A Mechanistic Model for Pressure Prediction in Deviated Wells During UBD. Operations
|
|
|
- Dylan Jenkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Mechanistic Model for Pressure Prediction in Deviated Wells During UBD Operations Shihui N *,1, Tie YAN 1, Xueliang BI 1, Guoqing YU 1 College of Petroleum Engineering, Northeast Petroleum University, Daqing, eilongjiang, , P.R China Daqing Oil Filed Co., td. of PetroChina, Daqing, eilongjiang, , P.R China Abstract Underbalanced drilling (UBD) offers a major advantage in increasing the rate of penetration and reducing lost circulation. In order to improve recovery, drilling of deviated and horizontal wells increased. owever, little data is available regarding the effects of well deviation on the hydraulics of two phase flow in deviated and horizontal wellbores. Prediction of flow and pressure profiles while drilling underbalanced in such wells will help in designing and planning of the well. The main aim of this research is to develop a new mechanistic model to predict flow pattern and calculate flow behavior for each pattern in deviated wells. The proposed model was evaluated against field measurements and compared with empirical models. Simulation results show that the proposed model, which considering the effects of wellbore deviation, has an outstanding performance. Keywords mechanistic model; well deviation; flow pattern; pressure drop I. INTRODUCTION Under UBD conditions, two phase flow models are used to predict flow characteristic, such as pressure drop, flow pattern, liquid holdup and other parameters. The models can be divided into two categories: empirical correlations and mechanistic models. Although empirical models lead to acceptable results in certain wells, they fail or over predict for both vertical and horizontal operations sometimes[1]. Field applications show that mechanistic models, rather than empirical correlations, are being used with increasing frequency for design of multiphase production system because of the better accuracy[]. Based on this trend of improvement, the application of mechanistic models to predict wellbore pressure and two phase flow parameters can increase the success of UBD operations. Taking into account the effects of well deviation, an improved mechanistic model for pressure prediction through a deviated well is presented in the paper. II. DOMINANT UBD FOW PATTERNS The major flow patterns that exist in multiphase flow are dispersed bubble, bubble, slug, churn and annular[3]. In UBD, due to well control safety and surface fluid handling consideration, choke pressure increase would drastically decrease superficial gas velocities and shift flow pattern from annular to churn or slug. In addition, pressure and temperature change along with the wellbore of a typical UBD well. Churn and annular flow may occur only at conditions close to the surface. Therefore, for the upward flow in the annulus, UBD operations deal mostly with dispersed bubble, bubble, and slug flow. For downward flow through the drill string, slug, bubble, and dispersed bubble flow are also the dominant flow patterns, depending on the combination of injected gas and liquid flow rates[4]. III. FOW PATTERN PREDICTION MODES The following flow pattern models applied to both the drill string and the annulus with an inclination angle θ from horizontal. A. Downward Flow through the Drill string Bubble to Slug Transition asan proposed the following expression for transition boundary between bubble and slug flow [5]. 0 S v vsg sin (1) (1 / ) C0 armathy correlation is used to calculate the terminal rise velocity (ν ) for upward flow in vertical and inclined channels as follows [6]. 0.5 Gg v 1.53 () Where,C 0 is the velocity profile coefficient. When inclination is 10º-50º, C 0 =1.05; When inclination is 50º-60º, C 0 =1.15; When inclination is 60º-90º, C 0 =1.5., G is liquid density and gas density, respectively, kg/m3. g is the gravitational acceleration, m/s.αis gas void fraction. v S is superficial liquid velocity, m/s. σ is liquid surface tension, N/m. 1) Bubble or Slug to Dispersed Bubble Transition Caetano model is recommended for the bubble or slug to dispersed bubble flow transition [7-8], which is given by: f 1.6 vm DIT G g (3) 0.5 v SG vm DOI /IJSSST.a ISSN: x online, print
2 Fanning friction factor, f, is calculated using the no-slip liquid holdup( ) defined by: vs (4) vm Where, D IT is the inner pipe diameter, m. v M is mixture velocity, m/s. v SG is superficial gas velocity, m/s. B. Upward Flow through the Annuli Bubble to Slug Transition During bubble flow, discrete bubbles rise with the occasional appearance of a Taylor bubble. The discrete bubble rise velocity was defined in (). asan and Kabir stated that the presence of an inner tube tends to make the nose of the Taylor bubble sharper, causing an increase in the Taylor bubble rise velocity [9]. As a result, asan and Kabir15 developed (5) where the diameter of the outer tube should be used with the diameter ratio K(D OT /D IC ) to get the following expression for the Taylor bubble rise velocity in inclined annulus. DOT sin 1 cos 1. G v gd IC DIC Where, D OT is the outside pipe diameter and D IC is the inner casing diameter, m. asan and Kabir stated that the presence of an inner tube does not appear to influence the bubble concentration profile (C 0 ) and thus, the bubble-slug transition is defined by: 4 C0 vs v (6) sin 1) Bubble or Slug to dispersed bubble transition The hydraulic diameter (D h ) is substituted for the pipe inside diameter (D IT ) in (3), the transition from bubble or slug to dispersed bubble flow is defined as follows f 1.6 v M D h g G (7) 0.5 v SG v M The hydraulic diameter of the casing-tubing annulus is given by: Dh DIC DOT (8) ) Dispersed bubble to slug flow transition Taitel et al. determined that the maximum allowable gas void fraction under bubble flow condition is 0.5 [10]. igher values will convert the flow to slug, hence the transition boundary could be equated as follows. vs 0.93 (9) 3) Slug to churn transition Tengesdal et al. stated that the slug structure will be completely destroyed and churn flow will occur if the gas void fraction equals 0.78 [11]. Thus churn flow will occur. The transition from slug flow to churn flow can thus be represented by: v v 0.9 gd (10) S SG ep Where D ep is the equi-periphery diameter defined as follow. Dep DIC DOT (11) 4) Churn to annular transition Based on the minimum gas velocity required to prevent the entrained liquid droplets from falling back into the gas stream that would originate churn flow, Taitel et al proposed the following equation to predict the transition to annular flow [10]. 0.5 Gg 3.1 (1) G IV. FOW BEAVIOR PREDICTION MODES For steady state flow, the total pressure gradient is composed of gravity, friction, and convective acceleration losses and is calculated as follows. dp dp dp dp (13) dz dz dz dz T y Fric Acc dp Where is the total pressure gradient, Pa/m; dz T dp (5) dp is the gravity pressure gradient, Pa/m; dz dz y dp is the friction pressure gradient, Pa/m; and is dz Acc the acceleration pressure gradient, Pa/m. A. Downward Flow through the Drill string Bubble Flow Model for Drill string The drift flux approach is used to calculate liquid holdup considering the slippage between the phases and non-homogenous distribution of bubbles. The slip velocity using the drift flux approach can be expressed as follows[1]. vs C0vM (14) 1 With an inclination angle θ the proposed model as shown below: vs v sin (15) Combining (14) and (15) we get the following expression: v sin 1.vM (16) 1 Newton-Raphson method was used to solve for liquid holdup from (16). The gravity component is given by: dp M g sin (17) dz y Where, 1 (18) M G The frictional pressure loss is given by: dp fm MvM (19) dz Fric DIT Where f M is the Moody friction factor and is calculated using Reynolds number N RE. Fric DOI /IJSSST.a ISSN: x online, print
3 Moody friction factor is four times the Fanning friction factor and it is calculated using the Colebrook function[13] log (0) f D M IT NRE f M Where, ε is tube roughness, mm. The acceleration pressure gradient components is calculated using Beggs and Brill approach as follow [14]. dp MvM dp (1) d p d The acceleration term (E k ) is defined as follow. M vm Ek () p Then the total pressure drop is calculated by (3) : dp dp dp d y d Fric (3) d T 1 Ek 1) Dispersed bubble flow model for drill string Since nearly a uniform bubble distribution in the liquid, the flow can be treated as ahomogenous flow. Thus, the liquid holdup is very close to the no-slip holdup. The pressure gradient components are calculated as those in bubble flow. ) Slug flow model for drill string Assuming that the liquid and gas phases in the liquid slug behave analogously to fully developed bubble flow and that the bubble swarm effect in downward flow is negligible n 0[15], the liquid holdup in the liquid slug can be calculated by: 1 (4) S 0 M v The liquid holdup in the Taylor bubble in downward flow may be calculated by: 1 (5) 1 M v After extensive validations, asan recommended using C 0 1.and C Considering a slug unit formed by a Taylor bubble and a liquid slug regions, the liquid holdup in the slug unit may be approximated to: S S (6) The slug unit length can be calculated by the following expression based on the superficial gas velocity. 160DIT for 0.4m/s (7) 0 M v 64DIT for 0.4m/s (8) 0 M v The liquid slug length is given by: S 16Dh(9) Perez-Tellez showed that, for a fully developed Taylor bubble, the total hydrostatic and frictional pressure losses can be calculated by: Acc dp 1M S M g d (30) y dp ff s M v S M 1 (31) d Fric DIT Where is the mixture density in the liquid slug MS zone and the friction factor is calculated with Colebrook function using Reynolds number, kg/m 3 ; is the relative bubble length parameter, 1; M is the mixture density in the Taylor bubble zone, kg/m 3 ; and is the v in-situ liquid velocity in the Taylor bubble zone, which are function of the slug flow conditions, m/s. For fully developed Taylor bubble slug flow: and M G (3) and for developing Taylor bubble slug flow: d, 1, m d G d d (33) and v v d Since in UBD, the most common flow patterns in downward flow are dispersed bubble and bubble, the acceleration component in drillstring geometries is relatively small and may be either neglected or calculated using the approach suggested for bubble flow, (3). B. Upward Flow through the Annulus 1) Bubble Flow Model for Annular Geometries For a bubbly flow the holdup is calculated as reported by asan and Kabir as follows [9]. 1 (34) v C0vM The gravity pressure gradient is calculated using (17). For the frictional pressure loss is calculated from (19). Caetano suggested the use of the calculation developed by Gunn and Darling for a turbulent flow as follow: exp N 3000 /10 RE F P f F CA (35) expNRE 3000 /10 FP 4log N RE f 0.4 F CA Where F p and F CA are geometry parameters defined by (36) and (37). FP 16 / NRE, M (36) 161 K FCA (37) 4 1K 1K 1 K ln 1/ K The acceleration component is calculated using Beggs and Brill approach using (3). ) Dispersed Bubble Flow Model The dispersed bubble holdup is assumed equal to the no-slip holdup ( ). The same equations as in the bubble DOI /IJSSST.a ISSN: x online, print
4 flow are used to calculate the total pressure gradient. 3) Slug Flow Model The same model used by Perez-Tellez for the case of downward flow inside the drill string is used. The hydraulic diameter is used instead of the inner tubing diameter in (30) for calculating Reynolds number. In addition, the pressure drop due to acceleration across the mixing zone at the front of the liquid slug by: dp S v v S v T v (38) S dz Acc The average holdup over the entire slug unit either developed of fully developing Taylor bubble can be calculated by: 1 v S vg S 1 (39) v Where v GS for is in-situ gas velocity in the liquid slug, m/s. 4) Annular flow model As explained above, in common UBD operations, the window of occurrence of annular flow is quite limited and when it occurs, it takes place in the annulus at a few meters close to the surface. The simplified annular flow model proposed by Taitel and Barnea was implemented only to avoid convergence problems during the computations [16]. dp 4 i G1 gsin d T De (40) The annular film thickness can be defined as follow: 1/3 0.6 vsd e g G (41) D e is the equivalent pipe diameter and is calculated by: D D D (4) e IC IT The interfacial shear stress ( i ) is defined by: 0.5 fig i (43) 4 1 / De The interfacial shear friction factor is calculated as suggested by Alves et al as follows [17]. fi fsci (44) Where f sc is the superficial core friction factor (gas phase) and is calculated based on the core superficial velocity, density and viscosity. The interfacial correction parameter I is used to take into account the roughness of the interface. The parameter I is an average between the horizontal angle and the vertical angle and is calculated based on an inclination θ. I I cos IV sin (45) The horizontal correction parameter is given by enstock and anratty[18]. I 1 800FA (46) Where, F 0.707NRE, S NRE, S v A 0.9 NRE, S vg G Where N RE,S and N RE,SG are the superficial liquid and gas Reynolds number respectively. Both are calculated below: vsde NRE, S (48) GDe NRE, SG (49) G The vertical correction parameter is given by Wallis as follow [19]. IV / De(50) Considering that the liquid film thickness is constant, the liquid holdup can be estimated by: 4 (51) De D e V. BIT MODE Using the mechanical energy balance along with the gas weighting fraction and neglecting frictional pressure drop, Perez-Tellez formulated the following expression for calculating the pressure drop across the bit nozzles. 1 w G wgzrt Pbh n bh up MG Pup v P P ln 0 (5) Where v n is the nozzle velocity, m/s; w G is the gas weighting factor; P bh is the bottom hole pressure, Pa; P up is the upstream pressure, Pa; M G is the gas nolecular weight, kg. Using the continuity equation for the gas liquid mixture the following expression is reached to express the conservation of mass MvMAn q qgg constant (53) And the nozzle velocity is calculated by: qgg q vn (54) An The above three equations are solved numerically to obtain the bit nozzle upstream pressure given the bottom hole pressure. VI. MODE VAIDATION In order to demonstrate the validity of the model, a field case was simulated and results compared with measurements. Injection and bottom hole pressure at depth 308m and 38m was measured by a pressure recording tool, which is obtained from Table I. Drill string and operating parameters for the above two depths are shown in Table II,III. TABEI.MEARED PRESREAT 308m AND 38m Depth Parameters Value 308 Injection Pressure P in /MPa 11.7 DOI /IJSSST.a ISSN: x online, print
5 38 Bottom hole Pressure P bh /MPa 17. Injection Pressure P in /MPa 9.0 Bottom hole Pressure P bh /MPa 16.8 TABEII DRISTRINGAND ANNUAR GEOMETRIESATTETWO SIMUATED DEPTS Run 1# Casing Pipe Depth/m ID/mm Depth/m OD/mm ID/mm Total Depth Casing Run # Pipe Depth/m ID/mm Depth/m OD/mm ID/mm Total Depth TABE III OPERATING PARAMETERS Operating Parameters Run 1# Run # Depth /(m) Gas Flow Rate / (m 3 /min) iquid Flow Rate / (m 3 /min) iquid Density / (kg/m 3 ) Mud Viscosity / (mpa s) 3 3 Inclination angles are read from survey file, which are shown in Table IV. In order to find the angle at any depth, linear interpolation is used. Depth (m) TABE IV MEARED INCINATION ANGE Inc. Angle ( ) Depth (m) Inc. Angle ( ) Depth (m) Inc. Angle ( ) asan and Kabir, Beggs and Brill models were also tested in compare to the result of the new model. The error of the developed model s predictions, the empirical models results with filed measurements are shown in Table V. The average absolute error E a is given by: Pcalc Pmeas Ea 100% (55) P meas TABE V COMPARISONOF ABSOUTE AVERAGE ERROR Comparison Developed Model Beggs & Brill asan & Kabir Calc. Pres /MPa Run 1# Run # Ea Calc. Pres /MPa P in P bh P in P bh P in P bh Table V shows that the results of the developed model have a good match with the measured value where at the average absolute error Ea has an average value of less than 10%. The Beggs & Brill, asan & Kabir models are based on empirical correlations, the results shown in Table V indicate that the empirical models predict the bottom hole pressure reasonably, however the mechanistic model outperform both. VII. CONCUSIONS A model is developed for the prediction of flow pattern and flow behavior in deviated wellbores and pipelines under UBD conditions using mechanistic steady state model. In the annulus, dispersed bubble, bubble, slug, churn, annular flow are considered. And three flow patterns (dispersed bubble, bubble, slug) are taken into account in the drill string. The developed model has been validated against field data and existing empirical models. The model have a good match with the measured data, which has an average absolute error of less than 10%.The model comparison shows that the developed model performs better than empirical models when trying to design UBD operation within a pressure window. Ea DOI /IJSSST.a ISSN: x online, print
6 ACKNOWEDGEMENT This work was supported by Youth Science Foundation of Northeast Petroleum University (No. NEPUBS014-08) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No ). REFERENCES [1]. Mousavi,., Mostafavi, V., Modeling of Three Phase Flow in the Annuli During UBD Operations,SPE International Symposium and Exhibition on Formation Damage Control, ouisiana, Feb., 008, doi:10.118/11679-ms. []. Perez-Tellez, C., Smith, J. R., A New Comprehensive, Mechanistic Model for UBD Improves Wellbore Pressure Predictions, IPCEM, Mexico, 10-1 Feb,00, doi:10.118/7446-ms. [3]. age, A.C.V.M. and Time, R.W. An Experimental and Theoretical Investigation of Upward Two-Phase Flow in Annuli, SPE Journal, vol.7, 00, pp [4]. Barnea, D., Shoham, O., and Taitel, Y. Flow Pattern Transition for Vertical Downward Two Phase Flow, Chem. Engineering. Sci.,vol. 37, 198, pp [5]. asan, A.R. Void Fraction in Bubbly and Slug Flow in Downward Vertical and Inclined Systems, SPE Production & Facilities, vol.10, 1995, pp [6]. armathy, T.Z. Velocity of arge Drops and Bubbles in Media of Infinite or Restricted Extent, AIChE J.,vol. 6, 1960, pp [7]. Caetano, E.F., Shoham, O., and Brill, J.P. Upward Vertical Two phase Flow through Annulus Part I: Single-Phase Friction Factor, Taylor Bubble Rise Velocity, and Flow Pattern Prediction, Journal of Energy Resources Technology, vol. 114,199, pp [8]. Caetano, E.F., Shoham, O. and Brill J.P. Upward Vertical Two Phase Flow through an Annulus Part II: Modeling Bubble, Slug and Annular Flow. ASME J. Energy Resources Technology, vol. 114,199, pp [9]. asan, A.R. and Kabir, C.S. Tow-Phase Flow in Vertical and Inclined Annuli, Intl. J. Multiphase Flow, vol.18,199, pp [10]. Taitel, Y., Barnea, D. and Duckler, A.E. Modeling Flow Pattern Transitions for Steady Upward Gas-iquid Flow in Vertical Tubes, AIChE J., vol. 6,1980, pp [11]. Tengesdal, J. Ø., Kaya, A. S., and Sarica, C. Flow Pattern Transition and ydrodynamic Modeling of Churn Flow, SPE J., vol. 4, 1999, pp [1]. Kaya, A.S., Sarica, C., and Brill, J.P. Comprehensive Mechanistic Modeling of Two phase Flow in Deviated Wells, Annual and Technical Conferences and Exhibition, ouston, 3-6 Oct., 1999, doi:10.118/565-ms. [13]. Colebrook, C.F. Turbulent Flow in Pipes With Particular Reference to the Transition Region Between the Smooth and Rough Pipe aws, J. Inst. Civil Eng., vol. 11,1939, pp [14]. Beggs,.D. and Brill, J.P. A Study of Two-Phase Flow in Inclined Pipes, Trans. AIME, vol.5, 1973, pp [15]. Perez-Tellez, C. Improved Bottomhole Pressure Control for Underbalanced Drilling Operations, D.S. thesis, ouisiana State University,ouisiana State, USA, 00. [16]. Taitel, Y. nd Barnea, D. Counter Current Gas-iquid Vertical Flow, Model for Flow Pattern and Pressure Drop, Int. J. Multiphase Flow, vol. 9, 1983, pp [17]. Alves, I. M., Caetano, E. F., Minami, K., and Shoham, O. Modeling Annular Flow Behavior for Gas Wells, SPE Production Engineering,vol. 64,1991,pp [18]. enstock, W.. and anratty, T.J. The Interfacial Drag and the eight of the Wall ayer in Annular Flow, AIChE J., vol.,1976, pp [19]. Wallis, G.B, One Dimensional Two phase Flow, New York: McGraw-ill, DOI /IJSSST.a ISSN: x online, print
Numerical Analysis of Two Phase Flow Patterns in Vertical and Horizontal Pipes
 Numerical Analysis of Two Phase Flow Patterns in Vertical and Horizontal Pipes MOHAMMED A. ABDULWAHID, HASANAIN J. KAREEM, MUJTABA A. ALMUDHAFFAR Thermal Mechanical Engineering, Southern Technical University,
Numerical Analysis of Two Phase Flow Patterns in Vertical and Horizontal Pipes MOHAMMED A. ABDULWAHID, HASANAIN J. KAREEM, MUJTABA A. ALMUDHAFFAR Thermal Mechanical Engineering, Southern Technical University,
B. C. Houchens, F. Popa & A. Filippov. Abstract. 1 Introduction. Landmark, Halliburton, USA
 Computational Methods in Multiphase Flow VIII 347 Sensitivity of dispersed-bubble flow regime identification over a broad parameter space and to various closure relations for mechanistic models of gas
Computational Methods in Multiphase Flow VIII 347 Sensitivity of dispersed-bubble flow regime identification over a broad parameter space and to various closure relations for mechanistic models of gas
Section 2 Multiphase Flow, Flowing Well Performance
 Section 2 Multiphase Flow, Flowing Well Performance Multiphase Vertical Flow When producing an oil or gas well, the flow of the fluids up the tubing will be in most cases be 2 phase, liquid and gas. The
Section 2 Multiphase Flow, Flowing Well Performance Multiphase Vertical Flow When producing an oil or gas well, the flow of the fluids up the tubing will be in most cases be 2 phase, liquid and gas. The
Simulation of Gas Holdup in a Bubble Column with a Draft Tube for Gas Dispersion into an Annulus
 Simulation of Gas Holdup in a Bubble Column with a Draft Tube for Gas Dispersion into an Annulus Fukuji Yamashita Dept. of Applied Bioscience, Kanagawa Institute of Technology, Atsugi 243-292, Japan, yamasita@bio.kanagawa-it.ac.jp
Simulation of Gas Holdup in a Bubble Column with a Draft Tube for Gas Dispersion into an Annulus Fukuji Yamashita Dept. of Applied Bioscience, Kanagawa Institute of Technology, Atsugi 243-292, Japan, yamasita@bio.kanagawa-it.ac.jp
Application of mechanistic models in predicting flow behavior in deviated wells under UBD conditions
 ouisiana State Uniersity SU Digital Commons SU Master's Theses Graduate School 2003 Application of mechanistic models in predicting flow behaior in deiated wells under UBD conditions Faisal Abdullah AAdwani
ouisiana State Uniersity SU Digital Commons SU Master's Theses Graduate School 2003 Application of mechanistic models in predicting flow behaior in deiated wells under UBD conditions Faisal Abdullah AAdwani
Irrigation &Hydraulics Department lb / ft to kg/lit.
 CAIRO UNIVERSITY FLUID MECHANICS Faculty of Engineering nd Year CIVIL ENG. Irrigation &Hydraulics Department 010-011 1. FLUID PROPERTIES 1. Identify the dimensions and units for the following engineering
CAIRO UNIVERSITY FLUID MECHANICS Faculty of Engineering nd Year CIVIL ENG. Irrigation &Hydraulics Department 010-011 1. FLUID PROPERTIES 1. Identify the dimensions and units for the following engineering
Flow assurance in Oil-Gas Pipelines
 Fourth LACCEI International Latin American and Caribbean Conference for Engineering and Technology (LACCET 2006) Breaking Frontiers and Barriers in Engineering: Education, Research and Practice 21-23 June
Fourth LACCEI International Latin American and Caribbean Conference for Engineering and Technology (LACCET 2006) Breaking Frontiers and Barriers in Engineering: Education, Research and Practice 21-23 June
Numerical Simulations of a Train of Air Bubbles Rising Through Stagnant Water
 Numerical Simulations of a Train of Air Bubbles Rising Through Stagnant Water Hong Xu, Chokri Guetari ANSYS INC. Abstract Transient numerical simulations of the rise of a train of gas bubbles in a liquid
Numerical Simulations of a Train of Air Bubbles Rising Through Stagnant Water Hong Xu, Chokri Guetari ANSYS INC. Abstract Transient numerical simulations of the rise of a train of gas bubbles in a liquid
Air Bubble Departure on a Superhydrophobic Surface
 Air Bubble Departure on a Superhydrophobic Surface A. Kibar 1, R. Ozbay 2, C.H. Choi 2 1 Department of Mechanical and Material Technologies, Kocaeli University, 41285, Kocaeli, Turkey 2 Department of Mechanical
Air Bubble Departure on a Superhydrophobic Surface A. Kibar 1, R. Ozbay 2, C.H. Choi 2 1 Department of Mechanical and Material Technologies, Kocaeli University, 41285, Kocaeli, Turkey 2 Department of Mechanical
Workshop 1: Bubbly Flow in a Rectangular Bubble Column. Multiphase Flow Modeling In ANSYS CFX Release ANSYS, Inc. WS1-1 Release 14.
 Workshop 1: Bubbly Flow in a Rectangular Bubble Column 14. 5 Release Multiphase Flow Modeling In ANSYS CFX 2013 ANSYS, Inc. WS1-1 Release 14.5 Introduction This workshop models the dispersion of air bubbles
Workshop 1: Bubbly Flow in a Rectangular Bubble Column 14. 5 Release Multiphase Flow Modeling In ANSYS CFX 2013 ANSYS, Inc. WS1-1 Release 14.5 Introduction This workshop models the dispersion of air bubbles
Environmental Science: An Indian Journal
 Environmental Science: An Indian Journal Research Vol 14 Iss 1 Flow Pattern and Liquid Holdup Prediction in Multiphase Flow by Machine Learning Approach Chandrasekaran S *, Kumar S Petroleum Engineering
Environmental Science: An Indian Journal Research Vol 14 Iss 1 Flow Pattern and Liquid Holdup Prediction in Multiphase Flow by Machine Learning Approach Chandrasekaran S *, Kumar S Petroleum Engineering
Distribution of the Sizes of Rock Cuttings in Gas Drilling At Various Depths
 Copyright 2012 Tech Science Press CMES, vol.89, no.2, pp.79-96, 2012 Distribution of the Sizes of Rock Cuttings in Gas Drilling At Various Depths Jun Li 1, Shunji Yang 1, Boyun Guo 1,2, Yin Feng 2 and
Copyright 2012 Tech Science Press CMES, vol.89, no.2, pp.79-96, 2012 Distribution of the Sizes of Rock Cuttings in Gas Drilling At Various Depths Jun Li 1, Shunji Yang 1, Boyun Guo 1,2, Yin Feng 2 and
STUDY OF SLUG CONTROL TECHNIQUES IN PIPELINE SYSTEMS
 STUDY OF SLUG CONTROL TECHNIQUES IN PIPELINE SYSTEMS JOSÉ L. A,VIDAL Petrobrás Research Center - CENPES/PDEP/TOOL Av.Horácio de Macedo 95- Cidade Universitária 191-915 -Rio de Janeiro-RJ E-mail:josearias@petrobras.com.br
STUDY OF SLUG CONTROL TECHNIQUES IN PIPELINE SYSTEMS JOSÉ L. A,VIDAL Petrobrás Research Center - CENPES/PDEP/TOOL Av.Horácio de Macedo 95- Cidade Universitária 191-915 -Rio de Janeiro-RJ E-mail:josearias@petrobras.com.br
Numerical simulation of an intermediate sized bubble rising in a vertical pipe
 Computational Methods in Multiphase Flow V 111 Numerical simulation of an intermediate sized bubble rising in a vertical pipe J. Hua 1, S. Quan 2 & J. Nossen 1 1 Department of Process and Fluid Flow Technology,
Computational Methods in Multiphase Flow V 111 Numerical simulation of an intermediate sized bubble rising in a vertical pipe J. Hua 1, S. Quan 2 & J. Nossen 1 1 Department of Process and Fluid Flow Technology,
EDUCTOR. principle of operation
 EDUCTOR principle of operation condensate and mixing eductor s are designed to mix two liquids intimately in various proportions in operations where the pressure liquid is the greater proportion of the
EDUCTOR principle of operation condensate and mixing eductor s are designed to mix two liquids intimately in various proportions in operations where the pressure liquid is the greater proportion of the
GAS KICK MECHANISTIC MODEL. A Thesis RAHEEL ZUBAIRY
 GAS KICK MECHANISTIC MODEL A Thesis by RAHEEL ZUBAIRY Submitted to the Office of Graduate and Professional Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of MASTER
GAS KICK MECHANISTIC MODEL A Thesis by RAHEEL ZUBAIRY Submitted to the Office of Graduate and Professional Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of MASTER
The Mechanism Study of Vortex Tools Drainage Gas Recovery of Gas Well
 Advances in Petroleum Exploration and Development Vol. 7, No. 1, 214, pp. 62-66 DOI:1.3968/j.aped.1925543821471.1931 ISSN 1925-542X [Print] ISSN 1925-5438 [Online] www.cscanada.net www.cscanada.org The
Advances in Petroleum Exploration and Development Vol. 7, No. 1, 214, pp. 62-66 DOI:1.3968/j.aped.1925543821471.1931 ISSN 1925-542X [Print] ISSN 1925-5438 [Online] www.cscanada.net www.cscanada.org The
Experimental Analysis and CFD Simulation of Pressure Drop of Carbon Dioxide in Horizontal Micro Tube Heat Exchangers
 Internatıonal Journal of Natural and Engineering Sciences 8 (2): 15-20, 2014 ISSN: 1307-1149, E-ISSN: 2146-0086, www.nobel.gen.tr Experimental Analysis and CFD Simulation of Pressure Drop of Carbon Dioxide
Internatıonal Journal of Natural and Engineering Sciences 8 (2): 15-20, 2014 ISSN: 1307-1149, E-ISSN: 2146-0086, www.nobel.gen.tr Experimental Analysis and CFD Simulation of Pressure Drop of Carbon Dioxide
A model for the bubble lift-off diameter in subcooled boiling flow in a horizontal channel
 Advances in Fluid Mechanics X 215 A model for the bubble lift-off diameter in subcooled boiling flow in a horizontal channel S. Shabannejad & N. Ashgriz Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering,
Advances in Fluid Mechanics X 215 A model for the bubble lift-off diameter in subcooled boiling flow in a horizontal channel S. Shabannejad & N. Ashgriz Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering,
Flow transients in multiphase pipelines
 Flow transients in multiphase pipelines David Wiszniewski School of Mechanical Engineering, University of Western Australia Prof. Ole Jørgen Nydal Multiphase Flow Laboratory, Norwegian University of Science
Flow transients in multiphase pipelines David Wiszniewski School of Mechanical Engineering, University of Western Australia Prof. Ole Jørgen Nydal Multiphase Flow Laboratory, Norwegian University of Science
DETAILED ANALYSIS OF PRESSURE DROP IN A LARGE DIAMETER VERTICAL PIPE THESISPRESENTED TO THE DEPARTMENT OF PETROLEUM ENGINEERING
 DETAILED ANALYSIS OF PRESSURE DROP IN A LARGE DIAMETER VERTICAL PIPE A THESISPRESENTED TO THE DEPARTMENT OF PETROLEUM ENGINEERING AFRICAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF
DETAILED ANALYSIS OF PRESSURE DROP IN A LARGE DIAMETER VERTICAL PIPE A THESISPRESENTED TO THE DEPARTMENT OF PETROLEUM ENGINEERING AFRICAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF
Effect of channel slope on flow characteristics of undular hydraulic jumps
 River Basin Management III 33 Effect of channel slope on flow characteristics of undular hydraulic jumps H. Gotoh, Y. Yasuda & I. Ohtsu Department of Civil Engineering, College of Science and Technology,
River Basin Management III 33 Effect of channel slope on flow characteristics of undular hydraulic jumps H. Gotoh, Y. Yasuda & I. Ohtsu Department of Civil Engineering, College of Science and Technology,
Effect of Argon Gas Distribution on Fluid Flow in the Mold Using Time-Averaged k-ε Models
 Effect of Argon Gas Distribution on Fluid Flow in the Mold Using Time-Averaged k-ε Models B. G. Thomas, T. Shi and L. Zhang Department of Materials Science &. Engineering University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Effect of Argon Gas Distribution on Fluid Flow in the Mold Using Time-Averaged k-ε Models B. G. Thomas, T. Shi and L. Zhang Department of Materials Science &. Engineering University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Study on the Influencing Factors of Gas Mixing Length in Nitrogen Displacement of Gas Pipeline Kun Huang 1,a Yan Xian 2,b Kunrong Shen 3,c
 Applied Mechanics and Materials Online: 2013-06-13 ISSN: 1662-7482, Vols. 321-324, pp 299-304 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.321-324.299 2013 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Study on the Influencing
Applied Mechanics and Materials Online: 2013-06-13 ISSN: 1662-7482, Vols. 321-324, pp 299-304 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.321-324.299 2013 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Study on the Influencing
A Computational Assessment of Gas Jets in a Bubbly Co-Flow 1
 A Computational Assessment of Gas Jets in a Bubbly Co-Flow 1 Melissa Fronzeo*, 1 Michael Kinzel 1 The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, USA Abstract In this effort, Computational Fluid
A Computational Assessment of Gas Jets in a Bubbly Co-Flow 1 Melissa Fronzeo*, 1 Michael Kinzel 1 The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, USA Abstract In this effort, Computational Fluid
New Viscosity Correlation for Different Iraqi Oil Fields
 Iraqi Journal of Chemical and Petroleum Engineering Iraqi Journal of Chemical and Petroleum Engineering Vol.15 No.3 (September 2014) 71-76 ISSN: 1997-4884 University of Baghdad College of Engineering New
Iraqi Journal of Chemical and Petroleum Engineering Iraqi Journal of Chemical and Petroleum Engineering Vol.15 No.3 (September 2014) 71-76 ISSN: 1997-4884 University of Baghdad College of Engineering New
and its weight (in newtons) when located on a planet with an acceleration of gravity equal to 4.0 ft/s 2.
 1.26. A certain object weighs 300 N at the earth's surface. Determine the mass of the object (in kilograms) and its weight (in newtons) when located on a planet with an acceleration of gravity equal to
1.26. A certain object weighs 300 N at the earth's surface. Determine the mass of the object (in kilograms) and its weight (in newtons) when located on a planet with an acceleration of gravity equal to
Numerical Simulation of Instability of Geothermal Production Well
 GRC Transactions, Vol. 37, 2013 Numerical Simulation of Instability of Geothermal Production Well Ryuichi Itoi 1, Yasunari Katayama 3, Toshiaki Tanaka 1, Naoto Kumagai 2, and Takaichi Iwasaki 3 1 Department
GRC Transactions, Vol. 37, 2013 Numerical Simulation of Instability of Geothermal Production Well Ryuichi Itoi 1, Yasunari Katayama 3, Toshiaki Tanaka 1, Naoto Kumagai 2, and Takaichi Iwasaki 3 1 Department
Flow pattern, pressure drop and void fraction of two-phase gas liquid flow in an inclined narrow annular channel
 Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science 30 (2006) 345 354 www.elsevier.com/locate/etfs Flow pattern, pressure drop and void fraction of two-phase gas liquid flow in an inclined narrow annular channel Somchai
Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science 30 (2006) 345 354 www.elsevier.com/locate/etfs Flow pattern, pressure drop and void fraction of two-phase gas liquid flow in an inclined narrow annular channel Somchai
CFD Analysis ofwind Turbine Airfoil at Various Angles of Attack
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 13, Issue 4 Ver. II (Jul. - Aug. 2016), PP 18-24 www.iosrjournals.org CFD Analysis ofwind Turbine
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 13, Issue 4 Ver. II (Jul. - Aug. 2016), PP 18-24 www.iosrjournals.org CFD Analysis ofwind Turbine
A Successful Experience in Optimization of a Production Well in a Southern Iranian Oil Field
 Iranian Journal of Chemical Engineering Vol. 6, No. 2 (Spring), 2009, IAChE A Successful Experience in Optimization of a Production Well in a Southern Iranian Oil Field S. R. Shadizadeh, M. Zoveidavianpoor
Iranian Journal of Chemical Engineering Vol. 6, No. 2 (Spring), 2009, IAChE A Successful Experience in Optimization of a Production Well in a Southern Iranian Oil Field S. R. Shadizadeh, M. Zoveidavianpoor
STRUCTURED PACKING FLOODING: ITS MEASUREMENT AND PREDICTION
 STRUCTURED PACKING FLOODING: ITS MEASUREMENT AND PREDICTION M. J. Lockett, R. A. Victor, J. F. Billingham Praxair, Inc., PO Box 44, Tonawanda, NY 14151-0044, USA. E-mail: Mike_Lockett@Praxair.com A cryogenic
STRUCTURED PACKING FLOODING: ITS MEASUREMENT AND PREDICTION M. J. Lockett, R. A. Victor, J. F. Billingham Praxair, Inc., PO Box 44, Tonawanda, NY 14151-0044, USA. E-mail: Mike_Lockett@Praxair.com A cryogenic
KICK CIRCULATION ANALYSIS FOR EXTENDED-REACH AND HORIZONTAL WELLS. A Thesis MAXIMILIAN M. LONG
 KICK CIRCULATION ANALYSIS FOR EXTENDED-REACH AND HORIZONTAL WELLS A Thesis by MAXIMILIAN M. LONG Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the requirements
KICK CIRCULATION ANALYSIS FOR EXTENDED-REACH AND HORIZONTAL WELLS A Thesis by MAXIMILIAN M. LONG Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the requirements
Using Gas Lift to Unload Horizontal Gas Wells
 Gas Well Deliquification Workshop Sheraton Hotel, Denver, Colorado February 27 March 2, 211 Using Gas Lift to Unload Horizontal Gas Wells Rob Sutton Marathon Oil Company Conventional Gas Lift Application
Gas Well Deliquification Workshop Sheraton Hotel, Denver, Colorado February 27 March 2, 211 Using Gas Lift to Unload Horizontal Gas Wells Rob Sutton Marathon Oil Company Conventional Gas Lift Application
Hydraulics analysis of the Heidrun offshore field
 Hydraulics analysis of the Heidrun offshore field P.Andreussi & E. Sangnes University of Pisa, Italy M. Bonizzi TEA Sistemi, Italy M. Nordsveen, E. Sletfjerding &, I. Berg Martiniussen Statoil ASA, Norway
Hydraulics analysis of the Heidrun offshore field P.Andreussi & E. Sangnes University of Pisa, Italy M. Bonizzi TEA Sistemi, Italy M. Nordsveen, E. Sletfjerding &, I. Berg Martiniussen Statoil ASA, Norway
Comparison of MARS-KS to SPACE for counter current flow limitation model
 Comparison of MARS-KS to SPACE for counter current limitation model Won Woong Lee, Min Gil Kim, Jeong I Lee Department of Nuclear and Quantum engineering, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology
Comparison of MARS-KS to SPACE for counter current limitation model Won Woong Lee, Min Gil Kim, Jeong I Lee Department of Nuclear and Quantum engineering, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology
THE EFFECT OF DRAG REDUCING AGENTS ON PRESSURE GRADIENT IN MULTIPHASE, OILIWATER/GAS VERTICAL FLOW. C. KANG AND W. P. JEPSON
 _. -4_JI!I!I!!!!I-== -S------- THE EFFECT OF DRAG REDUCING AGENTS ON PRESSURE GRADIENT IN MULTIPHASE, OILIWATER/GAS VERTICAL FLOW. BY C. KANG AND W. P. JEPSON NSF, IlUCRC, CORROSION IN MULTIPHASE SYSTEMS
_. -4_JI!I!I!!!!I-== -S------- THE EFFECT OF DRAG REDUCING AGENTS ON PRESSURE GRADIENT IN MULTIPHASE, OILIWATER/GAS VERTICAL FLOW. BY C. KANG AND W. P. JEPSON NSF, IlUCRC, CORROSION IN MULTIPHASE SYSTEMS
9 Mixing. I Fundamental relations and definitions. Milan Jahoda revision Radim Petříček, Lukáš Valenz
 9 ixing ilan Jahoda revision 14-7-017 Radim Petříček, Lukáš Valenz I Fundamental relations and definitions ixing is a hydrodynamic process, in which different methods are used to bring about motion of
9 ixing ilan Jahoda revision 14-7-017 Radim Petříček, Lukáš Valenz I Fundamental relations and definitions ixing is a hydrodynamic process, in which different methods are used to bring about motion of
Evaluation of a Flow Simulator for Multiphase Pipelines
 Evaluation of a Flow Simulator for Multiphase Pipelines Jeppe Mathias Jansen Master of Science in Energy and Environment Submission date: June 2009 Supervisor: Ole Jørgen Nydal, EPT Co-supervisor: Kjartan
Evaluation of a Flow Simulator for Multiphase Pipelines Jeppe Mathias Jansen Master of Science in Energy and Environment Submission date: June 2009 Supervisor: Ole Jørgen Nydal, EPT Co-supervisor: Kjartan
CFD SIMULATIONS IN AN INTERNAL CIRCULATION AIRLIFT OPERATING UNDER HOMOGENEOUS REGIME
 CFD SIMULATIONS IN AN INTERNAL CIRCULATION AIRLIFT OPERATING UNDER HOMOGENEOUS REGIME P. A. S. Monteiro 1, P. Seleghim Jr. 1 1 University of São Paulo, Engineering School of São Carlos, Mechanical Engineering
CFD SIMULATIONS IN AN INTERNAL CIRCULATION AIRLIFT OPERATING UNDER HOMOGENEOUS REGIME P. A. S. Monteiro 1, P. Seleghim Jr. 1 1 University of São Paulo, Engineering School of São Carlos, Mechanical Engineering
The water supply for a hydroelectric plant is a reservoir with a large surface area. An outlet pipe takes the water to a turbine.
 Fluids 1a. [1 mark] The water supply for a hydroelectric plant is a reservoir with a large surface area. An outlet pipe takes the water to a turbine. State the difference in terms of the velocity of the
Fluids 1a. [1 mark] The water supply for a hydroelectric plant is a reservoir with a large surface area. An outlet pipe takes the water to a turbine. State the difference in terms of the velocity of the
Pressure Drop of Two-Phase Flow Through Horizontal Channel with Smooth Expansion
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2012 Pressure Drop of Two-Phase Flow Through Horizontal Channel with Smooth
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2012 Pressure Drop of Two-Phase Flow Through Horizontal Channel with Smooth
The Split of Two-Phase-Flow at Horizontal Side-T-junctions in Unbalanced Pipe Systems for Clean Extinguishing Agents
 The Split of Two-Phase-Flow at Horizontal Side-T-junctions in Unbalanced Pipe Systems for Clean Extinguishing Agents Abstract by Gudrun Fay Minimax GmbH & CO. KG Industriestraße 10-12, 23840 Bad Oldesloe,
The Split of Two-Phase-Flow at Horizontal Side-T-junctions in Unbalanced Pipe Systems for Clean Extinguishing Agents Abstract by Gudrun Fay Minimax GmbH & CO. KG Industriestraße 10-12, 23840 Bad Oldesloe,
Application of Simulation Technology to Mitsubishi Air Lubrication System
 50 Application of Simulation Technology to Mitsubishi Air Lubrication System CHIHARU KAWAKITA *1 SHINSUKE SATO *2 TAKAHIRO OKIMOTO *2 For the development and design of the Mitsubishi Air Lubrication System
50 Application of Simulation Technology to Mitsubishi Air Lubrication System CHIHARU KAWAKITA *1 SHINSUKE SATO *2 TAKAHIRO OKIMOTO *2 For the development and design of the Mitsubishi Air Lubrication System
Dynamics of stagnant Taylor bubbles in vertical upward pipe flow with Venturi obstruction and non-newtonian liquids
 Dynamics of stagnant Taylor bubbles in vertical upward pipe flow with Venturi obstruction and non-newtonian liquids Rune W. Time and A.H. Rabenjafimanantsoa University of Stavanger, Norway ABSTRACT Experiments
Dynamics of stagnant Taylor bubbles in vertical upward pipe flow with Venturi obstruction and non-newtonian liquids Rune W. Time and A.H. Rabenjafimanantsoa University of Stavanger, Norway ABSTRACT Experiments
W I L D W E L L C O N T R O L PRESSURE BASICS AND CONCEPTS
 PRESSURE BASICS AND CONCEPTS Pressure Basics and Concepts Learning Objectives You will be familiarized with the following basic pressure concepts: Defining pressure Hydrostatic pressure Pressure gradient
PRESSURE BASICS AND CONCEPTS Pressure Basics and Concepts Learning Objectives You will be familiarized with the following basic pressure concepts: Defining pressure Hydrostatic pressure Pressure gradient
ANNUAL REPORT UIUC, August 16, Bubble Formation, Breakup and Coalescence in Stopper-rod Nozzle Flow and Effect on Multiphase Mold Flow
 ANNUAL REPORT 202 UIUC, August 6, 202 Bubble Formation, Breakup and Coalescence in Stopper-rod Nozzle Flow and Effect on Multiphase Mold Flow POSTECH: Seong-Mook Cho, Seon-Hyo Kim, Hyoung-Jun Lee, Dae-Woo
ANNUAL REPORT 202 UIUC, August 6, 202 Bubble Formation, Breakup and Coalescence in Stopper-rod Nozzle Flow and Effect on Multiphase Mold Flow POSTECH: Seong-Mook Cho, Seon-Hyo Kim, Hyoung-Jun Lee, Dae-Woo
ISOLATION OF NON-HYDROSTATIC REGIONS WITHIN A BASIN
 ISOLATION OF NON-HYDROSTATIC REGIONS WITHIN A BASIN Bridget M. Wadzuk 1 (Member, ASCE) and Ben R. Hodges 2 (Member, ASCE) ABSTRACT Modeling of dynamic pressure appears necessary to achieve a more robust
ISOLATION OF NON-HYDROSTATIC REGIONS WITHIN A BASIN Bridget M. Wadzuk 1 (Member, ASCE) and Ben R. Hodges 2 (Member, ASCE) ABSTRACT Modeling of dynamic pressure appears necessary to achieve a more robust
OLGA. The Dynamic Three Phase Flow Simulator. Input. Output. Mass transfer Momentum transfer Energy transfer. 9 Conservation equations
 서유택 Flow Assurance The Dynamic Three Phase Flow Simulator 9 Conservation equations Mass (5) Momentum (3) Energy (1) Mass transfer Momentum transfer Energy transfer Input Boundary and initial conditions
서유택 Flow Assurance The Dynamic Three Phase Flow Simulator 9 Conservation equations Mass (5) Momentum (3) Energy (1) Mass transfer Momentum transfer Energy transfer Input Boundary and initial conditions
CONSIDERATION OF DENSITY VARIATIONS IN THE DESIGN OF A VENTILATION SYSTEM FOR ROAD TUNNELS
 - 56 - CONSIDERATION OF DENSITY VARIATIONS IN THE DESIGN OF A VENTILATION SYSTEM FOR ROAD TUNNELS Gloth O., Rudolf A. ILF Consulting Engineers Zürich, Switzerland ABSTRACT This article investigates the
- 56 - CONSIDERATION OF DENSITY VARIATIONS IN THE DESIGN OF A VENTILATION SYSTEM FOR ROAD TUNNELS Gloth O., Rudolf A. ILF Consulting Engineers Zürich, Switzerland ABSTRACT This article investigates the
OPTIMIZATION OF SINGLE STAGE AXIAL FLOW COMPRESSOR FOR DIFFERENT ROTATIONAL SPEED USING CFD
 http:// OPTIMIZATION OF SINGLE STAGE AXIAL FLOW COMPRESSOR FOR DIFFERENT ROTATIONAL SPEED USING CFD Anand Kumar S malipatil 1, Anantharaja M.H 2 1,2 Department of Thermal Power Engineering, VTU-RO Gulbarga,
http:// OPTIMIZATION OF SINGLE STAGE AXIAL FLOW COMPRESSOR FOR DIFFERENT ROTATIONAL SPEED USING CFD Anand Kumar S malipatil 1, Anantharaja M.H 2 1,2 Department of Thermal Power Engineering, VTU-RO Gulbarga,
FLOW PATTERNS IN VERTICAL AIR/WATER FLOW WITH AND WITHOUT SURFACTANT. Thesis. Submitted to. The School of Engineering of the UNIVERSITY OF DAYTON
 FLOW PATTERNS IN VERTICAL AIR/WATER FLOW WITH AND WITHOUT SURFACTANT Thesis Submitted to The School of Engineering of the UNIVERSITY OF DAYTON In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for The Degree
FLOW PATTERNS IN VERTICAL AIR/WATER FLOW WITH AND WITHOUT SURFACTANT Thesis Submitted to The School of Engineering of the UNIVERSITY OF DAYTON In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for The Degree
Influence of rounding corners on unsteady flow and heat transfer around a square cylinder
 Influence of rounding corners on unsteady flow and heat transfer around a square cylinder S. K. Singh Deptt. of Mech. Engg., M. B. M. Engg. College / J. N. V. University, Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India Abstract
Influence of rounding corners on unsteady flow and heat transfer around a square cylinder S. K. Singh Deptt. of Mech. Engg., M. B. M. Engg. College / J. N. V. University, Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India Abstract
Effect of 180 bends on gas/liquid flows in vertical upward and downward pipes
 Computational Methods in Multiphase Flow VII 435 Effect of 180 bends on gas/liquid flows in vertical upward and downward pipes A. Almabrok, L. Lao & H. Yeung Department of Offshore, Process and Energy
Computational Methods in Multiphase Flow VII 435 Effect of 180 bends on gas/liquid flows in vertical upward and downward pipes A. Almabrok, L. Lao & H. Yeung Department of Offshore, Process and Energy
Effect of Diameter on the Aerodynamics of Sepaktakraw Balls, A Computational Study
 ISSN 1750-9823 (print) International Journal of Sports Science and Engineering Vol. 03 (2009) No. 01, pp. 017-021 Effect of Diameter on the Aerodynamics of Sepaktakraw Balls, A Computational Study Zahari
ISSN 1750-9823 (print) International Journal of Sports Science and Engineering Vol. 03 (2009) No. 01, pp. 017-021 Effect of Diameter on the Aerodynamics of Sepaktakraw Balls, A Computational Study Zahari
Flow and Mixing in the Liquid between Bubbles
 Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2009 Boston Flow and Mixing in the Liquid between Bubbles Bruce A. Finlayson, Professor Emeritus of Chemical Engineering Department of Chemical Engineering,
Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2009 Boston Flow and Mixing in the Liquid between Bubbles Bruce A. Finlayson, Professor Emeritus of Chemical Engineering Department of Chemical Engineering,
3 1 PRESSURE. This is illustrated in Fig. 3 3.
 P = 3 psi 66 FLUID MECHANICS 150 pounds A feet = 50 in P = 6 psi P = s W 150 lbf n = = 50 in = 3 psi A feet FIGURE 3 1 The normal stress (or pressure ) on the feet of a chubby person is much greater than
P = 3 psi 66 FLUID MECHANICS 150 pounds A feet = 50 in P = 6 psi P = s W 150 lbf n = = 50 in = 3 psi A feet FIGURE 3 1 The normal stress (or pressure ) on the feet of a chubby person is much greater than
Permeability. Darcy's Law
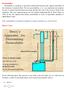 Permeability Permeability is a property of the porous medium that measures the capacity and ability of the formation to transmit fluids. The rock permeability, k, is a very important rock property because
Permeability Permeability is a property of the porous medium that measures the capacity and ability of the formation to transmit fluids. The rock permeability, k, is a very important rock property because
Measurement of both gas and liquid velocity profiles for bubble-induced turbulent flow
 Measurement of both gas and liquid velocity profiles for bubble-induced turbulent flow H. Takiguchi 1*, M. Furuya 1, T. Arai 1, T. Kanai 1 1: Central research institute of electric power industry (CRIEPI)
Measurement of both gas and liquid velocity profiles for bubble-induced turbulent flow H. Takiguchi 1*, M. Furuya 1, T. Arai 1, T. Kanai 1 1: Central research institute of electric power industry (CRIEPI)
Gas Lift Workshop Doha Qatar 4-88 February Gas Lift Optimisation of Long Horizontal Wells. by Juan Carlos Mantecon
 Gas Lift Workshop Doha Qatar 4-88 February 2007 Gas Lift Optimisation of Long Horizontal Wells by Juan Carlos Mantecon 1 Long Horizontal Wells The flow behavior of long horizontal wells is similar to pipelines
Gas Lift Workshop Doha Qatar 4-88 February 2007 Gas Lift Optimisation of Long Horizontal Wells by Juan Carlos Mantecon 1 Long Horizontal Wells The flow behavior of long horizontal wells is similar to pipelines
Experimental Investigation of CCFL in Pressurizer Surge Line with Air-Water
 Experimental Investigation of CCFL in Pressurizer Surge Line with Air-Water ZW Wang, WX Tian, JT Yu, DL Zhang, G H Su, SZ Qiu, RH Chen School of Nuclear Science and Technology, Xi an Jiao Tong University
Experimental Investigation of CCFL in Pressurizer Surge Line with Air-Water ZW Wang, WX Tian, JT Yu, DL Zhang, G H Su, SZ Qiu, RH Chen School of Nuclear Science and Technology, Xi an Jiao Tong University
MODELING OF RADIAL GAS FRACTION PROFILES FOR BUBBLE FLOW IN VERTICAL PIPES
 FR0108111 MODELING OF RADIAL GAS FRACTION PROFILES FOR BUBBLE FLOW IN VERTICAL PIPES D. LUCAS, E. KREPPER, H.-M. PRASSER Forschungszentrum Rossendorf e.v., Institute of Safety Research, P.O.Box 510 119,
FR0108111 MODELING OF RADIAL GAS FRACTION PROFILES FOR BUBBLE FLOW IN VERTICAL PIPES D. LUCAS, E. KREPPER, H.-M. PRASSER Forschungszentrum Rossendorf e.v., Institute of Safety Research, P.O.Box 510 119,
PRESSURE DROP OF DIFFERENT FLOW PATTERN IN MULTIPHASE FLOW SYSTEM
 PRESSURE DROP OF DIFFERENT FLOW PATTERN IN MULTIPHASE FLOW SYSTEM MOHAMMAD HAFIZEZAZMI BIN AJAMAIN Thesis submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the award of the degree of Bachelor of
PRESSURE DROP OF DIFFERENT FLOW PATTERN IN MULTIPHASE FLOW SYSTEM MOHAMMAD HAFIZEZAZMI BIN AJAMAIN Thesis submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the award of the degree of Bachelor of
. In an elevator accelerating upward (A) both the elevator accelerating upward (B) the first is equations are valid
 IIT JEE Achiever 2014 Ist Year Physics-2: Worksheet-1 Date: 2014-06-26 Hydrostatics 1. A liquid can easily change its shape but a solid cannot because (A) the density of a liquid is smaller than that of
IIT JEE Achiever 2014 Ist Year Physics-2: Worksheet-1 Date: 2014-06-26 Hydrostatics 1. A liquid can easily change its shape but a solid cannot because (A) the density of a liquid is smaller than that of
Unit A-2: List of Subjects
 ES312 Energy Transfer Fundamentals Unit A: Fundamental Concepts ROAD MAP... A-1: Introduction to Thermodynamics A-2: Engineering Properties Unit A-2: List of Subjects Basic Properties and Temperature Pressure
ES312 Energy Transfer Fundamentals Unit A: Fundamental Concepts ROAD MAP... A-1: Introduction to Thermodynamics A-2: Engineering Properties Unit A-2: List of Subjects Basic Properties and Temperature Pressure
I.CHEM.E. SYMPOSIUM SERIES NO. 97 BUOYANCY-DRIVEN NATURAL VENTILATION OP ENCLOSED SPACES
 BUOYANCY-DRIVEN NATURAL VENTILATION OP ENCLOSED SPACES M. R. Marshall* and P. L. Stewart-Darling* A simple mathematical model for the buoyancy driven ventilation of an enclosed space, using a two-pipe
BUOYANCY-DRIVEN NATURAL VENTILATION OP ENCLOSED SPACES M. R. Marshall* and P. L. Stewart-Darling* A simple mathematical model for the buoyancy driven ventilation of an enclosed space, using a two-pipe
International Journal of Petroleum and Geoscience Engineering Volume 03, Issue 02, Pages , 2015
 International Journal of Petroleum and Geoscience Engineering Volume 03, Issue 02, Pages 116- ISSN: 2289-4713 Improving Reservoir Recovery Factor Using Enhanced Electrical Submersible Pump Design; a Case
International Journal of Petroleum and Geoscience Engineering Volume 03, Issue 02, Pages 116- ISSN: 2289-4713 Improving Reservoir Recovery Factor Using Enhanced Electrical Submersible Pump Design; a Case
Investigation of momentum exchange term closures for the Eulerian-Eulerian model applied to bubbly flows
 Graduate Theses and Dissertations Iowa State University Capstones, Theses and Dissertations 2016 Investigation of momentum exchange term closures for the Eulerian-Eulerian model applied to bubbly flows
Graduate Theses and Dissertations Iowa State University Capstones, Theses and Dissertations 2016 Investigation of momentum exchange term closures for the Eulerian-Eulerian model applied to bubbly flows
Air entrainment in Dip coating under vacuum
 Air entrainment in Dip coating under vacuum M.I. Khan, R. Patel, H. Benkreira, IRC, School of Engineering, Design and Technology, University of Bradford, BD7 1DP, Abstract Air entrainment studies in dip
Air entrainment in Dip coating under vacuum M.I. Khan, R. Patel, H. Benkreira, IRC, School of Engineering, Design and Technology, University of Bradford, BD7 1DP, Abstract Air entrainment studies in dip
! =! [4 (2) ! n] 16 th Australasian Fluid Mechanics Conference Crown Plaza, Gold Coast, Australia 2-7 December 2007
![! =! [4 (2) ! n] 16 th Australasian Fluid Mechanics Conference Crown Plaza, Gold Coast, Australia 2-7 December 2007 ! =! [4 (2) ! n] 16 th Australasian Fluid Mechanics Conference Crown Plaza, Gold Coast, Australia 2-7 December 2007](/thumbs/76/74342437.jpg) 16 th Australasian Fluid Mechanics Conference Crown Plaza, Gold Coast, Australia 2-7 December 2007 Liquid Film Falling on Horizontal Circular Cylinders F. Jafar, G. Thorpe and O.F. Turan School of Architectural,
16 th Australasian Fluid Mechanics Conference Crown Plaza, Gold Coast, Australia 2-7 December 2007 Liquid Film Falling on Horizontal Circular Cylinders F. Jafar, G. Thorpe and O.F. Turan School of Architectural,
A New Model for Predicting Liquid Holdup in Two-Phase. Flow under High Gas and Liquid Velocities
 A New Model or Predicting iquid Holdup in Two-Phase Flow under High Gas and iquid Velocities Zilong iu a,b,c, Ruiquan iao a,b,c,*, Wei uo a,b,c, Joseph X. F. Ribeiro a,b,c a. Petroleum Engineering College,
A New Model or Predicting iquid Holdup in Two-Phase Flow under High Gas and iquid Velocities Zilong iu a,b,c, Ruiquan iao a,b,c,*, Wei uo a,b,c, Joseph X. F. Ribeiro a,b,c a. Petroleum Engineering College,
MODELING AND SIMULATION OF VALVE COEFFICIENTS AND CAVITATION CHARACTERISTICS IN A BALL VALVE
 Proceedings of the 37 th International & 4 th National Conference on Fluid Mechanics and Fluid Power FMFP2010 December 16-18, 2010, IIT Madras, Chennai, India FMFP2010 341 MODELING AND SIMULATION OF VALVE
Proceedings of the 37 th International & 4 th National Conference on Fluid Mechanics and Fluid Power FMFP2010 December 16-18, 2010, IIT Madras, Chennai, India FMFP2010 341 MODELING AND SIMULATION OF VALVE
T H E U N I V E R S I T Y O F T U L S A THE GRADUATE SCHOOL DESIGN AND PERFORMANCE OF MULTIPHASE DISTRIBUTION MANIFOLD. Angel R.
 T H E U N I V E R S I T Y O F T U S A THE RADUATE SCHOO DESIN AND PERFORMANCE OF MUTIPHASE DISTRIBUTION MANIFOD by Angel R. Bustamante A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for
T H E U N I V E R S I T Y O F T U S A THE RADUATE SCHOO DESIN AND PERFORMANCE OF MUTIPHASE DISTRIBUTION MANIFOD by Angel R. Bustamante A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for
Experimental Investigation Of Flow Past A Rough Surfaced Cylinder
 (AET- 29th March 214) RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Experimental Investigation Of Flow Past A Rough Surfaced Cylinder Monalisa Mallick 1, A. Kumar 2 1 (Department of Civil Engineering, National Institute
(AET- 29th March 214) RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Experimental Investigation Of Flow Past A Rough Surfaced Cylinder Monalisa Mallick 1, A. Kumar 2 1 (Department of Civil Engineering, National Institute
WALL BOILING MODELING EXTENSION TOWARDS CRITICAL HEAT FLUX. ABSTRACT
 WALL BOILING MODELING EXTENSION TOWARDS CRITICAL HEAT FLUX C. Lifante 1, Th. Frank 1 and A. Burns 2,3 1 ANSYS Germany GmbH, Staudenfeldweg 12, 83624 Otterfing, Germany 2 ANSYS UK, 97 Milton Park, Abingdon,
WALL BOILING MODELING EXTENSION TOWARDS CRITICAL HEAT FLUX C. Lifante 1, Th. Frank 1 and A. Burns 2,3 1 ANSYS Germany GmbH, Staudenfeldweg 12, 83624 Otterfing, Germany 2 ANSYS UK, 97 Milton Park, Abingdon,
Multiphase Flow Prof. Gargi Das Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Multiphase Flow Prof. Gargi Das Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Module No. # 01 Lecture No. # 02 Estimation of Flow Patterns Well very good morning to all of
Multiphase Flow Prof. Gargi Das Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Module No. # 01 Lecture No. # 02 Estimation of Flow Patterns Well very good morning to all of
Development of High-speed Gas Dissolution Device
 Development of High-speed Gas Dissolution Device Yoichi Nakano*, Atsushi Suehiro**, Tetsuhiko Fujisato***, Jun Ma**** Kesayoshi Hadano****, Masayuki Fukagawa***** *Ube National College of Technology, Tokiwadai
Development of High-speed Gas Dissolution Device Yoichi Nakano*, Atsushi Suehiro**, Tetsuhiko Fujisato***, Jun Ma**** Kesayoshi Hadano****, Masayuki Fukagawa***** *Ube National College of Technology, Tokiwadai
Experimental Analysis on Vortex Tube Refrigerator Using Different Conical Valve Angles
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 7-067X, p-issn: 7-00X, www.ijerd.com Volume 3, Issue 4 (August ), PP. 33-39 Experimental Analysis on Vortex Tube Refrigerator Using
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 7-067X, p-issn: 7-00X, www.ijerd.com Volume 3, Issue 4 (August ), PP. 33-39 Experimental Analysis on Vortex Tube Refrigerator Using
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 14 Fluids Fluids at rest pressure vs. depth Pascal s principle Archimedes s principle Buoynat forces Fluids in motion: Continuity & Bernoulli equations 1. How deep
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 14 Fluids Fluids at rest pressure vs. depth Pascal s principle Archimedes s principle Buoynat forces Fluids in motion: Continuity & Bernoulli equations 1. How deep
INSTRUMENT INSTRUMENTAL ERROR (of full scale) INSTRUMENTAL RESOLUTION. Tutorial simulation. Tutorial simulation
 Lab 1 Standing Waves on a String Learning Goals: To distinguish between traveling and standing waves To recognize how the wavelength of a standing wave is measured To recognize the necessary conditions
Lab 1 Standing Waves on a String Learning Goals: To distinguish between traveling and standing waves To recognize how the wavelength of a standing wave is measured To recognize the necessary conditions
Two Phase Fluid Flow (ENGINEERING DESIGN GUIDELINE)
 Page : 1 of 61 Rev: 01 Guidelines for Processing Plant www.klmtechgroup.com Rev 01 KLM Technology #03-12 Block Aronia, Jalan Sri Perkasa 2 Taman Tampoi Utama 81200 Johor Bahru (ENGINEERING DESIGN GUIDELINE)
Page : 1 of 61 Rev: 01 Guidelines for Processing Plant www.klmtechgroup.com Rev 01 KLM Technology #03-12 Block Aronia, Jalan Sri Perkasa 2 Taman Tampoi Utama 81200 Johor Bahru (ENGINEERING DESIGN GUIDELINE)
Two phase discharge flow prediction in safety valves
 Dempster W, Elmayyah W/ ICPVT-13 1 Two phase discharge flow prediction in safety valves William Dempster a, Wael Elmayyah b a Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, University of Strathclyde,
Dempster W, Elmayyah W/ ICPVT-13 1 Two phase discharge flow prediction in safety valves William Dempster a, Wael Elmayyah b a Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, University of Strathclyde,
Numerical Simulation And Aerodynamic Performance Comparison Between Seagull Aerofoil and NACA 4412 Aerofoil under Low-Reynolds 1
 Advances in Natural Science Vol. 3, No. 2, 2010, pp. 244-20 www.cscanada.net ISSN 171-7862 [PRINT] ISSN 171-7870 [ONLINE] www.cscanada.org *The 3rd International Conference of Bionic Engineering* Numerical
Advances in Natural Science Vol. 3, No. 2, 2010, pp. 244-20 www.cscanada.net ISSN 171-7862 [PRINT] ISSN 171-7870 [ONLINE] www.cscanada.org *The 3rd International Conference of Bionic Engineering* Numerical
Hard or Soft Shut-in : Which is the Best Approach?
 HARD - SOFT shut-in? Hard or Soft Shut-in : Which is the Best Approach? March '93 INTRODUCTION There is now reasonable acceptance through-out the industry for the use of a hard shut-in procedure following
HARD - SOFT shut-in? Hard or Soft Shut-in : Which is the Best Approach? March '93 INTRODUCTION There is now reasonable acceptance through-out the industry for the use of a hard shut-in procedure following
Gas Kick Behavior During Bullheading Operations in Vertical Wells.
 Louisiana State University LSU Digital Commons LSU Historical Dissertations and Theses Graduate School 1995 Gas Kick Behavior During Bullheading Operations in Vertical Wells. William Leo Koederitz Louisiana
Louisiana State University LSU Digital Commons LSU Historical Dissertations and Theses Graduate School 1995 Gas Kick Behavior During Bullheading Operations in Vertical Wells. William Leo Koederitz Louisiana
STIPumpCard. User Manual
 STIPumpCard User Manual Contents 1. Introduction...1 1.1. What is STIPumpCard?... 1 1.2. Main User Interface... 2 2. Input Parameters...4 2.1. Project... 4 2.2. Simulation Settings GroupBox... 4 2.3. Pump
STIPumpCard User Manual Contents 1. Introduction...1 1.1. What is STIPumpCard?... 1 1.2. Main User Interface... 2 2. Input Parameters...4 2.1. Project... 4 2.2. Simulation Settings GroupBox... 4 2.3. Pump
THE EFFECTS OF INLET FLOW CONDITIONS ON GAS-LIQUID TWO-PHASE FLOW IN A MICRO TUBE. Yuji Suzuki Dept. of Mech. Eng., The univ.
 Proceedings of HT007 007 ASME-JSME Thermal Engineering Summer Heat Transfer Conference July -, 007, Vancouver, British Columbia, CANADA HT007-39 THE EFFECTS OF INLET FLOW CONDITIONS ON GAS-LIQUID TWO-PHASE
Proceedings of HT007 007 ASME-JSME Thermal Engineering Summer Heat Transfer Conference July -, 007, Vancouver, British Columbia, CANADA HT007-39 THE EFFECTS OF INLET FLOW CONDITIONS ON GAS-LIQUID TWO-PHASE
Using the Artificial Gas Lift to Increase the Productivity of Noor Oil Field / Mishrif Formation
 Iraqi Journal of Chemical and Petroleum Engineering Iraqi Journal of Chemical and Petroleum Engineering Vol.16 No.2 (June 2015) 39-44 ISSN: 1997-4884 University of Baghdad College of Engineering Using
Iraqi Journal of Chemical and Petroleum Engineering Iraqi Journal of Chemical and Petroleum Engineering Vol.16 No.2 (June 2015) 39-44 ISSN: 1997-4884 University of Baghdad College of Engineering Using
Analysis and Research of Mooring System. Jiahui Fan*
 nd International Conference on Computer Engineering, Information Science & Application Technology (ICCIA 07) Analysis and Research of Mooring System Jiahui Fan* School of environment, North China Electric
nd International Conference on Computer Engineering, Information Science & Application Technology (ICCIA 07) Analysis and Research of Mooring System Jiahui Fan* School of environment, North China Electric
Numerical Investigation of Air Bubbles Evolution and Coalescence from Submerged Orifices Based on OpenFOAM
 Numerical Investigation of Air Bubbles Evolution and Coalescence from Submerged Orifices Based on OpenFOAM Pan Feng, He Ying, Li-zhong Mu 2018-7-6 Dalian University of Technology, China Outline Background
Numerical Investigation of Air Bubbles Evolution and Coalescence from Submerged Orifices Based on OpenFOAM Pan Feng, He Ying, Li-zhong Mu 2018-7-6 Dalian University of Technology, China Outline Background
Design Tapered Electric Submersible Pumps For Gassy Wells Desheng Zhou, SPE, Rajesh Sachdeva, SPE, IHS INC.
 SPE 113661 Design Tapered Electric Submersible Pumps For Gassy Wells Desheng Zhou, SPE, Rajesh Sachdeva, SPE, IS INC. Copyright 8, Society of Petroleum Engineers This paper was prepared for presentation
SPE 113661 Design Tapered Electric Submersible Pumps For Gassy Wells Desheng Zhou, SPE, Rajesh Sachdeva, SPE, IS INC. Copyright 8, Society of Petroleum Engineers This paper was prepared for presentation
of air-lift reactors based on bubble dynamics
 Indian Journal of Chemical Technology Vol. 5, July 1998, pp. 187-191 Modelling of air-lift reactors based on bubble dynamics Saikat Chakraborty+, Kajari Kargupta & Avijit Bhowal* Department of Chemical
Indian Journal of Chemical Technology Vol. 5, July 1998, pp. 187-191 Modelling of air-lift reactors based on bubble dynamics Saikat Chakraborty+, Kajari Kargupta & Avijit Bhowal* Department of Chemical
HOW FAST/FAR DOES FLY LINE FALL? N. Perkins of the University of Michigan, March 2003
 HOW FAST/FAR DOES FLY LINE FALL? N. Perkins of the University of Michigan, March 003 This report summarizes a simple model for the free fall dynamics of a length of fly line. The line is assumed to remain
HOW FAST/FAR DOES FLY LINE FALL? N. Perkins of the University of Michigan, March 003 This report summarizes a simple model for the free fall dynamics of a length of fly line. The line is assumed to remain
Modeling Turbulent Entrainment of Air at a Free Surface C.W. Hirt 5/24/12 Flow Science, Inc.
 Flow Science Report 01-12 Modeling Turbulent Entrainment of Air at a Free Surface C.W. Hirt 5/24/12 Flow Science, Inc. Overview In free-surface flows the turbulence in the liquid may be sufficient to disturb
Flow Science Report 01-12 Modeling Turbulent Entrainment of Air at a Free Surface C.W. Hirt 5/24/12 Flow Science, Inc. Overview In free-surface flows the turbulence in the liquid may be sufficient to disturb
Khosla's theory. After studying a lot of dam failure constructed based on Bligh s theory, Khosla came out with the following;
 Khosla's theory After studying a lot of dam failure constructed based on Bligh s theory, Khosla came out with the following; Following are some of the main points from Khosla's Theory From observation
Khosla's theory After studying a lot of dam failure constructed based on Bligh s theory, Khosla came out with the following; Following are some of the main points from Khosla's Theory From observation
Dynamics of bubble rising at small Reynolds numbers
 MATEC Web of Conferences 3, 01004 ( 015) DOI: 10.1051/ matecconf/ 015301004 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 015 Dynamics of bubble rising at small Reynolds numbers Vladimir Arkhipov
MATEC Web of Conferences 3, 01004 ( 015) DOI: 10.1051/ matecconf/ 015301004 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 015 Dynamics of bubble rising at small Reynolds numbers Vladimir Arkhipov
NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF PRESSURE DROP IN HYDRAULIC SPOOL VALVE
 NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF PRESSURE DROP IN HYDRAULIC SPOOL VALVE M.O. Abdalla *, T. Nagarajan and F.M. Hashim Mechanical Engineering Department, Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS, 31750 Tronoh, Perak, Malaysia
NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF PRESSURE DROP IN HYDRAULIC SPOOL VALVE M.O. Abdalla *, T. Nagarajan and F.M. Hashim Mechanical Engineering Department, Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS, 31750 Tronoh, Perak, Malaysia
MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF PERFORMANCE OF A LIQUD PISTON COMPRESSOR
 9. Pompa Vana Kompressör Kongresi 5-7 Mayıs 2016, İstanbul MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF PERFORMANCE OF A LIQUD PISTON COMPRESSOR Süleyman Doğan Öner Email: oner@ug.bilkent.edu.tr İbrahim Nasuh Yıldıran Email:
9. Pompa Vana Kompressör Kongresi 5-7 Mayıs 2016, İstanbul MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF PERFORMANCE OF A LIQUD PISTON COMPRESSOR Süleyman Doğan Öner Email: oner@ug.bilkent.edu.tr İbrahim Nasuh Yıldıran Email:
THEORETICAL EVALUATION OF FLOW THROUGH CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR STAGE
 THEORETICAL EVALUATION OF FLOW THROUGH CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR STAGE S.Ramamurthy 1, R.Rajendran 1, R. S. Dileep Kumar 2 1 Scientist, Propulsion Division, National Aerospace Laboratories, Bangalore-560017,ramamurthy_srm@yahoo.com
THEORETICAL EVALUATION OF FLOW THROUGH CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR STAGE S.Ramamurthy 1, R.Rajendran 1, R. S. Dileep Kumar 2 1 Scientist, Propulsion Division, National Aerospace Laboratories, Bangalore-560017,ramamurthy_srm@yahoo.com
COURSE NUMBER: ME 321 Fluid Mechanics I Fluid statics. Course teacher Dr. M. Mahbubur Razzaque Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BUET
 COURSE NUMBER: ME 321 Fluid Mechanics I Fluid statics Course teacher Dr. M. Mahbubur Razzaque Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BUET 1 Fluid statics Fluid statics is the study of fluids in
COURSE NUMBER: ME 321 Fluid Mechanics I Fluid statics Course teacher Dr. M. Mahbubur Razzaque Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BUET 1 Fluid statics Fluid statics is the study of fluids in
