Marine ALIEN & INVASIVE SPECIES
|
|
|
- Baldwin Stephens
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Marine ALIEN & INVASIVE SPECIES
2 Contents What are marine alien and invasive species?... 1 Categories Boccardia proboscidea Discinisca tenuis Dodecaceria fewkesi Carcinus maenas Ficopomatus enigmaticus Semimytilus algosus Mytilus galloprovincialis Crassostrea gigas Litopenaeus vannamei Penaeus monodon Penaeus indicus Metridium dianthus Ostrea edulis Sagartia ornata Ciona robusta Balanus glandula Glossary
3 What are marine alien and invasive species? Alien invasive species are plants, animals, pathogens and other organisms that are exotic, non-indigenous or non-native to an ecosystem, and which may cause economic or environmental harm or adversely affect human health. They spread aggressively, which subsequently threatens indigenous ecosystem functioning and biodiversity. Marine alien species are species whose presence in a region is attributed to human actions that enable them to overcome geographical barriers and invasive species are alien species that have self-replacing populations over several generations that have spread from their point of introduction. Coastal systems such as rocky intertidal shores, sandy bays, estuaries and harbours are becoming increasingly impacted and transformed by these species. The transfer of marine alien species involves a variety of vectors and pathways, such as live food and aquaria, ballast water discharge and hull fouling or biofouling of ships, and species or associated species farmed in aquaculture facilities. In marine ecosystems, alien species may become invasive and displace native species, causing the loss of the genetic make-up of native organisms, modify habitats, change community structure, affect foodweb properties, ecosystem processes, obstruct the provision of ecosystem services, impact human health and further cause substantial economic losses. The South African National Biodiversity Institute (SANBI) is mandated by the National Environmental Management: Biodiversity Act (NEM:BA), Act 10 of 2004, Alien and Invasive Species (AIS) regulations, to monitor and report on the state of biodiversity and to provide scientific advice to inform policy 1
4 and decision-making. As part of this mandate, SANBI s Marine Programme reports on the status of marine alien and invasive species and monitors for new introductions in South Africa, as well as providing scientific advice on their management. The AIS regulations list four different categories of invasive species that must be managed, controlled or eradicated from areas where they may cause harm to the environment, or that are prohibited to be brought into South Africa. 2
5 Categories Category 1a: Listed Invasive Species are those species which must be combatted or eradicated. Any form of trade or planting is strictly prohibited. Category 1b: Listed Invasive Species are those species which must be controlled and where possible, removed and destroyed. Any form or trade or planting is strictly prohibited. Category 2: Category 3: Invasive species or species deemed to be potentially invasive, in which a permit is required to carry out a restricted activity. Category 2 species include commercially import species such as pine, wattle and gum trees. Invasive species which may remain in prescribed areas or provinces. Further planting, propagation or trade is prohibited. 3
6 Boccardia proboscidea Category 1b Shell worm Description: The tube-dwelling shell worm is approximately 20 mm long. Its body is yellow when it is alive with visible red blood vessels. The head has a pair of extended feeding tentacles and black eyes. The gills are found on segment 1 and 2, then on segment 6 onwards. The tail is a rounded disc with dorsal notch. Vector/Pathway: Fouling on aquaculture species. Impacts: Reduce the condition of cultured abalones. Habitat: Populations have been reported from widely differing habitats including mudflats, sandy harbours, seagrass beds, amongst barnacles, in coralline algae, Kelp (Macrocystis pyrigera) holdfasts, sandstone or sedimentary rocks, shale and limestone reefs, sewage outfalls and gastropod shells inhabited by hermit crabs. 4
7 Photograph: Carol Simon 5
8 Discinisca tenuis Category 1b Disc lamp shell Description: The shell is flat, round with transparent horny discs up to 20 mm across. They show circular growth lines and may be fringed by long, straight hairs. In their native range they are usually found in large clumps. Vector/Pathway: Aquaculture. Impacts: Reduce the visual appeal of oysters for market. Habitat: Introduced populations are usually attached to oysters or other shellfish as single individuals or in small groups. 6
9 Photograph: Charles Griffiths 7
10 Dodecaceria fewkesi Category 1b Black coral worms Description: Colonies of the black coral worm form hard, grey, semi-circular reefs about 100 mm across. They comprise of hard, chalky tubes. Each colony houses mm long individual jet-black worms, each with a long pair of feeding limbs, behind which lie 4 5 pairs of extended tube-like gills. The colonies are derived asexually from single individuals, hence retaining the sex of the founder. Vector/Pathway: Shipping. Impacts: It forms hard coral-like colonies and is a potential ecosystem engi neer. Habitat: It is found on hard substrata like harbour wharfs, harbour walls and rocks. 8
11 Photograph: Charles Griffiths 9
12 Carcinus maenas Category 1b European shore crab Description: The adult crab reaches up to about 60 mm long and 90 mm wide. The colour of the crab is variable, from a dark brownish-green to a bluish colour. It is distinguished by the three teeth on the front margin of the carapace between the eyes and five along the margins. They have a row of lighter coloured spots which are yellowish white to darker in colour ventrally. The male abdomen is triangular and the female is subtriangular but rounded laterally. Vector/Pathway: Shipping. Impacts: Competes with native crab species and preys on clams, mussels and other species in natural settings and in aquaculture. Habitat: The impact of this crab is potentially most intense in estuaries and bays with soft sediment. 10
13 Photograph: Nicolas Dijkerman 11
14 Ficopomatus enigmaticus Category 1b Reef-building worm Description: The reef-building worms are usually mm in length. They form clusters of large intertwining reef-like masses that may be approximately 7 m in diameter. The tubes are flared at the openings and have collar-like rings along their lengths. Their colour is white in the early stages, but brown stains occur when they are older. The tubes are often covered with green algae. Vector/Pathway: Ship fouling. Impacts: Forms large colonies that foul the hulls of boats. Habitat: Populations occupy lagoons, marinas and estuaries. 12
15 Photograph: Charles Griffiths 13
16 Semimytilus algosus Category 1b Bisexual mussel Description: The bisexual mussel is small, elon gated, relatively fat and smooth, with a brown-green shell; its maximum growth is 50 mm. Most specimens are hermaphroditic, having a male gonad on one side and female one on the other. Mussels have small rope-like tentacles that they use to attach to hard substrates or to each other in colonies. Vector/Pathway: Fouling on large fishing vessels, oil rigs and aquaculture. Impacts: Displacement of native limpets. Habitat: Populations occupy the lower intertidal zone. 14
17 Photograph: SANBI 15
18 Mytilus galloprovincialis Category 2 Mediterranean mussel Description: The Mediterranean mussel is a large, smooth-shelled black to blue mussel, typically from 50 mm up to 120 mm long. It is a bivalve with two shells that are equal and nearly square. The outside of the shell is black-violet in colour; on one side the rim of the shell ends with a pointed and slightly bent umbo (the highest point of each valve of a bivalve shell) while the other side is rounded. It is fat in cross-section compared to the black mussel. Vector/Pathway: Aquaculture, shipping. Impacts: They monopolise space on intertidal rocks. They displace indigenous mussels and large limpets. Habitat: The mussel has dominated the rocky shores and has displaced indigenous mussels and limpets. 16
19 Photograph: SANBI 17
20 Crassostrea gigas Category 2 Giant Pacific oyster Description: The shell of the giant Pacific oyster is long and can reach a length of mm, but their individual size is extremely variable. The left (upper) valve is slightly curved; the right (lower) valve is deep and cup-shaped. The two valves are solid but unequal in size and shape. One shape is usually cemented to a hard substratum. The valves are carved, with large, irregular, rounded circular folds. Circular ribs are present on both valves starting from the umbo (the highest point of each valve of a bivalve shell). Usually whitish in colour, they also display purple streaks and spots. The inner surface is partly milky white. Vector/Pathway: Aquaculture. Impacts: Outcompetes and replaces native bivalves and shellfish for food and space. Habitat: It is able to grow in very varied environments, ranging from estuarine areas (brackish waters) to offshore oceanic waters. 18
21 Photograph: SANBI 19
22 Litopenaeus vannamei Category 2 Whiteleg shrimp Description: The colour of the whiteleg shrimp is typically translucent-white but varies in cases of nutritional deficiencies. The postlarvae ranges from mm in carapace length. The body is divided into specialised regions: head and main internal organs, highly muscularised and specialised abdomen for swimming, and telson (a tail-like structure). Each region bears specialised appendages, either for feeding and crawling or for swimming and breathing. The swimming limbs of the tail fan are used for escape propulsion. Vector/Pathway: Aquaculture. Impacts: There are no known impacts but in areas where it has invaded it is reported to potentially compete with native shrimp species because it approaches food items faster and more aggressively. Habitat: This marine shrimp likes muddy bottoms at depths from the shoreline down to about 72 m. 20
23 Photograph: Sam Siril Nicholas 21
24 Penaeus monodon Category 2 (except KwaZulu-Natal) Giant tiger prawn Description: The largest giant tiger shrimp available commercially reaches total lengths of mm. It is light to dark olive green in colour throughout its body. The head extends beyond the tip of the first pair of appendages. It is s-shaped, with 6 8 dorsal teeth and 2 4 ventral teeth. Vector/Pathway: Aquaculture. Impacts: Compete with, or prey directly upon native shrimp species. Habitat: Populations are found occupying shallow coastal estuaries, lagoons and mangrove areas; sand or muddy sand bottom nearshore marine habitats. 22
25 Photograph: Sam Siril Nicholas 23
26 Penaeus indicus Category 2 (except KwaZulu-Natal) (formerly Fenneropenaeus indicus) Indian prawn Description: The Indian prawn is light in colour with tiny blue and reddish-brown pigment spots. Prawns have a head (thorax), a tail and an abdomen with six segments. The head region is slightly curved at the tip but s-shaped. It also bears 7 9 upper and 3 6 lower teeth. The head region has a spine that bears one pair of eyes, two pairs of feeding appendages and five pairs of walking legs. Vector/Pathway: Aquaculture. Impacts: Vector to viruses and bacteria that affect shrimps. Habitat: Adult populations have been found in widely differing habitats including: mangals, large bays, offshore, sandy beaches and sheltered mangrove areas. 24
27 Photograph: Sam Siril Nicholas 25
28 Metridium dianthus Category 3 Feather duster anemone Description: This anemone is white, brick redorange, or tan-brown often with a white circle around its mouth. It grows up to about 100 mm tall and has up to 100 slender tentacles. Recognised by the lobed oral disc and hundreds of short limbs, which give the species a characteristic fluffy appearance. They are often found in closely packed groups and can reproduce by basal laceration, whereby small sections tear free from the base of the column and develop into new individuals. Vector/Pathway: Fouling on petroleum infrastructure. Impacts: Compete with local species for food. Habitat: It is usually found attached to rocks or other hard surfaces. The depth range is from the subtidal zone and down to 100 m. 26
29 Photograph: Charles Griffiths 27
30 Ostrea edulis Category 3 European flat oyster Description: The European flat oyster grows up to a maximum length of 110 mm. Living specimens are yellowish white. It is flat or slightly curved shell, with concentric (semi-circular) grooves and ridges, with ten or more ribs on the lower but none on the upper shell. The inner surfaces are pearly white or bluish-grey, often with darker blue areas. The left shell is concave and fixed to the substratum, the right shell is flat and sits inside the left. Vector/Pathway: Aquaculture. Impacts: Potential vector for the oyster disease bonamiosis and the oyster pathogen marteiliosis. Habitat: Populations are found occupying sheltered locations, usually in shallow water. 28
31 Photograph: Charles Griffiths 29
32 Sagartia ornata Category 3 Brooding sea anemone Description: The mouth of the brooding sea anemone is creamy-white; the rest of the oral disc is brownish internally and greenish externally, with creamy circular stripes. The oral disc is typically flat with the mouth slit-like to egg-shaped. It has up to 200 tentacles arranged in 4 5 cycles. The internal cycle of tentacles is longer than the external cycle. The last two cycles are considerably smaller than the others. It readily releases sticky white threads when disturbed. Vector/Pathway: Ballast water. Impacts: The brooding sea anemone is an ecosystem engineer as it alters the surrounding consolidating sand and traps coarse sediment, thus affecting the natural biota. Habitat: Populations are found intertidally on sandy shores partially covering the underlying rocks and in cordgrass beds. 30
33 Photograph: Charles Griffiths 31
34 Ciona robusta Category 3 (formerly Ciona intestinalis) Sea vase tunicate Description: The body of the sea vase tunicate is long reaching a maximum length of 100 mm. It is attached to the substratum by the posterior end or more frequently by the left side near the posterior end of the body. It has two tube-like structures that are situated at the anterior end of the body nearly equal in length. The tunic of the sea vase ascidian is cartilaginous and so robust that such individuals in a preserved state can be held upright. The body wall is very delicate and transparent such that the internal structure of the body can be seen through it. Also, its body wall is barely pigmented. It is faintly greenish with eye spots on the margins of the openings. The surface of the robust test may be covered partly by multiple colonies of some sea squirts or some bivalves and thus the tunic becomes quite non-transparent. Vector/Pathway: Shipping, fouling, natural dispersal. Impact: Preys directly on oyster larvae; inhibits oyster settlement by covering them and thereby reducing the amount of free substrate available for attachment. Habitat: The species is well established in artificial habitats including marinas and harbours. 32
35 Photograph: Tammy Robinson 33
36 Balanus glandula Category 3 Pacific barnacle Description: The pacific barnacle is small and approximately mm long. Its shell colour is greyish blue. Adult Pacific barnacles are encased in a cone-shaped shell of 4 8 hard chalky plates and live attached to rocks or hard surfaces. When they are emerged in water, the feathery legs are extended through an opening at the top where they combine to capture food particles. When exposed to air these feathery legs are withdrawn and the shell is sealed by four additional shell plates. The Pacific barnacle has a combination of six shell plates and that is how it is distinguished from other barnacles. It also possesses a chalky base and an m-shaped opening. Vector/Pathway: Fouling in ship hulls or ballast. Impacts: Displaces populations of formerly abundant indigenous barnacle species. Habitat: It is mainly found on intertidal rocks, in the open ocean and protected waters. 34
37 Photograph: Charles Griffiths 35
38 Glossary Abalone an edible mollusc of warm seas, with a shallow earshaped shell lined with mother-of-pearl and pierced with a line of respiratory holes. Antennular peduncle small appendages by which an animal is attached to the rest of the body. Aquaculture is the farming of fish, crustaceans, molluscs, aquatic plants, algae and other aquatic organisms. Bivalve an aquatic mollusc which has a compressed body enclosed within a hinged shell, such as oysters, mussels, and scallops. Carapace the hard upper shell of a tortoise, crustacean or arachnid. Coralline algae a branching reddish seaweed with a calcareous jointed stem. Fouling is the accumulation of unwanted material on solid surfaces to the detriment of function. Laterally at, towards, or from the side or sides; sideways. Larvae the young of any invertebrate animal. Mangals a swampy forest of mangroves. Pathogen a bacterium, virus, or other microorganism that can cause disease. 36
39 Rostrum anterior prolongation of the head. Substrate/substratum a substance or surface that an organism grows and lives on and is supported by. Subtriangular nearly but not quite triangular. Tentacles a slender, flexible limb or appendage in an animal, especially around the mouth of an invertebrate, used for grasping or moving about, or bearing sense organs. Umbo the highest point of each valve of a bivalve shell. Ventrally on or relating to the underside of an animal or plant; abdominal. 37
40 Additional information See SANBI s Seakeys species pages for marine species, including alien and invasive species, at: Contact the SANBI Marine Programme (Marine Alien and Invasive Species Project): Tel.: invasivespecies@sanbi.org.za Editing and design: SANBI Graphics & Editing, December 2017.
Chapter 7. Marine Animals Without a Backbone
 Chapter 7 Marine Animals Without a Backbone Molluscs Characteristics of Phylum: More than 200,000 species Name means "soft body" Basic body plan head, muscular foot and visceral mass in most species Mantle-
Chapter 7 Marine Animals Without a Backbone Molluscs Characteristics of Phylum: More than 200,000 species Name means "soft body" Basic body plan head, muscular foot and visceral mass in most species Mantle-
Saltwater detective guide
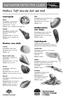 Saltwater detective guide Molluscs: Soft muscular foot and shell Gastropods Snail Description: rounded shell, grey/brown/cream colours. Various sizes: 5 30 mm Habitat: sand or mudflats and Whelk Description:
Saltwater detective guide Molluscs: Soft muscular foot and shell Gastropods Snail Description: rounded shell, grey/brown/cream colours. Various sizes: 5 30 mm Habitat: sand or mudflats and Whelk Description:
ABCs & Name the parts!
 ABCs & Name the parts! Objective: These two activities are used to introduce the students to the variety of marine life living in European waters while learning their ABCs and practicing their letter writing.
ABCs & Name the parts! Objective: These two activities are used to introduce the students to the variety of marine life living in European waters while learning their ABCs and practicing their letter writing.
Phylum Mollusca. Includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids.
 Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids. Bivalves Nautilus Characteristics Soft-bodied invertebrate Covered with protective mantle that may or may
Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids. Bivalves Nautilus Characteristics Soft-bodied invertebrate Covered with protective mantle that may or may
Bivalved molluscs filter feeders
 Class Bivalvia Bivalved molluscs have two shells (valves). Mussels, clams, oysters, scallops, shipworms. Mostly sessile filter feeders. No head or radula. Class Bivalvia Part of the mantle is modified
Class Bivalvia Bivalved molluscs have two shells (valves). Mussels, clams, oysters, scallops, shipworms. Mostly sessile filter feeders. No head or radula. Class Bivalvia Part of the mantle is modified
What is an insect? An insect is an invertebrate (an animal with no spine) that has three pairs of legs and three
 What is an insect? An insect is an invertebrate (an animal with no spine) that has three pairs of legs and three Small minnow mayfly body divisions. The mouth, antennae, and eyes are located on the head;
What is an insect? An insect is an invertebrate (an animal with no spine) that has three pairs of legs and three Small minnow mayfly body divisions. The mouth, antennae, and eyes are located on the head;
TAXONOMIC (DICHOTOMOUS) KEYS
 TAXONOMIC (DICHOTOMOUS) KEYS One method of classifying and identifying objects includes using a taxonomic key, sometimes called a dichotomous key. A taxonomic key looks at the similarities and differences
TAXONOMIC (DICHOTOMOUS) KEYS One method of classifying and identifying objects includes using a taxonomic key, sometimes called a dichotomous key. A taxonomic key looks at the similarities and differences
Name Date Period. Mollusk Review TORSION HEMOLYMPH SESSILE TROCHOPHORE ADDUCTOR KIDNEY HEMOCOEL MANTLE CHROMATOPHORES VISCERAL MASS
 Name Date Period Mollusk Review MOLLUSK VOCABULARY: Match the word with its definition. TORSION HEMOLYMPH SESSILE TROCHOPHORE ADDUCTOR KIDNEY HEMOCOEL MANTLE CHROMATOPHORES VISCERAL MASS Free-swimming
Name Date Period Mollusk Review MOLLUSK VOCABULARY: Match the word with its definition. TORSION HEMOLYMPH SESSILE TROCHOPHORE ADDUCTOR KIDNEY HEMOCOEL MANTLE CHROMATOPHORES VISCERAL MASS Free-swimming
 OCTOPUS Found throughout the world in tropical, warm and cold temperate waters - the octopus is a bottom dweller, spending much of its life in hiding, usually in a hole among rocks. All octopus species
OCTOPUS Found throughout the world in tropical, warm and cold temperate waters - the octopus is a bottom dweller, spending much of its life in hiding, usually in a hole among rocks. All octopus species
Habitat Fact Sheets. Rocky habitats are dominated by seaweeds and often mussels, which rely on the rocks for attachment.
 Habitat Fact Sheets Habitats in the Gulf of Maine serve many important roles for the environment and for humans as well. These include: cycling nutrients, filtering pollution, trapping sediments, storing
Habitat Fact Sheets Habitats in the Gulf of Maine serve many important roles for the environment and for humans as well. These include: cycling nutrients, filtering pollution, trapping sediments, storing
PHYLUM: PLATHYHELMINTHES
 PHYLUM: PLATHYHELMINTHES FLATWORMS Free living (living independently i.e. not attached) Bilaterally symmetrical with a definite front and back, and with left and right sides. Mobile creeping animals. Concentration
PHYLUM: PLATHYHELMINTHES FLATWORMS Free living (living independently i.e. not attached) Bilaterally symmetrical with a definite front and back, and with left and right sides. Mobile creeping animals. Concentration
Barnacles attach to hard surfaces and use their legs to catch tiny particles of food, including plankton from the water around them.
 Food Web Resources - Food Chain Cards Barnacles attach to hard surfaces and use their legs to catch tiny particles of food, including plankton from the water around them Barnacle Edible crabs use their
Food Web Resources - Food Chain Cards Barnacles attach to hard surfaces and use their legs to catch tiny particles of food, including plankton from the water around them Barnacle Edible crabs use their
Oyster Reef in the Classroom A Hands-On Laboratory Approach
 Grade Level: 7 Oyster Reef in the Classroom A Hands-On Laboratory Approach Subject Area: Life Science Virginia Standards of Learning: LS.4, LS.7, LS.8, LS. 11 Objectives: Students will: Understand the
Grade Level: 7 Oyster Reef in the Classroom A Hands-On Laboratory Approach Subject Area: Life Science Virginia Standards of Learning: LS.4, LS.7, LS.8, LS. 11 Objectives: Students will: Understand the
Bivalves: Mollusks that Matter
 Objective Bivalves: Mollusks that Matter Version 6/05 Students will understand the anatomy and physiology of mussels, and understand why they may pose health risks to humans. National Science Education
Objective Bivalves: Mollusks that Matter Version 6/05 Students will understand the anatomy and physiology of mussels, and understand why they may pose health risks to humans. National Science Education
Mollusks Soft-bodied Invertebrates
 Mollusks Soft-bodied Invertebrates Phylum Mollusca Very diverse - more species of molluscs than any other group in the ocean. Phylum includes: Bivalves (2 shells); ex. Clam Gastropods (1 shell, coiled);
Mollusks Soft-bodied Invertebrates Phylum Mollusca Very diverse - more species of molluscs than any other group in the ocean. Phylum includes: Bivalves (2 shells); ex. Clam Gastropods (1 shell, coiled);
Tide Pools Starfish eating a mussel
 Tide Pools Lesson 6 T ide pools form in rocks where water collects in depressions in the rocks during low tide. A variety of plants and animals live their entire life in a tide pool. Many animals that
Tide Pools Lesson 6 T ide pools form in rocks where water collects in depressions in the rocks during low tide. A variety of plants and animals live their entire life in a tide pool. Many animals that
27-4 Mollusks. Slide 1 of 43. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 1 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What Is a Mollusk? Mollusks are soft-bodied animals that usually have an internal or external shell. Mollusks include snails, slugs, clams, squids, octopi... They are group together
1 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What Is a Mollusk? Mollusks are soft-bodied animals that usually have an internal or external shell. Mollusks include snails, slugs, clams, squids, octopi... They are group together
`Mollusks. may or may not form a hard, calcium carbonate shell. Trochophore Larva
 `Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Soft-bodied invertebrate covered with protective mantle that may or may not form a hard, calcium carbonate shell Includes chitons, snails, slugs, clams, oysters, squid, octopus,
`Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Soft-bodied invertebrate covered with protective mantle that may or may not form a hard, calcium carbonate shell Includes chitons, snails, slugs, clams, oysters, squid, octopus,
Stonefly. Gilled Snails
 Mid-Michigan Macroinvertebrates Identification Guide & Descriptions Mayfly Nymphs have 3 tail filaments occasionally 2 tail filaments never paddle or fan-like Feathery gills line the sides of the abdomen
Mid-Michigan Macroinvertebrates Identification Guide & Descriptions Mayfly Nymphs have 3 tail filaments occasionally 2 tail filaments never paddle or fan-like Feathery gills line the sides of the abdomen
Lobsters, Crab and Shrimp
 Lobsters, Crab and Shrimp Crustaceans Phylum: Arthropoda ( jointed feet ) Invertebrate Exoskeleton (made of chitin) protects body and provides a place for muscles to attach to. Segmented body Jointed appendages
Lobsters, Crab and Shrimp Crustaceans Phylum: Arthropoda ( jointed feet ) Invertebrate Exoskeleton (made of chitin) protects body and provides a place for muscles to attach to. Segmented body Jointed appendages
DISCOVER THE. Sheppey. Shoreline. A family guide to the wildlife that can be found on the island s beaches
 DISCOVER THE Sheppey Shoreline A family guide to the wildlife that can be found on the island s beaches 1 Index 3 Introduction 4 Glossary of words and terms 6 The Strandline - Common piddock shell - Bladder
DISCOVER THE Sheppey Shoreline A family guide to the wildlife that can be found on the island s beaches 1 Index 3 Introduction 4 Glossary of words and terms 6 The Strandline - Common piddock shell - Bladder
Lecture Benthic Ecology
 Lecture Benthic Ecology Benthos Unlike the drifting plankton and swimming nekton, benthic organisms commonly referred to as benthos live on or near the ocean bottom A benthic habitat may be shallow or
Lecture Benthic Ecology Benthos Unlike the drifting plankton and swimming nekton, benthic organisms commonly referred to as benthos live on or near the ocean bottom A benthic habitat may be shallow or
Marine Ecosystems. Aquatic Ecosystems Section 2
 Marine Ecosystems Marine ecosystems are located mainly in coastal areas and in the open ocean. Organisms that live in coastal areas adapt to changes in water level and salinity. Organisms that live in
Marine Ecosystems Marine ecosystems are located mainly in coastal areas and in the open ocean. Organisms that live in coastal areas adapt to changes in water level and salinity. Organisms that live in
Dewees Island Game Fish & Shellfish
 Dewees Island Game Fish & Shellfish Red Drum Also called: spottail, spottail bass, channel bass, redfish, puppy drum Limit: 2 per person, per day Size: 15-inch minimum, 24-inch maximum Remarks: Red drum
Dewees Island Game Fish & Shellfish Red Drum Also called: spottail, spottail bass, channel bass, redfish, puppy drum Limit: 2 per person, per day Size: 15-inch minimum, 24-inch maximum Remarks: Red drum
Overview. What are Corals?
 Overview Coral Reefs extend back over 500 m.y. Grow in tropical seas with normal salinity Support a great variety of plant and animal life Cover less than 0.2% of sea floor Contain about 25% of marine
Overview Coral Reefs extend back over 500 m.y. Grow in tropical seas with normal salinity Support a great variety of plant and animal life Cover less than 0.2% of sea floor Contain about 25% of marine
Monterey Bay Aquarium Fieldtrip Worksheet
 Attach ticket stub here. Name: Class: B11 or B3A Lab day & time: Monterey Bay Aquarium Fieldtrip Worksheet General Information Address: 886 Cannery Row Monterey, California 93940 Hours: 10am 6pm (May vary
Attach ticket stub here. Name: Class: B11 or B3A Lab day & time: Monterey Bay Aquarium Fieldtrip Worksheet General Information Address: 886 Cannery Row Monterey, California 93940 Hours: 10am 6pm (May vary
Let s take a closer look at estuaries and learn why they are important.
 ave you ever wondered what happens where a river or stream flows into the ocean? When fresh water meets saltwater in a protected bay or inlet, a partially enclosed body of water called an estuary often
ave you ever wondered what happens where a river or stream flows into the ocean? When fresh water meets saltwater in a protected bay or inlet, a partially enclosed body of water called an estuary often
Exploring Tide Pools. Exploring Tide Pools. Visit for thousands of books and materials.
 Exploring Tide Pools A Reading A Z Level R Leveled Reader Word Count: 1,617 LEVELED READER R Exploring Tide Pools Written by Trica Oshant Hawkins Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials.
Exploring Tide Pools A Reading A Z Level R Leveled Reader Word Count: 1,617 LEVELED READER R Exploring Tide Pools Written by Trica Oshant Hawkins Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials.
Have You Wondered? College of Marine Sciences, Shanghai Ocean University
 Have You Wondered? 1. What role sponges play in marine ecosystems? 2. Why some animals are radially symmetrical? 3. If all gelatinous animals are jellyfishes? 4. What flatworms are? 5. What a lophophorate
Have You Wondered? 1. What role sponges play in marine ecosystems? 2. Why some animals are radially symmetrical? 3. If all gelatinous animals are jellyfishes? 4. What flatworms are? 5. What a lophophorate
Life on Fiji s Mangrove Trees. Alison Haynes
 Life on Fiji s Mangrove Trees Alison Haynes Life on Fiji s Mangrove Trees Alison Haynes L i f e o n F i j i s M a n g r o v e T r e e s 1 Acknowledgement My thanks to Johnson Seeto for the photograph
Life on Fiji s Mangrove Trees Alison Haynes Life on Fiji s Mangrove Trees Alison Haynes L i f e o n F i j i s M a n g r o v e T r e e s 1 Acknowledgement My thanks to Johnson Seeto for the photograph
ARTHROPODS JOINTED-LEGS ARTHROPODS ARE THE LARGEST GROUP OF ANIMALS!
 ARTHROPODS JOINTED-LEGS ARTHROPODS ARE THE LARGEST GROUP OF ANIMALS! WHO S WHO? SHRIMP ISOPOD SPIDER CRAB BARNACLE LOBSTER BASIC CHARACTERISTICS BILATERAL SYMMETRY SEGMENTED ANIMALS JOINTED BODY & PARTS
ARTHROPODS JOINTED-LEGS ARTHROPODS ARE THE LARGEST GROUP OF ANIMALS! WHO S WHO? SHRIMP ISOPOD SPIDER CRAB BARNACLE LOBSTER BASIC CHARACTERISTICS BILATERAL SYMMETRY SEGMENTED ANIMALS JOINTED BODY & PARTS
Biology. Slide 1 of 43. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 43 2 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What are the defining features of mollusks? 3 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What Is a Mollusk? Mollusks are soft-bodied animals that usually have an internal or external
Biology 1 of 43 2 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What are the defining features of mollusks? 3 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What Is a Mollusk? Mollusks are soft-bodied animals that usually have an internal or external
Examples of estuaries include bays, sounds, salt marshes, mangrove forests, mud flats, swamps, inlets, and sloughs.
 An estuary is a partially enclosed body of water where incoming seawater is mixed with fresh water coming from the land. Examples of estuaries include bays, sounds, salt marshes, mangrove forests, mud
An estuary is a partially enclosed body of water where incoming seawater is mixed with fresh water coming from the land. Examples of estuaries include bays, sounds, salt marshes, mangrove forests, mud
Shell Honour Created by I & L Weir Queensland, Australia May 2007
 Shell Honour Created by I & L Weir Queensland, Australia May 2007 Q1. What is the meaning of Mollusc? Animal with a soft body usually protected by a shell. E.g. Snails, mussels, oysters and cockles. Q2.
Shell Honour Created by I & L Weir Queensland, Australia May 2007 Q1. What is the meaning of Mollusc? Animal with a soft body usually protected by a shell. E.g. Snails, mussels, oysters and cockles. Q2.
I. Evolutionary Perspective. Chapter 12. II. Molluscan Characteristics. A. Regions of Molluscan Body 11/2/10
 I. Evolutionary Perspective Chapter 12 Molluscan Success Some of the world s best predators Large brains Complex sensory structures Rapid locomotion Grasping tentacles Tearing mouthparts Have been around
I. Evolutionary Perspective Chapter 12 Molluscan Success Some of the world s best predators Large brains Complex sensory structures Rapid locomotion Grasping tentacles Tearing mouthparts Have been around
INDICATOR BENTHIC MACROINVERTEBRATE SPECIES AND THEIR CHARACTERISTICS
 Coelenterata (Hydras) Turbellaria (Flatworms) A tube with tentacles Reproduces asexually by budding Movement: sessile, attached or fixed, not free moving Colour: clear to whitish Flattened shape Distinct
Coelenterata (Hydras) Turbellaria (Flatworms) A tube with tentacles Reproduces asexually by budding Movement: sessile, attached or fixed, not free moving Colour: clear to whitish Flattened shape Distinct
BIVALVE MOLLUSC CARE SOP# - MOLL1
 BIVALVE MOLLUSC CARE SOP# - MOLL1 PURPOSE: To describe methods of care of bivalve molluscs. POLICY: To provide optimum care for all animals. RESPONSIBILITY: Collector and user of the animals. If these
BIVALVE MOLLUSC CARE SOP# - MOLL1 PURPOSE: To describe methods of care of bivalve molluscs. POLICY: To provide optimum care for all animals. RESPONSIBILITY: Collector and user of the animals. If these
BeCome a BSAC Beachcomber!
 BeCome a BSAC Beachcomber! Welcome to the BSAC Beachcomber! Let s learn together and discover some fascinating facts about the amazing creatures living in the rock pools along our seashore... Who we are
BeCome a BSAC Beachcomber! Welcome to the BSAC Beachcomber! Let s learn together and discover some fascinating facts about the amazing creatures living in the rock pools along our seashore... Who we are
FAO SPECIES IDENTIFICATION SHEETS FISTULARIIDAE. Cornetfishes, flutemouths
 click for previous page FIST 1982 FAO SPECIES IDENTIFICATION SHEETS FISHING AREA 51 (W. Indian Ocean) FISTULARIIDAE Cornetfishes, flutemouths Body elongate and depressed. Mouth small, at end of a long
click for previous page FIST 1982 FAO SPECIES IDENTIFICATION SHEETS FISHING AREA 51 (W. Indian Ocean) FISTULARIIDAE Cornetfishes, flutemouths Body elongate and depressed. Mouth small, at end of a long
1 P a g e. Crabs of the Maroochy Wetlands Sanctuary. Compiled by Robyn Howard August 2011
 Identifying Crabs at Maroochy Wetlands Sanctuary The old saying Rules were meant to be broken seems to apply when it comes to crab identification. In general, the Ocypodid family have long eye-stalks and
Identifying Crabs at Maroochy Wetlands Sanctuary The old saying Rules were meant to be broken seems to apply when it comes to crab identification. In general, the Ocypodid family have long eye-stalks and
FAO SPECIES IDENTIFICATION SHEETS. FAMILY: PENAEIDAE FISHING AREA 51 (W. Indian Ocean) Parapenaeopsis maxillipedo Alcock, 1905
 click for previous page PEN Para 8 FAO SPECIES IDENTIFICATION SHEETS FAMILY: PENAEIDAE FISHING AREA 51 (W. Indian Ocean) Parapenaeopsis maxillipedo Alcock, 1905 1983 OTHER SCIENTIFIC NAMES STILL IN USE:
click for previous page PEN Para 8 FAO SPECIES IDENTIFICATION SHEETS FAMILY: PENAEIDAE FISHING AREA 51 (W. Indian Ocean) Parapenaeopsis maxillipedo Alcock, 1905 1983 OTHER SCIENTIFIC NAMES STILL IN USE:
Warm-up # 7 A day 5/17 - B day 5/18 UPDATE YOUR TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Warm-up # 7 A day 5/17 - B day 5/18 UPDATE YOUR TABLE OF CONTENTS Question: List all examples of surface water on Earth. Answer: Rivers and streams, lakes and reservoirs, (ponds) wetlands, estuaries and
Warm-up # 7 A day 5/17 - B day 5/18 UPDATE YOUR TABLE OF CONTENTS Question: List all examples of surface water on Earth. Answer: Rivers and streams, lakes and reservoirs, (ponds) wetlands, estuaries and
Lesson 10: Oyster Reefs and Their Inhabitants
 Lesson 10: Oyster Reefs and Their Inhabitants Focus Question: What animals use oyster reefs for habitats? Objective: observe properties of animals found within a bag of oysters; Infer about the quality
Lesson 10: Oyster Reefs and Their Inhabitants Focus Question: What animals use oyster reefs for habitats? Objective: observe properties of animals found within a bag of oysters; Infer about the quality
Point Rating: 3 Size: 10 mm Description: Caddisfly larvae are builders. They make sticky silk from their spit and use it to spin webs for trapping
 Point Rating: 3 Size: 10 mm Description: Caddisfly larvae are builders. They make sticky silk from their spit and use it to spin webs for trapping other insects. Other species use the silk as glue that
Point Rating: 3 Size: 10 mm Description: Caddisfly larvae are builders. They make sticky silk from their spit and use it to spin webs for trapping other insects. Other species use the silk as glue that
Title: May 31 2:42 PM (1 of 23) Phylum Mollusca
 Title: May 31 2:42 PM (1 of 23) Phylum Mollusca Title: May 31 3:25 PM (2 of 23) often referred to as mollusks second largest phylum has 7 classes only looking at 4 bilateral symmetry, true body cavity
Title: May 31 2:42 PM (1 of 23) Phylum Mollusca Title: May 31 3:25 PM (2 of 23) often referred to as mollusks second largest phylum has 7 classes only looking at 4 bilateral symmetry, true body cavity
Phylum Mollusca. By: Christa Jewett, Instructor
 Phylum Mollusca By: Christa Jewett, Instructor For since the creation of the world God s invisible qualities His eternal power and divine nature have been clearly seen, being understood from what has been
Phylum Mollusca By: Christa Jewett, Instructor For since the creation of the world God s invisible qualities His eternal power and divine nature have been clearly seen, being understood from what has been
Crayfish Dissection. Materials:gloves, preserved crayfish, paper towel, dissecting pan, scissors, forceps, dissecting. Background: LME-305
 Living Science LME-305 Crayfish Dissection Materials:gloves, preserved crayfish, paper towel, dissecting pan, scissors, forceps, dissecting needle, dissecting pins, and pen or pencil Background: Like all
Living Science LME-305 Crayfish Dissection Materials:gloves, preserved crayfish, paper towel, dissecting pan, scissors, forceps, dissecting needle, dissecting pins, and pen or pencil Background: Like all
Hester-Dendy Sampling Method Leaf Bag Sampling Method D-Net Sampling Method
 Hester-Dendy Sampling Method 1. Submerge the Hester-Dendy Sampler by attaching it to a rock or cement block with zip strips. Make careful notes about the sampler location. Measure out to the location from
Hester-Dendy Sampling Method 1. Submerge the Hester-Dendy Sampler by attaching it to a rock or cement block with zip strips. Make careful notes about the sampler location. Measure out to the location from
Invasive Species Student Worksheet
 1 Invasive Species Student Worksheet Asian long-horned beetle (Anoplophora glabripennis). Kyle T. Ramirez Kyle T. Ramirez Introduction Invasive Species A species that establishes itself in an area that
1 Invasive Species Student Worksheet Asian long-horned beetle (Anoplophora glabripennis). Kyle T. Ramirez Kyle T. Ramirez Introduction Invasive Species A species that establishes itself in an area that
Common Arthropods of the Inter0dal Zone
 CM 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 Common Arthropods of the Inter0dal Zone This visual guide is intended to aid you in iden1fying crabs and shrimp commonly captured while
CM 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 Common Arthropods of the Inter0dal Zone This visual guide is intended to aid you in iden1fying crabs and shrimp commonly captured while
Crustacean and Molluscs - production and diseases in Europe. Ed Peeler Isabelle Arzul Grant Stentiford
 Crustacean and Molluscs - production and diseases in Europe Ed Peeler Isabelle Arzul Grant Stentiford Disease emergence & host switching Disease spread through trade in live animals Spill over from farmed
Crustacean and Molluscs - production and diseases in Europe Ed Peeler Isabelle Arzul Grant Stentiford Disease emergence & host switching Disease spread through trade in live animals Spill over from farmed
Unit 18.2: Mollusks and Annelids
 Unit 18.2: Mollusks and Annelids Lesson Objectives Describe invertebrates in the phylum Mollusca. Summarize the characteristics of annelids. Vocabulary Annelida deposit feeder gills heart mantle Mollusca
Unit 18.2: Mollusks and Annelids Lesson Objectives Describe invertebrates in the phylum Mollusca. Summarize the characteristics of annelids. Vocabulary Annelida deposit feeder gills heart mantle Mollusca
SALINITY. It's the amount of dissolved salts the water contains.
 AQUATIC ECOSYSTEMS SALINITY The types of organisms in an aquatic ecosystem depend upon the water s Salinity. It's the amount of dissolved salts the water contains. Salinity determines the two main aquatic
AQUATIC ECOSYSTEMS SALINITY The types of organisms in an aquatic ecosystem depend upon the water s Salinity. It's the amount of dissolved salts the water contains. Salinity determines the two main aquatic
ANECDOTES ABOUT ANIMALS AND PLANTS ON THE SEASHORE
 Explorer Education Programme ANECDOTES ABOUT ANIMALS AND PLANTS ON THE SEASHORE Students and teachers can use the following stories and anecdotes to help remember facts about the animals and plants they
Explorer Education Programme ANECDOTES ABOUT ANIMALS AND PLANTS ON THE SEASHORE Students and teachers can use the following stories and anecdotes to help remember facts about the animals and plants they
Invasion of Asian Tiger Shrimp (Penaeus monodon Fabricius, 1798) in the Western Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico
 Invasion of Asian Tiger Shrimp (Penaeus monodon Fabricius, 1798) in the Western Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico Pam Fuller, USGS David Knott, Poseidon Taxonomic Services Peter R. Kingsley-Smith, SC DNR James
Invasion of Asian Tiger Shrimp (Penaeus monodon Fabricius, 1798) in the Western Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico Pam Fuller, USGS David Knott, Poseidon Taxonomic Services Peter R. Kingsley-Smith, SC DNR James
Phylum Mollusca. More than 500,000 known species. Class Polyplacophora. Class Bivalvia. Class Gastropoda. Class Cephalopoda
 Phylum Mollusca Class Polyplacophora Class Gastropoda Class Bivalvia Class Cephalopoda chitons Snails Sea slugs nudibranchs clams Squid Octopus Cuttlefish Nautilus More than 500,000 known species A bag,
Phylum Mollusca Class Polyplacophora Class Gastropoda Class Bivalvia Class Cephalopoda chitons Snails Sea slugs nudibranchs clams Squid Octopus Cuttlefish Nautilus More than 500,000 known species A bag,
Mollusks- soft bodied
 Mollusks- soft bodied Objectives Understand the taxonomic relationships and major features of mollusks Learn the external and internal anatomy of the clam and squid Understand the major advantages and
Mollusks- soft bodied Objectives Understand the taxonomic relationships and major features of mollusks Learn the external and internal anatomy of the clam and squid Understand the major advantages and
An Unwelcome Newcomer
 An Unwelcome Newcomer An Unwelcome Newcomer This article is provided courtesy of the American Museum of Natural History. million eggs each year. Then Invasion of the Zebra Mussels the young mussels float
An Unwelcome Newcomer An Unwelcome Newcomer This article is provided courtesy of the American Museum of Natural History. million eggs each year. Then Invasion of the Zebra Mussels the young mussels float
Phylum Mollusca. Soft-bodied animals. Internal or external shell. Include snails, slugs, clams, squids and octopi
 Phylum Mollusca Soft-bodied animals Internal or external shell Include snails, slugs, clams, squids and octopi Trochophore: free-swimming larval stage of an aquatic mollusk True coeloms Have complex organ
Phylum Mollusca Soft-bodied animals Internal or external shell Include snails, slugs, clams, squids and octopi Trochophore: free-swimming larval stage of an aquatic mollusk True coeloms Have complex organ
FAO SPECIES IDENTIFICATION SHEETS. FAMILY: LETHRINIDAE FISHING AREA 51 (W. Indian Ocean) Lethrinus conchyliatus (Smith, 1959)
 click for previous page LETH Leth 9 1983 FAO SPECIES IDENTIFICATION SHEETS FAMILY: LETHRINIDAE FISHING AREA 51 (W. Indian Ocean) Lethrinus conchyliatus (Smith, 1959) OTHER SCIENTIFIC NAMES STILE IN USE:
click for previous page LETH Leth 9 1983 FAO SPECIES IDENTIFICATION SHEETS FAMILY: LETHRINIDAE FISHING AREA 51 (W. Indian Ocean) Lethrinus conchyliatus (Smith, 1959) OTHER SCIENTIFIC NAMES STILE IN USE:
A Survey of the Shore Crabs in Siletz Bay before the Invasion of the European Green Crab, Carcinus maenas
 Chapter 9 Abstract Methods and Materials DESCRIPTION OF THE SITE POPULATION STRUCTURE Results Discussion CRAB DISTRIBUTIONS IN SILETZ BAY POTENTIAL EFFECTS OF C. MAENAS IN SILETZ BAY Acknowledgments A
Chapter 9 Abstract Methods and Materials DESCRIPTION OF THE SITE POPULATION STRUCTURE Results Discussion CRAB DISTRIBUTIONS IN SILETZ BAY POTENTIAL EFFECTS OF C. MAENAS IN SILETZ BAY Acknowledgments A
6/23/2010. Characteristics of Invasive Species
 Aquatic Nuisance Species Aquatic Invasive Species Exotic Aquatics Biological Roulette By the end of the 21st century, biological invasions [will] become one of the most prominent ecological l issues on
Aquatic Nuisance Species Aquatic Invasive Species Exotic Aquatics Biological Roulette By the end of the 21st century, biological invasions [will] become one of the most prominent ecological l issues on
Mollusc Adaptation and Diversity
 Mollusc Adaptation and Diversity Grade Level: grades 9-12 Lesson Summary: Students will examine a variety of live and preserved molluscs. They will compare and contrast body forms and try to relate the
Mollusc Adaptation and Diversity Grade Level: grades 9-12 Lesson Summary: Students will examine a variety of live and preserved molluscs. They will compare and contrast body forms and try to relate the
Mollusks Are Soft and Unsegmented
 Mollusks Objectives Understand the taxonomic relationships and major features of mollusks Learn the external and internal anatomy of the clam and squid Understand the major advantages and limitations of
Mollusks Objectives Understand the taxonomic relationships and major features of mollusks Learn the external and internal anatomy of the clam and squid Understand the major advantages and limitations of
NATIVE OYSTER RESTORATION AT ELKHORN SLOUGH, CALIFORNIA Summary of Elkhorn Slough National Estuarine Research Reserve and Elkhorn Slough Foundation
 NATIVE OYSTER RESTORATION AT ELKHORN SLOUGH, CALIFORNIA Summary of Elkhorn Slough National Estuarine Research Reserve and Elkhorn Slough Foundation partnership project Pain%ng by Cory and Catska Ench,
NATIVE OYSTER RESTORATION AT ELKHORN SLOUGH, CALIFORNIA Summary of Elkhorn Slough National Estuarine Research Reserve and Elkhorn Slough Foundation partnership project Pain%ng by Cory and Catska Ench,
1. Distribute the activity sheet, and allow 20 minutes for the first use.
 A LOCAL WAY OF LEARNING Title: MISSING MANGROVE MESSAGE Author: Eulalie R. Rivera Elementary School Environmental Education Team Grade Level: 4-6 Concepts: 2.Ecosystem 6.Resources 9.Change Disciplines:
A LOCAL WAY OF LEARNING Title: MISSING MANGROVE MESSAGE Author: Eulalie R. Rivera Elementary School Environmental Education Team Grade Level: 4-6 Concepts: 2.Ecosystem 6.Resources 9.Change Disciplines:
Apogon abrogramma Fraser and Lachner, 1985
 Apogon abrogramma Fraser and Lachner, 1985 English Name: Faintstripe cardinalfish Family: APOGONIDAE Local Name: Ehrongu boadhi Order: Perciformes Size: Common to 7cm; max. 10cm Specimen: MRS/0203/88 Distinctive
Apogon abrogramma Fraser and Lachner, 1985 English Name: Faintstripe cardinalfish Family: APOGONIDAE Local Name: Ehrongu boadhi Order: Perciformes Size: Common to 7cm; max. 10cm Specimen: MRS/0203/88 Distinctive
A DAY AT THE WHITNEY LAB The Whitney Laboratory for Marine Bioscience An Institute for Marine Research and Biotechnology
 A DAY AT THE WHITNEY LAB The Whitney Laboratory for Marine Bioscience An Institute for Marine Research and Biotechnology STUDENT NAME: What s For Lunch? The Mission In this activity, you will make an educated
A DAY AT THE WHITNEY LAB The Whitney Laboratory for Marine Bioscience An Institute for Marine Research and Biotechnology STUDENT NAME: What s For Lunch? The Mission In this activity, you will make an educated
Ocean Series Coral Reefs
 Ocean Series Coral Reefs Coral is part of the animal kingdom, a member of the scientific phylum Cnidaria along with other marine creatures including sea jellies. Sea jellies have a soft gelatinous body
Ocean Series Coral Reefs Coral is part of the animal kingdom, a member of the scientific phylum Cnidaria along with other marine creatures including sea jellies. Sea jellies have a soft gelatinous body
Marine Environments. Copyright 2011 LessonSnips
 Marine Environments I must go down to the seas again, for the call of the running tide Is a wild call and a clear call that may not be denied Excerpt from a poem by John Masefield Continents and islands
Marine Environments I must go down to the seas again, for the call of the running tide Is a wild call and a clear call that may not be denied Excerpt from a poem by John Masefield Continents and islands
A-Z San Diego Animal Guide
 A-Z San Diego Animal Guide Anemone- Anémona Aa I have stinging tentacles to catch my prey. I am a cousin of jellyfish and corals. I get protection from the sun and predators by covering my body with seashells,
A-Z San Diego Animal Guide Anemone- Anémona Aa I have stinging tentacles to catch my prey. I am a cousin of jellyfish and corals. I get protection from the sun and predators by covering my body with seashells,
Guide to Families 29 BIVALVES TECHNICAL TERMS AND MEASUREMENTS. Dorsal margin. posterior adductor muscle scar lateral tooth
 Guide to Families 29 BIVALVES Coastal species are of great interest to fisheries and have potential for exportation for eating purposes. Bivalves are caught mainly by divers and are also fished for pearls.
Guide to Families 29 BIVALVES Coastal species are of great interest to fisheries and have potential for exportation for eating purposes. Bivalves are caught mainly by divers and are also fished for pearls.
Spiny skinned animals with radial symmetrical body plan. Rays emanating from a common center. Internal skeleton of hardened plates of calcium
 Echinodermata Spiny skinned animals with radial symmetrical body plan. Rays emanating from a common center. Internal skeleton of hardened plates of calcium carbonate. Water vascular system and tube feet
Echinodermata Spiny skinned animals with radial symmetrical body plan. Rays emanating from a common center. Internal skeleton of hardened plates of calcium carbonate. Water vascular system and tube feet
Oceans Humans both depend on it and threaten it with their activities
 Oceans Humans both depend on it and threaten it with their activities Oceans Water covers nearly ¾ of the Earth s surface More than 50% of the world s population lives within an hour of the coast Oceans
Oceans Humans both depend on it and threaten it with their activities Oceans Water covers nearly ¾ of the Earth s surface More than 50% of the world s population lives within an hour of the coast Oceans
Water Snail Class Gastropoda
 Water Snail Class Gastropoda Water snails are molluscs. They have small horny teeth that they use to feed on water plants and algae by scaping it off hard surfaces such as rocks and logs. They have a coiled
Water Snail Class Gastropoda Water snails are molluscs. They have small horny teeth that they use to feed on water plants and algae by scaping it off hard surfaces such as rocks and logs. They have a coiled
SCRIPPS BIRCH AQUARIUM WORKSHEET
 SCRIPPS BIRCH AQUARIUM WORKSHEET Name 1. Read over the Student Learning Outcomes and associated General Questions on this page, and refer back and take notes on this page as you walk through the aquarium,
SCRIPPS BIRCH AQUARIUM WORKSHEET Name 1. Read over the Student Learning Outcomes and associated General Questions on this page, and refer back and take notes on this page as you walk through the aquarium,
Reef Watch Guidelines
 Reef Watch Guidelines What is Reef Watch? Reef watch is a simple one-dive-one-survey method to record the health of coral reefs. The method is easily learnt and it is even easier to participate in the
Reef Watch Guidelines What is Reef Watch? Reef watch is a simple one-dive-one-survey method to record the health of coral reefs. The method is easily learnt and it is even easier to participate in the
Which fish is for which state?
 By Jacob Buhrle Which fish is for which state? Oregon Chinook Salmon Florida Sailfish (saltwater) Largemouth Bass (freshwater) Eat or be Eaten: Chinook Salmon They feed on terrestrial and aquatic insects,
By Jacob Buhrle Which fish is for which state? Oregon Chinook Salmon Florida Sailfish (saltwater) Largemouth Bass (freshwater) Eat or be Eaten: Chinook Salmon They feed on terrestrial and aquatic insects,
TIDE POOLS and CORAL REEFS
 THEMATIC UNIT TIDE POOLS and CORAL REEFS Written by Jeanne King Edited by Patricia Miriani Sima Illustrated by Cheryl Buhler Teacher Created Resources, Inc. 6421 Industry Way Westminster, CA 92683 www.teachercreated.com
THEMATIC UNIT TIDE POOLS and CORAL REEFS Written by Jeanne King Edited by Patricia Miriani Sima Illustrated by Cheryl Buhler Teacher Created Resources, Inc. 6421 Industry Way Westminster, CA 92683 www.teachercreated.com
THEJ FIRST ZOEA OF PORCELLANA. By W K. BROOKS and E. B. WILSON. With Plate* VI and VII.
 7 "83?* {Jn-fJatoj 11 "T THEJ FIRST ZOEA OF PORCELLANA. By W K BROOKS and E. B. WILSON. With Plate* VI and VII. 7z O THE FIRST ZOEA OF PORCELLANA. By W K. BROOKS and E. B. WILSON. With Plates VI and VII.
7 "83?* {Jn-fJatoj 11 "T THEJ FIRST ZOEA OF PORCELLANA. By W K BROOKS and E. B. WILSON. With Plate* VI and VII. 7z O THE FIRST ZOEA OF PORCELLANA. By W K. BROOKS and E. B. WILSON. With Plates VI and VII.
Oceans Alive Resource Book
 E-BOOK CODE: REAU5023 Special School Photocopy Master Edition Oceans Alive Resource Book Image courtesy Microsoft Design Gallery by Sandy Tasker Contents OCEANS ALIVE Contents... 3 The Wonderful World
E-BOOK CODE: REAU5023 Special School Photocopy Master Edition Oceans Alive Resource Book Image courtesy Microsoft Design Gallery by Sandy Tasker Contents OCEANS ALIVE Contents... 3 The Wonderful World
CUSTOM CREATED FOR NAMUKA BAY BY DAEIRA CONSERVATION NAMUKA BAY 2018 REEF GUIDE
 CUSTOM CREATED FOR NAMUKA BAY BY DAEIRA CONSERVATION NAMUKA BAY 2018 REEF GUIDE WELCOME Welcome to the reef at Namuka Bay! ABOUT DAEIRA CONSERVATION Located on the southern coast of Viti Levu, Fiji, Namuka
CUSTOM CREATED FOR NAMUKA BAY BY DAEIRA CONSERVATION NAMUKA BAY 2018 REEF GUIDE WELCOME Welcome to the reef at Namuka Bay! ABOUT DAEIRA CONSERVATION Located on the southern coast of Viti Levu, Fiji, Namuka
28 2 Groups of Arthropods
 28 2 Groups of Arthropods 1 of 42 28 2 Groups of Arthropods Arthropods are classified based on the number and structure of their body segments and appendages particularly their mouthparts. The three major
28 2 Groups of Arthropods 1 of 42 28 2 Groups of Arthropods Arthropods are classified based on the number and structure of their body segments and appendages particularly their mouthparts. The three major
Remarks: Allen & Swainston (1988) have erroneously recorded this species from northwestern Australia.
 click for previous page 71 Literature: Masuda et al. (1975, 1984); Kyushin et al. (1977); Smith (1977); Randall et al. (1978, as P. townsendi); Rau & Rau (1980); Kyushin et al. (1982); Fischer & Bianchi
click for previous page 71 Literature: Masuda et al. (1975, 1984); Kyushin et al. (1977); Smith (1977); Randall et al. (1978, as P. townsendi); Rau & Rau (1980); Kyushin et al. (1982); Fischer & Bianchi
Chapter 29 Echinoderms and Invertebrate Chordates. Section Echinoderms. I. What Is An Echinoderm? 11/1/2010. Biology II Mrs.
 Chapter 29 Echinoderms and Invertebrate Chordates Section 29.1 - Echinoderms Biology II Mrs. Michaelsen I. What Is An Echinoderm? A. Move by means of hydraulic, suction cuptipped appendages. B. Skin covered
Chapter 29 Echinoderms and Invertebrate Chordates Section 29.1 - Echinoderms Biology II Mrs. Michaelsen I. What Is An Echinoderm? A. Move by means of hydraulic, suction cuptipped appendages. B. Skin covered
Teacher Resource Guide
 Teacher Resource Guide By Liz Kreitinger Objective The object of this presentation is to create an understanding of the function and purpose of adaptations, while applying this concept to life under water.
Teacher Resource Guide By Liz Kreitinger Objective The object of this presentation is to create an understanding of the function and purpose of adaptations, while applying this concept to life under water.
Terms of Use. Copyright Natural Beach Living
 Terms of Use All rights reserved. No part of this packet may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form by any means - electronic, mechanical, photo-copies, recording, or otherwise
Terms of Use All rights reserved. No part of this packet may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form by any means - electronic, mechanical, photo-copies, recording, or otherwise
ì<(sk$m)=bdhehd< +^-Ä-U-Ä-U Scott Foresman Science 1.5 Food Chains Nonfiction Draw Conclusions Captions Labels Call Outs Glossary
 Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Draw Conclusions Captions Labels Call Outs Glossary Food Chains Scott Foresman Science 1.5 ì
Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Draw Conclusions Captions Labels Call Outs Glossary Food Chains Scott Foresman Science 1.5 ì
Fish. Water Dwelling Animals
 Fish Water Dwelling Animals Class Agnatha (Jawless fish) They are believed to be the most primitive and oldest vertebrates. Lamprey and hagfish are the only 2 living members of this class and are placed
Fish Water Dwelling Animals Class Agnatha (Jawless fish) They are believed to be the most primitive and oldest vertebrates. Lamprey and hagfish are the only 2 living members of this class and are placed
What are Arthropods? General Characteristics. General Characteristics 5/14/2013. Phylum Arthropoda Biology 11
 What are Arthropods? Phylum Arthropoda Biology 11 Segmented invertebrates Jointed appendages Exoskeleton Includes the most numerous and diverse animals on Earth They are found in virtually every habitat
What are Arthropods? Phylum Arthropoda Biology 11 Segmented invertebrates Jointed appendages Exoskeleton Includes the most numerous and diverse animals on Earth They are found in virtually every habitat
click for previous page 245 General Remarks STOMATOPODS by M. Tavares, Universidade Santa Úrsula, Brazil
 click for previous page 245 General Remarks STOMATOPODS by M. Tavares, Universidade Santa Úrsula, Brazil 246 Stomatopods TECHNICAL TERMS AND MEASUREMENTS antennule eye carapace thoracic stomites 5 6 7
click for previous page 245 General Remarks STOMATOPODS by M. Tavares, Universidade Santa Úrsula, Brazil 246 Stomatopods TECHNICAL TERMS AND MEASUREMENTS antennule eye carapace thoracic stomites 5 6 7
Rocky Shore Zones: the lower intertidal zone
 Rocky Shore Zones: the lower intertidal zone Topic Zones, Adaptations Duration Two sessions Vocabulary adaptation challenge feature lower intertidal zone zone Standards Practices Analyzing and Interpreting
Rocky Shore Zones: the lower intertidal zone Topic Zones, Adaptations Duration Two sessions Vocabulary adaptation challenge feature lower intertidal zone zone Standards Practices Analyzing and Interpreting
Progress in Marine Ecosystem Classification, Mapping and Targets: Testing the Boundaries
 Progress in Marine Ecosystem Classification, Mapping and Targets: Testing the Boundaries Kerry Sink 1, Natasha Karenyi 1,2 and Tamsyn Livingstone 3 1 South African National Biodiversity Institute 2 University
Progress in Marine Ecosystem Classification, Mapping and Targets: Testing the Boundaries Kerry Sink 1, Natasha Karenyi 1,2 and Tamsyn Livingstone 3 1 South African National Biodiversity Institute 2 University
Invasive Species Student Worksheet
 1 Invasive Species Student Worksheet Asian long-horned beetle (Anoplophora glabripennis). Kyle T. Ramirez Kyle T. Ramirez Introduction Invasive Species A species that establishes itself in an area that
1 Invasive Species Student Worksheet Asian long-horned beetle (Anoplophora glabripennis). Kyle T. Ramirez Kyle T. Ramirez Introduction Invasive Species A species that establishes itself in an area that
APPENDIX F DANGEROUS FISH AND MOLLUSKS
 APPENDIX F DANGEROUS FISH AND MOLLUSKS Since fish and mollusks may be one of your major sources of food, it is wise to know which ones are dangerous to you should you catch them. Know which ones are dangerous,
APPENDIX F DANGEROUS FISH AND MOLLUSKS Since fish and mollusks may be one of your major sources of food, it is wise to know which ones are dangerous to you should you catch them. Know which ones are dangerous,
Project Limulus on Napatree Point: Horseshoe Crab Surveys in 2017
 Project Limulus on Napatree Point: Horseshoe Crab Surveys in 2017 Laura Craver-Rogers & Kevin Rogers Napatree Point Conservation Area, Watch Hill Conservancy & Watch Hill Fire District Napatree Naturalist
Project Limulus on Napatree Point: Horseshoe Crab Surveys in 2017 Laura Craver-Rogers & Kevin Rogers Napatree Point Conservation Area, Watch Hill Conservancy & Watch Hill Fire District Napatree Naturalist
Coastal areas have become increasingly under threat in recent years. Climate change is having a huge effect on coastal areas, making them much more
 Why are some coastal environments under threat? Coastal areas have become increasingly under threat in recent years. Climate change is having a huge effect on coastal areas, making them much more likely
Why are some coastal environments under threat? Coastal areas have become increasingly under threat in recent years. Climate change is having a huge effect on coastal areas, making them much more likely
Kingdom Animalia Subkingdom Eumetazoa Bilateria Phylum Mollusca
 Kingdom Animalia Subkingdom Eumetazoa Bilateria Phylum Mollusca Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Illustrations 2014 Cengage Learning unless otherwise noted Phylum Mollusca Molluscs (mollis = soft)
Kingdom Animalia Subkingdom Eumetazoa Bilateria Phylum Mollusca Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Illustrations 2014 Cengage Learning unless otherwise noted Phylum Mollusca Molluscs (mollis = soft)
Over the next few weeks, we will be learning all about the Coral Reef Ecosystems that surround much of the Australian coastline.
 Over the next few weeks, we will be learning all about the Coral Reef Ecosystems that surround much of the Australian coastline. You will need to complete the tasks set out below and hand them in at the
Over the next few weeks, we will be learning all about the Coral Reef Ecosystems that surround much of the Australian coastline. You will need to complete the tasks set out below and hand them in at the
GEORGIA SOUTH CAROLINA GEORGIA SOUTH CAROLINA Concern Concern Endangered Unlisted
 Atlantic pigtoe mussel Fusconaia masoni Concern Concern Endangered Unlisted (Note: Top drawing shows details of external shell; bottom drawing shows interior hinge area with teeth. Line represents 1 cm.)
Atlantic pigtoe mussel Fusconaia masoni Concern Concern Endangered Unlisted (Note: Top drawing shows details of external shell; bottom drawing shows interior hinge area with teeth. Line represents 1 cm.)
