IIIYEAR/VISEMESTER ME2023 RENEWABLE SOURCES OF ENERGY UNIT II WIND ENERGY
|
|
|
- Sandra Alexina Blake
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Department Of Mechanical Engineering IIIYEAR/VISEMESTER ME2023 RENEWABLE SOURCES OF ENERGY UNIT II WIND ENERGY 9 Wind Data and Energy Estimation wind Energy Conversion Systems Wind Energy generators and its performance Wind Energy Storage Applications Hybrid systems UNIT-II WIND ENERGY Introduction: Winds are essentially created by the solar heating of the atmosphere. Several attempts have been made since 1940 to use wind to generate electric energy and development is still going on. However, techno-economic feasibility has yet to be satisfactorily established. Wind as a power source is attractive because it is plentiful, inexhaustible and non-polluting. Further, it does not impose extra heat burden on the environment. Unfortunately, it is non-steady and undependable. Control equipment has been devised to start the wind power plant whenever the wind speed reaches 30km/h. Methods have also been found to generate constant frequency power with varying wind speeds and consequently varying speeds of wind mill propellers. Wind power may prove practical for small power needs in isolated sites. But for maximum flexibility, it should be used in conjunction with other methods of power generation to ensure continuity. For a rotor of 17m diameter and a velocity of 48 km/h the theoretical power is 265kW and the practical would be roughly half of this value. There are some distinctive energy end-use features of wind power systems: Most wind power sites are in remote rural, island or marine areas.rural grid systems are likely to be weak in these areas, since they carry relatively low voltage supplies (e.g.33kv). Wind energy: Can be economically used for the generation of electrical energy. Winds are caused due to Heating and cooling of the main atmosphere which generates convection currents. The rotation of the earth with respect to atmosphere, and its motion around the sun. The potential of wind energy is abundant.
2 1.6X107 MW. (Same order of present energy consumption) Wind mill is drives generator to produce electricity. Water pumping for irrigation and drinking water Required Wind speed range is 8 to 36Km per hour In India, coastal areas of Saurashtra, western Rajasthan and some parts of central India. Wind Direction: A weather vane, or wind vane, is used to show the direction of the wind. A wind vane points toward the source of the wind. Wind direction is reported as the direction from which the wind blows, not the direction toward which the wind moves. A north wind blows from the north toward the south. Wind Speed: It is important in many cases to know how fast the wind is blowing. Wind speed can be measured using a wind gauge or anemometer. One type of anemometer is a device with three arms that spin on top of a shaft. Each arm has a cup on its end. The cups catch the wind and spin the shaft. The harder the wind blows, the faster the shaft spins. A device inside counts the number of rotations per minute and converts that figure into miles per hour. A display on the anemometer shows the speed of the wind. History of Wind Machines: Since ancient times, people have harnessed the wind s energy. Over 5,000 years ago, the ancient Egyptians used the wind to sail ships on the Nile River. Later, people built windmills to grind wheat and other grains. The early windmills looked like paddle wheels. Centuries later, the people in Holland improved the windmill. They gave it propellertype blades, still made with sails. Holland is famous for its windmills. In this country, the colonists used windmills to grind wheat and corn, to pump water, and to cut wood at sawmills. Today, people occasionally use windmills to grind grain and pump water, but they also use modern wind turbines to make electricity
3 Today s Wind Turbines: Like old-fashioned windmills, today s wind turbines use blades to capture the wind s kinetic energy. Wind turbines work because they slow down the speed of the wind. When the wind blows, it pushes against the blades of the wind turbine, making them spin. They power a generator to produce electricity. Most wind turbines have the same basic parts: blades, shafts, gears, a generator, and a cable. (Some turbines do not have gearboxes.) These parts work together to convert the wind s energy into electricity. 1. The wind blows and pushes against the blades on top of the tower, making them spin. 2. The turbine blades are connected to a low-speed drive shaft. When the blades spin, the shaft turns. The shaft is connected to a gearbox. The gears in the gearbox increase the speed of the spinning motion on a high-speed drive shaft. 3. The high-speed drive shaft is connected to a generator. As the shaft turns inside the generator, it produces electricity. 4. The electricity is sent through a cable down the turbine tower to a transmission line. The amount of electricity that a turbine produces depends on its size and the speed of the wind. Wind turbines come in many different sizes. A small turbine may power one home. Large wind turbines can produce enough electricity to power up to 1,000 homes. Large turbines are sometimes grouped together to provide power to the electricity grid. The grid is the network of power lines connected together across the entire country Wind Power Plants: Wind power plants, or wind farms, are clusters of wind turbines used to produce electricity. A wind farm usually has dozens of wind turbines scattered over a large area. Choosing the location of a wind farm is known as siting a wind farm. The wind speed and direction must be studied to determine where to put the turbines. As a rule, wind speed increases with height, as well as over open areas with no windbreaks. Turbines are usually built in rows facing into the prevailing wind. Placing turbines too far apart wastes space. If turbines are too close together, they block each other s wind.the site must have strong, steady winds. Scientists measure the winds in an area for several years before choosing a site. The best sites for wind farms are on hilltops, on the open plains, through mountain passes, and near the coasts of oceans or large lakes.the wind blows stronger and steadier over water than over land.there are no obstacles on the water to block the wind. There is a lot of wind energy available offshore.offshore wind farms are built in the shallow waters off the coast of major lakes and oceans. Offshore turbines produce more electricity than turbines on land, but they cost more to build and operate. The first offshore wind farm in the United States, off the coast of Massachusetts, was approved in April Construction is expected to begin in 2013.
4 Wind Production Every year, wind produces only a small amount of the electricity this country uses, but the amount is growing every year. One reason wind farms don t produce more electricity is that they can only run when the wind is blowing at certain speeds. On Midwestern wind farms, the wind is optimum for producing electricity between 65 and 90 percent of the time. Environmental Impacts In some areas, people worry about the birds and bats that may be injured by wind turbines. Some people believe wind turbines produce a lot of sound, and some think turbines affect their view of the landscape. On the other hand, wind is a clean, renewable energy source that produces no air pollution. And wind is free to use. Wind power is not the perfect answer to our electricity needs, but it is a valuable part of the solution. Turbine subsystems include: Rotors which convert wind energy into mechanical energy of the shaft ; Nacelle (enclosure) which contains all the conversion equipment, generator,gear shaft etc. Tower, to increase the height of the turbine systems so that higher wind speeds are captured. Control equipment, Cables and other Civil works.
5 Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines (HAWTs) Horizontal-axis wind turbines (HAWT) get their name from the fact that their axis of rotation ishorizontal. They have the main rotor shaft and electrical generator at the top of a tower, and arepointed into the wind. The variability of wind distribution and speed brings up the requirement ofa gear system connected to the rotor and the generator. The gear system enables a constant speedof rotation to the generator thus enabling constant frequency generation. Turbine blades are madestiff in order to prevent the blades from being pushed into the tower by high winds. Downwindmachines have also been built, as they no longer require a yaw mechanism to keep them facingthe wind, and also because in high winds the blades can turn out of the wind thereby increasing drag and coming to a stop. Most of the HAWTs are upwind as downwind systems cause regular turbulence which may lead to fatigue. HAWT advantages Variable blade pitch, which gives the turbine blades the optimum angle of attack. Changing the angle of attack provides greater control over power generated and enables maximum efficiency. As wind energy increases with height, the tall tower in the HAWT gives access to higher wind speed. In some cases increase of even 10m height leads to increase in wind speed by 20 % In HAWTs the blades move horizontally that is perpendicular to the wind and hence haveminimum drag and they receive power throughout the rotation. HAWT disadvantages Due to inherent large structures, construction costs are very high and so are transportation costs. Civil construction is costly due to erection of large towers. Wind turbine operation often leads to production of electronic noise which affects radar sites. In case of downwind HAWTs the regular turbulence produced leads to structural failure. HAWTs require an additional yaw control mechanism to turn the blades toward the wind. Types of HAWTs: Mono-Blade Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine (HAWT) Features: 1. They have lighter rotor and are cheaper. 2. Blade are m long and are made up of metal, glass reinforced plastics, laminated wood,composite carbon fiber/ fiberglass etc. 3. Power generation is within the range 15 kw to 50 kw and service life of plant is 30 years. Advantages: 1. Simple and lighter construction. 2. Favorable price
6 3. Easy to install and maintain. Disadvantages: 1. Tethering control necessary for higher loads. 2. Not suitable for higher power ratings. Applications: 1. Field irrigation 2. Sea-Water desalination Plants 3. Electric power supply for farms and remote loads. Twin-Blade HAWT 1. They have large sizes and power output in range of 1 MW, 2 MW and 3MW. 2. These high power units feed directly to the distribution network. Blade HAWT 1. 3 blade propeller type wind turbines have been installed in India as well as abroad. 2. The rotor has three blades assembled on a hub. The blade tips have a pitch control of 0 30 for controlling shaft speed. 3. The shaft is mounted on bearings. 4. The gear chain changes the speed from turbine shaft to generator shaft.vertical axis Wind Turbines Vertical-axis wind turbines (or VAWTs) have the main rotor shaft arranged vertically as theplane of rotation is vertical. Blades are also vertical in this arrangement. The biggest advantage of VAWTs is they don t require a yaw control mechanism to be pointed into the wind. Thusthese are useful in sites where wind direction is random or there is presence of large obstacleslike trees, houses etc. Also VAWTs don t require a tower structure and can be placed nearby aground enabling access to electrical components. Some drawbacks are the low efficiency of wind production and the fact that large drag is created for rotating the blades in a vertical axis. VAWT advantages A massive tower structure is not required, as VAWTs are mounted closer to the ground They don t require yaw mechanisms. These are located closer to the ground and hence easier to maintain. These have lower startup speeds than their horizontal counterparts. These can start at speeds as low as 10Kmph. These have a lower noise signature. VAWT disadvantages VAWTs have lower efficiency as compared to HAWTs because of the additional drag produced due to rotation of blades. Even though VAWTs are located closer to the ground, the equipment now resides at the bottom of the turbines structure thus making it inaccessible. Because of their low height they cannot capture the wind energy stored in higher altitudes. Internal Components of a Wind Turbine
7 Anemometer: This device is used for measurement of speed. The wind speed is also fed to the controller as it is one of the variables for controlling pitch angle and yaw Blades: These are aerodynamically designed structures such that when wind flows over them they are lifted as in airplane wings. The blades are also slightly turned for greater aerodynamic efficiency Brake: This is either a mechanical, electrical or hydraulic brake used for stopping the turbine in high wind conditions Controller: This is the most important part of the turbine as it controls everything from power output to pitch angle. The controller senses wind speed, wind direction, shaft speed and torque at one or more Gear box: This steps-up or steps down the speed of turbine and with suitable coupling transmits rotating mechanical energy at a suitable speed to the generator. Typically a gear box system steps up rotation speed from 50 to 60 rpm to 1200 to 1500 rpm Generator: This can be a synchronous or asynchronous Ac machine producing power at 50Hz High-speed shaft: Its function is to drive the generator. Low-speed shaft: The rotor turns the low-speed shaft at about 30 to 60 rotations per minute. Nacelle: The nacelle is the housing structure for high speed shaft, low speed shaft, gear box, generator, converter equipment etc. It is located atop the tower structure mostly in the shadow of the blades Pitch: This is basically the angle the blades make with the wind. Changing the pitch angle changes weather the blades turn in or turn out of the wind stream. Rotor: The hub and the blades together compose the rotor. Tower: Towers are basically made up of tubular steel or steel lattice. Taller the towers greater is the amount of power generated as the wind speed generally goes on increasing with height. oints. Also the temp of generator and power output produced is sensed Wind direction: Generally erratic in nature, hence the rotor is made to face into the wind by means of control systems. Wind vane: Basically the job of a wind sensor, measuring the wind speed and communicating the same to the yaw drive, so as to turn the turbine into the wind flow direction. Yaw drive: This drive controls the orientation of the blades towards the wind. In case the turbine is out of the wind, then the yaw drive rotates the turbine in the wind direction. Power Speed Characteristics The mechanical power that can be extracted from the wind depends heavily on the wind speed,and for each wind speed there is always an optimum turbine speed at which the wind powerextracted at the shaft of the turbine is maximum, at any other speed apart from this optimumspeed we get substandard operation of the system. So our chief goal would be to find out theoptimum turbine speed
8 over the operational range of the wind stream speeds. This thing isbasically area specific, because the wind speeds would vary from place to place. Now themechanical power transmitted at the shaft is: As we know Cp is a function of the TSR & the pitch angle. For a wind turbine with radius R, theabove formula can be written as, Torque Speed Characteristics Turbine Performance: The Power Curve The power curve of a wind turbine indicates the electrical power output for the turbine at different wind speeds. The graph shows a power curve for atypical 600 kw wind turbine. Power curves are found by field measurements of power output versus wind speed. Anemometers placed on a mast reasonably close to the wind turbine to measure the wind speed.
9 Turbine Efficiency (Power Coefficient) The power coefficient tells you how efficiently a turbine converts the energy in the wind to electricity. Very simply, we just divide the electrical power output by the wind energy input to measure how efficient a wind turbine is. The graph shows a power coefficient curve for a typical wind turbine. The average efficiency is about 20 per cent. It varies with the wind speed, but is largest at around 9m/s. At low wind speeds efficiency is not as important because there is not much energy to harvest. By design, at high wind speeds, the turbine wastes excess energy above the generator rating. Hybrid Systems Hybrid means, in general, heterogeneous in nature or composition and the term hybrid systems means systems with behavior defined by entities or processes of distinct characteristics. Here the term hybrid refers to combinations or compositions of continuous and discrete parts and a hybrid dynamical system is understood to mean a dynamical system where the behavior of interest is determined by interacting continuous and discrete dynamics. Hybrid dynamical systems generate variables or signals, that are mixed signals consisting of combinations of continuous or discrete value or time signals, and through them interaction with other systems and the environment occurs.
TOPICS TO BE COVERED
 UNIT-3 WIND POWER TOPICS TO BE COVERED 3.1 Growth of wind power in India 3.2 Types of wind turbines Vertical axis wind turbines (VAWT) and horizontal axis wind turbines (HAWT) 3.3 Types of HAWTs drag and
UNIT-3 WIND POWER TOPICS TO BE COVERED 3.1 Growth of wind power in India 3.2 Types of wind turbines Vertical axis wind turbines (VAWT) and horizontal axis wind turbines (HAWT) 3.3 Types of HAWTs drag and
Study Of Wind Turbines
 Study Of Wind Turbines Dr. Sumit Gupta,AbhishekMathur, AjayKr.Panwar, AjayKr. Thagriya,Dilipsatoliya Professor, Department of Physics,Maharishi Arvind Institute of Engineering & Technology, Jaipur ABSTRACT:There
Study Of Wind Turbines Dr. Sumit Gupta,AbhishekMathur, AjayKr.Panwar, AjayKr. Thagriya,Dilipsatoliya Professor, Department of Physics,Maharishi Arvind Institute of Engineering & Technology, Jaipur ABSTRACT:There
Wind Energy Technology. What works & what doesn t
 Wind Energy Technology What works & what doesn t Orientation Turbines can be categorized into two overarching classes based on the orientation of the rotor Vertical Axis Horizontal Axis Vertical Axis Turbines
Wind Energy Technology What works & what doesn t Orientation Turbines can be categorized into two overarching classes based on the orientation of the rotor Vertical Axis Horizontal Axis Vertical Axis Turbines
LECTURE 18 WIND POWER SYSTEMS. ECE 371 Sustainable Energy Systems
 LECTURE 18 WIND POWER SYSTEMS ECE 371 Sustainable Energy Systems 1 HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT The first wind turbine used to generate electricity was built by La Cour of Denmark in 1891 2 HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT
LECTURE 18 WIND POWER SYSTEMS ECE 371 Sustainable Energy Systems 1 HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT The first wind turbine used to generate electricity was built by La Cour of Denmark in 1891 2 HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT
Wind Energy. Definition of Wind Energy. Wind energy is energy from moving air.
 Wind Energy Definition of Wind Energy Wind energy is energy from moving air. Air has mass. When it moves, it has kinetic energy. Kinetic energy is the energy of motion. How does wind form? Wind forms when
Wind Energy Definition of Wind Energy Wind energy is energy from moving air. Air has mass. When it moves, it has kinetic energy. Kinetic energy is the energy of motion. How does wind form? Wind forms when
Wind Power generation
 Lecture 28 Wind Power generation Basic technology Wind electric generator converts kinetic energy available in wind to electrical energy by using rotor, gear box and generator. Wind Power The terms "wind
Lecture 28 Wind Power generation Basic technology Wind electric generator converts kinetic energy available in wind to electrical energy by using rotor, gear box and generator. Wind Power The terms "wind
Small Scale Wind Technologies Part 2. Centre for Renewable Energy at Dundalk IT CREDIT
 Small Scale Wind Technologies Part 2 Centre for Renewable Energy at Dundalk IT CREDIT 1 Part 2 Small and large scale wind turbine technologies 2 Overview of small scale grid connected system Wind Turbine
Small Scale Wind Technologies Part 2 Centre for Renewable Energy at Dundalk IT CREDIT 1 Part 2 Small and large scale wind turbine technologies 2 Overview of small scale grid connected system Wind Turbine
CACTUS MOON EDUCATION, LLC
 CACTUS MOON EDUCATION, LLC ENERGY FROM THE WIND WIND ENERGY TECHNOLOGIES EDUCATION MODULE www.cactusmooneducation.com TEACHER S NOTES (wnd01tn) _ Cactus Moon Education, LLC. ENERGY FROM THE WIND WIND ENERGY
CACTUS MOON EDUCATION, LLC ENERGY FROM THE WIND WIND ENERGY TECHNOLOGIES EDUCATION MODULE www.cactusmooneducation.com TEACHER S NOTES (wnd01tn) _ Cactus Moon Education, LLC. ENERGY FROM THE WIND WIND ENERGY
Wind Energy Resource and Technologies
 Wind Energy Resource and Technologies Dr. Ram Chandra DBT s Energy Bioscience Overseas Fellow Centre for Rural Development and Technology Indian Institute of Technology Delhi Hauz Khas, New Delhi 110 016
Wind Energy Resource and Technologies Dr. Ram Chandra DBT s Energy Bioscience Overseas Fellow Centre for Rural Development and Technology Indian Institute of Technology Delhi Hauz Khas, New Delhi 110 016
V MW Offshore leadership
 V120-4.5 MW Offshore leadership OptiSpeed allows the rotor speed to vary within a range of approximately 60 per cent in relation to nominal rpm. Thus with OptiSpeed, the rotor speed can vary by as much
V120-4.5 MW Offshore leadership OptiSpeed allows the rotor speed to vary within a range of approximately 60 per cent in relation to nominal rpm. Thus with OptiSpeed, the rotor speed can vary by as much
Wind turbine Varying blade length with wind speed
 IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, PP 01-05 www.iosrjournals.org Wind turbine Varying blade length with wind speed Mohammed Ashique
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, PP 01-05 www.iosrjournals.org Wind turbine Varying blade length with wind speed Mohammed Ashique
Energy Utilisation of Wind
 Ing. Pavel Dostál, Ph.D., Ostrava University 1 Energy Utilisation of Wind Choice of locality Energy and wind output Wind-power installations Wind-power installations: types and classification Basic parts
Ing. Pavel Dostál, Ph.D., Ostrava University 1 Energy Utilisation of Wind Choice of locality Energy and wind output Wind-power installations Wind-power installations: types and classification Basic parts
III. Wind Energy CHE 443 III. Wind Energy
 WIND ENERGY Wind energy is the kinetic energy of air moving from one place to another in the form of wind. Wind is created as the results of uneven heating of the earth by the sun: Warm air rises leaving
WIND ENERGY Wind energy is the kinetic energy of air moving from one place to another in the form of wind. Wind is created as the results of uneven heating of the earth by the sun: Warm air rises leaving
Aerodynamically Efficient Wind Turbine Blade S Arunvinthan 1, Niladri Shekhar Das 2, E Giriprasad 3 (Avionics, AISST- Amity University, India)
 International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6734, ISSN (Print): 2319 6726 Volume 3 Issue 4ǁ April 2014ǁ PP.49-54 Aerodynamically Efficient Wind Turbine Blade S Arunvinthan
International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6734, ISSN (Print): 2319 6726 Volume 3 Issue 4ǁ April 2014ǁ PP.49-54 Aerodynamically Efficient Wind Turbine Blade S Arunvinthan
JJT WIND AMPLIFIER
 JJT-001-2014 WIND AMPLIFIER Sevvel P 1, Santhosh P 2 1 Assoicate Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Magna College of Engineering Email.Id : sevvel_ready@yahoo.co.in 2 Final year Mechanical
JJT-001-2014 WIND AMPLIFIER Sevvel P 1, Santhosh P 2 1 Assoicate Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Magna College of Engineering Email.Id : sevvel_ready@yahoo.co.in 2 Final year Mechanical
V MW Versatile megawattage
 V80-1.8 MW Versatile megawattage This system features microprocessors that rotate the blades around their longitudinal axes, thus ensuring continuous adjustment to maintain optimal blade angles in relation
V80-1.8 MW Versatile megawattage This system features microprocessors that rotate the blades around their longitudinal axes, thus ensuring continuous adjustment to maintain optimal blade angles in relation
Evaluation of aerodynamic criteria in the design of a small wind turbine with the lifting line model
 Evaluation of aerodynamic criteria in the design of a small wind turbine with the lifting line model Nicolas BRUMIOUL Abstract This thesis deals with the optimization of the aerodynamic design of a small
Evaluation of aerodynamic criteria in the design of a small wind turbine with the lifting line model Nicolas BRUMIOUL Abstract This thesis deals with the optimization of the aerodynamic design of a small
WIND TURBINE DESIGN. Dušan Medveď
 WIND TURBINE DESIGN ABSTRACT Dušan Medveď This paper deals with main design of wind turbine concerning with structure of wind turbines, option between vertical and horizontal axis wind turbines to optimising
WIND TURBINE DESIGN ABSTRACT Dušan Medveď This paper deals with main design of wind turbine concerning with structure of wind turbines, option between vertical and horizontal axis wind turbines to optimising
Vertical Wind Energy Engineering Design and Evaluation of a Twisted Savonius Wind Turbine
 Design and Evaluation of a Twisted Savonius Wind Turbine Ian Duffett Jeff Perry Blaine Stockwood Jeremy Wiseman Outline Problem Definition Introduction Concept Selection Design Fabrication Testing Results
Design and Evaluation of a Twisted Savonius Wind Turbine Ian Duffett Jeff Perry Blaine Stockwood Jeremy Wiseman Outline Problem Definition Introduction Concept Selection Design Fabrication Testing Results
Wind Power Systems. Energy Systems Research Laboratory, FIU
 Wind Power Systems Historical Development of Wind Power In the US - first wind-electric systems built in the late 1890 s By 1930s and 1940s, hundreds of thousands were in use in rural areas not yet served
Wind Power Systems Historical Development of Wind Power In the US - first wind-electric systems built in the late 1890 s By 1930s and 1940s, hundreds of thousands were in use in rural areas not yet served
Fundamentals of Wind Energy
 Fundamentals of Wind Energy Alaska Wind Energy Applications Training Symposium Bethel, Alaska E. Ian Baring-Gould National Renewable Energy Laboratory TOPICS Introduction Energy and Power Wind Characteristics
Fundamentals of Wind Energy Alaska Wind Energy Applications Training Symposium Bethel, Alaska E. Ian Baring-Gould National Renewable Energy Laboratory TOPICS Introduction Energy and Power Wind Characteristics
CFD Analysis of Giromill Type Vertical Axis Wind Turbine
 242 CFD Analysis Giromill Type Vertical Axis Wind Turbine K. Sainath 1, T. Ravi 2, Suresh Akella 3, P. Madhu Sudhan 4 1 Associate Pressor, Department Mechanical Engineering, Sreyas Inst. Engg. & Tech.,
242 CFD Analysis Giromill Type Vertical Axis Wind Turbine K. Sainath 1, T. Ravi 2, Suresh Akella 3, P. Madhu Sudhan 4 1 Associate Pressor, Department Mechanical Engineering, Sreyas Inst. Engg. & Tech.,
Modulation of Vertical Axis Wind Turbine
 Modulation of Vertical Axis Wind Turbine Apurwa Gokhale 1, Nehali Gosavi 2, Gurpreet Chhabda 3, Vikrant Ghadge 4, Dr. A.P.Kulkarni 5 1,2,3,4 Vishwakarma Institute of Information Technology, Pune. 5 Professor,
Modulation of Vertical Axis Wind Turbine Apurwa Gokhale 1, Nehali Gosavi 2, Gurpreet Chhabda 3, Vikrant Ghadge 4, Dr. A.P.Kulkarni 5 1,2,3,4 Vishwakarma Institute of Information Technology, Pune. 5 Professor,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY A PATH FOR HORIZING YOUR INNOVATIVE WORK FABRICATION AND TESTING OF CLOSE CASING VERTICAL AXIS WIND TURBINE WITH TUNNELLING
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY A PATH FOR HORIZING YOUR INNOVATIVE WORK FABRICATION AND TESTING OF CLOSE CASING VERTICAL AXIS WIND TURBINE WITH TUNNELLING
REMOTE SENSING APPLICATION in WIND ENERGY
 REMOTE SENSING APPLICATION in WIND ENERGY Siraj Ahmed Professor & Head Department of Mechanical Engineering Maulana Azad National Iinstitute of Technology Bhopal, India sirajahmed@manit.ac.in Contents
REMOTE SENSING APPLICATION in WIND ENERGY Siraj Ahmed Professor & Head Department of Mechanical Engineering Maulana Azad National Iinstitute of Technology Bhopal, India sirajahmed@manit.ac.in Contents
Can Wind Energy Be Captured in New York City? Case Study on Urban Wind based on a Feasibility Study by Orange Line Studio. Spark 101 Educator Resource
 Can Wind Energy Be Captured in New York City? Case Study on Urban Wind based on a Feasibility Study by Orange Line Studio Spark 101 Educator Resource Copyright 2013 Defining Key Concepts What is wind power?
Can Wind Energy Be Captured in New York City? Case Study on Urban Wind based on a Feasibility Study by Orange Line Studio Spark 101 Educator Resource Copyright 2013 Defining Key Concepts What is wind power?
PREDICTION THE EFFECT OF TIP SPEED RATIO ON WIND TURBINE GENERATOR OUTPUT PARAMETER
 Int. J. Mech. Eng. & Rob. Res. 2012 Hari Pal Dhariwal et al., 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2278 0149 www.ijmerr.com Vol. 1, No. 3, October 2012 2012 IJMERR. All Rights Reserved PREDICTION THE EFFECT OF TIP
Int. J. Mech. Eng. & Rob. Res. 2012 Hari Pal Dhariwal et al., 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2278 0149 www.ijmerr.com Vol. 1, No. 3, October 2012 2012 IJMERR. All Rights Reserved PREDICTION THE EFFECT OF TIP
Wind farm performance
 Wind farm performance Ali Marjan Wind Energy Submission date: June 2016 Supervisor: Lars Sætran, EPT Norwegian University of Science and Technology Department of Energy and Process Engineering Wind
Wind farm performance Ali Marjan Wind Energy Submission date: June 2016 Supervisor: Lars Sætran, EPT Norwegian University of Science and Technology Department of Energy and Process Engineering Wind
AN ISOLATED SMALL WIND TURBINE EMULATOR
 AN ISOLATED SMALL WIND TURBINE EMULATOR Md. Arifujjaman Graduate Student Seminar: Master of Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Memorial University of Newfoundland St. John s, NL, Canada
AN ISOLATED SMALL WIND TURBINE EMULATOR Md. Arifujjaman Graduate Student Seminar: Master of Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Memorial University of Newfoundland St. John s, NL, Canada
How Does A Wind Turbine's Energy Production Differ from Its Power Production? 1
 Siting Wind Power: Wind Power Curves & Community Considerations (Teacher Notes) (Assessing the Feasibility of Wind Power for Pennsylvania) Notes on Part 1 A Beaufort scale is included on the next page
Siting Wind Power: Wind Power Curves & Community Considerations (Teacher Notes) (Assessing the Feasibility of Wind Power for Pennsylvania) Notes on Part 1 A Beaufort scale is included on the next page
Speed Control of Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine
 Speed Control of Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine G Priyadharshini 1, E Pavithra 2, M Sanjay 3 1,2,3Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology, Erode, India ---------------------------------------------------------------------***---------------------------------------------------------------------
Speed Control of Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine G Priyadharshini 1, E Pavithra 2, M Sanjay 3 1,2,3Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology, Erode, India ---------------------------------------------------------------------***---------------------------------------------------------------------
Windmills using aerodynamic drag as propelling force; a hopeless concept. ing. A. Kragten. April 2009 KD 416
 Windmills using aerodynamic drag as propelling force; a hopeless concept It is allowed to copy this report for private use. ing. A. Kragten April 2009 KD 416 Engineering office Kragten Design Populierenlaan
Windmills using aerodynamic drag as propelling force; a hopeless concept It is allowed to copy this report for private use. ing. A. Kragten April 2009 KD 416 Engineering office Kragten Design Populierenlaan
Test Summary Report Giraffe 2.0 Hybrid Wind-Solar Power Station - for wind: according to IEC Annex M - for solar: measurement report
 Contact person Tanja Tränkle 2016-06-29 4P05805-R01 rev. 1 1 (7) Safety +46 10 516 57 19 Tanja.Trankle@sp.se Innoventum AB Morgan Widung / Marcus Ulmefors Turning Torso office 275 Lilla Varvsgatan 14 211
Contact person Tanja Tränkle 2016-06-29 4P05805-R01 rev. 1 1 (7) Safety +46 10 516 57 19 Tanja.Trankle@sp.se Innoventum AB Morgan Widung / Marcus Ulmefors Turning Torso office 275 Lilla Varvsgatan 14 211
ì<(sk$m)=bdiiid< +^-Ä-U-Ä-U
 Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Cause and Effect Captions Text Boxes Call Outs Glossary Natural Resources Scott Foresman Science 4.10 ì
Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Cause and Effect Captions Text Boxes Call Outs Glossary Natural Resources Scott Foresman Science 4.10 ì
As the Rotor Turns: Wind Power & You (Student Handout) (An Investigation of Wind Power as an Energy Resource in Pennsylvania)
 As the Rotor Turns: Wind Power & You (Student Handout) (An Investigation of Wind Power as an Energy Resource in Pennsylvania) Part 1: How is wind created? 1. Use the scale above to make an observation
As the Rotor Turns: Wind Power & You (Student Handout) (An Investigation of Wind Power as an Energy Resource in Pennsylvania) Part 1: How is wind created? 1. Use the scale above to make an observation
Increasing the power output of the Darrieus Vertical Axis Wind Turbine
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36. Increasing the power output of the Darrieus Vertical Axis Wind Turbine R. Ramkissoon 1 and K. Manohar
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36. Increasing the power output of the Darrieus Vertical Axis Wind Turbine R. Ramkissoon 1 and K. Manohar
Research on Small Wind Power System Based on H-type Vertical Wind Turbine Rong-Qiang GUAN a, Jing YU b
 06 International Conference on Mechanics Design, Manufacturing and Automation (MDM 06) ISBN: 978--60595-354-0 Research on Small Wind Power System Based on H-type Vertical Wind Turbine Rong-Qiang GUAN a,
06 International Conference on Mechanics Design, Manufacturing and Automation (MDM 06) ISBN: 978--60595-354-0 Research on Small Wind Power System Based on H-type Vertical Wind Turbine Rong-Qiang GUAN a,
FABRICATION OF VERTICAL AXIS WIND TURBINE WITH WIND REDUCER AND EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS
 87 CHAPTER-4 FABRICATION OF VERTICAL AXIS WIND TURBINE WITH WIND REDUCER AND EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS 88 CHAPTER-4 FABRICATION OF VERTICAL AXIS WIND TURBINE WITH WIND REDUCER AND EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS
87 CHAPTER-4 FABRICATION OF VERTICAL AXIS WIND TURBINE WITH WIND REDUCER AND EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS 88 CHAPTER-4 FABRICATION OF VERTICAL AXIS WIND TURBINE WITH WIND REDUCER AND EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS
Weightlifter Nacelle Only
 Weightlifter Nacelle Only i n s t r u c t i o n s About KidWind The KidWind Project is a team of teachers, students, engineers, and practitioners exploring the science behind wind energy in classrooms
Weightlifter Nacelle Only i n s t r u c t i o n s About KidWind The KidWind Project is a team of teachers, students, engineers, and practitioners exploring the science behind wind energy in classrooms
Terms and Definitions for Small Wind Site Assessor
 Terms and Definitions for Small Wind Site Assessor AEO/ AEP: Annual energy output, also known as AEP, annual energy production of the wind electric system. Alpha: Surface friction coefficient, used to
Terms and Definitions for Small Wind Site Assessor AEO/ AEP: Annual energy output, also known as AEP, annual energy production of the wind electric system. Alpha: Surface friction coefficient, used to
Urban wind turbines do they have a future? Or will they be white elephants?
 Urban wind turbines do they have a future? Or will they be white elephants? Presented by Brian Kirke As part of the What On Earth series, UniSA, 1 November 2012 WWEA* is optimistic about small wind (defined
Urban wind turbines do they have a future? Or will they be white elephants? Presented by Brian Kirke As part of the What On Earth series, UniSA, 1 November 2012 WWEA* is optimistic about small wind (defined
Exploring Wind Energy
 2013-2014 Exploring Wind Energy Student Guide SECONDARY Introduction to Wind What is Wind? Wind is simply air in motion. It is produced by the uneven heating of the Earth s surface by energy from the sun.
2013-2014 Exploring Wind Energy Student Guide SECONDARY Introduction to Wind What is Wind? Wind is simply air in motion. It is produced by the uneven heating of the Earth s surface by energy from the sun.
PRELIMINARY PROJECT EVALUATION OF TWISTED SAVONIUS WIND TURBINE
 2009 Vertical Wind Energy Engineering Ian Duffett 009723628 Jeff Perry 200211837 Blaine Stockwood 009224597 Jeremy Wiseman - 200336428 PRELIMINARY PROJECT EVALUATION OF TWISTED SAVONIUS WIND TURBINE Initial
2009 Vertical Wind Energy Engineering Ian Duffett 009723628 Jeff Perry 200211837 Blaine Stockwood 009224597 Jeremy Wiseman - 200336428 PRELIMINARY PROJECT EVALUATION OF TWISTED SAVONIUS WIND TURBINE Initial
Courseware Sample F0
 Electric Power / Controls Courseware Sample 85303-F0 A ELECTRIC POWER / CONTROLS COURSEWARE SAMPLE by the Staff of Lab-Volt Ltd. Copyright 2009 Lab-Volt Ltd. All rights reserved. No part of this publication
Electric Power / Controls Courseware Sample 85303-F0 A ELECTRIC POWER / CONTROLS COURSEWARE SAMPLE by the Staff of Lab-Volt Ltd. Copyright 2009 Lab-Volt Ltd. All rights reserved. No part of this publication
Challenges in the Quest for Clean Energies
 Challenges in the Quest for Clean Energies 3. Wind Technologies Sheela K Ramasesha Sheela K Ramasesha is currently working on renewable energy technologies with primary focus on photovoltaics at Divecha
Challenges in the Quest for Clean Energies 3. Wind Technologies Sheela K Ramasesha Sheela K Ramasesha is currently working on renewable energy technologies with primary focus on photovoltaics at Divecha
Rural Small Wind Energy:
 Rural Small Wind Energy: Resource Overview and System Components Phil Hofmeyer, Ph.D. Asst. Professor of Renewable Energy Morrisville State College MVCC Small Wind Energy Conference June 27, 2009 Hi, I
Rural Small Wind Energy: Resource Overview and System Components Phil Hofmeyer, Ph.D. Asst. Professor of Renewable Energy Morrisville State College MVCC Small Wind Energy Conference June 27, 2009 Hi, I
Outline. Wind Turbine Siting. Roughness. Wind Farm Design 4/7/2015
 Wind Turbine Siting Andrew Kusiak 2139 Seamans Center Iowa City, Iowa 52242-1527 andrew-kusiak@uiowa.edu Tel: 319-335-5934 Fax: 319-335-5669 http://www.icaen.uiowa.edu/~ankusiak Terrain roughness Escarpments
Wind Turbine Siting Andrew Kusiak 2139 Seamans Center Iowa City, Iowa 52242-1527 andrew-kusiak@uiowa.edu Tel: 319-335-5934 Fax: 319-335-5669 http://www.icaen.uiowa.edu/~ankusiak Terrain roughness Escarpments
A Numerical Simulation Comparing the Efficiencies of Tubercle Versus Straight Leading Edge Airfoils for a Darrieus Vertical Axis Wind Turbine
 A Numerical Simulation Comparing the Efficiencies of Tubercle Versus Straight Leading Edge Airfoils for a Darrieus Vertical Axis Wind Turbine By: Ross Neal Abstract: The efficiencies of sinusoidal and
A Numerical Simulation Comparing the Efficiencies of Tubercle Versus Straight Leading Edge Airfoils for a Darrieus Vertical Axis Wind Turbine By: Ross Neal Abstract: The efficiencies of sinusoidal and
Influence of the Number of Blades on the Mechanical Power Curve of Wind Turbines
 European Association for the Development of Renewable Energies, Environment and Power quality International Conference on Renewable Energies and Power Quality (ICREPQ 9) Valencia (Spain), 15th to 17th
European Association for the Development of Renewable Energies, Environment and Power quality International Conference on Renewable Energies and Power Quality (ICREPQ 9) Valencia (Spain), 15th to 17th
CHAPTER 9 PROPELLERS
 CHAPTER 9 CHAPTER 9 PROPELLERS CONTENTS PAGE How Lift is Generated 02 Helix Angle 04 Blade Angle of Attack and Helix Angle Changes 06 Variable Blade Angle Mechanism 08 Blade Angles 10 Blade Twist 12 PROPELLERS
CHAPTER 9 CHAPTER 9 PROPELLERS CONTENTS PAGE How Lift is Generated 02 Helix Angle 04 Blade Angle of Attack and Helix Angle Changes 06 Variable Blade Angle Mechanism 08 Blade Angles 10 Blade Twist 12 PROPELLERS
Job Sheet 1 Blade Aerodynamics
 Job Sheet 1 Blade Aerodynamics The rotor is the most important part of a wind turbine. It is through the rotor that the energy of the wind is converted into mechanical energy, which turns the main shaft
Job Sheet 1 Blade Aerodynamics The rotor is the most important part of a wind turbine. It is through the rotor that the energy of the wind is converted into mechanical energy, which turns the main shaft
青岛宝通进出口贸易有限公司. Wind Products List and Introductions
 Wind Products List and Introductions 400W Wind Turbine e 1.1 400W diffuse wind turbine technical parameters Blade material & quality Reinforced fiber glass*8 Wind rotor diameter (m) 1.25 Rated power/maximum
Wind Products List and Introductions 400W Wind Turbine e 1.1 400W diffuse wind turbine technical parameters Blade material & quality Reinforced fiber glass*8 Wind rotor diameter (m) 1.25 Rated power/maximum
BMM4753 RENEWABLE ENERGY RESOURCES
 BMM4753 RENEWABLE ENERGY RESOURCES Prof Dr Shahrani Haji Anuar Energy Sustainability Focus Group 1 Summary 5.1 Introduction 5.2 Overview 5.3 Formation of wind 5.4 Classification of wind 5.5 Factors affecting
BMM4753 RENEWABLE ENERGY RESOURCES Prof Dr Shahrani Haji Anuar Energy Sustainability Focus Group 1 Summary 5.1 Introduction 5.2 Overview 5.3 Formation of wind 5.4 Classification of wind 5.5 Factors affecting
Aerodynamic principle
 Aerodynamic principle In this document, I want to give you a short overview about the different aerodynamical principles based on which wind turbines and EneBird Wind Power Plants work. You won't need
Aerodynamic principle In this document, I want to give you a short overview about the different aerodynamical principles based on which wind turbines and EneBird Wind Power Plants work. You won't need
Design of a Microcontroller-Based Pitch Angle Controller for a Wind Powered Generator
 Journal of Engineering and Science Research 1 (2): 133-138, e-issn RMP Publications, DOI: Design of a Microcontroller-Based Pitch Angle Controller for a Wind Powered Generator Glenn V. Magwili, Michael
Journal of Engineering and Science Research 1 (2): 133-138, e-issn RMP Publications, DOI: Design of a Microcontroller-Based Pitch Angle Controller for a Wind Powered Generator Glenn V. Magwili, Michael
Introduction to Wind Energy Systems
 Introduction to Wind Energy Systems Hermann-Josef Wagner Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economy Ruhr-University Bochum, Germany lee@lee.rub.de Summer School of Physical Societies, Varenna 01.08.2012
Introduction to Wind Energy Systems Hermann-Josef Wagner Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economy Ruhr-University Bochum, Germany lee@lee.rub.de Summer School of Physical Societies, Varenna 01.08.2012
Power curves - use of spinner anemometry. Troels Friis Pedersen DTU Wind Energy Professor
 Power curves - use of spinner anemometry Troels Friis Pedersen DTU Wind Energy Professor Spinner anemometry using the airflow over the spinner to measure wind speed, yaw misalignment and flow inclination
Power curves - use of spinner anemometry Troels Friis Pedersen DTU Wind Energy Professor Spinner anemometry using the airflow over the spinner to measure wind speed, yaw misalignment and flow inclination
International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology Vol. 2, Issue 5, May 2013
 PERFORMANCE PREDICTION OF HORIZONTAL AXIS WIND TURBINE BLADE HardikPatel 1, SanatDamania 2 Master of Engineering Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Government Engineering College, Valsad, Gujarat,
PERFORMANCE PREDICTION OF HORIZONTAL AXIS WIND TURBINE BLADE HardikPatel 1, SanatDamania 2 Master of Engineering Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Government Engineering College, Valsad, Gujarat,
Wind Power. Kevin Clifford METR 112 April 19, 2011
 Wind Power Kevin Clifford METR 112 April 19, 2011 Outline Introduction Wind Turbines Determining Wind Power Output The Price of Wind Power Wind Power Availability across the World and US California Wind
Wind Power Kevin Clifford METR 112 April 19, 2011 Outline Introduction Wind Turbines Determining Wind Power Output The Price of Wind Power Wind Power Availability across the World and US California Wind
Efficiency Improvement of a New Vertical Axis Wind Turbine by Individual Active Control of Blade Motion
 Efficiency Improvement of a New Vertical Axis Wind Turbine by Individual Active Control of Blade Motion In Seong Hwang, Seung Yong Min, In Oh Jeong, Yun Han Lee and Seung Jo Kim* School of Mechanical &
Efficiency Improvement of a New Vertical Axis Wind Turbine by Individual Active Control of Blade Motion In Seong Hwang, Seung Yong Min, In Oh Jeong, Yun Han Lee and Seung Jo Kim* School of Mechanical &
Wind loads investigations of HAWT with wind tunnel tests and site measurements
 loads investigations of HAWT with wind tunnel tests and site measurements Shigeto HIRAI, Senior Researcher, Nagasaki R&D Center, Technical Headquarters, MITSUBISHI HEAVY INDSUTRIES, LTD, Fukahori, Nagasaki,
loads investigations of HAWT with wind tunnel tests and site measurements Shigeto HIRAI, Senior Researcher, Nagasaki R&D Center, Technical Headquarters, MITSUBISHI HEAVY INDSUTRIES, LTD, Fukahori, Nagasaki,
Designing Wave Energy Converting Device. Jaimie Minseo Lee. The Academy of Science and Technology The Woodlands College Park High School, Texas
 Designing Wave Energy Converting Device Jaimie Minseo Lee The Academy of Science and Technology The Woodlands College Park High School, Texas Table of Contents Abstract... i 1.0 Introduction... 1 2.0 Test
Designing Wave Energy Converting Device Jaimie Minseo Lee The Academy of Science and Technology The Woodlands College Park High School, Texas Table of Contents Abstract... i 1.0 Introduction... 1 2.0 Test
Comparison of Wind Turbines Regarding their Energy Generation.
 Comparison of Wind Turbines Regarding their Energy Generation. P. Mutschler, Member, EEE, R. Hoffmann Department of Power Electronics and Control of Drives Darmstadt University of Technology Landgraf-Georg-Str.
Comparison of Wind Turbines Regarding their Energy Generation. P. Mutschler, Member, EEE, R. Hoffmann Department of Power Electronics and Control of Drives Darmstadt University of Technology Landgraf-Georg-Str.
DESIGN, DEVELOPMENT, FABRICATION AND TESTING OF SMALL VERTICAL AXIS WIND TURBINE USING 7% CAMBERED PLATE
 DESIGN, DEVELOPMENT, FABRICATION AND TESTING OF SMALL VERTICAL AXIS WIND TURBINE USING 7% CAMBERED PLATE Vilas Warudkar *, Baijnath Ahirwar, Dharmendra Kumar Shah and Siraj Ahmed Department of Mechanical
DESIGN, DEVELOPMENT, FABRICATION AND TESTING OF SMALL VERTICAL AXIS WIND TURBINE USING 7% CAMBERED PLATE Vilas Warudkar *, Baijnath Ahirwar, Dharmendra Kumar Shah and Siraj Ahmed Department of Mechanical
Exercise 3. Power Versus Wind Speed EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION OUTLINE. Air density DISCUSSION
 Exercise 3 Power Versus Wind Speed EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will know how to calculate the power contained in the wind, and how wind power varies with wind speed. You
Exercise 3 Power Versus Wind Speed EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will know how to calculate the power contained in the wind, and how wind power varies with wind speed. You
V MW. Exceptional performance and reliability at high-wind-speed sites. vestas.com
 V90-3.0 MW Exceptional performance and reliability at high-wind-speed sites vestas.com We deliver on the promise of wind power SUPERIOR YIELD AT HIGH-WIND-SPEED SITES High standards for weight and performance
V90-3.0 MW Exceptional performance and reliability at high-wind-speed sites vestas.com We deliver on the promise of wind power SUPERIOR YIELD AT HIGH-WIND-SPEED SITES High standards for weight and performance
Technology Fundamentals Wind turbines
 In the first in a new series, John Twidell explains the fundamentals of wind power technology. He summarizes the engineering and operational principles of wind turbines, and looks at some of the latest
In the first in a new series, John Twidell explains the fundamentals of wind power technology. He summarizes the engineering and operational principles of wind turbines, and looks at some of the latest
2MW baseline wind turbine: model development and verification (WP1) The University of Tokyo & Hitachi, Ltd.
 2MW baseline wind turbine: model development and verification (WP1) The University of Tokyo & Hitachi, Ltd. Downwind turbine technology, IEA Wind Task 40 First Progress Meeting, Tokyo, Japan 11 Dec, 2017
2MW baseline wind turbine: model development and verification (WP1) The University of Tokyo & Hitachi, Ltd. Downwind turbine technology, IEA Wind Task 40 First Progress Meeting, Tokyo, Japan 11 Dec, 2017
Fontes Renováveis Não-Convencionais. Parte II
 Fontes Renováveis Não-Convencionais Parte II Prof. Antonio Simões Costa Prof. Tom Overbye, U. of Illinois Power in the Wind Consider the kinetic energy of a packet of air with mass m moving at velocity
Fontes Renováveis Não-Convencionais Parte II Prof. Antonio Simões Costa Prof. Tom Overbye, U. of Illinois Power in the Wind Consider the kinetic energy of a packet of air with mass m moving at velocity
ROTORS for WIND POWER
 ROTORS for WIND POWER P.T. Smulders Wind Energy Group Faculty of Physics University of Technology, Eindhoven ARRAKIS 1 st edition October 1991 revised edition January 2004 CONTENTS ROTORS for WIND POWER...
ROTORS for WIND POWER P.T. Smulders Wind Energy Group Faculty of Physics University of Technology, Eindhoven ARRAKIS 1 st edition October 1991 revised edition January 2004 CONTENTS ROTORS for WIND POWER...
Chapter 2 Wind: Origin and Local Effects
 Chapter 2 Wind: Origin and Local Effects All renewable energy (except tidal and geothermal power), and even the energy in fossil fuels, ultimately comes from the sun. About 1 2 % of the energy coming from
Chapter 2 Wind: Origin and Local Effects All renewable energy (except tidal and geothermal power), and even the energy in fossil fuels, ultimately comes from the sun. About 1 2 % of the energy coming from
Sheet 7 The Wind Turbine
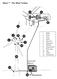 Sheet 7 The Wind Turbine 1. Blade 2. Rotor 3. Pitch 4. Shaft 5. Gear box 6. Generator 7. Nacelle 8. Anemometer 9. Wind vane 10. Yaw 11. Tower 12. Foundations Name: Date: Sheet 8 How a Turbine Works Look
Sheet 7 The Wind Turbine 1. Blade 2. Rotor 3. Pitch 4. Shaft 5. Gear box 6. Generator 7. Nacelle 8. Anemometer 9. Wind vane 10. Yaw 11. Tower 12. Foundations Name: Date: Sheet 8 How a Turbine Works Look
General Specification. V MW 60 Hz OptiSlip Wind Turbine. Item no R3 Class 1
 General Specification V80 1.8 MW 60 Hz OptiSlip Wind Turbine Item no. 944411.R3 Class 1 (6a) Date: 28. May 2002 Class: 1 Item no.: 944411.R3 Page: 2 of 18 Contents... Page 1. Introduction...3 2. Wind Climate...3
General Specification V80 1.8 MW 60 Hz OptiSlip Wind Turbine Item no. 944411.R3 Class 1 (6a) Date: 28. May 2002 Class: 1 Item no.: 944411.R3 Page: 2 of 18 Contents... Page 1. Introduction...3 2. Wind Climate...3
Wind Energy for Kids
 Wind Energy for Kids 1 What is wind power? Inside this pack you will find out what makes the wind blow, how a modern wind turbine makes electricity, how we measure the speed and direction of the wind,
Wind Energy for Kids 1 What is wind power? Inside this pack you will find out what makes the wind blow, how a modern wind turbine makes electricity, how we measure the speed and direction of the wind,
Dick Bowdler Acoustic Consultant
 Dick Bowdler Acoustic Consultant 01383 882 644 077 8535 2534 dick@dickbowdler.co.uk WIND SHEAR AND ITS EFFECT ON NOISE ASSESSMENT OF WIND TURBINES June 2009 The Haven, Low Causeway, Culross, Fife. KY12
Dick Bowdler Acoustic Consultant 01383 882 644 077 8535 2534 dick@dickbowdler.co.uk WIND SHEAR AND ITS EFFECT ON NOISE ASSESSMENT OF WIND TURBINES June 2009 The Haven, Low Causeway, Culross, Fife. KY12
The Wind Resource: Prospecting for Good Sites
 The Wind Resource: Prospecting for Good Sites Bruce Bailey, President AWS Truewind, LLC 255 Fuller Road Albany, NY 12203 bbailey@awstruewind.com Talk Topics Causes of Wind Resource Impacts on Project Viability
The Wind Resource: Prospecting for Good Sites Bruce Bailey, President AWS Truewind, LLC 255 Fuller Road Albany, NY 12203 bbailey@awstruewind.com Talk Topics Causes of Wind Resource Impacts on Project Viability
Centre for Offshore Renewable Energy Engineering, School of Energy, Environment and Agrifood, Cranfield University, Cranfield, MK43 0AL, UK 2
 Fluid Structure Interaction Modelling of A Novel 10MW Vertical-Axis Wind Turbine Rotor Based on Computational Fluid Dynamics and Finite Element Analysis Lin Wang 1*, Athanasios Kolios 1, Pierre-Luc Delafin
Fluid Structure Interaction Modelling of A Novel 10MW Vertical-Axis Wind Turbine Rotor Based on Computational Fluid Dynamics and Finite Element Analysis Lin Wang 1*, Athanasios Kolios 1, Pierre-Luc Delafin
Wind Turbine on Telecom Tower
 Wind Turbine on Telecom Tower Load Estimation and Structural Design Approach Anil Agarwal (IIT Hyderabad) Srinivas Aluri (Hara Industries) Project overview 2 Motivation Telecom towers get average 13.5
Wind Turbine on Telecom Tower Load Estimation and Structural Design Approach Anil Agarwal (IIT Hyderabad) Srinivas Aluri (Hara Industries) Project overview 2 Motivation Telecom towers get average 13.5
Efficiency of Upwind and Downwind Thai Sail Windmill
 Journal of Engineering and Science Research 1 (2): 01-06, 2017 e-issn 2289-7127 RMP Publications, 2017 DOI: 10.26666/rmp.jesr.2017.2.1 Efficiency of Upwind and Downwind Thai Sail Windmill Teerawat Klabklay
Journal of Engineering and Science Research 1 (2): 01-06, 2017 e-issn 2289-7127 RMP Publications, 2017 DOI: 10.26666/rmp.jesr.2017.2.1 Efficiency of Upwind and Downwind Thai Sail Windmill Teerawat Klabklay
A Novel Vertical-Axis Wind Turbine for Distributed & Utility Deployment
 A Novel Vertical-Axis Wind Turbine for Distributed & Utility Deployment J.-Y. Park*, S. Lee* +, T. Sabourin**, K. Park** * Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Inha University, Korea + KR Wind Energy Research
A Novel Vertical-Axis Wind Turbine for Distributed & Utility Deployment J.-Y. Park*, S. Lee* +, T. Sabourin**, K. Park** * Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Inha University, Korea + KR Wind Energy Research
Optimization of Blades of Horizontal Wind Turbines by Choosing an Appropriate Airfoil and Computer Simulation
 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2017 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Optimization
International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2017 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Optimization
Detailed study 3.4 Topic Test Investigations: Flight
 Name: Billanook College Detailed study 3.4 Topic Test Investigations: Flight Ivanhoe Girls Grammar School Questions 1 and 2 relate to the information shown in the diagram in Figure 1. z Question 1 y Figure
Name: Billanook College Detailed study 3.4 Topic Test Investigations: Flight Ivanhoe Girls Grammar School Questions 1 and 2 relate to the information shown in the diagram in Figure 1. z Question 1 y Figure
DEFINITIONS. Aerofoil
 Aerofoil DEFINITIONS An aerofoil is a device designed to produce more lift (or thrust) than drag when air flows over it. Angle of Attack This is the angle between the chord line of the aerofoil and the
Aerofoil DEFINITIONS An aerofoil is a device designed to produce more lift (or thrust) than drag when air flows over it. Angle of Attack This is the angle between the chord line of the aerofoil and the
Preliminary Research on Modelling and Control of Two Line Kites for Power Generation
 Preliminary Research on Modelling and Control of Two Line Kites for Power Generation Ashley Yan Electrical Engineering Department Unitec Institute of Technology Private Bag 92025, Victoria Street West,
Preliminary Research on Modelling and Control of Two Line Kites for Power Generation Ashley Yan Electrical Engineering Department Unitec Institute of Technology Private Bag 92025, Victoria Street West,
PATENT AGENT EXAMINATION PAPER A
 Page 1 of 21 PATENT AGENT EXAMINATION PAPER A 2009 Dear Candidate, Paper A is a patent drafting exercise in which the candidate is requested to prepare a full patent specification, with significant weight
Page 1 of 21 PATENT AGENT EXAMINATION PAPER A 2009 Dear Candidate, Paper A is a patent drafting exercise in which the candidate is requested to prepare a full patent specification, with significant weight
Low Wind High Yields Series
 Low Wind High Yields Series Wind Turbines USER S MANUAL Introduction Low Wind High Yields Series rotor blades apply the latest advanced thermoplastic engineering and are manufactured by precision injection
Low Wind High Yields Series Wind Turbines USER S MANUAL Introduction Low Wind High Yields Series rotor blades apply the latest advanced thermoplastic engineering and are manufactured by precision injection
Power efficiency and aerodynamic forces measurements on the Dettwiler-wind turbine
 Institut für Fluiddynamik ETH Zentrum, ML H 33 CH-8092 Zürich P rof. Dr. Thomas Rösgen Sonneggstrasse 3 Telefon +41-44-632 2646 Fax +41-44-632 1147 roesgen@ifd.mavt.ethz.ch www.ifd.mavt.ethz.ch Power efficiency
Institut für Fluiddynamik ETH Zentrum, ML H 33 CH-8092 Zürich P rof. Dr. Thomas Rösgen Sonneggstrasse 3 Telefon +41-44-632 2646 Fax +41-44-632 1147 roesgen@ifd.mavt.ethz.ch www.ifd.mavt.ethz.ch Power efficiency
Development and evaluation of a pitch regulator for a variable speed wind turbine PINAR TOKAT
 Development and evaluation of a pitch regulator for a variable speed wind turbine PINAR TOKAT Department of Energy and Environment Division of Electric Power Engineering CHALMERS UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Development and evaluation of a pitch regulator for a variable speed wind turbine PINAR TOKAT Department of Energy and Environment Division of Electric Power Engineering CHALMERS UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Alstom Ocean Energy Path towards Industrailsation. Ken Street 18 th April 2013
 Alstom Ocean Energy Path towards Industrailsation Ken Street 18 th April 2013 Three main activities in four Sectors Equipment & services for power generation Equipment & services for rail transport ALSTOM
Alstom Ocean Energy Path towards Industrailsation Ken Street 18 th April 2013 Three main activities in four Sectors Equipment & services for power generation Equipment & services for rail transport ALSTOM
Wind power generation
 6.2 Wind power generation Wind energy was the source of power for sailing ships and has been used for at least 3,000 years in windmills. However, this form of energy fell into disuse with the spread of
6.2 Wind power generation Wind energy was the source of power for sailing ships and has been used for at least 3,000 years in windmills. However, this form of energy fell into disuse with the spread of
Introduction to Pumps
 Introduction to Pumps 1 Introduction to Pumps 1.0 INTRODUCTION There are many different types of pump now available for use in pumped fluid systems. A knowledge of these pump types and their performance
Introduction to Pumps 1 Introduction to Pumps 1.0 INTRODUCTION There are many different types of pump now available for use in pumped fluid systems. A knowledge of these pump types and their performance
Energy capture performance
 Energy capture performance Cost of energy is a critical factor to the success of marine renewables, in order for marine renewables to compete with other forms of renewable and fossil-fuelled power generation.
Energy capture performance Cost of energy is a critical factor to the success of marine renewables, in order for marine renewables to compete with other forms of renewable and fossil-fuelled power generation.
7 th International Conference on Wind Turbine Noise Rotterdam 2 nd to 5 th May 2017
 7 th International Conference on Wind Turbine Noise Rotterdam 2 nd to 5 th May 2017 Sound power level measurements 3.0 ir. L.M. Eilders, Peutz bv: l.eilders@peutz.nl ing. E.H.A. de Beer, Peutz bv: e.debeer@peutz.nl
7 th International Conference on Wind Turbine Noise Rotterdam 2 nd to 5 th May 2017 Sound power level measurements 3.0 ir. L.M. Eilders, Peutz bv: l.eilders@peutz.nl ing. E.H.A. de Beer, Peutz bv: e.debeer@peutz.nl
A NOVEL FLOATING OFFSHORE WIND TURBINE CONCEPT: NEW DEVELOPMENTS
 A NOVEL FLOATING OFFSHORE WIND TURBINE CONCEPT: NEW DEVELOPMENTS L. Vita, U.S.Paulsen, T.F.Pedersen Risø-DTU Technical University of Denmark, Roskilde, Denmark luca.vita@risoe.dk Abstract: A novel concept
A NOVEL FLOATING OFFSHORE WIND TURBINE CONCEPT: NEW DEVELOPMENTS L. Vita, U.S.Paulsen, T.F.Pedersen Risø-DTU Technical University of Denmark, Roskilde, Denmark luca.vita@risoe.dk Abstract: A novel concept
Analysis of Traditional Yaw Measurements
 Analysis of Traditional Yaw Measurements Curiosity is the very basis of education and if you tell me that curiosity killed the cat, I say only the cat died nobly. Arnold Edinborough Limitations of Post-
Analysis of Traditional Yaw Measurements Curiosity is the very basis of education and if you tell me that curiosity killed the cat, I say only the cat died nobly. Arnold Edinborough Limitations of Post-
Chain Drives. 1. As no slip takes place during chain drive, hence perfect velocity ratio is obtained
 1. Introduction Chain Drives In Belt and Rope drives slipping may occur. In order to avoid slipping, steel chains are used. The chains are made up of a number of rigid links which are hinged together by
1. Introduction Chain Drives In Belt and Rope drives slipping may occur. In order to avoid slipping, steel chains are used. The chains are made up of a number of rigid links which are hinged together by
Design and fabrication and testing of a low speed wind turbine generator using tapered type rotor blade made from fibre reinforced plastic
 International Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy 2014; 3(1): 20-25 Published online February 20, 2014 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijrse) doi: 10.11648/j.ijrse.20140301.14 Design and
International Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy 2014; 3(1): 20-25 Published online February 20, 2014 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijrse) doi: 10.11648/j.ijrse.20140301.14 Design and
firefly Class Pack Materials for 10 fireflies or Students Activity Guide Grades Time required Concepts Objectives 45 minutes to 1 hour
 firefly Class Pack Activity Guide Materials for 10 fireflies or 10 30 Students Grades 3 12 Concepts Math Forces and Motion Earth Science Energy and Transformations Engineering, Art, and Design Using Basic
firefly Class Pack Activity Guide Materials for 10 fireflies or 10 30 Students Grades 3 12 Concepts Math Forces and Motion Earth Science Energy and Transformations Engineering, Art, and Design Using Basic
POWERED FLIGHT HOVERING FLIGHT
 Once a helicopter leaves the ground, it is acted upon by the four aerodynamic forces. In this chapter, we will examine these forces as they relate to flight maneuvers. POWERED FLIGHT In powered flight
Once a helicopter leaves the ground, it is acted upon by the four aerodynamic forces. In this chapter, we will examine these forces as they relate to flight maneuvers. POWERED FLIGHT In powered flight
Energy Output. Outline. Characterizing Wind Variability. Characterizing Wind Variability 3/7/2015. for Wind Power Management
 Energy Output for Wind Power Management Spring 215 Variability in wind Distribution plotting Mean power of the wind Betz' law Power density Power curves The power coefficient Calculator guide The power
Energy Output for Wind Power Management Spring 215 Variability in wind Distribution plotting Mean power of the wind Betz' law Power density Power curves The power coefficient Calculator guide The power
