Mammalogy Lecture 19 - Thermoregulation
|
|
|
- Amanda Sharp
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mammalogy Lecture 19 - Thermoregulation I. Introduction. Obviously, mammals are endotherms; they regulate body temperature via metabolic processes by burning energy. Thermal Neutral Zone When T A is low, energy is expended to keep warm. When T A is high, energy is expended to keep cool But for every endothermic species, there is a thermal neutral zone, the range of ambient temperatures across which there s no higher cost of homeothermy. T LC - highest temperature at which an endotherm expends energy to stay warm T UC - lowest temperature at which an endotherm expends energy to stay cool Obviously, when ambient temperatures are either below T LC or above T UC, there is a metabolic cost to homeothermy (maintaining a constant body temperature). II. Adaptations for Cold Temperatures in Zone A A. Large Size - Size is critical because of the relationship between body size, S/V and cooling. Remember that heat loss is directly related to S/V ratio - small animals cool faster. In general, more northerly species are larger than southerly species. This also typically holds true within a species. - Bergman s Rule Arctic wolves are larger than populations in more temperate regions. Alaskan Moose are larger than those from more moderate localities.
2 B. High Basal Metabolic Rate - Cold adapted species have a higher than expected basal metabolic rate. For example, Red foxes, Vulpes vulpes, have a BMR that s nearly twice as high as similar sized canids in warmer regions. C. Insulation - Extra layers to reduce heat loss Pelage - forms a barrier of warm air next to the surface of the animal. Many artiodactyls have hollow hair - hollow hair is a better insulator than solid hair Blubber - subcutaneous fat is commonly used as an insulating mechanism in marine mammals. D. Regional Heterothermy Extremities may be allowed to cool, sometimes to very low temperatures. This is accomplished by vasoconstriction. Urocitellus paryii - toe pads may be 2 o - 5 o C Ondatra zibethicus extremities are allowed to cool to water temperature
3 E. Systemic Heterothermy Adaptive Hypothermia Many mammals deal with cold via Adaptive Hypothermia - Allow T B to Drop Characterized by: - Decreased heart rate - Vasoconstriction - severe reduction of blood flow to the extremities - Decreased breathing rate - Suppression of shivering - Decreased oxygen consumption (decreased metabolic rate) - Decreased body temperature There is usually great energy savings associated with hypothermia. Maintenance of high T B at very low temperatures is energetically costly and without adaptive hypothermia, many small mammals would be unable to persist in many cold localities. The cost, however is that, recovery from adaptive hypothermia requires the metabolism of a special type of fatty tissue: thermogenic fat or brown fat. This differs from regular or white fat in many ways, two of these are that there s a very high concentration of mitochondria and very highly vascularized. Once brown fat stores are depleted, the animal looses the ability to arouse from adaptive hypothermia. The finite nature of brown fat reserves represents an additional cost to the strategy of adaptive hypothermia: the risk of being unable to arouse from torpor. Classify Adaptive Hypothermia two ways: depth or duration 1. May be shallow (Torpor) or deep (Hibernation). a. Shallow - T B may only drop very slightly or may drop as much low as 15 0 C b. Deep - T B may drop precipitously, as low as few degrees above ambient. In Great Basin pocket mice, Perognathus parvus, T body drops to ca C 2. May be Seasonal or Daily a. Seasonal - Tends to be deep but is not always. Ursus exhibit seasonal hypothermia, but it s not deep. Triggered by a variety of stimuli. - food limitation - photoperiod - may require a cold preparatory period of 6-8 weeks of cold temperature
4 b. Daily - Follow a circadian rhythm Usually only shallow. Only a slight decrease in T B, breathing, & MR (e.g., Peromyscus & Kangaroo mice Microdipodops). This capacity for daily torpor in P. maniculatus has been cited as critical adaptation that allows this otherwise very generalized mouse species to occupy such extremes habitats as boreal through desert habitats. Although daily torpor is more common in small mammals, it s not restricted to small mammals. For example American badger, Taxidae taxus, enters shortterm torpor frequently during the winter. Heart rate is cut in half from 55 to 25. Body temperatures drop around 10 0 to 29 0 C Temperate bat species of Myotis exhibit both daily and seasonal hypothermia A common usage, which old editions of your book used, is that torpor is a very general term for any period of dormancy. Hibernation is deep torpor seen in the winter. Others use the terminology we used here, where torpor is restricted to shallow hypothermia and hibernation is deep hypothermia. III. Strategies for Heat Look back at TNZ curve, and focus on zone C. Because mammals are endotherms, they are pre-adapted for dealing with cold. However, they are rather poorly prepared for dealing with heat. A. The simplest way of dealing with heat is to avoid exposure to it. 1. Almost all desert rodents are nocturnal and therefore are active during the coolest part of the day. 2. Many desert species, especially rodents, are somewhat fossorial. They shelter in burrows throughout the day and burrow temperatures are as much as 35 o C lower than surface. 3. Daily or Seasonal Dormancy: Long-term dormancy during the summer is called estivation (aestivation). Daily torpor in Peromyscus eremicus allows this otherwise generalized rodent to inhabit deserts. B. For many desert mammals, avoiding exposure to heat is not an option, so they have to deal with it.
5 1. Typically have lower BMR than expected based on size, so less heat is generated. For example, desert species of ground squirrels fall below the curve of metabolic rate on body size. This is true for an Idaho species, Urocitellus mollis, and it s true for Xerospermophilus mohavensis. 2. Large mammals can t find the refuges that are available to small mammals. Thus, especially African cetartiodactyls deal with hyperthermia, elevated T body. It then becomes necessary to protect vital organs from high temperatures. The brain is the most sensitive organ. African bovids have evolved countercurrent exchange mechanisms to keep the brain cool. The carotid artery passes through a rete mirabile, a complex series of capillaries, which then supply the brain with blood. Venous blood returning from the brain passes through capillaries in the olfactory epithelium where it is cooled by evaporation of the mucous membranes in the nasal cavities. This cooled venous blood enters the rete mirabile and the hyperthermic arterial blood in the carotid artery dumps its heat to the cool venous blood. This is the site of the counter-current heat exchange. This keeps the brain several degrees cooler than the core body temperature. Perissodactyls lack this, and Mitchell and Lust (2008. Biol. Lett. 4:415) have proposed that this explains the high diversity of terrestrial cetartiodactyls. C. The most universal method of dealing with heat involves evaporative cooling. As water evaporates heat is absorbed - thus the surface of which the water evaporates is cooled. a - The most common method - producing sweat. b - Panting. There is some effect by evaporation of saliva, but the major effect is derived from evaporation of moisture in the lungs, where blood is in close contact with surface tissues. This is called pulmonary evaporation, and is a huge source of water loss.
6 c - Saliva - Many Macropodids, for example, moisten their forearms with saliva. These regions are highly vascularized and vessels are dilated during heat stress. The evaporating saliva cools the venous blood in the extremities. Many cervids do this as well. Evaporative cooling is perhaps most effective.
Comparative Physiology 2007 First Midterm Exam. 1) 16 pts. 2) 12 pts. 3) 40 pts. 4) 10 pts. 5) 17 pts. 6) 5 pts. Total
 Name Comparative Physiology 2007 First Midterm Exam 1) 16 pts 2) 12 pts 3) 40 pts 4) 10 pts 5) 17 pts 6) 5 pts Total 1. All vertebrates yawn, yet we don t know why. A) Propose a possible functional explanation
Name Comparative Physiology 2007 First Midterm Exam 1) 16 pts 2) 12 pts 3) 40 pts 4) 10 pts 5) 17 pts 6) 5 pts Total 1. All vertebrates yawn, yet we don t know why. A) Propose a possible functional explanation
Fish 475: Marine Mammalogy
 Fish 475: Marine Mammalogy Adaptations to Life at Sea I: 19 April 2010 Course website: http://faculty.washington.edu/glennvb/fish475 Major challenges of life at sea for homeothermic animals of terrestrial
Fish 475: Marine Mammalogy Adaptations to Life at Sea I: 19 April 2010 Course website: http://faculty.washington.edu/glennvb/fish475 Major challenges of life at sea for homeothermic animals of terrestrial
Hibernation. Created by The Curriculum Corner
 Hibernation Created by The Curriculum Corner What is hibernation? The Curriculum Corner What is hibernation? The Curriculum Corner What is hibernation? When an animal sleeps all winter Some animals who
Hibernation Created by The Curriculum Corner What is hibernation? The Curriculum Corner What is hibernation? The Curriculum Corner What is hibernation? When an animal sleeps all winter Some animals who
Comparing Respiratory Systems
 Comparing Respiratory Systems Respiration Respiration is a process involving the movement of oxygen gas into cells and carbon dioxide out of cells, (This better called BREATHING ) in order to facilitate
Comparing Respiratory Systems Respiration Respiration is a process involving the movement of oxygen gas into cells and carbon dioxide out of cells, (This better called BREATHING ) in order to facilitate
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange elephant seals gills AP Biology
 alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange O 2 & CO 2 exchange exchange between environment & cells provides O 2 for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange O 2 & CO 2 exchange exchange between environment & cells provides O 2 for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high
AP Biology. Chapter 42. Gas Exchange. Optimizing gas exchange. Gas exchange. Gas exchange in many forms. Evolution of gas exchange structures
 alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange & C exchange exchange between environment & cells provides for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high surface area
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange & C exchange exchange between environment & cells provides for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high surface area
Tioga ISD Athletic Department Heat Policy
 Tioga ISD Athletic Department Heat Policy Practice of competition in hot and humid environmental conditions poses special problems for student-athletes. Heat stress and resulting heat illness is a primary
Tioga ISD Athletic Department Heat Policy Practice of competition in hot and humid environmental conditions poses special problems for student-athletes. Heat stress and resulting heat illness is a primary
Biology 131 Laboratory Spring Thermoregulation. 1. Measure the thermal status of terrestrial and marine mammals.
 Thermoregulation Objectives 1. Measure the thermal status of terrestrial and marine mammals. 2. Compare the effectiveness of fur, blubber, skin, and neoprene as insulators. 3. Evaluate the effect of exercise
Thermoregulation Objectives 1. Measure the thermal status of terrestrial and marine mammals. 2. Compare the effectiveness of fur, blubber, skin, and neoprene as insulators. 3. Evaluate the effect of exercise
RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE
 RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE Respiration Respiration delivery of oxygen to and removal of carbon dioxide from the tissue External respiration ventilation and exchange of gases in the lung Internal
RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE Respiration Respiration delivery of oxygen to and removal of carbon dioxide from the tissue External respiration ventilation and exchange of gases in the lung Internal
Name. Lab Partners. The Dive Response. In this lab exercise, you will be designing and conducting your own experiments!
 Name Lab Partners The Dive Response In this lab exercise, you will be designing and conducting your own experiments! Note: A formal report is due for this lab (see handout). Objectives 1. Characterize
Name Lab Partners The Dive Response In this lab exercise, you will be designing and conducting your own experiments! Note: A formal report is due for this lab (see handout). Objectives 1. Characterize
Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems
 alveoli gills Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? respiration for respiration Need O 2 in for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need CO 2
alveoli gills Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? respiration for respiration Need O 2 in for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need CO 2
LOCOMOTION, ENERGETICS & THERMOREGULATION
 Simone Baumann-Pickering May 7, 2013 sbaumann@ucsd.edu (858) 534-7280 Marine Mammal Biology SIO 133 LOCOMOTION, ENERGETICS & THERMOREGULATION HYPERPHALANGY (POLY/)HYPERDACTILY A) Risso s dolphin B) Killer
Simone Baumann-Pickering May 7, 2013 sbaumann@ucsd.edu (858) 534-7280 Marine Mammal Biology SIO 133 LOCOMOTION, ENERGETICS & THERMOREGULATION HYPERPHALANGY (POLY/)HYPERDACTILY A) Risso s dolphin B) Killer
AP Biology. Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems. Gas exchange. Why do we need a respiratory system? Optimizing gas exchange. Gas exchange in many forms
 alveoli Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems gills elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? Need O 2 in food respiration for respiration for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need
alveoli Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems gills elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? Need O 2 in food respiration for respiration for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need
B14 gas exchange note, reading and questions.notebook April 13, 2011
 Review All organisms (plants and animals) need energy to carry out their life processes. The chemi reaction which provides this energy is called. In larger animals it is sometimes called respiration because
Review All organisms (plants and animals) need energy to carry out their life processes. The chemi reaction which provides this energy is called. In larger animals it is sometimes called respiration because
(a) (i) Describe how a large difference in oxygen concentration is maintained between a fish gill and the surrounding water.
 1. Answers should be written in continuous prose. Credit will be given for biological accuracy, the organisation and presentation of information and the way in which an answer is expressed. Fick s law
1. Answers should be written in continuous prose. Credit will be given for biological accuracy, the organisation and presentation of information and the way in which an answer is expressed. Fick s law
I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface:
 I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface: Common characteristics of respiratory surfaces: a) Moist: allows for the RAPID diffusion of dissolved gasses across its surface. Whereas the respiratory
I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface: Common characteristics of respiratory surfaces: a) Moist: allows for the RAPID diffusion of dissolved gasses across its surface. Whereas the respiratory
PMT. Smaller species of annelid do not have gills. Explain why these small worms do not need gills to obtain sufficient oxygen
 1. There are many different species of annelid worm. Some are very small, only a few millimetres in length. Others, such as lugworms, are much larger. The drawing shows a lugworm and part of one of its
1. There are many different species of annelid worm. Some are very small, only a few millimetres in length. Others, such as lugworms, are much larger. The drawing shows a lugworm and part of one of its
Hypothermia. Hypothermia. By: Louis Durkin MD 1 Credit Course Approved by NJ OEMS For EMT-Basic Only
 Hypothermia By: Louis Durkin MD 1 Credit Course Approved by NJ OEMS For EMT-Basic Only Objectives Explain the basic physiology of thermoregulation Define the basic metabolic rate Explain common measurements
Hypothermia By: Louis Durkin MD 1 Credit Course Approved by NJ OEMS For EMT-Basic Only Objectives Explain the basic physiology of thermoregulation Define the basic metabolic rate Explain common measurements
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
Don t loose your cool! Cold Water Immerison SECTION 1
 Don t loose your cool! Cold Water Immerison SECTION 1 Cold Water Incident Case Study SECTION 2 Convict Lake Tragedy Relevance to you as: 1) A potential victim 2) A rescuer 3) An educator 4) A policy maker
Don t loose your cool! Cold Water Immerison SECTION 1 Cold Water Incident Case Study SECTION 2 Convict Lake Tragedy Relevance to you as: 1) A potential victim 2) A rescuer 3) An educator 4) A policy maker
Environmental Considerations
 Environmental Considerations I. Hyperthermia a. Heat stress i. Take extreme caution in hot, humid weather ii. Every year athletes die from heat related causes iii. Body temperature must be obtained by
Environmental Considerations I. Hyperthermia a. Heat stress i. Take extreme caution in hot, humid weather ii. Every year athletes die from heat related causes iii. Body temperature must be obtained by
Then the partial pressure of oxygen is x 760 = 160 mm Hg
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: the uptake of molecular oxygen (O2) from the environment and the discharge of
1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: the uptake of molecular oxygen (O2) from the environment and the discharge of
EXPOSURE TO THE COLD. November 6, 2013
 EXPOSURE TO THE COLD November 6, 2013 WHAT IS COLD STRESS Cold stress is the transfer of body heat out to a colder environment When you are exposed to a cold environment, most of your body's energy is
EXPOSURE TO THE COLD November 6, 2013 WHAT IS COLD STRESS Cold stress is the transfer of body heat out to a colder environment When you are exposed to a cold environment, most of your body's energy is
How Do Fish Swim? The density of water makes it very difficult to move in, but fish can move very smoothly and quickly.
 How Do Fish Swim? The density of water makes it very difficult to move in, but fish can move very smoothly and quickly. A swimming fish is relying on its skeleton for framework, its muscles for power,
How Do Fish Swim? The density of water makes it very difficult to move in, but fish can move very smoothly and quickly. A swimming fish is relying on its skeleton for framework, its muscles for power,
Animals in the winter environment. Source:
 Animals in the winter environment Source: http://sp.7savers.coml The big challenge Options for overwintering success Migration Hibernation Resistance Homeotherms Modes of energy transfer Heat in = Heat
Animals in the winter environment Source: http://sp.7savers.coml The big challenge Options for overwintering success Migration Hibernation Resistance Homeotherms Modes of energy transfer Heat in = Heat
Lab #2: Blood pressure and peripheral circulation
 Lab #2: Blood pressure and peripheral circulation Vertebrates have a closed circulatory system where the blood is always enclosed within blood vessels or the heart. Blood is pumped from the heart (the
Lab #2: Blood pressure and peripheral circulation Vertebrates have a closed circulatory system where the blood is always enclosed within blood vessels or the heart. Blood is pumped from the heart (the
Collin County Community College. Lung Physiology
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 9 Respiratory System 1 Lung Physiology Factors affecting Ventillation 1. Airway resistance Flow = Δ P / R Most resistance is encountered
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 9 Respiratory System 1 Lung Physiology Factors affecting Ventillation 1. Airway resistance Flow = Δ P / R Most resistance is encountered
Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation
 Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing and the first step in the respiratory process. Pulmonary ventilation brings in air with a new supply
Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing and the first step in the respiratory process. Pulmonary ventilation brings in air with a new supply
Damage to the AVA shunts can result from laminitis. Winter Laminitis and the Cold 1
 Winter Laminitis and the Cold 1 Here in the UK our winters are long and wet. We are blessed really not to have too many extremes but it can be relentlessly miserable and this seems to set the scene for
Winter Laminitis and the Cold 1 Here in the UK our winters are long and wet. We are blessed really not to have too many extremes but it can be relentlessly miserable and this seems to set the scene for
Human Biology Respiratory System
 Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Guide to Cold Stress at Work
 Guide to Cold Stress at Work WCB Website: www.wcb.pe.ca Toll free in Atlantic Canada: 1-800-237-5049 Revised: Jan/06 Cold Stress at Work Working in the cold is part of the job for many Prince Edward Islanders.
Guide to Cold Stress at Work WCB Website: www.wcb.pe.ca Toll free in Atlantic Canada: 1-800-237-5049 Revised: Jan/06 Cold Stress at Work Working in the cold is part of the job for many Prince Edward Islanders.
CHAPTER 3: The cardio-respiratory system
 : The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
: The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
3. (a) countercurrent mechanism; helps maintain diffusion gradient; 2
 1. (a) (i) Fish has ventilation system which replaces water; highly oxygenated water (circulatory system brings in) blood with low concentration of oxygen/blood removes oxygen; counter current system/description;
1. (a) (i) Fish has ventilation system which replaces water; highly oxygenated water (circulatory system brings in) blood with low concentration of oxygen/blood removes oxygen; counter current system/description;
FISD LIGHTNING GUIDELINES
 FISD LIGHTNING GUIDELINES 1. The chain of command that will make the call to remove individuals from the field will be as follows: Practices: The athletic trainer and the head coach or coaches will make
FISD LIGHTNING GUIDELINES 1. The chain of command that will make the call to remove individuals from the field will be as follows: Practices: The athletic trainer and the head coach or coaches will make
AN OVERVIEW OF RESPIRATION AND AN INTRODUCTION TO DIFFUSION AND SOLUBILITY OF GASES 1
 AN OVERVIEW OF RESPIRATION AND AN INTRODUCTION TO DIFFUSION AND SOLUBILITY OF GASES 1 Summary: This set of notes gives an overview of respiration and then follows the overview with a detailed discussion
AN OVERVIEW OF RESPIRATION AND AN INTRODUCTION TO DIFFUSION AND SOLUBILITY OF GASES 1 Summary: This set of notes gives an overview of respiration and then follows the overview with a detailed discussion
Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment
 Name: Date: Mark: / 45 Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
Name: Date: Mark: / 45 Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
EXISTENCE at the EXTREME Supported by
 EXISTENCE at the EXTREME Supported by This resource explains how an indigenous population has created an engineering solution to the problems they encounter in extreme cold, including building safe shelters
EXISTENCE at the EXTREME Supported by This resource explains how an indigenous population has created an engineering solution to the problems they encounter in extreme cold, including building safe shelters
3.3.2 Gas Exchange SPECIFICATION
 alevelbiology.co.uk 3.3.2 Gas Exchange SPECIFICATION Adaptations of gas exchange surfaces, shown by gas exchange: Across the body surface of a single-celled organism In the tracheal system of an insect
alevelbiology.co.uk 3.3.2 Gas Exchange SPECIFICATION Adaptations of gas exchange surfaces, shown by gas exchange: Across the body surface of a single-celled organism In the tracheal system of an insect
- How do the carotid bodies sense arterial blood gases? o The carotid bodies weigh 25mg, yet they have their own artery. This means that they have
 - How do the carotid bodies sense arterial blood gases? o The carotid bodies weigh 25mg, yet they have their own artery. This means that they have the highest blood flow of all organs, which makes them
- How do the carotid bodies sense arterial blood gases? o The carotid bodies weigh 25mg, yet they have their own artery. This means that they have the highest blood flow of all organs, which makes them
West African Lungfish A living fossil s biological and behavioral adaptations
 VideoMedia Spotlight West African Lungfish A living fossil s biological and behavioral adaptations For the complete video with media resources, visit: http://education.nationalgeographic.org/media/west-african-lungfish/
VideoMedia Spotlight West African Lungfish A living fossil s biological and behavioral adaptations For the complete video with media resources, visit: http://education.nationalgeographic.org/media/west-african-lungfish/
The Respiratory System. Medical Terminology
 The Respiratory System Medical Terminology The respiratory system is where gas exchange occurs via respiration; inhalation/exhalation. pick up oxygen from inhaled air expels carbon dioxide and water sinus
The Respiratory System Medical Terminology The respiratory system is where gas exchange occurs via respiration; inhalation/exhalation. pick up oxygen from inhaled air expels carbon dioxide and water sinus
Gas Exchange & Circulation
 Why is gas exchange important? Gas Exchange & Circulation Read Ch. 42 start with 42.5: Gas Exchange in Animals Respiration: C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2! Energy + CO 2 + H 2 O Photosynthesis: Energy + CO 2 + H 2
Why is gas exchange important? Gas Exchange & Circulation Read Ch. 42 start with 42.5: Gas Exchange in Animals Respiration: C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2! Energy + CO 2 + H 2 O Photosynthesis: Energy + CO 2 + H 2
Clam and Rat. By: Maddie Bonifas
 Clam and Rat By: Maddie Bonifas Clam (part 1) Corbicula Fluminea (scientific name) Circulatory System Major Organs Involved: Stomach Heart Arteries Veins Foot Gills Open Body Cavity Functions Stomach:
Clam and Rat By: Maddie Bonifas Clam (part 1) Corbicula Fluminea (scientific name) Circulatory System Major Organs Involved: Stomach Heart Arteries Veins Foot Gills Open Body Cavity Functions Stomach:
Staying Warm in the Winter
 Staying Warm in the Winter When winter arrives it doesn t mean an end to enjoying the outdoors. Staying active during the winter months is essential! Instead, it s important to keep warm while working
Staying Warm in the Winter When winter arrives it doesn t mean an end to enjoying the outdoors. Staying active during the winter months is essential! Instead, it s important to keep warm while working
Class Osteichthyes. Bony Fish
 Class Osteichthyes Bony Fish General Characteristics of Class internal skeleton ossified (turned to bone) Paired fins made of rays and spines, or lobed fins swim bladder or lung present bony scales (ganoid,
Class Osteichthyes Bony Fish General Characteristics of Class internal skeleton ossified (turned to bone) Paired fins made of rays and spines, or lobed fins swim bladder or lung present bony scales (ganoid,
GAS EXCHANGE & CIRCULATION CHAPTER 42 ( )
 Winter 08 1 of 10 GAS EXCHANGE & CIRCULATION CHAPTER 42 (867 891) MOVEMENT OF GASES Both O 2 and CO 2 move by The movement down a If a gas produced in one location, it diffuses away But diffusion is usually
Winter 08 1 of 10 GAS EXCHANGE & CIRCULATION CHAPTER 42 (867 891) MOVEMENT OF GASES Both O 2 and CO 2 move by The movement down a If a gas produced in one location, it diffuses away But diffusion is usually
Pulmonary Circulation Linda Costanzo Ph.D.
 Pulmonary Circulation Linda Costanzo Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The differences between pressures in the pulmonary and systemic circulations. 2. How
Pulmonary Circulation Linda Costanzo Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The differences between pressures in the pulmonary and systemic circulations. 2. How
25/4/2016. Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten
 25/4/2016 Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten Respiratory System Introduction: - We breath while we are sleeping, talking, working and resting. - Respiratory diseases are abundant
25/4/2016 Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten Respiratory System Introduction: - We breath while we are sleeping, talking, working and resting. - Respiratory diseases are abundant
Gas Exchange in Animals. Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2. Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial
 Gas Exchange in Animals Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2 Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial Respiratory surface! skin, gills, lungs Circulatory System O2/CO2
Gas Exchange in Animals Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2 Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial Respiratory surface! skin, gills, lungs Circulatory System O2/CO2
Ratio Deco. Overview. Global Perspective
 Ratio Deco Overview Ratio deco is simply an on the fly system of applying a set of rules to develop a decompression strategy that will work for you in your range of diving. These rules are derived from
Ratio Deco Overview Ratio deco is simply an on the fly system of applying a set of rules to develop a decompression strategy that will work for you in your range of diving. These rules are derived from
It is of vital importance that a source of clean, oxygen-rich air is available 24 hours a day. Like Robert gets when he sleeps at night..
 Gas Exchange is critical to all organisms It is of vital importance that a source of clean, oxygen-rich air is available 24 hours a day. Like Robert gets when he sleeps at night.. Avoid breathing contaminated
Gas Exchange is critical to all organisms It is of vital importance that a source of clean, oxygen-rich air is available 24 hours a day. Like Robert gets when he sleeps at night.. Avoid breathing contaminated
Gaseous exchange. Grade 11
 z Gaseous exchange Grade 11 z Terminology 1. Breathing 2. Gaseous exchange 3. Diffusion 4. Spongy mesophyll cells 5. Tracheae 6. Gills 7. Alveoli 8. Larynx 9. Diaphragm 10. Endothelium 1. Pleura 2. Squamous
z Gaseous exchange Grade 11 z Terminology 1. Breathing 2. Gaseous exchange 3. Diffusion 4. Spongy mesophyll cells 5. Tracheae 6. Gills 7. Alveoli 8. Larynx 9. Diaphragm 10. Endothelium 1. Pleura 2. Squamous
Biology. Slide 1 of 53. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 53 Chapter 33 Comparing Chordates 2 of 53 This chapter is a good revision of the material we saw during Unit III. 3 of 53 4 of 53 Controlling Body Temperature The control of body temperature
Biology 1 of 53 Chapter 33 Comparing Chordates 2 of 53 This chapter is a good revision of the material we saw during Unit III. 3 of 53 4 of 53 Controlling Body Temperature The control of body temperature
Shivering - no patient should ever shiver in care. Shivering is a useless way to produce heat.
 Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Basic Program Outlines Outline Topic: ENVIRONMENTAL and DIVING ACCIDENTS Revised: 11/2013 DEFINITIONS Shivering - no patient should ever
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Basic Program Outlines Outline Topic: ENVIRONMENTAL and DIVING ACCIDENTS Revised: 11/2013 DEFINITIONS Shivering - no patient should ever
Cardiovascular Laboratory Biol 106. In this exercise, you will:
 Cardiovascular Laboratory Biol 106 In this exercise, you will: 1) measure an electrical cardiogram of your own heart. 2) Investigate the human dive response 3) Dissect a mammalian heart 4) observe the
Cardiovascular Laboratory Biol 106 In this exercise, you will: 1) measure an electrical cardiogram of your own heart. 2) Investigate the human dive response 3) Dissect a mammalian heart 4) observe the
Circulation and Gas Exchange Chapter 42
 Circulation and Gas Exchange Chapter 42 Circulatory systems link exchange surfaces with cells throughout the body Diffusion is only efficient over small distances In small and/or thin animals, cells can
Circulation and Gas Exchange Chapter 42 Circulatory systems link exchange surfaces with cells throughout the body Diffusion is only efficient over small distances In small and/or thin animals, cells can
Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation
 Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation - Physical principles of gases: Pressure of a gas is caused by the movement of its molecules against a surface (more concentration
Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation - Physical principles of gases: Pressure of a gas is caused by the movement of its molecules against a surface (more concentration
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system
 CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
Table of Contents. By Adam Hollingworth
 By Adam Hollingworth Table of Contents Oxygen Cascade... 2 Diffusion... 2 Laws of Diffusion... 2 Diffusion & Perfusion Limitations... 3 Oxygen Uptake Along Pulmon Capillary... 4 Measurement of Diffusing
By Adam Hollingworth Table of Contents Oxygen Cascade... 2 Diffusion... 2 Laws of Diffusion... 2 Diffusion & Perfusion Limitations... 3 Oxygen Uptake Along Pulmon Capillary... 4 Measurement of Diffusing
 Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Pco2 *20times = 0.6, 2.4, so the co2 carried in the arterial blood in dissolved form is more than the o2 because of its solubility.
 Physiology, sheet #9 Oxygen, is first dissolved in the plasma and the cytosol of the rbc, we have around blood constitutes 7% of our body weight, oxygen, in the capillaries is present in the rbc s and
Physiology, sheet #9 Oxygen, is first dissolved in the plasma and the cytosol of the rbc, we have around blood constitutes 7% of our body weight, oxygen, in the capillaries is present in the rbc s and
Section Two Diffusion of gases
 Section Two Diffusion of gases Lecture 5: Partial pressure and the composition of gasses in air. Factors affecting diffusion of gases. Ventilation perfusion ratio effect on alveolar gas concentration.
Section Two Diffusion of gases Lecture 5: Partial pressure and the composition of gasses in air. Factors affecting diffusion of gases. Ventilation perfusion ratio effect on alveolar gas concentration.
Capnography in the Veterinary Technician Toolbox. Katie Pinner BS, LVT Bush Advanced Veterinary Imaging Richmond, VA
 Capnography in the Veterinary Technician Toolbox Katie Pinner BS, LVT Bush Advanced Veterinary Imaging Richmond, VA What are Respiration and Ventilation? Respiration includes all those chemical and physical
Capnography in the Veterinary Technician Toolbox Katie Pinner BS, LVT Bush Advanced Veterinary Imaging Richmond, VA What are Respiration and Ventilation? Respiration includes all those chemical and physical
Recitation question # 05
 Recitation and Lab # 05 The goal of this recitations / labs is to review material related to the CV and respiratory lectures for the second test of this course. Info required to answer this recitation
Recitation and Lab # 05 The goal of this recitations / labs is to review material related to the CV and respiratory lectures for the second test of this course. Info required to answer this recitation
REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE & EXCRETION 11 SEPTEMBER 2013
 REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE & EXCRETION 11 SEPTEMBER 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Revise gaseous exchange in different animals and examine the structure of the kidney Key Concepts Important
REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE & EXCRETION 11 SEPTEMBER 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Revise gaseous exchange in different animals and examine the structure of the kidney Key Concepts Important
Cold Weather Safety Program
 Title: Cold Weather Safety program Effective Date: 12/6/2014 Control Number: THG_0052 Revision Number: 1 Date: 10/23/2015 Annual Review Completed: 5/13/2015 Cold Weather Safety Program CONTENTS I. INTRODUCTION
Title: Cold Weather Safety program Effective Date: 12/6/2014 Control Number: THG_0052 Revision Number: 1 Date: 10/23/2015 Annual Review Completed: 5/13/2015 Cold Weather Safety Program CONTENTS I. INTRODUCTION
Systems of distribution
 Systems of distribution Outline Distribution of respiratory gases, and in blood Respiratory systems - transport of oxygen to tissues - radically different designs in mammals, birds, insects Vertebrate
Systems of distribution Outline Distribution of respiratory gases, and in blood Respiratory systems - transport of oxygen to tissues - radically different designs in mammals, birds, insects Vertebrate
Introduction to Biological Science - BIOL Gas Exchange
 Gas Exchange A. Influence of concentration gradient on gas diffusion rate 1. You have two tubes of permeable membrane. a. Add an arrow to illustrate concurrent fluid flow in Tubes A and B. Tube A Tube
Gas Exchange A. Influence of concentration gradient on gas diffusion rate 1. You have two tubes of permeable membrane. a. Add an arrow to illustrate concurrent fluid flow in Tubes A and B. Tube A Tube
Control of Respiration. Central Control of Ventilation
 Central Control of Goal: maintain sufficient ventilation with minimal energy Process steps: mechanics + aerodynamics Points of Regulation Breathing rate and depth, coughing, swallowing, breath holding
Central Control of Goal: maintain sufficient ventilation with minimal energy Process steps: mechanics + aerodynamics Points of Regulation Breathing rate and depth, coughing, swallowing, breath holding
Respiration. The resspiratory system
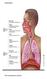 Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
Respiratory Systems: Ventilation & Gas Exchange
 Respiratory Systems: Ventilation & Gas Exchange Ventilation of Respiratory Surfaces Non-directional ventilation: Medium flows past gas exchange surface in an unpredictable pattern. Tidal Ventilation External
Respiratory Systems: Ventilation & Gas Exchange Ventilation of Respiratory Surfaces Non-directional ventilation: Medium flows past gas exchange surface in an unpredictable pattern. Tidal Ventilation External
Physiology of Respiration
 Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
Lab Orientation and the Surface to volume ratio in animals
 LAB ORIENTATION AND THE SURFACE TO VOLUME RATIO IN ANIMALS - 1 Lab Orientation and the Surface to volume ratio in animals by Antoine Morin and Gabriel Blouin-Demers Lab Orientation Details of your activities
LAB ORIENTATION AND THE SURFACE TO VOLUME RATIO IN ANIMALS - 1 Lab Orientation and the Surface to volume ratio in animals by Antoine Morin and Gabriel Blouin-Demers Lab Orientation Details of your activities
GRASSLANDS BIOME OR HABITAT
 GRASSLANDS BIOME OR HABITAT This area is covered mostly with grasses, has few large trees, and at times has very little water. Dominant colors in the grasslands are browns. An example of a grassland habitat
GRASSLANDS BIOME OR HABITAT This area is covered mostly with grasses, has few large trees, and at times has very little water. Dominant colors in the grasslands are browns. An example of a grassland habitat
Magdalen Court School
 Introduction Working in a cold environment whether it be cold weather, cold water, or an indoor freezer is part of the job for many British Columbia workers. One of the major hazards you face when working
Introduction Working in a cold environment whether it be cold weather, cold water, or an indoor freezer is part of the job for many British Columbia workers. One of the major hazards you face when working
2. State the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a normal breathing.
 CLASS XI BIOLOGY Breathing And Exchange of Gases 1. Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Answer: Vital Capacity (VC): The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration.
CLASS XI BIOLOGY Breathing And Exchange of Gases 1. Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Answer: Vital Capacity (VC): The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration.
Respiratory physiology II.
 Respiratory physiology II. Learning objectives: 29. Pulmonary gas exchange. 30. Oxygen transport in the blood. 31. Carbon-dioxide transport in the blood. 1 Pulmonary gas exchange The transport mechanism
Respiratory physiology II. Learning objectives: 29. Pulmonary gas exchange. 30. Oxygen transport in the blood. 31. Carbon-dioxide transport in the blood. 1 Pulmonary gas exchange The transport mechanism
Then the partial pressure of oxygen is. b) Gases will diffuse down a pressure gradient across a respiratory surface if it is: i) permeable ii) moist
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: Relies on the diffusion of gases down pressure gradients. At sea level, atmosphere
1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: Relies on the diffusion of gases down pressure gradients. At sea level, atmosphere
How Animals Survive (Circulation and Gas Exchange)
 How Animals Survive (Circulation and Gas Exchange) by Flourence Octaviano on February 16, 2018 lesson duration of 30 minutes under Earth and Life Science generated on February 16, 2018 at 12:45 am Tags:
How Animals Survive (Circulation and Gas Exchange) by Flourence Octaviano on February 16, 2018 lesson duration of 30 minutes under Earth and Life Science generated on February 16, 2018 at 12:45 am Tags:
Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System
 Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System Animals require a continuous supply of oxygen (O 2 ) for cellular respiration, and they must expel carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), the waste product of this
Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System Animals require a continuous supply of oxygen (O 2 ) for cellular respiration, and they must expel carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), the waste product of this
Civil Air Patrol Auxiliary of the United States Air Force
 Mountain Flying Qualification Course Civil Air Patrol Auxiliary of the United States Air Force Physiological Effects of Altitude Physiological Effects of Altitude OXYGEN DEPRIVATION (HYPOXIA) SINUS PRESSURE
Mountain Flying Qualification Course Civil Air Patrol Auxiliary of the United States Air Force Physiological Effects of Altitude Physiological Effects of Altitude OXYGEN DEPRIVATION (HYPOXIA) SINUS PRESSURE
Chapter 35: Respiratory Systems
 Chapter 35: Respiratory Systems AP Curriculum Alignment Cells are restricted in size by the necessity of maintain a large surface area to volume. The cells of the alveoli, which are the functioning units
Chapter 35: Respiratory Systems AP Curriculum Alignment Cells are restricted in size by the necessity of maintain a large surface area to volume. The cells of the alveoli, which are the functioning units
Lung Volumes and Capacities
 Lung Volumes and Capacities Normally the volume of air entering the lungs during a single inspiration is approximately equal to the volume leaving on the subsequent expiration and is called the tidal volume.
Lung Volumes and Capacities Normally the volume of air entering the lungs during a single inspiration is approximately equal to the volume leaving on the subsequent expiration and is called the tidal volume.
REBOUND. on the. It was the winter of 2000/2001, and it seemed like the snow
 JILLIAN COOPER / istockphoto.com 12 January / February 2018 on the While concerns remain, American marten are making a comeback in New Hampshire REBOUND by Jillian Kilborn It was the winter of 2000/2001,
JILLIAN COOPER / istockphoto.com 12 January / February 2018 on the While concerns remain, American marten are making a comeback in New Hampshire REBOUND by Jillian Kilborn It was the winter of 2000/2001,
The physiological functions of respiration and circulation. Mechanics. exercise 7. Respiratory Volumes. Objectives
 exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
Henleaze Swimming Club Winter Swimming Guide
 Henleaze Swimming Club Winter Swimming Guide The Joy of Winter Swimming A Guide Why is winter swimming so good for you? Scientists have found lots of evidence of health benefits from regular cold water
Henleaze Swimming Club Winter Swimming Guide The Joy of Winter Swimming A Guide Why is winter swimming so good for you? Scientists have found lots of evidence of health benefits from regular cold water
Nina Elisabeth N Storvik Theres Arulf
 Nina Elisabeth N Storvik Theres Arulf 1 Program Accident scene command and initial assessment Patient examination ABCDE -approach CPR Recovery position Bleedings Hypothermia - Frostbite Fractures Burns
Nina Elisabeth N Storvik Theres Arulf 1 Program Accident scene command and initial assessment Patient examination ABCDE -approach CPR Recovery position Bleedings Hypothermia - Frostbite Fractures Burns
Chapter 22 Gas Exchange
 Chapter 22 Gas Exchange PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction: Surviving in Thin Air
Chapter 22 Gas Exchange PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction: Surviving in Thin Air
Cold Weather Emergencies
 Cold Weather Emergencies Introduction Medical emergencies can result from exposure to heat or cold. Certain populations are at higher risk for heat and cold emergencies. Children Older people People with
Cold Weather Emergencies Introduction Medical emergencies can result from exposure to heat or cold. Certain populations are at higher risk for heat and cold emergencies. Children Older people People with
CHAPTER 6. Oxygen Transport. Copyright 2008 Thomson Delmar Learning
 CHAPTER 6 Oxygen Transport Normal Blood Gas Value Ranges Table 6-1 OXYGEN TRANSPORT Oxygen Dissolved in the Blood Plasma Dissolve means that the gas maintains its precise molecular structure About.003
CHAPTER 6 Oxygen Transport Normal Blood Gas Value Ranges Table 6-1 OXYGEN TRANSPORT Oxygen Dissolved in the Blood Plasma Dissolve means that the gas maintains its precise molecular structure About.003
Modeling Gas Dynamics in California Sea Lions
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Modeling Gas Dynamics in California Sea Lions Andreas Fahlman Department of Life Sciences Texas A&M University-Corpus Christi
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Modeling Gas Dynamics in California Sea Lions Andreas Fahlman Department of Life Sciences Texas A&M University-Corpus Christi
(Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System
 (Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System I. (Slide 2) The Respiratory Tract A) Major structures and regions of the respiratory Tract/Route INTO body 1) nose 2) nasal cavity 3) pharynx 4) glottis 5)
(Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System I. (Slide 2) The Respiratory Tract A) Major structures and regions of the respiratory Tract/Route INTO body 1) nose 2) nasal cavity 3) pharynx 4) glottis 5)
SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION
 SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION WHEN WE BREATHE, WHAT DO WE BREATHE IN? O2, N2, CO2, O3, NO2 (gas fumes), CO, pollutant, fragrants, toxins, etc. WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF BREATHING IN? WHAT DOES OUR BODY WANT? O2 WHY?
SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION WHEN WE BREATHE, WHAT DO WE BREATHE IN? O2, N2, CO2, O3, NO2 (gas fumes), CO, pollutant, fragrants, toxins, etc. WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF BREATHING IN? WHAT DOES OUR BODY WANT? O2 WHY?
Approximate Grade Level: Objectives: Common Core State Standards: Class Sessions (45 minutes): Teaching Materials/Worksheets: Student Supplies:
 Habitats Grade Level: 1-3 Teacher Guidelines Instructional Pages Activity Page Practice Page Answer Key pages 1 2 pages 3 5 pages 6 page 7 page 8-9 Classroom Procedure: 1. List and display student responses
Habitats Grade Level: 1-3 Teacher Guidelines Instructional Pages Activity Page Practice Page Answer Key pages 1 2 pages 3 5 pages 6 page 7 page 8-9 Classroom Procedure: 1. List and display student responses
PICU Resident Self-Study Tutorial The Basic Physics of Oxygen Transport. I was told that there would be no math!
 Physiology of Oxygen Transport PICU Resident Self-Study Tutorial I was told that there would be no math! INTRODUCTION Christopher Carroll, MD Although cells rely on oxygen for aerobic metabolism and viability,
Physiology of Oxygen Transport PICU Resident Self-Study Tutorial I was told that there would be no math! INTRODUCTION Christopher Carroll, MD Although cells rely on oxygen for aerobic metabolism and viability,
NORTHERN DIVER WETSUIT MANUAL
 WETSUIT MANUAL NORTHERN DIVER WETSUIT MANUAL This manual describes materials, construction, use, care, maintenance, repair, and inherent risks involved in the use of neoprene wetsuits for SCUBA Diving.
WETSUIT MANUAL NORTHERN DIVER WETSUIT MANUAL This manual describes materials, construction, use, care, maintenance, repair, and inherent risks involved in the use of neoprene wetsuits for SCUBA Diving.
60bbm and less 60-50bbm 50-30bbm 30-20bbm 20-10bbm (incorporates a significant aerobic component)
 TRAINING SPECIFICS IN RELATION TO AEROBIC & ANAEROBIC CONDITIONING OF SWIMMERS By Leigh Nugent, National Youth Coach Training specificity is a term mentioned often in the literature published on the physiological
TRAINING SPECIFICS IN RELATION TO AEROBIC & ANAEROBIC CONDITIONING OF SWIMMERS By Leigh Nugent, National Youth Coach Training specificity is a term mentioned often in the literature published on the physiological
Chapter 16 Respiratory System
 Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
National Weather Service
 National Weather Service Gulf of California Moisture Surges Gulf of California moisture surges, or simply Gulf Surges, are one of the most researched components of the North American Monsoon. As early
National Weather Service Gulf of California Moisture Surges Gulf of California moisture surges, or simply Gulf Surges, are one of the most researched components of the North American Monsoon. As early
Guidelines on Working in Cold Conditions Re-endorsed by Annual Conference 2017
 Guidelines on Working in Cold Conditions Re-endorsed by Annual Conference 2017 What is cold? Cold is experienced when the body is in circumstances that deplete the body s heat and potentially reduce its
Guidelines on Working in Cold Conditions Re-endorsed by Annual Conference 2017 What is cold? Cold is experienced when the body is in circumstances that deplete the body s heat and potentially reduce its
