Stomach 9. Stomach 9. (Carotid Sinus)
|
|
|
- Prudence Hudson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Death Touch Secrets In the following pages you will learn some of the most devastating striking points known to man. As well as learning the Dim Mak effects of striking these points, we will also cover the purely physical medical implications and damage caused by striking these points. Please respect this knowledge and use it only when absolutely necessary when your life, or the life of another is in danger and no other course of action will remove that danger. The information contained on the following pages is for educational purposes only in the pursuit of perfection in the Martial Arts. The Writer does not advocate the use of any of this information except in a life threatening situation.
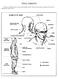
2 Contents 1. Stomach 9 2. Throat 3. Stomach 5 4. Governor Vessel Conceptor Vessel Eyes 7. Mind Point 8. Gallbladder 3 9. Conceptor Vessel Neurological Shutdown Points 11. Bladder Small Intestine Triple Heater Small Intestine Liver Conceptor Vessel Gallbladder Spleen Lung Pericardium Ears 22. Nasal Bone 23. Spleen
3 Stomach 9 Stomach 9 (Carotid Sinus) St 9 causes death instantly, is very easy to get at, and offers extremely easy methods of access, so this point is probably the highest on the list of dangerous points.. This point will work every time by causing either KO or death as a result of heart stoppage. All you have to do is raise the knife edge of one hand to access it. You can use many different weapons to gain access to this point. The elbow can be used with devastating results. It can also be accessed during a chokeout or a sleeper hold. It can be accessed with a punch or a strike with the tips of the fingers. Or, to access the side of his neck use a reverse knife-edge strike or thrust the back of your palm into the point.
4 Medical Implications of a strike to front or side of throat: Throat The results from a well-focused blow to the front or side of the throat are a combination of multiple effects and results. The following is a listing of each separate possible effect and result: Effects Contusion of the internal Jugular Vein Contusion of the internal Carotid Artery Contusion of the Vertebratal Vein Contusion of the Hypoglassal Nerve Contusion of the Vagus Nerve Contusion of the Phrenic Nerve Contusion of the Laryngenial Nerve Hematoma in Carotid Sheath Fracture of the Spinous Process Fracture of the Thyroid Cartilage Fracture of the Cricoid Cartilage Possible injury to Brachial Plexus 1. The internal jugular vein pulsates during respiration, distends during expiration. and collapses to a ribbon-like structure during inspiration. If the blow is struck on expiration, the vein would be full of blood and hard. Rupturing the internal jugular vein from striking it against the hard surface of the cervical vertebra would result in a quick death due to a massive haemorrhage (haematoma).
5 Throat (Continued) 2. Severe contusion of the carotid vein may result in thrombosis, (blood clot in the vessel) due to the vessel wall spasm, which produces a restriction in biood flow. This may eventually end in cerebral thrombosis (blood clot in the vessels of the brain) and death. 3. Laceration or contusion of the VERTEBRAL ARTERY is only possible When the blow is heavy enough to chip or fracture the spinous vertebral processes that the artery runs through. Results are the same as the previous two variations in vessel damage. 4. The two most important functions of the VAGUS NERVE we are concerned with here are that of heart contraction and lung constriction. Since there are two branches of the vagus nerve (one on each side of the neck) injury to one may not by itself be completely fatal because of the partial overiapping of the two nerve branches once they reach their destination. However, damage to one side of the nerve could cause spasms of the lungs and heart, ultimately ending in shortness of breath, irregular heart palpitations, and death.
6 Throat (Continued) V. The PHRENIC NERVE runs from the fourth cervical vertebra, vertically down the neck into the thorax (chest) where it finally merges into the diaphragm. The main function of the phrenic nerve is to supply the diaphragm with necessary responses for breathing. When it is injured, the same feeling that one gets when the "wind" has been knocked out will exist until normal function resumes or death occurs. VI. The LARYNGEAL NERVES (nerves of the vocal cords, etc.) are a branch of the vagus nerve. They control the main functions of the larynx, which are to open and close the vocal cords and epiglottis so that no foreign objects are permitted to pass through the trachea. When a foreign object (food, teeth, blood, etc.) agitates the nerve surrounding the larynx or inside of the throat, the vocal cords close and the epiglottis covers the opening of the wind pipe to prevent anything from being sucked into the pipe. When this is done no air can go in or out of the lungs until the nerve relaxes and opens the wind pipe for normal breathing. If the nerve does not relax, death by suffocation will follow. VII. The HYPOGLOSSAL NERVE is the main nerve of the tongue. If it is damaged, loss of control of the tongue will be inevitable with suffocation - and death if it is swallowed. VIII. A HAEMATOMA IN THE SHEATH that encompasses the internal jugular, carotid vein and vagus nerve in the neck is the result of blood leakage from a torn blood vessel. If the tear does not seal itself immediately, death by strangulation will soon follow. The haematoma will grow larger with each pulsation of the heart and eventually start pressing against the trachea until it has com-pressed it enough to stimulate the laryngeal nerves to close it off. The out-side appearance will be that of a huge swelling on the side of the neck IX. A chipped or fractured SPINOUS PROCESS of the vertebra is one of the most dangerous occurences, not because of the fracture but because of what lies between it and the outside surface of the skin, which in this case is everything previously mentioned. Also there would be the possibility of spinal cord shock (injury to the spinal cord without any known disruption of the spinal cord fibers-whiplash)
7 Throat (Continued) X. Fracture of the THYROID OR CRICOID CARTILAGE is the result of a frontal blow to the throat. The most important thing to remember here is that surrounding the cartilages are many nerve branches of the larynx (laryngenial nerves). Of course, stimulation of these nerves by a fracture of the cartilage will activate the vocal cords and epiglottis to close off the air supply to the lungs, resulting in a slow death by suffocation or at least Unconsciousness from lack of air. Because of the close proximity of all the above mentioned effects and results, it is easy to see how two or more of the effects would exist and cause death to or at least total disability of the attacker.
8 Stomach 5 Stomach 5 This is easy to get to and works like a charm to knock out your attacker. You can either use a punch to the side of the jaw or a palm strike. I prefer the palm strike since you do not have to be that accurate. It works best if someone is coming at you with great force, perhaps with two hands, to grab you. You use the force of his own arms to bounce your palms off his arms and into the side of his jaw. The harder they attack, the harder they are struck. You do not have to use that much power to cause a KO here. Medical Implications; FRACTURE OR DISLOCATION OF THE MANDIBLE (lower jaw) FRACTURE OR DISLOCATION OF THE ZYGOMA (cheekbone) CONTROL OF THE TONGUE WOULD BE LOST possibly leading to asphyxiation
9 Governor Vessel 26 The power of this point, just under the nose, can be demonstrated by having a strong person lean forward while in a strong stance. Try to push his waist to upright using his forehead, and you will find that it is almost impossible. Now, place just one finger laterally across Gv 26 and press upward. He is upright in no time at all, and you have not used that much pressure on the point. In a realistic situation, however, we attack this point with the palm heel or a one-knuckle punch. Governor Vessel 26 Again, a smaller person can bide his or her time until the shot is available, then thrust the palm heel up under the nose with devastating results. This strike will work even using a stiff type of attack with only triceps power, but by using the whole body, you will kill the attacker with this point Medical Implications: A SPLIT LIP, CHIPPED OR MISSING TEETH AND EYEWATERING PAIN are the minimal possible results. The eye watering pain is due to the close proximity of the nerves to the surface of the skin. A BURSTING FRACTURE OF THE MAXILLA (upper jaw) is the outcome because of the spherical nature of the skull. The skull will compress to its limit and then burst, producing a bursting fracture. The fracture is usually on one side or the other, distal to the point of impact, but may be a fracture at the impact site also. The simple task of eating will become a very painful one. UNCONSCIOUSNESS AND/OR CONCUSSION frequently follow such a blow. Unconsciousness may be a result of a concussion or more than likely may be caused by the fast exit of blood from the brain into the internal organs (due to shock). RESPIRATORY PARALYSIS AND DEATH may develop from broken or dislocated teeth and blood caught in or near the wind pipe (trachea) may cause a spasm of the vocal cords with closing off of the air supply.
10 Conceptor Vessel 22 Conceptor Vessel 22 This point will stop an attacker instantly. At the very least he will drop to the ground in a coughing fit, gasping for air, and at most he will die. The point can be accessed using a palm heel, the tips of the fingers, an elbow, or a one-knuckle punch. The attack should have intent behind it, simply strike it using brute force.
11 Eyes Eyes There are points in the eyes, of course, but what does it matter-the eyes are extremely sensitive to even a light scrape across the eyeball. In fact, the best type of attack to the eye is a scrape, which will produce temporary or permanent blindness and extreme pain, causing the recipient to drop Medical Implications: The possible results are so many in this area, that we will concern our-selves with only the more obvious trauma. RUPTURE OF THE EYE BULB WITH PROTRUSION OF THE 'WATERY AND GELATINOUS LIKE CONTENTS will result when the bulb is no longer able to withstand the direct pressure piercing it. TEMPORARY TO PERMANENT BLINDNESS (Probably permanent) is the common result. Tremendous shocking pain will prevail in one or both eyes. An uncontrollable watering of the eyes will always be functional whenever a foreign object enters or touches the eye, which naturally produces temporary blurred vision in the uninjured eye. A TORN EYELID (usually the top one) is the effect of a sharp fingernail piercing an eyelid that has blinked at the last instant before the nail has struck. Infection following trauma of this kind is the usual aftermath because of small debris (dirt, germs, hair, etc.) that enters the eye with the fingernail. Sometimes infection can be a more serious complication than the blow itself.
12 Mind Point The Mind Point This is one of the "extra points." It is near the back of the jaw, just forward of the earlobe. It is struck at an angle of about 45 degrees to the front of the body toward the backbone. This is quite an amazing knockout point, requiring only medium power to cause KO. It is usually struck using a cross fist
13 Gallbladder 3 Gallbladder 3 (Temple) The temple is traditionally a well-known point to strike to, and Gb 3 is the temple. It can be struck all by itself to cause death or KO. The point is struck straight in using a oneknuckle punch. Medical Implications I. A FRACTURE IN THE TEMPORAL REGION OF THE SKULL WITH MIDDLE MENINGEAL HEMORRHAGE (Meningeal Artery) commonly occur together; however, one may prevail without the other. The meningeal artery supplies the skull and dura (membrane that covers the brain) with blood. The artery follows its groove in the skull case and is easily pinched or severed if disruption of this groove occurs from a skull fracture. II. HEADACHE, NAUSEA, VOMITING, COMA AND DEATH may ensue immediately or may be the delayed result, as long as two weeks later. If the artery were severed there would be immediate compression of the brain due to the massive hemorrhage there, indicated by a gradual deepen-ing stupor. If diagnosis is not made soon, the patient will go into a coma and finally death will result. If the artery is only pinched with slow blood leakage, a small extradural hematoma will produce delayed results, similar to a complete severence of the meningeal artery. Rupture of the meningeal artery may be prevailent without an accompanying skull fracture due to the severe jarring action displacing the vein from its groove. III. RUPTURE OF THE TYMPANIC MEMBRANE (EARDRUM) may occur if the fracture line runs through the internal ear section of the skull. This will be evident from bleeding of the ear, nose, and mouth, and also from the vomiting of blood that has been swallowed and an obvious impairment of hearing. IV. A FRACTURE OF THE ZYGOMATIC PROCESS will be the out-come if the blow is one inch lower than the temporal bone (temple). Opening and closing of the mouth will be noticeably painful.
14 Conceptor Vessel 23 Conceptor Vessel 23 (Throat) This point will stop any attacker when struck up and into the neck at an angle of 45 degrees. You can use a knife-edge strike or the tips of the fingers with equally devastating results.
15 Neurological Shutdown Points Neurological Shutdown Points Neurological shutdown points are not really points, but rather areas of the face and neck comprising several points. A stinging slap to the side of the jaw that includes part of the ear and neck using a palm strike will cause KO instantly. The tongue of the recipient usually turns blue and hangs out. Immediate resuscitation is required here. Should the attacker come at you with both hands, both of your palms slam the inside of his both arms outward, then your right one (or left) rebounds to strike (slap) him on the side ofthe face. The attacker drops immediately.
16 Bladder 10 Bladder 10 (Back of neck) This point is the old rabbit chop and works like a charm for taking someone down to his knees or flat out on the ground, depending upon how hard you hit him. It can be accessed while in a grappling type of situation with one hand around the back of the opponent's neck, using the reverse knife-edge strike to the point. The result is instant.
17 Bladder 10 (Continued) Medical Implications: Multiple FRACTURE OF THE CERVICAL VERTEBRA with bieeding in a pinched spinal cord will cause partial to complete paralysis encompassing any or all portions of the body and limbs below the point of impact. Respiratory paralysis may lie due to a compressed phrenic nerve. Death may be immediate or occur later. Inability to move the head from side to side, dizziness and headache are the minimal possibilities from a medium-strength blow. A CONCUSSION may exist due to the transmission of shock waves through the brain stem into the brain. Shock (caused by too much stress On the nervous system) may by itself cause death. This is sometimes referred m as a violent interruption of the body's homostatic balance.
18 Small Intestine 17 Small Intestine 17 (Just under hinge of jaw) Just under the hinge of the jaw, this point is another wonderful KO point. The knife edge or reverse knife edge is used here. It can be accessed from a choker hold or whenever you can get at the point, which is usually when you have closed with the opponent. A sharp upward strike into the neck and chin will cause a KO, with the recipient not even knowing it happened
19 Triple Heater 23 Triple Heater 23 The strike is done downward over the bone at the comer of the eye, usually using a palm heel strike.
20 Small Intestine 16 Small Intestine 16 This is a point that is easily accessed and very dangerous. It can be got at in much the same way that St 9 is accessed, only the direction is straight in to the side of the neck.
21 Liver 14 Liver 14 As you move down the body, this is one of the more deadly points. Located just under the pectoral crease by about 1 inch, midline down from the nipple, it is easily accessed from the front of the body, and the results are devastating. The immediate effect is collapsed lungs, resulting in KO and, eventually, death
22 Conceptor Vessel 14 (Solar Plexus) One of the most dangerous points that stops the heart, this point, located where the solar plexus is situated, is struck straight in with a slightly upward flick Conceptor Vessel 14
23 Conceptor Vessel 14 (Solar Plexus) Medical Implications: As indicated, different angles of the kick or strike will produce varied results. If the kick is directed toward the right side of the opponent's body, the liver and gallbladder will be damaged. If it is in the center of the solar plexus, the duodenum and pancreas will be thrust against the front of the lumbar spine. The abdominal aorta (huge vein) follows the lumbar spine vertically and is very snug against the front side of the vertebra. If the heel kick was strong enough to injure the vein, shock (extreme loss of blood) and death would follow almost immediately. The stomach (and some reports claim that the spleen) will be involved when the blow is to the left side of the solar plexus. The level, angle and strength of the kick will determine how many of these organs will be damaged.
24 Conceptor Vessel 14 (Solar Plexus) I. A DEEP FISSURE IN THE LIVER may very well be fatal. Peritonitis in the name given to free floating blood and / or bile in the peritoneal cavity (body cavity). Hiccupping from blood or bile irritating the diaphragm and an increasing tenderness and pain in the abdomen will continue until surgery of the abdomen corrects the symptoms which may very easily evolve into death. II. THE GALL BLADDER WOULD BE TORN with gastric acids and digestive juices being spilled into the body cavity. (Prior to a meal, the gall bladder fills with proper digestive juices for digestion of the meal and stores the juices until food is induced. The gall bladder would burst rather easily if enough pressure was exerted upon it during the predigestion period.) The juices would immediately start to digest the internal organs they came in contact with, and only surgery would prevent death.
25 Conceptor Vessel 14 (Solar Plexus) III. RUPTURE OF THE STOMACH with the spilling of its contents and blood into the body cavity would again result in peritonitis. Days of intestinal disturbances, gastric disorders and vomiting, shock, and eventual death will occur. IV. A compression injury of the DUODENUM against the lumbar spine will progress the same as III above.
26 Conceptor Vessel 14 (Solar Plexus) V. AN INJURED PANCREAS may result if the kick were well timed (when the opponent was inhaling) and the solar plexus were relaxed and easily penetrated. The pancreas might also be compressed, along with the duodenum, against the lumbar spine producing a split surface of the organ. Respiratory paralysis -spasm of the abdominal and intercostal rib muscles, which inhibits normal movements of the diaphragm in breathing, unconsciousness, shock, and death are the likely results. VI. PARTIAL COLLAPSE OF THE LUNG, due to a minute plural tear from the percussive shock (jarring) present in the chest cavity at the moment of impact, will result in shallow breathing and great pain during respiration. VII. SHOCK is a term used in internal injuries to describe the extreme loss of blood and bile into the body cavity. Shock maybe immediately fatal or be latent, (48 hours later) until abdominal splinting occurs. Abdominal splinting means that when the cavity fills with blood, It will he evident be-cause of a growing tenderness and increasing rigidity of the abdomen, with the elevation of body temperature and possible vomiting of blood from rupture of the stomach or duodenum. Death is the common result of shock, because usually by the time the injured person arrives at the hospital he has lapsed into unconsciousness from lack of blood and cannot tell the doctor his symptoms.
27 Gallbladder 24 Gallbladder 24 Also a dangerous point that will cause KO or death, this point is located 1 inch below Liv 14, midline down from the nipple, about 2 inches below the pectoral crease. It is struck straight in.
28 Spleen 17 Spleen 17 Located to the outer side of the pectoral in a lateral line to the nipple (not quite under the arm), it is struck from out to in, laterally across the body, usually using an elbow.
29 Medical Implications I. A green stick fracture of the ribs will cause only pain in breathing, but a complete break in the rib, with protruding ends, will tear the lung's pleura (membrane sac covering the lungs) and puncture the lung, resulting in a COLLAPSED LUNG. Blood in the lung cavity (hemothorax) will be present until it is removed. II. Spleen 17 (Continued) Shortness of breath and muscle spasms of the chest and rib cage, with severe pain while breathing will predominate. If the lung collapses all the way, death is sure to follow. A lung may be collapsed from the violent jarring produced by the kick or strike, without the presence of a fractured rib. When the pleura tear is very small, it will usually seal itself soon without any great after effects. The great danger involved with a completely collapsed lung (besides air starvation) is an uncontrollable spasm of the heart, which is caused by the pressure difference when the lung collapses. The heart is held in place (partially) by the lungs on either side and the heart's suspensory ligaments. When there is no pressure on one side to help hold the heart in place, the lung on the other side will pull the heart toward it (heart shift), re-sulting in a severe muscle spasm of the heart and usually either a quick or lingering death. Intercostal muscle spasms (muscles between the ribs) with loss of breath would be the minimal damage. A complication of this blow would be a puncture of the diaphragm.
30 Lung 5 Lung 5 This is one of the best set-up and qi drainage points. Located at the elbow crease on the outside of the inner arm, it is easy to get at using the back of the palm slicing downward. It will cause considerable damage to the arm and central nervous system, as well as to the qi system of the body. This strike will cause KO.
31 PERICARDIUM 6 (PC 6) Pericardium 6 (Neigwan) Pc 6, or neigwan, is the best utility set-up point, causing both qi drainage and nausea. You can virtually use this point as a set-up to any other point strike. Located midline on the inside of your forearm, about one hand's width back from the wrist crease, it can be accessed via a strike or a wrist lock.
32 Ears Medical Implications of a strike to the ears with Cupped hands: 1. UNCONSCIOUSNESS OR A CONCUSSION will occur from any well-focused blow to the head. This is especially true when the head is not al-lowed to roll with the blow. The palms striking on both sides of the head simultaneously will act as a stabilizing device to the head and therefore doubles the percussive shock and pain. Whenever there is the possibility of a concussion there is the possibility of death. II. RUPTURE OF THE TYMPANIC MEMBRANE (Eardrum) will result from the large volume of air being forced through the external audi-tory canal, through the thin-skinned membrane of the eardrum, and finally through the eustachian tube which opens into the back of the throat. The outside bf the ear will be swollen because of the broken blood vessels and small capillaries there. Capillaries inside the auditory can'al will be ruptured and swell because of the expanding volume of air that has rushed through the narrow passageway leading to the eardrum. Loss of hearing would be from partial to complete, depending upon the total degree of injury to the internal ear. The eustachian tube is much narrower than the auditory canal (the size of a pencil lead), and therefore will suffer greater expanding pressures as the air passes through it. The eustachian tube will undoubtedly swell completely shut. There will be an extreme amount of pain from the double palm strike to the ears. If the blows are not pulled, shock will be a prominent result. III. POSSIBLE FRACTURE AND/OR DISLQCATION OF THE JAW HINGE may occur if the blow is slightly lower. IV. CONTUSION OF THE FACIAL NERVE AND,NEIN, with possible paralysis of one side of the face, are experienced if the blow abrades them against the edge of the jawbone. This paralysis would probably be temporary unless a sharp section of the bone' fracture punctured or severed the facial nerve. Likewise, if the vein was punctured there would be a small haematoma (walnut-size lump) and eventually one side of the face would turn black and blue.
33 Medical Implications Nasal Bone 1. A COMPOUND FRACTURE AND/OR DISLOCATION OF THE NASAL BONE AND SEPTUM (dividing partition of the nostrils) are a consequence of all four knuckles raking across the upper part of the nose. Needless to say, there will be massive hemorrhage because of the many blood vessels in this area. Shock and pain may render your opponent un-conscious. Temporary blindness may be a result of the extreme watering of the eyes because of the stimulated pain receptors in the nasal region. We must realize that many times the blow may not be a death-dealing one, but the accidental consequences may end in death. In this case we are talking about unconsciousness which invariably occurs before the opponent hits the ground. The effect is a grave one because the head is relaxed when it strikes the ground and may end in a serious concussion or skull fracture if the surface is fairly solid. Death may also ensue be-cause of the huge amount of blood clogging the trachea (wind pipe) during unconsciousness. II. FRACTURE INTO THE ORBITAL SOCKET ( eye socket) with possible cerebral involvement may be a complication of the blow. If the fracture line has continued into the brain casing (cribiform plate of the ethmoid bone), a slight tear in the dura will release small amounts of cerebro-spinal fluid. The fluid will travel through the sinuses and finally exit through the nostrils or be swallowed. Cerebrospinal fluid (clear fluid that circulates in the closed cavity of the brain and spinal cord) is sometimes mistaken for a normal secretion for quite some time, until severe headaches motivate the individual to seek medical advice. When bone (or for that matter any part of the body) is struck, the force of the blow is transferred from the weapon to the target in the form of oscillating vibrations. In the case of bone the oscillations follow the path of least resitence. The oscillations are further apart in wide or thick borre and closer together in thin or narrow bone. As oscillations narrow the vibration becomes more violent and causes a fracture through the weakest portion of bone. The olefactory nerves (nerves of smell) are spread throughout the roof of the nasal section (cribiform plate of the ethmoid bone) and may become torn or severed from the fractured bone. A dulling of the sense of smell will occur.
34 Medical Implications: Spleen I. The spleen is located on the left side of the rib cage right beside the left kidney, under the diaphragm and parallel to the ninth, tenth and eleventh ribs. II. The function of the spleen that we are chiefly concerned with here is its ability to act as a reservoir for the storage of blood and to return it to normal circulation in harmony with the body's needs. During shock or fright, blood drains into the spleen and other internal organs. Under normal and stress situations the spleen is partially or nearly totally full of blood (according to the environment and emotions). (The spleen is also one of the main organs that fights against bodily infection, a very important function.) III. A fracture of the ribs with lacerations of the diaphragm and spleen is the beginning of a slow but sure death. Shock due to the loss of blood with weakness, nausea, severe pain and ten-derness from the point of impact to the left side of the abdomen are the first symptoms; unconsciousness, coma, and death usually follow within forty-eight hours. Spasm of the diaphragm will also be present. Abdominal splinting is the hardening of the abdomen to a board-like rigidity due to the accumulation of a large amount of blood between the muscles and the abdominal cavity. Abdominal splinting will be a symptom in nearly all abdominal injuries. Pain in the abdomen and nausea occurs from the irritation of blood and bile in the abdominal cavity. III. Even if the ribs are not fractured, a delayed rupture of the spleen may occur any time from within twenty-four hours to two years. A small fissure or bruise, caused at the time of injury, can eventually increase in size and ultimately result in a massive hemorrhage with death the ultimate end. A delayed rupture of the spleen is almost always fatal because it is unexpected. A blow from the front or side can result in rupture of the spleen, especially if the opponent is inhaling when contact is made. During inhalation the muscles of the trunk are relaxed and very soft. This is evident by the easy penetration of a blow on inhalation.
Effective Strikes are KING!
 VITAL TARGETS The body is divided into three sections: high, middle, and low. Each section contains vital targets. The effects of striking these targets follow: Effective Strikes are KING! Effective striking
VITAL TARGETS The body is divided into three sections: high, middle, and low. Each section contains vital targets. The effects of striking these targets follow: Effective Strikes are KING! Effective striking
B-immobility from structural or organic damage
 DRAGON'S TOUCH weaknesses of the human anatomy by: Hei Long This volume (and the ones to follow) concentrates on the 43 major pressure points of the body. Of course, there are quite a few more, but these
DRAGON'S TOUCH weaknesses of the human anatomy by: Hei Long This volume (and the ones to follow) concentrates on the 43 major pressure points of the body. Of course, there are quite a few more, but these
Review. 1. Which of the following statements regarding the Adam s apple is FALSE?
 Chapter 25 Review 1. Which of the following statements regarding the Adam s apple is FALSE? A. It is inferior to the cricoid cartilage. B. It is formed by the thyroid cartilage. C. It is the uppermost
Chapter 25 Review 1. Which of the following statements regarding the Adam s apple is FALSE? A. It is inferior to the cricoid cartilage. B. It is formed by the thyroid cartilage. C. It is the uppermost
8 Pieces of Brocade. 1. Two hands lifting the sky with finger interlocked to harmonize the triple warmers.
 8 Pieces of Brocade Preparing/standing form: Move left feet one step to the left side, feet with shoulder width, relax and bend knee slightly, stand strict, tongue touch the upper jaw, close lower jaw,
8 Pieces of Brocade Preparing/standing form: Move left feet one step to the left side, feet with shoulder width, relax and bend knee slightly, stand strict, tongue touch the upper jaw, close lower jaw,
SCRIPT FOR FULL MINDFULNESS PRACTICE BODY SCAN 40 MINUTES
 SCRIPT FOR FULL MINDFULNESS PRACTICE BODY SCAN 40 MINUTES Before we begin, take time to get yourself comfortable. To do the body scan, you can either sit in a chair, or, if you prefer, lie on your back
SCRIPT FOR FULL MINDFULNESS PRACTICE BODY SCAN 40 MINUTES Before we begin, take time to get yourself comfortable. To do the body scan, you can either sit in a chair, or, if you prefer, lie on your back
Paul Viscogliosi MD WTF anti-doping & Medical Committee Chair WTF Vice-Chairman Technical Committee
 Paul Viscogliosi MD WTF anti-doping & Medical Committee Chair WTF Vice-Chairman Technical Committee Management of injuries during the fight 1. The central Referee has to manage two things in case of injury:
Paul Viscogliosi MD WTF anti-doping & Medical Committee Chair WTF Vice-Chairman Technical Committee Management of injuries during the fight 1. The central Referee has to manage two things in case of injury:
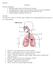
Human Biology Respiratory System
 Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
FIRST AID. Study Topics. At a minimum, the following topics are to be studied for the first aid exam.
 FIRST AID Study Topics At a minimum, the following topics are to be studied for the first aid exam. TOPIC Avoid getting air in stomach during rescue breathing Burns Kinds of Burns & Care Calling for Help
FIRST AID Study Topics At a minimum, the following topics are to be studied for the first aid exam. TOPIC Avoid getting air in stomach during rescue breathing Burns Kinds of Burns & Care Calling for Help
The Human Body. Everyone Needs Healthy Systems. Blood Vessels
 The Human Body Everyone Needs Healthy Systems There are several systems that make up the human body. Although their functions differ, they all work together to keep your body running smoothly. Some of
The Human Body Everyone Needs Healthy Systems There are several systems that make up the human body. Although their functions differ, they all work together to keep your body running smoothly. Some of
Structures of the Respiratory System include:
 Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
First Aid - immediate care that is given to the victim of an injury or illness until experts can take over - Oftentimes, it s the difference between
 First Aid First Aid - immediate care that is given to the victim of an injury or illness until experts can take over - Oftentimes, it s the difference between life and death or recovery vs permanent disability
First Aid First Aid - immediate care that is given to the victim of an injury or illness until experts can take over - Oftentimes, it s the difference between life and death or recovery vs permanent disability
LESSON 2: THE FIRST LIFE- SAVING STEPS
 LESSON 2: THE FIRST LIFE- SAVING STEPS automatic external defibrillators (AEDs) cardiac arrest heart attack heimlich maneuver rescue breathing stroke INTRODUCTION In emergency situations, the people involved
LESSON 2: THE FIRST LIFE- SAVING STEPS automatic external defibrillators (AEDs) cardiac arrest heart attack heimlich maneuver rescue breathing stroke INTRODUCTION In emergency situations, the people involved
Accidents happen anywhere
 Bulletin 2325 Maine Farm Safety Program by Dawna L. Cyr, farm safety project assistant, and Steven B. Johnson, Ph.D., Extension crops specialist Basic First Aid Accidents happen anywhere and anytime. The
Bulletin 2325 Maine Farm Safety Program by Dawna L. Cyr, farm safety project assistant, and Steven B. Johnson, Ph.D., Extension crops specialist Basic First Aid Accidents happen anywhere and anytime. The
Wilderness First Responder Course Peak 7 Adventures
 Wilderness First Responder Course Peak 7 Adventures The practice of the healing arts (including Wilderness First Responder) does not lend itself well to a cook book approach. There are endless variations
Wilderness First Responder Course Peak 7 Adventures The practice of the healing arts (including Wilderness First Responder) does not lend itself well to a cook book approach. There are endless variations
TARGETS: THE ARMS YIN METAL
 TARGETS: THE ARMS The targets of the arms are vital to developing an understanding of karate. We must consider that our techniques are usually a reaction to an opponent s attack, and an opponent s arms
TARGETS: THE ARMS The targets of the arms are vital to developing an understanding of karate. We must consider that our techniques are usually a reaction to an opponent s attack, and an opponent s arms
Respiration. The ins and outs
 Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
2/28/18. Respiratory System. 1 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Introduction. Anatomy. Physiology. Respiratory System
 Introduction Respiratory System Chapter 28 Respiration: We inhale air, extract oxygen from it, exhale air Cardiovascular and respiratory systems work together Failure of either system: - Disruption of
Introduction Respiratory System Chapter 28 Respiration: We inhale air, extract oxygen from it, exhale air Cardiovascular and respiratory systems work together Failure of either system: - Disruption of
CONTROL OF EXTERNAL BLEEDING
 CONTROL OF EXTERNAL BLEEDING Responsibility Never hesitate to call 911 Life Safety is most important! It is the responsibility of every individual to learn to recognize the warning signs of a medical emergency.
CONTROL OF EXTERNAL BLEEDING Responsibility Never hesitate to call 911 Life Safety is most important! It is the responsibility of every individual to learn to recognize the warning signs of a medical emergency.
FUNDAMENTAL CRITERIA FOR FIRST AID INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 1 FUNDAMENTAL CRITERIA FOR FIRST AID INTRODUCTION Soldiers may have to depend upon their first aid knowledge and skills to save themselves or other soldiers. They may be able to save a life, prevent
CHAPTER 1 FUNDAMENTAL CRITERIA FOR FIRST AID INTRODUCTION Soldiers may have to depend upon their first aid knowledge and skills to save themselves or other soldiers. They may be able to save a life, prevent
8 Pieces of Brocade. 1. Two hands lifting up the sky with finger interlocked to harmonize the triple Burners.
 8 Pieces of Brocade Preparing/standing form: Move left feet one step to the left side, feet with shoulder width, relax and bend knee slightly, stand straight, tongue touch the upper jaw, close lower jaw,
8 Pieces of Brocade Preparing/standing form: Move left feet one step to the left side, feet with shoulder width, relax and bend knee slightly, stand straight, tongue touch the upper jaw, close lower jaw,
Bleeding: Chapter 22 page 650
 Bleeding: Chapter 22 page 650 The Significance of Bleeding When patient have serious external blood loss it is often difficult to determine the amount of blood that is present because it may be absorbed
Bleeding: Chapter 22 page 650 The Significance of Bleeding When patient have serious external blood loss it is often difficult to determine the amount of blood that is present because it may be absorbed
FM P r e f a c e
 *FM 21-150 i ii iii Preface This field manual contains information and guidance pertaining to rifle-bayonet fighting and hand-to-hand combat. The hand-to-hand combat portion of this manual is divided into
*FM 21-150 i ii iii Preface This field manual contains information and guidance pertaining to rifle-bayonet fighting and hand-to-hand combat. The hand-to-hand combat portion of this manual is divided into
Chapter 16 Respiratory System
 Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Stanford Kenpo Karate Association BLUE BELT. Version 10/2008 by T. Shem
 BLUE BELT Kenpo Blue Belt Requirements Techniques Supplemental Techniques 1. Thousand Mallets Crossing Swords A 2. Driving the Spike Chinese Eclipse 3. Siege of the Temple Ox Cart B 4. Tangled Wings --
BLUE BELT Kenpo Blue Belt Requirements Techniques Supplemental Techniques 1. Thousand Mallets Crossing Swords A 2. Driving the Spike Chinese Eclipse 3. Siege of the Temple Ox Cart B 4. Tangled Wings --
Breathing: The normal rate is about 14 to 20 times a minute. Taking in of air is called Inspiration and the forcing out of air is called Expiration.
 Biology 12 Respiration Divisions of Respiration Breathing: entrance and exit of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration: exchange of gases(o2 and CO2) between air (in alveoli) and blood Internal
Biology 12 Respiration Divisions of Respiration Breathing: entrance and exit of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration: exchange of gases(o2 and CO2) between air (in alveoli) and blood Internal
Seven Star Women s Kung Fu Basics Handout
 Seven Star Women s Kung Fu Basics Handout THREE PRIMARY TARGETS 1. Eyes 2. Throat 3. Knees ALL TARGETS LISTED FROM THE HEAD DOWN 1. Forehead 2. Occipital Bone 3. Zygomatic Temporal Nerve (Temple) 4. Bridge
Seven Star Women s Kung Fu Basics Handout THREE PRIMARY TARGETS 1. Eyes 2. Throat 3. Knees ALL TARGETS LISTED FROM THE HEAD DOWN 1. Forehead 2. Occipital Bone 3. Zygomatic Temporal Nerve (Temple) 4. Bridge
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Remove an Upper Airway Obstruction in an Adult , Clear an Upper Airway Obstruction.
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 5 Remove an Upper Airway Obstruction in an Adult. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 5-1 through 5-7. TASK TAUGHT LESSON 081-831-0019, Clear an Upper Airway Obstruction. After completing
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 5 Remove an Upper Airway Obstruction in an Adult. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 5-1 through 5-7. TASK TAUGHT LESSON 081-831-0019, Clear an Upper Airway Obstruction. After completing
UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 9.01 GENERAL FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. Brings oxygenated air to the alveoli B. Removes air containing carbon dioxide C. Filters, warms, and humidifies
UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 9.01 GENERAL FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. Brings oxygenated air to the alveoli B. Removes air containing carbon dioxide C. Filters, warms, and humidifies
Frog Dissection. PreLab: 1. Where do frogs get their energy? Draw a simple food chain to illustrate.
 Name Date Frog Dissection Class # PreLab: Amphibian Reading As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but they must return to water to reproduce. Eggs are laid
Name Date Frog Dissection Class # PreLab: Amphibian Reading As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but they must return to water to reproduce. Eggs are laid
BASIC KNOWLEDGE OF LABORATORY FIRST AID
 BASIC KNOWLEDGE OF LABORATORY FIRST AID RV: 02/02/2015 prevencio@uv.es Page 1 of 7 . General issues to be considered by the rescuer in the event of an accident are described below: - Proceed as follows:
BASIC KNOWLEDGE OF LABORATORY FIRST AID RV: 02/02/2015 prevencio@uv.es Page 1 of 7 . General issues to be considered by the rescuer in the event of an accident are described below: - Proceed as follows:
Frog Dissection. External Observation
 Frog Dissection External Observation Use the diagram below to locate and identify the external features of the head. Find the mouth, external nares, tympani (ear drum), eyes, and nictitating membranes
Frog Dissection External Observation Use the diagram below to locate and identify the external features of the head. Find the mouth, external nares, tympani (ear drum), eyes, and nictitating membranes
How to Make a Proper Fist
 How to Make a Proper Fist Bend your index finger so that the first knuckle touches the second knuckle of your thumb, tucking in the fold of skin that is between your thumb and index finger. Then fold your
How to Make a Proper Fist Bend your index finger so that the first knuckle touches the second knuckle of your thumb, tucking in the fold of skin that is between your thumb and index finger. Then fold your
PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Parts of the Respiratory System The RS can be divided into two parts: 1. Respiratory Tract, (path that air follows). Nasal passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi,
PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Parts of the Respiratory System The RS can be divided into two parts: 1. Respiratory Tract, (path that air follows). Nasal passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi,
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system. Objective sheet 3 Notes
 1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
Chapter 9 Airway Respirations Metabolism Oxygen Requirements Respiratory Anatomy Respiratory Anatomy Respiratory Anatomy Diaphragm
 1 Chapter 9 Airway 2 Respirations Every cell of the body requires to survive Oxygen must come in and carbon must go out 3 Metabolism Metabolism--Process where the body s cells convert food to Adequate
1 Chapter 9 Airway 2 Respirations Every cell of the body requires to survive Oxygen must come in and carbon must go out 3 Metabolism Metabolism--Process where the body s cells convert food to Adequate
Universal Precautions
 First Aid Safety First Aid is a matter of Personal Choice. The Company does not require employees to provide first aid for fellow employees. We have a medical provider close by to provide these services.
First Aid Safety First Aid is a matter of Personal Choice. The Company does not require employees to provide first aid for fellow employees. We have a medical provider close by to provide these services.
Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment
 Name: Date: Mark: / 45 Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
Name: Date: Mark: / 45 Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
The Respiratory System. Medical Terminology
 The Respiratory System Medical Terminology The respiratory system is where gas exchange occurs via respiration; inhalation/exhalation. pick up oxygen from inhaled air expels carbon dioxide and water sinus
The Respiratory System Medical Terminology The respiratory system is where gas exchange occurs via respiration; inhalation/exhalation. pick up oxygen from inhaled air expels carbon dioxide and water sinus
THE AMERICAN SAFETY & HEALTH INSTITUTE ADULT CPR EXAM
 THE AMERICAN SAFETY & HEALTH INSTITUTE ADULT CPR EXAM 1. During an adult victim s assessment, responder should check victim for responsiveness. If no response, responder should first: A. Check for signals
THE AMERICAN SAFETY & HEALTH INSTITUTE ADULT CPR EXAM 1. During an adult victim s assessment, responder should check victim for responsiveness. If no response, responder should first: A. Check for signals
TARGET FOCUS COMBAT. TARGETS Page I of VI
 TARGET FOCUS COMBAT Page I of VI Targets - 1. They are places where injuries typically occur. 2. They effect the way we breath, think and move! 3. They have a specific associated spinal reflex. It s important
TARGET FOCUS COMBAT Page I of VI Targets - 1. They are places where injuries typically occur. 2. They effect the way we breath, think and move! 3. They have a specific associated spinal reflex. It s important
Internal Anatomy of Fish
 Internal Anatomy of Fish The Systems of a Fish Skeletal System Muscular System Respiratory System Digestive System Circulatory System Nervous System Reproductive System Special Organs Skeletal System
Internal Anatomy of Fish The Systems of a Fish Skeletal System Muscular System Respiratory System Digestive System Circulatory System Nervous System Reproductive System Special Organs Skeletal System
Video. Respiration System. You will use 3 pages of your journal for this lesson. 1. One page for hand written notes onto a journal page
 Respiratory System Video Respiration System You will use 3 pages of your journal for this lesson. 1. One page for hand written notes onto a journal page 2. 2 nd page for diagram 3. 3 rd page for chart
Respiratory System Video Respiration System You will use 3 pages of your journal for this lesson. 1. One page for hand written notes onto a journal page 2. 2 nd page for diagram 3. 3 rd page for chart
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Initiate Rescue Breathing on an Adult. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 Initiate Rescue Breathing on an Adult. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-12. TASK TAUGHT 081-831-0018, Open the Airway. 081-831-0048, Perform Rescue Breathing. LESSON
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 Initiate Rescue Breathing on an Adult. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-12. TASK TAUGHT 081-831-0018, Open the Airway. 081-831-0048, Perform Rescue Breathing. LESSON
Top 10 Yoga Exercises to relieve Sciatica
 Top 10 Yoga Exercises to relieve Sciatica This is due to compression and inflammation of the spinal nerves. A sharp pain radiates from the lower back to to the leg and foot in a pattern determined by the
Top 10 Yoga Exercises to relieve Sciatica This is due to compression and inflammation of the spinal nerves. A sharp pain radiates from the lower back to to the leg and foot in a pattern determined by the
Breathing Process: Inhalation
 Airway Chapter 6 Breathing Process: Inhalation Active part of breathing Diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract, allowing the lungs to expand. The decrease in pressure allows lungs to fill with air.
Airway Chapter 6 Breathing Process: Inhalation Active part of breathing Diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract, allowing the lungs to expand. The decrease in pressure allows lungs to fill with air.
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System
 Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
BASIC LIFE SUPPORT CPR: Introduction. Why & When to Do it? CPR... ABCDEF
 BASIC LIFE SUPPORT CPR: Considered when an individual cannot adequately breathe and maintain circulation to vital organs. Introduction Why & When to Do it? Collapsed patients require assistance to maintain
BASIC LIFE SUPPORT CPR: Considered when an individual cannot adequately breathe and maintain circulation to vital organs. Introduction Why & When to Do it? Collapsed patients require assistance to maintain
Senior BLACK Belt Curriculum Your Senior BLACK curriculum will take approximately 18 months or 200 classes.
 A black belt is a white belt who never quit. Senior BLACK Belt Curriculum Your Senior BLACK curriculum will take approximately 18 months or 200 classes. Senior BLACK Belt Techniques 1) All WHITE Belt Techniques
A black belt is a white belt who never quit. Senior BLACK Belt Curriculum Your Senior BLACK curriculum will take approximately 18 months or 200 classes. Senior BLACK Belt Techniques 1) All WHITE Belt Techniques
Outline - Respiratory System. Function of the respiratory system Parts of the respiratory system Mechanics of breathing Regulation of breathing
 Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
 EXTERNAL BLEEDING Definition: This is where the blood vessels and the skin are cut and blood is escaping the body. Causes: Damage to the skin caused by trauma. Can be a laceration (clean cut), abrasion,
EXTERNAL BLEEDING Definition: This is where the blood vessels and the skin are cut and blood is escaping the body. Causes: Damage to the skin caused by trauma. Can be a laceration (clean cut), abrasion,
FIRST AID: Until Help Arrives
 FIRST AID: Until Help Arrives This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation. Featured are: INTRODUCTION: A brief description of the program and the subject
FIRST AID: Until Help Arrives This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation. Featured are: INTRODUCTION: A brief description of the program and the subject
SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION
 SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION WHEN WE BREATHE, WHAT DO WE BREATHE IN? O2, N2, CO2, O3, NO2 (gas fumes), CO, pollutant, fragrants, toxins, etc. WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF BREATHING IN? WHAT DOES OUR BODY WANT? O2 WHY?
SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION WHEN WE BREATHE, WHAT DO WE BREATHE IN? O2, N2, CO2, O3, NO2 (gas fumes), CO, pollutant, fragrants, toxins, etc. WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF BREATHING IN? WHAT DOES OUR BODY WANT? O2 WHY?
How To Start And WIN Any Fight!
 by Grandmaster Dr. Ted Gambordella First Punches That Never Fail Everything You Need To Know To Win Every Fight...You Ever Start! Neck Breaking Kicks That End It Period! Chokes & Throws Ground Finishes
by Grandmaster Dr. Ted Gambordella First Punches That Never Fail Everything You Need To Know To Win Every Fight...You Ever Start! Neck Breaking Kicks That End It Period! Chokes & Throws Ground Finishes
Other diseases or age process
 1 BLS For Healthcare Providers 2 Time is Critical! begins to die in 4 to 6 minutes Brain matter cannot regenerate itself In order to sustain life, the human body must have going in and out and must be
1 BLS For Healthcare Providers 2 Time is Critical! begins to die in 4 to 6 minutes Brain matter cannot regenerate itself In order to sustain life, the human body must have going in and out and must be
Preventing Further Injury
 Poolside First Aid Preventing Further Injury Provide appropriate first aid treatment after removing the patron from immediate danger Remain calm and in control of the situation Call for assistance and
Poolside First Aid Preventing Further Injury Provide appropriate first aid treatment after removing the patron from immediate danger Remain calm and in control of the situation Call for assistance and
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Perform Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation on a Child or Infant. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 6 Perform Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation on a Child or Infant. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 6-1 through 6-7. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 6 Perform Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation on a Child or Infant. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 6-1 through 6-7. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
External Anatomy Dissection Guide
 External Anatomy Dissection Guide Dissection is the cutting of a dead animal or a plant into separate parts for the purpose of careful and detailed examination and study. The external anatomy is as important
External Anatomy Dissection Guide Dissection is the cutting of a dead animal or a plant into separate parts for the purpose of careful and detailed examination and study. The external anatomy is as important
PERSONAL INJURY PATIENT HISTORY
 PERSONAL INJURY PATIENT HISTORY Name Date Address Phone Cell Phone E-Mail For text reminders, your cell phone provider: Date of Birth: Social Security Number: Date of the accident: Time: AM PM What city
PERSONAL INJURY PATIENT HISTORY Name Date Address Phone Cell Phone E-Mail For text reminders, your cell phone provider: Date of Birth: Social Security Number: Date of the accident: Time: AM PM What city
Do your share as a good citizen in your school, community, country, and the world
 Lesson 3 Controlling Bleeding What You Will Learn to Do Determine first aid procedures for bleeding victim Linked Core Abilities Do your share as a good citizen in your school, community, country, and
Lesson 3 Controlling Bleeding What You Will Learn to Do Determine first aid procedures for bleeding victim Linked Core Abilities Do your share as a good citizen in your school, community, country, and
Health, Safety, Security and Environment
 Document owner and change code Document Owner Aaron Perronne Title HSSE Manager Mark X Change Code Description X N/A First Issue A Typographical/Grammatical correction; formatting change; text clarification-no
Document owner and change code Document Owner Aaron Perronne Title HSSE Manager Mark X Change Code Description X N/A First Issue A Typographical/Grammatical correction; formatting change; text clarification-no
First Aid Exercises 1
 First Aid Exercises 1 1 A N S W E R T H E Q U E S T I O N S I N Y O U R O W N W O R D S! What are the emergency numbers you should remember? What kind of information should you give when you call for help?
First Aid Exercises 1 1 A N S W E R T H E Q U E S T I O N S I N Y O U R O W N W O R D S! What are the emergency numbers you should remember? What kind of information should you give when you call for help?
CPR Skills INTRODUCTION
 CPR Skills INTRODUCTION Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a lifesaving procedure for providing oxygen and circulation to someone who has suffered a cardiac and respiratory arrest. The essentials of
CPR Skills INTRODUCTION Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a lifesaving procedure for providing oxygen and circulation to someone who has suffered a cardiac and respiratory arrest. The essentials of
Green Belt Requirements
 Green Belt Requirements Techniques 1. Dancing Cat 2. Gun Attack A, B 3. Slashing Claws 4. Snapping the Vines 5. Rickshaw 6. Fallen Warrior A 7. Striking the Gong 8. Wielding the Torch 9. Soaring Eagle
Green Belt Requirements Techniques 1. Dancing Cat 2. Gun Attack A, B 3. Slashing Claws 4. Snapping the Vines 5. Rickshaw 6. Fallen Warrior A 7. Striking the Gong 8. Wielding the Torch 9. Soaring Eagle
Dragon Whips it s Tail Benefits
 2 Dragon Whips it s Tail Benefits This circulates, energizes and fills the 3 Dan Tians. Filling the third eye helps develop intuition and the sixth sense. 3 4 8 T r i gr a m O r ga n Q i g on g I n struction
2 Dragon Whips it s Tail Benefits This circulates, energizes and fills the 3 Dan Tians. Filling the third eye helps develop intuition and the sixth sense. 3 4 8 T r i gr a m O r ga n Q i g on g I n struction
Surface Rescue Swimmer Course
 Surface Rescue Swimmer Course Secondary Survey LT 5.5 December 2003 1 Objective List the procedures for a secondary survey. Demonstrate secondary survey procedures in a mock trauma (moulage) scenario without
Surface Rescue Swimmer Course Secondary Survey LT 5.5 December 2003 1 Objective List the procedures for a secondary survey. Demonstrate secondary survey procedures in a mock trauma (moulage) scenario without
6 th Kup - 5 th Kup (Green belt - blue tab)
 6 th Kup - 5 th Kup (Green belt - blue tab) Long stance - Double knife-hand strike : Hammer-fist strike : Back-fist strike : Spear-Hand Punch : Back stance Single fist guarding block : Double fist guarding
6 th Kup - 5 th Kup (Green belt - blue tab) Long stance - Double knife-hand strike : Hammer-fist strike : Back-fist strike : Spear-Hand Punch : Back stance Single fist guarding block : Double fist guarding
The Complete Book of One Steps
 By Grandmaster Dr. Ted Gambordella All the Basic One Steps You need from White to Green Belt. By Grandmaster Dr. Ted Gambordella 1 Since I began my martial arts training over 35 years ago. I have found
By Grandmaster Dr. Ted Gambordella All the Basic One Steps You need from White to Green Belt. By Grandmaster Dr. Ted Gambordella 1 Since I began my martial arts training over 35 years ago. I have found
U.S. Shooting Team Balance, Strength and Stability Workout. Training Work-Out
 U.S. Shooting Team Balance, Strength and Stability Workout Training Work-Out Modified by Dan Durben and Sommer Wood November 2006 from the program originally developed by Amber Darland for the USA Shooting
U.S. Shooting Team Balance, Strength and Stability Workout Training Work-Out Modified by Dan Durben and Sommer Wood November 2006 from the program originally developed by Amber Darland for the USA Shooting
YOU AND YOUR PARTNER ARE MEMBERS OF THE MINE RESCUE TEAM EXPLORING THE 3 EAST MAIN INTAKE AFTER AN EXPLOSION OCCURRED AT THE WILDCAT #4 MINE AND HAVE
 YOU AND YOUR PARTNER ARE MEMBERS OF THE MINE RESCUE TEAM EXPLORING THE 3 EAST MAIN INTAKE AFTER AN EXPLOSION OCCURRED AT THE WILDCAT #4 MINE AND HAVE LOCATED RON, THE WEEKLY EXAMINER. THE CAPTAIN INFORMS
YOU AND YOUR PARTNER ARE MEMBERS OF THE MINE RESCUE TEAM EXPLORING THE 3 EAST MAIN INTAKE AFTER AN EXPLOSION OCCURRED AT THE WILDCAT #4 MINE AND HAVE LOCATED RON, THE WEEKLY EXAMINER. THE CAPTAIN INFORMS
Hyung Standards: Chon-Ji through Choong-Moo
 There are three steps in learning a hyung: 1 Learn the steps 2 Perfect the stances and techniques 3 Apply the attacks and blocks, fight for your life. Ready Stance fists start in front of shoulder and
There are three steps in learning a hyung: 1 Learn the steps 2 Perfect the stances and techniques 3 Apply the attacks and blocks, fight for your life. Ready Stance fists start in front of shoulder and
SDTS Certification Grade Exam 7: Weapons Offensive Tactics (SDTS Module Combatives Module 9, 11)
 SDTS Certification Grade Exam 7: Weapons Offensive Tactics (SDTS Module Combatives Module 9, 11) Fight with the weapon All weapons are designed to work with your hand to hand training Grip strength and
SDTS Certification Grade Exam 7: Weapons Offensive Tactics (SDTS Module Combatives Module 9, 11) Fight with the weapon All weapons are designed to work with your hand to hand training Grip strength and
Adult, Child and Infant Exam
 CPR Pro for the Professional Rescuer Adult, Child and Infant Exam Instructions: Read each of the following questions carefully and then place an X over the correct answer on the separate answer sheet provided.
CPR Pro for the Professional Rescuer Adult, Child and Infant Exam Instructions: Read each of the following questions carefully and then place an X over the correct answer on the separate answer sheet provided.
Monday, ! Today: Respiratory system! 5/20/14! Transport of Blood! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing!
 Monday, 5.19.14! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing! Transport of Blood! What is transported! Nutrients! Oxygen! Carbon Dioxide! Hormones! Antibodies! What it is/does!
Monday, 5.19.14! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing! Transport of Blood! What is transported! Nutrients! Oxygen! Carbon Dioxide! Hormones! Antibodies! What it is/does!
LIFE SAVING GUIDE. of life savers
 LIFE SAVING GUIDE Training a nation of life savers HEARTSTART TAUGHT MY SON The British Heart Foundation has a vision to create a nation of life savers. As part of that vision, we re doing everything we
LIFE SAVING GUIDE Training a nation of life savers HEARTSTART TAUGHT MY SON The British Heart Foundation has a vision to create a nation of life savers. As part of that vision, we re doing everything we
3.6. The Respiratory System
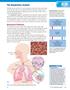 The Respiratory System Whether you are aware of it or not, you breathe in and out 15 times each minute on average. This rate increases automatically if your physical activity increases. With normal breathing,
The Respiratory System Whether you are aware of it or not, you breathe in and out 15 times each minute on average. This rate increases automatically if your physical activity increases. With normal breathing,
Clinical Respiratory System Quiz
 Quiz Description Clinical Respiratory System Quiz Q.1) Q.2) Q.3) Q.4) Q.5) Q.6) What is NOT true about Asthma? It can be triggered by air temperature and allergens. It is the inflammation of the throat.
Quiz Description Clinical Respiratory System Quiz Q.1) Q.2) Q.3) Q.4) Q.5) Q.6) What is NOT true about Asthma? It can be triggered by air temperature and allergens. It is the inflammation of the throat.
CPR & BASIC FIRST AID FOR CHILDREN CPR & BASIC FIRST AID FOR CHILDREN
 CPR & BASIC FOR CHILDREN Student Guide Contents First Aid provider 4 Legal Considerations 5 Disease Transmission & Universal Precautions 6 Unconscious & not breathing - CPR 7 CPR- Child & Infant Sequence
CPR & BASIC FOR CHILDREN Student Guide Contents First Aid provider 4 Legal Considerations 5 Disease Transmission & Universal Precautions 6 Unconscious & not breathing - CPR 7 CPR- Child & Infant Sequence
Yellow Belt Requirements
 Yellow Belt Requirements Techniques 1. Capturing Paws A 2. Sharpening the Blade A, B 3. Escape of the Lamb A 4. Chopping Bamboo A 5. Evading the Samurai A 6. Grasping Honor B 7. Entering the Shrine A 8.
Yellow Belt Requirements Techniques 1. Capturing Paws A 2. Sharpening the Blade A, B 3. Escape of the Lamb A 4. Chopping Bamboo A 5. Evading the Samurai A 6. Grasping Honor B 7. Entering the Shrine A 8.
Shaolin Chuan Fa Requirements for Purple Belt
 Shaolin Chuan Fa Requirements for Purple Belt Stances The heart of any movement is the stance, because your position and balance dictates your ability to perform the desired strike or kick, or to evade
Shaolin Chuan Fa Requirements for Purple Belt Stances The heart of any movement is the stance, because your position and balance dictates your ability to perform the desired strike or kick, or to evade
U.S. Shooting Team Balance, Strength and Stability Workout. Shooting Warm-Up
 U.S. Shooting Team Balance, Strength and Stability Workout Shooting Warm-Up Modified by Dan Durben and Sommer Wood from the program originally developed by Amber Darland for the USA Shooting National Rifle
U.S. Shooting Team Balance, Strength and Stability Workout Shooting Warm-Up Modified by Dan Durben and Sommer Wood from the program originally developed by Amber Darland for the USA Shooting National Rifle
Warm Ups. Standing Stretches
 Warm Ups Mild warm-ups are a necessity for everyone. The need for warm-ups increases with age as the body becomes less elastic over time. It is recommended that you execute the warm-up routine in this
Warm Ups Mild warm-ups are a necessity for everyone. The need for warm-ups increases with age as the body becomes less elastic over time. It is recommended that you execute the warm-up routine in this
First Aid. Pamphlet. About the Bureau of Mine Safety
 First Aid About the Bureau of Mine Safety The Bureau of Mine Safety (BMS) exists to actively promote the safety of miners of New Mexico. BMS will train over 2500 miners during 2011. This includes over
First Aid About the Bureau of Mine Safety The Bureau of Mine Safety (BMS) exists to actively promote the safety of miners of New Mexico. BMS will train over 2500 miners during 2011. This includes over
Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42. Gas Exchange pp Gas Exchange. Gas Exchange in Fish pp Gas Exchange in Fish
 Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42 Fig. 42.24 Gas Exchange pp.979-989 Gas exchange involves the uptake of oxygen and the discharge of carbon dioxide (i.e. respiration or breathing). It is necessary for cellular
Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42 Fig. 42.24 Gas Exchange pp.979-989 Gas exchange involves the uptake of oxygen and the discharge of carbon dioxide (i.e. respiration or breathing). It is necessary for cellular
Hyung Standards: Sam-Il through Moon-Moo
 General Comments: Always pivot on the ball of the foot. When you pivot on your heel you immobilize your hip. Sam-Il Double middle block starts with both fists at shoulder level. High double forearm block
General Comments: Always pivot on the ball of the foot. When you pivot on your heel you immobilize your hip. Sam-Il Double middle block starts with both fists at shoulder level. High double forearm block
Principles of Providing First Aid
 First Aid Principles of Providing First Aid Immediate care that is provided to the victim of injury or illness to minimize the adverse effects until experts take over. Proper first aid can mean the difference
First Aid Principles of Providing First Aid Immediate care that is provided to the victim of injury or illness to minimize the adverse effects until experts take over. Proper first aid can mean the difference
FIRST-AID LEAFLET SITUATIONS PROCEDURES
 Page 1 FIRST-AID LEAFLET SITUATIONS PROCEDURES CONTENTS: FIRST AID ARTIFICIAL RESPIRATION CONTROL OF BLEEDING FRACTURES BURNS SHOCK WOUNDS EYE INJURIES ABDOMINAL WOUNDS BACKBONE FRACTURE HEAT STROKE BLEEDING
Page 1 FIRST-AID LEAFLET SITUATIONS PROCEDURES CONTENTS: FIRST AID ARTIFICIAL RESPIRATION CONTROL OF BLEEDING FRACTURES BURNS SHOCK WOUNDS EYE INJURIES ABDOMINAL WOUNDS BACKBONE FRACTURE HEAT STROKE BLEEDING
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at gaseous exchange in humans in terms of o Ventilation o Inspiration o Expiration o Transport of gases o Homeostatic
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at gaseous exchange in humans in terms of o Ventilation o Inspiration o Expiration o Transport of gases o Homeostatic
Copyright 2001 Dr. Ted Gambordella
 1 INTRODUCTION CHOKES Chokes. If you are in a life or death fight situation and you absolutely want to make sure that the fight will NOT continue, and that you will be the Winner, Choke Them Out! Nothing
1 INTRODUCTION CHOKES Chokes. If you are in a life or death fight situation and you absolutely want to make sure that the fight will NOT continue, and that you will be the Winner, Choke Them Out! Nothing
Mine Foreman Training First Aid & CPR Unit 8 Part 1
 Mine Foreman Training First Aid & CPR Unit 8 Part 1 Power Point Program and Training Developed by Wayne Collett Office of Mine Safety & Licensing 2005 1 First aid is the immediate emergency care or treatment
Mine Foreman Training First Aid & CPR Unit 8 Part 1 Power Point Program and Training Developed by Wayne Collett Office of Mine Safety & Licensing 2005 1 First aid is the immediate emergency care or treatment
War Surgery Dr. Abdulwahid INTRODUCTION: AIRWAY, BREATHING
 War Surgery Dr. Abdulwahid INTRODUCTION: AIRWAY, BREATHING The aims of war surgery: Save life Avoid infectious complications Save limbs Minimize residual disability The outcome is influenced by: Type of
War Surgery Dr. Abdulwahid INTRODUCTION: AIRWAY, BREATHING The aims of war surgery: Save life Avoid infectious complications Save limbs Minimize residual disability The outcome is influenced by: Type of
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
Orbital decompression surgery. See also information leaflets on: ~ Thyroid Eye Disease ~ Upper lid lowering ~ Proptosis
 Orbital decompression surgery See also information leaflets on: ~ Thyroid Eye Disease ~ Upper lid lowering ~ Proptosis Qu: What is the orbit? The eye, its surrounding muscles, nerves and fatty tissue lie
Orbital decompression surgery See also information leaflets on: ~ Thyroid Eye Disease ~ Upper lid lowering ~ Proptosis Qu: What is the orbit? The eye, its surrounding muscles, nerves and fatty tissue lie
Rescue Swimmer Refresher Course. Practical First Aid Training/Mock Trauma LT 2.2
 Rescue Swimmer Refresher Course Practical First Aid Training/Mock Trauma LT 2.2 Enabling Objectives Respond to an emergency per current American Red Cross standards. Administer CPR per current American
Rescue Swimmer Refresher Course Practical First Aid Training/Mock Trauma LT 2.2 Enabling Objectives Respond to an emergency per current American Red Cross standards. Administer CPR per current American
What is a wound? An injury to the skin and some times other deeper soft tissues. Types:
 1 Dr. Samer Sara What is a wound? An injury to the skin and some times other deeper soft tissues. Types: Open wounds: Skin is torn or cut, often leads to bleeding. Closed wounds: Skin is not affected and
1 Dr. Samer Sara What is a wound? An injury to the skin and some times other deeper soft tissues. Types: Open wounds: Skin is torn or cut, often leads to bleeding. Closed wounds: Skin is not affected and
The Respiratory System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Organs of the Respiratory system
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Organs of the Respiratory system
First Aid Skills Checklist
 ,, Care Adult, Child, Baby the Scene the Person Shout for Help or EMS/9-1-1 Is it safe? What happened? How did it happen? How many ill or injured people are there? Is there someone to help me? Is there
,, Care Adult, Child, Baby the Scene the Person Shout for Help or EMS/9-1-1 Is it safe? What happened? How did it happen? How many ill or injured people are there? Is there someone to help me? Is there
Introduction. Sharp knife Disposable gloves Antiseptic wipes/hand wash Means of suspending carcass (if appropriate) Plastic bags Record book
 Introduction From the moment it is culled a deer carcass needs to be treated carefully on it s way to becoming food. One of the first steps in the process is the gralloch, during which part of the meat
Introduction From the moment it is culled a deer carcass needs to be treated carefully on it s way to becoming food. One of the first steps in the process is the gralloch, during which part of the meat
OUTLINE SHEET Respond to an emergency per current American Red Cross standards.
 INTRODUCTION OUTLINE SHEET 2.2-1 PRACTICAL FIRST AID TRAINING/MOCK TRAUMA PAGE 1 of 8 First Aid, in any situation, consists of emergency treatment of the sick or injured before medical help can be obtained.
INTRODUCTION OUTLINE SHEET 2.2-1 PRACTICAL FIRST AID TRAINING/MOCK TRAUMA PAGE 1 of 8 First Aid, in any situation, consists of emergency treatment of the sick or injured before medical help can be obtained.
Om Fairy LLC Page 1 This personal yoga practice was created for One Stressed Out Yogi.
 A Restorative Practice for One Stressed Out Yogini. In any of the postures below, if your joints are floating in the air (elbows, knees, ankles, etc.), you can utilize extra props for support, be it a
A Restorative Practice for One Stressed Out Yogini. In any of the postures below, if your joints are floating in the air (elbows, knees, ankles, etc.), you can utilize extra props for support, be it a
Silk-Reeling Exercises for All Parts of the Body
 Chapter IV Silk-Reeling Exercises for All Parts of the Body A. HEAD 1. Turning the head Movements: Start with the wuji commencing posture, the feet shoulderwidth apart. Keep the head upright, the shoulders
Chapter IV Silk-Reeling Exercises for All Parts of the Body A. HEAD 1. Turning the head Movements: Start with the wuji commencing posture, the feet shoulderwidth apart. Keep the head upright, the shoulders
