Chapter 22. Phylum Echnodermata 4/13/2009. Characteristics. Diversity. Group Diversity. Ecology, Economics, and Research.
|
|
|
- Ginger Griffith
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
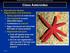
1 Characteristics Chapter 22 All members of the phylum have a calcareous skeleton. The spiny endoskeleton consists of plates. They have a unique water vascular system. They possess pedicellariae and dermal branchiae. They have radial or biradial symmetry Phylum Echnodermata Copyright The McGraw Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. They are an ancient group extending back to the Cambrian period. They likely descended from bilateral ancestors their larvae are bilateral. One theory is that they evolved radiality as an adaptation to sessile existence. The body plan is derived from crinoid like ancestors that became free moving descendants later. They lack ability to osmoregulate and this restricts them to marine environments. No parasitic echinoderms are known a few are commensals. Ecology, Economics, and Research Due to their spiny structure, echinoderms are not often preyed upon. A few fish and otters are adapted to feed on sea urchins. Humans sometimes eat the sea urchin gonads and the body wall of certain holothurians. Sea stars feed on molluscs, crustaceans and other invertebrates they may damage oyster beds. The embryology of sea urchin eggs is very observable. Artificial parthenogenesis was first described for sea urchin eggs they develop without fertilization if treated with hypertonic seawater or subjected to other stimuli. Group Asteroids or sea stars are mostly predators. Ophiuroids or brittle stars move by active arms and may be scavengers, browsers or commensal. Holothurians or sea cucumbers are mostly suspension or deposit feeders. Echinoids or sea urchins are found on hard bottoms while sand dollars prefer sand substrate they feed on detritus. Crinoids are sessile and flower like as young and detach as adults they are suspension feeders. Class Asteroidea Sea stars are common along shorelines and may aggregate on rocks. Some sea stars live on muddy or sandy bottoms, or among coral reefs. They range from a centimeter across to about a meter across and may be brightly colored. Asterias is common on the east coast of the U.S. Pisaster is common on the west coast. 1
2 Sea stars have a central disc with tapering arms extending outward. The body is flattened and flexible, with a pigmented and ciliated epidermis. The mouth is on the underside or oral side. A large radial nerve is in the center of each ambulacral groove. Under the nerve is an extension of the coelom and the radial canal of the water vascular system. In all other cases except crinoids, ossicles or other dermal tissue covers these structures. On the aboral side is a circular madreporite that is a sieve leading to the water vascular system From the madreporite, water drains from the stone canal that leads to the ring canal. This leads into radial canals connected to ampullae that lead to tube feet. The ambulacrum runs from the mouth to the tip of each arm. Usually there are five arms but there may be more. The ambulacral groove is bordered by rows of tube feet. The aboral surface is spiny at the base of the spines are groups of pincer like pedicellariae. Pedicellariae keep the body surface free of debris. Papulae (dermal branchiae or skin gills) are soft projections lined with peritoneum and serve in respiration Endoskeleton Under the epidermis is the mesodermal endoskeleton of small calcareous plates or ossicles. Ossicles are penetrated by a meshwork of spaces filled with fibers and dermal cells. Muscles in the body wall move the rays and partially close the ambulacral grooves. 2
3 Coelom, Excretion, and Respiration The spacious body coelom filled with fluid is one coelomic compartment. The fluid contains amebocytes (coelomocytes). Ciliated peritoneal lining of the coelom circulates the fluid around the cavity and into papulae. Respiratory gases and nitrogenous waste ammonia diffuse across the papulae and tube feet. Some wastes are picked up by coelomocytes, which migrate to the tips of papulae to be pinched off. Water Vascular System This system is another coelomic compartment and is unique to echinoderms. It consists of a system of canals, tube feet and dermal ossicles. This system functions in locomotion and foodgathering as well as respiration and excretion. The system opens to the outside at the madreporite on the aboral side. Water vascular System Polian vesicles may also be attached; they serve for fluid storage. Small lateral canals, each with a one way valve, connect the radial canal to the tube feet. The inner end of each tube foot or podium is an ampulla that lies within the body coelom. The outer end of each tube foot bears a sucker. The water vascular system operates hydraulically; valves in lateral canals prevent backflow. Water vascular System Locomotion Muscles in the ampulla contract forcing fluid into and extending the podium. Contraction of longitudinal muscles in the tube foot retracts it, forcing fluid back into the ampulla. Small muscles in the end of the tube foot raise the middle of the end, creating suction. The sea star can move while being firmly adhered to the substrate. Tube feet are innervated by a central nervous system; they move in one direction but not in unison. Cutting a radial nerve ends coordination in one arm; cutting a circumoral nerve ring stops all movement. Feeding and Digestive System Feeding The mouth on the oral side leads through a short esophagus to a large central stomach. The lower cardiac part of the stomach can be everted through the mouth during feeding. The upper stomach is smaller and is connected by ducts to a pair of pyloric ceca in each arm. The anus is inconspicuous and empties on the center at the top; some lack an intestine and anus. Marine2.html Sea stars consume a wide range of food; some eat sea urchins and regurgitate undigestible parts. Some feed on molluscs; they pull steadily until they can insert a stomach through the crack. Some sea stars food on small particles that are carried up ambulacral grooves to the mouth. 3
4 Nervous System Reproductive System, Regeneration, and Autonomy The oral system of a nerve ring and radial nerves coordinate the tube feet. A deep hyponeural system aboral to the oral system forms a ring around the anus and extends into the roof of each ray. The epidermal nerve plexus coordinates responses of the dermal branchiae to tactile stimulation. Tactile organs are scattered over the surface and an ocellus is at the tip of each arm. They react to touch, temperature, chemicals and light intensity; they are mainly active at night. /science/regeneration.htm Most have separate sexes; a pair of gonads is in each interradial space. Fertilization is external; in early summer, eggs and sperm are shed into the water. Echinoderms also regenerate lost parts; they can cast off injured arms and regenerate new ones. An arm can regenerate a new sea star if at least one fifth of the central disc is present. Development Development In most cases, embryonating eggs are dispersed in the water and hatch to free swimming larvae. Embryogenesis shows a typical primitive deuterostome pattern. The left hydrocoel becomes the water vascular system; the left axocoel becomes the stone canal and perihemal channels. The free swimming larva has cilia arranged in bands and is called a bipinnaria. Ciliated tracts become larval arms. When the larva grows three adhesive arms and a sucker at the anterior, it is called a brachiolaria. A brachiolaria then attaches to the substrate and undergoes metamorphosis into a radial juvenile. As its arms and tube feet appear, the animal detaches from its stalk and becomes a young sea star. Class Ophiuroidea This group is largest in number of species and probably in abundance. The arms of the brittle stars are slender and distinct from the central disc. They lack pedicellariae or papulae and the ambulacral groove is closed and coated with ossicles. Tube feet lack suckers. The madreporite is on the oral surface. The tube feet lack ampullae; protrusion is generated by proximal muscles. Each jointed arm has a column of articulated ossicles called vertebrae. Arms are moved in pairs for locomotion. Five movable plates act as jaws and surround the mouth; there is no anus. Skin is leathery and surface cilia are mostly lacking. Visceral organs are all in the central disc; the arms are too slender to accomodate them. The stomach is saclike; there is no intestine. The water vascular, nervous and hemal systems resemble those of sea stars. 4
5 Reproduction Five invaginations called bursae open to the oral surface by genital slits at the bases of the arms. Gonads on the wall of each bursa discharge ripe sex cells into the water for external fertilization. Sexes are usually separate but a few are hermaphroditic. The larva has ciliated bands that extend onto delicate and beautiful larval arms. In contrast to sea stars, they lack any attached phases during metamorphosis. Regeneration and autotomy are more pronounced than in sea stars they are very fragile. Biology Brittle stars are secretive and live on hard or sandy bottoms where little light penetrates, often under rocks or in kelp holdfasts. They browse on food or suspension feed. Class Echinoidea Sea urchins lack arms but their tests show the five part symmetry. The up folding brings the ambulacral areas up to the area of the anus. Most sea urchins have a hemispherical shape with radial symmetry and long spines. Sand dollars and heart urchins (irregular echinoids) have become bilateral with short spines. Regular urchins move by tube feet irregular urchins move by their spines. Echinoids occur from intertidal regions to deep ocean. The echinoid test has ten double rows of plates with movable, stiff spines. The tube feet extend along the five ambulacral rows. The spines articulate on ball and socket joints moved by small muscles at the bases. Among the several kinds of pedicellaria, the three jawed variety on long stalks is most common. Some species have pedicellariae with poison glands that secrete a toxin that paralyzes small prey. Five converging teeth and sometimes branched gills encircle the peristome. The anus, genital pores, and madreporite are aboral and in the periproct region. 5
6 Form and Function Inside the test is Aristotle s lantern, a complex set of chewing structures. Sand dollars and heart urchins have shifted the anus to the posterior and can be defined bilaterally. A ciliated siphon connects the esophagus to the intestine food can be concentrated in the intestine. Sea urchins eat algae sand dollars filter particles through their spines. Hemal and nervous systems resemble those in asteroids. Ambulacral grooves are closed and radial canals run just beneath the test in each radii. In irregular urchins, respiratory podia are arranged in fields called petaloids on the aboral surface. Reproduction Sexes are separate both eggs and sperm are shed into the sea for external fertilization. Some, including pencil urchins, brood young in depressions between the spines. Larvae of nonbrooding echinoids live a planktonic existence before becoming urchins. Class Holothuroidea As their name suggests, these animals resemble cucumbers. They are greatly elongated in the oral aboral axis. Ossicles are very reduced and the body is soft. Some species crawl on the ocean bottom, others are found under rocks or burrow. conservation.org/image_gallery/pages/uw216 12%20(sea%20cucumber)Andre%20Seale.html Video The body wall is leathery with tiny ossicles buried in it a few have dermal armor. In some, locomotor tube feet are distributed to all five ambulacral areas most have them only on the ambulacra that faces the substratum. The side that faces the substratum (the sole) has three ambulacra, adding a secondary bilaterality. 6
7 All tube feet, except oral tentacles, are absent in burrowing forms. Oral tentacles are tube feet surrounding the mouth. The coelomic cavity has many coelomocytes. The digestive system opens into a cloaca a respiratory tree also empties into the cloaca. A madreporite lies free in the coelom the hemal system is more developed than in other echinoderms. The respiratory tree also serves for excretion gas exchange also occurs through the skin and tube feet. Reproduction Sexes are separate but some are hermaphroditic. Sea cucumbers have a single gonad this is considered a primitive character. Fertilization is external and produces free swimming larvae. A few brood their young inside the body or on the body surface. Biology Defense Sea cucumbers cast out part of their viscera when irritated they must regenerate these tissues. The organs of Cuvier are expelled in the direction of an enemy they are sticky and have toxins. Sea cucumbers use both ventral tube feet and muscular body waves to move. Some trap particles on the mucus of their tentacles and suck off the food particles in their pharynx. Others graze the sea bottom with their tentacles. Commensal Relationship Class Crinoidea One small fish, Carapus, uses the cloaca and respiratory tree of a sea cucumber for shelter. Crinoids include both sea lilies and feather stars they have primitive characters. Crinoids are far more numerous in the fossil record. They are unique in being attached for most of their life. ea lilies have a flower shaped body at the tip of a stalk. Feather stars have long, many branched arms adults are free moving but may be sessile. Many crinoids are deep water species feather stars are found in more shallow water. 7
8 The body disc or calyx is covered with a leathery skin or tegmen of calcareous plates. The five arms branch to form more arms, each with lateral pinnules as in a feather. The calyx and arms form a crown. Sessile forms have a stalk formed of plates; it appears jointed and may bear cirri. A madreporite, spines and pedicellariae are absent. The upper surface has a mouth that opens into an esophagus and intestine; it then exits the anus. Tube feet and mucous nets allow it to feed on small organisms in the ambulacral grooves. It has a water vascular system, an oral ring and a radial nerve to each arm. Reproduction Phylogeny Sexes are separate; gonads are merely masses of cells in the genital cavity of the arms and pinnules. Gametes escape through ruptures in the pinnule wall; some brood their eggs. Larvae are free swimming before they become attached and metamorphose. Most living crinoids are cm long; some fossil species had stalks 20 meters long. The fossil record is extensive but there are still many theories about their evolution. From the larvae, we know the ancestor was bilateral and the coelom had three pairs of spaces. One theory states sessile groups derived independently from free moving adults with radial symmetry. Traditional views consider the first echinoderms sessile and radial, giving rise to free swimming forms. Early forms may have had endoskeletal plates and external ciliary grooves. Echinoids and holothuroids are related; the relationship of ophiuroids and asteroids is controversial. Fig
CHAPTER 22. Echinoderms 22-1
 CHAPTER 22 Echinoderms 22-1 Phylum Echinodermata: Diversity and Characteristics Characteristics All members have a calcareous skeleton Spiny endoskeleton consists of plates Unique water-vascular system
CHAPTER 22 Echinoderms 22-1 Phylum Echinodermata: Diversity and Characteristics Characteristics All members have a calcareous skeleton Spiny endoskeleton consists of plates Unique water-vascular system
 Echinoderms Name Means: Echino- Spiny Derm- Skin About 7,000 species No Head! No Brain! No ventral, dorsal, posterior, or anterior sides! Do have oral (mouth) and aboral sides. Symmetry: Larvae are
Echinoderms Name Means: Echino- Spiny Derm- Skin About 7,000 species No Head! No Brain! No ventral, dorsal, posterior, or anterior sides! Do have oral (mouth) and aboral sides. Symmetry: Larvae are
ADVANCED INVERTEBRATES HAVE COMPLEX BODIES AND INTERNAL SYSTEMS
 ADVANCED INVERTEBRATES HAVE COMPLEX BODIES AND INTERNAL SYSTEMS Arthropoda Most successful phylum on Earth Exoskeleton chitin Striated muscle Articulation Crayfish, lobsters, shrimp, crabs Echinodermata
ADVANCED INVERTEBRATES HAVE COMPLEX BODIES AND INTERNAL SYSTEMS Arthropoda Most successful phylum on Earth Exoskeleton chitin Striated muscle Articulation Crayfish, lobsters, shrimp, crabs Echinodermata
Spiny skinned animals with radial symmetrical body plan. Rays emanating from a common center. Internal skeleton of hardened plates of calcium
 Echinodermata Spiny skinned animals with radial symmetrical body plan. Rays emanating from a common center. Internal skeleton of hardened plates of calcium carbonate. Water vascular system and tube feet
Echinodermata Spiny skinned animals with radial symmetrical body plan. Rays emanating from a common center. Internal skeleton of hardened plates of calcium carbonate. Water vascular system and tube feet
TAKSONOMI HEWAN CHAPTER 8: ECHINODERMATA
 TAKSONOMI HEWAN CHAPTER 8: ECHINODERMATA Husni Mubarok, S.Pd., M.Si. Tadris Biologi IAIN Jember DEUTEROSTOMIA Termasuk sand dollar, bintang laut, landak laut/ bulu babi, hidup di laut, masuk dalam klade
TAKSONOMI HEWAN CHAPTER 8: ECHINODERMATA Husni Mubarok, S.Pd., M.Si. Tadris Biologi IAIN Jember DEUTEROSTOMIA Termasuk sand dollar, bintang laut, landak laut/ bulu babi, hidup di laut, masuk dalam klade
Class Asteroidea. Reproductive System, Regeneration, and Autonomy
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Compaies, Ic. Permissio required for reproductio or display. Class Asteroidea Reproductive System, Regeeratio, ad Autoomy Sexes separate i most sexes Pair of goads i each iterradial
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Compaies, Ic. Permissio required for reproductio or display. Class Asteroidea Reproductive System, Regeeratio, ad Autoomy Sexes separate i most sexes Pair of goads i each iterradial
Echinoderms. Phylum Echinodermata
 Echinoderms Phylum Echinodermata spiny skinned or hedgehog skin sea stars (starfish), sea urchins, sea cucumbers 6000 species radial symmetry in 2 o development bilateral symmetry in larva http://www.biologyreference.com/dn-ep/echinoderm.html
Echinoderms Phylum Echinodermata spiny skinned or hedgehog skin sea stars (starfish), sea urchins, sea cucumbers 6000 species radial symmetry in 2 o development bilateral symmetry in larva http://www.biologyreference.com/dn-ep/echinoderm.html
Z202-Unit 9/10 Chapter 22 Chaetognaths, Echinoderms & Hemichordates
 Z202-Unit 9/10 Chapter 22 Chaetognaths, Echinoderms & Hemichordates I. Diversity A. Evolutionary Diversity - Cambrian Explosion (535 to 530 mya) radiation in diversity seen in fossil record other explosions
Z202-Unit 9/10 Chapter 22 Chaetognaths, Echinoderms & Hemichordates I. Diversity A. Evolutionary Diversity - Cambrian Explosion (535 to 530 mya) radiation in diversity seen in fossil record other explosions
Phyla Echinodermata and Chordata
 10/27/14 Deuterostomes! v Echinoderms and Phyla Echinodermata and Chordata Deuterostome Review v Deuterostomes share developmental characteristics Radial cleavage Formation of the anus from the blastopore
10/27/14 Deuterostomes! v Echinoderms and Phyla Echinodermata and Chordata Deuterostome Review v Deuterostomes share developmental characteristics Radial cleavage Formation of the anus from the blastopore
Phyla Echinodermata and Chordata
 Phyla Echinodermata and Chordata Deuterostomes! v Echinoderms and chordates constitute the clade Deuterostomia v Echinoderms (phylum Echinodermata) include sea stars and sea urchins v Chordates (phylum
Phyla Echinodermata and Chordata Deuterostomes! v Echinoderms and chordates constitute the clade Deuterostomia v Echinoderms (phylum Echinodermata) include sea stars and sea urchins v Chordates (phylum
Chapter 29 Echinoderms and Invertebrate Chordates. Section Echinoderms. I. What Is An Echinoderm? 11/1/2010. Biology II Mrs.
 Chapter 29 Echinoderms and Invertebrate Chordates Section 29.1 - Echinoderms Biology II Mrs. Michaelsen I. What Is An Echinoderm? A. Move by means of hydraulic, suction cuptipped appendages. B. Skin covered
Chapter 29 Echinoderms and Invertebrate Chordates Section 29.1 - Echinoderms Biology II Mrs. Michaelsen I. What Is An Echinoderm? A. Move by means of hydraulic, suction cuptipped appendages. B. Skin covered
Protostome: Embryonic blastopore becomes mouth
 Classical hypothesis Molecular hypothesis Adoutte 2000 PNAS Protostome: Embryonic blastopore becomes mouth Schizocoelous development (typical of the protostome coelomates) 1 Deuterostome: Embryonic blastopore
Classical hypothesis Molecular hypothesis Adoutte 2000 PNAS Protostome: Embryonic blastopore becomes mouth Schizocoelous development (typical of the protostome coelomates) 1 Deuterostome: Embryonic blastopore
Chapter 28 Arthropods and Echinoderms. Body Terms. Evolution has led to:
 Chapter 28 Arthropods and Echinoderms Introduction to Arthropods jointed feet Most diverse and successful animals Over 750,000 species identified Segmented bodies Tough exoskeleton Jointed appendages Body
Chapter 28 Arthropods and Echinoderms Introduction to Arthropods jointed feet Most diverse and successful animals Over 750,000 species identified Segmented bodies Tough exoskeleton Jointed appendages Body
PLACOZOA Small multicellular hairy sticky flat things
 PLACOZOA Small multicellular hairy sticky flat things BODY PLAN 5 CELL TYPES Two species described in this phylum 1. Trichoplax adharens 2. Treptoplax reptans Smallest amount of DNA yet measured for any
PLACOZOA Small multicellular hairy sticky flat things BODY PLAN 5 CELL TYPES Two species described in this phylum 1. Trichoplax adharens 2. Treptoplax reptans Smallest amount of DNA yet measured for any
Protostomes vs Deuterostomes. Phylum Mollusca
 Protostomes vs Deuterostomes Animals that have a true coelom and complete digestive system can be divided into two main groups. This division is based on the way their embryos develop and the way in which
Protostomes vs Deuterostomes Animals that have a true coelom and complete digestive system can be divided into two main groups. This division is based on the way their embryos develop and the way in which
Title: May 31 2:42 PM (1 of 23) Phylum Mollusca
 Title: May 31 2:42 PM (1 of 23) Phylum Mollusca Title: May 31 3:25 PM (2 of 23) often referred to as mollusks second largest phylum has 7 classes only looking at 4 bilateral symmetry, true body cavity
Title: May 31 2:42 PM (1 of 23) Phylum Mollusca Title: May 31 3:25 PM (2 of 23) often referred to as mollusks second largest phylum has 7 classes only looking at 4 bilateral symmetry, true body cavity
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. CHAPTER 17. Annelids 17-1
 CHAPTER 17 Annelids 17-1 Characteristics of the Phylum Annelida Diversity Exhibit segmentation or metamerism Bodies composed of repeated units Each unit contains components of most MAJOR organ systems
CHAPTER 17 Annelids 17-1 Characteristics of the Phylum Annelida Diversity Exhibit segmentation or metamerism Bodies composed of repeated units Each unit contains components of most MAJOR organ systems
Phylum: Porifera (sponges)
 Phylum: Porifera (sponges) (8,761 known species) General Description: Simplest animals, multicellular No organs or body systems Skeleton composed of spongin (soft) and spicules (hard) Symmetry: Asymmetrical
Phylum: Porifera (sponges) (8,761 known species) General Description: Simplest animals, multicellular No organs or body systems Skeleton composed of spongin (soft) and spicules (hard) Symmetry: Asymmetrical
An introduction to the taxonomy of the Echinodermata
 An introduction to the taxonomy of the Echinodermata Yves Samyn Belgian Focal Point to the GTI Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences Classification of the Phylum Echinodermata in the Animal Kingdom
An introduction to the taxonomy of the Echinodermata Yves Samyn Belgian Focal Point to the GTI Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences Classification of the Phylum Echinodermata in the Animal Kingdom
Phylum Mollusca. Includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids.
 Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids. Bivalves Nautilus Characteristics Soft-bodied invertebrate Covered with protective mantle that may or may
Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids. Bivalves Nautilus Characteristics Soft-bodied invertebrate Covered with protective mantle that may or may
I. Evolutionary Perspective. Chapter 12. II. Molluscan Characteristics. A. Regions of Molluscan Body 11/2/10
 I. Evolutionary Perspective Chapter 12 Molluscan Success Some of the world s best predators Large brains Complex sensory structures Rapid locomotion Grasping tentacles Tearing mouthparts Have been around
I. Evolutionary Perspective Chapter 12 Molluscan Success Some of the world s best predators Large brains Complex sensory structures Rapid locomotion Grasping tentacles Tearing mouthparts Have been around
Figure 33.25a Free-living nematode
 Figure 33.25a Free-living nematode Bilateraly symmetrical Pseudocoelomates Body covered with secreated, flexible cuticle. No cilia Only longitudinal muscles. No protonephridia Muscular pharynx Gonochoristic
Figure 33.25a Free-living nematode Bilateraly symmetrical Pseudocoelomates Body covered with secreated, flexible cuticle. No cilia Only longitudinal muscles. No protonephridia Muscular pharynx Gonochoristic
ZOO 2040 Biology of Animals Topic 12 Lophophorates, Chaetognaths, Echinoderms, and Hemichordates
 Deuterostomes are a group of several higher phyla: the Lophophorates (Phoronida, Ectoprocta, and Brachiopoda), Chaetognatha, Echinodermata, Hemichordata, and Chordata (which includes vertebrates) Lophophorates
Deuterostomes are a group of several higher phyla: the Lophophorates (Phoronida, Ectoprocta, and Brachiopoda), Chaetognatha, Echinodermata, Hemichordata, and Chordata (which includes vertebrates) Lophophorates
Biology 11 - Chapter 31 Assignment
 Name: Class: Date: Biology 11 - Chapter 31 Assignment True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Echinoderms exhibit their invertebrate heritage by their hard exoskeletons made of calcium
Name: Class: Date: Biology 11 - Chapter 31 Assignment True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Echinoderms exhibit their invertebrate heritage by their hard exoskeletons made of calcium
What Is an Annelid? Annelids are worms with segmented bodies. They have a true coelom that is lined with tissue derived from mesoderm.
 What Is an Annelid? What Is an Annelid? Phylum: Annelidae Annelids are worms with segmented bodies. They have a true coelom that is lined with tissue derived from mesoderm. Three Germ Layers of an Annelid
What Is an Annelid? What Is an Annelid? Phylum: Annelidae Annelids are worms with segmented bodies. They have a true coelom that is lined with tissue derived from mesoderm. Three Germ Layers of an Annelid
Mollusks are soft bodied animals that have an internal or external shell, a similar body plan consisting of four basic parts: a foot, mantle, shell,
 Mollusca Mollusks are soft bodied animals that have an internal or external shell, a similar body plan consisting of four basic parts: a foot, mantle, shell, and visceral mass. Mollusks also possess a
Mollusca Mollusks are soft bodied animals that have an internal or external shell, a similar body plan consisting of four basic parts: a foot, mantle, shell, and visceral mass. Mollusks also possess a
Each unit contains components of most organ systems. Increased burrowing efficiency by permitting movement of segments
 CHAPTER 17 Annelids Characteristics of the Phylum Annelida Diversity Exhibit segmentation or Bodies composed of units Each unit contains components of most organ systems Increased burrowing efficiency
CHAPTER 17 Annelids Characteristics of the Phylum Annelida Diversity Exhibit segmentation or Bodies composed of units Each unit contains components of most organ systems Increased burrowing efficiency
27-4 Mollusks. Slide 1 of 43. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 1 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What Is a Mollusk? Mollusks are soft-bodied animals that usually have an internal or external shell. Mollusks include snails, slugs, clams, squids, octopi... They are group together
1 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What Is a Mollusk? Mollusks are soft-bodied animals that usually have an internal or external shell. Mollusks include snails, slugs, clams, squids, octopi... They are group together
Phylum Mollusca. Soft-bodied animals. Internal or external shell. Include snails, slugs, clams, squids and octopi
 Phylum Mollusca Soft-bodied animals Internal or external shell Include snails, slugs, clams, squids and octopi Trochophore: free-swimming larval stage of an aquatic mollusk True coeloms Have complex organ
Phylum Mollusca Soft-bodied animals Internal or external shell Include snails, slugs, clams, squids and octopi Trochophore: free-swimming larval stage of an aquatic mollusk True coeloms Have complex organ
Chapter 7. Marine Animals Without a Backbone
 Chapter 7 Marine Animals Without a Backbone Molluscs Characteristics of Phylum: More than 200,000 species Name means "soft body" Basic body plan head, muscular foot and visceral mass in most species Mantle-
Chapter 7 Marine Animals Without a Backbone Molluscs Characteristics of Phylum: More than 200,000 species Name means "soft body" Basic body plan head, muscular foot and visceral mass in most species Mantle-
Bivalved molluscs filter feeders
 Class Bivalvia Bivalved molluscs have two shells (valves). Mussels, clams, oysters, scallops, shipworms. Mostly sessile filter feeders. No head or radula. Class Bivalvia Part of the mantle is modified
Class Bivalvia Bivalved molluscs have two shells (valves). Mussels, clams, oysters, scallops, shipworms. Mostly sessile filter feeders. No head or radula. Class Bivalvia Part of the mantle is modified
 Kingdom: Animalia Phylum:Mollusca Classes: Bivalva, Gastropoda, Cephalopoda http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0a7j5prl8hc&feature=related http://www2.beavercreek.k12.oh.us/videos/45/pgr45_700k.asf What is
Kingdom: Animalia Phylum:Mollusca Classes: Bivalva, Gastropoda, Cephalopoda http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0a7j5prl8hc&feature=related http://www2.beavercreek.k12.oh.us/videos/45/pgr45_700k.asf What is
Biology. Slide 1 of 43. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 43 2 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What are the defining features of mollusks? 3 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What Is a Mollusk? Mollusks are soft-bodied animals that usually have an internal or external
Biology 1 of 43 2 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What are the defining features of mollusks? 3 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What Is a Mollusk? Mollusks are soft-bodied animals that usually have an internal or external
Mollusks Soft-bodied Invertebrates
 Mollusks Soft-bodied Invertebrates Phylum Mollusca Very diverse - more species of molluscs than any other group in the ocean. Phylum includes: Bivalves (2 shells); ex. Clam Gastropods (1 shell, coiled);
Mollusks Soft-bodied Invertebrates Phylum Mollusca Very diverse - more species of molluscs than any other group in the ocean. Phylum includes: Bivalves (2 shells); ex. Clam Gastropods (1 shell, coiled);
`Mollusks. may or may not form a hard, calcium carbonate shell. Trochophore Larva
 `Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Soft-bodied invertebrate covered with protective mantle that may or may not form a hard, calcium carbonate shell Includes chitons, snails, slugs, clams, oysters, squid, octopus,
`Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Soft-bodied invertebrate covered with protective mantle that may or may not form a hard, calcium carbonate shell Includes chitons, snails, slugs, clams, oysters, squid, octopus,
Chapter 12 Part 2. The Worms Platyhelminthes, Nematoda & Annelida
 Chapter 12 Part 2 The Worms Platyhelminthes, Nematoda & Annelida Phylum: Platyhelminthes Examples: Flatworms, Planaria sp., tapeworms and blood flukes Acoelomate, Invertebrate, Simplest critter w/ bilateral
Chapter 12 Part 2 The Worms Platyhelminthes, Nematoda & Annelida Phylum: Platyhelminthes Examples: Flatworms, Planaria sp., tapeworms and blood flukes Acoelomate, Invertebrate, Simplest critter w/ bilateral
 OCTOPUS Found throughout the world in tropical, warm and cold temperate waters - the octopus is a bottom dweller, spending much of its life in hiding, usually in a hole among rocks. All octopus species
OCTOPUS Found throughout the world in tropical, warm and cold temperate waters - the octopus is a bottom dweller, spending much of its life in hiding, usually in a hole among rocks. All octopus species
Unit 18.2: Mollusks and Annelids
 Unit 18.2: Mollusks and Annelids Lesson Objectives Describe invertebrates in the phylum Mollusca. Summarize the characteristics of annelids. Vocabulary Annelida deposit feeder gills heart mantle Mollusca
Unit 18.2: Mollusks and Annelids Lesson Objectives Describe invertebrates in the phylum Mollusca. Summarize the characteristics of annelids. Vocabulary Annelida deposit feeder gills heart mantle Mollusca
Chapter 35. Table of Contents. Section 1 Mollusca. Section 2 Annelida. Mollusks and Annelids
 Mollusks and Annelids Table of Contents Section 1 Mollusca Section 2 Annelida Section 1 Mollusca Objectives Describe the key characteristics of mollusks. Describe the body plan of mollusks. Name the characteristics
Mollusks and Annelids Table of Contents Section 1 Mollusca Section 2 Annelida Section 1 Mollusca Objectives Describe the key characteristics of mollusks. Describe the body plan of mollusks. Name the characteristics
Symmetry. Asymmetrical- no shape. Radial- same in half when cut any angle. Bilateral- having a distinct right and left side
 Symmetry Asymmetrical- no shape Radial- same in half when cut any angle Bilateral- having a distinct right and left side Invertebrates 95% of Animals No Backbone The simplest animals and they do not have
Symmetry Asymmetrical- no shape Radial- same in half when cut any angle Bilateral- having a distinct right and left side Invertebrates 95% of Animals No Backbone The simplest animals and they do not have
Chapter 6 SPONGES. Invertebrates. Sponges. Pore-Bearers. Movement of Water
 Invertebrates Chapter 6 Animals Without Backbones Animals that lack a backbone are called invertebrates. It is estimated that 97% of all species of animals are invertebrates. With the exception of insects,
Invertebrates Chapter 6 Animals Without Backbones Animals that lack a backbone are called invertebrates. It is estimated that 97% of all species of animals are invertebrates. With the exception of insects,
Animal Evolution: Chordate and Vertebrate Evolution and Diversity (Learning Outline)
 Animal Evolution: Chordate and Vertebrate Evolution and Diversity (Learning Outline) 1. Distinguishing features of the phylum Chordata and representative organisms. 2. Highlights of evolutionary steps
Animal Evolution: Chordate and Vertebrate Evolution and Diversity (Learning Outline) 1. Distinguishing features of the phylum Chordata and representative organisms. 2. Highlights of evolutionary steps
Mollusks- soft bodied
 Mollusks- soft bodied Objectives Understand the taxonomic relationships and major features of mollusks Learn the external and internal anatomy of the clam and squid Understand the major advantages and
Mollusks- soft bodied Objectives Understand the taxonomic relationships and major features of mollusks Learn the external and internal anatomy of the clam and squid Understand the major advantages and
Unit 19.2: Fish. Vocabulary fish spawning swim bladder
 Unit 19.2: Fish Lesson Objectives Describe structure and function in fish. Explain how fish reproduce and develop. Give an overview of the five living classes of fish. Summarize the evolution of fish.
Unit 19.2: Fish Lesson Objectives Describe structure and function in fish. Explain how fish reproduce and develop. Give an overview of the five living classes of fish. Summarize the evolution of fish.
Biol Echinoderms & Chordates. But first a few words about Development
 Biol 1309 Echinoderms & Chordates 1 But first a few words about Development Blastula- zygote first develops into a hollow ball of cells Deuterostome - mouth second Protostome - mouth first Cleavage - describes
Biol 1309 Echinoderms & Chordates 1 But first a few words about Development Blastula- zygote first develops into a hollow ball of cells Deuterostome - mouth second Protostome - mouth first Cleavage - describes
Coelomate Worms: Sipunculans, Pogonophorans, Echiurans and Vestimenifera
 Coelomate Worms Coelomate Worms: Sipunculans, Pogonophorans, Echiurans and Vestimenifera Ectoderm Mesoderm Dt Endoderm Coelom Often dismissed as minor or lesser Comprise less than 600 species total Never
Coelomate Worms Coelomate Worms: Sipunculans, Pogonophorans, Echiurans and Vestimenifera Ectoderm Mesoderm Dt Endoderm Coelom Often dismissed as minor or lesser Comprise less than 600 species total Never
Chapter 28 Mollusks & Annelids. BIOLOGY II Miss. Loulousis
 Chapter 28 Mollusks & Annelids BIOLOGY II Miss. Loulousis Mollusks have a true coelom Snails, slugs, oysters, clams, scallops, octopuses, and squids are all mollusks Annelid earthworm next section Mollusks
Chapter 28 Mollusks & Annelids BIOLOGY II Miss. Loulousis Mollusks have a true coelom Snails, slugs, oysters, clams, scallops, octopuses, and squids are all mollusks Annelid earthworm next section Mollusks
Molluscs. Chapter 16
 Molluscs Chapter 16 Phylum Mollusca Phylum Mollusca includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids. Phylum Mollusca Molluscs have a mesoderm lined body cavity a coelom. They are
Molluscs Chapter 16 Phylum Mollusca Phylum Mollusca includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids. Phylum Mollusca Molluscs have a mesoderm lined body cavity a coelom. They are
Name Date Period. Mollusk Review TORSION HEMOLYMPH SESSILE TROCHOPHORE ADDUCTOR KIDNEY HEMOCOEL MANTLE CHROMATOPHORES VISCERAL MASS
 Name Date Period Mollusk Review MOLLUSK VOCABULARY: Match the word with its definition. TORSION HEMOLYMPH SESSILE TROCHOPHORE ADDUCTOR KIDNEY HEMOCOEL MANTLE CHROMATOPHORES VISCERAL MASS Free-swimming
Name Date Period Mollusk Review MOLLUSK VOCABULARY: Match the word with its definition. TORSION HEMOLYMPH SESSILE TROCHOPHORE ADDUCTOR KIDNEY HEMOCOEL MANTLE CHROMATOPHORES VISCERAL MASS Free-swimming
27/12/2012. Learning Outcome G4
 Learning Outcome G4 Learning Outcome G4 Analyse the increasing complexity of the Phylum Mollusca, the Phylum Echinodermata, and the Phylum Arthropoda Phylum Mollusca, Echinodermata & Arthropoda Students
Learning Outcome G4 Learning Outcome G4 Analyse the increasing complexity of the Phylum Mollusca, the Phylum Echinodermata, and the Phylum Arthropoda Phylum Mollusca, Echinodermata & Arthropoda Students
Kingdom Animalia. Eukaryotic Multicellular Heterotrophs Lack Cell Walls
 Kingdom Animalia Eukaryotic Multicellular Heterotrophs Lack Cell Walls Must do: Feed, Respiration, Circulation, Excretion, Response, Movement, and Reproduction Symmetry Asymmetrical- no shape Radial- same
Kingdom Animalia Eukaryotic Multicellular Heterotrophs Lack Cell Walls Must do: Feed, Respiration, Circulation, Excretion, Response, Movement, and Reproduction Symmetry Asymmetrical- no shape Radial- same
Origin and Importance! ! Fish were the first vertebrates to appear on Earth about 500 million years ago.
 2/9/14 Origin and Importance Evolution Marine Fish Fish were the first vertebrates to appear on Earth about 500 million years ago. Fish are the most economically important organism and are a vital source
2/9/14 Origin and Importance Evolution Marine Fish Fish were the first vertebrates to appear on Earth about 500 million years ago. Fish are the most economically important organism and are a vital source
Chordates 1. Biology 2
 Chordates 1 Biology 2 Kingdom Animals Eukaryotic Multicellular - Many cell types Heterotrophic Feed by ingestion No cell walls Diploid life cycle Phylogenetic Tree Deuterostome Bilateral Symmetry 3 tissues
Chordates 1 Biology 2 Kingdom Animals Eukaryotic Multicellular - Many cell types Heterotrophic Feed by ingestion No cell walls Diploid life cycle Phylogenetic Tree Deuterostome Bilateral Symmetry 3 tissues
Lobsters, Crab and Shrimp
 Lobsters, Crab and Shrimp Crustaceans Phylum: Arthropoda ( jointed feet ) Invertebrate Exoskeleton (made of chitin) protects body and provides a place for muscles to attach to. Segmented body Jointed appendages
Lobsters, Crab and Shrimp Crustaceans Phylum: Arthropoda ( jointed feet ) Invertebrate Exoskeleton (made of chitin) protects body and provides a place for muscles to attach to. Segmented body Jointed appendages
ZOOLOGY SEGMENTED WORMS (Phylum Annelida)
 ZOOLOGY SEGMENTED WORMS (Phylum Annelida) I. Compared and Contrasted to Phylum Mollusca. A. They are like the molluscs in that they 1. are eucoelomate animals. 2. have specialized sense organs. 3. have
ZOOLOGY SEGMENTED WORMS (Phylum Annelida) I. Compared and Contrasted to Phylum Mollusca. A. They are like the molluscs in that they 1. are eucoelomate animals. 2. have specialized sense organs. 3. have
Class Polychaeta: Marine Worms
 Class Polychaeta: Marine Worms Animal Phyla Phylum Mollusca (Snails, Clams, Octopods and Allies): Radula: rasping tongue Shell: 3 layers, mostly calcium carbonate Inner-most = nacre = mother of pearl Mantle:
Class Polychaeta: Marine Worms Animal Phyla Phylum Mollusca (Snails, Clams, Octopods and Allies): Radula: rasping tongue Shell: 3 layers, mostly calcium carbonate Inner-most = nacre = mother of pearl Mantle:
Mollusks Are Soft and Unsegmented
 Mollusks Objectives Understand the taxonomic relationships and major features of mollusks Learn the external and internal anatomy of the clam and squid Understand the major advantages and limitations of
Mollusks Objectives Understand the taxonomic relationships and major features of mollusks Learn the external and internal anatomy of the clam and squid Understand the major advantages and limitations of
Fish. Water Dwelling Animals
 Fish Water Dwelling Animals Class Agnatha (Jawless fish) They are believed to be the most primitive and oldest vertebrates. Lamprey and hagfish are the only 2 living members of this class and are placed
Fish Water Dwelling Animals Class Agnatha (Jawless fish) They are believed to be the most primitive and oldest vertebrates. Lamprey and hagfish are the only 2 living members of this class and are placed
The Animals: Kingdom Animalia
 The Animals: Kingdom Animalia Kingdom Animalia (Animals) What is an Animal? Zoology- The study of Animals General Characteristics of 1. Animals are multicellular and eukaryotic. Animals 2. Animals consume
The Animals: Kingdom Animalia Kingdom Animalia (Animals) What is an Animal? Zoology- The study of Animals General Characteristics of 1. Animals are multicellular and eukaryotic. Animals 2. Animals consume
Chordates. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Chordates Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Vertebrates are members of the kingdom Animalia and the phylum Chordata ([link]). Recall that animals that possess bilateral symmetry can be divided into two groups protostomes
Chordates Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Vertebrates are members of the kingdom Animalia and the phylum Chordata ([link]). Recall that animals that possess bilateral symmetry can be divided into two groups protostomes
BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring Larval Development. Larval Development. Lecture 18
 BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring 2010 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 18 Larval Development 1. Often presented as a progression of stages a. Representative
BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring 2010 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 18 Larval Development 1. Often presented as a progression of stages a. Representative
1. Overview of Chordates
 Chapter 34A: The Origin & Evolution of Vertebrates I 1. Overview of the Chordates 2. Invertebrate Chordates 1. Overview of Chordates Echinodermata ANCESTRAL DEUTEROSTOME NOTOCHORD Common ancestor of chordates
Chapter 34A: The Origin & Evolution of Vertebrates I 1. Overview of the Chordates 2. Invertebrate Chordates 1. Overview of Chordates Echinodermata ANCESTRAL DEUTEROSTOME NOTOCHORD Common ancestor of chordates
A. Porifera (sponges): B. Cnidaria (jellies, hydra, sea anemones, and corals):
 Invertebrates Notes A. Porifera (sponges): Porifera literally means. Most sponges are. They are that collect food particles from the water as they pass through flagellated cells called. These cells then
Invertebrates Notes A. Porifera (sponges): Porifera literally means. Most sponges are. They are that collect food particles from the water as they pass through flagellated cells called. These cells then
Mollusks and Annelids. Chapter 23+
 Mollusks and Annelids Chapter 23+ 1 Annelids and Mollusks Coelomates Trochophore larvae Bilateral symmetry More complex organ systems 2 Moving On Up 3 Coelom Coelomates Evolutionary milestone True body
Mollusks and Annelids Chapter 23+ 1 Annelids and Mollusks Coelomates Trochophore larvae Bilateral symmetry More complex organ systems 2 Moving On Up 3 Coelom Coelomates Evolutionary milestone True body
Readings in Chapter 2, 3, and 7.
 Early Vertebrates Readings in Chapter 2, 3, and 7. Using the Tree of Life Web Project www.tolweb.org org A project to put the entire tree of life, a phylogeny of all life, on the web. Biologists world-wide
Early Vertebrates Readings in Chapter 2, 3, and 7. Using the Tree of Life Web Project www.tolweb.org org A project to put the entire tree of life, a phylogeny of all life, on the web. Biologists world-wide
Is a seahorse a fish, amphibian, or reptile? FISH
 Ch. 30 Loulousis Is a seahorse a fish, amphibian, or reptile? FISH Vertebral Column (Endoskeleton) Gills Single-loop circulation Kidneys Also share all the characteristics of chordates such as notochord,
Ch. 30 Loulousis Is a seahorse a fish, amphibian, or reptile? FISH Vertebral Column (Endoskeleton) Gills Single-loop circulation Kidneys Also share all the characteristics of chordates such as notochord,
Kingdom Animalia Subkingdom Eumetazoa Bilateria Phylum Mollusca
 Kingdom Animalia Subkingdom Eumetazoa Bilateria Phylum Mollusca Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Illustrations 2014 Cengage Learning unless otherwise noted Phylum Mollusca Molluscs (mollis = soft)
Kingdom Animalia Subkingdom Eumetazoa Bilateria Phylum Mollusca Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Illustrations 2014 Cengage Learning unless otherwise noted Phylum Mollusca Molluscs (mollis = soft)
Chapter 10. Part 1: Cartilaginous Fishes
 Chapter 10 Part 1: Cartilaginous Fishes Objectives Understand how hagfishes and lampreys differ from all other fishes. Describe how sharks, skates, and rays are related. Differentiate between cartilaginous
Chapter 10 Part 1: Cartilaginous Fishes Objectives Understand how hagfishes and lampreys differ from all other fishes. Describe how sharks, skates, and rays are related. Differentiate between cartilaginous
Mollusca: Class Cephalopoda. Lecture 11
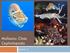 Mollusca: Class Cephalopoda Lecture 11 Cephalophod Characteristics Characteristics of class All marine Most 6-70 cm up to 20m Architeuthis Shell divided by septa, chambers connected by siphuncle Closed
Mollusca: Class Cephalopoda Lecture 11 Cephalophod Characteristics Characteristics of class All marine Most 6-70 cm up to 20m Architeuthis Shell divided by septa, chambers connected by siphuncle Closed
Aquatic vertebrates that are characterized by:
 Aquatic vertebrates that are characterized by: Paired fins Used for movement Scales Used for protection Gills Used for exchanging gases Fishes were the first vertebrates to evolve The evolution of jaws
Aquatic vertebrates that are characterized by: Paired fins Used for movement Scales Used for protection Gills Used for exchanging gases Fishes were the first vertebrates to evolve The evolution of jaws
Phylum Chordata:
 The Chordates: Putting a Backbone Into Spineless Animals Note: These links do not work. Use the links within the outline to access the mages in the popup windows. This text is the same as the scrolling
The Chordates: Putting a Backbone Into Spineless Animals Note: These links do not work. Use the links within the outline to access the mages in the popup windows. This text is the same as the scrolling
Body Plan of the Chordates. Notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal gill slits, blocks of muscle, post-anal tail
 Chordata The Major Groups Invertebrate Chordates Fishes Class: Agnatha Class Condrichthyes Class Osteichthyes Class: Amphibia Class: Reptilia Class: Aves Class: Mammalia Body Plan of the Chordates Notochord,
Chordata The Major Groups Invertebrate Chordates Fishes Class: Agnatha Class Condrichthyes Class Osteichthyes Class: Amphibia Class: Reptilia Class: Aves Class: Mammalia Body Plan of the Chordates Notochord,
Dogfish Shark Dissection
 Dogfish Shark Dissection Name Date Period Fun Facts: Materials: The teeth of sharks are modified scales embedded in the skin of its mouth Sharks have pits on their face used to detect electric fields Sharks
Dogfish Shark Dissection Name Date Period Fun Facts: Materials: The teeth of sharks are modified scales embedded in the skin of its mouth Sharks have pits on their face used to detect electric fields Sharks
Chapter 5 Marine Protozoans and Invertebrates
 Chapter 5 Marine Protozoans and Invertebrates I. The Protozoans A. Kindgom Protista a catch-all category B. Characteristics 1. Mode of nutrition 2. Single-celled or multicellular? 3. Cell structure 4.
Chapter 5 Marine Protozoans and Invertebrates I. The Protozoans A. Kindgom Protista a catch-all category B. Characteristics 1. Mode of nutrition 2. Single-celled or multicellular? 3. Cell structure 4.
Chapter 34A: The Origin & Evolution of Vertebrates I. 1. Overview of the Chordates 2. Invertebrate Chordates
 Chapter 34A: The Origin & Evolution of Vertebrates I 1. Overview of the Chordates 2. Invertebrate Chordates 1. Overview of Chordates Echinodermata Phylogeny of ANCESTRAL DEUTEROSTOME NOTOCHORD Common ancestor
Chapter 34A: The Origin & Evolution of Vertebrates I 1. Overview of the Chordates 2. Invertebrate Chordates 1. Overview of Chordates Echinodermata Phylogeny of ANCESTRAL DEUTEROSTOME NOTOCHORD Common ancestor
Animal Diversity. Kingdom Animalia
 7ch11 Animal Diversity Kingdom Animalia Animal Characteristics 1. animals are eukaryotes and are multicellular 2. cells are specialized for different functions (vision,digestion,reproduction) 3. protein,
7ch11 Animal Diversity Kingdom Animalia Animal Characteristics 1. animals are eukaryotes and are multicellular 2. cells are specialized for different functions (vision,digestion,reproduction) 3. protein,
What is a Fish? Fishes are aquatic vertebrates. Most fishes have paired fins, scales, and gills.
 What is a Fish? Fishes are aquatic vertebrates. Most fishes have paired fins, scales, and gills. Feeding and Digestion Every mode of feeding is seen in fish herbivores, carnivores, parasites, filter feeders,
What is a Fish? Fishes are aquatic vertebrates. Most fishes have paired fins, scales, and gills. Feeding and Digestion Every mode of feeding is seen in fish herbivores, carnivores, parasites, filter feeders,
Marine Fishes. Chapter 8
 Marine Fishes Chapter 8 Fish Gills The construction of the gill is the same in all fish gill arch supports the entire structure, gill rakers are on the forward surface of the gill arch and gill filaments
Marine Fishes Chapter 8 Fish Gills The construction of the gill is the same in all fish gill arch supports the entire structure, gill rakers are on the forward surface of the gill arch and gill filaments
Characteristics of Animals pp Topic 7: Animal Diversity Ch Symmetry pp Characteristics of Animals
 Topic 7: Animal Diversity Ch. 32-34 Characteristics of Animals pp.704-705 Animals: Are eukaryotic Are multicellular Are ingestive heterotrophs Have no cell walls Most are motile Most have tissues organized
Topic 7: Animal Diversity Ch. 32-34 Characteristics of Animals pp.704-705 Animals: Are eukaryotic Are multicellular Are ingestive heterotrophs Have no cell walls Most are motile Most have tissues organized
Fish Dissection. Background
 Fish Dissection The Fish Dissection program at Hatfield Marine Science Center is a 50-minute hands-on program for 4th through 12th grade students. Students will work in small groups as they examine a variety
Fish Dissection The Fish Dissection program at Hatfield Marine Science Center is a 50-minute hands-on program for 4th through 12th grade students. Students will work in small groups as they examine a variety
Phylum Platyhelminthes. You will need: five colours of pencil crayon or pen (preferably blue, green, red, orange and purple)
 Phylum Platyhelminthes You will need: five colours of pencil crayon or pen (preferably blue, green, red, orange and purple) Phylum Platyhelminthes bilaterally symmetrical have all 3 embryonic germ layers:
Phylum Platyhelminthes You will need: five colours of pencil crayon or pen (preferably blue, green, red, orange and purple) Phylum Platyhelminthes bilaterally symmetrical have all 3 embryonic germ layers:
Phylum Mollusca. More than 500,000 known species. Class Polyplacophora. Class Bivalvia. Class Gastropoda. Class Cephalopoda
 Phylum Mollusca Class Polyplacophora Class Gastropoda Class Bivalvia Class Cephalopoda chitons Snails Sea slugs nudibranchs clams Squid Octopus Cuttlefish Nautilus More than 500,000 known species A bag,
Phylum Mollusca Class Polyplacophora Class Gastropoda Class Bivalvia Class Cephalopoda chitons Snails Sea slugs nudibranchs clams Squid Octopus Cuttlefish Nautilus More than 500,000 known species A bag,
Internal Anatomy of Fish
 Internal Anatomy of Fish The Systems of a Fish Skeletal System Muscular System Respiratory System Digestive System Circulatory System Nervous System Reproductive System Special Organs Skeletal System
Internal Anatomy of Fish The Systems of a Fish Skeletal System Muscular System Respiratory System Digestive System Circulatory System Nervous System Reproductive System Special Organs Skeletal System
Phylum Mollusca Classes
 Lecture Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Classes Aculifera with spicules Aplacophora - mollusks without shells Polyplacophora ( Amphineura) chiton, eight plates, intertidal Conchifera with shells Monoplacophora
Lecture Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Classes Aculifera with spicules Aplacophora - mollusks without shells Polyplacophora ( Amphineura) chiton, eight plates, intertidal Conchifera with shells Monoplacophora
26-3 Cnidarians Slide 1 of 47
 1 of 47 What Is a Cnidarian? What is a cnidarian? 2 of 47 What Is a Cnidarian? What Is a Cnidarian? Cnidarians are soft-bodied, carnivorous animals that have stinging tentacles arranged in circles around
1 of 47 What Is a Cnidarian? What is a cnidarian? 2 of 47 What Is a Cnidarian? What Is a Cnidarian? Cnidarians are soft-bodied, carnivorous animals that have stinging tentacles arranged in circles around
Exercise 18B Class Chondrichthyes Cartilaginous Fishes
 AP Biology Chapter 24 Exercise #18: Chordates: Fish Cartilaginous Fishes Lab Guide Exercise 18B Class Chondrichthyes Cartilaginous Fishes This group contains about 970 species that are characterized by
AP Biology Chapter 24 Exercise #18: Chordates: Fish Cartilaginous Fishes Lab Guide Exercise 18B Class Chondrichthyes Cartilaginous Fishes This group contains about 970 species that are characterized by
Phylum Platyhelminthes Phylum Nematoda Phylum Mollusca. By: Jerzylin, Beata & Jennifer
 Phylum Platyhelminthes Phylum Nematoda Phylum Mollusca By: Jerzylin, Beata & Jennifer Phylum Platyhelminthes Common Characteristics: Triploblastic Bilateral Symmetry Protostome No true stomach structure
Phylum Platyhelminthes Phylum Nematoda Phylum Mollusca By: Jerzylin, Beata & Jennifer Phylum Platyhelminthes Common Characteristics: Triploblastic Bilateral Symmetry Protostome No true stomach structure
Classification. Phylum Chordata
 AP Biology Chapter 23 Exercise #17: Chordates: Urochordata & Cephalochordata Lab Guide Chordates show remarkable diversity. Most are vertebrates. All animals that belong to this phylum MUST, at some point
AP Biology Chapter 23 Exercise #17: Chordates: Urochordata & Cephalochordata Lab Guide Chordates show remarkable diversity. Most are vertebrates. All animals that belong to this phylum MUST, at some point
Taxonomy of Fishes. Chapter 18. I. SuperClass Agnatha. A. Class Myxini. Kingdom Animalia. The Fishes
 Taxonomy of Fishes Chapter 18 The Fishes Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata SuperClass Agnatha - jawless fish Class Chondrichthyes - cartilagenous fish Class Osteichthyes - bony fish I. SuperClass Agnatha
Taxonomy of Fishes Chapter 18 The Fishes Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata SuperClass Agnatha - jawless fish Class Chondrichthyes - cartilagenous fish Class Osteichthyes - bony fish I. SuperClass Agnatha
LECTURE 6 - OUTLINE. Evolution & Classification - Part II. Agnatha (cont.) Gnathostomata
 LECTURE 6 - OUTLINE Evolution & Classification - Part II Agnatha (cont.) 6. Myxini 7. Cephalaspidomorphi Gnathostomata 1. Phylogenetic relationships 2. Placodermi 3. Acanthodii BIOL 4340 Lecture 6-1 Class
LECTURE 6 - OUTLINE Evolution & Classification - Part II Agnatha (cont.) 6. Myxini 7. Cephalaspidomorphi Gnathostomata 1. Phylogenetic relationships 2. Placodermi 3. Acanthodii BIOL 4340 Lecture 6-1 Class
The Animal Kingdom. Animal Kingdom. Characteristics of All Animals. Major Characteristics Used To Classify Animals
 The Animal Kingdom Animal Kingdom Phylums: 1. Sponges 2. Cnidaria Jelly Fish, Hydra 3. Flatworms Flukes, Tapeworms 4. Roundworms- Hookworms 5. Segmented Worms- Earthworms 6. Rotifera- Rotifers 7. Mullusca
The Animal Kingdom Animal Kingdom Phylums: 1. Sponges 2. Cnidaria Jelly Fish, Hydra 3. Flatworms Flukes, Tapeworms 4. Roundworms- Hookworms 5. Segmented Worms- Earthworms 6. Rotifera- Rotifers 7. Mullusca
Perch Dissection Lab
 Perch Dissection Lab Introduction: The fish in the class Osteichthyes have bony skeletons. There are three groups of the bony fish - -- ray-finned fish, lobe-finned fish, and the lung fish. The perch is
Perch Dissection Lab Introduction: The fish in the class Osteichthyes have bony skeletons. There are three groups of the bony fish - -- ray-finned fish, lobe-finned fish, and the lung fish. The perch is
Basic mollusc body plan
 Phylum Mollusca Phylum Mollusca 3 embryonic germ layers true coelom complete gut second largest phylum of animals, around 100,000 species mainly aquatic, but some terrestrial species Basic mollusc body
Phylum Mollusca Phylum Mollusca 3 embryonic germ layers true coelom complete gut second largest phylum of animals, around 100,000 species mainly aquatic, but some terrestrial species Basic mollusc body
Chapter 12 Marine Fishes
 Chapter 12 Marine Fishes Marine Protochordates Phylum: Chordata (nerve cord) Subphylum: Protochordata first chordates/primitive Primitive species of marine vertebrates Do not have advanced features (backbone)
Chapter 12 Marine Fishes Marine Protochordates Phylum: Chordata (nerve cord) Subphylum: Protochordata first chordates/primitive Primitive species of marine vertebrates Do not have advanced features (backbone)
ARTHROPODS JOINTED-LEGS ARTHROPODS ARE THE LARGEST GROUP OF ANIMALS!
 ARTHROPODS JOINTED-LEGS ARTHROPODS ARE THE LARGEST GROUP OF ANIMALS! WHO S WHO? SHRIMP ISOPOD SPIDER CRAB BARNACLE LOBSTER BASIC CHARACTERISTICS BILATERAL SYMMETRY SEGMENTED ANIMALS JOINTED BODY & PARTS
ARTHROPODS JOINTED-LEGS ARTHROPODS ARE THE LARGEST GROUP OF ANIMALS! WHO S WHO? SHRIMP ISOPOD SPIDER CRAB BARNACLE LOBSTER BASIC CHARACTERISTICS BILATERAL SYMMETRY SEGMENTED ANIMALS JOINTED BODY & PARTS
Perch Dissection Lab
 Name: Block: Due Date: Perch Dissection Lab Background The fish in the class Osteichthyes have bony skeletons. There are three groups of the bony fish: ray-finned, lobe-finned, and the lungfish. The perch
Name: Block: Due Date: Perch Dissection Lab Background The fish in the class Osteichthyes have bony skeletons. There are three groups of the bony fish: ray-finned, lobe-finned, and the lungfish. The perch
Echinodermata. To familiarize the marine guide with the echinoderms of Southern Africa
 WildlifeCampus - Marine Field Guiding 1 Module # 4 Component # 1 Objective Echinodermata To familiarize the marine guide with the echinoderms of Southern Africa Expected Outcomes: The learner will be able
WildlifeCampus - Marine Field Guiding 1 Module # 4 Component # 1 Objective Echinodermata To familiarize the marine guide with the echinoderms of Southern Africa Expected Outcomes: The learner will be able
General Characters of Trematodes
 Parasitology Department General Characters of Trematodes By Hala Elwakil, MD Intended Learning Outcomes By the end of this lecture, the student will be able to know: 1. General morphology of trematodes
Parasitology Department General Characters of Trematodes By Hala Elwakil, MD Intended Learning Outcomes By the end of this lecture, the student will be able to know: 1. General morphology of trematodes
February 17, Unit 2. Biodiversity. Chordata, the vertebrates
 Unit 2 Biodiversity Chordata, the vertebrates Phylum Chordata Examples: Sea squirts, fish, birds, dinosaurs, humans. General characteristics: 1. Bilaterally symmetrical 2. Coelomate 3. One way digestive
Unit 2 Biodiversity Chordata, the vertebrates Phylum Chordata Examples: Sea squirts, fish, birds, dinosaurs, humans. General characteristics: 1. Bilaterally symmetrical 2. Coelomate 3. One way digestive
BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring Cycloneuralia Characters. Pseudo- coelomates (Ecdysozoa): Lecture 19
 BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring 2010 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 19 Cycloneuralia Characters 18(2): Ambiguous spiral cleavage. 92: Terminal mouth
BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring 2010 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 19 Cycloneuralia Characters 18(2): Ambiguous spiral cleavage. 92: Terminal mouth
