarawa, A.R. Mohamed, K.T. Lee, I. Dahlan, Fuel 86 (2007) J. Adanez, V. Fierro, F.G. Labiano, J.M. Palacios. Fuel, 76 (1997) N. Karatepe, A.E. Meriçücboyu, R. Yavuz, S. Küçükbayrak, Thermochim. Acta 335 (1999) N. Karatepe, N. Erdoğan, A.E. Meriçboyu, S. Küçükbayrak, Chem. Eng. Sci. 59 (2004) A. Garea, J.L. Herrera, J.A. Marques, A. Irabien, Chem. Eng. Sci. 56 (2001) C.S. Ho, S.M. Shih, C.F. Liu, H.M. Chu, C.D. Lee, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 41 (2002) M.J. Renedo, J. Fernández, Fuel 83 (2004) M. Bausach, M.P. Titus, C. Fite, F. Cunill, J.F. Izquierdo, J.Tejero, M.Iborra, AIChE Journal 51 (2005) F.J.G. Ortiz, P. Ollero, Sep. Purif. Technol. 62 (2008) H.G. Shin, H. Kim, T.M. Noh, D.W. Kim, Y.N. Kim, Int. J. Miner. Process. 98 (2011) H.G. Shin, H.Kim, Y.N. Kim, H.S. Lee, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 25 (2009) H.G. Shin, H. Kim, Y.N. Kim, H.S. Lee, Curr. Appl. Phys. 9 (2009) K.L. Murray, N.A. Seaton, M.A. Day, Langmuir 15 (1999) G. Leofanti, M. Padovan, G. Tozzola, B. Venturelli, Catal. Today 41 (1998) B. Johannesson, P. Utgenannt, Cem. Concr. Res. 31 (2001)
Reactivity Improvement of Ca (OH) 2 Sorbent Using Diatomaceous Earth (DE) From Aceh Province
 Research Inventy: International Journal of Engineering And Science Vol.8, Issue 2 (May 2018), PP -05-10 Issn (e): 2278-4721, Issn (p):2319-6483, www.researchinventy.com Reactivity Improvement of Ca (OH)
Research Inventy: International Journal of Engineering And Science Vol.8, Issue 2 (May 2018), PP -05-10 Issn (e): 2278-4721, Issn (p):2319-6483, www.researchinventy.com Reactivity Improvement of Ca (OH)
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Metal-organic framework-derived CoSe2/(NiCo)Se2
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Metal-organic framework-derived CoSe2/(NiCo)Se2
Effect of Moisture Content of Wet Fly Ash on Basic Properties of Mortar and Concrete
 Fourth International Conference on Sustainable Construction Materials and Technologies http://www.claisse.info/proceedings.htm SCMT4 Las Vegas, USA, August 7-11, 216 Effect of Moisture Content of Wet Fly
Fourth International Conference on Sustainable Construction Materials and Technologies http://www.claisse.info/proceedings.htm SCMT4 Las Vegas, USA, August 7-11, 216 Effect of Moisture Content of Wet Fly
McIlvaine Company Hot Topic Hour. April 9, Dry Sorbent Injection Options and Issues
 McIlvaine Company Hot Topic Hour April 9, 2015 Dry Sorbent Injection Options and Issues Marty Dillon Flue Gas Treatment Specialist Lhiost North America Presentation Overview Lhoist Overview Dry Sorbent
McIlvaine Company Hot Topic Hour April 9, 2015 Dry Sorbent Injection Options and Issues Marty Dillon Flue Gas Treatment Specialist Lhiost North America Presentation Overview Lhoist Overview Dry Sorbent
Interconnected hierarchical NiCo 2 O 4 microspheres as high performance. electrode material for supercapacitor
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Interconnected hierarchical microspheres as high performance electrode material for
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Interconnected hierarchical microspheres as high performance electrode material for
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Information Scalable and Ascendant Synthesis of Coated Carbon
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Information Scalable and Ascendant Synthesis of Coated Carbon
A variable-pressure constant-volume method was employed to determine the gas permeation
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 S.1. Gas permeation experiments A variable-pressure constant-volume method was employed to
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 S.1. Gas permeation experiments A variable-pressure constant-volume method was employed to
Supporting Information. Metal organic framework-derived Fe/C Nanocubes toward efficient microwave absorption
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Metal organic framework-derived Fe/C Nanocubes toward
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Metal organic framework-derived Fe/C Nanocubes toward
Supplementary Material
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Material Biomass Chitosan Derived Cobalt/Nitrogen Doped Carbon
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Material Biomass Chitosan Derived Cobalt/Nitrogen Doped Carbon
Injector Dynamics Assumptions and their Impact on Predicting Cavitation and Performance
 Injector Dynamics Assumptions and their Impact on Predicting Cavitation and Performance Frank Husmeier, Cummins Fuel Systems Presented by Laz Foley, ANSYS Outline Overview Computational Domain and Boundary
Injector Dynamics Assumptions and their Impact on Predicting Cavitation and Performance Frank Husmeier, Cummins Fuel Systems Presented by Laz Foley, ANSYS Outline Overview Computational Domain and Boundary
Understanding Hydrated Lime Properties In Acid Gas Control
 Understanding Hydrated Lime Properties In Acid Gas Control Mike Tate McIlvaine Company Hot Topic Hour June 21, 2012 Understanding Sorbent Properties Material Handling Chemistry Reactivity Effect on Particulate
Understanding Hydrated Lime Properties In Acid Gas Control Mike Tate McIlvaine Company Hot Topic Hour June 21, 2012 Understanding Sorbent Properties Material Handling Chemistry Reactivity Effect on Particulate
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Fig S1 a top-down SEM image of PS template. b. cross-sectional SEM of PS template (with diameter of 440 nm). Fig. S2 The cross-sectional SEM of the dense Ge film(a) and 3DOM Ge
Supplementary Information Fig S1 a top-down SEM image of PS template. b. cross-sectional SEM of PS template (with diameter of 440 nm). Fig. S2 The cross-sectional SEM of the dense Ge film(a) and 3DOM Ge
11/22/ (4) Harmonization: <846> SPECIFIC SURFACE AREA
 BRIEFING 846 Specific Surface Area, USP 27 page 2385. The European Pharmacopoeia is the coordinating pharmacopeia for the international harmonization of the Specific Surface Area General Chapter, as part
BRIEFING 846 Specific Surface Area, USP 27 page 2385. The European Pharmacopoeia is the coordinating pharmacopeia for the international harmonization of the Specific Surface Area General Chapter, as part
Supporting information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry Please do 2018 not adjust margins Supporting information Self-assembled 3D flower-like
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry Please do 2018 not adjust margins Supporting information Self-assembled 3D flower-like
Experimental Analysis on Vortex Tube Refrigerator Using Different Conical Valve Angles
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 7-067X, p-issn: 7-00X, www.ijerd.com Volume 3, Issue 4 (August ), PP. 33-39 Experimental Analysis on Vortex Tube Refrigerator Using
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 7-067X, p-issn: 7-00X, www.ijerd.com Volume 3, Issue 4 (August ), PP. 33-39 Experimental Analysis on Vortex Tube Refrigerator Using
Tunable CoFe-Based Active Sites on 3D Heteroatom Doped. Graphene Aerogel Electrocatalysts via Annealing Gas Regulation for
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Tunable CoFe-Based Active Sites on 3D Heteroatom Doped Graphene Aerogel
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Tunable CoFe-Based Active Sites on 3D Heteroatom Doped Graphene Aerogel
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Template-Preparation of Three-Dimensional Molybdenum
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Template-Preparation of Three-Dimensional Molybdenum
BASF s Mercury Sorbent HX A Mercury MATS Compliant Technology William Hizny, Fabien Rioult PhD, Xiaolin Yang PhD
 BASF s Mercury Sorbent HX A Mercury MATS Compliant Technology William Hizny, Fabien Rioult PhD, Xiaolin Yang PhD EUEC 2014 February 3-5, 2014 Phoenix, AZ 1 Overview Mercury Sorbent HX MATS compliant mercury
BASF s Mercury Sorbent HX A Mercury MATS Compliant Technology William Hizny, Fabien Rioult PhD, Xiaolin Yang PhD EUEC 2014 February 3-5, 2014 Phoenix, AZ 1 Overview Mercury Sorbent HX MATS compliant mercury
HYPERVELOCITY IMPACT AND OUTGASSING TESTS ON ETHYLENE- CO-METHACRYLIC ACID IONOMERS FOR SPACE APPLICATIONS
 HYPERVELOCITY IMPACT AND OUTGASSING TESTS ON ETHYLENE- CO-METHACRYLIC ACID IONOMERS FOR SPACE APPLICATIONS L. Castelnovo 1, A. M. Grande 1, L. Di Landro 1, G. Sala 1, C. Giacomuzzo 2, A. Francesconi 2
HYPERVELOCITY IMPACT AND OUTGASSING TESTS ON ETHYLENE- CO-METHACRYLIC ACID IONOMERS FOR SPACE APPLICATIONS L. Castelnovo 1, A. M. Grande 1, L. Di Landro 1, G. Sala 1, C. Giacomuzzo 2, A. Francesconi 2
EFFECT OF FLY ASH GRADATION ON WORKABILITY, STRENGTH AND DURABILITY OF PORTLAND CEMENT FLY ASH MORTARS
 EFFECT OF FLY ASH GRADATION ON WORKABILITY, STRENGTH AND DURABILITY OF PORTLAND CEMENT FLY ASH MORTARS Xian P. Liu, Pei M. Wang and Jie Sun Key Laboratory of Advanced Civil Engineering Materials (Tongji
EFFECT OF FLY ASH GRADATION ON WORKABILITY, STRENGTH AND DURABILITY OF PORTLAND CEMENT FLY ASH MORTARS Xian P. Liu, Pei M. Wang and Jie Sun Key Laboratory of Advanced Civil Engineering Materials (Tongji
Waste to energy conversion Dr. Prasenjit Mondal Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee. Lecture 25 Gas Cleanup 2
 Waste to energy conversion Dr. Prasenjit Mondal Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Lecture 25 Gas Cleanup 2 Hi friends. Now we will start discussion on the second
Waste to energy conversion Dr. Prasenjit Mondal Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Lecture 25 Gas Cleanup 2 Hi friends. Now we will start discussion on the second
5 th Oxyfuel Combustion Research Network Meeting. Acid Gas Control by Dry Sorbent Injection in Air and Oxy-Fuel Combustion
 Institut für Feuerungs- und Kraftwerkstechnik Prof. Dr. techn. G. Scheffknecht 5 th Oxyfuel Combustion Research Network Meeting Hongyi Hotel, Wuhan, China 27 th /30 th October 2015 Acid Gas Control by
Institut für Feuerungs- und Kraftwerkstechnik Prof. Dr. techn. G. Scheffknecht 5 th Oxyfuel Combustion Research Network Meeting Hongyi Hotel, Wuhan, China 27 th /30 th October 2015 Acid Gas Control by
Layered polyaniline/graphene film from sandwich-structured polyaniline/graphene/polyaniline nanosheets for high-performance pseudosupercapacitors
 Supporting Information for: Layered polyaniline/graphene film from sandwich-structured polyaniline/graphene/polyaniline nanosheets for high-performance pseudosupercapacitors Zhongqiu Tong a, Yongning Yang
Supporting Information for: Layered polyaniline/graphene film from sandwich-structured polyaniline/graphene/polyaniline nanosheets for high-performance pseudosupercapacitors Zhongqiu Tong a, Yongning Yang
METHOD 3C - DETERMINATION OF CARBON DIOXIDE, METHANE, NITROGEN, AND OXYGEN FROM STATIONARY SOURCES
 METHOD 3C - DETERMINATION OF CARBON DIOXIDE, METHANE, NITROGEN, AND OXYGEN FROM STATIONARY SOURCES 1. Applicability and Principle 1.1 Applicability. This method applies to the analysis of carbon dioxide
METHOD 3C - DETERMINATION OF CARBON DIOXIDE, METHANE, NITROGEN, AND OXYGEN FROM STATIONARY SOURCES 1. Applicability and Principle 1.1 Applicability. This method applies to the analysis of carbon dioxide
DSC 204 HP Phoenix. High-Pressure Differential Scanning Calorimetry up to 15 MPa Method, Technique and Applications
 DSC 204 HP Phoenix High-Pressure Differential Scanning Calorimetry up to 15 MPa Method, Technique and Applications DSC 204 HP Phoenix The ability to apply pressure improves the capabilities of Differential
DSC 204 HP Phoenix High-Pressure Differential Scanning Calorimetry up to 15 MPa Method, Technique and Applications DSC 204 HP Phoenix The ability to apply pressure improves the capabilities of Differential
CFD Analysis of the Anti-Surge Effects by Water Hammering
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS CFD Analysis of the Anti-Surge Effects by Water Hammering To cite this article: Tae-oh Kim et al 2015 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci.
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS CFD Analysis of the Anti-Surge Effects by Water Hammering To cite this article: Tae-oh Kim et al 2015 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci.
Supporting information. A metal-organic framework based multifunctional catalytic platform for organic transformation and environmental remediation
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting information A metal-organic framework based multifunctional catalytic platform
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting information A metal-organic framework based multifunctional catalytic platform
Key Laboratory of Material Chemistry for Energy Conversion and Storage (Ministry
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information for Dramatically enhanced visible-light driven H 2 evolution
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information for Dramatically enhanced visible-light driven H 2 evolution
Optical measurement in carbon nanotubes formation by pulsed laser ablation
 Thin Solid Films 457 (004) 7 11 Optical measurement in carbon nanotubes formation by pulsed laser ablation Tomoaki Ikegami, Futoshi Nakanishi*, Makoto Uchiyama, Kenji Ebihara Graduate School of Science
Thin Solid Films 457 (004) 7 11 Optical measurement in carbon nanotubes formation by pulsed laser ablation Tomoaki Ikegami, Futoshi Nakanishi*, Makoto Uchiyama, Kenji Ebihara Graduate School of Science
Particle Control under Wall Saturation in Long-pulse High-density H-mode Plasmas of JT-60U
 Particle Control under Wall Saturation in Long-pulse High-density H-mode Plasmas of JT-6U H. Kubo, T. Nakano, N. Asakura, H. Takenaga, K. Tsuzuki, N. Oyama, H. Kawashima, K. Shimizu, H. Urano, K. Fujimoto,
Particle Control under Wall Saturation in Long-pulse High-density H-mode Plasmas of JT-6U H. Kubo, T. Nakano, N. Asakura, H. Takenaga, K. Tsuzuki, N. Oyama, H. Kawashima, K. Shimizu, H. Urano, K. Fujimoto,
To What Extend is Helium Adsorbed on Porous Solids at Ambient Temperatures?
 To What Extend is Helium Adsorbed on Porous Solids at Ambient Temperatures? J. U. Keller, St. Bohn, R. Staudt* Inst. Fluid- and Thermodynamics University of Siegen, 57068 Siegen e-mail: keller@ift.maschinenbau.uni-siegen.de
To What Extend is Helium Adsorbed on Porous Solids at Ambient Temperatures? J. U. Keller, St. Bohn, R. Staudt* Inst. Fluid- and Thermodynamics University of Siegen, 57068 Siegen e-mail: keller@ift.maschinenbau.uni-siegen.de
arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 16 Aug 2014
![arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 16 Aug 2014 arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 16 Aug 2014](/thumbs/90/101993511.jpg) Preprint typeset in JINST style - HYPER VERSION RPC Gap Production and Performance for CMS RE4 Upgrade arxiv:1408.3720v1 [physics.ins-det] 16 Aug 2014 Sung Keun Park, Min Ho Kang and Kyong Sei Lee Korea
Preprint typeset in JINST style - HYPER VERSION RPC Gap Production and Performance for CMS RE4 Upgrade arxiv:1408.3720v1 [physics.ins-det] 16 Aug 2014 Sung Keun Park, Min Ho Kang and Kyong Sei Lee Korea
Visual Observation of Nucleate Boiling and Sliding Phenomena of Boiling Bubbles on a Horizontal Tube Heater
 Proceedings of the 2 nd World Congress on Mechanical, Chemical, and Material Engineering (MCM'16) Budapest, Hungary August 22 23, 216 Paper No. HTFF 146 DOI:.11159/htff16.146 Visual Observation of Nucleate
Proceedings of the 2 nd World Congress on Mechanical, Chemical, and Material Engineering (MCM'16) Budapest, Hungary August 22 23, 216 Paper No. HTFF 146 DOI:.11159/htff16.146 Visual Observation of Nucleate
SO 3 HCI SO 2. reduce emissions. solutions for. Air Pollution Control.
 SO 3 HCI SO 2 reduce emissions Hg solutions for Air Pollution Control www.sturtevantinc.com Reduce Emissions with Sturtevant Many boilers and coal fired power plants are injecting dry sorbents into flue
SO 3 HCI SO 2 reduce emissions Hg solutions for Air Pollution Control www.sturtevantinc.com Reduce Emissions with Sturtevant Many boilers and coal fired power plants are injecting dry sorbents into flue
Supporting Information. In-Situ Facile Bubble-Templated Fabrication of New-Type Urchin-Like (Li, Mo)- Doped Lix(Mo0.3V0.7)2O5 for Zn 2+ Storage
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information In-Situ Facile Bubble-Templated Fabrication of New-Type
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information In-Situ Facile Bubble-Templated Fabrication of New-Type
D DAVID PUBLISHING. Manufacturing Ultra High Performance Concretes by Silica Fume, Ultra Fine Fly Ash and Metakaolin Addition. 1.
 Journal of Materials Science and Engineering A 7 (5-6) (2017) 136-142 doi: 10.17265/2161-6213/2017.5-6.003 D DAVID PUBLISHING Manufacturing Ultra High Performance Concretes by Silica Fume, Tony Song, Ion
Journal of Materials Science and Engineering A 7 (5-6) (2017) 136-142 doi: 10.17265/2161-6213/2017.5-6.003 D DAVID PUBLISHING Manufacturing Ultra High Performance Concretes by Silica Fume, Tony Song, Ion
The analysis of complex multicomponent
 The analysis of complex multicomponent gas mixtures for emission monitoring 31 July 2017 Test and Measurement Prelly Marebane Fit-for-purpose reference materials for air pollution monitoring in SA and
The analysis of complex multicomponent gas mixtures for emission monitoring 31 July 2017 Test and Measurement Prelly Marebane Fit-for-purpose reference materials for air pollution monitoring in SA and
Dust explosion severity characteristics of Indonesian Sebuku coal in oxy-fuel atmospheres
 Dust explosion severity characteristics of Indonesian Sebuku coal in oxy-fuel atmospheres Frederik Norman,1, Sepideh Hosseinzadeh 2, Eric Van den Bulck 2, Jan Berghmans 1, Filip Verplaetsen 1 1 Adinex
Dust explosion severity characteristics of Indonesian Sebuku coal in oxy-fuel atmospheres Frederik Norman,1, Sepideh Hosseinzadeh 2, Eric Van den Bulck 2, Jan Berghmans 1, Filip Verplaetsen 1 1 Adinex
Electronic Supplementary Information for. Highly Stable Mesoporous Silica Nanospheres Embedded with
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 17 Electronic Supplementary Information for Highly Stable Mesoporous Silica Nanospheres Embedded
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 17 Electronic Supplementary Information for Highly Stable Mesoporous Silica Nanospheres Embedded
CFD Simulation and Experimental Validation of a Diaphragm Pressure Wave Generator
 CFD Simulation and Experimental Validation of a Diaphragm Pressure Wave Generator T. Huang 1, A. Caughley 2, R. Young 2 and V. Chamritski 1 1 HTS-110 Ltd Lower Hutt, New Zealand 2 Industrial Research Ltd
CFD Simulation and Experimental Validation of a Diaphragm Pressure Wave Generator T. Huang 1, A. Caughley 2, R. Young 2 and V. Chamritski 1 1 HTS-110 Ltd Lower Hutt, New Zealand 2 Industrial Research Ltd
Characterizing a Cu/Mn Alloy for Extracting Oxygen from Inert Gas. Streams
 Characterizing a Cu/Mn Alloy for Extracting Oxygen from Inert Gas Streams Grace Lenhard Prattsburgh Central School LLE advisors: Walter Shmayda and Matthew Sharpe Laboratory for Laser Energetics University
Characterizing a Cu/Mn Alloy for Extracting Oxygen from Inert Gas Streams Grace Lenhard Prattsburgh Central School LLE advisors: Walter Shmayda and Matthew Sharpe Laboratory for Laser Energetics University
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information 3D-composite structure of FeP nanorods supported
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information 3D-composite structure of FeP nanorods supported
White Paper. Chemical Sensor vs NDIR - Overview: NDIR Technology:
 Title: Comparison of Chemical Sensor and NDIR Technologies TSN Number: 25 File:\\MII- SRV1\Metron\Bridge_Analyzers\Customer_Service_Documentation\White_Papers\25_G en EGA NDIR vs Chemical Sensor.docx Created
Title: Comparison of Chemical Sensor and NDIR Technologies TSN Number: 25 File:\\MII- SRV1\Metron\Bridge_Analyzers\Customer_Service_Documentation\White_Papers\25_G en EGA NDIR vs Chemical Sensor.docx Created
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Fe 3 O 4 Quantum Dots Decorated MoS 2 Nanosheet
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Fe 3 O 4 Quantum Dots Decorated MoS 2 Nanosheet
acrolein, acetaldehyde and acetone( cm -1 ); methanol (1306 cm -1 ); ethylene (949 cm -1 ); and isoprene (893 cm -1 ).
 acrolein, acetaldehyde and acetone(1550 1800 cm -1 ); methanol (1306 cm -1 ); ethylene (949 cm -1 ); and isoprene (893 cm -1 ). 5 Figure 4a 6 Figure 4b Figure 4c 7 Figure 5 Questions in Student Handout
acrolein, acetaldehyde and acetone(1550 1800 cm -1 ); methanol (1306 cm -1 ); ethylene (949 cm -1 ); and isoprene (893 cm -1 ). 5 Figure 4a 6 Figure 4b Figure 4c 7 Figure 5 Questions in Student Handout
Dr. Rogers Chapter 5 Homework Chem 111 Fall 2003
 Dr. Rogers Chapter 5 Homework Chem 111 Fall 2003 From textbook: 7-33 odd, 37-45 odd, 55, 59, 61 1. Which gaseous molecules (choose one species) effuse slowest? A. SO 2 (g) B. Ar(g) C. NO(g) D. Ne(g) E.
Dr. Rogers Chapter 5 Homework Chem 111 Fall 2003 From textbook: 7-33 odd, 37-45 odd, 55, 59, 61 1. Which gaseous molecules (choose one species) effuse slowest? A. SO 2 (g) B. Ar(g) C. NO(g) D. Ne(g) E.
SIMULATION OF CORE LIFTING PROCESS FOR LOST GAS CALCULATION IN SHALE RESERVOIRS
 SCA213-5 1/12 SIMULATION OF CORE LIFTING PROCESS FOR LOST GAS CALCULATION IN SHALE RESERVOIRS Kurt Wilson, A.S. Padmakar, Firoze Mondegarian, Chevron This paper was prepared for presentation at the International
SCA213-5 1/12 SIMULATION OF CORE LIFTING PROCESS FOR LOST GAS CALCULATION IN SHALE RESERVOIRS Kurt Wilson, A.S. Padmakar, Firoze Mondegarian, Chevron This paper was prepared for presentation at the International
A07 Surfactant Induced Solubilization and Transfer Resistance in Gas-Water and Gas-Oil Systems
 A07 Surfactant Induced Solubilization and Transfer Resistance in Gas-Water and Gas-Oil Systems R Farajzadeh* (TU Delft), A. Banaei (TU Delft), J. Kinkela (TU Delft), T. deloos (TU Delft), S. Rudolph (TU
A07 Surfactant Induced Solubilization and Transfer Resistance in Gas-Water and Gas-Oil Systems R Farajzadeh* (TU Delft), A. Banaei (TU Delft), J. Kinkela (TU Delft), T. deloos (TU Delft), S. Rudolph (TU
Artisan Technology Group is your source for quality new and certified-used/pre-owned equipment
 Artisan Technology Group is your source for quality new and certified-used/pre-owned equipment FAST SHIPPING AND DELIVERY TENS OF THOUSANDS OF IN-STOCK ITEMS EQUIPMENT DEMOS HUNDREDS OF MANUFACTURERS SUPPORTED
Artisan Technology Group is your source for quality new and certified-used/pre-owned equipment FAST SHIPPING AND DELIVERY TENS OF THOUSANDS OF IN-STOCK ITEMS EQUIPMENT DEMOS HUNDREDS OF MANUFACTURERS SUPPORTED
Practical approach and problems in in-situ RGA calibration
 Practical approach and problems in in-situ RGA calibration Oleg Malyshev and Keith Middleman Vacuum Science Group, ASTeC Accelerator Science and Technology Centre STFC Daresbury Laboratory UK Workshop
Practical approach and problems in in-situ RGA calibration Oleg Malyshev and Keith Middleman Vacuum Science Group, ASTeC Accelerator Science and Technology Centre STFC Daresbury Laboratory UK Workshop
Description of saturation curves and boiling process of dry air
 EPJ Web of Conferences 180, 0114 (018) EFM 017 https://doi.org/10.1051/epjconf/0181800114 Description of saturation curves and boiling process of dry air Magda Vestfálová 1,*, Markéta Petříková 1, Martin
EPJ Web of Conferences 180, 0114 (018) EFM 017 https://doi.org/10.1051/epjconf/0181800114 Description of saturation curves and boiling process of dry air Magda Vestfálová 1,*, Markéta Petříková 1, Martin
EFFECTS OF CHEMICAL ADDITIVES ON THE PRESSURE DROP IN THE PIPES
 International Journal of Bio-Technology andresearch (IJBTR) ISSN(P): 2249-6858; ISSN(E): 2249-796X Vol. 4, Issue 1, Feb 2014, 1-6 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. EFFECTS OF CHEMICAL ADDITIVES ON THE PRESSURE DROP IN THE
International Journal of Bio-Technology andresearch (IJBTR) ISSN(P): 2249-6858; ISSN(E): 2249-796X Vol. 4, Issue 1, Feb 2014, 1-6 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. EFFECTS OF CHEMICAL ADDITIVES ON THE PRESSURE DROP IN THE
Scales of Motion and Atmospheric Composition
 Scales of Motion and Atmospheric Composition Atmos 3200/Geog 3280 Mountain Weather and Climate Sebastian Hoch & C. David Whiteman Drusberg and Glaernisch, Switzerland, Sebastian Hoch Atmospheric Scales
Scales of Motion and Atmospheric Composition Atmos 3200/Geog 3280 Mountain Weather and Climate Sebastian Hoch & C. David Whiteman Drusberg and Glaernisch, Switzerland, Sebastian Hoch Atmospheric Scales
The Origin and Time Dependence of the Amount and Composition of Non- Constituent Gases Present in Crystal Growth Systems
 The Origin and Time Dependence of the Amount and Composition of Non- Constituent Gases Present in Crystal Growth Systems Witold Palosz A Desorption of inert gases from, and their diffusion through the
The Origin and Time Dependence of the Amount and Composition of Non- Constituent Gases Present in Crystal Growth Systems Witold Palosz A Desorption of inert gases from, and their diffusion through the
Green Building Bricks Made with Clays and Sugar Cane Bagasse Ash
 Green Building Bricks Made with Clays and Sugar Cane Bagasse Ash Danupon Tonnayopas Department of Mining and Materials Engineering Faculty of Engineering Prince of Songkla University Introduction Performances
Green Building Bricks Made with Clays and Sugar Cane Bagasse Ash Danupon Tonnayopas Department of Mining and Materials Engineering Faculty of Engineering Prince of Songkla University Introduction Performances
Refinement. R[F 2 >2(F 2 )] = wr(f 2 ) = S = reflections
![Refinement. R[F 2 >2(F 2 )] = wr(f 2 ) = S = reflections Refinement. R[F 2 >2(F 2 )] = wr(f 2 ) = S = reflections](/thumbs/94/120849244.jpg) Acta Crystallographica Section E Structure Reports Online ISSN 1600-5368 Zr 3 NiSb 7 : a new antimony-enriched ZrSb 2 derivative V. Romaka, a * A. Tkachuk b and L. Romaka a 11118 measured reflections 1722
Acta Crystallographica Section E Structure Reports Online ISSN 1600-5368 Zr 3 NiSb 7 : a new antimony-enriched ZrSb 2 derivative V. Romaka, a * A. Tkachuk b and L. Romaka a 11118 measured reflections 1722
SUPERIOR RESULTS WITH UNIQUE FEATURES
 Gemini VII 2390 SUPERIOR RESULTS WITH UNIQUE FEATURES Gemini VII 2390 Series Surface Area Analyzers Rapid and Precise Surface Area Analysis Surface area and pore volume are important physical properties
Gemini VII 2390 SUPERIOR RESULTS WITH UNIQUE FEATURES Gemini VII 2390 Series Surface Area Analyzers Rapid and Precise Surface Area Analysis Surface area and pore volume are important physical properties
PRELIMINARY TEST RESULTS ON A CLOSED-LOOP CONTAMINANT REMOVAL SYSTEM FOR PROCESSING OF METALLIC MELTS
 PRELIMINARY TEST RESULTS ON A CLOSED-LOOP CONTAMINANT REMOVAL SYSTEM FOR PROCESSING OF METALLIC MELTS Pramod K. Sharma, Gregory S. Hickey, and Kin F. Man Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute
PRELIMINARY TEST RESULTS ON A CLOSED-LOOP CONTAMINANT REMOVAL SYSTEM FOR PROCESSING OF METALLIC MELTS Pramod K. Sharma, Gregory S. Hickey, and Kin F. Man Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute
CHAPTER 3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
 CHAPTER 3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION The research included the development and verification of the earlier apparatus, and the collection and validation of moisture diffusion data under both isothermal and
CHAPTER 3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION The research included the development and verification of the earlier apparatus, and the collection and validation of moisture diffusion data under both isothermal and
Potential Solutions for Mercury Control in the Cement Industry Portland Cement Association Meeting
 Potential Solutions for Mercury Control in the Cement Industry Portland Cement Association Meeting August 24, 2009 Agenda Albemarle Sorbent Technologies Quick Overview Mercury Sorbents Control Options
Potential Solutions for Mercury Control in the Cement Industry Portland Cement Association Meeting August 24, 2009 Agenda Albemarle Sorbent Technologies Quick Overview Mercury Sorbents Control Options
Flow behavior of wakes in a three-phase slurry bubble column with viscous liquid medium
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 28(3), 974-979 (2011) DOI: 10.1007/s11814-010-0403-4 INVITED REVIEW PAPER Flow behavior of wakes in a three-phase slurry bubble column with viscous liquid medium Dae Ho Lim*, Ji Hwa
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 28(3), 974-979 (2011) DOI: 10.1007/s11814-010-0403-4 INVITED REVIEW PAPER Flow behavior of wakes in a three-phase slurry bubble column with viscous liquid medium Dae Ho Lim*, Ji Hwa
ENVIRONMENTAL AND POLLUTANTS GAS ANALYZERS
 XIX IMEKO World Congress Fundamental and Applied Metrology September 6, 9, Lisbon, Portugal ENVIRONMENTAL AND POLLUTANTS GAS ANALYZERS Ana Madeira, Florbela A. Dias and Eduarda Filipe 3 Instituto Português
XIX IMEKO World Congress Fundamental and Applied Metrology September 6, 9, Lisbon, Portugal ENVIRONMENTAL AND POLLUTANTS GAS ANALYZERS Ana Madeira, Florbela A. Dias and Eduarda Filipe 3 Instituto Português
Fabrication of Novel Lamellar Alternating Nitrogen-Doped
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Fabrication of Novel Lamellar Alternating Nitrogen-Doped Microporous Carbon
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Fabrication of Novel Lamellar Alternating Nitrogen-Doped Microporous Carbon
Barrier Development and Evaluation Methodology. D.S. Musgrave 1 1 Thermal Visions, Inc., Granville, USA
 Barrier Development and Evaluation Methodology D.S. Musgrave 1 1 Thermal Visions, Inc., Granville, USA 1. Introduction: Vacuum insulation is now a rapidly expanding market and technical advances are being
Barrier Development and Evaluation Methodology D.S. Musgrave 1 1 Thermal Visions, Inc., Granville, USA 1. Introduction: Vacuum insulation is now a rapidly expanding market and technical advances are being
Supporting Information for: Screen-Printed Graphite Electrodes as Low-Cost Devices for Oxygen Gas Detection in Room- Temperature Ionic Liquids
 Supporting Information for: Screen-Printed Graphite Electrodes as Low-Cost Devices for Oxygen Gas Detection in Room- Temperature Ionic Liquids Junqiao Lee 1, Ghulam Hussain 1, Craig E. Banks 2 and Debbie
Supporting Information for: Screen-Printed Graphite Electrodes as Low-Cost Devices for Oxygen Gas Detection in Room- Temperature Ionic Liquids Junqiao Lee 1, Ghulam Hussain 1, Craig E. Banks 2 and Debbie
Separation of N 2 /SF 6 binary mixtures using polyethersulfone (PESf) hollow fiber membrane
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 9(8), 1081-1085 (01) DOI: 10.1007/s11814-011-094-z INVITED REVIEW PAPER Separation of binary mixtures using polyethersulfone (PESf) hollow fiber membrane Dae-Hoon Kim*, Yong-Hae Ko**,
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 9(8), 1081-1085 (01) DOI: 10.1007/s11814-011-094-z INVITED REVIEW PAPER Separation of binary mixtures using polyethersulfone (PESf) hollow fiber membrane Dae-Hoon Kim*, Yong-Hae Ko**,
Air bubble movement over and under hydrophobic surfaces in water
 Air bubble movement over and under hydrophobic surfaces in water Ali Kibar 1, Ridvan Ozbay 2, Mohammad Amin Sarshar 2, Yong Tae Kang 3, Chang-Hwan Choi 2, 3 1 Department of Mechanical and Material Technologies,
Air bubble movement over and under hydrophobic surfaces in water Ali Kibar 1, Ridvan Ozbay 2, Mohammad Amin Sarshar 2, Yong Tae Kang 3, Chang-Hwan Choi 2, 3 1 Department of Mechanical and Material Technologies,
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 Supplementary Information Mo modulation effect on the hydrogen binding
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 Supplementary Information Mo modulation effect on the hydrogen binding
Experimental Analysis of Inclined Narrow Plate-Fins Heat Sink under Natural Convection
 Experimental Analysis of Inclined Narrow Plate-Fins Heat Sink under Natural Convection A.A.WALUNJ 1, D.D.PALANDE 2 1,2 PG student, Mechanical Department, MCOERC, Nashik Abstract Steady state natural convection
Experimental Analysis of Inclined Narrow Plate-Fins Heat Sink under Natural Convection A.A.WALUNJ 1, D.D.PALANDE 2 1,2 PG student, Mechanical Department, MCOERC, Nashik Abstract Steady state natural convection
EFFECTS OF SIDEWALL OPENINGS ON THE WIND LOADS ON PIPE-FRAMED GREENHOUSES
 The Seventh Asia-Pacific Conference on Wind Engineering, November 8-12, 29, Taipei, Taiwan EFFECTS OF SIDEWALL OPENINGS ON THE WIND LOADS ON PIPE-FRAMED GREENHOUSES Yasushi Uematsu 1, Koichi Nakahara 2,
The Seventh Asia-Pacific Conference on Wind Engineering, November 8-12, 29, Taipei, Taiwan EFFECTS OF SIDEWALL OPENINGS ON THE WIND LOADS ON PIPE-FRAMED GREENHOUSES Yasushi Uematsu 1, Koichi Nakahara 2,
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Dual active nitrogen doped hierarchical porous hollow carbon nanospheres
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Dual active nitrogen doped hierarchical porous hollow carbon nanospheres
1 SE/P-02. Experimental and Analytical Studies on Thermal-Hydraulic Performance of a Vacuum Vessel Pressure Suppression System in ITER
 1 SE/P-2 Experimental and Analytical Studies on Thermal-Hydraulic Performance of a Vacuum Vessel Pressure Suppression System in ITER K. Takase 1), H. Akimoto 1) 1) Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute,
1 SE/P-2 Experimental and Analytical Studies on Thermal-Hydraulic Performance of a Vacuum Vessel Pressure Suppression System in ITER K. Takase 1), H. Akimoto 1) 1) Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute,
Automatic Permeability Testing: The Challenges and Solutions Author: Alyce Hartvigsen, PBI-Dansensor A/S, Ringsted, Denmark
 Automatic Permeability Testing: The Challenges and Solutions Author: Alyce Hartvigsen, PBI-Dansensor A/S, Ringsted, Denmark In recent years, numerous product developments and major changes in the distribution
Automatic Permeability Testing: The Challenges and Solutions Author: Alyce Hartvigsen, PBI-Dansensor A/S, Ringsted, Denmark In recent years, numerous product developments and major changes in the distribution
AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF TRANSCRITICAL CO 2 INJECTION
 Paper ID IDILASS8-3- ILASS8-A55 ILASS 28 Sep. 8-, 28, Como Lake, Italy AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF TRANSCRITICAL CO 2 INJECTION Paul Seebald and Paul E. Sojka Maurice J. Zucrow Laboratories, School of Mechanical
Paper ID IDILASS8-3- ILASS8-A55 ILASS 28 Sep. 8-, 28, Como Lake, Italy AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF TRANSCRITICAL CO 2 INJECTION Paul Seebald and Paul E. Sojka Maurice J. Zucrow Laboratories, School of Mechanical
Facile fabrication of well-defined polyaniline microtubes derived. from natural kapok fiber for supercapacitor with long-term.
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Facile fabrication of well-defined polyaniline microtubes derived from natural kapok fiber
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Facile fabrication of well-defined polyaniline microtubes derived from natural kapok fiber
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information Branched polyethylenimine grafted electrospun polyacrylonitrile
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information Branched polyethylenimine grafted electrospun polyacrylonitrile
Facile synthesis of N-rich carbon quantum dots by spontaneous. polymerization and incision of solvents as efficient bioimaging probes
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Facile synthesis of N-rich carbon quantum dots by spontaneous polymerization
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Facile synthesis of N-rich carbon quantum dots by spontaneous polymerization
The Preparation of Low Concentration Hydrogen Sulfide Standards Gulf Coast Conference September 12, 2002 Galveston, TX Paper 050,12:45 pm Moody F
 The Preparation of Low Concentration Hydrogen Sulfide Standards Gulf Coast Conference September 12, 2002 Galveston, TX Paper 050,12:45 pm Moody F Robert Benesch, Malik Haouchine, and Tracey Jacksier, Ph.D.
The Preparation of Low Concentration Hydrogen Sulfide Standards Gulf Coast Conference September 12, 2002 Galveston, TX Paper 050,12:45 pm Moody F Robert Benesch, Malik Haouchine, and Tracey Jacksier, Ph.D.
A Practice of Developing New Environment-friendly System by Composites
 A Practice of Developing New Environment-friendly System by Composites Yun-Hae Kim, Dong-Hun Yang, Young-Dae Jo, Seung-Jun An, Se-Ho Park, Sung-Won Yoon Department of Materials Engineering, Korea Maritime
A Practice of Developing New Environment-friendly System by Composites Yun-Hae Kim, Dong-Hun Yang, Young-Dae Jo, Seung-Jun An, Se-Ho Park, Sung-Won Yoon Department of Materials Engineering, Korea Maritime
Application Note 13: Electron Microscope Decontamination
 The Chlorine Dioxide People Providing you with gaseous chlorine dioxide solutions for your decontamination needs Application Note 13: Electron Microscope Decontamination M Uses: An electron microscope
The Chlorine Dioxide People Providing you with gaseous chlorine dioxide solutions for your decontamination needs Application Note 13: Electron Microscope Decontamination M Uses: An electron microscope
CHE 4115 Chemical Processes Laboratory 2 Experiment 1. Batch Distillation
 CHE 4115 Chemical Processes Laboratory 2 Experiment 1 Batch Distillation BACKGROUND Distillation is one of the most commonly used unit operations in chemical engineering. In general, a distillation operation
CHE 4115 Chemical Processes Laboratory 2 Experiment 1 Batch Distillation BACKGROUND Distillation is one of the most commonly used unit operations in chemical engineering. In general, a distillation operation
GENERAL INFORMATION FOR TGS SENSORS. Technical Information on Usage of TGS Sensors for Toxic and Explosive Gas Leak Detectors
 Technical Information on Usage of TGS Sensors for Toxic and Explosive Gas Leak Detectors Figaro TGS sensors are a type of thick film metal oxide semiconductor which offer low cost, long life, and good
Technical Information on Usage of TGS Sensors for Toxic and Explosive Gas Leak Detectors Figaro TGS sensors are a type of thick film metal oxide semiconductor which offer low cost, long life, and good
Remote Plasma Cleaning from a TEM Sample Holder with an Evactron De-Contaminator ABSTRACT
 Remote Plasma Cleaning from a TEM Sample Holder with an Evactron De-Contaminator Christopher G. Morgan, David Varley, and Ronald Vane, XEI Scientific, Inc., 1755 E. Bayshore Rd., Suite 17, Redwood City,
Remote Plasma Cleaning from a TEM Sample Holder with an Evactron De-Contaminator Christopher G. Morgan, David Varley, and Ronald Vane, XEI Scientific, Inc., 1755 E. Bayshore Rd., Suite 17, Redwood City,
Experimental Study of an Air Lift Pump
 Engineering, Technology & Applied Science Research Vol. 7, No. 3, 217, 1676-168 1676 Experimental Study of an Air Lift Pump Fawzy Sh. Abou Taleb Mechanical Engineering Department Engineering College Northern
Engineering, Technology & Applied Science Research Vol. 7, No. 3, 217, 1676-168 1676 Experimental Study of an Air Lift Pump Fawzy Sh. Abou Taleb Mechanical Engineering Department Engineering College Northern
CHEMISTRY - CLUTCH CH.5 - GASES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: UNITS OF PRESSURE Pressure is defined as the force exerted per unit of surface area. Pressure = Force Area The SI unit for Pressure is the, which has the units of. The SI
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: UNITS OF PRESSURE Pressure is defined as the force exerted per unit of surface area. Pressure = Force Area The SI unit for Pressure is the, which has the units of. The SI
Accurate Measurement of Steam Flow Properties
 Accurate Measurement of Steam Flow Properties Kewen Li and Roland N. Horne Stanford Geothermal Program, Stanford University (Proceedings of 1999 GRC Annual Meeting on October 17-20, Reno, California, USA)
Accurate Measurement of Steam Flow Properties Kewen Li and Roland N. Horne Stanford Geothermal Program, Stanford University (Proceedings of 1999 GRC Annual Meeting on October 17-20, Reno, California, USA)
John Downs Cabot Specialty Fluids SPE European Formation Damage Conference
 John Downs Cabot Specialty Fluids Water vapour in natural gas Natural gas is saturated with water vapour at reservoir conditions Equilbrium water vapour content of gas: - Increases with temperature (and
John Downs Cabot Specialty Fluids Water vapour in natural gas Natural gas is saturated with water vapour at reservoir conditions Equilbrium water vapour content of gas: - Increases with temperature (and
Wear of the blade diamond tools in truing vitreous bond grinding wheels Part II. Truing and grinding forces and wear mechanism
 Wear 250 (2001) 593 603 Wear of the blade diamond tools in truing vitreous bond grinding wheels Part II. Truing and grinding forces and wear mechanism Albert J. Shih a,, William I. Clark a, Jeffrey L.
Wear 250 (2001) 593 603 Wear of the blade diamond tools in truing vitreous bond grinding wheels Part II. Truing and grinding forces and wear mechanism Albert J. Shih a,, William I. Clark a, Jeffrey L.
Quartz etch process to improve etch depth linearity and uniformity using Mask Etcher IV
 Quartz etch process to improve etch depth linearity and uniformity using Mask Etcher IV Sunil Srinivasan *, Jason Plumhoff, Russ Westerman, Dave Johnson, Chris Constantine Unaxis USA, Inc. 10050 16 th
Quartz etch process to improve etch depth linearity and uniformity using Mask Etcher IV Sunil Srinivasan *, Jason Plumhoff, Russ Westerman, Dave Johnson, Chris Constantine Unaxis USA, Inc. 10050 16 th
ETCHING OF COPPER COATED MYLAR TUBES WITH CF4 GAS. Karl M. Ecklund, Keith W. Hartman, Michael J. Hebert, Stanley G. Wojcicki
 SLAC-PUB-16219 ICFA INSTRUMENTATION B ULLETIN ETCHING OF COPPER COATED MYLAR TUBES WITH CF4 GAS Karl M. Ecklund, Keith W. Hartman, Michael J. Hebert, Stanley G. Wojcicki Department of Physics, Stanford
SLAC-PUB-16219 ICFA INSTRUMENTATION B ULLETIN ETCHING OF COPPER COATED MYLAR TUBES WITH CF4 GAS Karl M. Ecklund, Keith W. Hartman, Michael J. Hebert, Stanley G. Wojcicki Department of Physics, Stanford
Reflux Condensation with Various Non-Condensable Gases
 Proceedings of the 3 rd World Congress on Mechanical, Chemical, and Material Engineering (MCM'17) Rome, Italy June 8 10, 2017 Paper No. HTFF 168 ISSN: 2369-8136 DOI: 10.11159/htff17.168 Reflux Condensation
Proceedings of the 3 rd World Congress on Mechanical, Chemical, and Material Engineering (MCM'17) Rome, Italy June 8 10, 2017 Paper No. HTFF 168 ISSN: 2369-8136 DOI: 10.11159/htff17.168 Reflux Condensation
Laboratory Hardware. Custom Gas Chromatography Solutions WASSON - ECE INSTRUMENTATION. Engineered Solutions, Guaranteed Results.
 Laboratory Hardware Custom Gas Chromatography Solutions Engineered Solutions, Guaranteed Results. WASSON - ECE INSTRUMENTATION Laboratory Hardware Wasson-ECE Instrumentation offers hardware-only solutions
Laboratory Hardware Custom Gas Chromatography Solutions Engineered Solutions, Guaranteed Results. WASSON - ECE INSTRUMENTATION Laboratory Hardware Wasson-ECE Instrumentation offers hardware-only solutions
You should be able to: Describe Equipment Barometer Manometer. 5.1 Pressure Read and outline 5.1 Define Barometer
 A P CHEMISTRY - Unit 5: Gases Unit 5: Gases Gases are distinguished from other forms of matter, not only by their power of indefinite expansion so as to fill any vessel, however large, and by the great
A P CHEMISTRY - Unit 5: Gases Unit 5: Gases Gases are distinguished from other forms of matter, not only by their power of indefinite expansion so as to fill any vessel, however large, and by the great
LOW PRESSURE EFFUSION OF GASES revised by Igor Bolotin 03/05/12
 LOW PRESSURE EFFUSION OF GASES revised by Igor Bolotin 03/05/ This experiment will introduce you to the kinetic properties of low-pressure gases. You will make observations on the rates with which selected
LOW PRESSURE EFFUSION OF GASES revised by Igor Bolotin 03/05/ This experiment will introduce you to the kinetic properties of low-pressure gases. You will make observations on the rates with which selected
Chemistry Chapter 11 Test Review
 Chemistry Chapter 11 Test Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Pressure is the force per unit a. volume. c. length. b. surface area.
Chemistry Chapter 11 Test Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Pressure is the force per unit a. volume. c. length. b. surface area.
Evaluation of Hydropath Clearwell Technology On Carbonate Brine Scaling Using Tube Blocking Method
 Flow Assurance R-4-319 November 24 Evaluation of Hydropath Clearwell Technology On Carbonate Brine Scaling Using Tube Blocking Method Final Report Authors: S. Brown & J. Rohan Work By: J. Rohan Westport
Flow Assurance R-4-319 November 24 Evaluation of Hydropath Clearwell Technology On Carbonate Brine Scaling Using Tube Blocking Method Final Report Authors: S. Brown & J. Rohan Work By: J. Rohan Westport
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI)
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) FeP@C Nanoarray Vertically Grown on Graphene Nanosheets:
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) FeP@C Nanoarray Vertically Grown on Graphene Nanosheets:
Supplementary Information:
 Supplementary Information: UV-responsive nano-sponge for oil absorption and desorption Do Hyun Kim 1,2, Min Chan Jung 3, So-Hye Cho 2, Sang Hoon Kim 2, Ho-Young Kim 3, Heon Ju Lee 2, Kyu Hwan Oh 1, and
Supplementary Information: UV-responsive nano-sponge for oil absorption and desorption Do Hyun Kim 1,2, Min Chan Jung 3, So-Hye Cho 2, Sang Hoon Kim 2, Ho-Young Kim 3, Heon Ju Lee 2, Kyu Hwan Oh 1, and
Macro-scale Mathematical Model for Hydration and TEWL in intact Stratum Corneum
 Macro-scale Mathematical Model for Hydration and TEWL in intact Stratum Corneum Bob Imhof 1, Perry Xiao 1, 2 and Lori Ciortea 1 1 Biox Systems Ltd, London, UK 2 South Bank University, London, UK 1 The
Macro-scale Mathematical Model for Hydration and TEWL in intact Stratum Corneum Bob Imhof 1, Perry Xiao 1, 2 and Lori Ciortea 1 1 Biox Systems Ltd, London, UK 2 South Bank University, London, UK 1 The
THERMODYNAMICS OF A GAS PHASE REACTION: DISSOCIATION OF N 2 O 4
 THERMODYNAMICS OF A GAS PHASE REACTION: DISSOCIATION OF N 2 O 4 OBJECTIVES 1. To measure the equilibrium constant, enthalpy, entropy, and Gibbs free energy change of the reaction N2O4(g) = 2 NO2(g). 2.
THERMODYNAMICS OF A GAS PHASE REACTION: DISSOCIATION OF N 2 O 4 OBJECTIVES 1. To measure the equilibrium constant, enthalpy, entropy, and Gibbs free energy change of the reaction N2O4(g) = 2 NO2(g). 2.
