INSPECTION OF MEDICAL DEVICES
|
|
|
- Gerard Glenn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 INSPECTION OF MEDICAL DEVICES Safety And Maintenance For Industrial Systems Sapienza Università di Roma, Ing. Silvia Ruggieri 1
2 Safe MD development Physiological effects of electricity and Consequences of dangerous voltage IEC vs. IEC Commonly used terms and definitions How is testing performed? Final test AGENDA 2
3 Achievements: Significant improvement of health care in all medical specialties Reducing the number of seriously ill people Reduction of mortality Consequences: increased complexity of medical devices and their applications increased incidence of adverse effects of implementation of MD in the U.S. approx. 10,000 cases of patient injury due to the application of MT MEDICAL DEVICES 3
4 Causes of unintended consequences: improper handling insufficient or improper staff practice (training) in handling with MD insufficient experience example, medical staff rarely read manuals for the users (User Manual) equipment malfunction Demand for MD developers: developement of safe devices (failure-safe) MEDICAL DEVICES 4
5 In a clinical environment patient is exposed to various risks, more than a typical workplace or at home frequent invasive (blood) operations - penetration through skin or mucous membranes presence of potentially hazardous chemicals and substances - anesthetics, medicines, medical gases sources of infection - particularly "hospital infection" various sources of energy that penetrate into or through the patient: current, voltage, ionizing and non-ionizing radiation, sound and ultrasound, electric and magnetic field, UV radiation, lasers, microwave radiation, mechanical stress, etc. DANGER TO PATIENTS 5
6 Electrical MD security is considered: physiological effects of electricity possibility (risk) of failures and their consequences methods of patients and staff protection standards describing electrical safety electrical safety testing modes Understanding the possible dangers and risks Implementation in achieving security SAFE MD DEVELOPMENT 6
7 Body (tissue) becoming a part of an electrical circuit The amount (amplitude) of electricity often depends on the ratio of voltage present and the sum of all (serially connected) impedance Usually, the highest impedance is the impedance of the skin The consequence of current flow: nerve and/or muscle tissue stimulation heating of tissues (a result of tissue resistance) burns PHYSIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF ELECTRICITY 7
8 I t curves for sensory and motor responses PULSED CURRENT 8
9 Further consideration are based on the following parameters Human body with contact to el. circuit at left and right hand Body weight: 70 kg Applied current time: 1 s to 3 s Current frequency: 60 Hz PHYSIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF CURRENT 9
10 THRESHOLD OF PERCEPTION Current density is just large enough to excite nerve endings in the skin Subject feels tingling sensation Lowes values with moistered hands (decreases contact resistance): 0.5 ma at 60 Hz 2 ma to 10 ma DC The subject meight feel a slight warming PHYSIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF CURRENT (1) 10
11 LET-GO CURRENT The let-go current is defined as the maximal current at which the subject can withdraw voluntarily For higher current nerves and muscles are vigorously stimulated Involuntary contraction or reflex withdrawals may cause secondary physical injuries (falling off the ladder) The minimal threshold for the let-go current is 6 ma PHYSIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF CURRENT (2) 11
12 RESPIRATORY PARALYSIS, PAIN, FATIGUE Higher current causes involuntary contraction of muscles and stimulation of nerves what can lead to pain and cause fatigue Example: stimulation of respiratory muscles lead to involuntary contraction with the result of asphyxiation if current is not interrupted Of course, today s ethics commission would never allow these experiments on human beings. PHYSIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF CURRENT (3) 12
13 VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION The heart is especially susceptible to electric current. Just 75 ma to 400 ma (AC) can rapidly disorganize the cardiac rhythm and death occurs within minutes Only a brief high-current pulse from a defibrillator can depolarize all the cells of the heart muscle simultaneously Within the U.S. occur approximately 1,000 death per year due to cord-connected appliances PHYSIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF CURRENT (4) 13
14 SUSTAINED MYOCARDIAL CONTRACTION When current is high enough to stimulate the entire heart muscle, it stops beating Usually the heart-beat ensues when the current is interrupted Minimal currents range from 1 A to 6 A (AC), like used in defibrillators PHYSIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF CURRENT (5) 14
15 BURNS AND PHYSICAL INJURY Resistive heating cause burns Current can puncture the skin Brain and nerve tissue may lose all functional excitability Simultaneously stimulated muscles may contract strong enough to pull the attachment away from the bone or bread the bone PHYSIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF CURRENT (6) 15
16 Unintended consequences are usually a result of human involvement in the circuit, in some way connecting to the grid (inattention, failure) Several levels of action perception contractions (let-go) paralysis (respiratory), pain, fatigue ventricular fibrillation tetanic contraction burns and physical injuries ELECTRICITY GRID 16
17 Fibrilation Convulsion Consequences depende on the voltage current relation, but also on individual susceptibility Expected values Intact skin R K = 2~5 kω Damaged skin - injuries, surgical procedures R O = 100Ω ~ 1kΩ CONSEQUENCES OF DANGEROUS VOLTAGE 17
18 Fibrilation Convulsion Focus on the worst possible scenario, for example, a person holding two conductors at different potentials in his hands resulting muscle spasms, inability to release captured conductors In case of intact skin, R ext = 2~5 kω, cramps can occur even at a voltage of few dozen ma In case of damaged skin - injuries, surgical procedures, R int = 100Ω ~ 1kΩ, fibrillation may occur at voltages of several volts and current of few dozen ma CONSEQUENCES OF DANGEROUS VOLTAGE 18
19 The consequences of current passage through the tissue depend on the contact point with the source of voltage Even greater power will not necessarily cause fatal consequences, eg. fibrillation, when going through the limbs MICROSHOCK VS. MACROSHOCK 19
20 Macroshock is caused by current passing through the body through the skin, and the current that can cause harmful effects is relatively high and significantly depends on the point of contact Microshock is caused by the passage of relatively low current, but the source of electricity was brought directly into contact with the heart, for example, during cardiac catheterization (catheter in the heart is a diagnostic procedure). Another point of contact can be anywhere on the body (eg limbs). Current of 10 μa is considered safe limit to prevent microshock MICROSHOCK VS. MACROSHOCK 20
21 Macroshock = current spreads through the body Two factors reduce danger in case of an electric shock High skin resistance (15k Ohm to 1 MOhm at 1 cm2) Spatial distribution Many medical devices Reduce the skin resistance with ionic gel (good electrode contact), or Bypass the natural protection by bypassing the skin (thermometer in the mouth, intravenous catheters, etc.) Many fluids conduct electricity (blood, urine, intravenous solution, etc.) Result Patients in medical-care facilities are much more susceptible to macroshocks MACROSHOCK HAZARDS 21
22 Ground fault with short circuit to a metal chassis: A. not grounded chassis macroshock B. grounded chassis safe Figure: Macroshock due to a ground fault from hot line to equipment cases for (a) ungrounded cases and (b) grounded chassis. MACROSHOCK HAZARDS PROTECTION 22
23 Microshock = all current flows through the heart Microshock accidents generally result from leakage-currents in line-operated equipment differences in voltage between grounded conductive surfaces due to large currents in the grounding system Microshock currents can flow either into or out of the electric connection to the heart Result Patient is only in danger of microshock if there is some electric connection to the heart MICROSHOCK HAZARDS 23
24 Leakage-current flows: A. through the ground wire no microshock occurs B. through the patient if he touches the chassis and has a grounded catheter etc. C. through the patient if he is touching ground and has a connected catheter etc. Figure: Microshock leakage-current pathways. Assume 100 μa of leakage current from the power line to the instrument chassis, (a) Intact ground, and 99.8 μa flows through the ground, (b) Broken ground, and 100 μa flows through the heart, (c) Broken ground, and 100 μa flows through the heart in the opposite direction. MICROSHOCK HAZARDS PROTECTION 24
25 ZONE 1: no reactions (~1mA) ZONE 2: no dangerous physiological effect (~10mA) ZONE 3: reversible disorders, muscle contractions, breathing difficulties (~100mA) ZONE 4: probable cardiac arrest, respiratory arrest, severe burns (~200mA) LET'S DO SOME CALCULATIONS 25
26 Reasonably safe current value: MD WITHOUT APPLIED PARTS I c = 10 ma ~ 20 ma Maximum safe contact voltage for the patient: U L = 25 V ca, 60 V cc Esternal contact: R ~ 10 kω ZONE 2 LET'S DO SOME CALCULATIONS 26
27 Reasonably safe current value: MD WITH APPLIED PARTS OF THE CF TYPE I c 10 μa Maximum safe contact voltage for the patient: U L = 10 mv Internal contact: R ~ 1 kω For heart current value > 10 μa: VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION!!! LET'S DO SOME CALCULATIONS 27
28 Generally, patients are only occasionally and accidentally exposed to risk of getting in touching with devices whose conductive parts may be energized. In hospitals, especially in intensive care units, patients are deliberately connected to the diagnostic and/or therapeutic electrical devices/equipment: particularly careful with the isolation of any conductive parts connected to the heart or its vicinity from all other conductive parts all conductive parts in the vicinity of the patient must be connected to a single point grounding (eg, metal bed, cupboard, etc.) periodic testing of the grounding impedance must be provided Tolerable difference in potential between the grounded conductive parts in clinical areas: in the general minor of 500 mv intensive care and other critical cases minor of 40 mv PROTECTIVE GROUNDING 28
29 Under normal conditions, increasing patient safety is provided by: formation of isolated parts of the grid installation of automatic monitoring of impedance grounding (line isolation monitor) POWER IN CLINICAL ENVIRONMENTS 29
30 The principle of redundancy can be applied to the safety of medical devices and equipment For example, it is required that electrical medical equipment is safe even in case of a breakdown on the conductive contact with patient Grounding impedance must be sufficiently low so that the patient may not get in touch with any dangerous voltage EQUIPMENT SAFE DURING THE FIRST FAILURE 30
31 Occur between conductors that are not in direct contact (touch) and are at different potentials For devices that are powered from the grid, leakage currents are: capacitive character (spreading capacity) operative character (current through the insulation, dust, humidity...) LEAKAGE CURRENTS 31
32 Pathways of leakage current through the patient with intact ground lead LEAKAGE CURRENTS PATHWAYS 32
33 Pathways of leakage current through the patient with broken protective ground lead, patien connected to ground through a catheter LEAKAGE CURRENTS PATHWAYS 33
34 Pathways of leakage current through the patient with broken protective ground lead, patien connected to ground by an electrode or unintentianally. LEAKAGE CURRENTS PATHWAYS 34
35 The International Electrotechnical Commission, or IEC, has done the industry a great service by introducing a series of standards for the safety and efficacy of medical electrical equipment, better known as IEC As IEC was put into practice, though, experts observed that these standards overlooked the necessity of ongoing testing of the equipment after it had entered the field. Thus, a new set of standards for this very purpose was introduced: IEC HOW DETECT AND ERADICATE POTENTIAL ELECTRIC HAZARDS? 35
36 IEC 60601, Medical Electrical Equipment General Requirements for Safety was introduced in 1977 and put forth a set of requirements for the manufacturers of medical equipment. These requirements were designed to detect and eradicate any potential electric hazards presented by the equipment being produced (e.g. leakage currents, protective grounding, etc.). Assuming the equipment was utilized properly for the duration of its lifespan, these tests were meant to curb possible defects later on. They were further utilized on equipment already in service as a means of routine tests and after-repair tests; however, this practice presented some unforeseen difficulties: for example, IEC outlines type-testing in laboratory conditions, but often those conditions are not available or applicable once the device is already in use. And so, thirty years after IEC appeared on the scene, in 2007, IEC 62353, Medical Electrical Equipment Recurrent Test and Test After Repair of Medical Electrical Equipment emerged to accommodate the needs of in-service devices. IEC is specifically designed around testing equipment in the field, and is therefore more practical, more effective, and more safe than using IEC in those particular circumstances. IEC VS. IEC
37 Electrical equipment, designed for treatment, monitoring or diagnoses of patients, powered from not more than one connection to mains supply and which are necessarily in physical or electrical contact with the patient or transfers energy to or from the patient or detects such energy transfer to or from the patient. Combination of equipment of which at least one is classed as medical electrical equipment and as such specified by the manufacturer to be connected by functional connection or use of a multiple portable socketoutlet. WHAT IS AN ELECTRICAL MEDICAL DEVICE? 37
38 WHAT IS AN ELECTRICAL MEDICAL DEVICE? 38
39 WHAT IS AN ELECTRICAL MEDICAL DEVICE? 39
40 Applied part: Part of the medical equipment, which is designed to come into physical contact with the patient, or parts that are likely to be brought into contact with the patient. COMMONLY USED TERMS AND DEFINITIONS IN IEC /
41 F-Type applied part: Applied part which is electrically isolated from earth and other parts of the medical equipment. i.e. floating. F-Type applied parts are either type BF or type CF applied parts Type B applied part: Applied Part complying with specified requirements for protection against electric shock. Type B applied parts are those parts, which are usually Earth referenced. Type B are those parts not suitable for direct cardiac application. Type BF applied part: F-Type applied part complying with a higher degree of protection against electric shock than type B applied parts. Type BF applied parts are those parts not suitable for direct cardiac application. Type CF applied part: F-Type applied part complying with the highest degree of protection against electric shock. Type CF applied parts are those parts suitable for direct cardiac application. COMMONLY USED TERMS AND DEFINITIONS IN IEC /
42 Patient environment: Volumetric area in which a patient can come into contact with medical equipment or contact can occur between other persons touching medical equipment and the patient, both intentional and unintentional. COMMONLY USED TERMS AND DEFINITIONS IN IEC /
43 Class I: Equipment protection against electric shock by (earthed) additional protection to basic insulation through means of connecting exposed conductive parts to the protective earth in the fixed wiring of the installation BASIC INSULATION + PERMANENT CONNECTION OF THE PROTECTIVE EARTH CONDUCTOR AND OF THE METALLIC PARTS Class II: Also referred to as double insulated. Equipment protection against electric shock is achieved by additional protection to basic insulation through means of supplementary insulation, there being no provision for the connection of exposed metalwork of the equipment to a protective conductor and no reliance upon precautions to be taken in the fixed wiring of the installation BASIC INSULATION + DOUBLE OR REINFORCED INSULATION EMD CLASSIFICATION 43
44 IEC requires testing before initial start-up, after repair, and periodically. The manufacturer is obligated to provide information about the testing of the device, with which the operator of the testing should carefully comply. WHEN ARE THE TESTS SPECIFIED BY IEC PERFORMED? 44
45 Tests of device safety must be performed by qualified technician who have received adequate training for attending to devices under testing conditions. Individuals who perform safety tests must be able to recognize any threats posed by devices that do not meet safety standards. WHO SHOULD PERFORM THESE TESTS? 45
46 Before testing, accompanying documentation must be examined Whenever and wherever possible, the device must be disconnected from the mains supply power; otherwise, special measures must be implemented for the prevention of hazards resulting from working on live devices. All tests carried out must be documented in depth. Testing documents must at the very least contain the following entries: Designation of the test location (e.g. company, department, authority) Name of the person(s) who performed and evaluated the test Designation of the tested device and accessories (e.g. type, serial number, inventory number) Executed tests including measured values, measuring methods and utilized measuring instruments Function test Final evaluation Date and ignature of the person who prepared the evaluation Identification of the tested device (if required by the operating service provider) HOW IS TESTING PERFORMED? 46
47 In most cases, 70% of all faults are detected during visual an inspection. The following inspections can be included: 1. Housing / Enclosure - Look for damage, cracks etc. 2. Integrity - Look for obstruction of moving parts, connector pins etc. 3. Cabling (supply, applied parts etc.), Look for cuts, wrong connections etc. 4. Fuse rating - check correct values after replacement. 5. Markings and labelling - check the integrity of safety markings. 6. Integrity of mechanical parts - check for any obstructions. VISUAL INSPECTION 47
48 1. Protective Conductor Resistance Measurement 2. Leakage Current Measurement: 1. Device Leakage Current 2. Leakage Current from the Application Part 3. Insulation Resistance Measurement (not obligatory) ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENT TESTS 48
49 1) Protective Conductor Resistance Measurement Protective conductor resistance measurements are performed on Class I devices to ensure that all accessible conductive parts (which, in the event of a fault, may become live) are appropriately secured to the protective conductor terminal. All devices must conform to the following protective conductor connection limit values: ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENT TESTS (1) 49
50 2) Leakage Current Measurement Leakage current measurement requirements only apply universally to AC components; DC leakage current measurements must be determined and explicitly expounded upon in accompanying documentation by manufacturers (complying also with IEC DC limit values). The measured value must be corrected to the value which corresponds to the measurement at nominal line voltage. The following leakage currents are measured: 1. Device Leakage Current 2. Leakage Current from the Application Part ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENT TESTS (2) 50
51 There are three methods to choose from for measuring leakage current; selection of which should be based on the design of the device: ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENT TESTS (2) 51
52 ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENT TESTS (2) 52
53 ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENT TESTS (2) 53
54 ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENT TESTS (2) 54
55 3) Insulation Resistance Measurement Insulation resistance is a helpful measurement to find insulation faults caused by dust, wetness or pollution but the measurement may be forbidden by some manufacturers to avoid damage on sensitive parts. Furthermore, there is no limit value specified in IEC 62353, but the following values can serve as a reliable guideline: ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENT TESTS (3) 55
56 4) Function Test Function tests regarding safety will be specified by the manufacturer, and should be executed accordingly. Function tests also fall under essential performance characteristics and special requirements of IEC Most of the time, additional test instruments will be required (such as with infusion pumps and defibrillators). ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENT TESTS (4) 56
57 DOCUMENT EXAMPLE 57
58 IN 45 MINUTES, YOU MUST EXECUTE A RISK ANALYSIS OF 1 ELECTROMEDICAL DEVICE THAT CHOOSE FROM THESE LISTED: EXTERNAL DEFIBRILLATOR ECG MONITOR OPERATING TABLE SCIALYTIC LAMP ELECTROSURGERY FINAL TEST 1/2 58
59 IN THE REST OF TIME, YOU MUST DESCRIBE HOW YOU WILL MAKE THE SAFETY TEST ON THE ELECTROMEDICAL DEVICE YOU CHOSE BEFORE AND COMPILE THE MAINTENANCE REPORT FROM YOU PREPARED. FINAL TEST 2/2 59
CHAPTER 2: ELECTRICAL SAFETY
 Contents: CHAPTER 2: ELECTRICAL SAFETY 2.1 Physiological Effects of Electricity 2.2 Macroshock and Microshock 2.3 Approaches Towards Protection Against Shock 2.4 Medical Safety Test 2.5 Medical Equipment:
Contents: CHAPTER 2: ELECTRICAL SAFETY 2.1 Physiological Effects of Electricity 2.2 Macroshock and Microshock 2.3 Approaches Towards Protection Against Shock 2.4 Medical Safety Test 2.5 Medical Equipment:
Electrical Safety in Hospitals
 Electrical Safety in Hospitals Safety in Clinical Environment Electrical hazards Electrical shocks (micro and macro) due to equipment failure, failure of power delivery systems, ground failures, burns,
Electrical Safety in Hospitals Safety in Clinical Environment Electrical hazards Electrical shocks (micro and macro) due to equipment failure, failure of power delivery systems, ground failures, burns,
5 th year (Control department)
 Benha Faculty of Engineering Benha University 5 th year (Control department) Clinical Equipment Management(E527) Examiner: Dr.Waleed A.A Salem Final Written Examination 2012 / 2013 Time : Three Hours Answer
Benha Faculty of Engineering Benha University 5 th year (Control department) Clinical Equipment Management(E527) Examiner: Dr.Waleed A.A Salem Final Written Examination 2012 / 2013 Time : Three Hours Answer
Definitions found in several locations:
 Definitions found in several locations: NFPA 70 - National Electric Code NFPA 70B Recommended Practice for Electrical Equipment Maintenance. NFPA 70E Electrical Safety in the Workplace OSHA 1910 Subpart
Definitions found in several locations: NFPA 70 - National Electric Code NFPA 70B Recommended Practice for Electrical Equipment Maintenance. NFPA 70E Electrical Safety in the Workplace OSHA 1910 Subpart
This training session covers electrical safety for unqualified persons. Unqualified persons are machine operators, operators of powered industrial
 This training session covers electrical safety for unqualified persons. Unqualified persons are machine operators, operators of powered industrial trucks, construction workers, and others who are not qualified
This training session covers electrical safety for unqualified persons. Unqualified persons are machine operators, operators of powered industrial trucks, construction workers, and others who are not qualified
Electrical. OSHA Office of Training and Education 1
 Electrical OSHA Office of Training and Education 1 Introduction An average of one worker is electrocuted on the job every day There are four main types of electrical injuries: Electrocution (death due
Electrical OSHA Office of Training and Education 1 Introduction An average of one worker is electrocuted on the job every day There are four main types of electrical injuries: Electrocution (death due
Electrical Safety. Toolbox Talk
 Electrical Safety Toolbox Talk Establishing an Electrical Safety Program There are five objectives of an safety program: 1. Make personnel more aware of rules, responsibilities and procedures for working
Electrical Safety Toolbox Talk Establishing an Electrical Safety Program There are five objectives of an safety program: 1. Make personnel more aware of rules, responsibilities and procedures for working
Sikkerhed og certifisering for sundhedsteknologisk udstyr
 Sikkerhed og certifisering for sundhedsteknologisk udstyr Temadag på Sundhedsteknologiuddannelsens 6. semester Kim Dremstrup Nielsen, IST, AAU Program 9.00-10.00 Elsikkerhed, IEC 60601 mm. Lektor Kim Dremstrup
Sikkerhed og certifisering for sundhedsteknologisk udstyr Temadag på Sundhedsteknologiuddannelsens 6. semester Kim Dremstrup Nielsen, IST, AAU Program 9.00-10.00 Elsikkerhed, IEC 60601 mm. Lektor Kim Dremstrup
Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter(GFCI) Policy
 NewStar Netronics, LLC American Products for the World Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter(GFCI) Policy 3926 East 3 rd Street Tulsa, OK 74112 Phone (918)894-5006 Fax (918)836-9909 tech@newstarnetronics.com
NewStar Netronics, LLC American Products for the World Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter(GFCI) Policy 3926 East 3 rd Street Tulsa, OK 74112 Phone (918)894-5006 Fax (918)836-9909 tech@newstarnetronics.com
Circuit model of medical equipment for electrical safety purposes
 Risk Analysis IX 507 Circuit model of medical equipment for electrical safety purposes E. Zennaro 1, C. Mazzetti 1, F. Fiamingo 2 & G. L. Amicucci 2 1 Department of Astronautics, Electrical and Energetics
Risk Analysis IX 507 Circuit model of medical equipment for electrical safety purposes E. Zennaro 1, C. Mazzetti 1, F. Fiamingo 2 & G. L. Amicucci 2 1 Department of Astronautics, Electrical and Energetics
Please print or type all responses except where a signature is required. DESIGN PROJECT TITLE: SEMESTER AND COURSE REFERENCE NUMBER: STUDENT NAME:
 ENGR 196, 296, 396 PROJECT FORM (Circle the correct course number) Prior to signing up for an ENGR 196, 296, 396 hands on project, the student must acquire the signature of the faculty member who will
ENGR 196, 296, 396 PROJECT FORM (Circle the correct course number) Prior to signing up for an ENGR 196, 296, 396 hands on project, the student must acquire the signature of the faculty member who will
REPORTING AND TREATMENT REQUIRED AS A RESULT OF AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT CS-OHS-5
 Form S1745 (Amd 7/97) CS ENERGY PROCEDURE FOR REPORTING AND TREATMENT REQUIRED AS A RESULT OF AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT CS-OHS-5 Responsible Officer: Authorised Person Approved : GM Production Contents 1.
Form S1745 (Amd 7/97) CS ENERGY PROCEDURE FOR REPORTING AND TREATMENT REQUIRED AS A RESULT OF AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT CS-OHS-5 Responsible Officer: Authorised Person Approved : GM Production Contents 1.
The best safeguard against accidents is a genuine safety culture - awareness and constant vigilance on the part of all those involved, and the
 The best safeguard against accidents is a genuine safety culture - awareness and constant vigilance on the part of all those involved, and the establishment of safety as a permanent and natural feature
The best safeguard against accidents is a genuine safety culture - awareness and constant vigilance on the part of all those involved, and the establishment of safety as a permanent and natural feature
Dealing with Electrical Hazards in the Workplace
 Dealing with Electrical Hazards in the Workplace Presented By: Tom Norwood Sr. Safety Specialist A SUBSIDIARY OF MEGGER TRAINING INSTITUTE, INC. Dallas, Texas Introduction Several hundred electrical fatalities
Dealing with Electrical Hazards in the Workplace Presented By: Tom Norwood Sr. Safety Specialist A SUBSIDIARY OF MEGGER TRAINING INSTITUTE, INC. Dallas, Texas Introduction Several hundred electrical fatalities
Electrical Safety. Unqualified Worker
 Electrical Safety Unqualified Worker Session Objectives Understand the hazards of electricity Identify and avoid common electrical hazards Follow safe work practices around electrical equipment How Does
Electrical Safety Unqualified Worker Session Objectives Understand the hazards of electricity Identify and avoid common electrical hazards Follow safe work practices around electrical equipment How Does
Norrsken Family Booklet
 Section 1: Introduction Low Energy Designs produce efficient and effective LED based lighting products for commercial, retail and industry purposes. Each product may contain specific details on its operation
Section 1: Introduction Low Energy Designs produce efficient and effective LED based lighting products for commercial, retail and industry purposes. Each product may contain specific details on its operation
Electrical Safety. Introduction
 Electrical Safety 1 Introduction There are four main types of electrical injuries: Electrocution (death due to electrical shock) Electrical shock Burns Falls Around 300 workers were electrocuted in 2008
Electrical Safety 1 Introduction There are four main types of electrical injuries: Electrocution (death due to electrical shock) Electrical shock Burns Falls Around 300 workers were electrocuted in 2008
Dr Morris Odell. Victorian Institute of Forensic Medicine VIFM
 TASERS and STUN GUNS Dr Morris Odell Victorian Institute of Forensic Medicine Intentional Electric Shock Devices Less than Lethal weapons Stun guns Tasers Cattle prods, Electric fences, Man traps Conducted
TASERS and STUN GUNS Dr Morris Odell Victorian Institute of Forensic Medicine Intentional Electric Shock Devices Less than Lethal weapons Stun guns Tasers Cattle prods, Electric fences, Man traps Conducted
Leakage Current Testing Is it right for your application?
 Leakage Current Testing Is it right for your application? Introduction The Leakage Current test (LCT for short) is most often specified to be performed as a type test in a design or engineering laboratory
Leakage Current Testing Is it right for your application? Introduction The Leakage Current test (LCT for short) is most often specified to be performed as a type test in a design or engineering laboratory
Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science. Electrical Safety. for Staff and Students in EECS Instructional Laboratories
 NEVER WORK ALONE Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science Electrical Safety for Staff and Students in EECS Instructional Laboratories If you will be working with energized circuits or equipment
NEVER WORK ALONE Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science Electrical Safety for Staff and Students in EECS Instructional Laboratories If you will be working with energized circuits or equipment
Preview to the 2018 NFPA 70E, the Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace
 Preview to the 2018 NFPA 70E, the Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace Preview to the 2018 NFPA 70E, the Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace Technical Committee Members James Dollard,
Preview to the 2018 NFPA 70E, the Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace Preview to the 2018 NFPA 70E, the Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace Technical Committee Members James Dollard,
DX 3 RCDs. Technical data Nature and consequences of electrical risks Direct and indirect contact. Direct contacts
 RCDs Nature and consequences of electrical risks Direct and indirect contact All electrical risks for people are the result of direct or indirect contact. What are these contacts? And how can we protect
RCDs Nature and consequences of electrical risks Direct and indirect contact All electrical risks for people are the result of direct or indirect contact. What are these contacts? And how can we protect
SKAGIT COUNTY AUTOMATED EXTERNAL DEFIBRILLATOR [AED] POLICY
![SKAGIT COUNTY AUTOMATED EXTERNAL DEFIBRILLATOR [AED] POLICY SKAGIT COUNTY AUTOMATED EXTERNAL DEFIBRILLATOR [AED] POLICY](/thumbs/78/76760010.jpg) SKAGIT COUNTY AUTOMATED EXTERNAL DEFIBRILLATOR [AED] POLICY Purpose: To provide guidance in the management and administration of the Skagit County AED program. Check ONE box only: X For treatment of victims
SKAGIT COUNTY AUTOMATED EXTERNAL DEFIBRILLATOR [AED] POLICY Purpose: To provide guidance in the management and administration of the Skagit County AED program. Check ONE box only: X For treatment of victims
Policies, Procedures, Guidelines and Protocols
 Policies, Procedures, Guidelines and Protocols Document Details Title Portable Electrical Equipment Management Policy Trust Ref No 701-29768 Local Ref (optional) Main points the document Responsibilities
Policies, Procedures, Guidelines and Protocols Document Details Title Portable Electrical Equipment Management Policy Trust Ref No 701-29768 Local Ref (optional) Main points the document Responsibilities
Hazards and Risks Associated With the Use of Electricity in the Workplace
 Hazards and Risks Associated With the Use of Electricity in the Workplace A simple electrical circuit can be described by reference to three parameters: voltage, current and resistance. These three parameters
Hazards and Risks Associated With the Use of Electricity in the Workplace A simple electrical circuit can be described by reference to three parameters: voltage, current and resistance. These three parameters
The definition of a competent person given in the Electricity at Work Regulations 1989 (EWR) is as follows:
 Electrical Safety Guidance Note 1 - General Guidance Competent Person The definition of a competent person given in the Electricity at Work Regulations 1989 (EWR) is as follows: "A person in the possession
Electrical Safety Guidance Note 1 - General Guidance Competent Person The definition of a competent person given in the Electricity at Work Regulations 1989 (EWR) is as follows: "A person in the possession
Ground Fault Protection for Electrical Tools
 Hanover Risk Solutions Ground Fault Protection for Electrical Tools Effective electrical tool and equipment grounding are extremely important on construction sites. Injuries and deaths can result from
Hanover Risk Solutions Ground Fault Protection for Electrical Tools Effective electrical tool and equipment grounding are extremely important on construction sites. Injuries and deaths can result from
CS ENERGY PROCEDURE FOR ELECTRIC SHOCK TREATMENT AND REPORTING CS-OHS-05
 CS-OHS-05 10/04/2012 CS ENERGY PROCEDURE FOR ELECTRIC SHOCK TREATMENT AND REPORTING CS-OHS-05 Responsible Officer: Group Manager Health and Safety Responsible Executive: Executive General Manager Corporate
CS-OHS-05 10/04/2012 CS ENERGY PROCEDURE FOR ELECTRIC SHOCK TREATMENT AND REPORTING CS-OHS-05 Responsible Officer: Group Manager Health and Safety Responsible Executive: Executive General Manager Corporate
Ultima. X Series Gas Monitor
 Ultima X Series Gas Monitor Safety Manual SIL 2 Certified " The Ultima X Series Gas Monitor is qualified as an SIL 2 device under IEC 61508 and must be installed, used, and maintained in accordance with
Ultima X Series Gas Monitor Safety Manual SIL 2 Certified " The Ultima X Series Gas Monitor is qualified as an SIL 2 device under IEC 61508 and must be installed, used, and maintained in accordance with
Industrial Relations
 Industrial & Management Engineering Department Industrial Relations IM 111 Dr Yehia Youssef IM111 Lecture 7 1 Definitions Hazard: A hazard is anything that can cause harm to people. Examples are dangerous
Industrial & Management Engineering Department Industrial Relations IM 111 Dr Yehia Youssef IM111 Lecture 7 1 Definitions Hazard: A hazard is anything that can cause harm to people. Examples are dangerous
Guidelines to the standard IEC60601
 EUROPEAN POWER SUPPLY MANUFACTURERS ASSOCIATION (Visit the EPSMA website at www.epsma.org) Medical Approvals for Power Supplies Guidelines to the standard IEC60601 Revision Date: 2009-09-12 This document
EUROPEAN POWER SUPPLY MANUFACTURERS ASSOCIATION (Visit the EPSMA website at www.epsma.org) Medical Approvals for Power Supplies Guidelines to the standard IEC60601 Revision Date: 2009-09-12 This document
ES18 Security Theory/Regulations Answer Schedule
 ES18 Security Theory/Regulations Answer Schedule Notes:1. means that the preceding statement/answer earns 1 mark. 2. This schedule sets out the expected answers to the examination questions. The marker
ES18 Security Theory/Regulations Answer Schedule Notes:1. means that the preceding statement/answer earns 1 mark. 2. This schedule sets out the expected answers to the examination questions. The marker
SEGMENT NINE - Electricity
 71 SEGMENT NINE - Electricity After studying this segment you should have a greater understanding of the potential danger posed by electricity and the steps taken in the workplace to ensure that electrical
71 SEGMENT NINE - Electricity After studying this segment you should have a greater understanding of the potential danger posed by electricity and the steps taken in the workplace to ensure that electrical
Rigel 601 CHECKBOX. Instruction Manual. 348A551 Issue 2.0. April Seaward Electronic Ltd. Issue 2.0
 Rigel 601 CHECKBOX Instruction Manual 348A551 Issue 2.0 April 2006 2006 Seaward Electronic Ltd. Issue 2.0 Limited Warranty & Limitation of Liability Rigel Medical guarantees this product for a period of
Rigel 601 CHECKBOX Instruction Manual 348A551 Issue 2.0 April 2006 2006 Seaward Electronic Ltd. Issue 2.0 Limited Warranty & Limitation of Liability Rigel Medical guarantees this product for a period of
2018 NFPA 70E Significant Changes 7/27/2017. EFCOG Electrical Safety Task Group Workshop, July 2017
 Significant Changes EFCOG Electrical Safety Task Group Workshop, July 2017 Appreciation Thanks to: Paul Dobrowsky creating the base PPT program Chair, Dave Dini for leading the Committee through the process
Significant Changes EFCOG Electrical Safety Task Group Workshop, July 2017 Appreciation Thanks to: Paul Dobrowsky creating the base PPT program Chair, Dave Dini for leading the Committee through the process
Original Date of Issue: 04/09
 POLICIES AND PROCEDURES DEPARTMENT: Environmental Health and Safety SUBJECT: Electrical Safety Program Original Date of Issue: 04/09 Reviewed 12/2011 Revised 12/2011 BACKGROUND ELECTRIC SHOCK It is well
POLICIES AND PROCEDURES DEPARTMENT: Environmental Health and Safety SUBJECT: Electrical Safety Program Original Date of Issue: 04/09 Reviewed 12/2011 Revised 12/2011 BACKGROUND ELECTRIC SHOCK It is well
WHS-05 Electric Shock Response
 Table of Contents 1 Purpose... 3 2 Scope... 3 3 References... 3 4 Roles and Responsibilities... 3 5 Definitions... 4 6 Records... 4 7 Rescue and first aid... 4 8 Medical emergency response (Code Blue)...
Table of Contents 1 Purpose... 3 2 Scope... 3 3 References... 3 4 Roles and Responsibilities... 3 5 Definitions... 4 6 Records... 4 7 Rescue and first aid... 4 8 Medical emergency response (Code Blue)...
POLICY FOR THE CONTROL OF SUBSTANCES HAZARDOUS TO HEALTH (COSHH)
 POLICY FOR THE CONTROL OF SUBSTANCES HAZARDOUS TO HEALTH (COSHH) INTRODUCTION & LEGISLATION Using chemicals or other hazardous substances at work can put people s health at risk. The law requires employers
POLICY FOR THE CONTROL OF SUBSTANCES HAZARDOUS TO HEALTH (COSHH) INTRODUCTION & LEGISLATION Using chemicals or other hazardous substances at work can put people s health at risk. The law requires employers
Safe Schools: A Health and Safety Check
 Name of School: Optional Information Date of Inspection: Vocational Program/Course/Room: Signature of Inspector: Use of Electrical Equipment Self-Inspection Checklist Guidelines: This checklist covers
Name of School: Optional Information Date of Inspection: Vocational Program/Course/Room: Signature of Inspector: Use of Electrical Equipment Self-Inspection Checklist Guidelines: This checklist covers
Electrical Safety PPT-SM-ELECTSFTY V.A.0.0
 Electrical Safety 1 Electrical Safety OSHA s electrical safety standard covers Work on or near exposed energized equipment Proper use of electrical protective equipment Safe use of portable electric equipment
Electrical Safety 1 Electrical Safety OSHA s electrical safety standard covers Work on or near exposed energized equipment Proper use of electrical protective equipment Safe use of portable electric equipment
! Warning, refer to accompanying documents.
 About this Manual To the best of our knowledge and at the time written, the information contained in this document is technically correct and the procedures accurate and adequate to operate this instrument
About this Manual To the best of our knowledge and at the time written, the information contained in this document is technically correct and the procedures accurate and adequate to operate this instrument
PAT Testing Procedures WYMONDHAM RUGBY FOOTBALL CLUB. Wymondham RFC PAT Testing Procedure Version 1 Revision 3 Wednesday, 27 July 2016 Page 1
 WYMONDHAM RUGBY FOOTBALL CLUB PAT Testing Procedures Wednesday, 27 July 2016 Page 1 Contents 1 Introduction 2 Explanation of Terms Used 3 What Does the Law Require? 4 Controlling the Risk 5 Maintenance
WYMONDHAM RUGBY FOOTBALL CLUB PAT Testing Procedures Wednesday, 27 July 2016 Page 1 Contents 1 Introduction 2 Explanation of Terms Used 3 What Does the Law Require? 4 Controlling the Risk 5 Maintenance
Management Plan for Electrical Safety ISD #535
 Management Plan for Electrical Safety ISD #535 Health & Safety Office Maintenance Service Building 10 SE 9 ½ Street Rochester, MN 55904 507-328-4507 MANAGEMENT PLAN FOR ELECTRICAL SAFETY Table of Contents
Management Plan for Electrical Safety ISD #535 Health & Safety Office Maintenance Service Building 10 SE 9 ½ Street Rochester, MN 55904 507-328-4507 MANAGEMENT PLAN FOR ELECTRICAL SAFETY Table of Contents
Med Aire Alternating Pressure Pump and Pad System
 User Manual Med Aire Alternating Pressure Pump and Pad System 14002E 14001E Symbols & Statements NOTE Indicates some tips or some information users should be aware of. CAUTION Indicates correct operating
User Manual Med Aire Alternating Pressure Pump and Pad System 14002E 14001E Symbols & Statements NOTE Indicates some tips or some information users should be aware of. CAUTION Indicates correct operating
Essential Performance for MED rd ed. PSES San Diego chapter meeting December 11, 2012
 Essential Performance for MED 601-1 3 rd ed. Grant Schmidbauer, Nemko USA, Inc. PSES San Diego chapter meeting December 11, 2012 2012 PSES San Diego Chapter http://www.psessymposium.org/ 1 3.27 Essential
Essential Performance for MED 601-1 3 rd ed. Grant Schmidbauer, Nemko USA, Inc. PSES San Diego chapter meeting December 11, 2012 2012 PSES San Diego Chapter http://www.psessymposium.org/ 1 3.27 Essential
It is essential that the maintenance staff is qualified for electrical works and follows safety procedures.
 MAINTENANCE OF POWER FACTOR CORRECTION EQUIPMENTS Procedures, suggestions and traceability The purpose of this document is to propose a maintenance method that allows to identify the elements to be maintained
MAINTENANCE OF POWER FACTOR CORRECTION EQUIPMENTS Procedures, suggestions and traceability The purpose of this document is to propose a maintenance method that allows to identify the elements to be maintained
Electronics Lab Advanced Electrical Engineering Lab Course II Spring 2006
 Safety Instructions Electronics Lab Advanced Electrical Engineering Lab Course II Spring 2006 Instructor: H. Elgala, Dr. D. Knipp Ta http://www.faculty.iu-bremen.de/course/c300221a/ee_module_2 Purpose
Safety Instructions Electronics Lab Advanced Electrical Engineering Lab Course II Spring 2006 Instructor: H. Elgala, Dr. D. Knipp Ta http://www.faculty.iu-bremen.de/course/c300221a/ee_module_2 Purpose
Reference Number PDS 10 (RIC Standard: EP SP)
 Discipline Engineering Standard NSW Category Electrical Title Reference Number PDS 10 (RIC Standard: EP 00 00 00 08 SP) Document Control Status Date Prepared Reviewed Endorsed Approved Mar 05 Standards
Discipline Engineering Standard NSW Category Electrical Title Reference Number PDS 10 (RIC Standard: EP 00 00 00 08 SP) Document Control Status Date Prepared Reviewed Endorsed Approved Mar 05 Standards
The Best Use of Lockout/Tagout and Control Reliable Circuits
 Session No. 565 The Best Use of Lockout/Tagout and Control Reliable Circuits Introduction L. Tyson Ross, P.E., C.S.P. Principal LJB Inc. Dayton, Ohio Anyone involved in the design, installation, operation,
Session No. 565 The Best Use of Lockout/Tagout and Control Reliable Circuits Introduction L. Tyson Ross, P.E., C.S.P. Principal LJB Inc. Dayton, Ohio Anyone involved in the design, installation, operation,
Welding With Arc Welding Equipment
 Optional Information Name of School: Date of Inspection: Vocational Program/Course/Room: Signature of Inspector: Welding With Arc Welding Equipment Self Inspection Checklist Guidelines: This checklist
Optional Information Name of School: Date of Inspection: Vocational Program/Course/Room: Signature of Inspector: Welding With Arc Welding Equipment Self Inspection Checklist Guidelines: This checklist
MANUAL DIRECT PURGE OPTION. UNION Instruments GmbH CWD2005 PLUS. General information, safety standards and regulations for direct purge option
 MANUAL DIRECT PURGE OPTION UNION Instruments GmbH CWD2005 PLUS General information, safety standards and regulations for direct purge option Version: V1.00 Stand: 24.03.2010 Union Instruments GmbH Zeppelinstr.
MANUAL DIRECT PURGE OPTION UNION Instruments GmbH CWD2005 PLUS General information, safety standards and regulations for direct purge option Version: V1.00 Stand: 24.03.2010 Union Instruments GmbH Zeppelinstr.
Administrative Procedures Automated External Defibrillator (AED)
 Administrative Procedures Automated External Defibrillator (AED) PURPOSE: The purpose of these procedures is to give guidance to those employees of the Lynden School District who are trained and willing
Administrative Procedures Automated External Defibrillator (AED) PURPOSE: The purpose of these procedures is to give guidance to those employees of the Lynden School District who are trained and willing
Comfortmax Thermax Hot/Cold Water Circulation System. Instructions for Use
 Comfortmax Thermax Hot/Cold Water Circulation System Instructions for Use THIS DEVICE CAN BE COLD ENOUGH TO CAUSE SERIOUS INJURY. SERIOUS ADVERSE REACTIONS AND SAFETY HAZARDS MAY OCCUR WHEN USING THIS
Comfortmax Thermax Hot/Cold Water Circulation System Instructions for Use THIS DEVICE CAN BE COLD ENOUGH TO CAUSE SERIOUS INJURY. SERIOUS ADVERSE REACTIONS AND SAFETY HAZARDS MAY OCCUR WHEN USING THIS
ELECTRICAL (COMPREHENSIVE) SAFETY PROGRAM REGULATORY STANDARD: OSHA - 29 CFR CFR , ,
 ELECTRICAL (COMPREHENSIVE) SAFETY PROGRAM REGULATORY STANDARD: OSHA - 29 CFR 1910.331 335-29 CFR 1926.302, 1926.416, 1926.417 BASIS: The National Safety Council estimates that there are at least 300 deaths
ELECTRICAL (COMPREHENSIVE) SAFETY PROGRAM REGULATORY STANDARD: OSHA - 29 CFR 1910.331 335-29 CFR 1926.302, 1926.416, 1926.417 BASIS: The National Safety Council estimates that there are at least 300 deaths
General Requirements of the NEC Advanced Course. Building Officials and Inspectors Educational Association
 General Requirements of the NEC Advanced Course Building Officials and Inspectors Educational Association General Requirements -NEC Course Outcome Explain general requirements found in Article 110 of the
General Requirements of the NEC Advanced Course Building Officials and Inspectors Educational Association General Requirements -NEC Course Outcome Explain general requirements found in Article 110 of the
User s Guide Temperature Sensor Converter TSC-599
 User s Guide Temperature Sensor Converter TSC-599 ILX Lightwave Corporation 31950 Frontage Road Bozeman, MT, U.S.A. 59715 U.S. & Canada: 1-800-459-9459 International Inquiries: 406-556-2481 Fax 406-586-9405
User s Guide Temperature Sensor Converter TSC-599 ILX Lightwave Corporation 31950 Frontage Road Bozeman, MT, U.S.A. 59715 U.S. & Canada: 1-800-459-9459 International Inquiries: 406-556-2481 Fax 406-586-9405
Transmitter CS 21 Operation Manual
 Transmitter CS 21 Operation Manual Content Page For your Safety 3 General Description 3 Detection Principle 4 Operational Notes 4 Design 4 Mounting Position of CS21 5 Mounting 6 Installation of Electrical
Transmitter CS 21 Operation Manual Content Page For your Safety 3 General Description 3 Detection Principle 4 Operational Notes 4 Design 4 Mounting Position of CS21 5 Mounting 6 Installation of Electrical
PLANT/EQUIPMENT/ASSET HAZARD REPORT
 Asset Description: EL-08001-011 : Harrison 550 CNC Lathe Large Sale Type For what use is this asset being sold? Re-Use þ Spare Parts Scrap Note 1: Assets are sold only for the use indicated. Any other
Asset Description: EL-08001-011 : Harrison 550 CNC Lathe Large Sale Type For what use is this asset being sold? Re-Use þ Spare Parts Scrap Note 1: Assets are sold only for the use indicated. Any other
11/2/2017. Course Objectives. Overview
 Course Objectives The objective of this CBT module is to insure that personnel receive basic training in electrical safety. Every employee's work involves electricity. This may vary from typical electrical
Course Objectives The objective of this CBT module is to insure that personnel receive basic training in electrical safety. Every employee's work involves electricity. This may vary from typical electrical
Code of Practice for the Inspection and Testing of Portable Electrical Equipment (PAT)
 Code of Practice for the Inspection and Testing of Portable Electrical Equipment (PAT) Reviews and Revisions Action Date Reason Reviewer Updated details of External PAT Contractor 17/02/16 New contract
Code of Practice for the Inspection and Testing of Portable Electrical Equipment (PAT) Reviews and Revisions Action Date Reason Reviewer Updated details of External PAT Contractor 17/02/16 New contract
PLEASE READ CAREFULLY BEFORE INSTALLING OR USING MEGA POOL SAVER MPS 1100
 MPS-1100 User Manual Mega Pool Saver Ltd PLEASE READ CAREFULLY BEFORE INSTALLING OR USING MEGA POOL SAVER MPS 1100 For further up to date instructions on how to install Mega Pool Saver MPS 1100, please
MPS-1100 User Manual Mega Pool Saver Ltd PLEASE READ CAREFULLY BEFORE INSTALLING OR USING MEGA POOL SAVER MPS 1100 For further up to date instructions on how to install Mega Pool Saver MPS 1100, please
: Electric Power Generation, Transmission, and Distribution. Region IV - OSHA
 1910.269: Electric Power Generation, Transmission, and Distribution Region IV - OSHA Scope This standard covers the operation and maintenance of electric power generation, control, transformation transmission,
1910.269: Electric Power Generation, Transmission, and Distribution Region IV - OSHA Scope This standard covers the operation and maintenance of electric power generation, control, transformation transmission,
C&G Level 3 Award in the Periodic Inspection, Testing and Certification of Electrical Installations
 C&G 2395-01 Level 3 Award in the Periodic Inspection, Testing and Certification of Electrical Installations Test instruments and recommended testing sequence 1 Outcomes of this Session describe the different
C&G 2395-01 Level 3 Award in the Periodic Inspection, Testing and Certification of Electrical Installations Test instruments and recommended testing sequence 1 Outcomes of this Session describe the different
Transmitter CS 21 Operation Manual
 Transmitter CS 21 Operation Manual 1194 Oak Valley Drive, Suite 20, Ann Arbor, MI 48108 800-959-0573 734-769-1888 Content Page For your Safety 3 General Description 3 Detection Principle 4 Operation 4
Transmitter CS 21 Operation Manual 1194 Oak Valley Drive, Suite 20, Ann Arbor, MI 48108 800-959-0573 734-769-1888 Content Page For your Safety 3 General Description 3 Detection Principle 4 Operation 4
10 Best Practices for Electrosurgical Unit Testing
 10 Best Practices for Electrosurgical Unit Testing Tips to quickly and effectively test electrosurgical devices to ensure performance and safety White Paper Let s start with the basics. Electrosurgical
10 Best Practices for Electrosurgical Unit Testing Tips to quickly and effectively test electrosurgical devices to ensure performance and safety White Paper Let s start with the basics. Electrosurgical
ECE Lab Safety. Module All Jan 2018
 ECE Lab Safety Module All Jan 2018 Agenda Lab Policies Electrical Safety Distribution Grounding Physiology CPR/AED Biological Safety Jewelry Lead Eye Safety Test online, 25 random multiple choice questions,
ECE Lab Safety Module All Jan 2018 Agenda Lab Policies Electrical Safety Distribution Grounding Physiology CPR/AED Biological Safety Jewelry Lead Eye Safety Test online, 25 random multiple choice questions,
Respiration. Figure 22: Schematic representation of the respiratory system
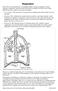 Respiration One of the seven characteristics of something which is living is respiration. Strictly speaking, respiration is the process that takes place at cellular level and is one of three different
Respiration One of the seven characteristics of something which is living is respiration. Strictly speaking, respiration is the process that takes place at cellular level and is one of three different
PLANT/EQUIPMENT/ASSET HAZARD REPORT
 Asset Description: EL-09100-060 : Gantry hoist system Sale Type For what use is this asset being sold? Re-Use Spare Parts Scrap Note 1: Assets are sold only for the use indicated. Any other use is at the
Asset Description: EL-09100-060 : Gantry hoist system Sale Type For what use is this asset being sold? Re-Use Spare Parts Scrap Note 1: Assets are sold only for the use indicated. Any other use is at the
Instruction Manual Contact Pressure Vacuum Gauge
 MS10 Instruction Manual Contact Pressure Vacuum Gauge Table of Contents 1. Safety Instructions 2. Intended Applications 3. Product Description and Functions 4. Installation 5. Commissioning 6. Maintenance
MS10 Instruction Manual Contact Pressure Vacuum Gauge Table of Contents 1. Safety Instructions 2. Intended Applications 3. Product Description and Functions 4. Installation 5. Commissioning 6. Maintenance
Portable Appliance Testing
 The University of Edinburgh E Brief description of the paper University Health and Safety Committee Tuesday 18 th November 2014 Portable Appliance Testing This Paper presents the review of the University
The University of Edinburgh E Brief description of the paper University Health and Safety Committee Tuesday 18 th November 2014 Portable Appliance Testing This Paper presents the review of the University
This presentation provides an overview of modern methods for minimizing the arc-flash hazard.
 Electricity is all around us. An uncontrolled release of electric energy is extremely dangerous, posing a threat to human life, causing equipment damage, and jeopardizing the manufacturing process that
Electricity is all around us. An uncontrolled release of electric energy is extremely dangerous, posing a threat to human life, causing equipment damage, and jeopardizing the manufacturing process that
Fingertip Pulse Oximeter
 Instruction Manual Fingertip Pulse Oximeter Item # 40-810-000 Item # 40-811-000 Item # 40-812-000 Item # 40-813-000 Please read this guidebook completely before operating this unit. Limited Two-Year Warranty
Instruction Manual Fingertip Pulse Oximeter Item # 40-810-000 Item # 40-811-000 Item # 40-812-000 Item # 40-813-000 Please read this guidebook completely before operating this unit. Limited Two-Year Warranty
Calibration Requirements for Direct Reading Confined Space Gas Detectors
 : Calibration Requirements for Direct Reading Confined Space Gas Detectors However, the definition of bump test has always been a little slippery. Some manufacturers differentiate between a bump test that
: Calibration Requirements for Direct Reading Confined Space Gas Detectors However, the definition of bump test has always been a little slippery. Some manufacturers differentiate between a bump test that
Electrical Safety. Hazard Awareness
 Electrical Safety Hazard Awareness What does Hazard mean? Hazard means: any potential or actual threat to the wellbeing of people, machinery or environment Electrical hazard safety means: taking precautions
Electrical Safety Hazard Awareness What does Hazard mean? Hazard means: any potential or actual threat to the wellbeing of people, machinery or environment Electrical hazard safety means: taking precautions
Digital Melting Point Apparatus
 Digital Melting Point Apparatus Heating Plateau Ramping Start/Stop Plateau set Ramp stop Hold User Guide Version 1.1 Heating Viewing tube Sample Chamber IEC power inlet socket Power on/off Temperature
Digital Melting Point Apparatus Heating Plateau Ramping Start/Stop Plateau set Ramp stop Hold User Guide Version 1.1 Heating Viewing tube Sample Chamber IEC power inlet socket Power on/off Temperature
SC505 Sof Care Inflator. Operating Instructions and Service Manual
 SC505 Sof Care Inflator Gaymar Industries, Inc. 10 Centre Drive Orchard Park, NY 14127 Toll Free +1 800.828.7341 + 1 716.662.2551 Fax +1 800.993.7890 Outside USA +1 716.662.8636 Outside USA Fax +1 716.662.0730
SC505 Sof Care Inflator Gaymar Industries, Inc. 10 Centre Drive Orchard Park, NY 14127 Toll Free +1 800.828.7341 + 1 716.662.2551 Fax +1 800.993.7890 Outside USA +1 716.662.8636 Outside USA Fax +1 716.662.0730
Electrical. Version 1.0
 This document is intended to provide basic safety guidelines for the Physical Plant Department at Community College of Allegheny County. The information provided in this guide may vary by site. Version
This document is intended to provide basic safety guidelines for the Physical Plant Department at Community College of Allegheny County. The information provided in this guide may vary by site. Version
Leader s Guide ERI Safety Videos
 1717 SAFE ELECTRICAL WORK PRACTICES & THE 2018 NFPA 70E Leader s Guide ERI Safety Videos SAFE ELECTRICAL WORK PRACTICES & THE 2018 NFPA 70E This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting
1717 SAFE ELECTRICAL WORK PRACTICES & THE 2018 NFPA 70E Leader s Guide ERI Safety Videos SAFE ELECTRICAL WORK PRACTICES & THE 2018 NFPA 70E This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting
NIMBUS range. with people in mind
 NIMBUS range Advanced Mattress Replacement systems with people in mind OPTIMUM PRESSURE RELIEF AND COMFORT In clinical use for more than 20 years, Nimbus Alternating Mattress Replacement Systems have consistently
NIMBUS range Advanced Mattress Replacement systems with people in mind OPTIMUM PRESSURE RELIEF AND COMFORT In clinical use for more than 20 years, Nimbus Alternating Mattress Replacement Systems have consistently
CIRCUIT BREAKER TESTING - JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS
 Title: Circuit Breaker Testing Purpose and Scope: Provide guidelines for testing of Circuit Breakers. Staffing Resources: Staff will have the minimum requirement of an Electrical Fitter/Mechanic Licence
Title: Circuit Breaker Testing Purpose and Scope: Provide guidelines for testing of Circuit Breakers. Staffing Resources: Staff will have the minimum requirement of an Electrical Fitter/Mechanic Licence
SECTION 51 NFPA 70E POLICY. Health & Safety Policy and Procedures Manual
 SECTION 51 NFPA 70E POLICY Health & Safety Policy and 1. Protection Against Arc Flash A. Policy: An arc flash is a dangerous condition associated with the release of energy caused by an electric arc. An
SECTION 51 NFPA 70E POLICY Health & Safety Policy and 1. Protection Against Arc Flash A. Policy: An arc flash is a dangerous condition associated with the release of energy caused by an electric arc. An
MODEL GT820 OXYGEN SENSOR
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL MODEL GT820 OXYGEN SENSOR 70046 The information and technical data disclosed by this document may be used and disseminated only for the purposes and to the extent specifically authorized
INSTRUCTION MANUAL MODEL GT820 OXYGEN SENSOR 70046 The information and technical data disclosed by this document may be used and disseminated only for the purposes and to the extent specifically authorized
Hazardous Energy Control (Lockout-Tagout)
 Hazardous Energy Control (Lockout-Tagout) The purpose of this program is to prevent inadvertent operation or energization of machines, equipment, or processes in order to protect employees and establish
Hazardous Energy Control (Lockout-Tagout) The purpose of this program is to prevent inadvertent operation or energization of machines, equipment, or processes in order to protect employees and establish
Technical Data Sheet MF010-O-LC
 Technical Data Sheet MF010-O-LC - 1 - 1. Properties The oxygen measuring system MF010-O-LC determines the oxygen content in gas mixtures up to a temperature of 250 C. It is particularly suitable for the
Technical Data Sheet MF010-O-LC - 1 - 1. Properties The oxygen measuring system MF010-O-LC determines the oxygen content in gas mixtures up to a temperature of 250 C. It is particularly suitable for the
To comply with the OHS Act, the responsible manager must carry out and document the following:
 Owner: Manager Health, Wellbeing and Safety Last Update: 10 January 2018 Contents 1. Purpose... 1 2. Minimum Compliance Requirements... 1 3. Definitions... 2 4. Legislative requirements under the OHS Act
Owner: Manager Health, Wellbeing and Safety Last Update: 10 January 2018 Contents 1. Purpose... 1 2. Minimum Compliance Requirements... 1 3. Definitions... 2 4. Legislative requirements under the OHS Act
Electrical Safety Work Practices
 Work Practices I. SCOPE This program covers any SOUTHWESTERN COMMUNITY COLLEGE employee that may work or be exposed to exposed electrical systems: To assure that employees are not exposed to potentially
Work Practices I. SCOPE This program covers any SOUTHWESTERN COMMUNITY COLLEGE employee that may work or be exposed to exposed electrical systems: To assure that employees are not exposed to potentially
POWERPRESS UNIT. User Manual. Gradient Pneumatic Sequential Compressor. Neomedic
 TIMER (MIN) POWERPRESS UNIT 40 70 40 80 90 10 60 100 MIN MAX PRESSURE (mmhg) User Manual Neomedic 9601 Owens mouth Ave. #8 Chatsworth, CA 91311 Toll Free: 866-990-1168 Tel: 818-998-1023 Fax: 818-998-0277
TIMER (MIN) POWERPRESS UNIT 40 70 40 80 90 10 60 100 MIN MAX PRESSURE (mmhg) User Manual Neomedic 9601 Owens mouth Ave. #8 Chatsworth, CA 91311 Toll Free: 866-990-1168 Tel: 818-998-1023 Fax: 818-998-0277
2.017 Lab Rules and Safety Rm September 9, 2009 (Version 2) Dr. Harrison H. Chin
 2.017 Lab Rules and Safety Rm. 5-007 September 9, 2009 (Version 2) Dr. Harrison H. Chin LAB RULES 1. WORK SAFELY IN THE LAB 2. POWER TOOL USE IS RESTRICTED 3. DO NOT WORK WITH CHEMICALS ALONE 4. CLEAN
2.017 Lab Rules and Safety Rm. 5-007 September 9, 2009 (Version 2) Dr. Harrison H. Chin LAB RULES 1. WORK SAFELY IN THE LAB 2. POWER TOOL USE IS RESTRICTED 3. DO NOT WORK WITH CHEMICALS ALONE 4. CLEAN
MONTGOMERY COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS Office of the Chief Operating Officer Automated External Defibrillator (AED) Guidelines for High Schools
 MONTGOMERY COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS Office of the Chief Operating Officer 2013-2014 Automated External Defibrillator (AED) Guidelines for High Schools Purpose: To provide guidance in the management and administration
MONTGOMERY COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS Office of the Chief Operating Officer 2013-2014 Automated External Defibrillator (AED) Guidelines for High Schools Purpose: To provide guidance in the management and administration
LABORATORY SAFETY MANUAL
 SCHOOL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING & TELECOMMUNICATIONS LABORATORY SAFETY MANUAL FOR UNDERGRADUATE STUDENTS 2004 EE&T UG Safety Manual 1 Introduction School UG Laboratory Safety Manual The aim of this manual
SCHOOL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING & TELECOMMUNICATIONS LABORATORY SAFETY MANUAL FOR UNDERGRADUATE STUDENTS 2004 EE&T UG Safety Manual 1 Introduction School UG Laboratory Safety Manual The aim of this manual
Technical Data. General specifications. Rated operating distance s n 5 mm
 0102 Model Number Features 5 mm flush Usable up to SIL 2 acc. to IEC 61508 Accessories EXG-18 Quick mounting bracket with dead stop BF 18 Mounting flange, 18 mm Technical Data specifications Switching
0102 Model Number Features 5 mm flush Usable up to SIL 2 acc. to IEC 61508 Accessories EXG-18 Quick mounting bracket with dead stop BF 18 Mounting flange, 18 mm Technical Data specifications Switching
UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS FIELD MEDICAL TRAINING BATTALION Camp Lejeune, NC
 UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS FIELD MEDICAL TRAINING BATTALION Camp Lejeune, NC 28542-0042 FMST 504 Conduct Triage TERMINAL LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Given multiple casualties in a tactical environment, conduct
UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS FIELD MEDICAL TRAINING BATTALION Camp Lejeune, NC 28542-0042 FMST 504 Conduct Triage TERMINAL LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Given multiple casualties in a tactical environment, conduct
MISSOURI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY Procedure: 3.6
 Procedure This electrical safety procedure structures safety procedures to meet the requirements of the NFPA-70E Standard. The program is designed for qualified employees who occasionally must perform
Procedure This electrical safety procedure structures safety procedures to meet the requirements of the NFPA-70E Standard. The program is designed for qualified employees who occasionally must perform
MODELS (2 foot Version) (4 foot Version)
 INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL DUROSITE LED LINEAR FIXTURE Document No: 9100-127-2571-99 Rev A April, 2016 MODELS (2 foot Version) (4 foot Version) ALL LAE ALL LBE These instructions contain important
INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL DUROSITE LED LINEAR FIXTURE Document No: 9100-127-2571-99 Rev A April, 2016 MODELS (2 foot Version) (4 foot Version) ALL LAE ALL LBE These instructions contain important
Guidelines on Monitoring in Anaesthesia
 Page 1 of 8 Guidelines on Monitoring in Anaesthesia Version Effective Date 1 OCT 1992 2 FEB 2002 3 APR 2012 4 JUL 2013 5 MAY 2017 Document No. HKCA P1 v5 Prepared by College Guidelines Committee Endorsed
Page 1 of 8 Guidelines on Monitoring in Anaesthesia Version Effective Date 1 OCT 1992 2 FEB 2002 3 APR 2012 4 JUL 2013 5 MAY 2017 Document No. HKCA P1 v5 Prepared by College Guidelines Committee Endorsed
LYMPHA PRESS MANUFACTURED BY MEGO AFEK IMPORTED BY LYMPHA PRESS USA, Ltd. USERS MANUAL LYMPHA PRESS MODEL 201-M
 LYMPHA PRESS MANUFACTURED BY MEGO AFEK IMPORTED BY LYMPHA PRESS USA, Ltd. USERS MANUAL LYMPHA PRESS MODEL 201-M THE LYMPHA PRESS MODEL 201-M IS A THERAPEUTIC DEVICE FOR THE CONTROL OF LYMPHEDEMA OF THE
LYMPHA PRESS MANUFACTURED BY MEGO AFEK IMPORTED BY LYMPHA PRESS USA, Ltd. USERS MANUAL LYMPHA PRESS MODEL 201-M THE LYMPHA PRESS MODEL 201-M IS A THERAPEUTIC DEVICE FOR THE CONTROL OF LYMPHEDEMA OF THE
HSE guidelines. SMay 2015 ELECTRICAL SAFETY HSE LIFE THE NATIONAL OIL&GAS INDUSTRY STANDARD FOR PROFESSIONALS
 HSE guidelines SMay 2015 ELECTRICAL SAFETY HSE LIFE THE NATIONAL OIL&GAS INDUSTRY STANDARD FOR PROFESSIONALS Work safely or do not work at all There are strict procedures when working on electrical installations
HSE guidelines SMay 2015 ELECTRICAL SAFETY HSE LIFE THE NATIONAL OIL&GAS INDUSTRY STANDARD FOR PROFESSIONALS Work safely or do not work at all There are strict procedures when working on electrical installations
IEC :2012 Risk Management Client Completion Form
 IEC 60601-1:2012 Risk Management Client Completion Form F 028c (2018-09-28) IEC 60601-1:2012 Medical electrical equipment: General requirements for basic safety and essential performance (Edition 3.1 Consolidated
IEC 60601-1:2012 Risk Management Client Completion Form F 028c (2018-09-28) IEC 60601-1:2012 Medical electrical equipment: General requirements for basic safety and essential performance (Edition 3.1 Consolidated
SAFE-WORK PRACTICES Working On Or Near Energized Electrical Equipment CAT A-1 SOP #4
 SUNCOR ENERGY PRODUCTS DISTRIBUTION TERMINAL OPERATING MANUAL STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE SAFE-WORK PRACTICES Working On Or Near Energized Electrical Equipment Lifesaving Rules Supporting Document Verify
SUNCOR ENERGY PRODUCTS DISTRIBUTION TERMINAL OPERATING MANUAL STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE SAFE-WORK PRACTICES Working On Or Near Energized Electrical Equipment Lifesaving Rules Supporting Document Verify
Preventive Maintenance
 A Health and Safety Guideline for Your Workplace Why? Preventive maintenance is predetermined work performed to a schedule with the aim of preventing the wear and tear or sudden failure of equipment components.
A Health and Safety Guideline for Your Workplace Why? Preventive maintenance is predetermined work performed to a schedule with the aim of preventing the wear and tear or sudden failure of equipment components.
