TAKSONOMI HEWAN CHAPTER 8: ECHINODERMATA
|
|
|
- Kerry Reed
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TAKSONOMI HEWAN CHAPTER 8: ECHINODERMATA Husni Mubarok, S.Pd., M.Si. Tadris Biologi IAIN Jember
2
3
4 DEUTEROSTOMIA Termasuk sand dollar, bintang laut, landak laut/ bulu babi, hidup di laut, masuk dalam klade Deuterostome. Simetri Bilateral pd tahap larva. Simetri Radial/Biradial pd thap Dewasa Bergerak & makan menggunakan network dr kanal internal utk memompa air ke daerah tubuh lainnya Classical deuterostome developmental features are radial regulative cleavage; formation of the mouth from a second opening (deuterostomy); and coelom formation by enterocoely. All deuterostomes are coelomate.
5 DEUTEROSTOMIA
6 Echinodermata Chordata
7 PHYLUM ECHINODERMATA
8 General Characteristics Unique water-vascular system of coelomic origin extends from body surface as series of tentacle-like projections (podia, or tube feet) protracted by increase of fluid pressure within them Opening to exterior (madreporite or hydropore) usually present Living in marine habitats Free-living taxa Body unsegmented (nonmetameric) with pentaradial symmetry; body rounded, cylindrical, or star-shaped, with five or more radiating areas, or ambulacra, alternating with interambulacral areas; no head Triploblastic body
9 General Characteristics As adults they show secondary radial symmetry pentaradial (5 parts). Perhaps an adaptation for sessile living in early echinoderms. Crinoids Today s echinoderms are mostly motile. Many are still radial. Some have again become superficially bilateral (skeletal & organ systems still pentaradial). Sea cucumbers. A few sea urchins.
10 General Characteristics Canals of the water vascular system lead to the tube feet. Tube feet may have suckers, allowing the echinoderm to move while remaining firmly attached to the substrate important in areas with lots of wave action.
11 General Characteristics Coelom extensive, forming perivisceral cavity and cavity of watervascular system; coelom of enterocoelous type; coelomic fluid with amebocytes Endoskeleton of dermal calcareous ossicles with spines or of calcareous spicules in dermis; covered by epidermis (ciliated in most); pedicellariae (in some) Ossicles: small calcareous elements embedded in the dermis of the body wall of echinoderms. They form part of the endoskeleton and provide rigidity and protection A pedicellaria (plural: pedicellariae) is a small wrench- or claw-shaped appendage with movable jaws, called valves, commonly found on echinoderms (phylum Echinodermata), particularly in sea stars (class Asteroidea) and sea urchins (class Echinoidea). Digestive system usually complete; axial or coiled; anus absent in ophiuroids
12 Echinoderms have an endoskeleton of calcareous ossicles often with spines. Endoskeleton is covered by an epidermis. Some have a very substantial endoskeleton (sea urchins), others have only a few scattered dermal ossicles (some sea cucumbers).
13
14
15
16
17
18 Autotomy and regeneration of lost parts conspicuous; asexual reproduction by fragmentation in some Sexes separate (except a few hermaphroditic) with large gonads, single in holothuroids but multiple in most; simple ducts, with no elaborate copulatory apparatus or secondary sexual structures; fertilization usually external General Characteristics
19
20 General Characteristics Eggs (which may be brooded or laid as benthic egg masses) hatch into bilateral, free-swimming larvae. The type of larva is specific to each echinoderm class. Echinoderms are bilaterally symmetrical as larvae. This means their ancestors were bilaterally symmetrical.
21
22 Excretory organs absent Respiration by papulae, tube feet, respiratory tree (holothuroids), and bursae (ophiuroids) Blood-vascular system (hemal system) much reduced, playing little if any role in circulation, and surrounded by extensions of coelom (perihemal sinuses); main circulation of body fluids (coelomic fluids) by peritoneal cilia
23 Nervous system with circumoral ring and radial nerves; usually two or three systems of networks located at different levels in the body, varying in degree of development according to group No brain; few specialized sensory organs; sensory system of tactile and chemoreceptors, podia, terminal tentacles, photoreceptors, and statocysts
24 KLASIFIKASI ECHINODERMATA
25
26
27
28 Sea stars have arms (rays) arranged around a central disc. The body is flattened, flexible, and covered with a ciliated, pigmented epidermis. Class Asteroidea
29 Class Asteroidea The mouth is on the underside of the sea star. Ambulacral grooves stretch out from the mouth along each ray. Tube feet border each groove
30 The aboral surface is often rough and spiny. Around the base of each spine there are pincerlike pedicellariae that keep the surface free of debris and sometimes help with food capture. Class Asteroidea
31 The upper part of the stomach connects to a pair of digestive glands (pyloric ceca/ cecum) in each arm.
32 Most sea stars are carnivorous; feeding on molluscs, crustaceans, polychaetes, echinoderms, other inverts & sometimes small fish. Class Asteroidea - Feeding
33
34
35 Class Asteroidea Reproduction Most sea stars have separate sexes with a pair of gonads in each ray. Fertilization is external. Echinoderms can regenerate lost parts. Sea stars can readily replace an arm if it is lost. This may take several months They can also cast off an injured arm.
36 Class Asteroidea Reproduction Some species can even regenerate an entire individual from a broken off arm. Usually, a small piece of the central disc must be included. Linckia can regenerate a whole new individual from a broken arm with no central disc attached.
37 Class Asteroidea Reproduction Metamorphosis involves a reorganization into a radial juvenile. Left/right becomes oral/aboral.
38 Class Ophiuroidea No pedicillariae or skin gills. Madreporite is on the oral surface. Tube feet have no suckers, their primary function is to aid in feeding. Brittle stars move using their arms rather than tube feet.
39
40 Class Echinoidea Class Echinoidea includes sea urchins and sand dollars. The endoskeleton is well developed in echinoids. Dermal ossicles have become close-fitting plates that form the test.
41 Class Echinoidea
42 Echinoids lack arms, but still show the pentamerous plan in the five ambulacral areas with pores in the test for the tube feet. Class Echinoidea
43 Most echinoids are regular having a hemispherical shape, radial symmetry, and medium to long spines. Regular urchins move using their tube feet with some help from spines. Class Echinoidea
44 Class Echinoidea
45 Irregular echinoids include the sand dollars and heart urchins that include some species that have become bilateral. Spines are usually short and are used in locomotion.
46 Some urchins have very reduced tests, and bright coloration. The pedicellariae in these species contain painful toxins. Echinoids live in all seas from the intertidal to the deep sea. Urchins usually prefer rocky substrate, while sand dollars and heart urchins like to burrow into sandy substrate
47 Echinoids have a complex chewing mechanism called Aristotle s lantern. Teeth are attached here. Sea urchins are usually omnivorous feeding mostly on algae. Sand dollars use their short spines to move sand & its organic contents to the sides, the food particles drop between the spines, and ciliated tracts on the oral side carry the particles to the mouth.
48 Class Holothuroidea Sea cucumbers (Class Holothuroidea) are elongated along the oral/aboral axis. Bilateral Ossicles are greatly reduced in most species. The body wall is usually leathery with tiny ossicles embedded in it, but can be very thin.
49
50
51
52 Class Holothuroidea Oral tentacles are modified tube feet located around the mouth. Food particles are gathered by the oral tentacles. Tentacles are put into the pharynx one by one so food can be sucked off.
53 Sea cucumbers move using ventral tube feet and waves of contraction along the muscular body wall. Sea cucumbers have a very unusual defense mechanism: They are able to cast out part of their viscera. The lost parts regenerate. Some have organs of Cuvier that can be expelled in the direction of an enemy. These tubules become long and sticky, sometimes containing toxins.
54 Crinoids include sea lilies and feather stars. At metamorphosis, juveniles become sessile and stalked. Adults are freemoving in some species. Long, many branched arms. Class Crinoidea
55
56
57
58
59 SOFT SKILL Jadi Apakah Patrick Bintang Laut Lebih Pintar dari Spongebob??
CHAPTER 22. Echinoderms 22-1
 CHAPTER 22 Echinoderms 22-1 Phylum Echinodermata: Diversity and Characteristics Characteristics All members have a calcareous skeleton Spiny endoskeleton consists of plates Unique water-vascular system
CHAPTER 22 Echinoderms 22-1 Phylum Echinodermata: Diversity and Characteristics Characteristics All members have a calcareous skeleton Spiny endoskeleton consists of plates Unique water-vascular system
 Echinoderms Name Means: Echino- Spiny Derm- Skin About 7,000 species No Head! No Brain! No ventral, dorsal, posterior, or anterior sides! Do have oral (mouth) and aboral sides. Symmetry: Larvae are
Echinoderms Name Means: Echino- Spiny Derm- Skin About 7,000 species No Head! No Brain! No ventral, dorsal, posterior, or anterior sides! Do have oral (mouth) and aboral sides. Symmetry: Larvae are
ADVANCED INVERTEBRATES HAVE COMPLEX BODIES AND INTERNAL SYSTEMS
 ADVANCED INVERTEBRATES HAVE COMPLEX BODIES AND INTERNAL SYSTEMS Arthropoda Most successful phylum on Earth Exoskeleton chitin Striated muscle Articulation Crayfish, lobsters, shrimp, crabs Echinodermata
ADVANCED INVERTEBRATES HAVE COMPLEX BODIES AND INTERNAL SYSTEMS Arthropoda Most successful phylum on Earth Exoskeleton chitin Striated muscle Articulation Crayfish, lobsters, shrimp, crabs Echinodermata
Spiny skinned animals with radial symmetrical body plan. Rays emanating from a common center. Internal skeleton of hardened plates of calcium
 Echinodermata Spiny skinned animals with radial symmetrical body plan. Rays emanating from a common center. Internal skeleton of hardened plates of calcium carbonate. Water vascular system and tube feet
Echinodermata Spiny skinned animals with radial symmetrical body plan. Rays emanating from a common center. Internal skeleton of hardened plates of calcium carbonate. Water vascular system and tube feet
Chapter 22. Phylum Echnodermata 4/13/2009. Characteristics. Diversity. Group Diversity. Ecology, Economics, and Research.
 Characteristics Chapter 22 All members of the phylum have a calcareous skeleton. The spiny endoskeleton consists of plates. They have a unique water vascular system. They possess pedicellariae and dermal
Characteristics Chapter 22 All members of the phylum have a calcareous skeleton. The spiny endoskeleton consists of plates. They have a unique water vascular system. They possess pedicellariae and dermal
Protostome: Embryonic blastopore becomes mouth
 Classical hypothesis Molecular hypothesis Adoutte 2000 PNAS Protostome: Embryonic blastopore becomes mouth Schizocoelous development (typical of the protostome coelomates) 1 Deuterostome: Embryonic blastopore
Classical hypothesis Molecular hypothesis Adoutte 2000 PNAS Protostome: Embryonic blastopore becomes mouth Schizocoelous development (typical of the protostome coelomates) 1 Deuterostome: Embryonic blastopore
Echinoderms. Phylum Echinodermata
 Echinoderms Phylum Echinodermata spiny skinned or hedgehog skin sea stars (starfish), sea urchins, sea cucumbers 6000 species radial symmetry in 2 o development bilateral symmetry in larva http://www.biologyreference.com/dn-ep/echinoderm.html
Echinoderms Phylum Echinodermata spiny skinned or hedgehog skin sea stars (starfish), sea urchins, sea cucumbers 6000 species radial symmetry in 2 o development bilateral symmetry in larva http://www.biologyreference.com/dn-ep/echinoderm.html
An introduction to the taxonomy of the Echinodermata
 An introduction to the taxonomy of the Echinodermata Yves Samyn Belgian Focal Point to the GTI Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences Classification of the Phylum Echinodermata in the Animal Kingdom
An introduction to the taxonomy of the Echinodermata Yves Samyn Belgian Focal Point to the GTI Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences Classification of the Phylum Echinodermata in the Animal Kingdom
Phyla Echinodermata and Chordata
 10/27/14 Deuterostomes! v Echinoderms and Phyla Echinodermata and Chordata Deuterostome Review v Deuterostomes share developmental characteristics Radial cleavage Formation of the anus from the blastopore
10/27/14 Deuterostomes! v Echinoderms and Phyla Echinodermata and Chordata Deuterostome Review v Deuterostomes share developmental characteristics Radial cleavage Formation of the anus from the blastopore
Phyla Echinodermata and Chordata
 Phyla Echinodermata and Chordata Deuterostomes! v Echinoderms and chordates constitute the clade Deuterostomia v Echinoderms (phylum Echinodermata) include sea stars and sea urchins v Chordates (phylum
Phyla Echinodermata and Chordata Deuterostomes! v Echinoderms and chordates constitute the clade Deuterostomia v Echinoderms (phylum Echinodermata) include sea stars and sea urchins v Chordates (phylum
Z202-Unit 9/10 Chapter 22 Chaetognaths, Echinoderms & Hemichordates
 Z202-Unit 9/10 Chapter 22 Chaetognaths, Echinoderms & Hemichordates I. Diversity A. Evolutionary Diversity - Cambrian Explosion (535 to 530 mya) radiation in diversity seen in fossil record other explosions
Z202-Unit 9/10 Chapter 22 Chaetognaths, Echinoderms & Hemichordates I. Diversity A. Evolutionary Diversity - Cambrian Explosion (535 to 530 mya) radiation in diversity seen in fossil record other explosions
Chapter 29 Echinoderms and Invertebrate Chordates. Section Echinoderms. I. What Is An Echinoderm? 11/1/2010. Biology II Mrs.
 Chapter 29 Echinoderms and Invertebrate Chordates Section 29.1 - Echinoderms Biology II Mrs. Michaelsen I. What Is An Echinoderm? A. Move by means of hydraulic, suction cuptipped appendages. B. Skin covered
Chapter 29 Echinoderms and Invertebrate Chordates Section 29.1 - Echinoderms Biology II Mrs. Michaelsen I. What Is An Echinoderm? A. Move by means of hydraulic, suction cuptipped appendages. B. Skin covered
Chapter 28 Arthropods and Echinoderms. Body Terms. Evolution has led to:
 Chapter 28 Arthropods and Echinoderms Introduction to Arthropods jointed feet Most diverse and successful animals Over 750,000 species identified Segmented bodies Tough exoskeleton Jointed appendages Body
Chapter 28 Arthropods and Echinoderms Introduction to Arthropods jointed feet Most diverse and successful animals Over 750,000 species identified Segmented bodies Tough exoskeleton Jointed appendages Body
PLACOZOA Small multicellular hairy sticky flat things
 PLACOZOA Small multicellular hairy sticky flat things BODY PLAN 5 CELL TYPES Two species described in this phylum 1. Trichoplax adharens 2. Treptoplax reptans Smallest amount of DNA yet measured for any
PLACOZOA Small multicellular hairy sticky flat things BODY PLAN 5 CELL TYPES Two species described in this phylum 1. Trichoplax adharens 2. Treptoplax reptans Smallest amount of DNA yet measured for any
Class Asteroidea. Reproductive System, Regeneration, and Autonomy
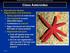 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Compaies, Ic. Permissio required for reproductio or display. Class Asteroidea Reproductive System, Regeeratio, ad Autoomy Sexes separate i most sexes Pair of goads i each iterradial
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Compaies, Ic. Permissio required for reproductio or display. Class Asteroidea Reproductive System, Regeeratio, ad Autoomy Sexes separate i most sexes Pair of goads i each iterradial
Phylum: Porifera (sponges)
 Phylum: Porifera (sponges) (8,761 known species) General Description: Simplest animals, multicellular No organs or body systems Skeleton composed of spongin (soft) and spicules (hard) Symmetry: Asymmetrical
Phylum: Porifera (sponges) (8,761 known species) General Description: Simplest animals, multicellular No organs or body systems Skeleton composed of spongin (soft) and spicules (hard) Symmetry: Asymmetrical
I. Evolutionary Perspective. Chapter 12. II. Molluscan Characteristics. A. Regions of Molluscan Body 11/2/10
 I. Evolutionary Perspective Chapter 12 Molluscan Success Some of the world s best predators Large brains Complex sensory structures Rapid locomotion Grasping tentacles Tearing mouthparts Have been around
I. Evolutionary Perspective Chapter 12 Molluscan Success Some of the world s best predators Large brains Complex sensory structures Rapid locomotion Grasping tentacles Tearing mouthparts Have been around
Mollusks- soft bodied
 Mollusks- soft bodied Objectives Understand the taxonomic relationships and major features of mollusks Learn the external and internal anatomy of the clam and squid Understand the major advantages and
Mollusks- soft bodied Objectives Understand the taxonomic relationships and major features of mollusks Learn the external and internal anatomy of the clam and squid Understand the major advantages and
27/12/2012. Learning Outcome G4
 Learning Outcome G4 Learning Outcome G4 Analyse the increasing complexity of the Phylum Mollusca, the Phylum Echinodermata, and the Phylum Arthropoda Phylum Mollusca, Echinodermata & Arthropoda Students
Learning Outcome G4 Learning Outcome G4 Analyse the increasing complexity of the Phylum Mollusca, the Phylum Echinodermata, and the Phylum Arthropoda Phylum Mollusca, Echinodermata & Arthropoda Students
 OCTOPUS Found throughout the world in tropical, warm and cold temperate waters - the octopus is a bottom dweller, spending much of its life in hiding, usually in a hole among rocks. All octopus species
OCTOPUS Found throughout the world in tropical, warm and cold temperate waters - the octopus is a bottom dweller, spending much of its life in hiding, usually in a hole among rocks. All octopus species
27-4 Mollusks. Slide 1 of 43. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 1 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What Is a Mollusk? Mollusks are soft-bodied animals that usually have an internal or external shell. Mollusks include snails, slugs, clams, squids, octopi... They are group together
1 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What Is a Mollusk? Mollusks are soft-bodied animals that usually have an internal or external shell. Mollusks include snails, slugs, clams, squids, octopi... They are group together
Chapter 6 SPONGES. Invertebrates. Sponges. Pore-Bearers. Movement of Water
 Invertebrates Chapter 6 Animals Without Backbones Animals that lack a backbone are called invertebrates. It is estimated that 97% of all species of animals are invertebrates. With the exception of insects,
Invertebrates Chapter 6 Animals Without Backbones Animals that lack a backbone are called invertebrates. It is estimated that 97% of all species of animals are invertebrates. With the exception of insects,
Mollusks are soft bodied animals that have an internal or external shell, a similar body plan consisting of four basic parts: a foot, mantle, shell,
 Mollusca Mollusks are soft bodied animals that have an internal or external shell, a similar body plan consisting of four basic parts: a foot, mantle, shell, and visceral mass. Mollusks also possess a
Mollusca Mollusks are soft bodied animals that have an internal or external shell, a similar body plan consisting of four basic parts: a foot, mantle, shell, and visceral mass. Mollusks also possess a
Figure 33.25a Free-living nematode
 Figure 33.25a Free-living nematode Bilateraly symmetrical Pseudocoelomates Body covered with secreated, flexible cuticle. No cilia Only longitudinal muscles. No protonephridia Muscular pharynx Gonochoristic
Figure 33.25a Free-living nematode Bilateraly symmetrical Pseudocoelomates Body covered with secreated, flexible cuticle. No cilia Only longitudinal muscles. No protonephridia Muscular pharynx Gonochoristic
Molluscs. Chapter 16
 Molluscs Chapter 16 Phylum Mollusca Phylum Mollusca includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids. Phylum Mollusca Molluscs have a mesoderm lined body cavity a coelom. They are
Molluscs Chapter 16 Phylum Mollusca Phylum Mollusca includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids. Phylum Mollusca Molluscs have a mesoderm lined body cavity a coelom. They are
Symmetry. Asymmetrical- no shape. Radial- same in half when cut any angle. Bilateral- having a distinct right and left side
 Symmetry Asymmetrical- no shape Radial- same in half when cut any angle Bilateral- having a distinct right and left side Invertebrates 95% of Animals No Backbone The simplest animals and they do not have
Symmetry Asymmetrical- no shape Radial- same in half when cut any angle Bilateral- having a distinct right and left side Invertebrates 95% of Animals No Backbone The simplest animals and they do not have
Biol Echinoderms & Chordates. But first a few words about Development
 Biol 1309 Echinoderms & Chordates 1 But first a few words about Development Blastula- zygote first develops into a hollow ball of cells Deuterostome - mouth second Protostome - mouth first Cleavage - describes
Biol 1309 Echinoderms & Chordates 1 But first a few words about Development Blastula- zygote first develops into a hollow ball of cells Deuterostome - mouth second Protostome - mouth first Cleavage - describes
Chapter 5 Marine Protozoans and Invertebrates
 Chapter 5 Marine Protozoans and Invertebrates I. The Protozoans A. Kindgom Protista a catch-all category B. Characteristics 1. Mode of nutrition 2. Single-celled or multicellular? 3. Cell structure 4.
Chapter 5 Marine Protozoans and Invertebrates I. The Protozoans A. Kindgom Protista a catch-all category B. Characteristics 1. Mode of nutrition 2. Single-celled or multicellular? 3. Cell structure 4.
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. CHAPTER 17. Annelids 17-1
 CHAPTER 17 Annelids 17-1 Characteristics of the Phylum Annelida Diversity Exhibit segmentation or metamerism Bodies composed of repeated units Each unit contains components of most MAJOR organ systems
CHAPTER 17 Annelids 17-1 Characteristics of the Phylum Annelida Diversity Exhibit segmentation or metamerism Bodies composed of repeated units Each unit contains components of most MAJOR organ systems
Phylum Mollusca. Includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids.
 Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids. Bivalves Nautilus Characteristics Soft-bodied invertebrate Covered with protective mantle that may or may
Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids. Bivalves Nautilus Characteristics Soft-bodied invertebrate Covered with protective mantle that may or may
ZOO 2040 Biology of Animals Topic 12 Lophophorates, Chaetognaths, Echinoderms, and Hemichordates
 Deuterostomes are a group of several higher phyla: the Lophophorates (Phoronida, Ectoprocta, and Brachiopoda), Chaetognatha, Echinodermata, Hemichordata, and Chordata (which includes vertebrates) Lophophorates
Deuterostomes are a group of several higher phyla: the Lophophorates (Phoronida, Ectoprocta, and Brachiopoda), Chaetognatha, Echinodermata, Hemichordata, and Chordata (which includes vertebrates) Lophophorates
Bivalved molluscs filter feeders
 Class Bivalvia Bivalved molluscs have two shells (valves). Mussels, clams, oysters, scallops, shipworms. Mostly sessile filter feeders. No head or radula. Class Bivalvia Part of the mantle is modified
Class Bivalvia Bivalved molluscs have two shells (valves). Mussels, clams, oysters, scallops, shipworms. Mostly sessile filter feeders. No head or radula. Class Bivalvia Part of the mantle is modified
What Is an Annelid? Annelids are worms with segmented bodies. They have a true coelom that is lined with tissue derived from mesoderm.
 What Is an Annelid? What Is an Annelid? Phylum: Annelidae Annelids are worms with segmented bodies. They have a true coelom that is lined with tissue derived from mesoderm. Three Germ Layers of an Annelid
What Is an Annelid? What Is an Annelid? Phylum: Annelidae Annelids are worms with segmented bodies. They have a true coelom that is lined with tissue derived from mesoderm. Three Germ Layers of an Annelid
Title: May 31 2:42 PM (1 of 23) Phylum Mollusca
 Title: May 31 2:42 PM (1 of 23) Phylum Mollusca Title: May 31 3:25 PM (2 of 23) often referred to as mollusks second largest phylum has 7 classes only looking at 4 bilateral symmetry, true body cavity
Title: May 31 2:42 PM (1 of 23) Phylum Mollusca Title: May 31 3:25 PM (2 of 23) often referred to as mollusks second largest phylum has 7 classes only looking at 4 bilateral symmetry, true body cavity
Biology 11 - Chapter 31 Assignment
 Name: Class: Date: Biology 11 - Chapter 31 Assignment True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Echinoderms exhibit their invertebrate heritage by their hard exoskeletons made of calcium
Name: Class: Date: Biology 11 - Chapter 31 Assignment True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Echinoderms exhibit their invertebrate heritage by their hard exoskeletons made of calcium
Chordates 1. Biology 2
 Chordates 1 Biology 2 Kingdom Animals Eukaryotic Multicellular - Many cell types Heterotrophic Feed by ingestion No cell walls Diploid life cycle Phylogenetic Tree Deuterostome Bilateral Symmetry 3 tissues
Chordates 1 Biology 2 Kingdom Animals Eukaryotic Multicellular - Many cell types Heterotrophic Feed by ingestion No cell walls Diploid life cycle Phylogenetic Tree Deuterostome Bilateral Symmetry 3 tissues
Mollusks Are Soft and Unsegmented
 Mollusks Objectives Understand the taxonomic relationships and major features of mollusks Learn the external and internal anatomy of the clam and squid Understand the major advantages and limitations of
Mollusks Objectives Understand the taxonomic relationships and major features of mollusks Learn the external and internal anatomy of the clam and squid Understand the major advantages and limitations of
Class Polychaeta: Marine Worms
 Class Polychaeta: Marine Worms Animal Phyla Phylum Mollusca (Snails, Clams, Octopods and Allies): Radula: rasping tongue Shell: 3 layers, mostly calcium carbonate Inner-most = nacre = mother of pearl Mantle:
Class Polychaeta: Marine Worms Animal Phyla Phylum Mollusca (Snails, Clams, Octopods and Allies): Radula: rasping tongue Shell: 3 layers, mostly calcium carbonate Inner-most = nacre = mother of pearl Mantle:
February 17, Unit 2. Biodiversity. Chordata, the vertebrates
 Unit 2 Biodiversity Chordata, the vertebrates Phylum Chordata Examples: Sea squirts, fish, birds, dinosaurs, humans. General characteristics: 1. Bilaterally symmetrical 2. Coelomate 3. One way digestive
Unit 2 Biodiversity Chordata, the vertebrates Phylum Chordata Examples: Sea squirts, fish, birds, dinosaurs, humans. General characteristics: 1. Bilaterally symmetrical 2. Coelomate 3. One way digestive
Characteristics of Animals pp Topic 7: Animal Diversity Ch Symmetry pp Characteristics of Animals
 Topic 7: Animal Diversity Ch. 32-34 Characteristics of Animals pp.704-705 Animals: Are eukaryotic Are multicellular Are ingestive heterotrophs Have no cell walls Most are motile Most have tissues organized
Topic 7: Animal Diversity Ch. 32-34 Characteristics of Animals pp.704-705 Animals: Are eukaryotic Are multicellular Are ingestive heterotrophs Have no cell walls Most are motile Most have tissues organized
Kingdom Animalia. Eukaryotic Multicellular Heterotrophs Lack Cell Walls
 Kingdom Animalia Eukaryotic Multicellular Heterotrophs Lack Cell Walls Must do: Feed, Respiration, Circulation, Excretion, Response, Movement, and Reproduction Symmetry Asymmetrical- no shape Radial- same
Kingdom Animalia Eukaryotic Multicellular Heterotrophs Lack Cell Walls Must do: Feed, Respiration, Circulation, Excretion, Response, Movement, and Reproduction Symmetry Asymmetrical- no shape Radial- same
Protostomes vs Deuterostomes. Phylum Mollusca
 Protostomes vs Deuterostomes Animals that have a true coelom and complete digestive system can be divided into two main groups. This division is based on the way their embryos develop and the way in which
Protostomes vs Deuterostomes Animals that have a true coelom and complete digestive system can be divided into two main groups. This division is based on the way their embryos develop and the way in which
A. Porifera (sponges): B. Cnidaria (jellies, hydra, sea anemones, and corals):
 Invertebrates Notes A. Porifera (sponges): Porifera literally means. Most sponges are. They are that collect food particles from the water as they pass through flagellated cells called. These cells then
Invertebrates Notes A. Porifera (sponges): Porifera literally means. Most sponges are. They are that collect food particles from the water as they pass through flagellated cells called. These cells then
Chapter 7. Marine Animals Without a Backbone
 Chapter 7 Marine Animals Without a Backbone Molluscs Characteristics of Phylum: More than 200,000 species Name means "soft body" Basic body plan head, muscular foot and visceral mass in most species Mantle-
Chapter 7 Marine Animals Without a Backbone Molluscs Characteristics of Phylum: More than 200,000 species Name means "soft body" Basic body plan head, muscular foot and visceral mass in most species Mantle-
Name Date Period. Mollusk Review TORSION HEMOLYMPH SESSILE TROCHOPHORE ADDUCTOR KIDNEY HEMOCOEL MANTLE CHROMATOPHORES VISCERAL MASS
 Name Date Period Mollusk Review MOLLUSK VOCABULARY: Match the word with its definition. TORSION HEMOLYMPH SESSILE TROCHOPHORE ADDUCTOR KIDNEY HEMOCOEL MANTLE CHROMATOPHORES VISCERAL MASS Free-swimming
Name Date Period Mollusk Review MOLLUSK VOCABULARY: Match the word with its definition. TORSION HEMOLYMPH SESSILE TROCHOPHORE ADDUCTOR KIDNEY HEMOCOEL MANTLE CHROMATOPHORES VISCERAL MASS Free-swimming
Phylum Platyhelminthes Phylum Nematoda Phylum Mollusca. By: Jerzylin, Beata & Jennifer
 Phylum Platyhelminthes Phylum Nematoda Phylum Mollusca By: Jerzylin, Beata & Jennifer Phylum Platyhelminthes Common Characteristics: Triploblastic Bilateral Symmetry Protostome No true stomach structure
Phylum Platyhelminthes Phylum Nematoda Phylum Mollusca By: Jerzylin, Beata & Jennifer Phylum Platyhelminthes Common Characteristics: Triploblastic Bilateral Symmetry Protostome No true stomach structure
BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring Cycloneuralia Characters. Pseudo- coelomates (Ecdysozoa): Lecture 19
 BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring 2010 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 19 Cycloneuralia Characters 18(2): Ambiguous spiral cleavage. 92: Terminal mouth
BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring 2010 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 19 Cycloneuralia Characters 18(2): Ambiguous spiral cleavage. 92: Terminal mouth
Animal Diversity. Kingdom Animalia
 7ch11 Animal Diversity Kingdom Animalia Animal Characteristics 1. animals are eukaryotes and are multicellular 2. cells are specialized for different functions (vision,digestion,reproduction) 3. protein,
7ch11 Animal Diversity Kingdom Animalia Animal Characteristics 1. animals are eukaryotes and are multicellular 2. cells are specialized for different functions (vision,digestion,reproduction) 3. protein,
26-3 Cnidarians Slide 1 of 47
 1 of 47 What Is a Cnidarian? What is a cnidarian? 2 of 47 What Is a Cnidarian? What Is a Cnidarian? Cnidarians are soft-bodied, carnivorous animals that have stinging tentacles arranged in circles around
1 of 47 What Is a Cnidarian? What is a cnidarian? 2 of 47 What Is a Cnidarian? What Is a Cnidarian? Cnidarians are soft-bodied, carnivorous animals that have stinging tentacles arranged in circles around
 Kingdom: Animalia Phylum:Mollusca Classes: Bivalva, Gastropoda, Cephalopoda http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0a7j5prl8hc&feature=related http://www2.beavercreek.k12.oh.us/videos/45/pgr45_700k.asf What is
Kingdom: Animalia Phylum:Mollusca Classes: Bivalva, Gastropoda, Cephalopoda http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0a7j5prl8hc&feature=related http://www2.beavercreek.k12.oh.us/videos/45/pgr45_700k.asf What is
Each unit contains components of most organ systems. Increased burrowing efficiency by permitting movement of segments
 CHAPTER 17 Annelids Characteristics of the Phylum Annelida Diversity Exhibit segmentation or Bodies composed of units Each unit contains components of most organ systems Increased burrowing efficiency
CHAPTER 17 Annelids Characteristics of the Phylum Annelida Diversity Exhibit segmentation or Bodies composed of units Each unit contains components of most organ systems Increased burrowing efficiency
Animals. Invertebrate Diversity & Evolution
 Animals Invertebrate Diversity & Evolution Animal Characteristics Multicellular Heterotrophic (can be classified by their feeding strategies) Classified by feeding strategies Filter feeders (suspension
Animals Invertebrate Diversity & Evolution Animal Characteristics Multicellular Heterotrophic (can be classified by their feeding strategies) Classified by feeding strategies Filter feeders (suspension
Mollusks Soft-bodied Invertebrates
 Mollusks Soft-bodied Invertebrates Phylum Mollusca Very diverse - more species of molluscs than any other group in the ocean. Phylum includes: Bivalves (2 shells); ex. Clam Gastropods (1 shell, coiled);
Mollusks Soft-bodied Invertebrates Phylum Mollusca Very diverse - more species of molluscs than any other group in the ocean. Phylum includes: Bivalves (2 shells); ex. Clam Gastropods (1 shell, coiled);
1. Animals are (diploid) with tissues arranged into organs and organ systems. 3. Animals require for aerobic respiration.
 Chapter 25 Animals: The Invertebrates I. Overview of the Animal Kingdom A. General Characteristics of Animals 1. Animals are (diploid) with tissues arranged into organs and organ systems. 2. Animals are.
Chapter 25 Animals: The Invertebrates I. Overview of the Animal Kingdom A. General Characteristics of Animals 1. Animals are (diploid) with tissues arranged into organs and organ systems. 2. Animals are.
`Mollusks. may or may not form a hard, calcium carbonate shell. Trochophore Larva
 `Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Soft-bodied invertebrate covered with protective mantle that may or may not form a hard, calcium carbonate shell Includes chitons, snails, slugs, clams, oysters, squid, octopus,
`Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Soft-bodied invertebrate covered with protective mantle that may or may not form a hard, calcium carbonate shell Includes chitons, snails, slugs, clams, oysters, squid, octopus,
Kingdom Animalia. Lab Exercise 23. Objectives. Introduction
 Lab Exercise Kingdom Animalia Objectives - Be able to recognize and name the major groups of animals - Be able to identify key characteristics that separate animal taxa - Be able to use a dichotomous key
Lab Exercise Kingdom Animalia Objectives - Be able to recognize and name the major groups of animals - Be able to identify key characteristics that separate animal taxa - Be able to use a dichotomous key
Chapter 12 Part 2. The Worms Platyhelminthes, Nematoda & Annelida
 Chapter 12 Part 2 The Worms Platyhelminthes, Nematoda & Annelida Phylum: Platyhelminthes Examples: Flatworms, Planaria sp., tapeworms and blood flukes Acoelomate, Invertebrate, Simplest critter w/ bilateral
Chapter 12 Part 2 The Worms Platyhelminthes, Nematoda & Annelida Phylum: Platyhelminthes Examples: Flatworms, Planaria sp., tapeworms and blood flukes Acoelomate, Invertebrate, Simplest critter w/ bilateral
Life History of Aquatic Organisms (AFI-31306) Lecture: Adaptive radiation in molluscs Martin Lankheet, EZO
 Life History of Aquatic Organisms (AFI-31306) Lecture: Adaptive radiation in molluscs Martin Lankheet, EZO Position in the course THEME Lectures Tutorials Practicals Introduction to Life Life-history trade-offs
Life History of Aquatic Organisms (AFI-31306) Lecture: Adaptive radiation in molluscs Martin Lankheet, EZO Position in the course THEME Lectures Tutorials Practicals Introduction to Life Life-history trade-offs
Overview of Invertebrates
 Overview of Invertebrates General Features of Animals Heterotrophic Multicellular (eukaryotic) Cells lack rigid cell walls Cells are usually quite flexible. Cells (except sponges) are organized into structural
Overview of Invertebrates General Features of Animals Heterotrophic Multicellular (eukaryotic) Cells lack rigid cell walls Cells are usually quite flexible. Cells (except sponges) are organized into structural
Chapter 28 Mollusks & Annelids. BIOLOGY II Miss. Loulousis
 Chapter 28 Mollusks & Annelids BIOLOGY II Miss. Loulousis Mollusks have a true coelom Snails, slugs, oysters, clams, scallops, octopuses, and squids are all mollusks Annelid earthworm next section Mollusks
Chapter 28 Mollusks & Annelids BIOLOGY II Miss. Loulousis Mollusks have a true coelom Snails, slugs, oysters, clams, scallops, octopuses, and squids are all mollusks Annelid earthworm next section Mollusks
Arthropoda diversity
 Arthropoda diversity -Subphylum Trilobitomorpha no living representatives (only fossil record) - Subphylum Chelicerata - Subphylum Mandibulata Horseshoe crab Sea spiders Crustacea Class Crustacea. ~ 45.000
Arthropoda diversity -Subphylum Trilobitomorpha no living representatives (only fossil record) - Subphylum Chelicerata - Subphylum Mandibulata Horseshoe crab Sea spiders Crustacea Class Crustacea. ~ 45.000
Phylum Mollusca. Soft-bodied animals. Internal or external shell. Include snails, slugs, clams, squids and octopi
 Phylum Mollusca Soft-bodied animals Internal or external shell Include snails, slugs, clams, squids and octopi Trochophore: free-swimming larval stage of an aquatic mollusk True coeloms Have complex organ
Phylum Mollusca Soft-bodied animals Internal or external shell Include snails, slugs, clams, squids and octopi Trochophore: free-swimming larval stage of an aquatic mollusk True coeloms Have complex organ
Biology. Slide 1 of 43. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 43 2 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What are the defining features of mollusks? 3 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What Is a Mollusk? Mollusks are soft-bodied animals that usually have an internal or external
Biology 1 of 43 2 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What are the defining features of mollusks? 3 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What Is a Mollusk? Mollusks are soft-bodied animals that usually have an internal or external
What is an animal? Introduction to Animals 2. Phylum Mollusca. Phylum Mollusca 4/20/2016
 What is an animal? Introduction to Animals 2 Multicellular chemoorganoheterotrophs Eukaryotes that lack cell walls and chloroplasts Have mitochondria Are motile at some point in their lives Snails, Octopus,
What is an animal? Introduction to Animals 2 Multicellular chemoorganoheterotrophs Eukaryotes that lack cell walls and chloroplasts Have mitochondria Are motile at some point in their lives Snails, Octopus,
Chapter 35. Table of Contents. Section 1 Mollusca. Section 2 Annelida. Mollusks and Annelids
 Mollusks and Annelids Table of Contents Section 1 Mollusca Section 2 Annelida Section 1 Mollusca Objectives Describe the key characteristics of mollusks. Describe the body plan of mollusks. Name the characteristics
Mollusks and Annelids Table of Contents Section 1 Mollusca Section 2 Annelida Section 1 Mollusca Objectives Describe the key characteristics of mollusks. Describe the body plan of mollusks. Name the characteristics
ZOOLOGY SEGMENTED WORMS (Phylum Annelida)
 ZOOLOGY SEGMENTED WORMS (Phylum Annelida) I. Compared and Contrasted to Phylum Mollusca. A. They are like the molluscs in that they 1. are eucoelomate animals. 2. have specialized sense organs. 3. have
ZOOLOGY SEGMENTED WORMS (Phylum Annelida) I. Compared and Contrasted to Phylum Mollusca. A. They are like the molluscs in that they 1. are eucoelomate animals. 2. have specialized sense organs. 3. have
PHYLUM: PLATHYHELMINTHES
 PHYLUM: PLATHYHELMINTHES FLATWORMS Free living (living independently i.e. not attached) Bilaterally symmetrical with a definite front and back, and with left and right sides. Mobile creeping animals. Concentration
PHYLUM: PLATHYHELMINTHES FLATWORMS Free living (living independently i.e. not attached) Bilaterally symmetrical with a definite front and back, and with left and right sides. Mobile creeping animals. Concentration
The Animals: Kingdom Animalia
 The Animals: Kingdom Animalia Kingdom Animalia (Animals) What is an Animal? Zoology- The study of Animals General Characteristics of 1. Animals are multicellular and eukaryotic. Animals 2. Animals consume
The Animals: Kingdom Animalia Kingdom Animalia (Animals) What is an Animal? Zoology- The study of Animals General Characteristics of 1. Animals are multicellular and eukaryotic. Animals 2. Animals consume
BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring Larval Development. Larval Development. Lecture 18
 BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring 2010 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 18 Larval Development 1. Often presented as a progression of stages a. Representative
BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring 2010 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 18 Larval Development 1. Often presented as a progression of stages a. Representative
What are Arthropods? General Characteristics. General Characteristics 5/14/2013. Phylum Arthropoda Biology 11
 What are Arthropods? Phylum Arthropoda Biology 11 Segmented invertebrates Jointed appendages Exoskeleton Includes the most numerous and diverse animals on Earth They are found in virtually every habitat
What are Arthropods? Phylum Arthropoda Biology 11 Segmented invertebrates Jointed appendages Exoskeleton Includes the most numerous and diverse animals on Earth They are found in virtually every habitat
Unit 18.2: Mollusks and Annelids
 Unit 18.2: Mollusks and Annelids Lesson Objectives Describe invertebrates in the phylum Mollusca. Summarize the characteristics of annelids. Vocabulary Annelida deposit feeder gills heart mantle Mollusca
Unit 18.2: Mollusks and Annelids Lesson Objectives Describe invertebrates in the phylum Mollusca. Summarize the characteristics of annelids. Vocabulary Annelida deposit feeder gills heart mantle Mollusca
Henry Guan, Akash Kashyap, and Angus Qian
 Henry Guan, Akash Kashyap, and Angus Qian http://peterbe.mobi/plog/interior-octopus/octopus.jpg Akash Kashyap Overview 85, 000 species Marine, Terrestrial, Freshwater habitats Very Diverse Classes: Chitons,
Henry Guan, Akash Kashyap, and Angus Qian http://peterbe.mobi/plog/interior-octopus/octopus.jpg Akash Kashyap Overview 85, 000 species Marine, Terrestrial, Freshwater habitats Very Diverse Classes: Chitons,
Phylum Platyhelminthes. You will need: five colours of pencil crayon or pen (preferably blue, green, red, orange and purple)
 Phylum Platyhelminthes You will need: five colours of pencil crayon or pen (preferably blue, green, red, orange and purple) Phylum Platyhelminthes bilaterally symmetrical have all 3 embryonic germ layers:
Phylum Platyhelminthes You will need: five colours of pencil crayon or pen (preferably blue, green, red, orange and purple) Phylum Platyhelminthes bilaterally symmetrical have all 3 embryonic germ layers:
Chordates. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Chordates Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Vertebrates are members of the kingdom Animalia and the phylum Chordata ([link]). Recall that animals that possess bilateral symmetry can be divided into two groups protostomes
Chordates Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Vertebrates are members of the kingdom Animalia and the phylum Chordata ([link]). Recall that animals that possess bilateral symmetry can be divided into two groups protostomes
Kingdom Animalia Subkingdom Eumetazoa Bilateria Phylum Mollusca
 Kingdom Animalia Subkingdom Eumetazoa Bilateria Phylum Mollusca Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Illustrations 2014 Cengage Learning unless otherwise noted Phylum Mollusca Molluscs (mollis = soft)
Kingdom Animalia Subkingdom Eumetazoa Bilateria Phylum Mollusca Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Illustrations 2014 Cengage Learning unless otherwise noted Phylum Mollusca Molluscs (mollis = soft)
Unit 19.2: Fish. Vocabulary fish spawning swim bladder
 Unit 19.2: Fish Lesson Objectives Describe structure and function in fish. Explain how fish reproduce and develop. Give an overview of the five living classes of fish. Summarize the evolution of fish.
Unit 19.2: Fish Lesson Objectives Describe structure and function in fish. Explain how fish reproduce and develop. Give an overview of the five living classes of fish. Summarize the evolution of fish.
Chapter 23: The Animal Kingdom
 Chapter 23: The Animal Kingdom Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 23-1 What is an animal? 23-2 Eukaryotic Multicellular
Chapter 23: The Animal Kingdom Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 23-1 What is an animal? 23-2 Eukaryotic Multicellular
Topic Page: Annelida. Annelid Charact erist ics.
 Topic Page: Annelida Definition: annelid from Philip's Encyclopedia Any member of the Annelida phylum of segmented worms. All have encircling grooves usually corresponding to internal partitions of the
Topic Page: Annelida Definition: annelid from Philip's Encyclopedia Any member of the Annelida phylum of segmented worms. All have encircling grooves usually corresponding to internal partitions of the
PHYLUM CHORDATA: Subphylum vertebrata
 PHYLUM CHORDATA: Subphylum vertebrata There are three basic characteristics that distinguish Phylum Chordata from all other animal phyla: The presence of a flexible, rod-like, internal supporting structure
PHYLUM CHORDATA: Subphylum vertebrata There are three basic characteristics that distinguish Phylum Chordata from all other animal phyla: The presence of a flexible, rod-like, internal supporting structure
Ch17_Animals. Animals Multicellular eukaryotes. What is an animal? Animal development. Main differences with plants Main differences with fungi
 Animals Multicellular eukaryotes Domain Domain Kingdoms Main differences with plants Main differences with fungi What is an animal? Domain Nutritional mode: Heterotrophic (Ingestive) Level of organization:
Animals Multicellular eukaryotes Domain Domain Kingdoms Main differences with plants Main differences with fungi What is an animal? Domain Nutritional mode: Heterotrophic (Ingestive) Level of organization:
Figure 32.8 Animal phylogeny based on sequencing of SSU-rRNA
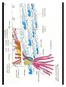 Figure 32.8 Animal phylogeny based on sequencing of SSU-rRNA Polychaetes Representative Annelids Oligochaetes Marine worms Hirudineans Terrestrial & aquatic Leeches - Aquatic & terrestrial Annelid Circulatory,
Figure 32.8 Animal phylogeny based on sequencing of SSU-rRNA Polychaetes Representative Annelids Oligochaetes Marine worms Hirudineans Terrestrial & aquatic Leeches - Aquatic & terrestrial Annelid Circulatory,
Life Lecture Notes Chapter 13 Mollusca unsegmented bodied critters Valve mantle ii. Bilateral symmetry Gills foot Radula Visceral mass
 Life Lecture Notes Chapter 13 I. Phylum Mollusca a. General Characteristics i. Soft unsegmented bodied critters often covered by a shell called a Valve which is produced by the mantle. ii. Bilateral symmetry
Life Lecture Notes Chapter 13 I. Phylum Mollusca a. General Characteristics i. Soft unsegmented bodied critters often covered by a shell called a Valve which is produced by the mantle. ii. Bilateral symmetry
chordates (S3.O1.d / S3.O2.e)
 Comparing invertebrates and Vocab Chap 29 & 33 chordates (S3.O1.d / S3.O2.e) 1. Radial symmetry 2. Bilateral symmetry 3. Cephalization 4. Coelom 5. Intracellular digestion 6. Extracellular digestion 7.
Comparing invertebrates and Vocab Chap 29 & 33 chordates (S3.O1.d / S3.O2.e) 1. Radial symmetry 2. Bilateral symmetry 3. Cephalization 4. Coelom 5. Intracellular digestion 6. Extracellular digestion 7.
Marine Biology 2/9/05
 Information on Common Animals in the Rocky Intertidal Zone HERMIT CRAB (Phylum Arthropoda) Feeding: Hermit crabs will eat just about anything; most are scavengers on dead organisms and detritus. Some species,
Information on Common Animals in the Rocky Intertidal Zone HERMIT CRAB (Phylum Arthropoda) Feeding: Hermit crabs will eat just about anything; most are scavengers on dead organisms and detritus. Some species,
Requirements for Animal Life. Phylum Bryozoa. Colonial Bryozoans. A lophophore is a structure used for:
 Requirements for Animal Life Animal phylogeny based on sequencing of SSU-rRNA The demands of 3 unique environments Marine, freshwater, terrestrial Gas exchange Nutrition Distribution and transport Disposal
Requirements for Animal Life Animal phylogeny based on sequencing of SSU-rRNA The demands of 3 unique environments Marine, freshwater, terrestrial Gas exchange Nutrition Distribution and transport Disposal
deuterostomes eucoelomates pseudocoelomates acoelomate
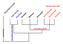 deuterostomes Mollusca Arthropoda Echinodermata Hemichordata Chordata eucoelomates Annelida Rotifera Platyhelminthes Nematoda acoelomate pseudocoelomates Phylum Hemichordata Share characteristics with
deuterostomes Mollusca Arthropoda Echinodermata Hemichordata Chordata eucoelomates Annelida Rotifera Platyhelminthes Nematoda acoelomate pseudocoelomates Phylum Hemichordata Share characteristics with
Ch17_Animals. Animals Multicellular eukaryotes. What is an animal? Animal development. Main differences with plants Main differences with fungi
 Animals Multicellular eukaryotes Domain Domain Kingdoms Main differences with plants Main differences with fungi What is an animal? Domain Nutritional mode: Heterotrophic (Ingestive) Level of organization:
Animals Multicellular eukaryotes Domain Domain Kingdoms Main differences with plants Main differences with fungi What is an animal? Domain Nutritional mode: Heterotrophic (Ingestive) Level of organization:
5 Marine Biology Notes. Marine Invertebrates (Animals Without a Backbone)
 5 Marine Biology Notes Marine Invertebrates (Animals Without a Backbone) Invertebrates Animals without a backbone are known as invertebrates. Those with a backbone are called vertebrates. About 97% of
5 Marine Biology Notes Marine Invertebrates (Animals Without a Backbone) Invertebrates Animals without a backbone are known as invertebrates. Those with a backbone are called vertebrates. About 97% of
Animal Evolution: Chordate and Vertebrate Evolution and Diversity (Learning Outline)
 Animal Evolution: Chordate and Vertebrate Evolution and Diversity (Learning Outline) 1. Distinguishing features of the phylum Chordata and representative organisms. 2. Highlights of evolutionary steps
Animal Evolution: Chordate and Vertebrate Evolution and Diversity (Learning Outline) 1. Distinguishing features of the phylum Chordata and representative organisms. 2. Highlights of evolutionary steps
2 Mollusks and Annelid Worms
 CHAPTER 15 2 Mollusks and Annelid Worms SECTION Invertebrates BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the four features of mollusks? What are
CHAPTER 15 2 Mollusks and Annelid Worms SECTION Invertebrates BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the four features of mollusks? What are
The Animal Kingdom. Animal Kingdom. Characteristics of All Animals. Major Characteristics Used To Classify Animals
 The Animal Kingdom Animal Kingdom Phylums: 1. Sponges 2. Cnidaria Jelly Fish, Hydra 3. Flatworms Flukes, Tapeworms 4. Roundworms- Hookworms 5. Segmented Worms- Earthworms 6. Rotifera- Rotifers 7. Mullusca
The Animal Kingdom Animal Kingdom Phylums: 1. Sponges 2. Cnidaria Jelly Fish, Hydra 3. Flatworms Flukes, Tapeworms 4. Roundworms- Hookworms 5. Segmented Worms- Earthworms 6. Rotifera- Rotifers 7. Mullusca
Classification. Phylum Chordata
 AP Biology Chapter 23 Exercise #17: Chordates: Urochordata & Cephalochordata Lab Guide Chordates show remarkable diversity. Most are vertebrates. All animals that belong to this phylum MUST, at some point
AP Biology Chapter 23 Exercise #17: Chordates: Urochordata & Cephalochordata Lab Guide Chordates show remarkable diversity. Most are vertebrates. All animals that belong to this phylum MUST, at some point
Mollusks and Annelids. Chapter 23+
 Mollusks and Annelids Chapter 23+ 1 Annelids and Mollusks Coelomates Trochophore larvae Bilateral symmetry More complex organ systems 2 Moving On Up 3 Coelom Coelomates Evolutionary milestone True body
Mollusks and Annelids Chapter 23+ 1 Annelids and Mollusks Coelomates Trochophore larvae Bilateral symmetry More complex organ systems 2 Moving On Up 3 Coelom Coelomates Evolutionary milestone True body
Invertebrates. Sponges: Porifera pore bearer 10/8/09
 Animals without backbones We ll cover characteristics of major phyla and some to class level (KPCOFGS) We ll also cover some natural history Refer to your notes that I posted on-line! Invertebrates Levels
Animals without backbones We ll cover characteristics of major phyla and some to class level (KPCOFGS) We ll also cover some natural history Refer to your notes that I posted on-line! Invertebrates Levels
Phylum Mollusca (soft bodied)
 Phylum Mollusca (soft bodied) Most described species in the animal kingdom next to Phylum Arthropoda ~100,000 species... Marine, freshwater and terrestrial. 35,000 fossil species. Most diverse group of
Phylum Mollusca (soft bodied) Most described species in the animal kingdom next to Phylum Arthropoda ~100,000 species... Marine, freshwater and terrestrial. 35,000 fossil species. Most diverse group of
Lobsters, Crab and Shrimp
 Lobsters, Crab and Shrimp Crustaceans Phylum: Arthropoda ( jointed feet ) Invertebrate Exoskeleton (made of chitin) protects body and provides a place for muscles to attach to. Segmented body Jointed appendages
Lobsters, Crab and Shrimp Crustaceans Phylum: Arthropoda ( jointed feet ) Invertebrate Exoskeleton (made of chitin) protects body and provides a place for muscles to attach to. Segmented body Jointed appendages
Marine Fishes. Chapter 8
 Marine Fishes Chapter 8 Fish Gills The construction of the gill is the same in all fish gill arch supports the entire structure, gill rakers are on the forward surface of the gill arch and gill filaments
Marine Fishes Chapter 8 Fish Gills The construction of the gill is the same in all fish gill arch supports the entire structure, gill rakers are on the forward surface of the gill arch and gill filaments
Coelomate Worms: Sipunculans, Pogonophorans, Echiurans and Vestimenifera
 Coelomate Worms Coelomate Worms: Sipunculans, Pogonophorans, Echiurans and Vestimenifera Ectoderm Mesoderm Dt Endoderm Coelom Often dismissed as minor or lesser Comprise less than 600 species total Never
Coelomate Worms Coelomate Worms: Sipunculans, Pogonophorans, Echiurans and Vestimenifera Ectoderm Mesoderm Dt Endoderm Coelom Often dismissed as minor or lesser Comprise less than 600 species total Never
2/17/2017. Lec. 11: Ch. 32 Deuterostomes
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Lec. 11: Ch. 32 Deuterostomes Deuterostomes Radial cleavage Indeterminant blastomeres Blastopore becomes anus Coelom forms by outpouching of the gut (enterocoelous) Phylum Echinodermata
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Lec. 11: Ch. 32 Deuterostomes Deuterostomes Radial cleavage Indeterminant blastomeres Blastopore becomes anus Coelom forms by outpouching of the gut (enterocoelous) Phylum Echinodermata
Lecture III.5a. Questions.
 Lecture III.5a. Questions. 1. Suppose that echinoderms were originally bilaterally symmetric. How would that change the synapomorphies in the cladogram on page 2? 2. If echinoderms were originally bilaterally
Lecture III.5a. Questions. 1. Suppose that echinoderms were originally bilaterally symmetric. How would that change the synapomorphies in the cladogram on page 2? 2. If echinoderms were originally bilaterally
