Classes at: - Topic: Gaseous State
|
|
|
- Phyllis Austin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY by: SHAILENDRA KR. Classes at: - SCIENCE TUTORIALS; Opp. Khuda Baksh Library, Ashok Rajpath, Patna PIN POINT STUDY CIRCLE; House No. 5A/65, Opp. Mahual Kothi, Alpana Market, Patna Topic: Gaseous State Meq. Approach 1. 5 g of ethane are confined in a bulb of 1 litre capacity. The bulb is so weak that it will burst if the pressure exceeds 10 atm. At what temperature will be the pressure of gas reach the bursting value. Ans: C 2. An iron cylinder contains helium at a pressure of 250 kpa at 300 K. The cylinder can withstand a pressure of Pa. The room in which cylinder is placed catches fire. Predict whether the cylinder will blow up before it melts or not, melting point of cylinder = 1800 K. Ans: 1200 K 3. A gas occupies 300 ml at 27 C and 730 mm pressure. What would be its volume at STP? Ans: ml 4. Calculate the volume occupied by 7 g N 2 at 27 C and 750 mm of Hg. Ans: litre 5. O 2 is present in one litre flask at a pressure of mm of Hg. Calculate no. of O 2 molecules at 0 C. Ans: In victor Meyer s experiment, 0.23 g of a volatile solute displaced air which measures 112 ml at NTP. Calculate the vapour density and mol. wt. of substance. Ans: Mol. wt. = and V.D = The pressure exerted by 12 g of an ideal gas at temperature t C in a vessel of volume V litre is one atm. When the temperature is increased by 10 degree at the same volume, the pressure increases by 10%. Calculate the temperature t and volume V. ( Molecular weight of the gas = 120) Ans: 0.82 litre 8. An LPG (liquefied petroleum gas) cylinder weighs 14.8 kg when empty, when full, it weighs 29.0 kg and shows a pressure of 2.5 atm. In the course of use at 27 C, the weight of full cylinder is reduced to 23.2 kg. Find out the volume of the gas in cubic meters used up at the normal usage conditions, and the final pressure inside the cylinder. Assume LPG to be n-butane with normal boiling point of 0 C. Ans: 2.4 m 3 Page No.: 1
2 9. A balloon blown up with 1 mole of gas has a volume of 480 ml at 5 C. The balloon is filled to (7/8)th of its maximum capacity. Suggest, (a) Will be balloon burst at 30 C? (b) The minimum temperature at which it will burst. (c) The pressure of gas inside the balloon at 5 C. (d) The pressure of gas when balloon bursts. Ans: (a) C (b) C (c) 47.5 atm (d) 47.5 atm. 10. A spherical balloon of 21 cm diameter is to be filled up with H 2 at NTP from a cylinder containing the gas at 20 atm at 27 C. The cylinder can hold 2.82 litre of water at NTP. Calculate the number of balloons that can be filled up. Ans: n = A balloon of diameter 20 meter weighs 100 kg. Calculate its pay-load, if it is filled with He at 1.0 atm and 27 C. Density of air is 1.2 kg m 3.[R = dm 3 atm K 1 mol 1 ] Ans: g 12. A gas occupies litre at 740 mm of Hg and 27 C. Calculate: (a) its volume at STP (b) molecular weight if gas weighs 3.0 g (c) new pressure of gas if the weight of gas is increased to 7.5 g and temperature becomes 280 K (d) The volume of vessel at 300 K. Ans: (a) 0.37 litre (b) (c) 2.27 atm (d) litre 13. A mixture of CO and CO 2 is found to have a density of 1.50 g/litre at 30 C and 730 mm. What is composition of mixture? Ans: m = 38.85, Mole % of CO = 32.19, Mole % of CO 2 = An open vessel at 27 C is heated until 3/5th of the air in it has been expelled. Assuming that the volume of the vessel remains constant, find out: (a) the temperature at which vessel was heated. (b) the air escaped out if vessel is heated to 900 K. (c) the temperature at which half of the air escapes out. Ans: (a) K = 477 C (b) 2/3n mole (c) K = 327 C 15. An open flask contains air at 27 C. Calculate the temperature at which it should be heated so that, (a) 1/3rd of air measured at 27 C escapes out. (b) 1/3rd of air measured at final temperature escapes out. Ans: (a) K = 177 C (b) K = 127 C % N 2 O 4 molecules are dissociated in a sample of gas at 27 C and 760 torr. Calculate the density of the equilibrium mixture. Page No.: 2
3 Ans: g litre 1 Ans: atm 17. A car tyre has a volume of 10 litre when inflated. The tyre is inflated to a pressure of 3 atm at 17 C with air. Due to driving the temperature of tyre increases to 47 C. (a) What would be the pressure at this temperature? (b) How many litre of air measured at 47 C and pressure of 1 atm should be let out to restore the tyre to 3 atm at 47 C? Ans: (a) P = 3.31 atm (b) V 2 = 3.1 litre 18. O 2 is collected over water at 20 C. The pressure inside shown by the gas is 740 mm of Hg. What is the pressure due to O 2 alone if v.p. of H 2 O is 18 mm at 20 C. Ans: 722 mm 19. Calculate the total pressure in a 10 litre cylinder which contains 0.4 g of helium, 1.6 g of oxygen and 1.4 g of nitrogen at 27 C. Also calculate the partial pressure of helium gas in the cylinder. Assume ideal behaviour of gases. Given R = litre atm K 1 mol 1. Ans: H 2 = atm, O 2 = atm, N 2 = atm 20. Equal weights of CH 4 and O 2 are mixed in an empty container of one litre at 27 C. Calculate the: (a) fractional of total pressure exerted by O 2. (b) total pressure if the weights of gases are 32 g each. Ans: (a) 1/3 (b) atm 21. Two glass bulbs of equal volume are connected by a narrow tube and filled with a gas at 0 C and pressure of 76 cm of Hg. One of the bulb is then placed in a water bath maintained at 62 C. What is the new value of the pressure inside the bulbs? the volume of the connecting tube is negligible. Ans: cm of Hg 22. The density of a mixture of O 2 and N 2 at NTP is 1.3 g litre 1. Calculate partial pressure of O 2. Ans: 0.28 atm 23. An evacuated glass vessel weighs 50.0 g when empty g when filled with a liquid of density 0.98 g ml 1 and 50.5 g when filled with an ideal gas at 760 mm Hg at 300 K. determine the molecular weight of the gas. Ans: Calculate the total pressure in a mixture of 4 g O 2 and 2 g H 2 confined in a bulb of 1 litre at 0 C. Ans: atm 25. At room temperature following reaction goes to completion : 2NO + O 2 2NO 2 N 2 O 4 Dimer N 2 O 4 at 262 K is solid. A 250 ml flask and a 100 ml flask are separated by a stop cock. At 300 K, the nitric oxide in the larger flask exerts a pressure of atm and smaller one contains O 2 at atm.the gases are mixed by opening the stop cock and after the end of the reaction, the flasks are cooled to 220 K. Neglecting the vapour pressure of dimer, find out the pressure and composition of gas remaining at 220 K. (Assume gases behave ideally). Page No.: 3
4 26. One litre of O 2 and one litre of H 2 are taken in a vessel of 2 litre capacity at NTP. The gases are made to combine to form water. Calculate: (a) the mole and weight of water formed (b) the amount of gas left in vessel. (c) the total pressure if the vessel is heated to 100 C. (d) mole of O 2 used for formation of water. Ans: (a) Mole of H 2 O formed = , wt. of H 2 O formed = (b) mole, Wt. of O 2 left = g (c) 1.02 atm (d) dm 3 of SO 2 diffuses through a porous partition in 60 second. What volume be O 2 will diffuse under similar conditions in 30 second? Ans: dm The composition of the equilibrium mixture Cl 2 2Cl), which is attained at 1200 C, is determined by measuring the rate of effusion through a pinhole. It is observed that at 1.80 mm Hg pressure, the mixture effuses 1.16 times as fast as Krypton effuses under the same conditions. Calculate the fraction of chlorine molecules dissociated into atoms. (Atomic wt. of Kr = 84) Ans: α = or 13.7% 29. At 27 C, H 2 is leaked through a tiny hole into a vessel for 20 minute. Another unknown gas at the same T and P as that of H 2 is leaked through the same hole for 20 minute. After the effusion of the gases, the mixture exerts a pressure of 6 atm. The H 2 content of the mixture is 0.7 mole. If volume of container is 3 litre, what is the mol.wt. of unknown gas? Ans: M = A 4:1 molar mixture of He and CH 4 is contained in a vessel at 20 bar pressure. Due to a hole in the vessel, the gas mixture leaks out. What is the composition of the mixture effusing out initially? Ans: 8 : Assuming O 2 molecule spherical in shape and occupying the radius 150 pm, calculate: (a) the volume of single molecule of gas. (b) the percentage of empty space in one mole of O 2 at NTP. (c) comment on the percentage of empty space. Ans: (a) cm 3 per mol (b) % (c) 99.96% is empty space and this accounts that most of space in container is empty in which a molecule can move. Also it suggests for compressibility of gases to higher extent. Page No.: 4
5 32. Calculate the root mean square speed and average speed for a sample of gas having 5,10 and 15 molecules each one in a set is moving with a speed of , and ms 1 respectively. Ans: u rms = m sec 1 & u AV = m sec Calculate root mean square speed, average speed and most probable speed of: (a) O 2 at STP (b) Ethane at 27 C and 720 mm of Hg (c) O 2 at 17 C (d) O 2 if its density is g ml 1 at 1 atm (e) O 2 if g of it occupies 5 litre at 750 mm (f) O 2 if 20 C and 82 cm Hg. Ans: (a) u AV = cm sec 1 (b) u AV = cm sec 1 u rms = cm sec 1 u rms = cm sec 1 u MP = cm sec 1 u MP = cm sec 1 (c) u AV = cm sec 1 (d) u AV = cm sec 1 u rms = cm sec 1 u rms = cm sec 1 u MP = cm sec 1 u MP = cm sec 1 (e) u AV = cm sec 1 (f) u AV = cm sec 1 u rms = cm sec 1 u rms = cm sec 1 u MP = cm sec 1 u MP = cm sec The average speed at T 1 K and the most probable speed at T 2 K of CO 2 gas is cmsec 1. Calculate the value of T 1 and T 2. Ans: T 2 = K & T 1 = K 35. The average speed of an ideal gas molecule at 27 C is 0.3 m sec 1. Calculate average speed at 927 C. Ans: u 2 = 0.6 m sec Calculate the pressure exerted by gas molecules, each of mass g in a container of volume one litre. The rms speed is 10 5 cm sec 1. Ans: P = dyne cm Calculate the root mean square speed, total and average translational kinetic energy in joule of the molecules in 8 g methane at 27 C. Ans: u rms = cm sec 1, Total kinetic energy = joule Average kinetic energy = joule 38. (a) Calculate the pressure exerted by 5 mole of CO 2 in one litre vessel at 47 C using van der Waals equation. Also report the pressure of gas if it behaves ideally in nature. Given that a = atm litre 2 mol 2, b = litre mol 1. Page No.: 5
6 (b) If volume occupied by CO 2 molecules is negligible, then calculate the pressure exerted by one mole of CO 2 gas at 273 K. Ans: (a) P = atm (if gas behaves ideally, then PV=nRT, P 1 = =131.36atm) (b) atm 39. Calculate the compressibility factor for CO 2, if one mole of it occupies 0.4 litre at 300 K and 40 atm. Comment on the result. Ans: 0.65, since Z value is lesser than 1 and thus, nrt > PV. In order to have Z = 1, volume of CO 2 must have been more at same P and T or CO 2 is more compressible than ideal gas. 40. The density of the vapours of a substance at 1 atm pressure and 500 K is 0.36 kg m 3. The vapour effuses through a small hole at a rate of 1.33 times faster than oxygen under the same condition. (a) Determined (i) molecular weight, (ii) molar volume, (iii) compression factor(z) of the vapours and (iv) which forces among the gas molecules are dominating, the attractive or the repulsive? (b) If the vapours behaves ideally at 1000 K, determine the average translational kinetic energy of molecules. Ans: (a) (i) 18.1 (ii) m 3 (iii) (b) J/ molecule 41. Using van der Waal s equation, calculate the constant, a when two mole of a gas confined in a four litre flask exerts a pressure of 11.0 atmospheres at a temperature of 300 K. The value of b is 0.05 lit.mol 1. Ans: 6.46 atm litre 2 mol Atomic and molecular sizes are of the order of a few. Angstrom (1 Å = m). Assuming that N 2 molecules is spherical in shape with radius m, calculate : (i) the volume of single N 2 molecule. (ii) the percentage of empty space in one mole of N 2 gas at STP. Ans: (i) cm 3 (ii) 99.9% 43. Compressibility factor(z) for N 2 at 50 C and 800 atm pressure is Calculate mole of N 2 gas required to fill a gas cylinder of 100 ml capacity under the given conditions. Ans: Calculate molecular diameter if He from its van der Waal s constant b = 24 ml mol 1 Ans: 2.71 Å 45. The compression factor (compressibility factor) for 1 mole of a van der Waal s gas at 0 C and 100 C atmosphere pressure is found to be 0.5. Assuming that the volume of gas molecule is negligible, calculate the van der Waal s constant a. Ans: liter 2 mol 2 atm Page No.: 6
States of Matter. Q 7. Calculate the average of kinetic energy, in joules of the molecules in 8.0 g of methane at 27 o C. (IIT JEE Marks)
 Q 1. States of Matter Calculate density of NH 3 at 30 o C and 5 atm pressure Q 2. (IIT JEE 1978 3 Marks) 3.7 g of a gas at 25 o C occupied the same volume as 0.184g of hydrogen at 17 o C and at the same
Q 1. States of Matter Calculate density of NH 3 at 30 o C and 5 atm pressure Q 2. (IIT JEE 1978 3 Marks) 3.7 g of a gas at 25 o C occupied the same volume as 0.184g of hydrogen at 17 o C and at the same
PSI Chemistry: Gases Multiple Choice Review
 PSI Chemistry: Gases Multiple Choice Review Name Kinetic Molecular Theory 1. According to the kinetic-molecular theory, particles of matterare in constant motion (A) have different shapes (B) have different
PSI Chemistry: Gases Multiple Choice Review Name Kinetic Molecular Theory 1. According to the kinetic-molecular theory, particles of matterare in constant motion (A) have different shapes (B) have different
You should be able to: Describe Equipment Barometer Manometer. 5.1 Pressure Read and outline 5.1 Define Barometer
 A P CHEMISTRY - Unit 5: Gases Unit 5: Gases Gases are distinguished from other forms of matter, not only by their power of indefinite expansion so as to fill any vessel, however large, and by the great
A P CHEMISTRY - Unit 5: Gases Unit 5: Gases Gases are distinguished from other forms of matter, not only by their power of indefinite expansion so as to fill any vessel, however large, and by the great
Chapter 10: Gases. Characteristics of Gases
 Chapter 10: Gases Learning Outcomes: Calculate pressure and convert between pressure units with an emphasis on torr and atmospheres. Calculate P, V, n, or T using the ideal-gas equation. Explain how the
Chapter 10: Gases Learning Outcomes: Calculate pressure and convert between pressure units with an emphasis on torr and atmospheres. Calculate P, V, n, or T using the ideal-gas equation. Explain how the
Chapter 5: Gases 5.1 Pressure Why study gases? An understanding of real world phenomena. An understanding of how science works.
 Chapter 5: Gases 5.1 Pressure Why study gases? An understanding of real world phenomena. An understanding of how science works. A Gas Uniformly fills any container. Easily compressed. Mixes completely
Chapter 5: Gases 5.1 Pressure Why study gases? An understanding of real world phenomena. An understanding of how science works. A Gas Uniformly fills any container. Easily compressed. Mixes completely
Elements that exist as gases at 25 o C and 1 atmosphere H 2, N 2, O 2, F 2, Cl 2, He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn
 AP Chemistry Chapter 5 Sections 5. 5.9 Note Organizer Pressure, The Gas Laws of Boyle, Charles, and Avogadro, The Ideal Gas Law, Gas Stoichiometry, Dalton s Law of Partial Pressure, The Kinetic olecular
AP Chemistry Chapter 5 Sections 5. 5.9 Note Organizer Pressure, The Gas Laws of Boyle, Charles, and Avogadro, The Ideal Gas Law, Gas Stoichiometry, Dalton s Law of Partial Pressure, The Kinetic olecular
Worksheet 1.7: Gas Laws. Charles Law. Guy-Lassac's Law. Standard Conditions. Abbreviations. Conversions. Gas Law s Equation Symbols
 Name Block Worksheet 1.7: Gas Laws Boyle s Law Charles Law Guy-Lassac's Law Combined Gas Law For a given mass of gas at constant temperature, the volume of a gas varies inversely with pressure PV = k The
Name Block Worksheet 1.7: Gas Laws Boyle s Law Charles Law Guy-Lassac's Law Combined Gas Law For a given mass of gas at constant temperature, the volume of a gas varies inversely with pressure PV = k The
Lecture Presentation. Chapter 10. Gases. John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 10 John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Characteristics of Unlike liquids and solids, gases Expand to fill their containers. Are highly compressible.
Lecture Presentation Chapter 10 John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Characteristics of Unlike liquids and solids, gases Expand to fill their containers. Are highly compressible.
Expand to fill their containers, are highly compressible, have extremely low densities.
 Chem150 week6 Handout 1 Gases Characteristics of Gases: Unlike liquids and solids, they Expand to fill their containers, are highly compressible, have extremely low densities. Pressure is the amount of
Chem150 week6 Handout 1 Gases Characteristics of Gases: Unlike liquids and solids, they Expand to fill their containers, are highly compressible, have extremely low densities. Pressure is the amount of
Chapter 5. Nov 6 1:02 PM
 Chapter 5 Nov 6 1:02 PM Expand to fill their containers Fluid motion (they flow) Have low densities (1/1000 the density of equivalent liquids or solids) Compressible Can Effuse and Diffuse Effuse: The
Chapter 5 Nov 6 1:02 PM Expand to fill their containers Fluid motion (they flow) Have low densities (1/1000 the density of equivalent liquids or solids) Compressible Can Effuse and Diffuse Effuse: The
Dr. Rogers Chapter 5 Homework Chem 111 Fall 2003
 Dr. Rogers Chapter 5 Homework Chem 111 Fall 2003 From textbook: 7-33 odd, 37-45 odd, 55, 59, 61 1. Which gaseous molecules (choose one species) effuse slowest? A. SO 2 (g) B. Ar(g) C. NO(g) D. Ne(g) E.
Dr. Rogers Chapter 5 Homework Chem 111 Fall 2003 From textbook: 7-33 odd, 37-45 odd, 55, 59, 61 1. Which gaseous molecules (choose one species) effuse slowest? A. SO 2 (g) B. Ar(g) C. NO(g) D. Ne(g) E.
Kinetic Molecular Theory imaginary Assumptions of Kinetic Molecular Theory: Problems with KMT:
 AP Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block Kinetic Molecular Theory Explains properties of gases, liquids, and solids in terms of energy using an ideal gas, an imaginary which fits all the assumptions of kinetic
AP Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block Kinetic Molecular Theory Explains properties of gases, liquids, and solids in terms of energy using an ideal gas, an imaginary which fits all the assumptions of kinetic
Section 5.1 Pressure. Why study gases? An understanding of real world phenomena. An understanding of how science works.
 Chapter 5 Gases Section 5.1 Pressure Why study gases? An understanding of real world phenomena. An understanding of how science works. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved 2 Section 5.1 Pressure
Chapter 5 Gases Section 5.1 Pressure Why study gases? An understanding of real world phenomena. An understanding of how science works. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved 2 Section 5.1 Pressure
THE GAS STATE. Unit 4. CHAPTER KEY TERMS HOME WORK 9.1 Kinetic Molecular Theory States of Matter Solid, Liquid, gas.
 Unit 4 THE GAS STATE CHAPTER KEY TERMS HOME WORK 9. Kinetic Molecular Theory States of Matter Solid, Liquid, gas Page 4 # to 4 9. Boyles Law P α /V PV = Constant P V = P V Pressure Atmospheric Pressure
Unit 4 THE GAS STATE CHAPTER KEY TERMS HOME WORK 9. Kinetic Molecular Theory States of Matter Solid, Liquid, gas Page 4 # to 4 9. Boyles Law P α /V PV = Constant P V = P V Pressure Atmospheric Pressure
4.) There are no forces of attraction or repulsion between gas particles. This means that
 KINETIC MOLECULAR (K-M) THEORY OF MATTER NOTES - based on the idea that particles of matter are always in motion - assumptions of the K-M Theory 1.) Gases consist of large numbers of tiny particles that
KINETIC MOLECULAR (K-M) THEORY OF MATTER NOTES - based on the idea that particles of matter are always in motion - assumptions of the K-M Theory 1.) Gases consist of large numbers of tiny particles that
Problems of Chapter 3
 Problems of Chapter 3 Section 3.1 Molecular Model of an Ideal Gas 3. A sealed cubical container 20 cm on a side contains three times Avogadro s number of molecules at a temperature of 20 C. Find the force
Problems of Chapter 3 Section 3.1 Molecular Model of an Ideal Gas 3. A sealed cubical container 20 cm on a side contains three times Avogadro s number of molecules at a temperature of 20 C. Find the force
NOTES: Behavior of Gases
 NOTES: Behavior of Gases Properties of Gases Gases have weight Gases take up space Gases exert pressure Gases fill their containers Gases are mostly empty space The molecules in a gas are separate, very
NOTES: Behavior of Gases Properties of Gases Gases have weight Gases take up space Gases exert pressure Gases fill their containers Gases are mostly empty space The molecules in a gas are separate, very
temperature and pressure unchanging
 Gas Laws Review I. Variables Used to Describe a Gas A. Pressure (P) kpa, atm, mmhg (torr) -Pressure=force exerted per unit area (force/area) -Generated by collisions within container walls (more collisions=more
Gas Laws Review I. Variables Used to Describe a Gas A. Pressure (P) kpa, atm, mmhg (torr) -Pressure=force exerted per unit area (force/area) -Generated by collisions within container walls (more collisions=more
Chemistry 101 Chapter 5 GAS MIXTURES
 GAS MIXTURES Consider mixing equal volumes of 3 different gases, all at the same temperature and pressure in a container of the same size. 1 L He 1 L N 2 1 L O 2 1 L mixture t = 0 0 C t = 0 0 C t = 0 0
GAS MIXTURES Consider mixing equal volumes of 3 different gases, all at the same temperature and pressure in a container of the same size. 1 L He 1 L N 2 1 L O 2 1 L mixture t = 0 0 C t = 0 0 C t = 0 0
GASES. Unit #8. AP Chemistry
 GASES Unit #8 AP Chemistry I. Characteristics of Gases A. Gas Characteristics: 1. Fills its container a. no definite shape b. no definite vol. 2. Easily mixes w/ other gases 3. Exerts pressure on its surroundings
GASES Unit #8 AP Chemistry I. Characteristics of Gases A. Gas Characteristics: 1. Fills its container a. no definite shape b. no definite vol. 2. Easily mixes w/ other gases 3. Exerts pressure on its surroundings
Name Hour. The Behavior of Gases. Practice B
 Name Hour The Behavior of Gases Practice B B 1 Objective 1: Apply Boyle s Law, Charles s Law, and Gay-Lussac s Law to solve problems involving pressure and volume and temperature. 1. A high-altitude balloon
Name Hour The Behavior of Gases Practice B B 1 Objective 1: Apply Boyle s Law, Charles s Law, and Gay-Lussac s Law to solve problems involving pressure and volume and temperature. 1. A high-altitude balloon
EXPERIMENT 8 Ideal Gas Law: Molecular Weight of a Vapor
 EXPERIMENT 8 Ideal Gas Law: Molecular Weight of a Vapor Purpose: In this experiment you will use the ideal gas law to calculate the molecular weight of a volatile liquid compound by measuring the mass,
EXPERIMENT 8 Ideal Gas Law: Molecular Weight of a Vapor Purpose: In this experiment you will use the ideal gas law to calculate the molecular weight of a volatile liquid compound by measuring the mass,
CHEMISTRY - CLUTCH CH.5 - GASES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: UNITS OF PRESSURE Pressure is defined as the force exerted per unit of surface area. Pressure = Force Area The SI unit for Pressure is the, which has the units of. The SI
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: UNITS OF PRESSURE Pressure is defined as the force exerted per unit of surface area. Pressure = Force Area The SI unit for Pressure is the, which has the units of. The SI
Boyle s Law Practice
 Boyle s Law Practice Boyle s Law is an indirect relationship. Most of these problems can be done in your head without showing your work. 1. Herman has 30.0 L of helium gas trapped in a cylinder by a piston.
Boyle s Law Practice Boyle s Law is an indirect relationship. Most of these problems can be done in your head without showing your work. 1. Herman has 30.0 L of helium gas trapped in a cylinder by a piston.
(for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes)
 www.tutor-homework.com (for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes) 1. Which statement is inconsistent with the kinetic theory of an ideal gas? 1. The forces of repulsion between gas molecules
www.tutor-homework.com (for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes) 1. Which statement is inconsistent with the kinetic theory of an ideal gas? 1. The forces of repulsion between gas molecules
CP Chapter 13/14 Notes The Property of Gases Kinetic Molecular Theory
 CP Chapter 13/14 Notes The Property of Gases Kinetic Molecular Theory Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases The word kinetic refers to. Kinetic energy is the an object has because of its motion. Kinetic Molecular
CP Chapter 13/14 Notes The Property of Gases Kinetic Molecular Theory Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases The word kinetic refers to. Kinetic energy is the an object has because of its motion. Kinetic Molecular
Funsheet [WHAT IS PRESSURE AND TEMPERATURE] Gu 2015
![Funsheet [WHAT IS PRESSURE AND TEMPERATURE] Gu 2015 Funsheet [WHAT IS PRESSURE AND TEMPERATURE] Gu 2015](/thumbs/93/112589015.jpg) Funsheet 7.0 7.1 [WHAT IS PRESSURE AND TEMPERATURE] Gu 2015 1. Convert the following pressures. a) 101 kpa =? atm b) 55 Torr =? psi c) 60. mmhg =? bar d) 45 Torr =? kpa e) 5 psi =? atm f) 0.0056 atm =?
Funsheet 7.0 7.1 [WHAT IS PRESSURE AND TEMPERATURE] Gu 2015 1. Convert the following pressures. a) 101 kpa =? atm b) 55 Torr =? psi c) 60. mmhg =? bar d) 45 Torr =? kpa e) 5 psi =? atm f) 0.0056 atm =?
Each gas sample has the same A) density B) mass C) number of molecules D) number of atoms
 1. A real gas behaves most like an ideal gas at A) low pressure and high temperature B) average potential energy of its particles C) ionization energy of its particles D) activation energy of its particles
1. A real gas behaves most like an ideal gas at A) low pressure and high temperature B) average potential energy of its particles C) ionization energy of its particles D) activation energy of its particles
Chemistry Chapter 11 Test Review
 Chemistry Chapter 11 Test Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Pressure is the force per unit a. volume. c. length. b. surface area.
Chemistry Chapter 11 Test Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Pressure is the force per unit a. volume. c. length. b. surface area.
Unit 9 Packet: Gas Laws Introduction to Gas Laws Notes:
 Name: Unit 9 Packet: Gas Laws Introduction to Gas Laws Notes: Block: In chemistry, the relationships between gas physical properties are described as gas laws. Some of these properties are pressure, volume,
Name: Unit 9 Packet: Gas Laws Introduction to Gas Laws Notes: Block: In chemistry, the relationships between gas physical properties are described as gas laws. Some of these properties are pressure, volume,
Chapter 5 TEST: Gases
 Chapter 5 TEST: Gases 1) Gases generally have A) low density B) high density C) closely packed particles D) no increase in volume when temperature is increased E) no decrease in volume when pressure is
Chapter 5 TEST: Gases 1) Gases generally have A) low density B) high density C) closely packed particles D) no increase in volume when temperature is increased E) no decrease in volume when pressure is
States of Matter Review
 States of Matter Review May 13 8:16 PM Physical States of Matter (Phases) Solid Liquid Melting Gas Condensation Freezing Evaporation Deposition Sublimation Sep 13 6:04 PM 1 May 13 8:11 PM Gases Chapter
States of Matter Review May 13 8:16 PM Physical States of Matter (Phases) Solid Liquid Melting Gas Condensation Freezing Evaporation Deposition Sublimation Sep 13 6:04 PM 1 May 13 8:11 PM Gases Chapter
AP TOPIC 6: Gases. Revised August General properties and kinetic theory
 AP OPIC 6: Gases General properties and kinetic theory Gases are made up of particles that have (relatively) large amounts of energy. A gas has no definite shape or volume and will expand to fill as much
AP OPIC 6: Gases General properties and kinetic theory Gases are made up of particles that have (relatively) large amounts of energy. A gas has no definite shape or volume and will expand to fill as much
Gilbert Kirss Foster. Chapter 10. Properties of Gases The Air We Breathe
 Gilbert Kirss Foster Chapter 10 Properties of Gases The Air We Breathe Chapter Outline 10.1 The Properties of Gases 10.2 Effusion and the Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases 10.3 Atmospheric Pressure 10.4
Gilbert Kirss Foster Chapter 10 Properties of Gases The Air We Breathe Chapter Outline 10.1 The Properties of Gases 10.2 Effusion and the Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases 10.3 Atmospheric Pressure 10.4
Gas Law Worksheets - WS: Boyle s and Charles Law
 Gas Law Worksheets - WS: Boyle s and Charles Law Boyle s Law states that the volume of a gas varies inversely with its pressure if temperature is held constant. (If one goes up the, other goes down.) We
Gas Law Worksheets - WS: Boyle s and Charles Law Boyle s Law states that the volume of a gas varies inversely with its pressure if temperature is held constant. (If one goes up the, other goes down.) We
Honors Chemistry Unit 7 Gas Laws Notes
 Honors Chemistry Unit 7 Gas Laws Notes Kinetic Molecular Theory 1. List the five assumptions: Assumption Description Extra Info 1 Basically means: the particles themselves have compared to the space between
Honors Chemistry Unit 7 Gas Laws Notes Kinetic Molecular Theory 1. List the five assumptions: Assumption Description Extra Info 1 Basically means: the particles themselves have compared to the space between
Name: Class: Date: SHORT ANSWER Answer the following questions in the space provided.
 CHAPTER 11 REVIEW Gases SECTION 1 SHORT ANSWER Answer the following questions in the space provided. 1. Pressure =. For a constant force, when the surface area is tripled the pressure is (a) doubled. (b)
CHAPTER 11 REVIEW Gases SECTION 1 SHORT ANSWER Answer the following questions in the space provided. 1. Pressure =. For a constant force, when the surface area is tripled the pressure is (a) doubled. (b)
Chapter 9 Gases: Their Properties and Behavior
 Chapter 9 Gases: Their Properties and Behavior 國防醫學院生化學科王明芳老師 2011-11-15 & 2011-11-22 Chapter 9/1 Gases and Gas Pressure Gas mixtures are homogeneous and compressible. Air-the mixture of gases. Molecular
Chapter 9 Gases: Their Properties and Behavior 國防醫學院生化學科王明芳老師 2011-11-15 & 2011-11-22 Chapter 9/1 Gases and Gas Pressure Gas mixtures are homogeneous and compressible. Air-the mixture of gases. Molecular
Kinetic Molecular Theory Gases. Behavior of gases. Postulate two. Postulate one. Postulate three. Postulate four
 Kinetic Molecular Theory Gases Gas particles are so small that their individual volume can be considered to be negligible Gas particles are in constant motion and the collisions of the particles with the
Kinetic Molecular Theory Gases Gas particles are so small that their individual volume can be considered to be negligible Gas particles are in constant motion and the collisions of the particles with the
Gas Laws Packet Ideal Gas Law Worksheet PV = nrt
 Gas Laws Packet Ideal Gas Law Worksheet PV = nrt Use the ideal gas law, PV-nRT, and the universal gas constant R = 0.0821 L*atm to solve the following problems: K*mol If pressure is needed in kpa then
Gas Laws Packet Ideal Gas Law Worksheet PV = nrt Use the ideal gas law, PV-nRT, and the universal gas constant R = 0.0821 L*atm to solve the following problems: K*mol If pressure is needed in kpa then
Chemistry 1B Chapter 10 Worksheet - Daley. Name
 Name 1) The National Weather Service routinely supplies atmospheric pressure data to help pilots set their altimeters. The units the NWS uses for atmospheric pressure are inches of mercury. A barometric
Name 1) The National Weather Service routinely supplies atmospheric pressure data to help pilots set their altimeters. The units the NWS uses for atmospheric pressure are inches of mercury. A barometric
Ch. 14 The Behavior of Gases
 Ch. 14 The Behavior of Gases 14.1 PROPERTIES OF GASES Compressibility Compressibility: a measure of how much the volume of matter decreases under pressure Gases are easily compressed because of the spaces
Ch. 14 The Behavior of Gases 14.1 PROPERTIES OF GASES Compressibility Compressibility: a measure of how much the volume of matter decreases under pressure Gases are easily compressed because of the spaces
Chemistry Honors - Gases
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Chemistry Honors - Gases Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Why does a can collapse when a vacuum pump removes air
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Chemistry Honors - Gases Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Why does a can collapse when a vacuum pump removes air
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Test General Chemistry CH116 UMass Boston Summer 2013 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The pressure exerted by a column of
Test General Chemistry CH116 UMass Boston Summer 2013 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The pressure exerted by a column of
Kinetic-Molecular Theory of Matter
 Gases Properties of Gases Gas Pressure Gases What gases are important for each of the following: O 2, CO 2 and/or He? A. B. C. D. 1 2 Gases What gases are important for each of the following: O 2, CO 2
Gases Properties of Gases Gas Pressure Gases What gases are important for each of the following: O 2, CO 2 and/or He? A. B. C. D. 1 2 Gases What gases are important for each of the following: O 2, CO 2
Chemistry HP Unit 6 Gases. Learning Targets (Your exam at the end of Unit 6 will assess the following:) 6. Gases
 Chemistry HP Unit 6 Gases Learning Targets (Your exam at the end of Unit 6 will assess the following:) 6. Gases 6-1. Define pressure using a mathematical equation. 6-2. Perform calculations involving pressure,
Chemistry HP Unit 6 Gases Learning Targets (Your exam at the end of Unit 6 will assess the following:) 6. Gases 6-1. Define pressure using a mathematical equation. 6-2. Perform calculations involving pressure,
PROPERTIES OF GASES. [MH5; Ch 5, (only)]
![PROPERTIES OF GASES. [MH5; Ch 5, (only)] PROPERTIES OF GASES. [MH5; Ch 5, (only)]](/thumbs/76/74446950.jpg) PROPERTIES OF GASES [MH5; Ch 5, 5.1-5.5 (only)] FEATURES OF A GAS Molecules in a gas are a long way apart (under normal conditions). Molecules in a gas are in rapid motion in all directions. The forces
PROPERTIES OF GASES [MH5; Ch 5, 5.1-5.5 (only)] FEATURES OF A GAS Molecules in a gas are a long way apart (under normal conditions). Molecules in a gas are in rapid motion in all directions. The forces
Example 5.1 Converting between Pressure Units
 Example 5.1 Converting between Pressure Units For Practice 5.1 Your local weather report announces that the barometric pressure is 30.44 in Hg. Convert this pressure to psi. For More Practice 5.1 Convert
Example 5.1 Converting between Pressure Units For Practice 5.1 Your local weather report announces that the barometric pressure is 30.44 in Hg. Convert this pressure to psi. For More Practice 5.1 Convert
A. What are the three states of matter chemists work with?
 Chapter 10 and 12 The Behavior of Gases Chapter 10 The States of Matter A. What are the three states of matter chemists work with? Section 10.1 Pg 267 B. We will explain the behavior of gases using the
Chapter 10 and 12 The Behavior of Gases Chapter 10 The States of Matter A. What are the three states of matter chemists work with? Section 10.1 Pg 267 B. We will explain the behavior of gases using the
Example: 25 C = ( ) K = 298 K. Pressure Symbol: p Units: force per area 1Pa (Pascal) = 1 N/m 2
 Chapter 6: Gases 6.1 Measurements on Gases MH5, Chapter 5.1 Let s look at a certain amount of gas, i.e. trapped inside a balloon. To completely describe the state of this gas one has to specify the following
Chapter 6: Gases 6.1 Measurements on Gases MH5, Chapter 5.1 Let s look at a certain amount of gas, i.e. trapped inside a balloon. To completely describe the state of this gas one has to specify the following
UNIT 10 - GASES. Notes & Worksheets - Honors
 Ideal Gas Equation 1 WKSHT 1.) What is the pressure exerted by 2.0 moles of an ideal gas when it occupies a volume of 12.0 L at 373 K? 2.) A flashbulb of volume 2.6 cm 3 contains O 2 gas at a pressure
Ideal Gas Equation 1 WKSHT 1.) What is the pressure exerted by 2.0 moles of an ideal gas when it occupies a volume of 12.0 L at 373 K? 2.) A flashbulb of volume 2.6 cm 3 contains O 2 gas at a pressure
CP Chapter 13/14 Notes The Property of Gases Kinetic Molecular Theory
 CP Chapter 13/14 Notes The Property of Gases Kinetic Molecular Theory Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases The word kinetic refers to. Kinetic energy is the an object has because of its motion. Kinetic Molecular
CP Chapter 13/14 Notes The Property of Gases Kinetic Molecular Theory Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases The word kinetic refers to. Kinetic energy is the an object has because of its motion. Kinetic Molecular
Section 8: Gases. The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science TAC (c).
 Section 8: Gases The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science TAC 112.35(c). 8.01 Simple Gas Laws Chemistry (9)(A) 8.02 Ideal Gas Law Chemistry
Section 8: Gases The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science TAC 112.35(c). 8.01 Simple Gas Laws Chemistry (9)(A) 8.02 Ideal Gas Law Chemistry
Practice MC Test unit D (Ch 10) Gas Laws (pg 1 of 10)
 Practice MC Test unit D (Ch 10) Gas Laws (pg 1 of 10) This is practice - Do NOT cheat yourself of finding out what you are capable of doing. Be sure you follow the testing conditions outlined below. DO
Practice MC Test unit D (Ch 10) Gas Laws (pg 1 of 10) This is practice - Do NOT cheat yourself of finding out what you are capable of doing. Be sure you follow the testing conditions outlined below. DO
Question McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited
 Question 1 Which of the following cannot be explained by considering the empty space between the particles of a gas? A) Gases are more compressible than liquids. B) Gases have lower viscosities than liquids.
Question 1 Which of the following cannot be explained by considering the empty space between the particles of a gas? A) Gases are more compressible than liquids. B) Gases have lower viscosities than liquids.
Chapter 5. Pressure. Atmospheric Pressure. Gases. Force Pressure = Area
 Chapter 5 Gases Water for many homes is supplied by a well The pump removes air from the pipe, decreasing the air pressure in the pipe The pressure then pushes the water up the pipe Pressure Atmospheric
Chapter 5 Gases Water for many homes is supplied by a well The pump removes air from the pipe, decreasing the air pressure in the pipe The pressure then pushes the water up the pipe Pressure Atmospheric
Name Unit 9 Notes: Gas Laws Period. Complete throughout unit. Due on test day!
 Name Unit 9 Notes: Gas Laws Period Skills: 1. Gases and Entropy 2. Distinguish between Ideal and Real gases 3. Understand KMT and Avogadro s Law 4. Identify and Solve Boyle s Law Problems 5. Identify and
Name Unit 9 Notes: Gas Laws Period Skills: 1. Gases and Entropy 2. Distinguish between Ideal and Real gases 3. Understand KMT and Avogadro s Law 4. Identify and Solve Boyle s Law Problems 5. Identify and
Behavior of Gases. Gases are mostly The molecules in a gas are separate, very small and very
 Properties of Gases Gases have Gases Gases exert Gases fill their containers Behavior of Gases Gases are mostly The molecules in a gas are separate, very small and very Kinetic Theory of Matter: Gas molecules
Properties of Gases Gases have Gases Gases exert Gases fill their containers Behavior of Gases Gases are mostly The molecules in a gas are separate, very small and very Kinetic Theory of Matter: Gas molecules
Chemistry: It s a gas
 Chemistry: It s a gas Part IV Molar mass of a gas Density of a gas Dalton s Law: high altitudes and scuba diving Kinetic Molecular Theory: fast gases are hot! I have a chemistry test on Friday, there is
Chemistry: It s a gas Part IV Molar mass of a gas Density of a gas Dalton s Law: high altitudes and scuba diving Kinetic Molecular Theory: fast gases are hot! I have a chemistry test on Friday, there is
Honors Chemistry - Problem Set Chapter 13 Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT.
 Honors Chemistry - Problem Set Chapter 13 Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. 1. Atmospheric pressure is 760 mm Hg. 2. The SI unit of pressure is
Honors Chemistry - Problem Set Chapter 13 Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. 1. Atmospheric pressure is 760 mm Hg. 2. The SI unit of pressure is
Name /74. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch 11 Gases STUDY GUIDE Accelerated Chemistry SCANTRON Name /74 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements
Ch 11 Gases STUDY GUIDE Accelerated Chemistry SCANTRON Name /74 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements
Gases. Chapter 5: Gas Laws Demonstration. September 10, Chapter 5 Gasses.notebook. Dec 18 10:23 AM. Jan 1 4:11 PM. Crushing 55 gallon drum
 Chapter 5: Gases Dec 18 10:23 AM Gas Laws Demonstration Crushing 55 gallon drum Egg in a bottle Student in a bag Boiling Water Charles gas Law Water in a flask Ballon in a bottle Jan 1 4:11 PM 1 5.1 Pressure
Chapter 5: Gases Dec 18 10:23 AM Gas Laws Demonstration Crushing 55 gallon drum Egg in a bottle Student in a bag Boiling Water Charles gas Law Water in a flask Ballon in a bottle Jan 1 4:11 PM 1 5.1 Pressure
Judith Herzfeld 1996,1998. These exercises are provided here for classroom and study use only. All other uses are copyright protected.
 Judith Herzfeld 1996,1998 These exercises are provided here for classroom and study use only. All other uses are copyright protected. 2.7-110 A yardstick laid on a table with a few inches hanging over
Judith Herzfeld 1996,1998 These exercises are provided here for classroom and study use only. All other uses are copyright protected. 2.7-110 A yardstick laid on a table with a few inches hanging over
Simple Gas Laws. To facilitate comparison of gases, the following standards are used: STP: O C (273 K) and kpa. SATP: 25 C (298 K) and 101.
 Simple Gas Laws To facilitate comparison of gases, the following standards are used: STP: O C (273 K) and 101.3 kpa If assuming 1 mol, V = 22.4L SATP: 25 C (298 K) and 101.3 kpa If assuming 1 mol, V =
Simple Gas Laws To facilitate comparison of gases, the following standards are used: STP: O C (273 K) and 101.3 kpa If assuming 1 mol, V = 22.4L SATP: 25 C (298 K) and 101.3 kpa If assuming 1 mol, V =
Chapter 11. Recall: States of Matter. Properties of Gases. Gases
 Chapter 11 Gases Recall: States of Matter Solids and Liquids: are closely related because in each case the particles are interacting with each other Gases: Properties of Gases Gases can be compressed Gases
Chapter 11 Gases Recall: States of Matter Solids and Liquids: are closely related because in each case the particles are interacting with each other Gases: Properties of Gases Gases can be compressed Gases
Unit 8: Gases and States of Matter
 Unit 8: Gases and States of Matter Gases Particles that have no definite shape or volume. They adapt to the shape and volume of their container. Ideal gases are imaginary gases that comply with all the
Unit 8: Gases and States of Matter Gases Particles that have no definite shape or volume. They adapt to the shape and volume of their container. Ideal gases are imaginary gases that comply with all the
Multiple Choice (40%)
 AP Chemistry Test (Chapter 5) Please do not write on this test thank you! Multiple Choice (40%) 1) A sealed rigid container is filled with three ideal gases: A, B and C. The partial pressure of each gas
AP Chemistry Test (Chapter 5) Please do not write on this test thank you! Multiple Choice (40%) 1) A sealed rigid container is filled with three ideal gases: A, B and C. The partial pressure of each gas
To convert to millimeters of mercury, we derive a unit factor related to the equivalent relationship 29.9 in. Hg = 760 mm Hg.
 Example Exercise 11.1 Gas Pressure Conversion Meteorologists state that a falling barometer indicates an approaching storm. Given a barometric pressure of 27.5 in. Hg, express the pressure in each of the
Example Exercise 11.1 Gas Pressure Conversion Meteorologists state that a falling barometer indicates an approaching storm. Given a barometric pressure of 27.5 in. Hg, express the pressure in each of the
Chapter 12. The Gaseous State of Matter
 Chapter 12 The Gaseous State of Matter The air in a hot air balloon expands When it is heated. Some of the air escapes from the top of the balloon, lowering the air density inside the balloon, making the
Chapter 12 The Gaseous State of Matter The air in a hot air balloon expands When it is heated. Some of the air escapes from the top of the balloon, lowering the air density inside the balloon, making the
To play movie you must be in Slide Show Mode CLICK HERE EXERCISE! EXERCISE! To play movie you must be in Slide Show Mode CLICK HERE
 Boyle s Law Boyle s law Pressure and volume are inversely related (constant T, temperature, and n, # of moles of gas). PV k (kis a constant for a given sample of air at a specific temperature) P V P V
Boyle s Law Boyle s law Pressure and volume are inversely related (constant T, temperature, and n, # of moles of gas). PV k (kis a constant for a given sample of air at a specific temperature) P V P V
Gases NO CALCULATORS MAY BE USED FOR THESE QUESTIONS
 NO CALCULATORS MAY BE USED FOR THESE QUESTIONS Questions 1-3 refer to the following gases at 0 C and 1 atm. (A) Ar (B) NO 2 (C) Xe (D) H 2 (E) N 2 1. Has an average atomic or molecular speed closest to
NO CALCULATORS MAY BE USED FOR THESE QUESTIONS Questions 1-3 refer to the following gases at 0 C and 1 atm. (A) Ar (B) NO 2 (C) Xe (D) H 2 (E) N 2 1. Has an average atomic or molecular speed closest to
Chapter 14-Gases. Dr. Walker
 Chapter 14-Gases Dr. Walker State of Matter Gases are one of the four states of matter along with solids, liquids, and plasma Conversion to Gases From liquids Evaporation Example: Boiling water From solids
Chapter 14-Gases Dr. Walker State of Matter Gases are one of the four states of matter along with solids, liquids, and plasma Conversion to Gases From liquids Evaporation Example: Boiling water From solids
Chem 110 General Principles of Chemistry
 CHEM110 Worksheet - Gases Chem 110 General Principles of Chemistry Chapter 9 Gases (pages 337-373) In this chapter we - first contrast gases with liquids and solids and then discuss gas pressure. - review
CHEM110 Worksheet - Gases Chem 110 General Principles of Chemistry Chapter 9 Gases (pages 337-373) In this chapter we - first contrast gases with liquids and solids and then discuss gas pressure. - review
 Graham s Law of Diffusion 1. Dalton s law of partial pressure is not applied for 1) N CO ) NO O 3) CO O ) O, N. vessel contains Helium and Methane in : 1 molar ratio at 0 bar pressure. Due to leakage,
Graham s Law of Diffusion 1. Dalton s law of partial pressure is not applied for 1) N CO ) NO O 3) CO O ) O, N. vessel contains Helium and Methane in : 1 molar ratio at 0 bar pressure. Due to leakage,
Worksheet 12 - Partial Pressures and the Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases
 Worksheet 12 - Partial Pressures and the Kinetic olecular Theory of Gases Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures states that the sums of the pressures of each gas in the mixture add to give the total pressure
Worksheet 12 - Partial Pressures and the Kinetic olecular Theory of Gases Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures states that the sums of the pressures of each gas in the mixture add to give the total pressure
Ideal Gas Law Worksheet PV = nrt
 ame: Hour: Date: Ideal Gas Law Worksheet PV = nrt Use the ideal gas law, PV= nrt, and the universal gas constant R = 0.0821 L*atm to solve the following problems: K*mol P = pressure (in atm) V = volume
ame: Hour: Date: Ideal Gas Law Worksheet PV = nrt Use the ideal gas law, PV= nrt, and the universal gas constant R = 0.0821 L*atm to solve the following problems: K*mol P = pressure (in atm) V = volume
Characteristics of Gases
 Lecture 25-27 Gases Characteristics of Gases Unlike liquids and solids, gases Expand to fill their containers. Are highly compressible. Have extremely low densi@es. Pressure of a gas Force per unit area
Lecture 25-27 Gases Characteristics of Gases Unlike liquids and solids, gases Expand to fill their containers. Are highly compressible. Have extremely low densi@es. Pressure of a gas Force per unit area
Gases. Name: Class: Date: Matching
 Name: Class: Date: Gases Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. a. Boyle's law d. Graham's law b. Charles's law e. Gay-Lussac's law c. Dalton's law f. ideal gas law 1. For a given mass
Name: Class: Date: Gases Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. a. Boyle's law d. Graham's law b. Charles's law e. Gay-Lussac's law c. Dalton's law f. ideal gas law 1. For a given mass
General Properties of Gases
 GASES Chapter 13 Importance of Gases Airbags fill with N 2 gas in an accident. Gas is generated by the decomposition of sodium azide,, NaN 3. 2 NaN 3 ---> > 2 Na + 3 N 2 THREE STATES OF MATTER General
GASES Chapter 13 Importance of Gases Airbags fill with N 2 gas in an accident. Gas is generated by the decomposition of sodium azide,, NaN 3. 2 NaN 3 ---> > 2 Na + 3 N 2 THREE STATES OF MATTER General
Under ideal conditions, the rates at which different gases diffuse (spread out) are proportional to their molar masses.
 Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block Graham s Law of Diffusion- Under ideal conditions, the rates at which different gases diffuse (spread out) are proportional to their molar masses. In other words, gas molecules
Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block Graham s Law of Diffusion- Under ideal conditions, the rates at which different gases diffuse (spread out) are proportional to their molar masses. In other words, gas molecules
Chapter 10 Gases. Characteristics of Gases. Pressure. The Gas Laws. The Ideal-Gas Equation. Applications of the Ideal-Gas Equation
 Characteristics of Gases Chapter 10 Gases Pressure The Gas Laws The Ideal-Gas Equation Applications of the Ideal-Gas Equation Gas mixtures and partial pressures Kinetic-Molecular Theory Real Gases: Deviations
Characteristics of Gases Chapter 10 Gases Pressure The Gas Laws The Ideal-Gas Equation Applications of the Ideal-Gas Equation Gas mixtures and partial pressures Kinetic-Molecular Theory Real Gases: Deviations
Chemistry A Molecular Approach. Fourth Edition. Chapter 5. Gases. Copyright 2017, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
 Chemistry A Molecular Approach Fourth Edition Chapter 5 Gases Supersonic Skydiving and the Risk of Decompression Gas Gases are composed of particles that are moving around very fast in their container(s).
Chemistry A Molecular Approach Fourth Edition Chapter 5 Gases Supersonic Skydiving and the Risk of Decompression Gas Gases are composed of particles that are moving around very fast in their container(s).
Kinetic Molecular Theory
 Kinetic Molecular Theory Name Period Unit 7 HW 1 Worksheet (Goals 1 & 2) 1. Describe how gases, liquids, and solids compare using the following table. Volume (definite or indefinite) Molecular Motion (high,
Kinetic Molecular Theory Name Period Unit 7 HW 1 Worksheet (Goals 1 & 2) 1. Describe how gases, liquids, and solids compare using the following table. Volume (definite or indefinite) Molecular Motion (high,
The Kinetic-Molecular Theory of Gases based on the idea that particles are always in motion
 The Kinetic-Molecular Theory of Gases based on the idea that particles are always in motion Five assumptions: 1. Most of the volume occupied dby a gas is empty space 2. Collisions between gas particles
The Kinetic-Molecular Theory of Gases based on the idea that particles are always in motion Five assumptions: 1. Most of the volume occupied dby a gas is empty space 2. Collisions between gas particles
Chapter 6 10/14/13. Gas Law. Volume change with temperature and pressure.
 Chapter 6 10/14/13 Gas Law 1. Properties of a Gas a. Neither definite shape nor volume i. Uniformly fills any container i Exerts pressure on surroundings Volume change with temperature and pressure. b.
Chapter 6 10/14/13 Gas Law 1. Properties of a Gas a. Neither definite shape nor volume i. Uniformly fills any container i Exerts pressure on surroundings Volume change with temperature and pressure. b.
Date: Period: Gas Laws Worksheet #1 - Boyle s, Charles, Gay-Lussac s, and Combined Gas Law
 Name: Date: Period: Gas Laws Worksheet #1 - Boyle s, Charles, Gay-Lussac s, and Combined Gas Law Boyle s Law: V1P1 = V2P2 1. A gas sample contained in a cylinder equipped with a moveable piston occupied
Name: Date: Period: Gas Laws Worksheet #1 - Boyle s, Charles, Gay-Lussac s, and Combined Gas Law Boyle s Law: V1P1 = V2P2 1. A gas sample contained in a cylinder equipped with a moveable piston occupied
Basic Concepts of Chemistry Notes for Students [Chapter 10, page 1] D J Weinkauff - Nerinx Hall High School. Chapter 10 Gases
![Basic Concepts of Chemistry Notes for Students [Chapter 10, page 1] D J Weinkauff - Nerinx Hall High School. Chapter 10 Gases Basic Concepts of Chemistry Notes for Students [Chapter 10, page 1] D J Weinkauff - Nerinx Hall High School. Chapter 10 Gases](/thumbs/78/77082586.jpg) Basic Concepts of Chemistry Notes for Students [Chapter 10, page 1] Chapter 10 Gases We have talked a little about gases in Chapter 3 and we dealt briefly with them in our stoichiometric calculations in
Basic Concepts of Chemistry Notes for Students [Chapter 10, page 1] Chapter 10 Gases We have talked a little about gases in Chapter 3 and we dealt briefly with them in our stoichiometric calculations in
Experiment 13 Molar Mass of a Gas. Purpose. Background. PV = nrt
 Experiment 13 Molar Mass of a Gas Purpose In this experiment you will use the ideal gas law to calculate the molar mass of a volatile liquid compound by measuring the mass, volume, temperature, and pressure
Experiment 13 Molar Mass of a Gas Purpose In this experiment you will use the ideal gas law to calculate the molar mass of a volatile liquid compound by measuring the mass, volume, temperature, and pressure
2. Calculate the ratio of diffusion rates for carbon monoxide (CO) and carbon dioxide (CO2). υa = MB = 44 = 1.25
 Gas laws worksheet (2-08) (modified 3/17) Answer key Graham s Law 1. Calculate the ratio of effusion rates for nitrogen (N2) and neon (Ne). υa = MB = 20 = 0.845 υb MA 28 2. Calculate the ratio of diffusion
Gas laws worksheet (2-08) (modified 3/17) Answer key Graham s Law 1. Calculate the ratio of effusion rates for nitrogen (N2) and neon (Ne). υa = MB = 20 = 0.845 υb MA 28 2. Calculate the ratio of diffusion
Substances that are liquids or solids under ordinary conditions may also exist as gases. These are often referred to as vapors. Properties of Gases
 Common Student Misconceptions Students need to be told to always use temperature in Kelvin in gas problems. Students should always use units in gas-law problems to keep track of required conversions. Due
Common Student Misconceptions Students need to be told to always use temperature in Kelvin in gas problems. Students should always use units in gas-law problems to keep track of required conversions. Due
Gas Laws Chapter 14. Complete the following pressure conversion. Be sure to show how units cancel.
 Gas Laws Chapter 14 Complete the following pressure conversion. Be sure to show how units cancel. 1 atm = 760 mm Hg = 760 torr = 101.3 kpa = 14.7 psi = 1.013 bar 1. The air pressure for a certain tire
Gas Laws Chapter 14 Complete the following pressure conversion. Be sure to show how units cancel. 1 atm = 760 mm Hg = 760 torr = 101.3 kpa = 14.7 psi = 1.013 bar 1. The air pressure for a certain tire
Name Chemistry Pre-AP
 Name Chemistry Pre-AP Notes: Gas Laws and Gas Stoichiometry Period Part 1: The Nature of Gases and The Gas Laws I. Nature of Gases A. Kinetic-Molecular Theory The - theory was developed to account for
Name Chemistry Pre-AP Notes: Gas Laws and Gas Stoichiometry Period Part 1: The Nature of Gases and The Gas Laws I. Nature of Gases A. Kinetic-Molecular Theory The - theory was developed to account for
Chapter 10: Properties of Gases: The Air We Breathe
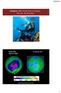 Chapter 10: Properties of Gases: The Air We Breathe South Pole Sept 24, 2006 15 February 2017 http://ozonewatch.gsfc.nasa.gov 1 Chapter Outline 10.1 10.2 10.3 The Properties of Gases Effusion and the Kinetic
Chapter 10: Properties of Gases: The Air We Breathe South Pole Sept 24, 2006 15 February 2017 http://ozonewatch.gsfc.nasa.gov 1 Chapter Outline 10.1 10.2 10.3 The Properties of Gases Effusion and the Kinetic
Chemistry Chapter 12. Characteristics of Gases. Characteristics of Gases 1/31/2012. Gases and Liquids
 Importance of Gases Chemistry Chapter 12 Gases and Liquids Airbags fill with N 2 gas in an accident. Gas is generated by the decomposition of sodium azide, NaN 3. 2 NaN 3 ---> 2 Na + 3 N 2 THREE STATES
Importance of Gases Chemistry Chapter 12 Gases and Liquids Airbags fill with N 2 gas in an accident. Gas is generated by the decomposition of sodium azide, NaN 3. 2 NaN 3 ---> 2 Na + 3 N 2 THREE STATES
Dalton s Law How is the total pressure of a mixture of gases related to the partial pressures of the component gases?
 Dalton s Law Chapter 4 The Behavior of Gases 4. Properties of Gases 4. The Gas Laws 4. Ideal Gases Dalton s Law How is the total pressure of a mixture of gases related to the partial pressures of the component
Dalton s Law Chapter 4 The Behavior of Gases 4. Properties of Gases 4. The Gas Laws 4. Ideal Gases Dalton s Law How is the total pressure of a mixture of gases related to the partial pressures of the component
C h e m i s t r y 1 A : C h a p t e r 5 P a g e 1
 C h e m i s t r y 1 A : C h a p t e r 5 P a g e 1 Chapter 5: Gases Homework: Read Chapter 5. Work out sample/practice exercises Keep up with MasteringChemistry assignments Gas Properties: Ideal Gas: Gases
C h e m i s t r y 1 A : C h a p t e r 5 P a g e 1 Chapter 5: Gases Homework: Read Chapter 5. Work out sample/practice exercises Keep up with MasteringChemistry assignments Gas Properties: Ideal Gas: Gases
More Practice with Gas Laws KEY
 More Practice with Gas Laws KEY Chemistry Directions: For each question, identify the applicable law and solve for the correct answer using dimensional analysis. Express your answer to the correct number
More Practice with Gas Laws KEY Chemistry Directions: For each question, identify the applicable law and solve for the correct answer using dimensional analysis. Express your answer to the correct number
Chapter 10: Properties of Gases: The Air We Breathe
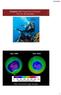 Chapter 10: Properties of Gases: The Air We Breathe Sept, 2006 Sept, 2016 http://ozonewatch.gsfc.nasa.gov 1 Chapter Outline 10.1 The Properties of Gases 10.2 The Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases* 10.3
Chapter 10: Properties of Gases: The Air We Breathe Sept, 2006 Sept, 2016 http://ozonewatch.gsfc.nasa.gov 1 Chapter Outline 10.1 The Properties of Gases 10.2 The Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases* 10.3
Section 8.1 Properties of Gases Goal: Describe the kinetic molecular theory of gases and the units of measurement used for gases.
 Chapter 8 Gases Practice Problems Section 8.1 Properties of Gases Goal: Describe the kinetic molecular theory of gases and the units of measurement used for gases. Summary: In a gas, particles are so far
Chapter 8 Gases Practice Problems Section 8.1 Properties of Gases Goal: Describe the kinetic molecular theory of gases and the units of measurement used for gases. Summary: In a gas, particles are so far
Chemistry 20 Unit 2 Gases FITB Notes. Topic A Characteristics of Gases
 Chemistry 20 Unit 2 Gases FITB Notes General Outcome: Topic A Characteristics of Gases We use technologies that were designed with the knowledge of the visible characteristics ( ) of gases ex. SCUBA equipment,
Chemistry 20 Unit 2 Gases FITB Notes General Outcome: Topic A Characteristics of Gases We use technologies that were designed with the knowledge of the visible characteristics ( ) of gases ex. SCUBA equipment,
